BIOBRIEF
Immediate Implant Placement and Provisionalization for Anterior Esthetics

THE SITUATION
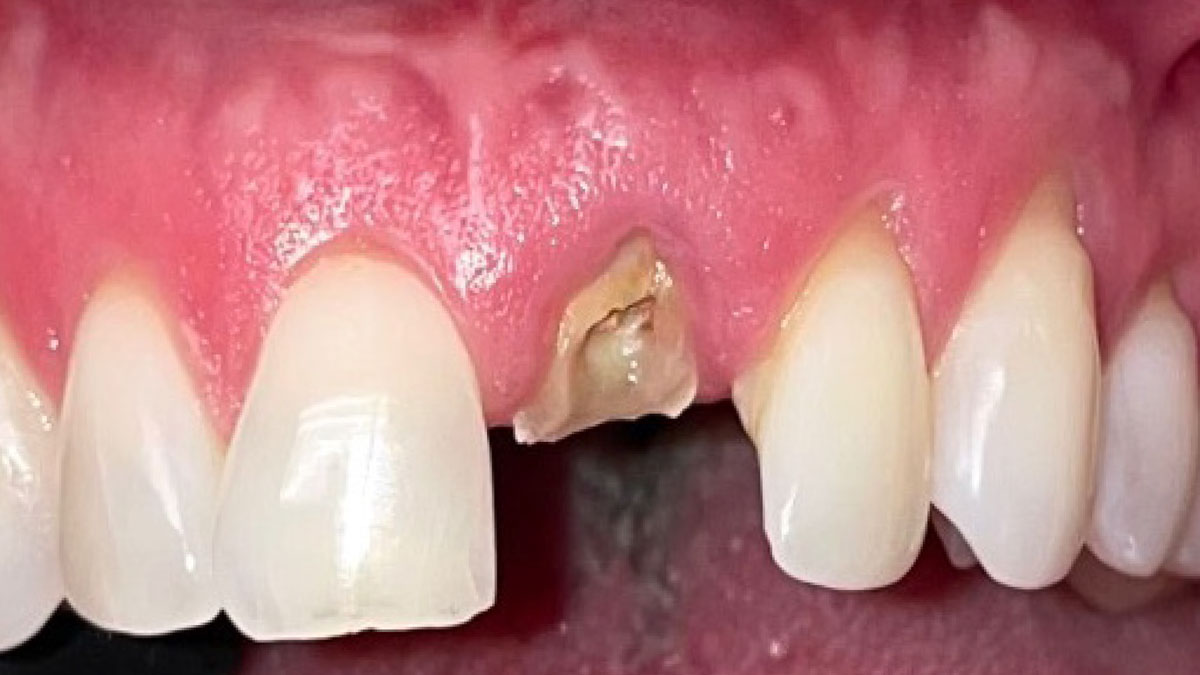
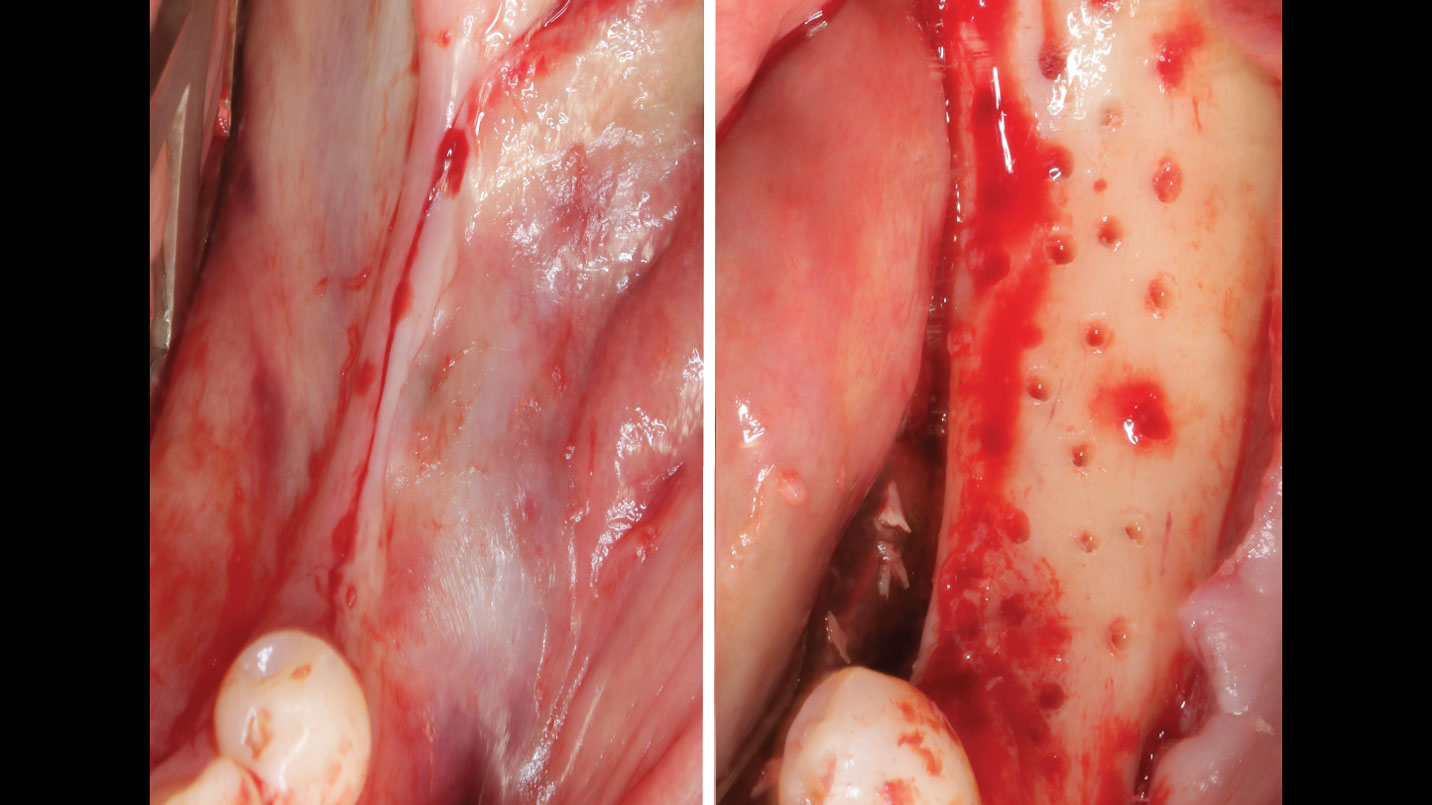
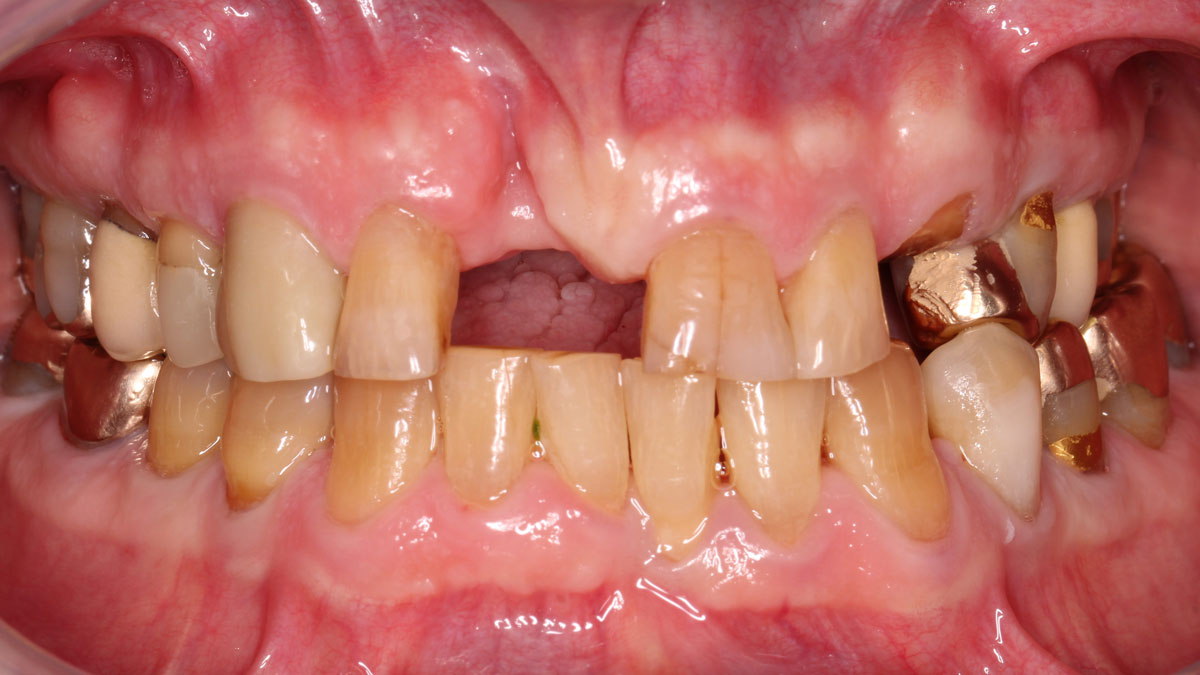
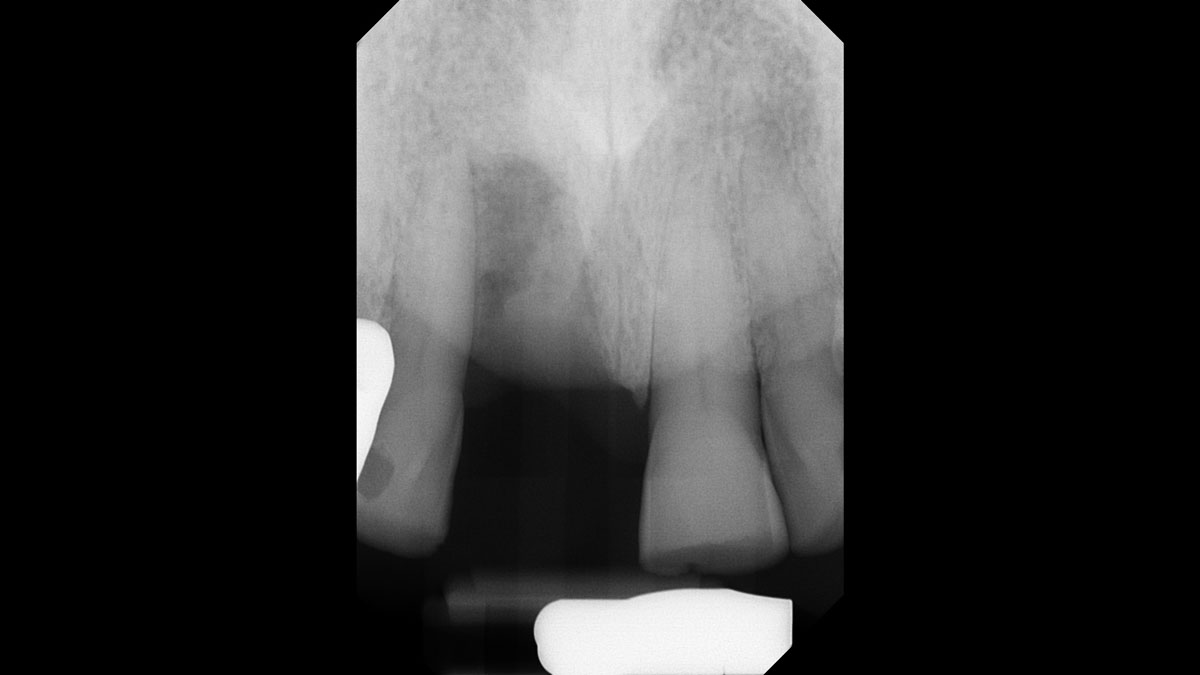
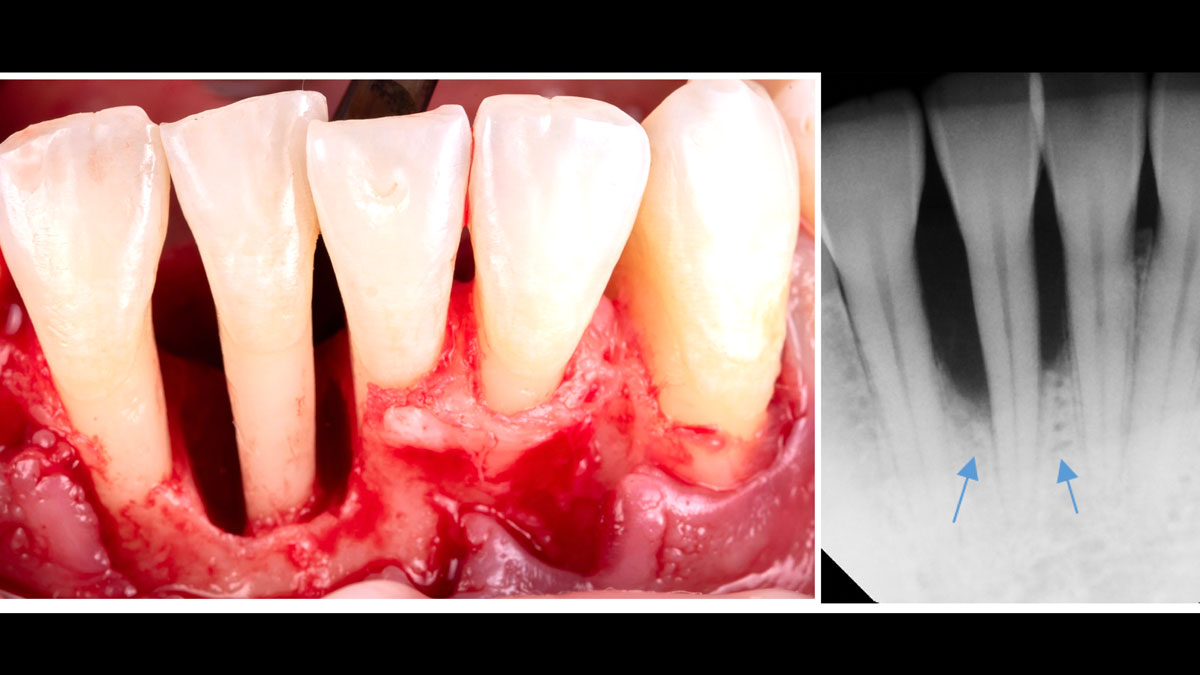
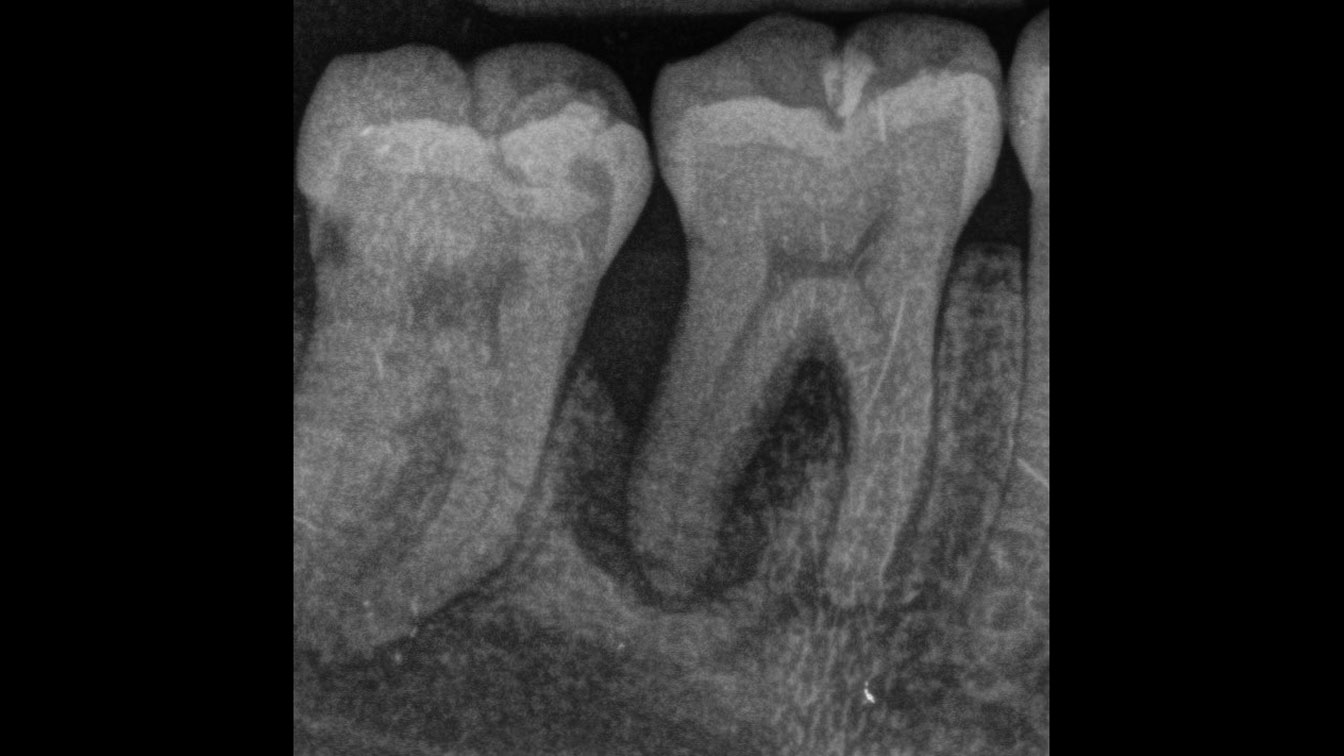
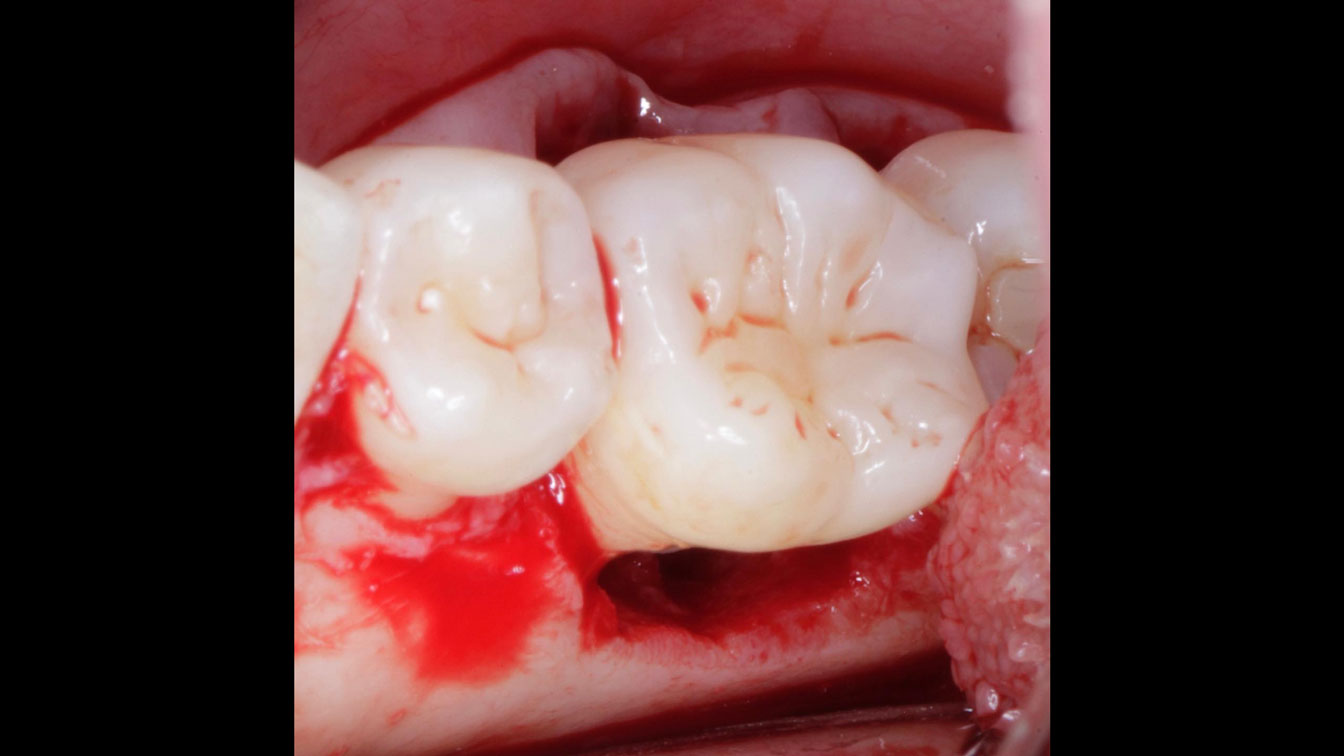
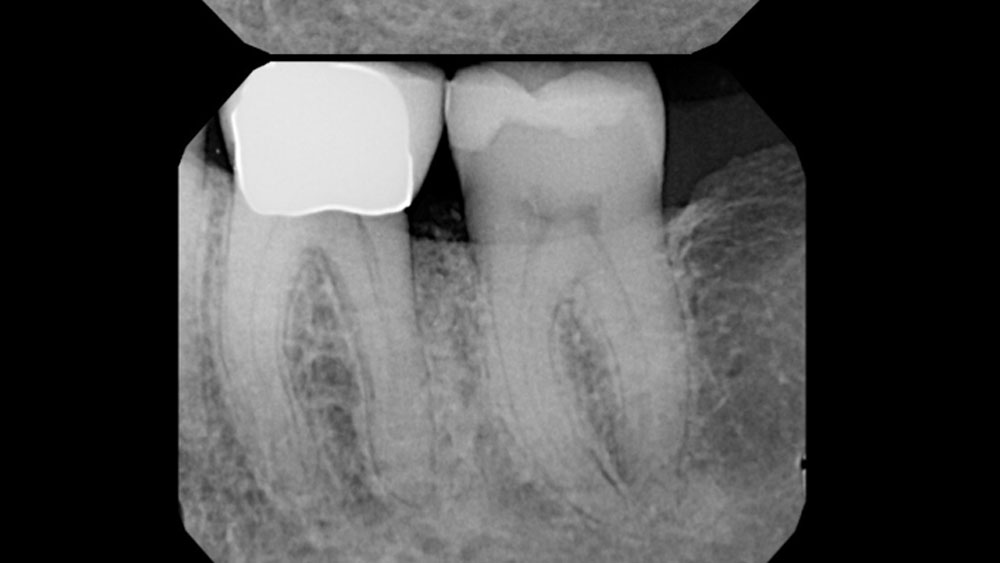
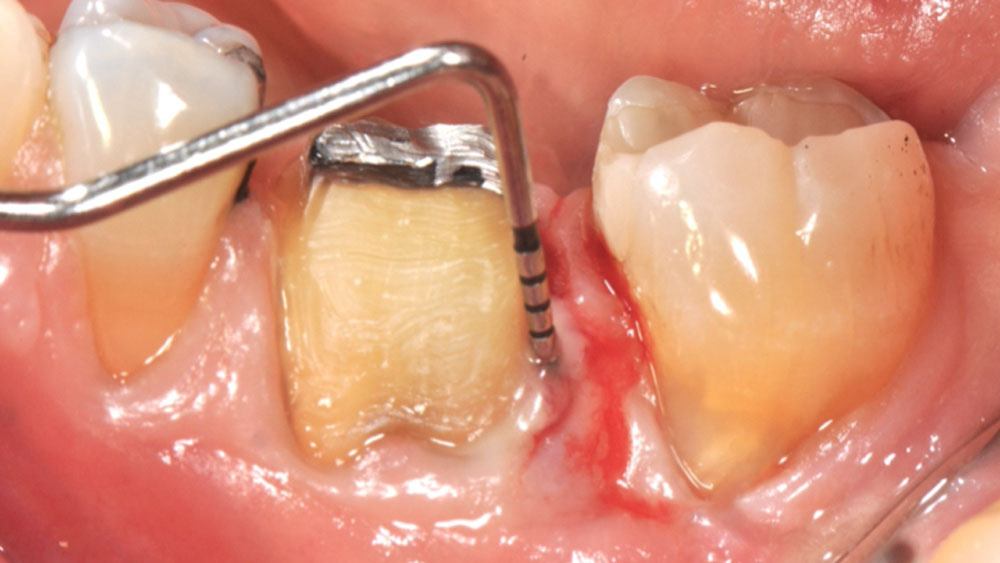
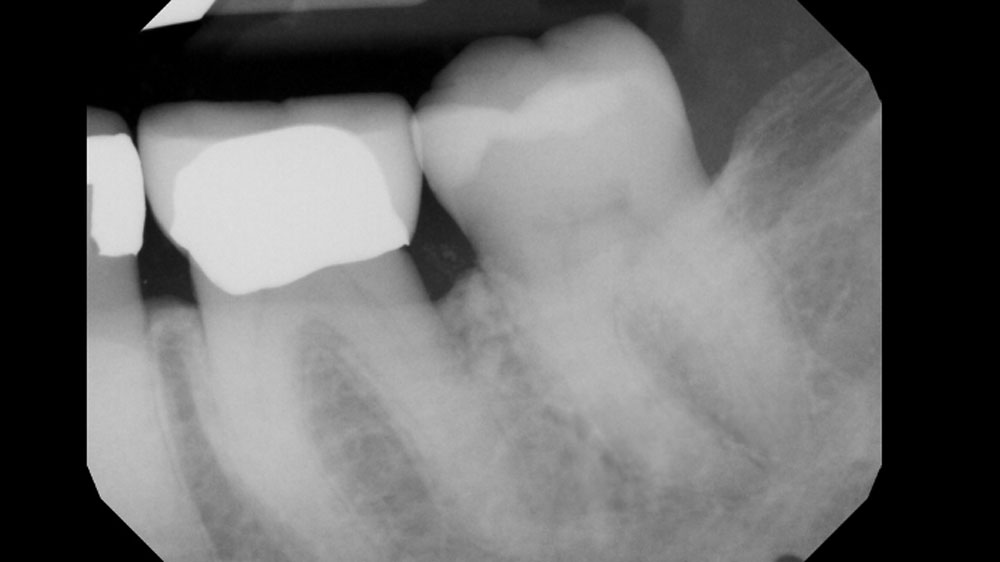
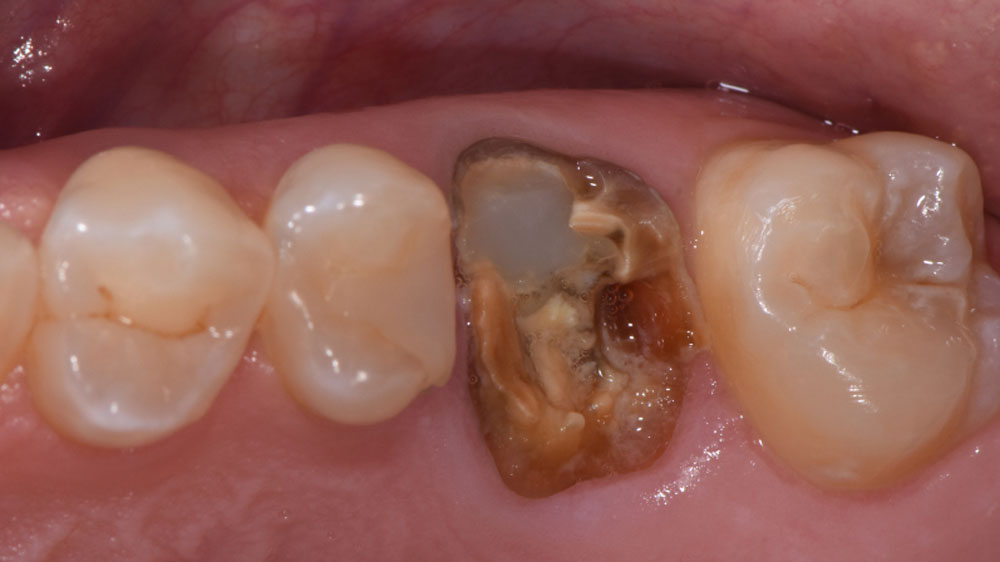
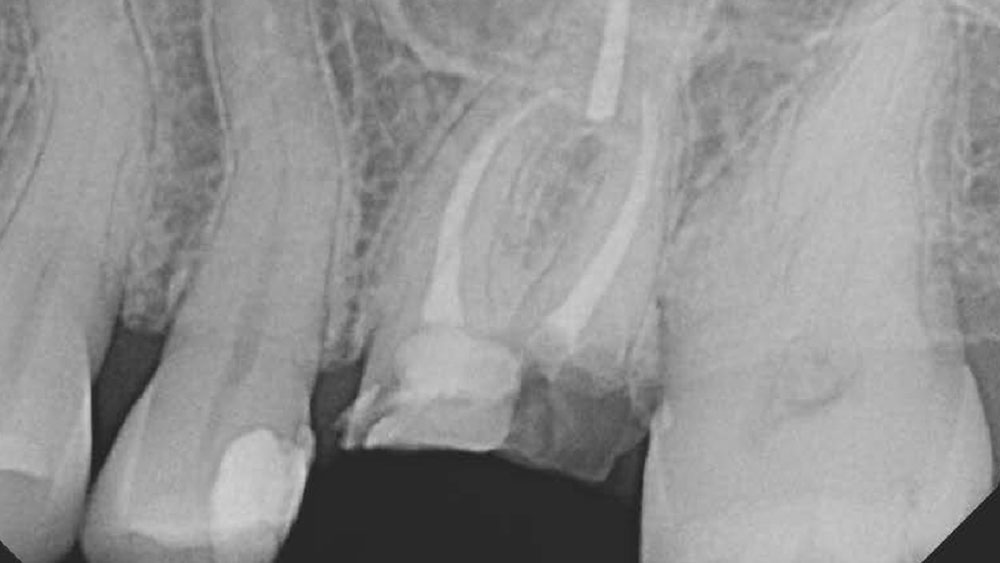
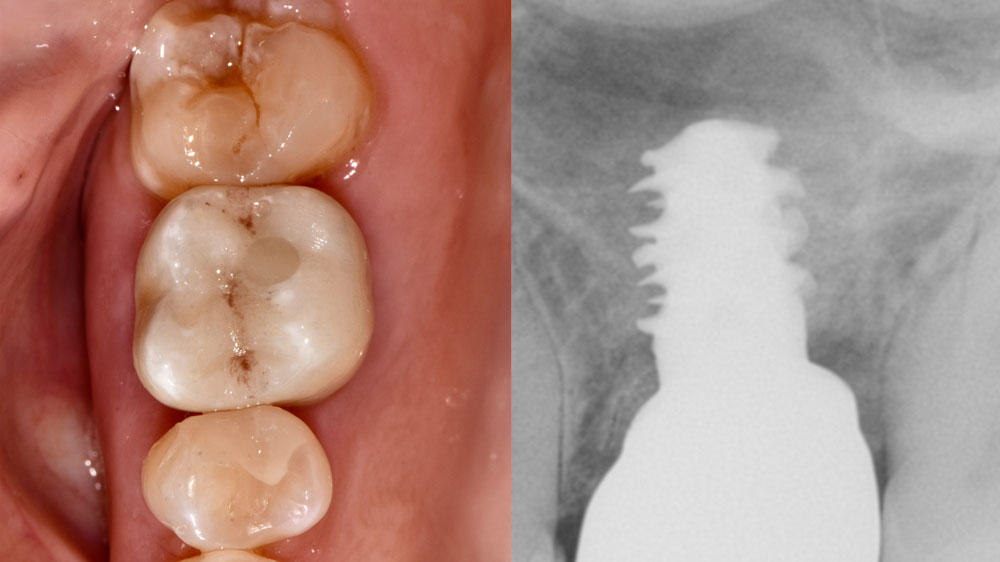
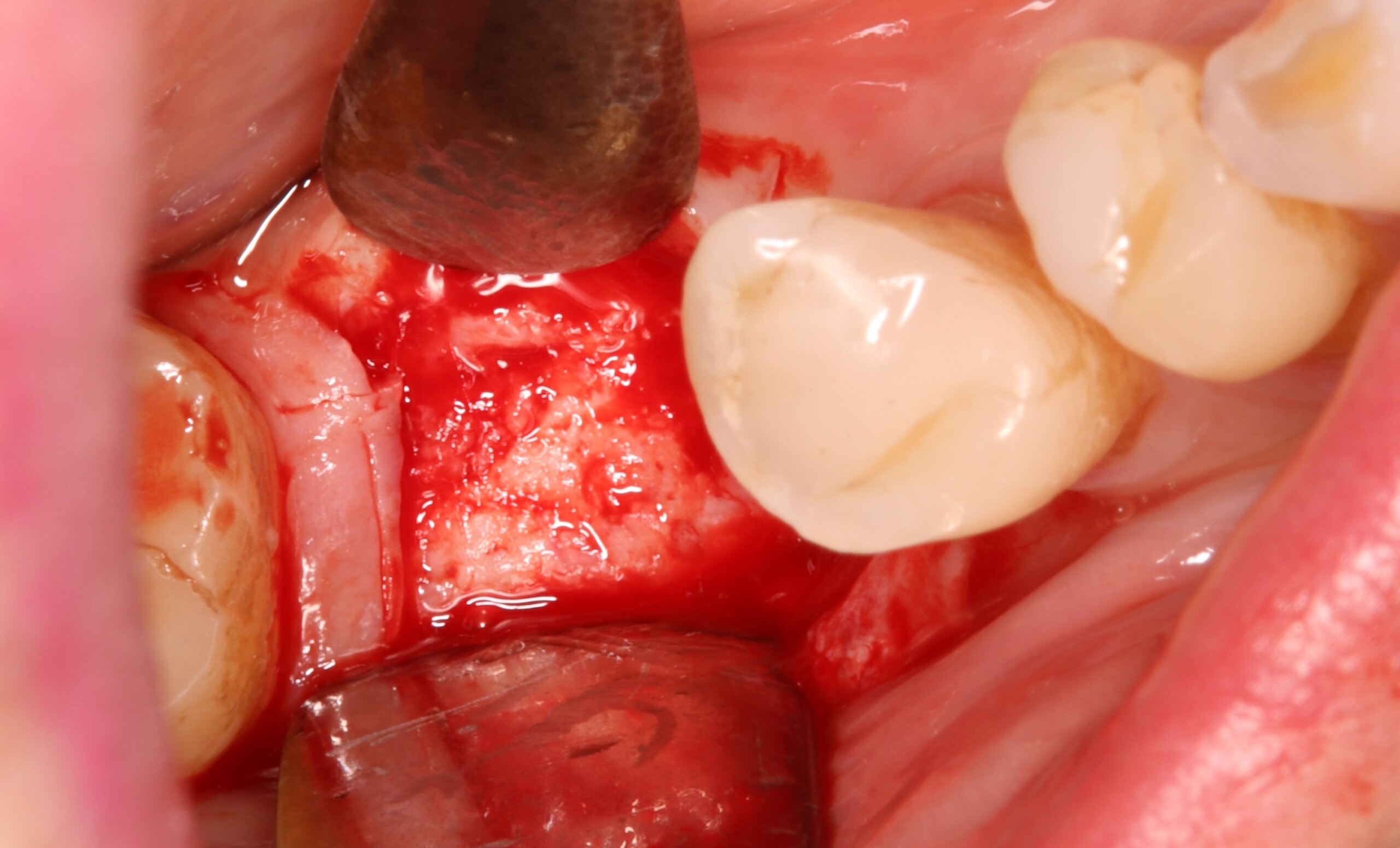
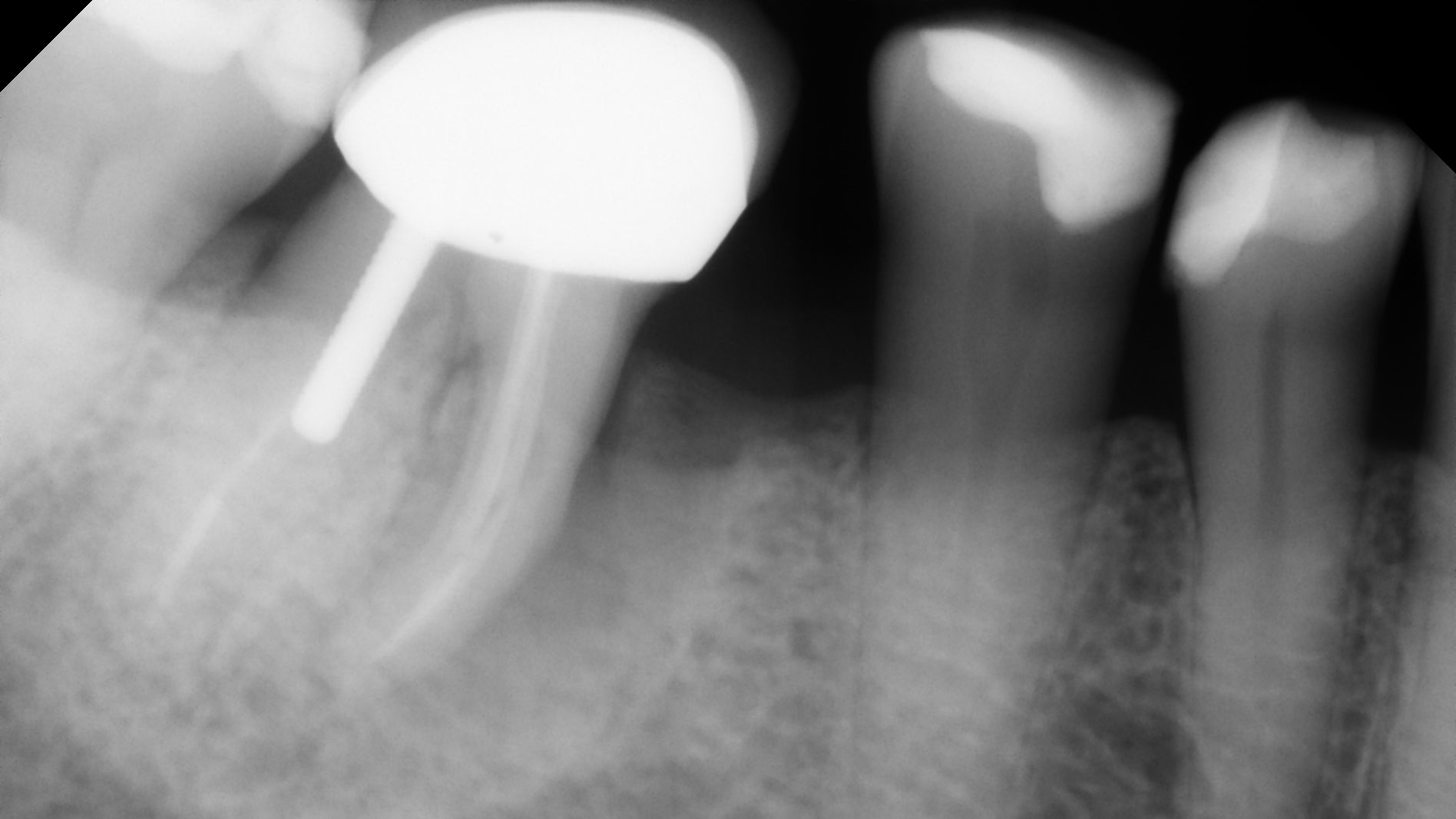
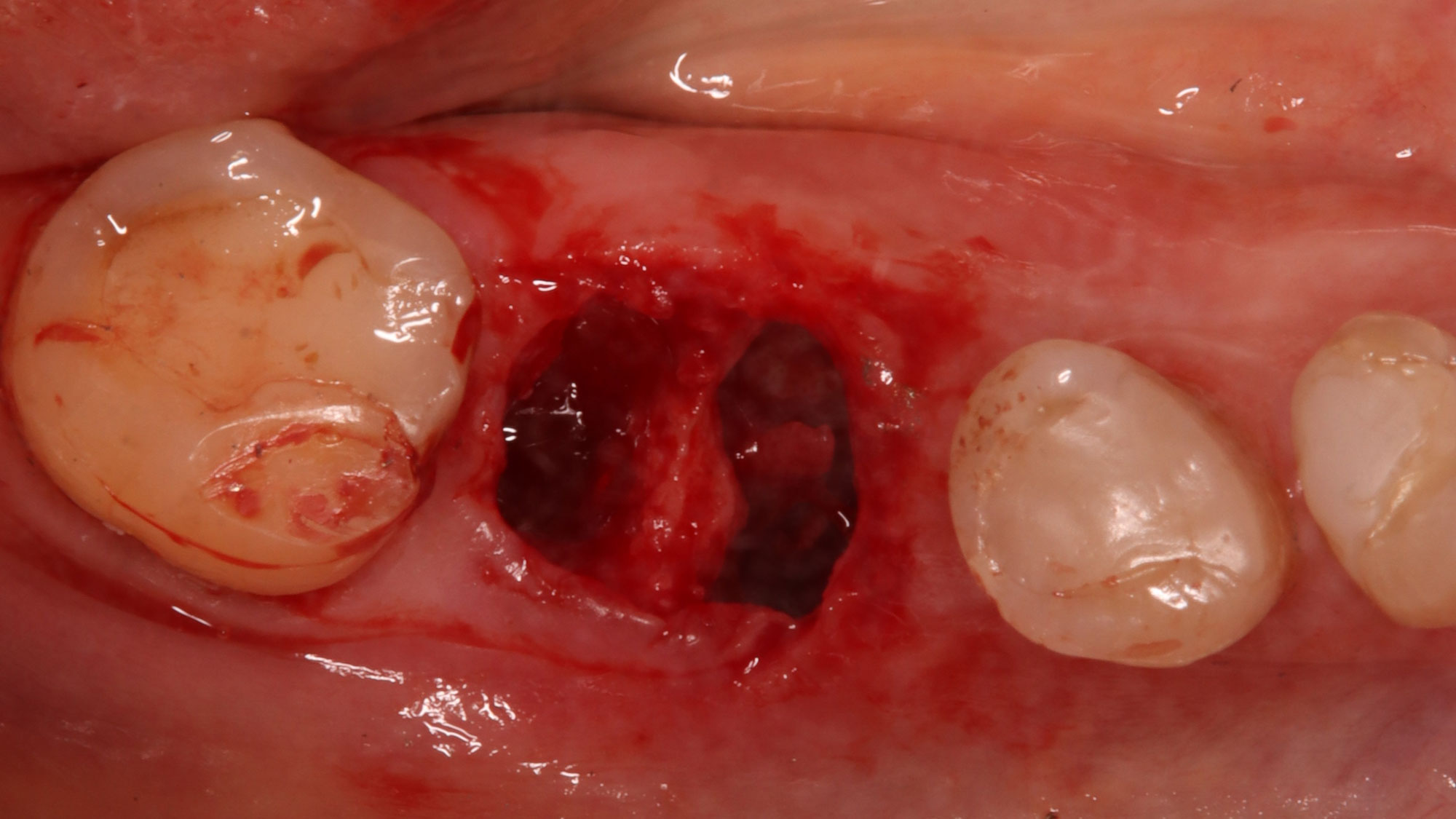
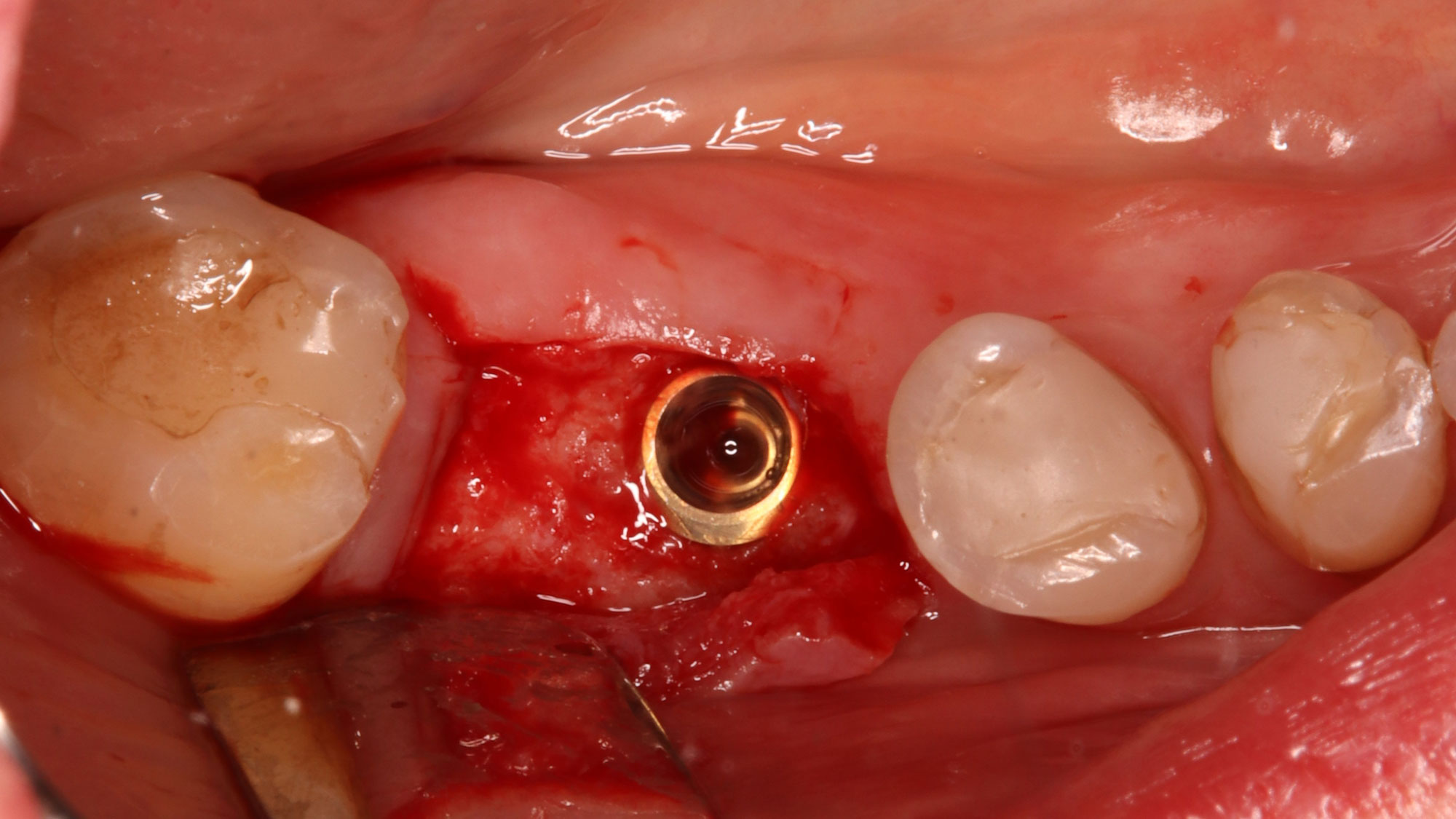
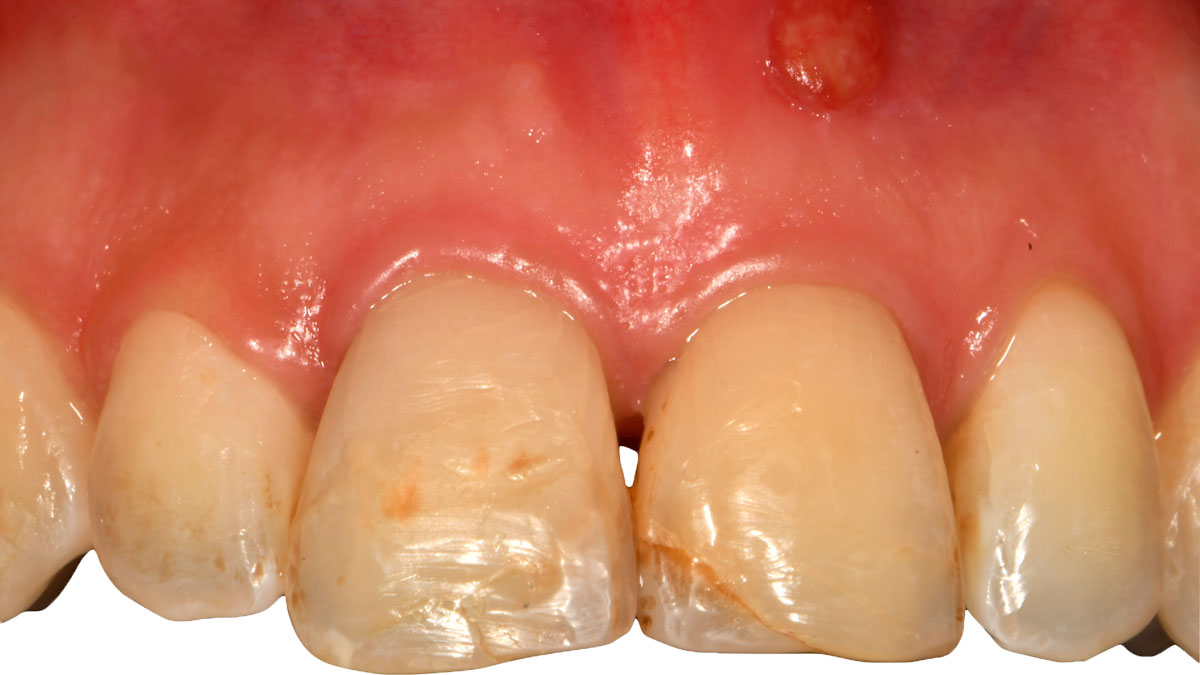
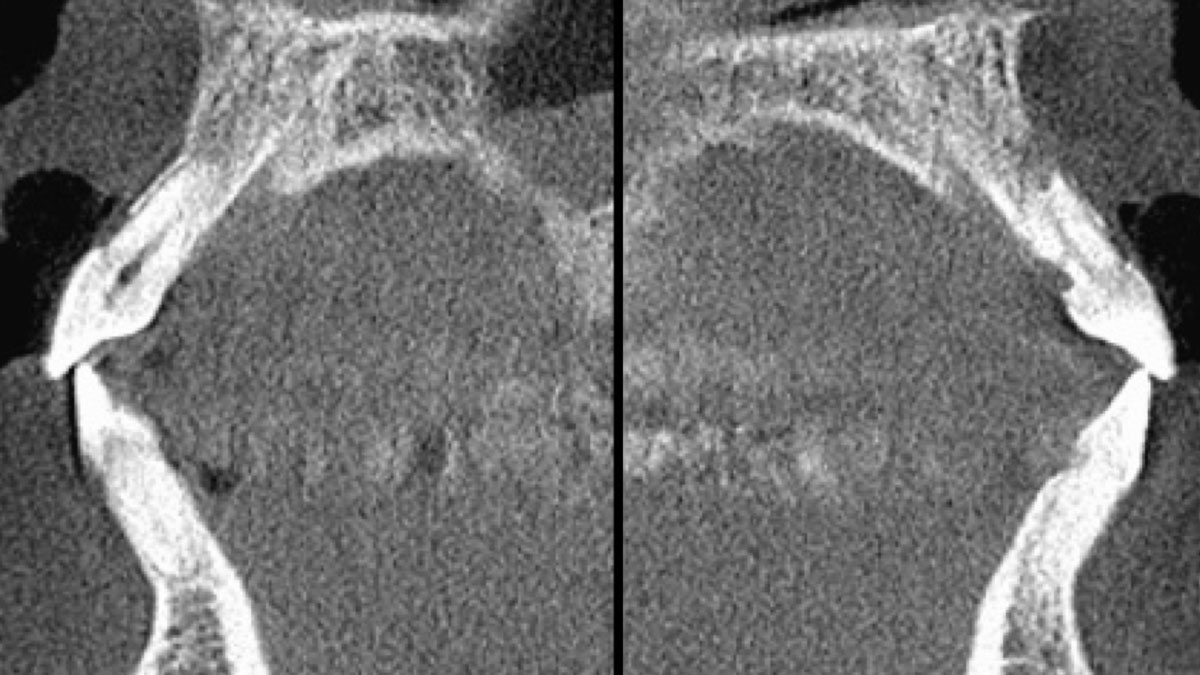
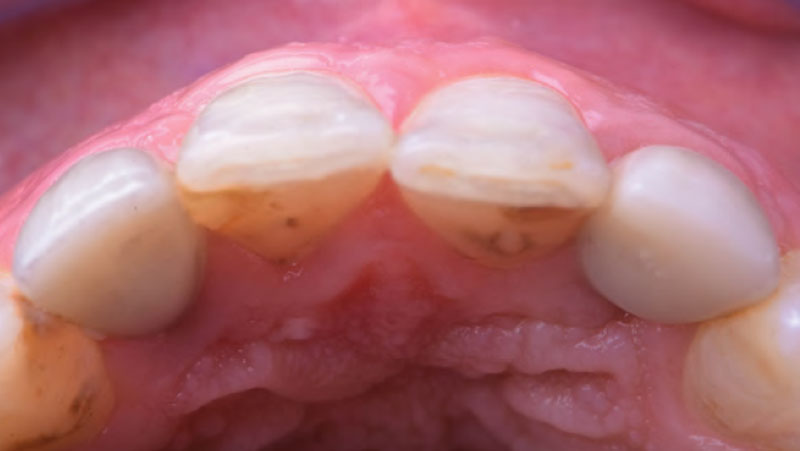
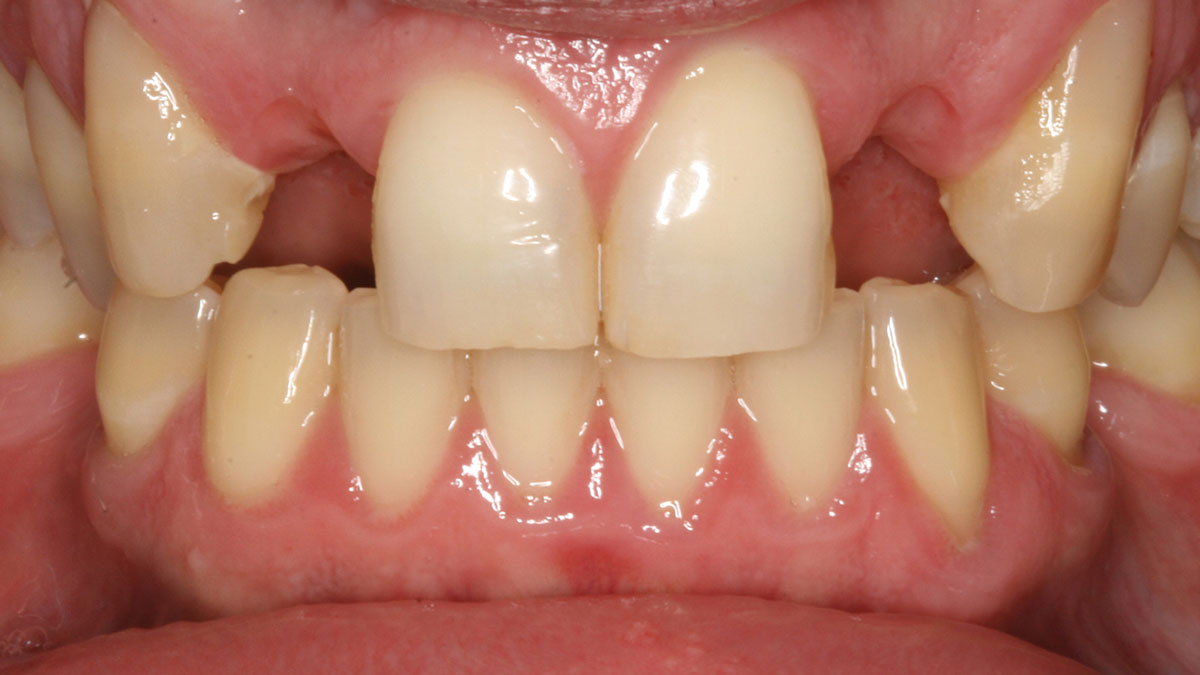
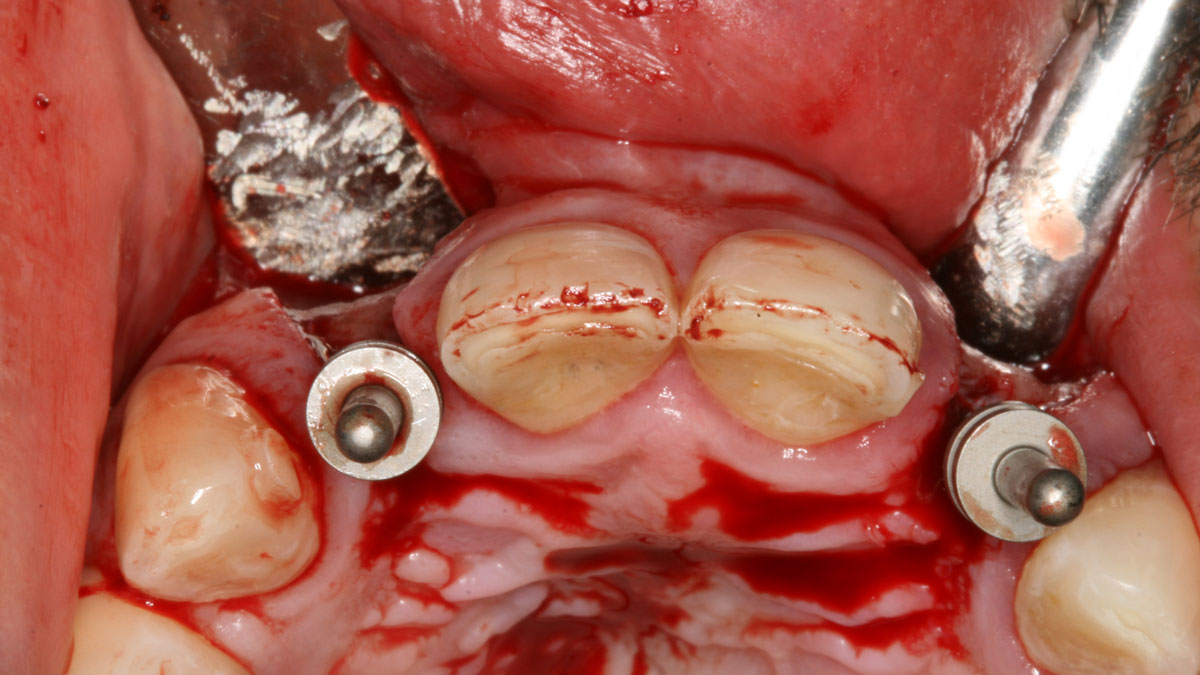
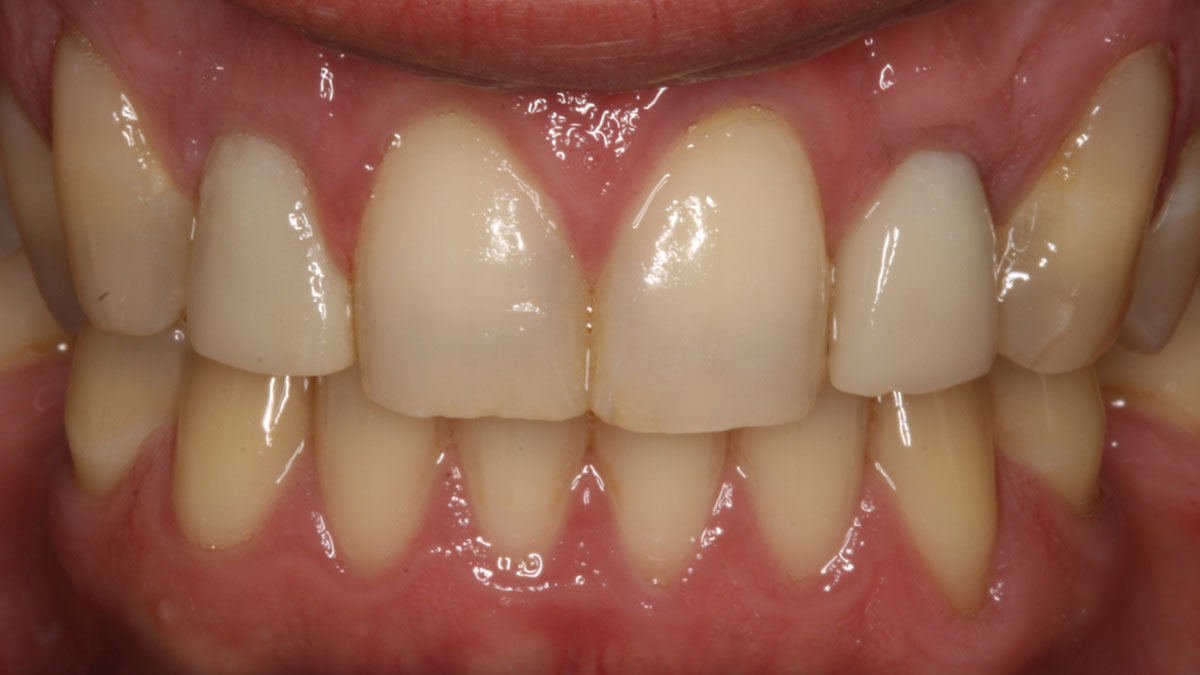
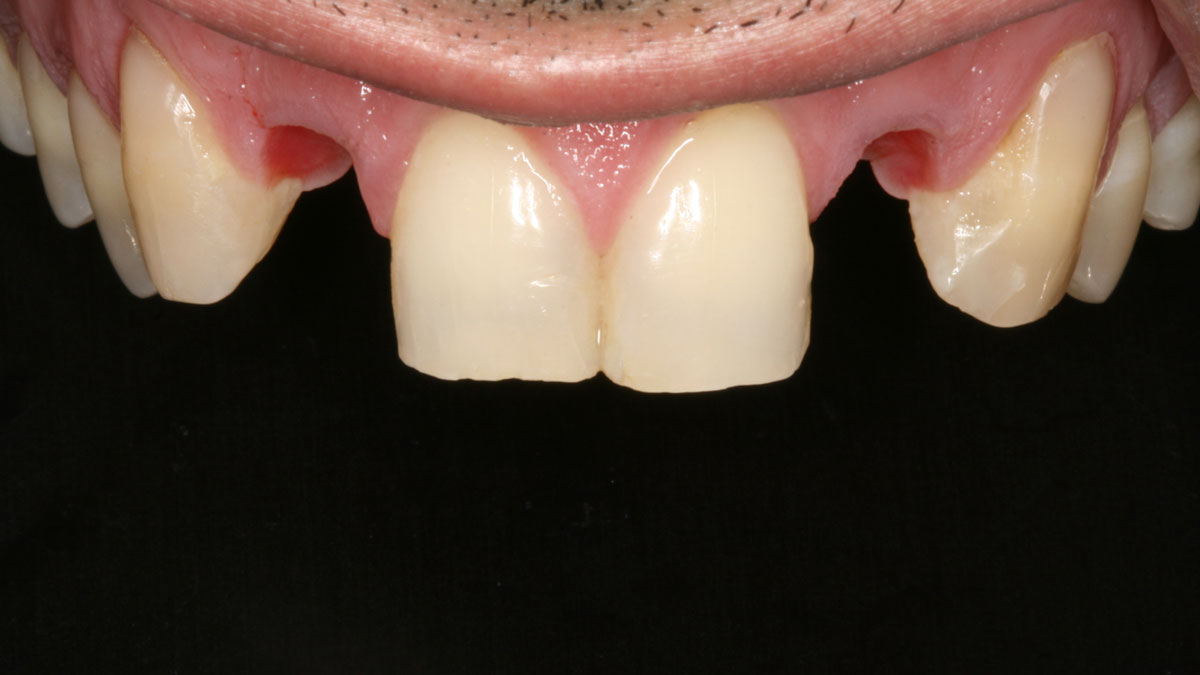
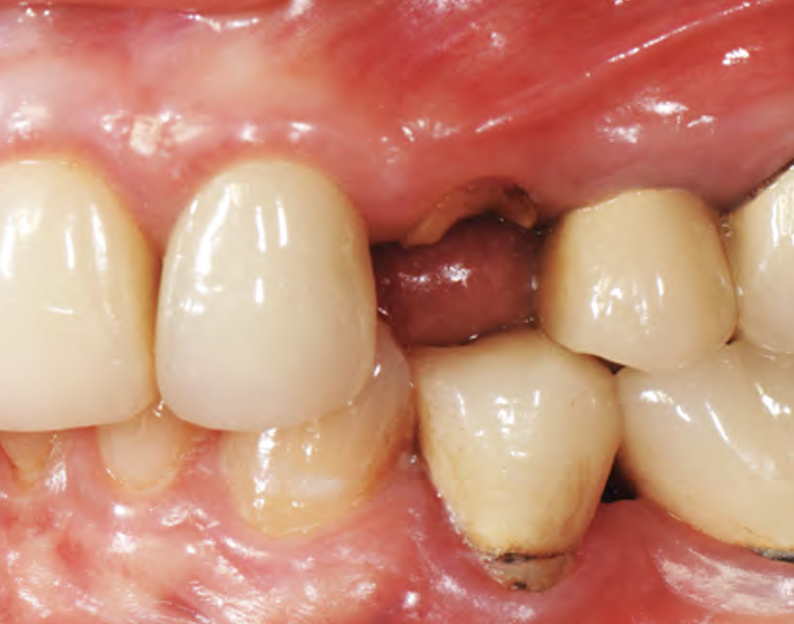
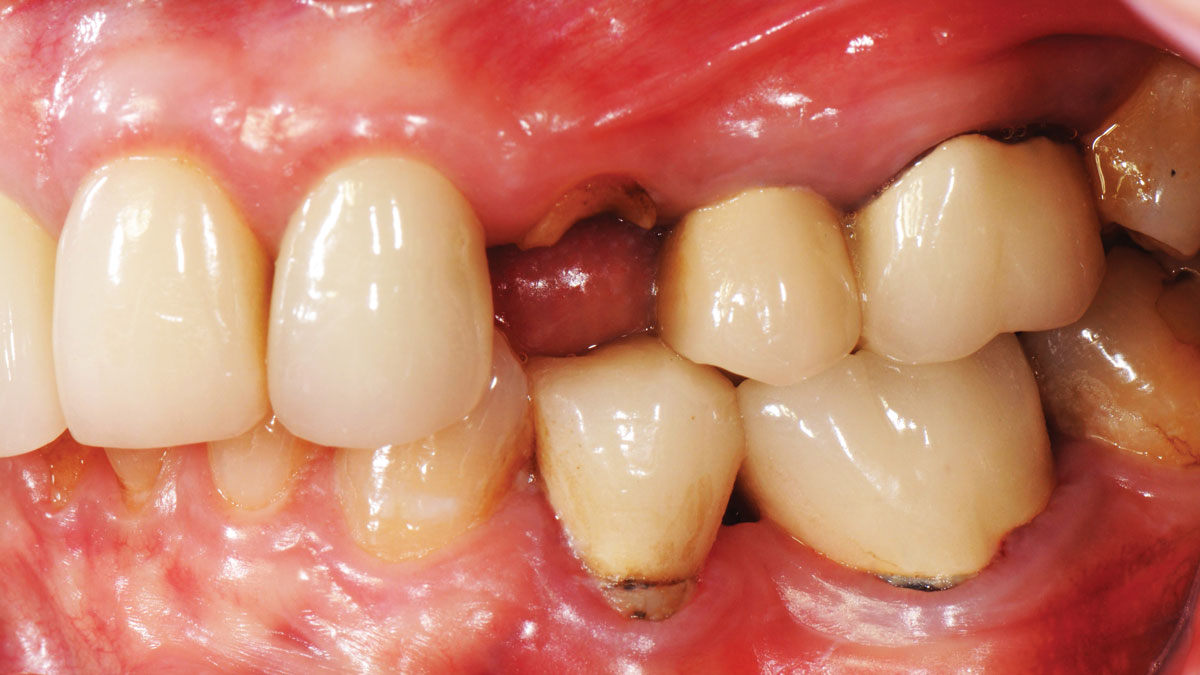
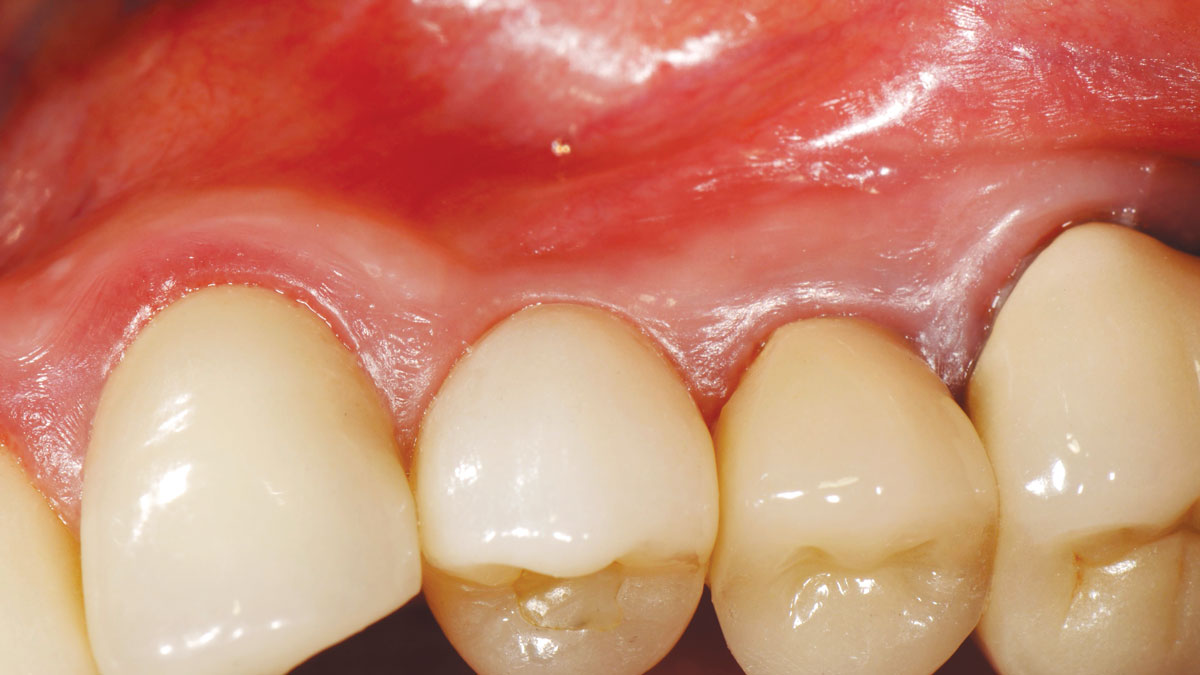
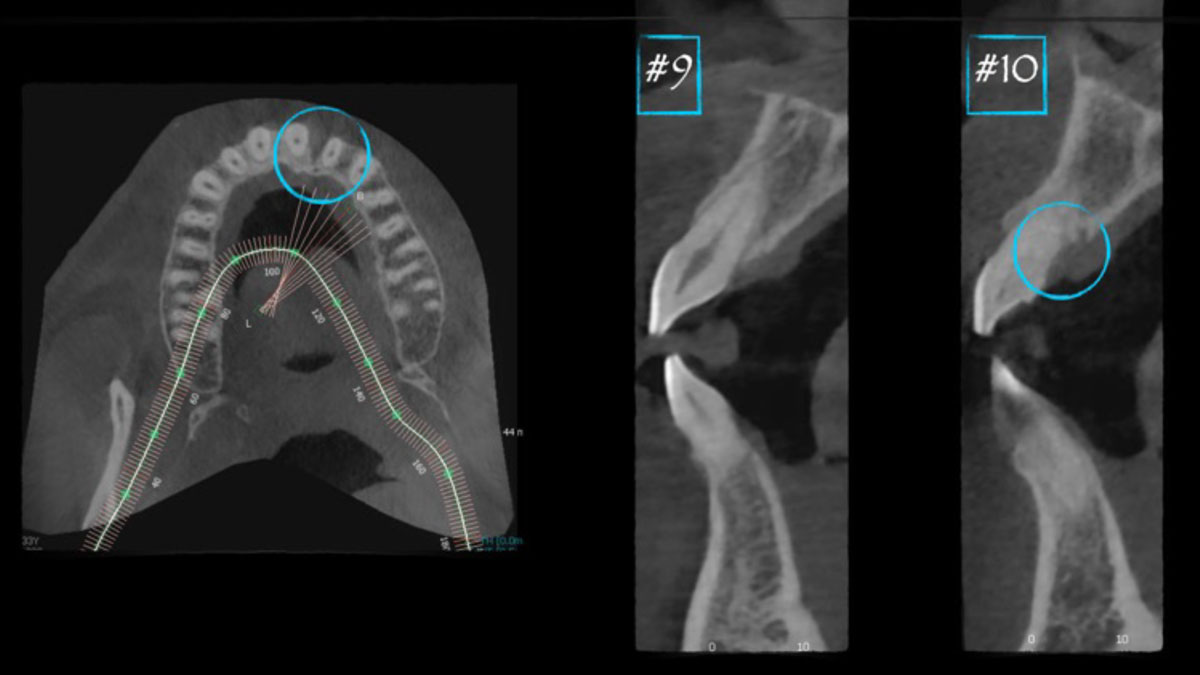
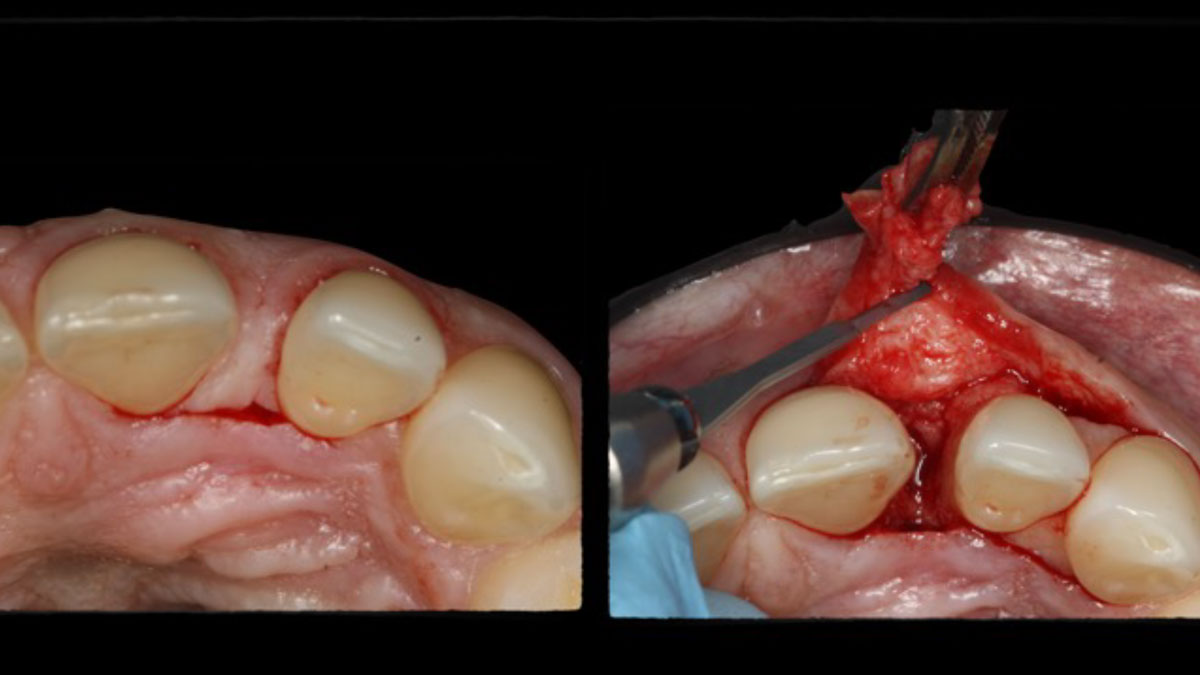
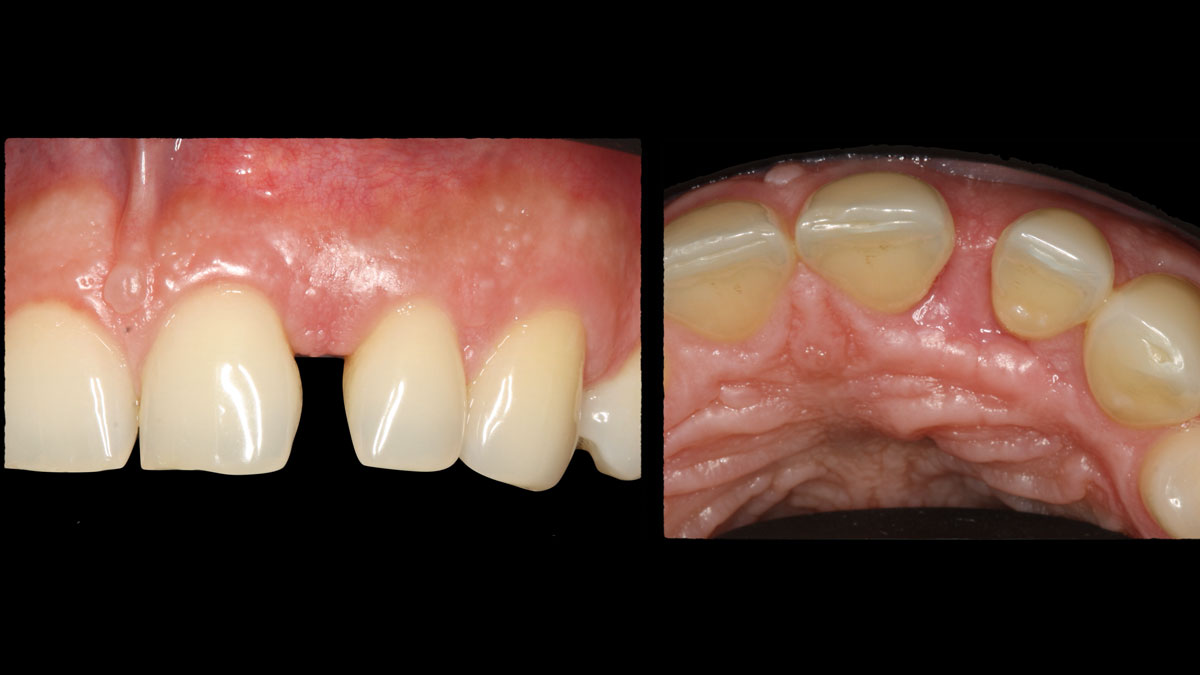
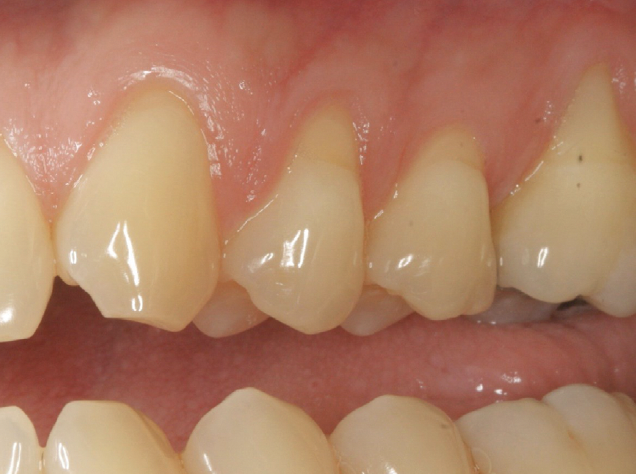
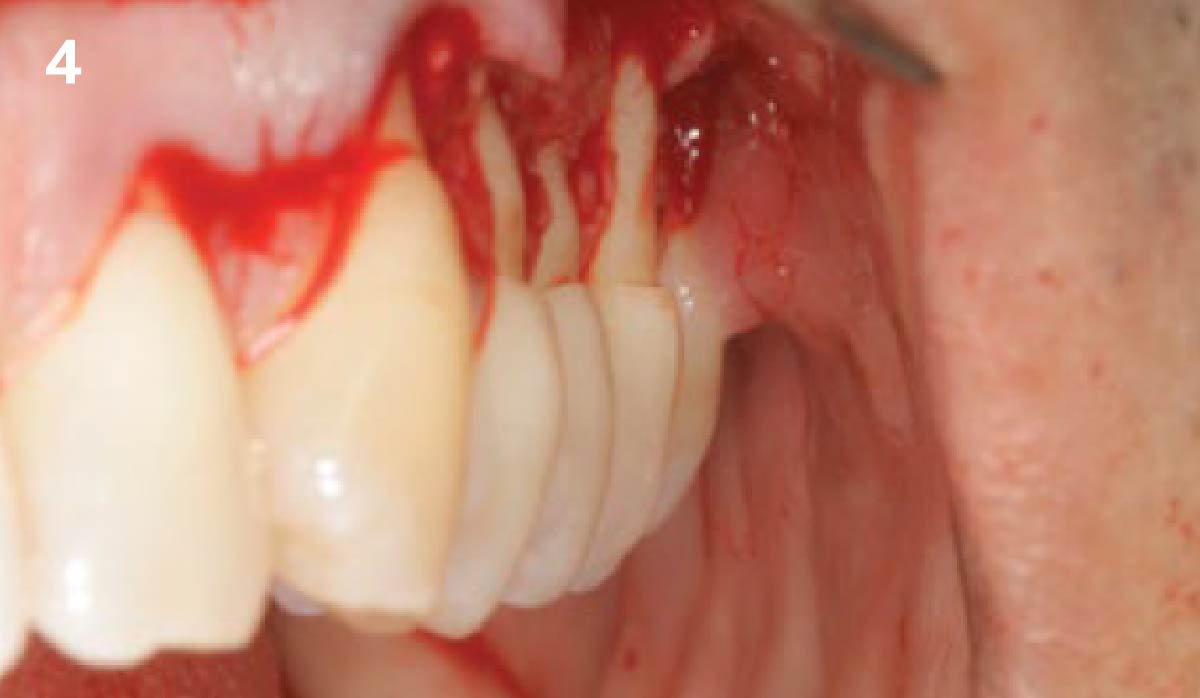
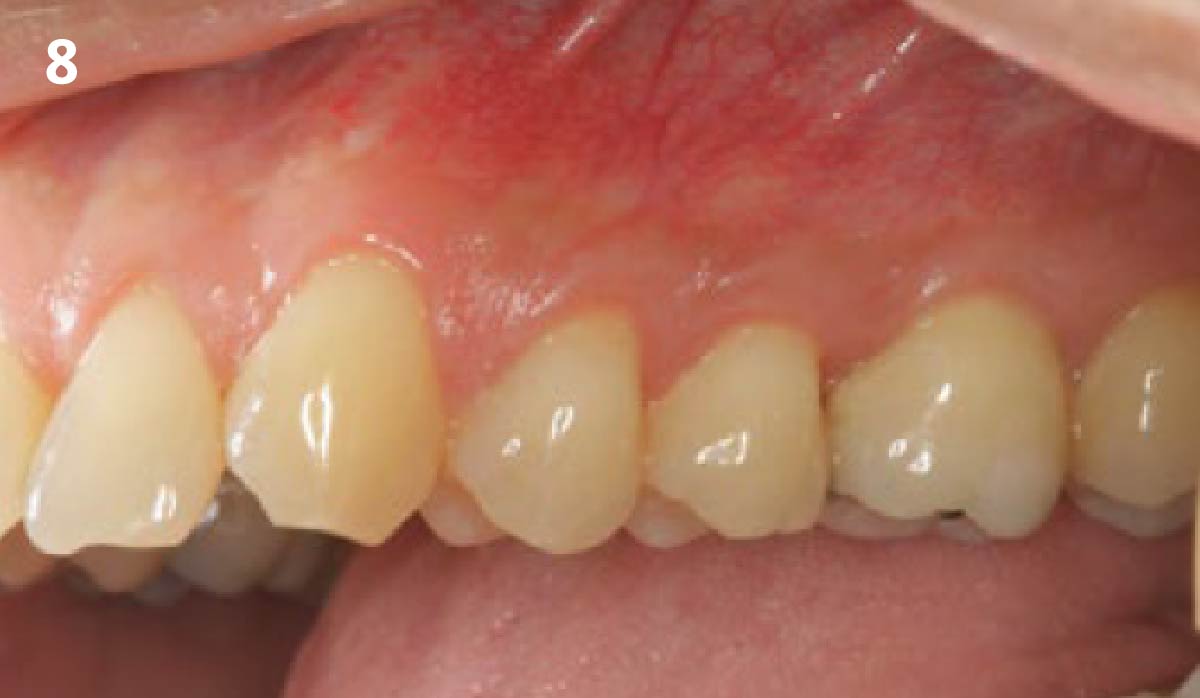
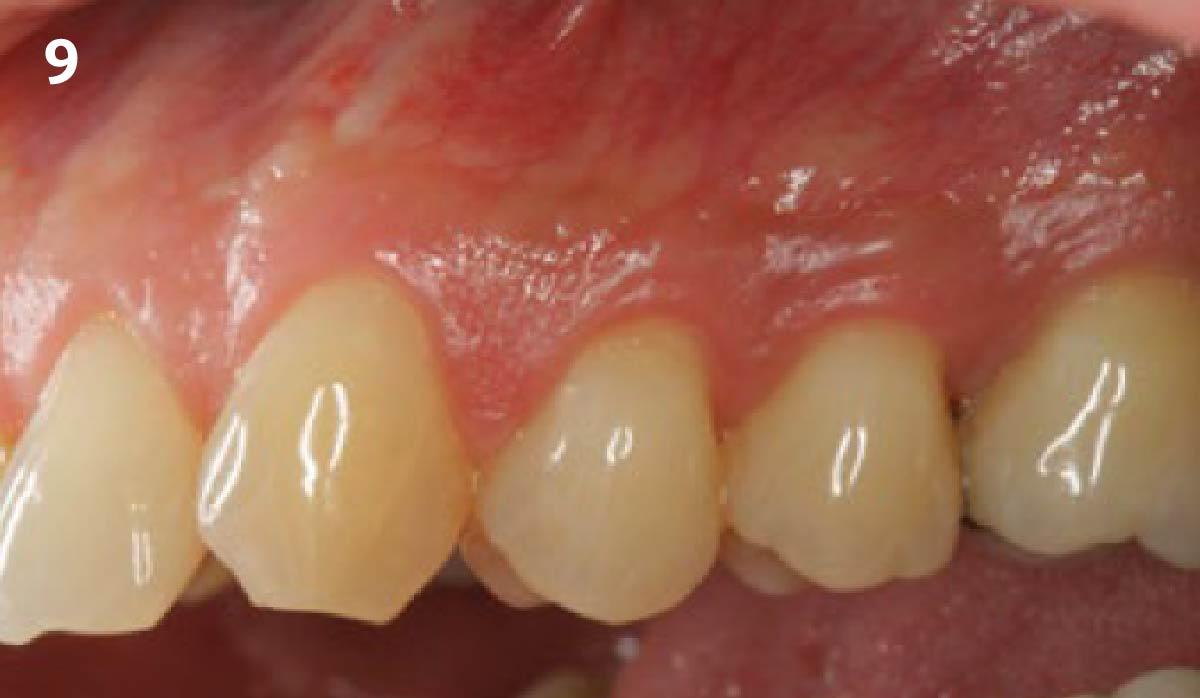
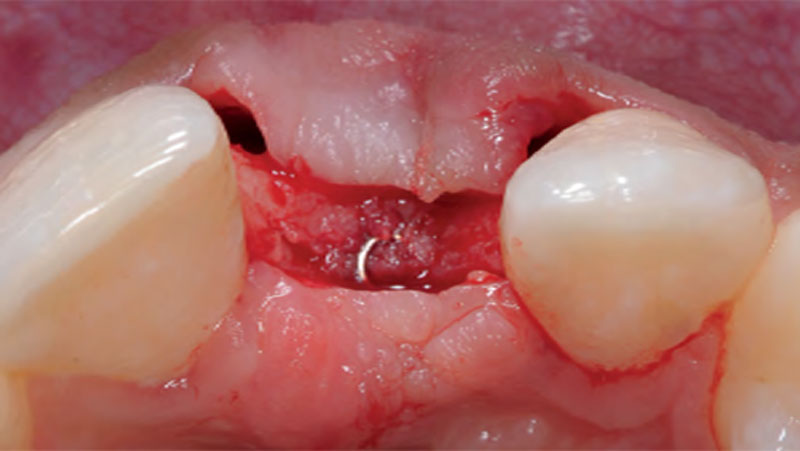
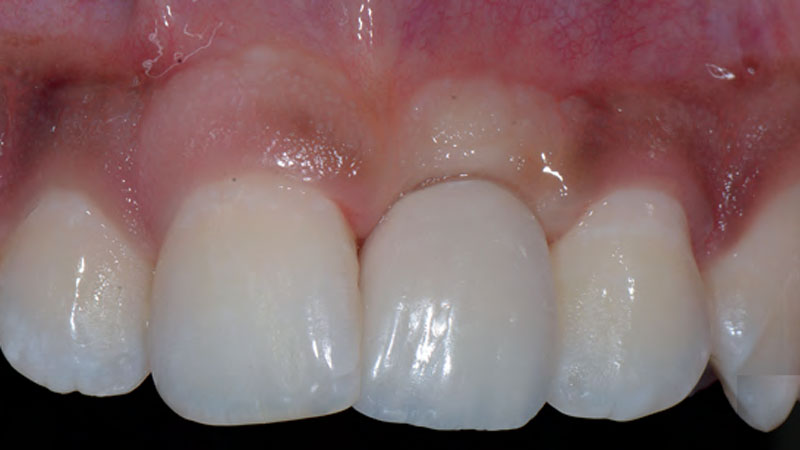
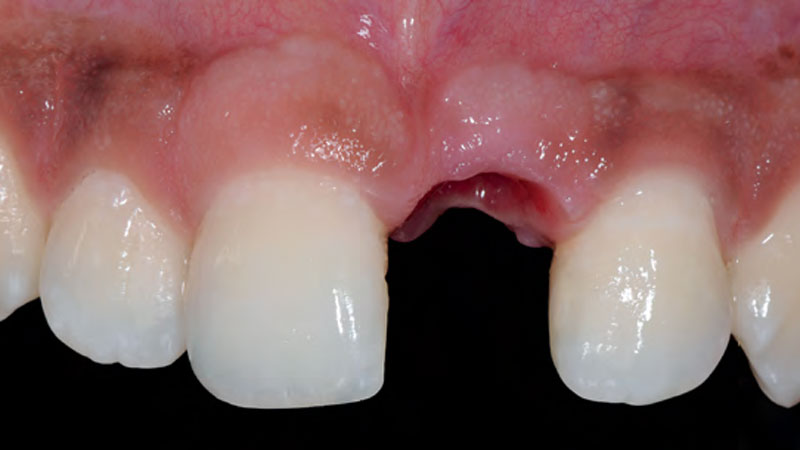
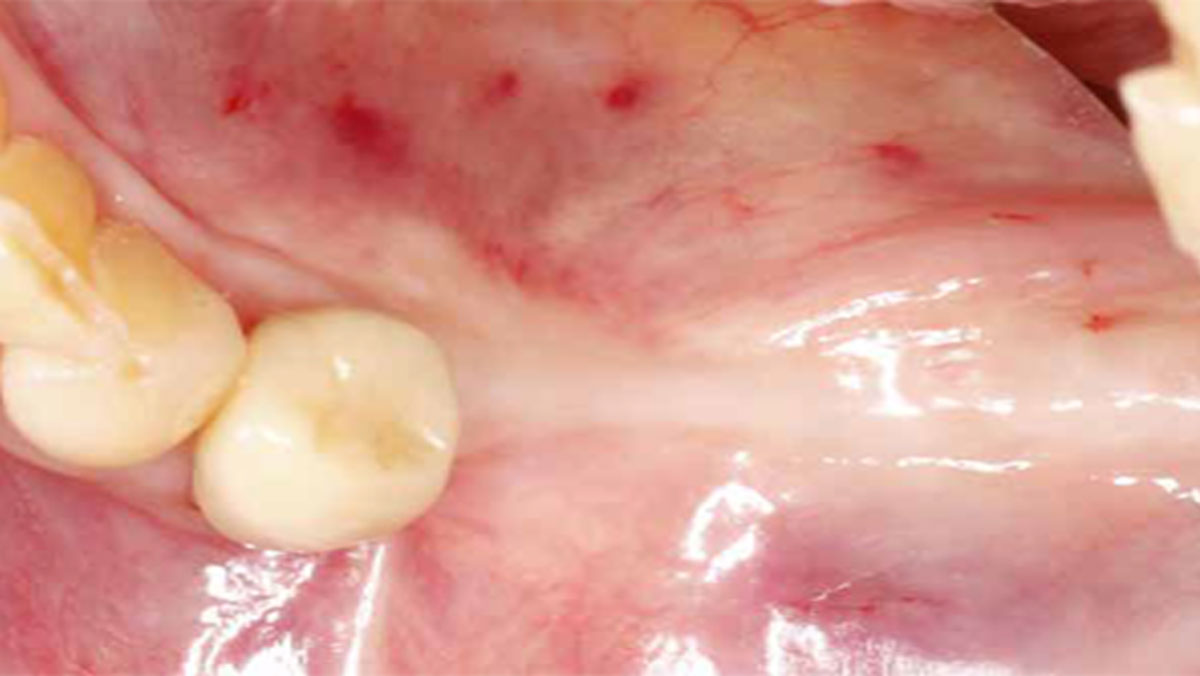
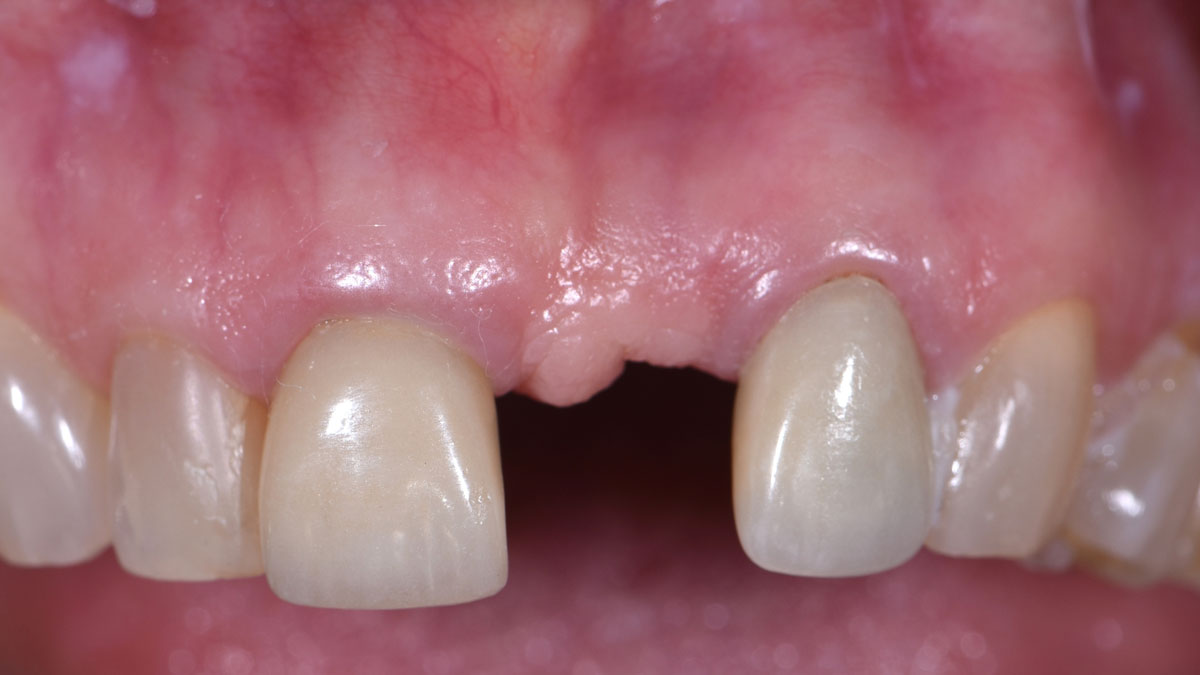
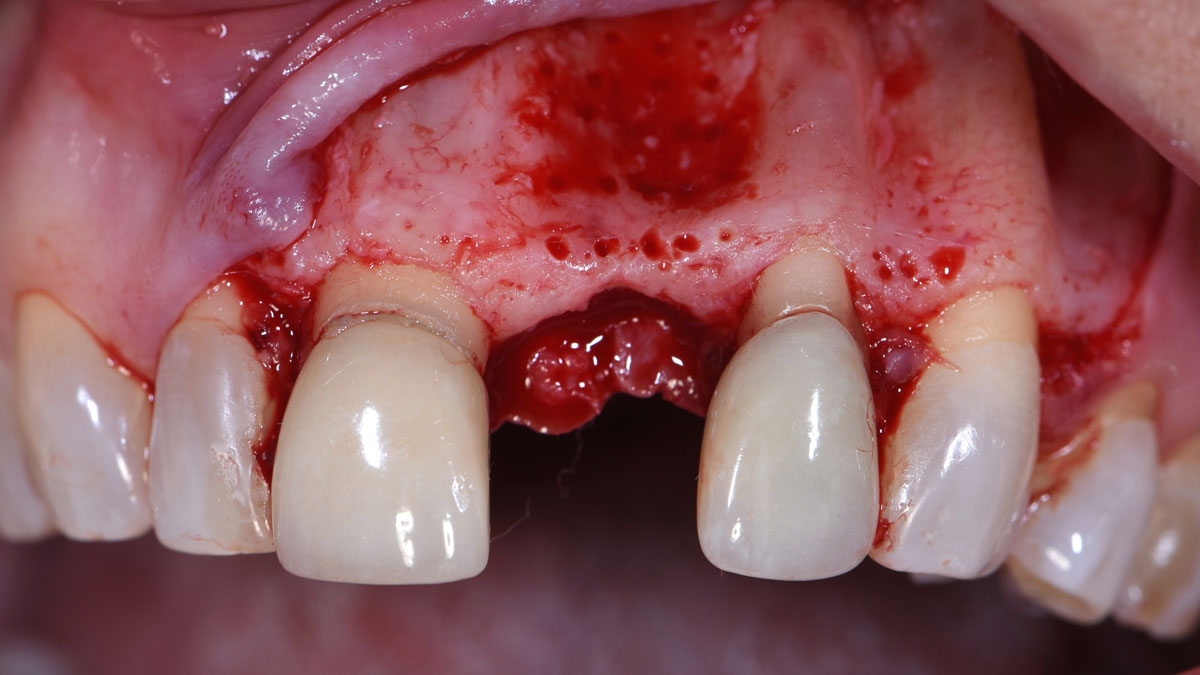
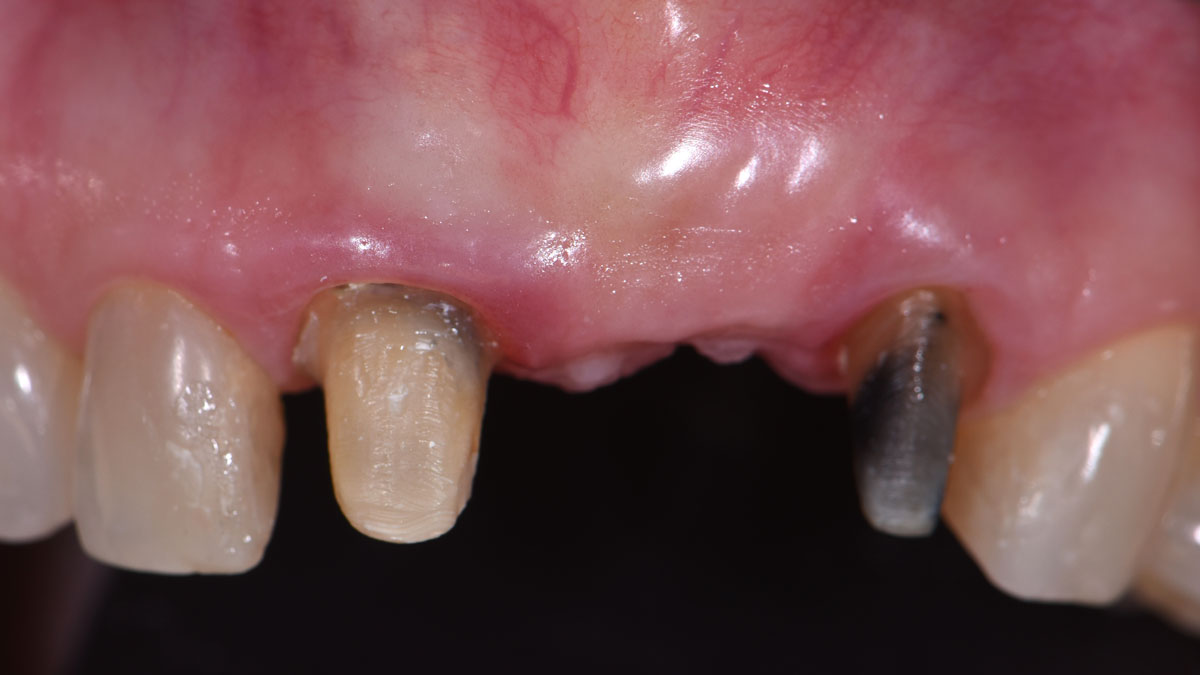
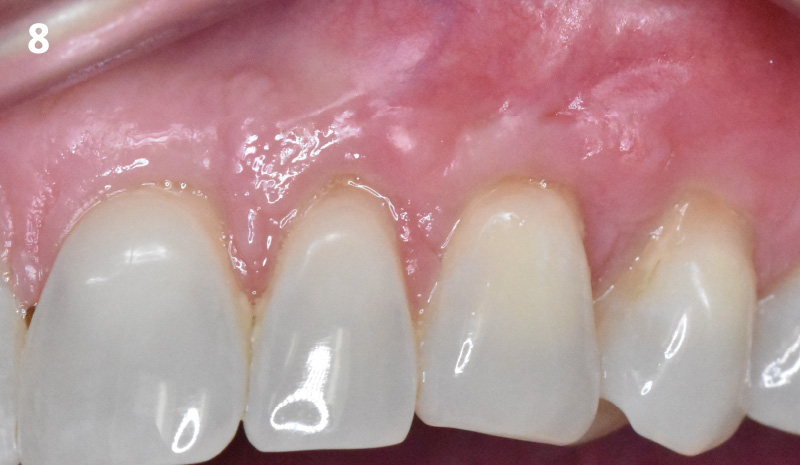
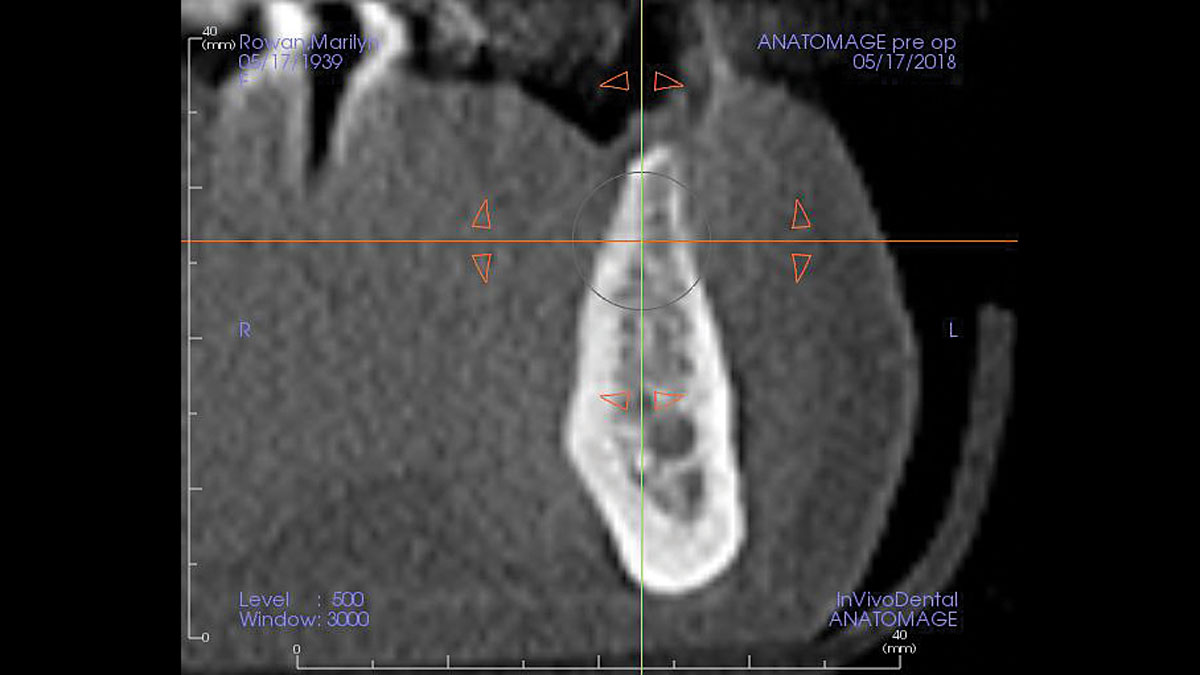
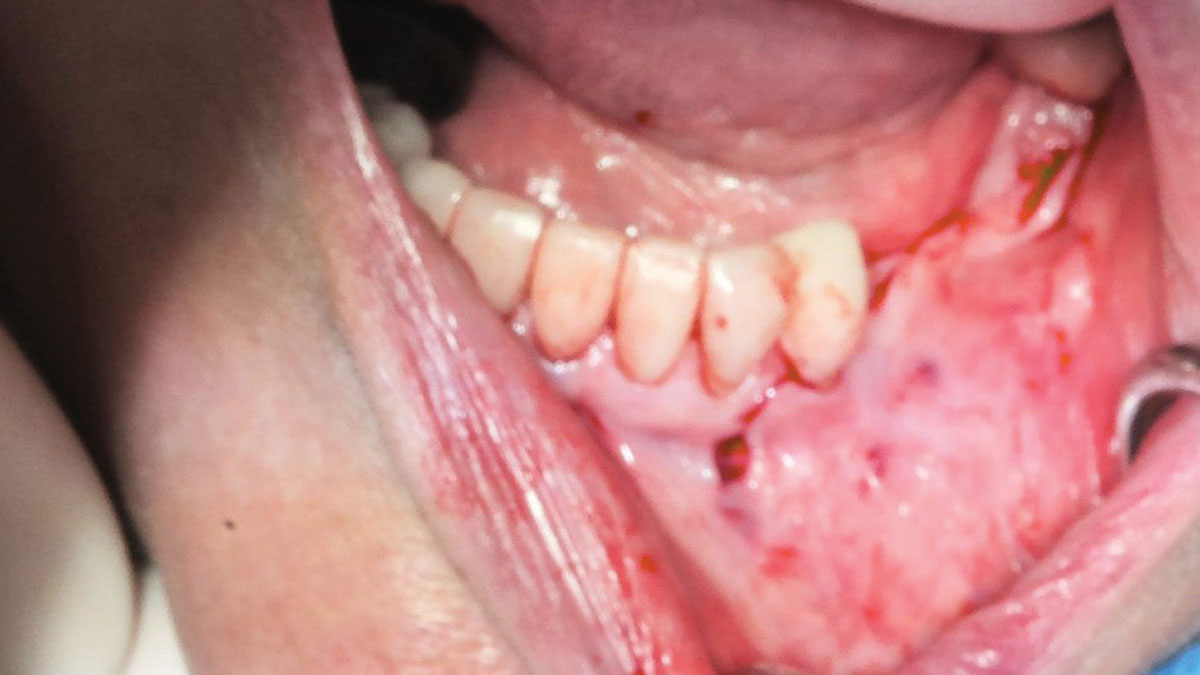
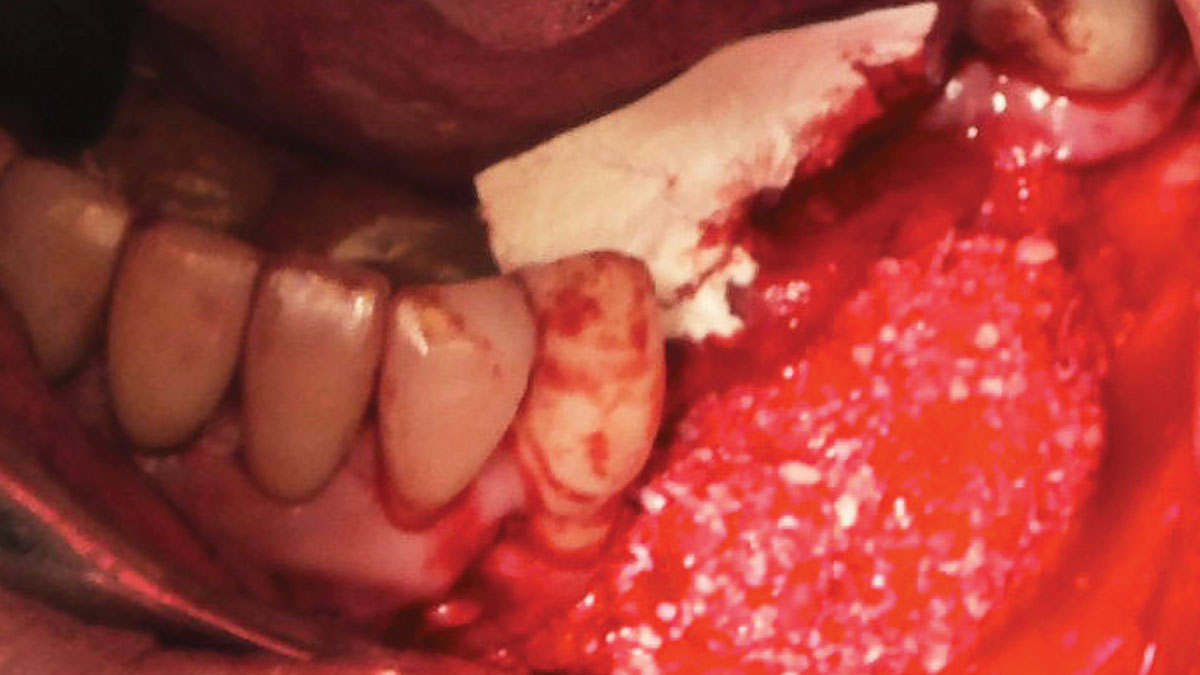
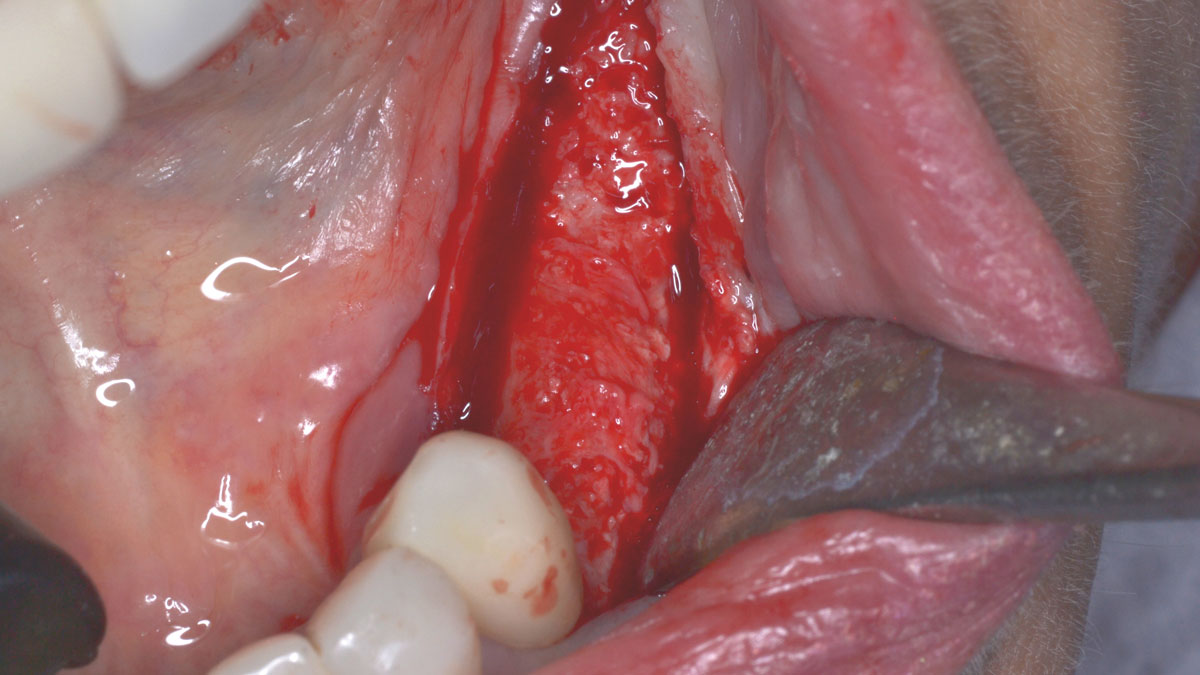
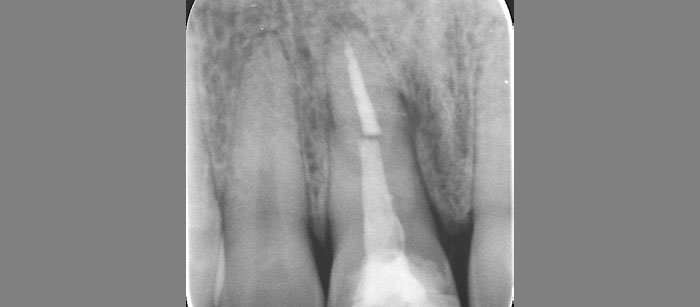
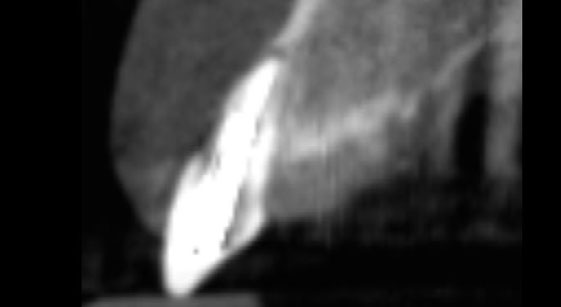
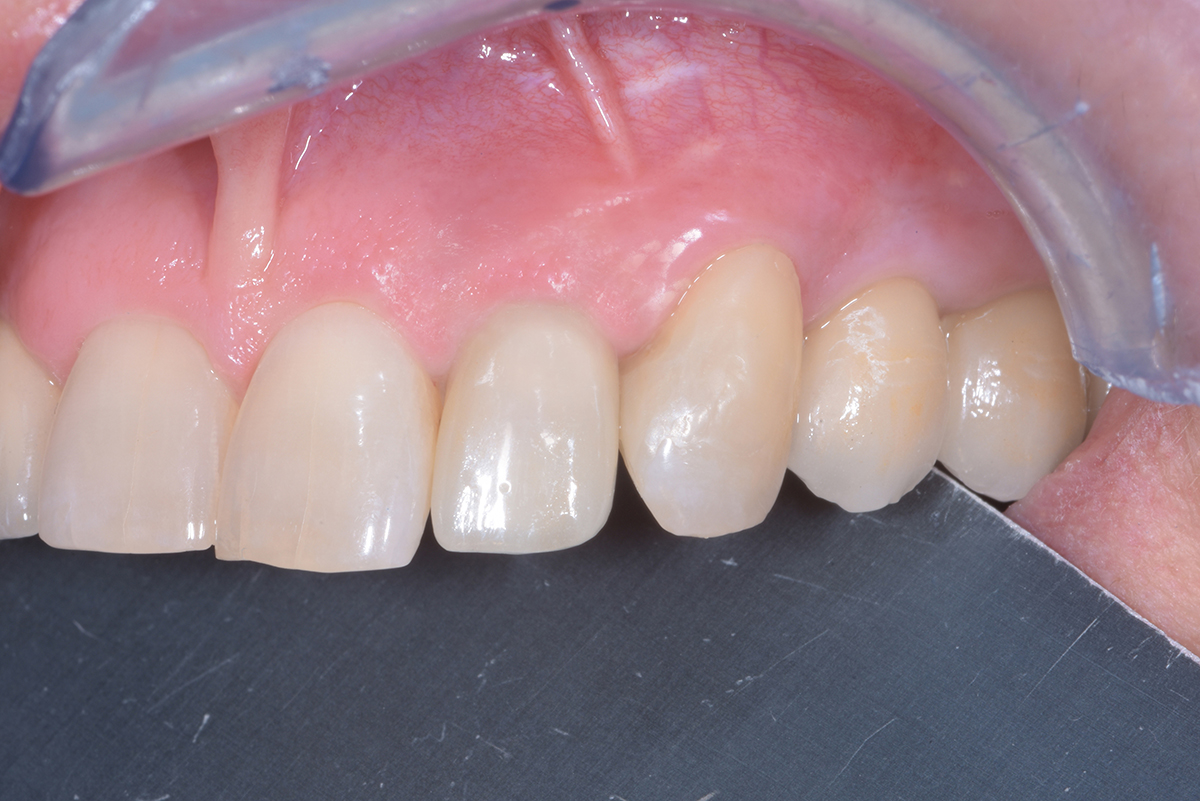
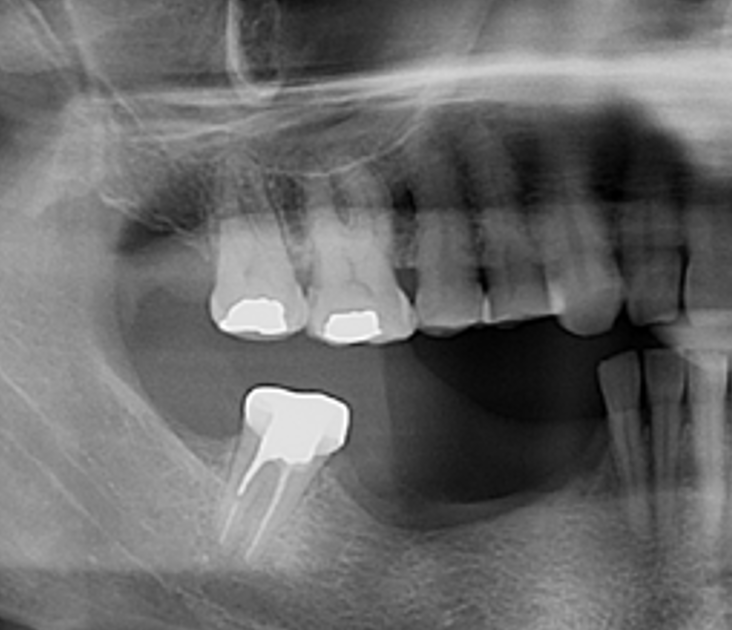
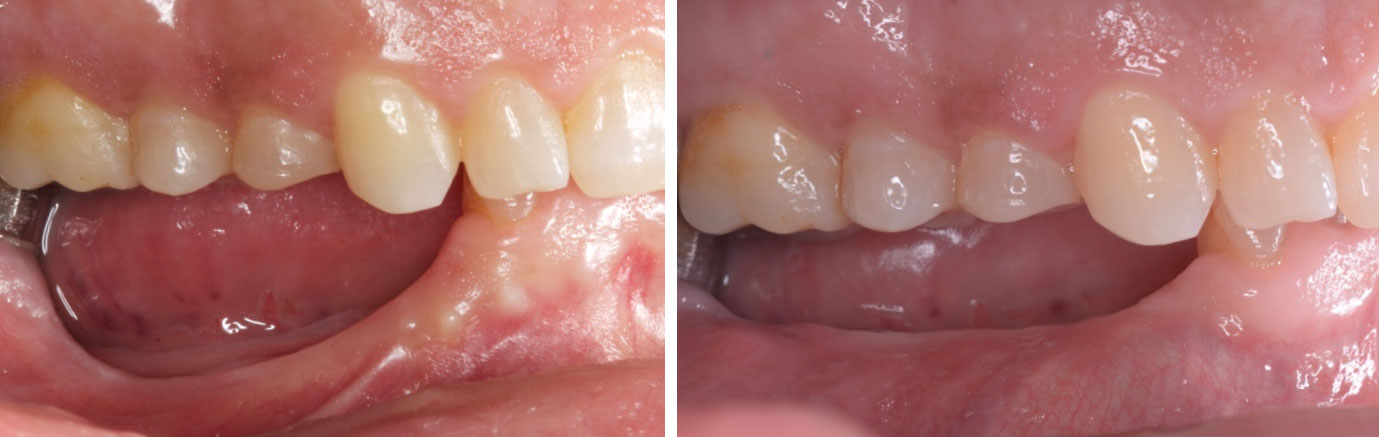
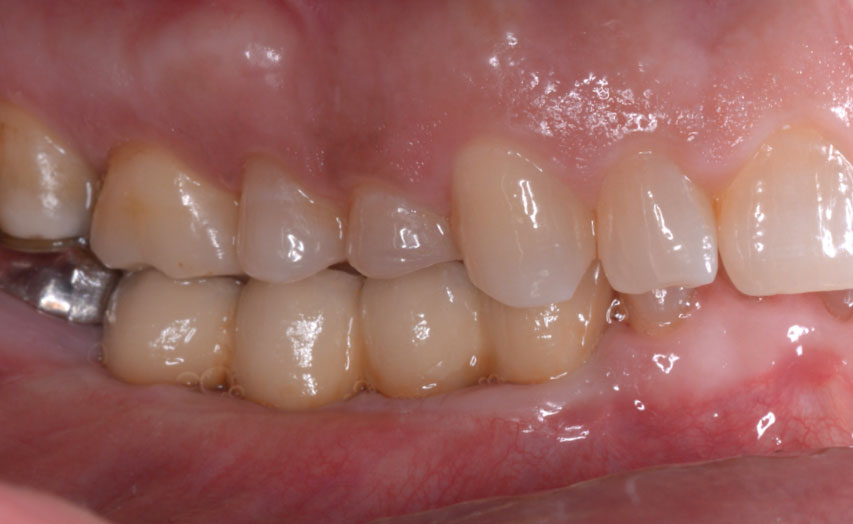
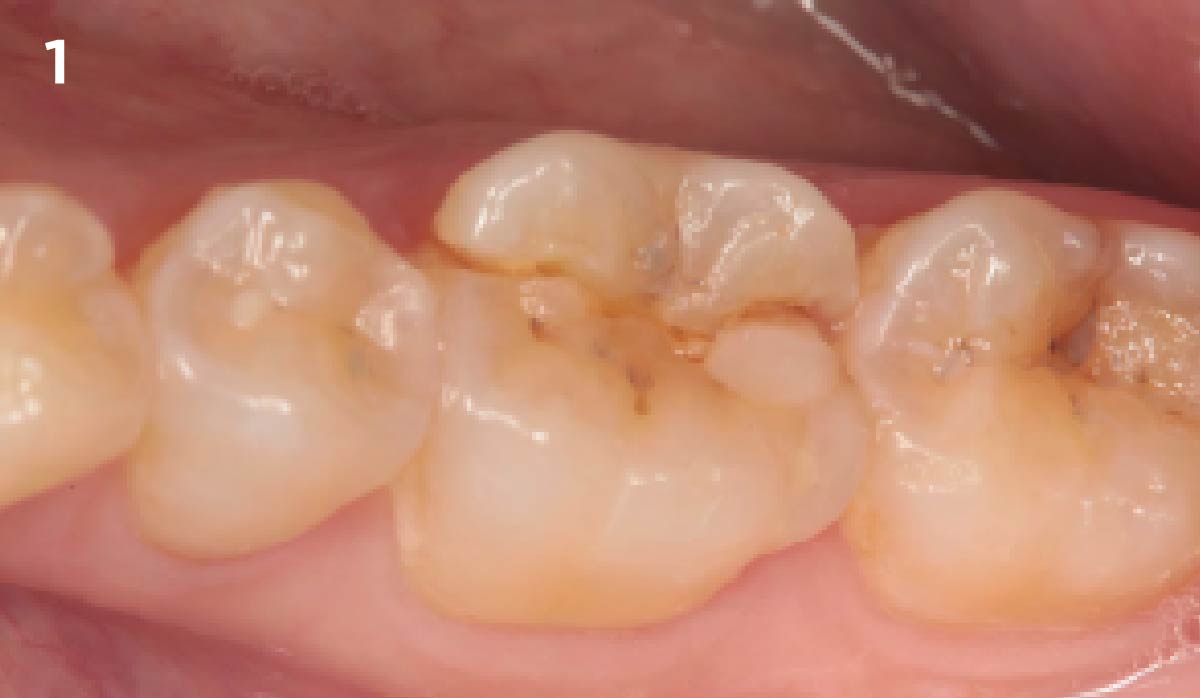
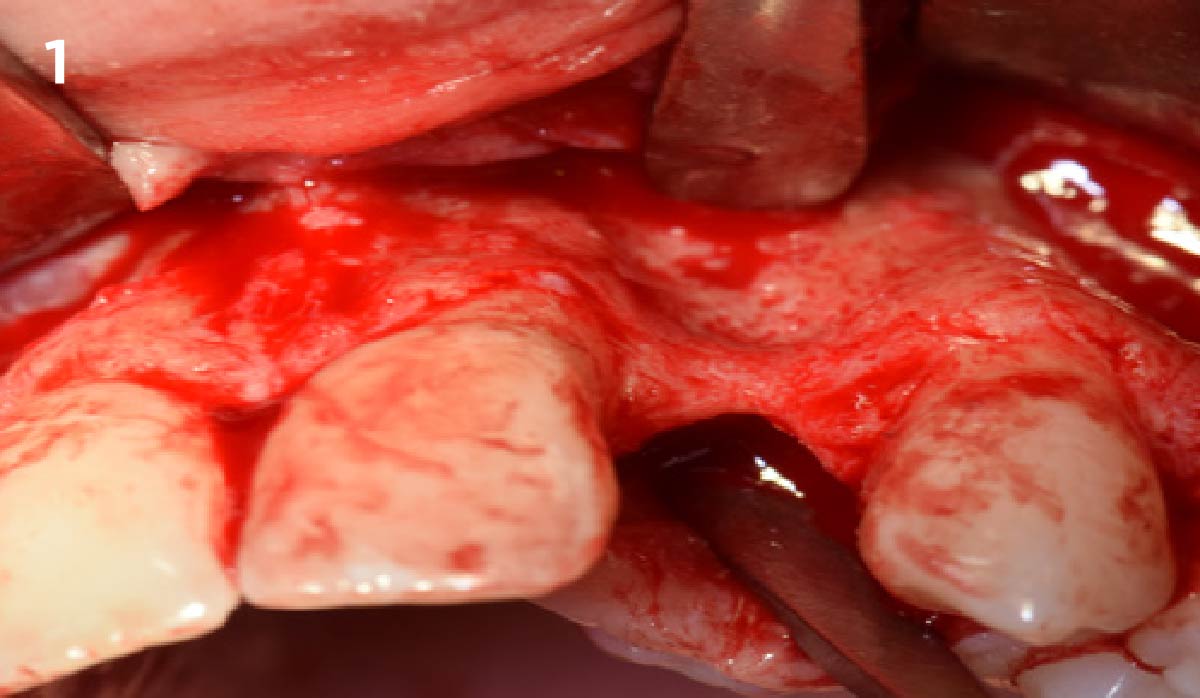
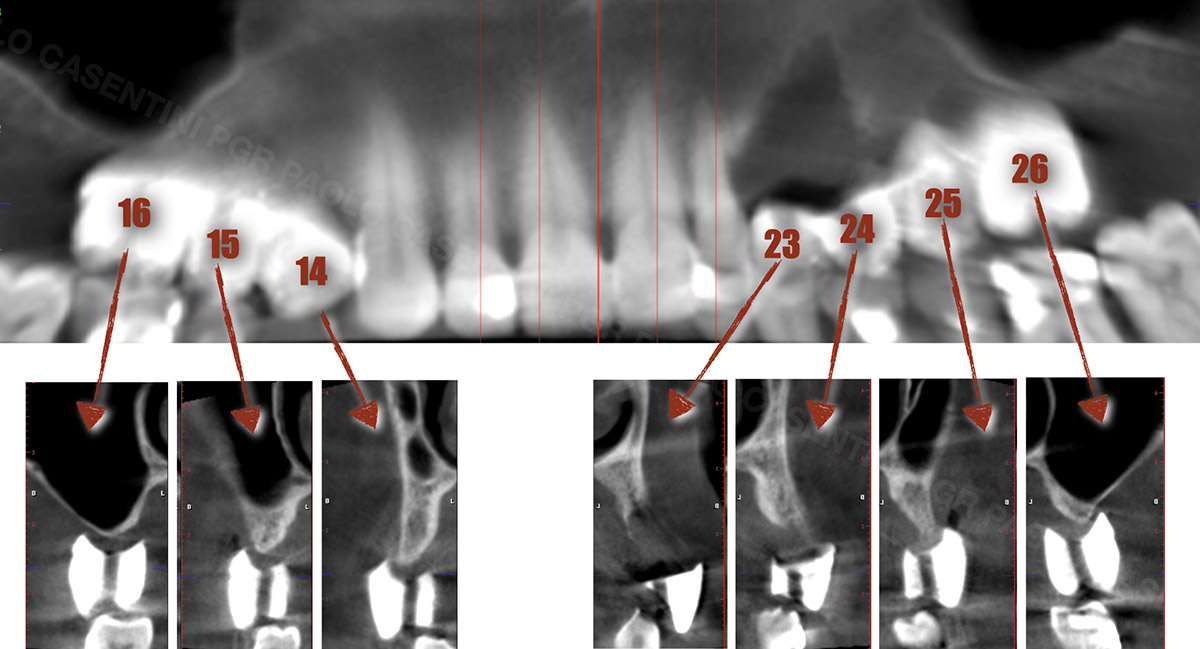
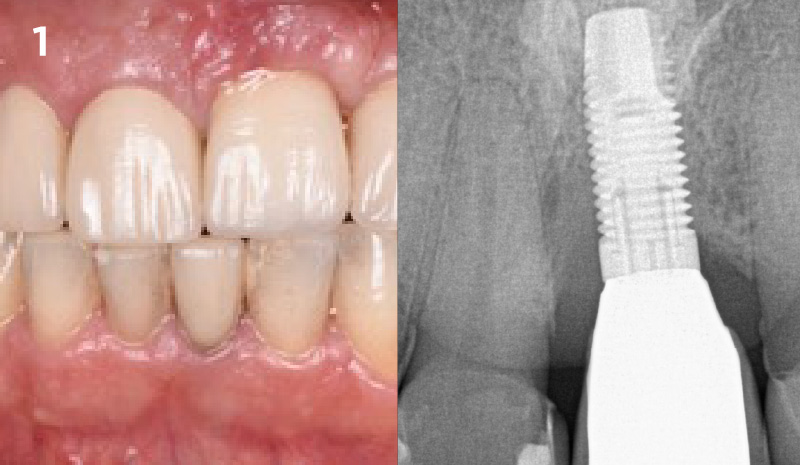
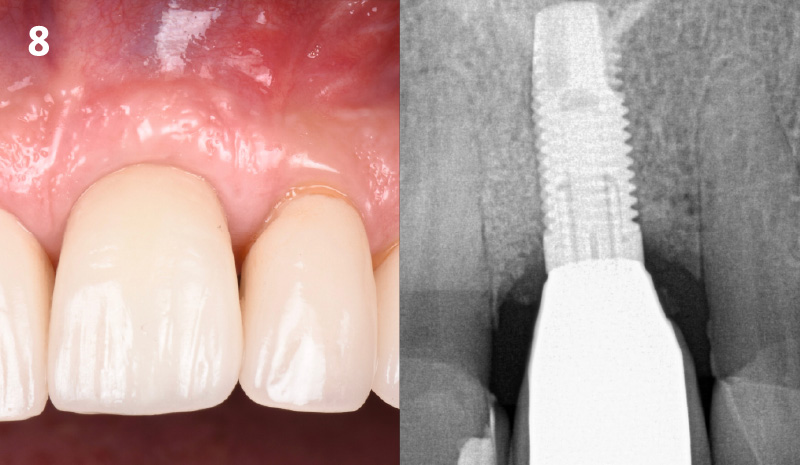
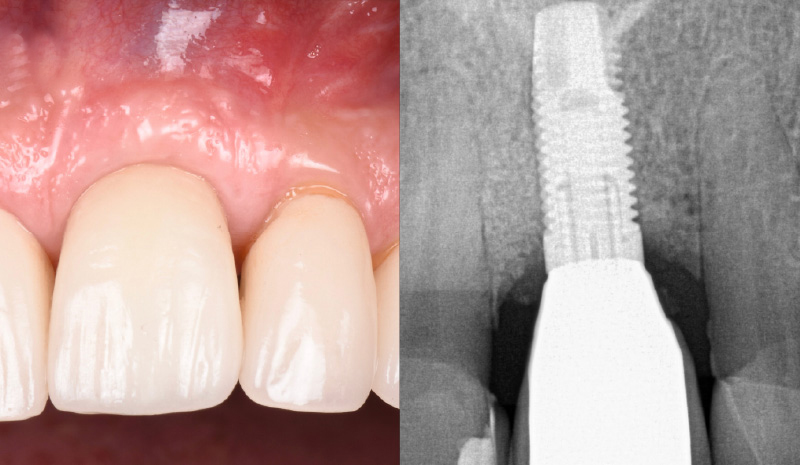
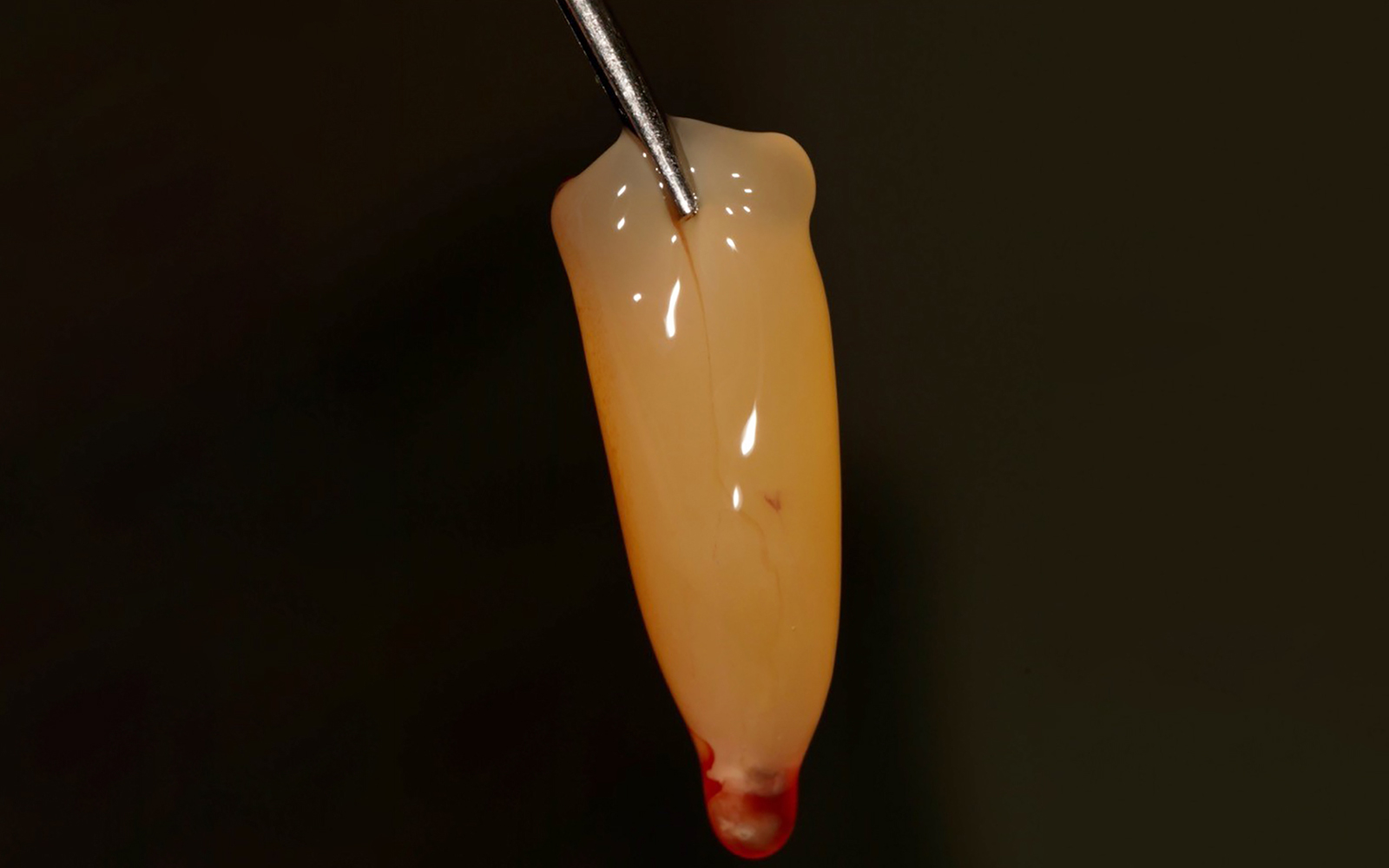
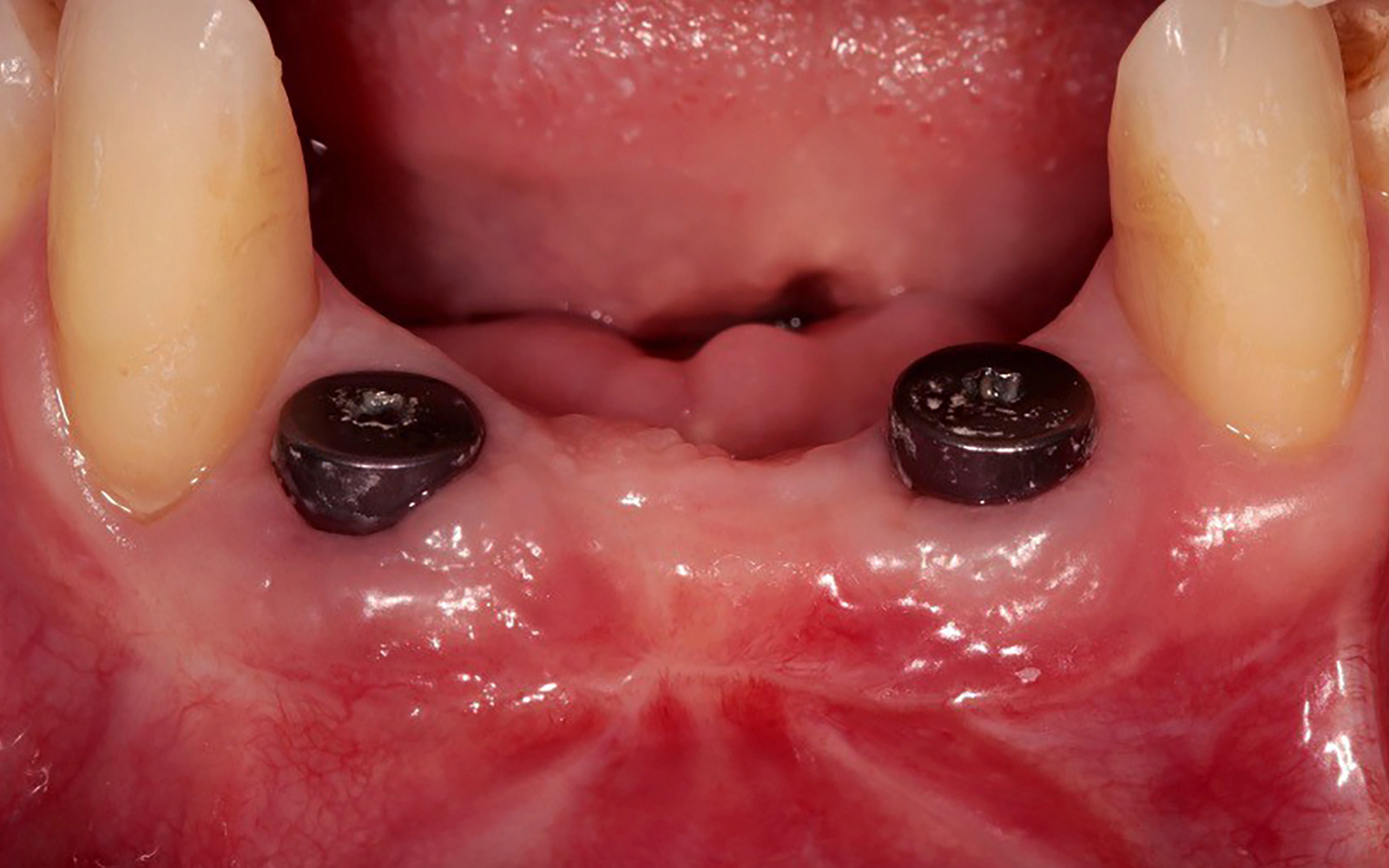
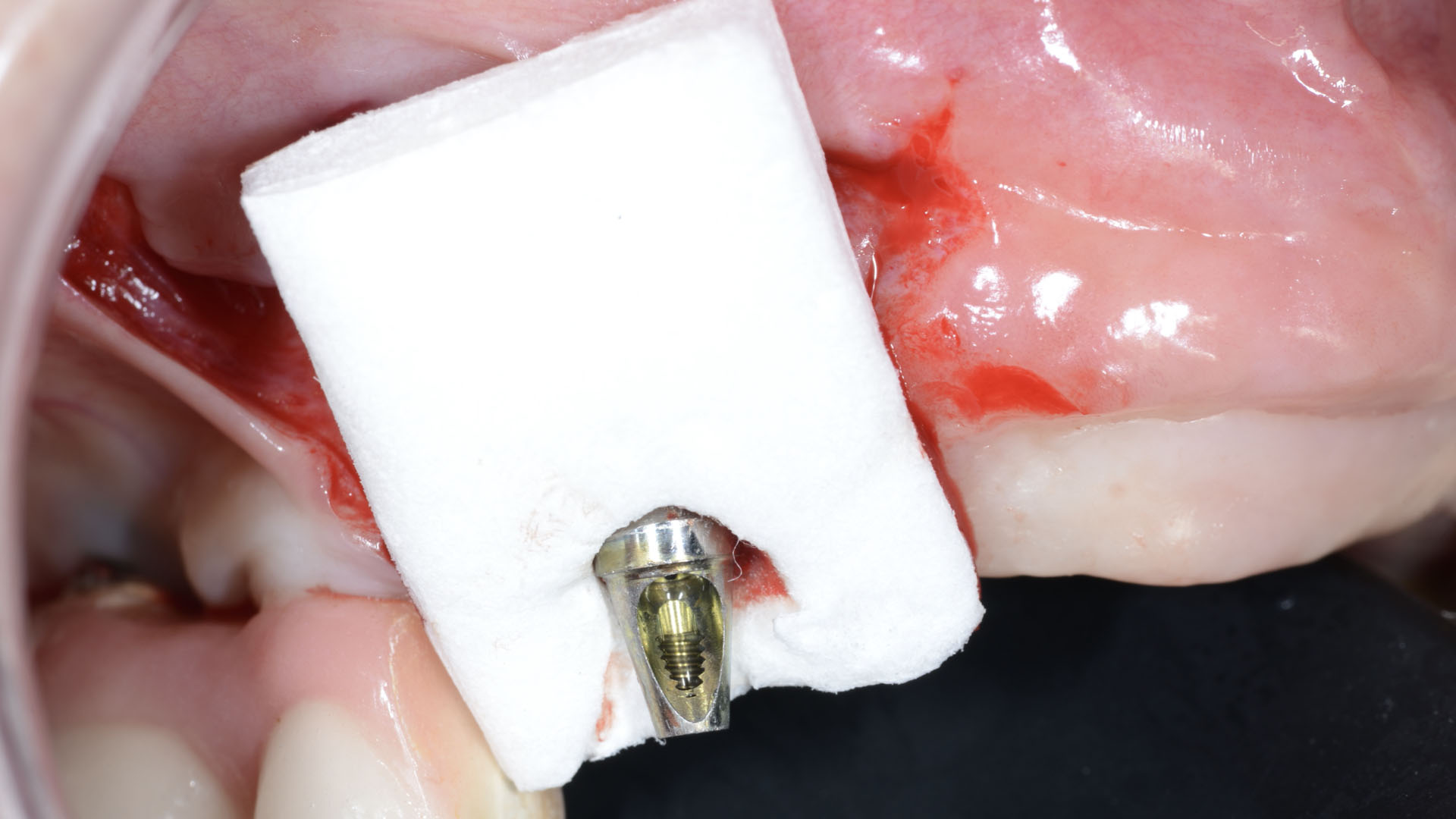
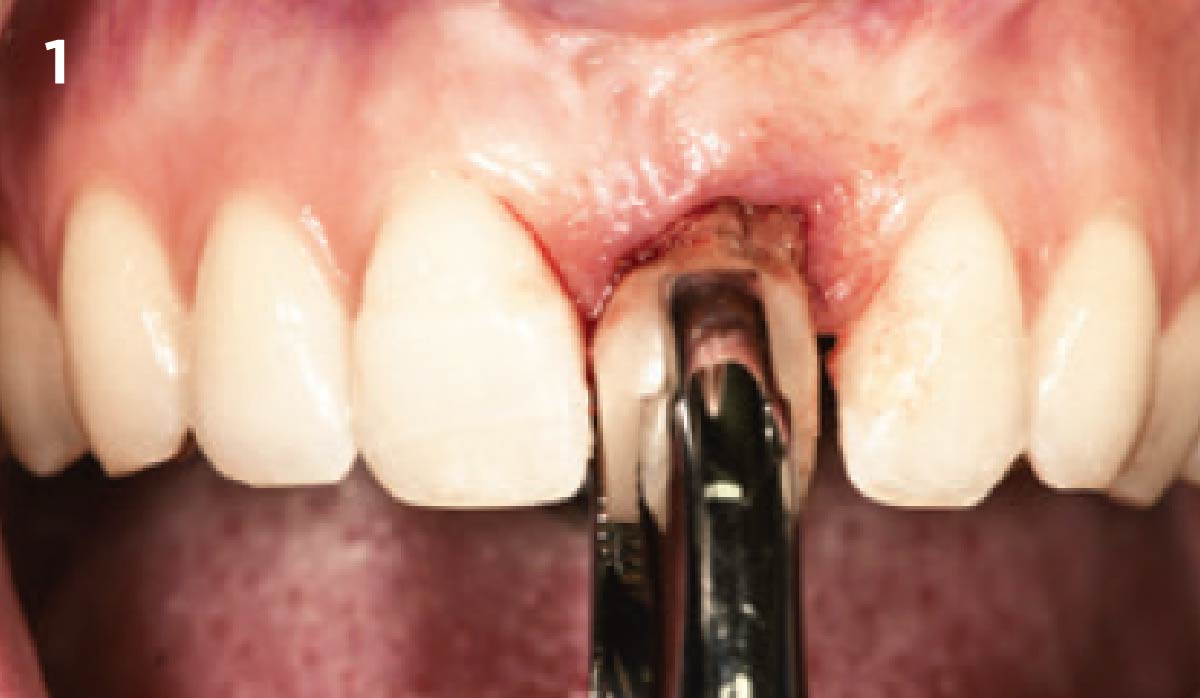
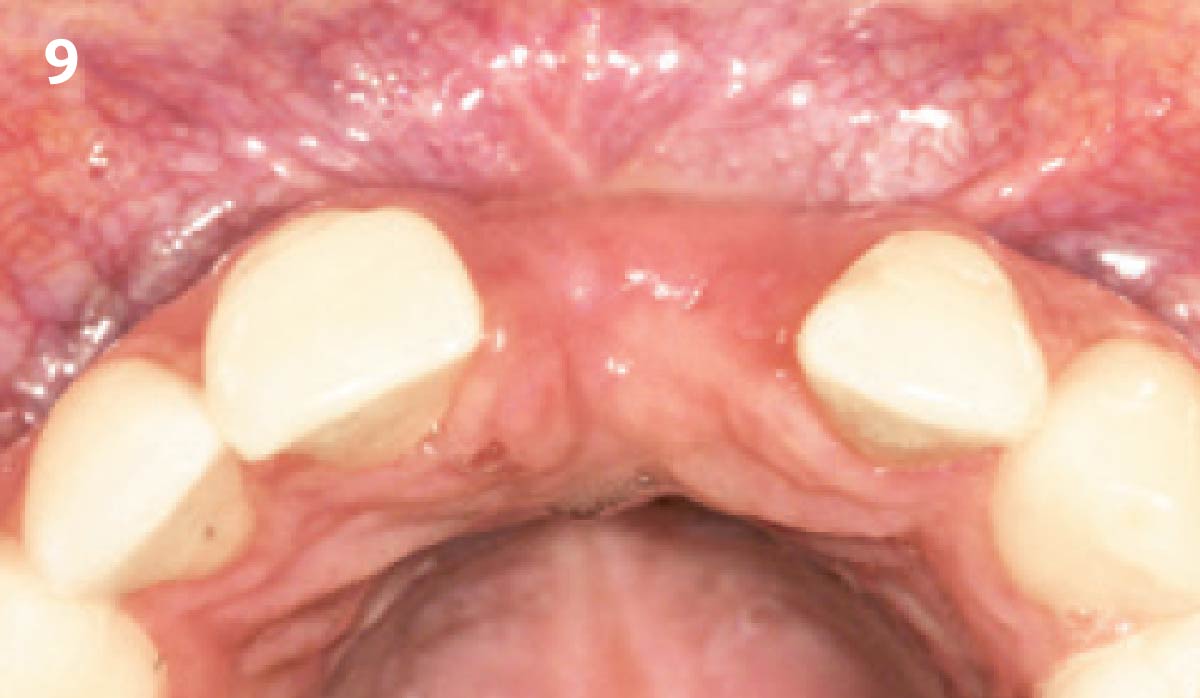
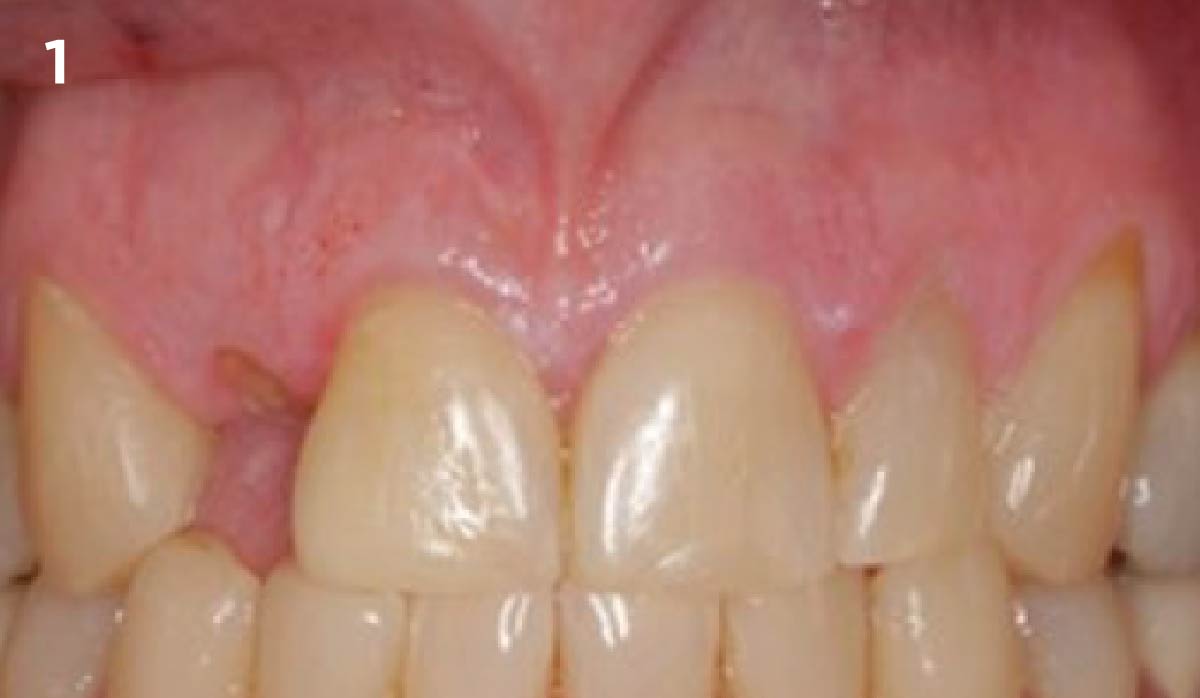
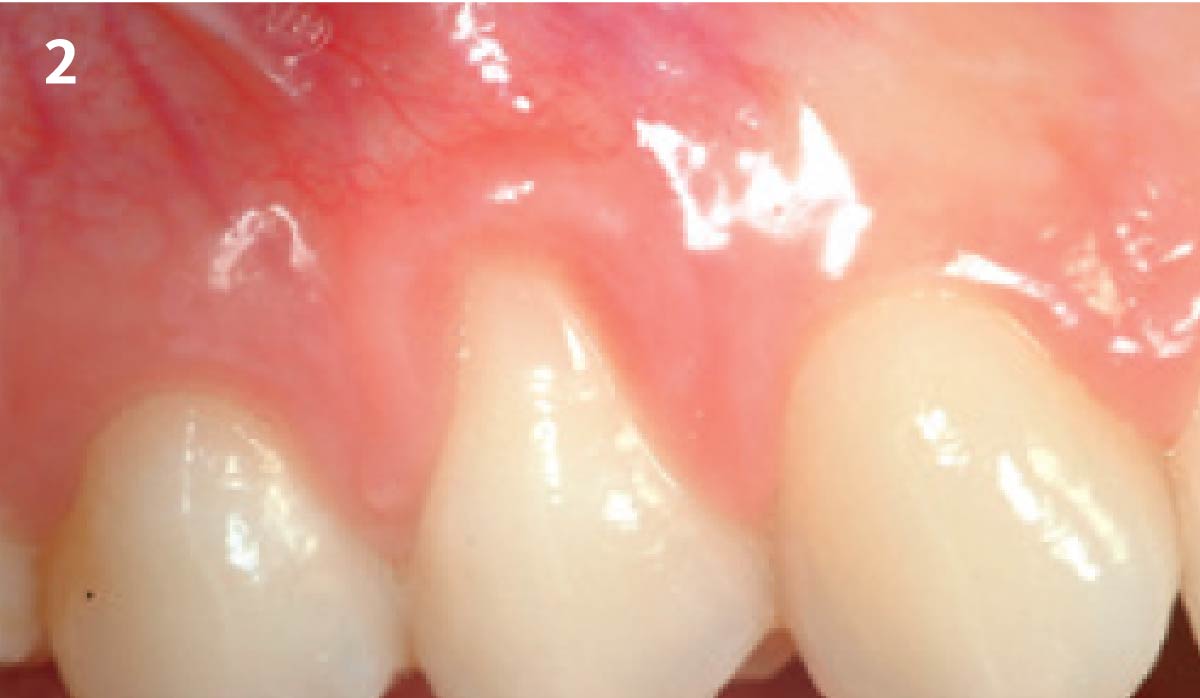
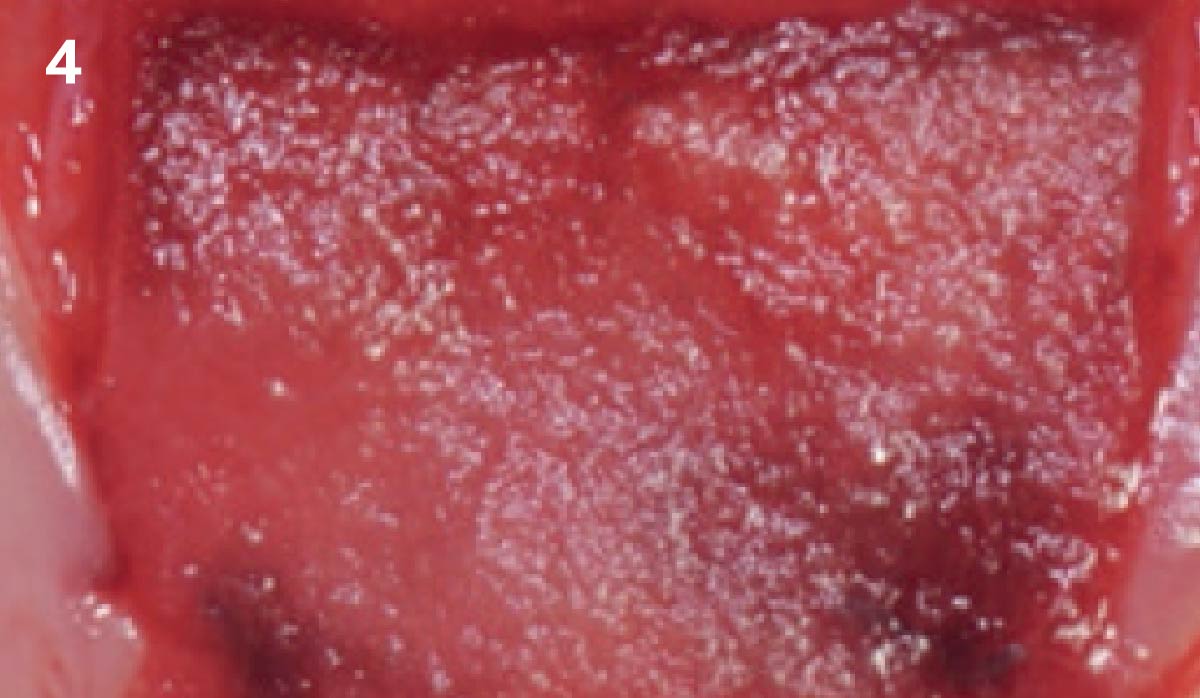
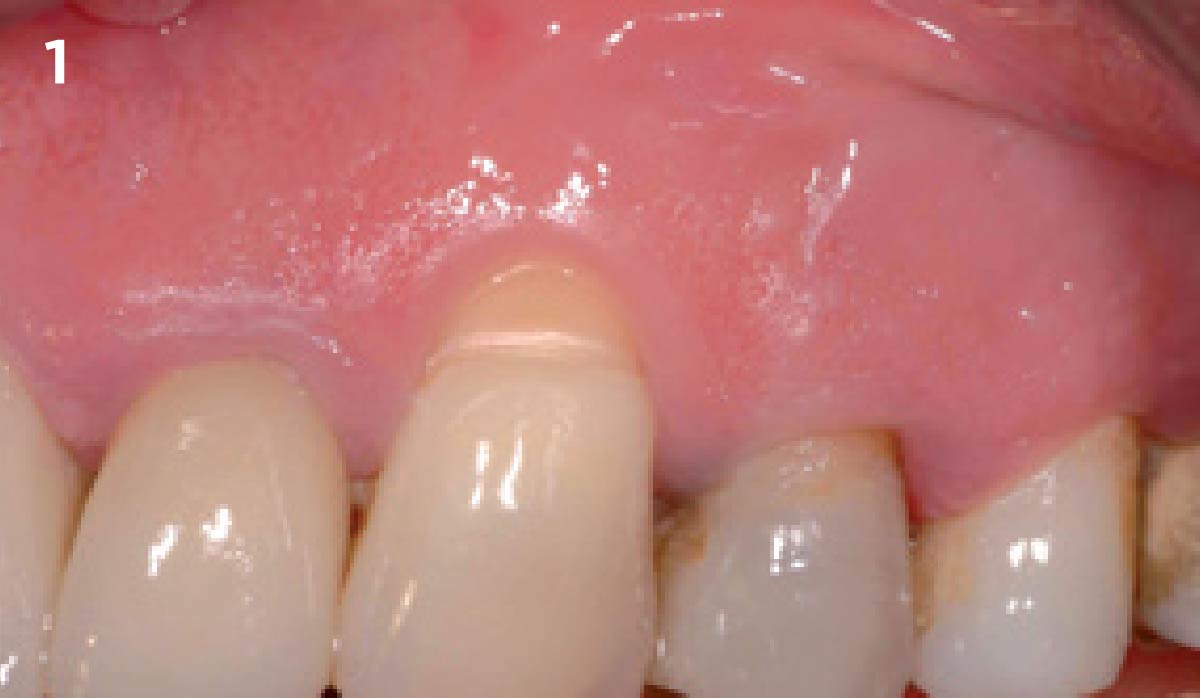
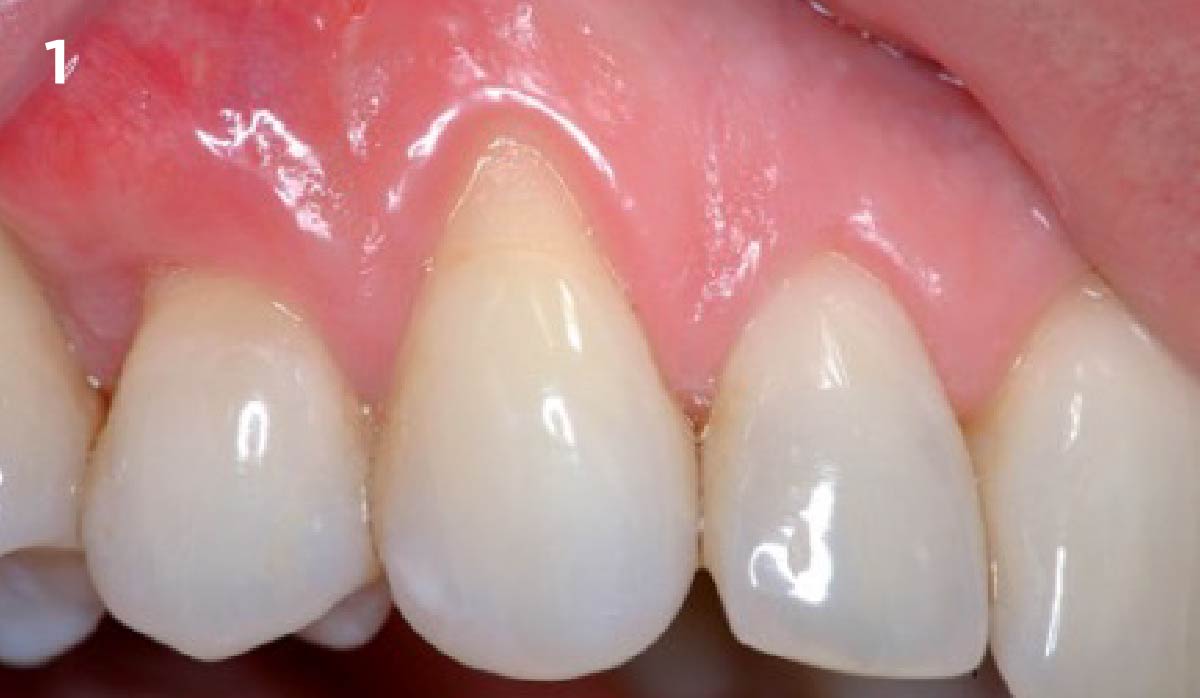
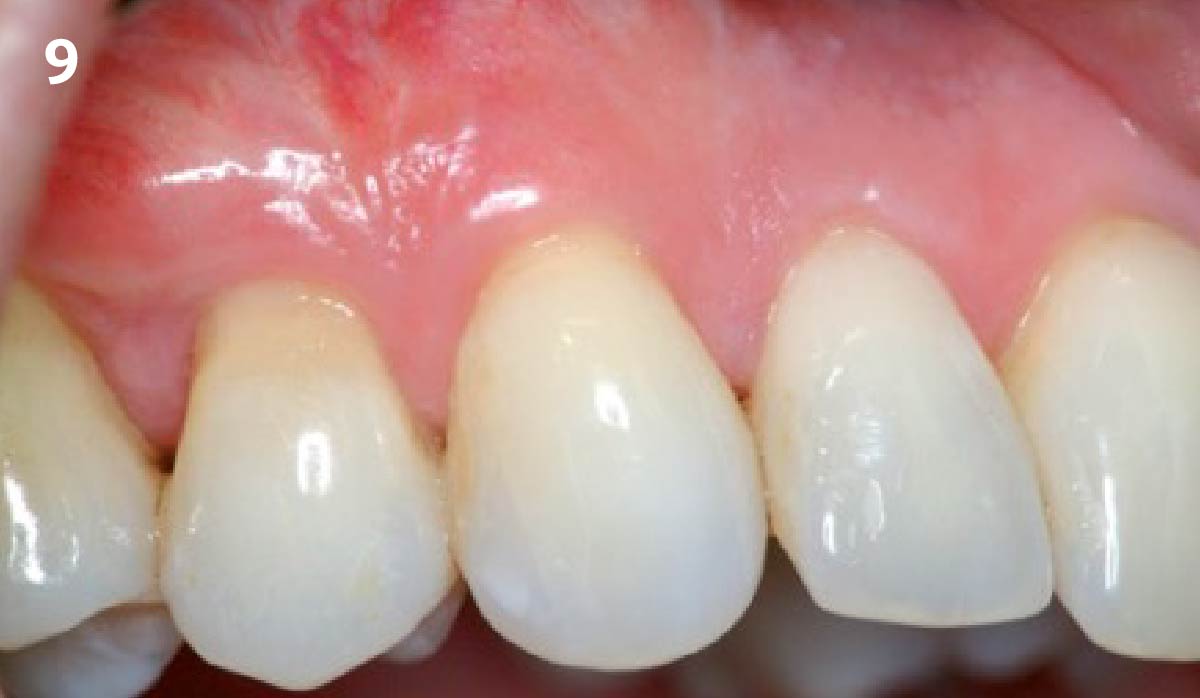
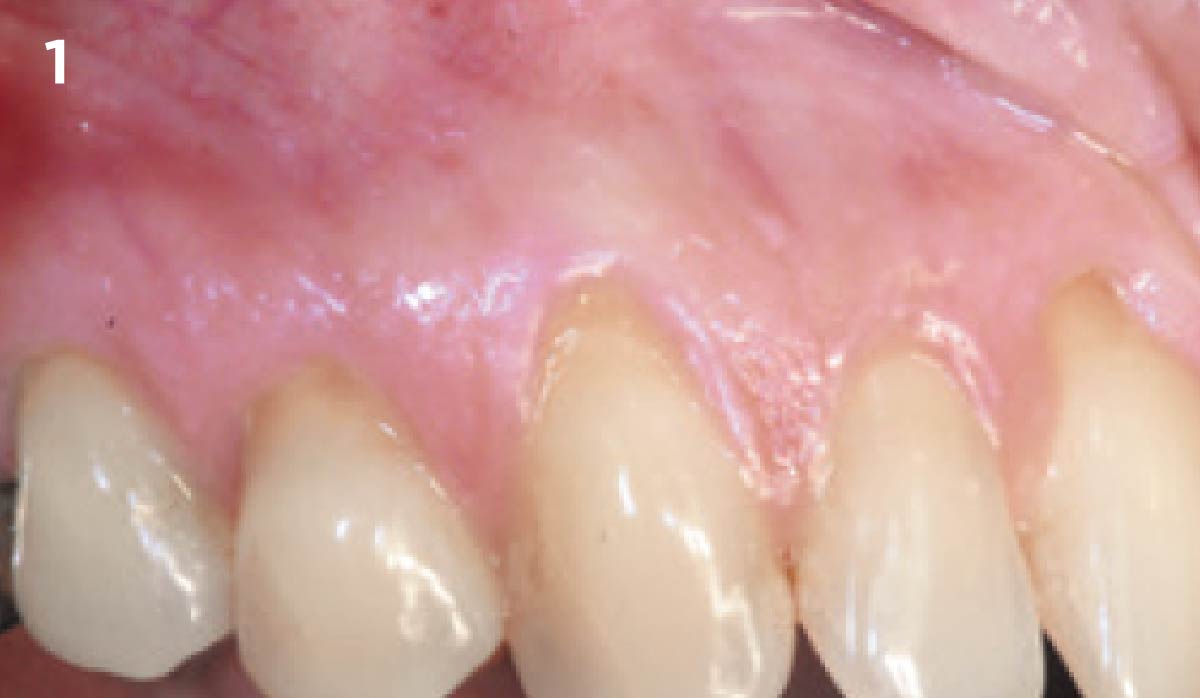
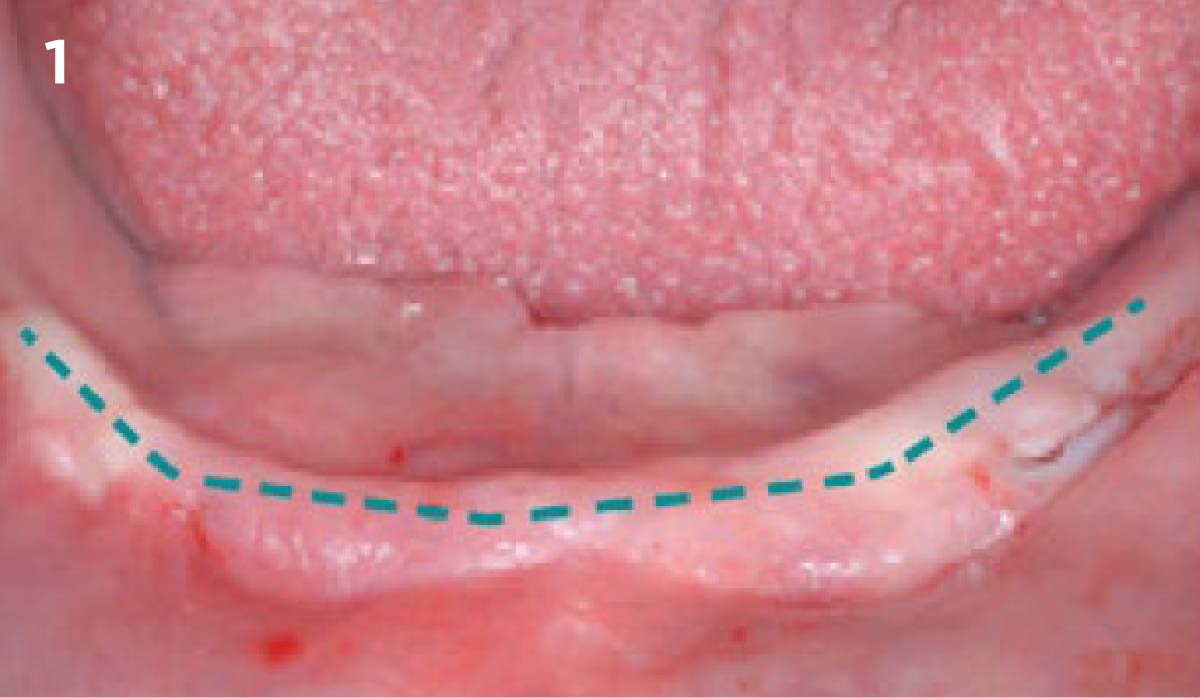
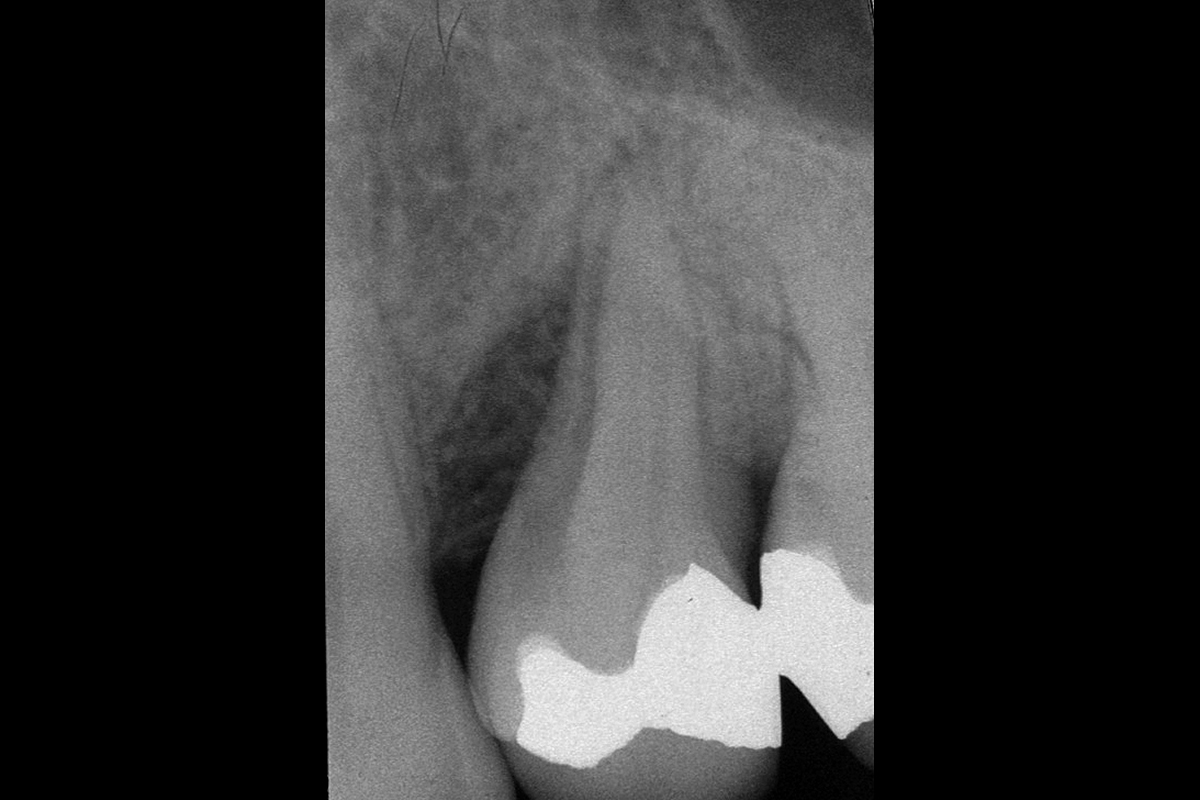
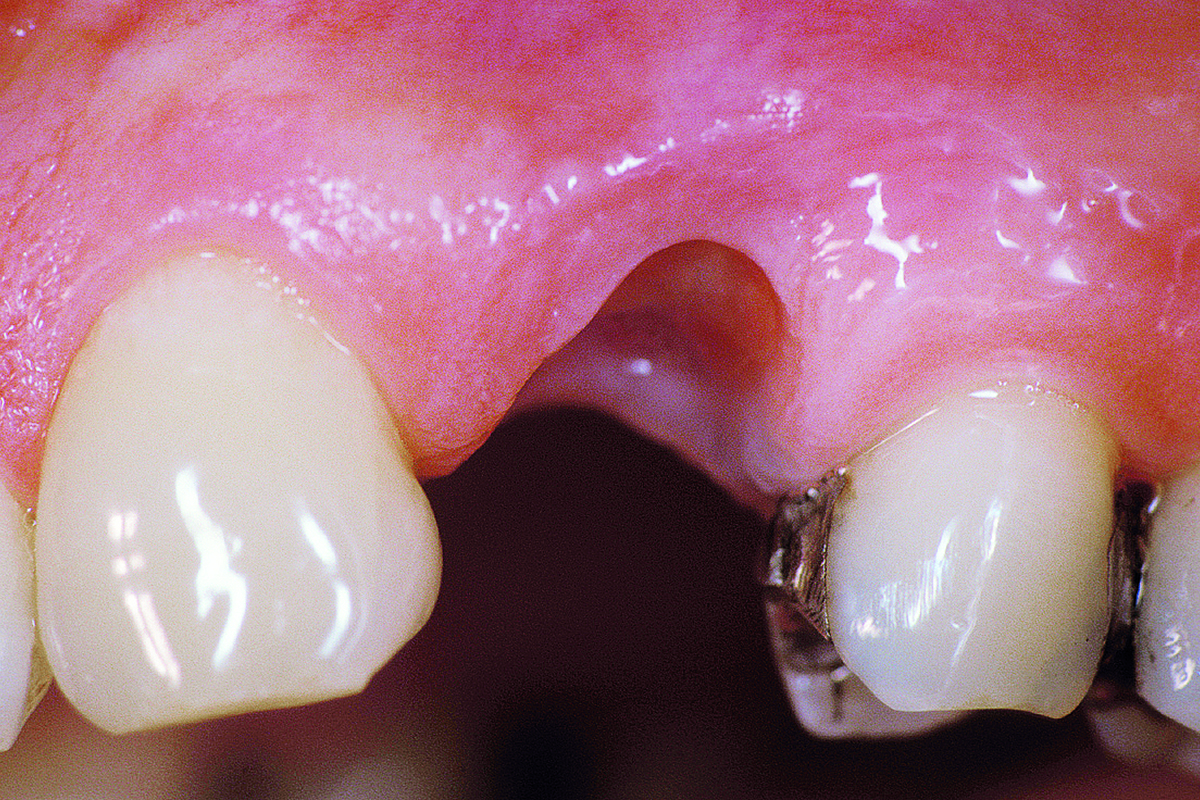
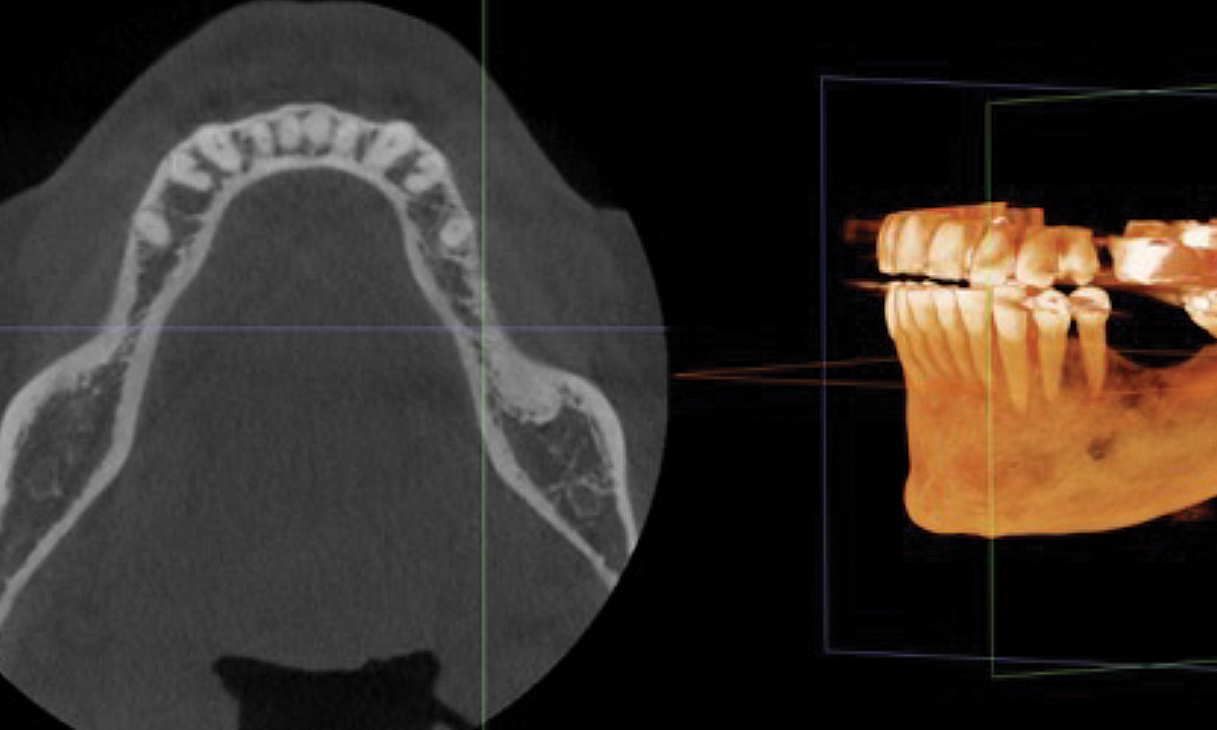
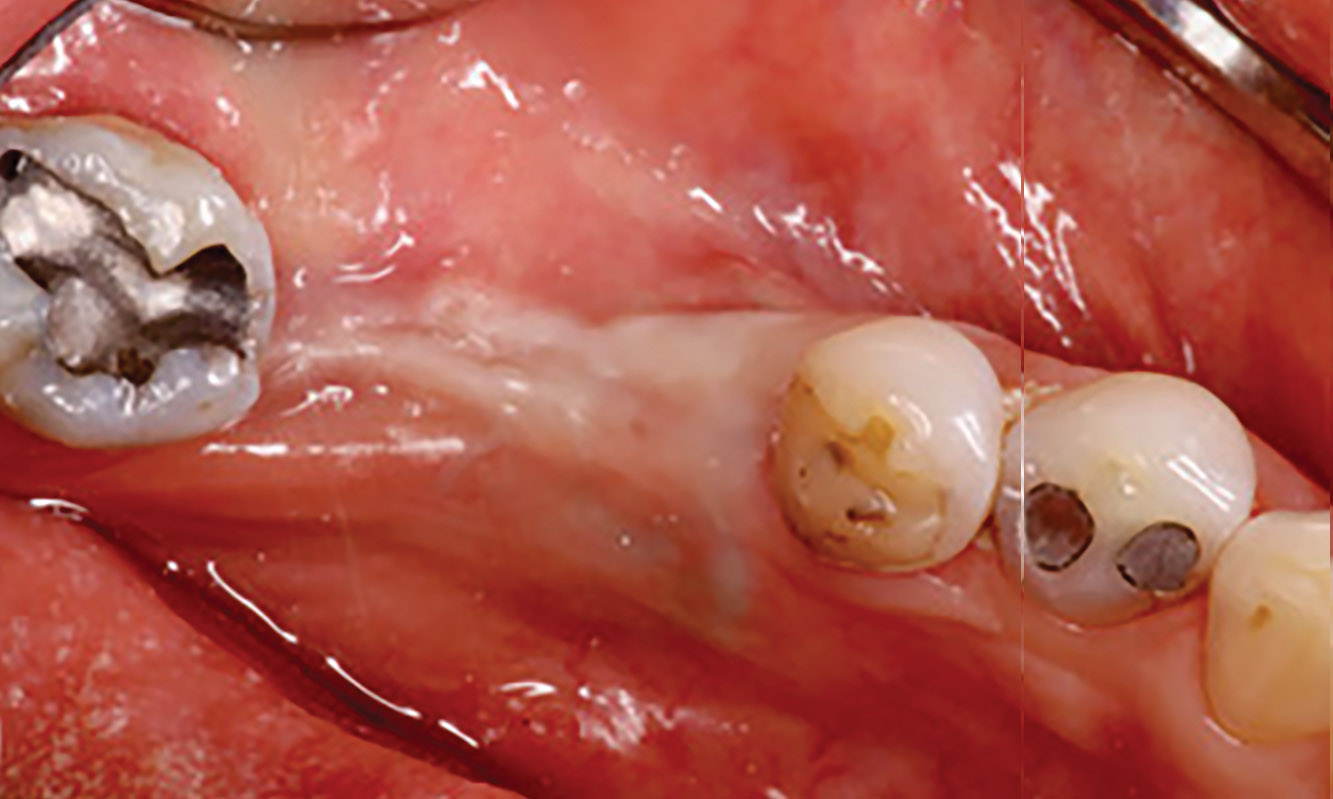
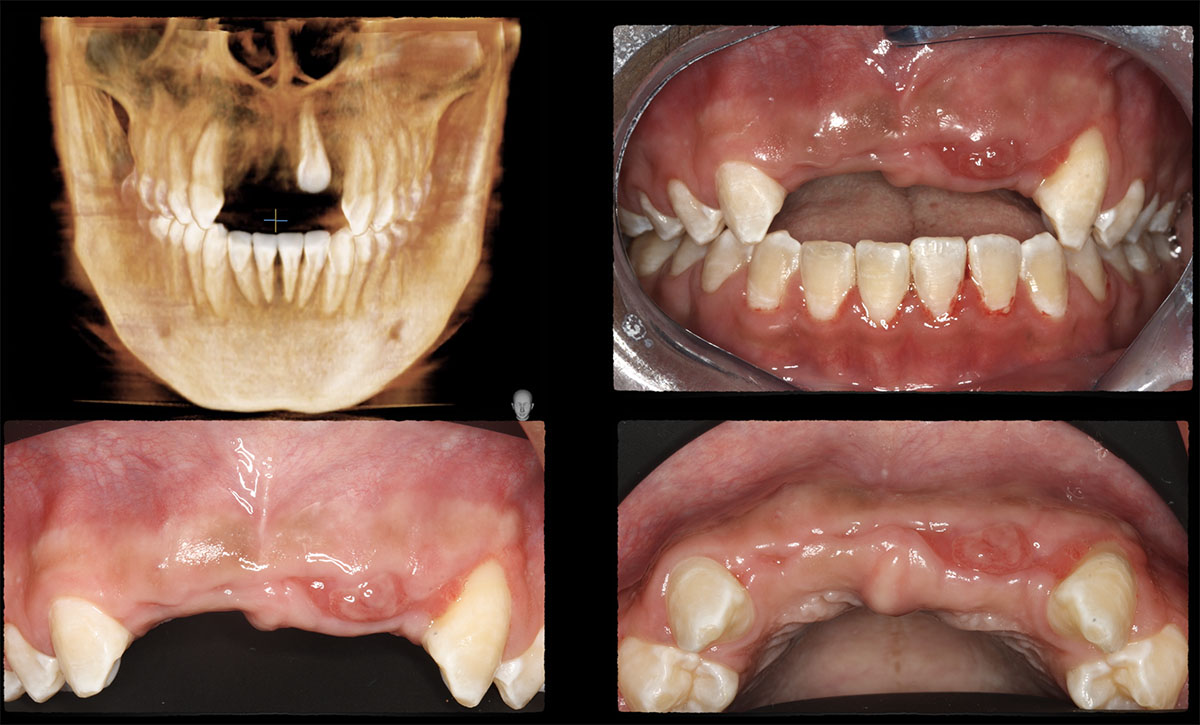
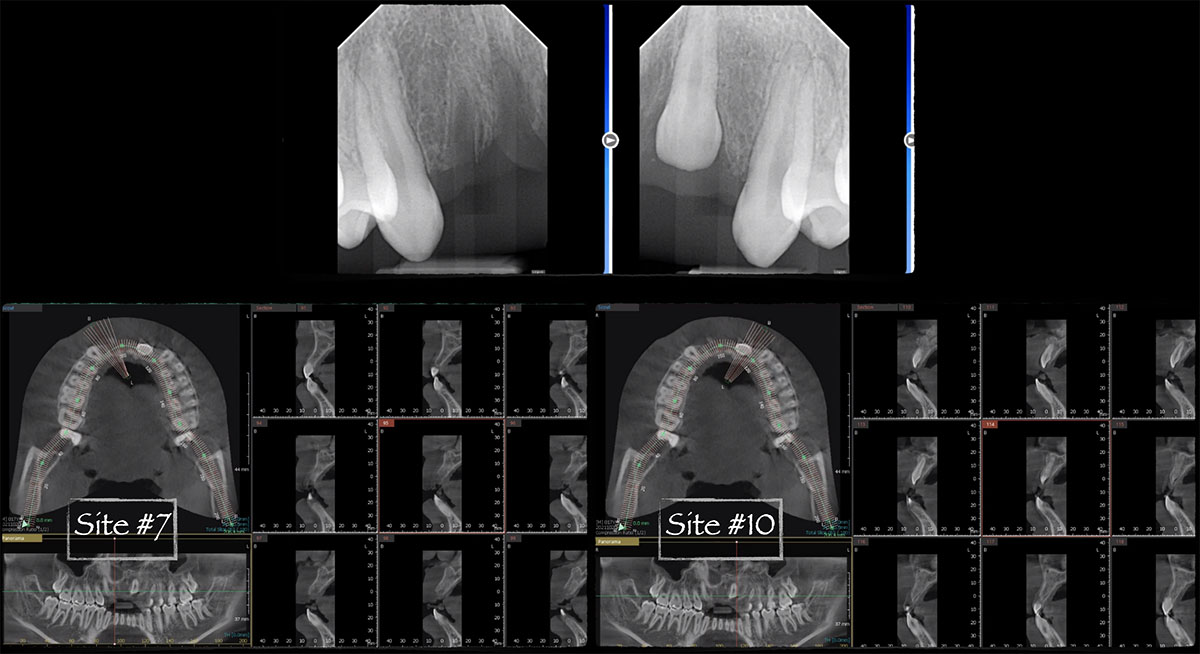
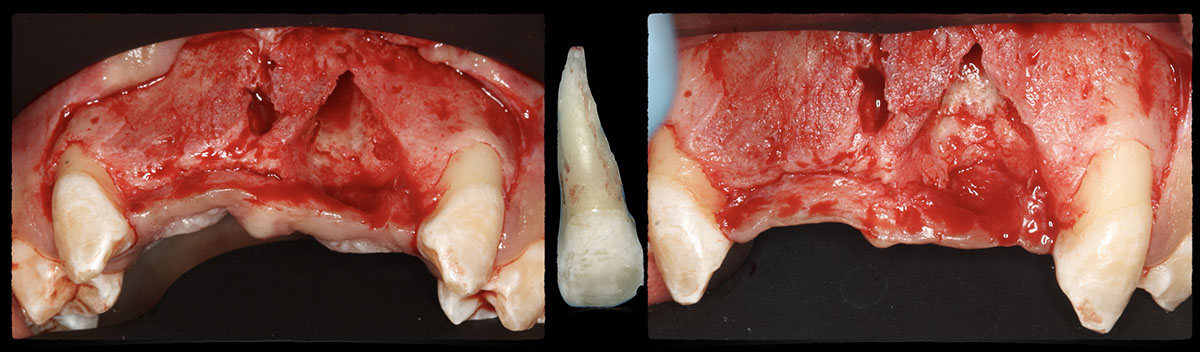
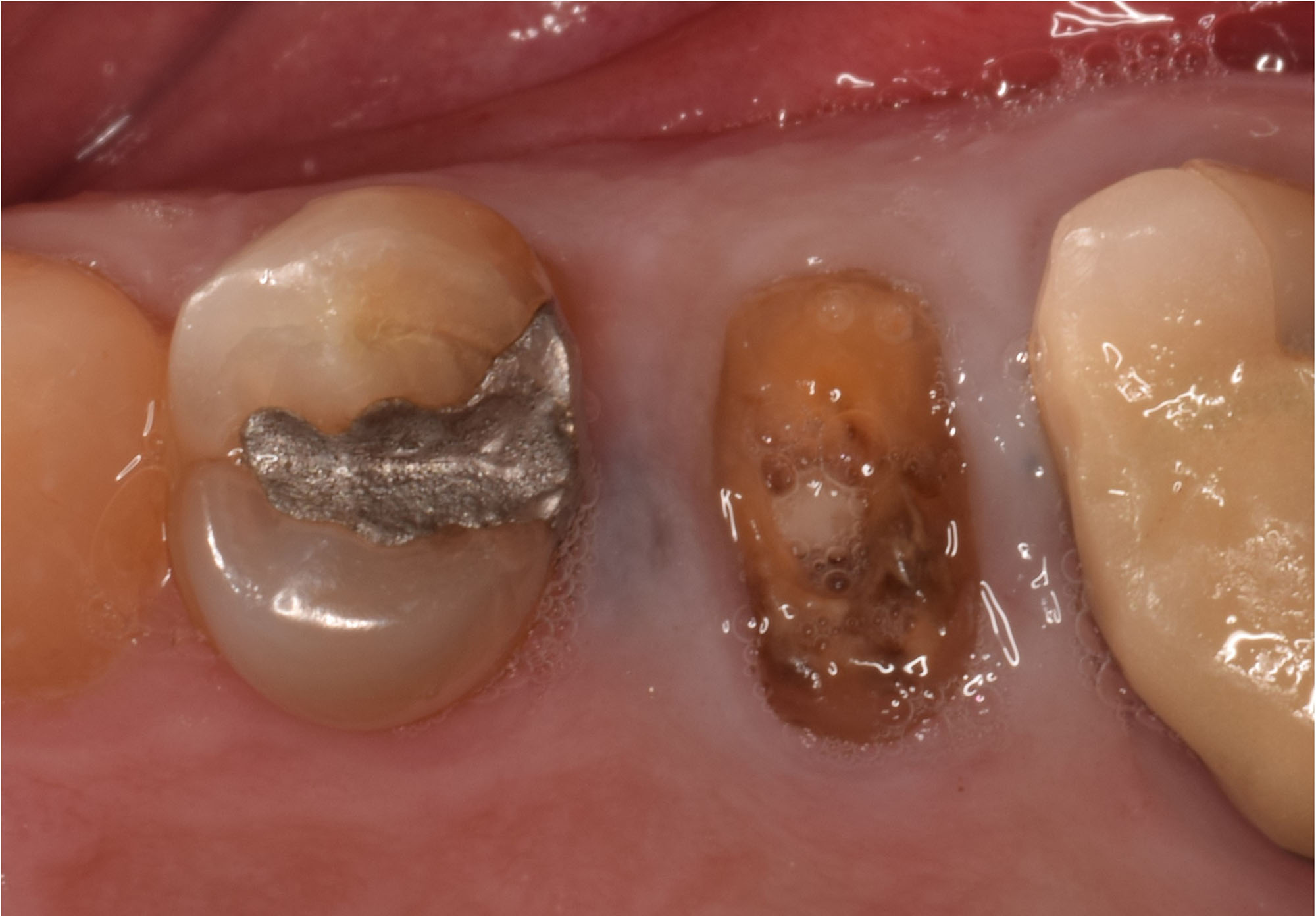
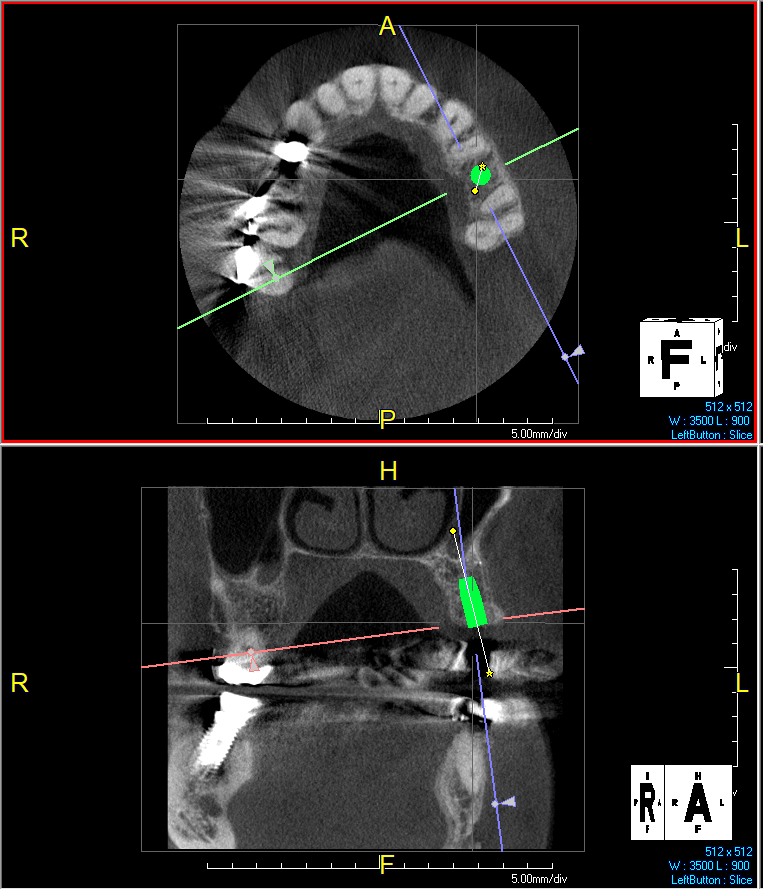
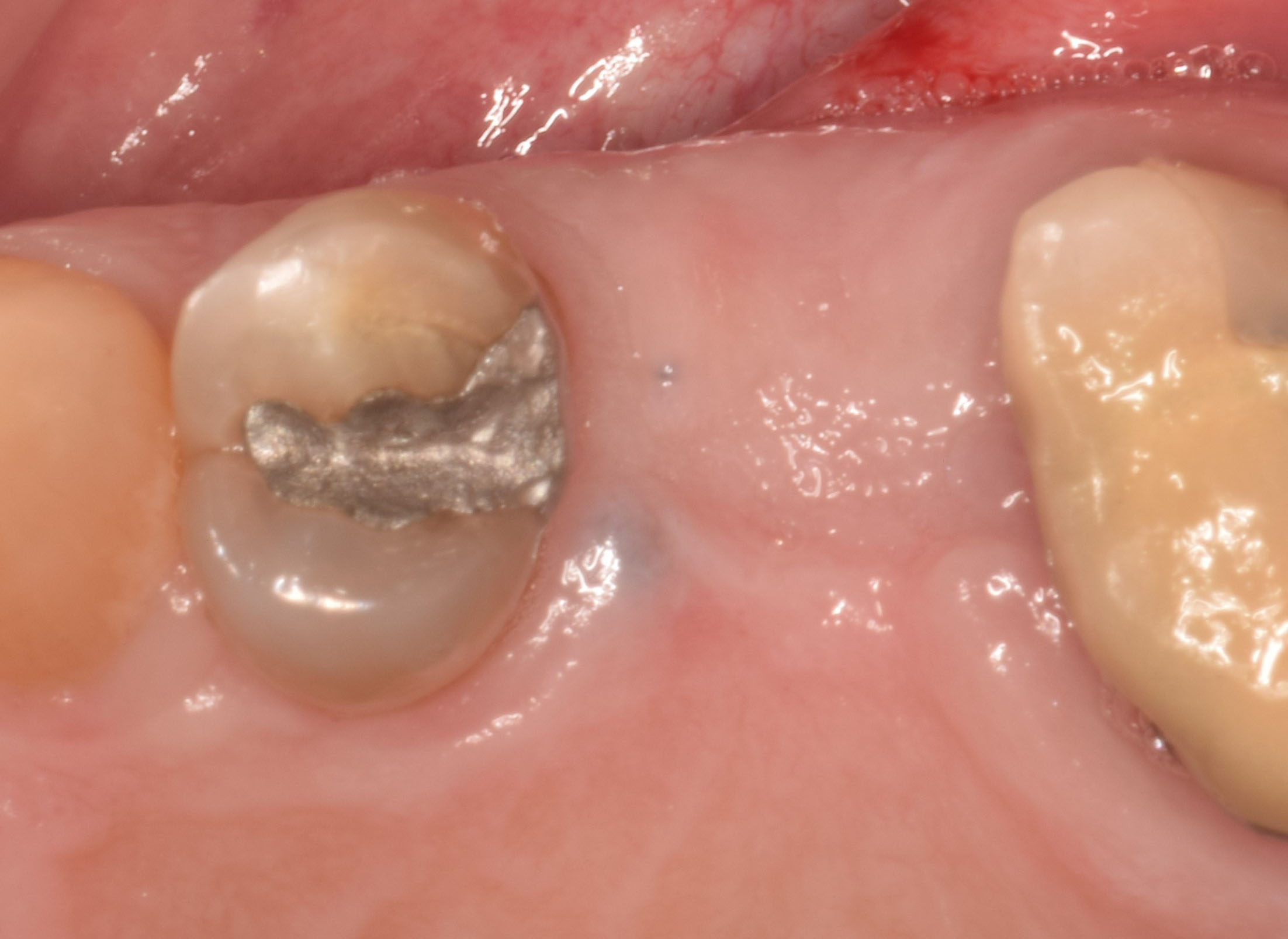
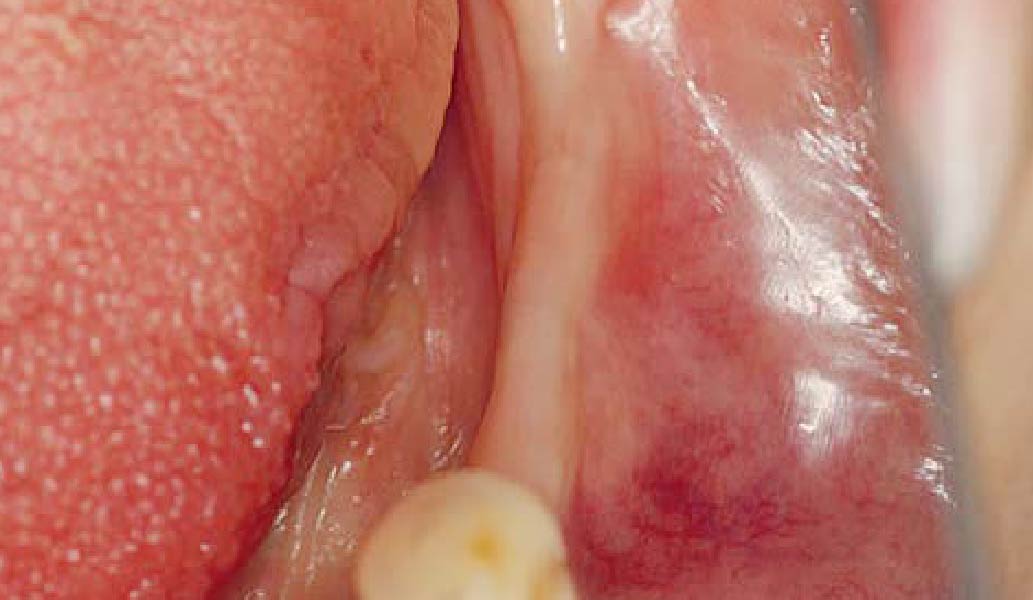
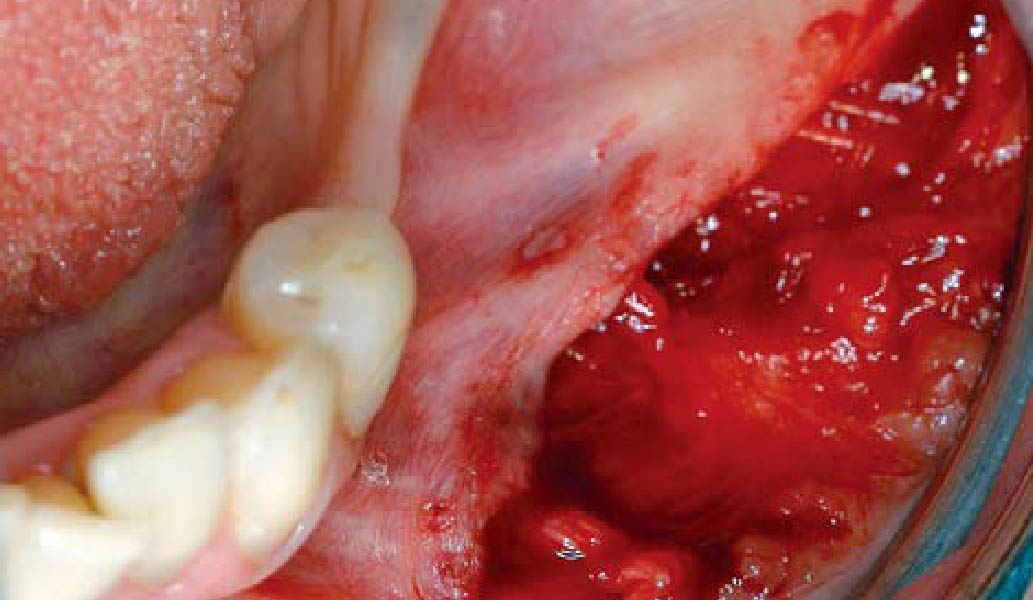
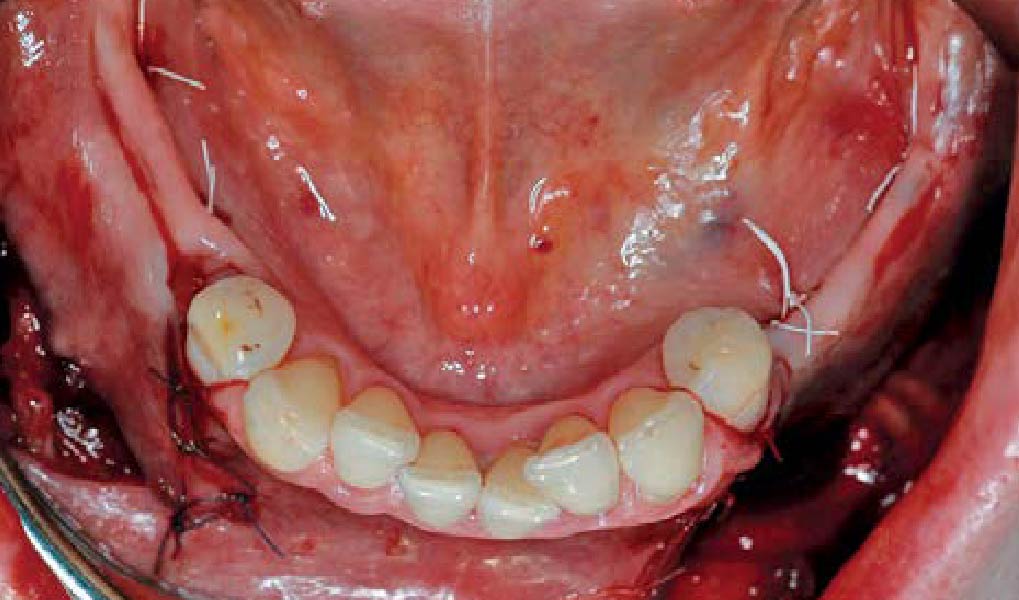
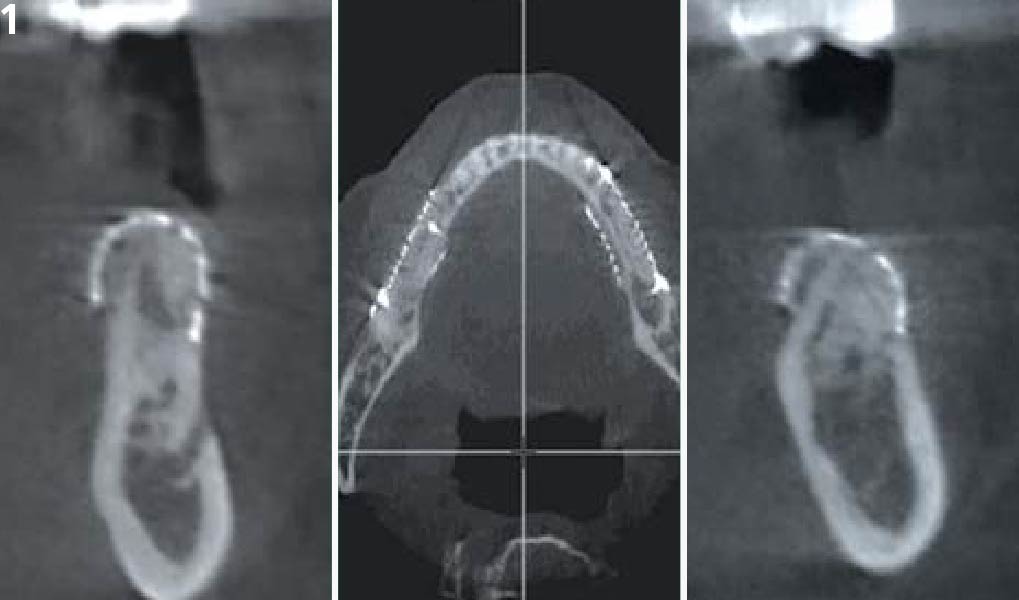
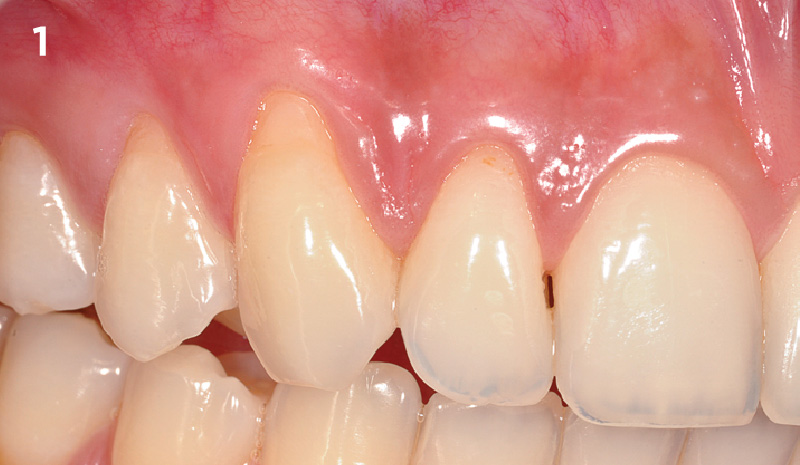
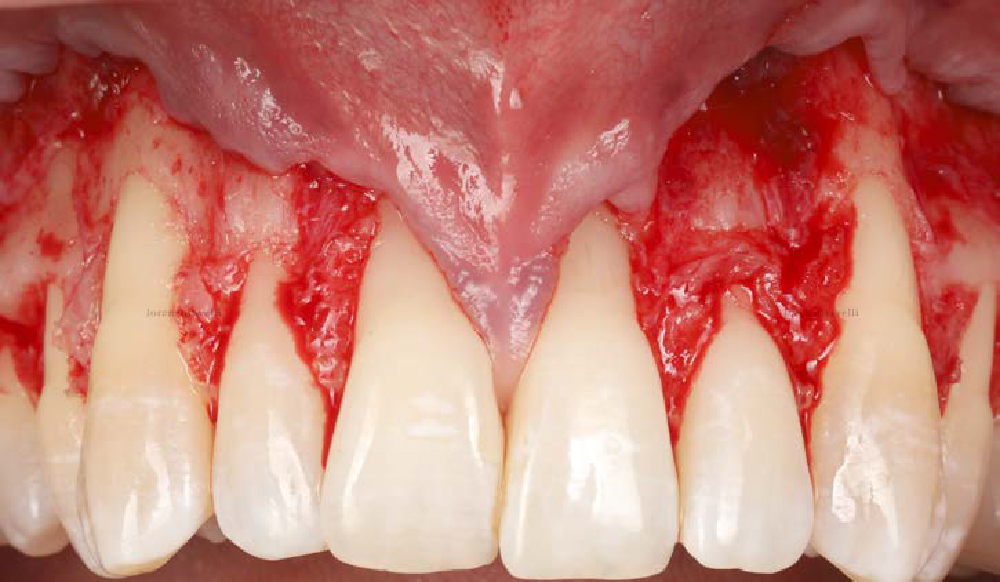
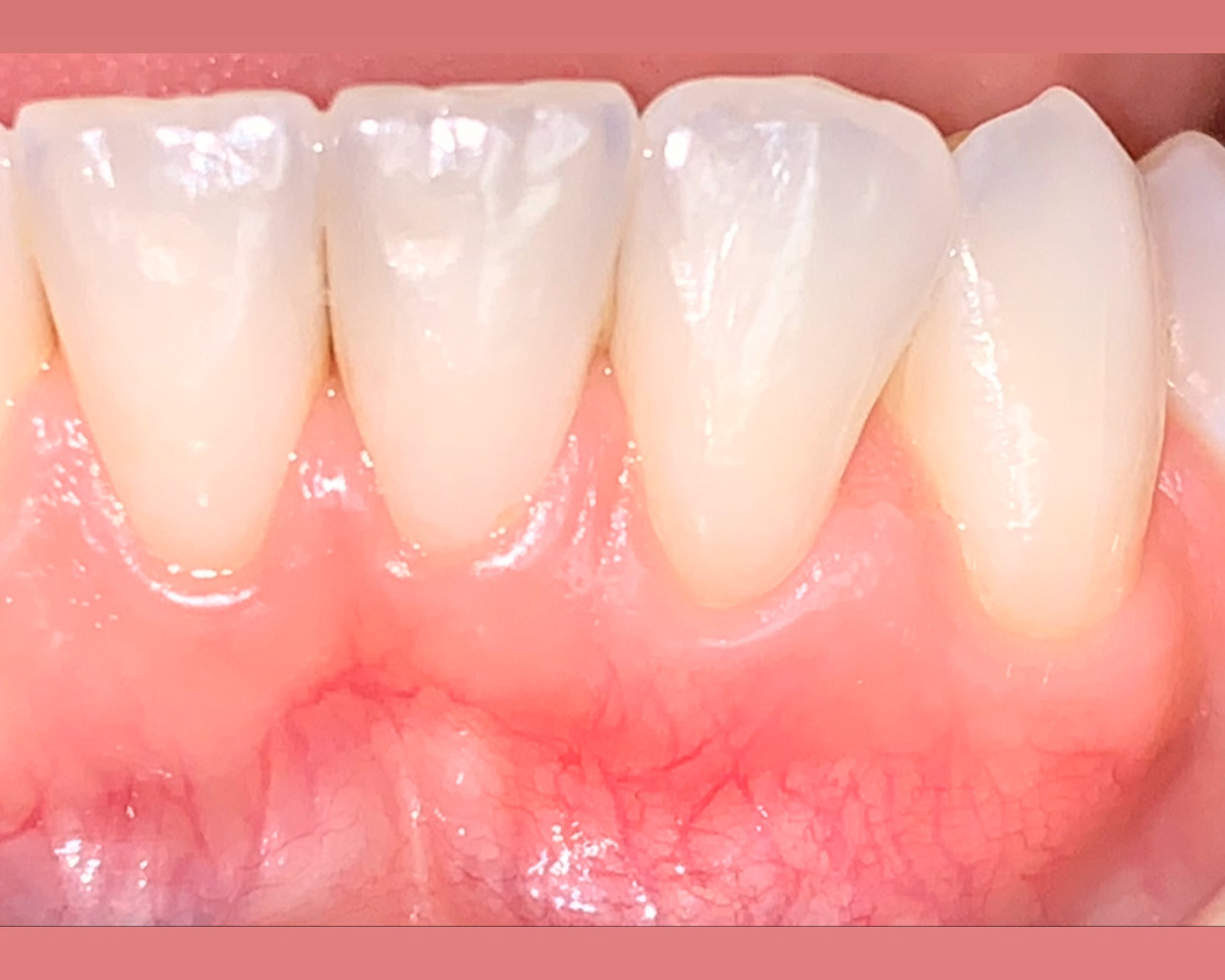
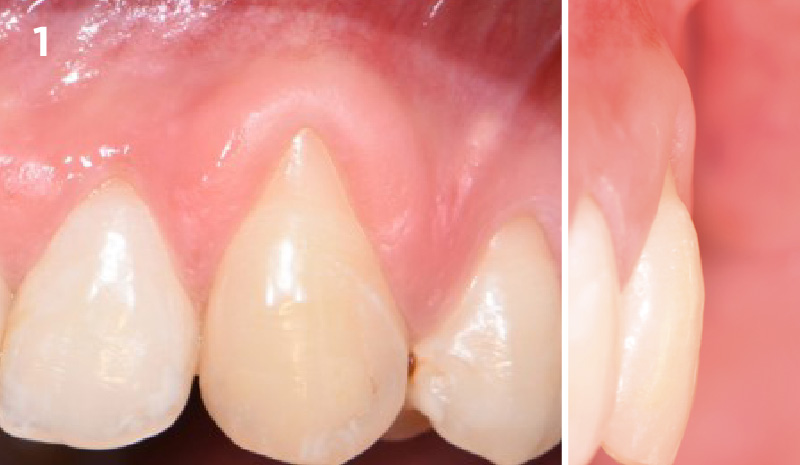
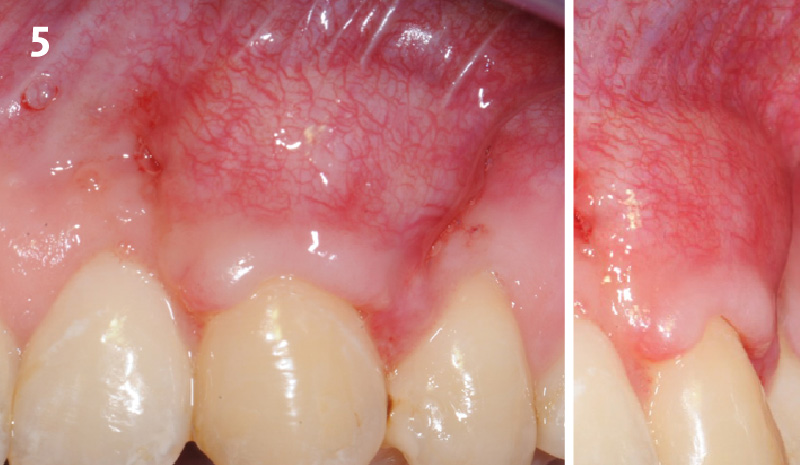
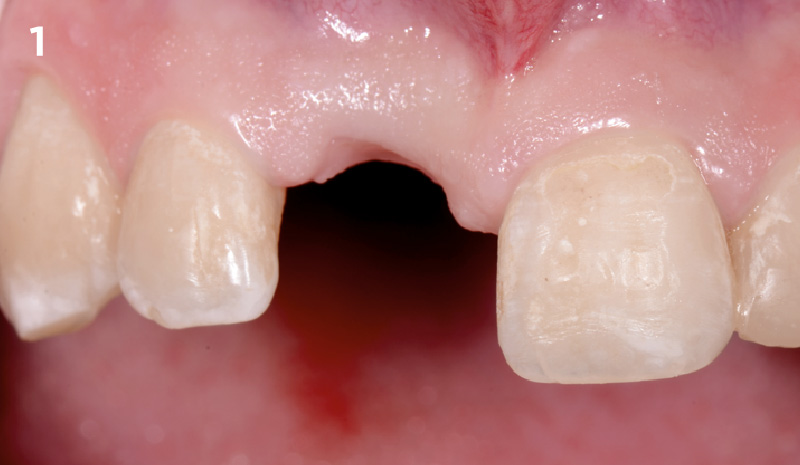
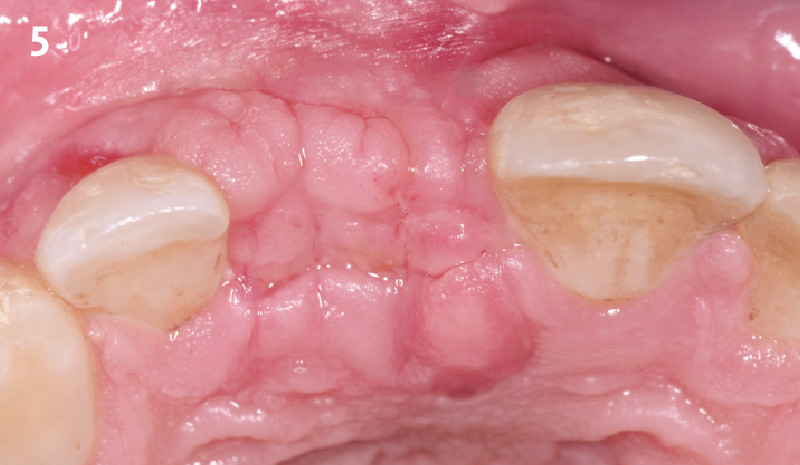
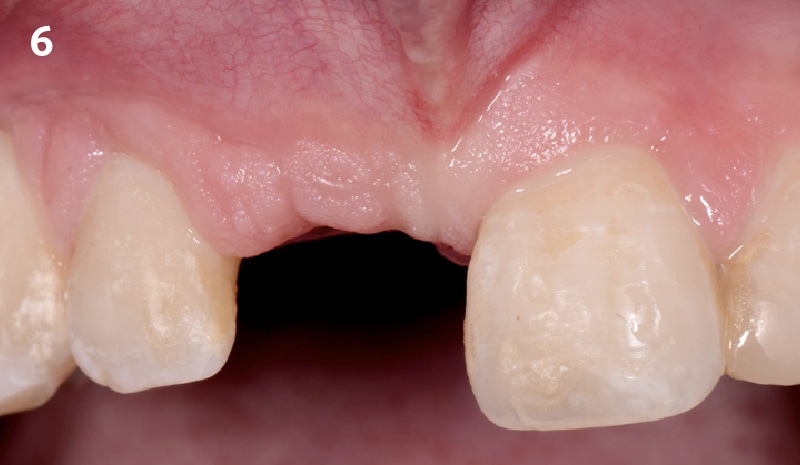
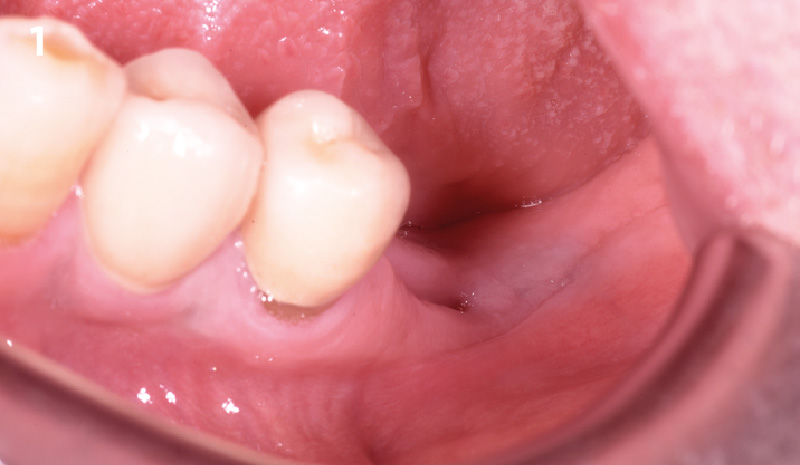
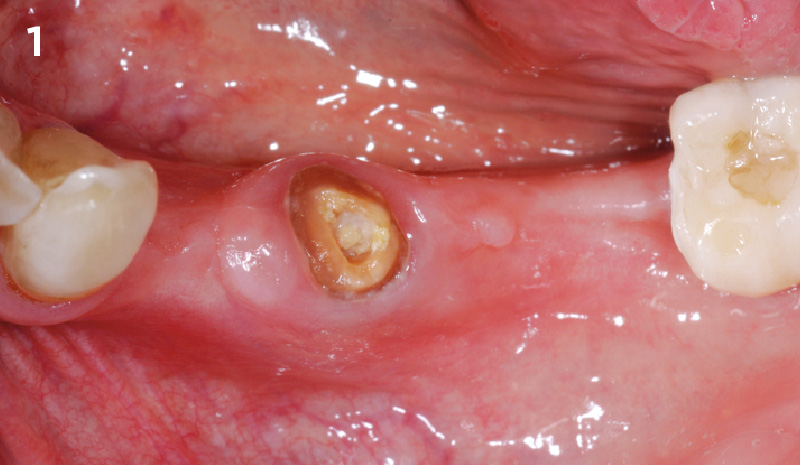
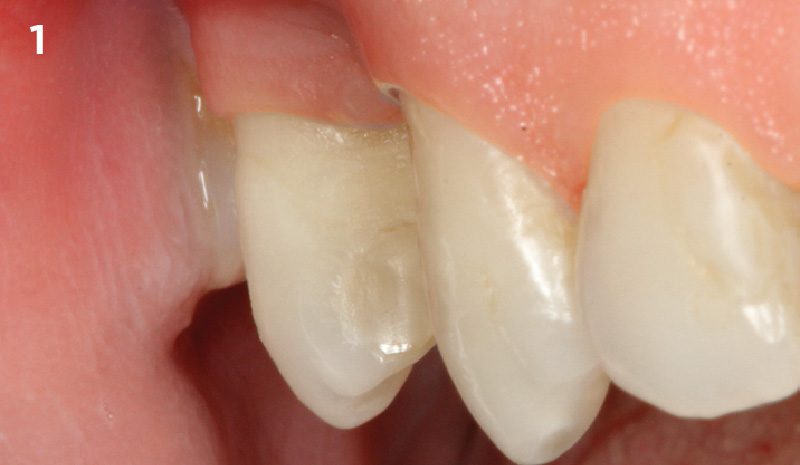
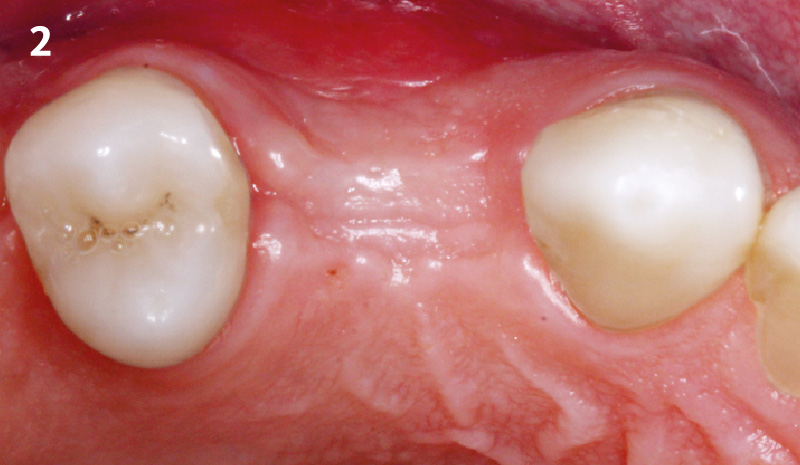
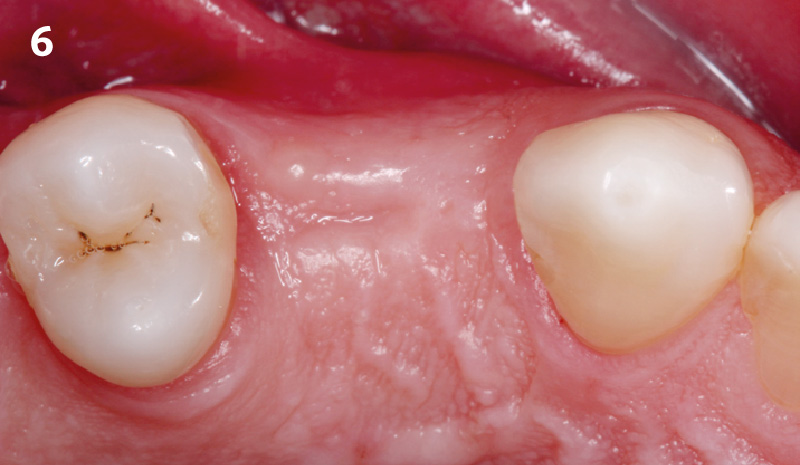
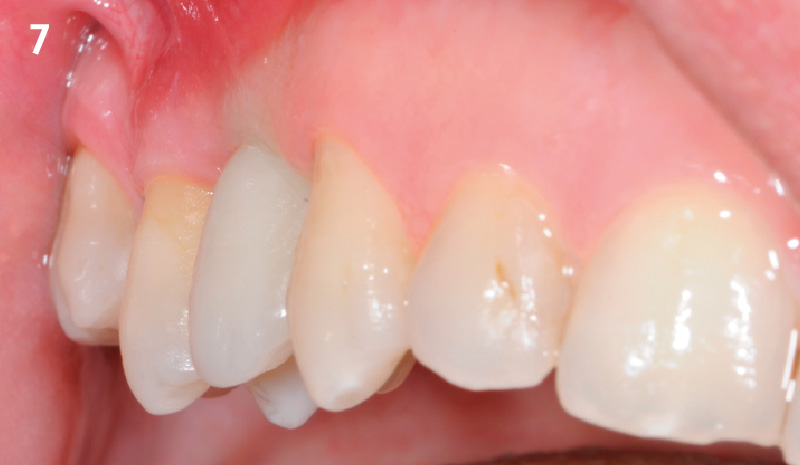
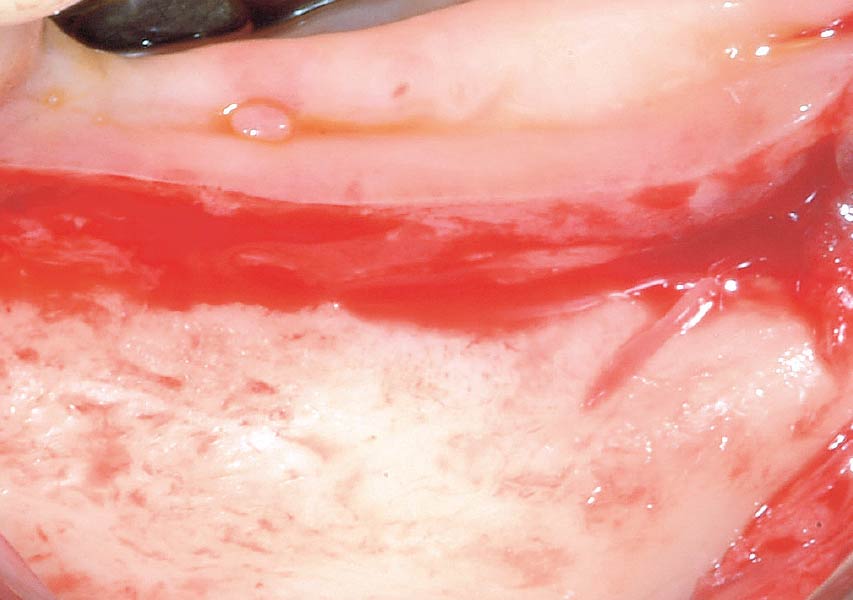
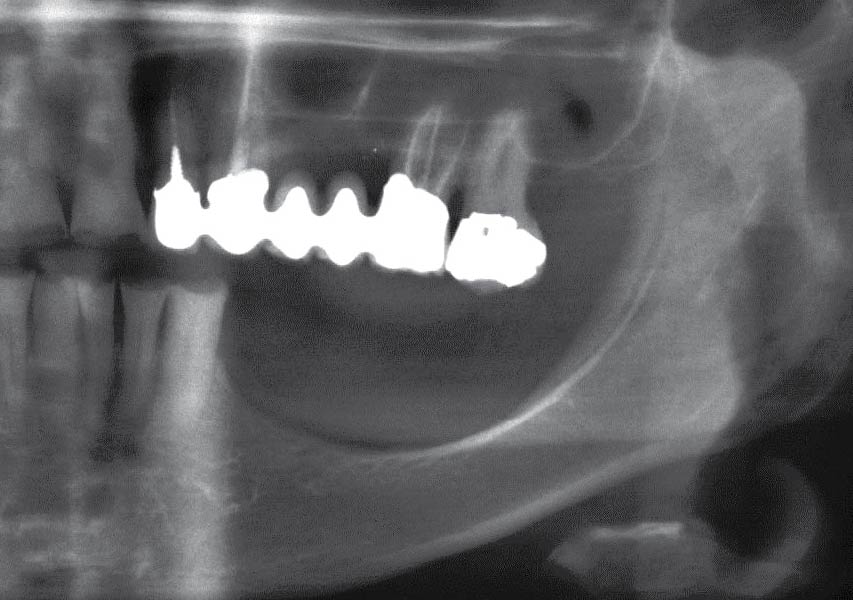
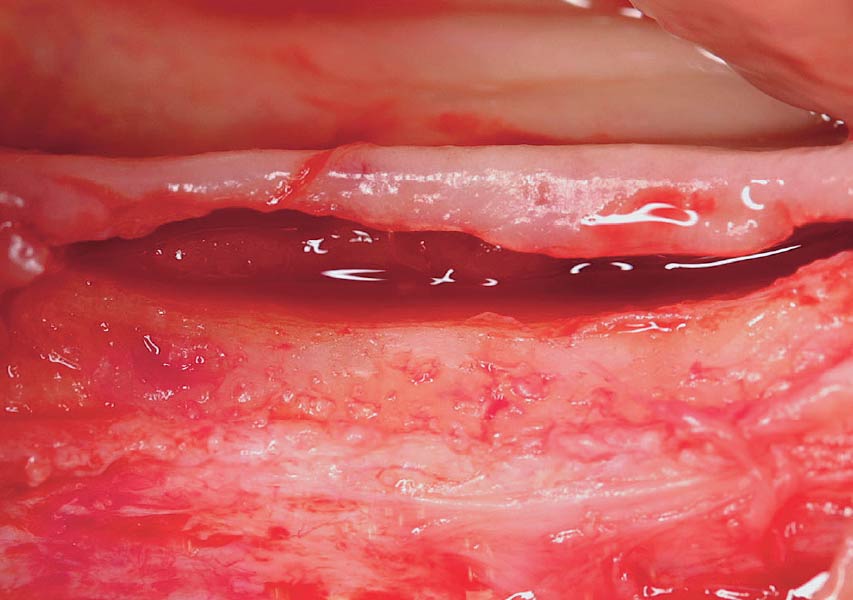
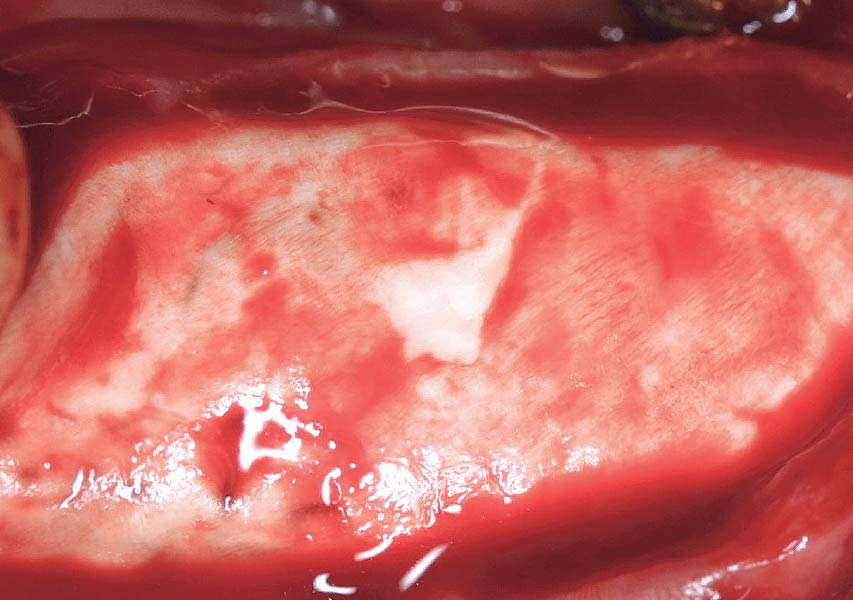
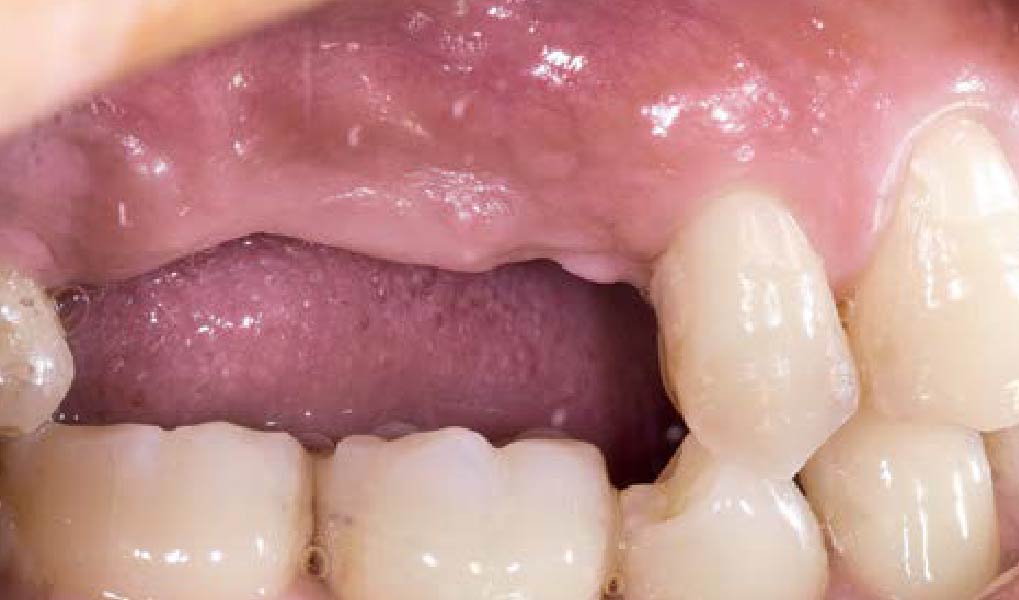
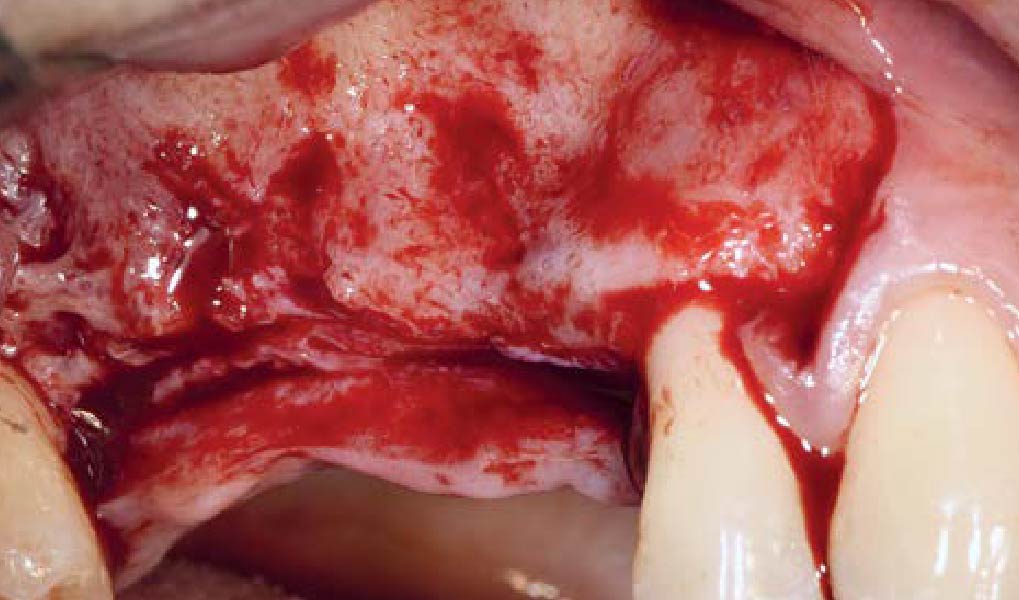
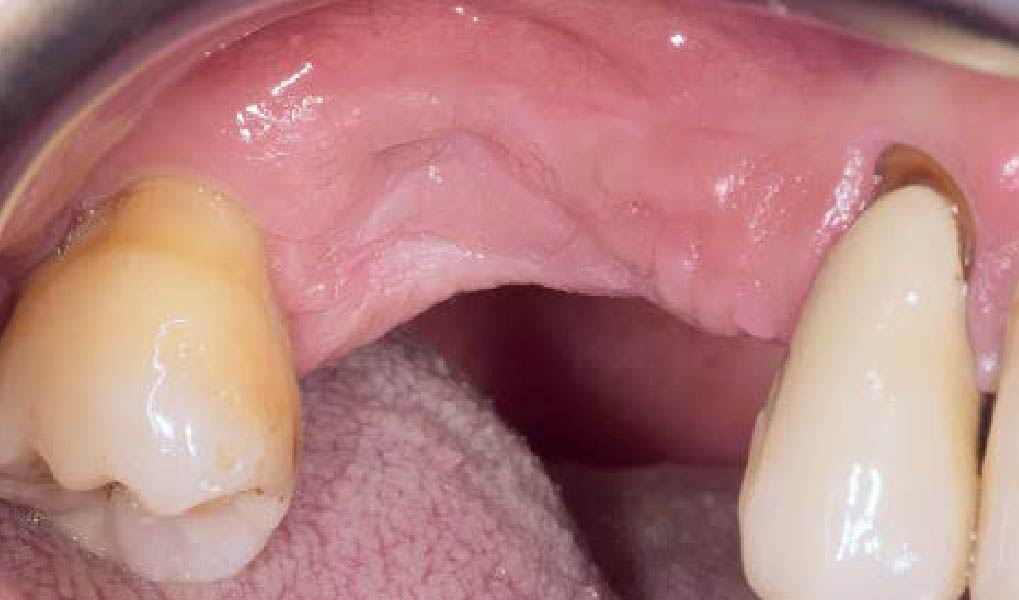
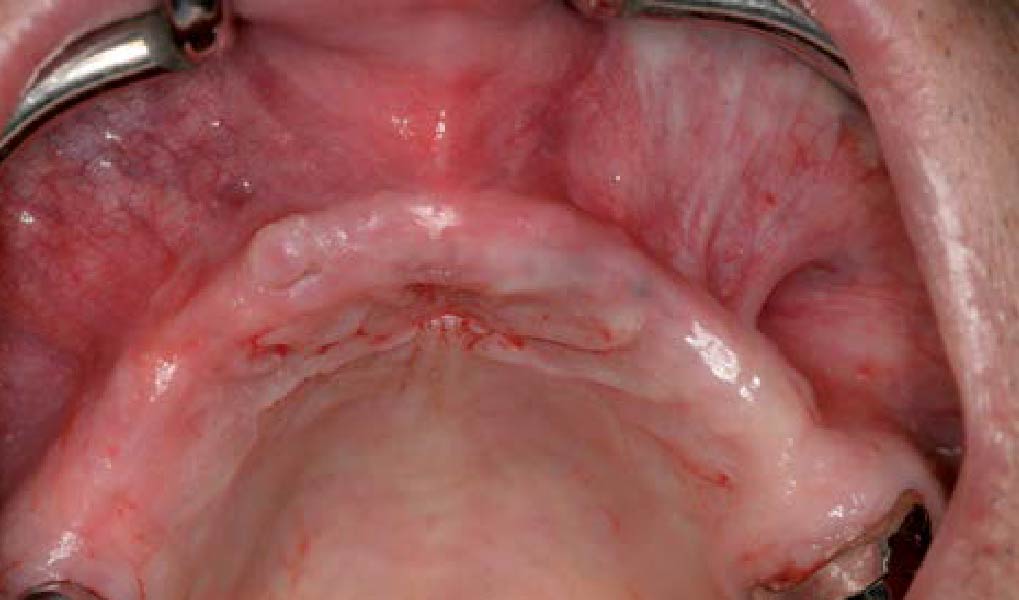
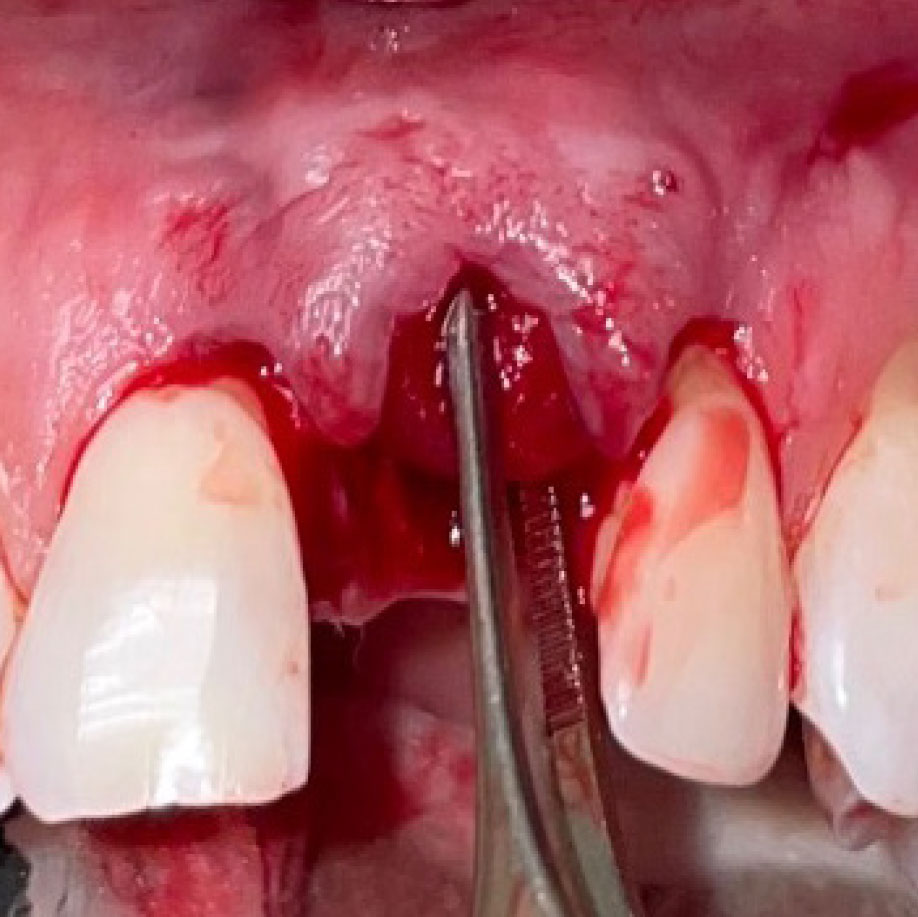
A healthy, 56-year-old female presented with fractured, endodontically treated tooth #9. The tooth was fractured at the gingival level and asymptomatic. Both the patient and the restorative dentist had high esthetic expectations, and preferred immediate implant placement with provisionalization if possible.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system Non-smoker | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of the smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival phenotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
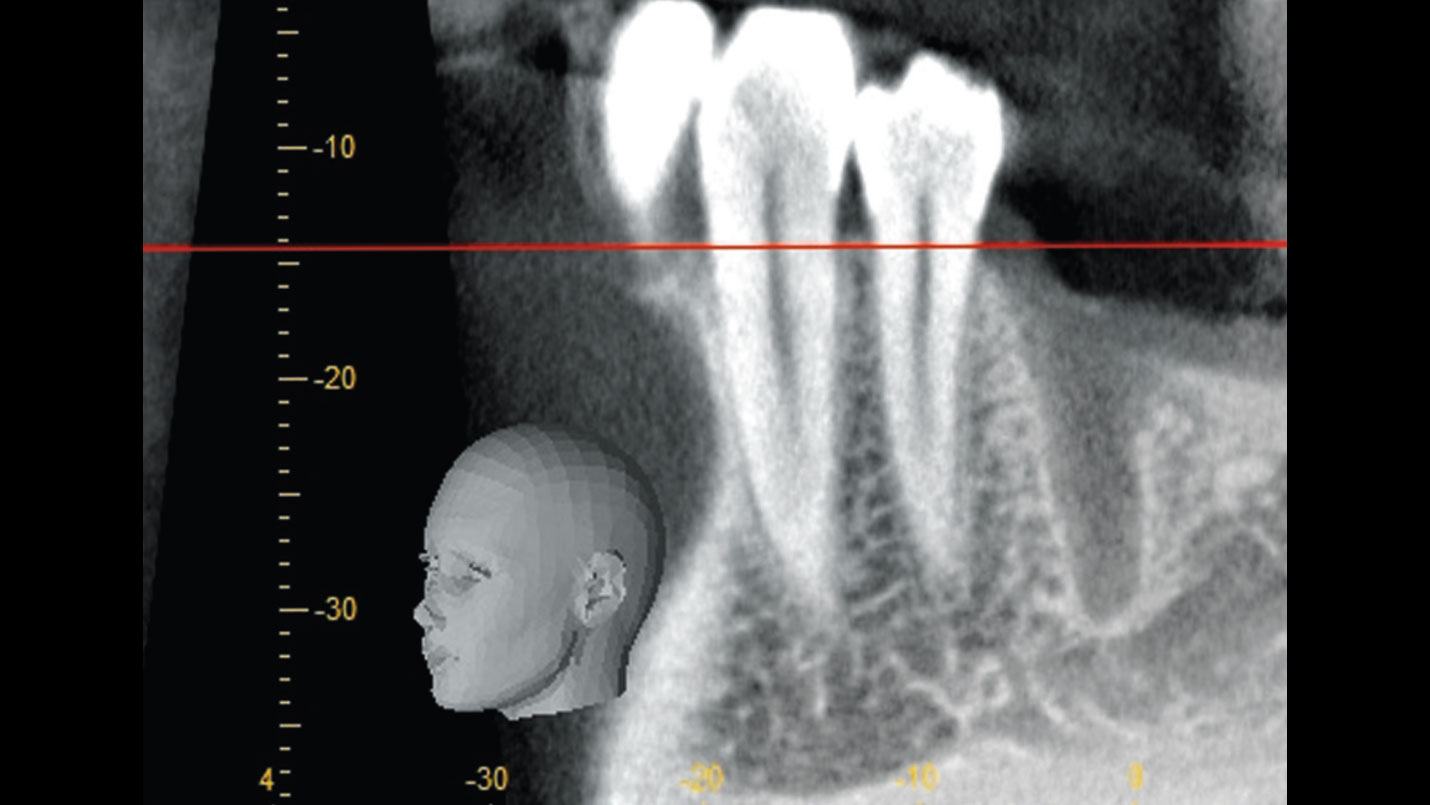
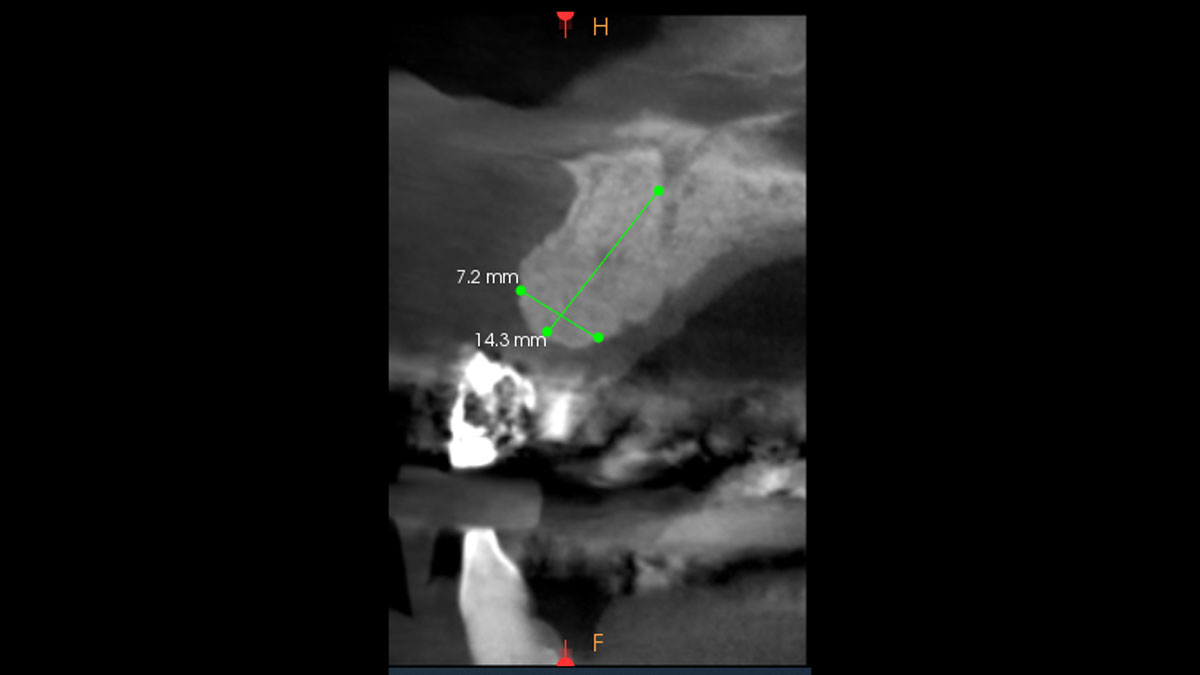
| Bone height at adjacent tooth | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
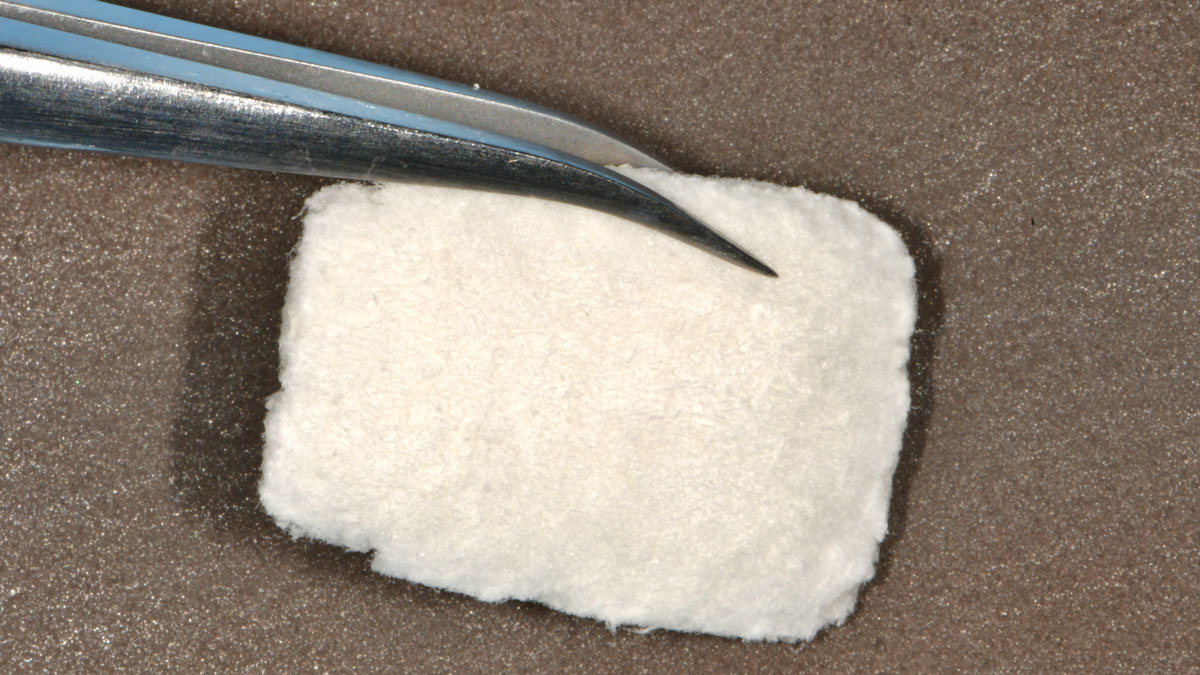
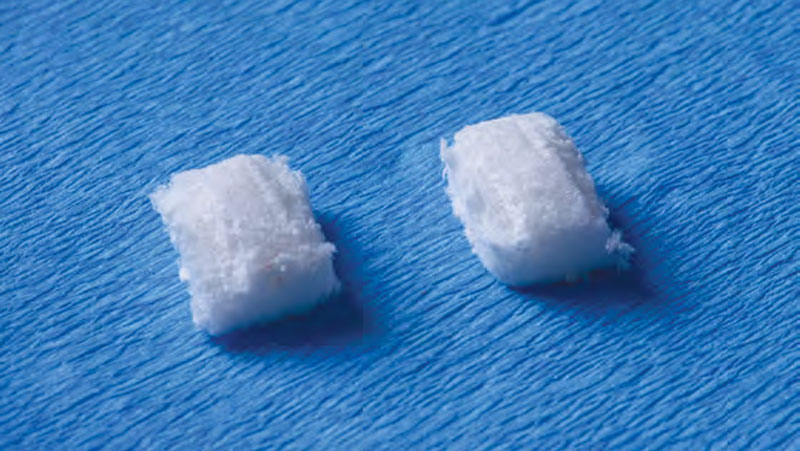
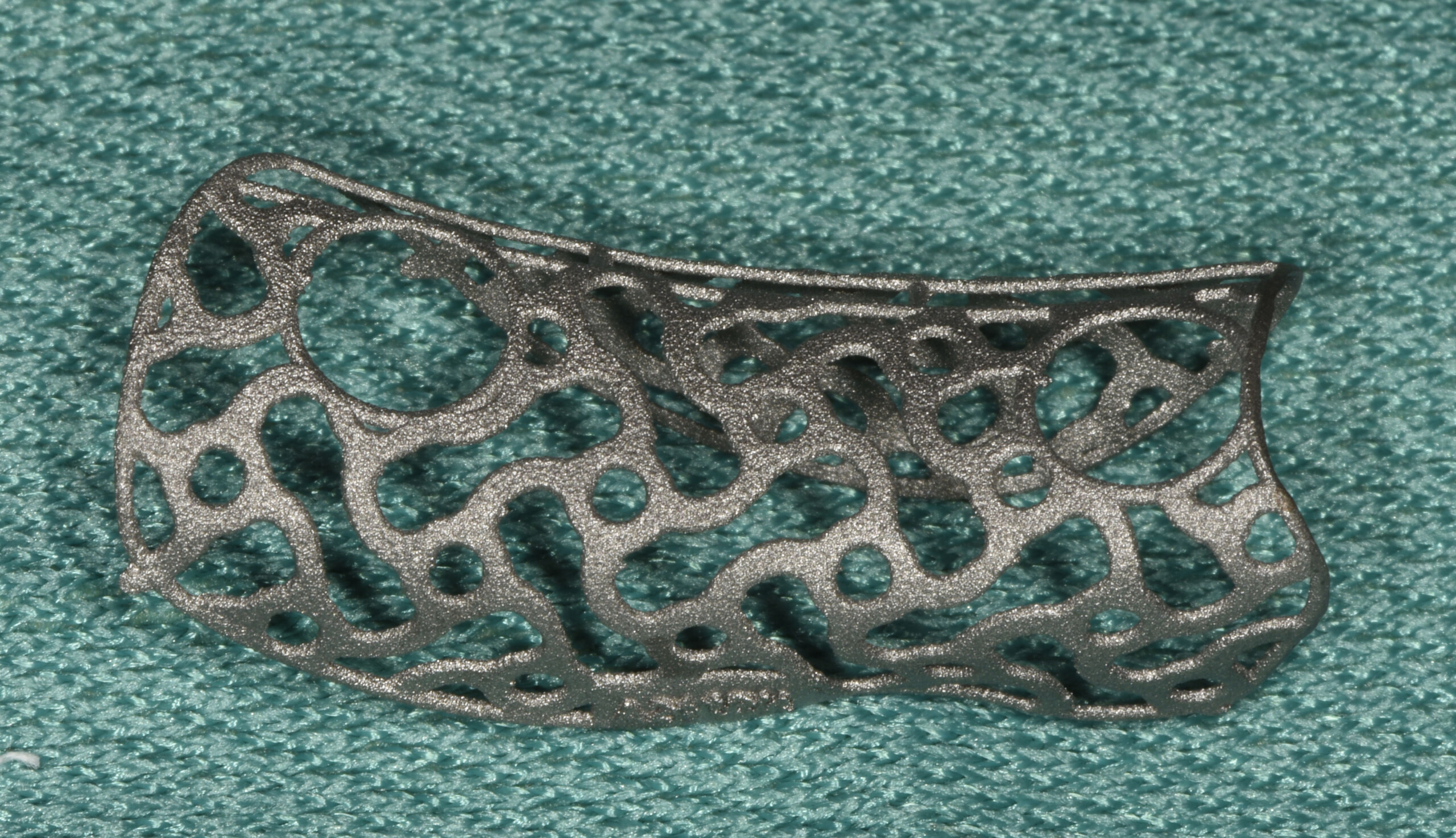
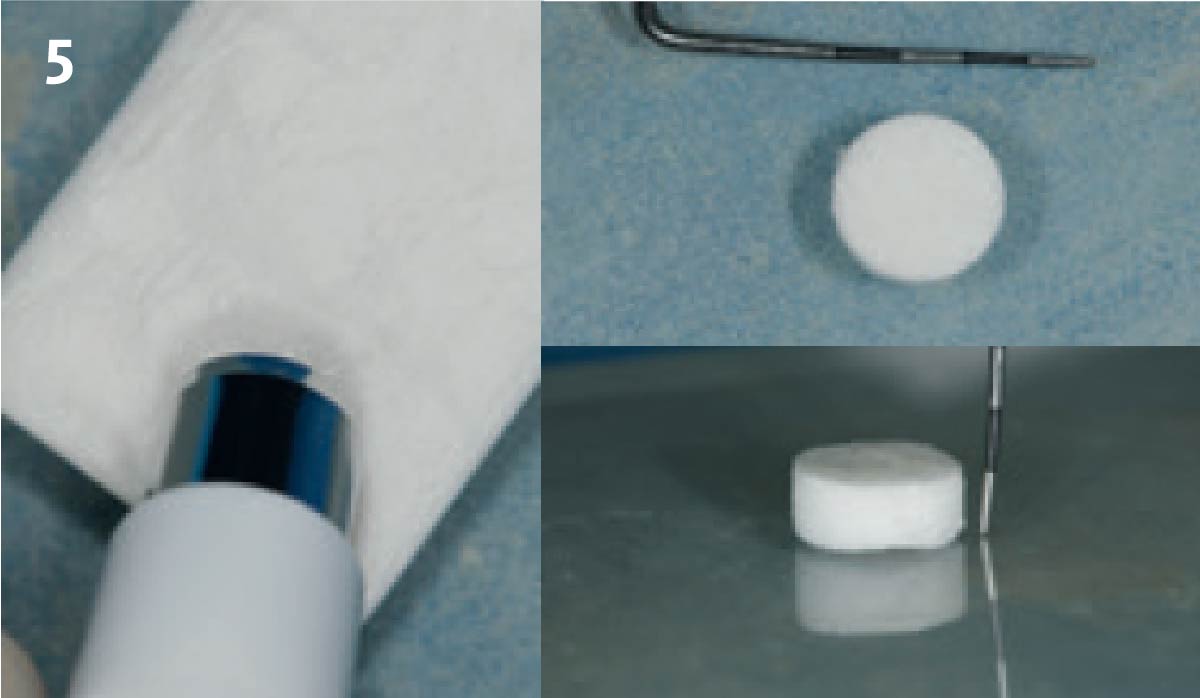
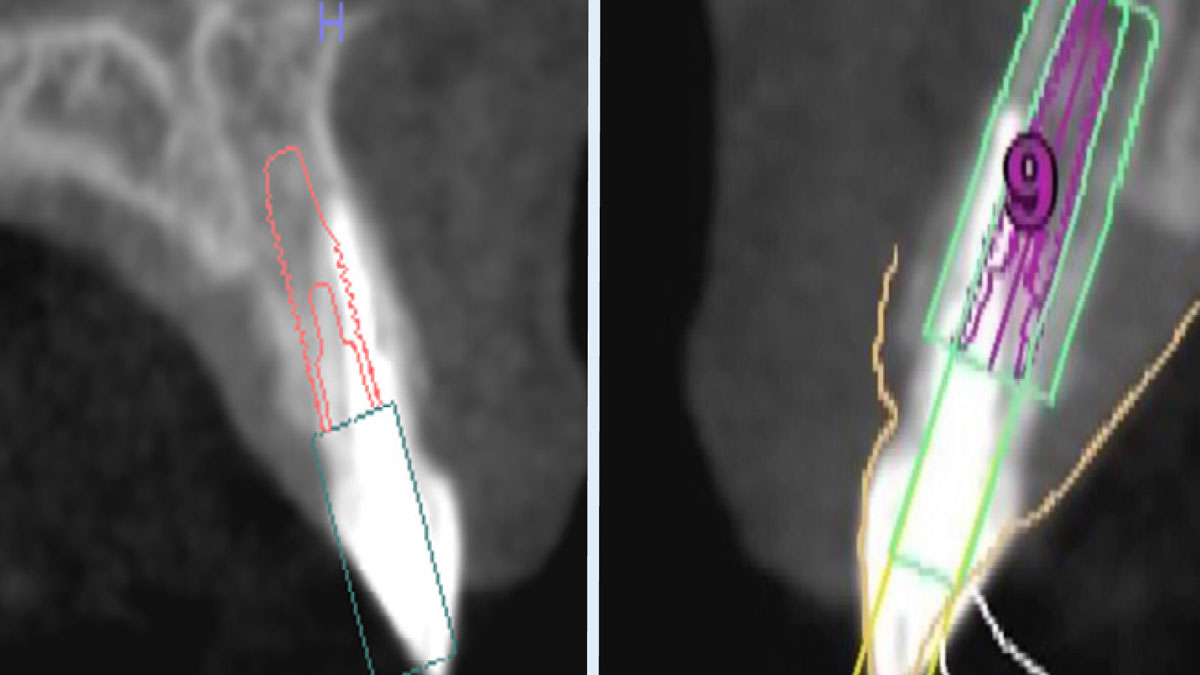
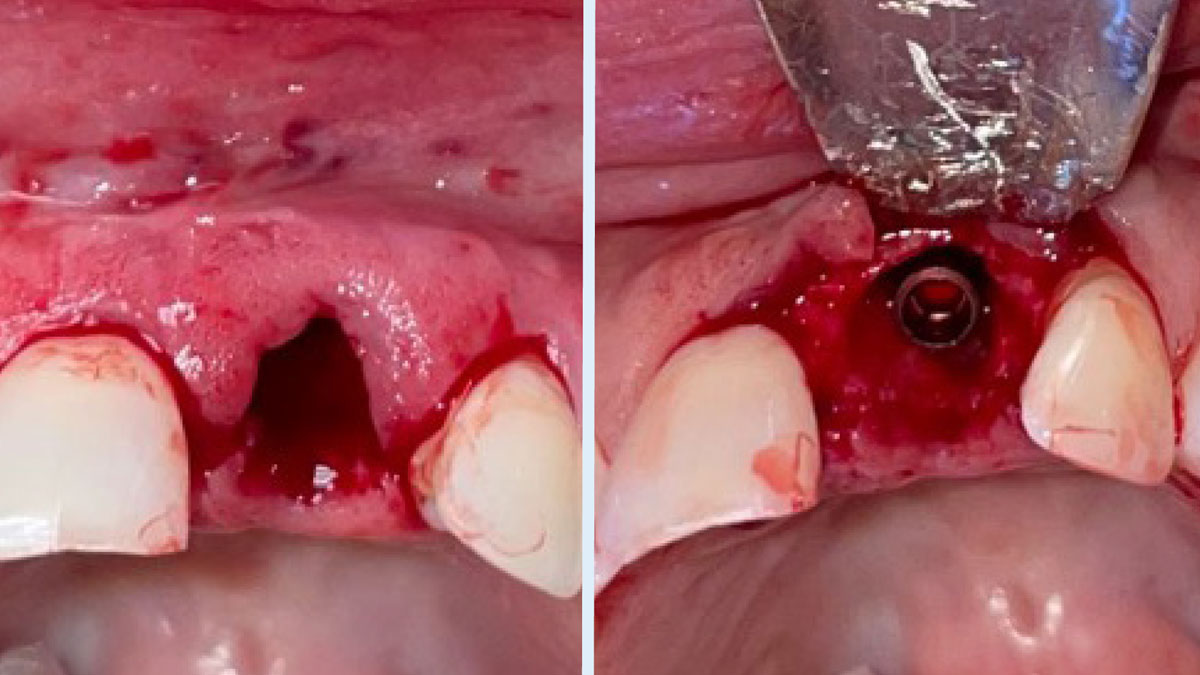
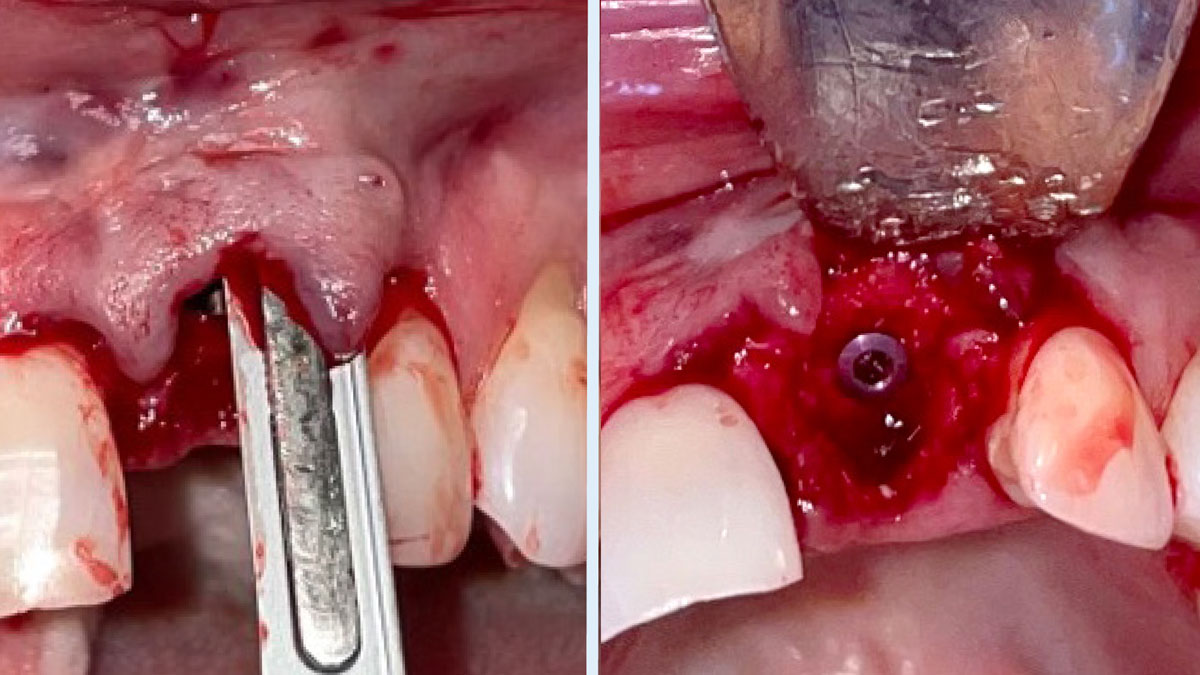
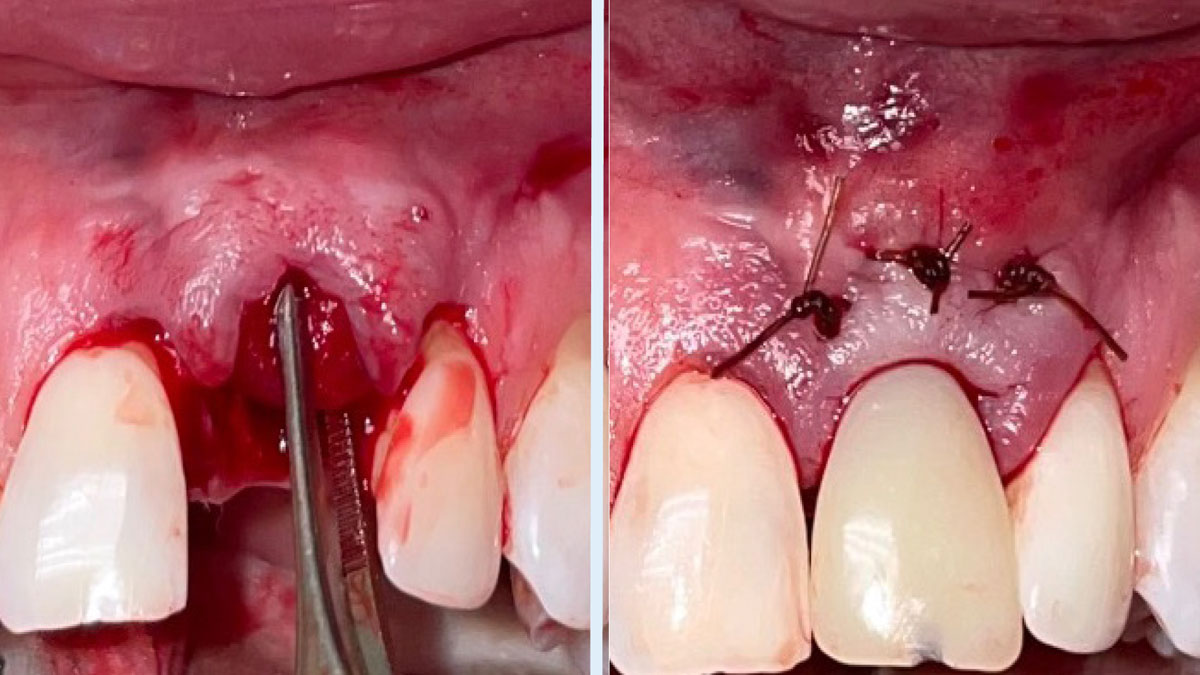
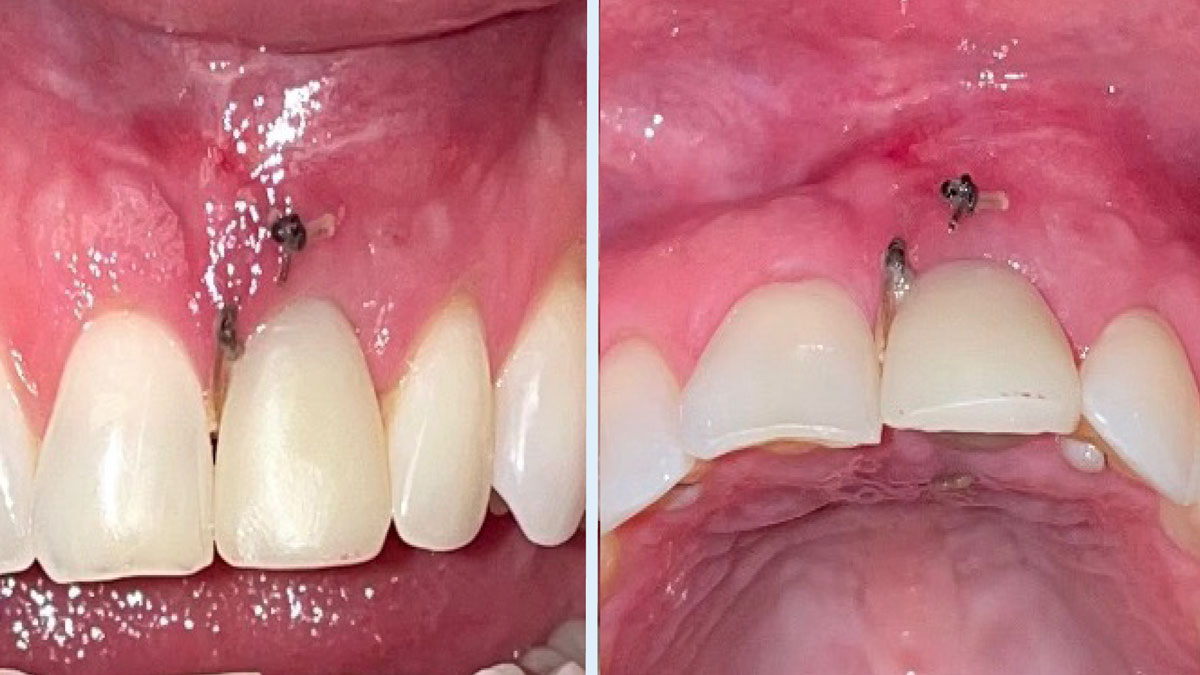
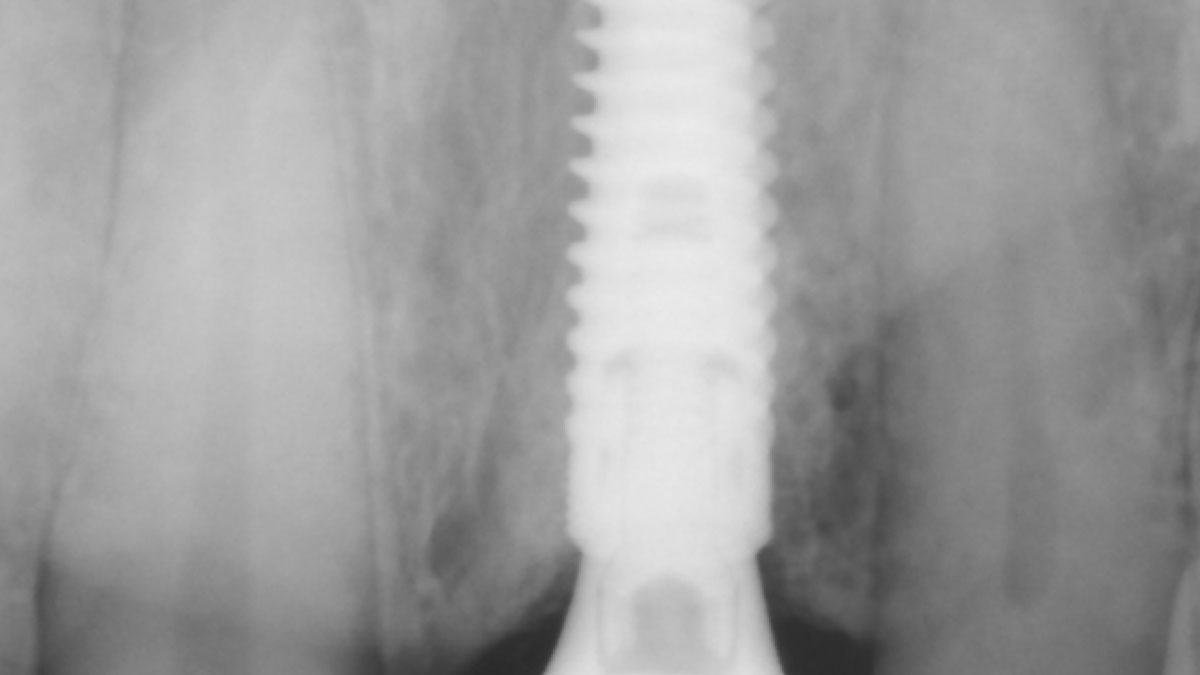
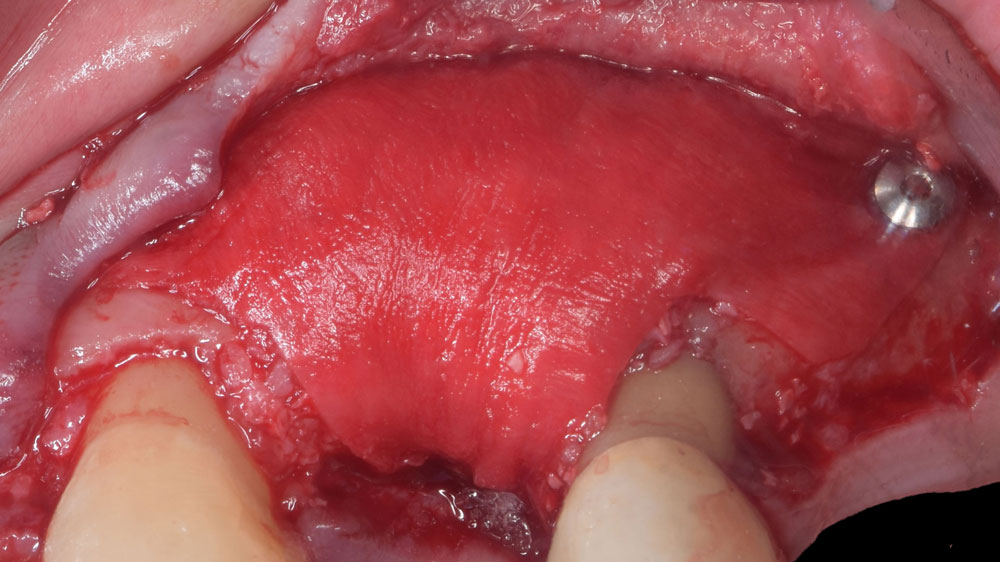
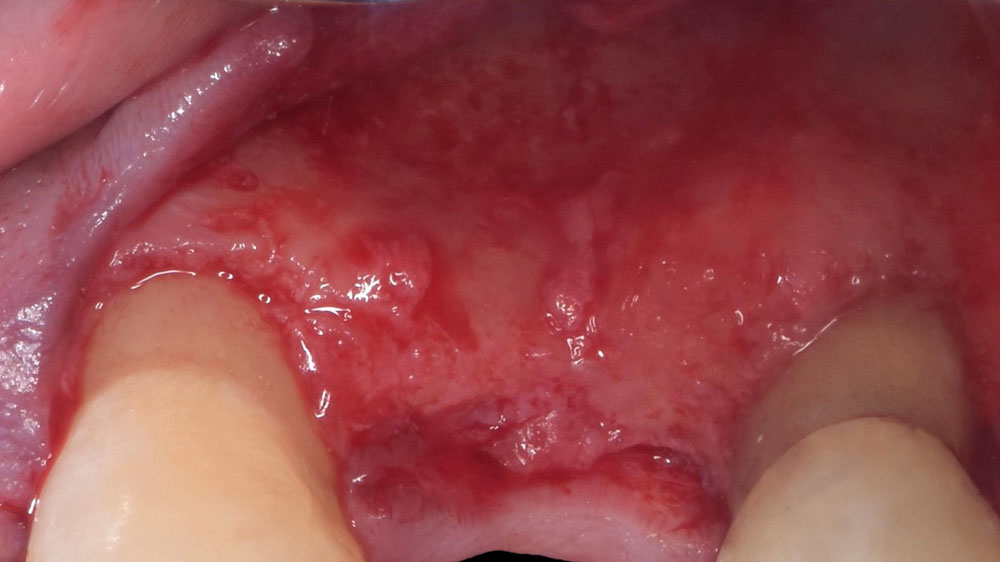
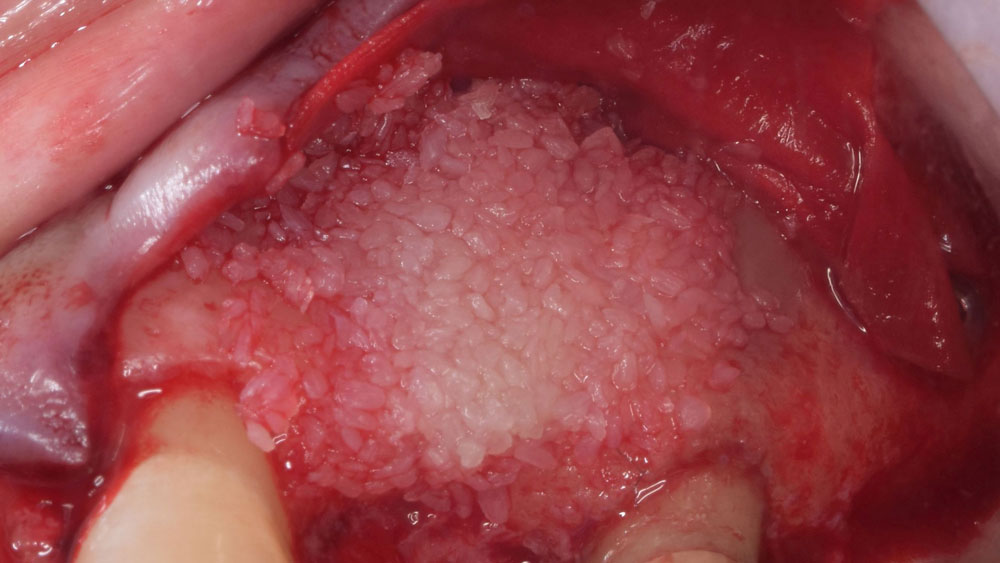
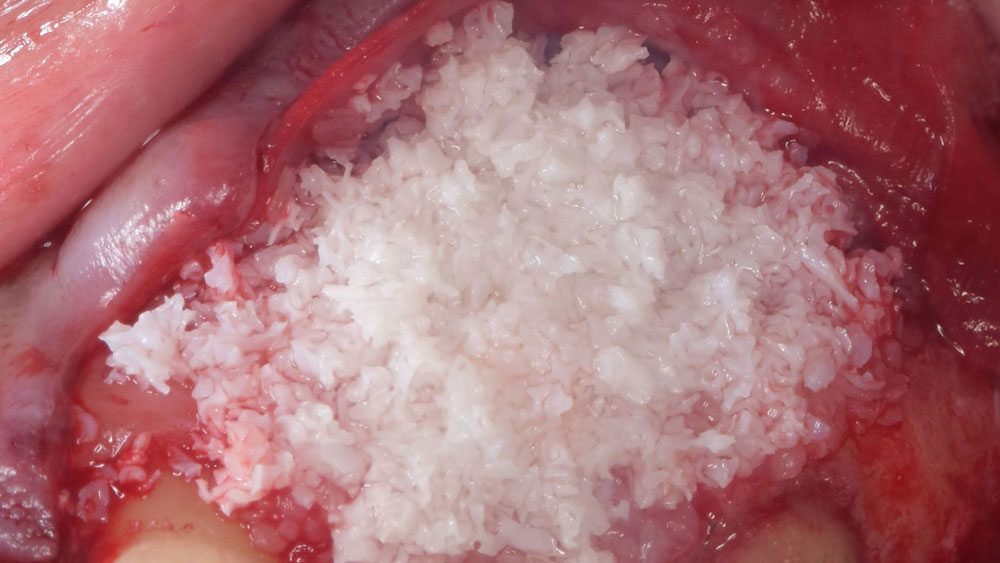
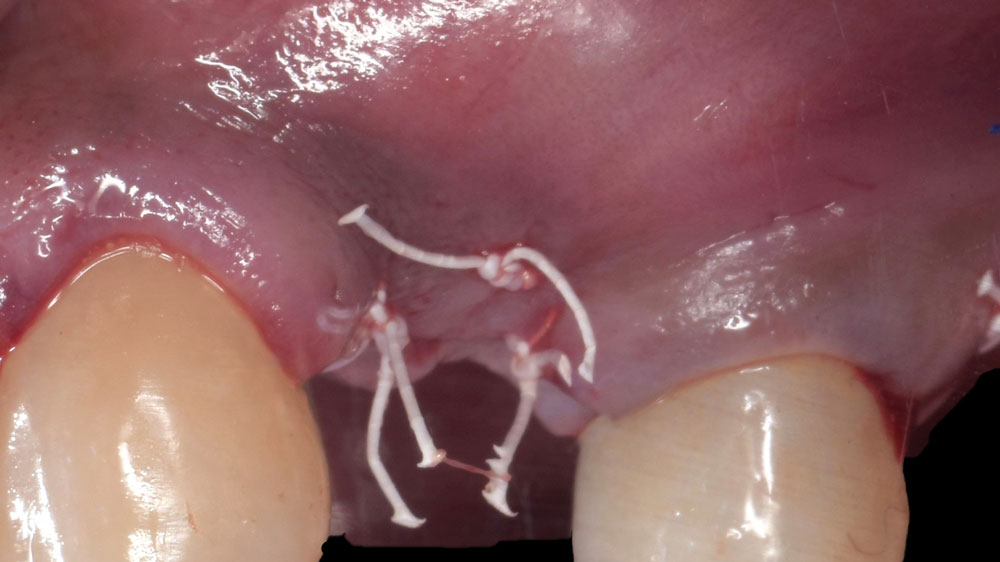
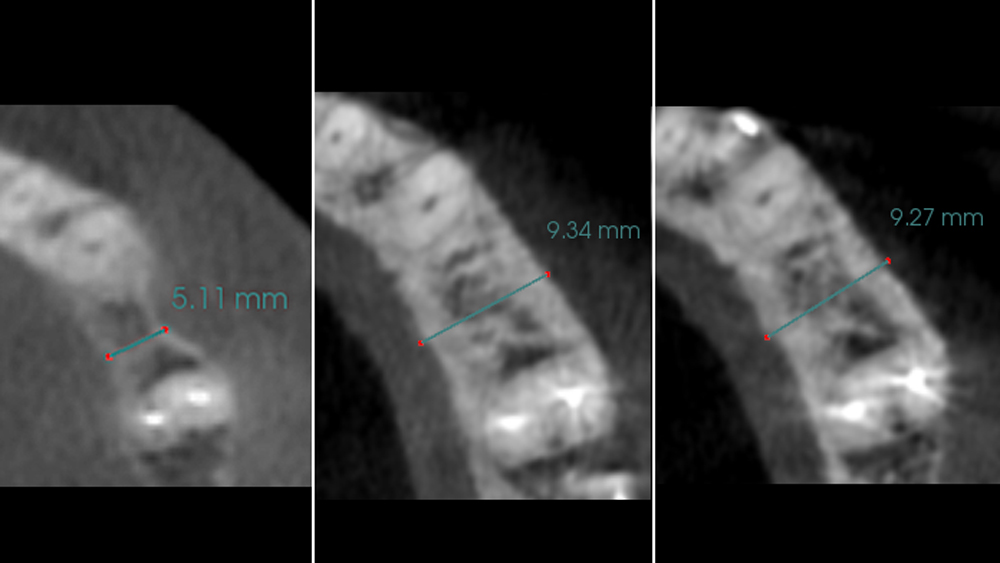
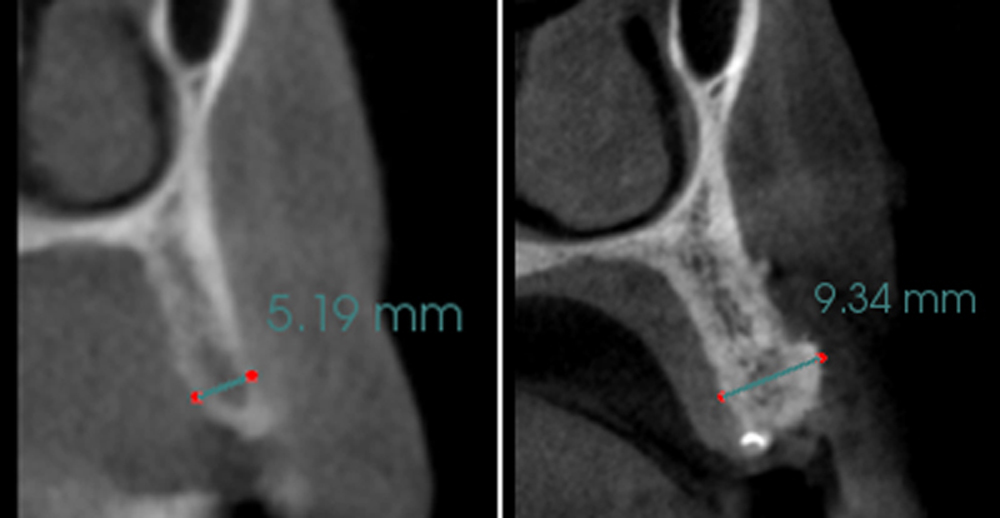
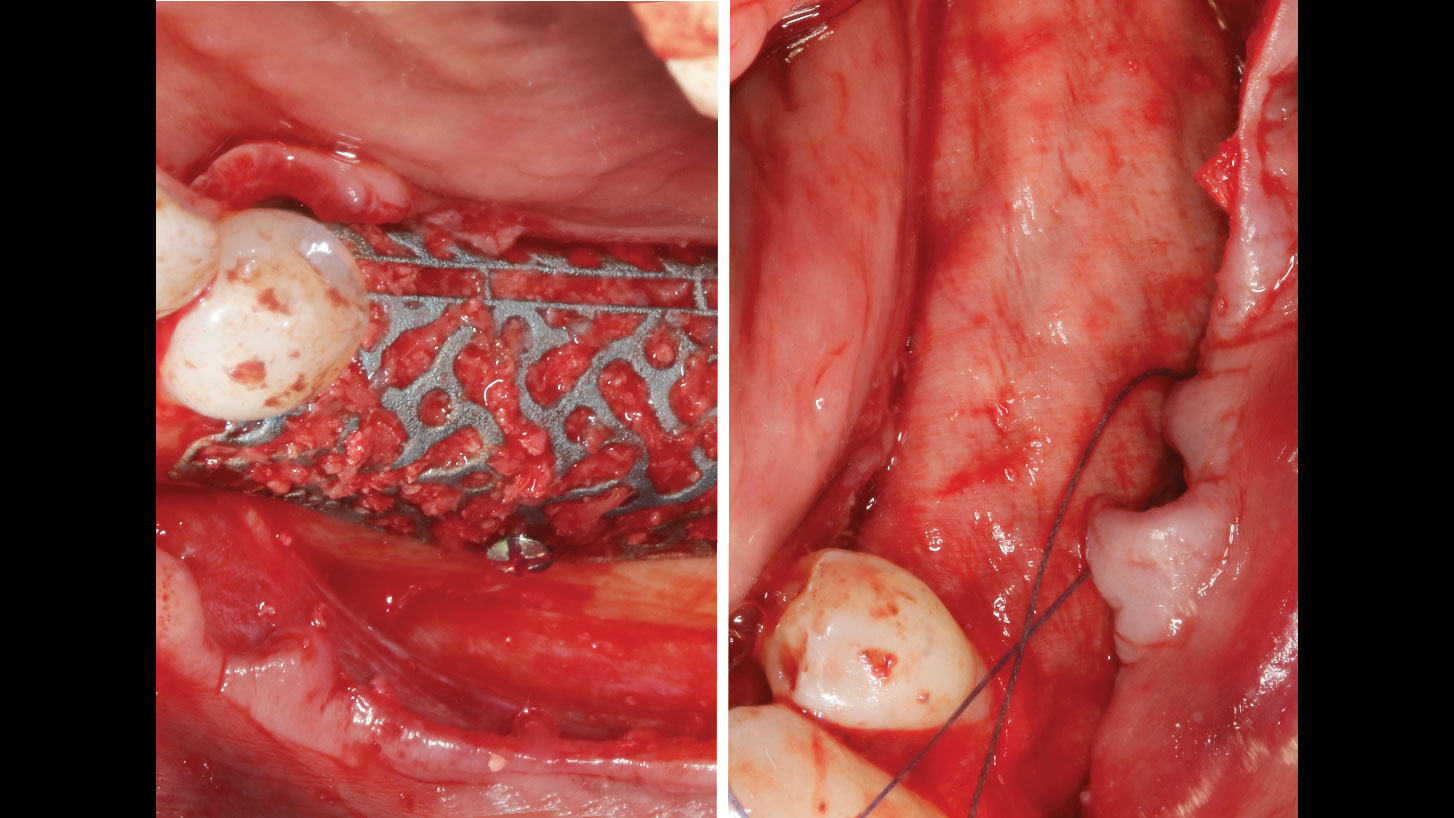
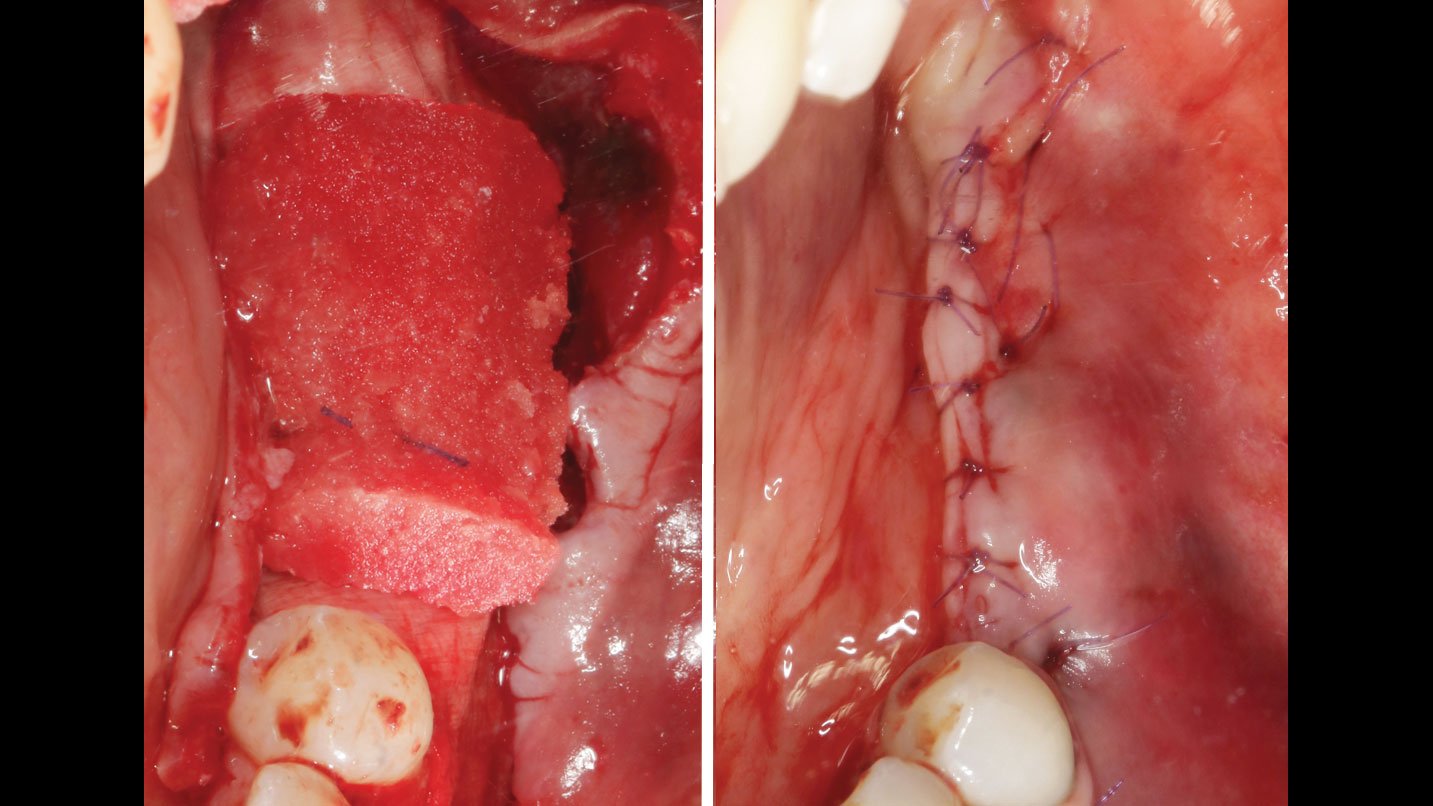
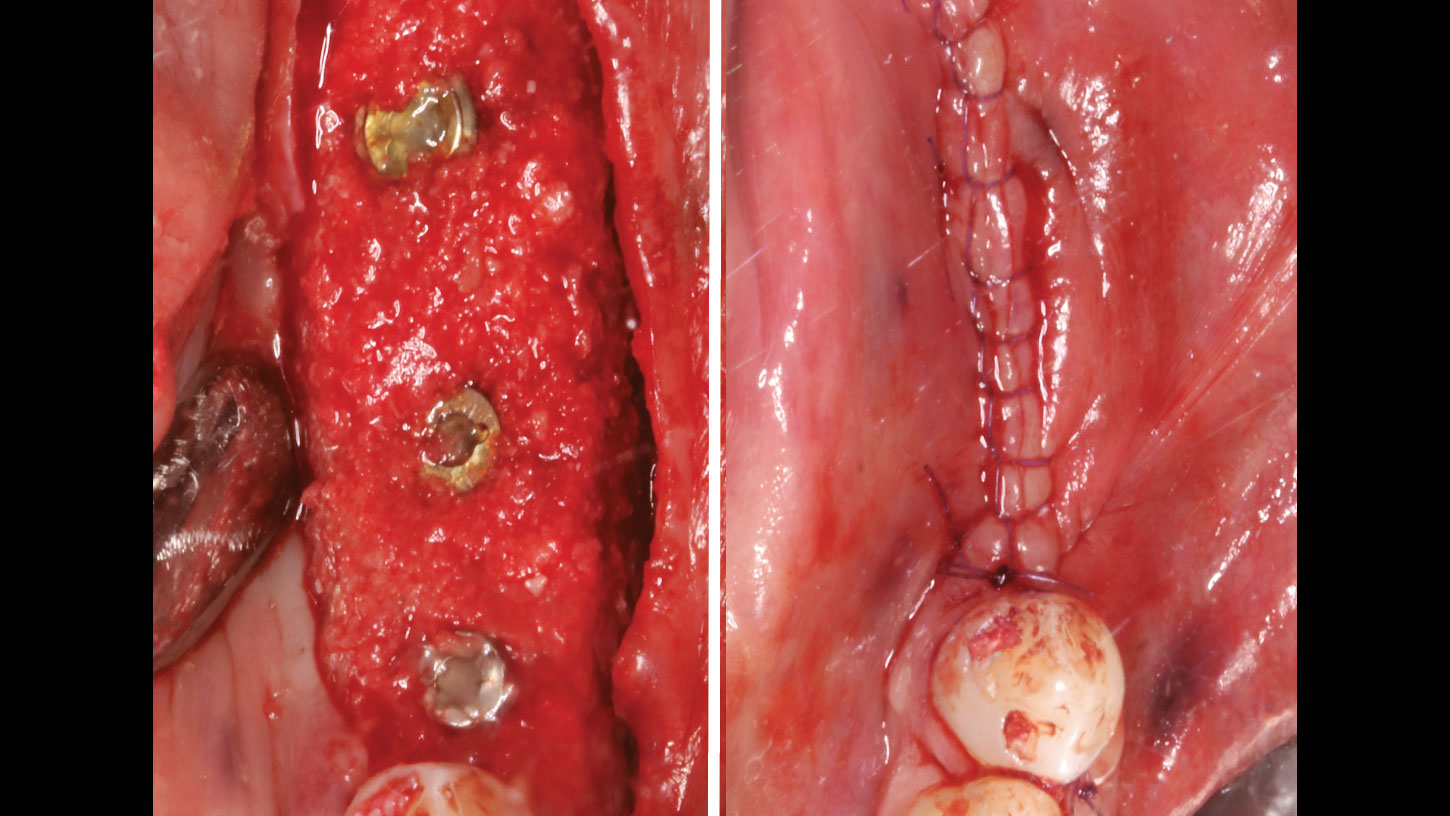
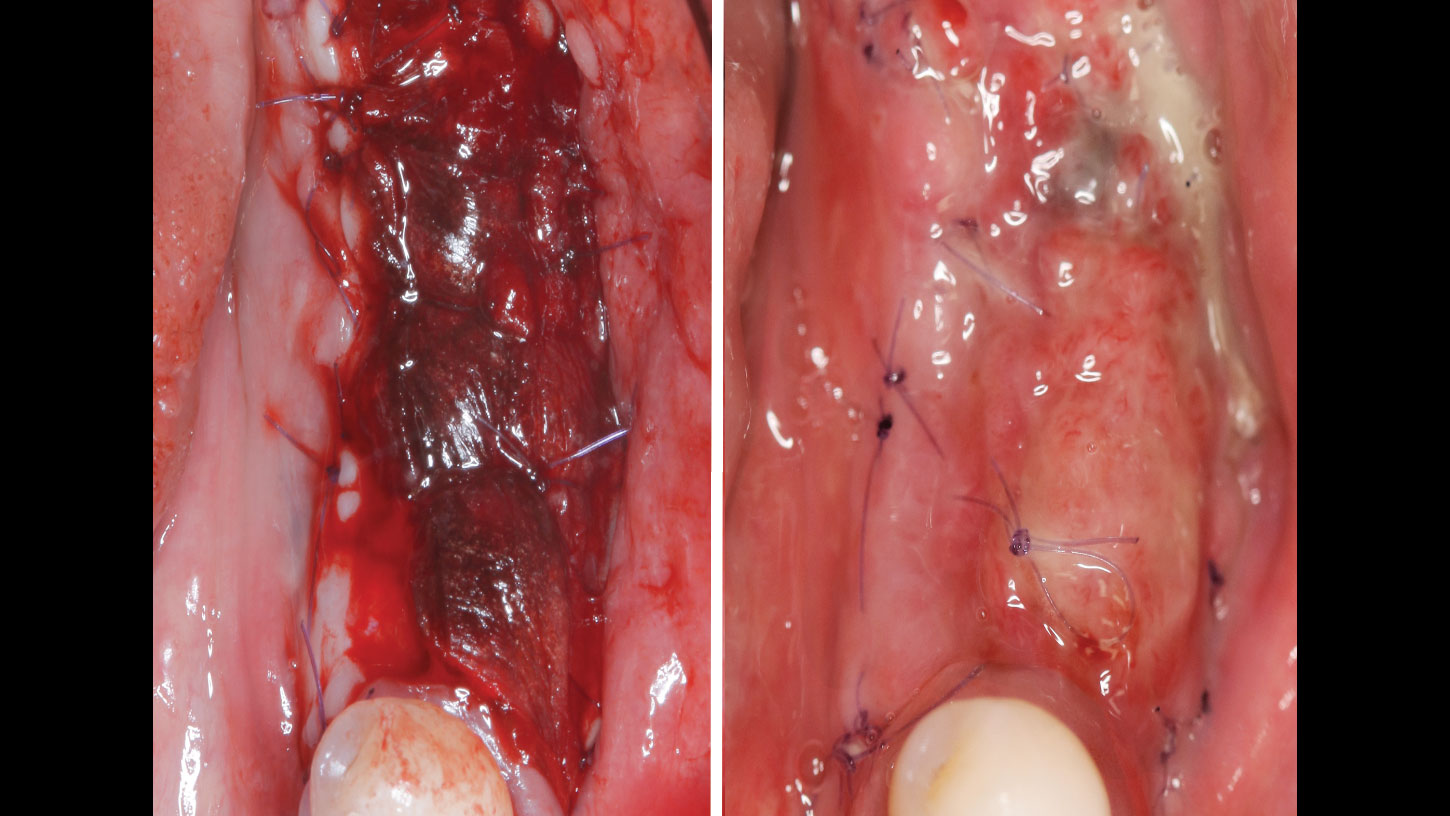
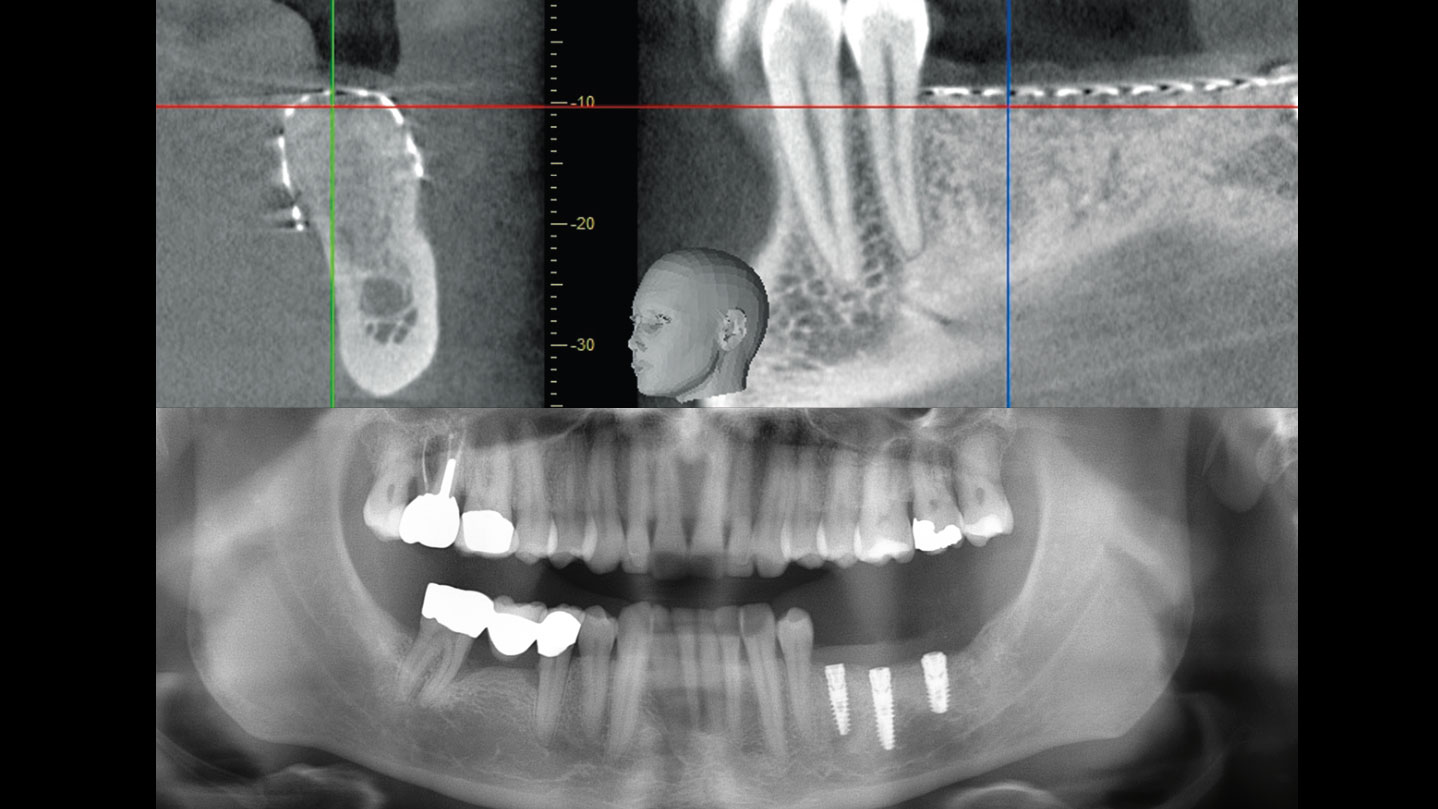
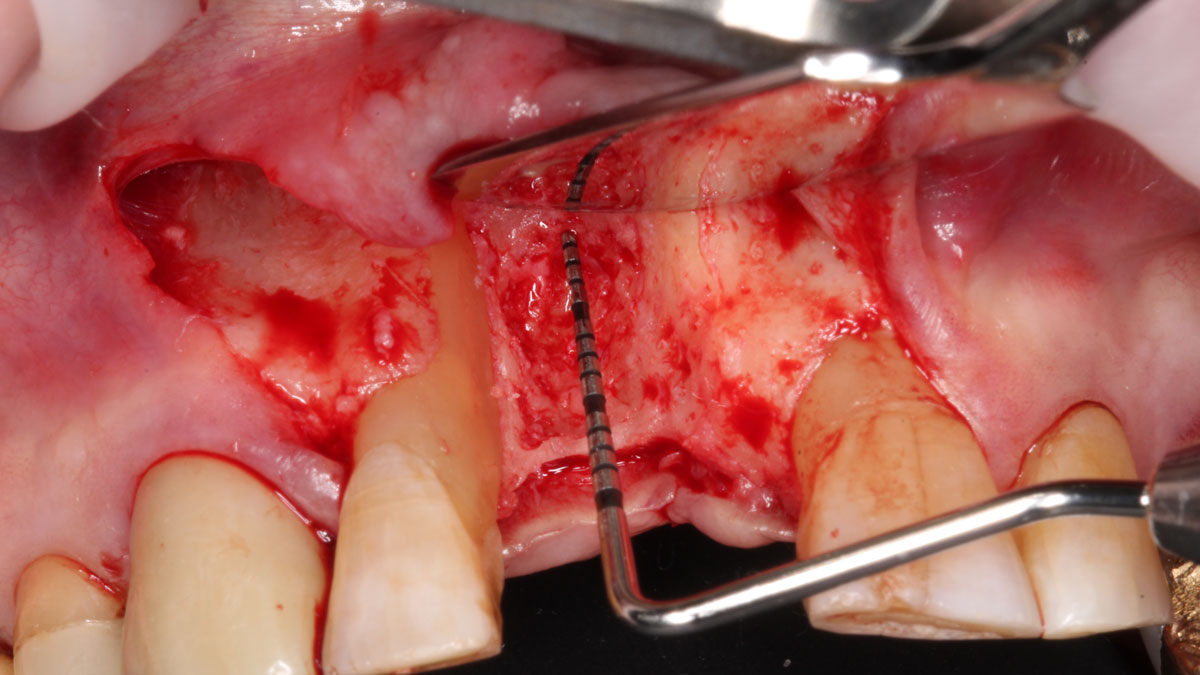
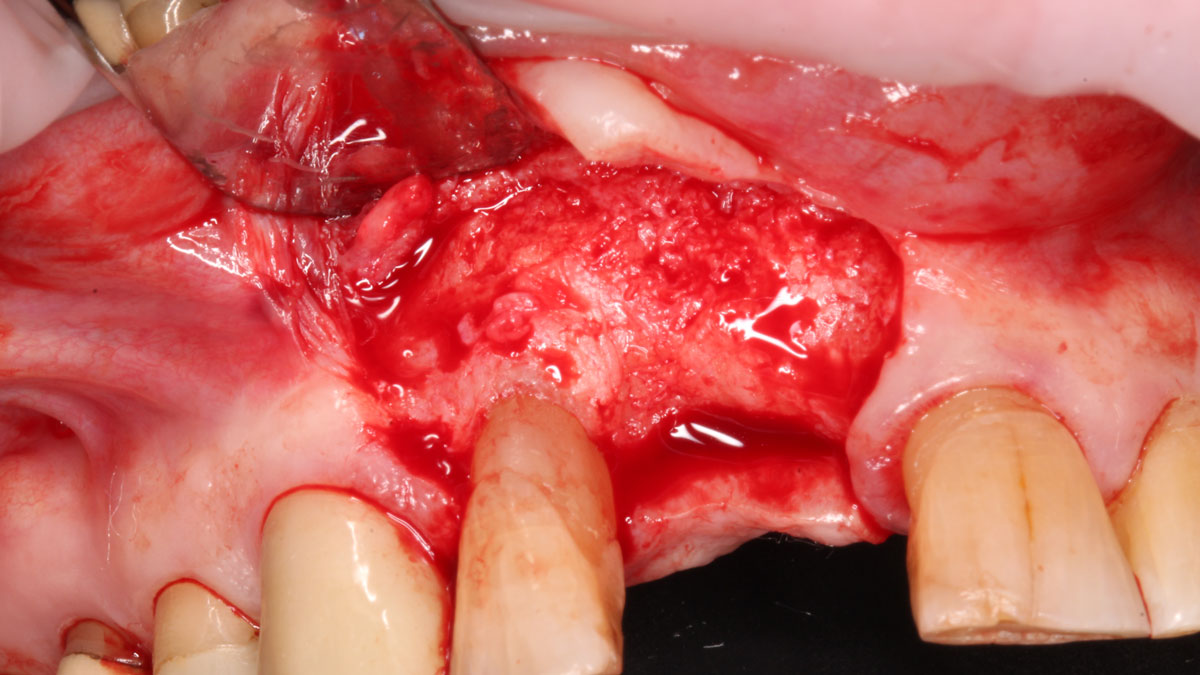
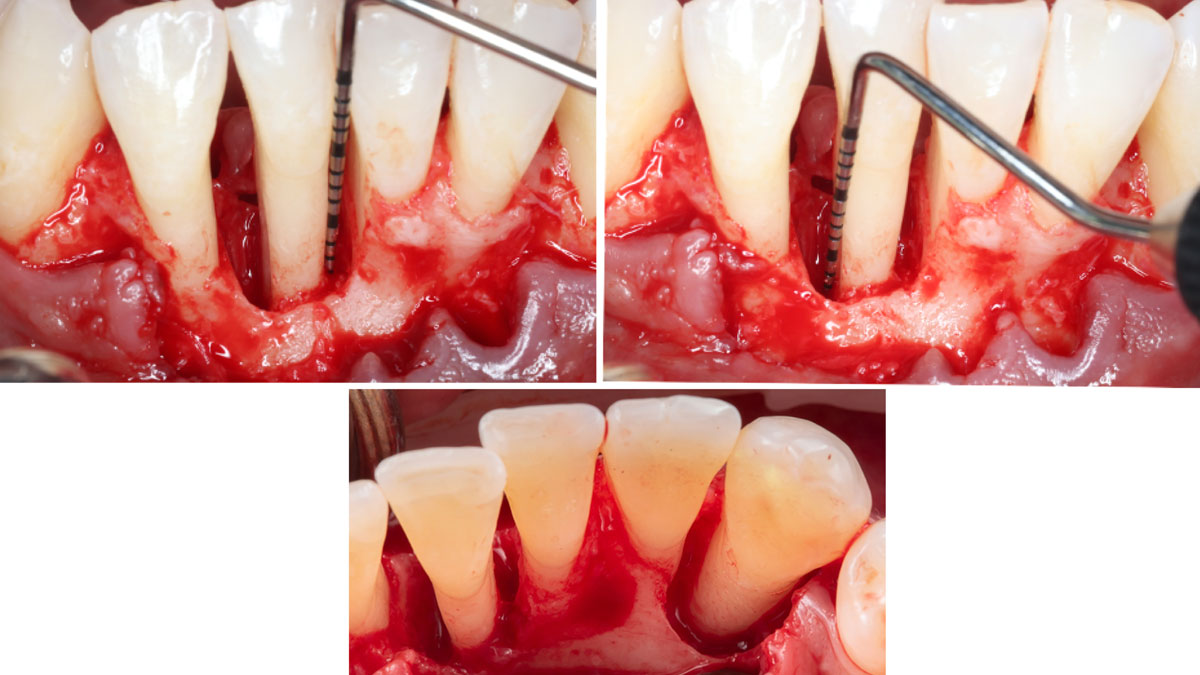
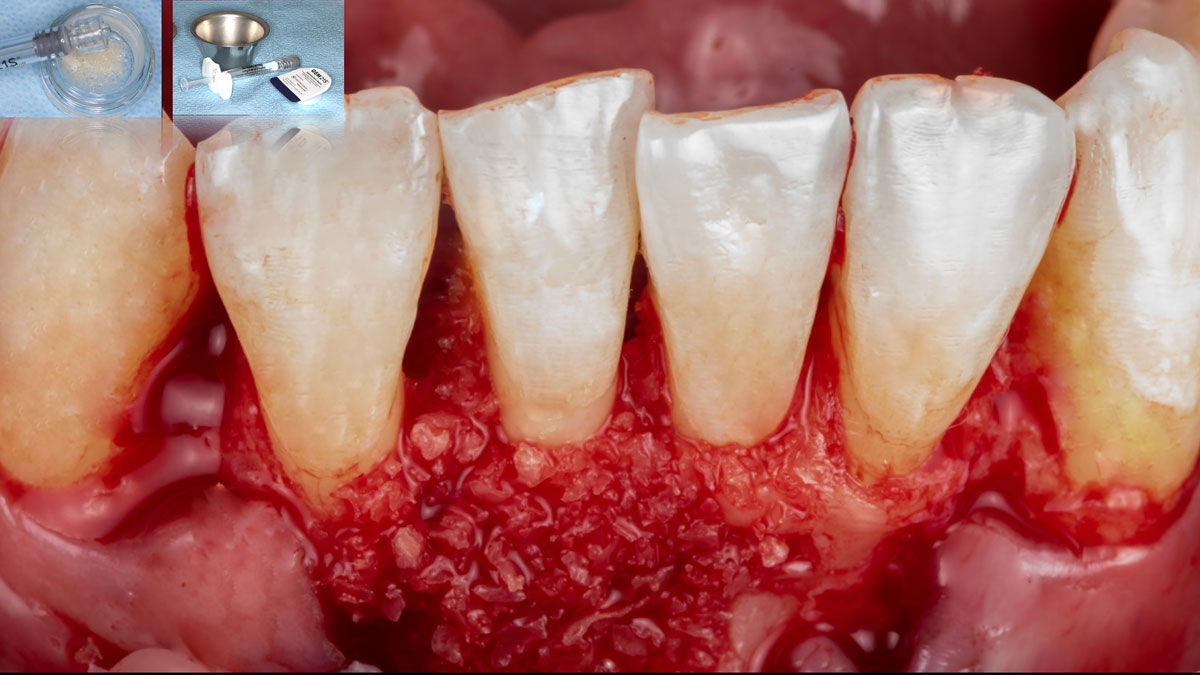
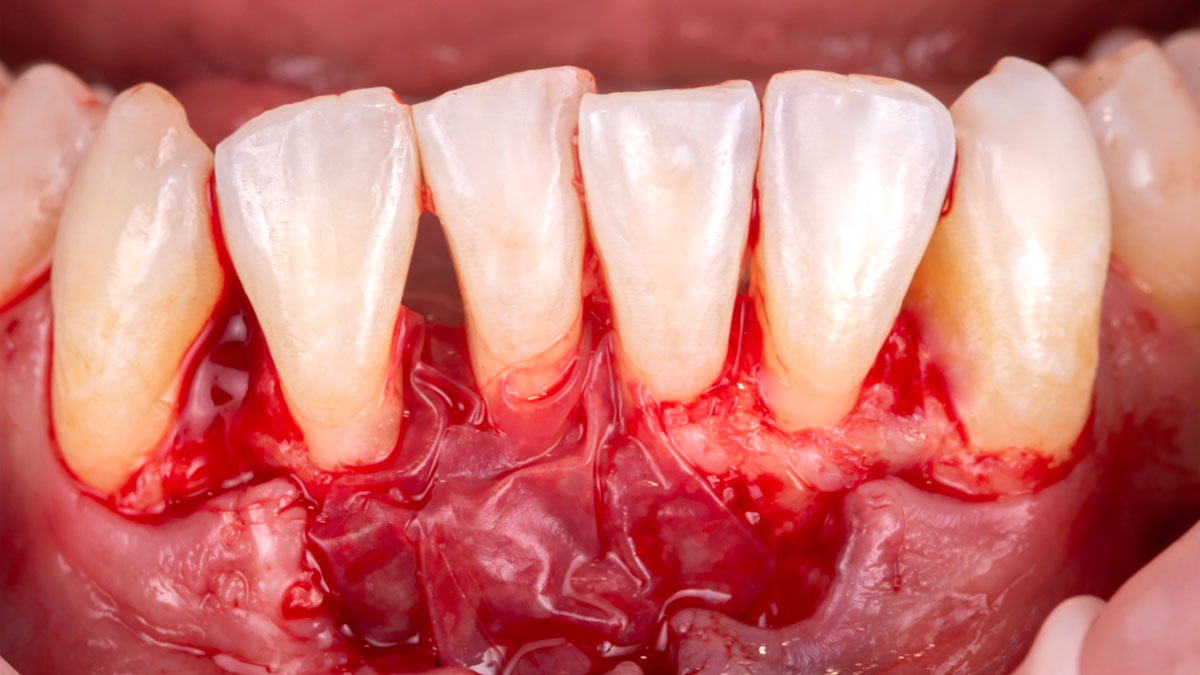
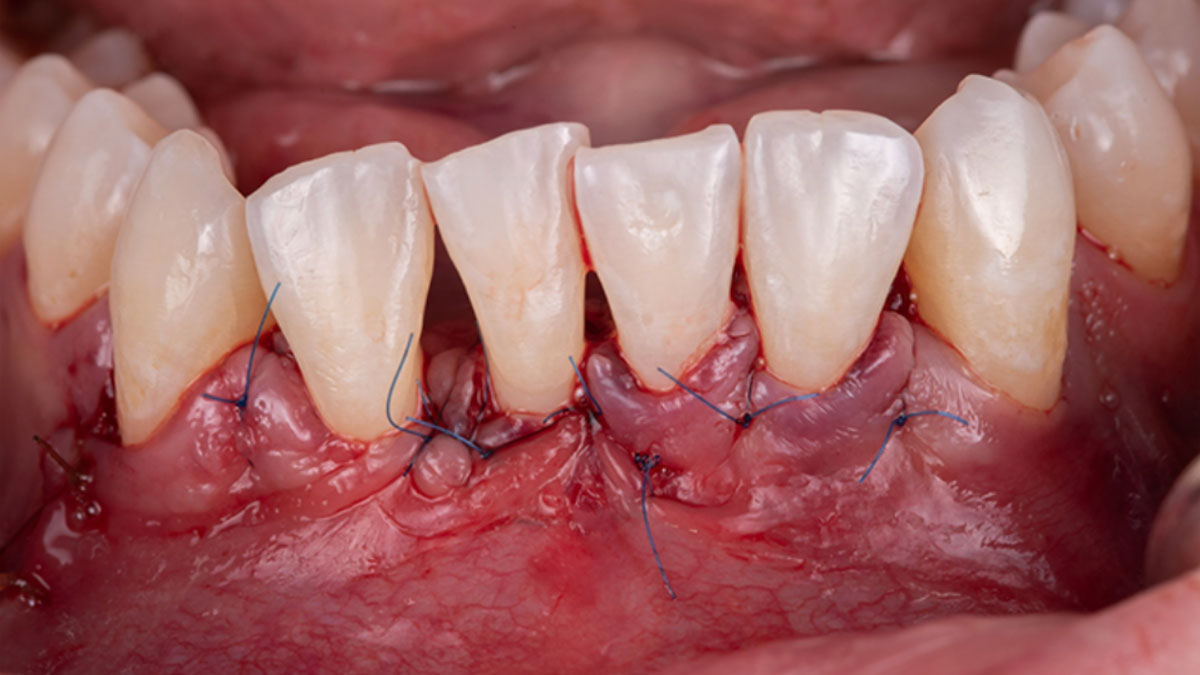
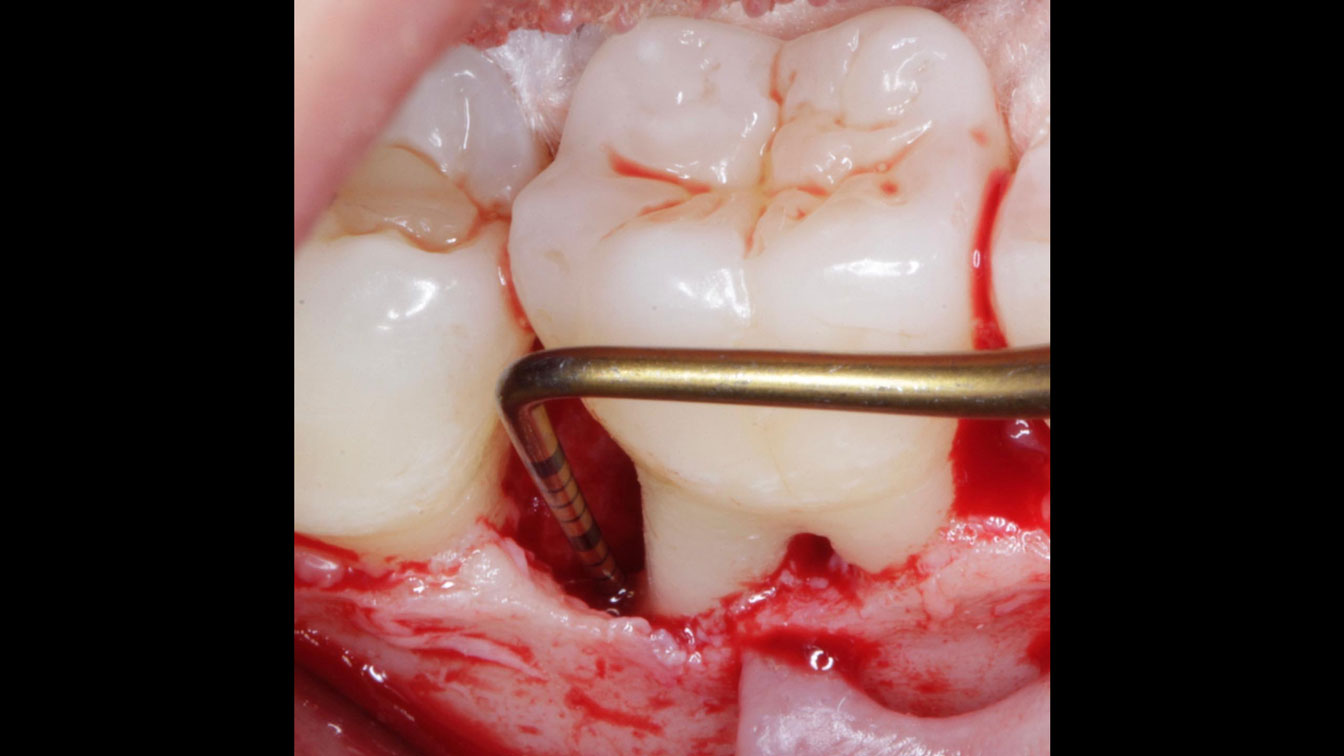
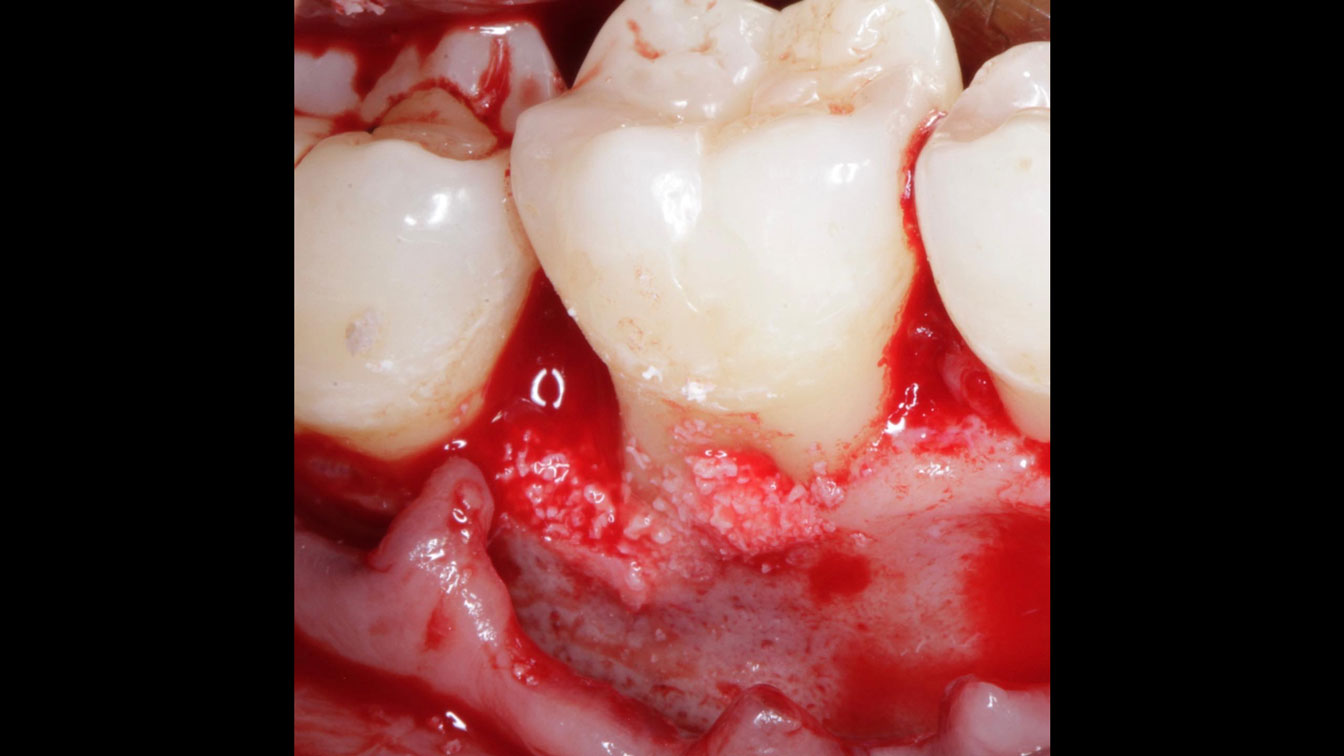
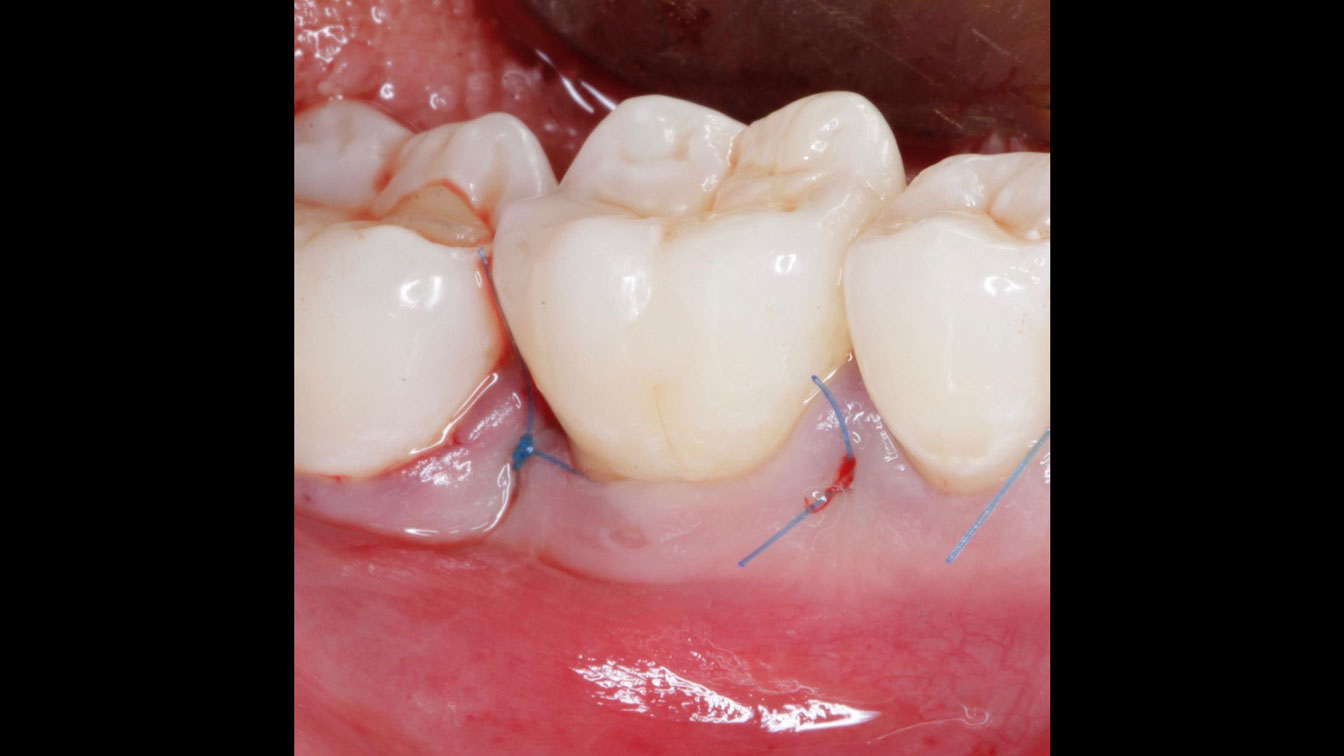
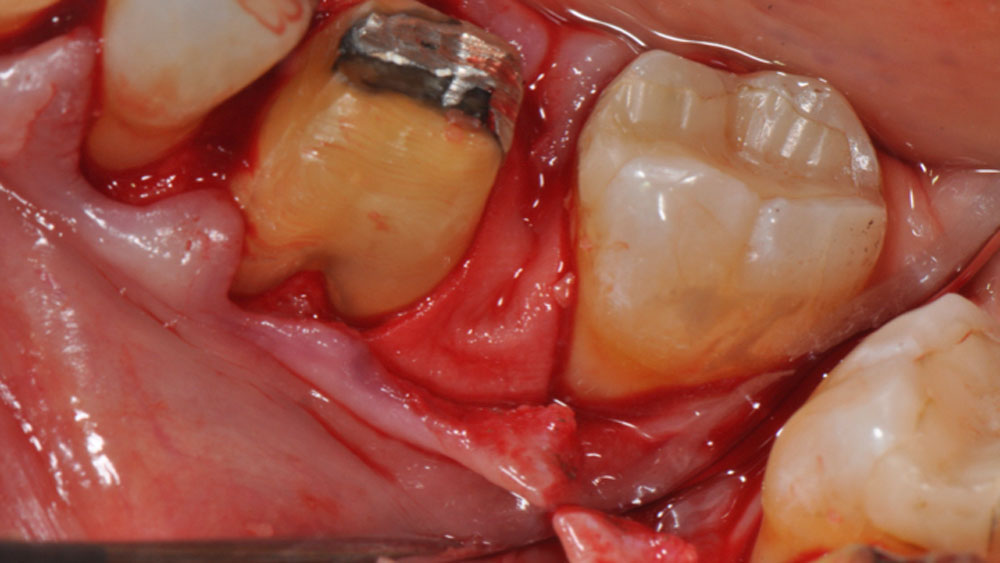
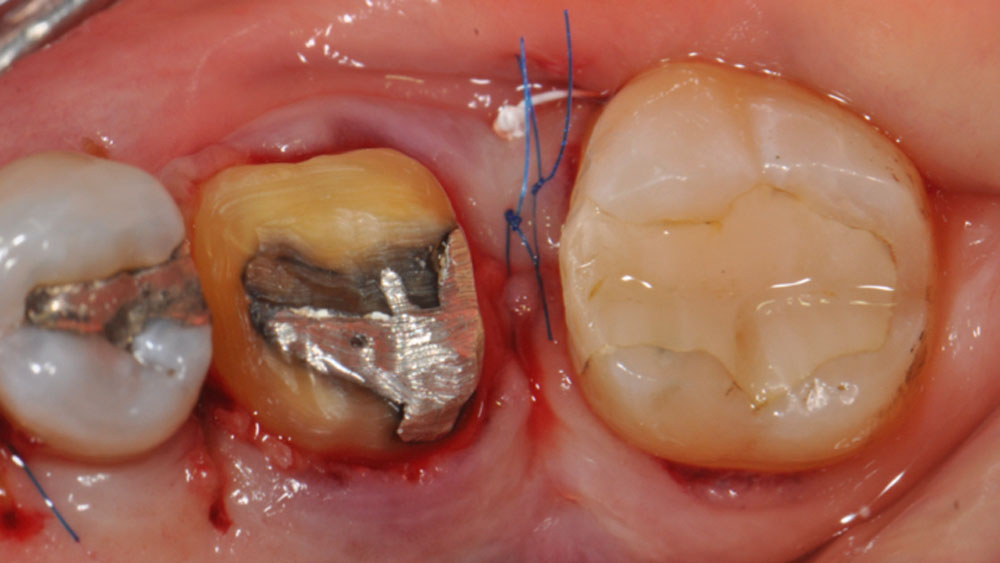
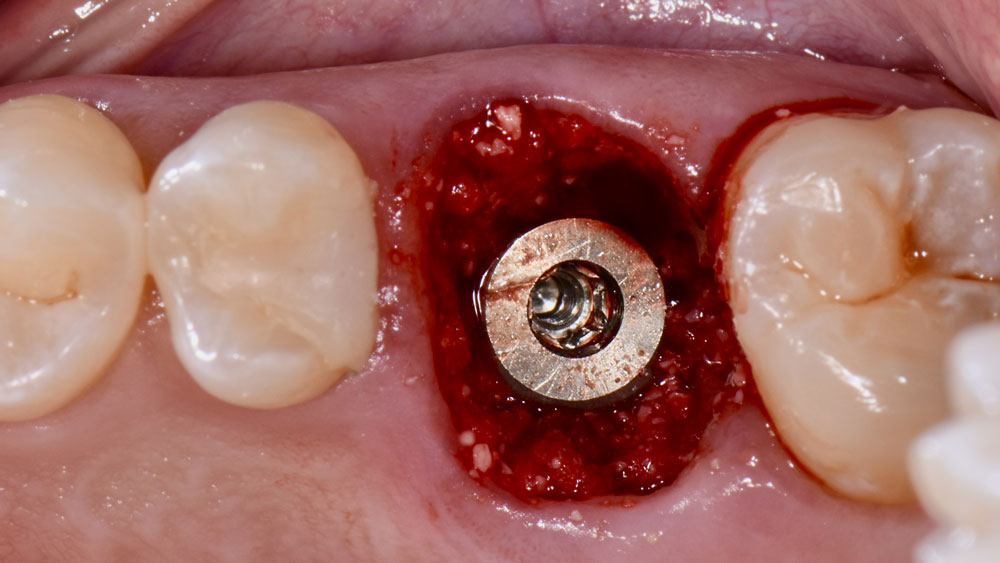
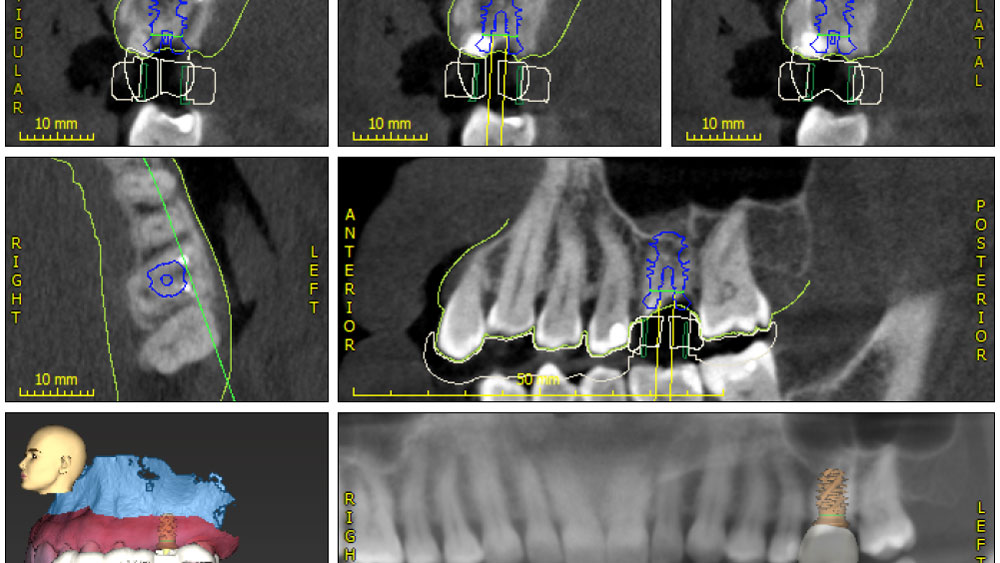
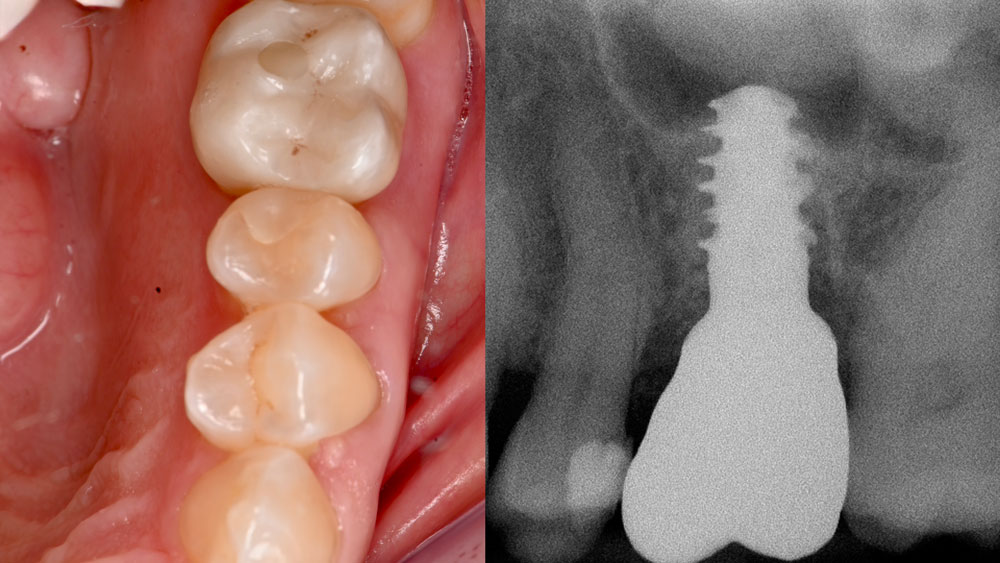
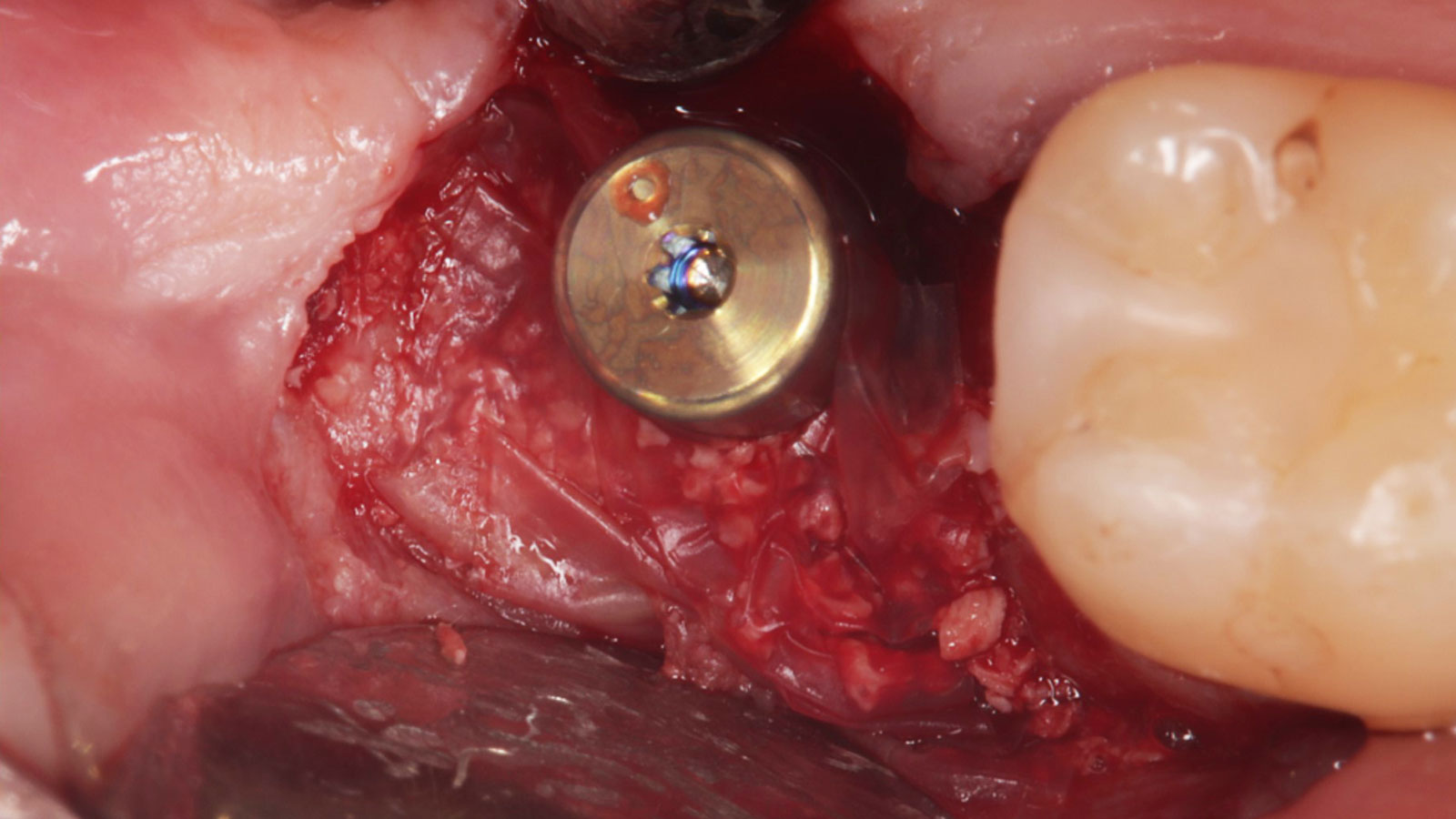
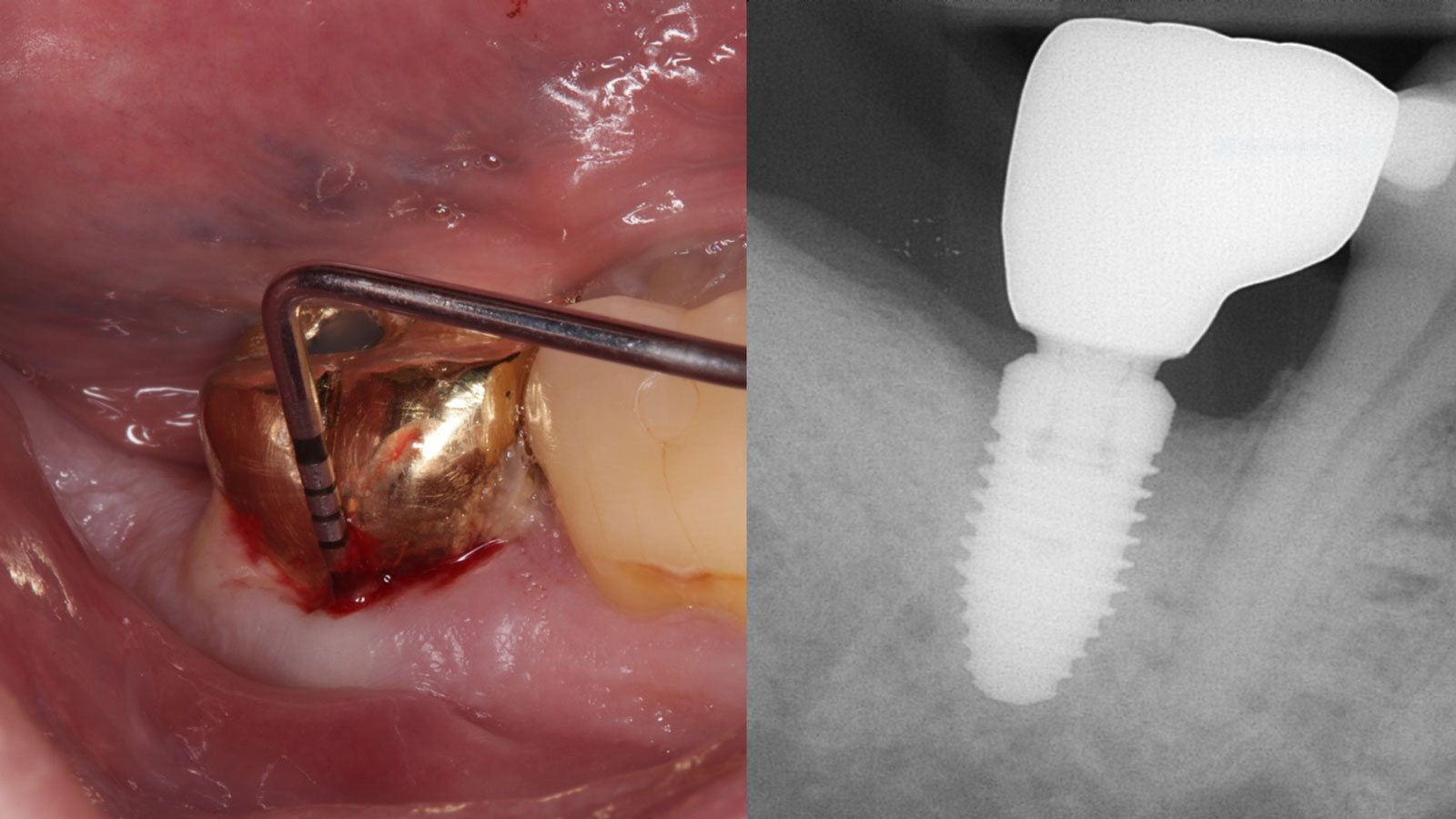
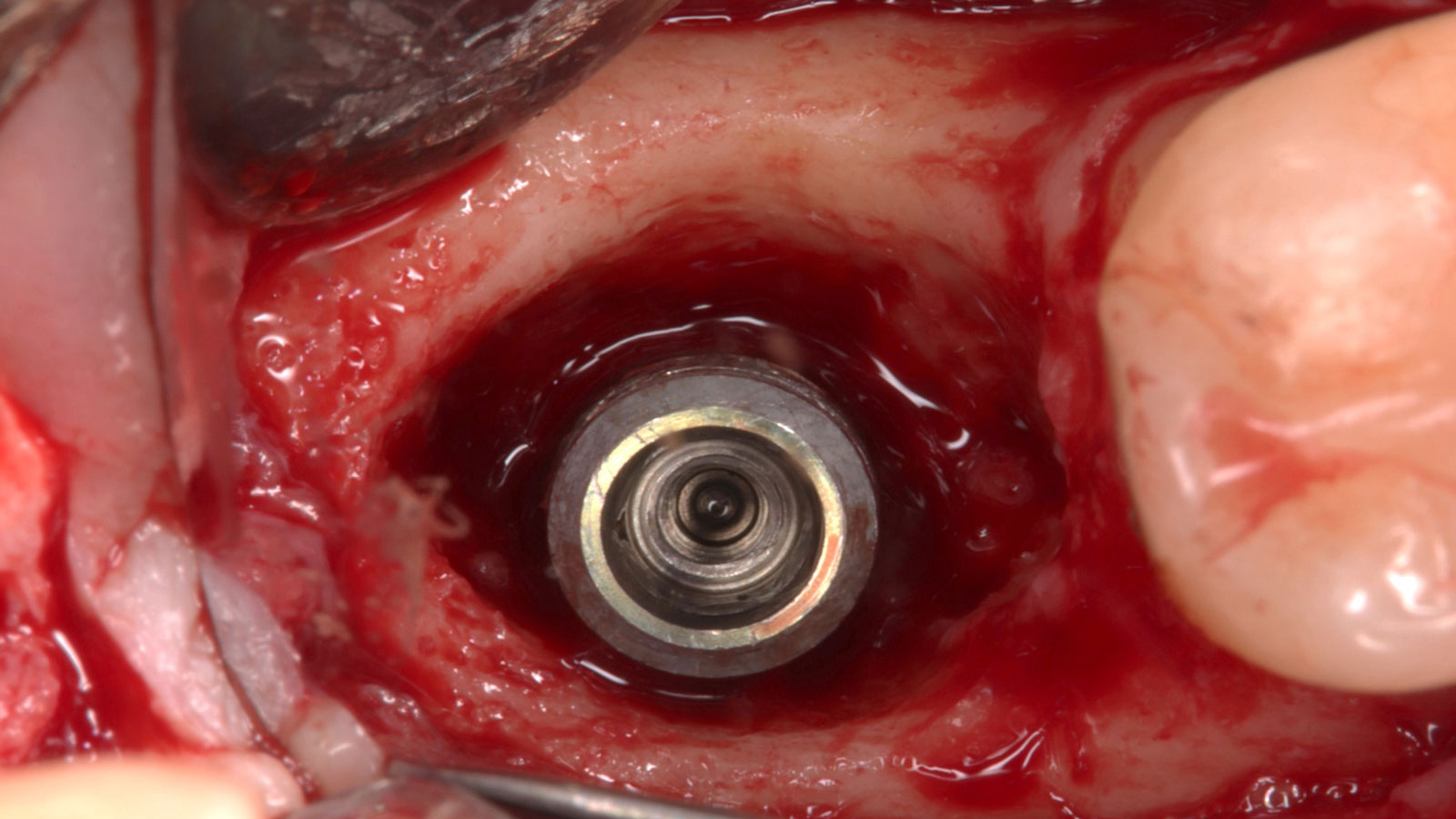
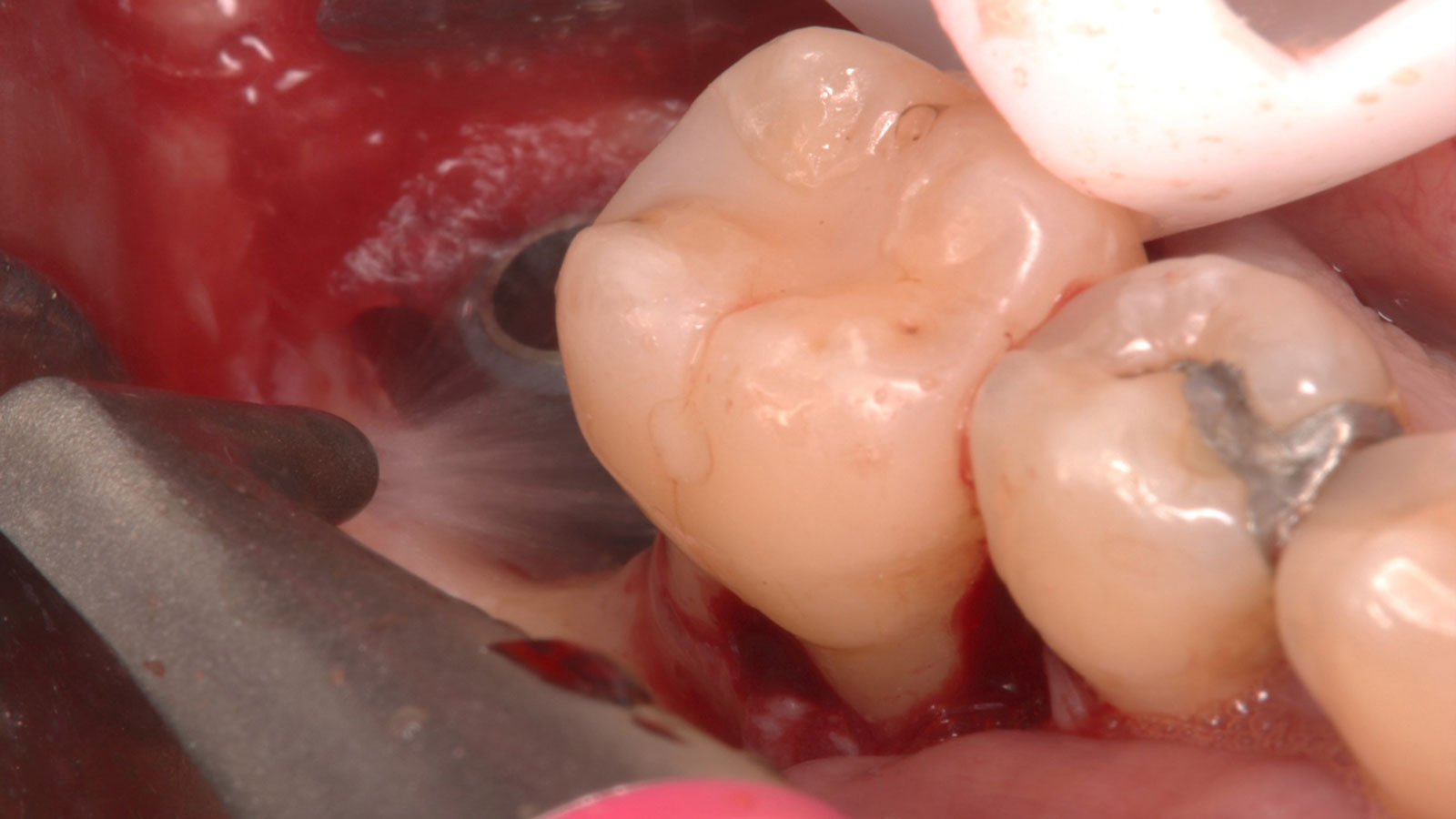
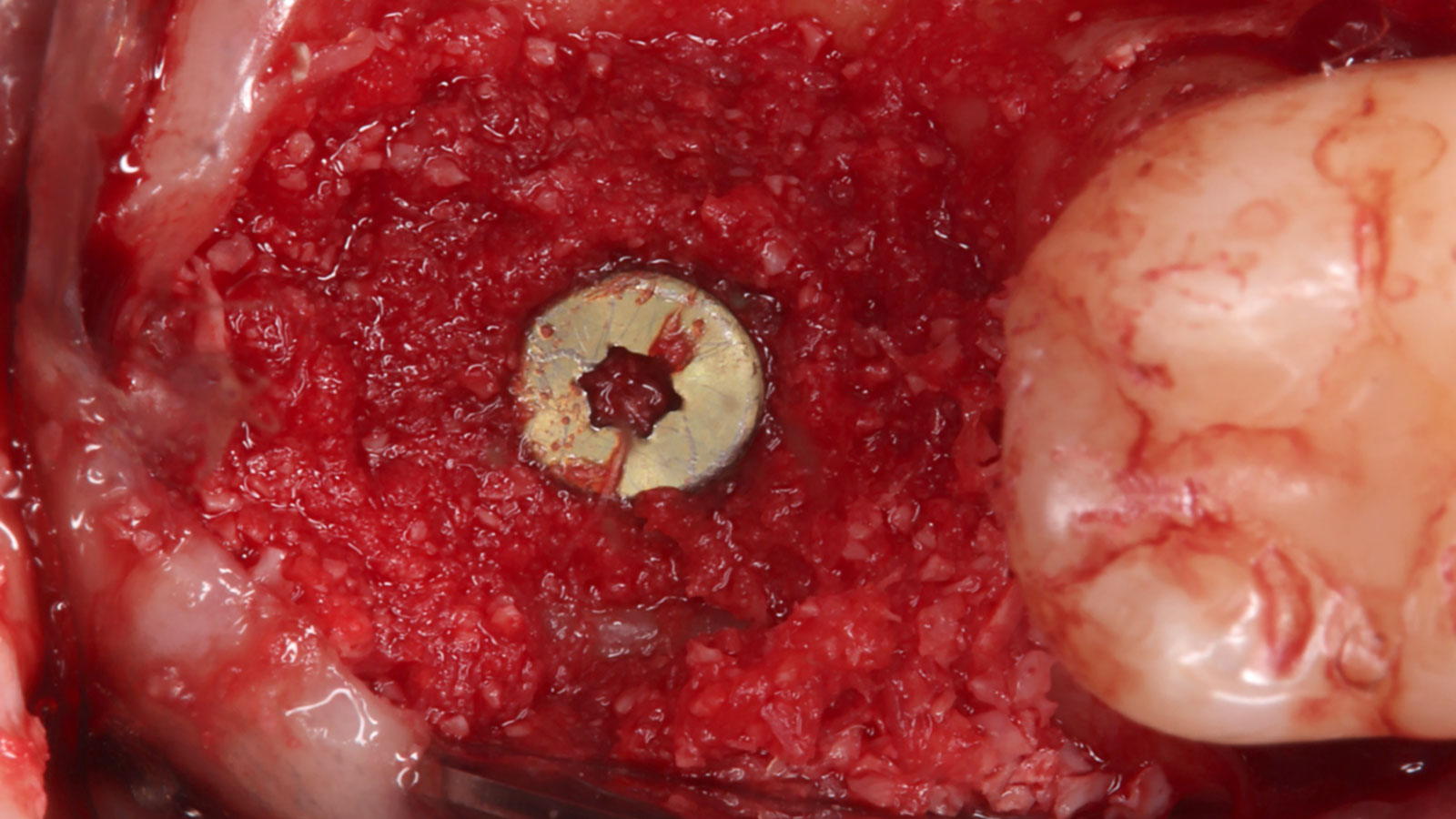
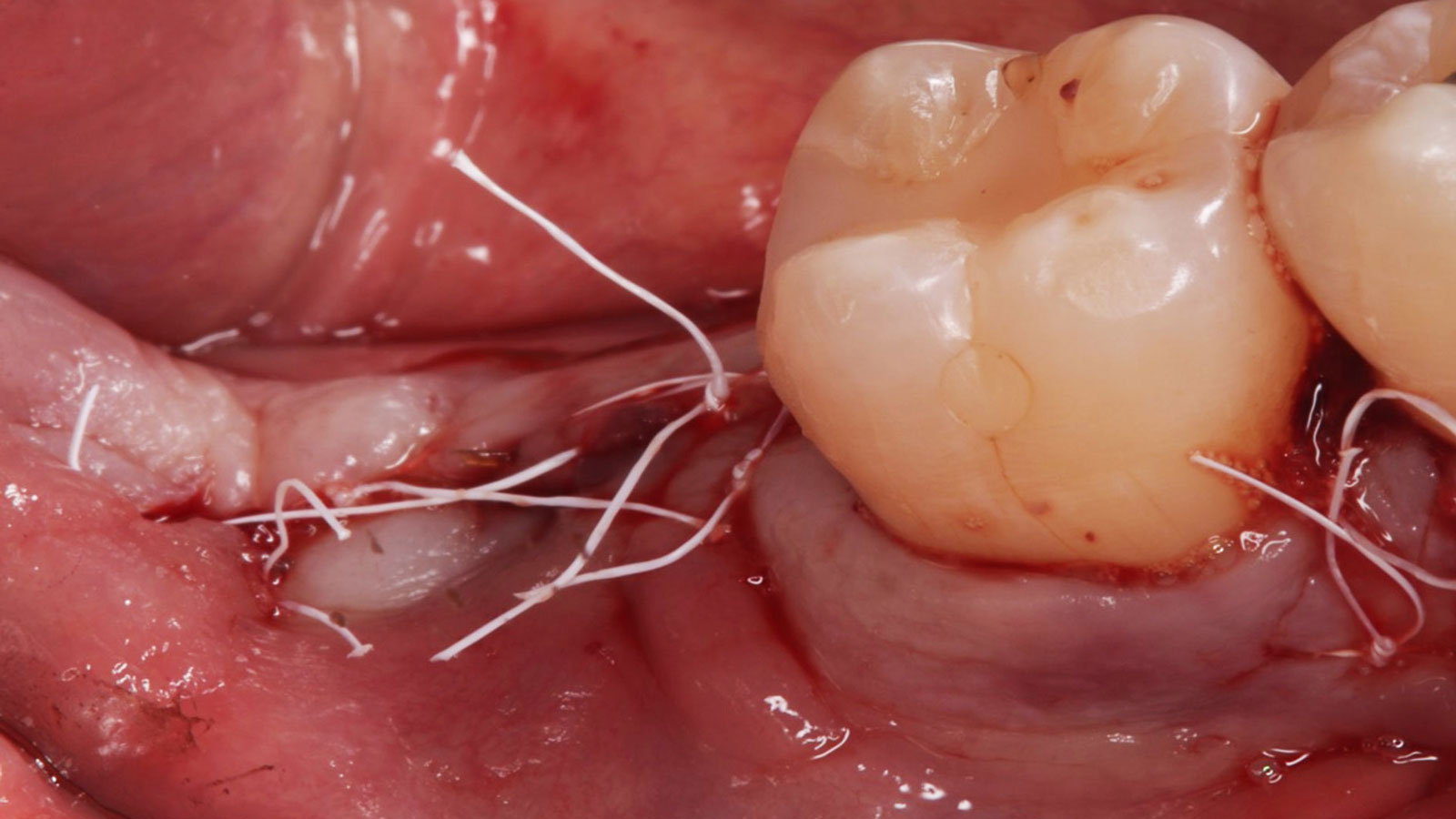
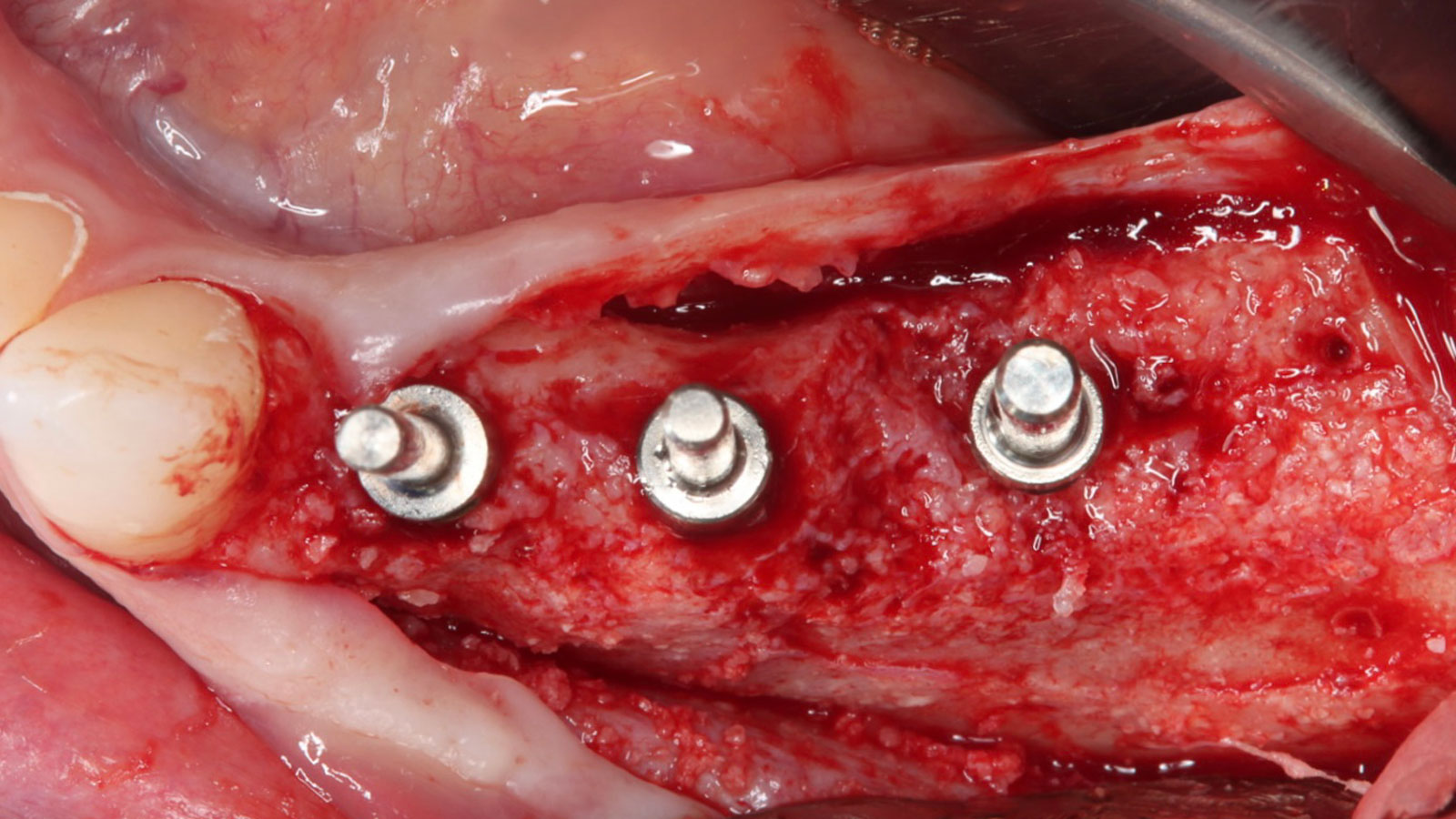
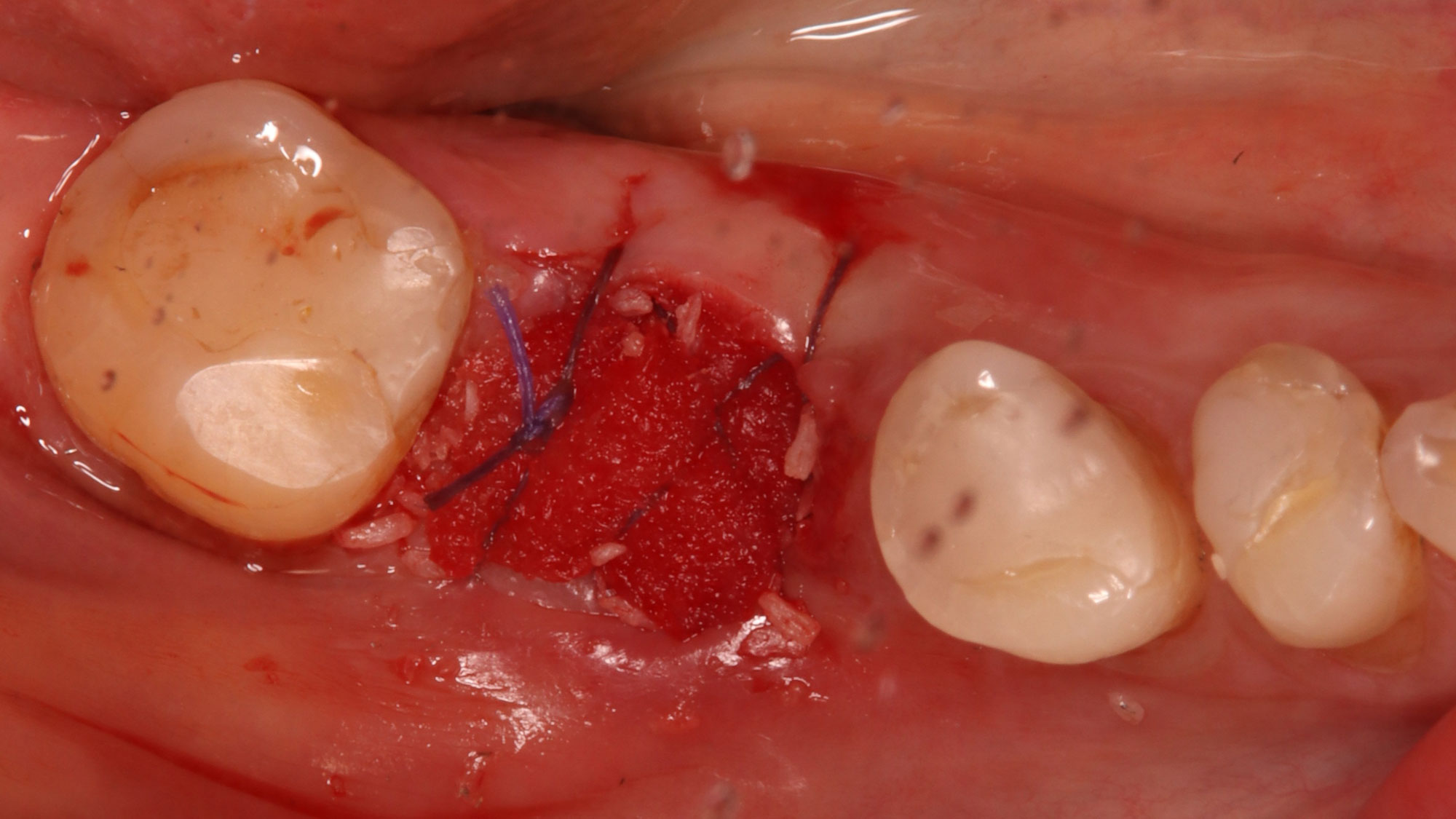
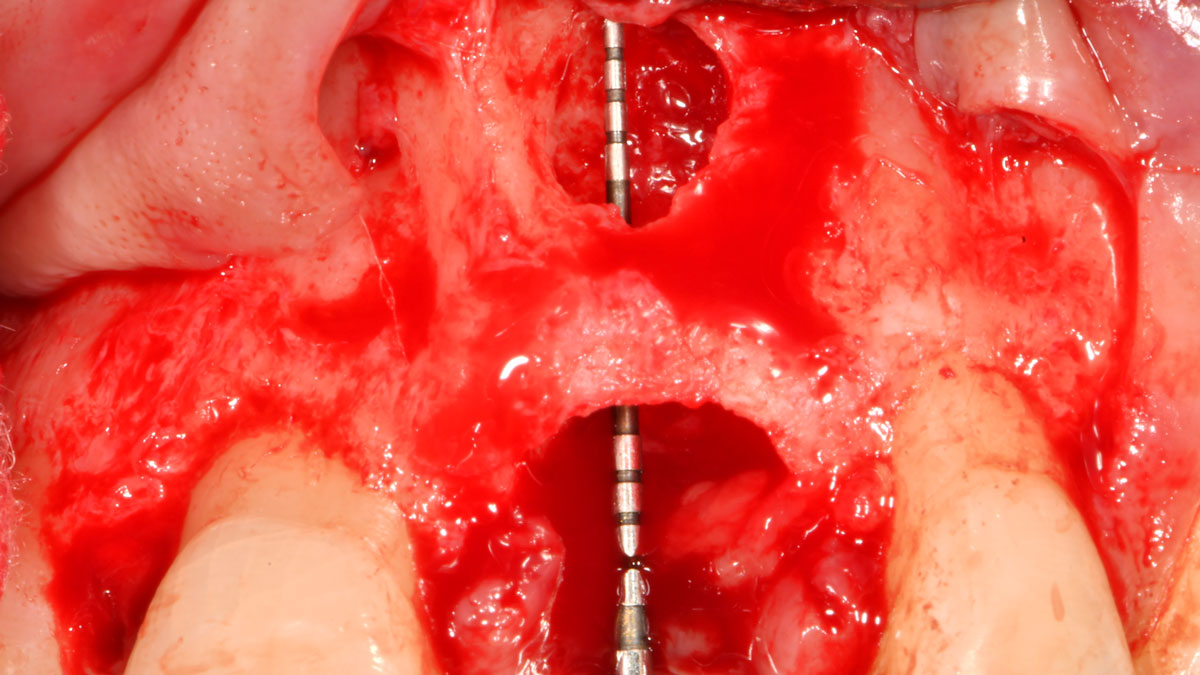
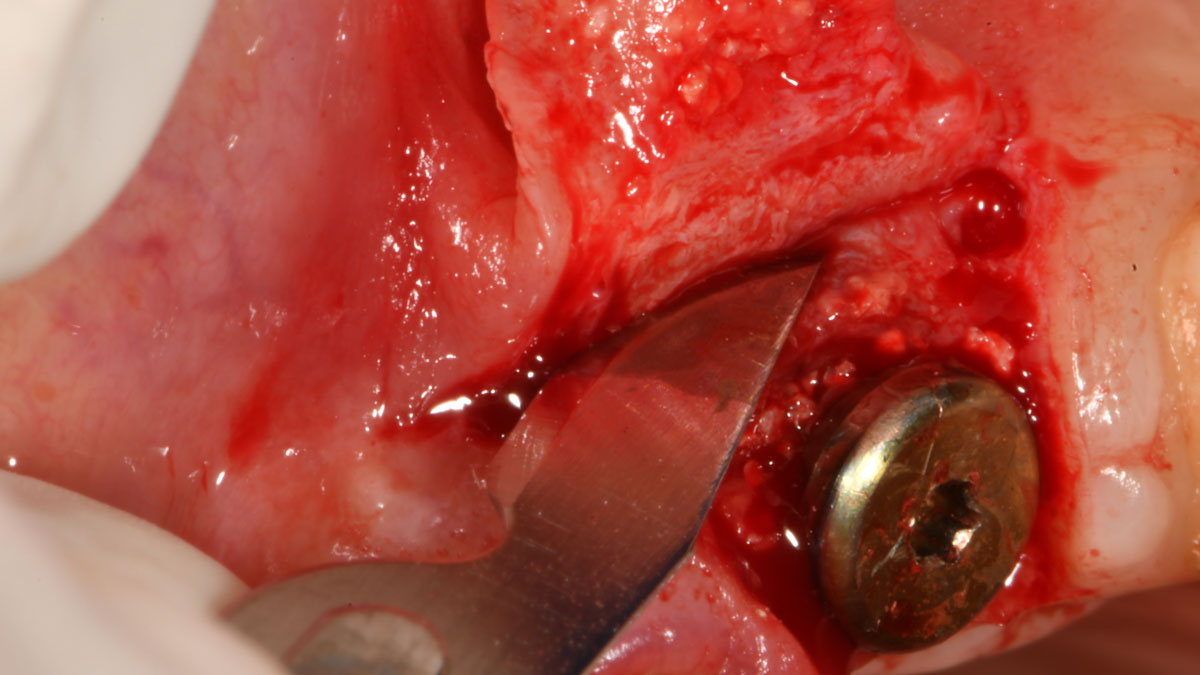
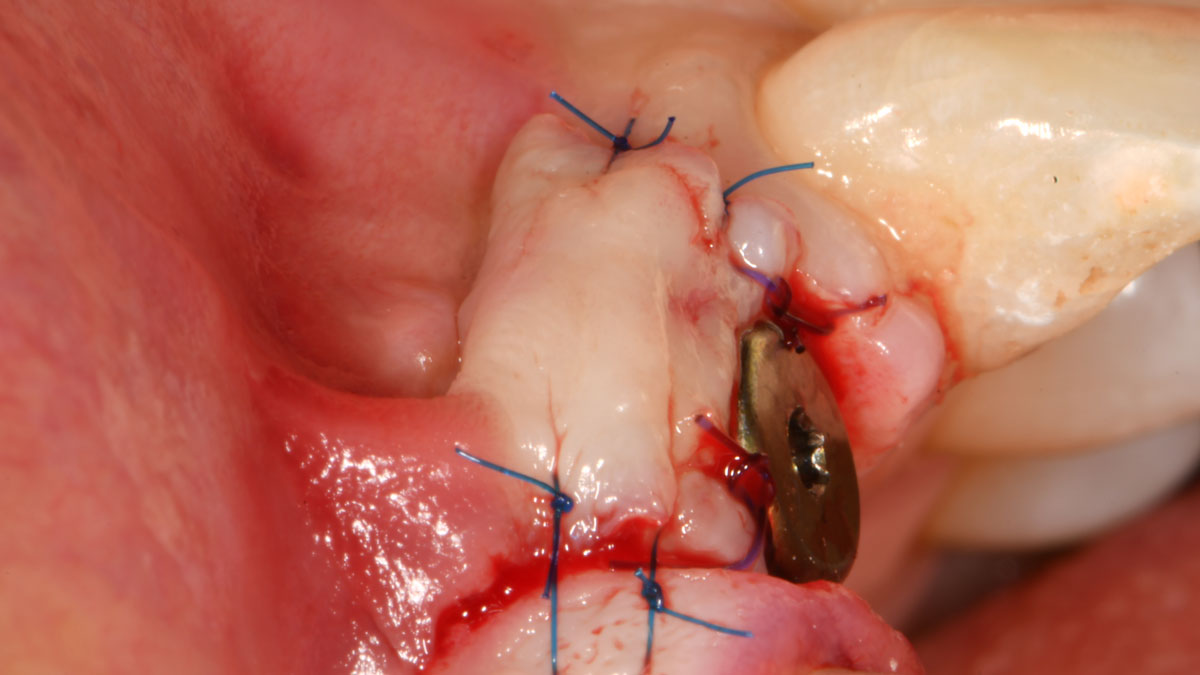
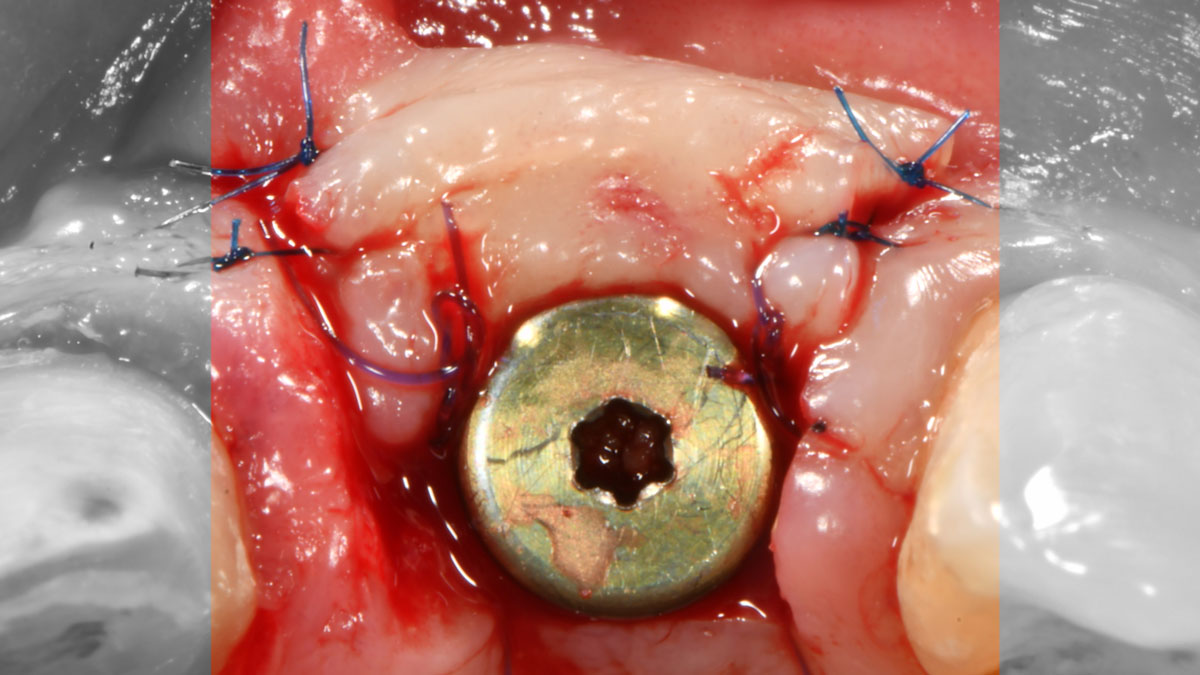
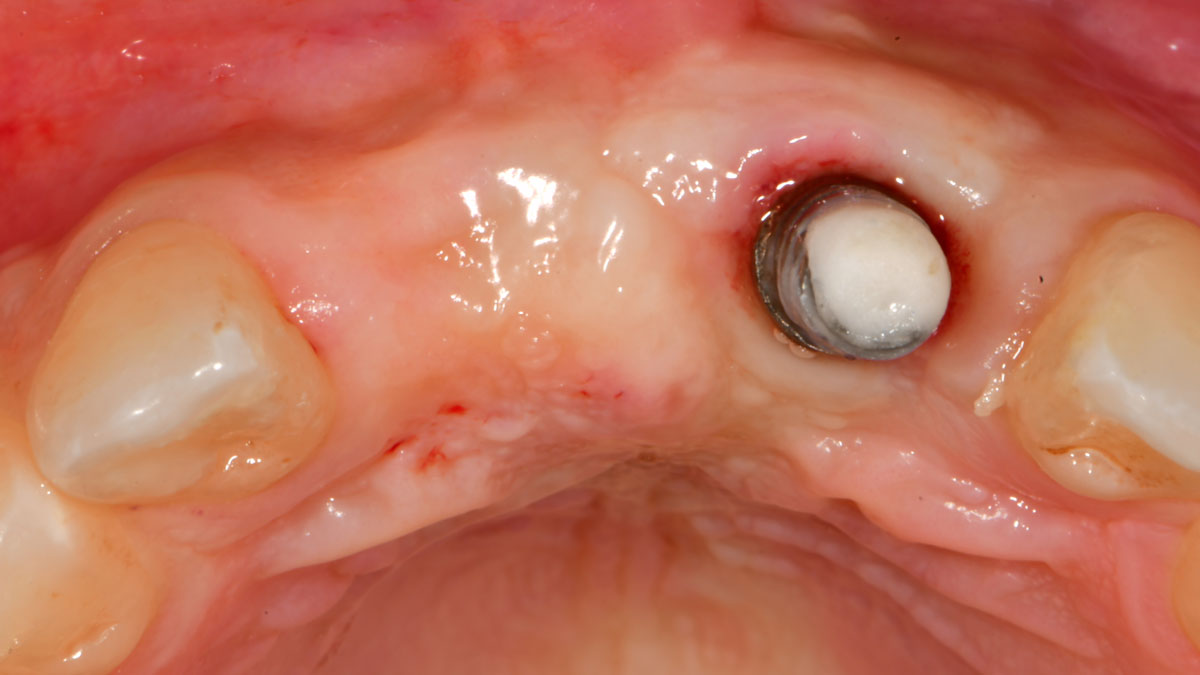
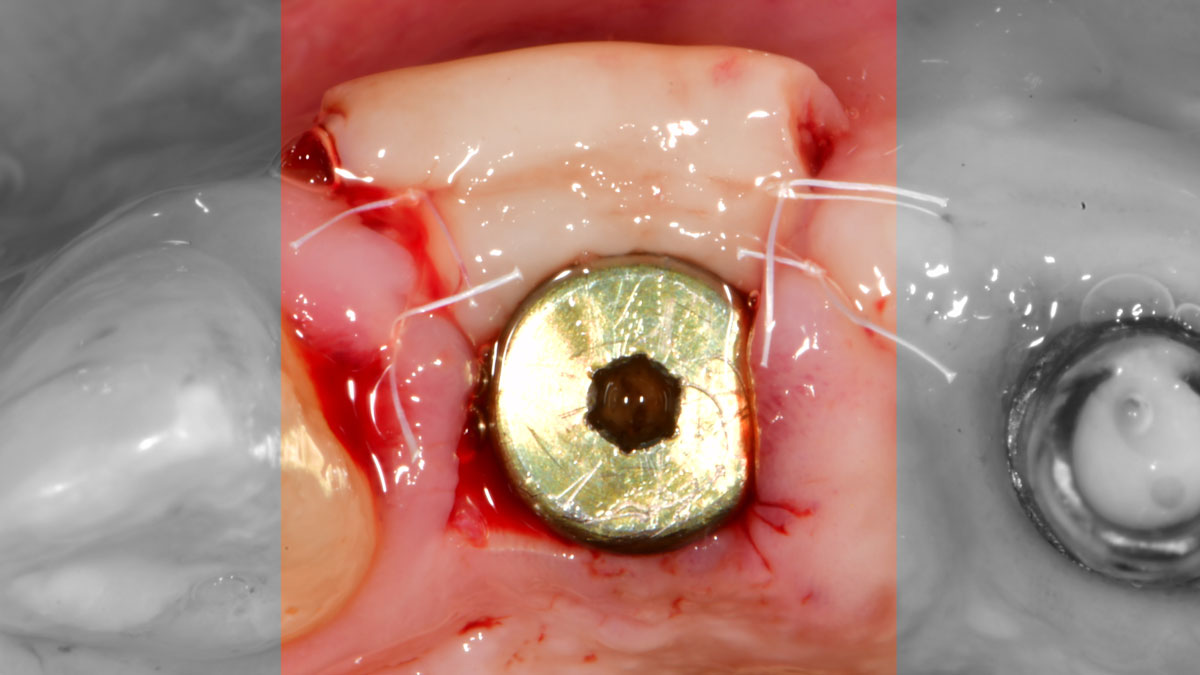
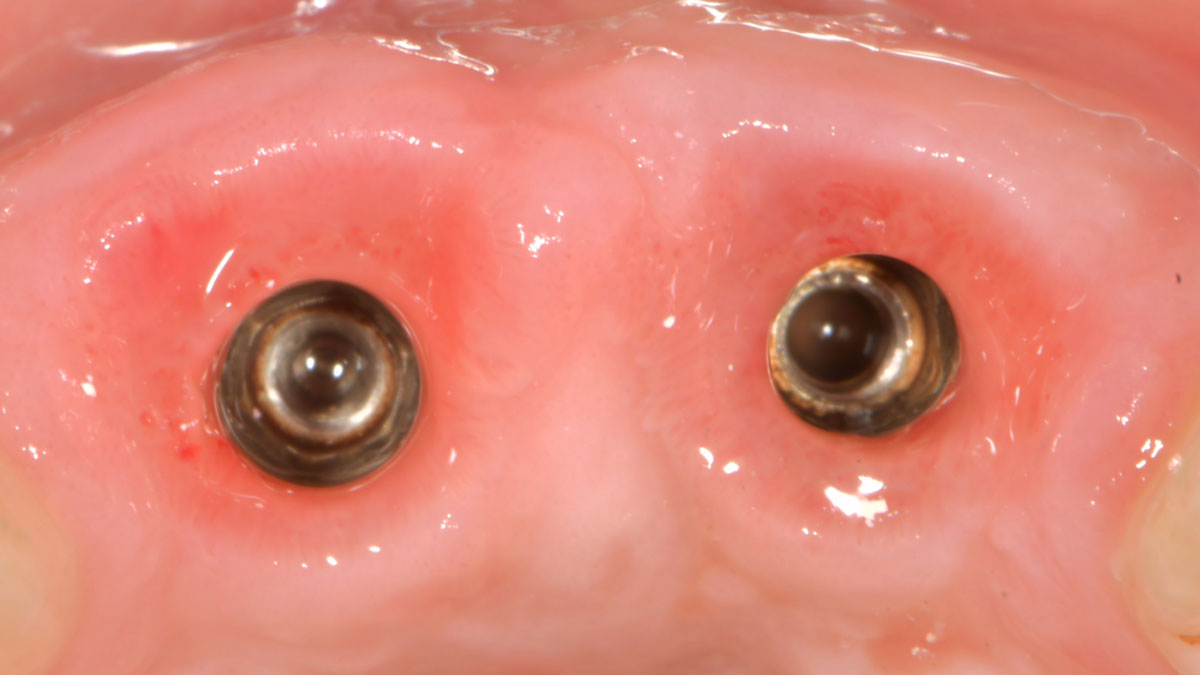
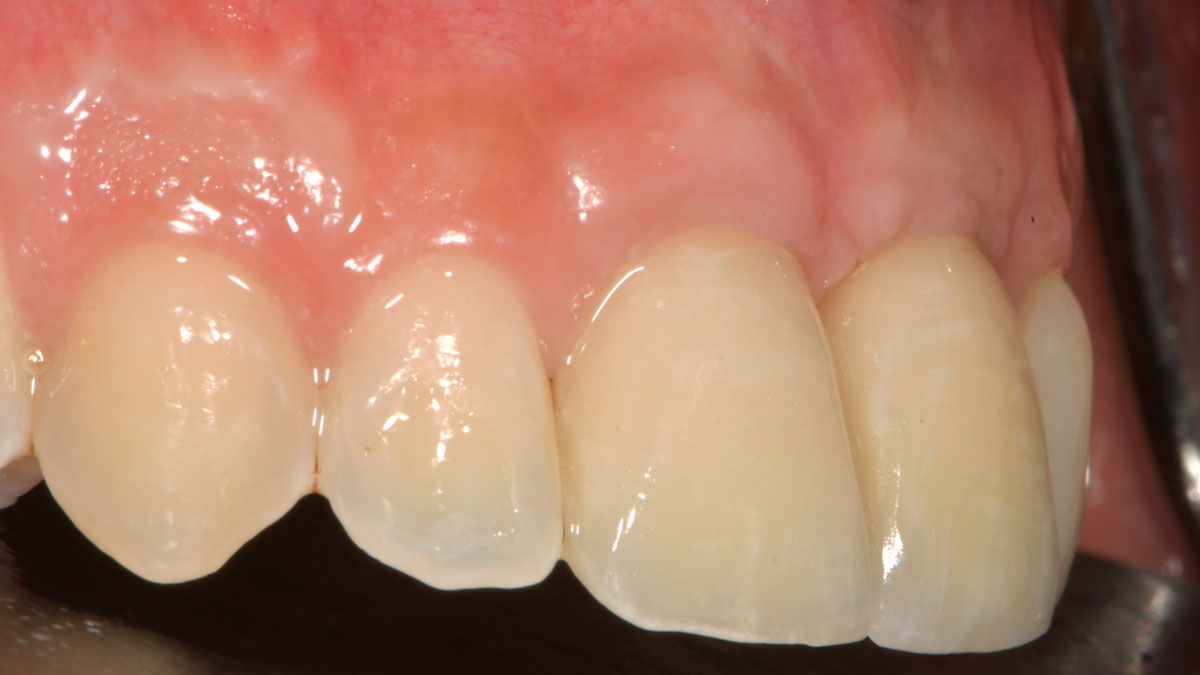
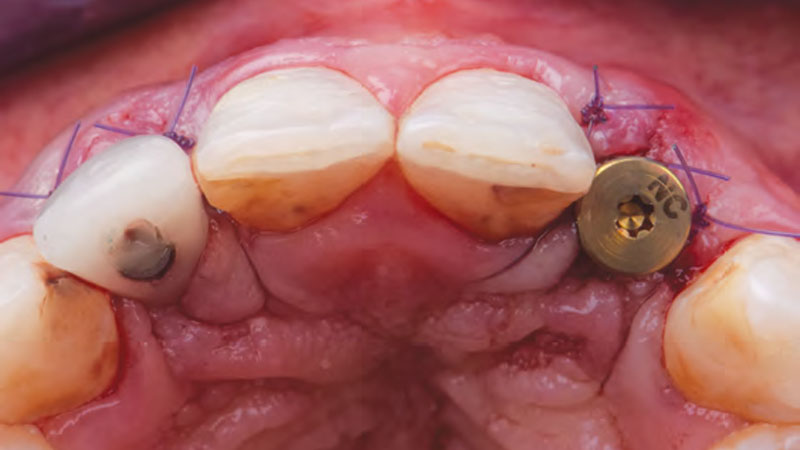
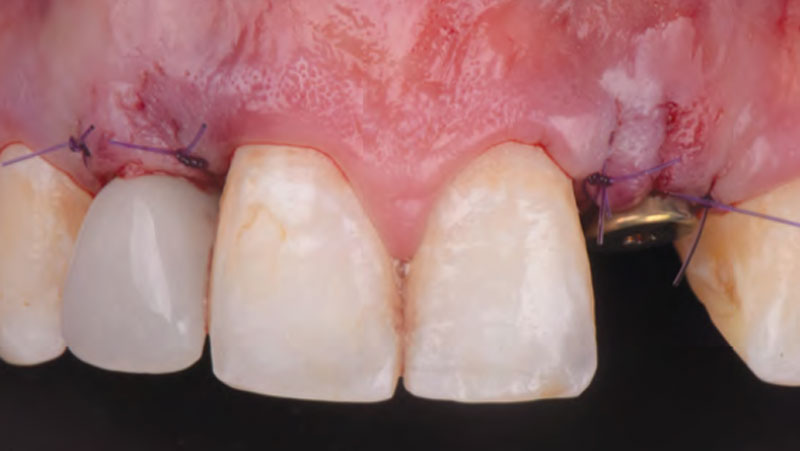
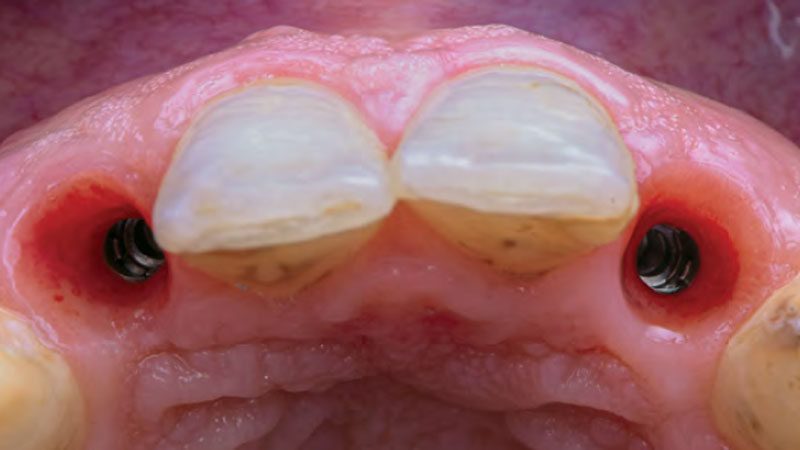
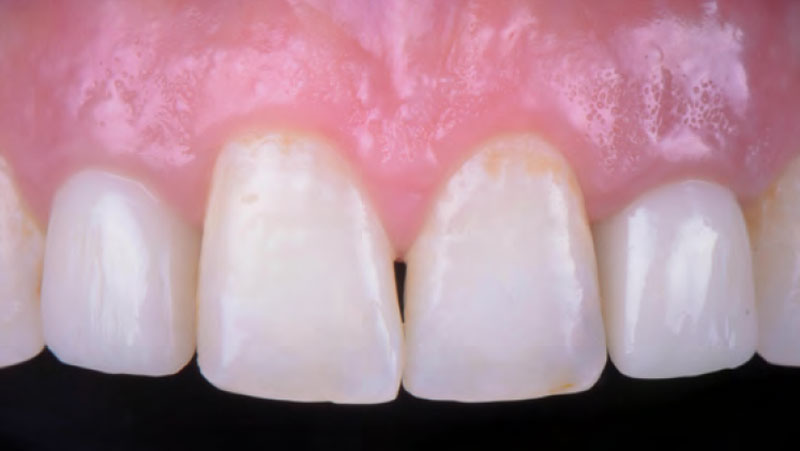
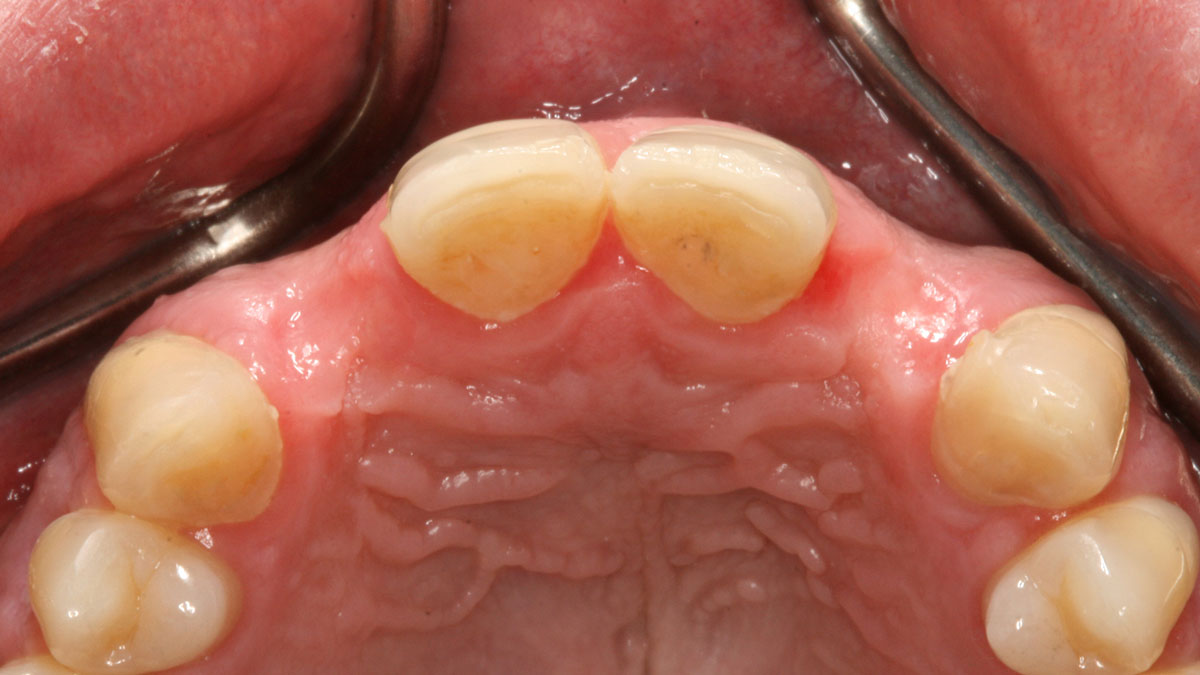
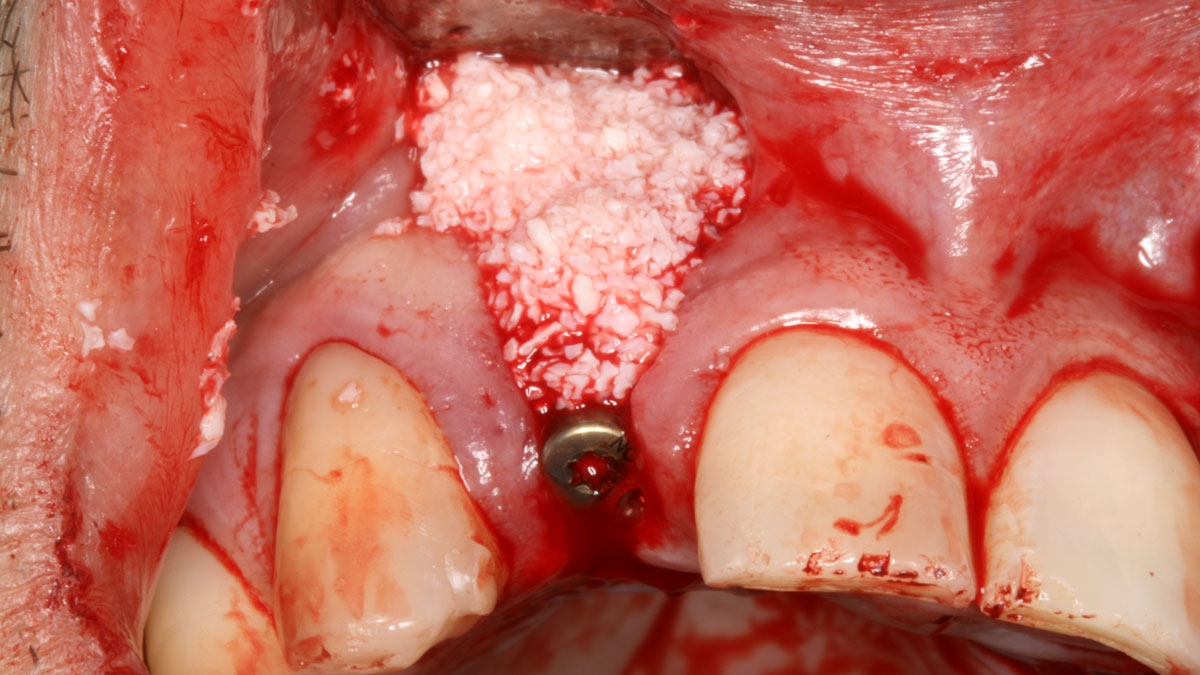
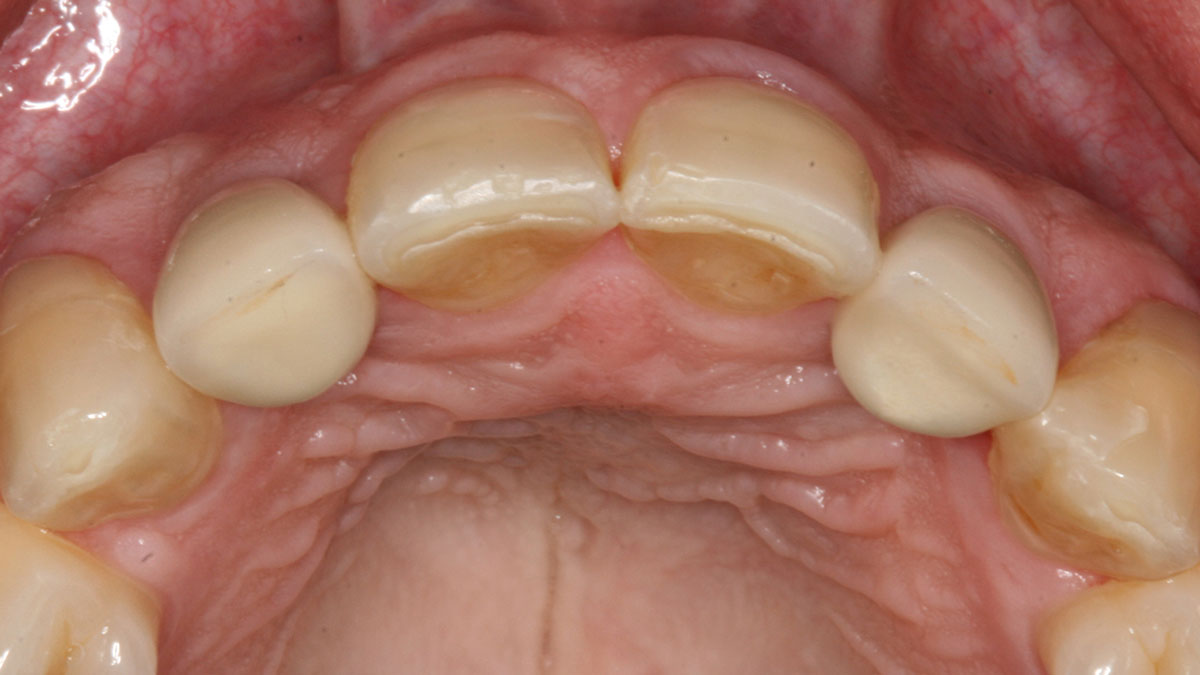
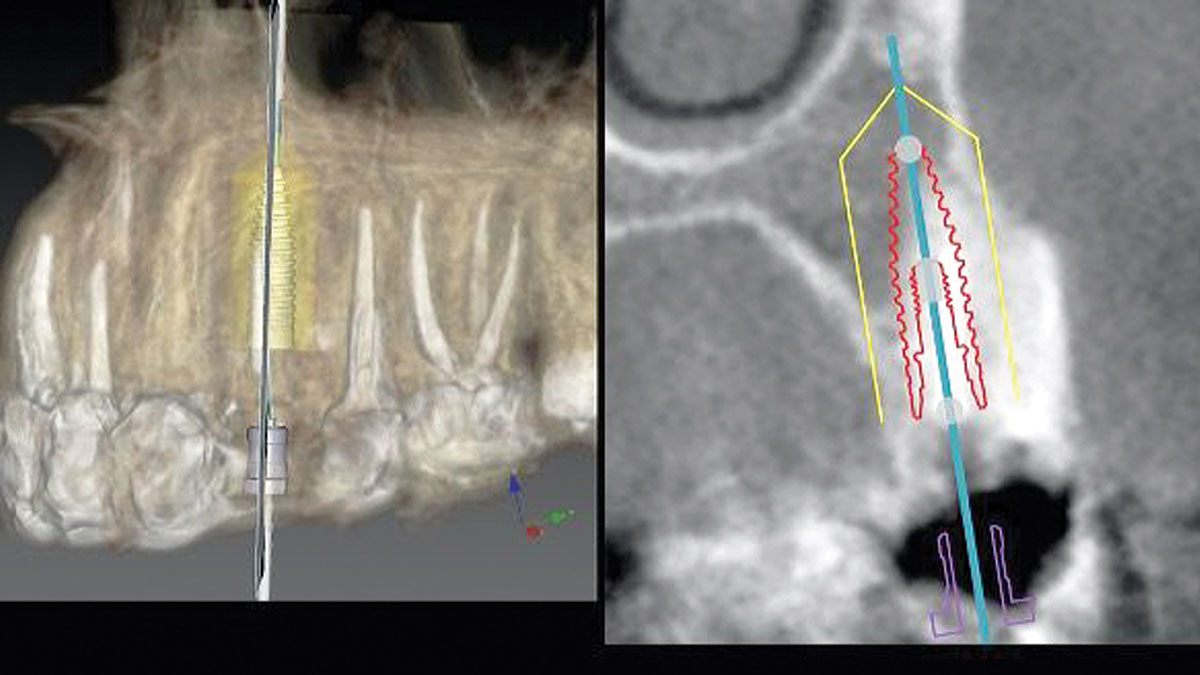
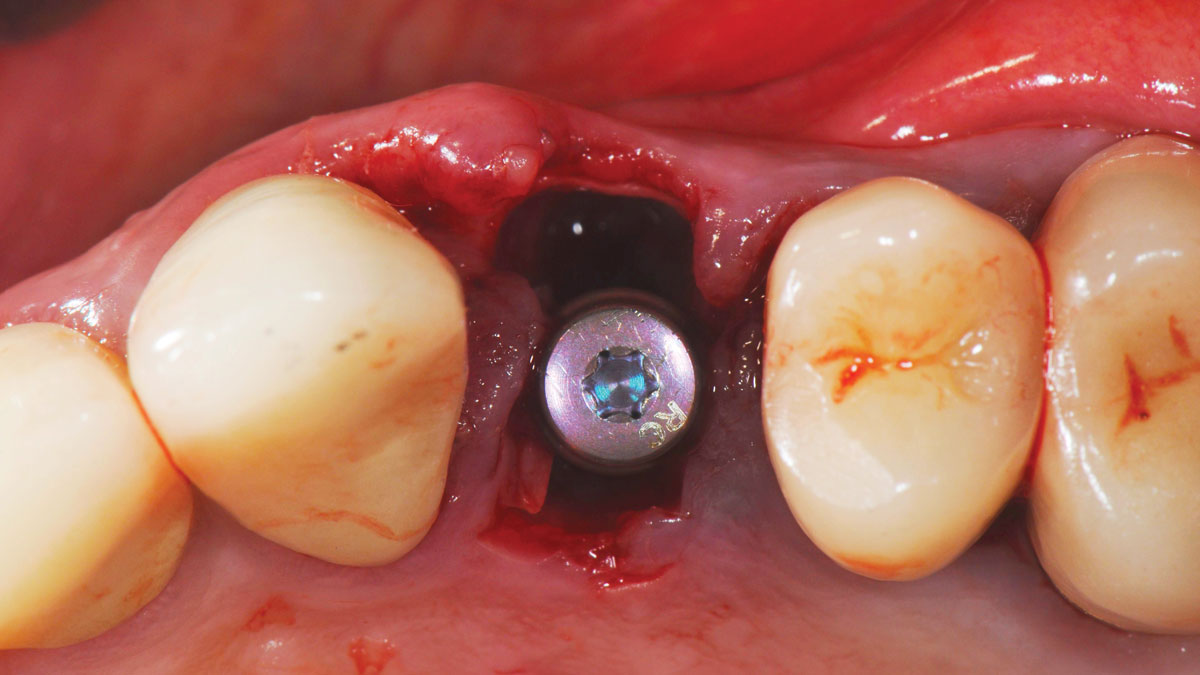
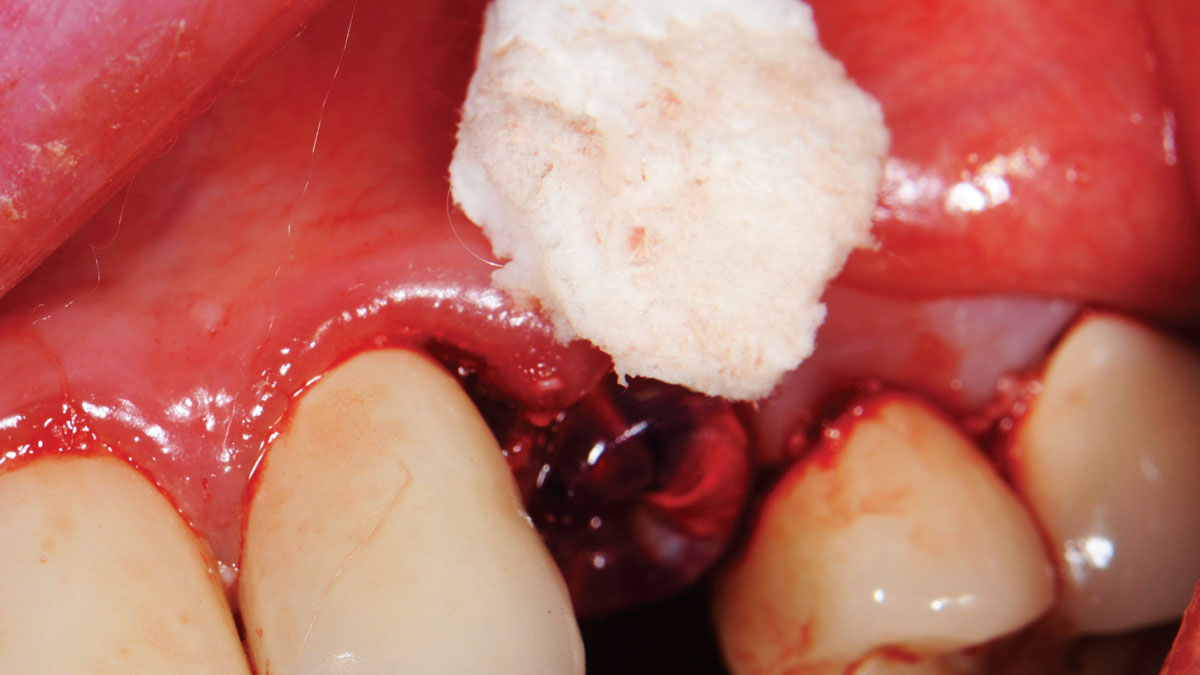
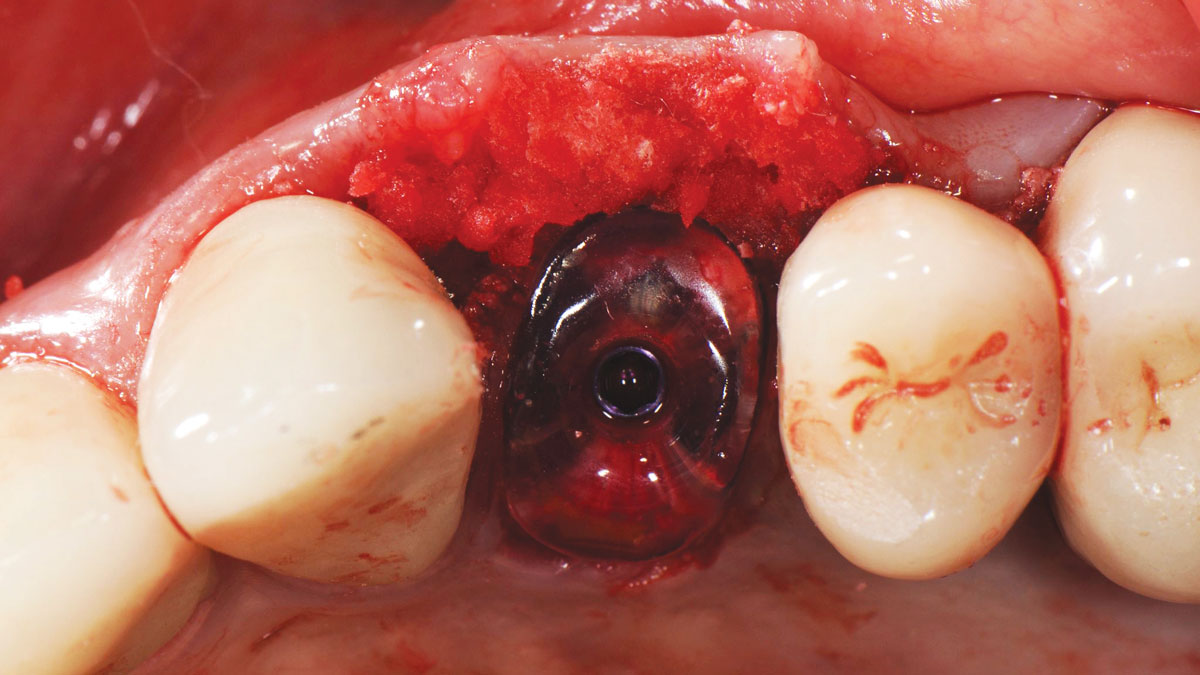
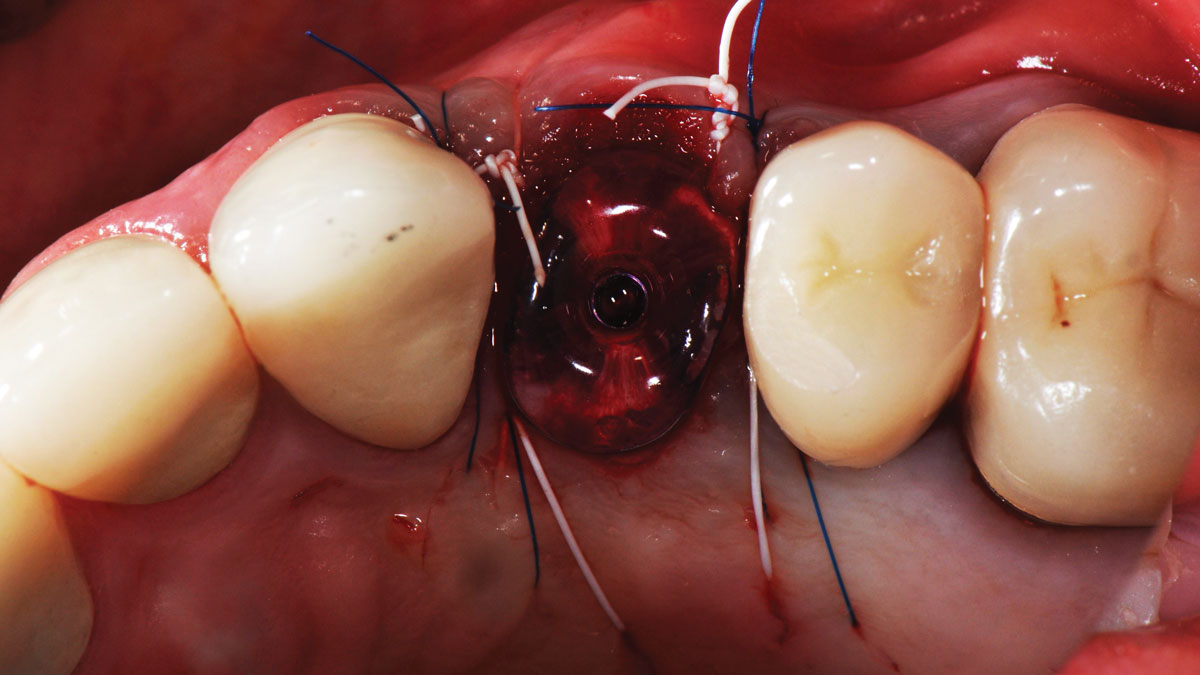
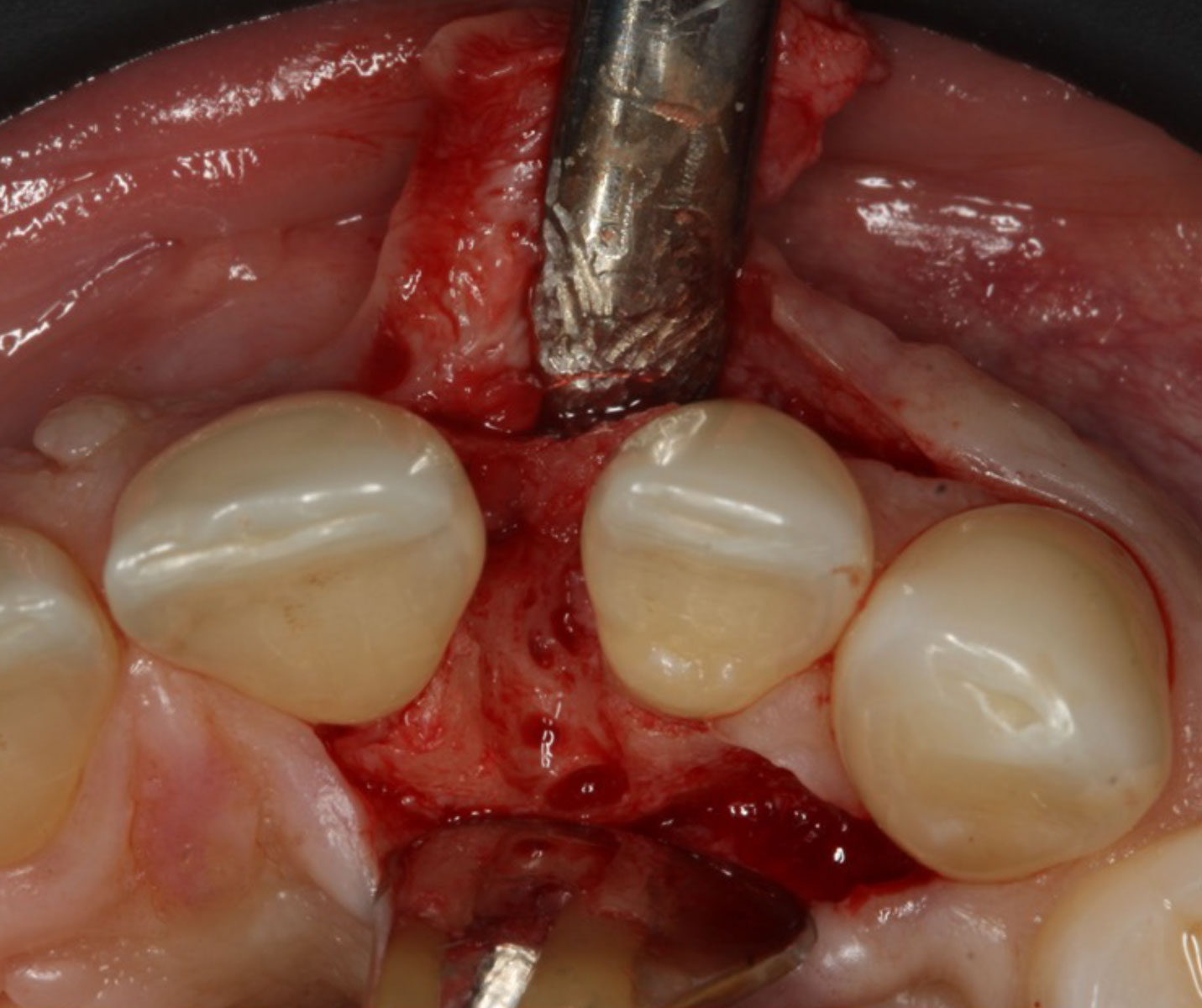
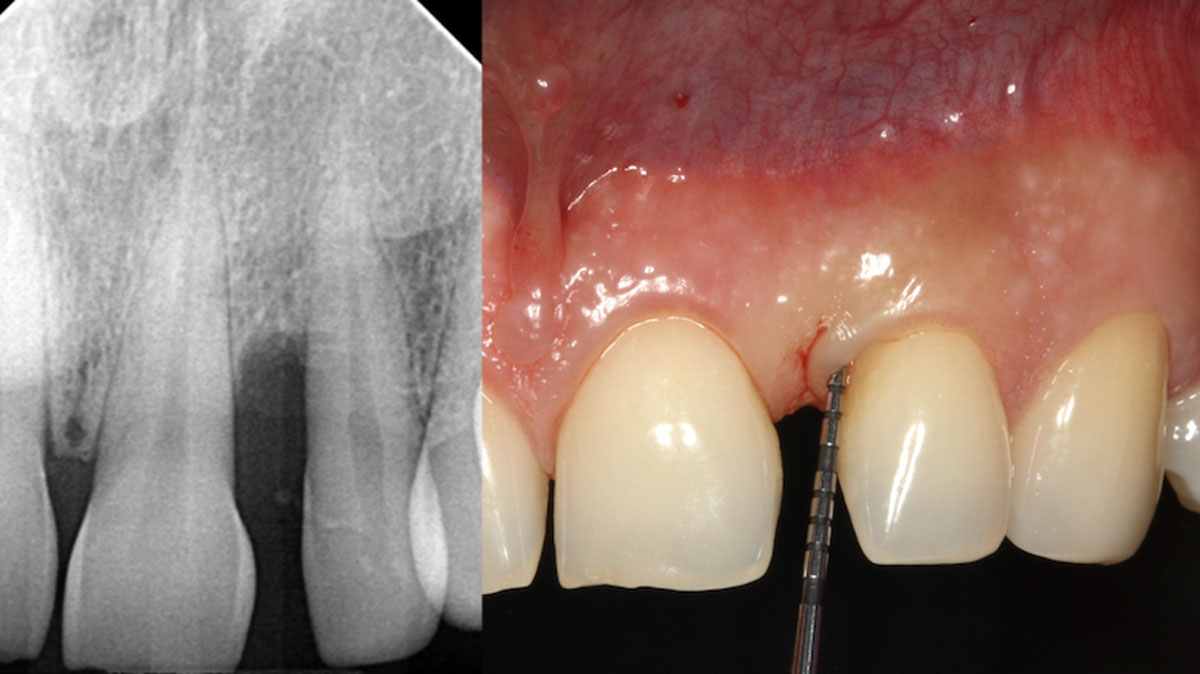
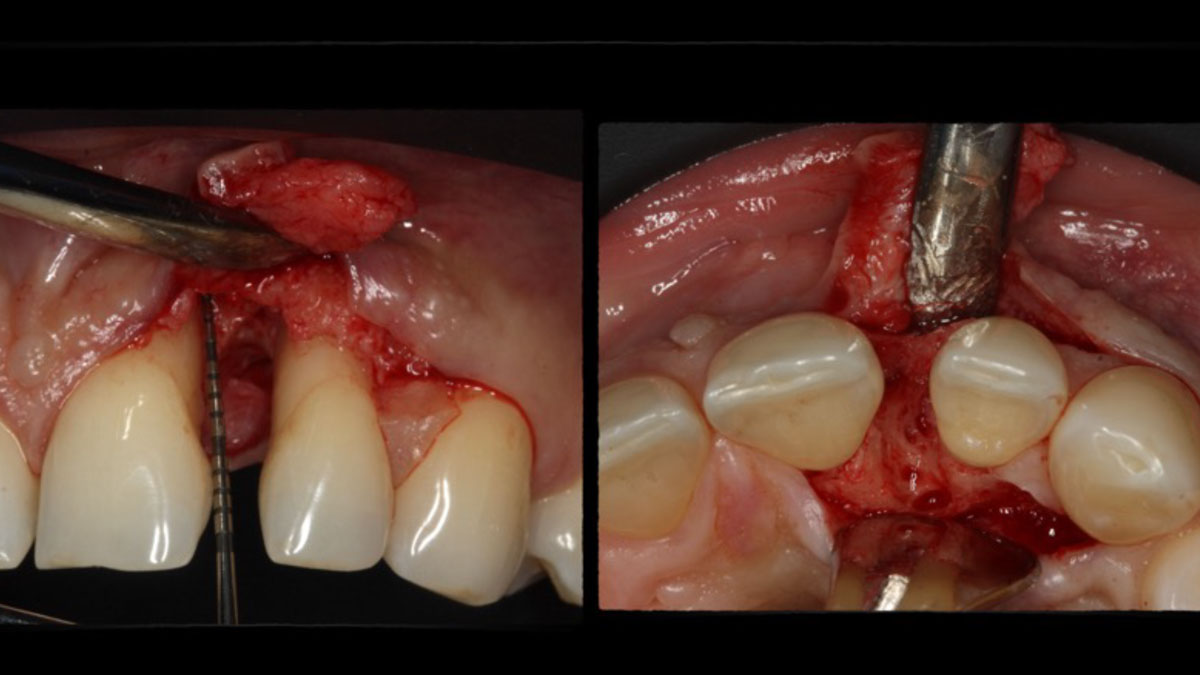
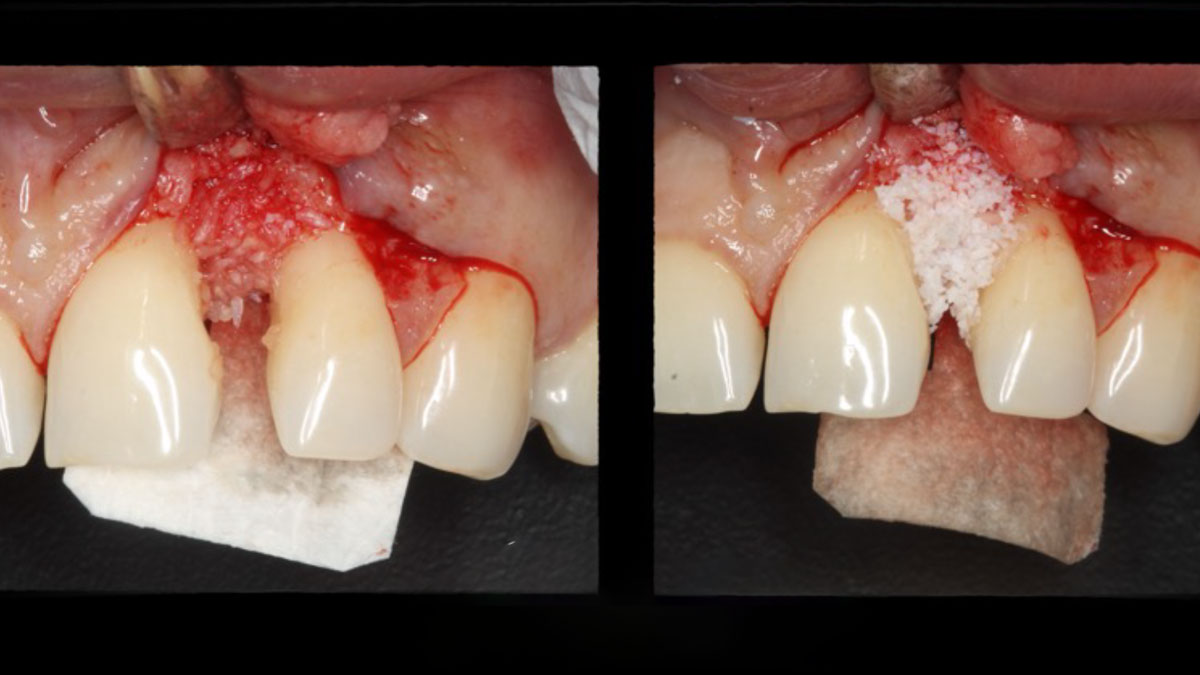
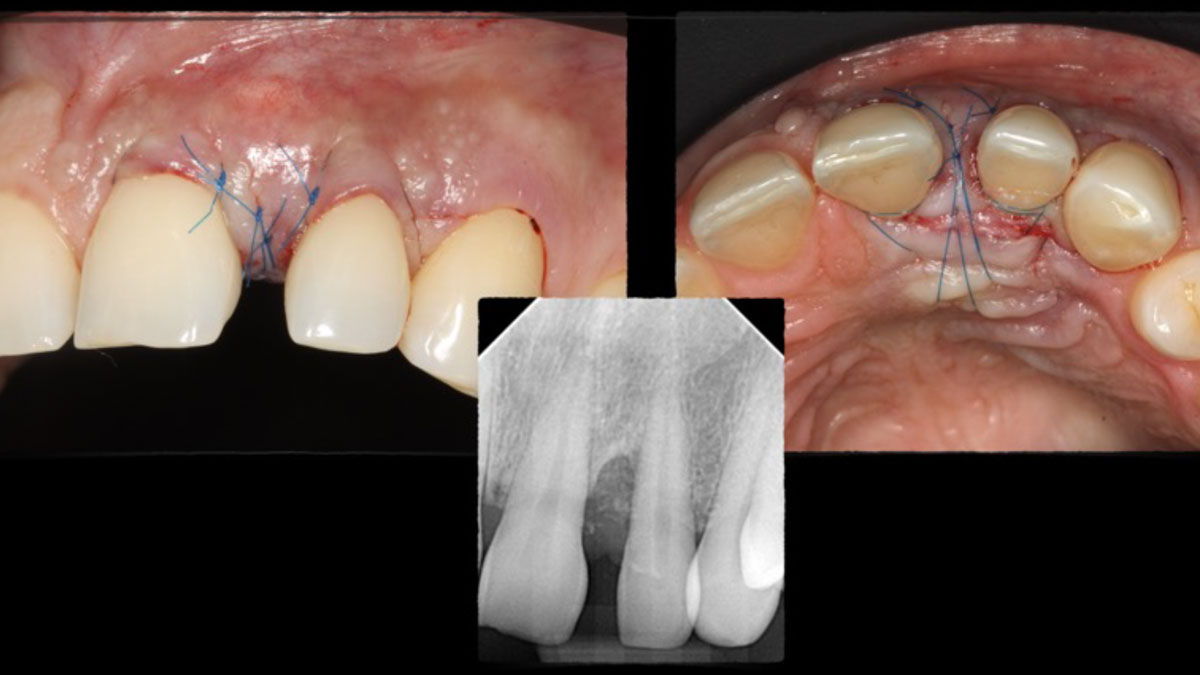
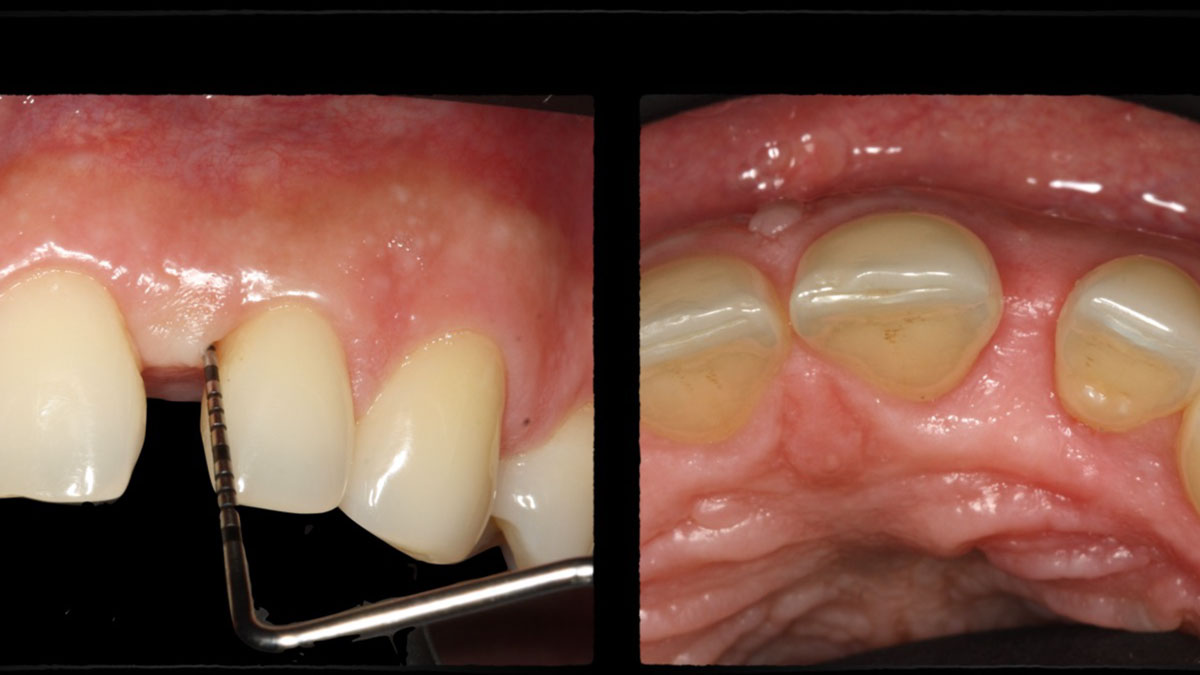
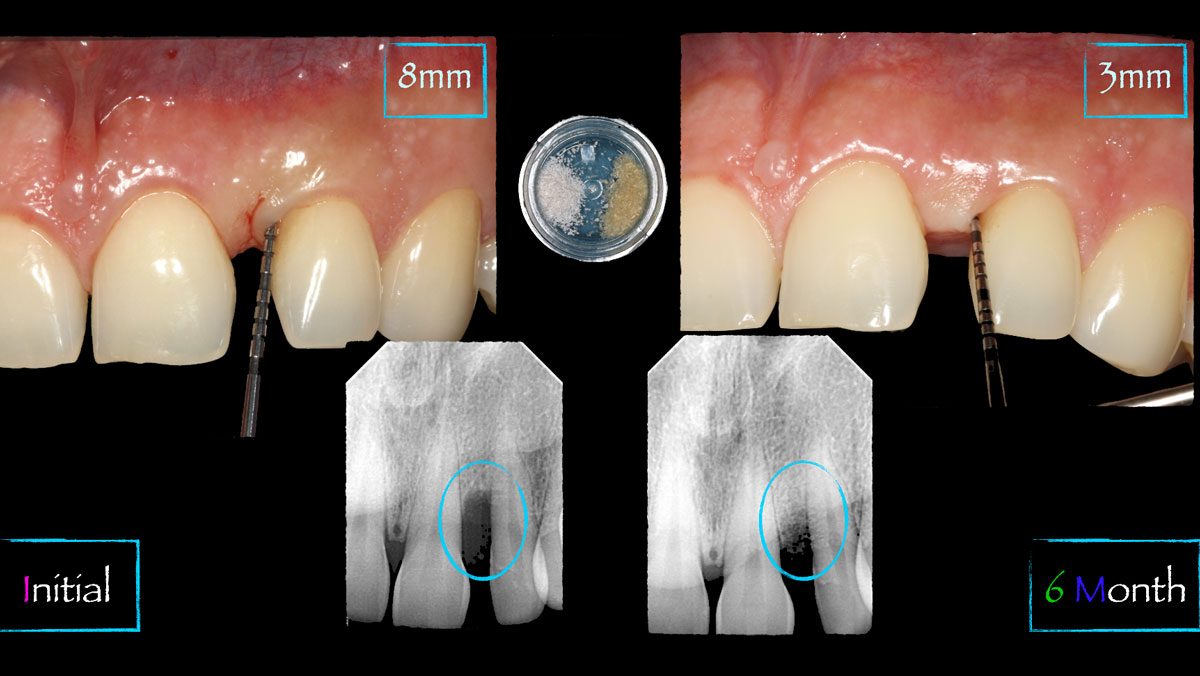
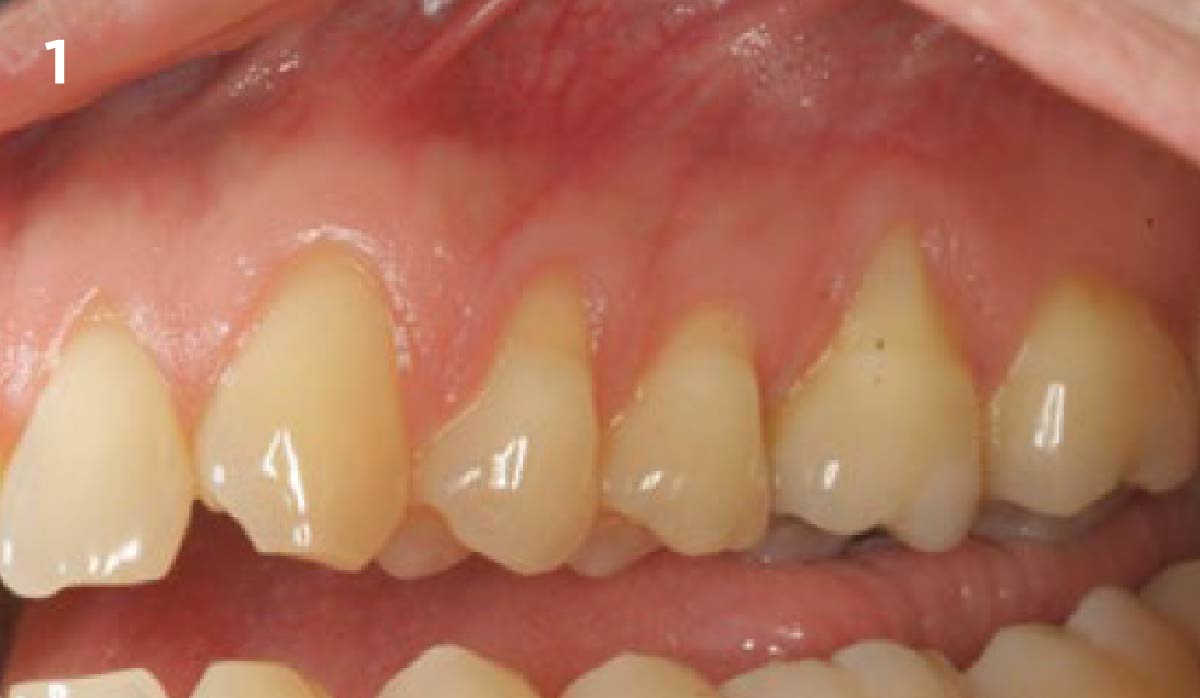
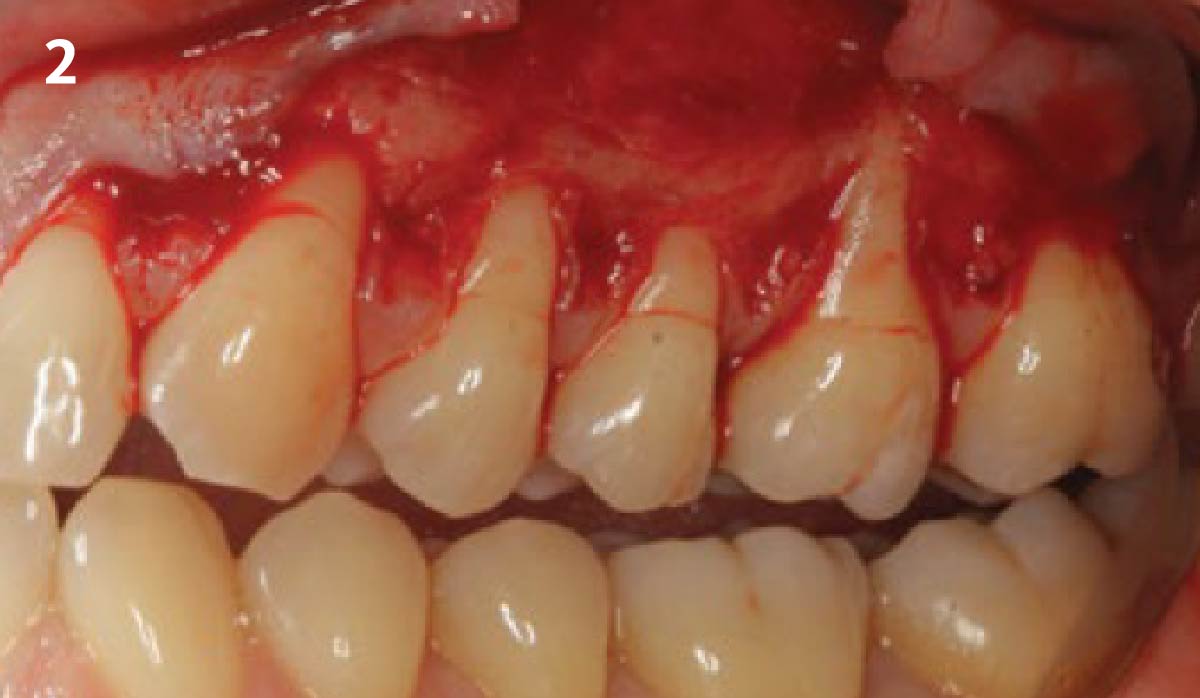
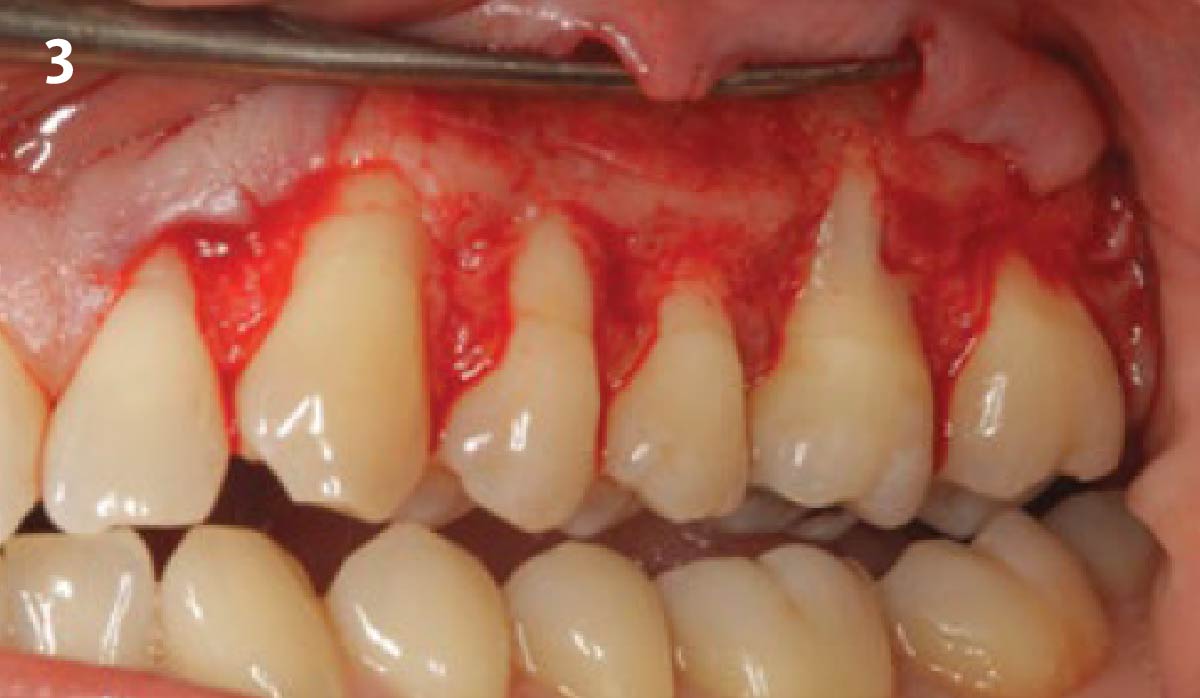
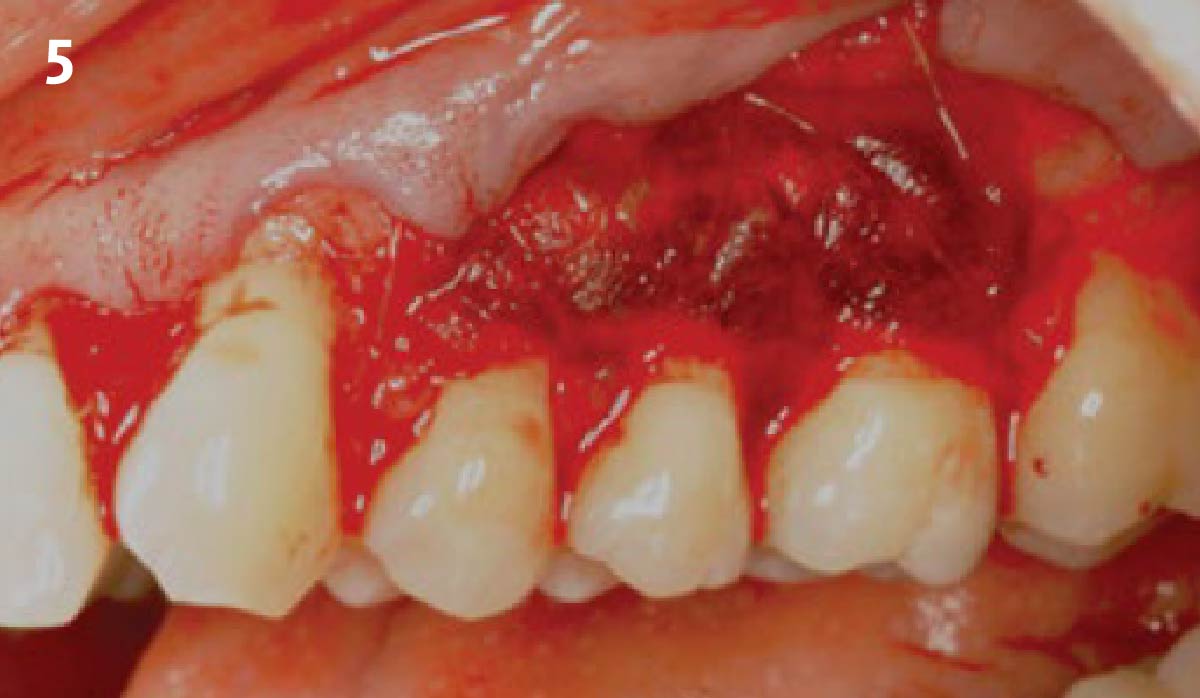
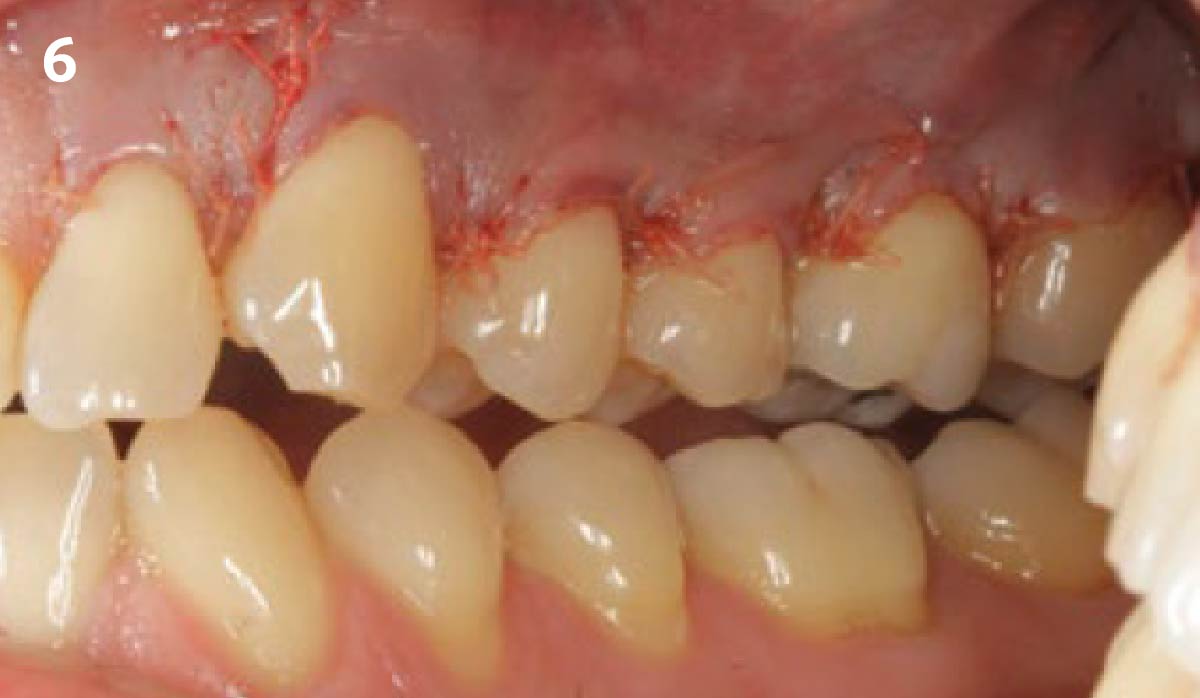
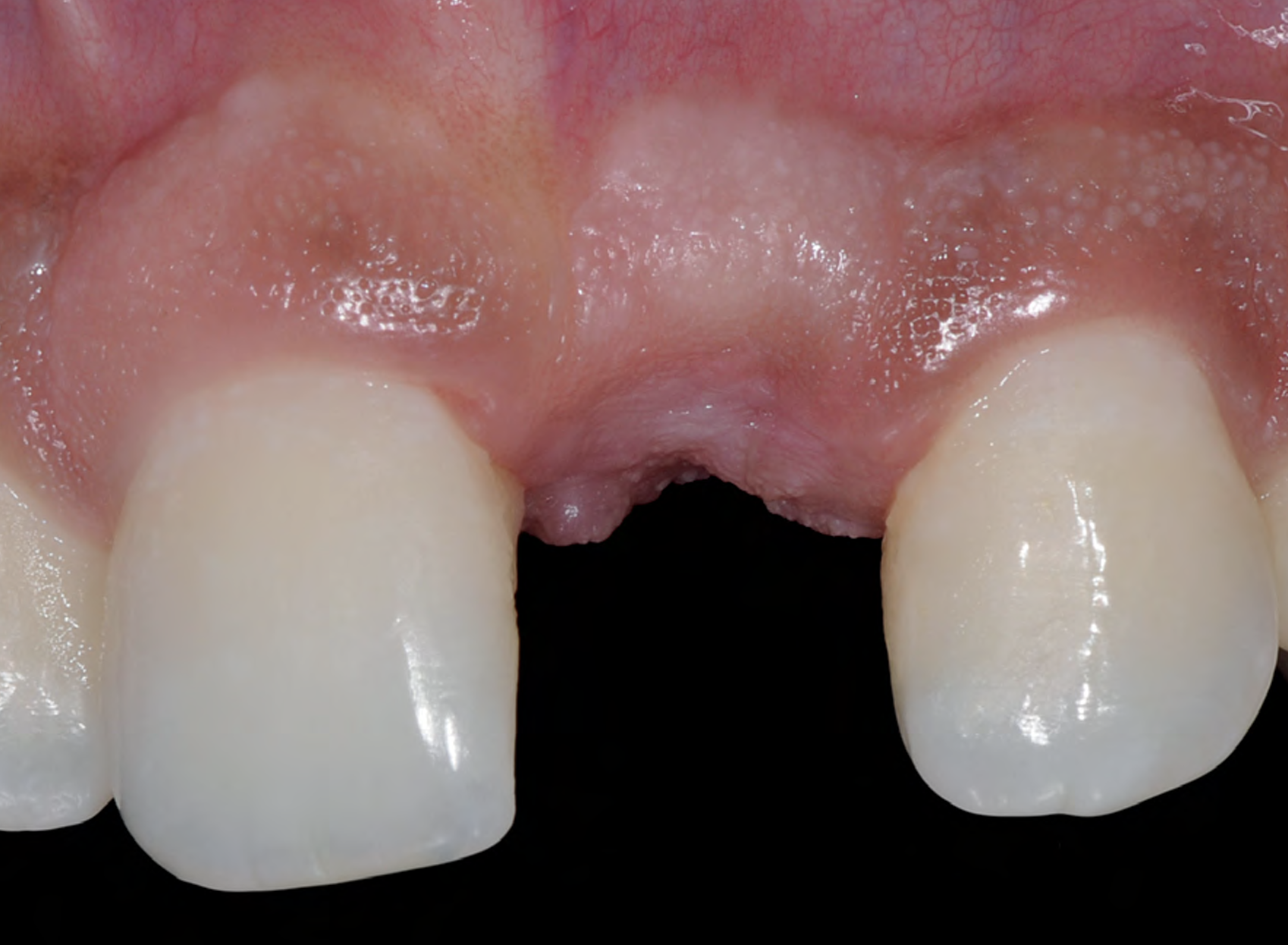
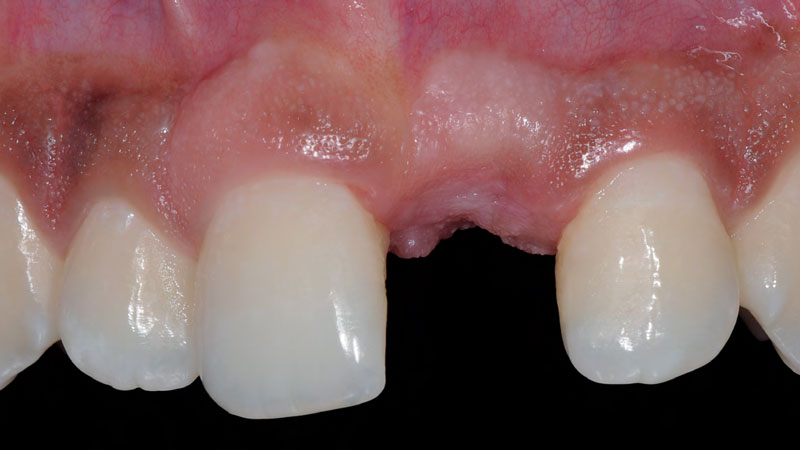
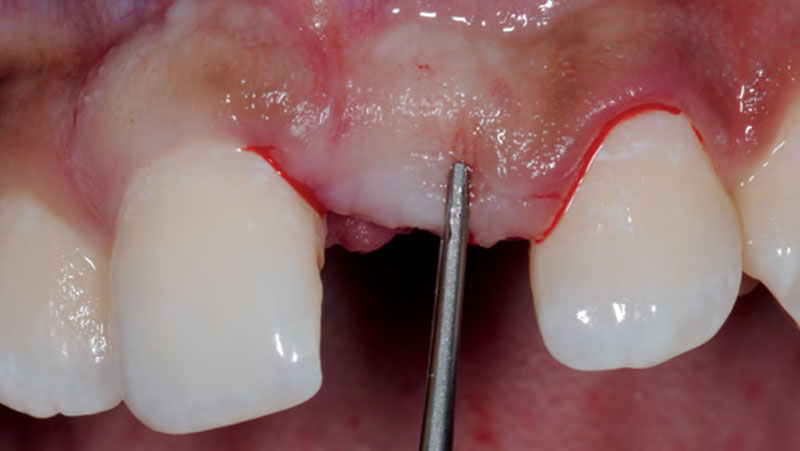
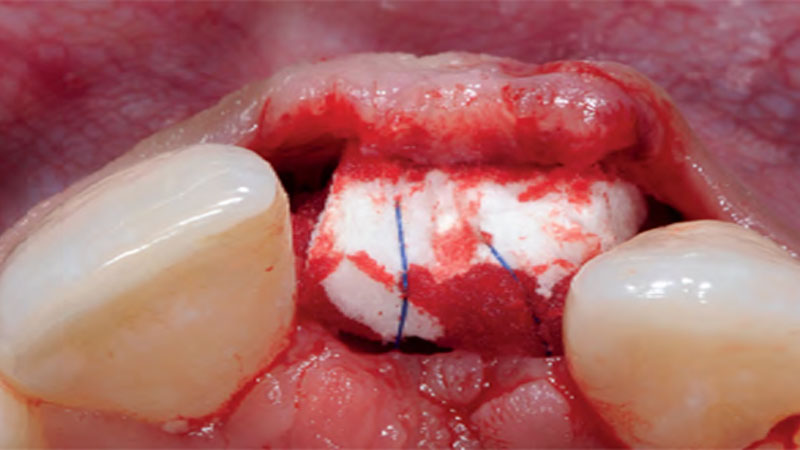
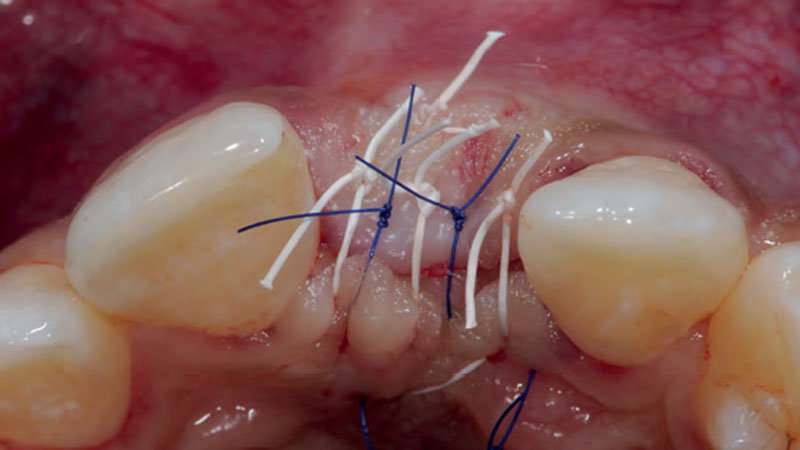
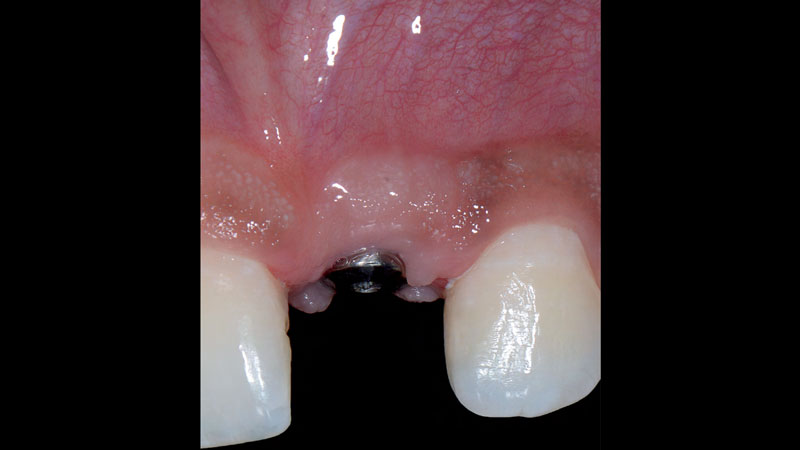
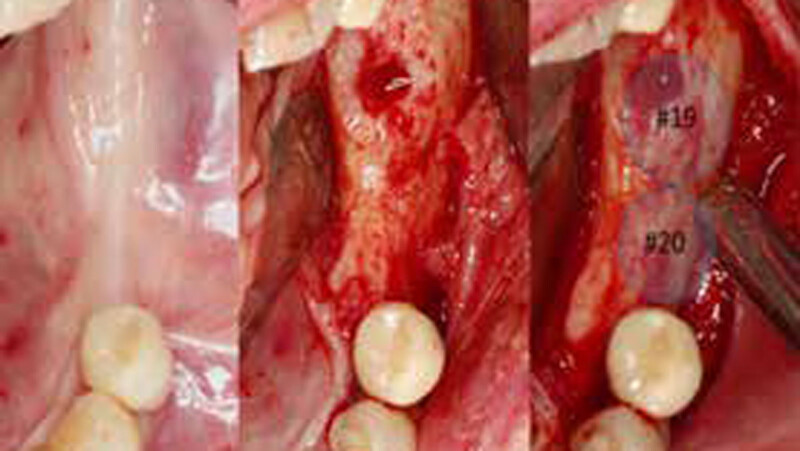
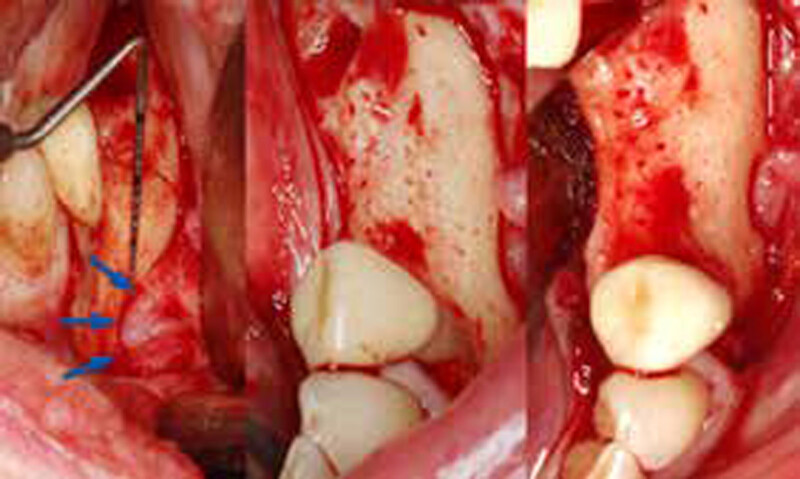
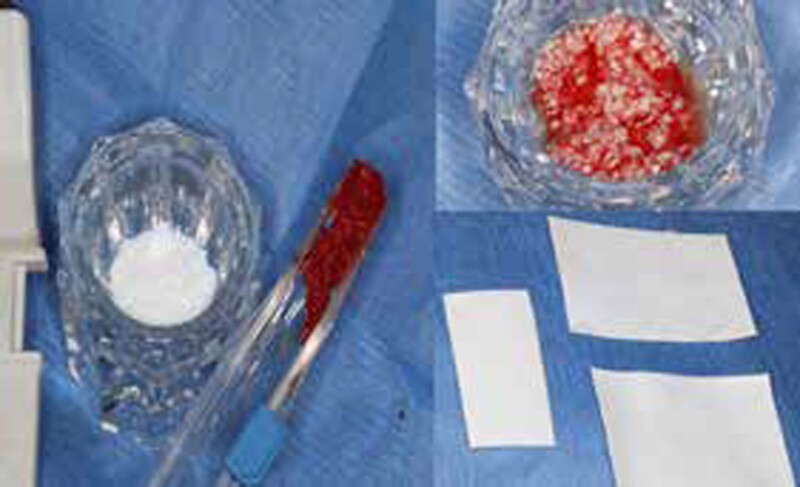
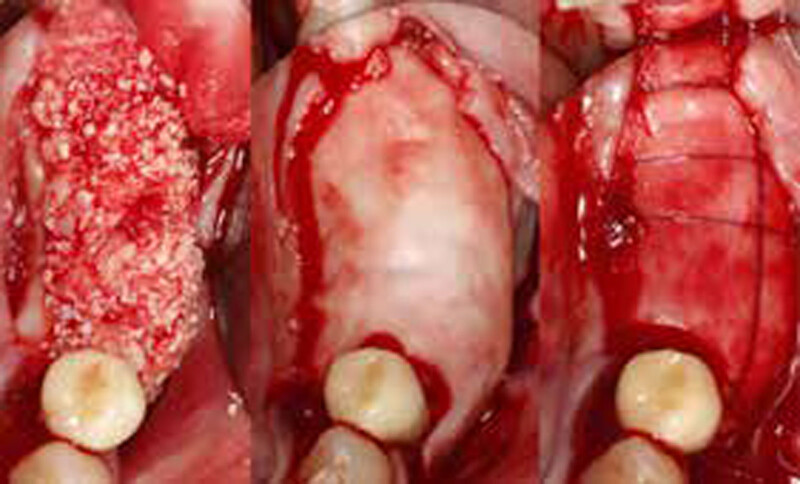
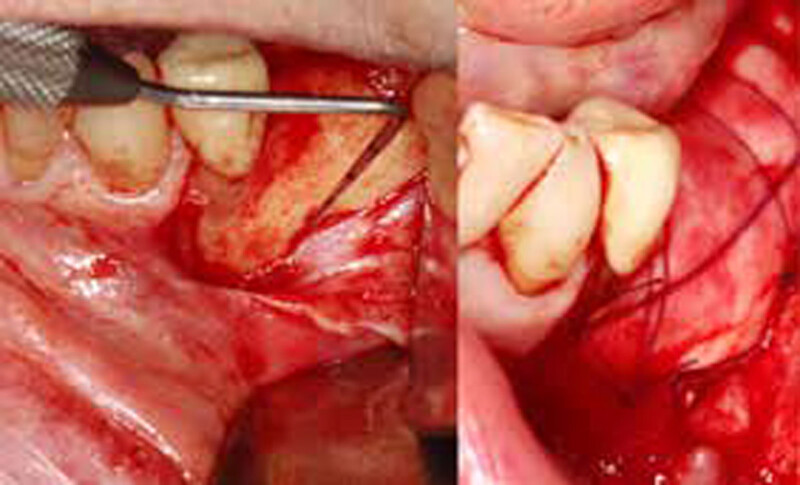
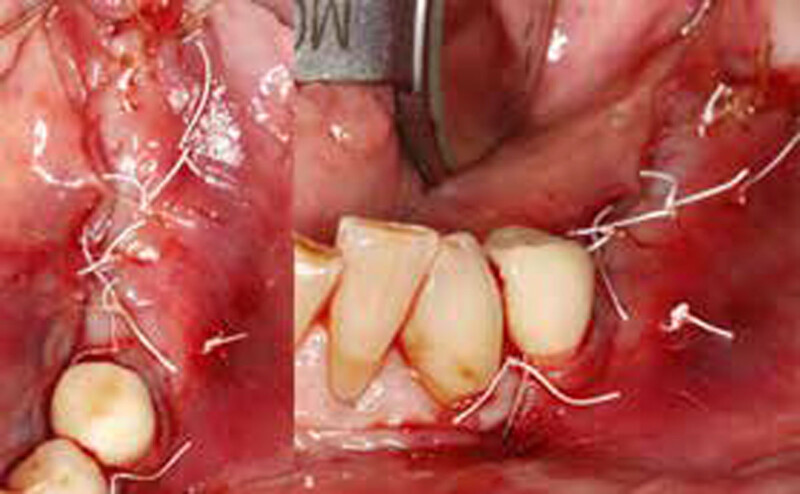
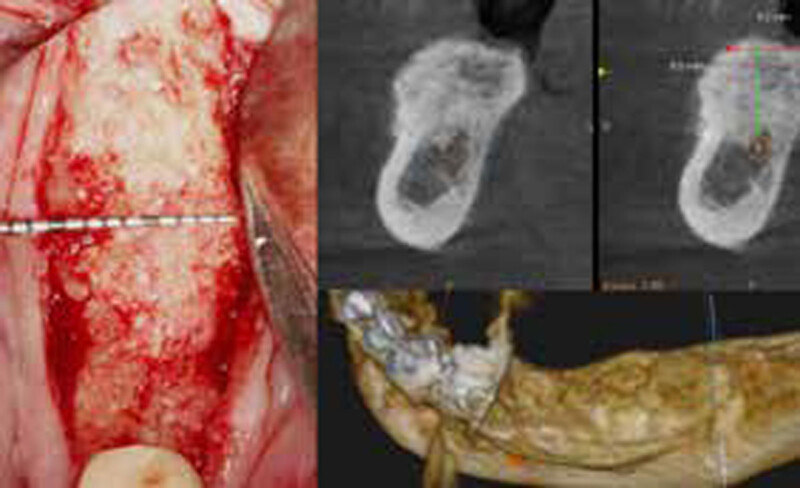
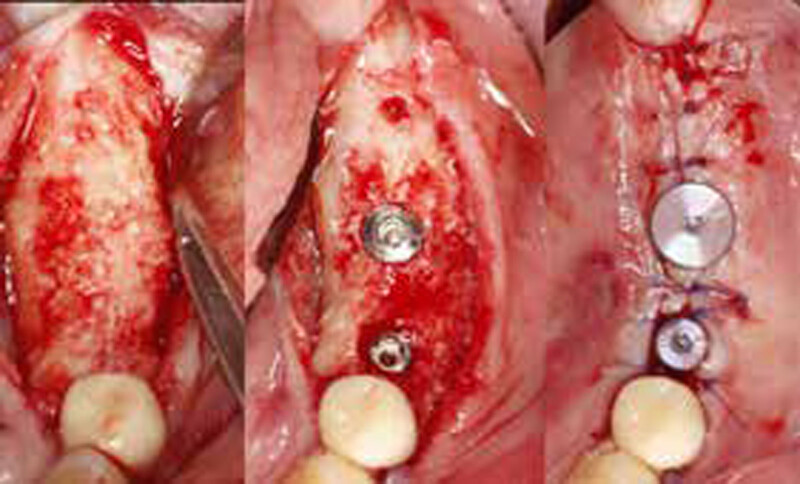
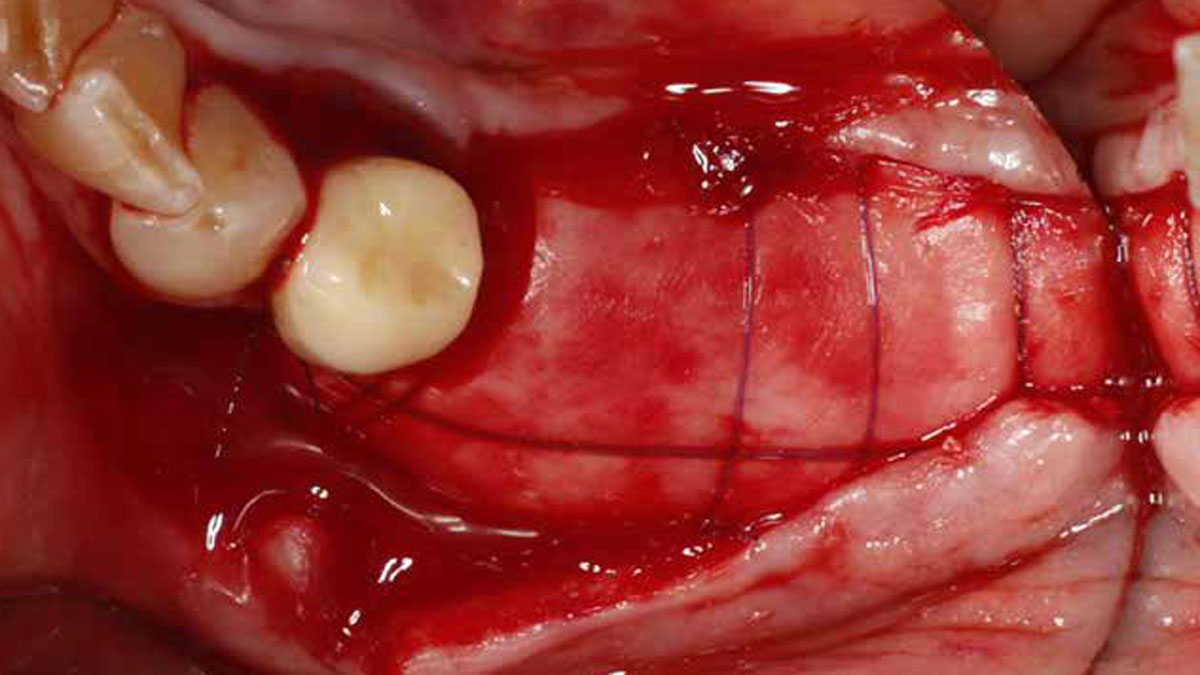
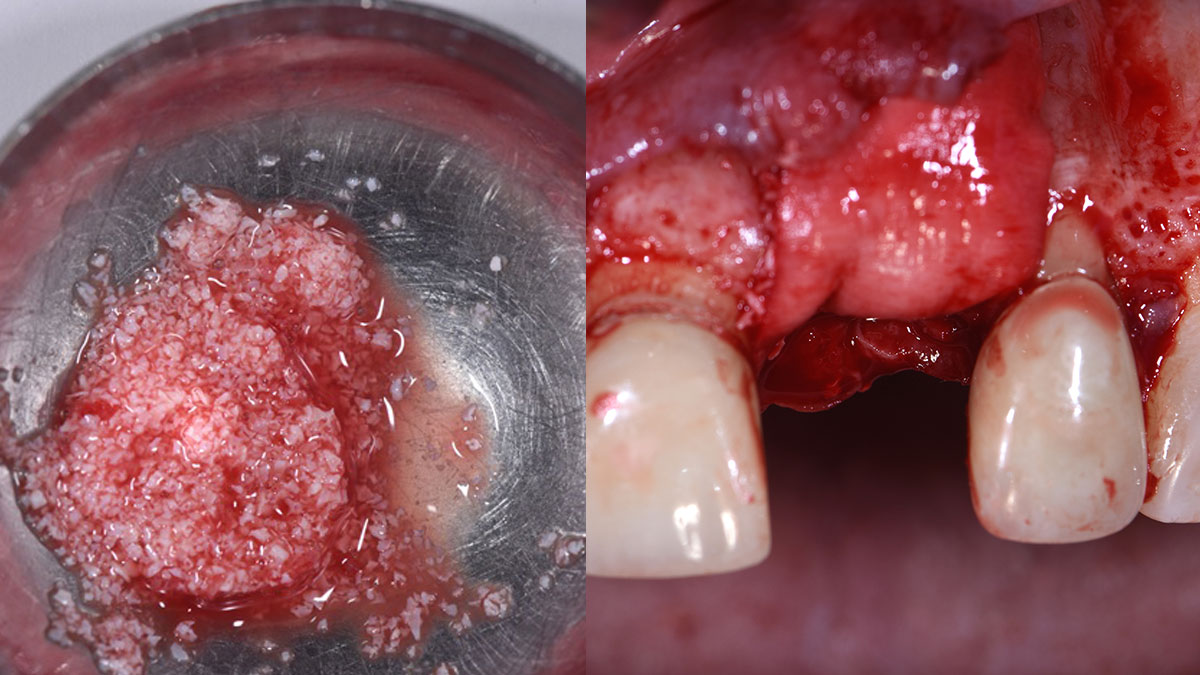
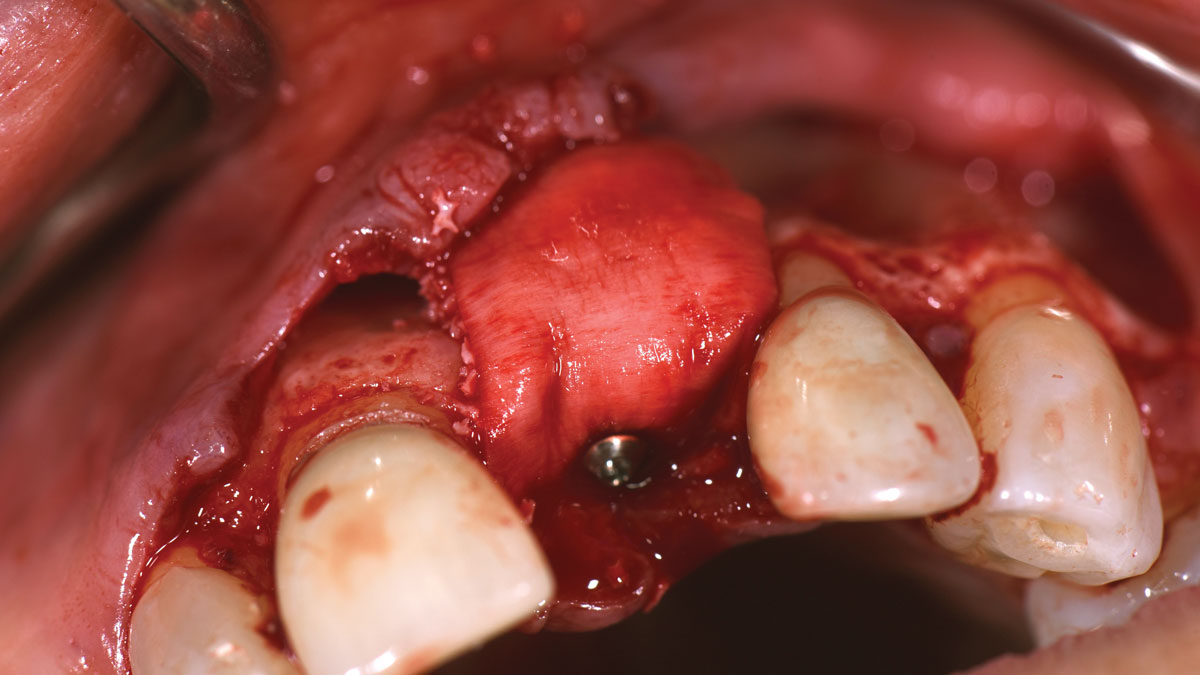
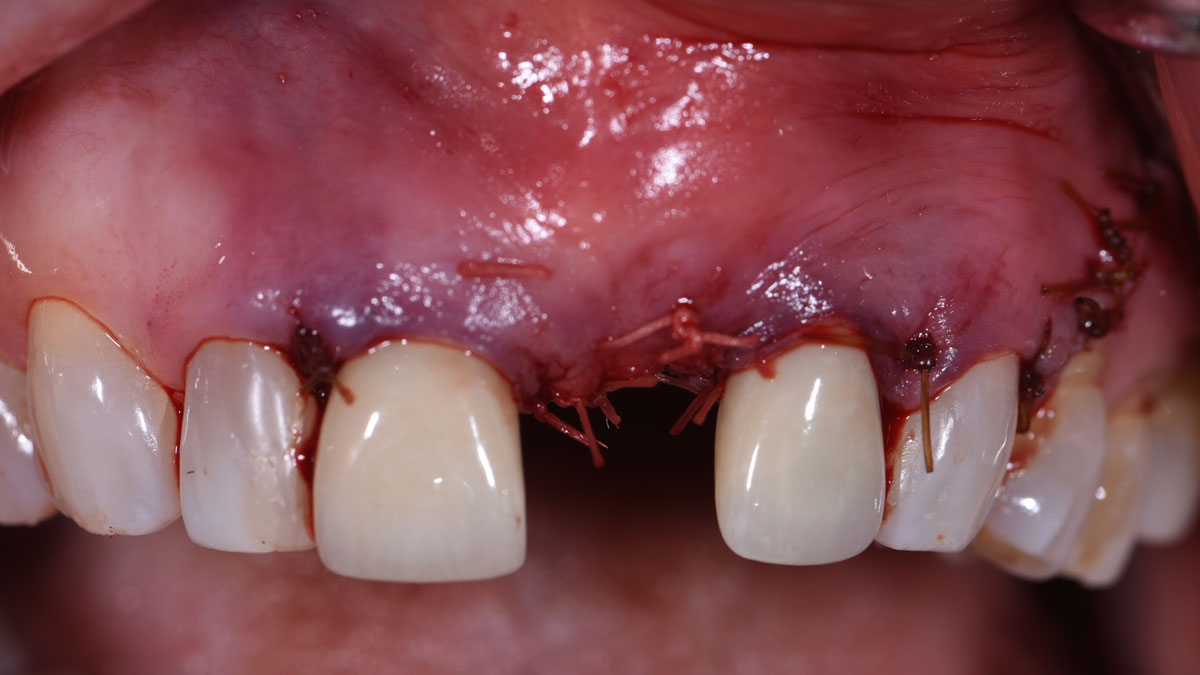
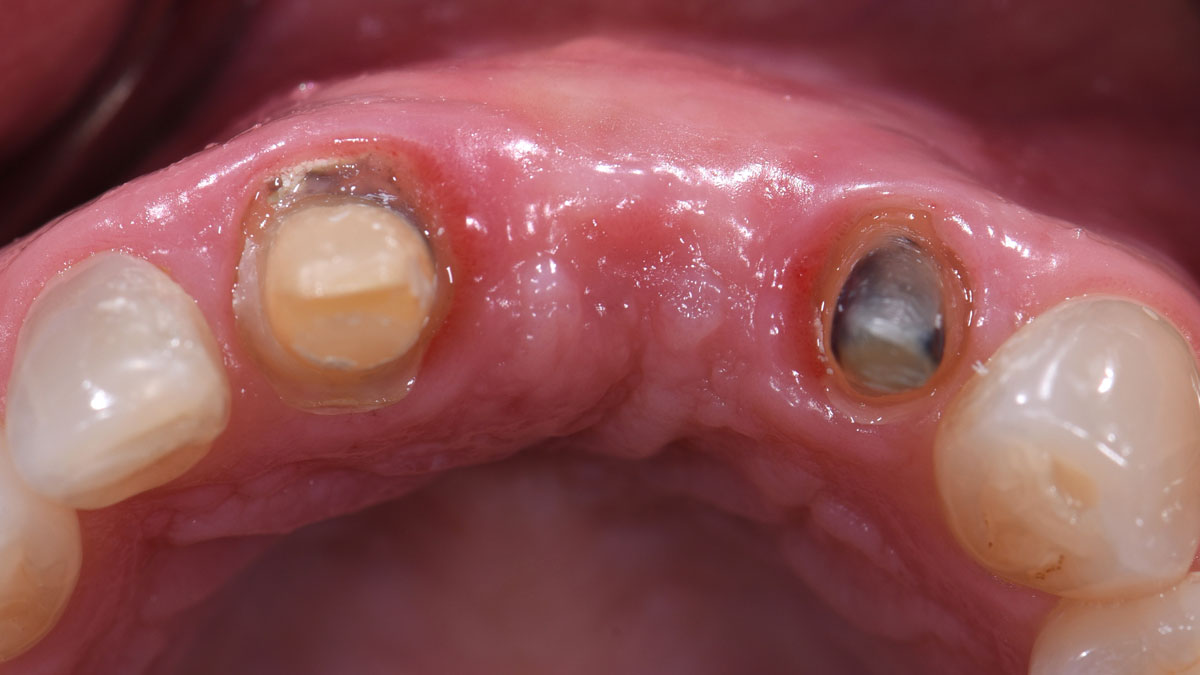
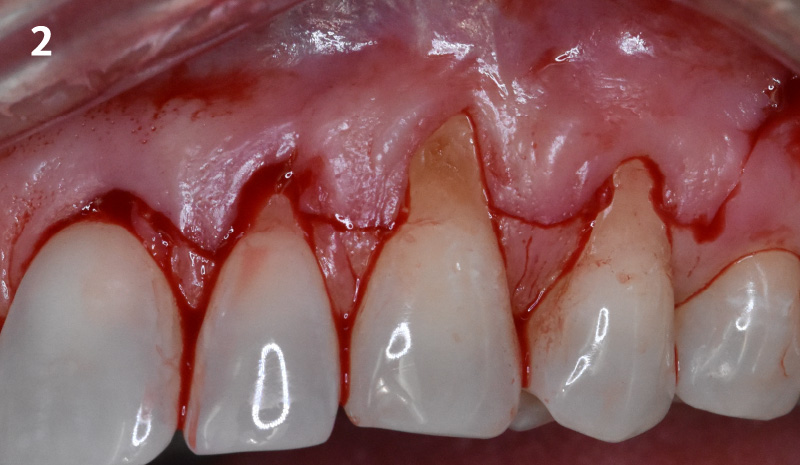
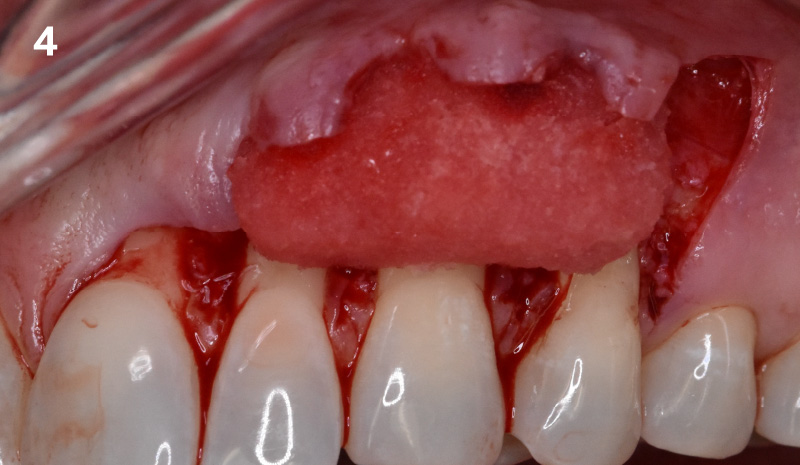
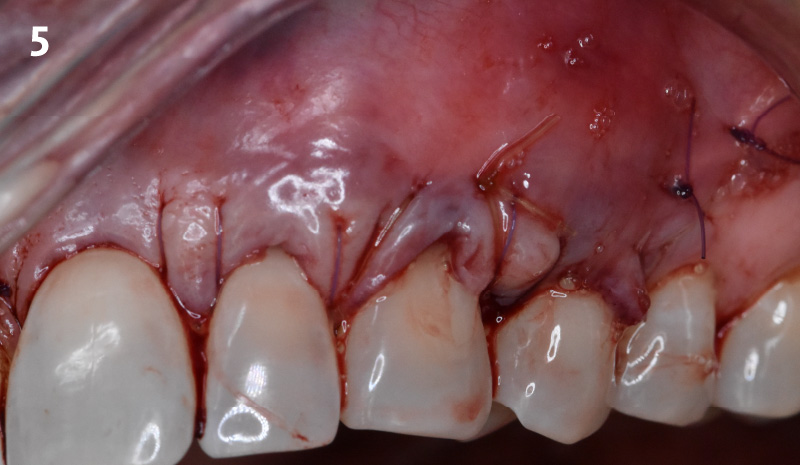
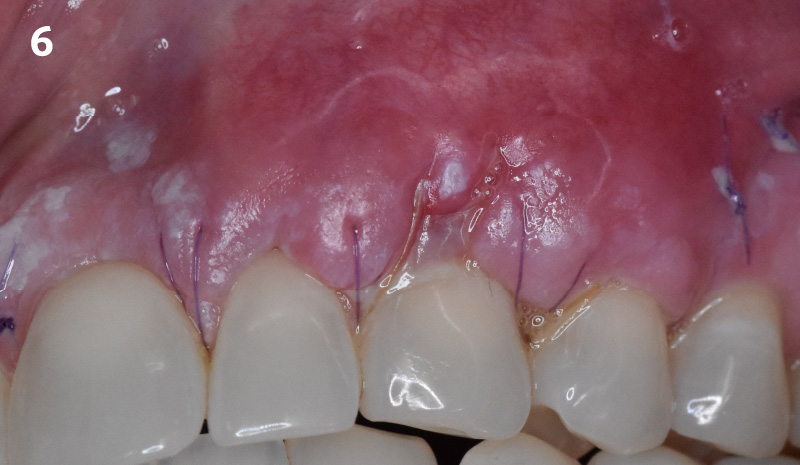
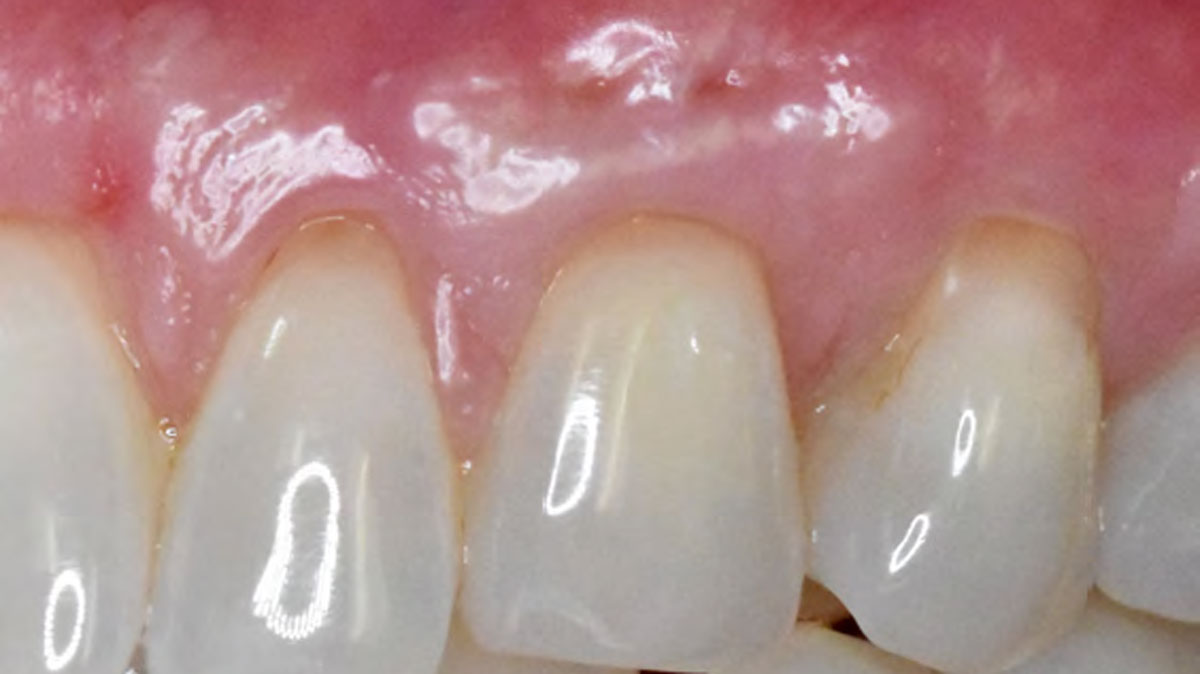
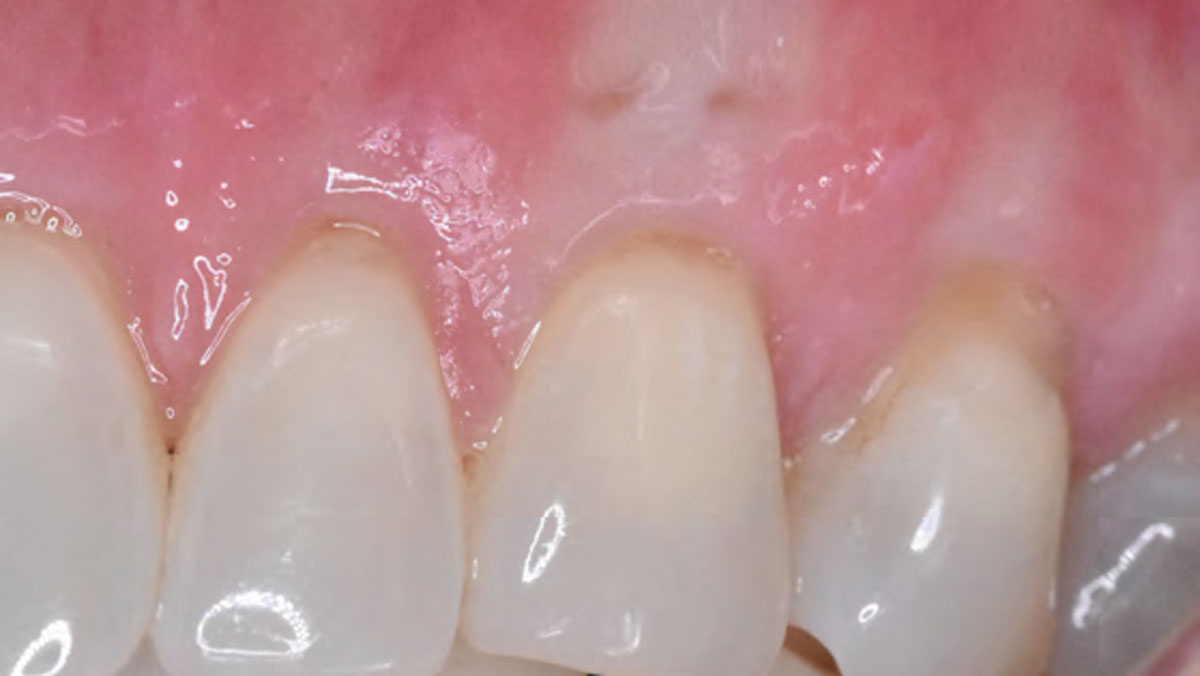
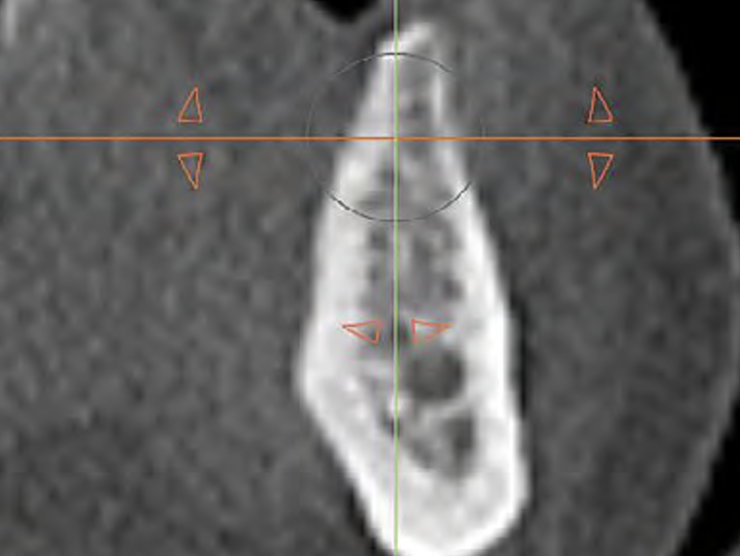
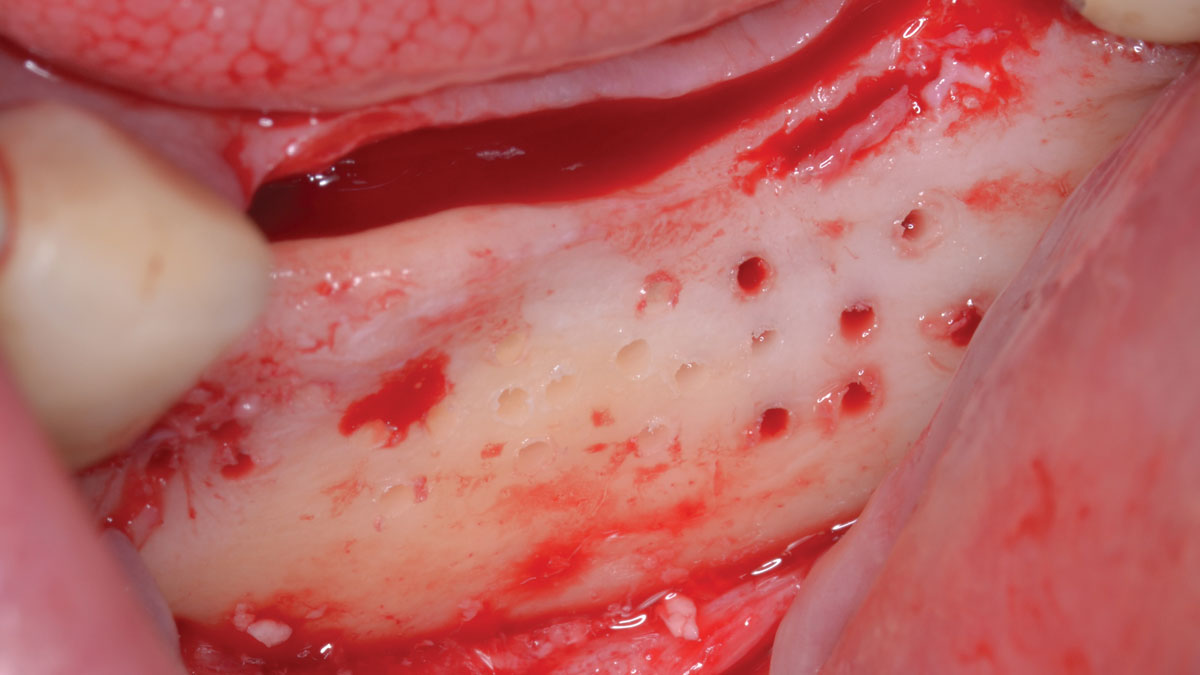
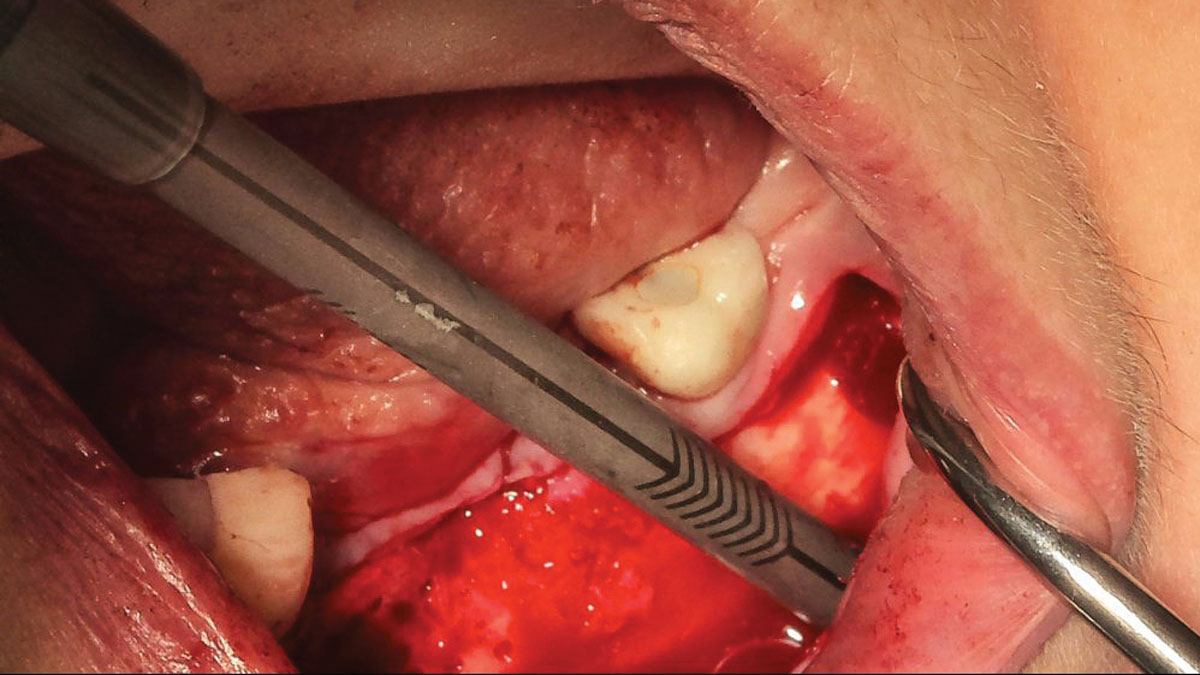
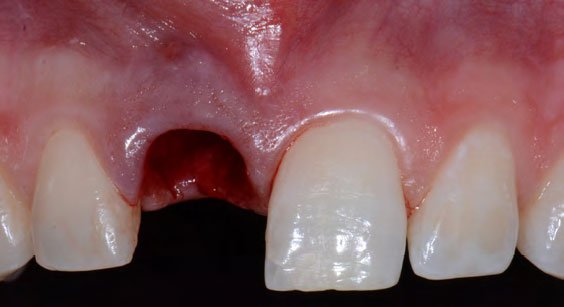
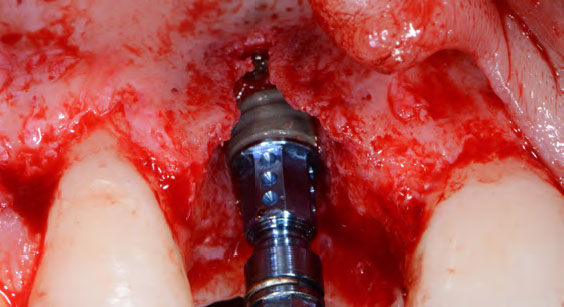
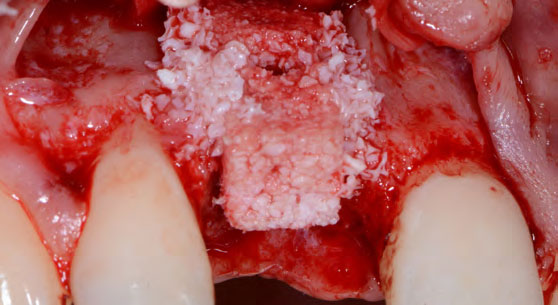
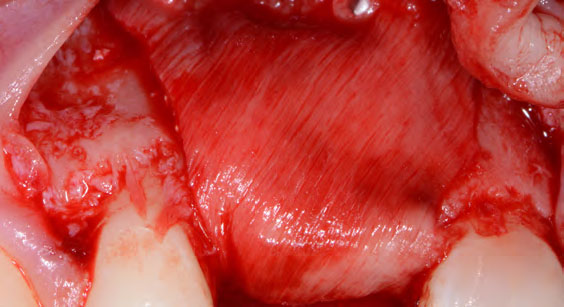
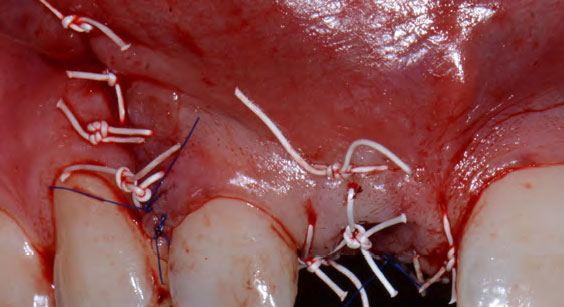
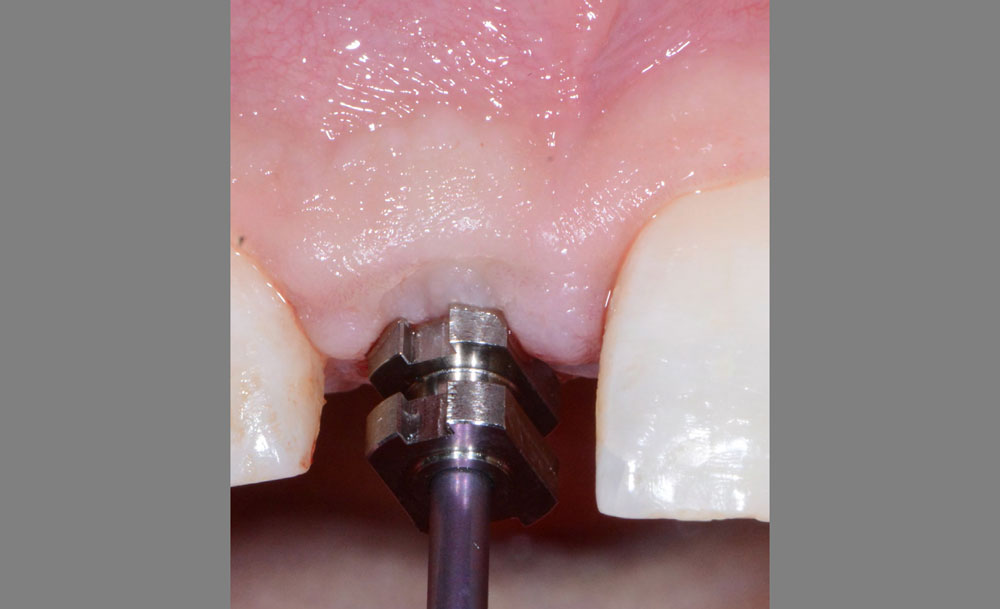
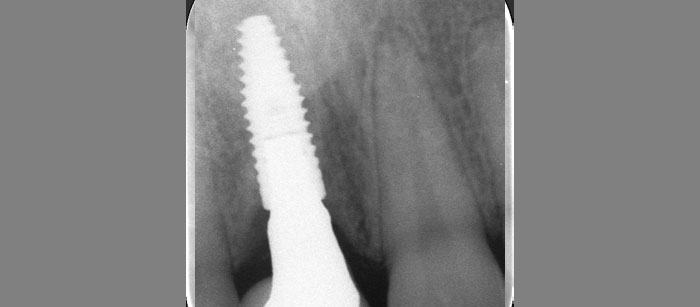
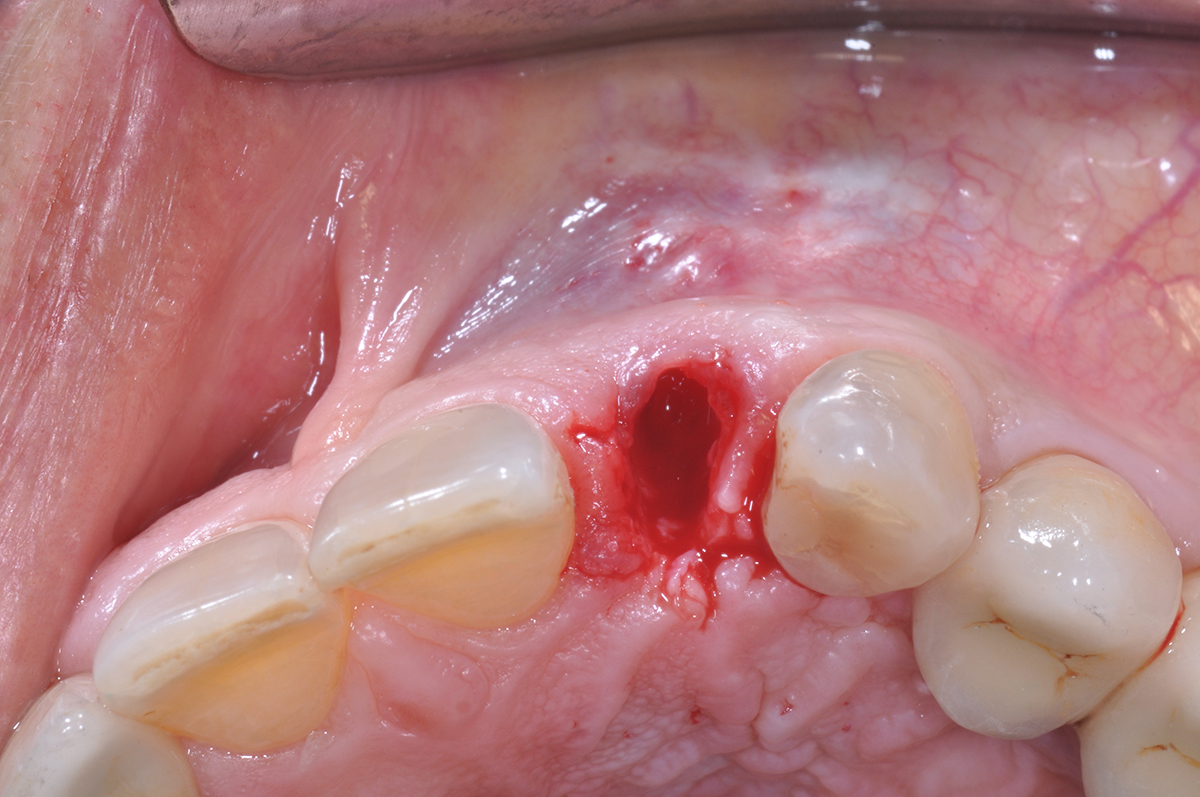
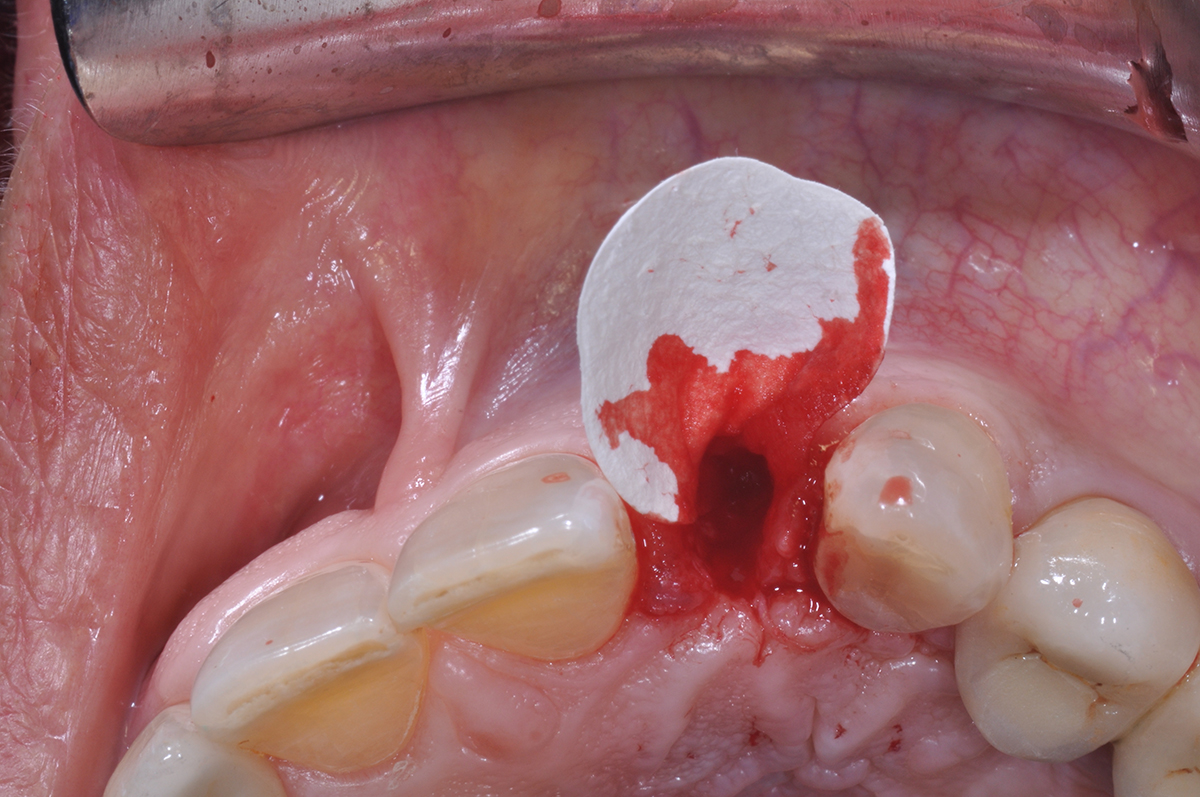
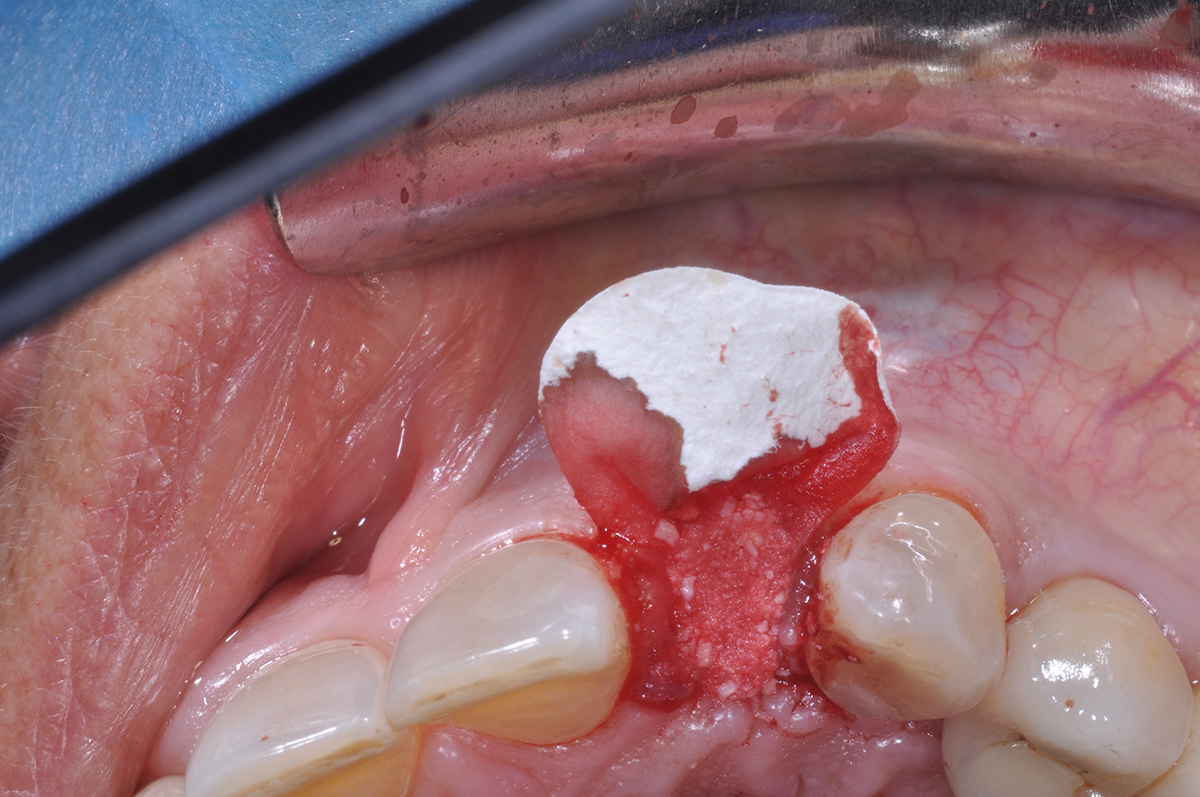
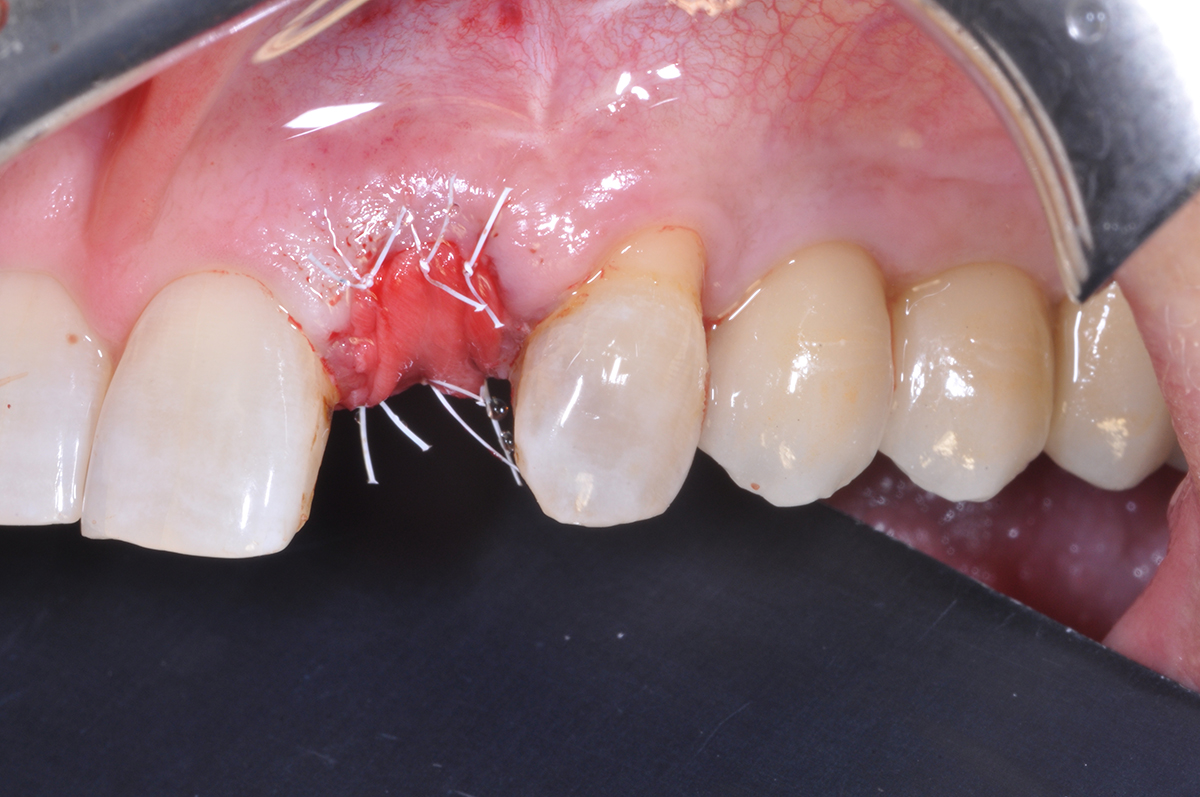
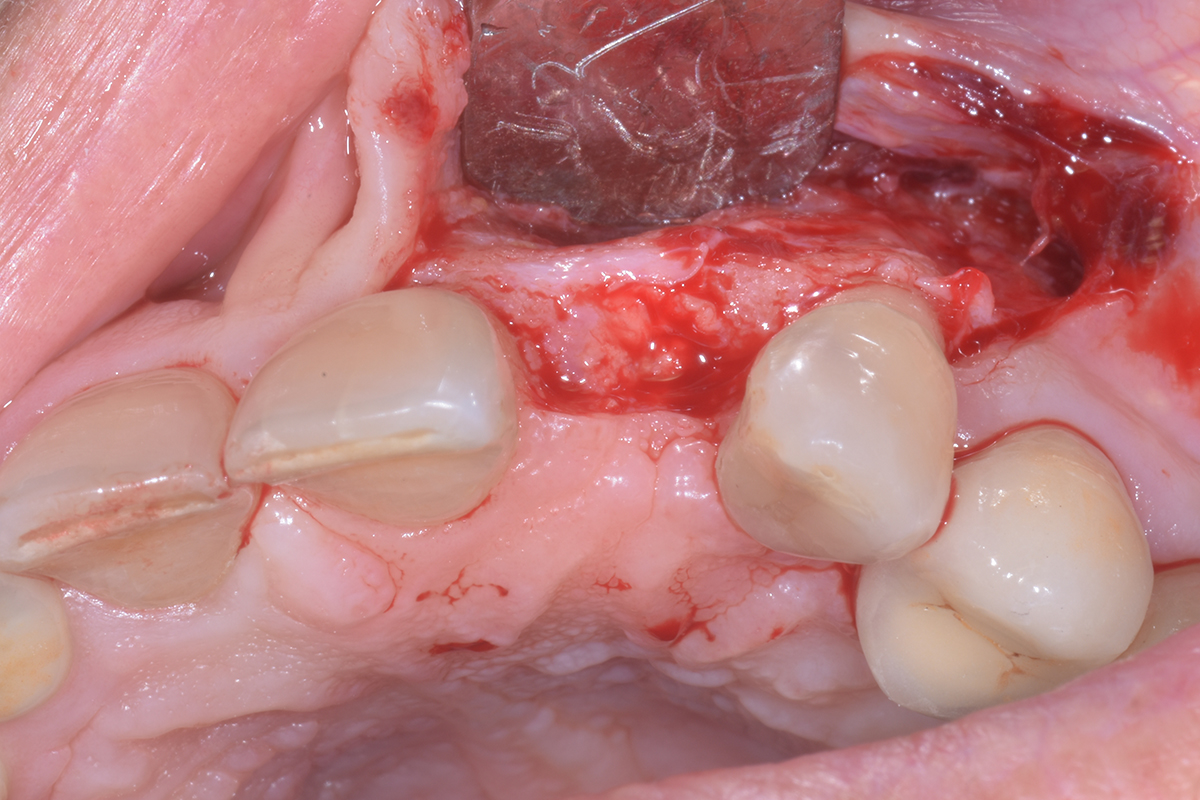
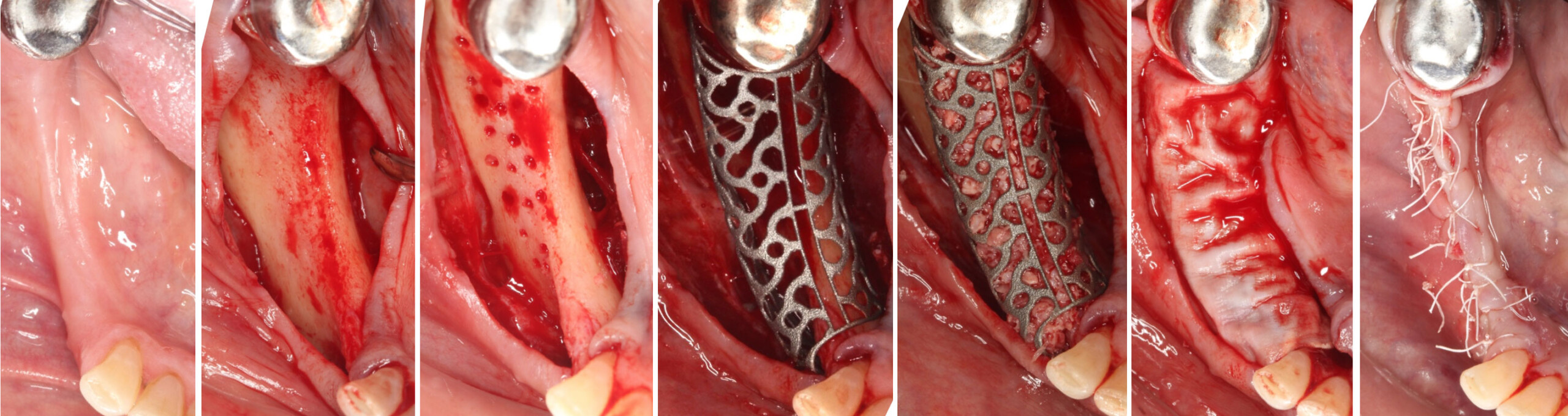
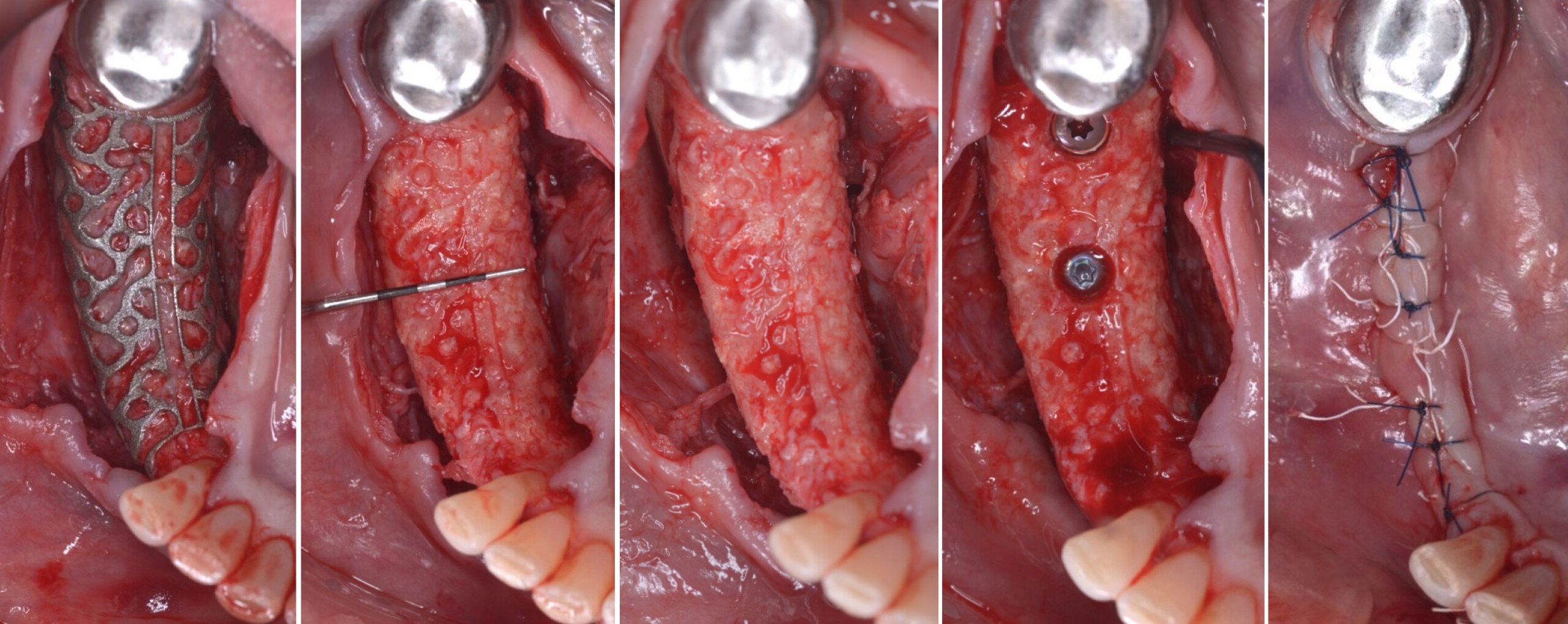
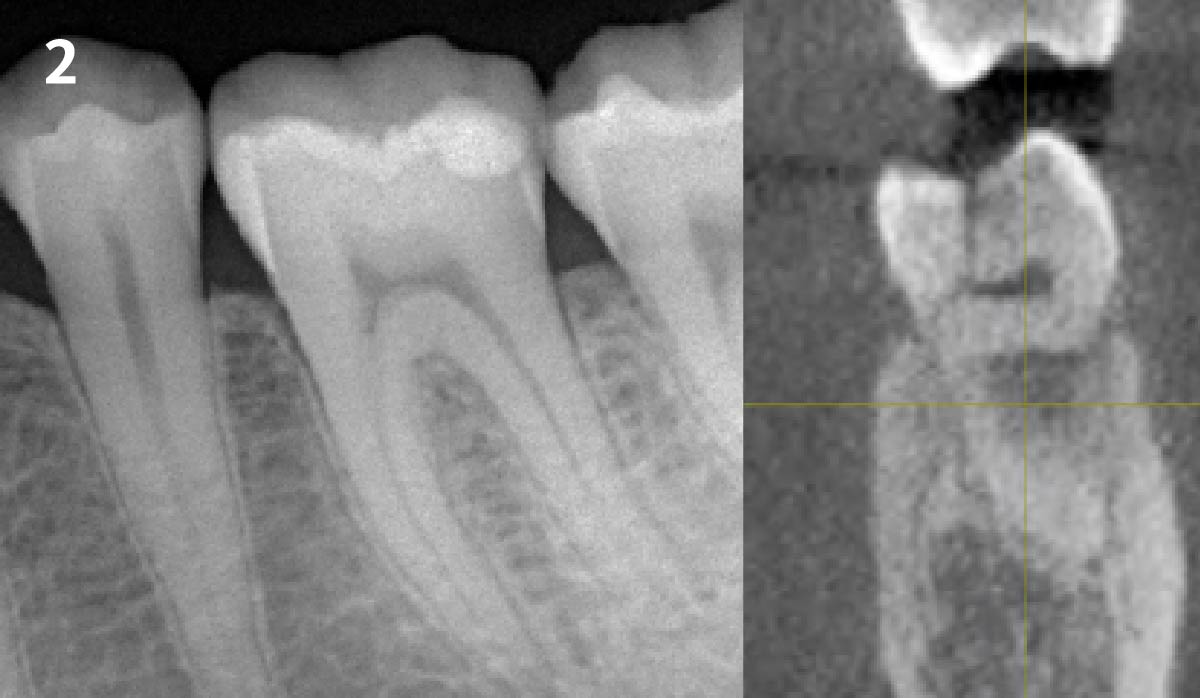
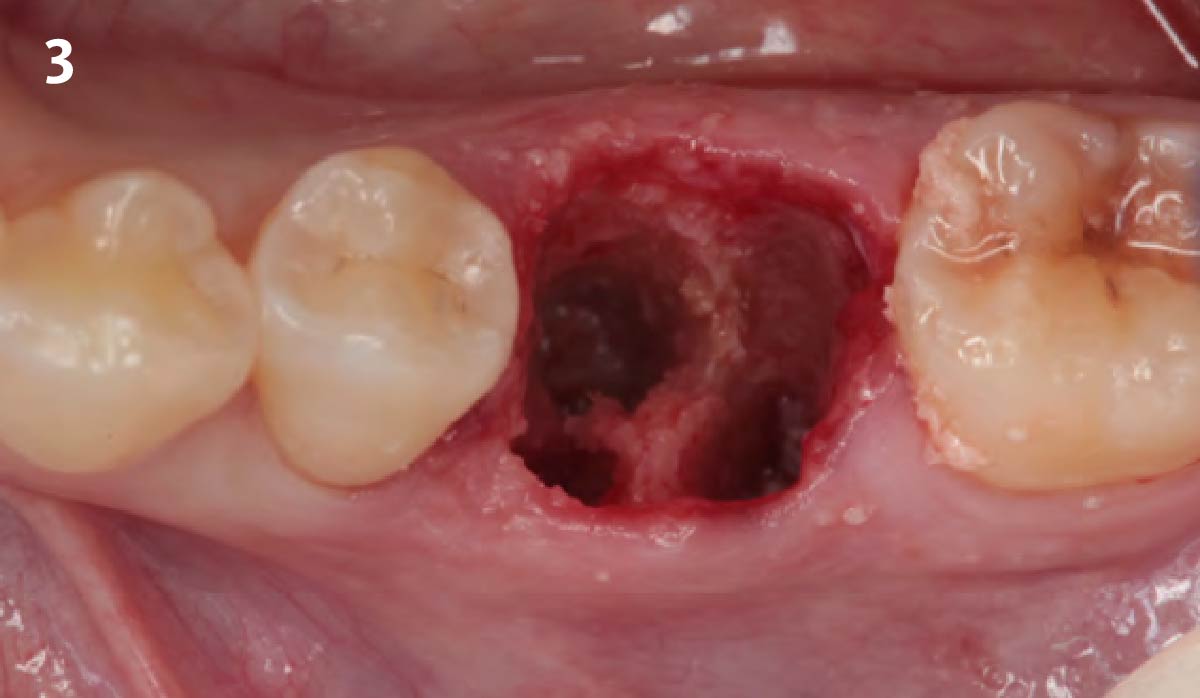
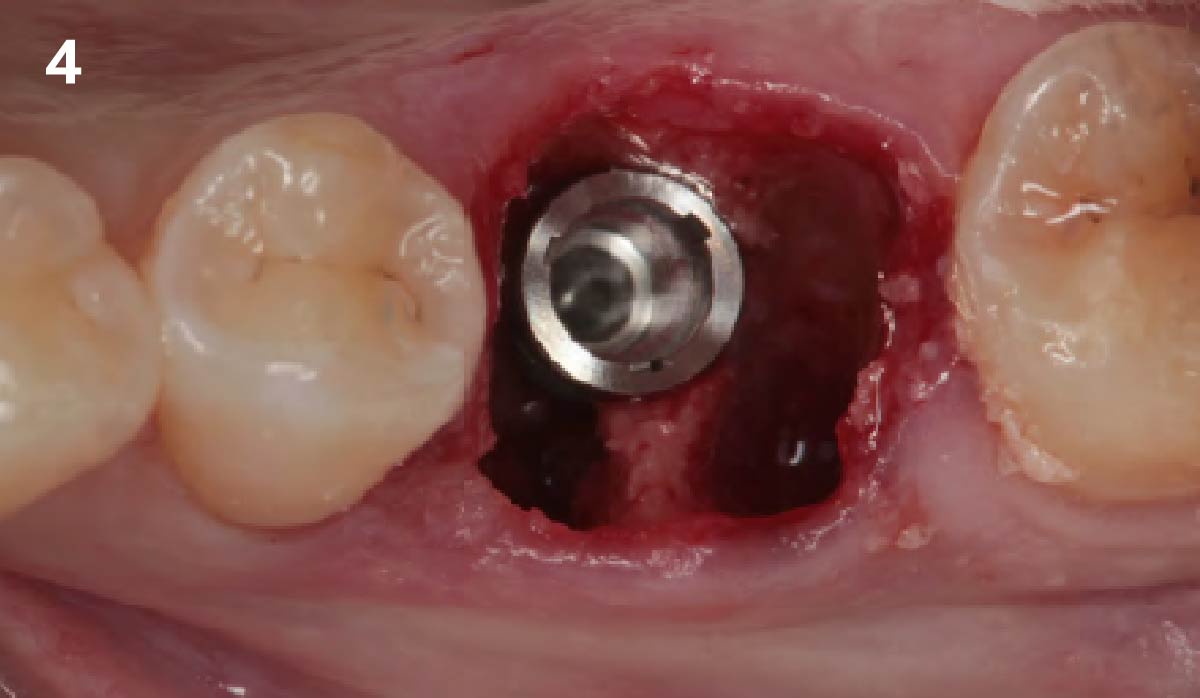
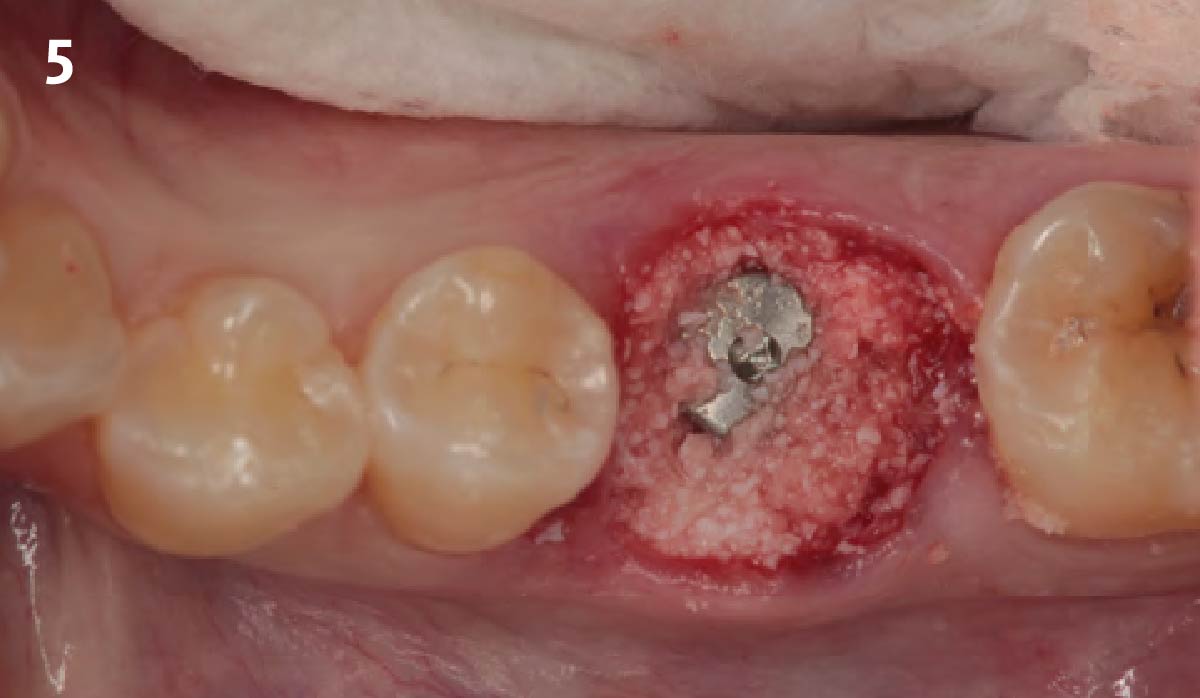
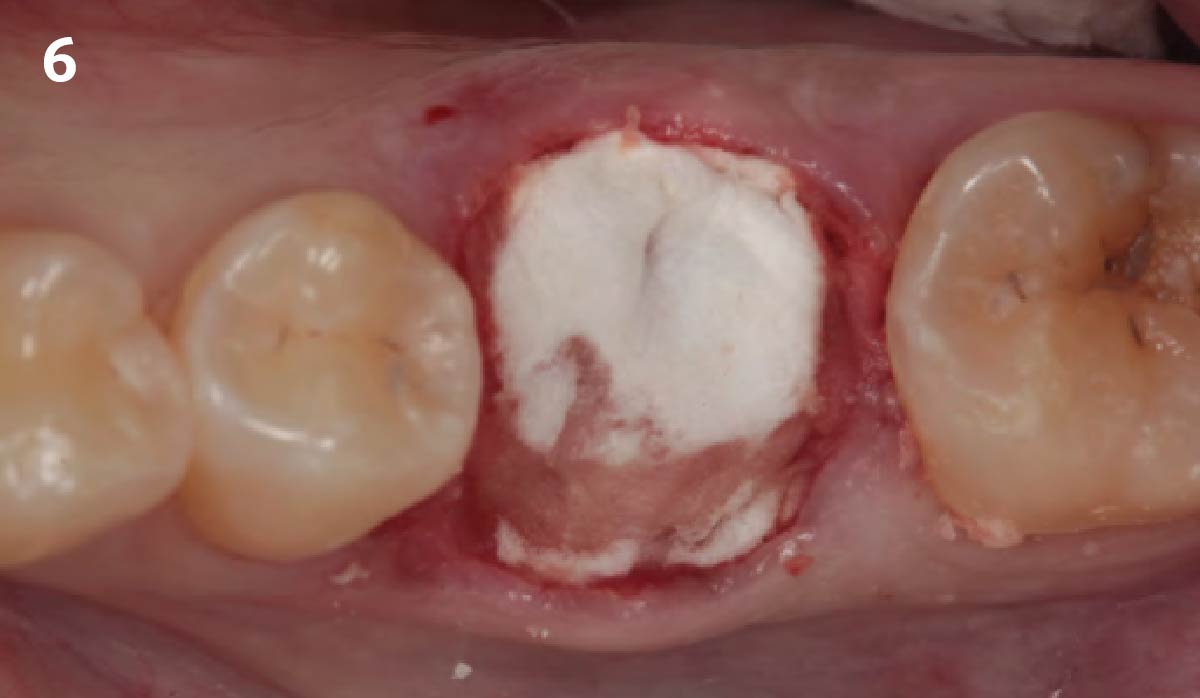
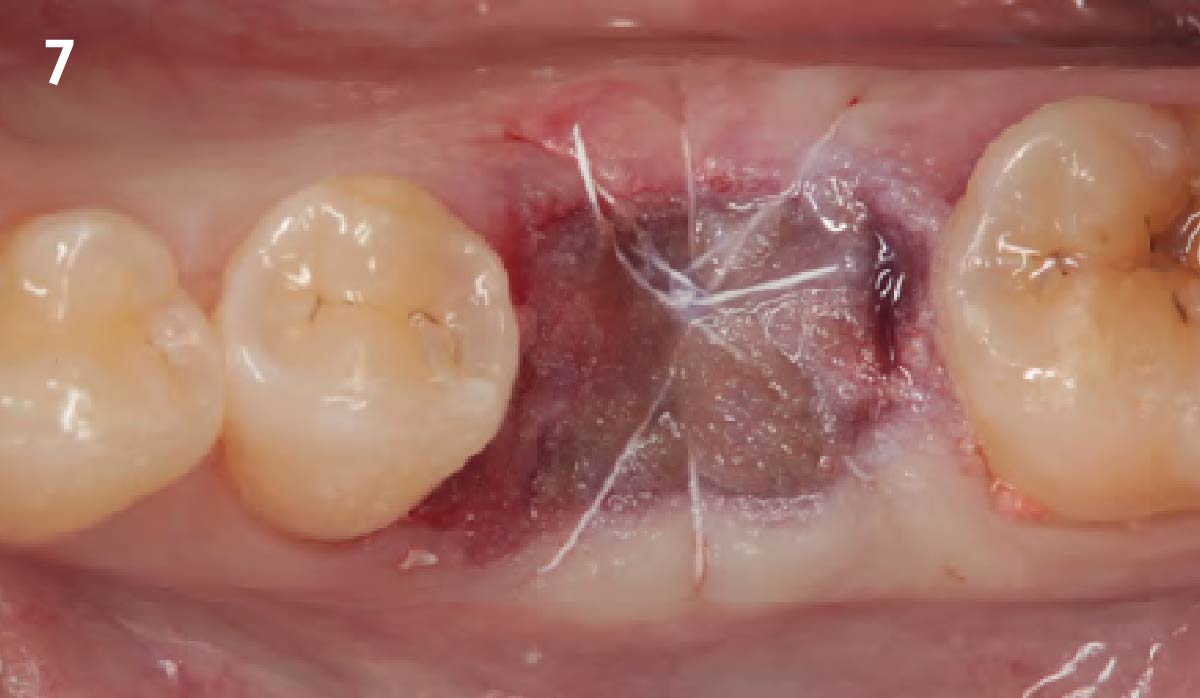
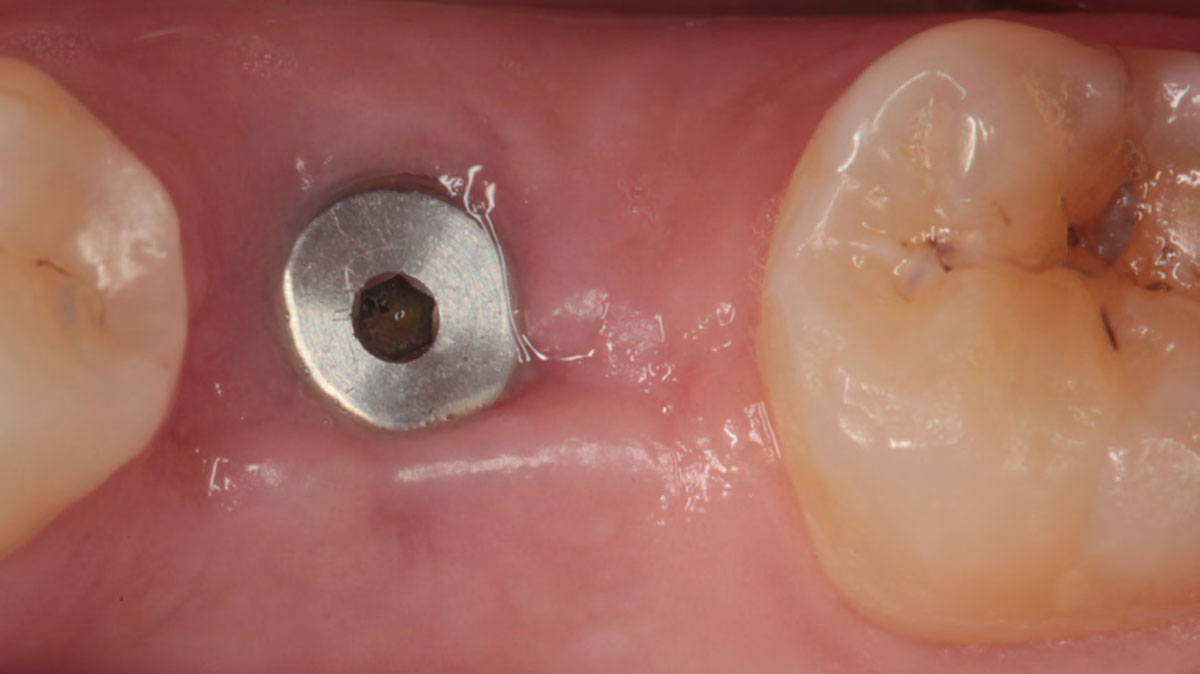
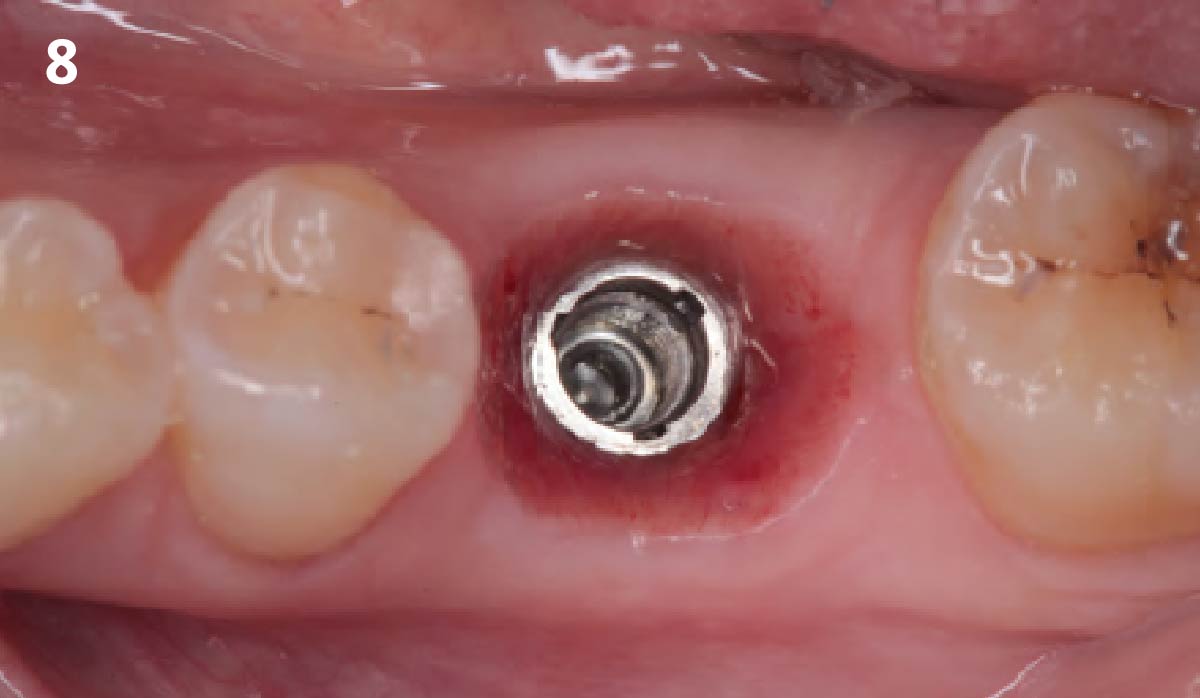
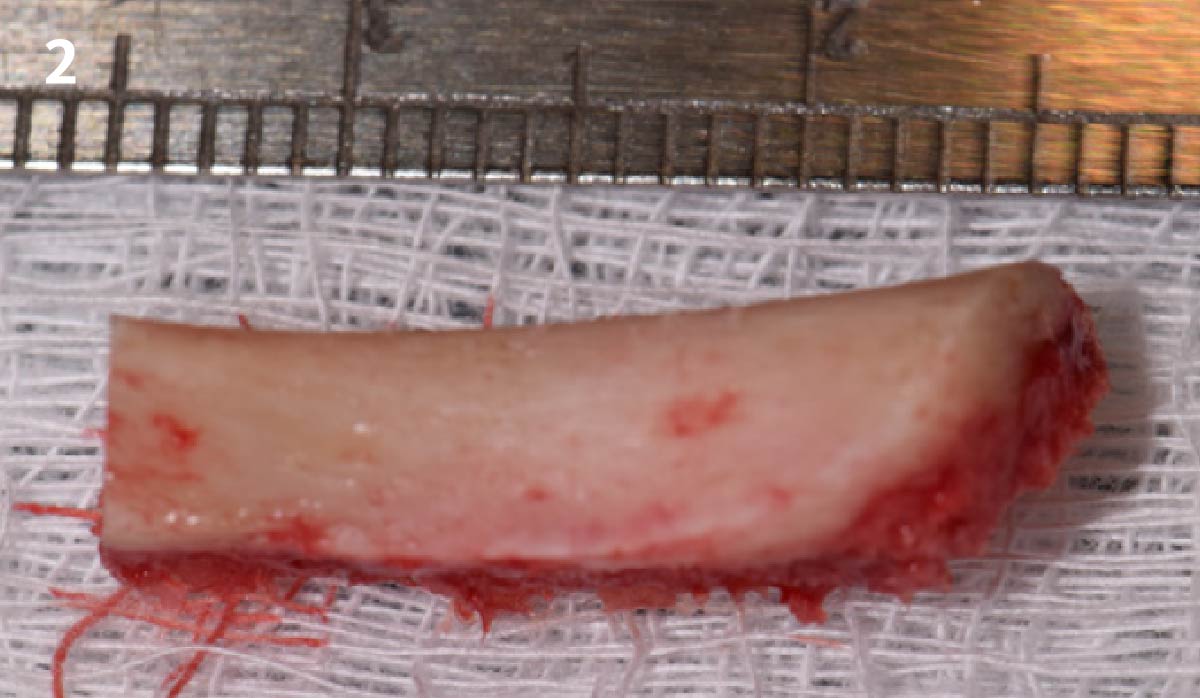
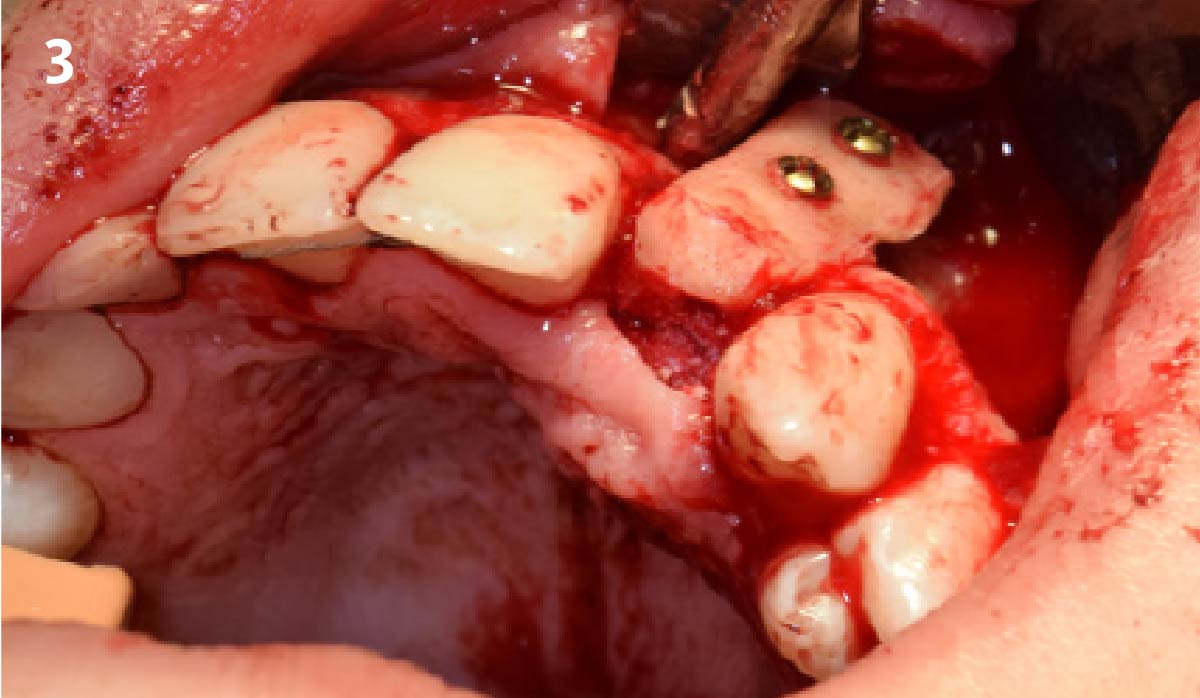
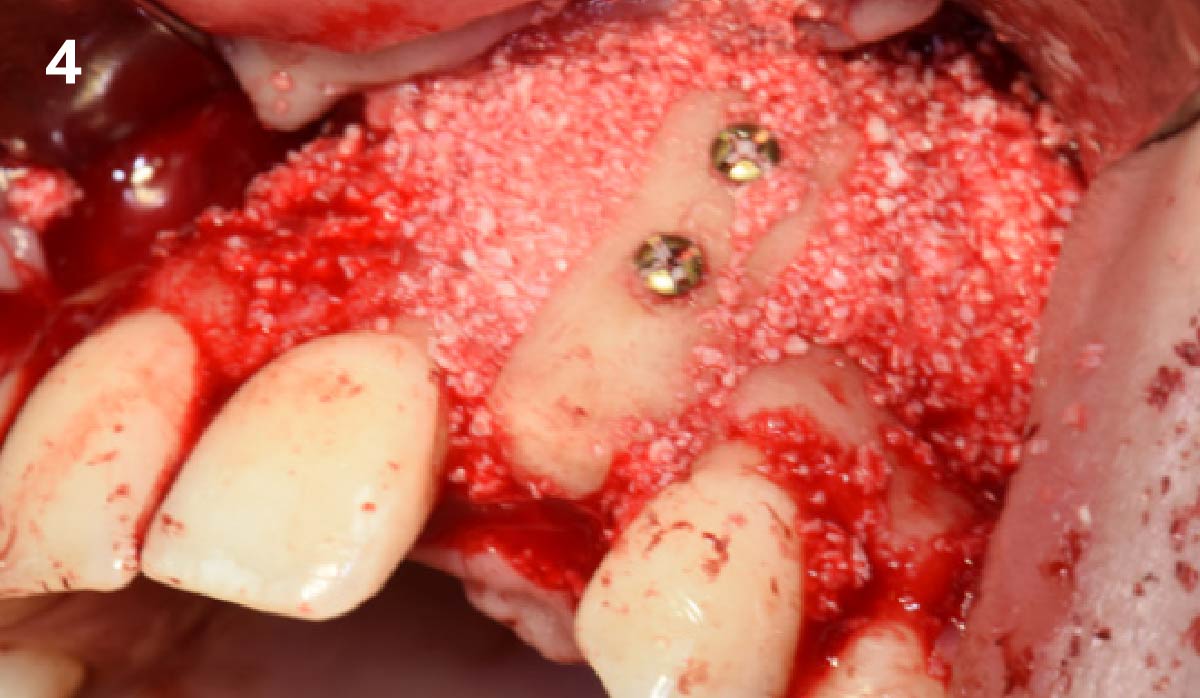
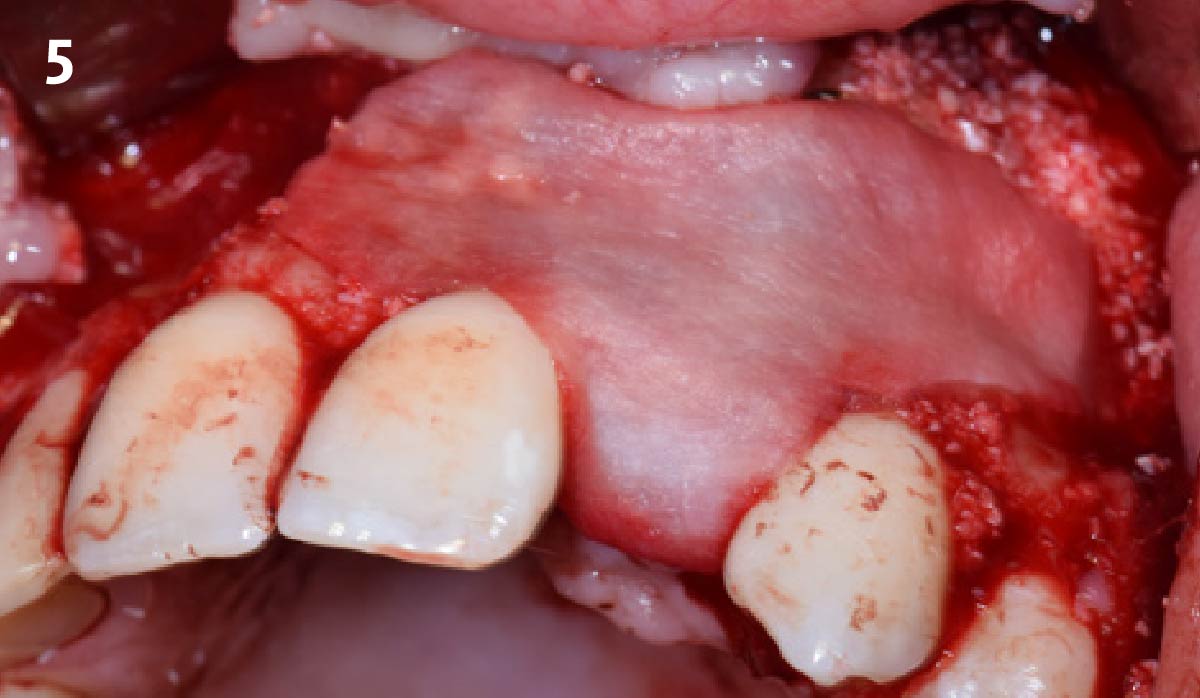
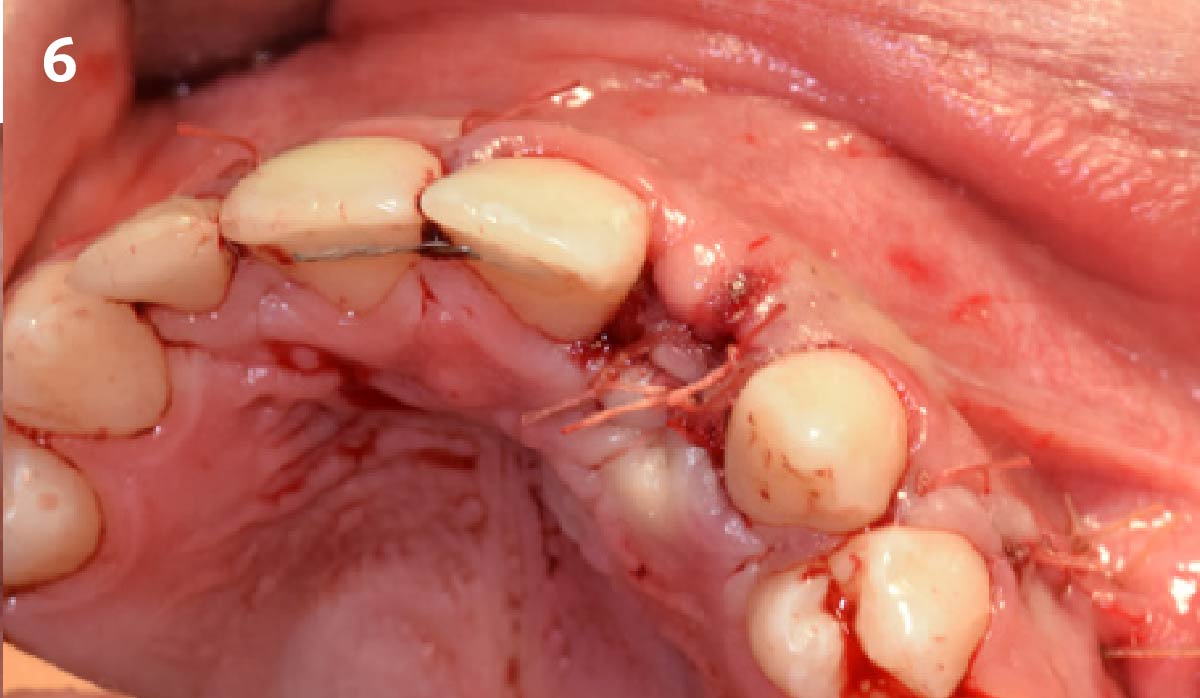
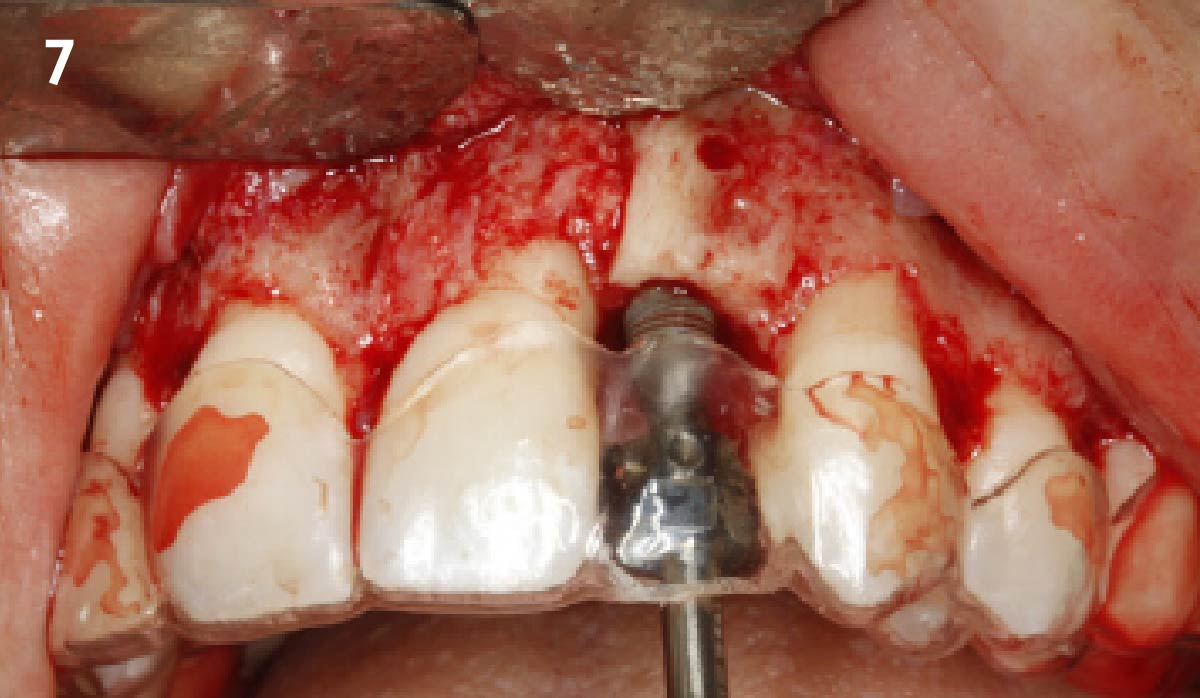
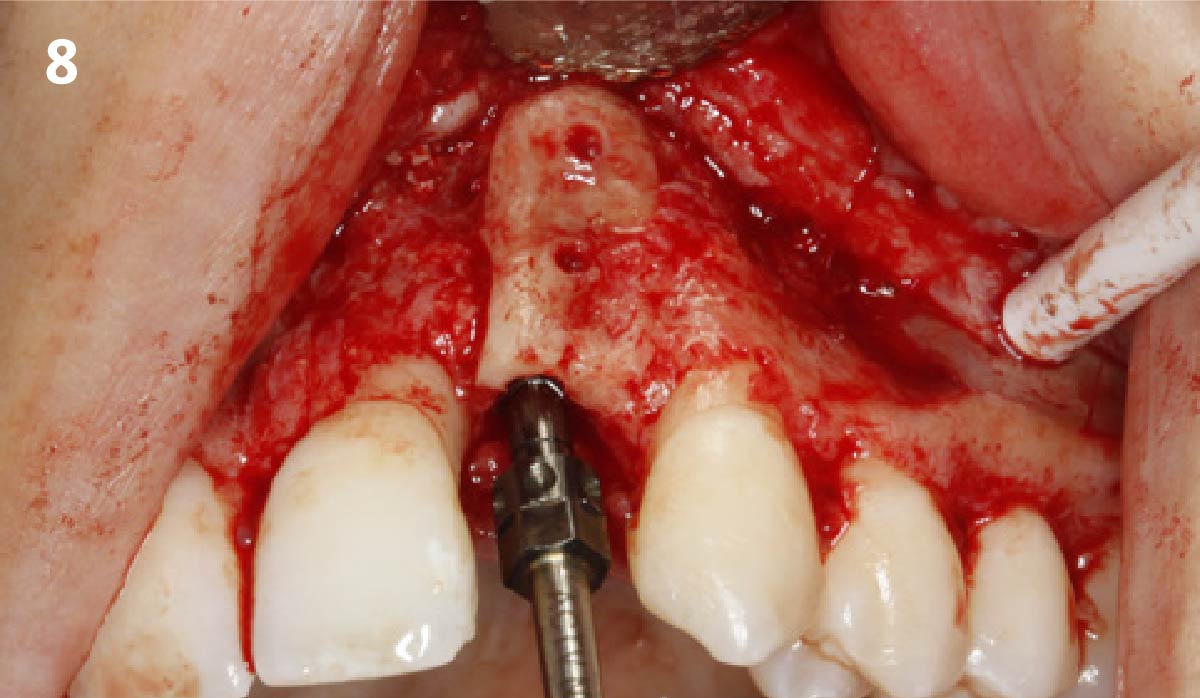
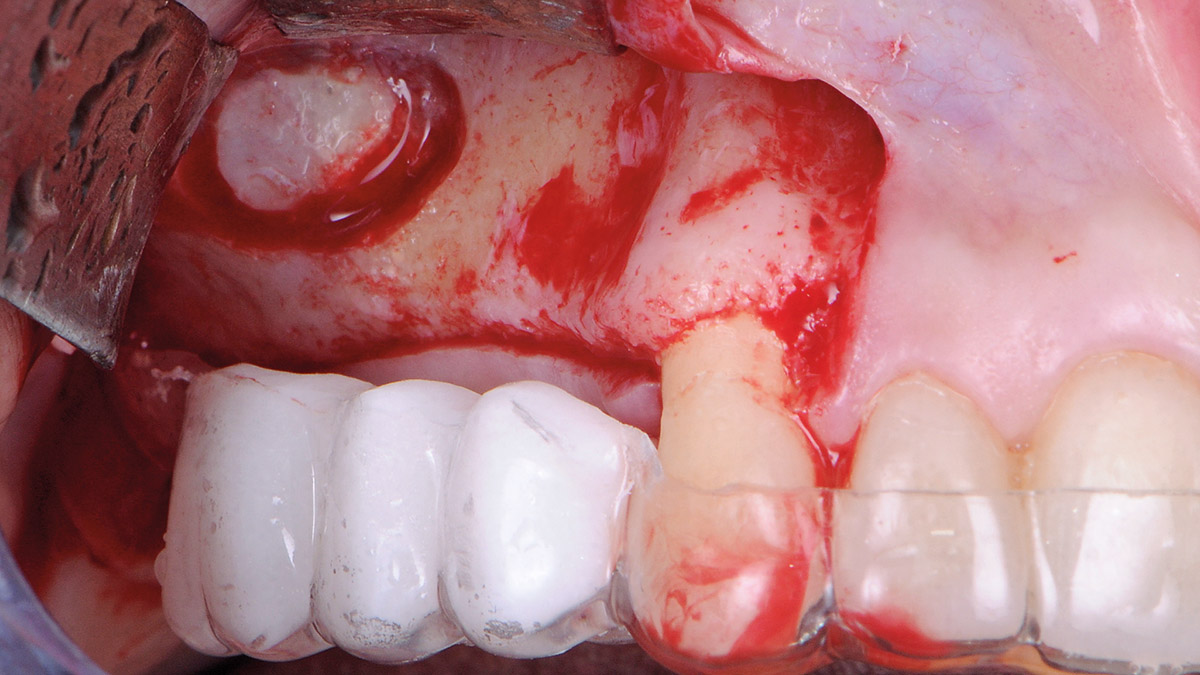
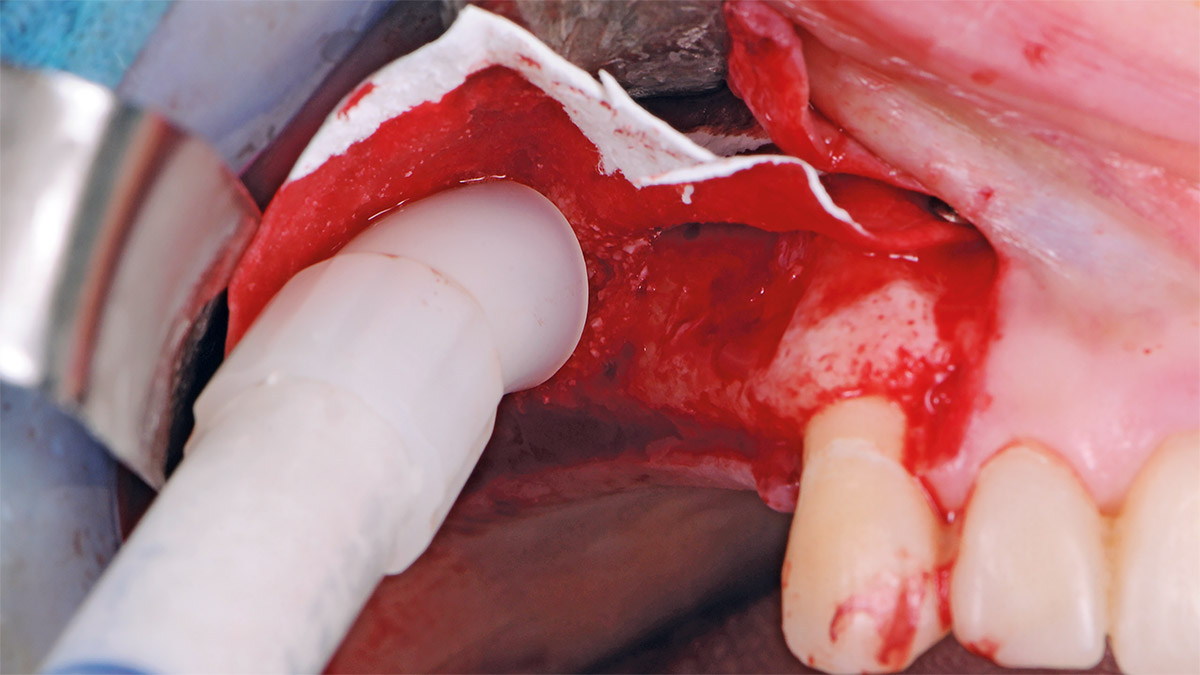
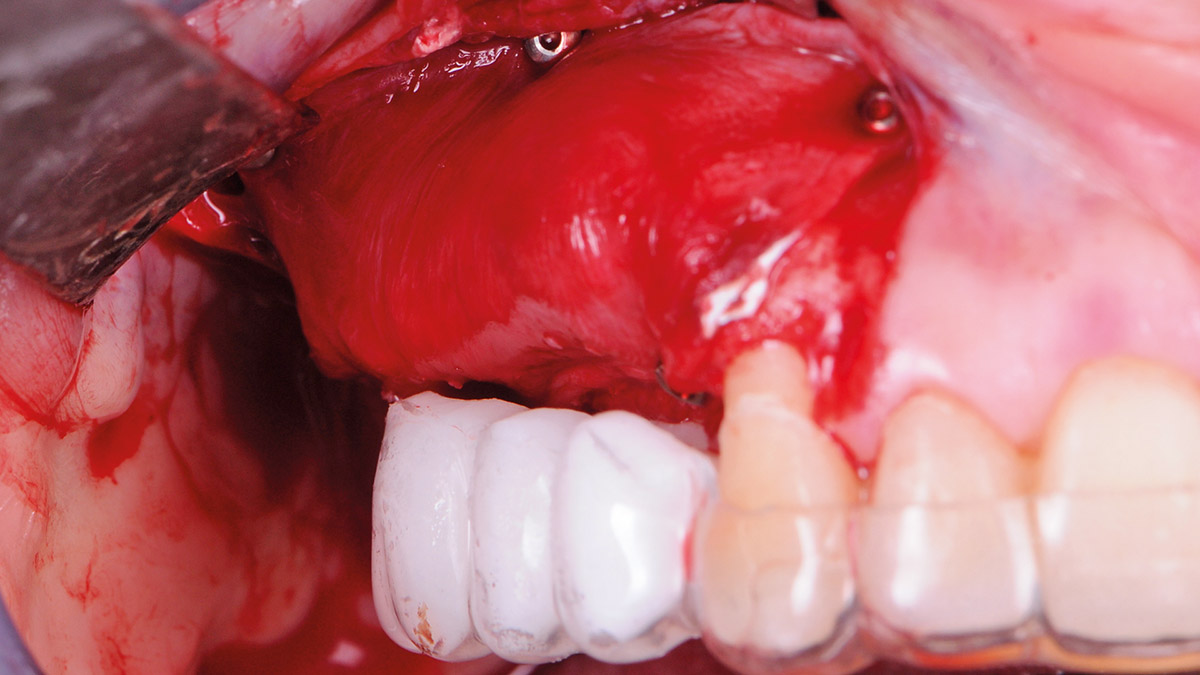
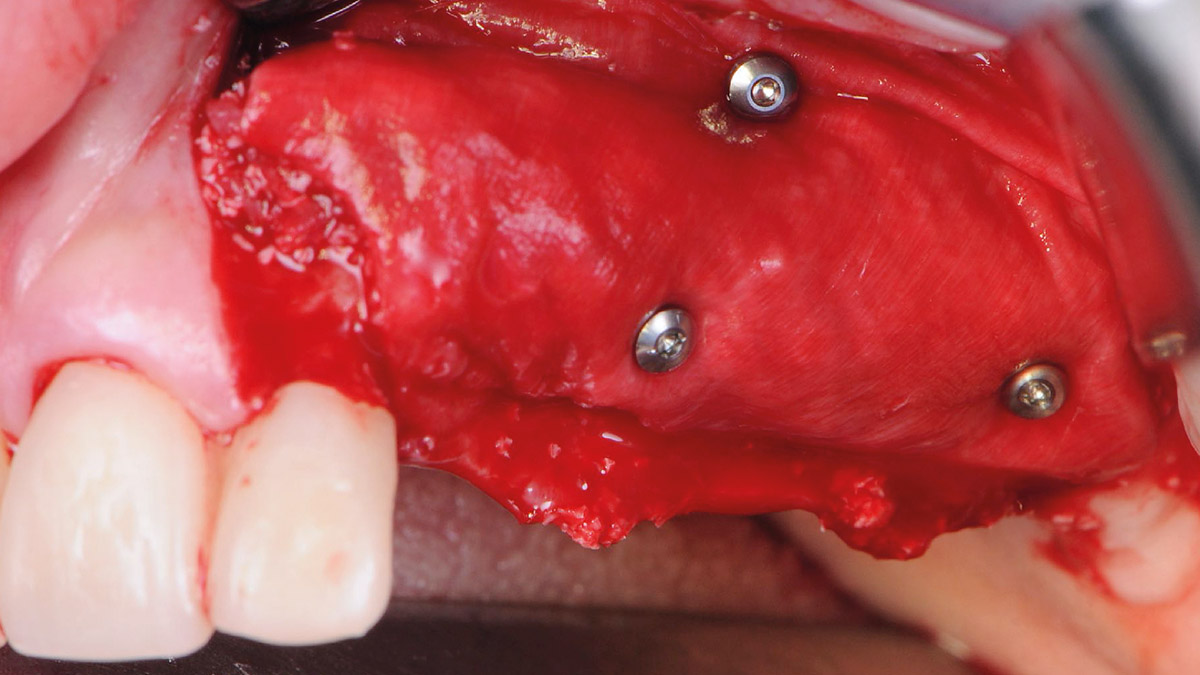
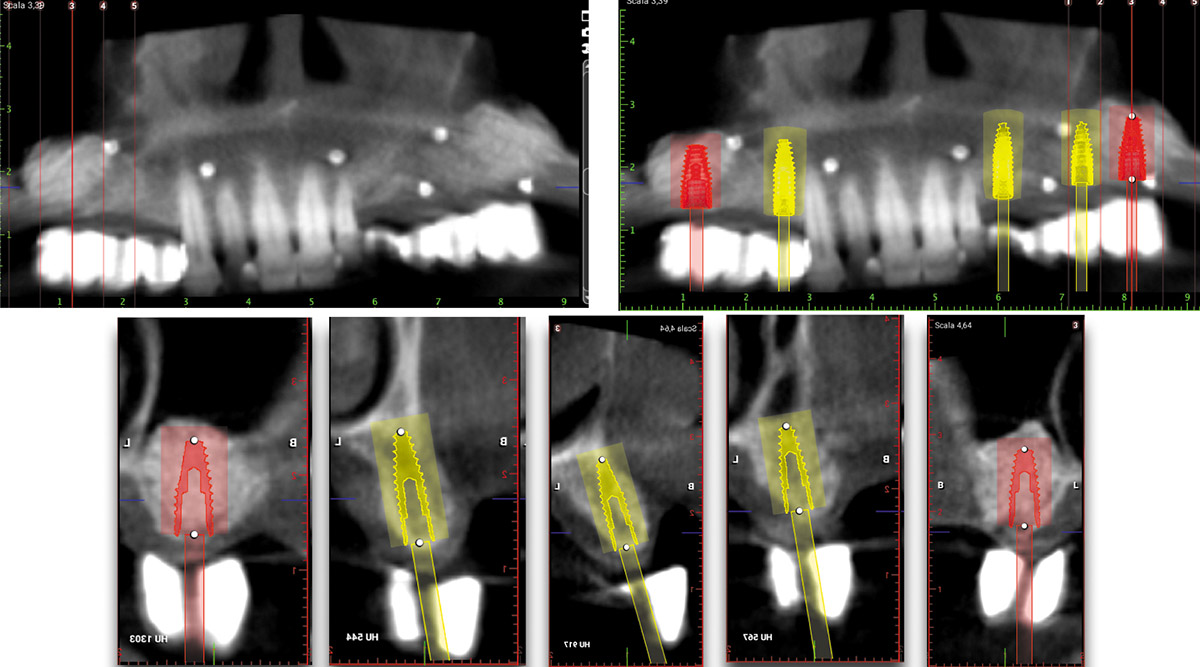
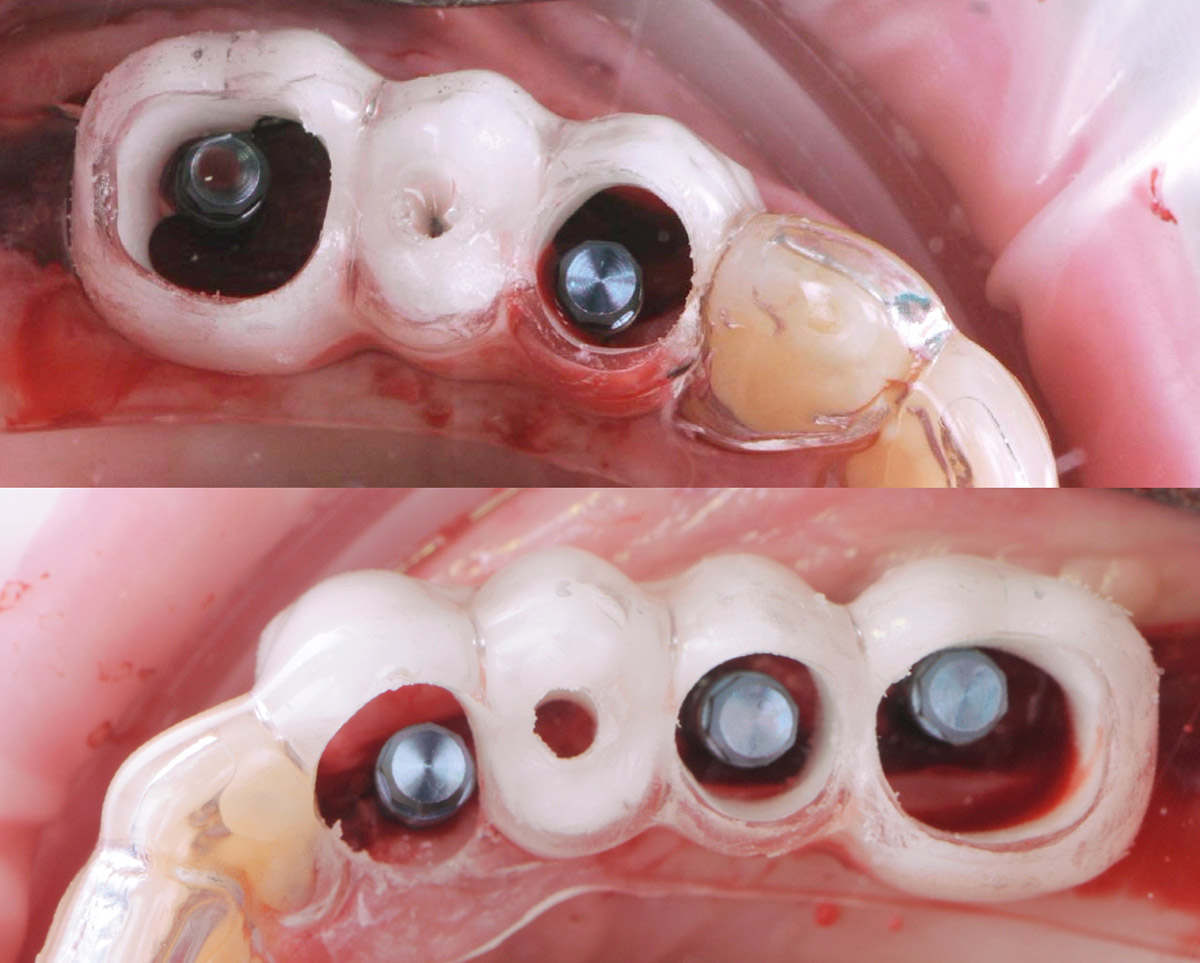
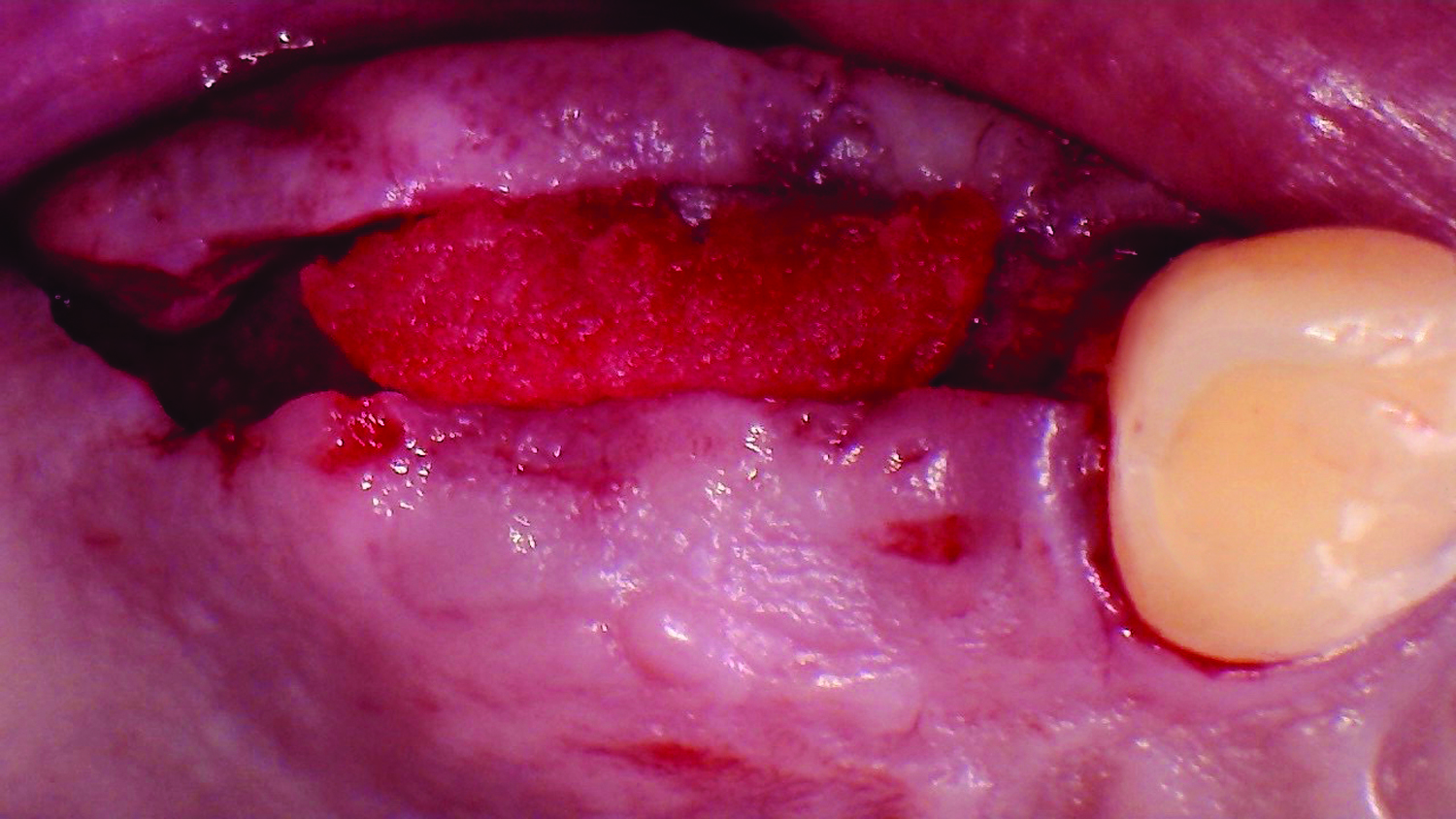
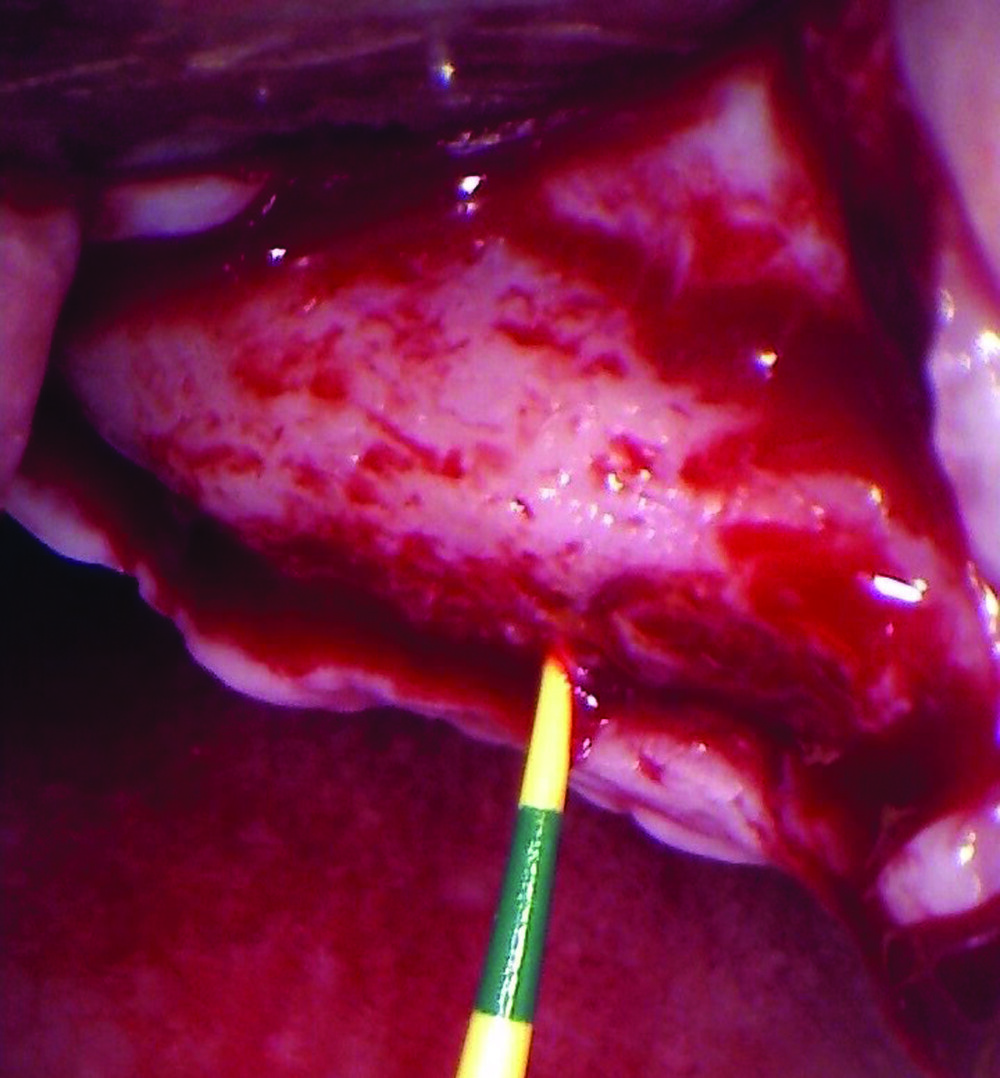
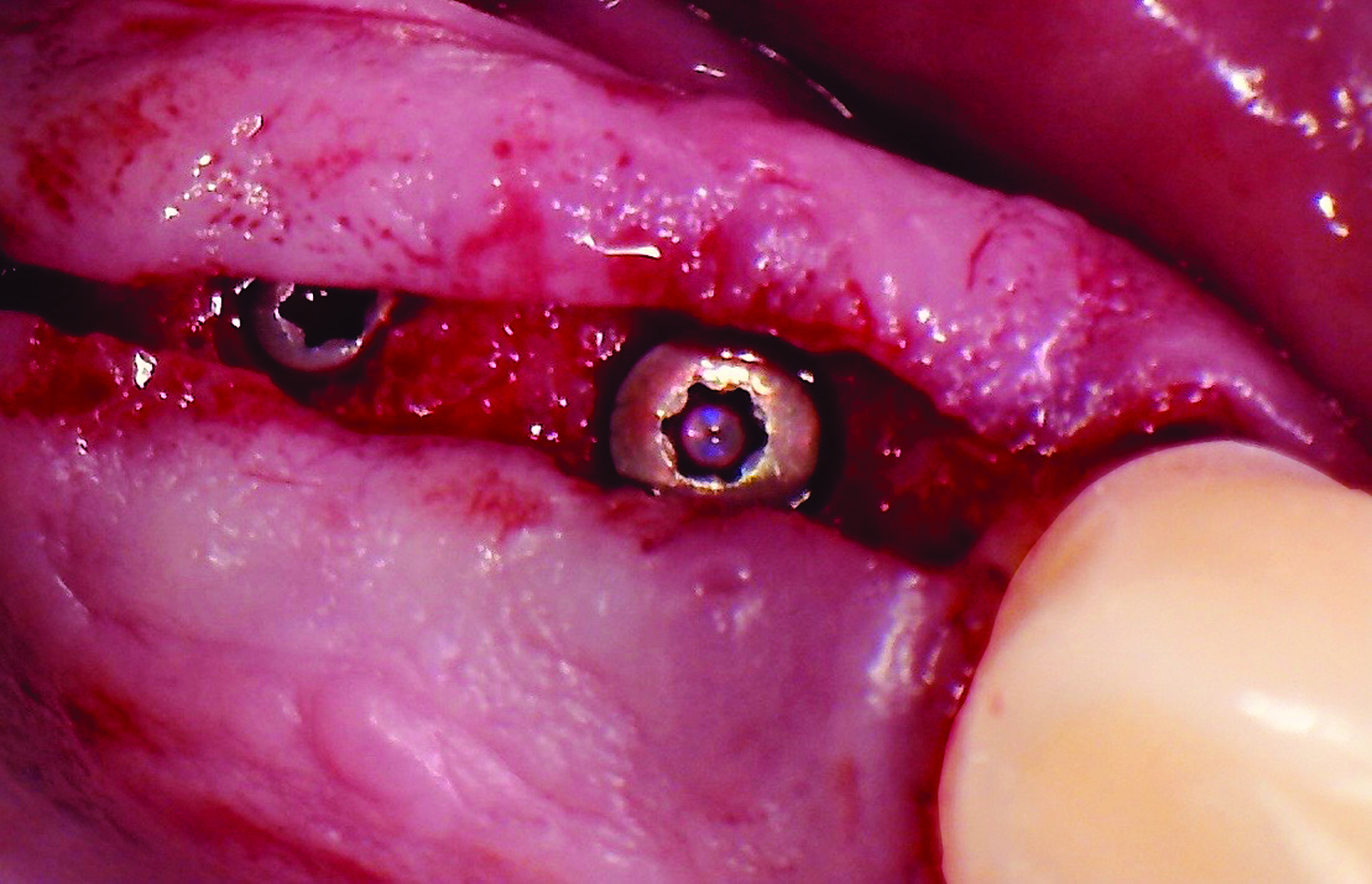
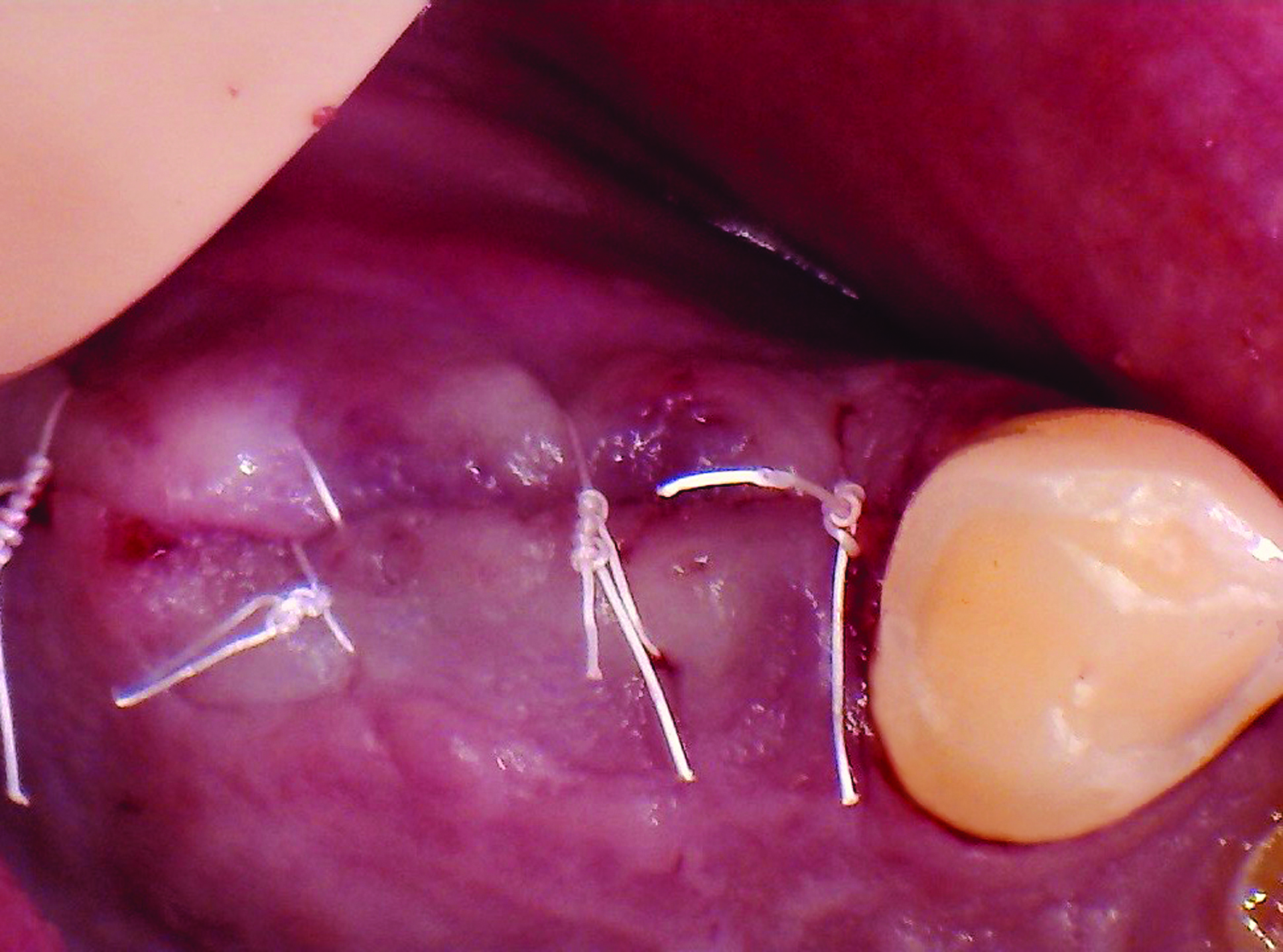
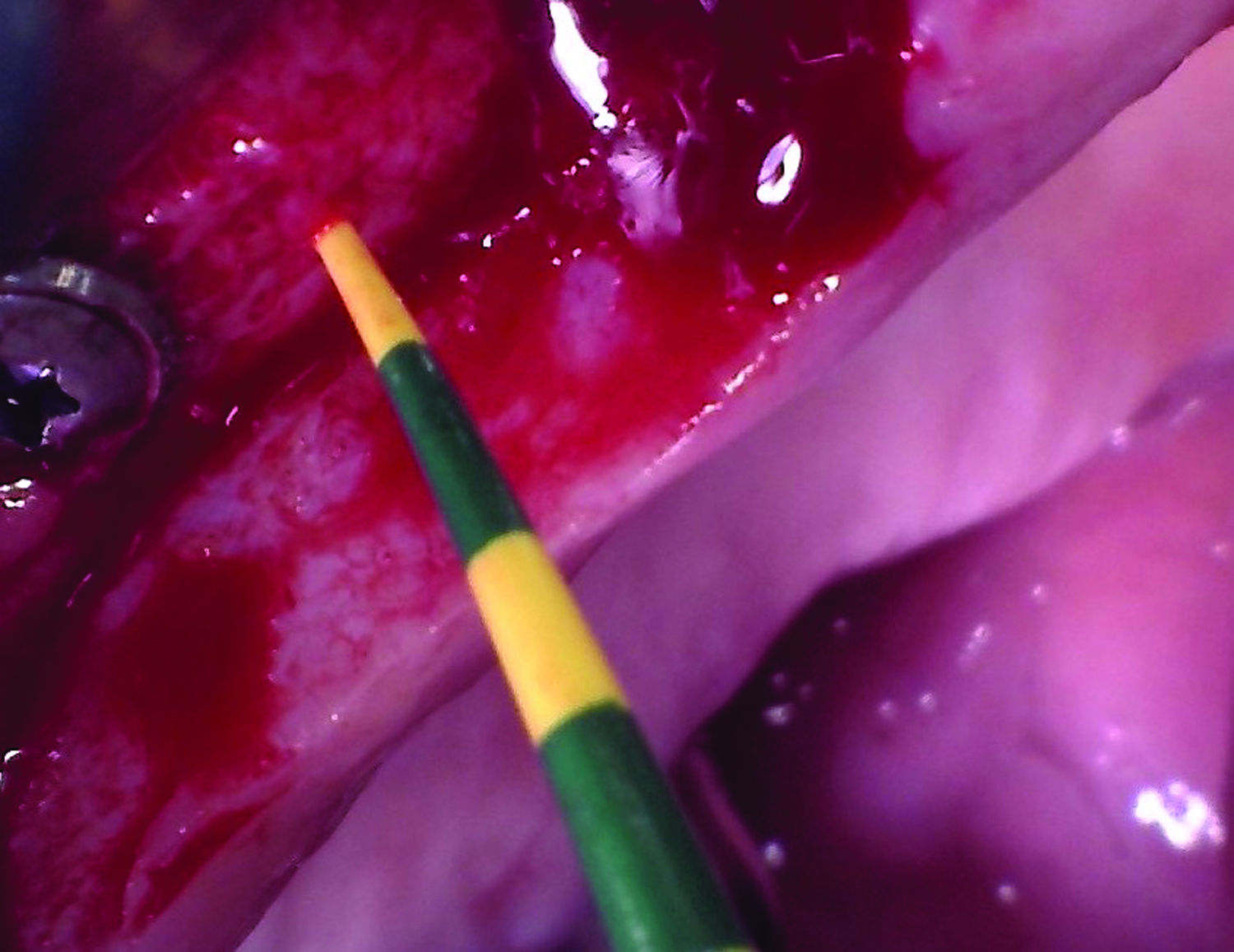
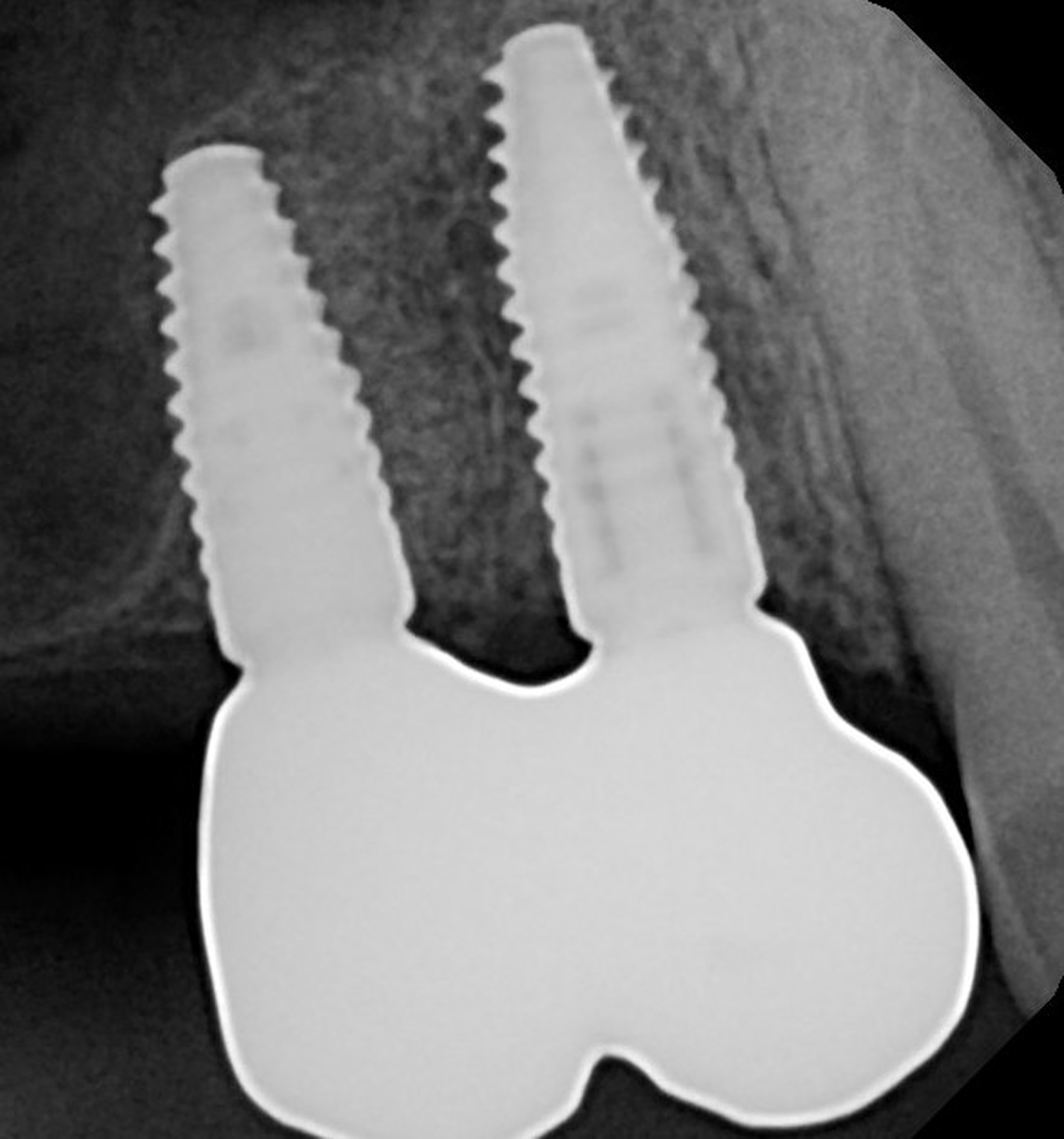
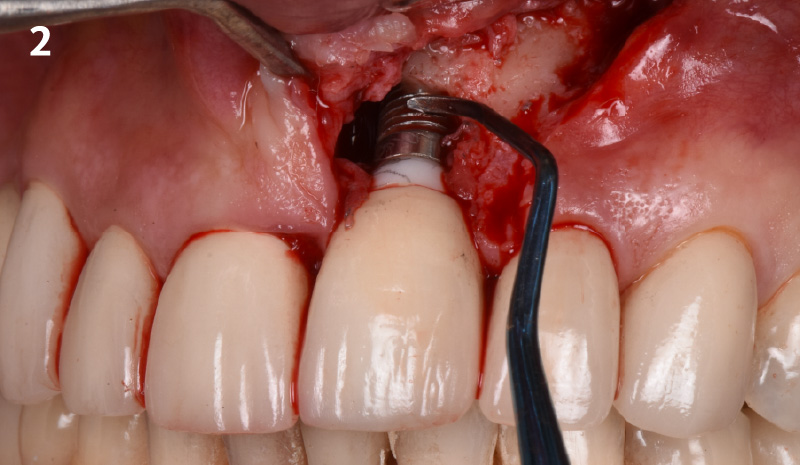
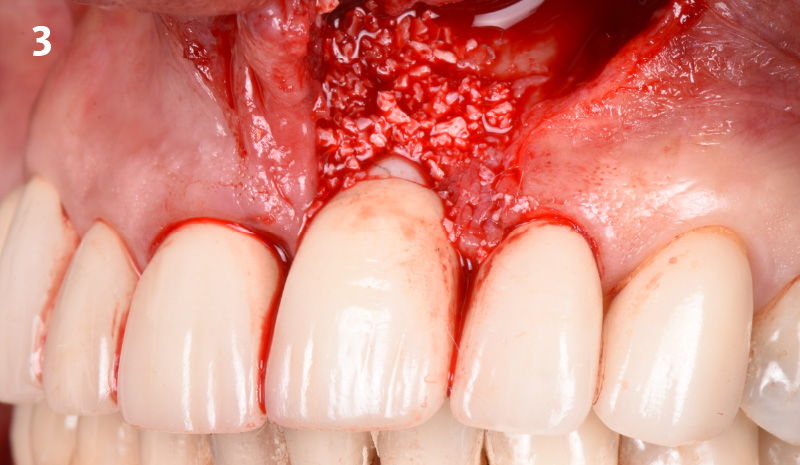
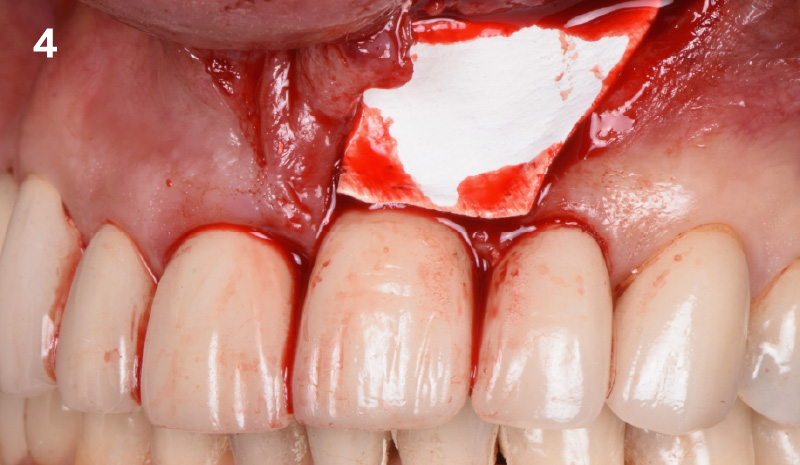
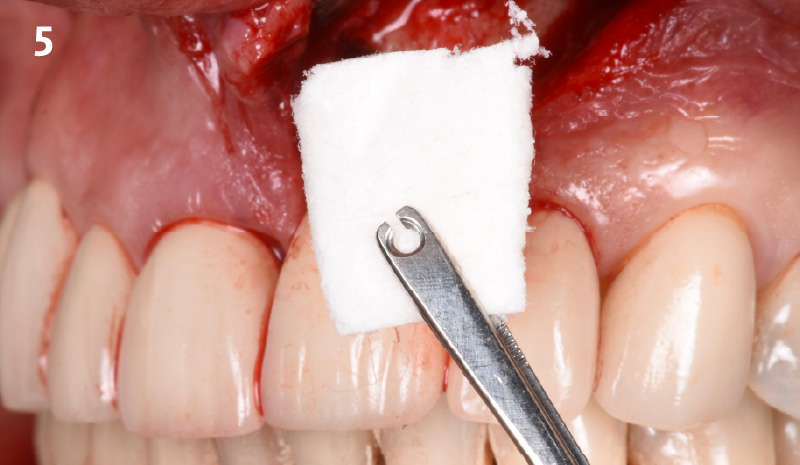
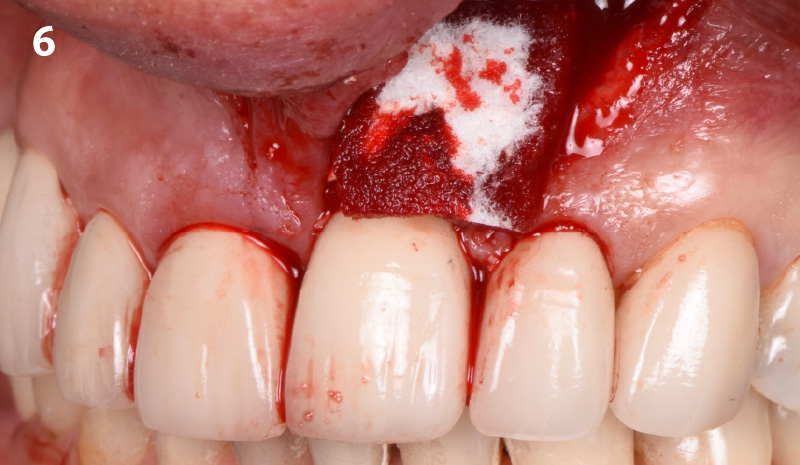
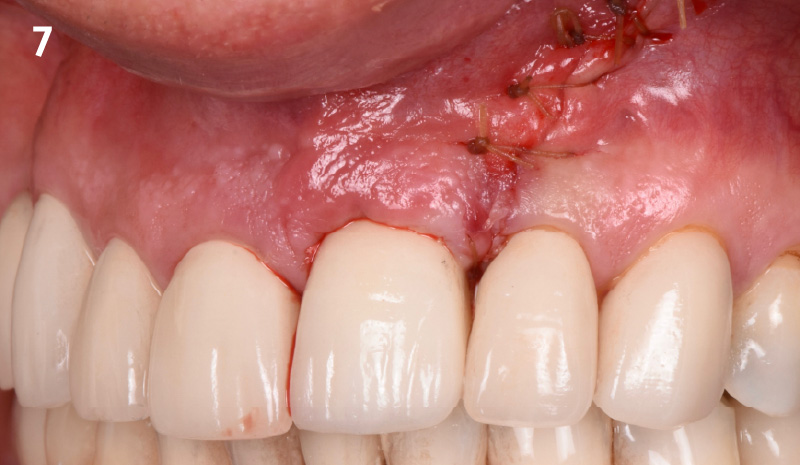
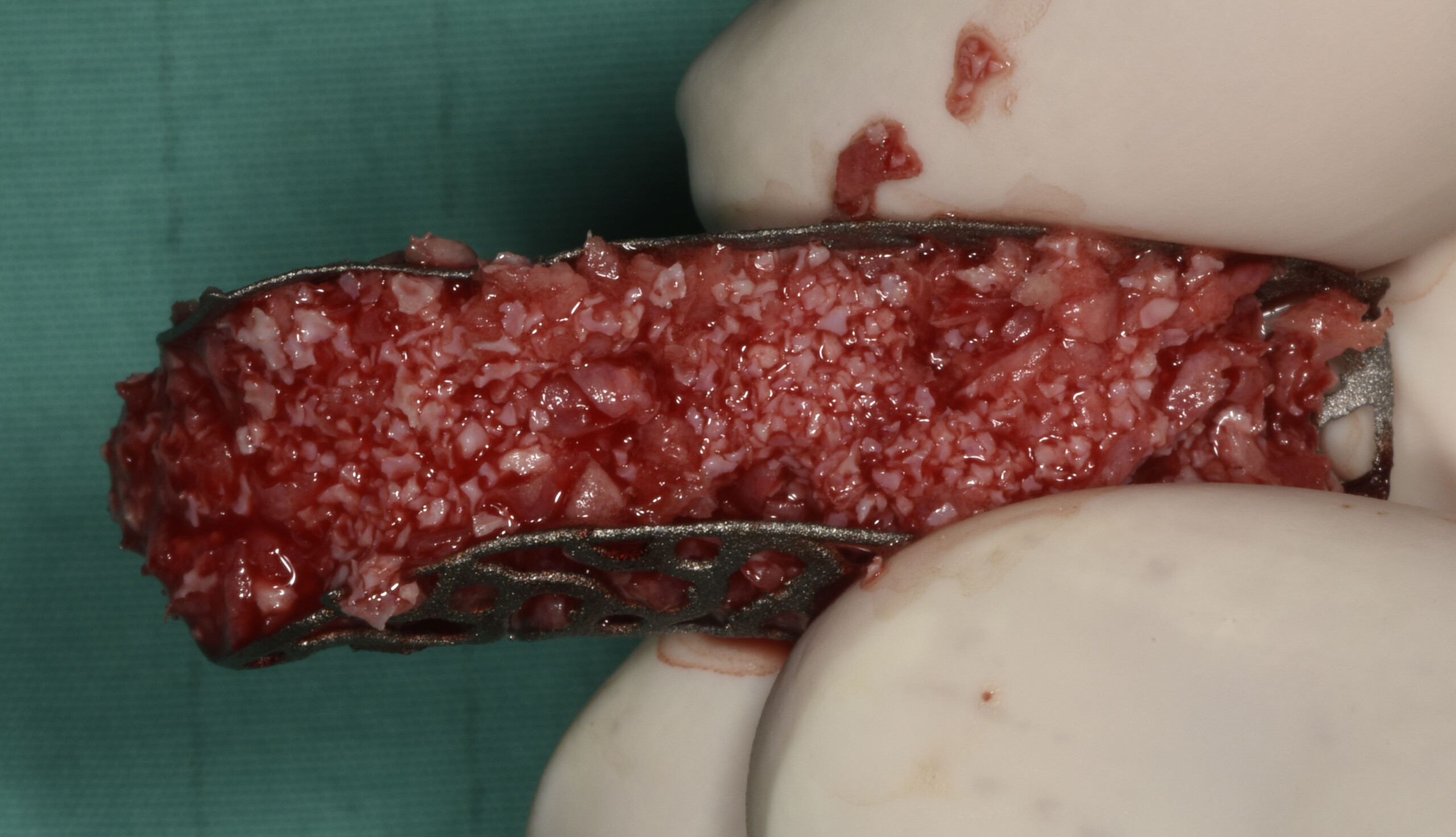
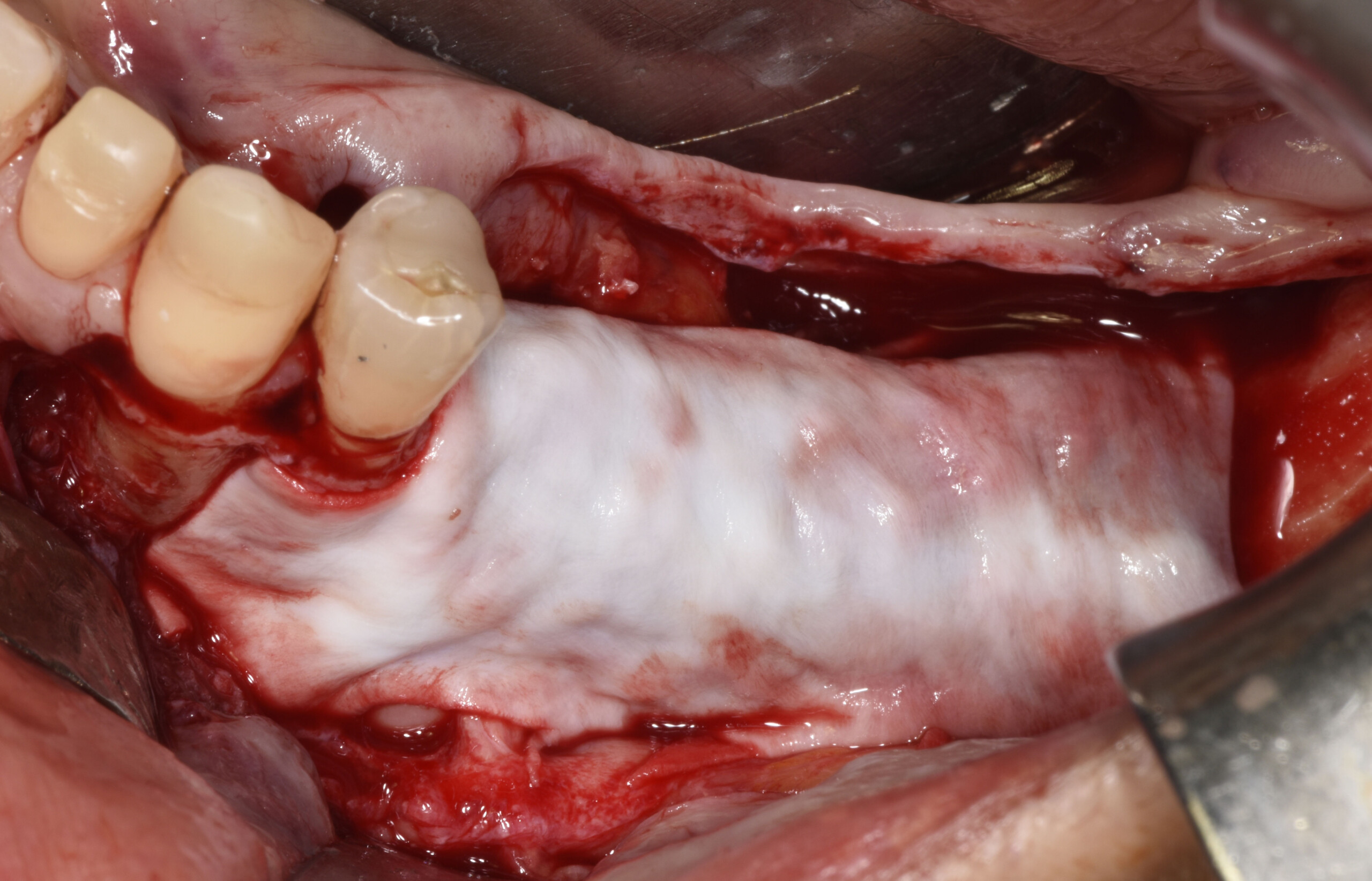
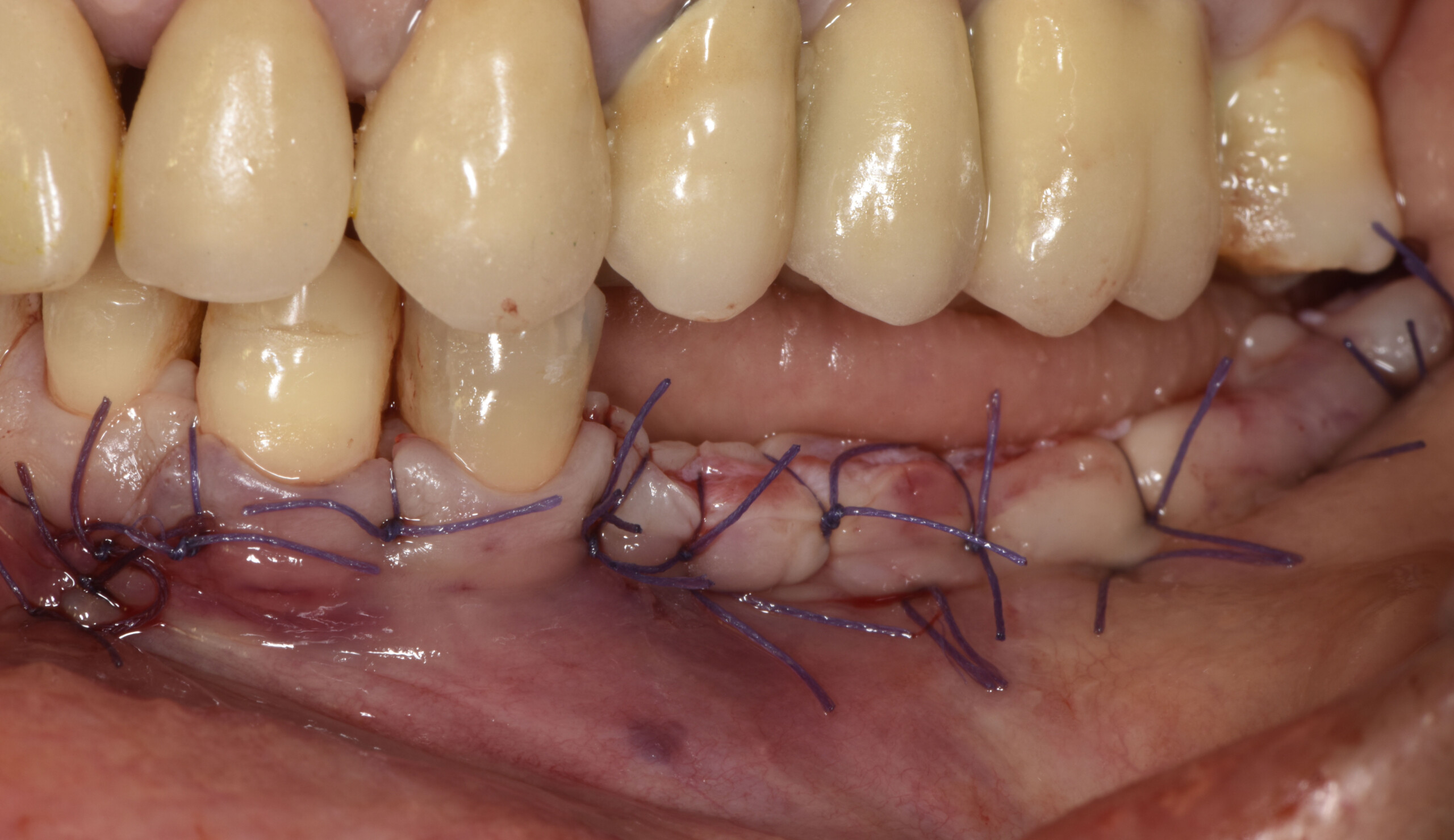
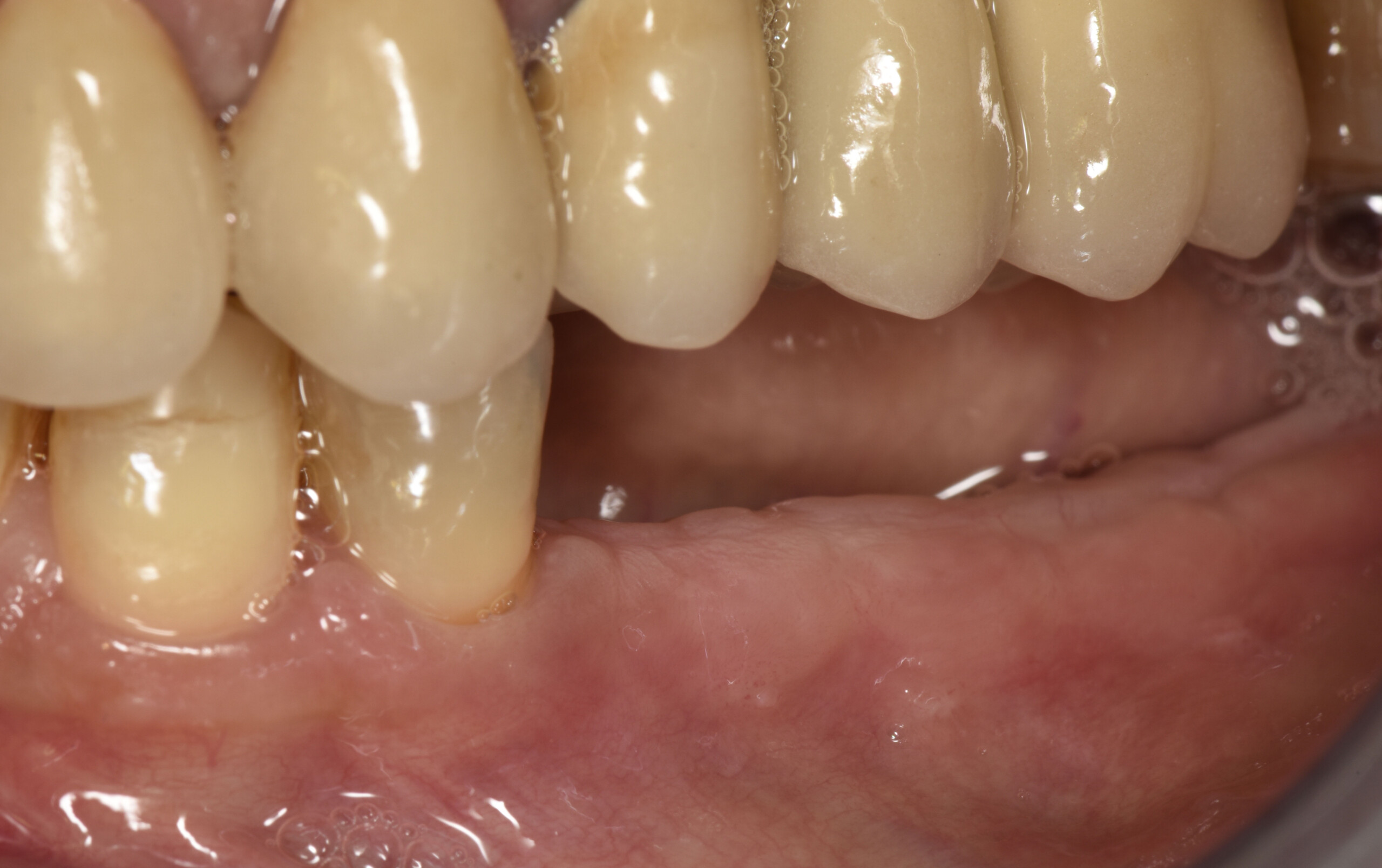
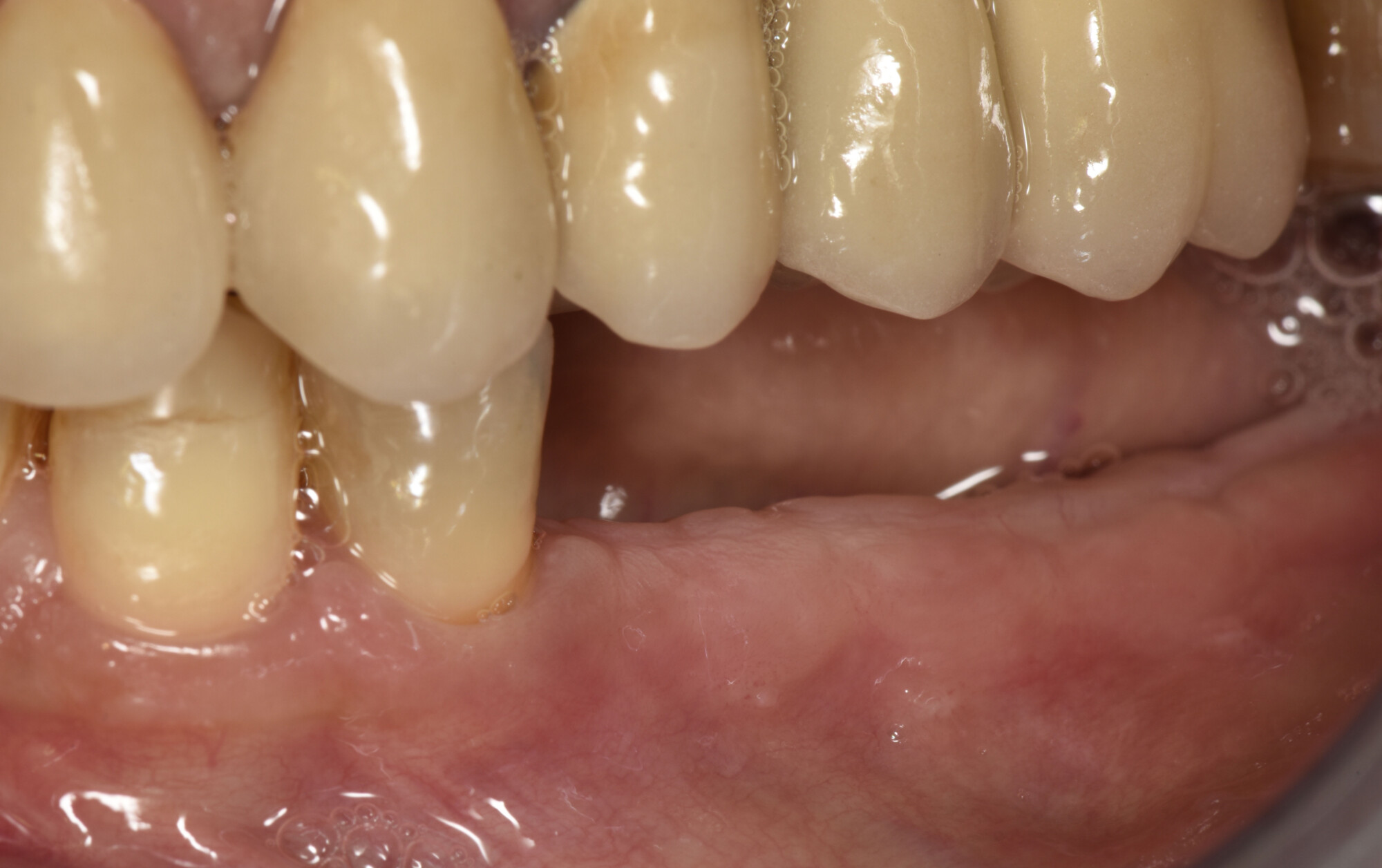
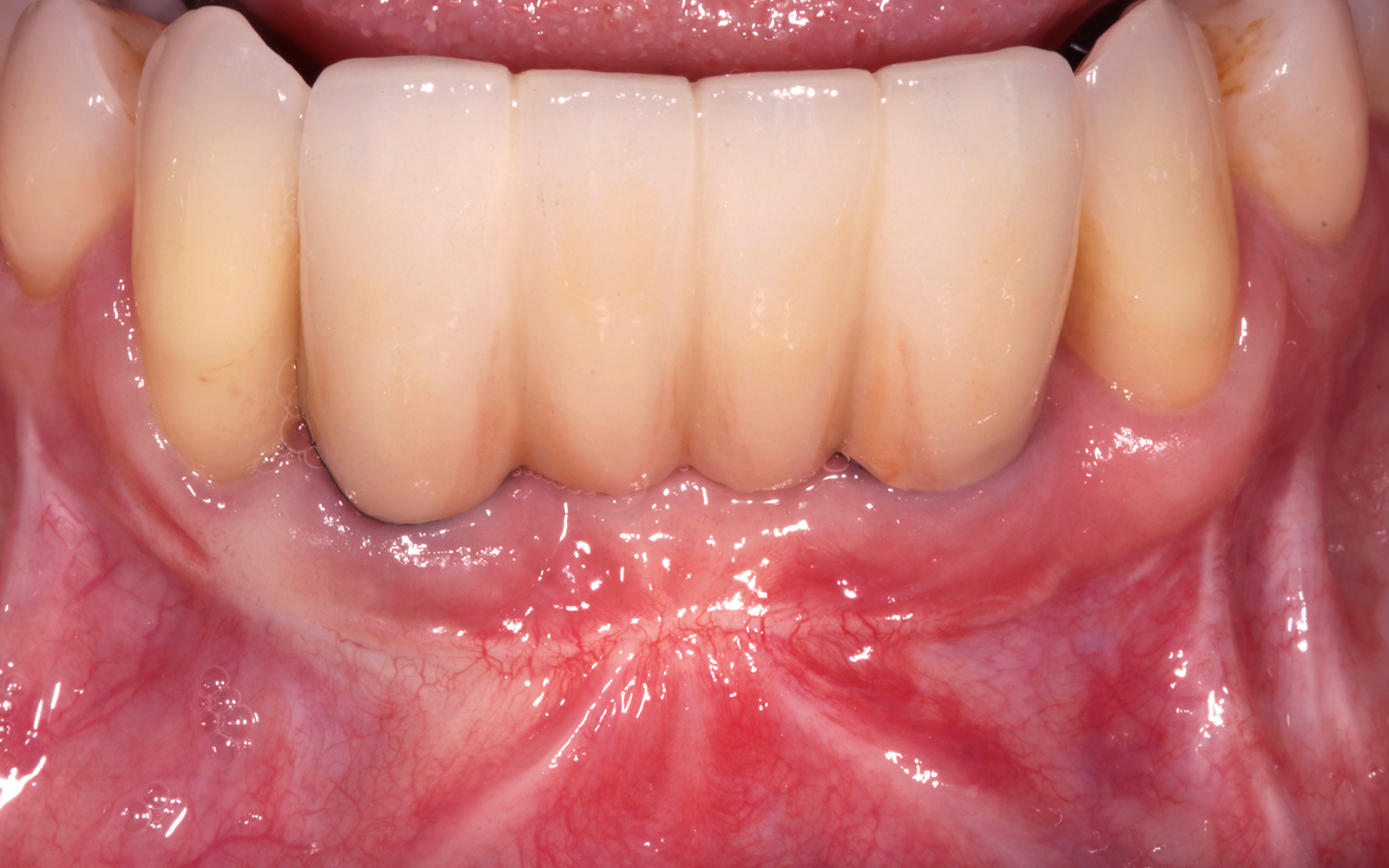
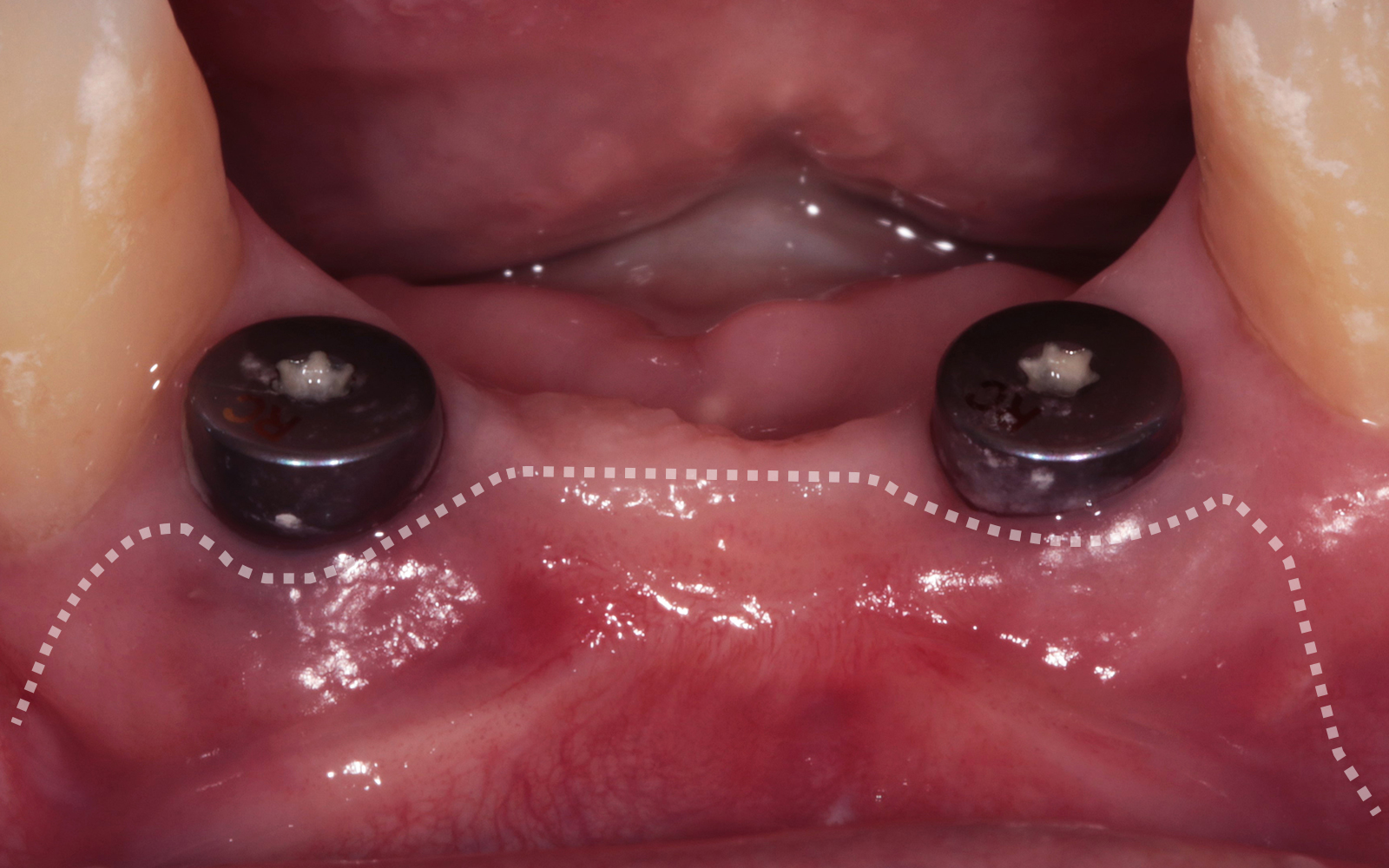
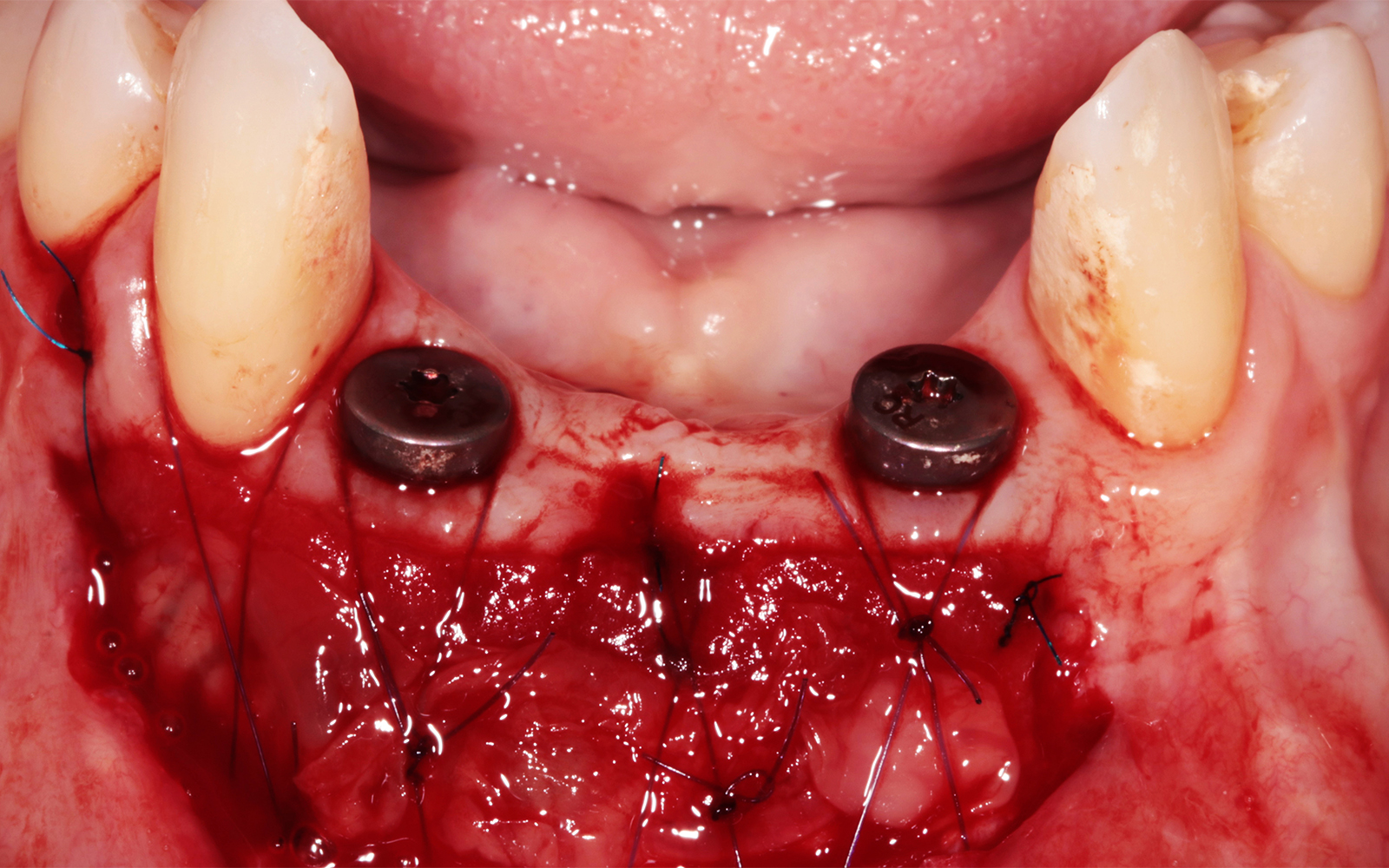
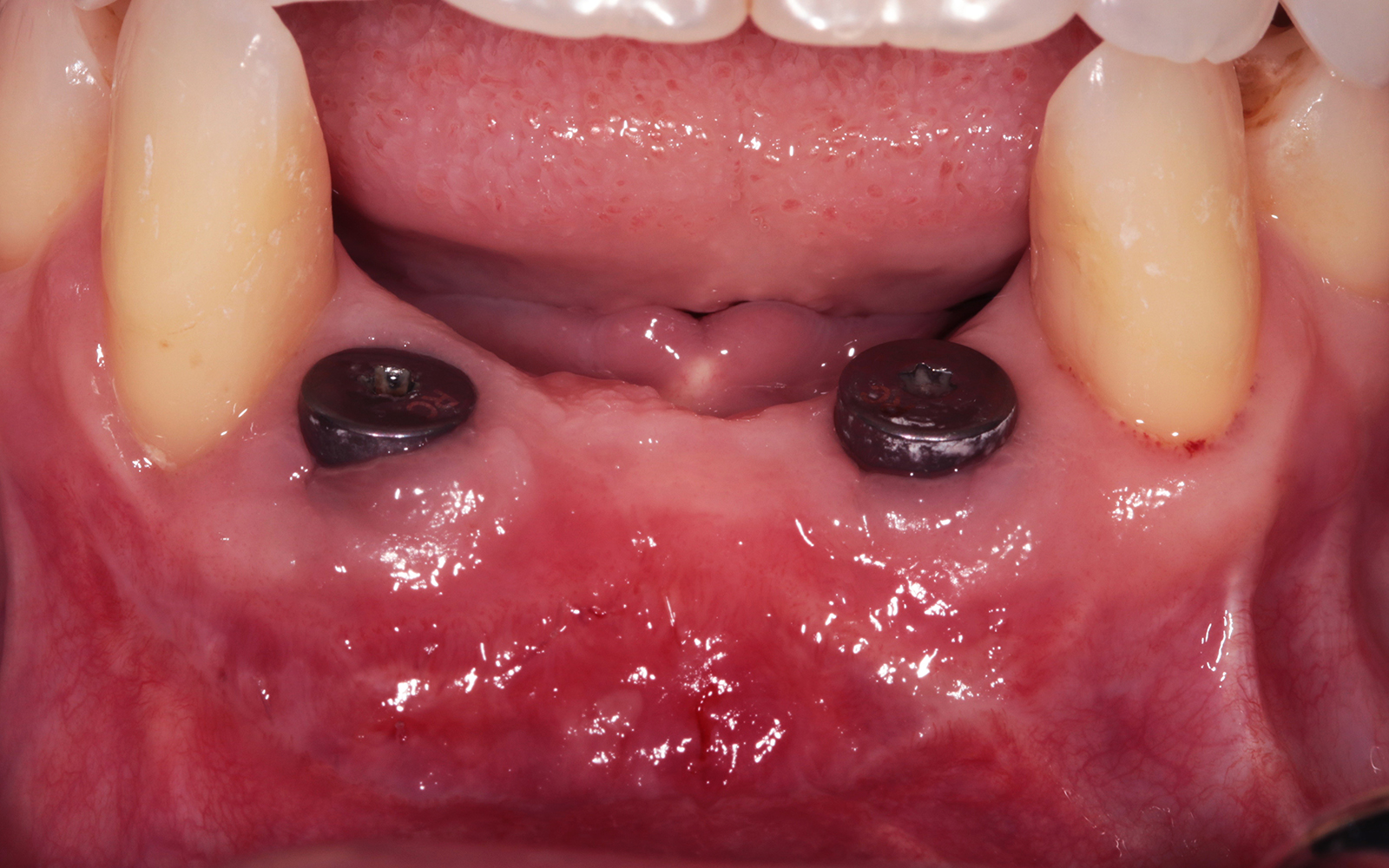
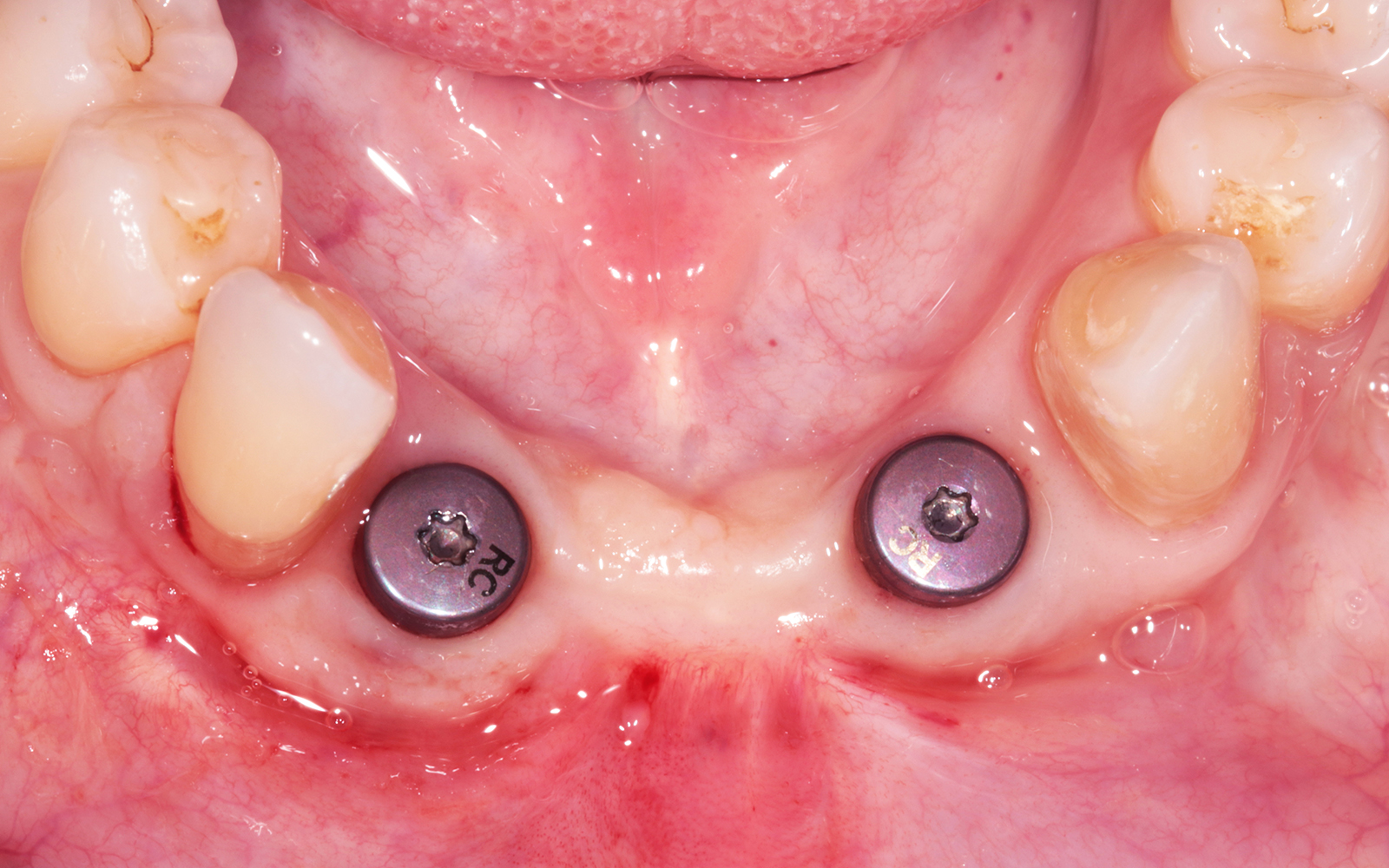
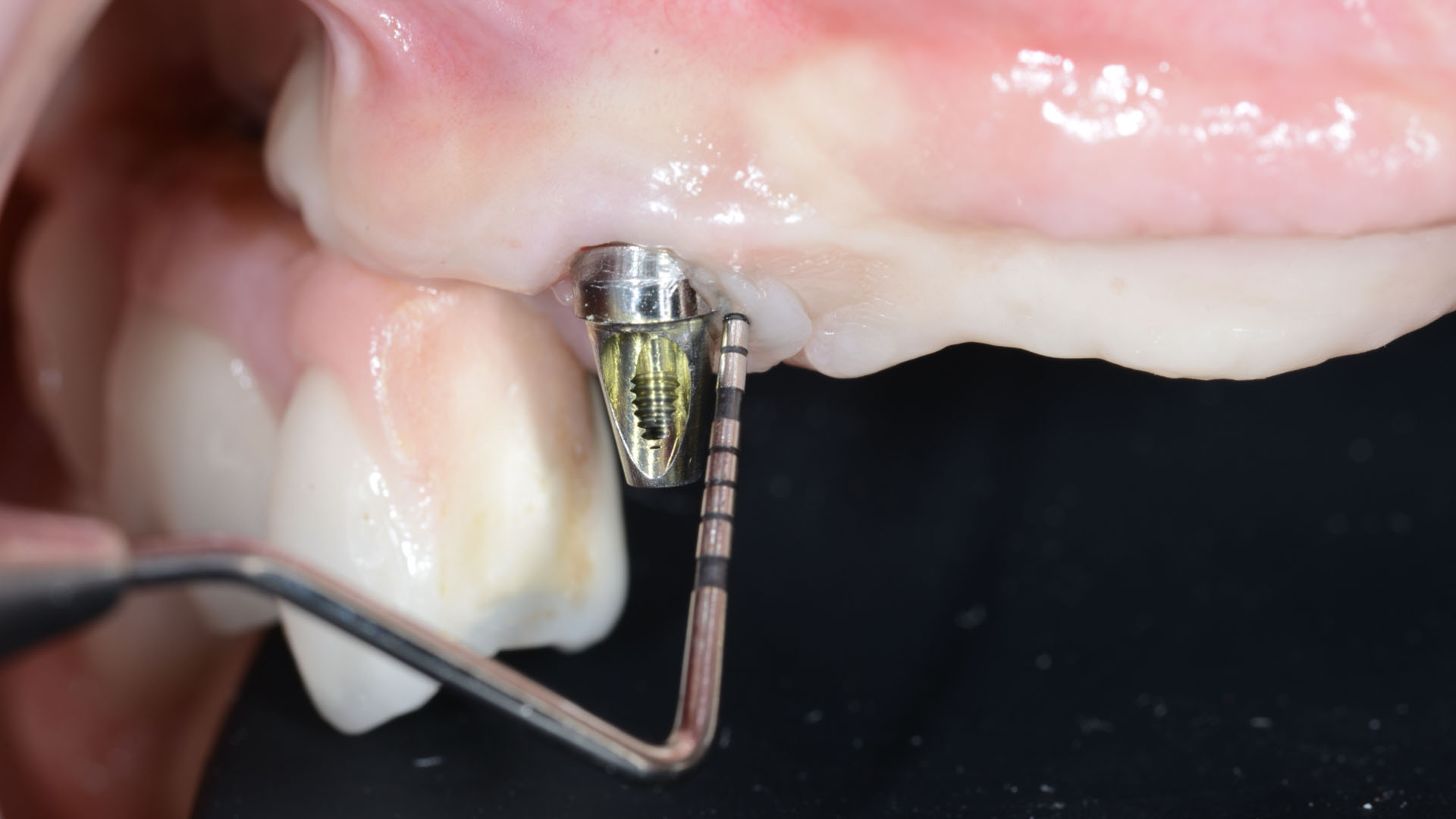
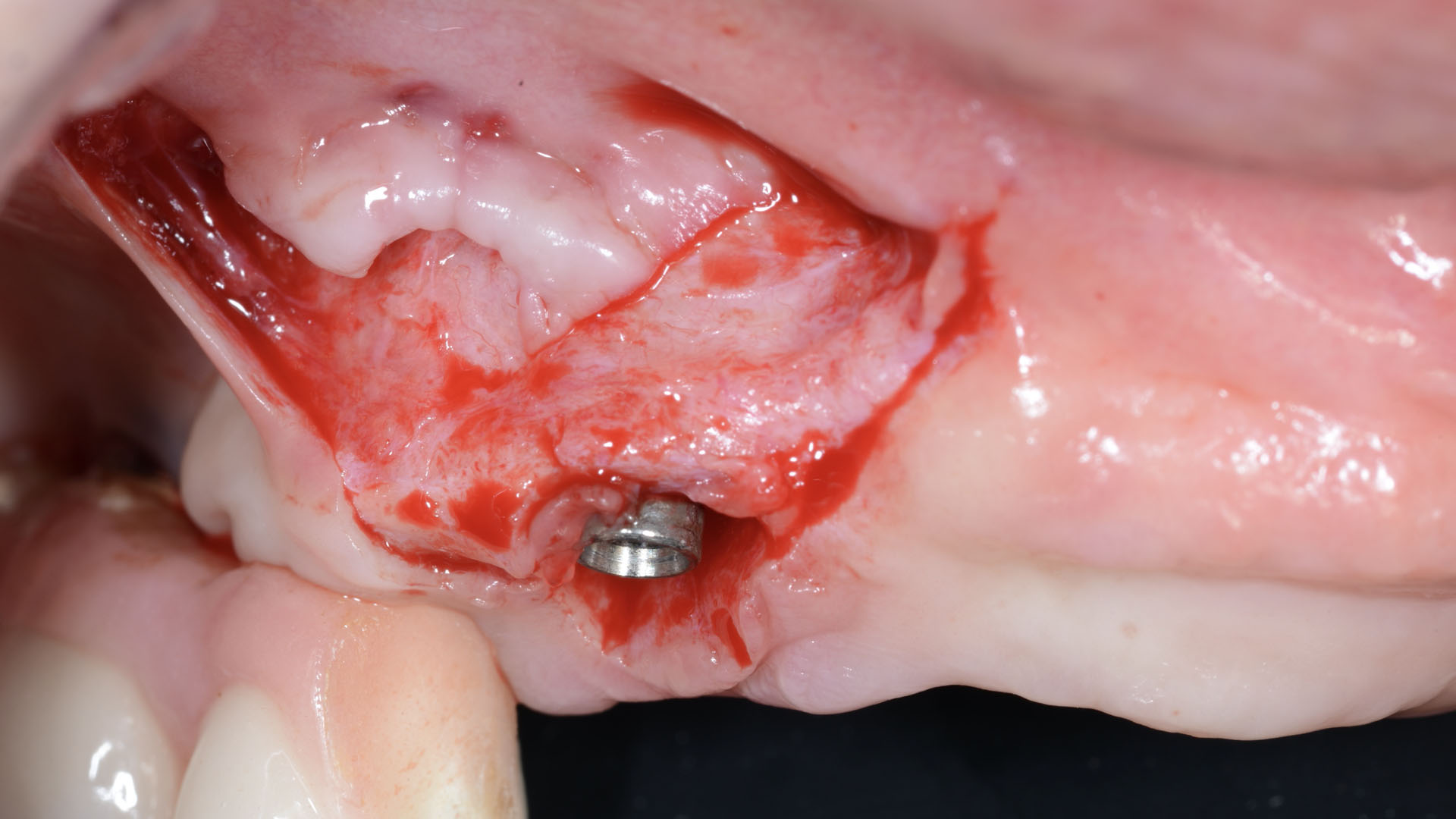
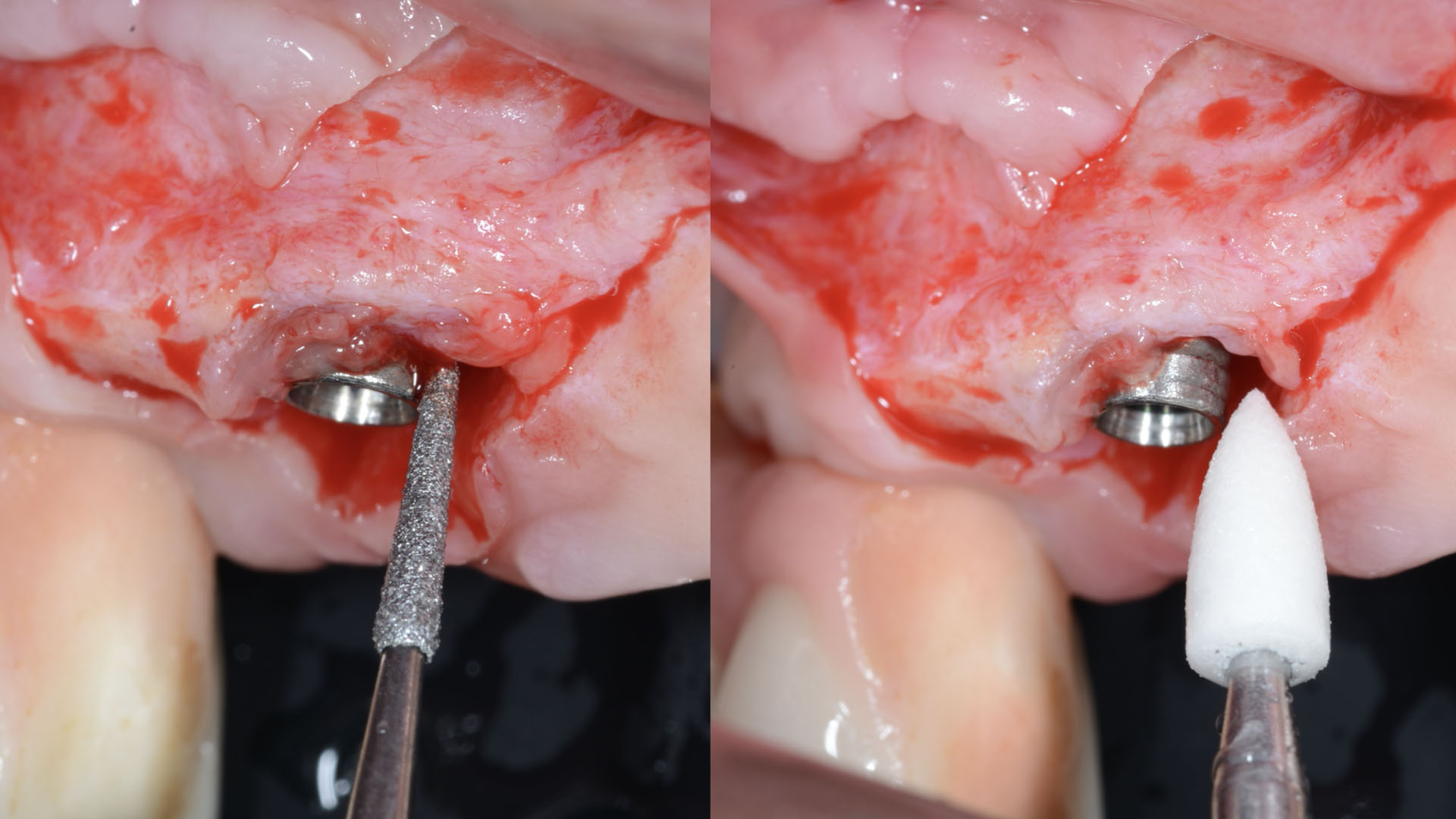
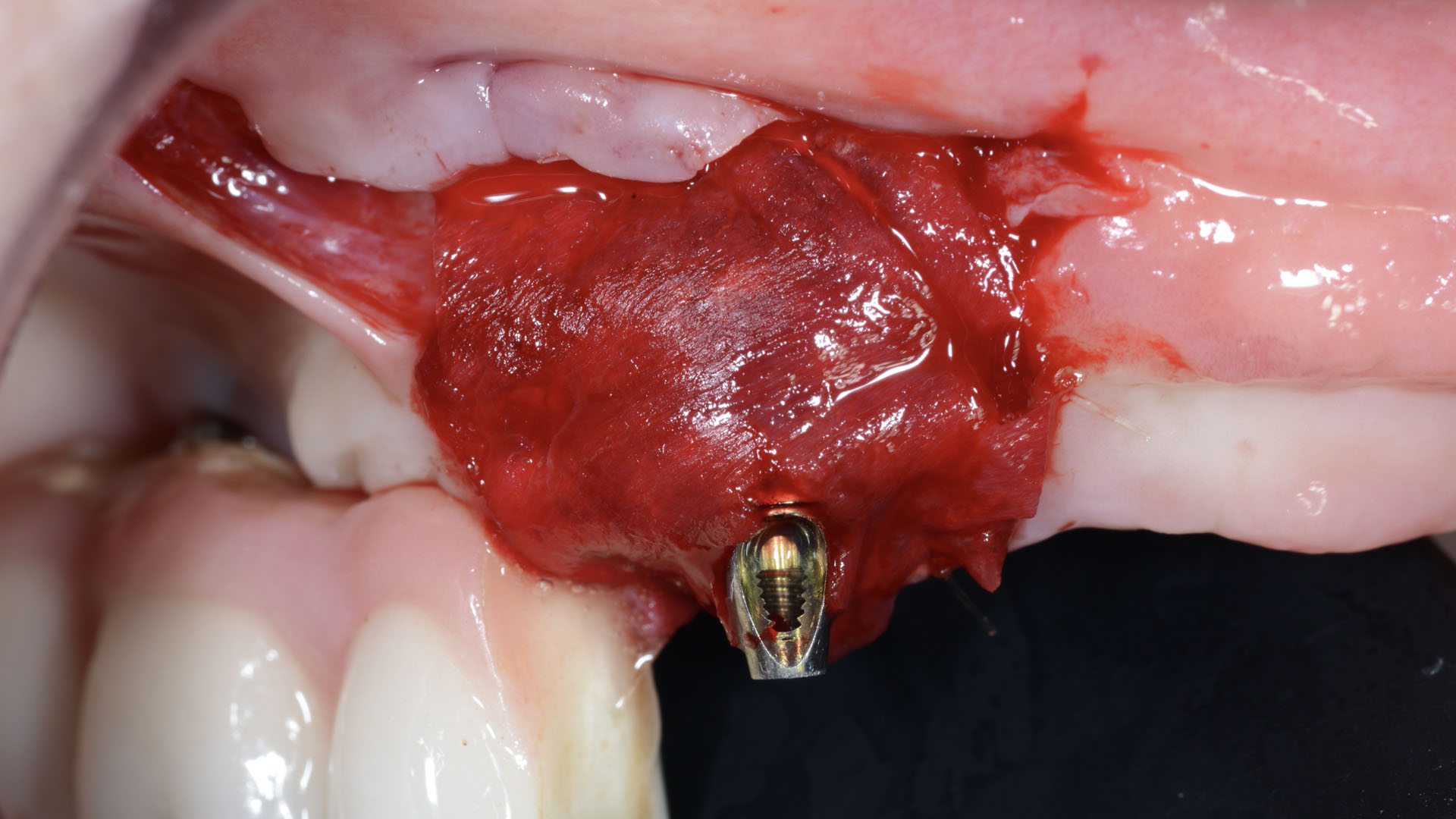
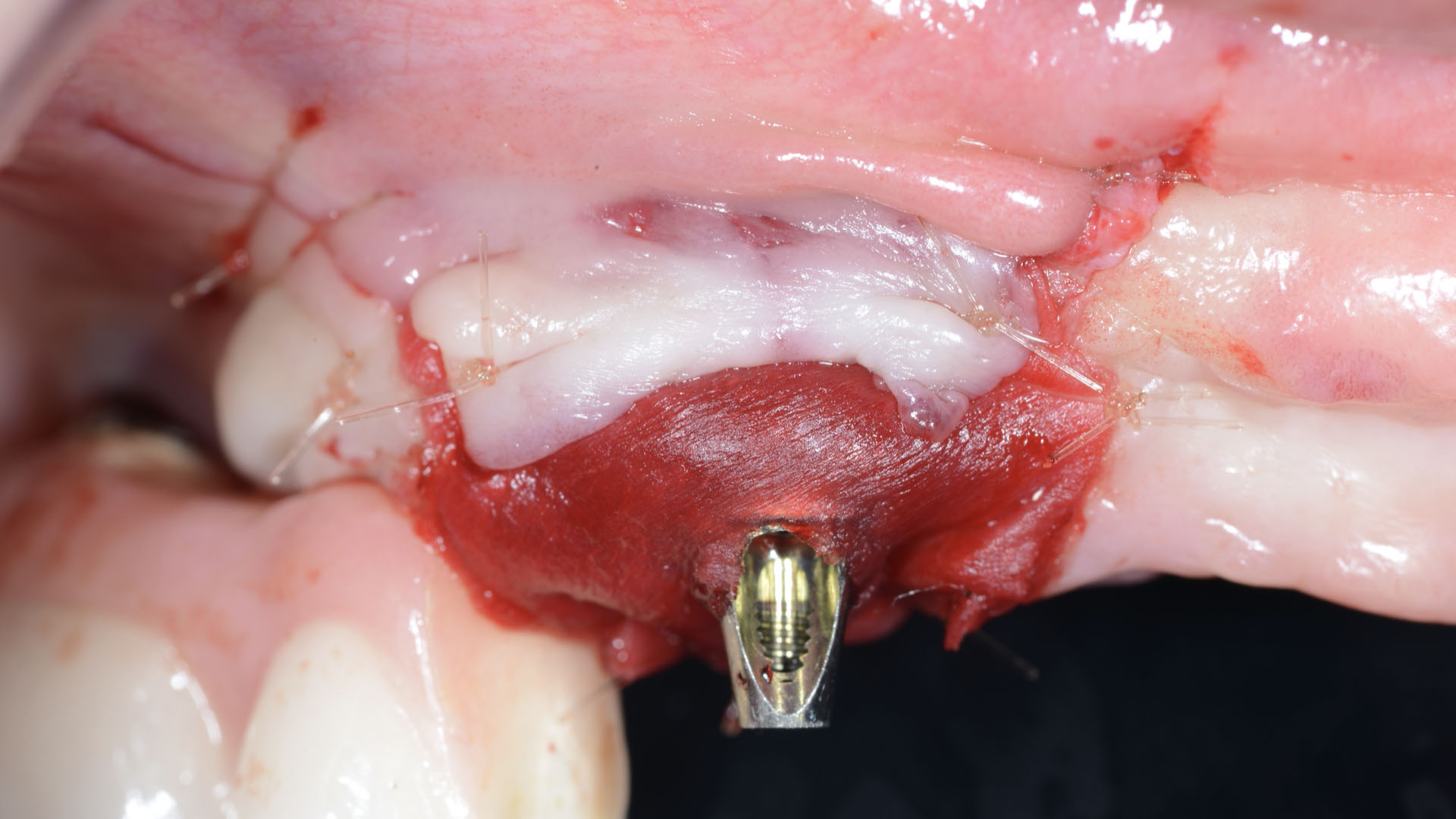
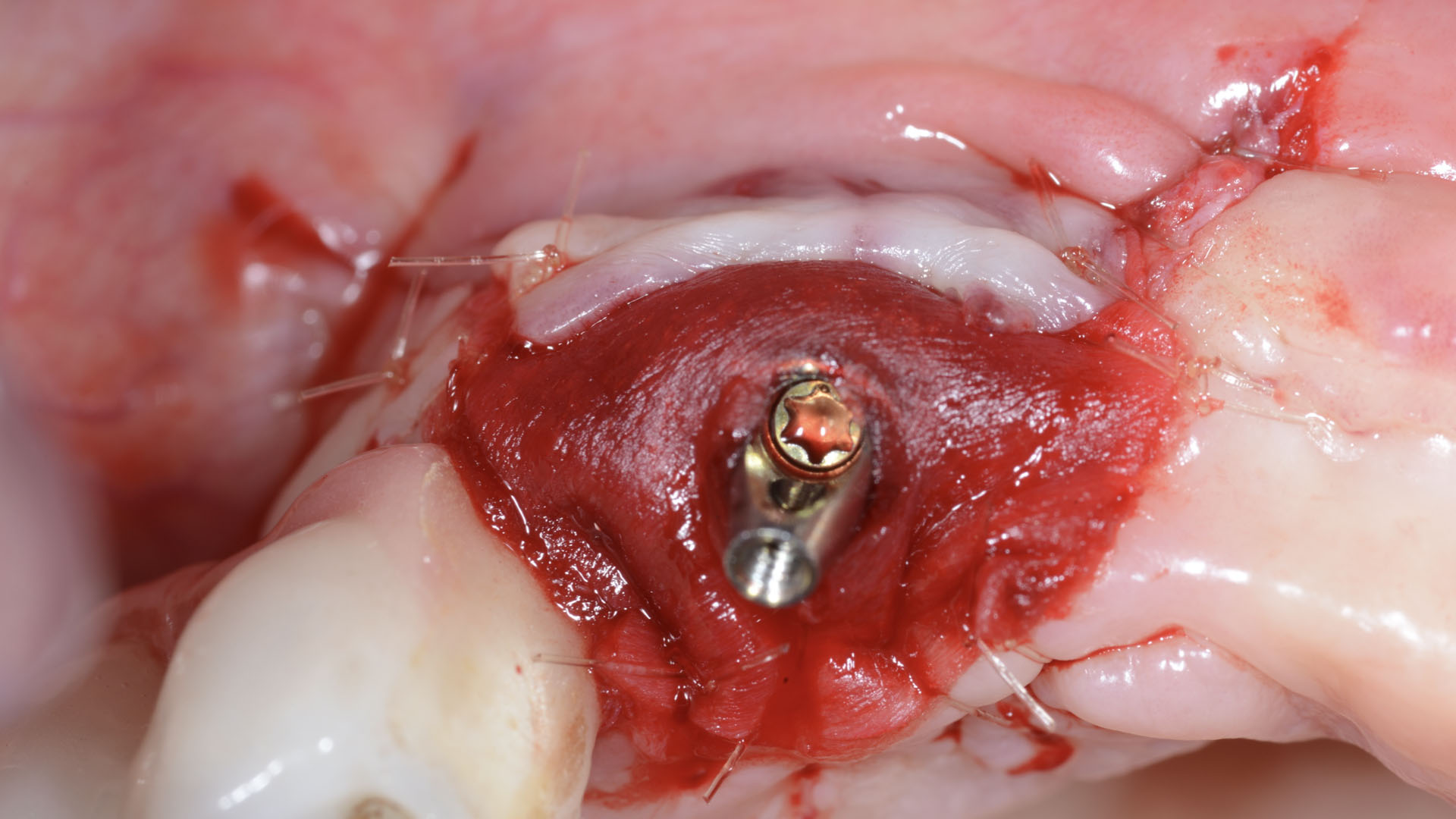
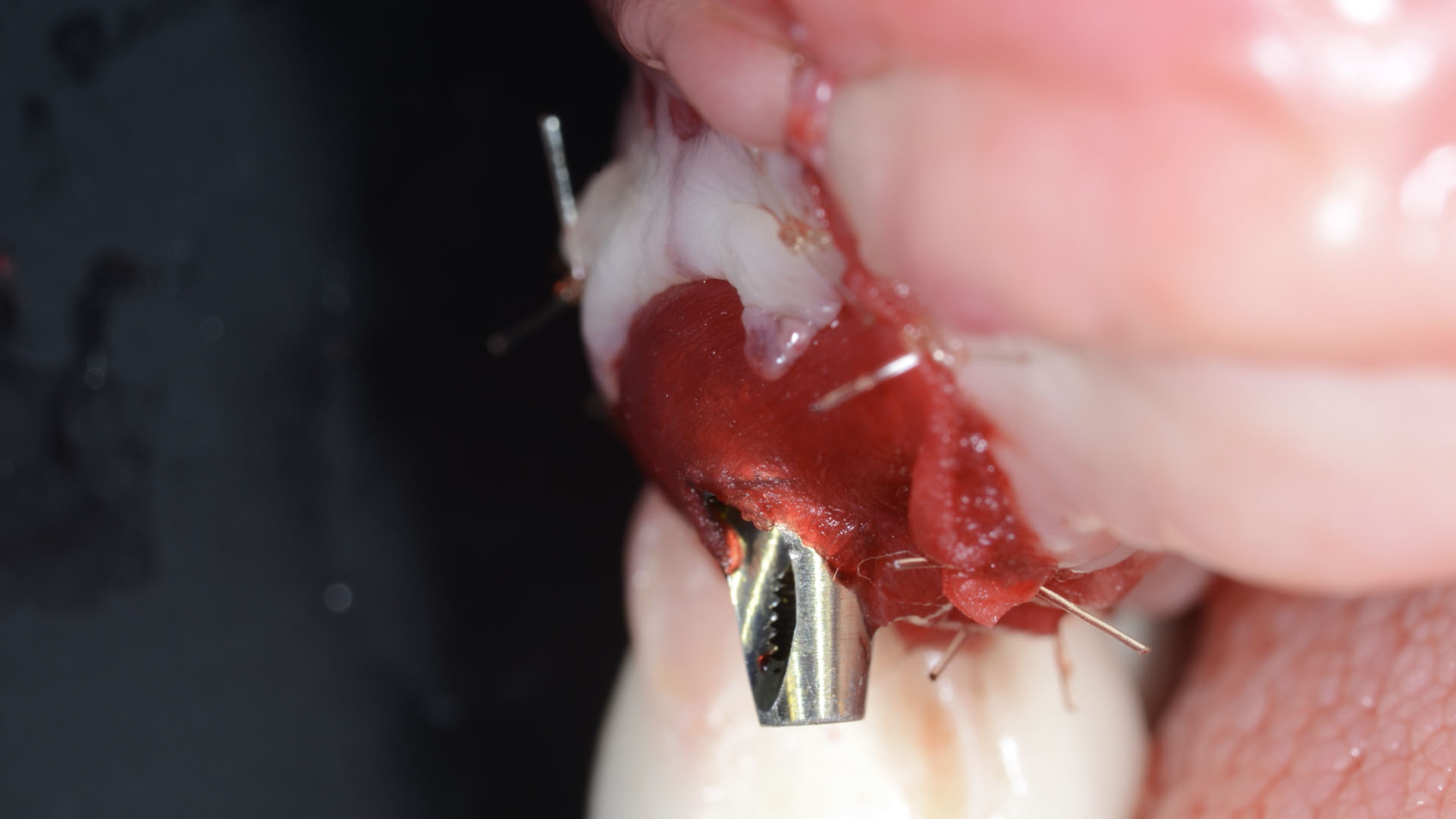
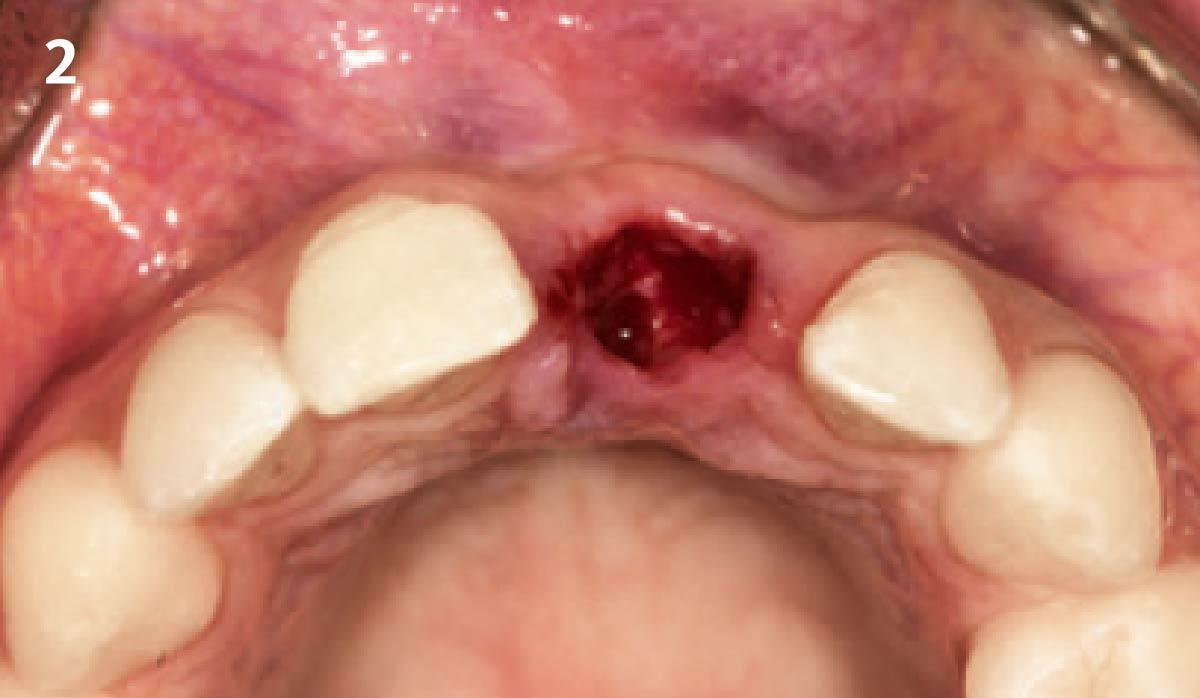
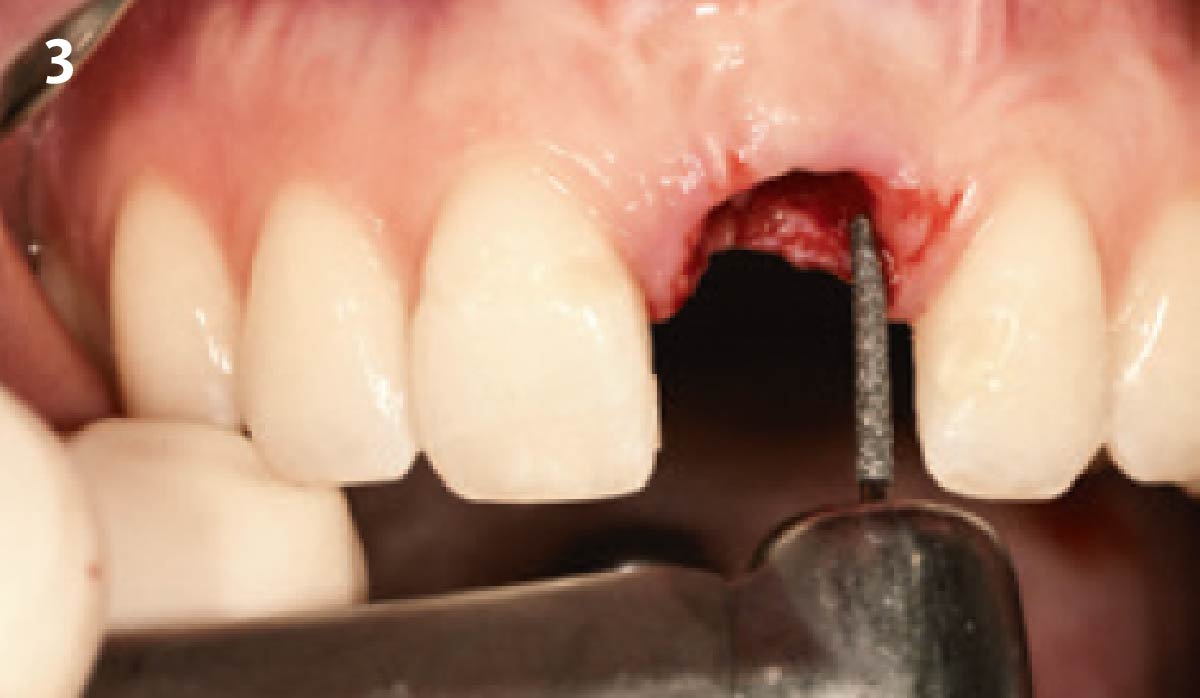
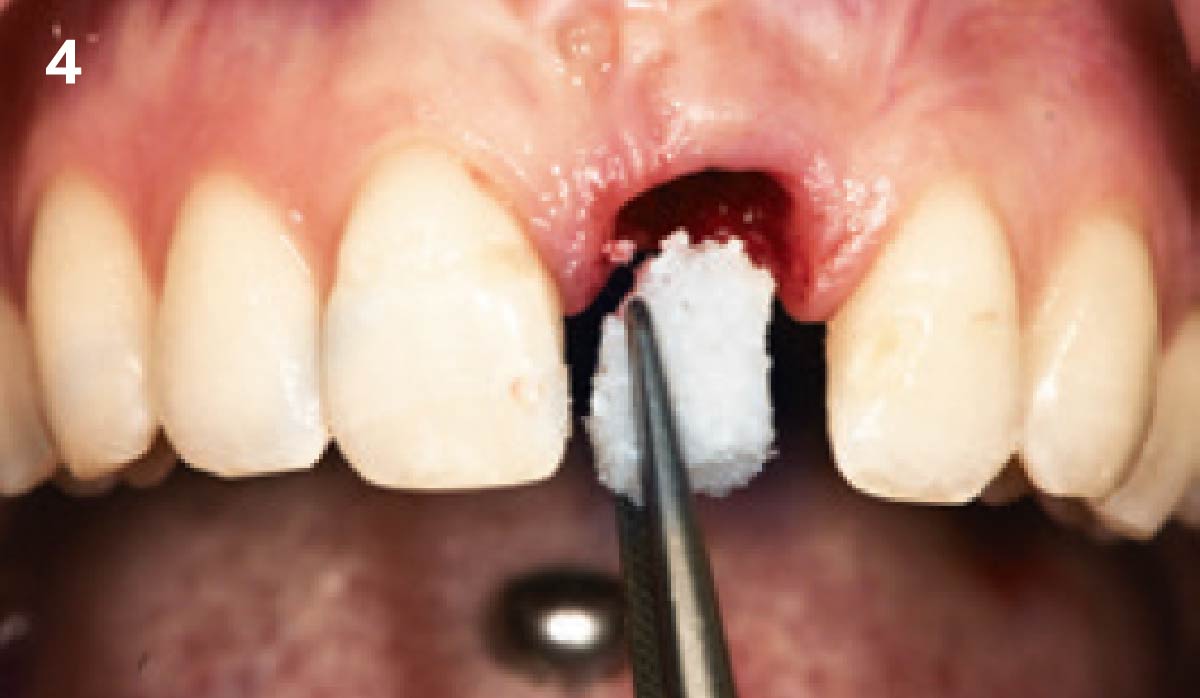
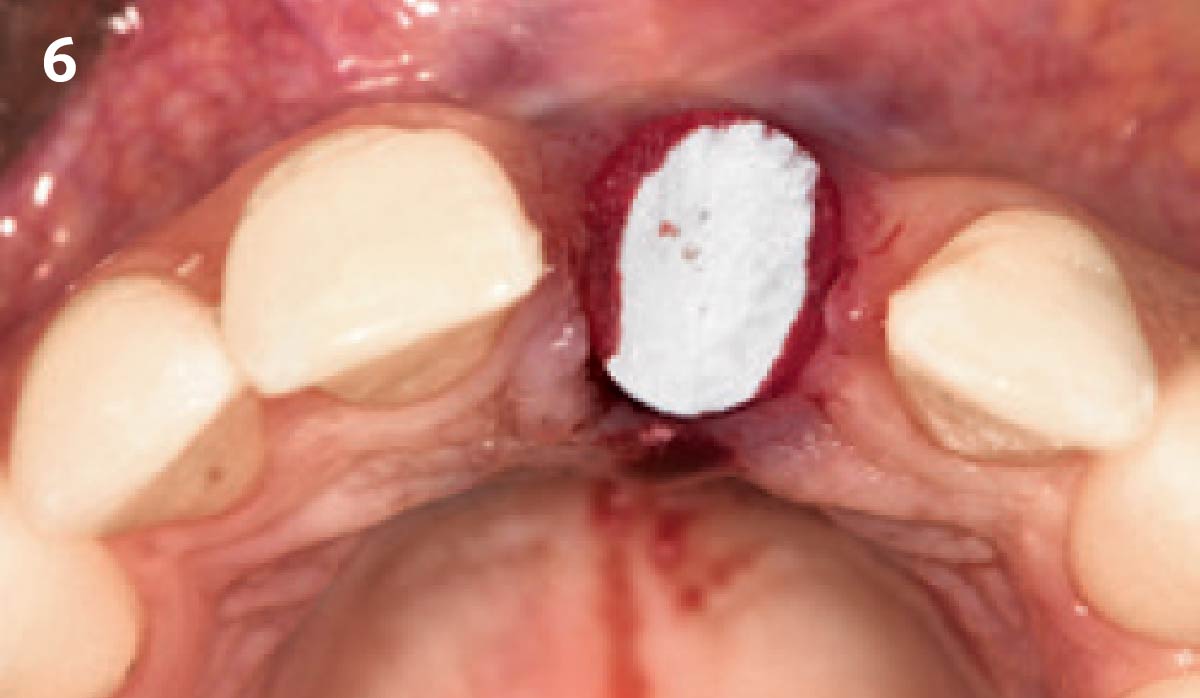
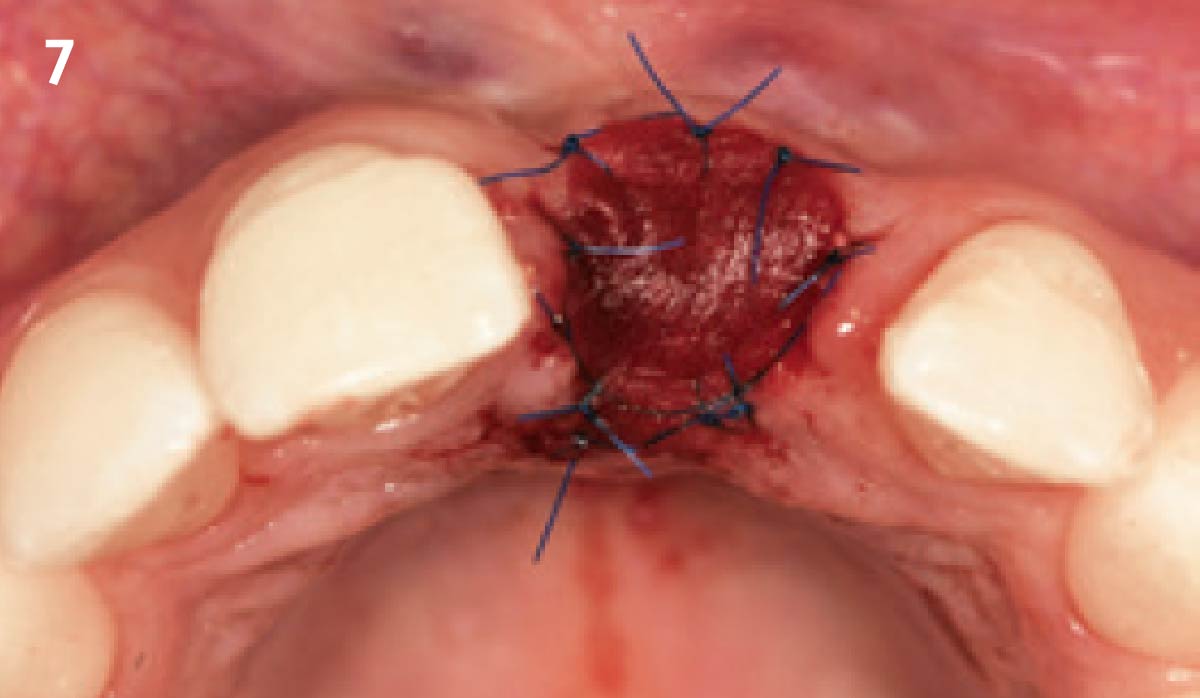
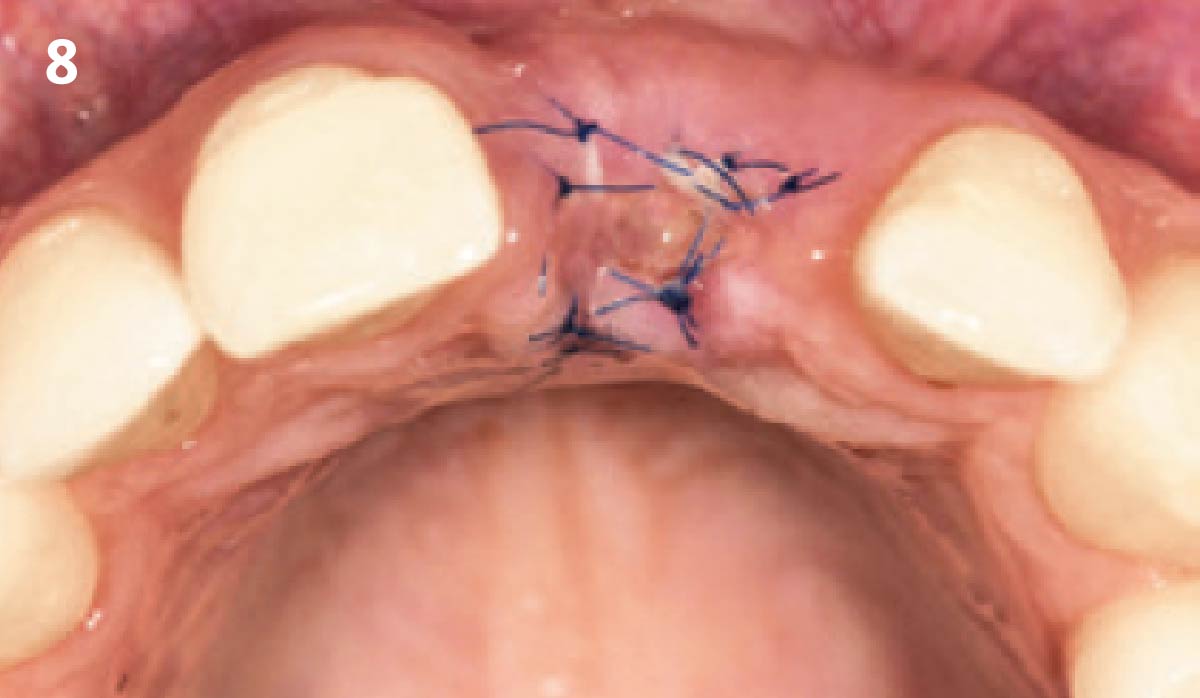
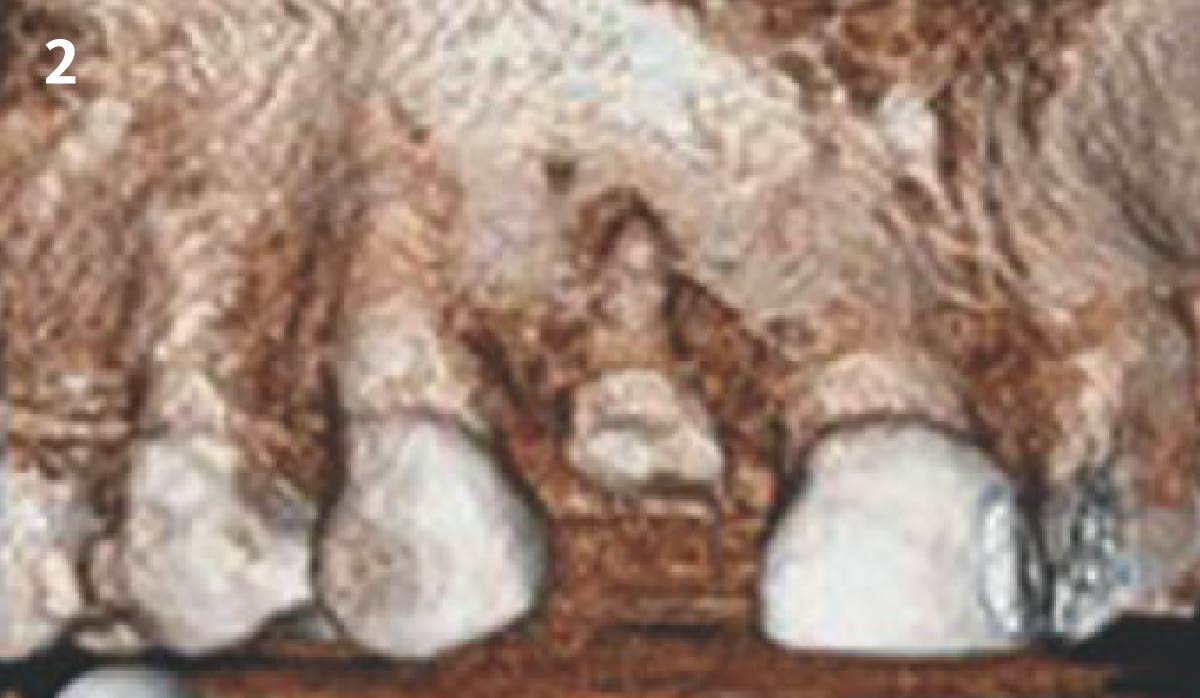
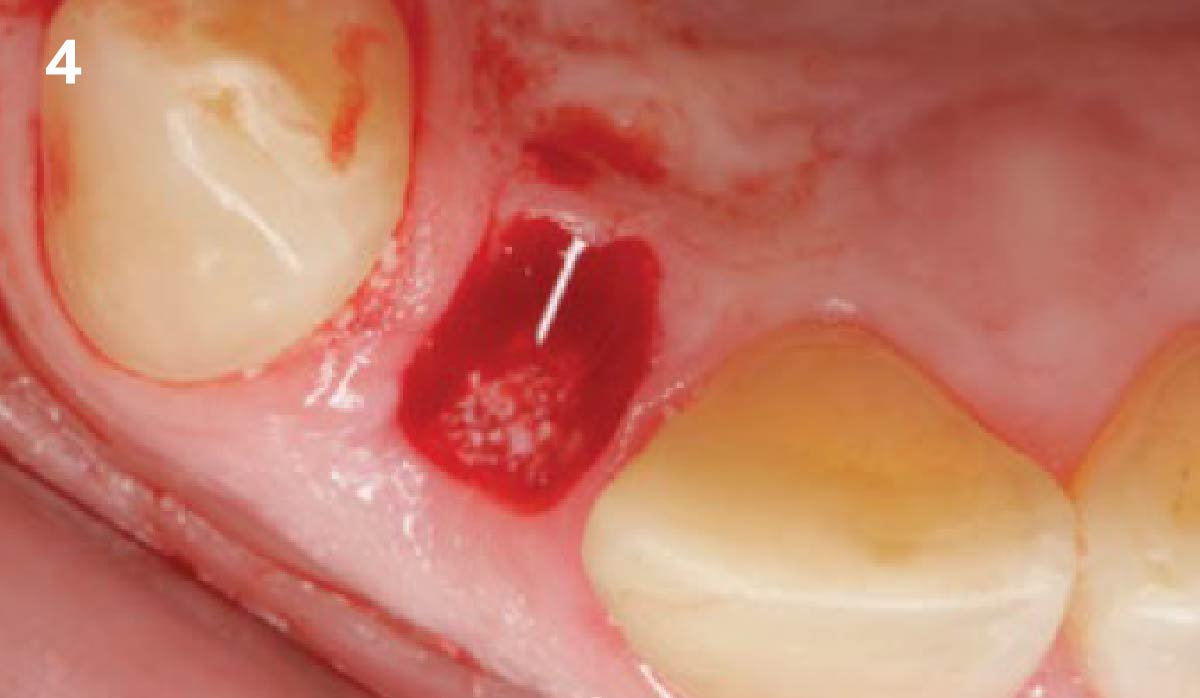
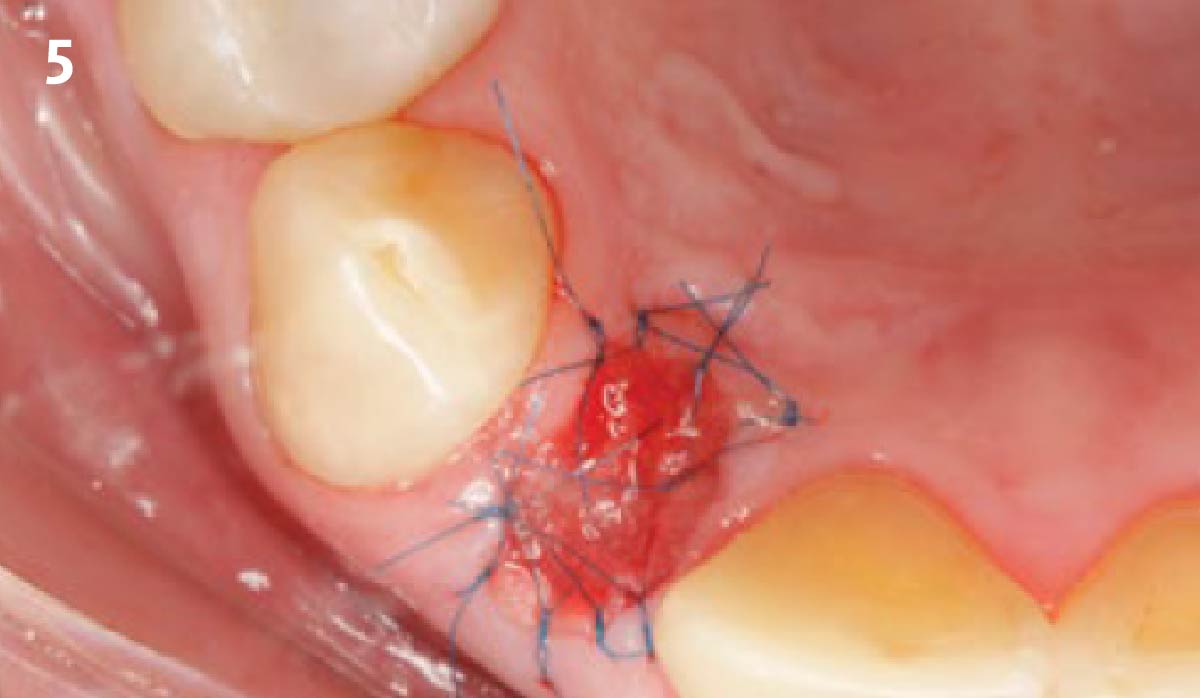
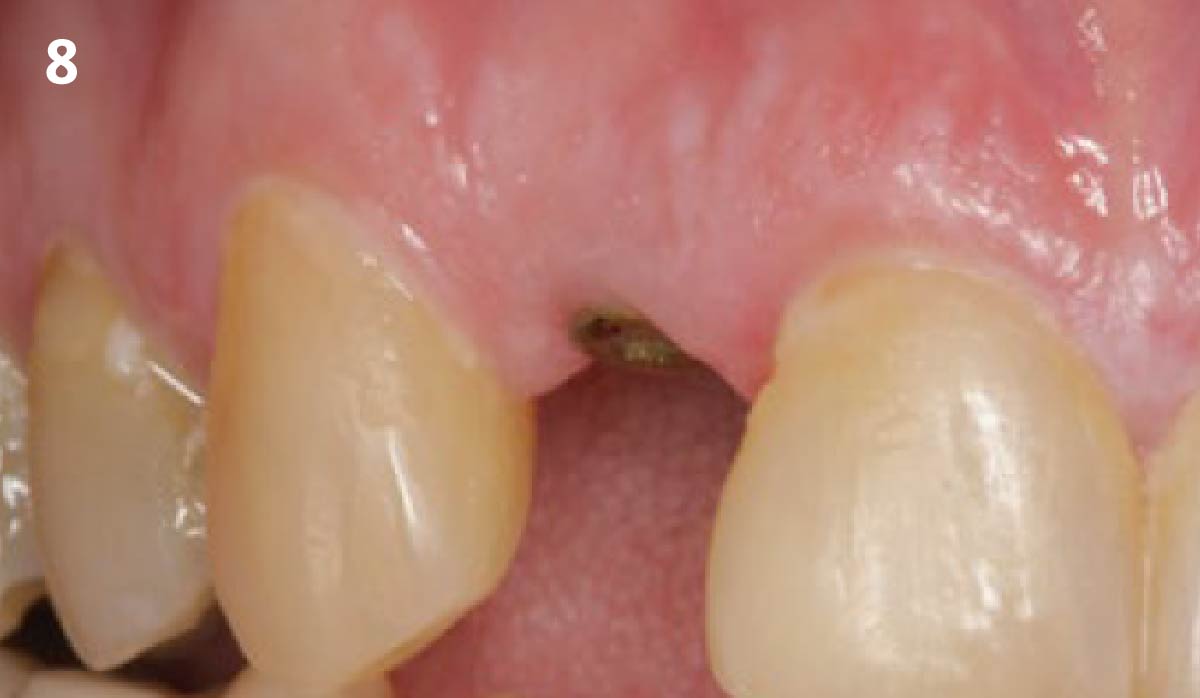
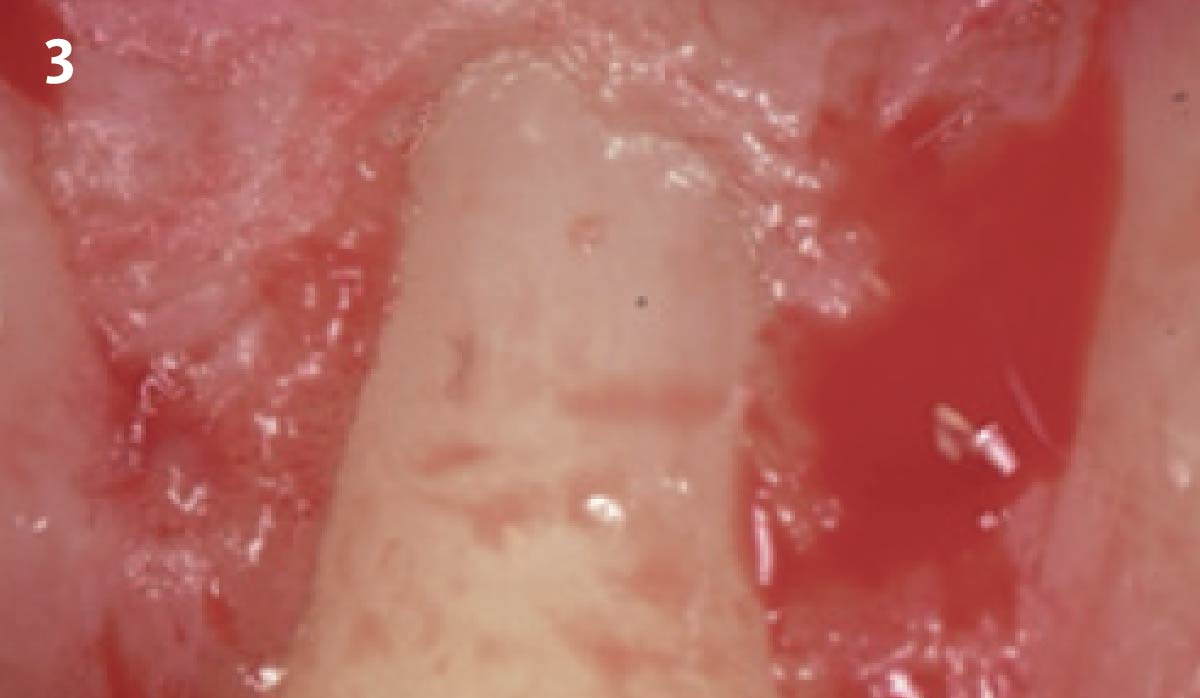
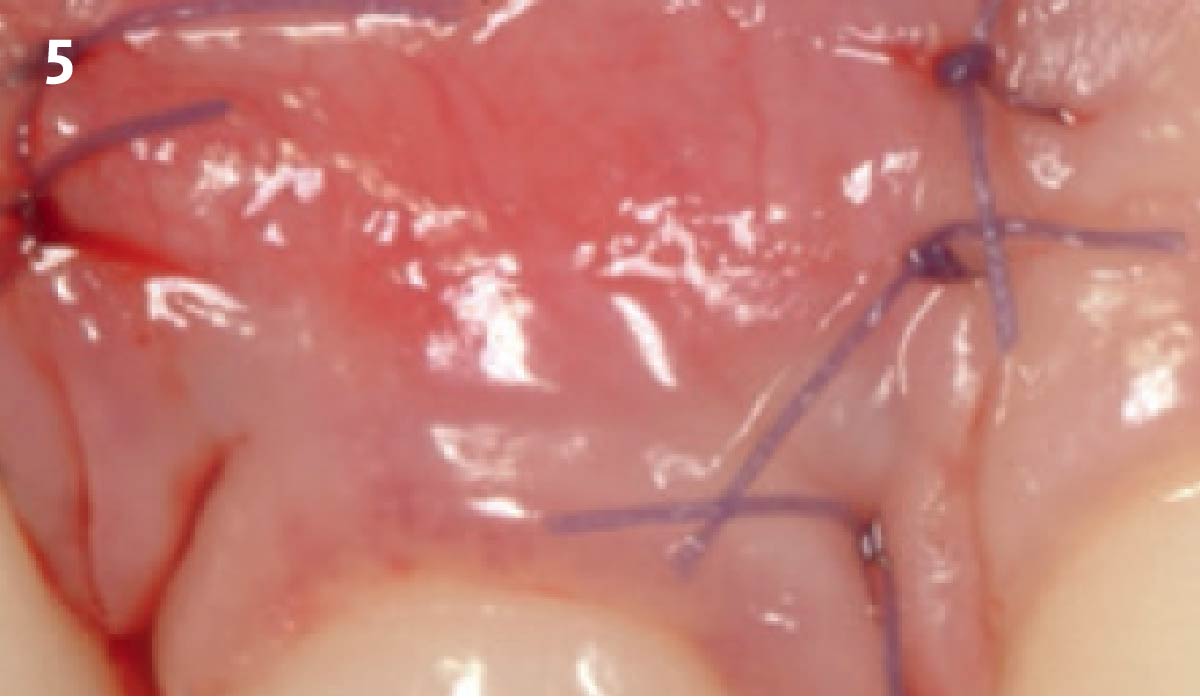
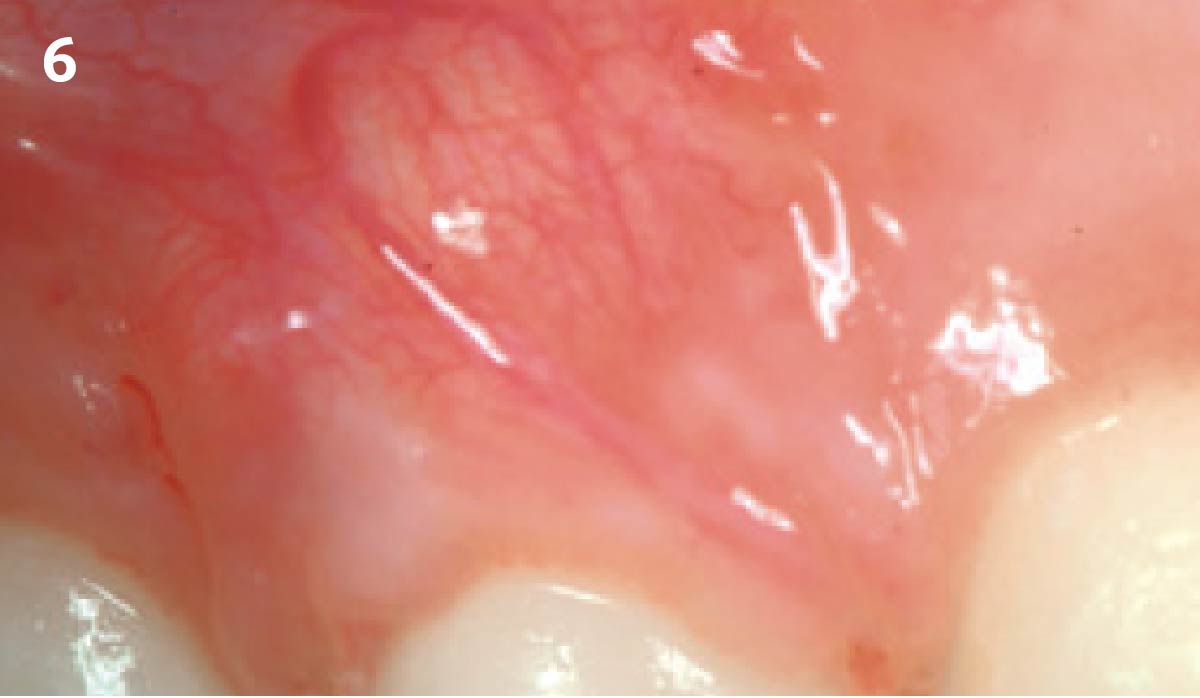
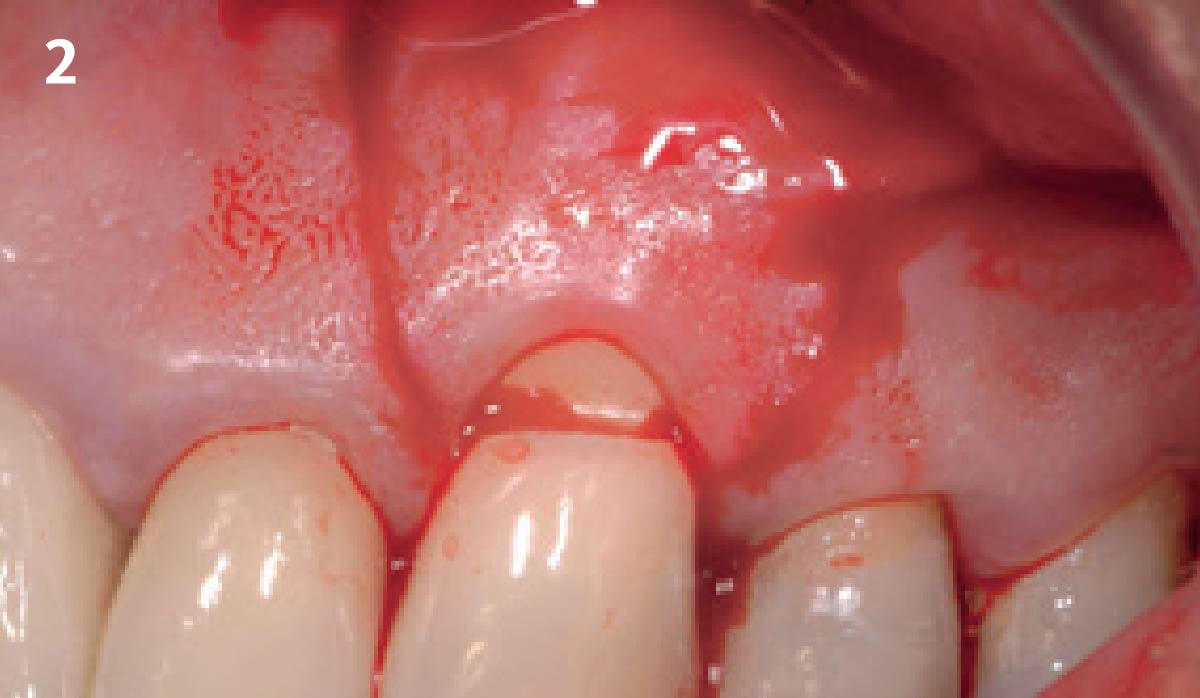
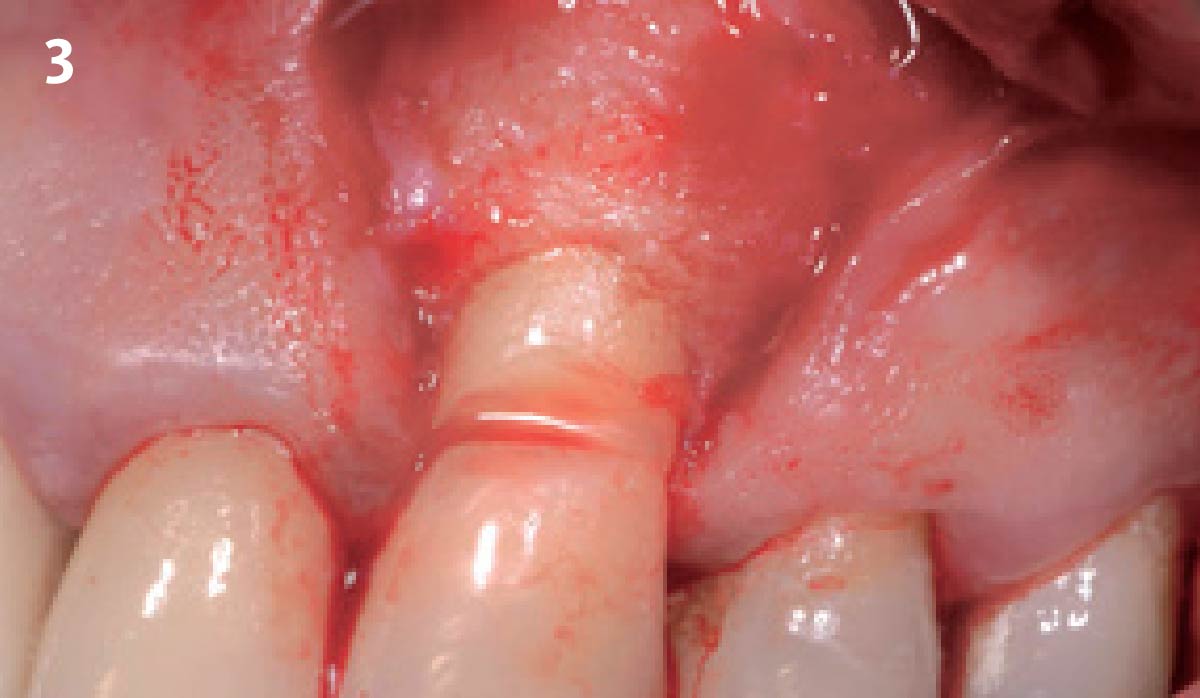
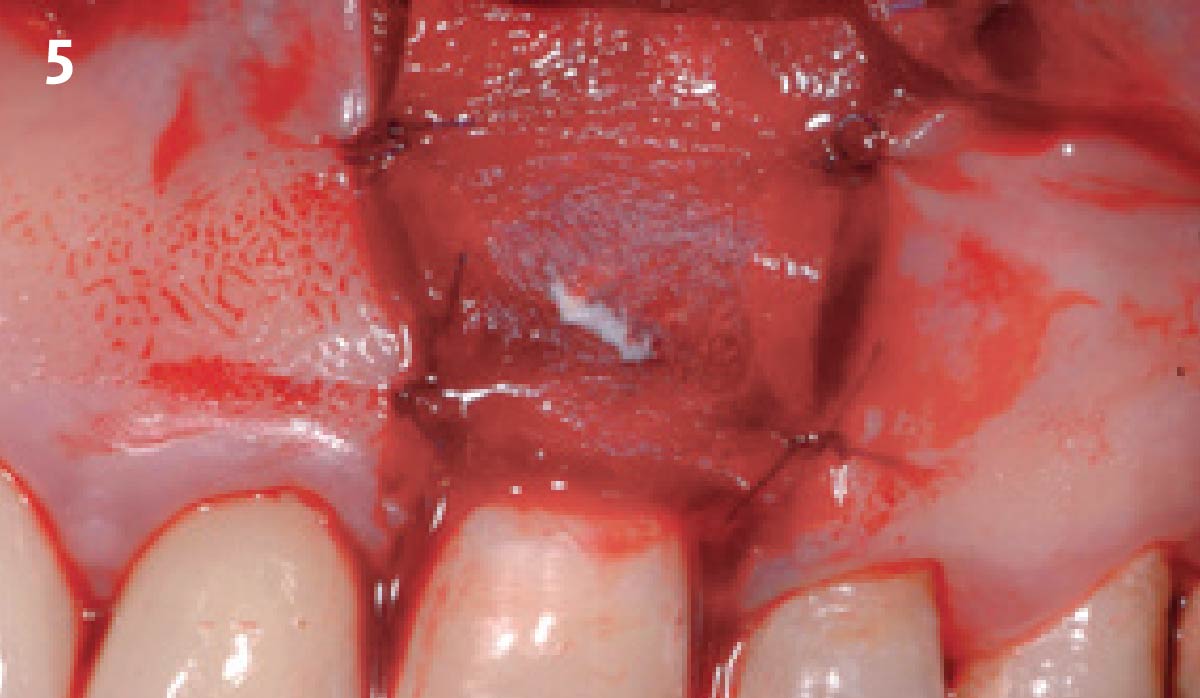
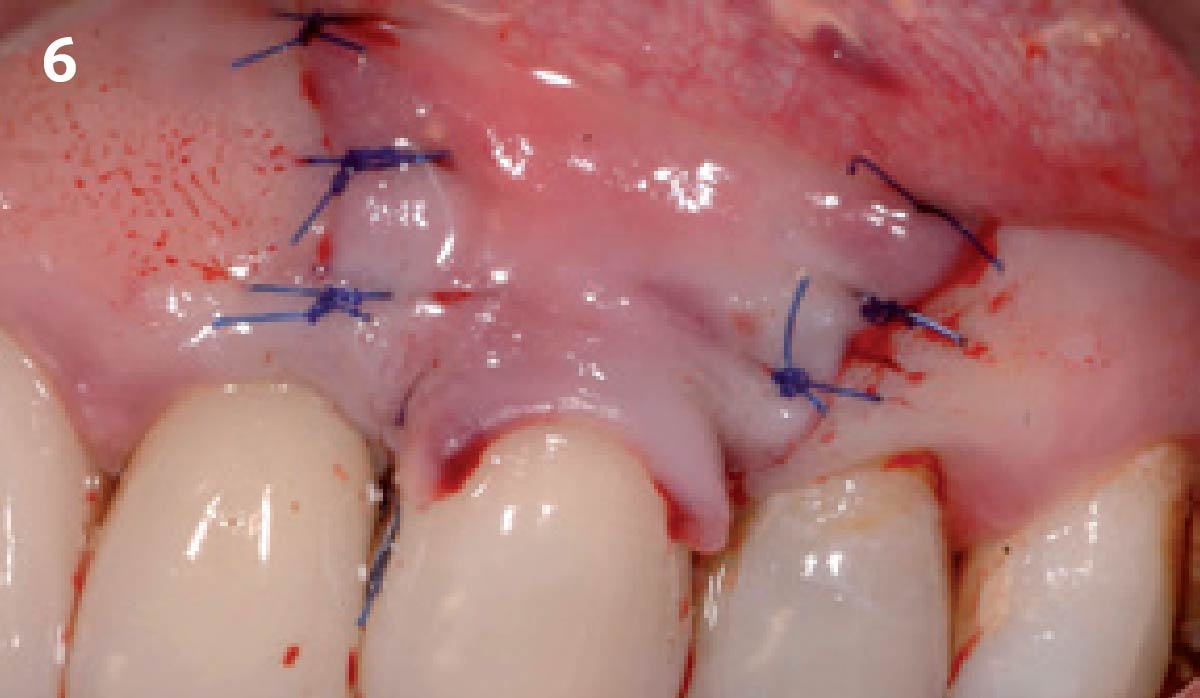
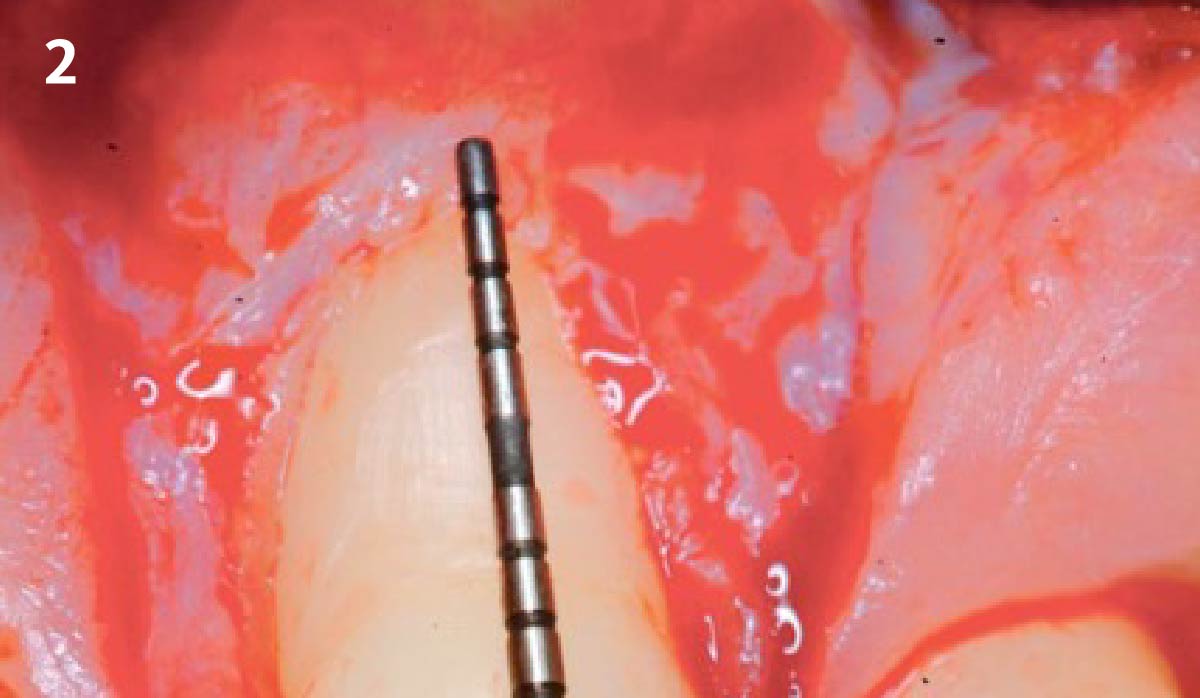
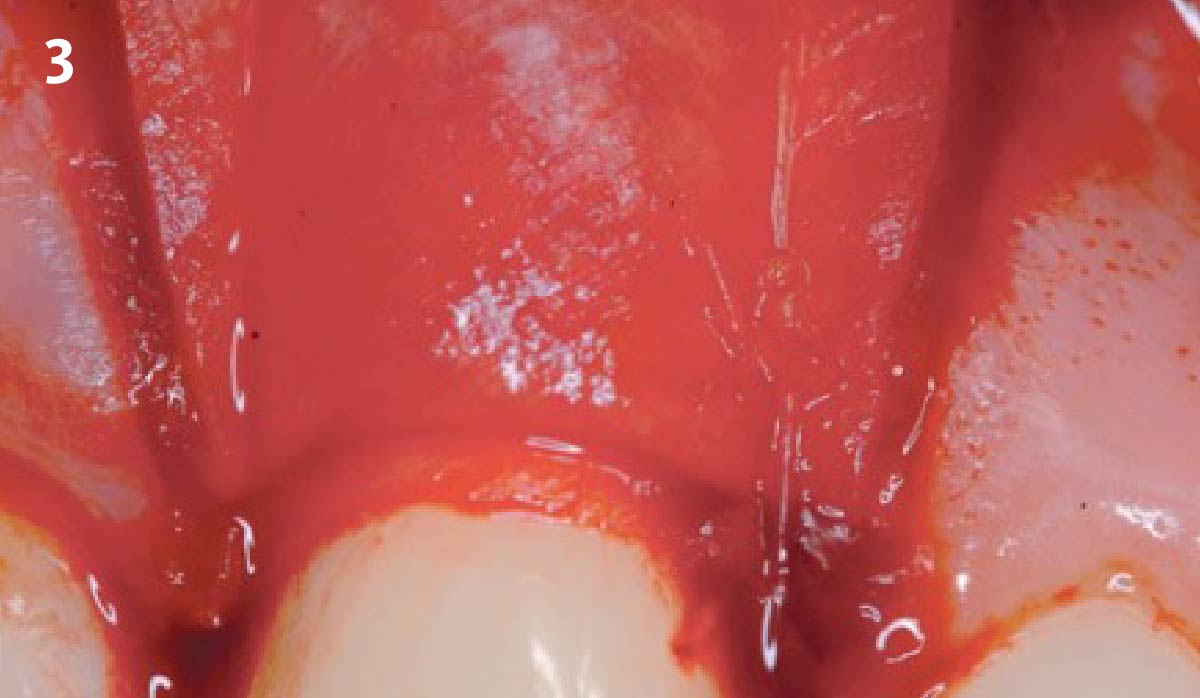
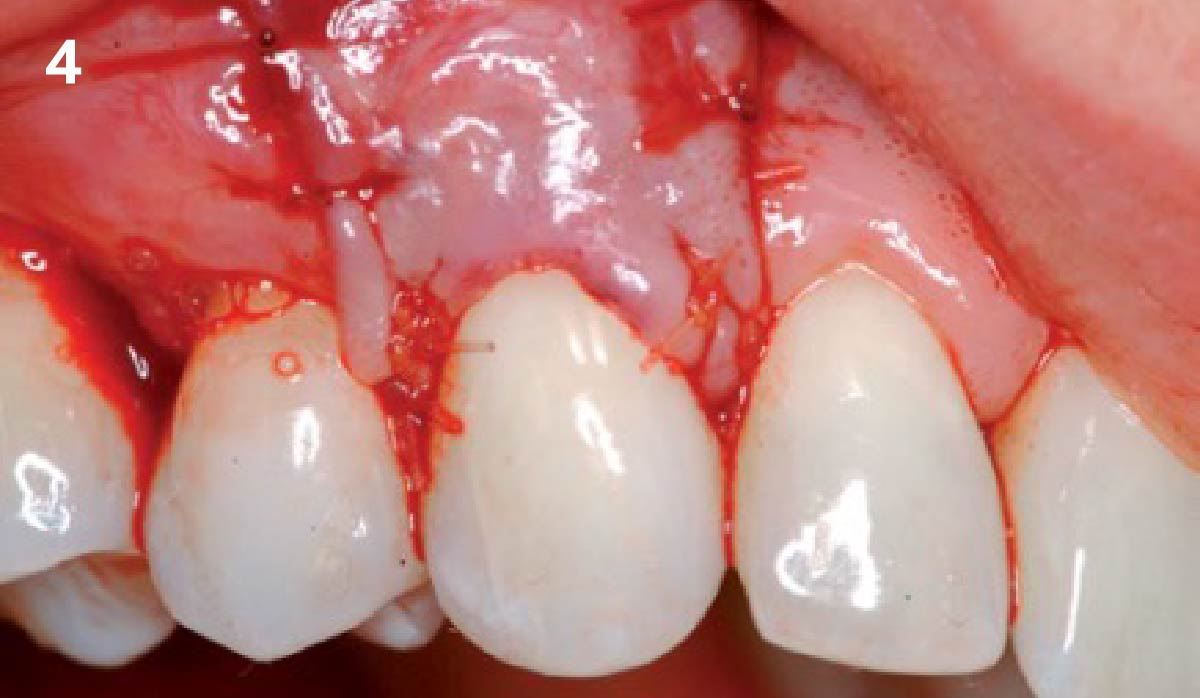
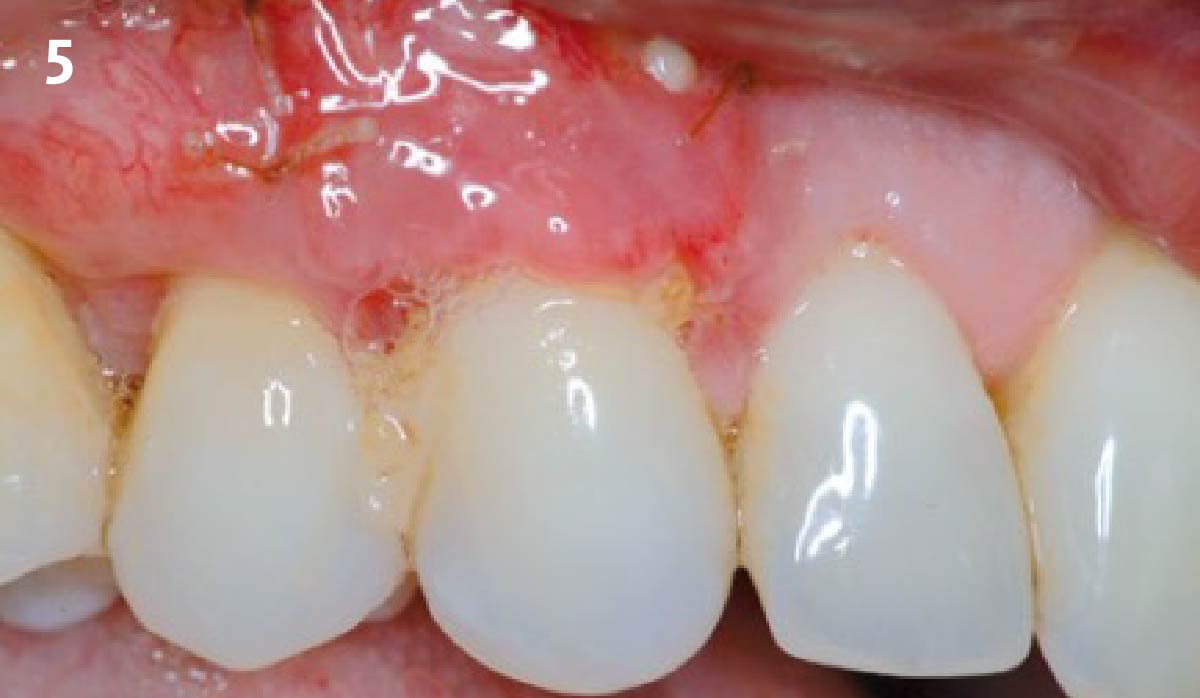
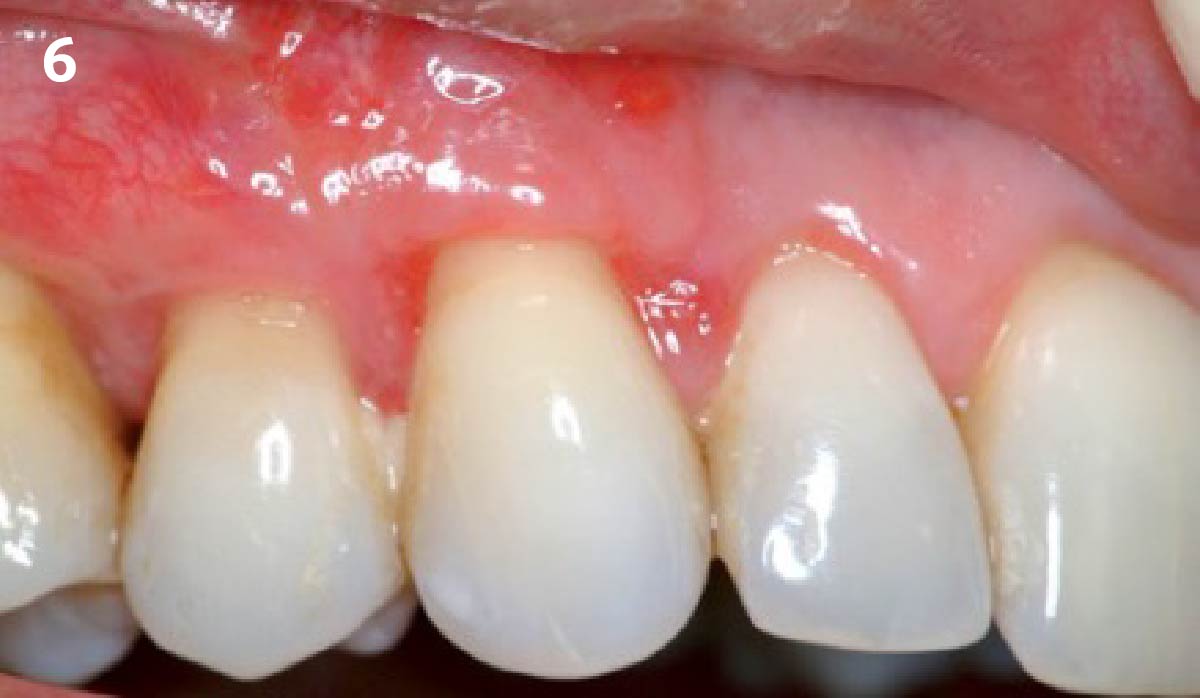
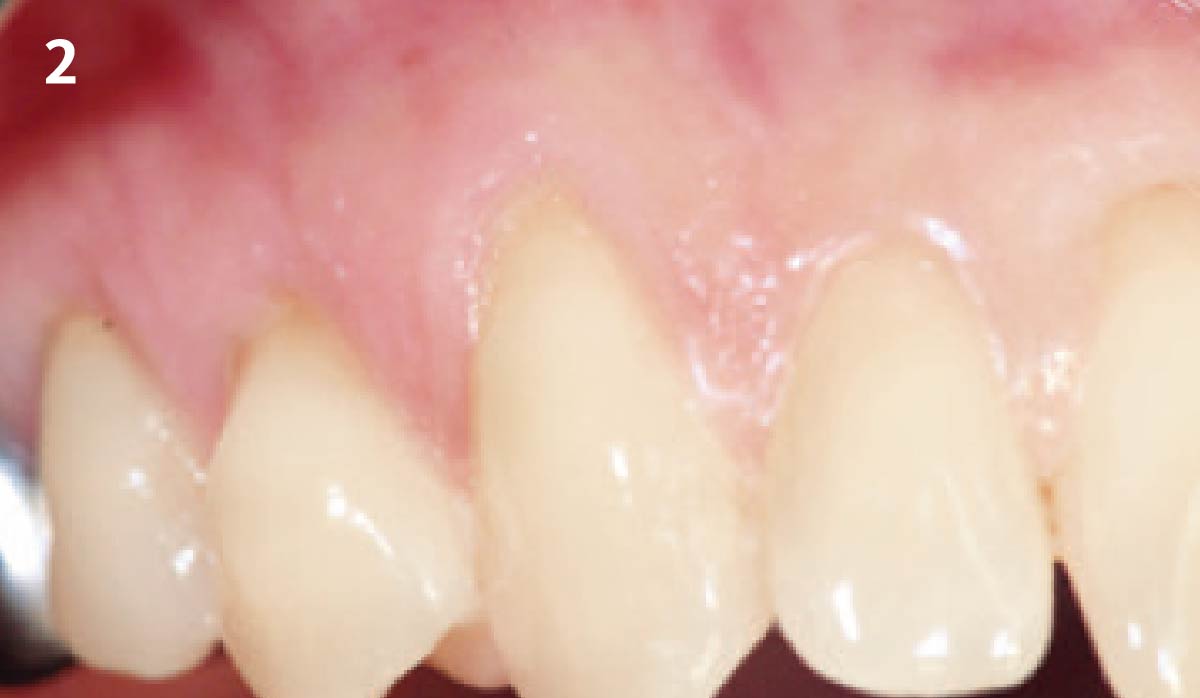
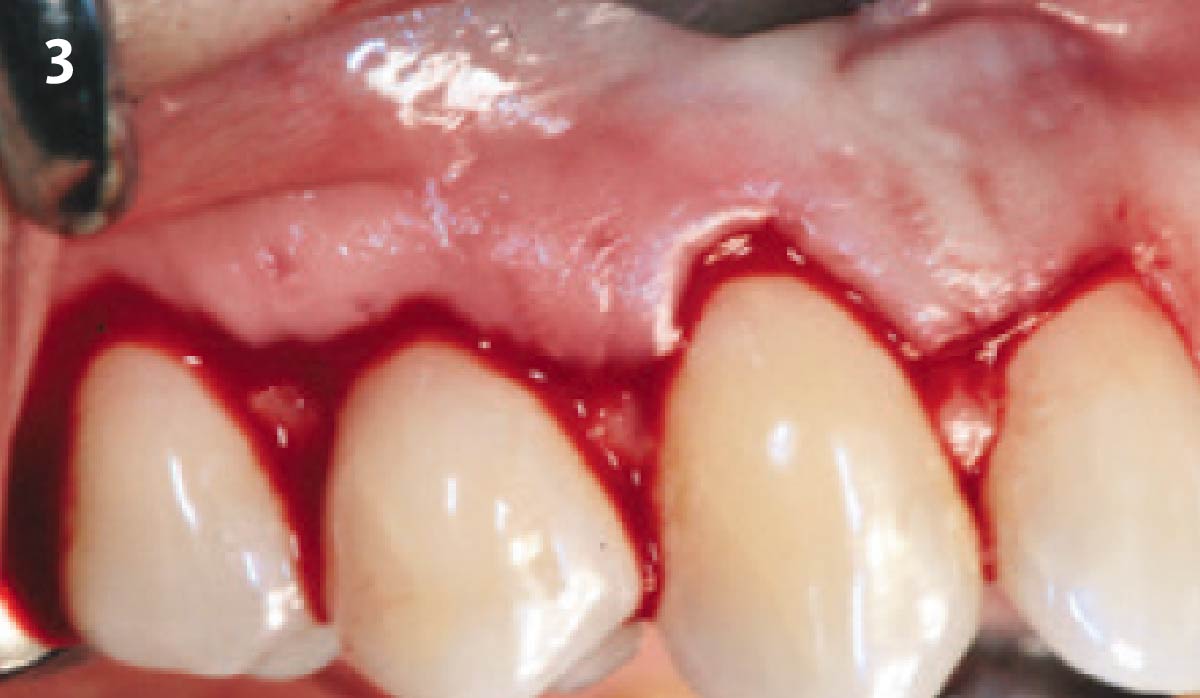
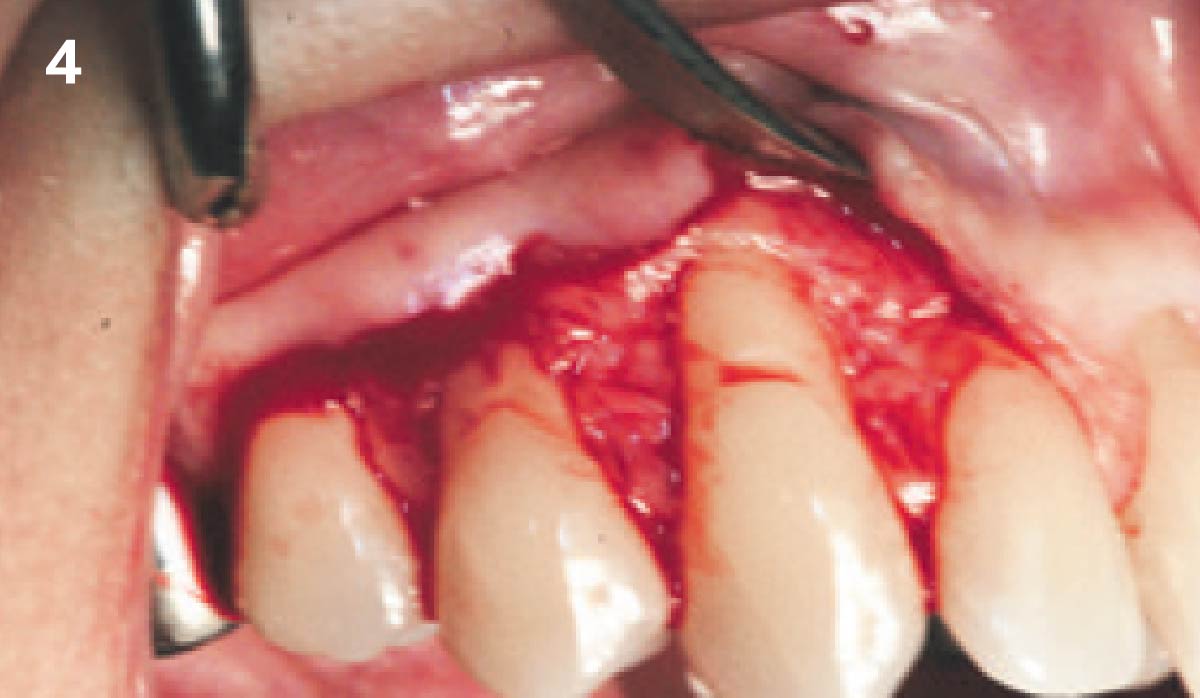
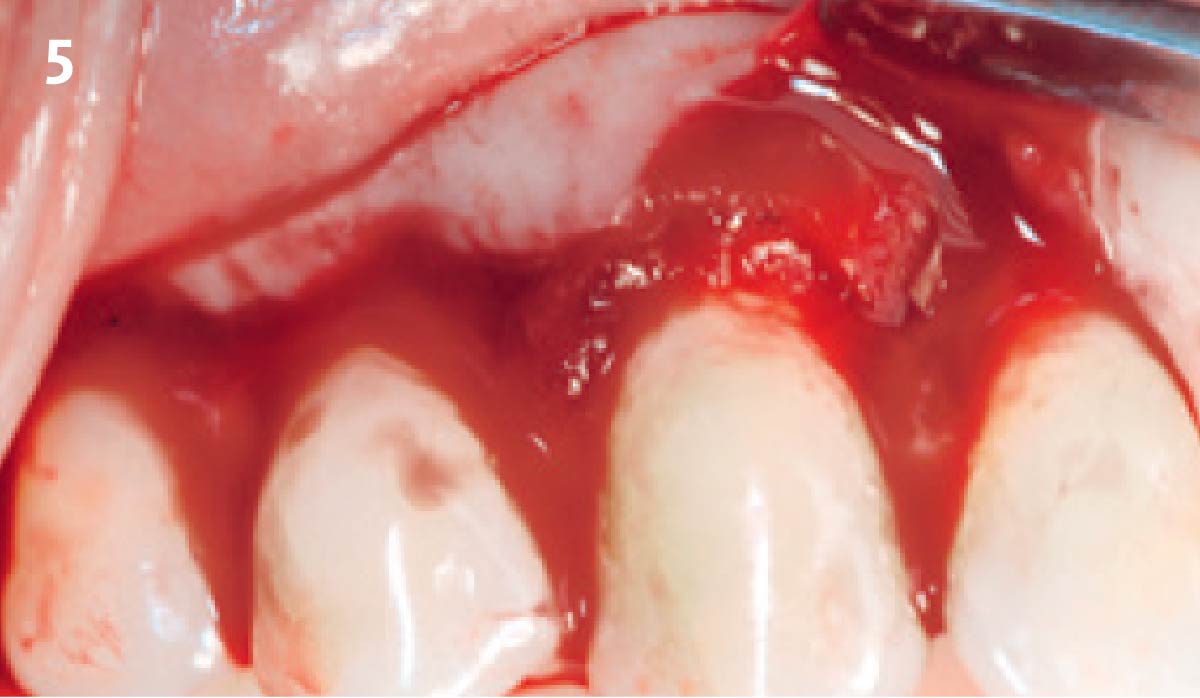
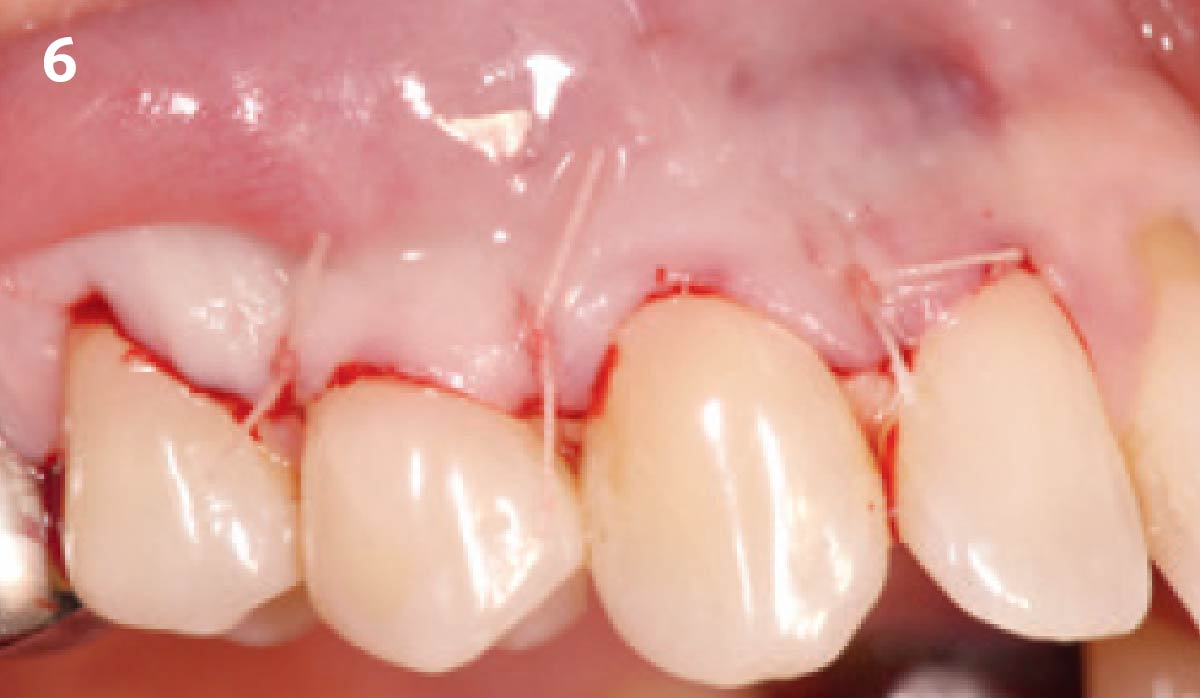
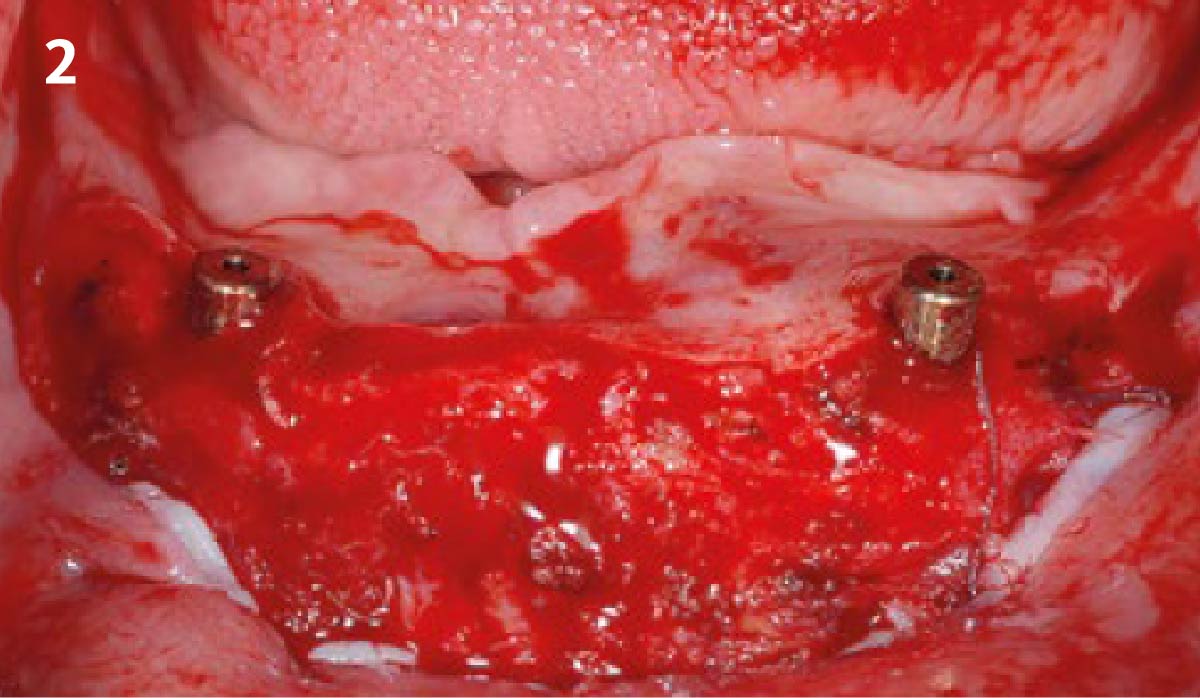
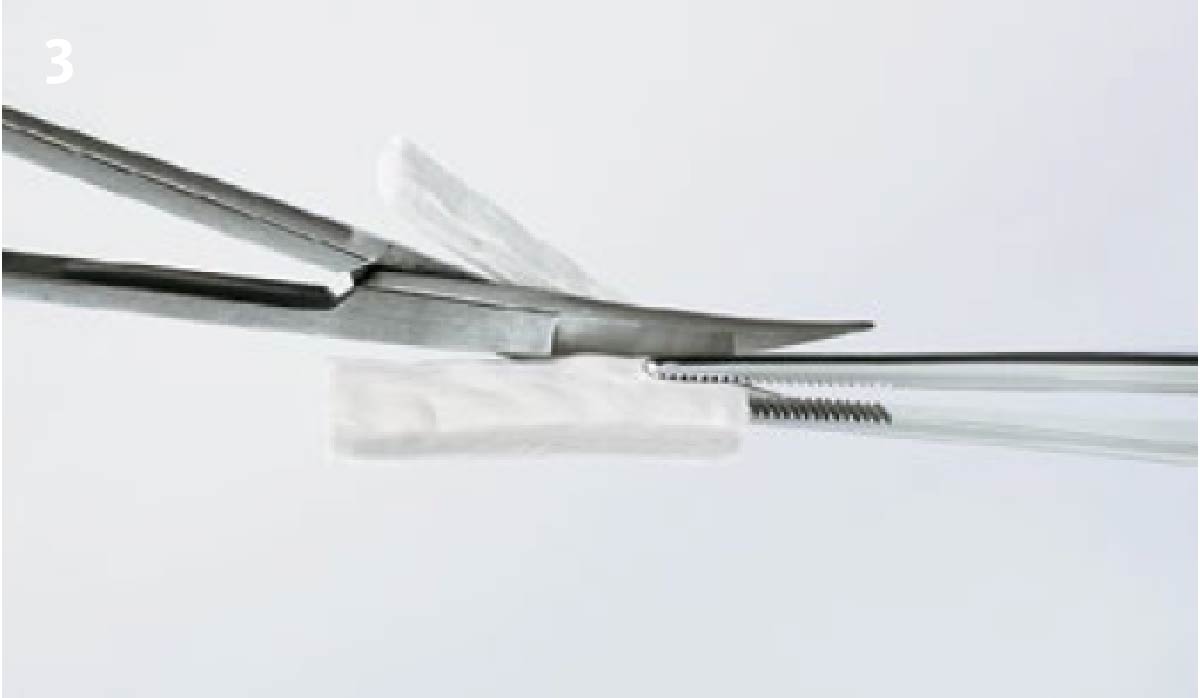
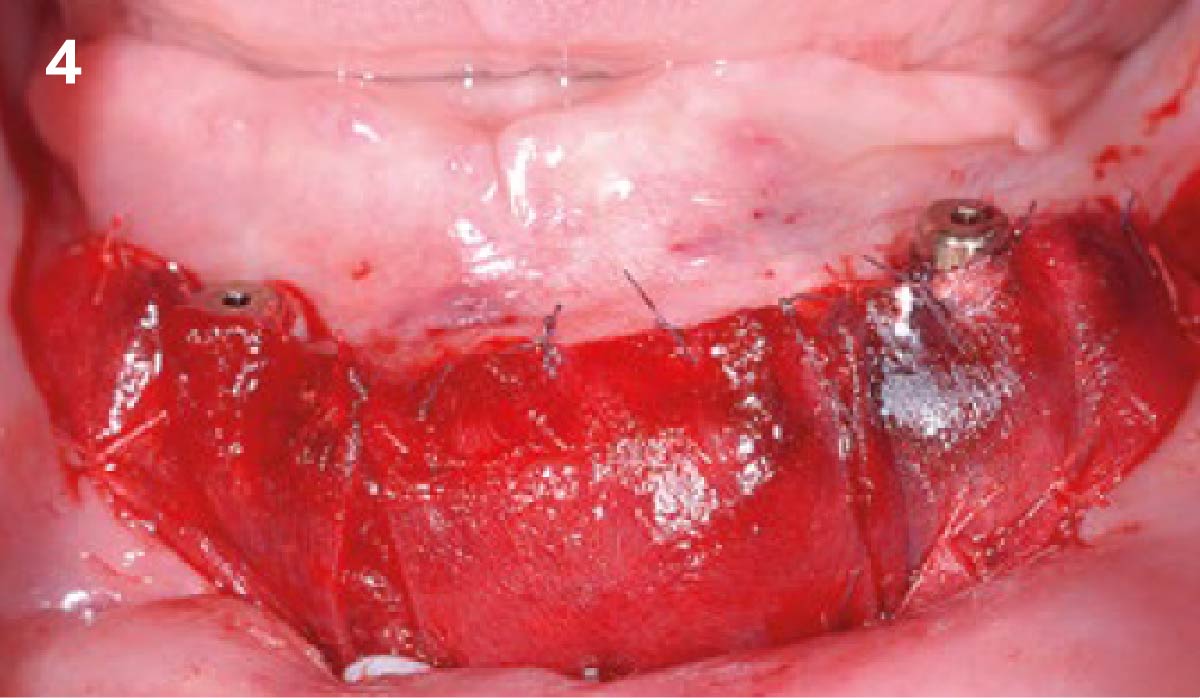
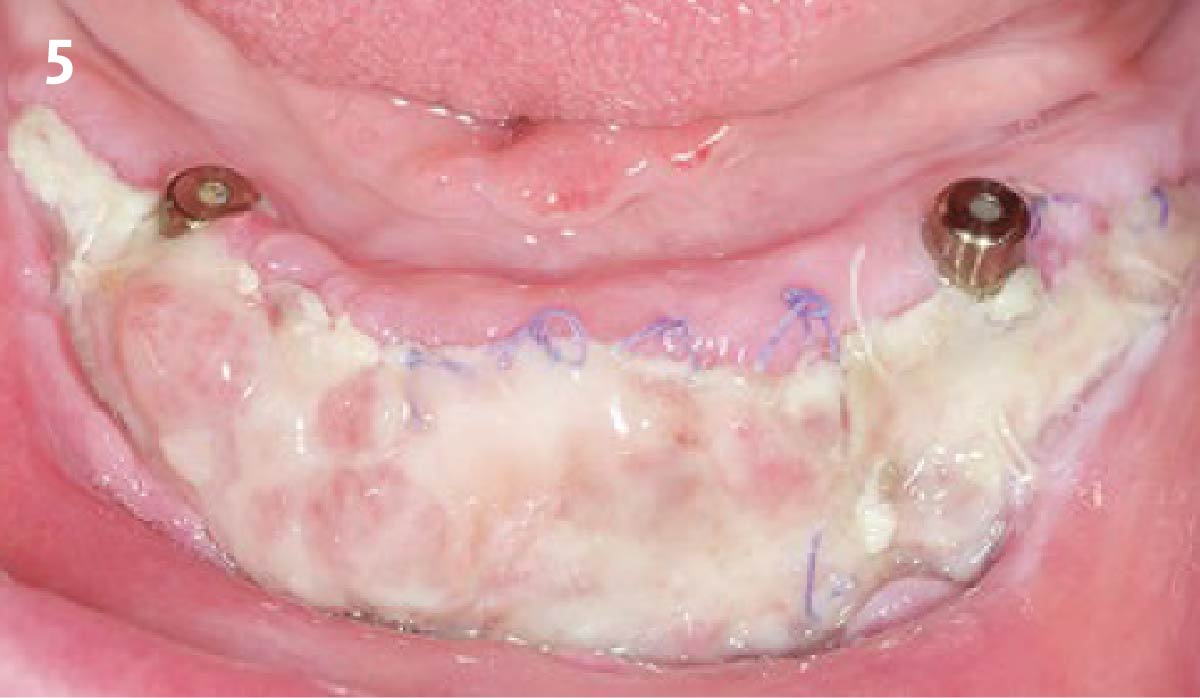
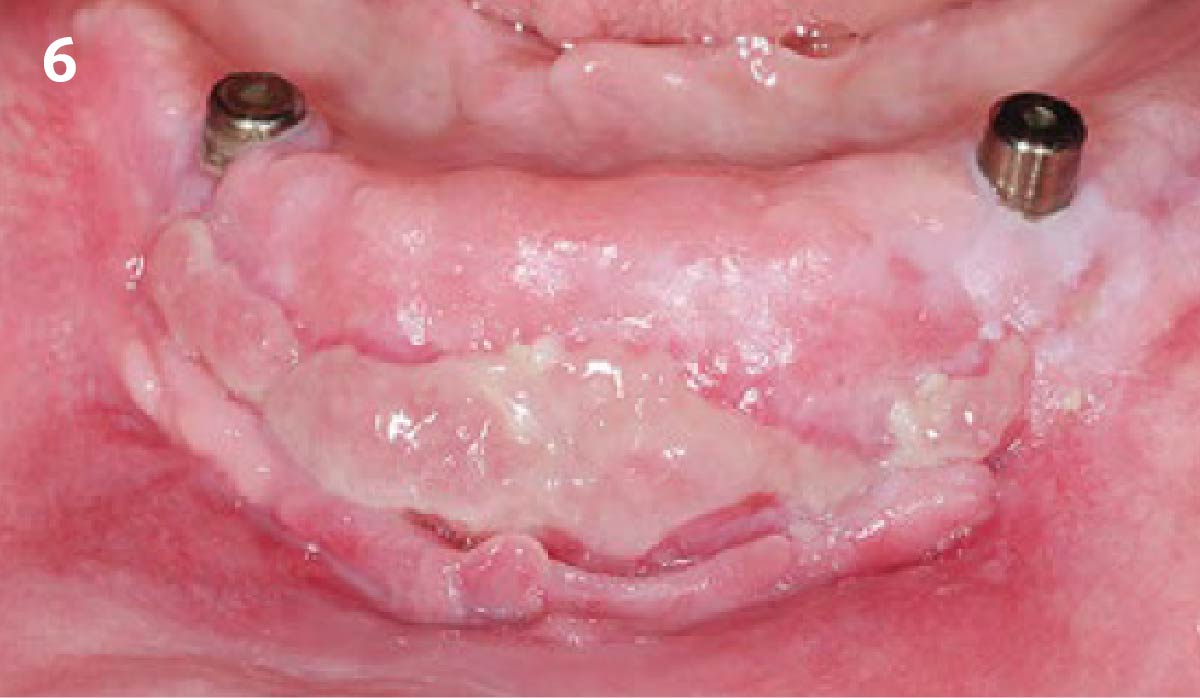
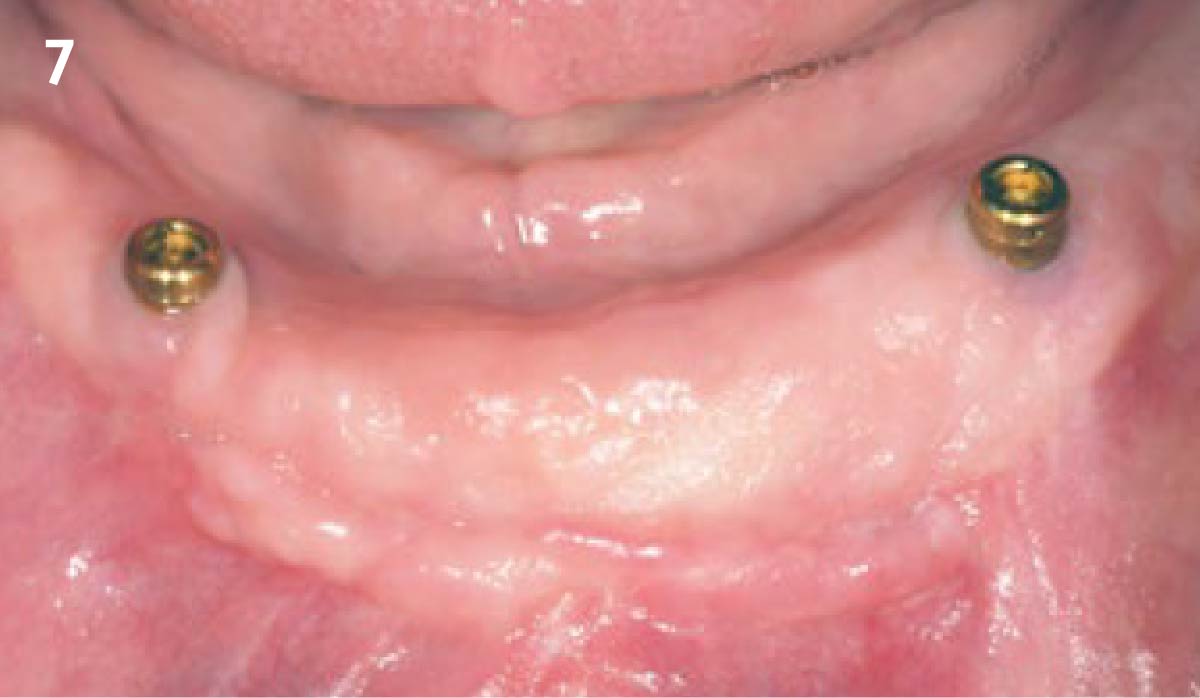
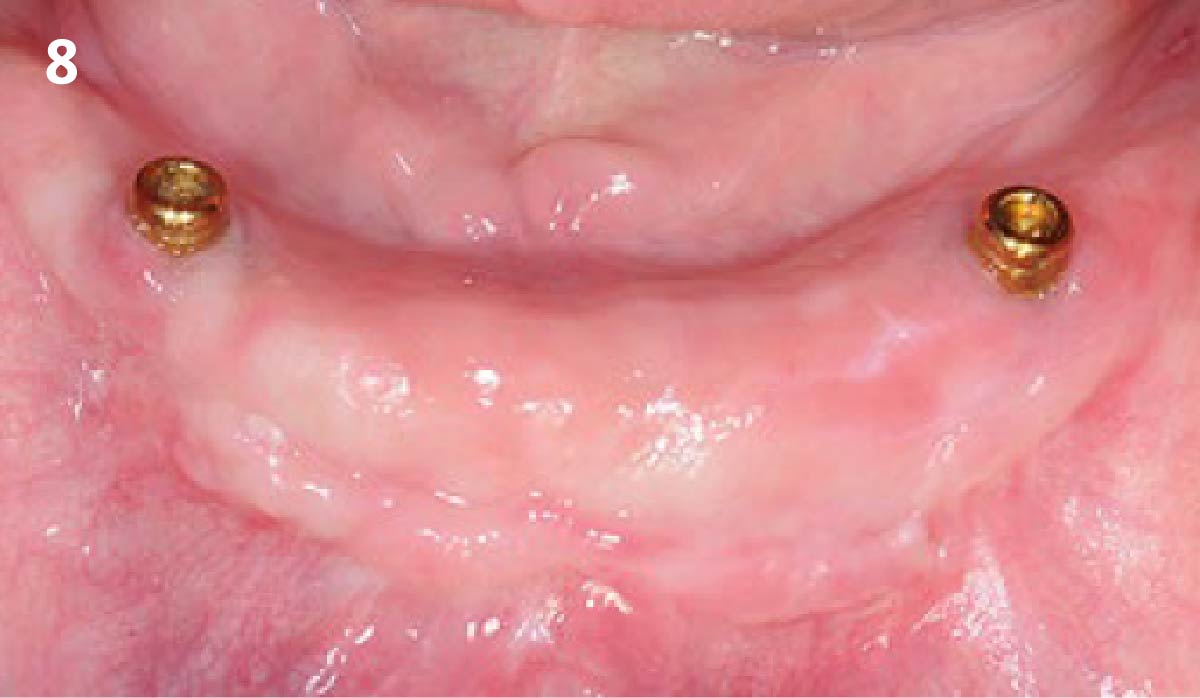
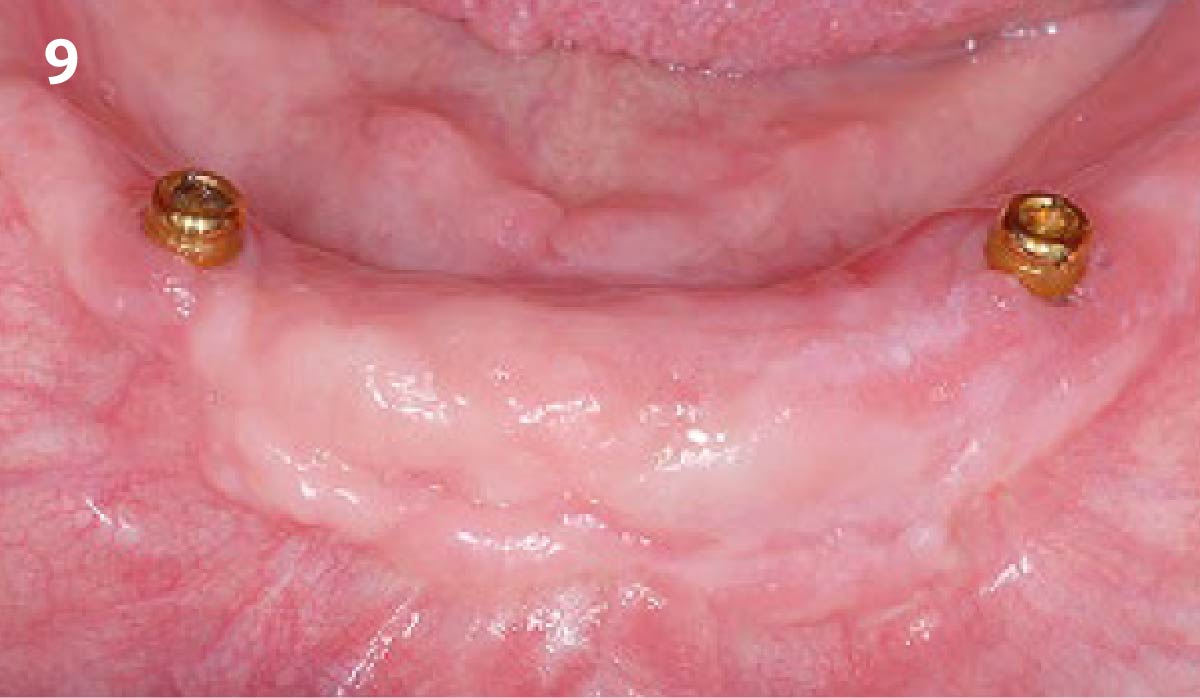
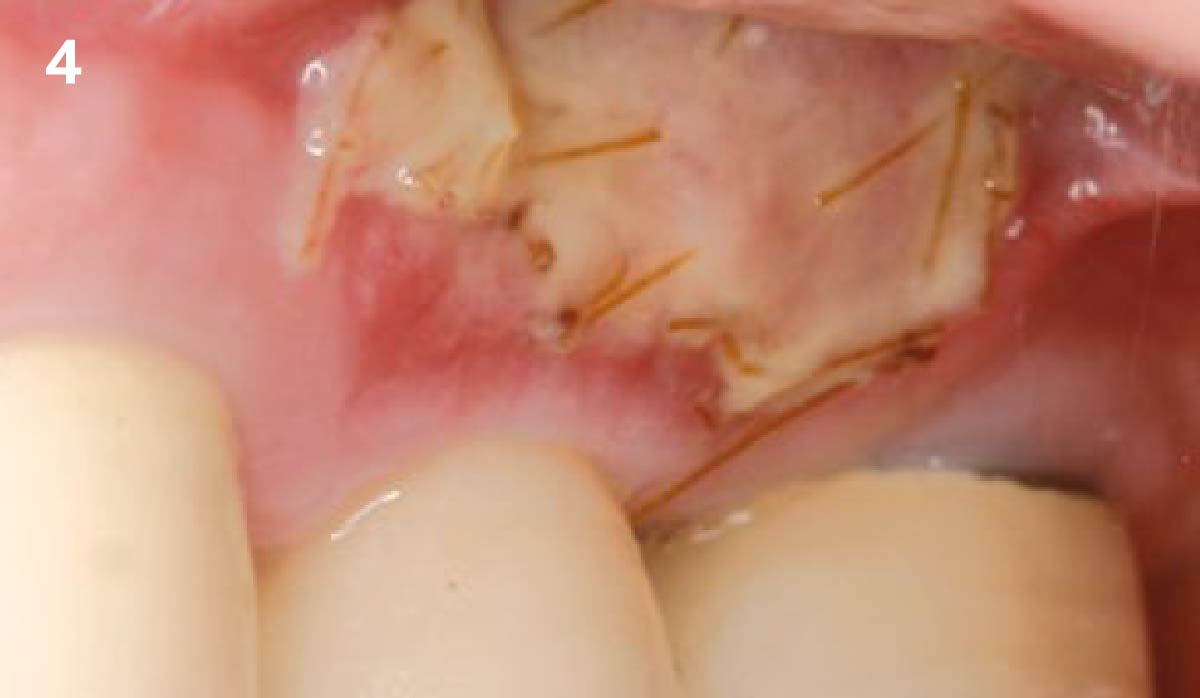
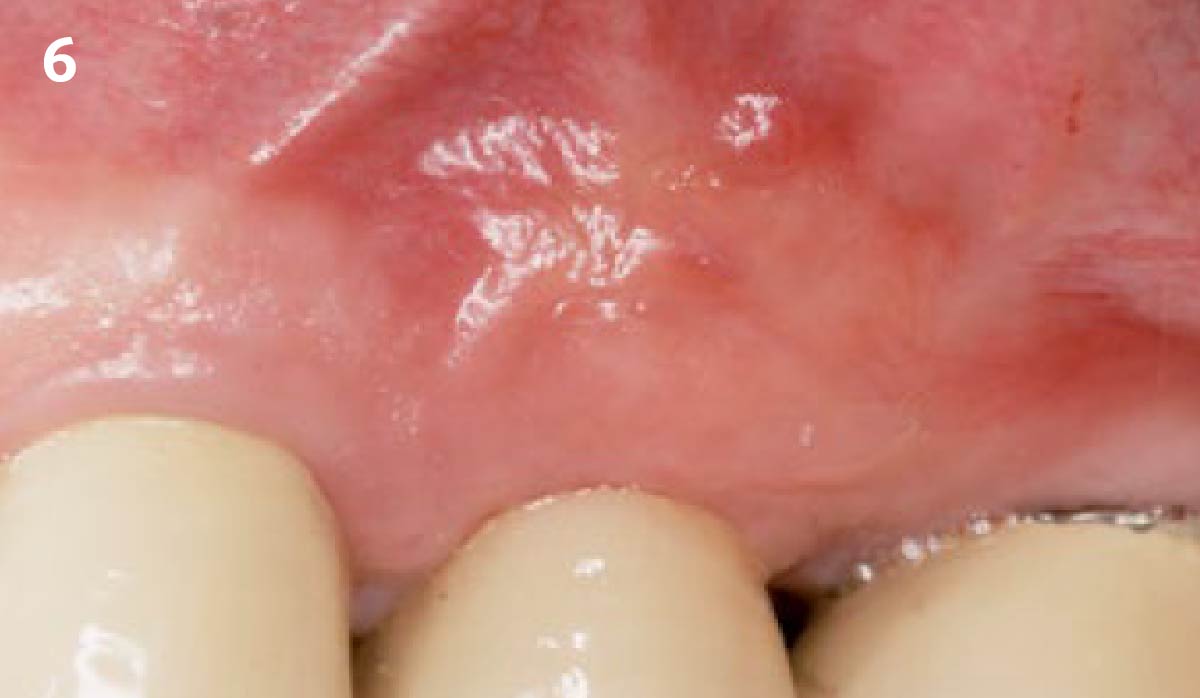
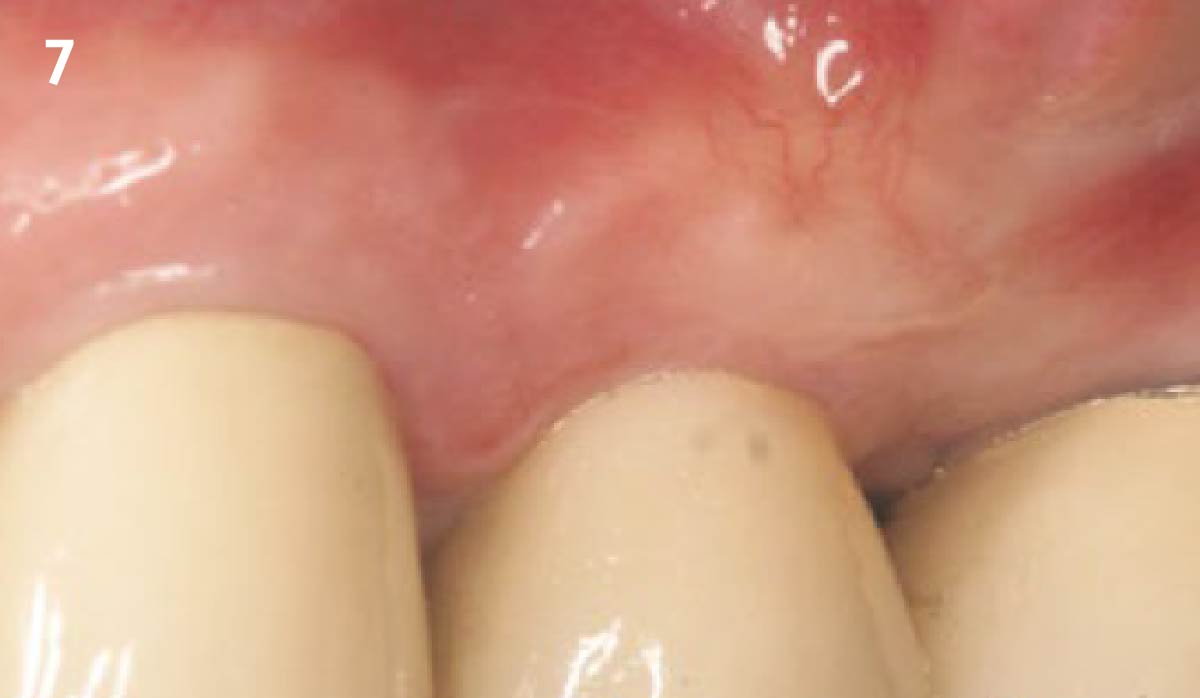
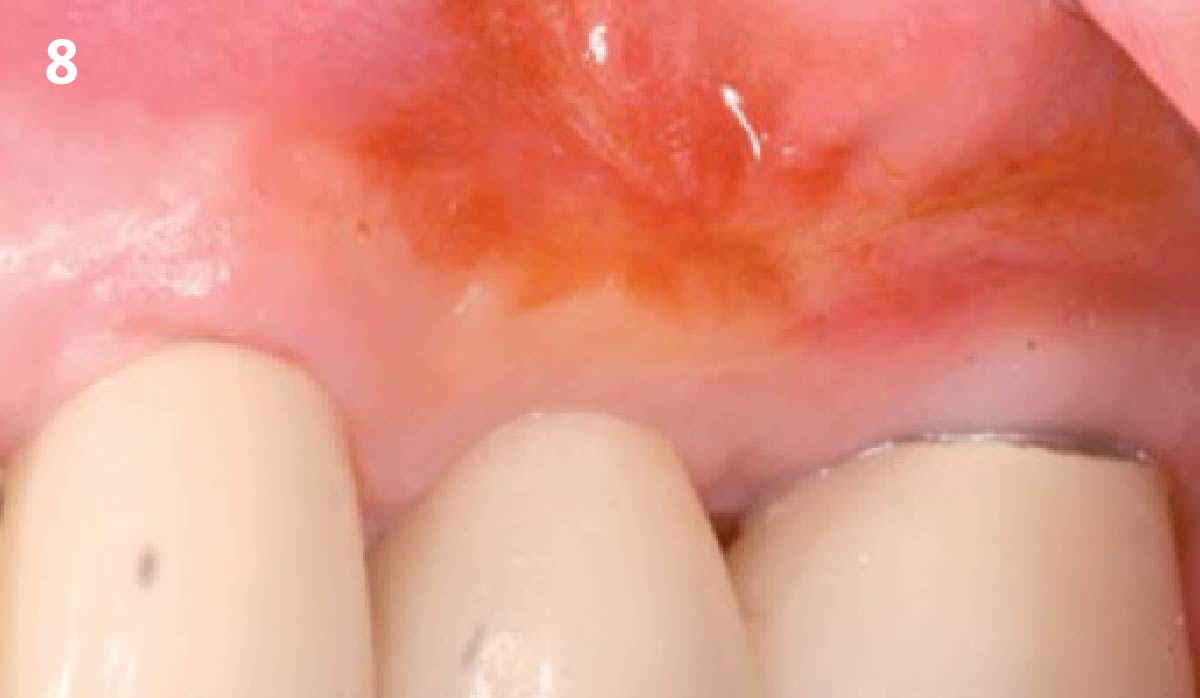
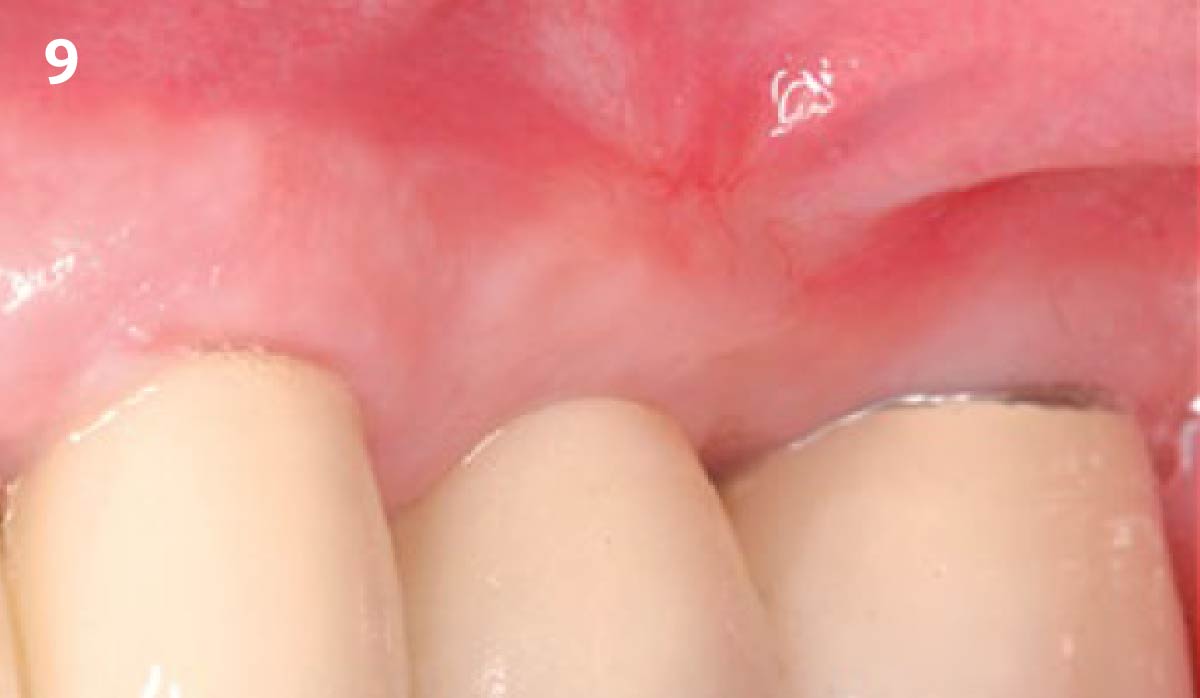
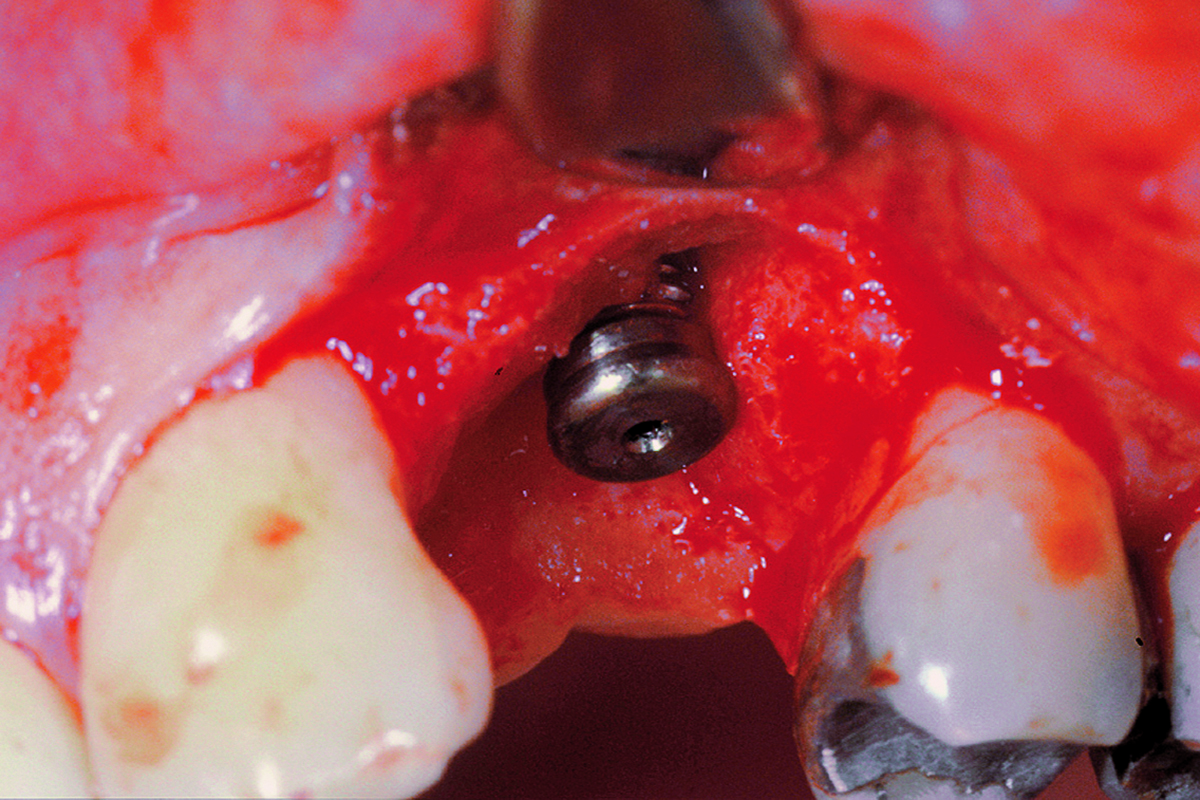
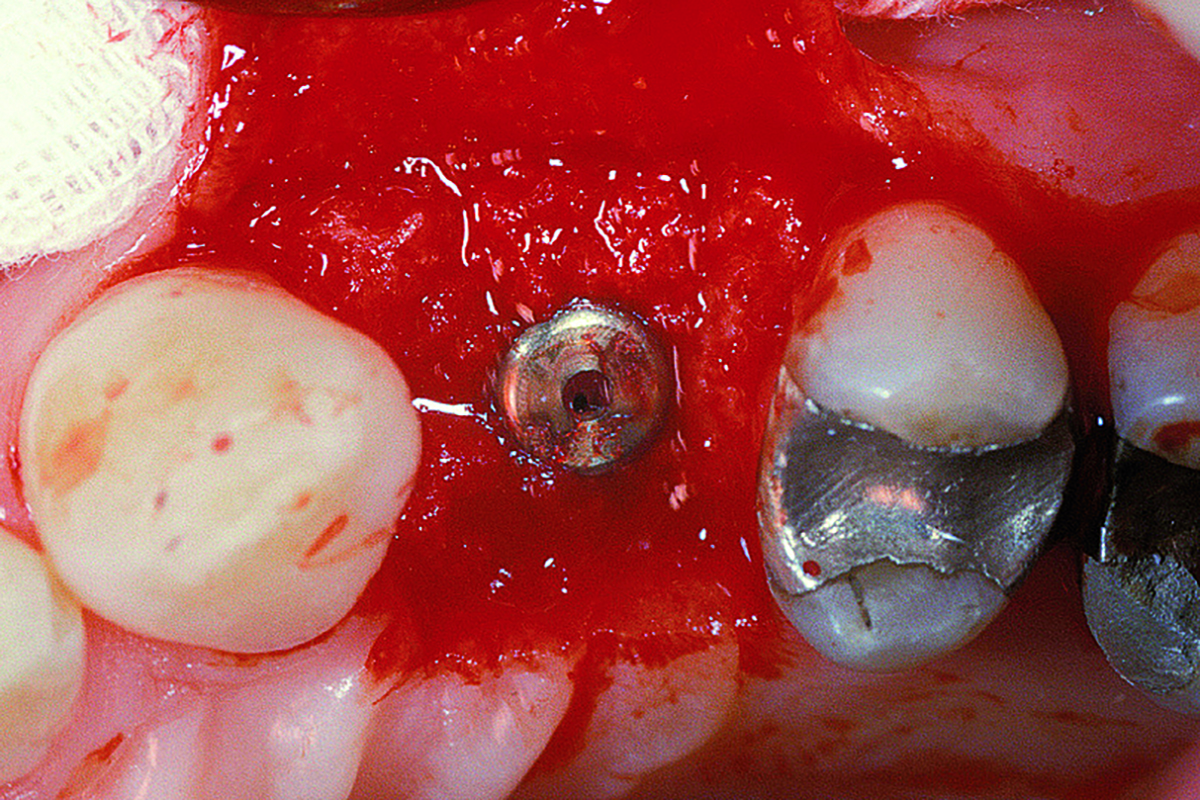
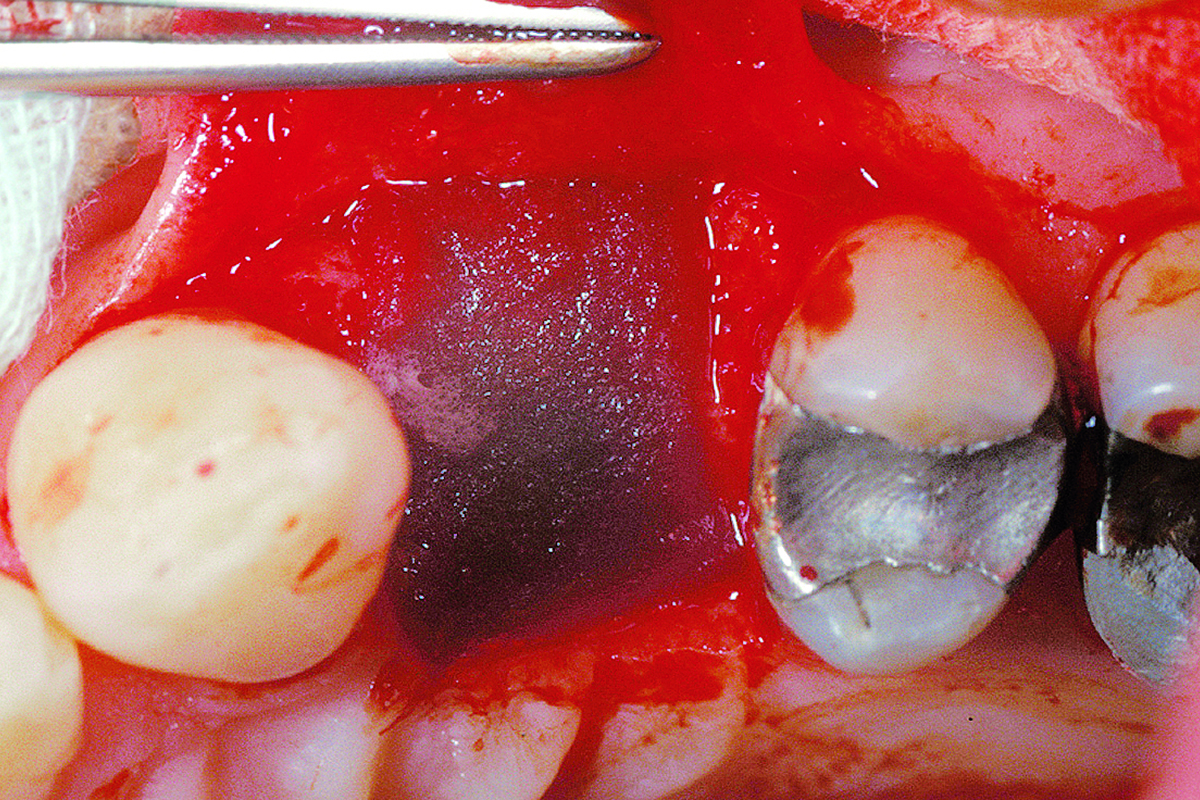
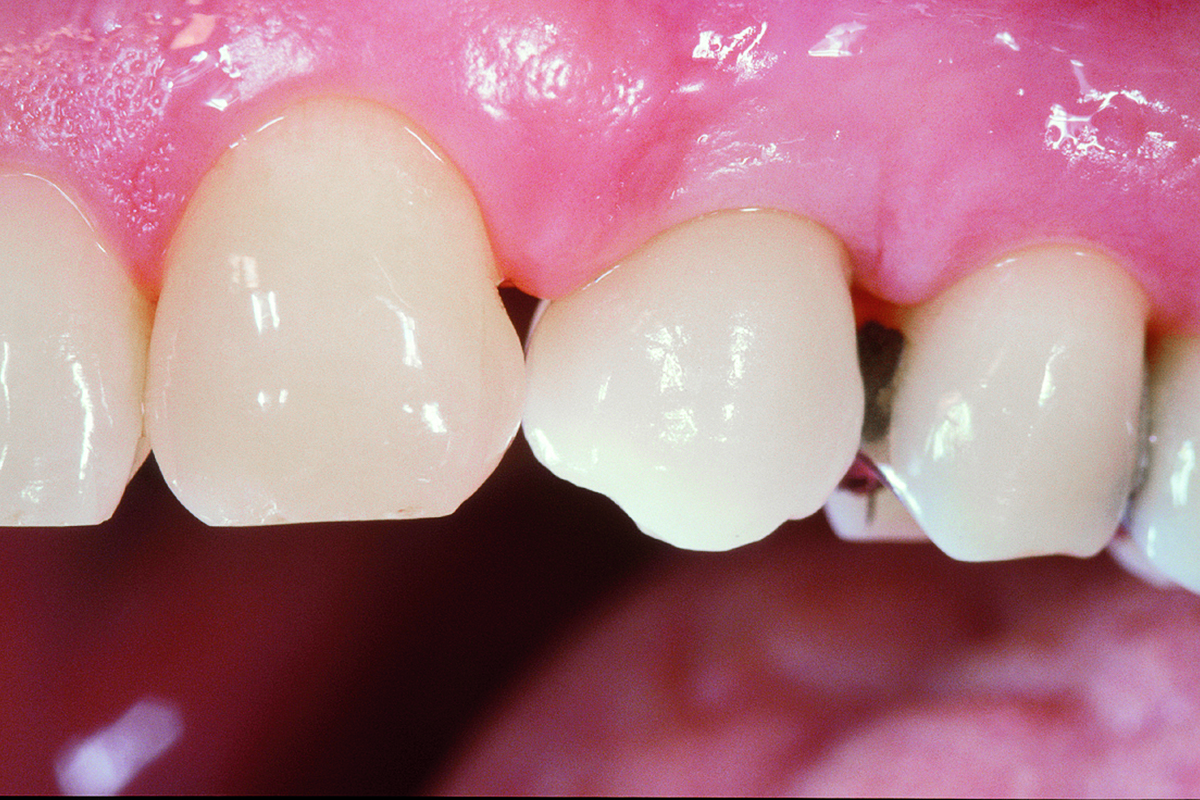
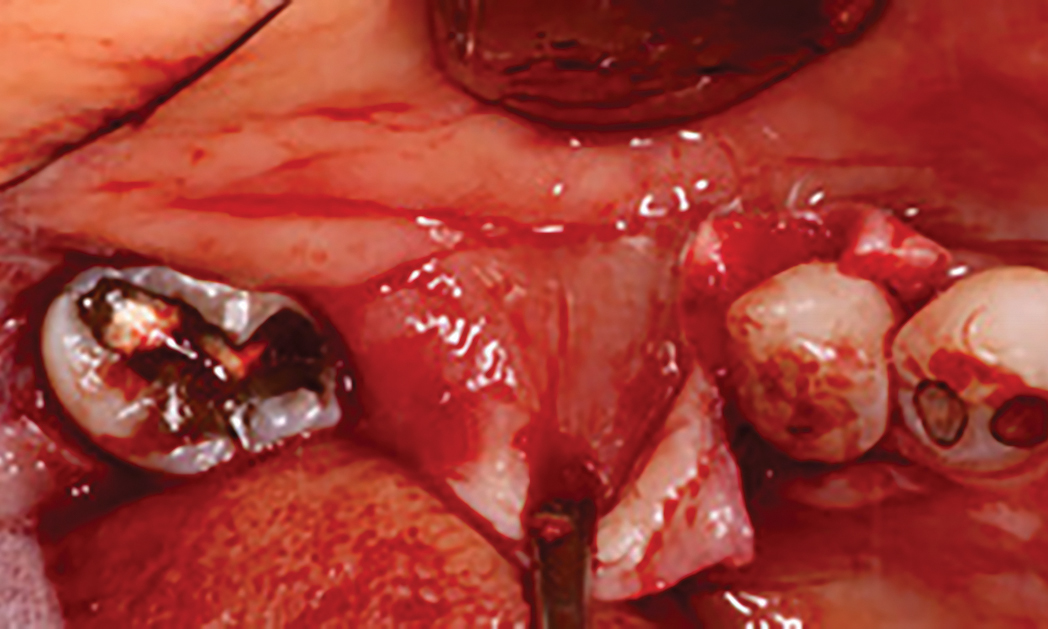
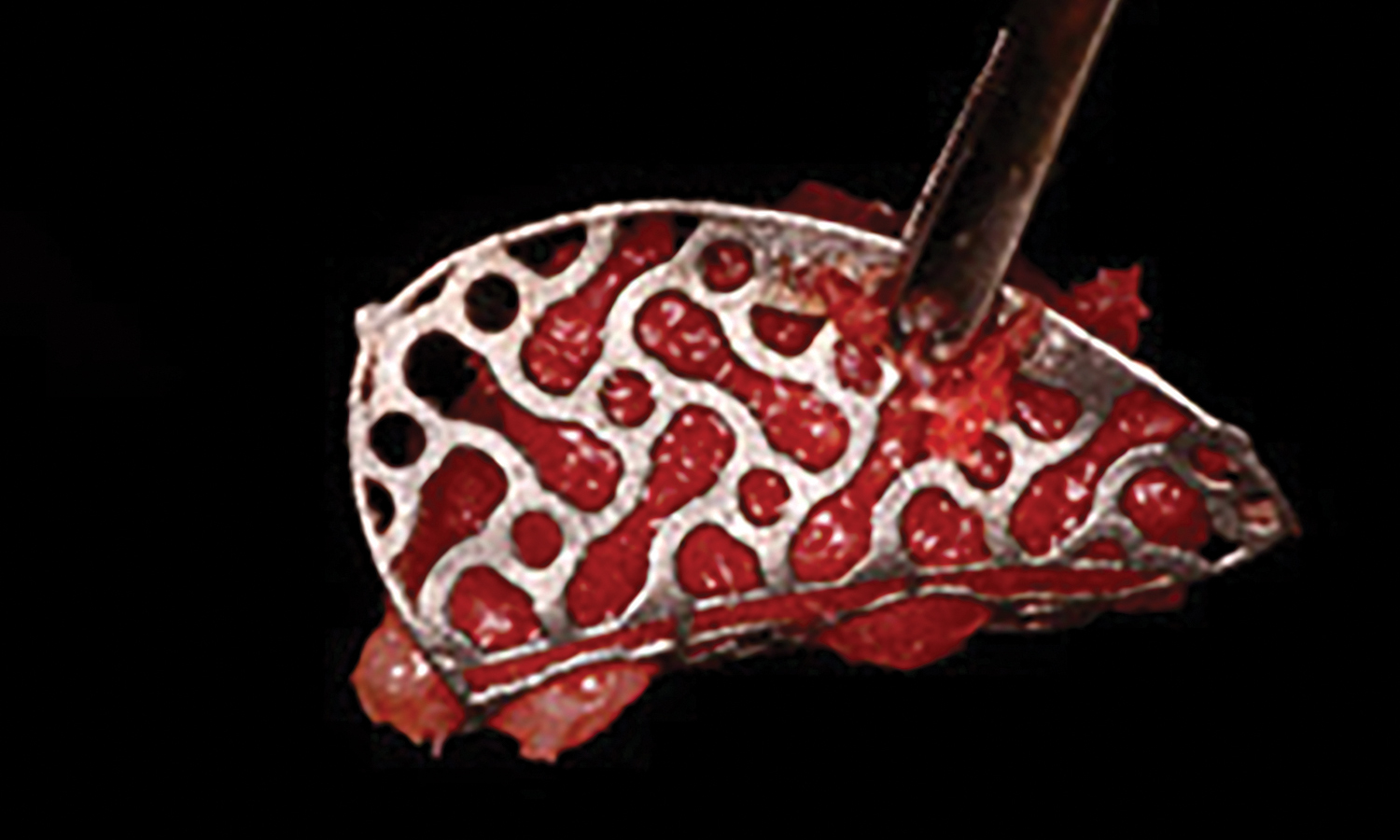
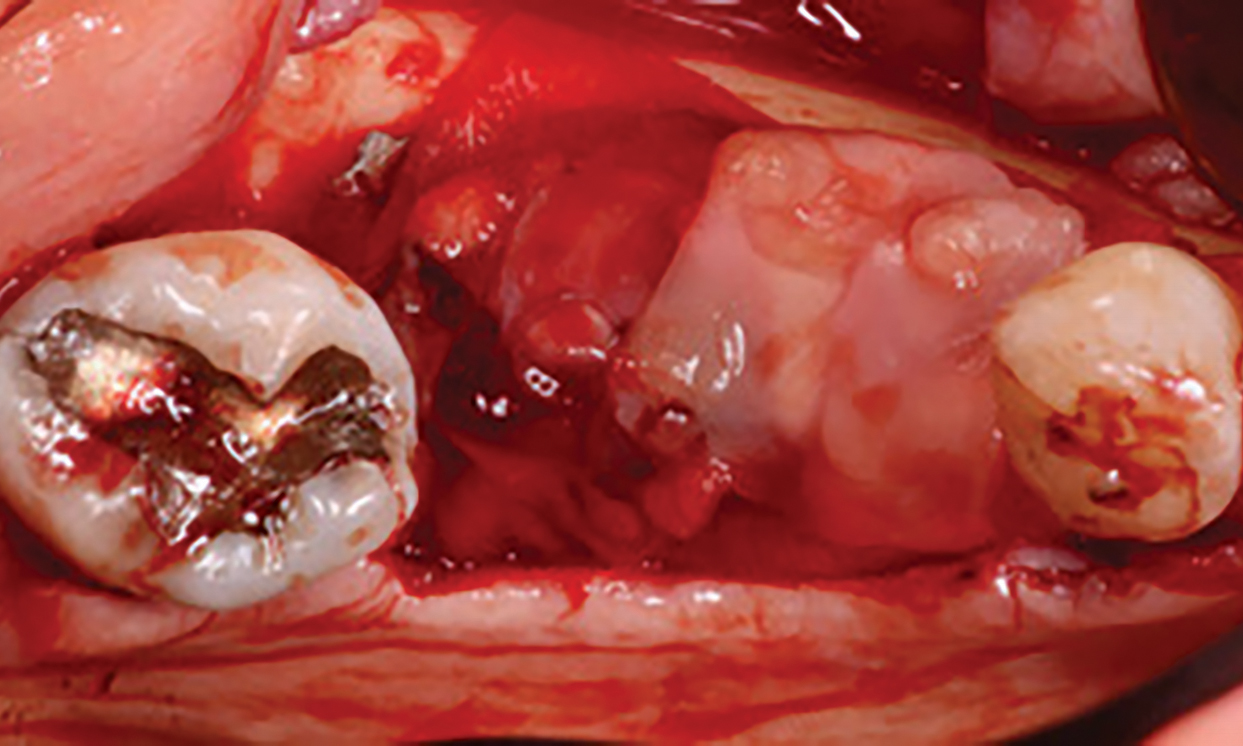
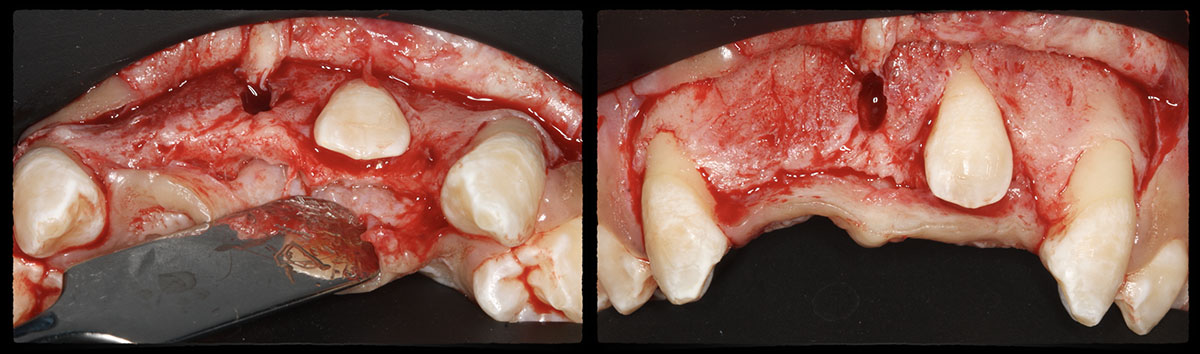
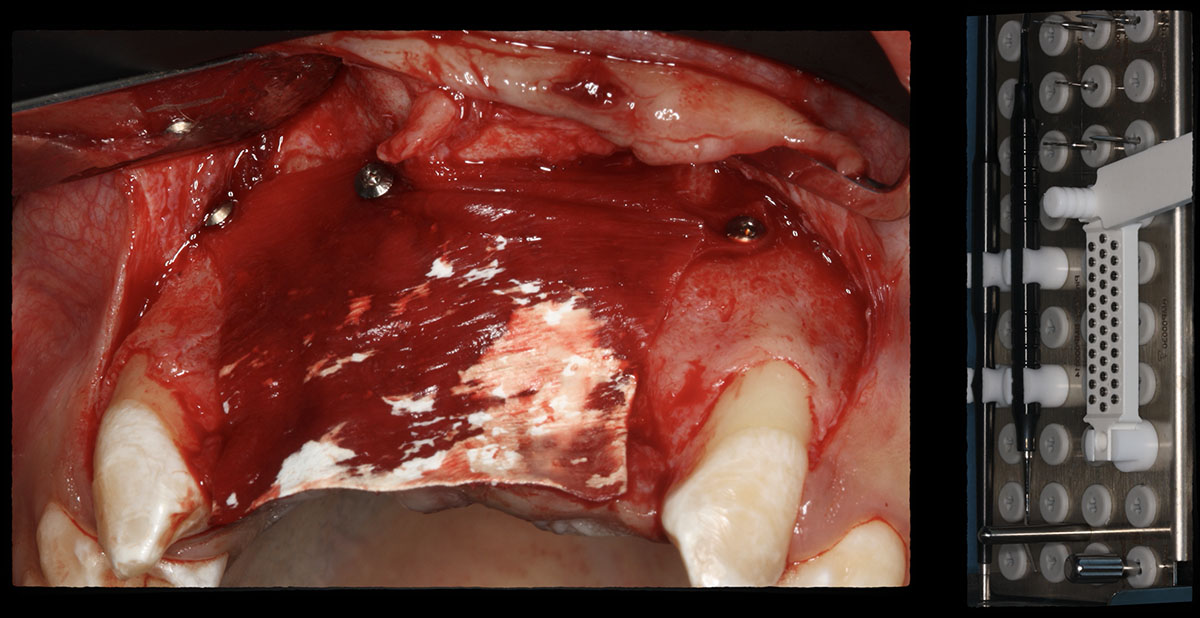
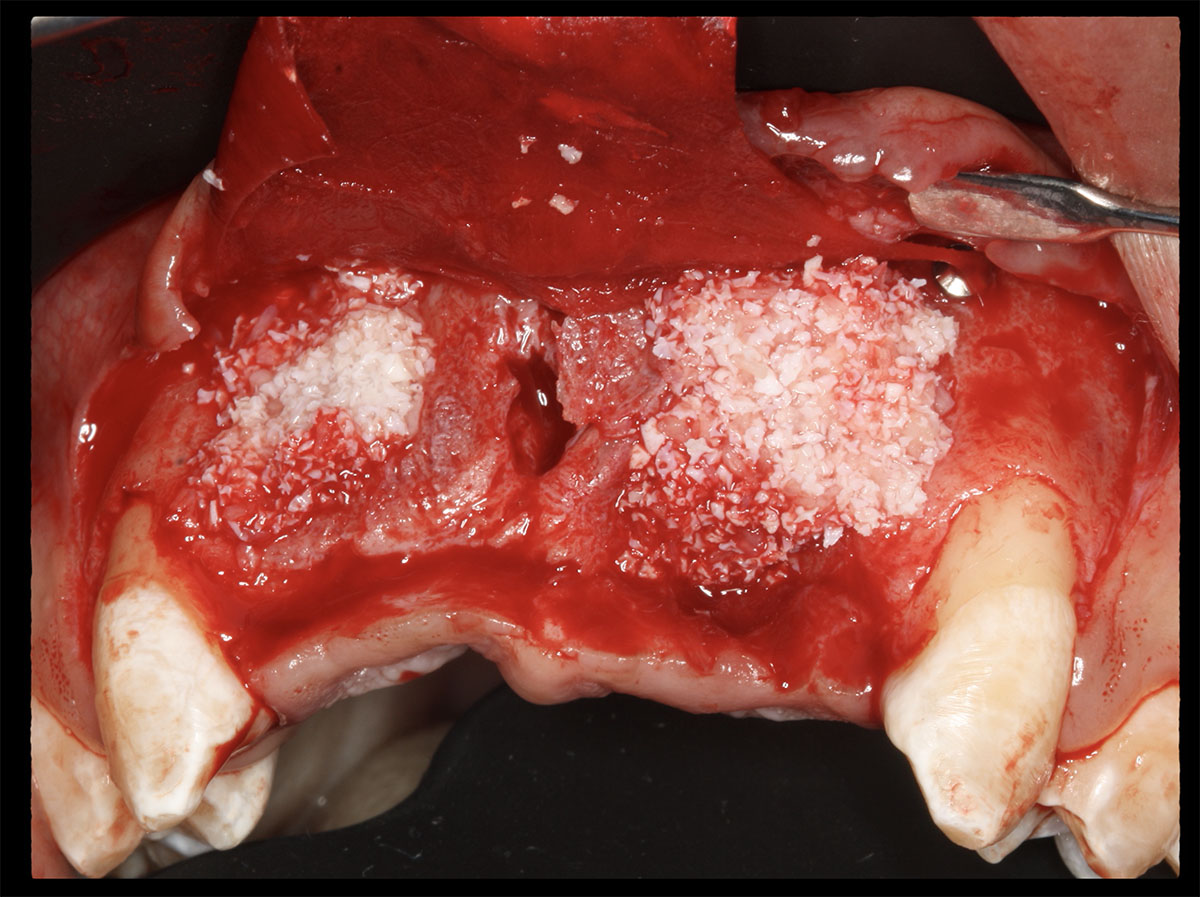
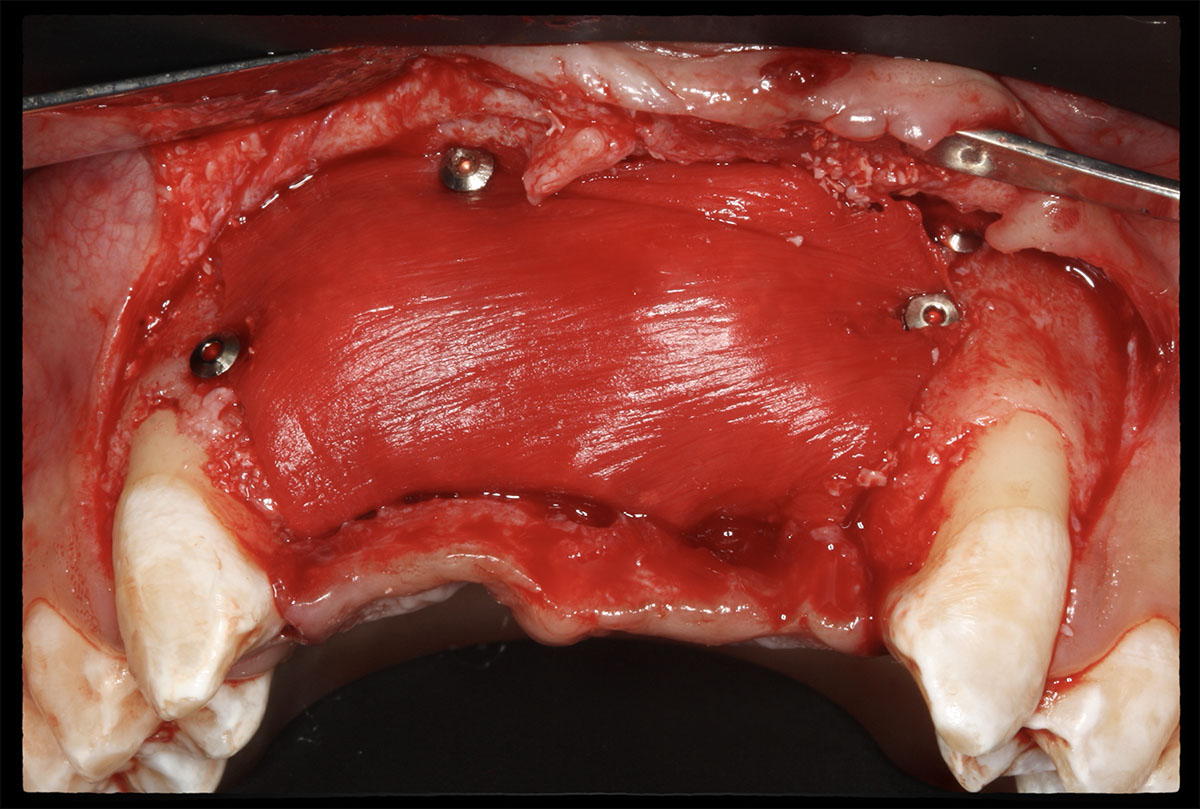
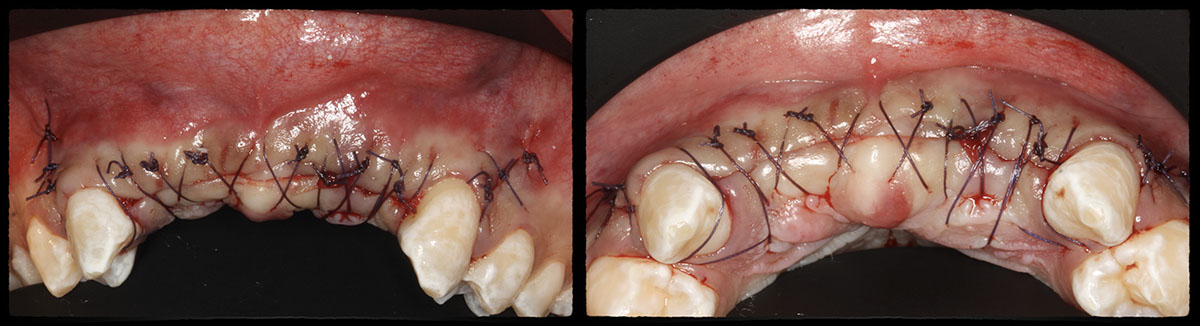
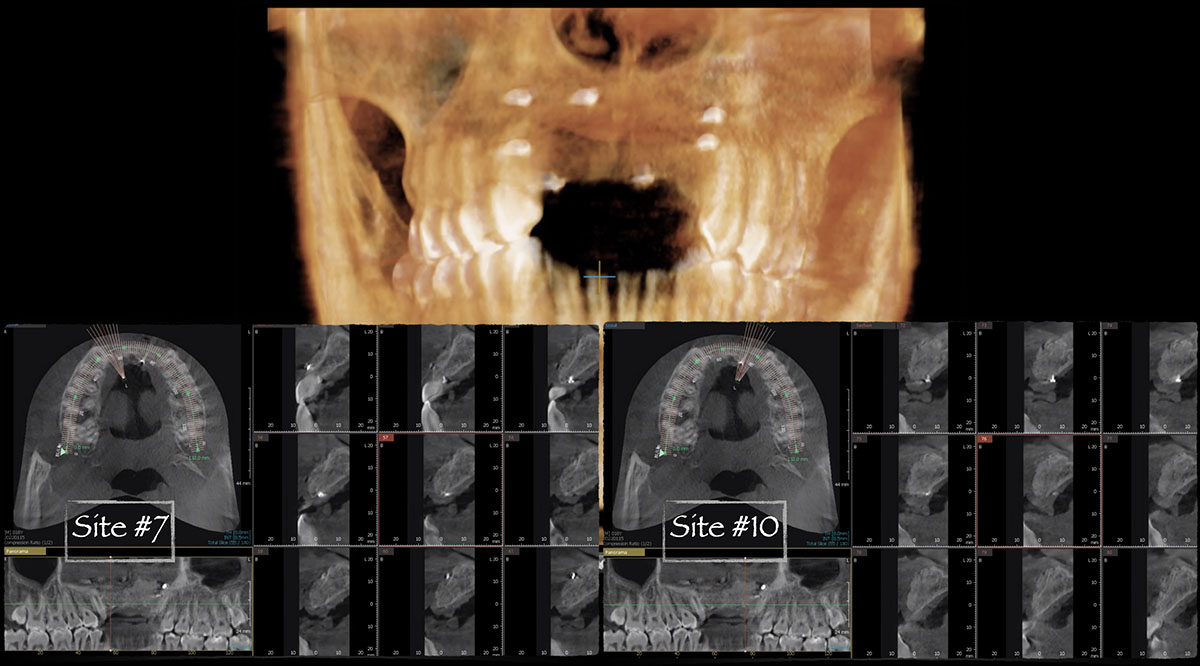
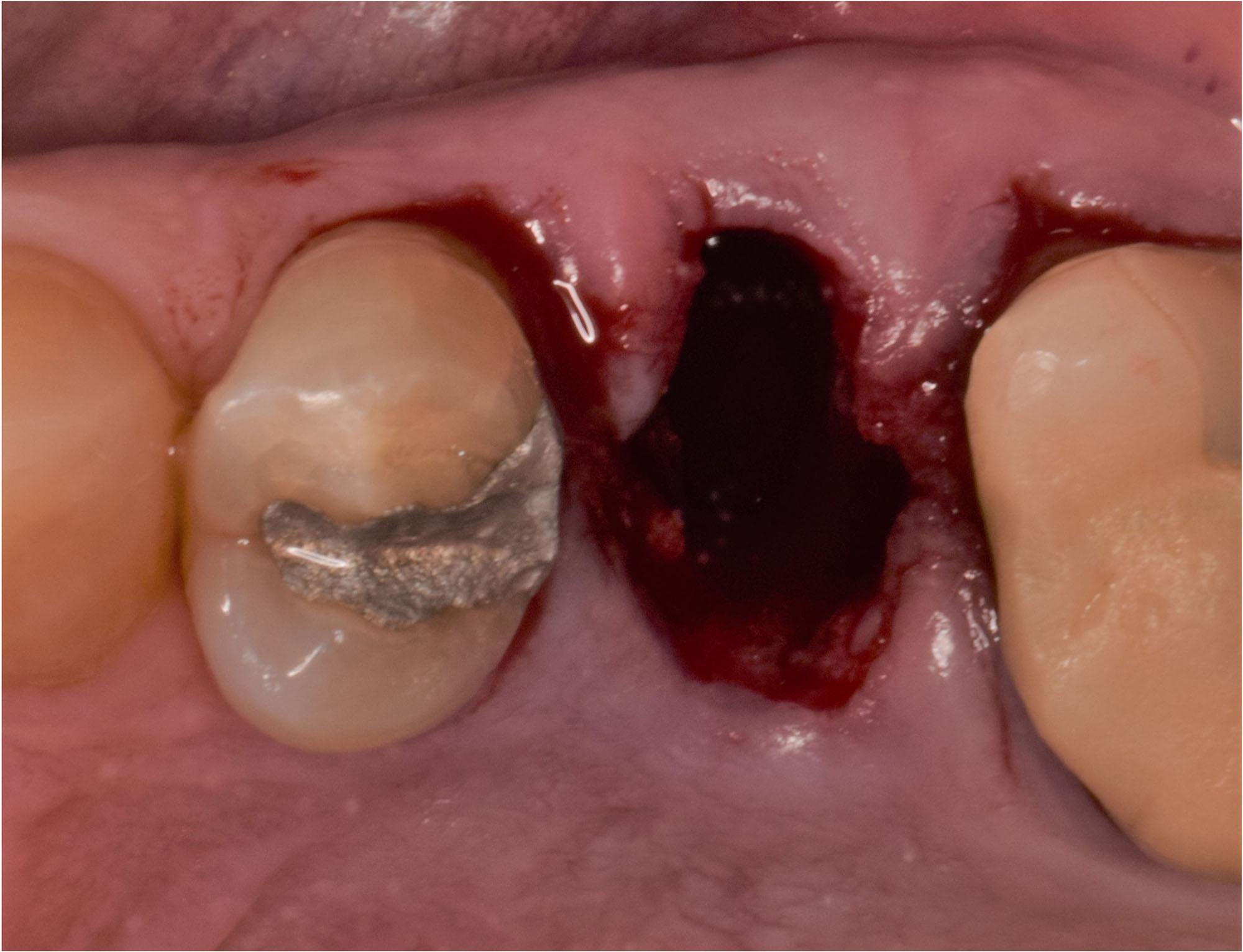
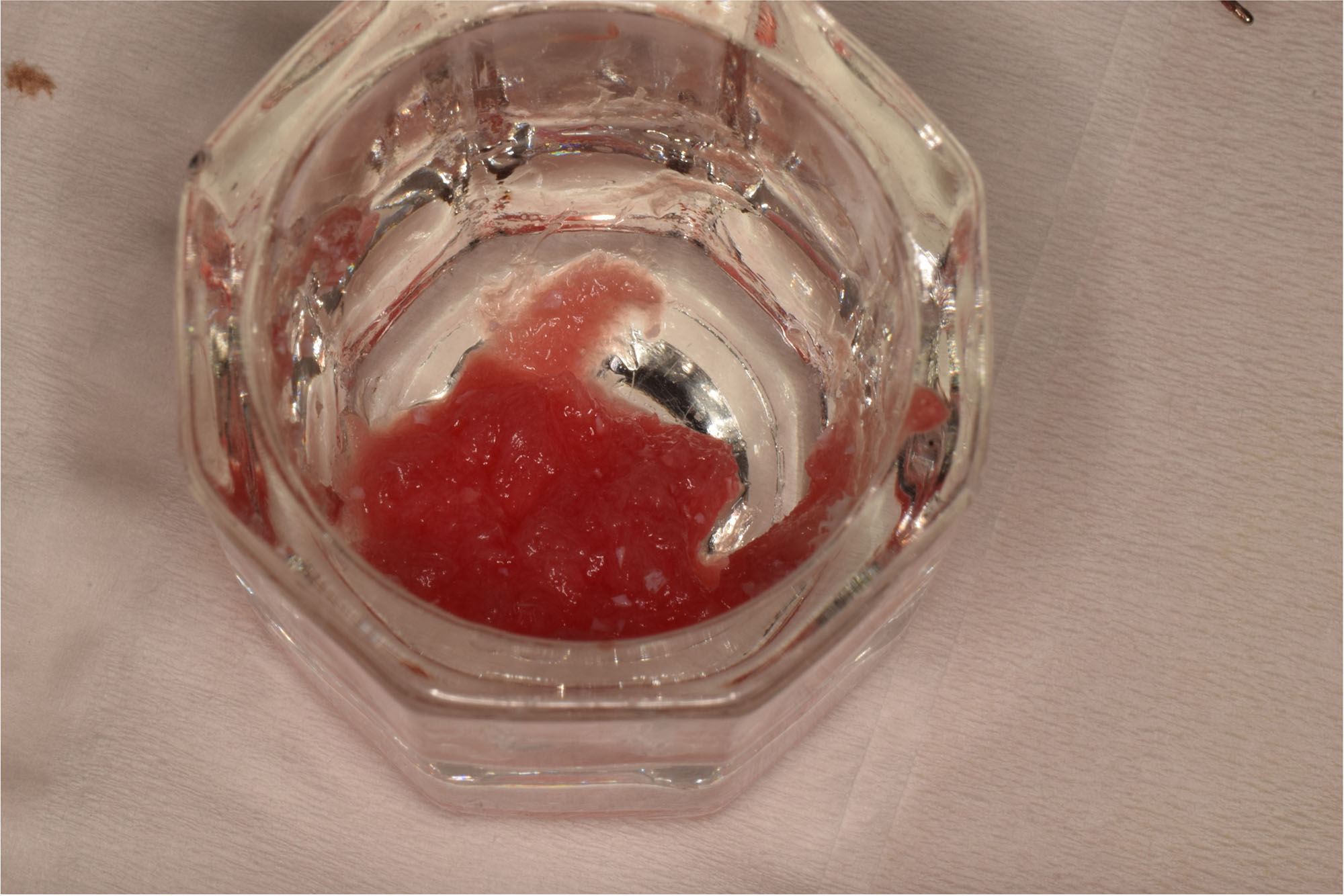
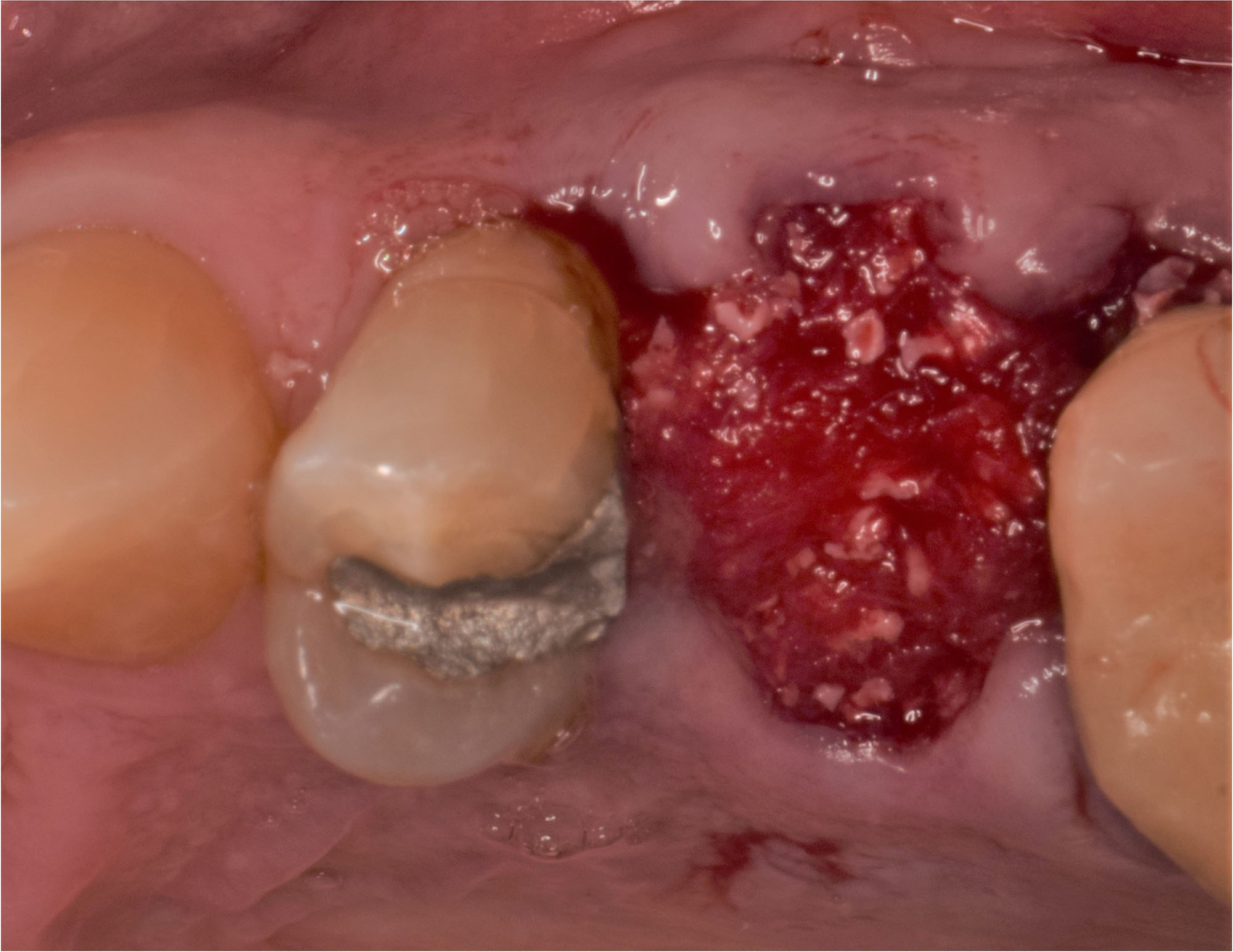
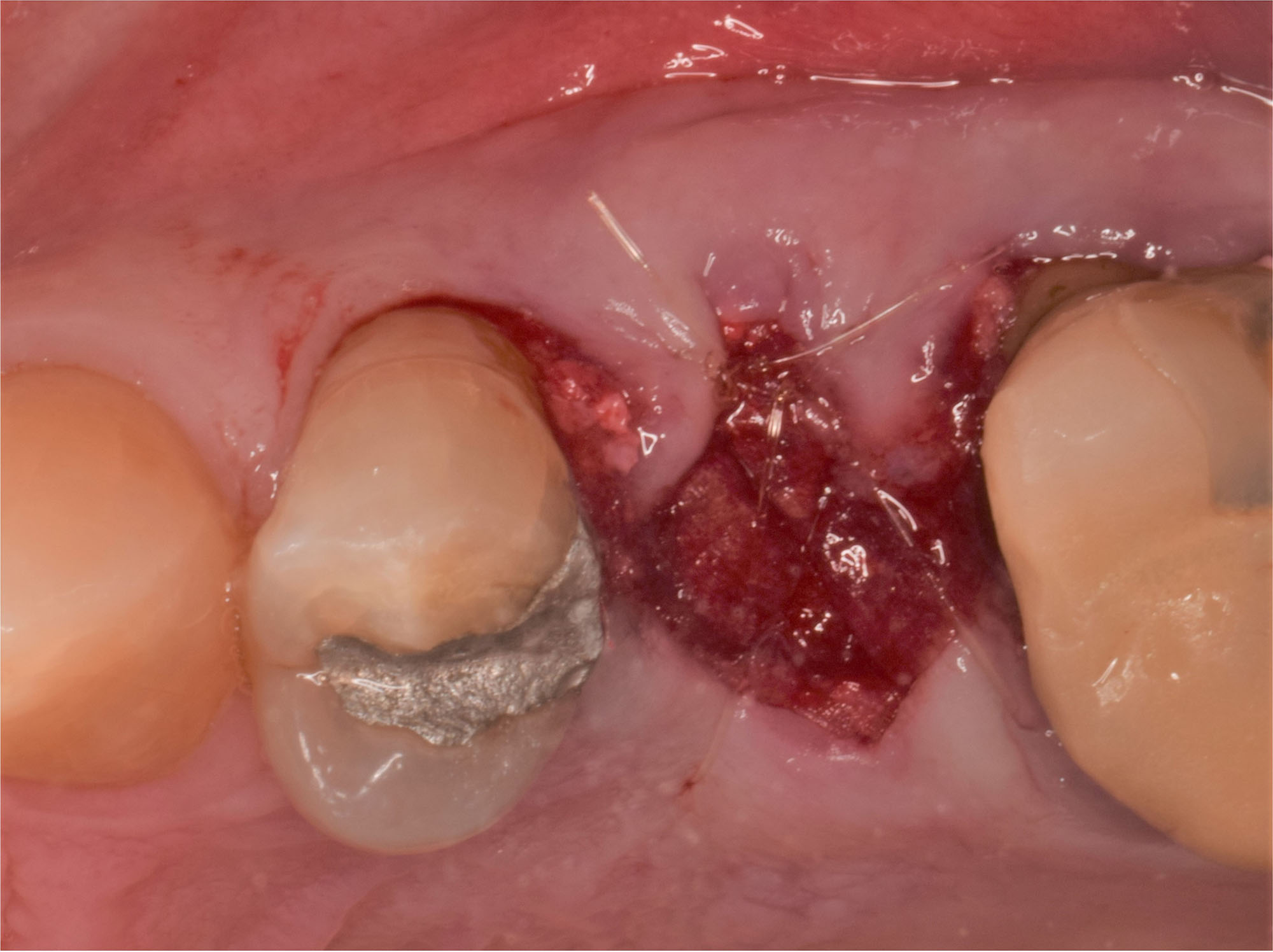
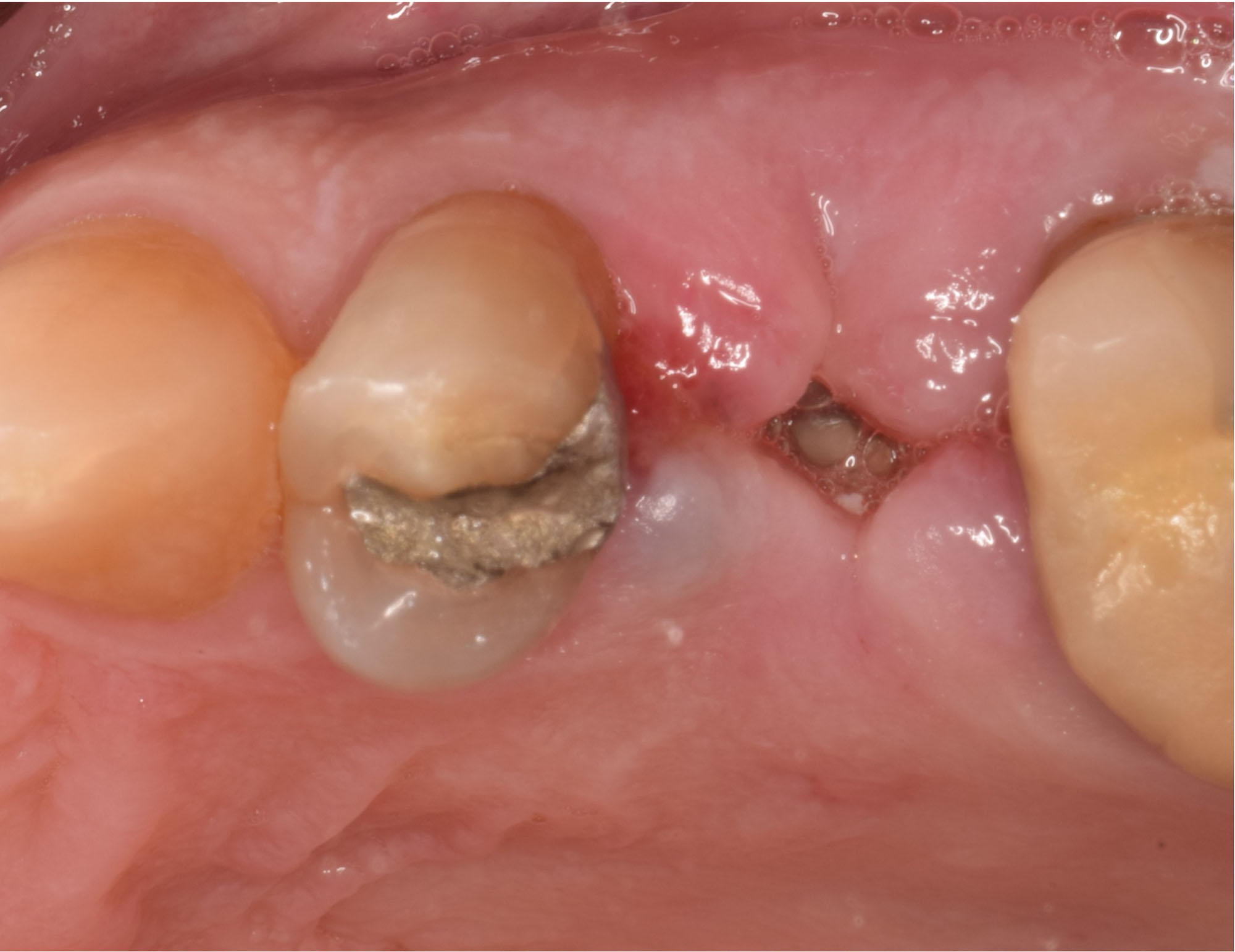
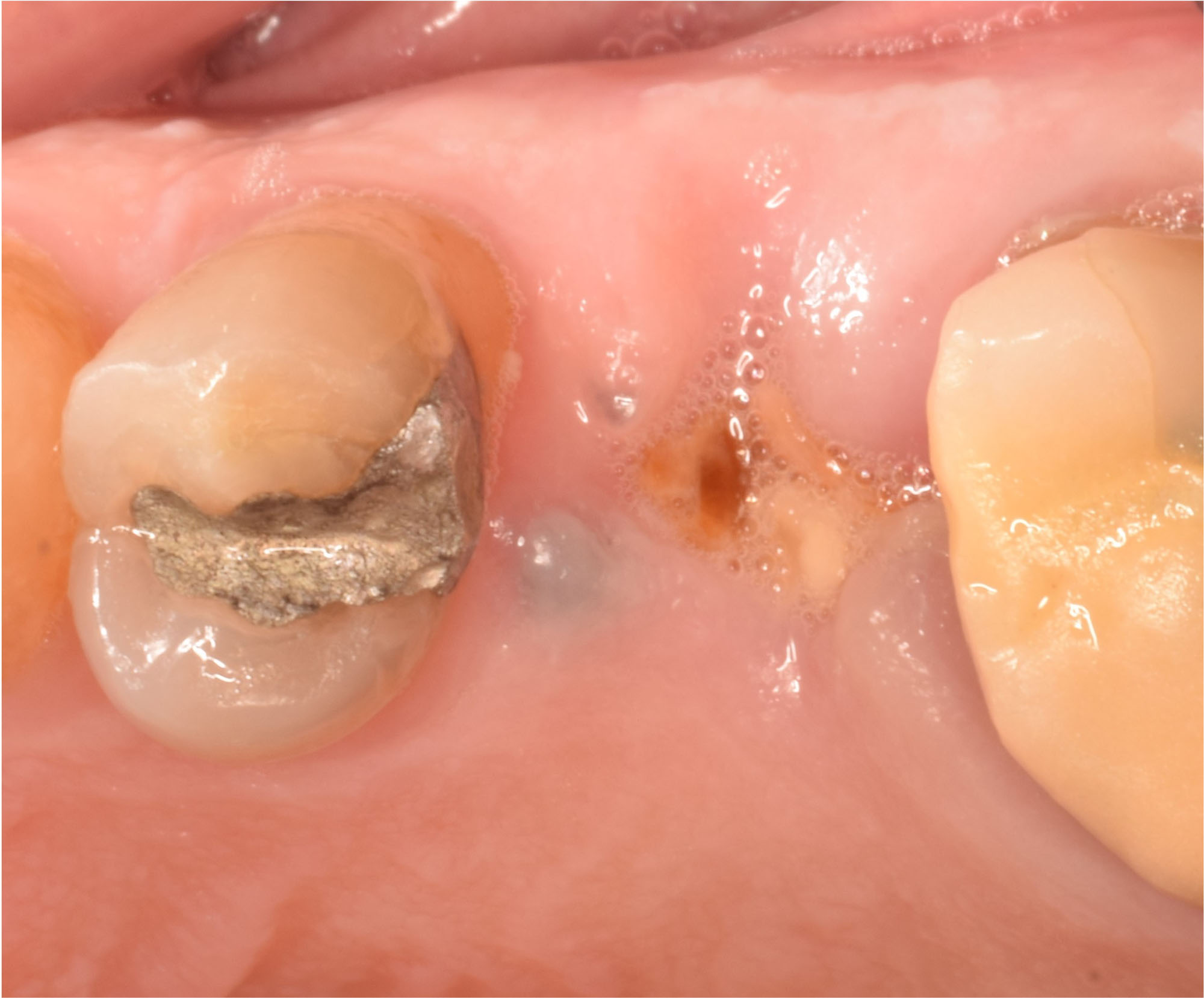
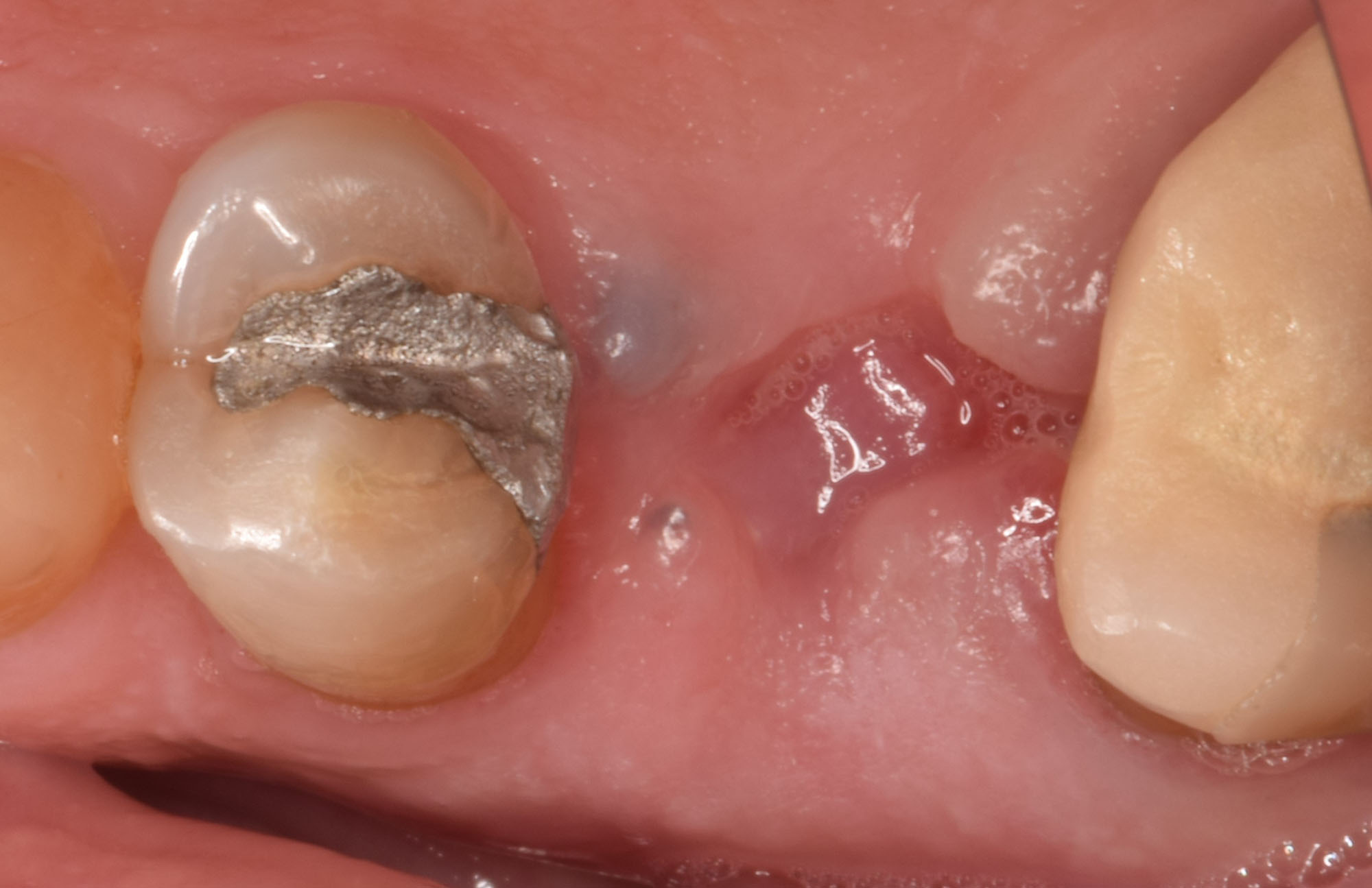
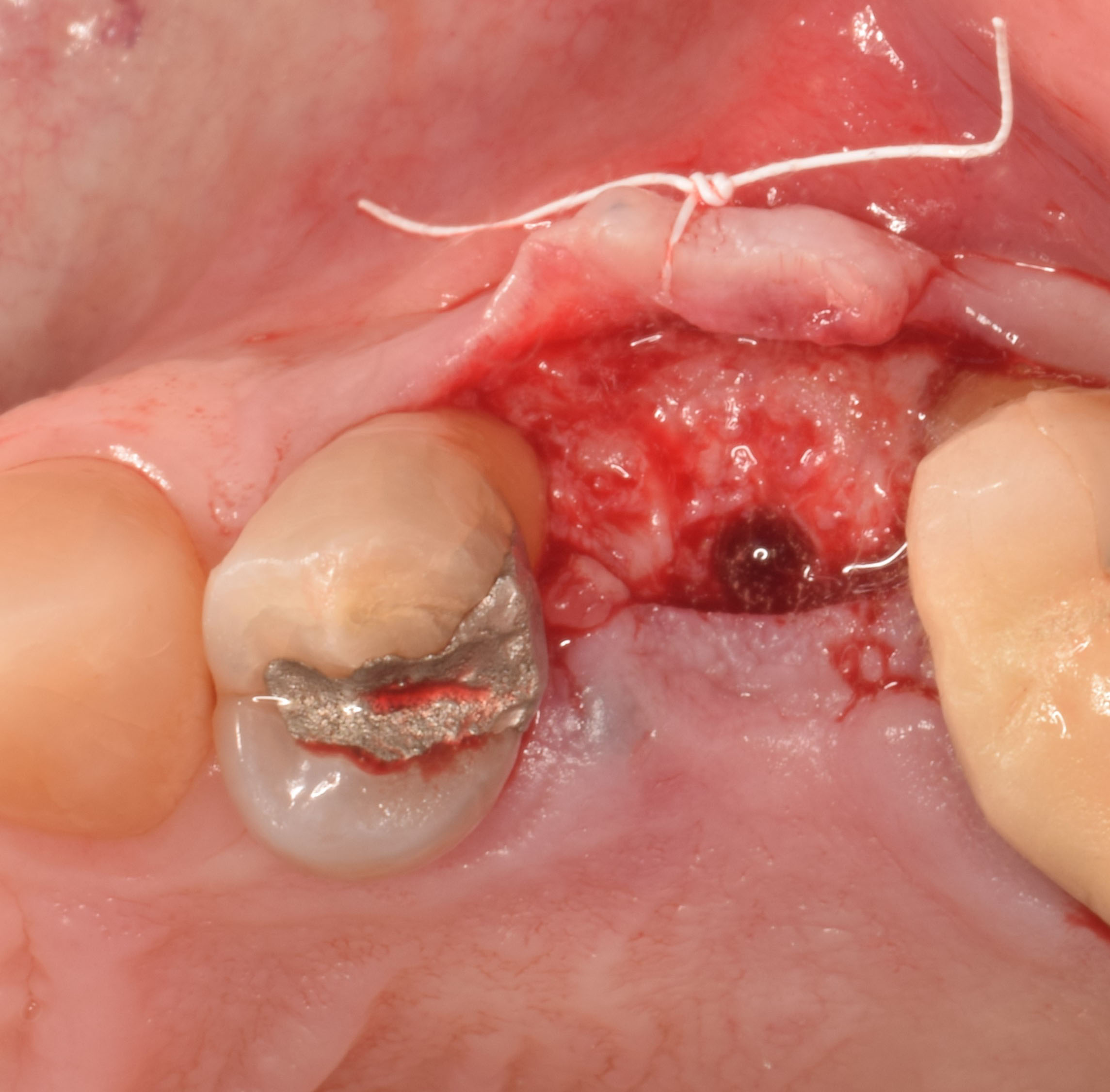
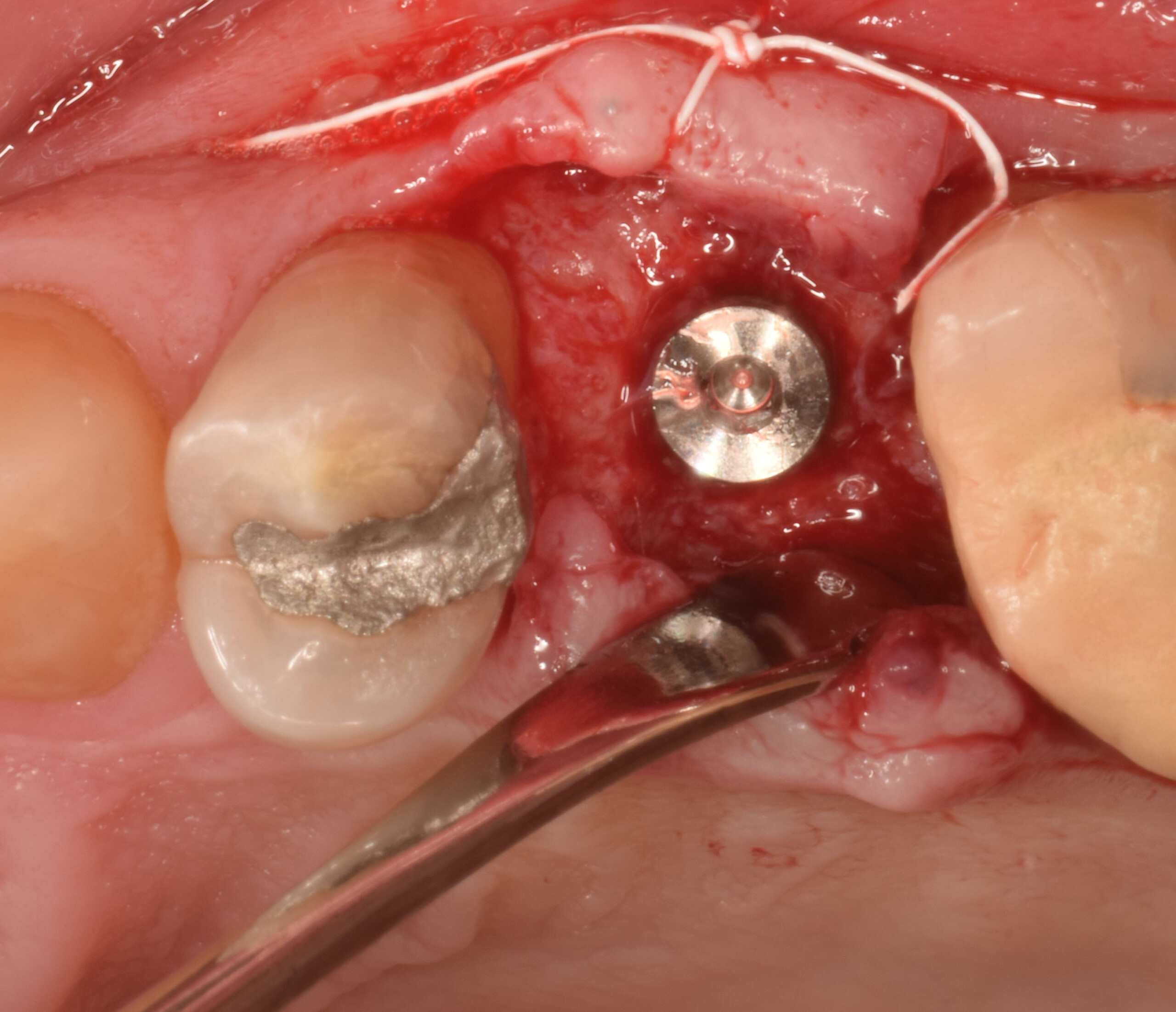
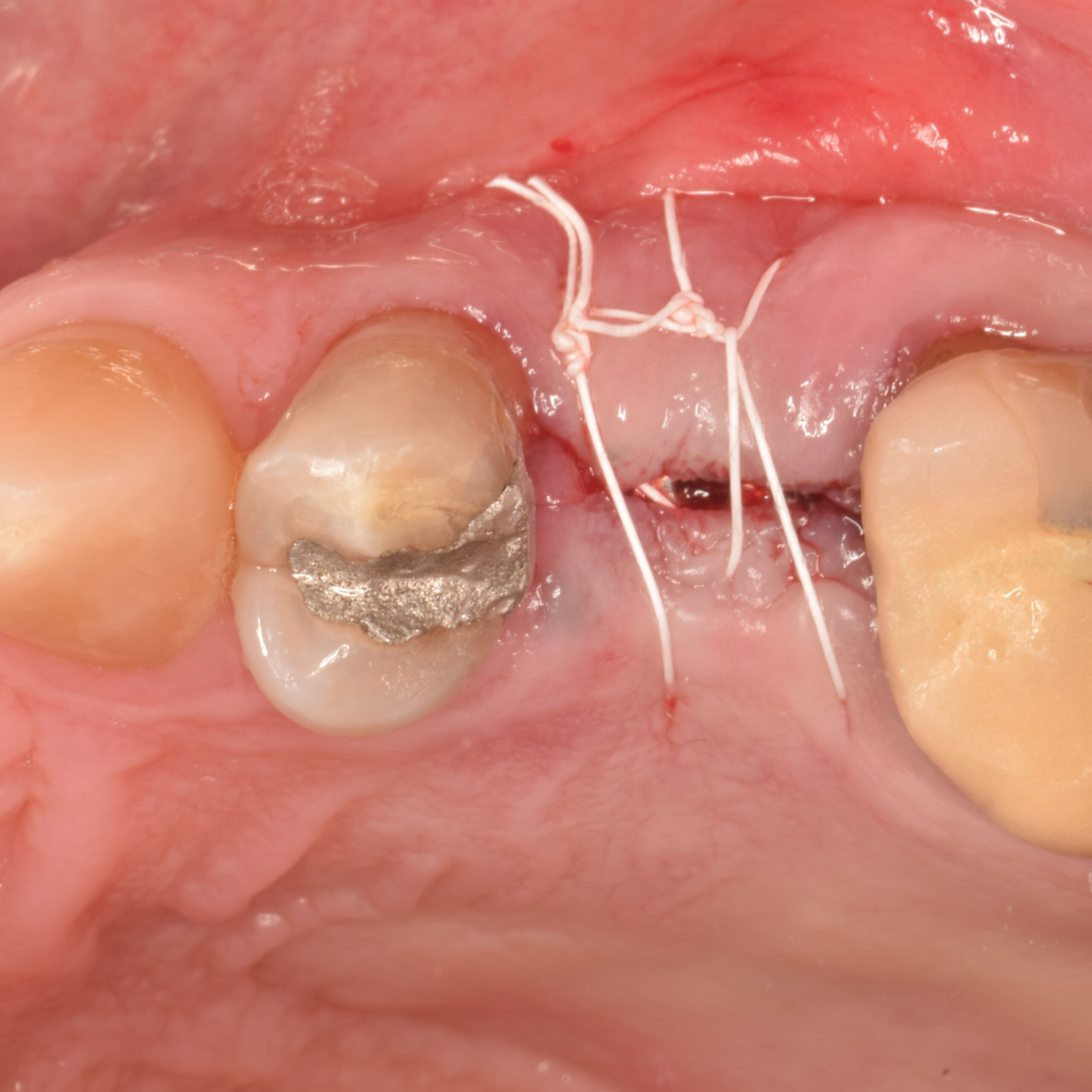
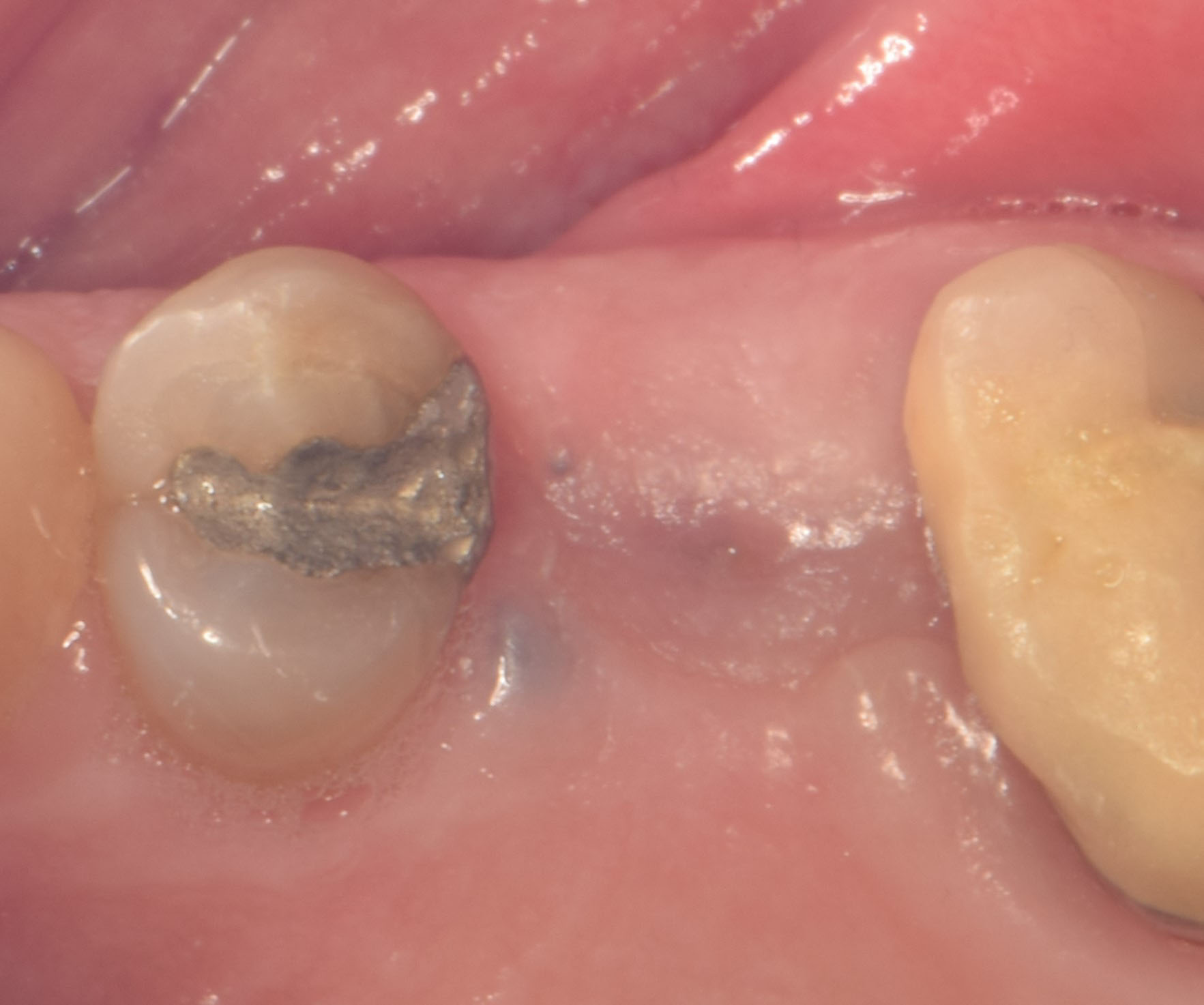
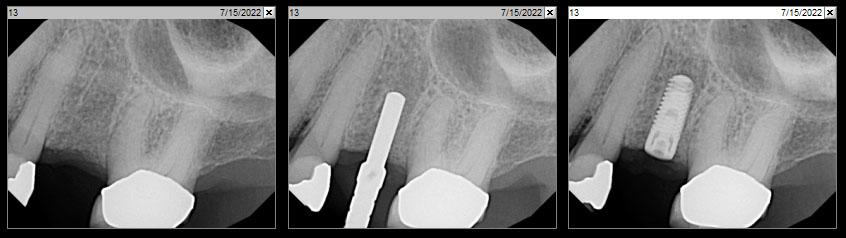
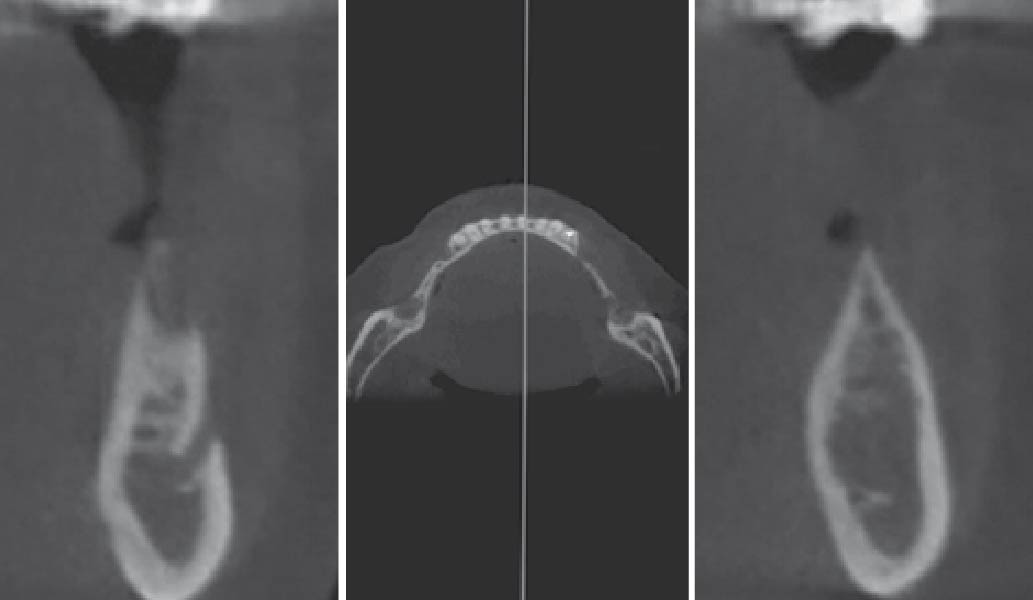
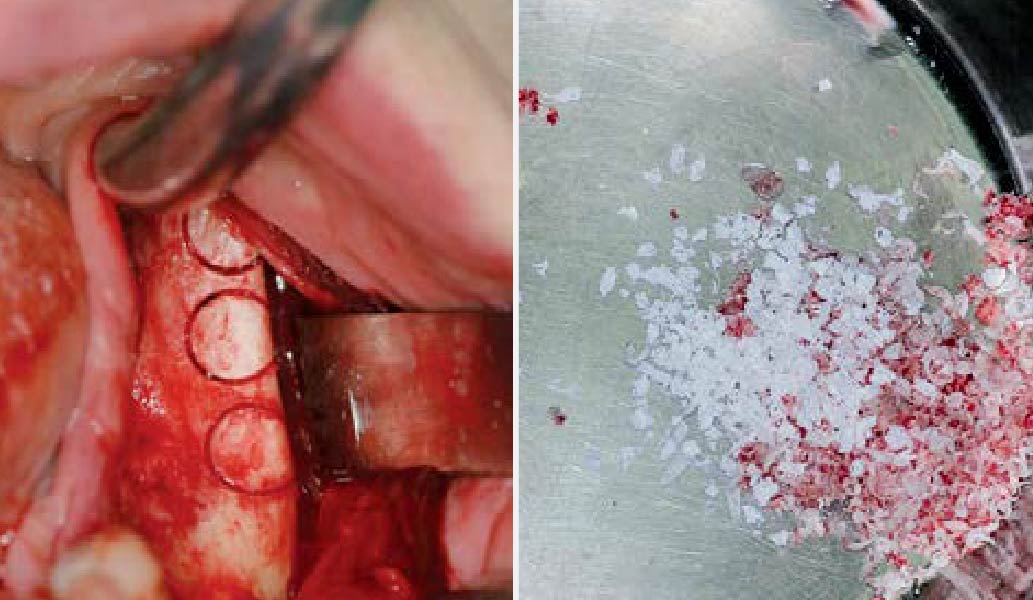
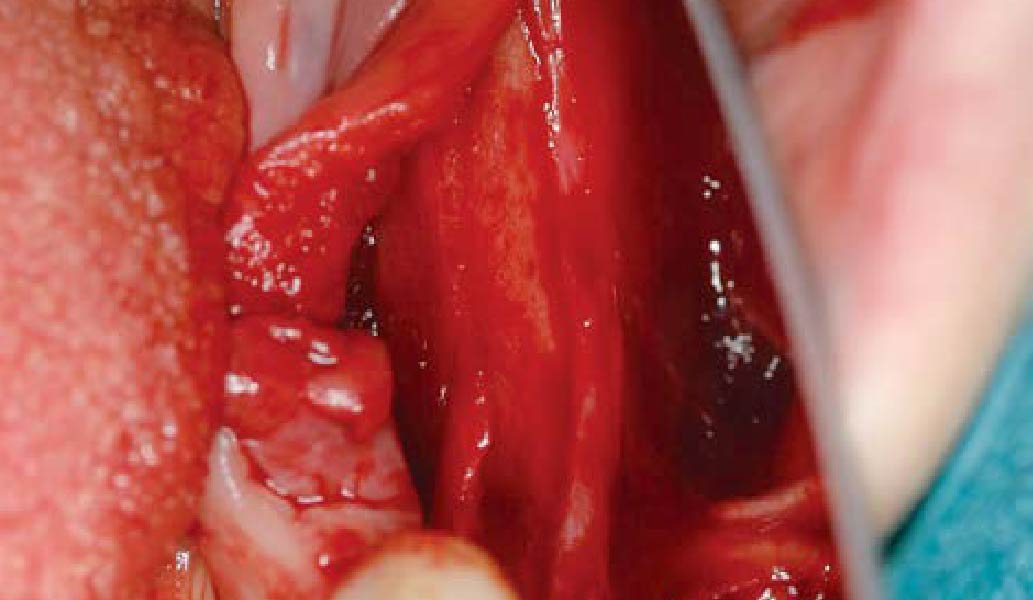
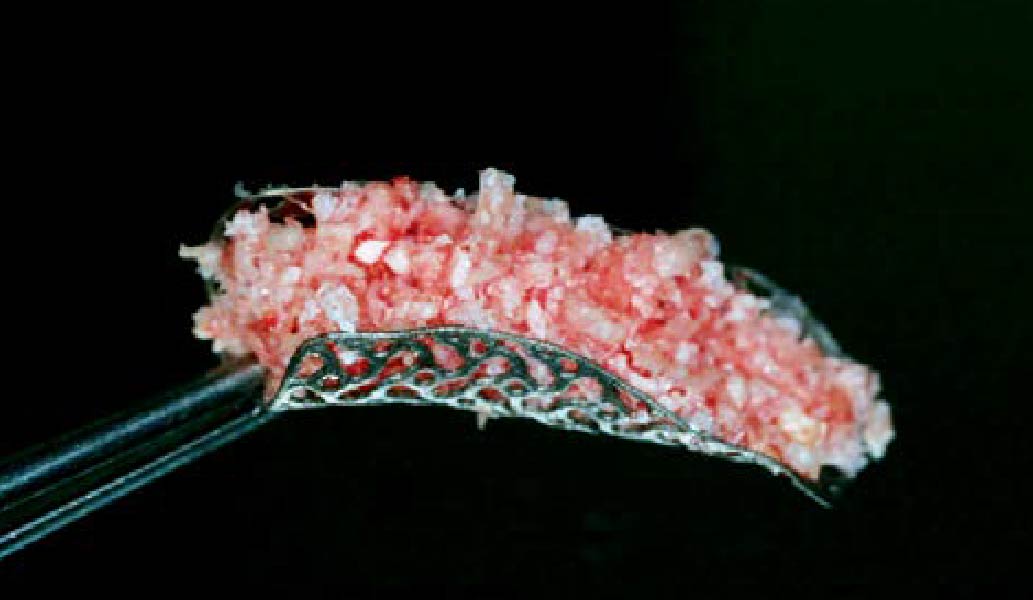
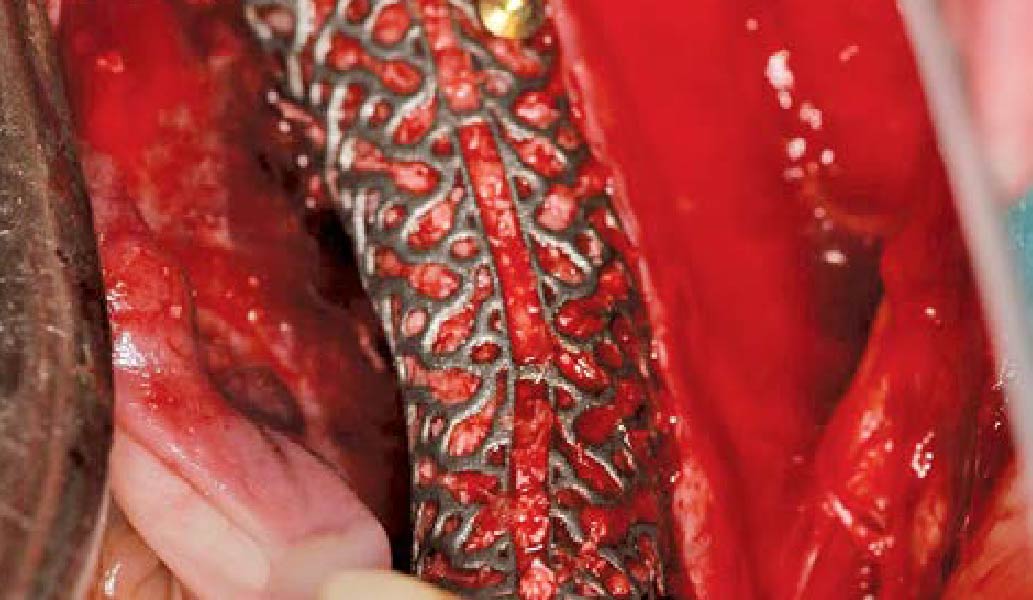
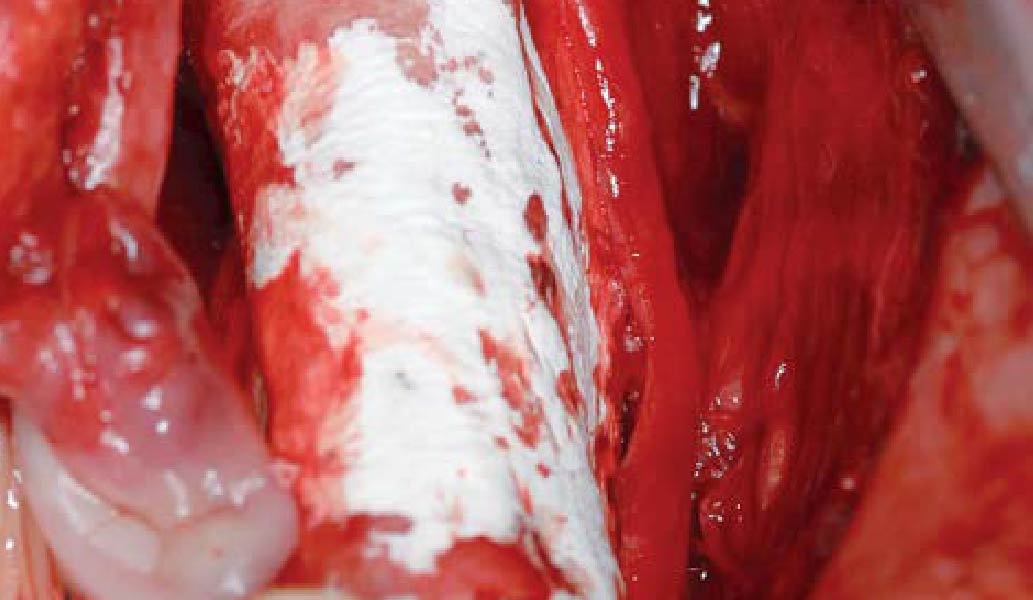
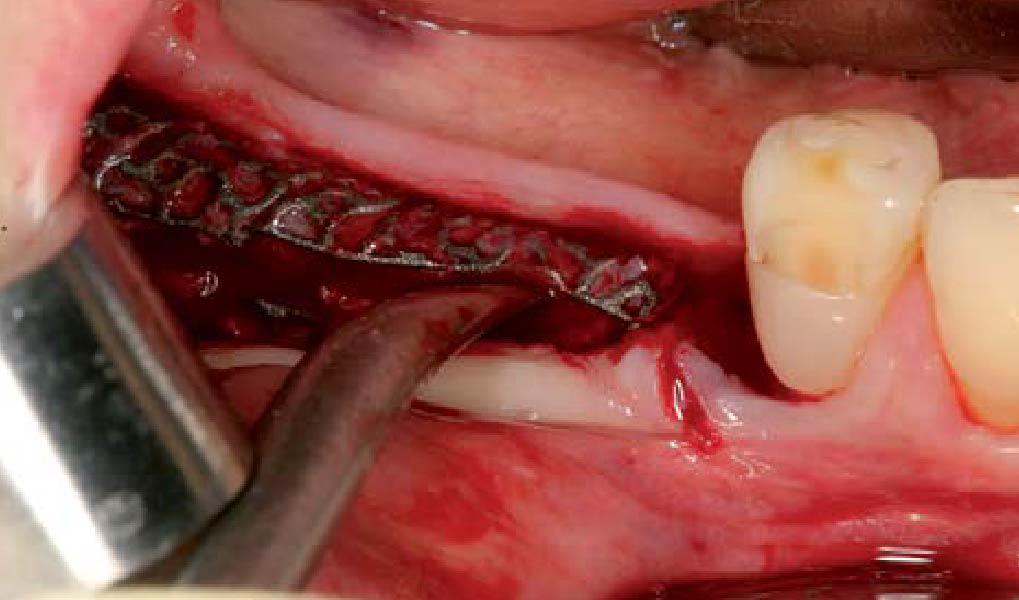
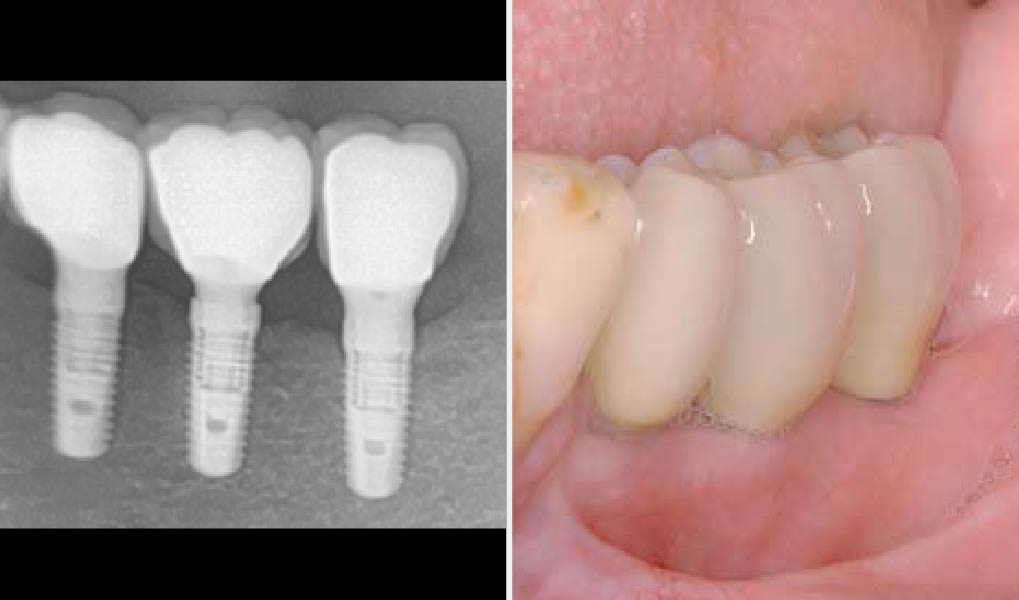
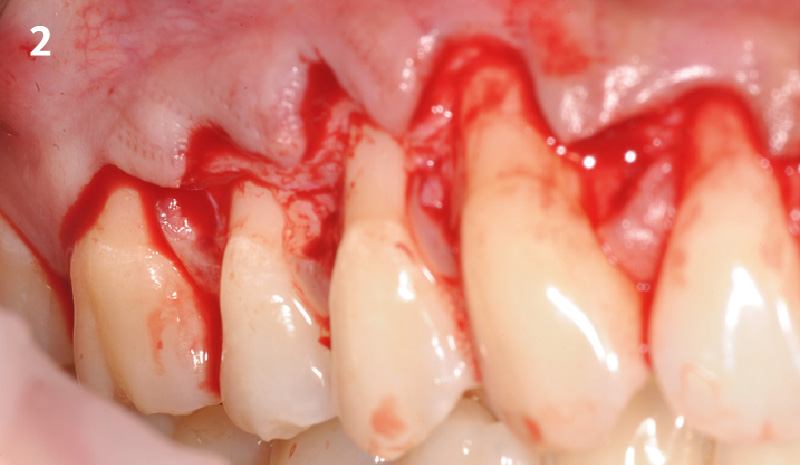
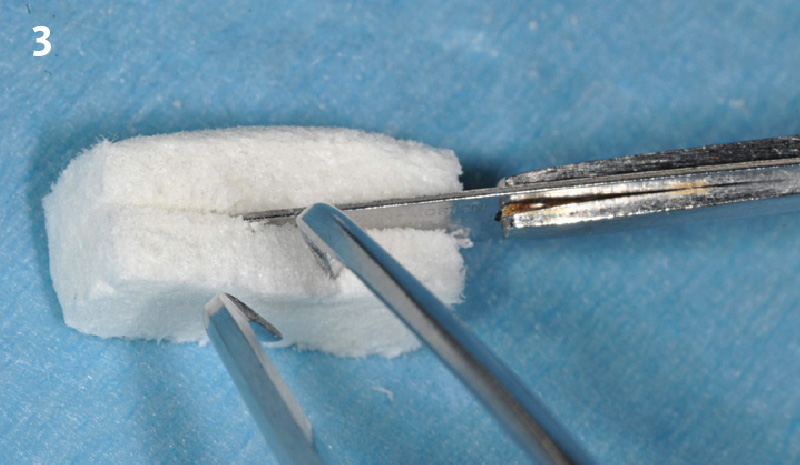
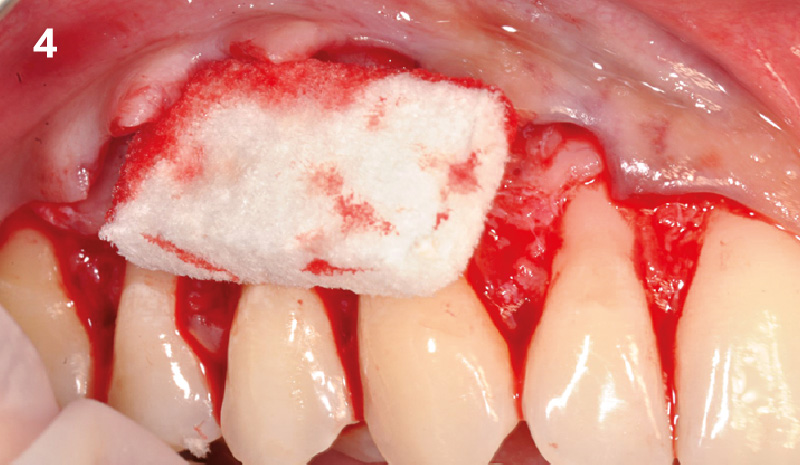
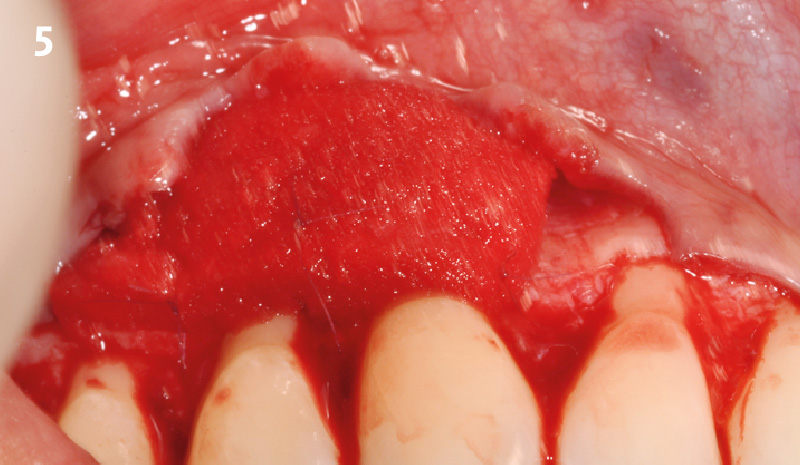
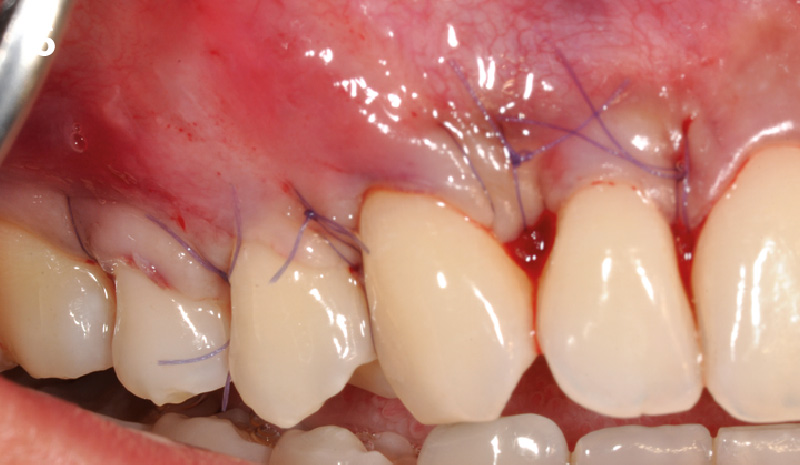
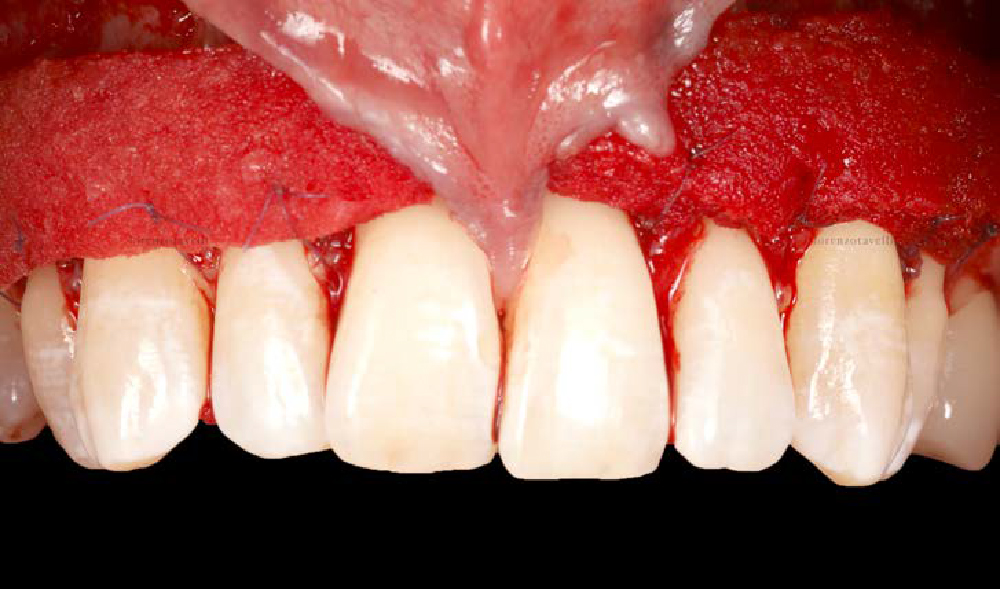
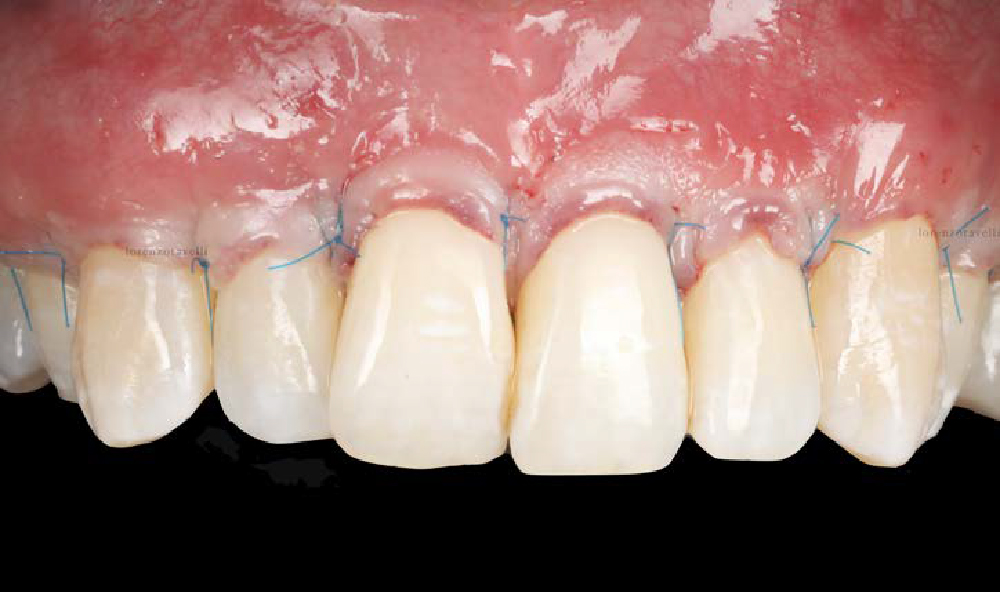
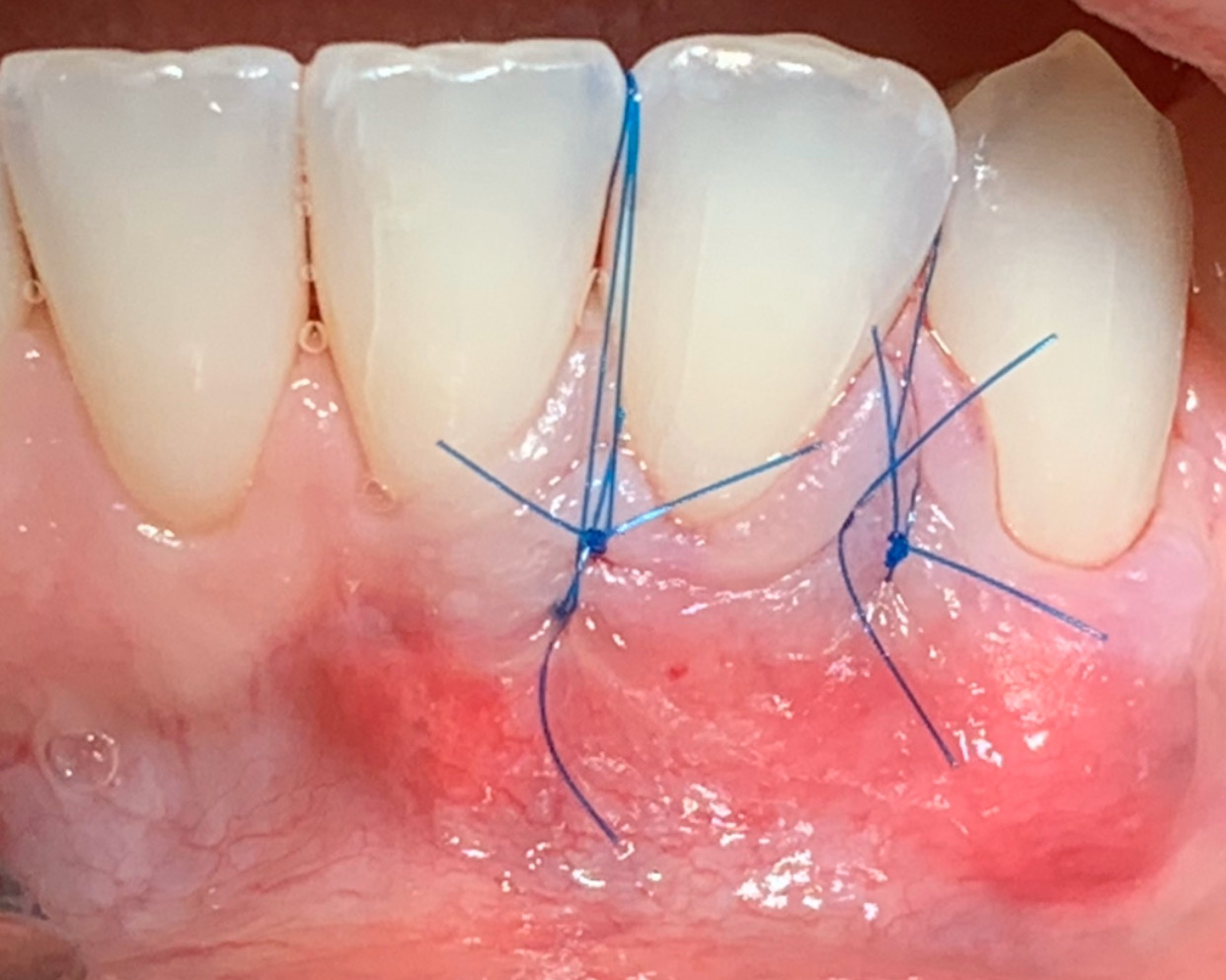
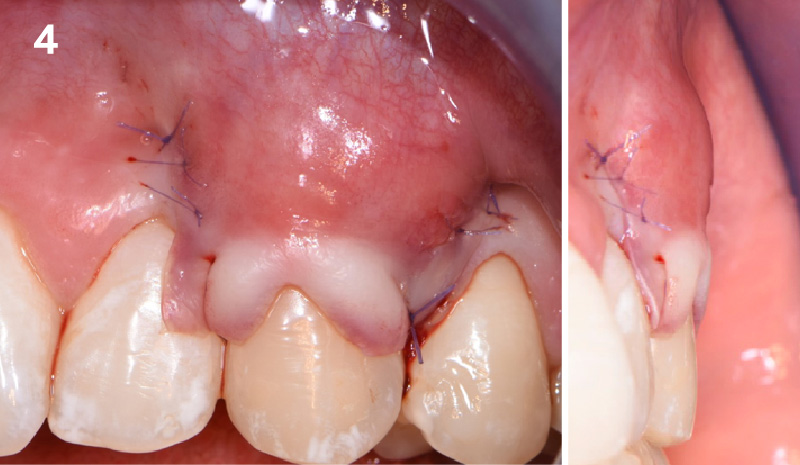
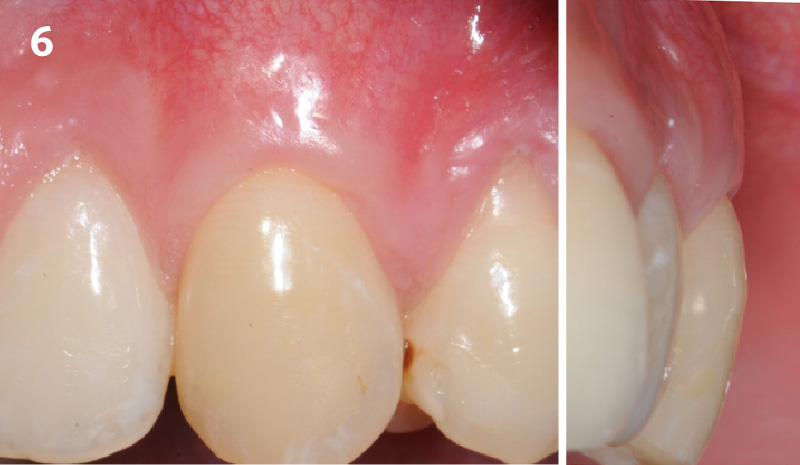
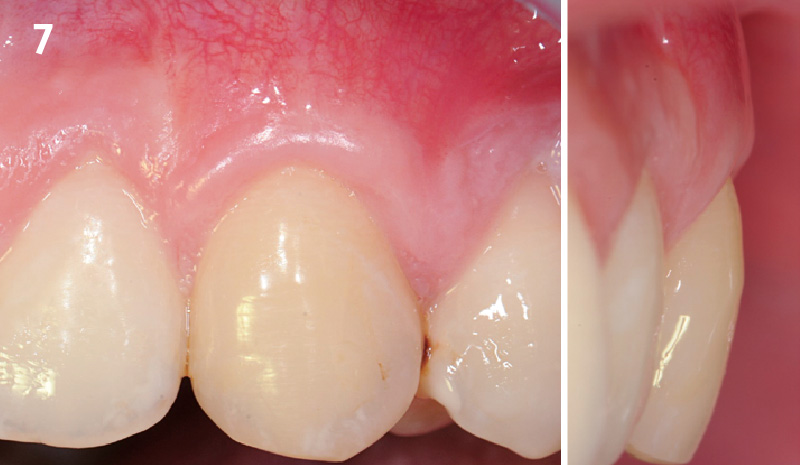
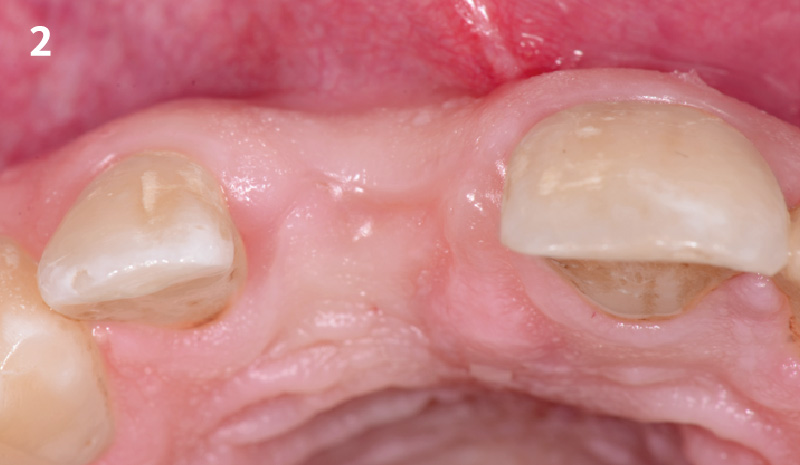
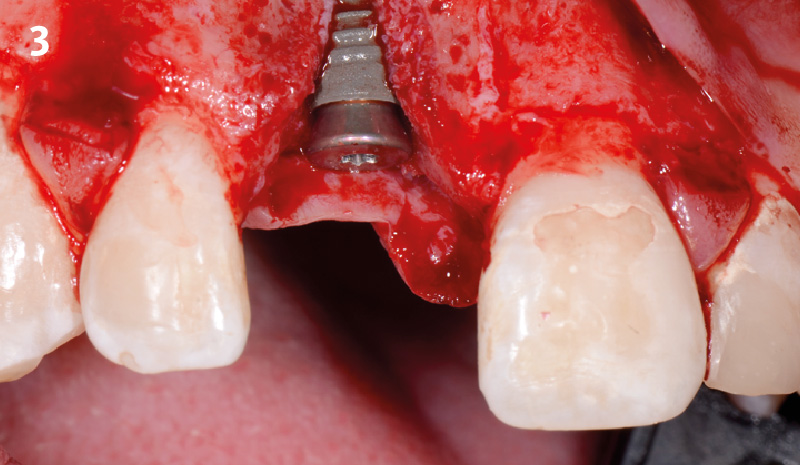
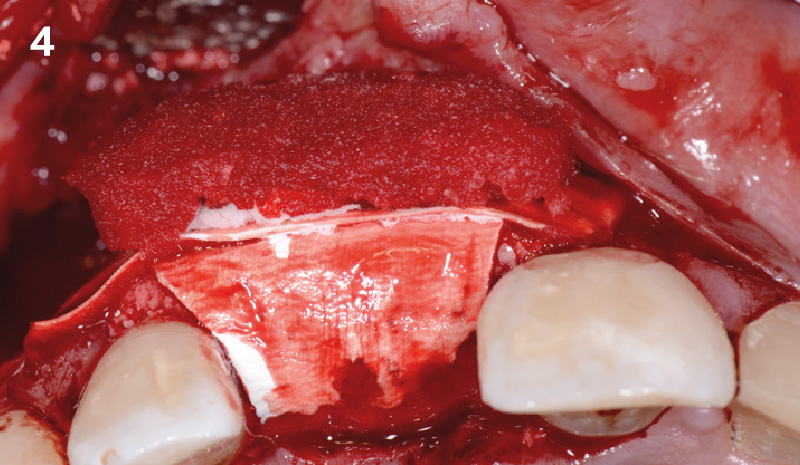
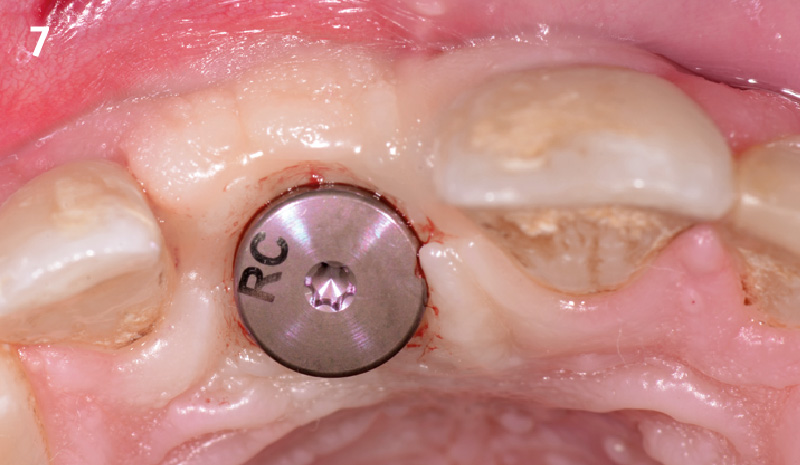
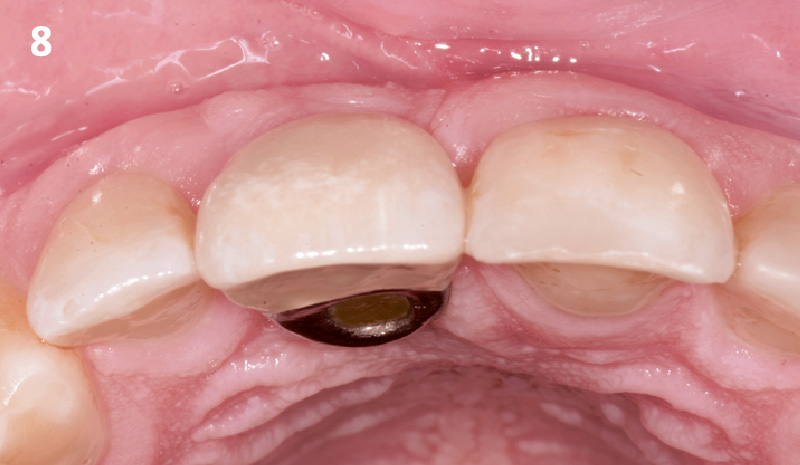
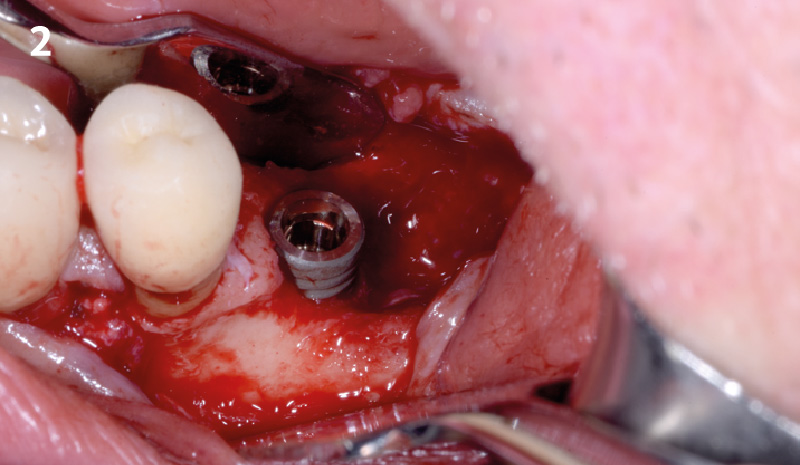
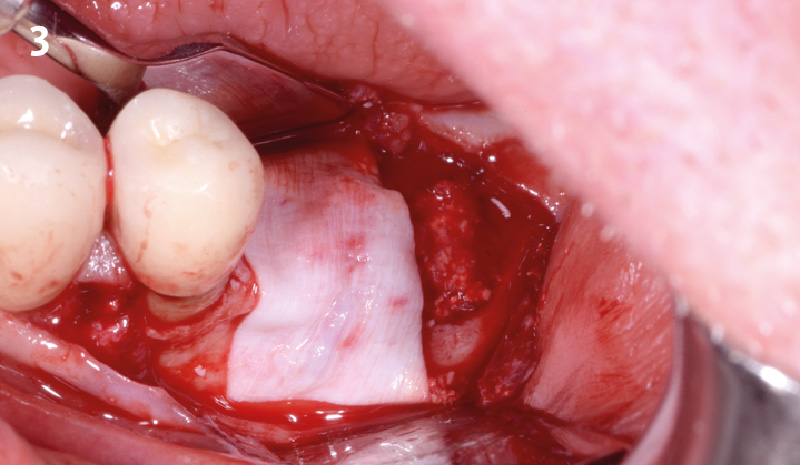
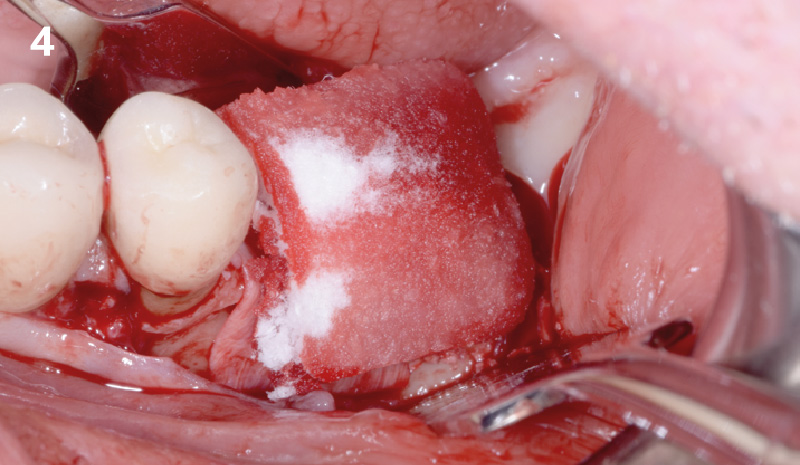
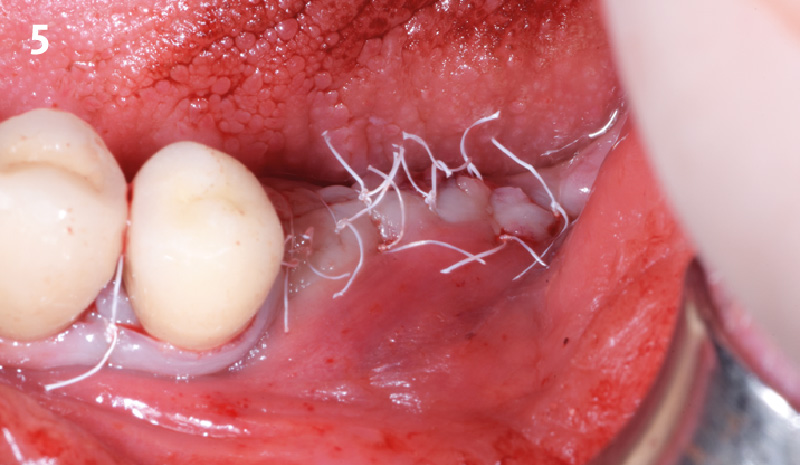
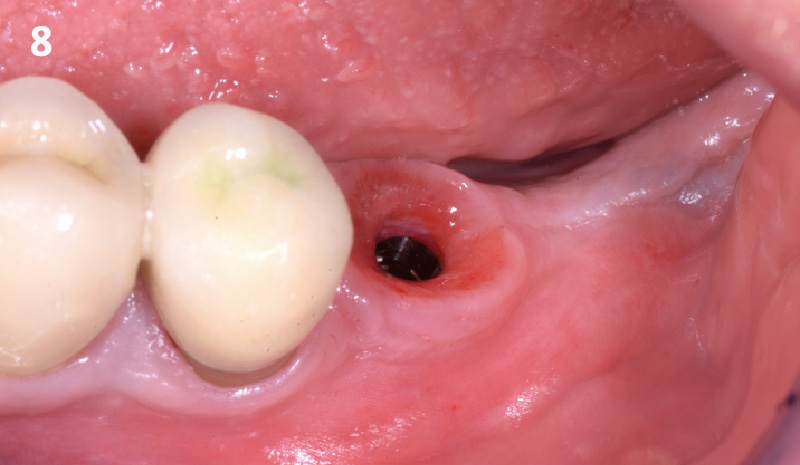
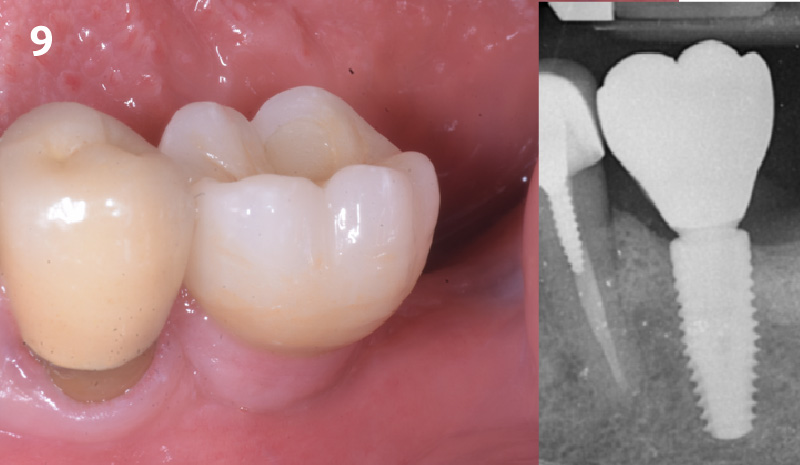
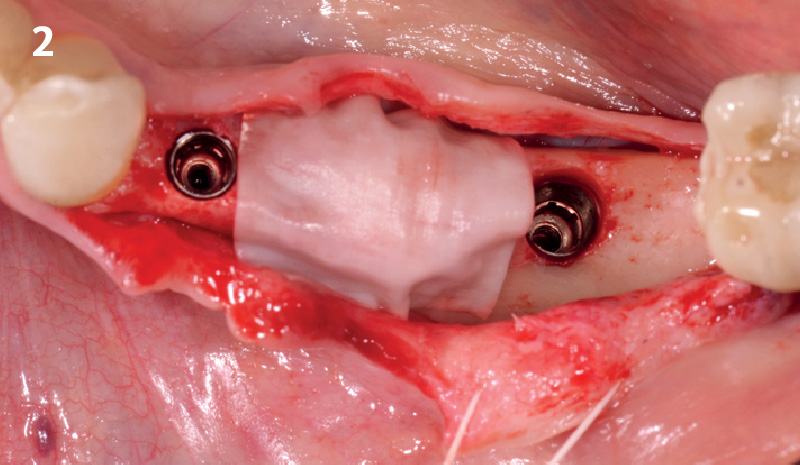
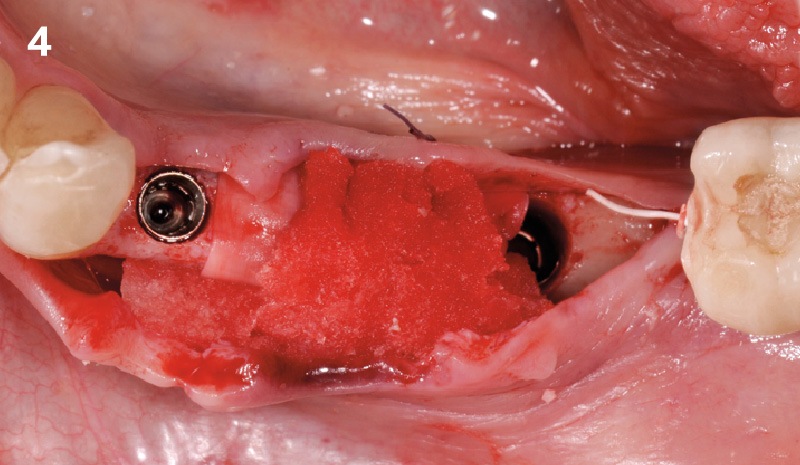
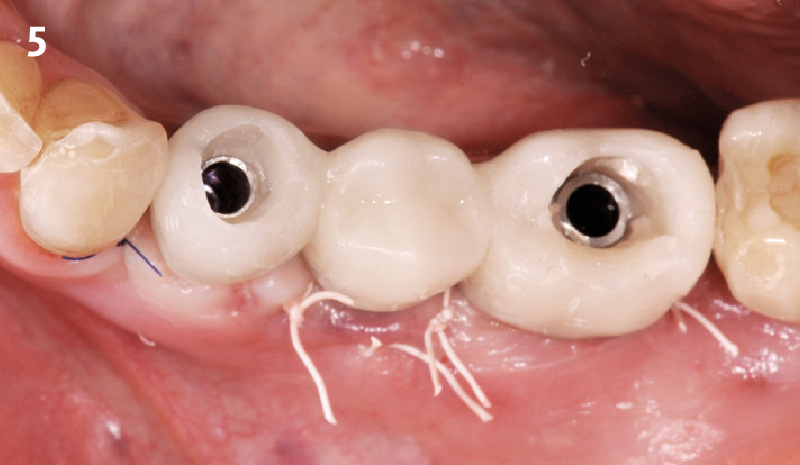
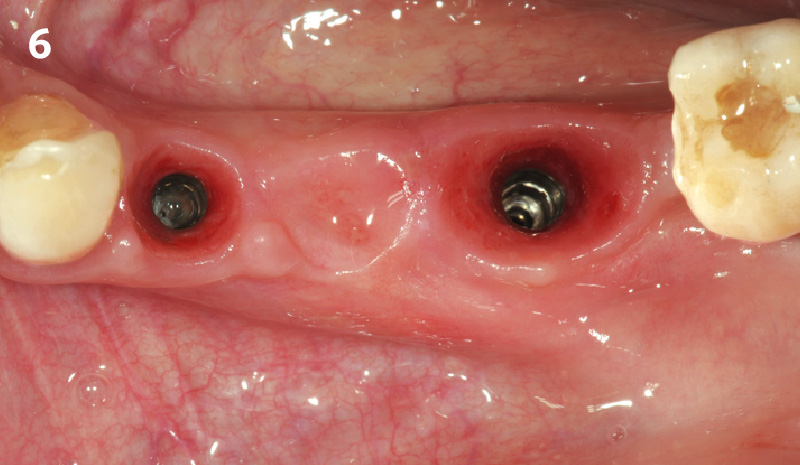
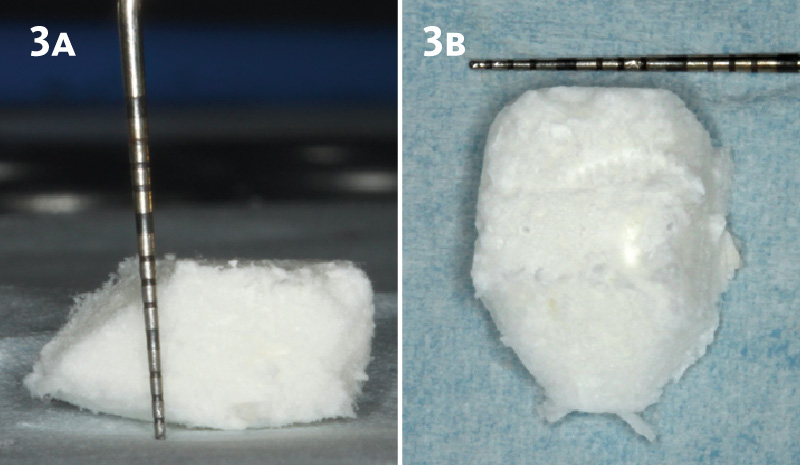
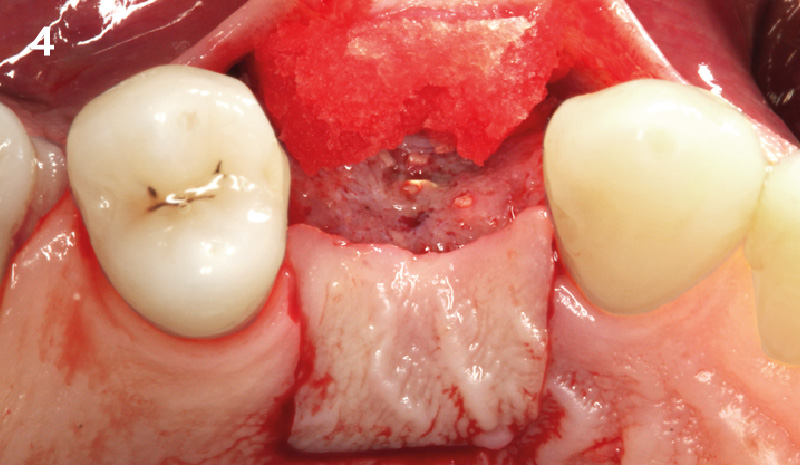
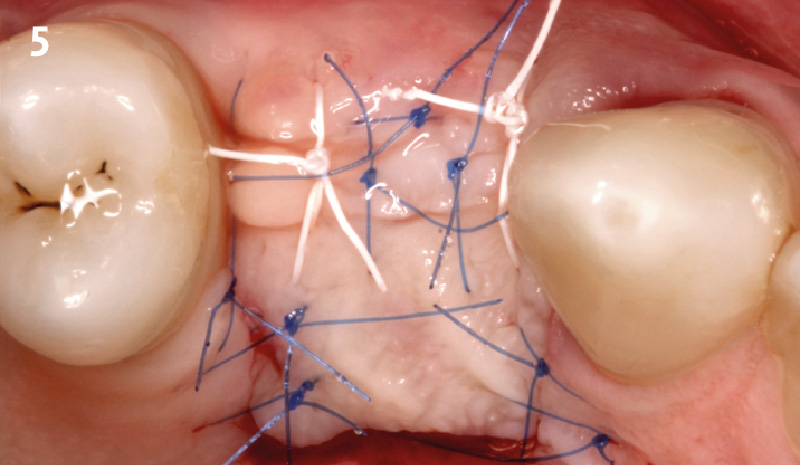
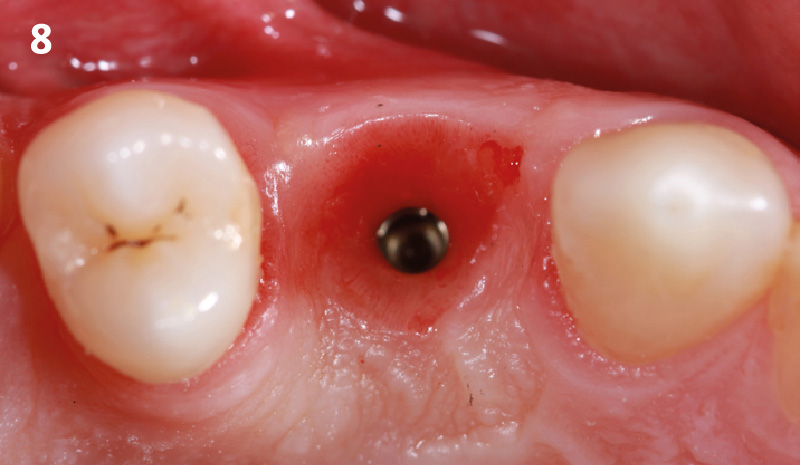
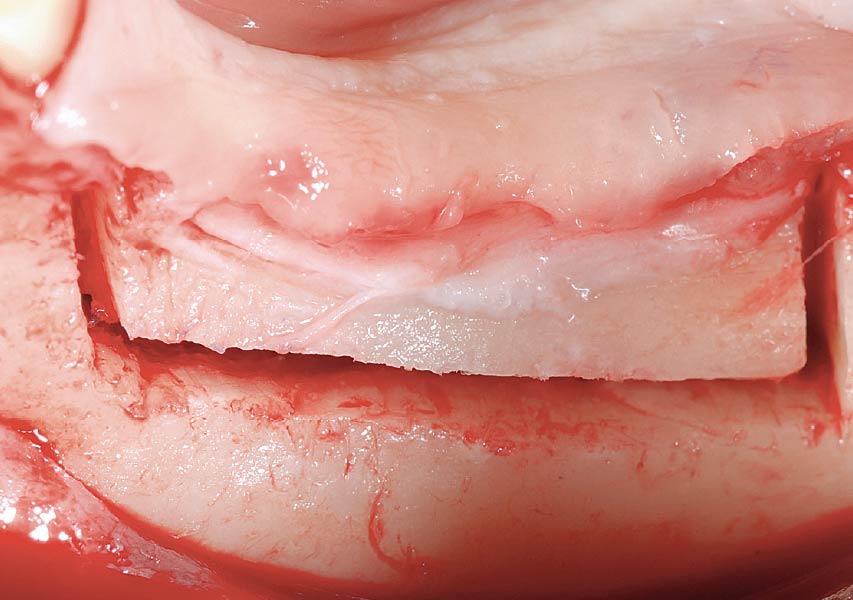
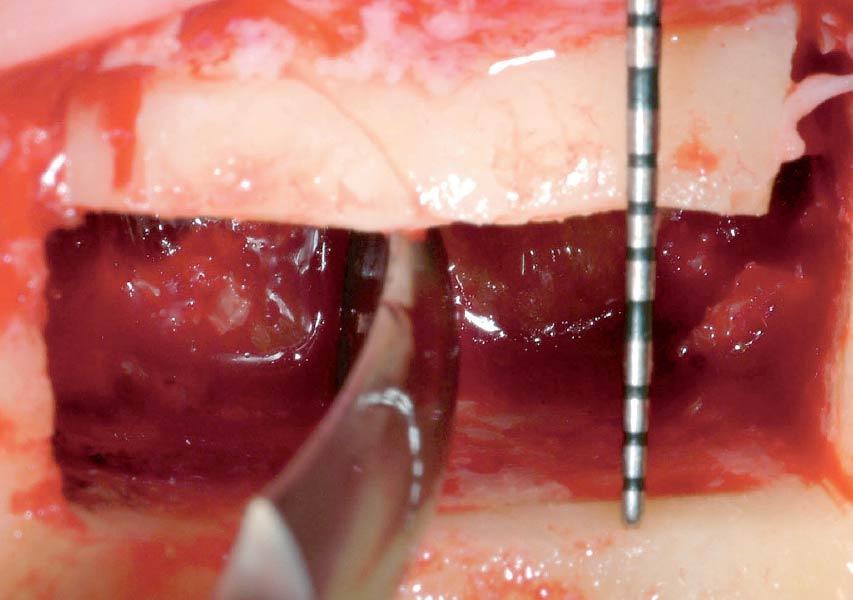
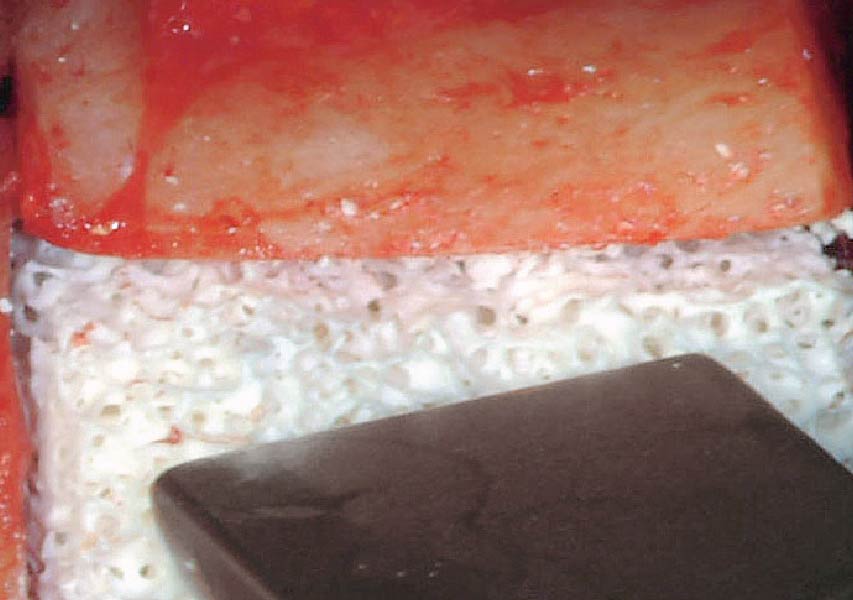
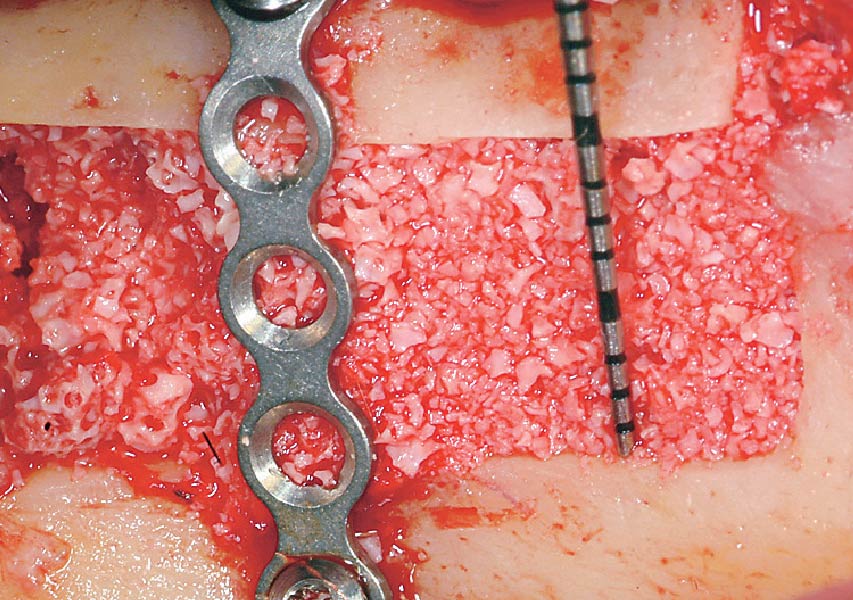
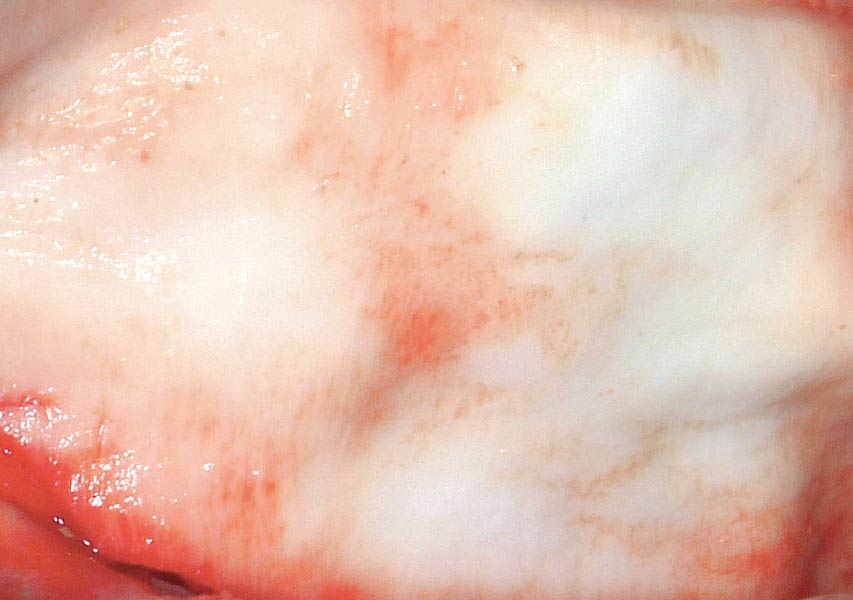
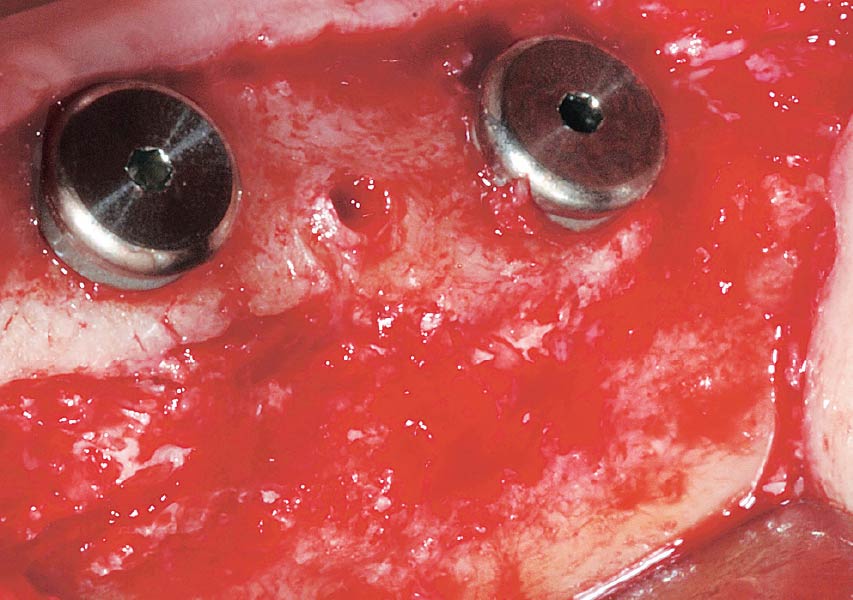
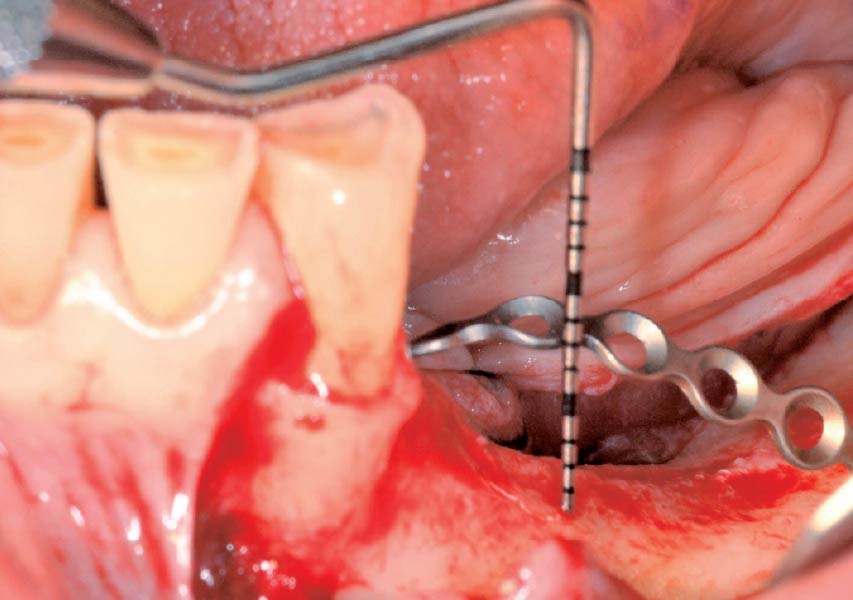
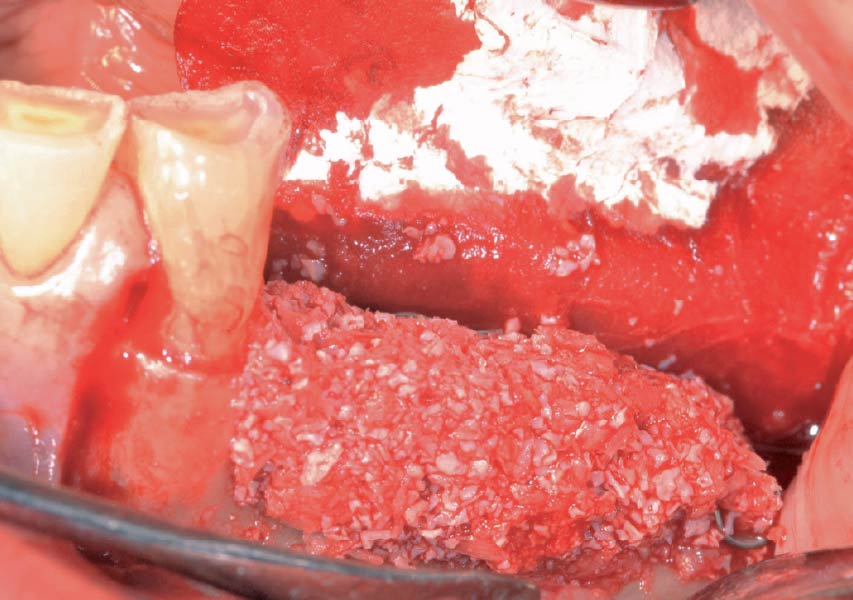
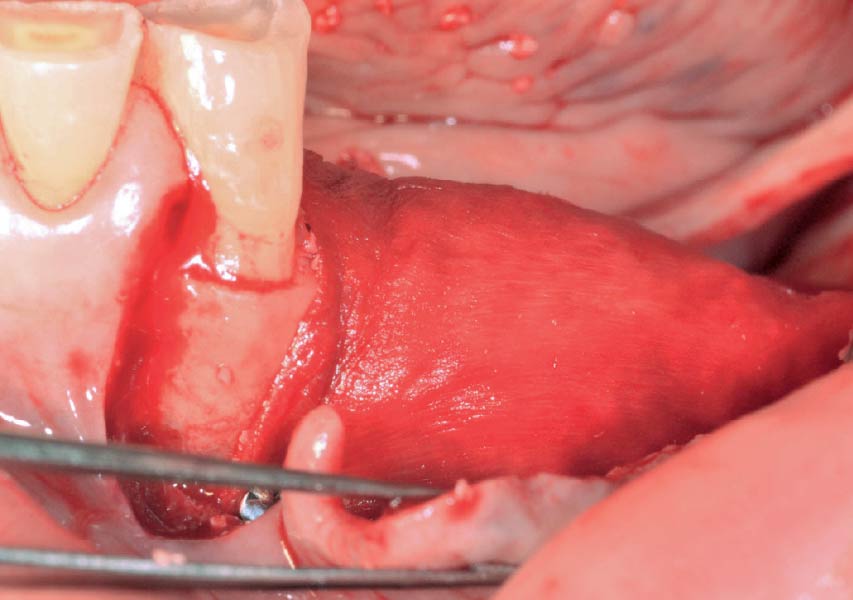
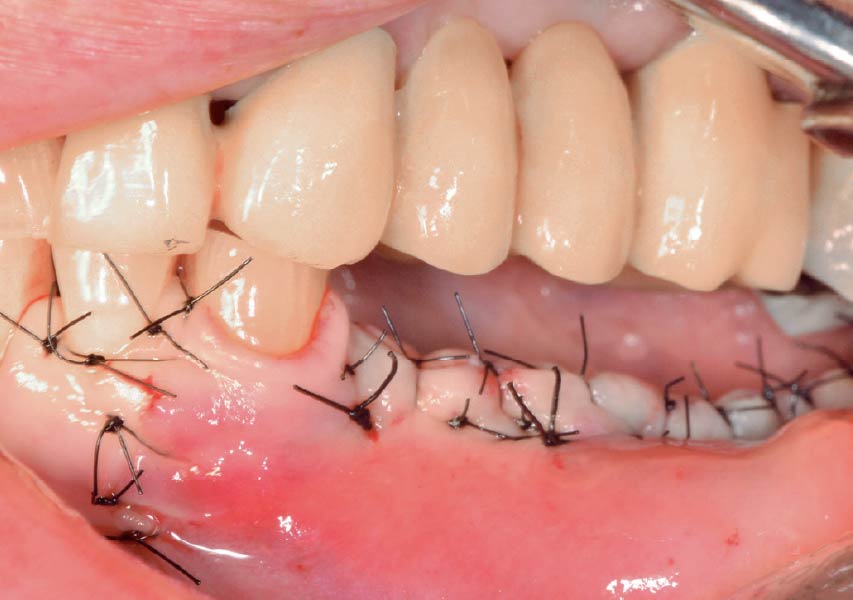
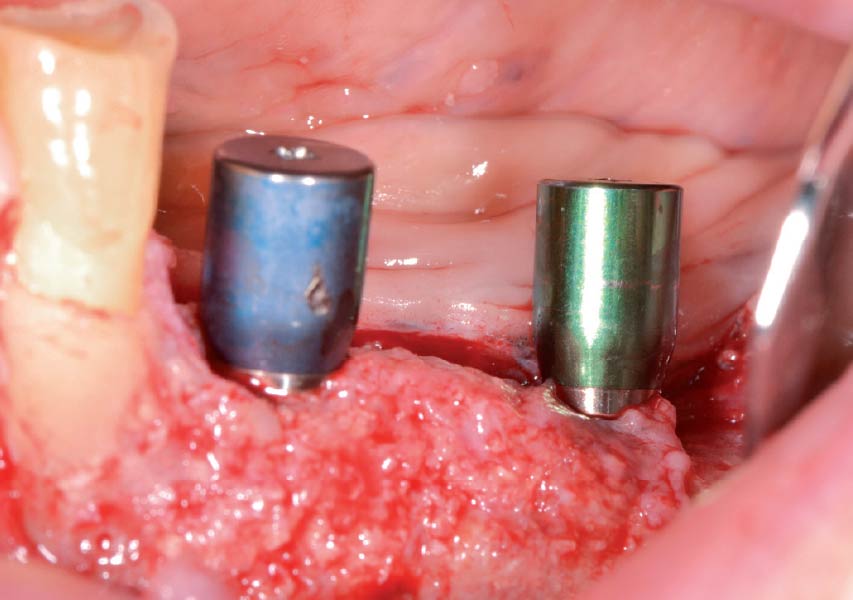
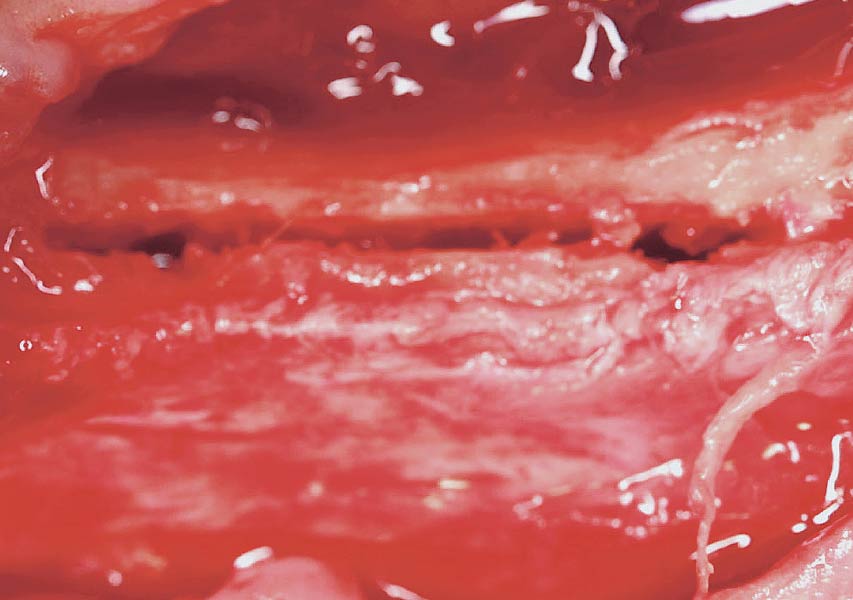
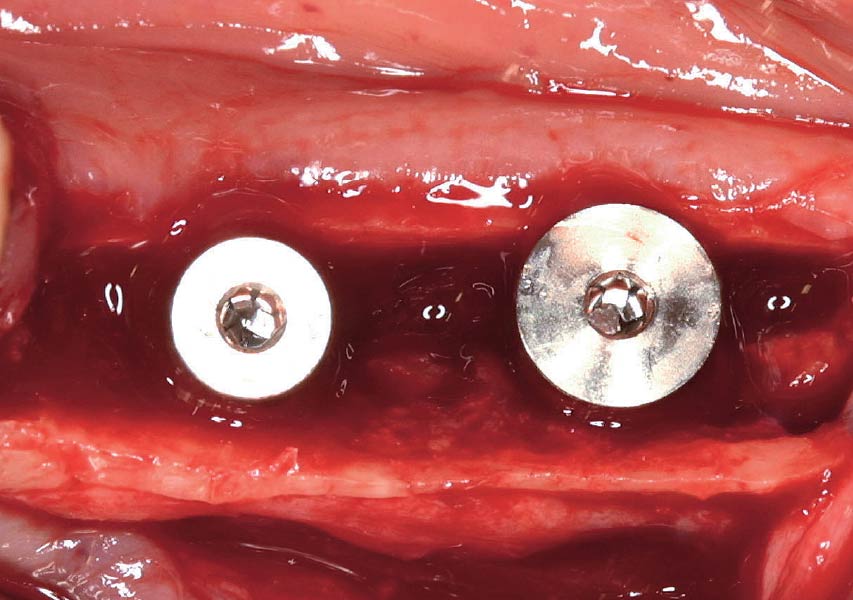
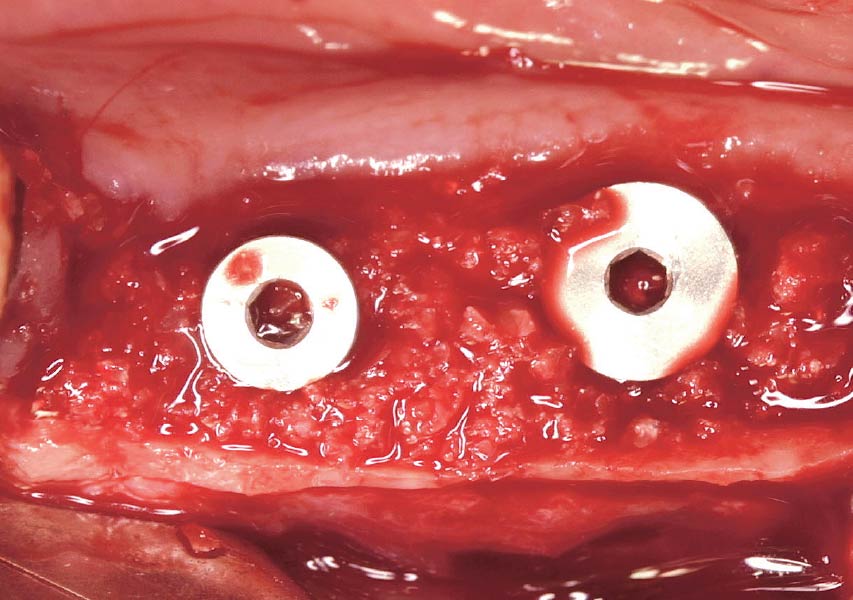
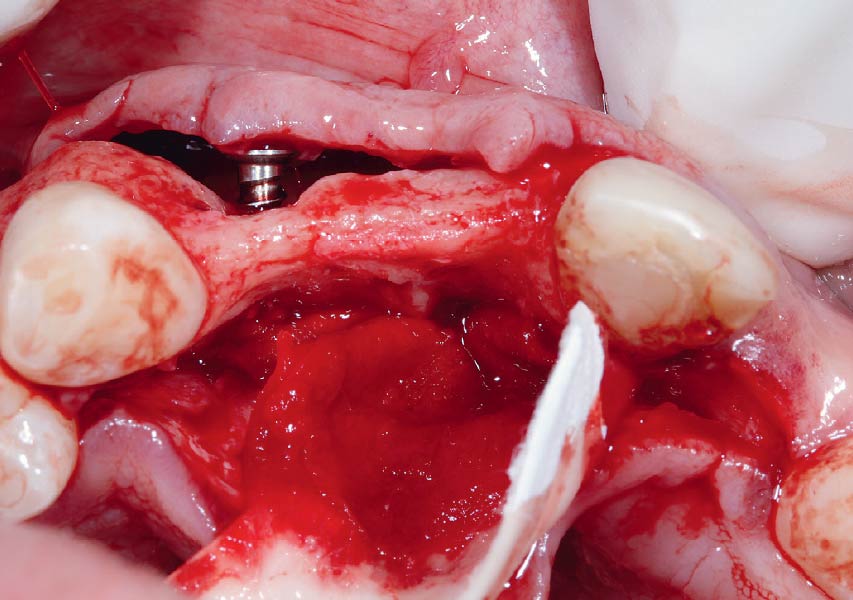
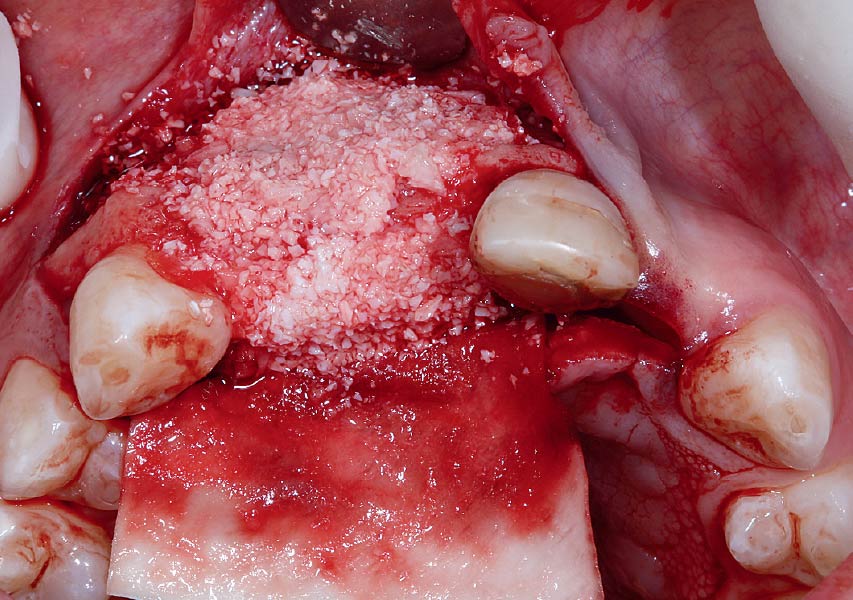
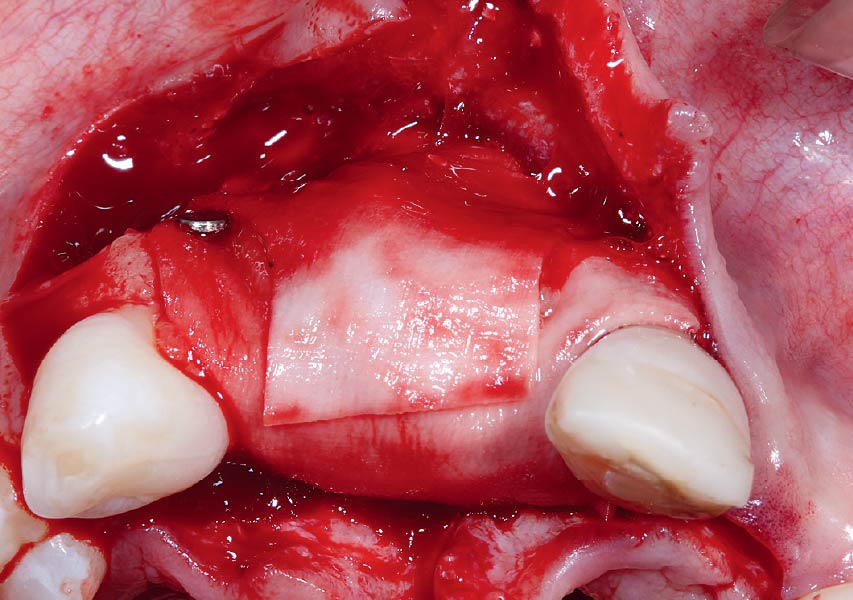
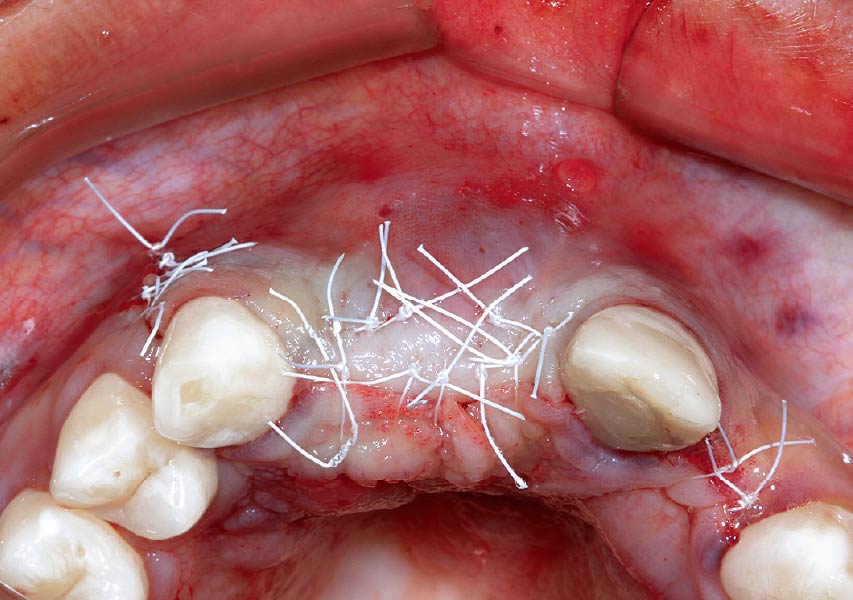
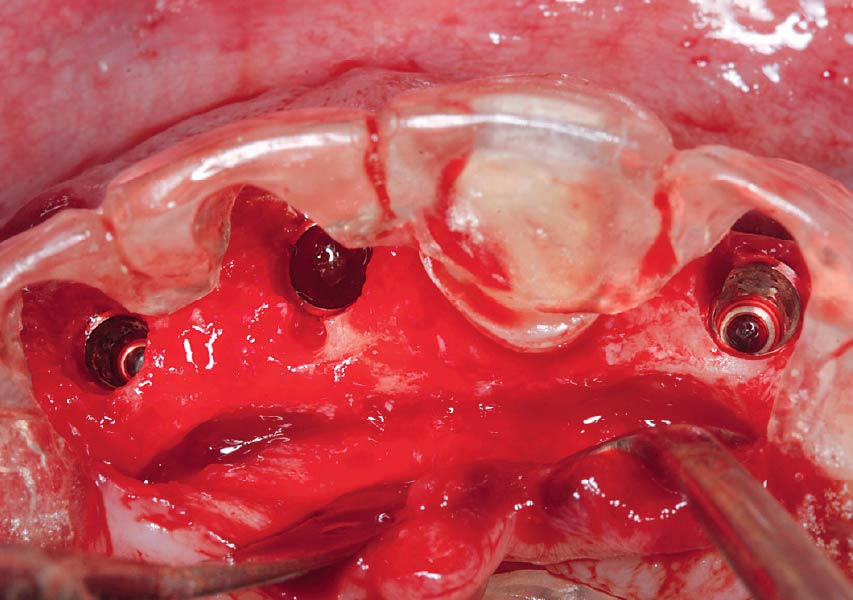
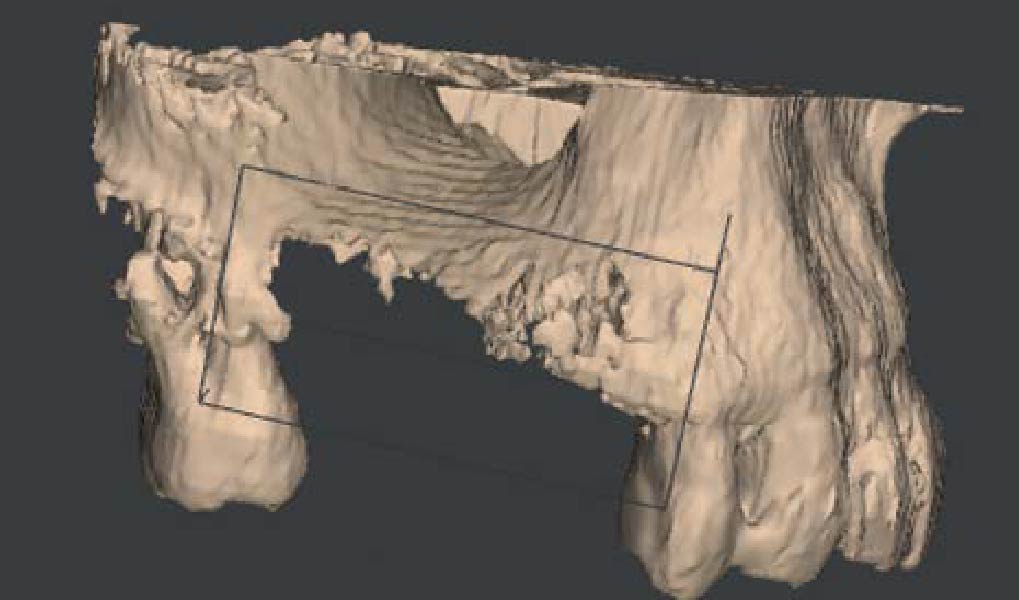
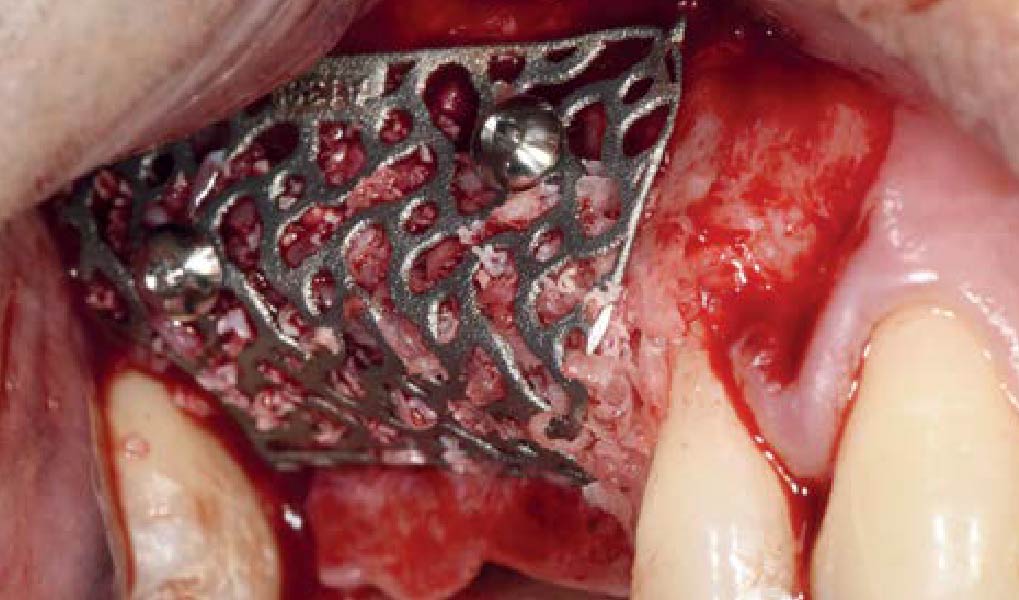
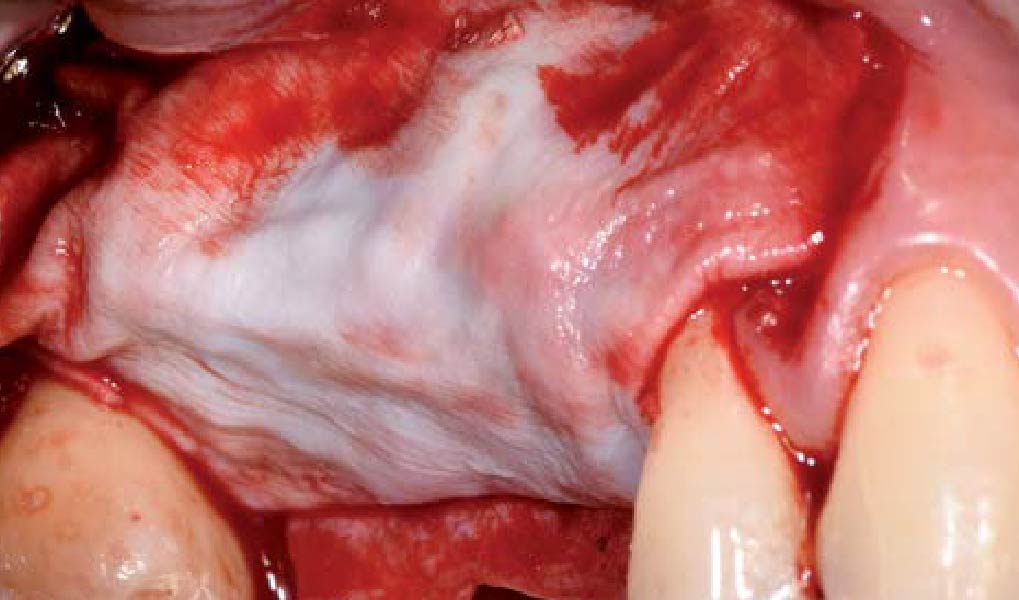
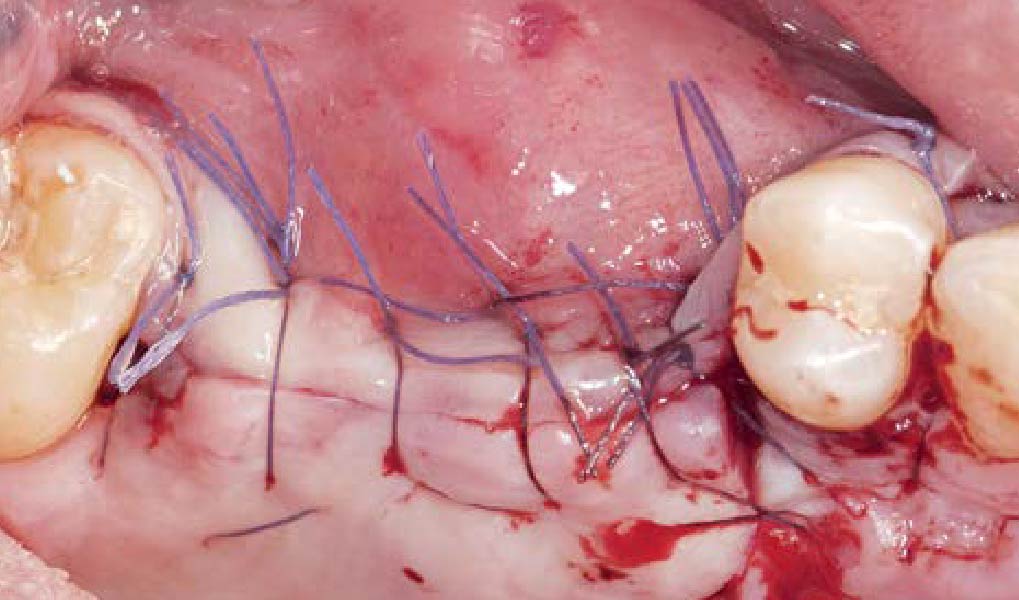
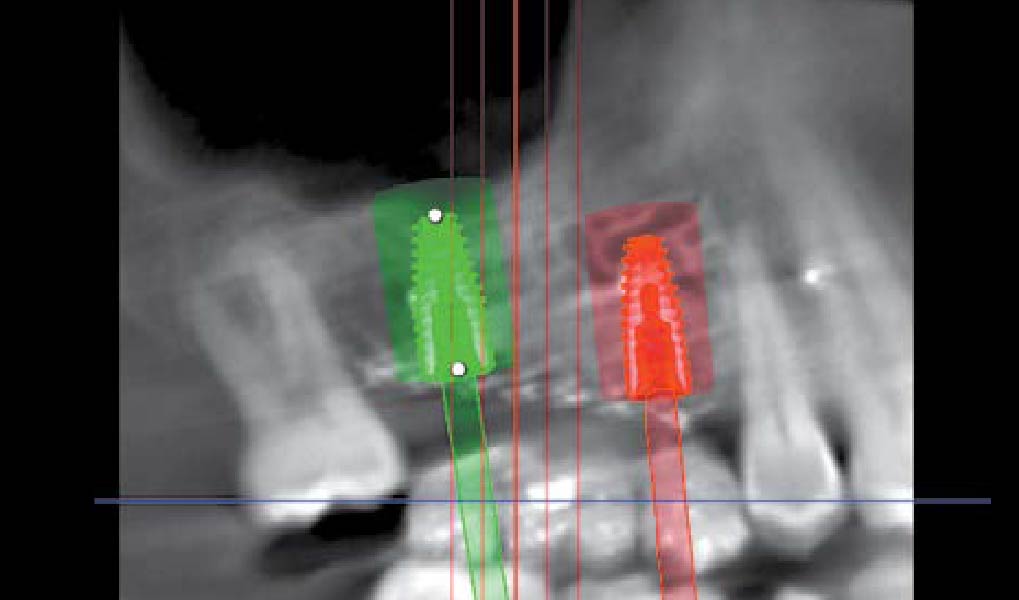
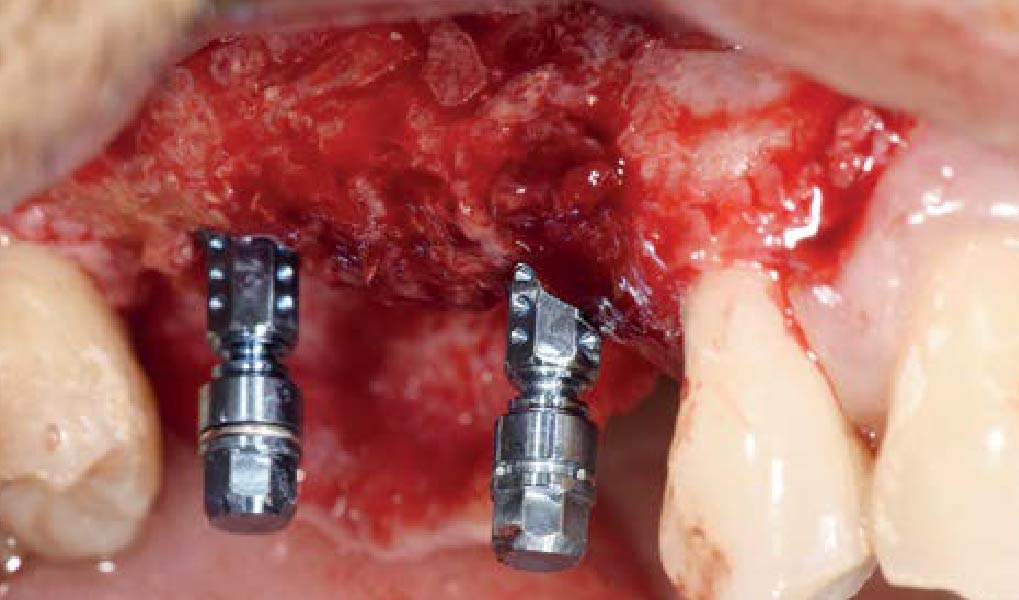
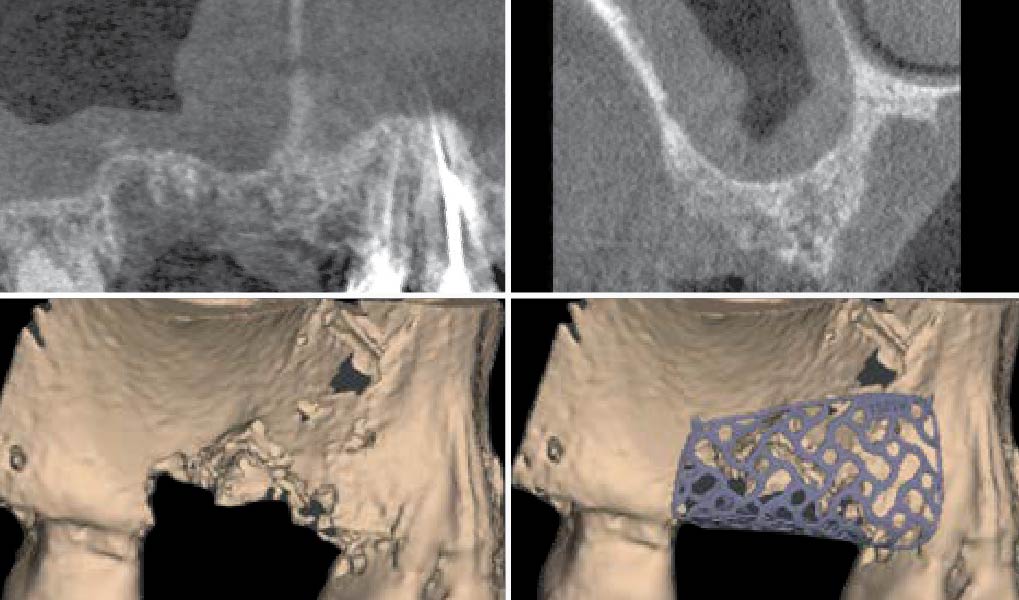
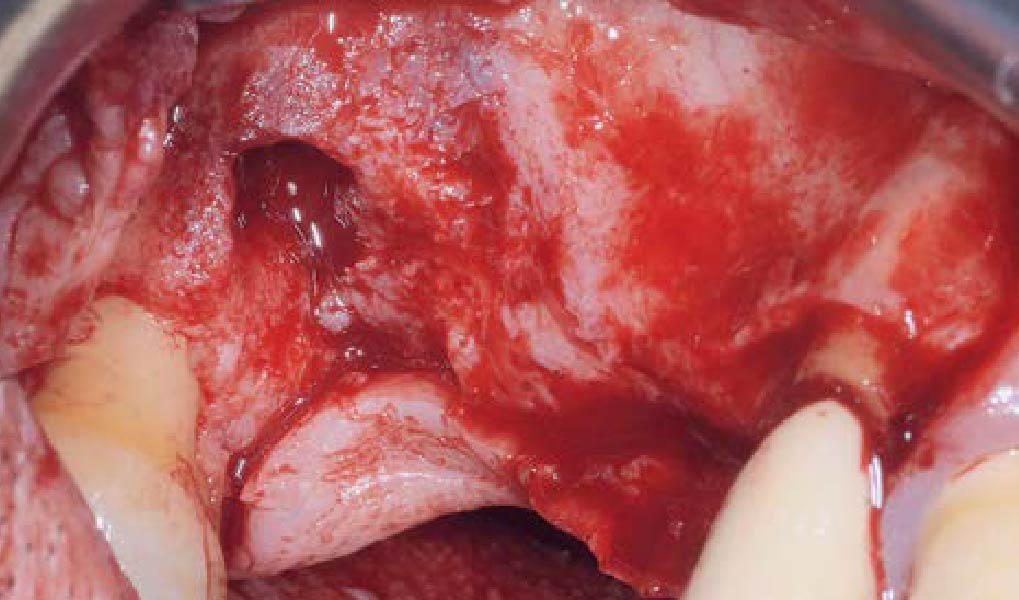
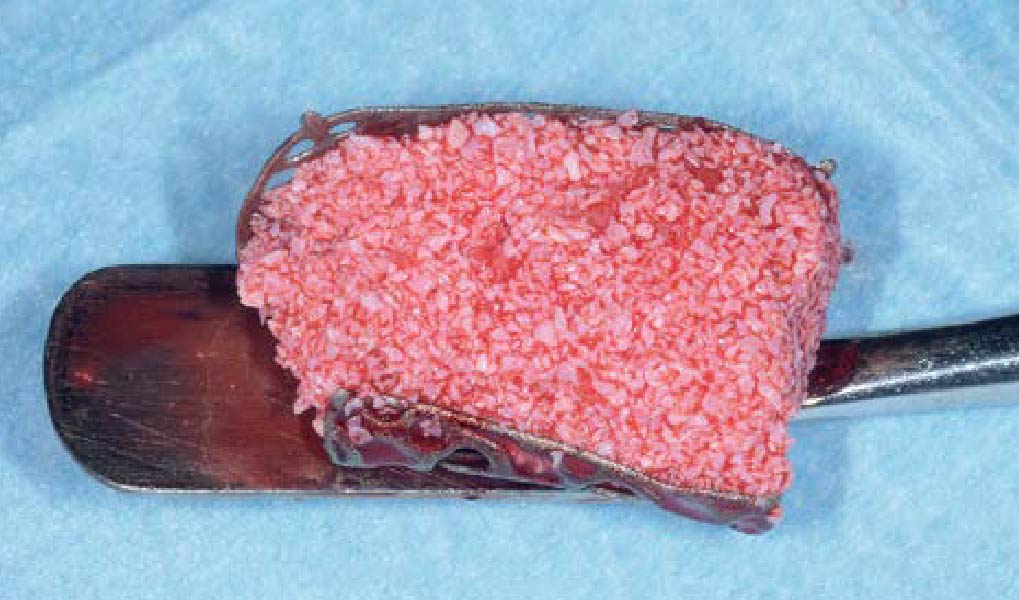
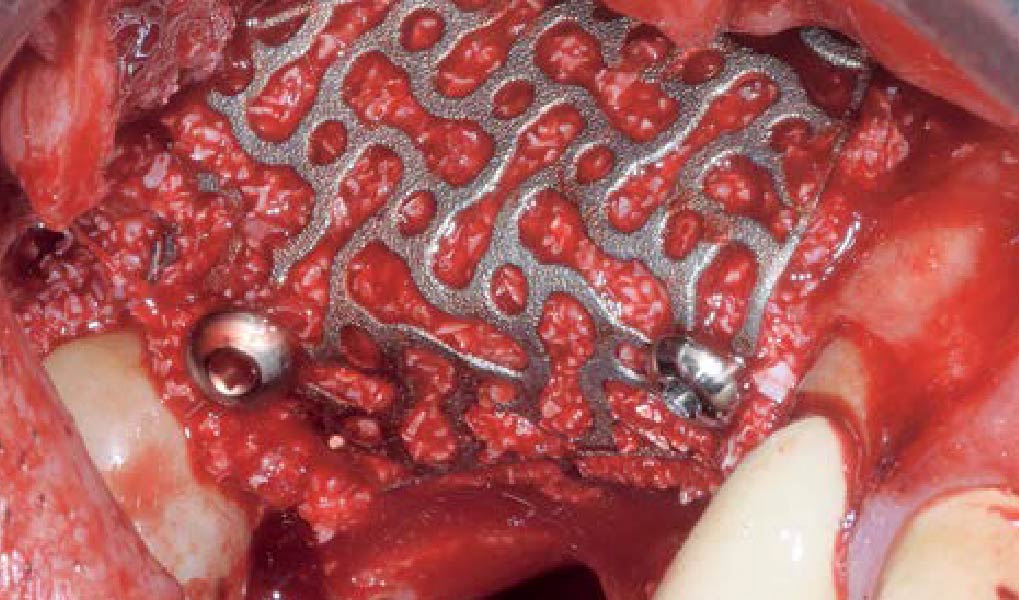
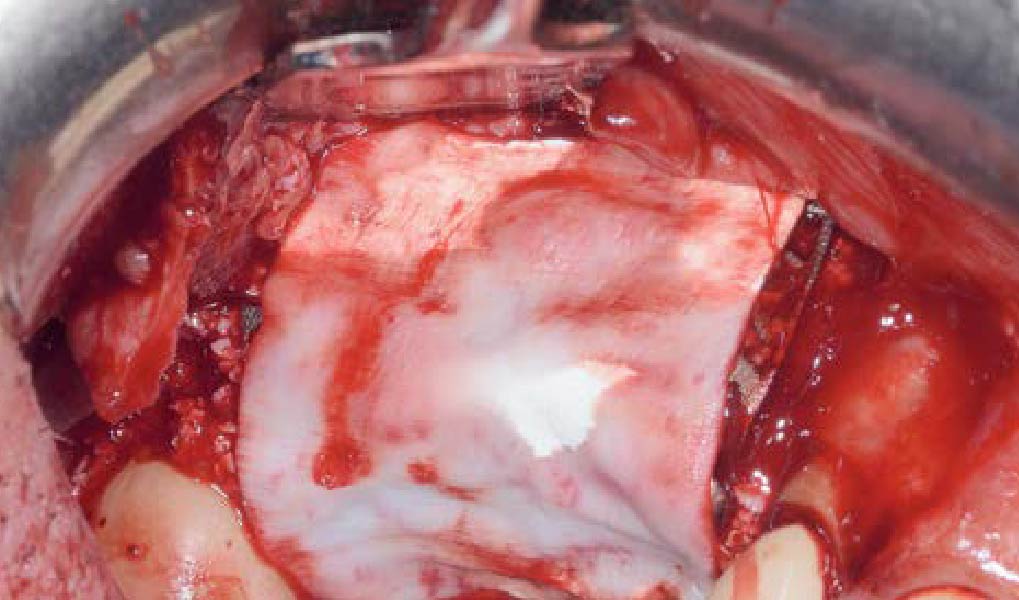
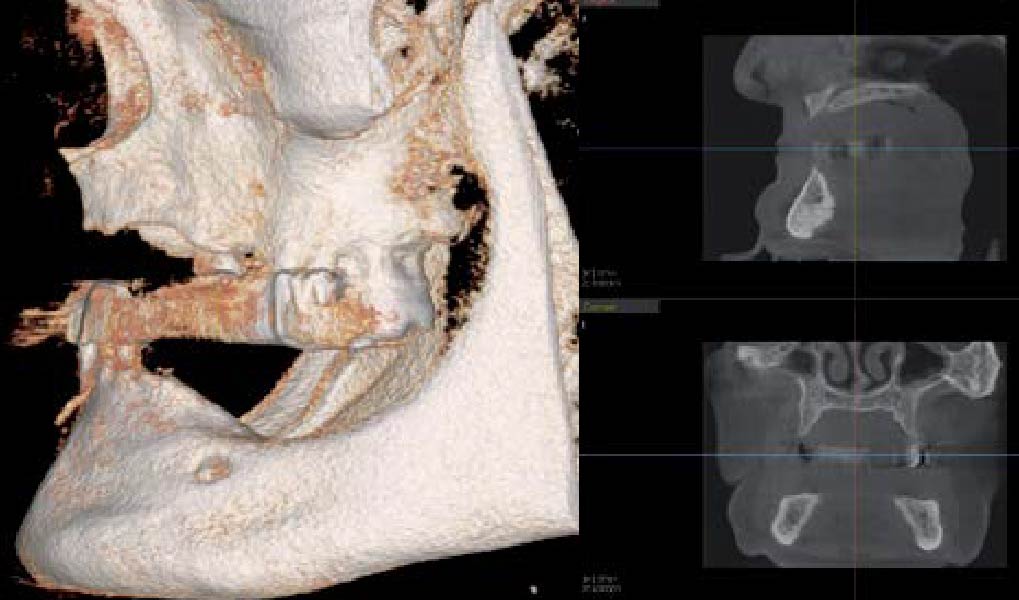
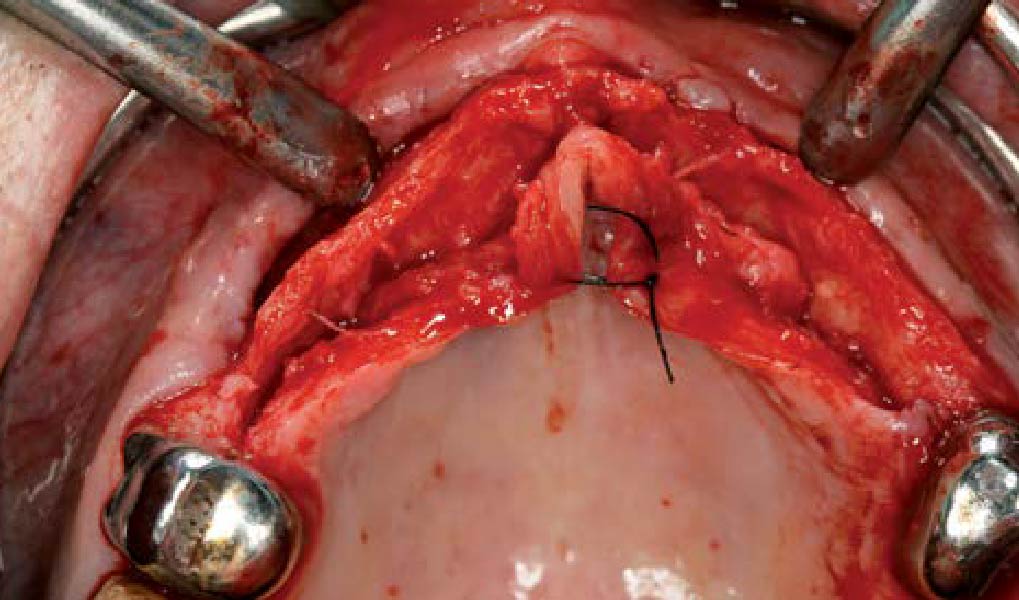
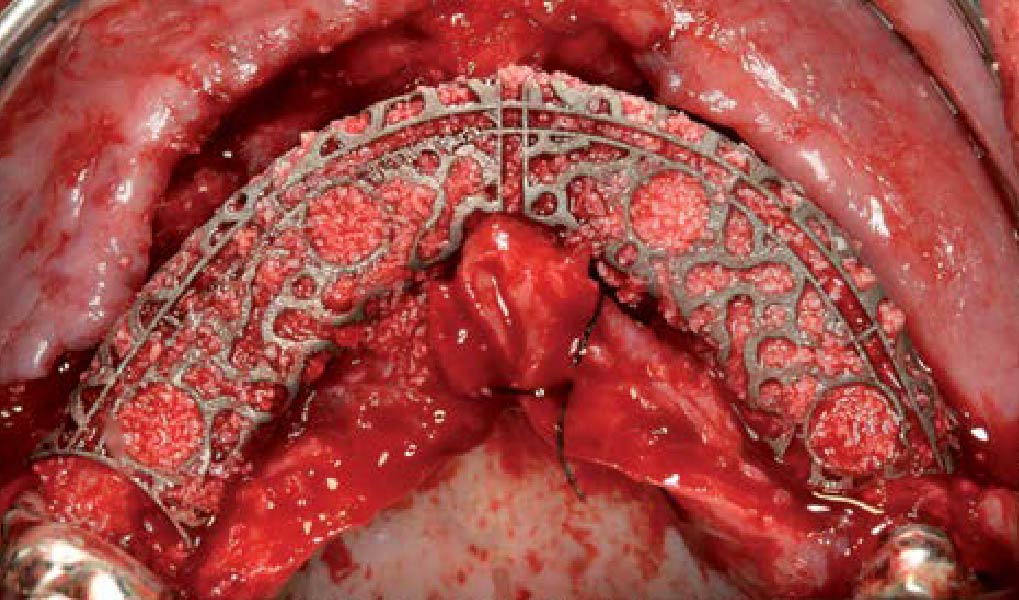
The goals of this case were to: 1) maximize pink and white esthetic scores, 2) preserve the pre-operative soft tissue architecture, 3) minimize hard and soft tissue remodeling over time following tooth extraction, and 4) promote long-term implant health and stability. To achieve these objectives, immediate implant placement with immediate provisionalization was planned. The extraction was performed with minimal flap elevation, and the implant was placed in a guided manner with palatal bias to maximize the facial gap. This gap was then grafted with a slowly resorbing bovine xenograft (Geistlich Bio-Oss Collagen®) to minimize remodeling of the labial bone plate. To further enhance soft tissue volume and contour, the facial soft tissue was augmented after using a Geistlich Fibro-Gide® collagen matrix. Finally, an immediate provisional crown was placed to contain the bone graft and provide support for the soft tissue.
“This was a challenging case in which the patient and her dentist had high esthetic expectations. The goal of this case was to preserve as much of the preoperative anatomy as possible and minimize the inevitable hard and soft tissue remodeling that occurs after a tooth is removed.”
— David E. Urbanek, DMD, MS
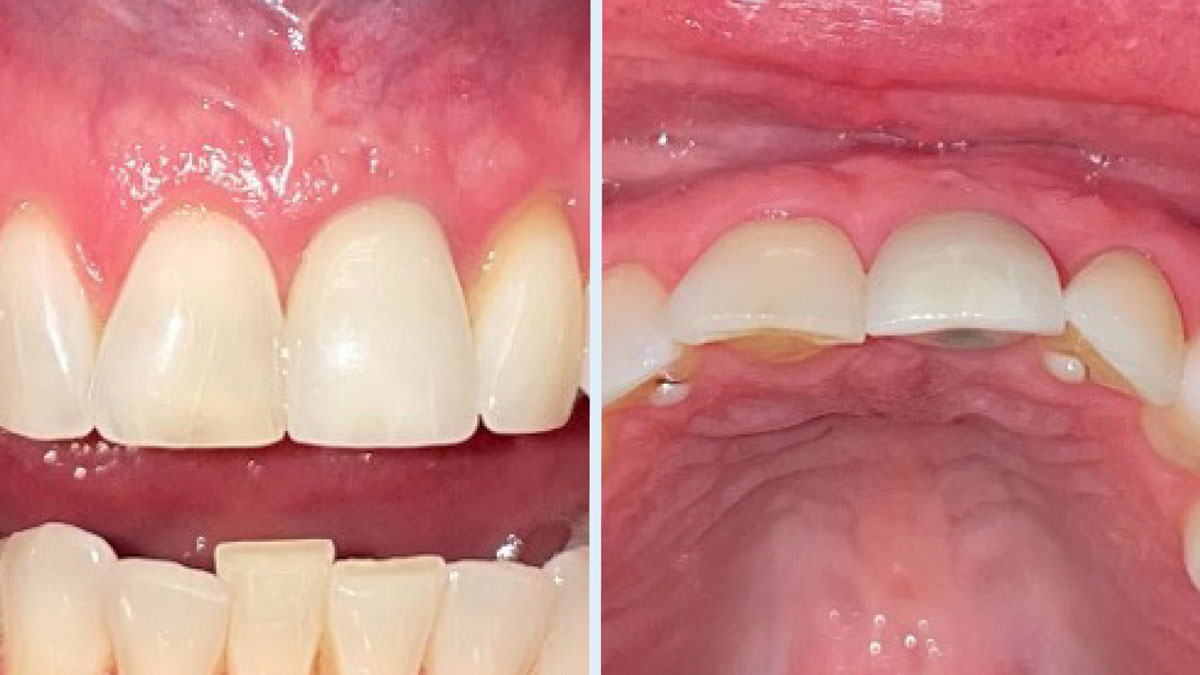
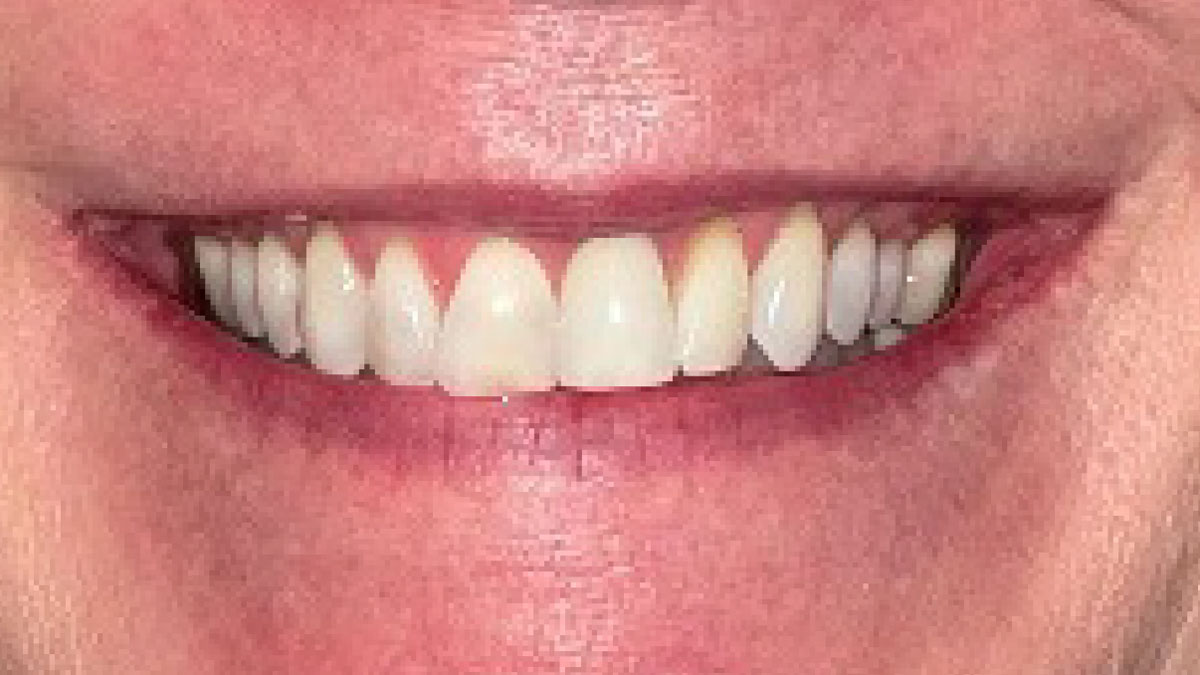
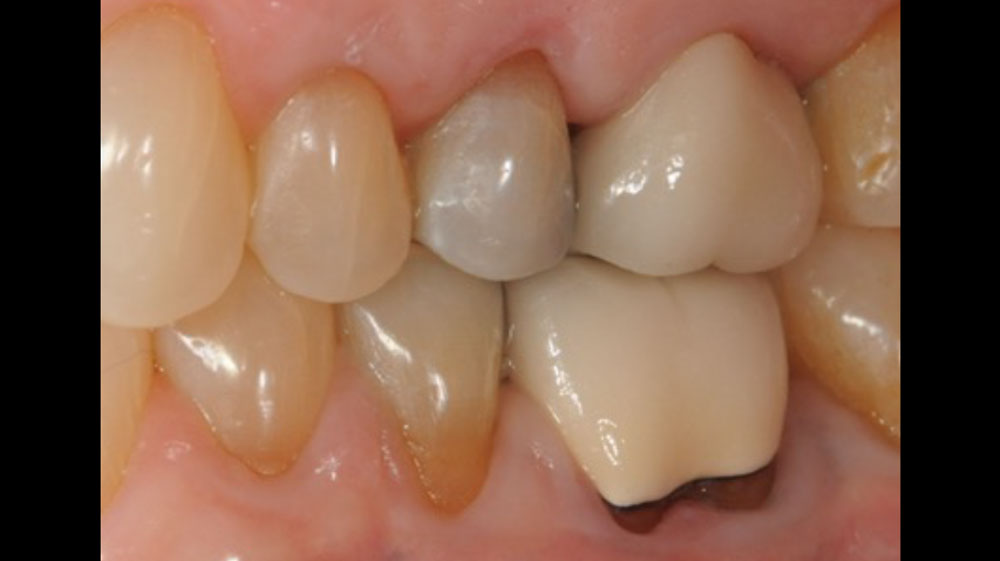
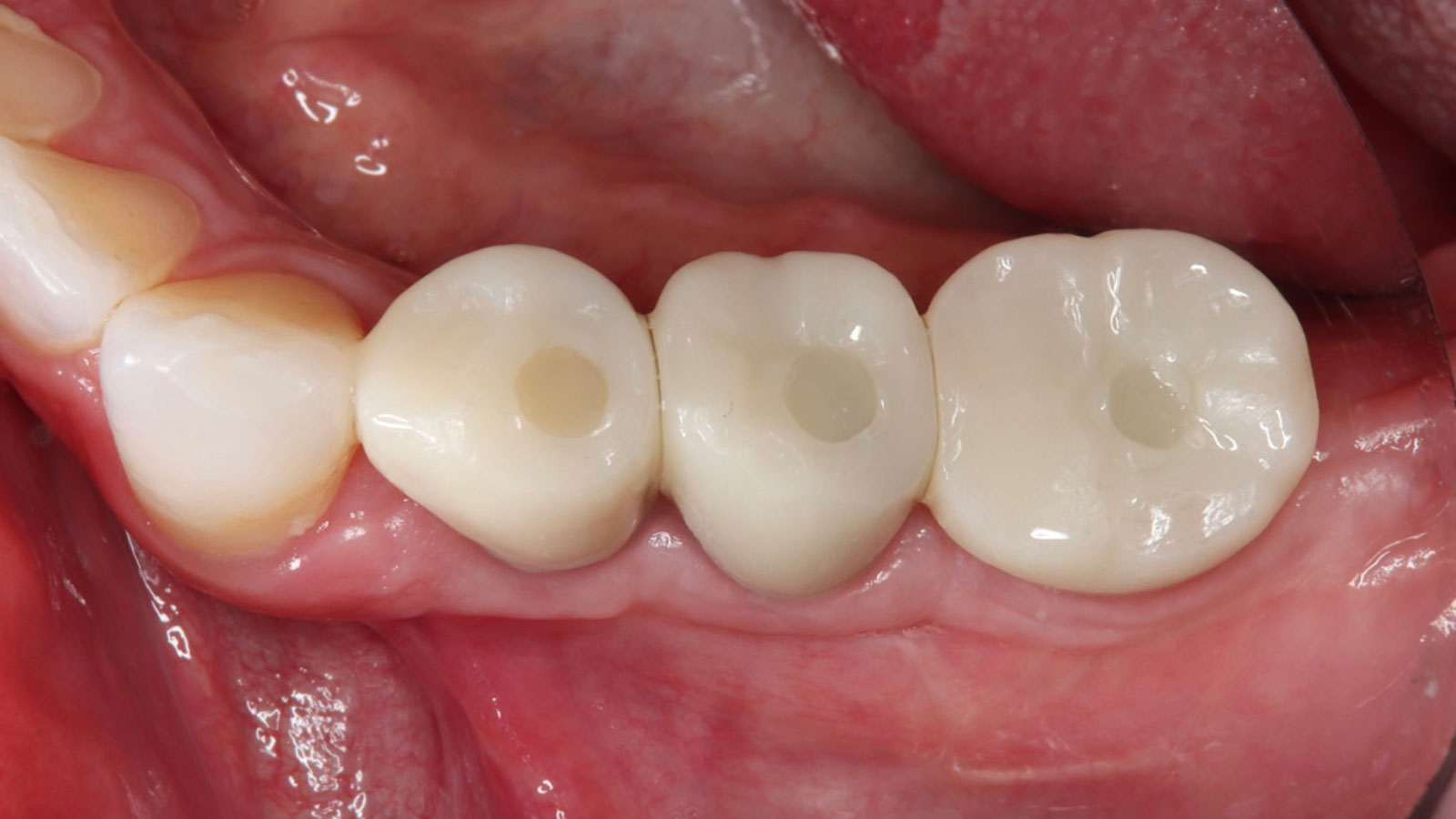
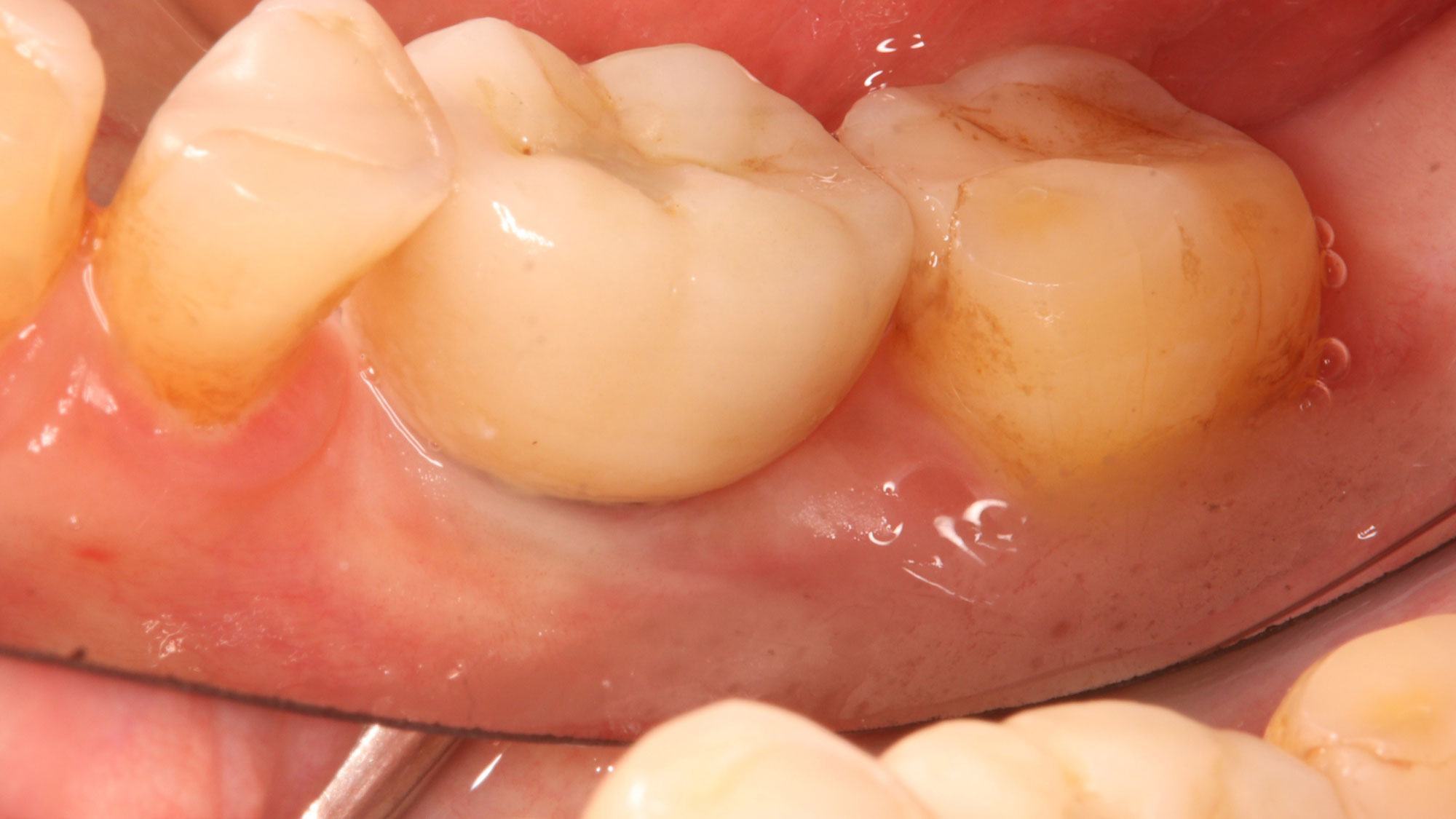
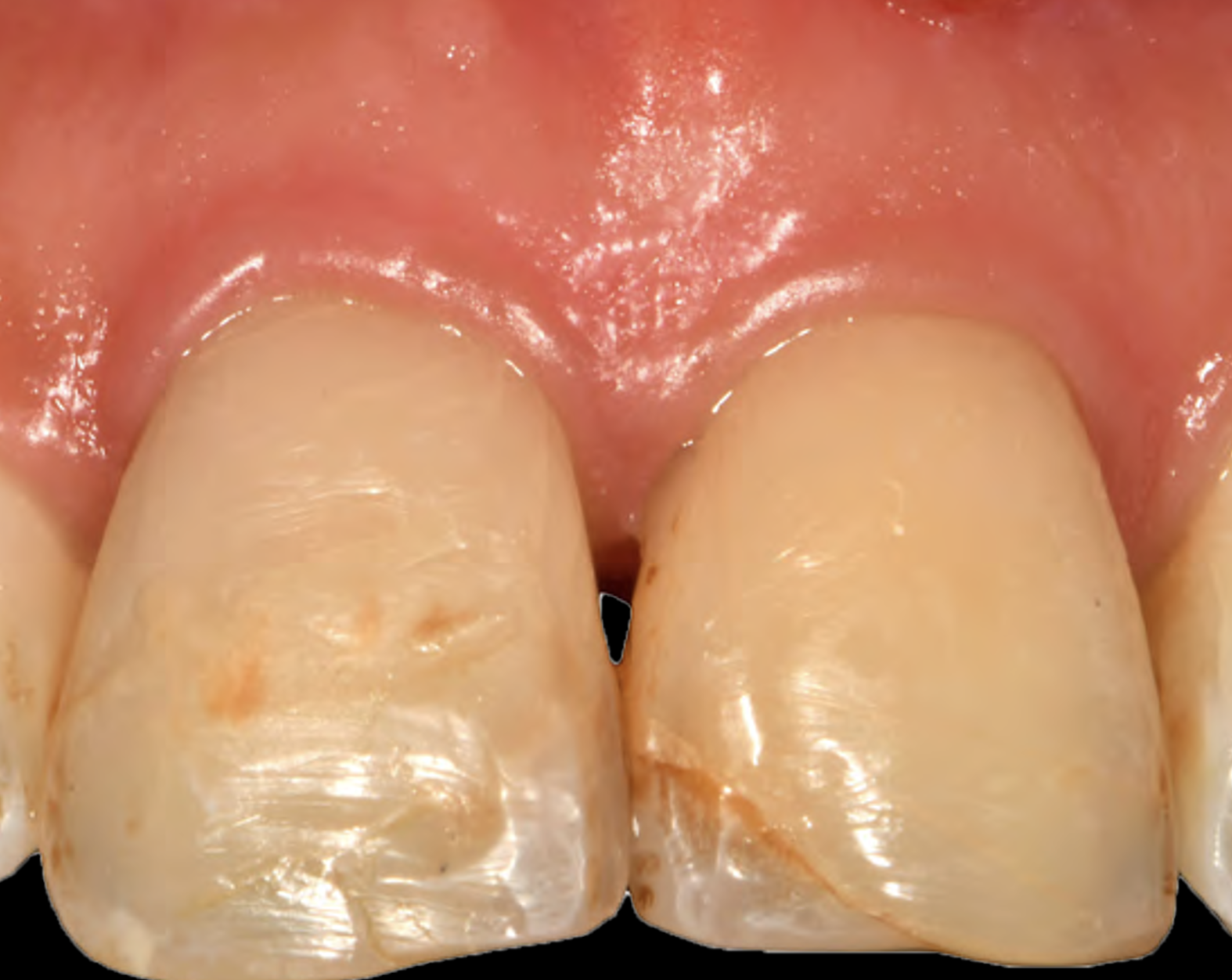
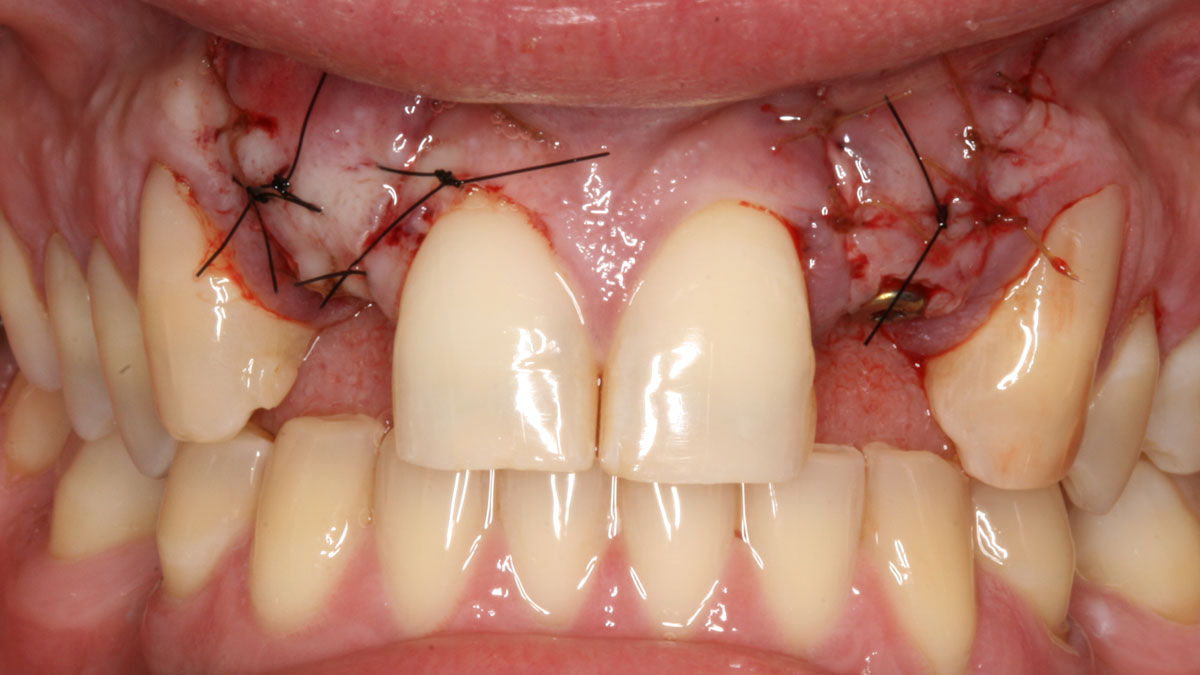
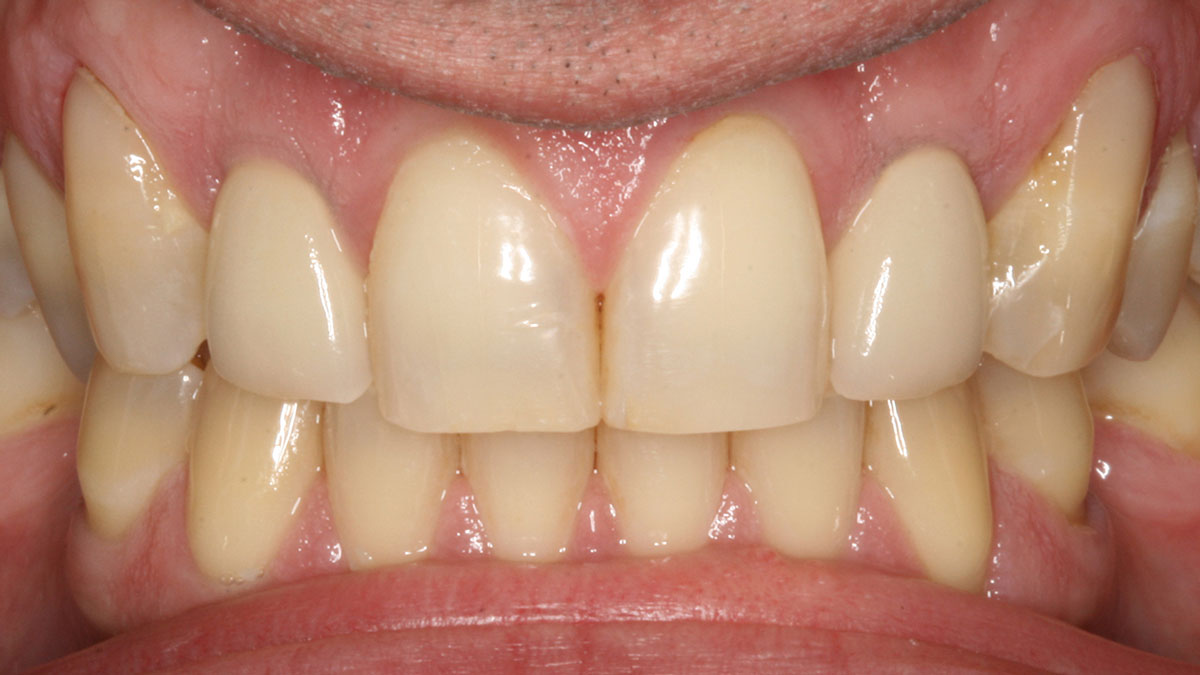
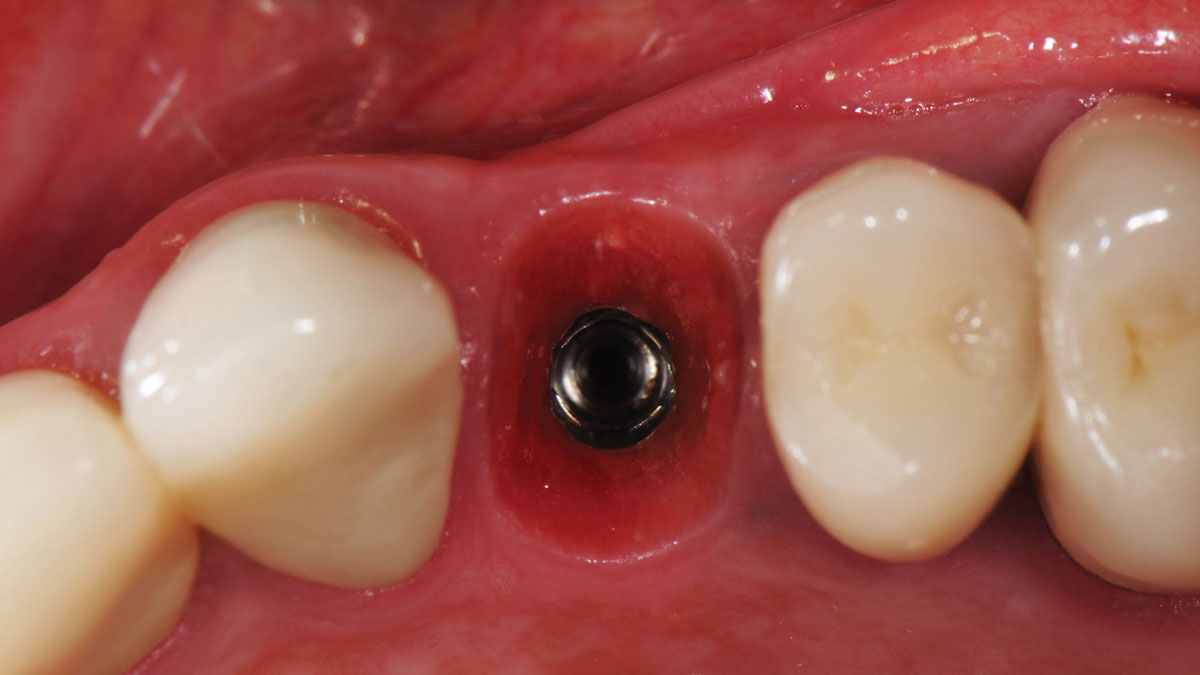
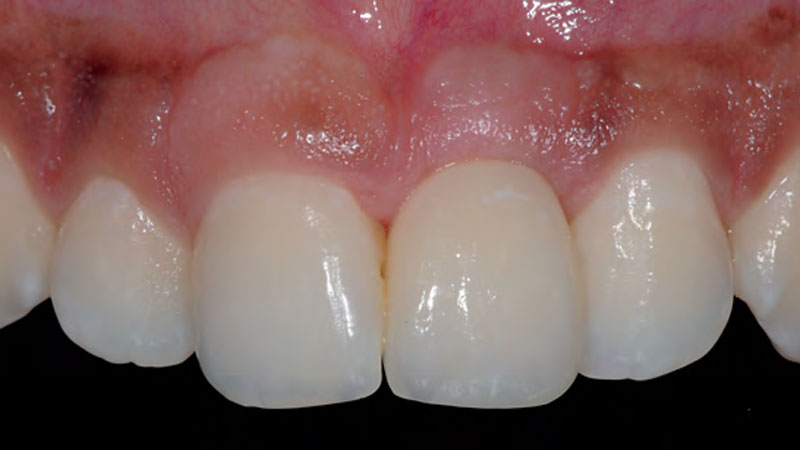
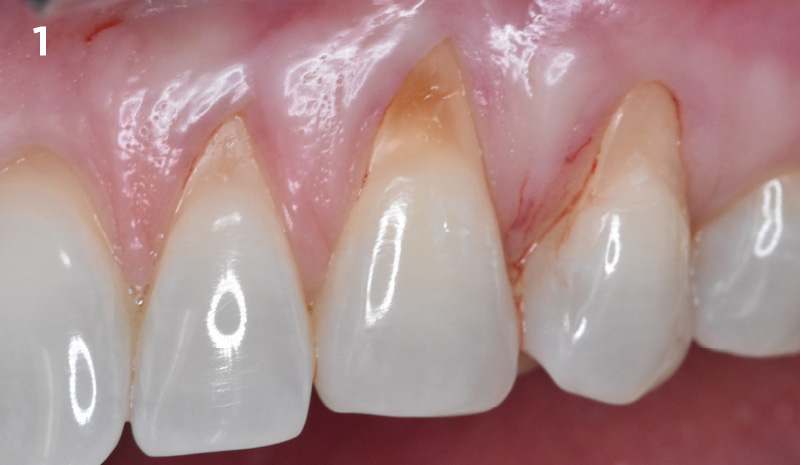
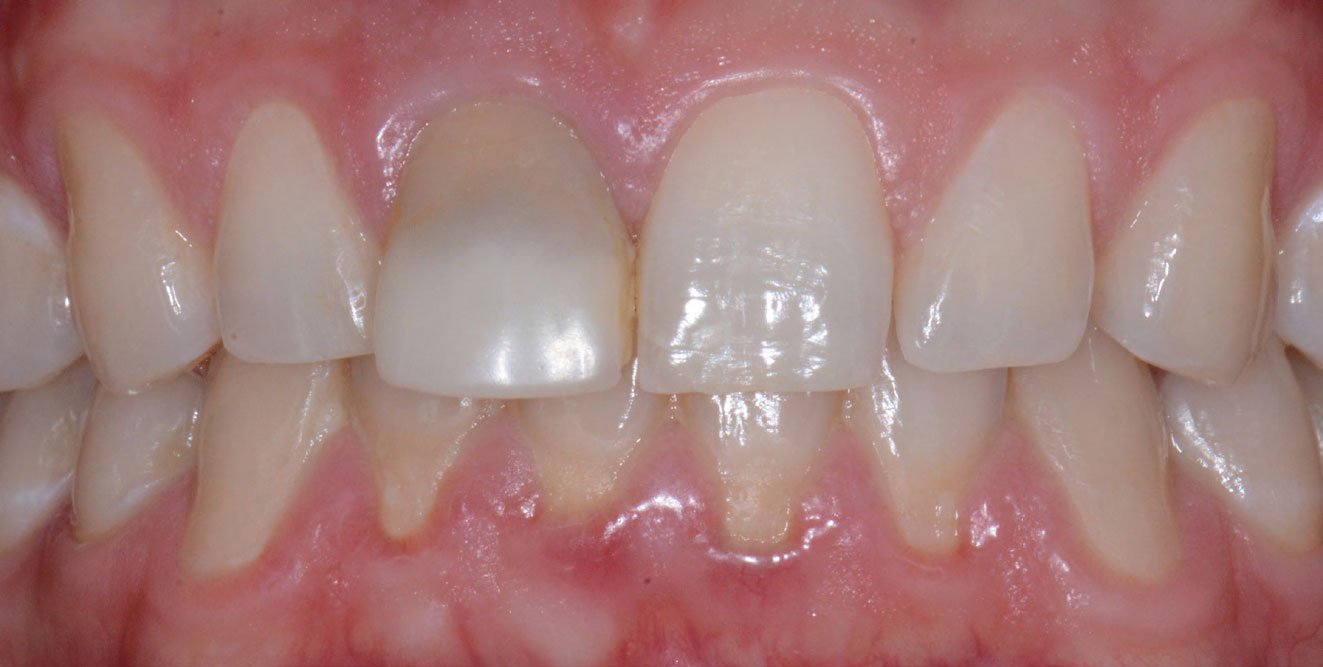
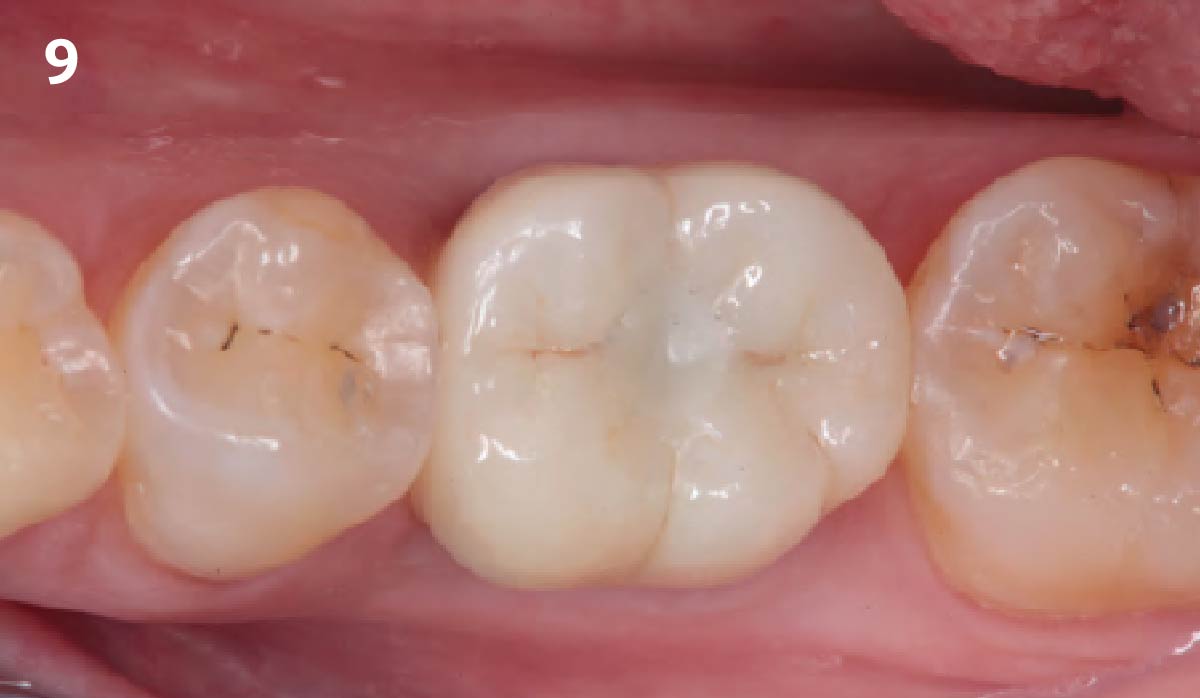
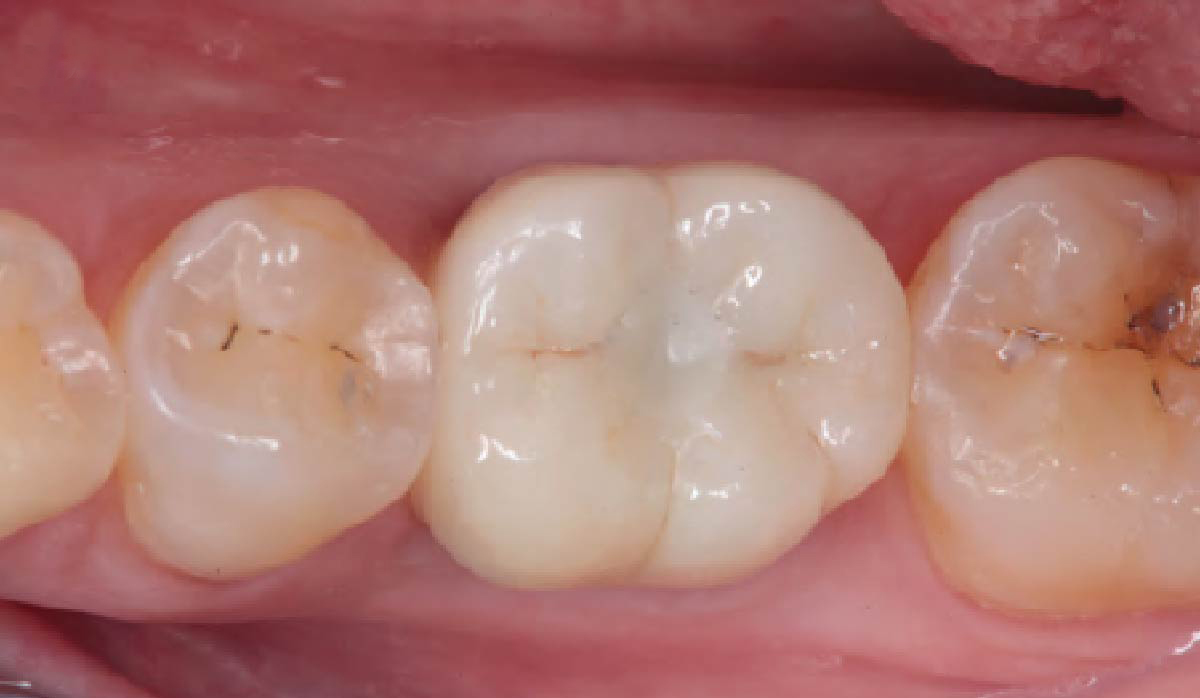
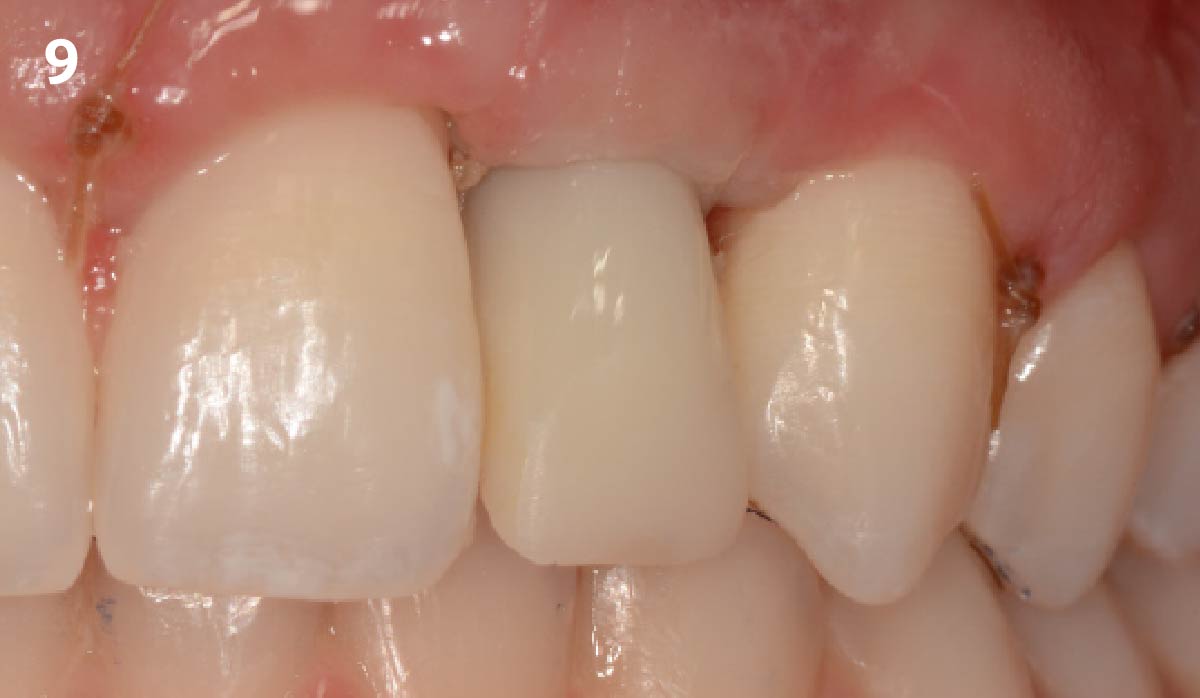
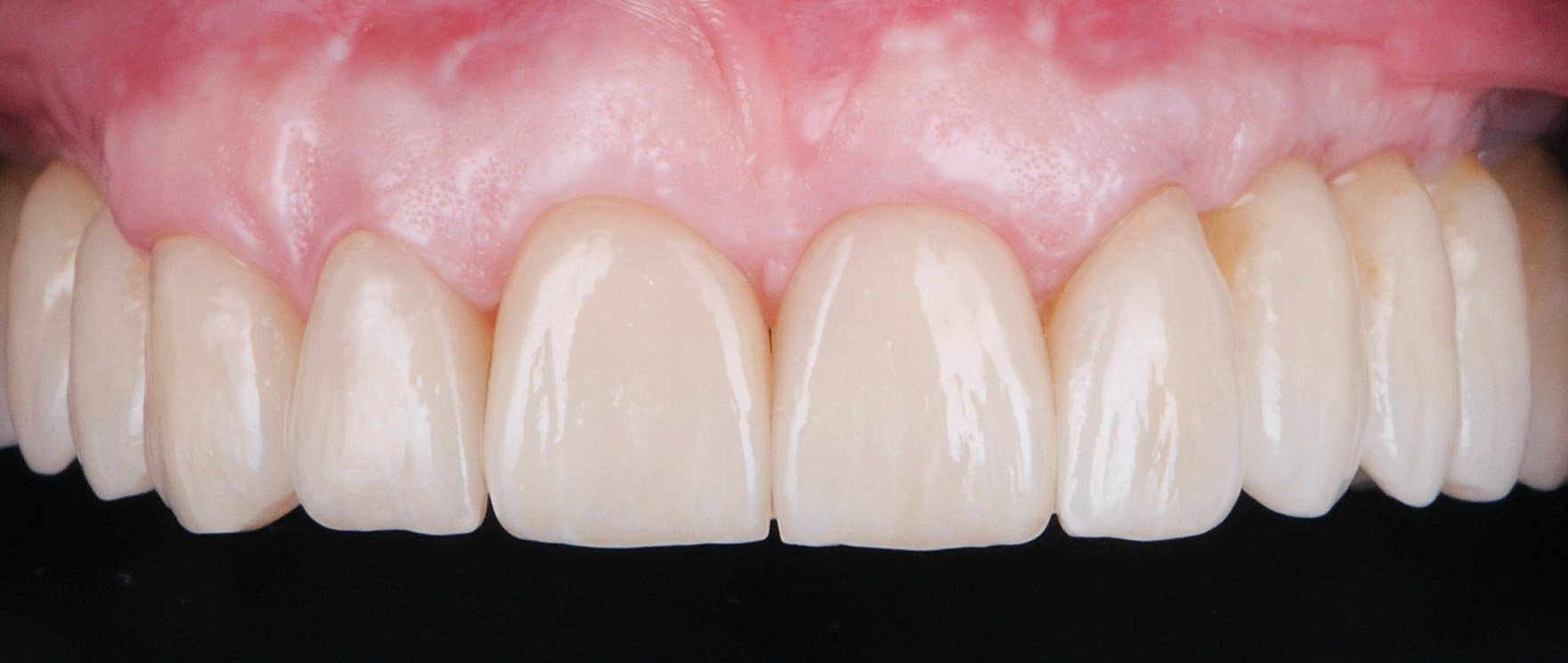
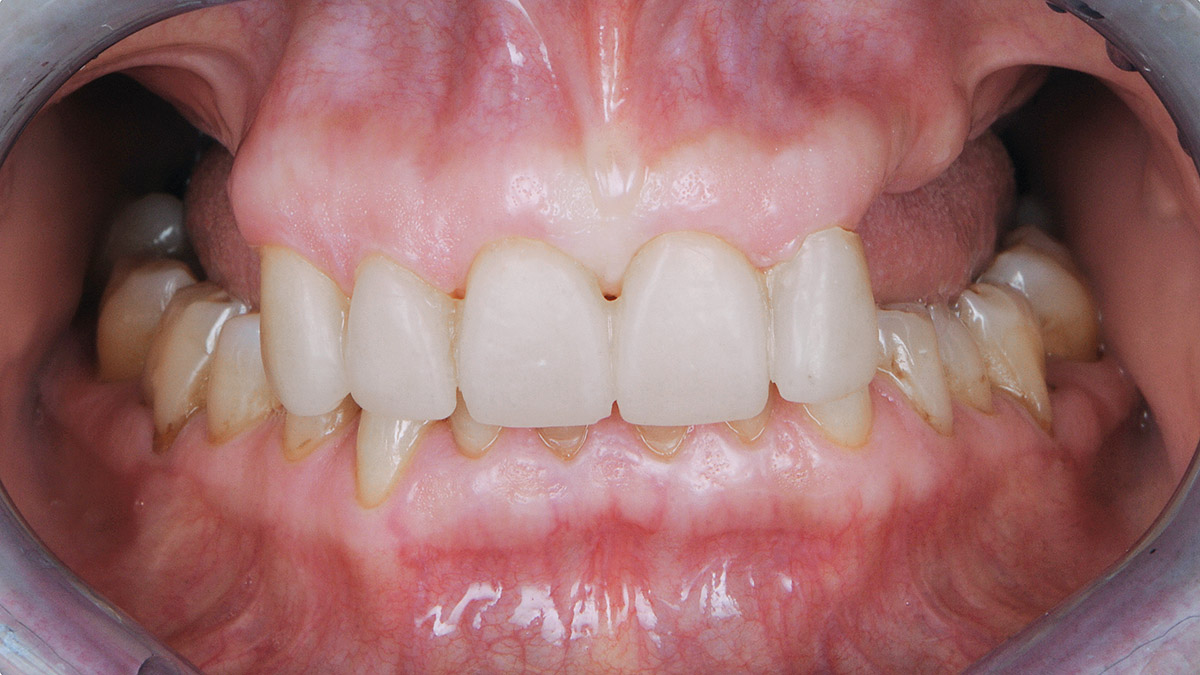
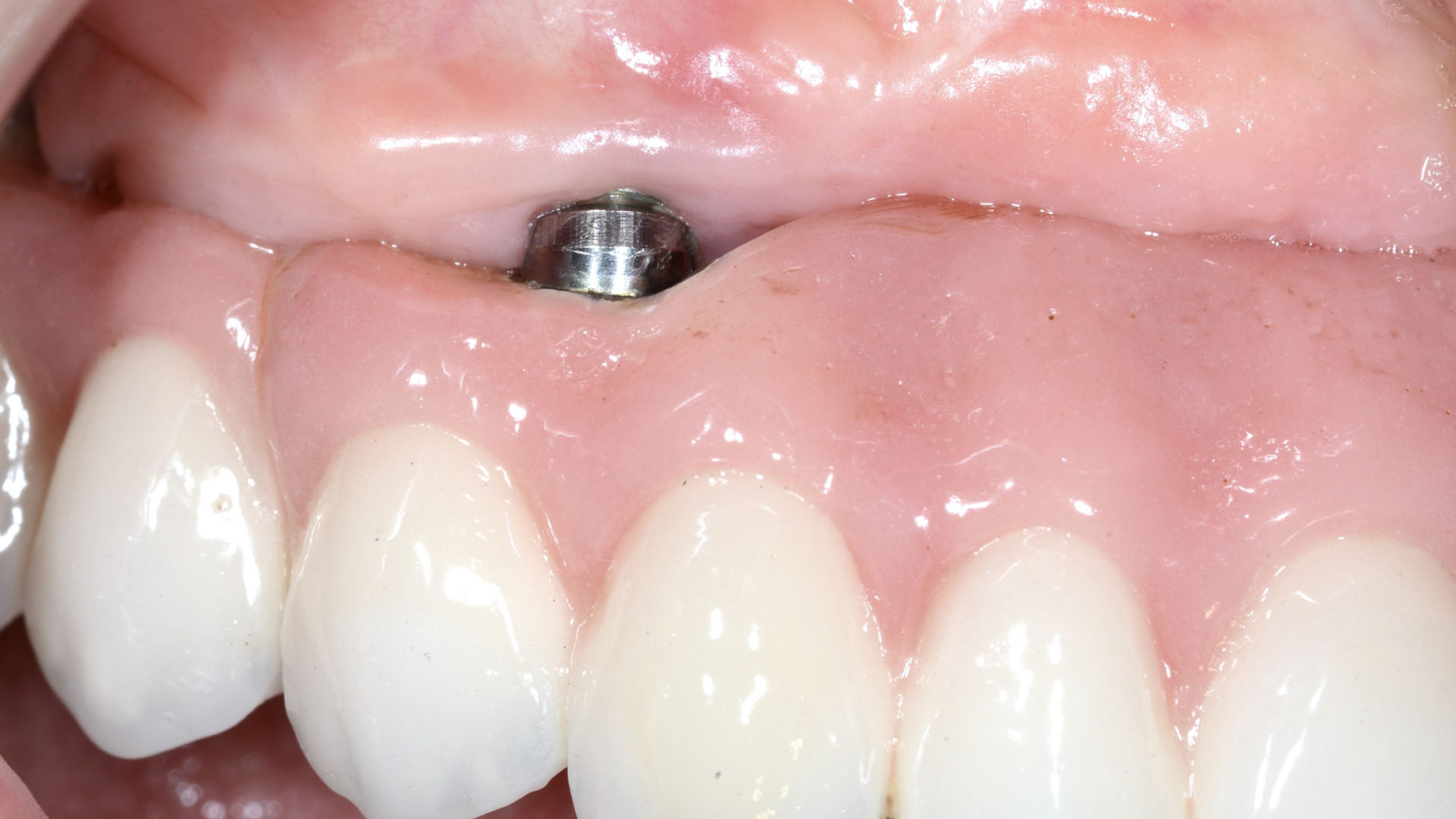
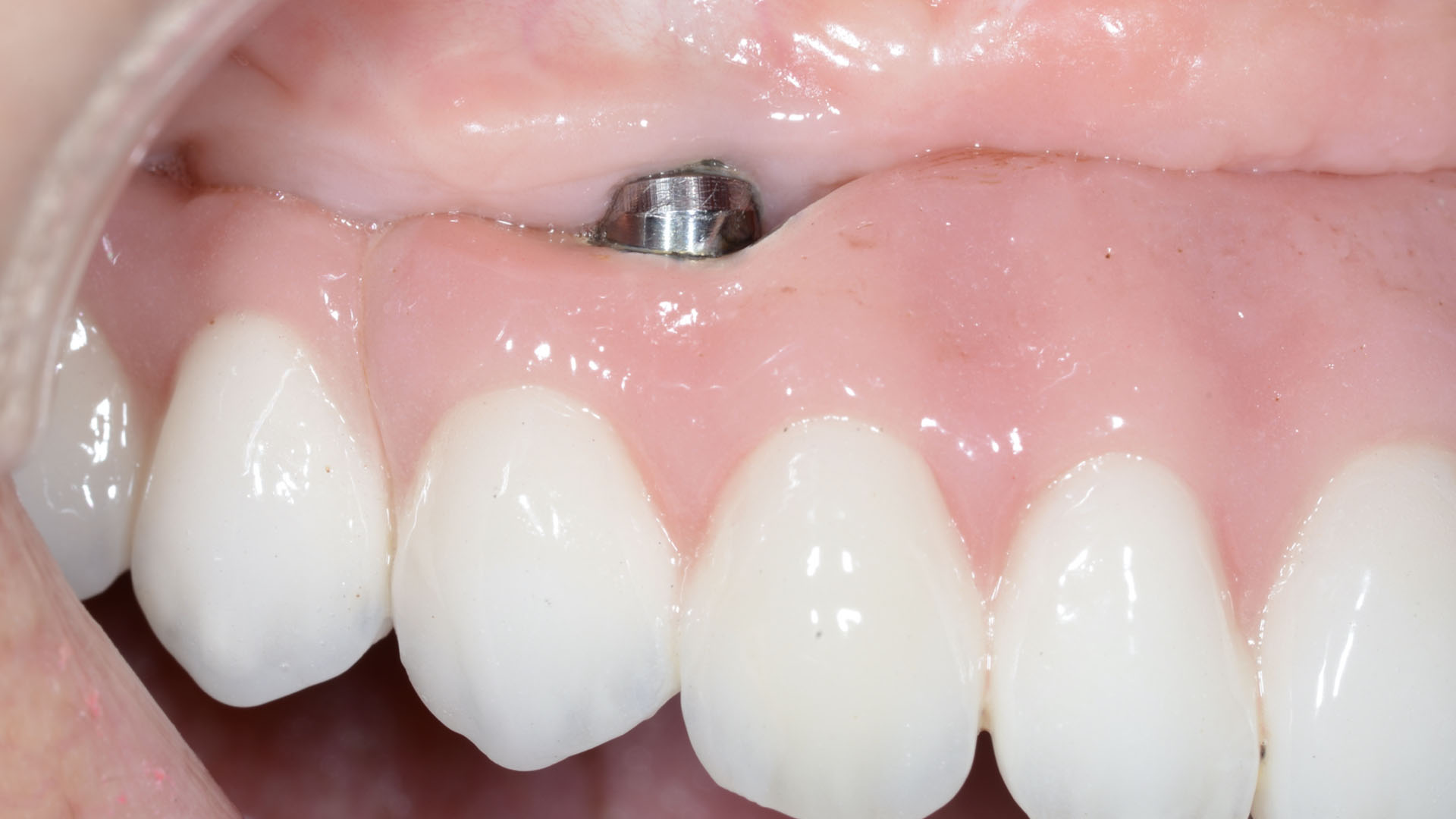
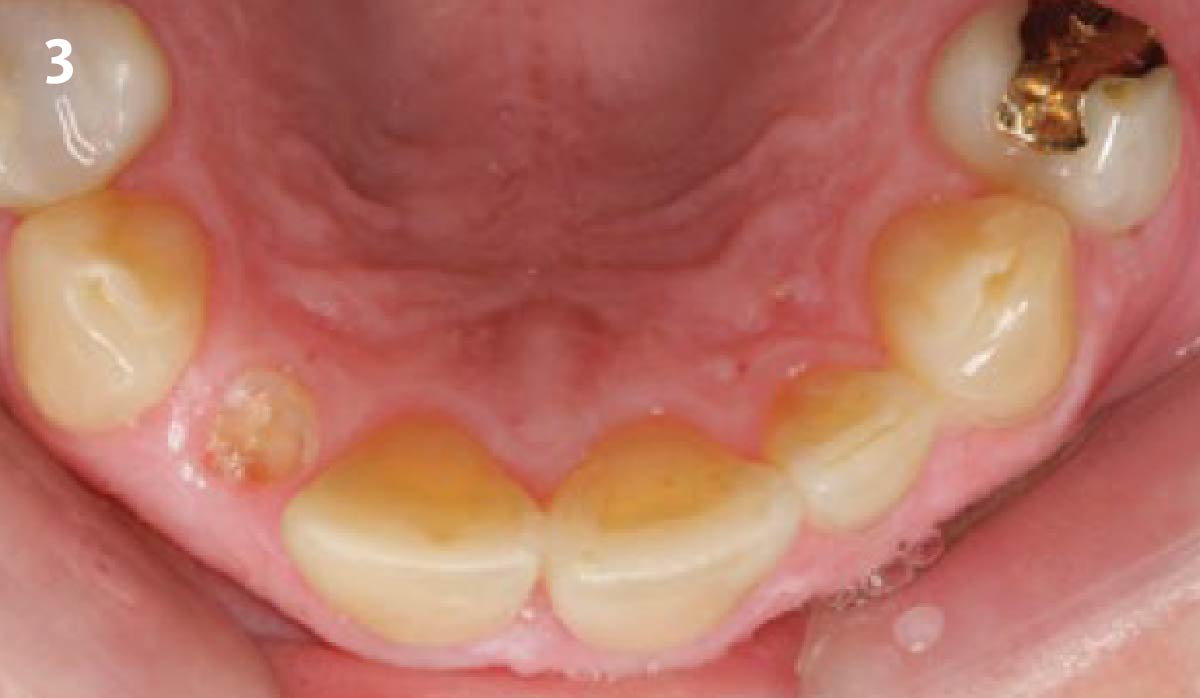
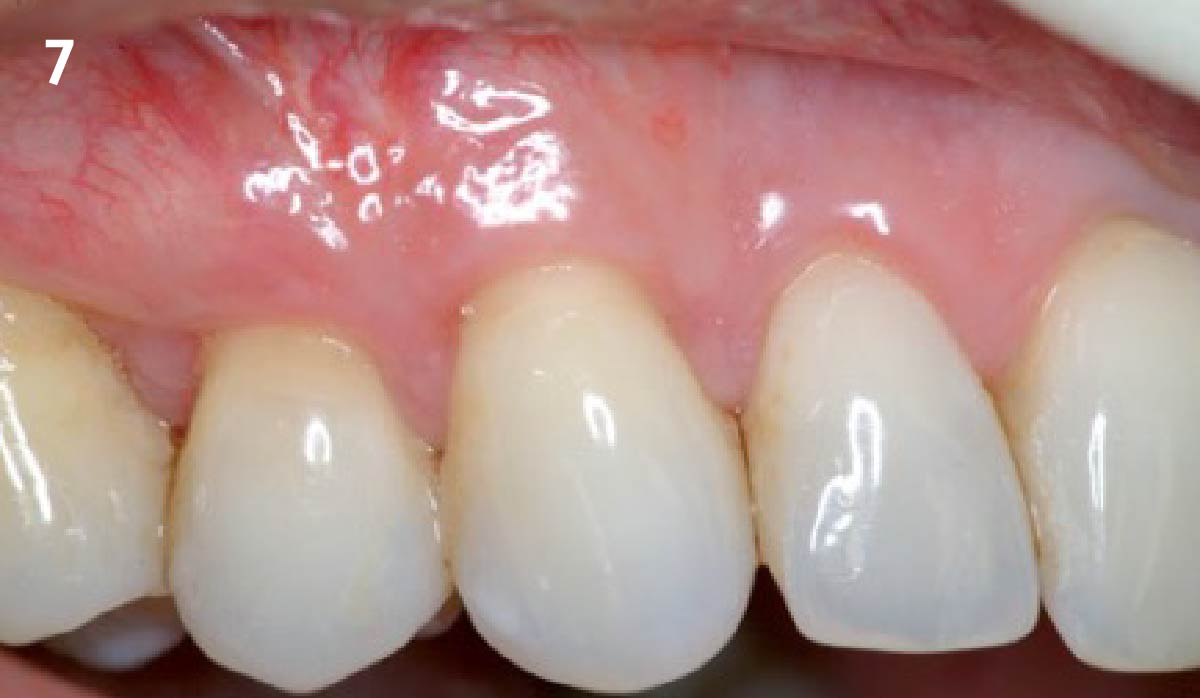
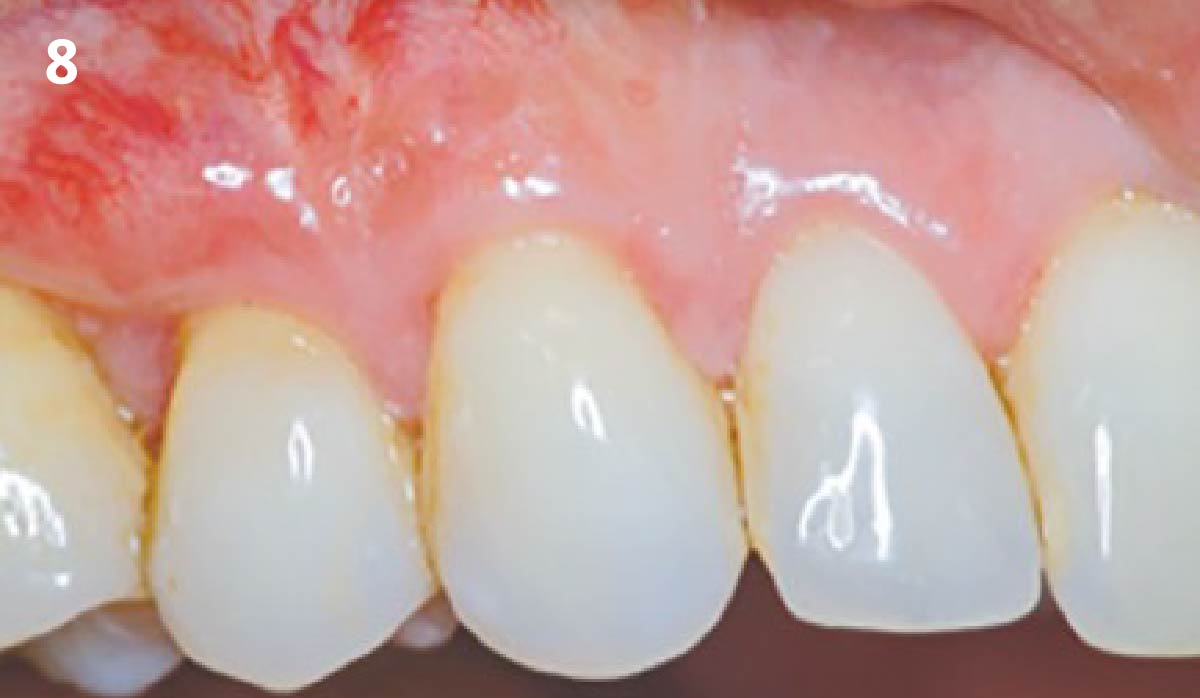
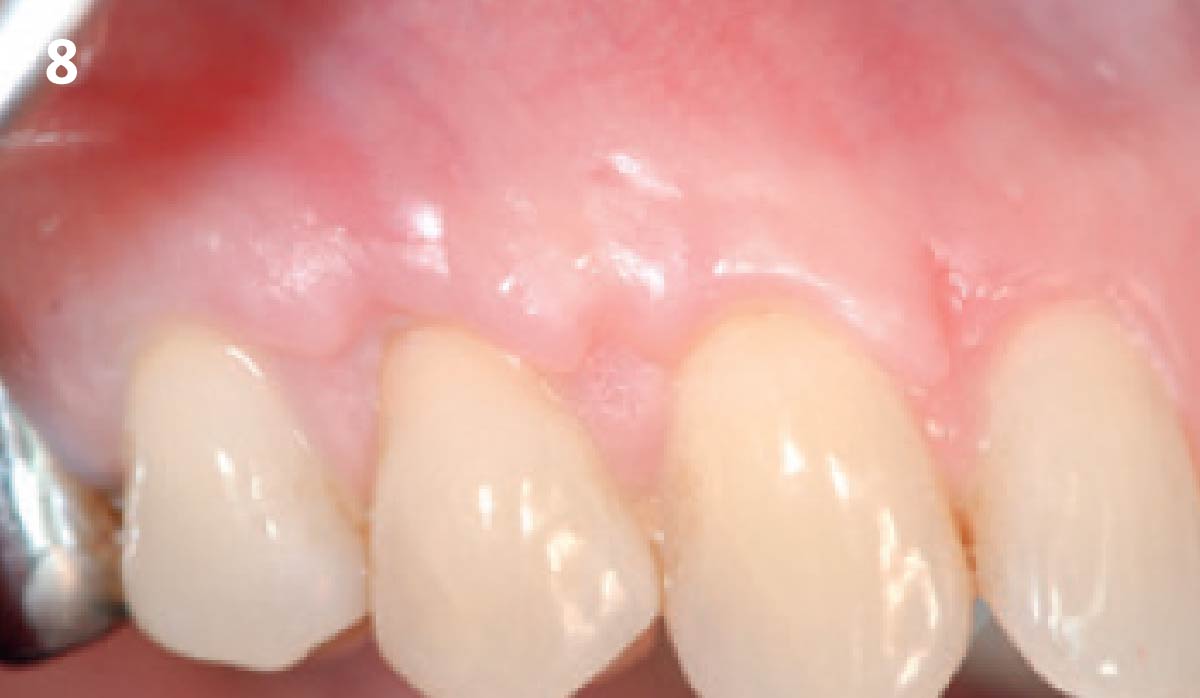
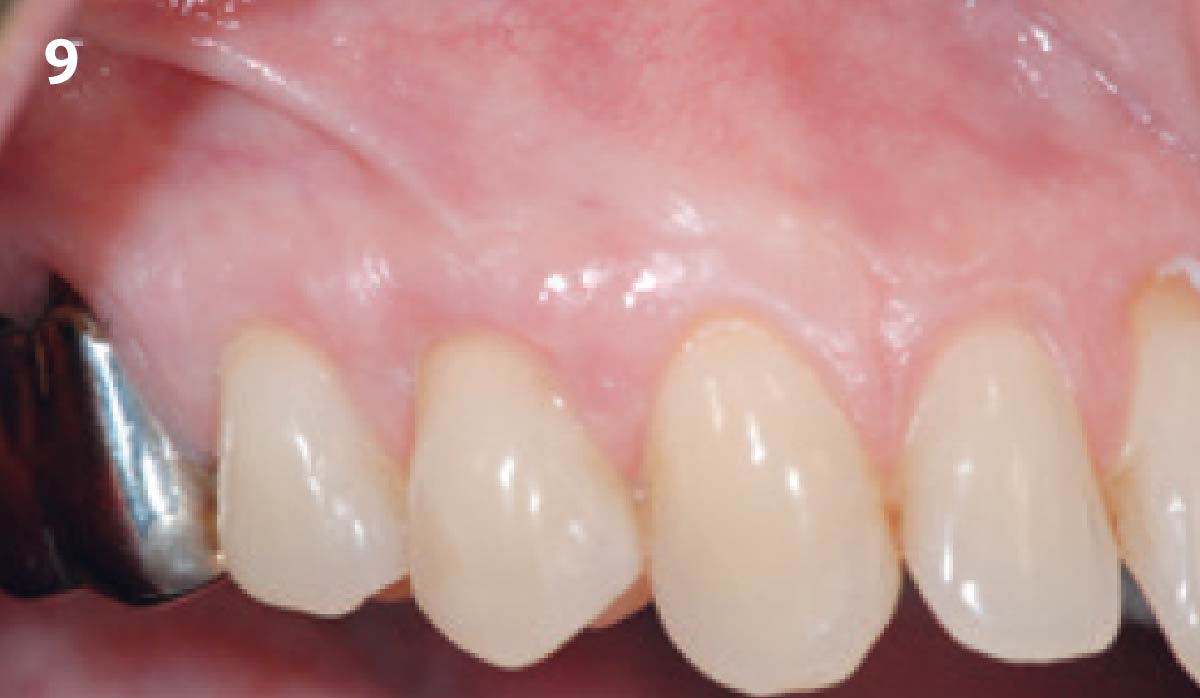
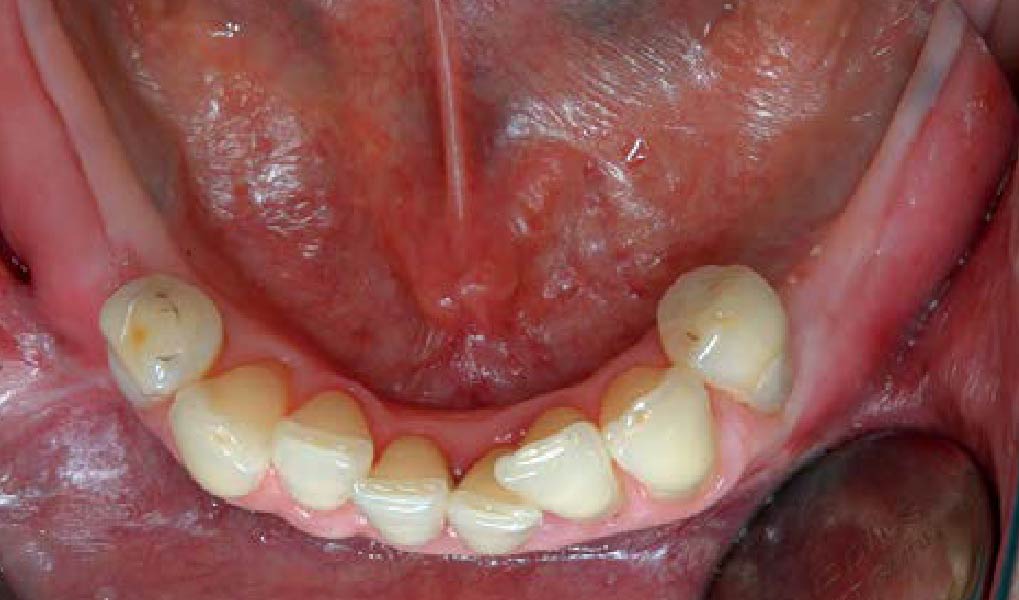
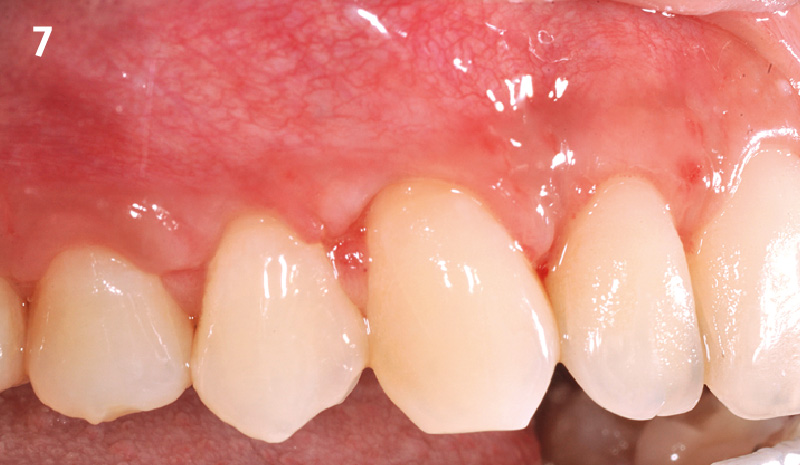
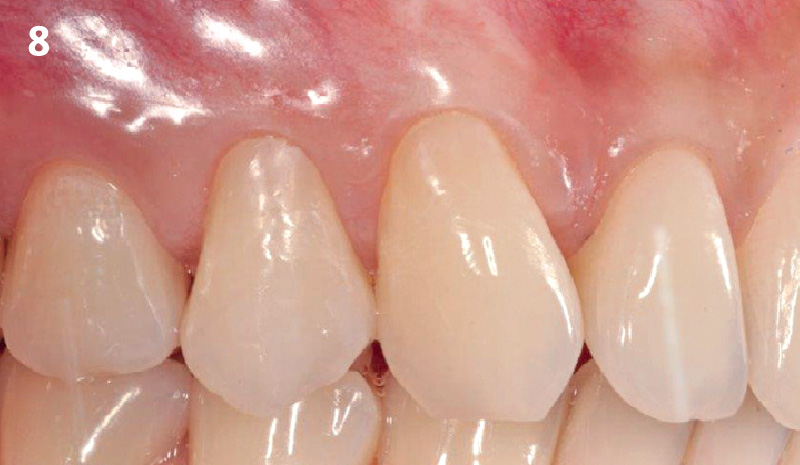
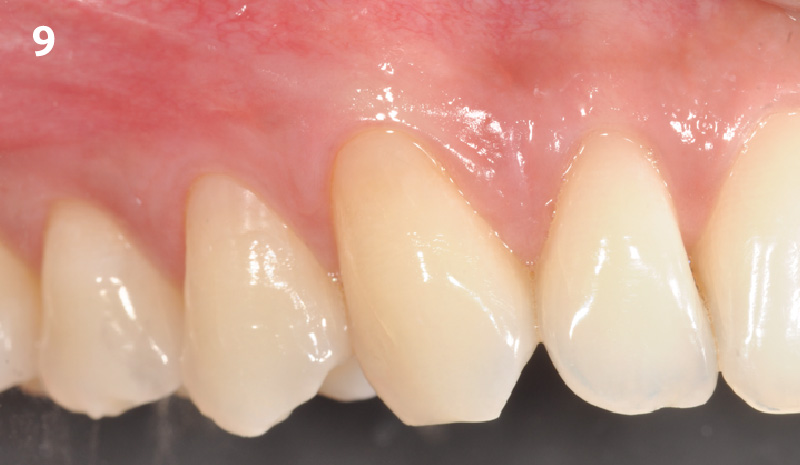
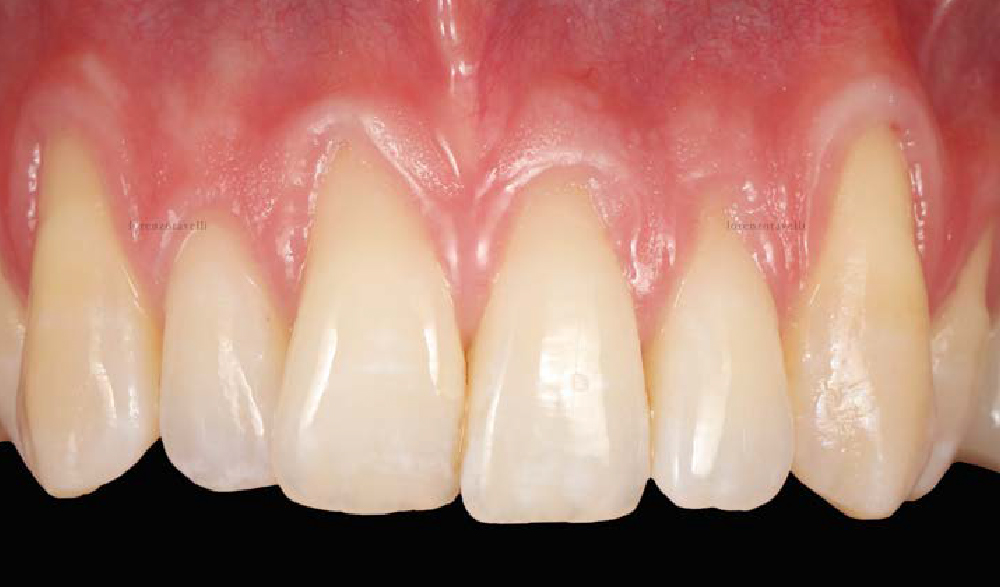
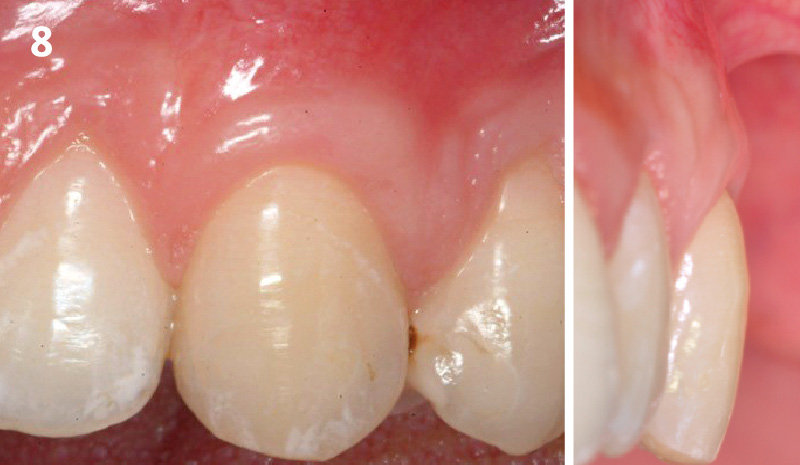
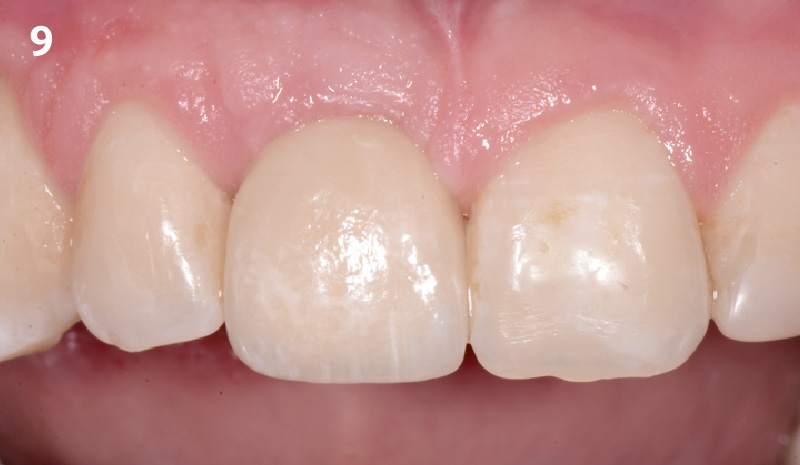
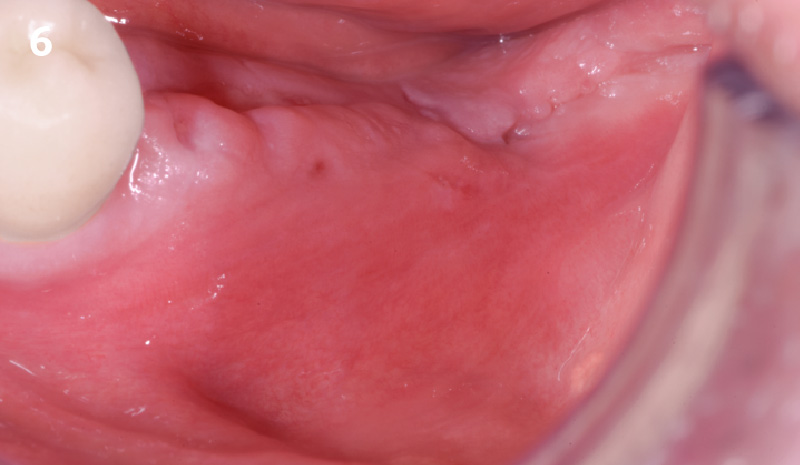
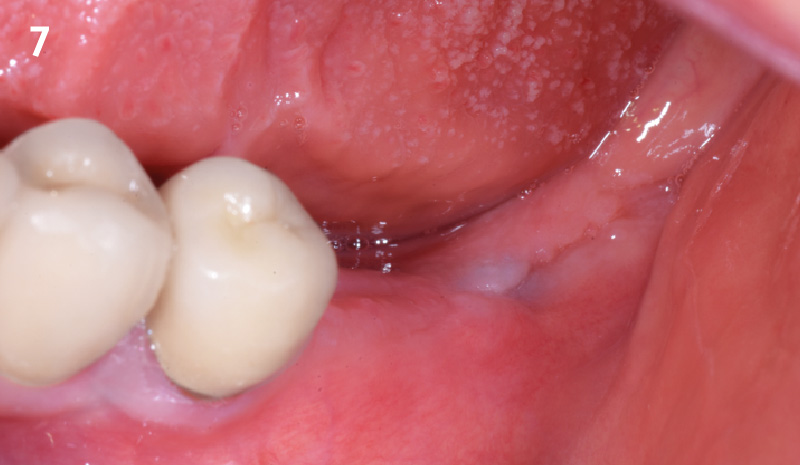
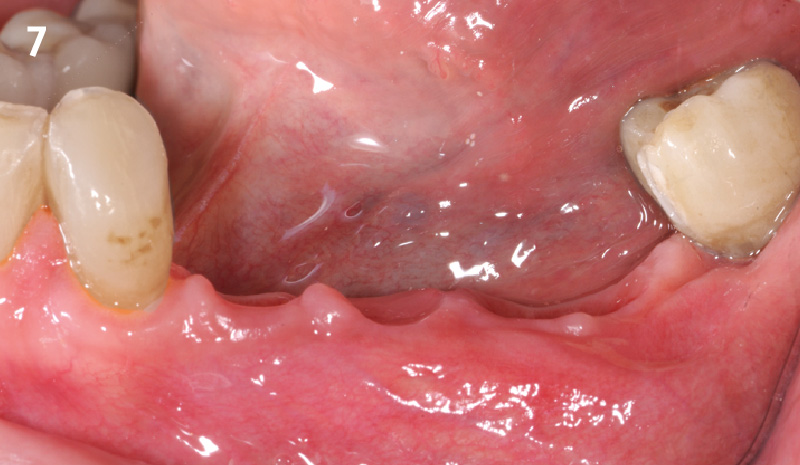
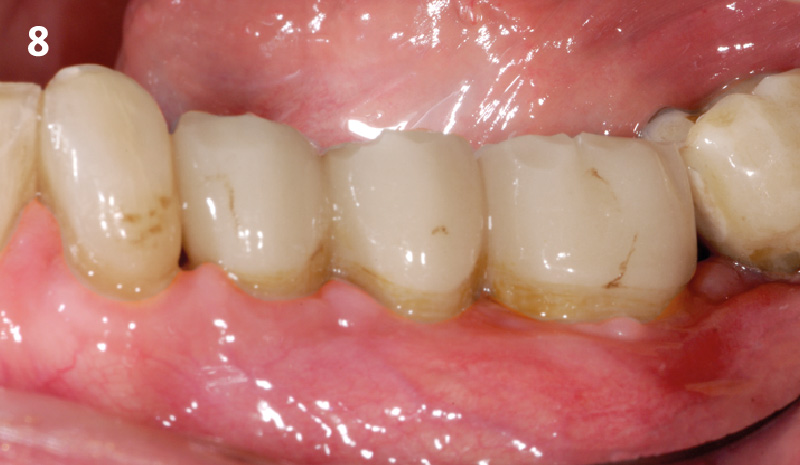
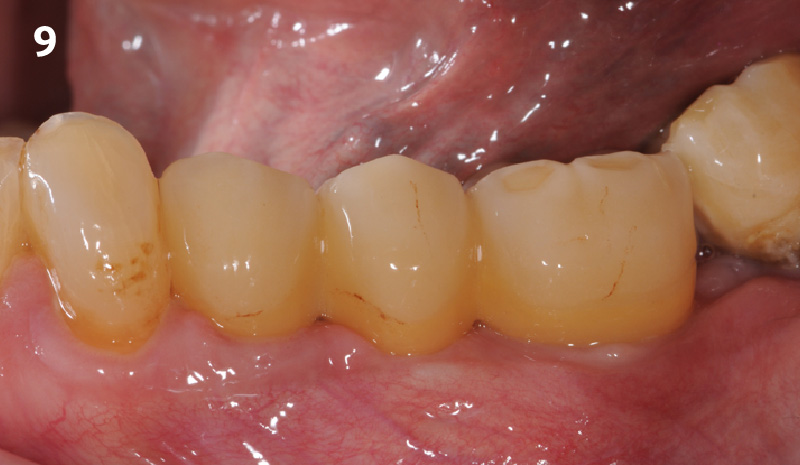
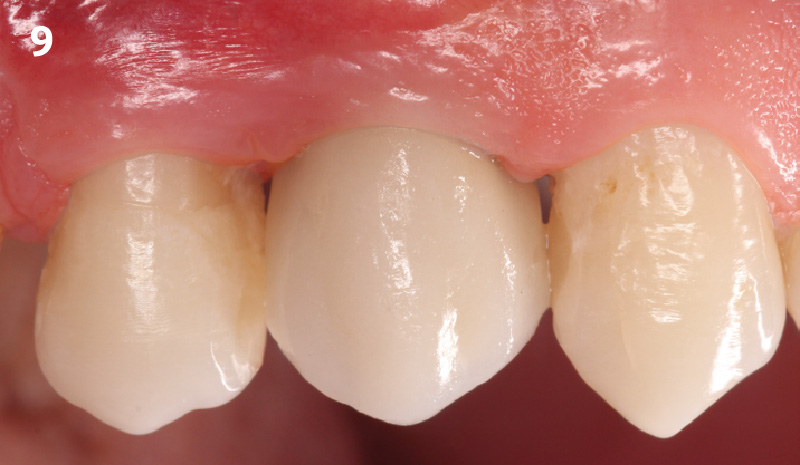
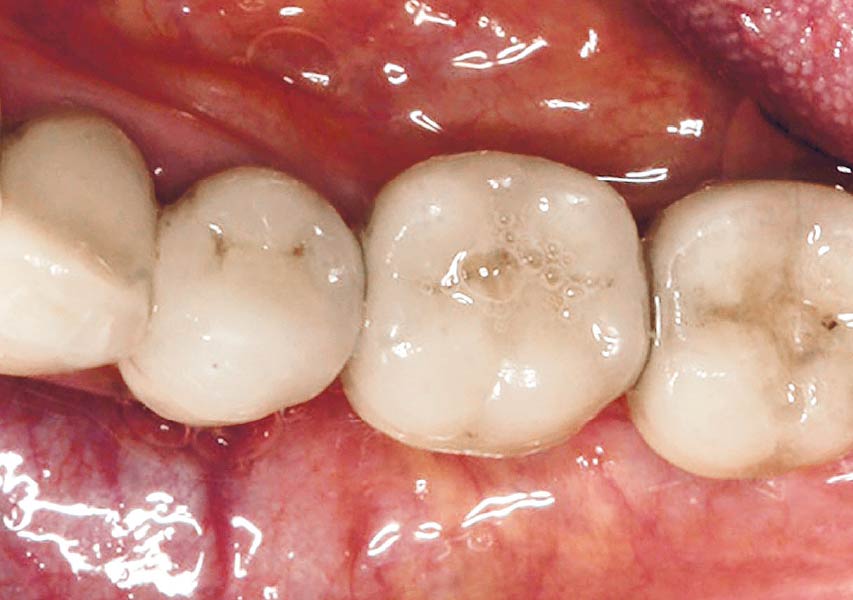
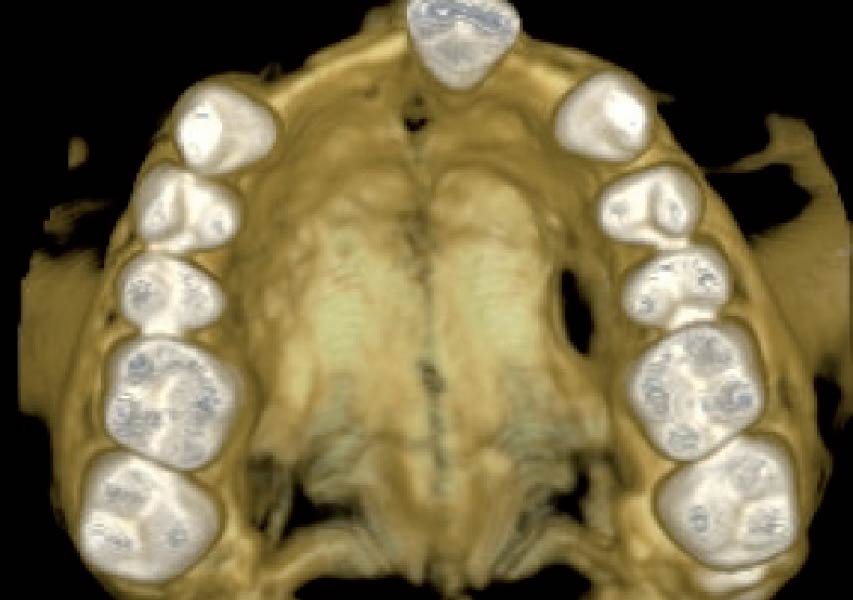
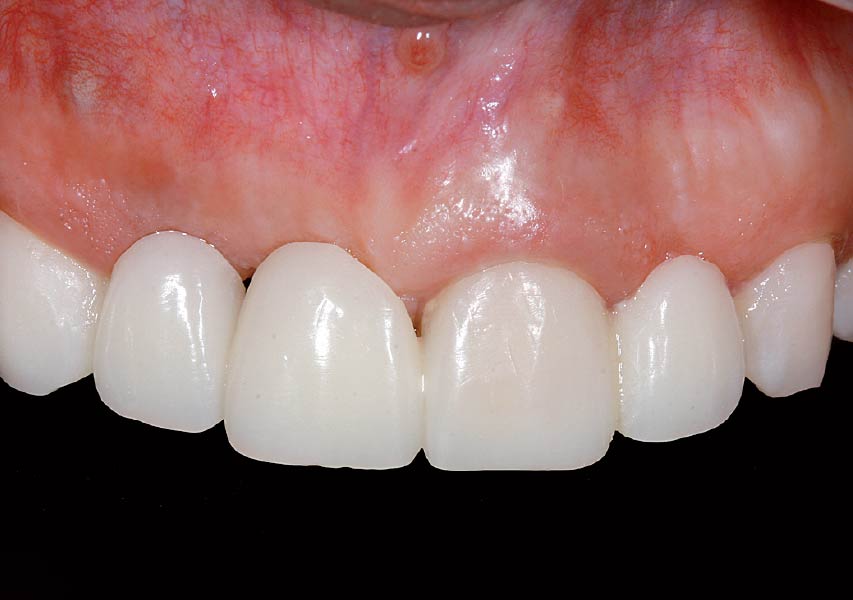
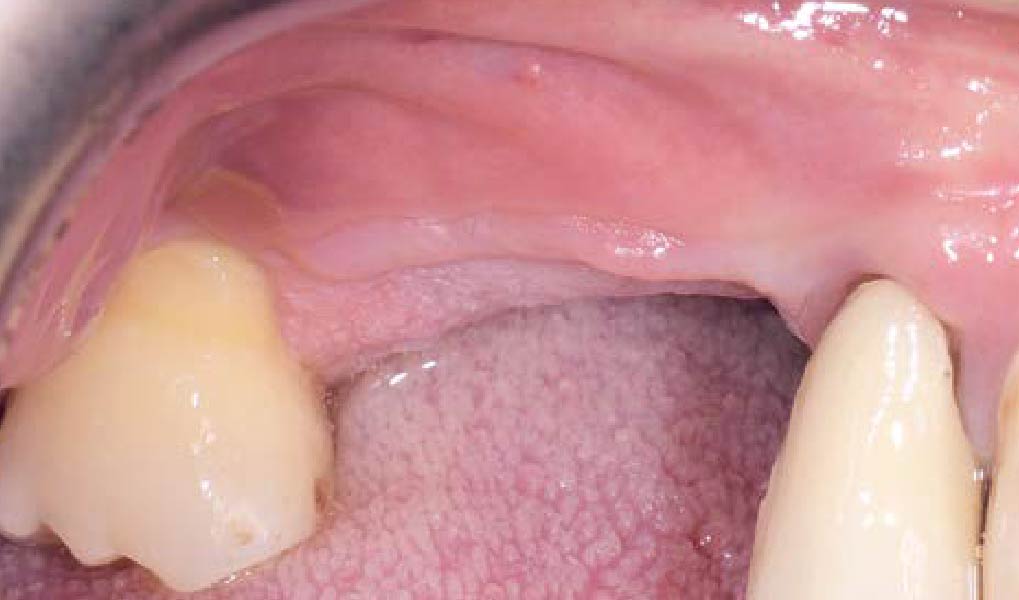
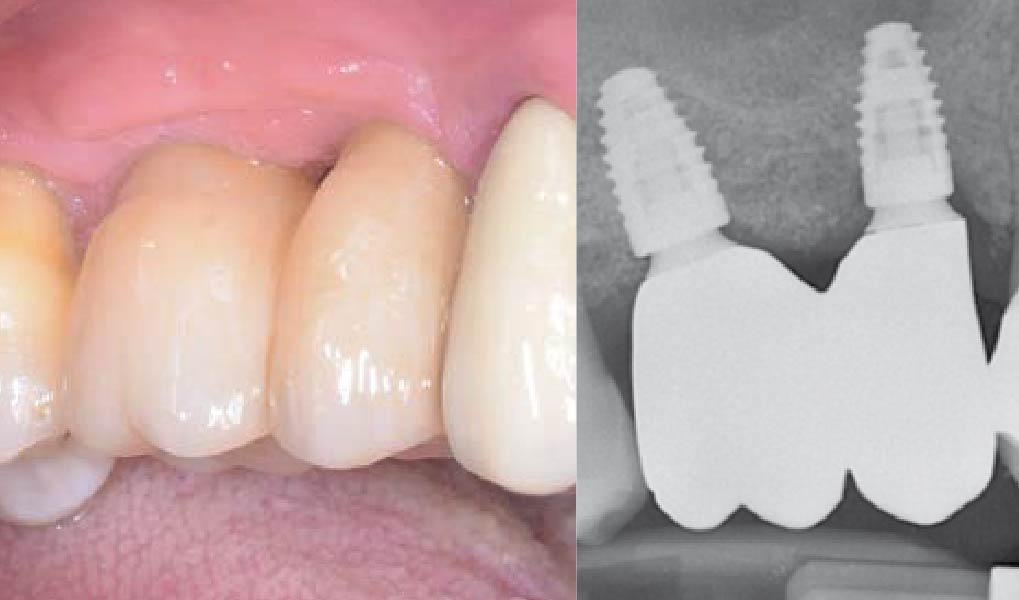
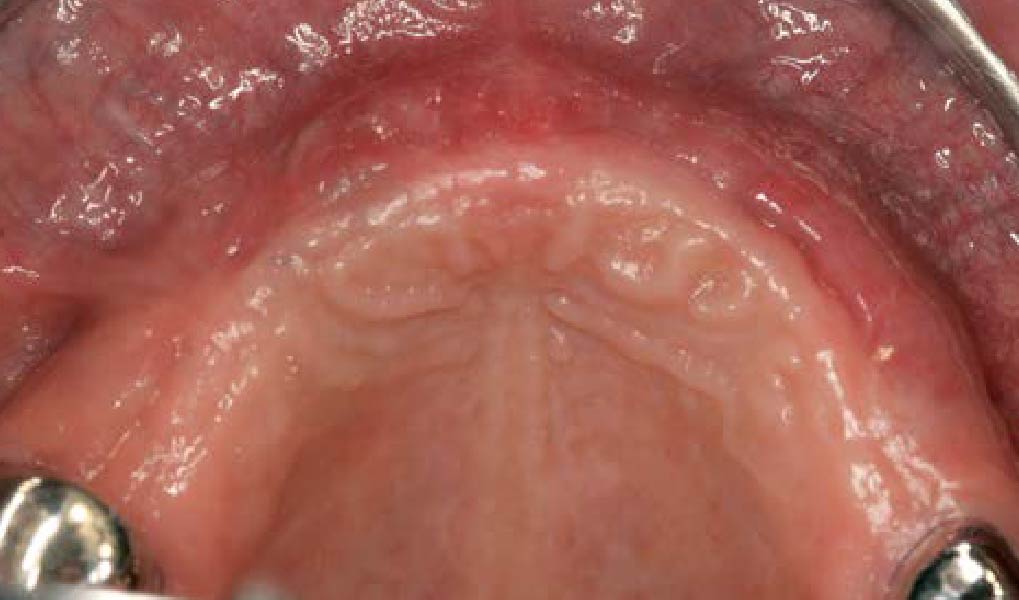
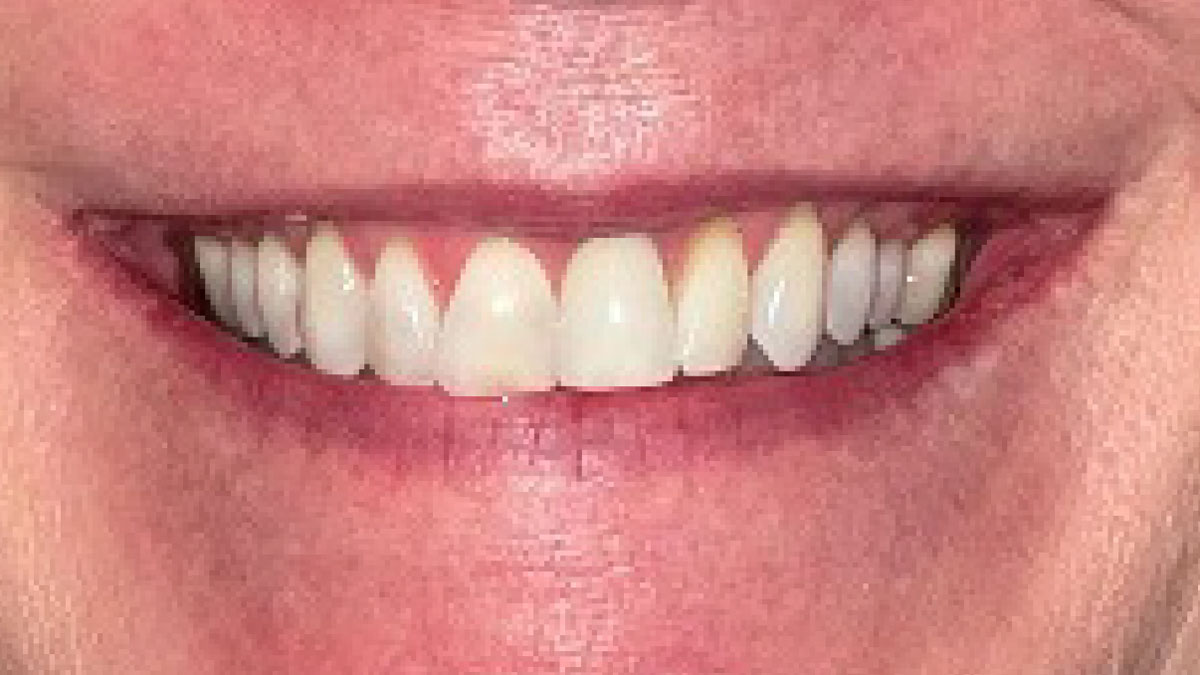
THE OUTCOME
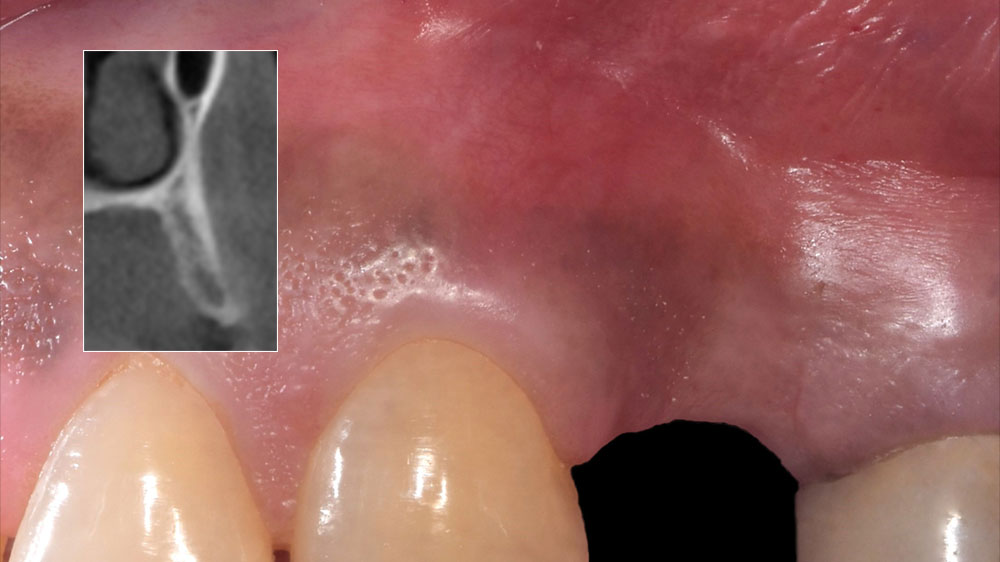
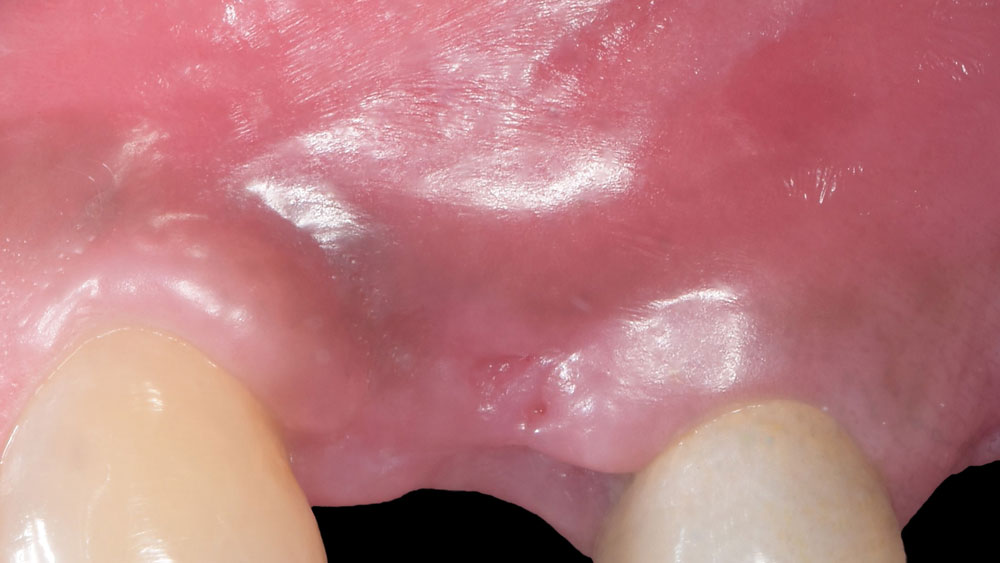
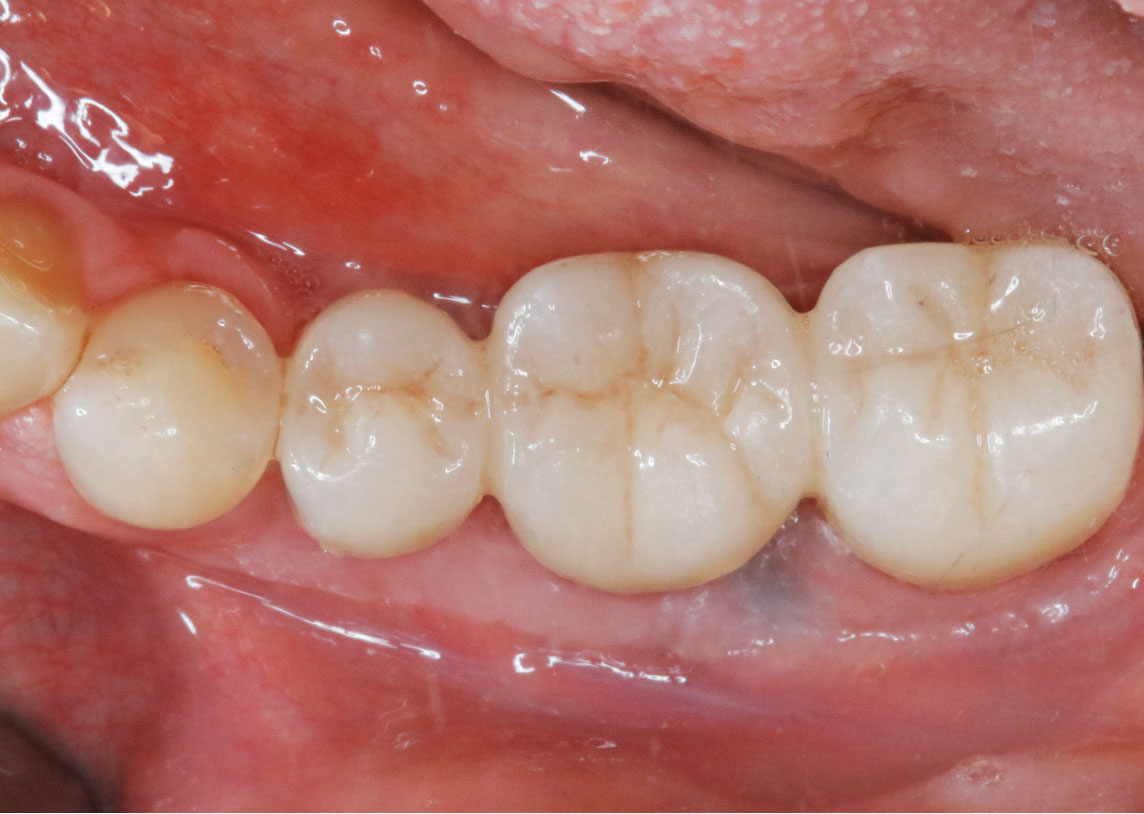
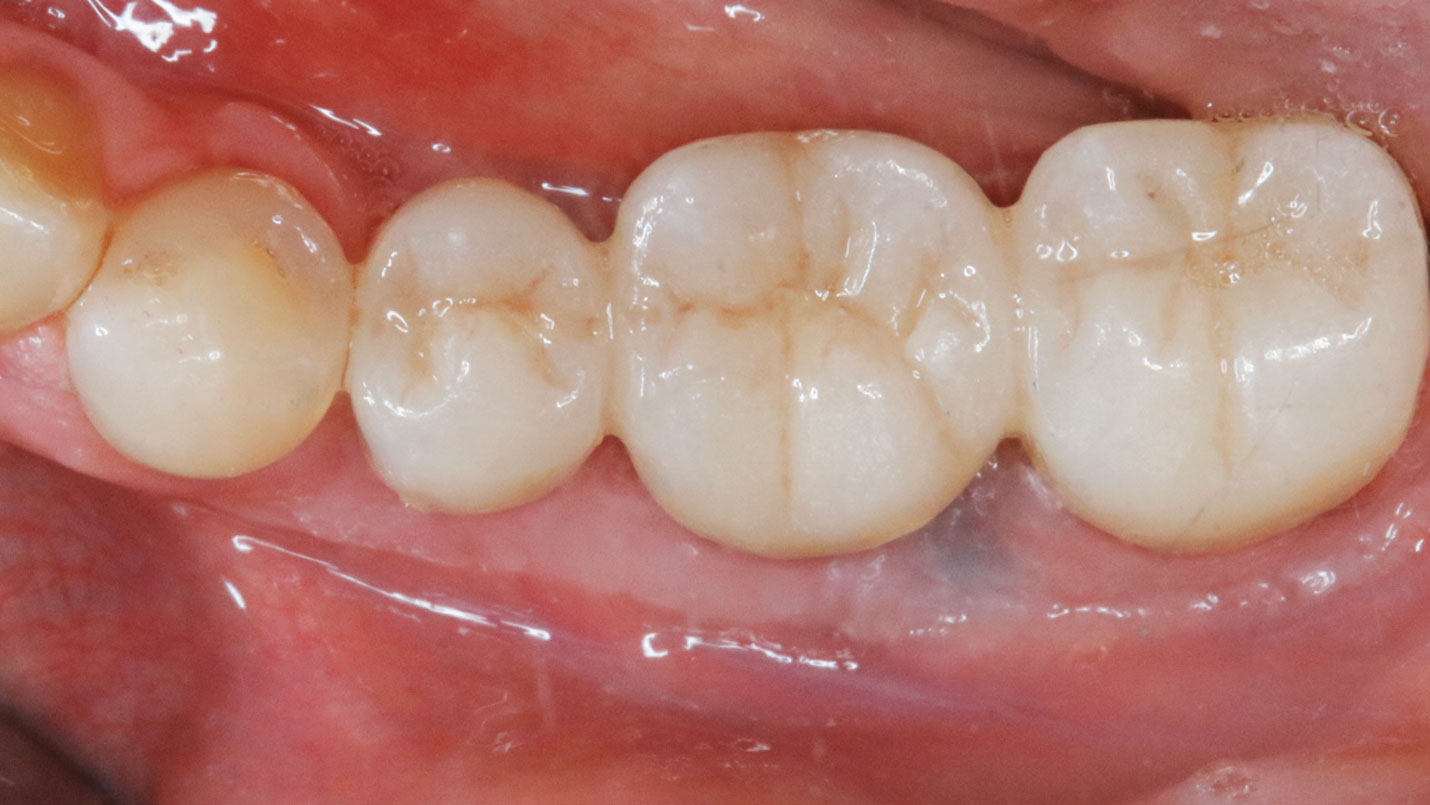
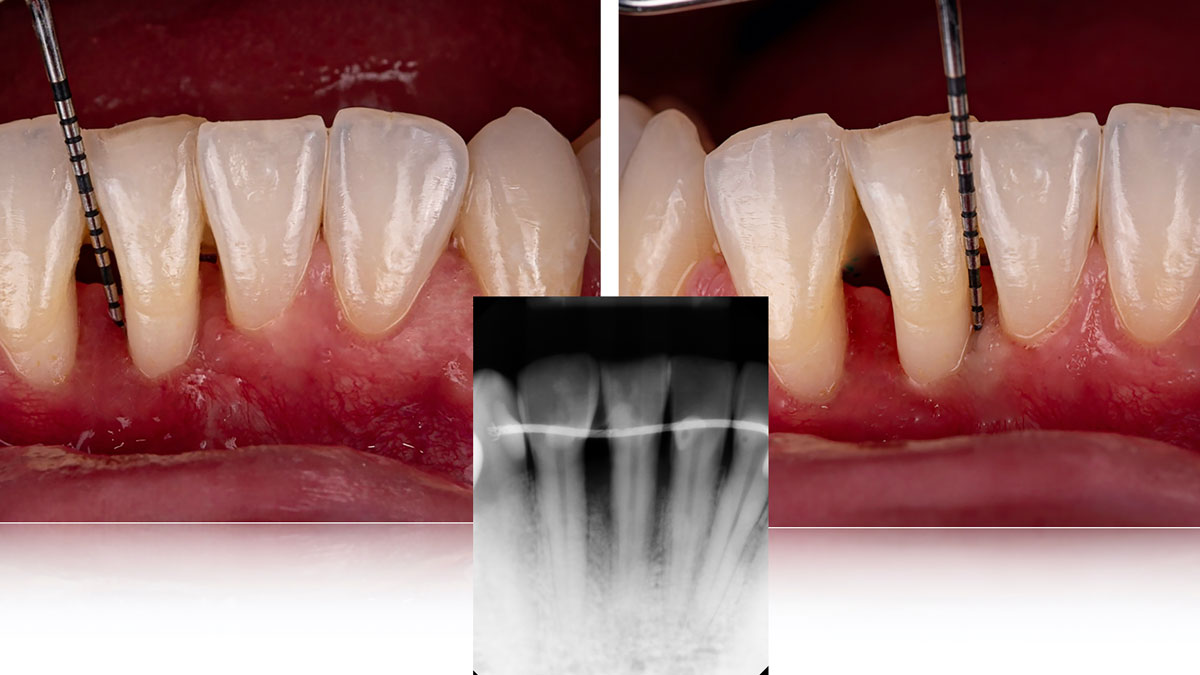
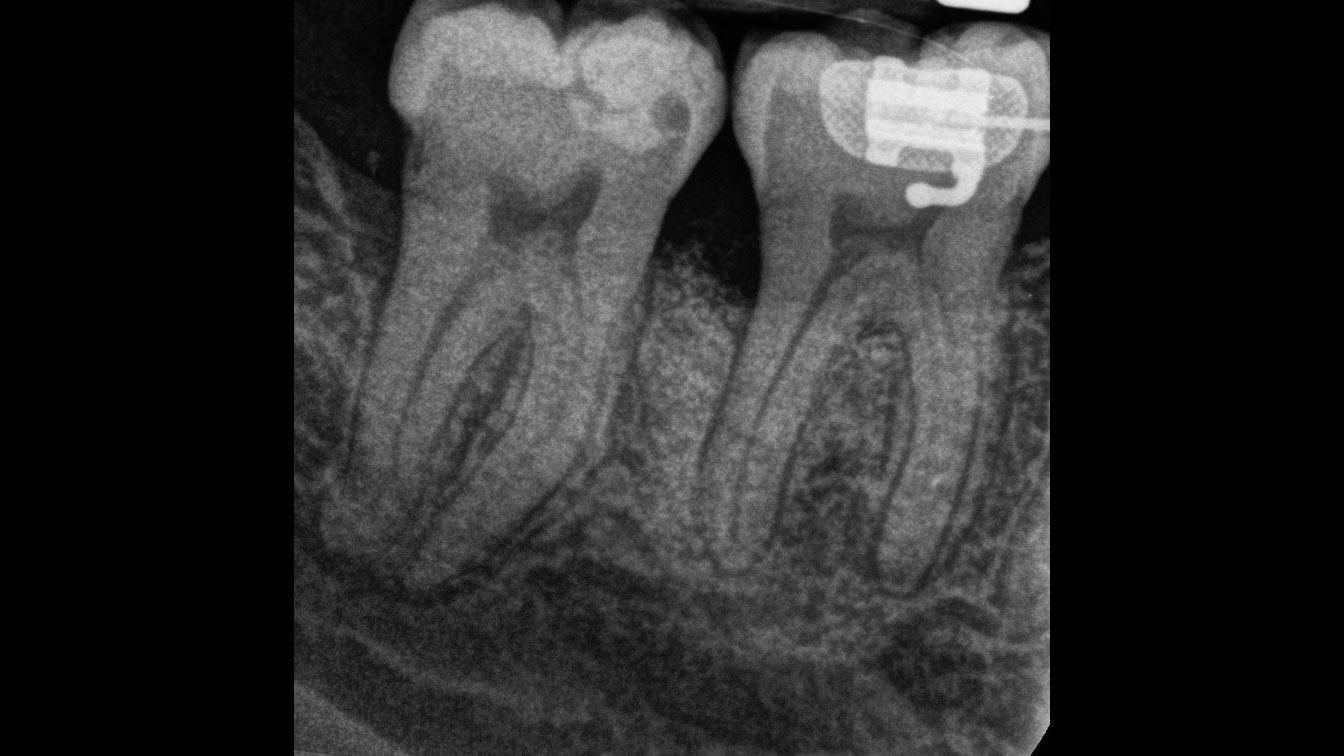
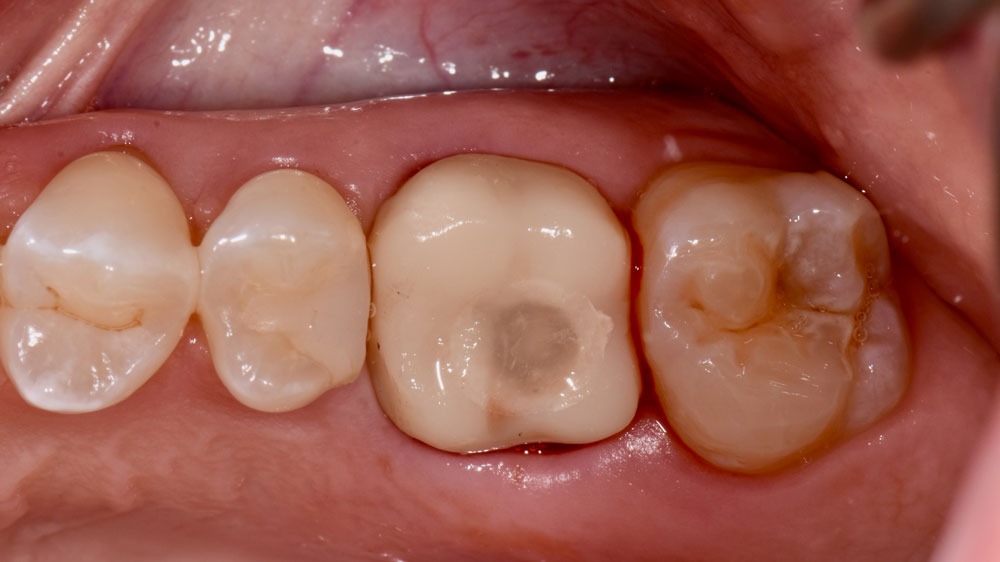
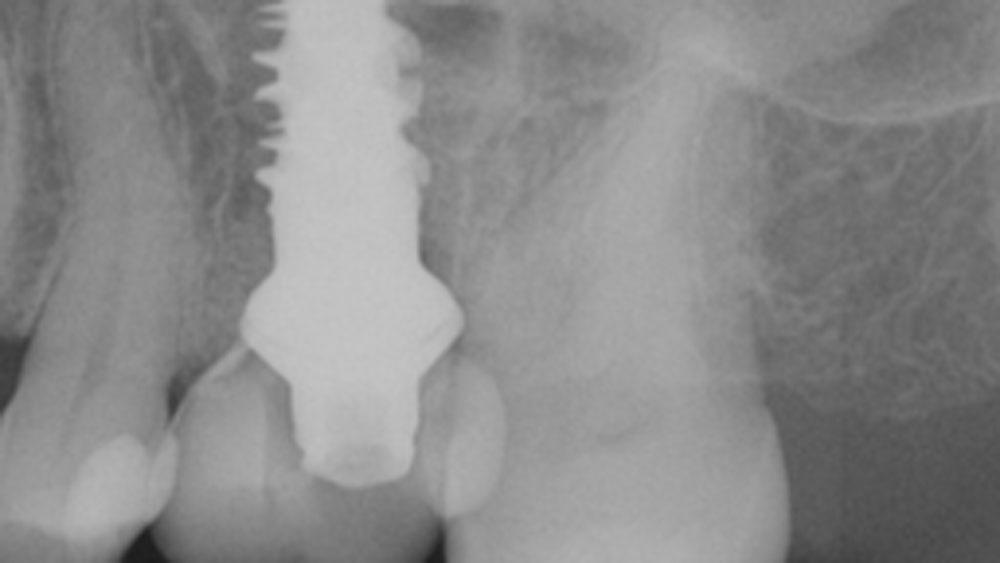
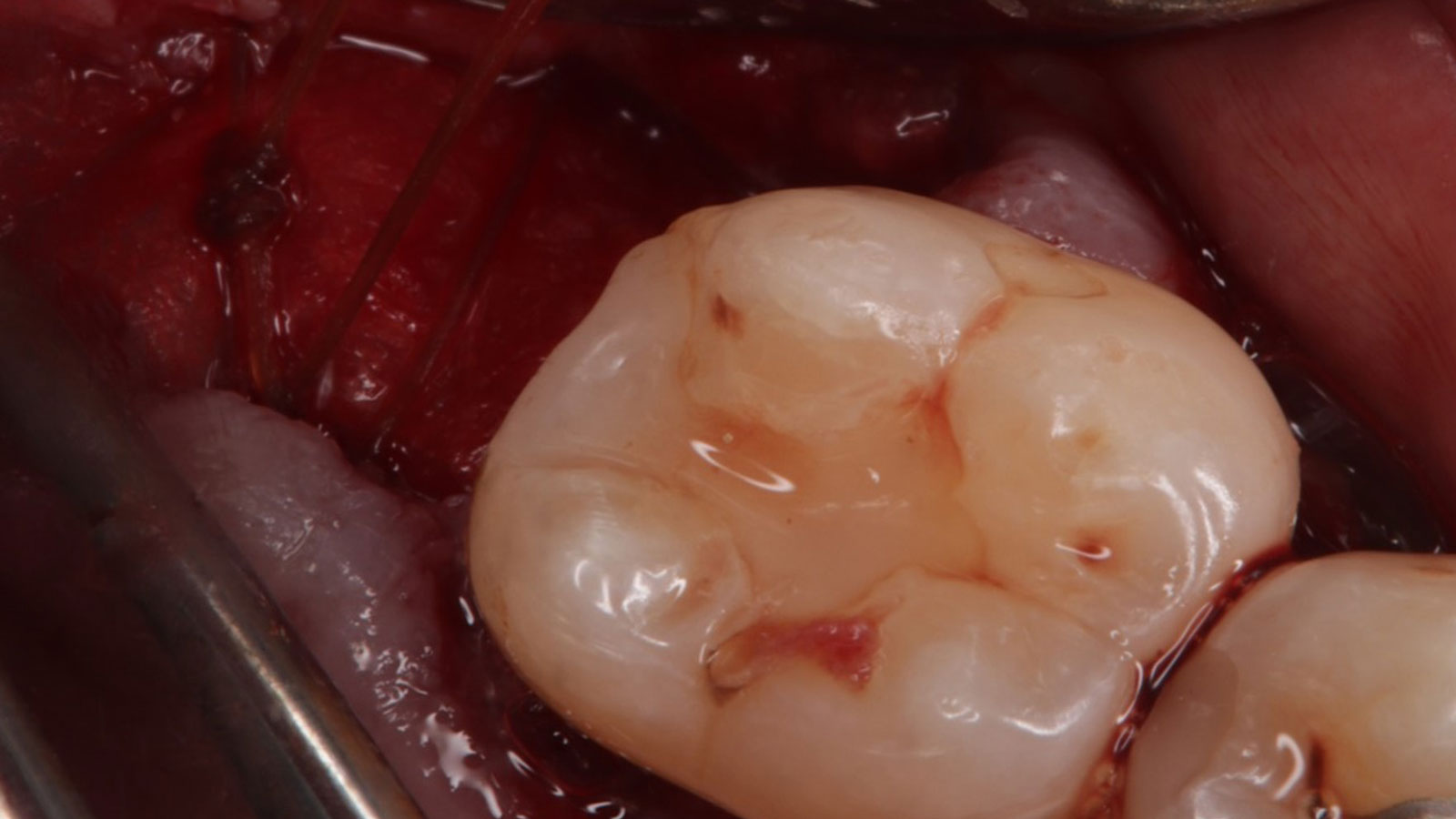
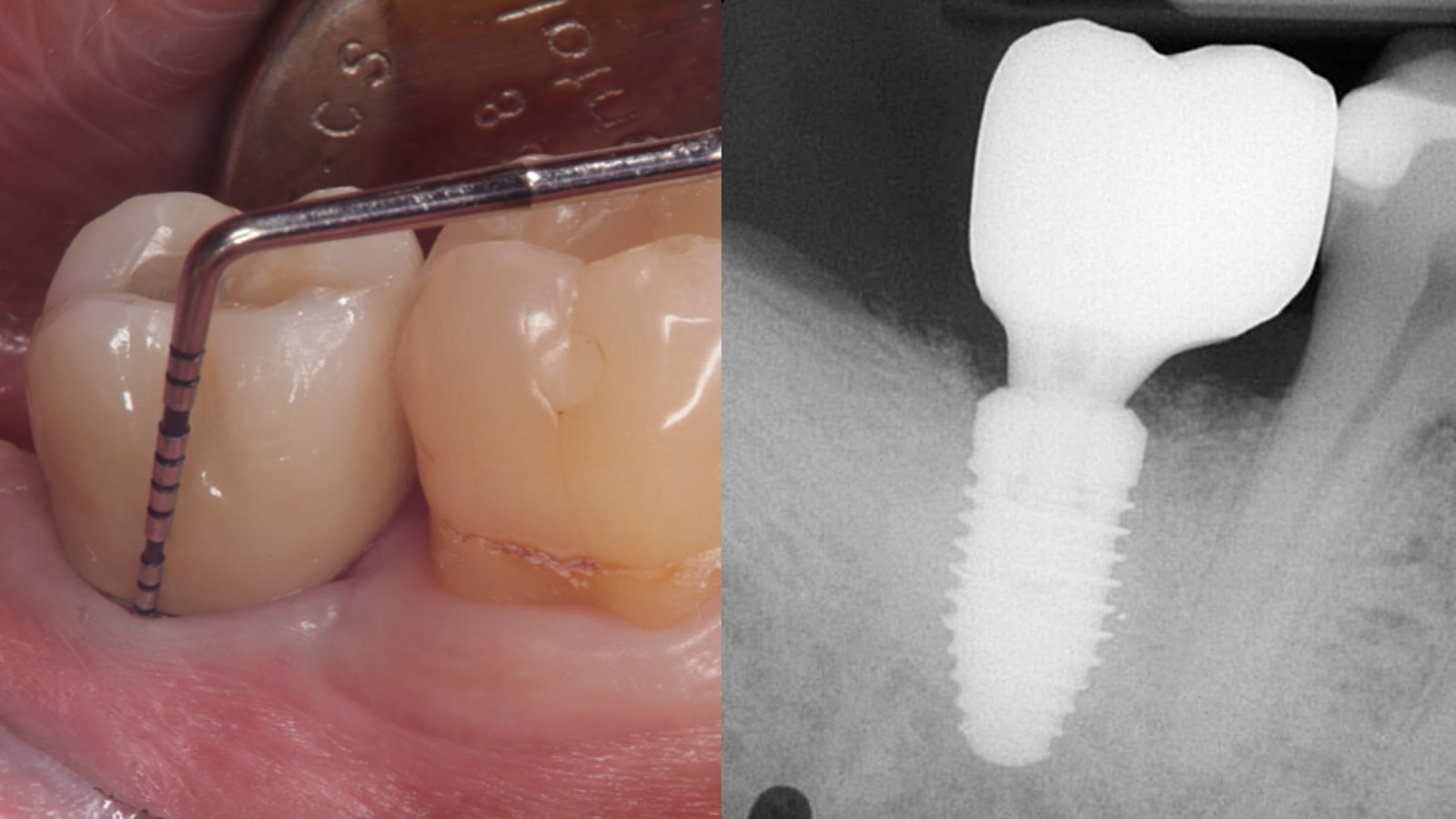
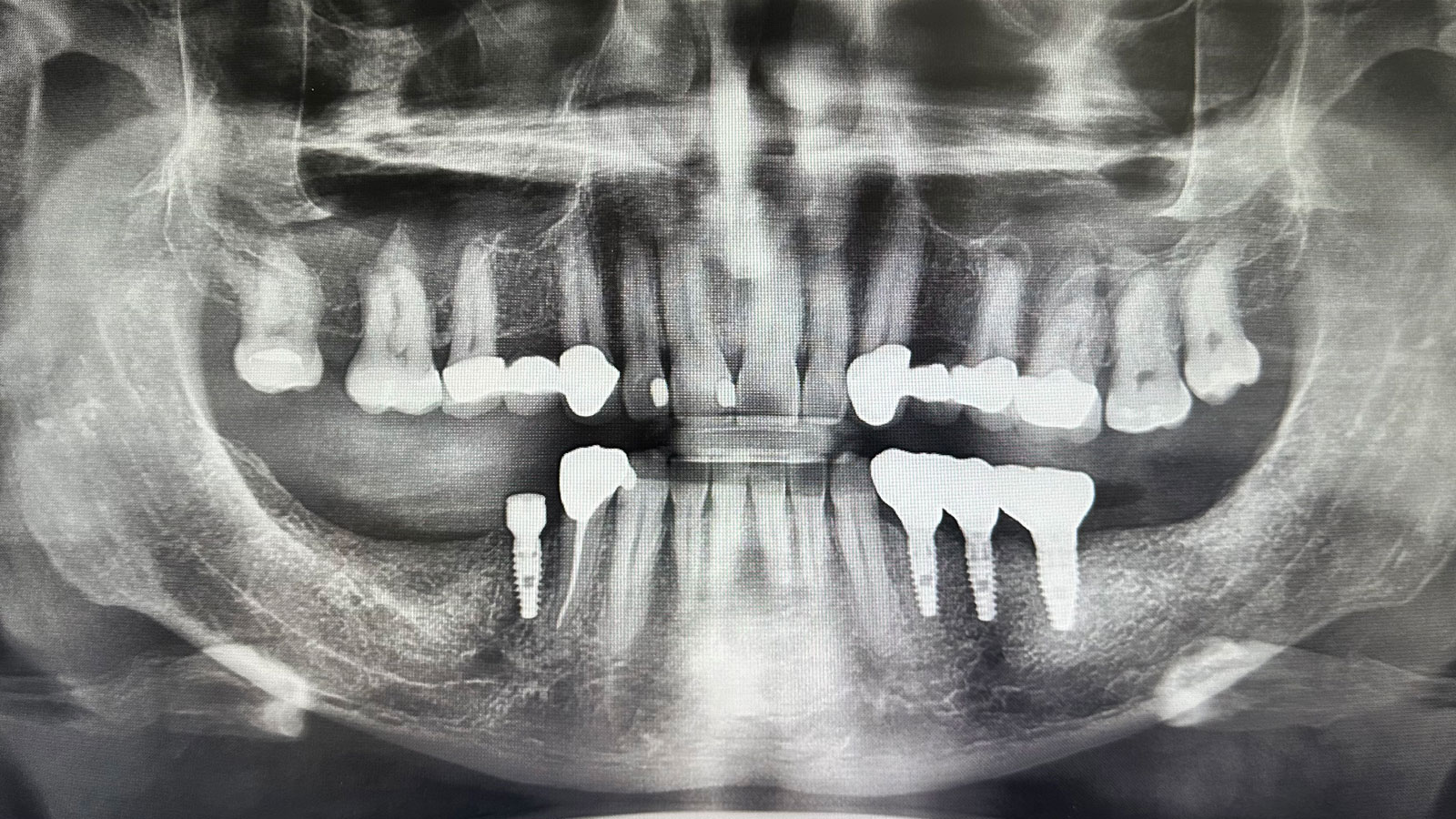
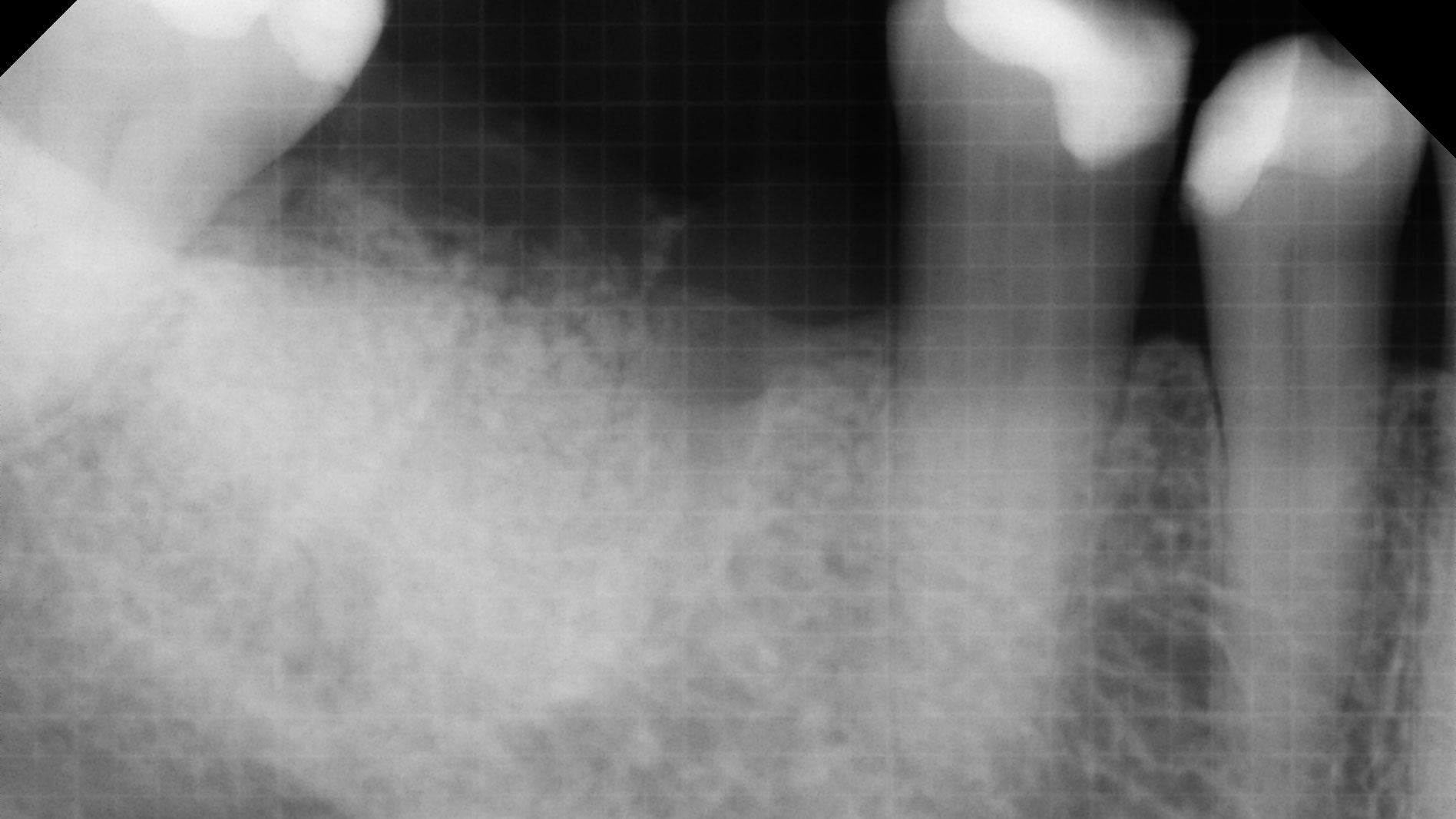
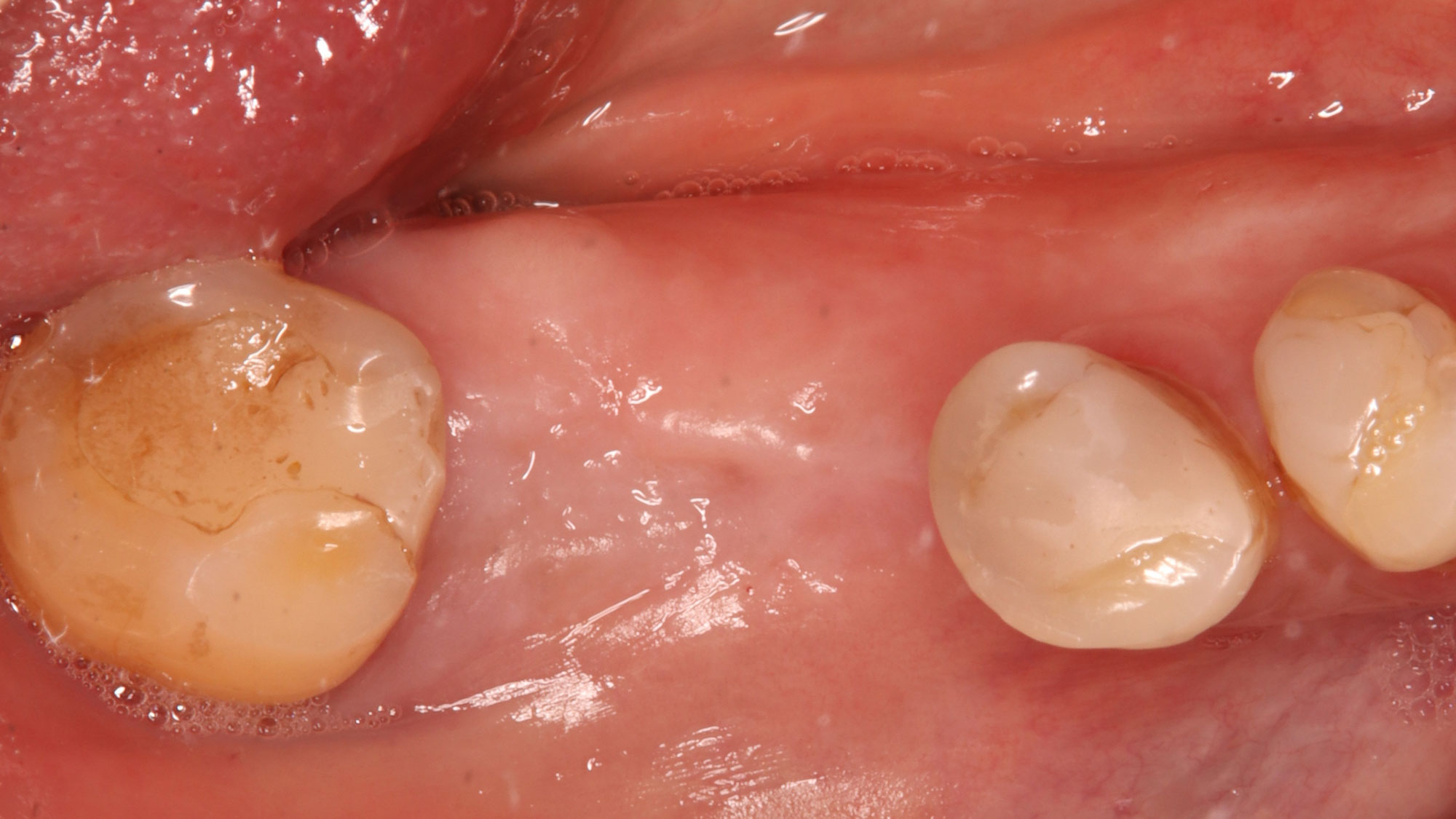
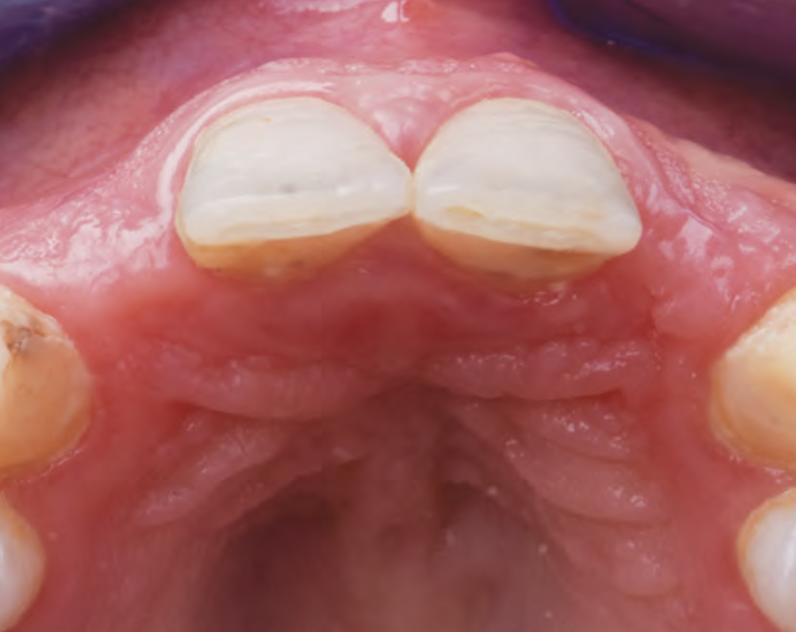
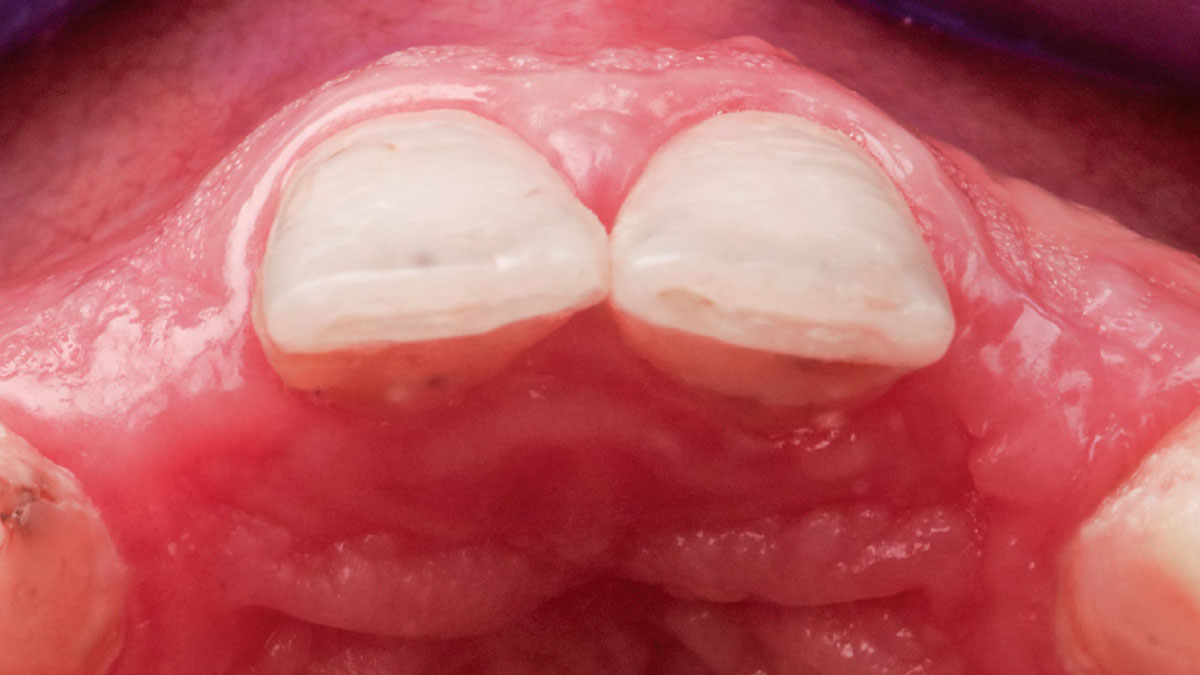
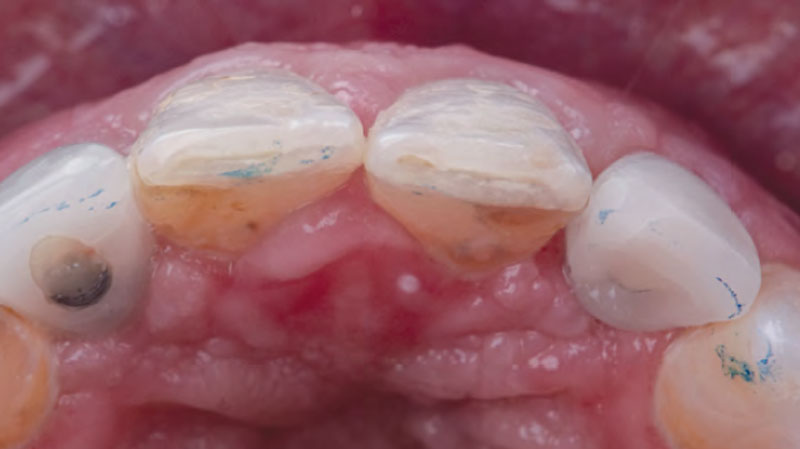
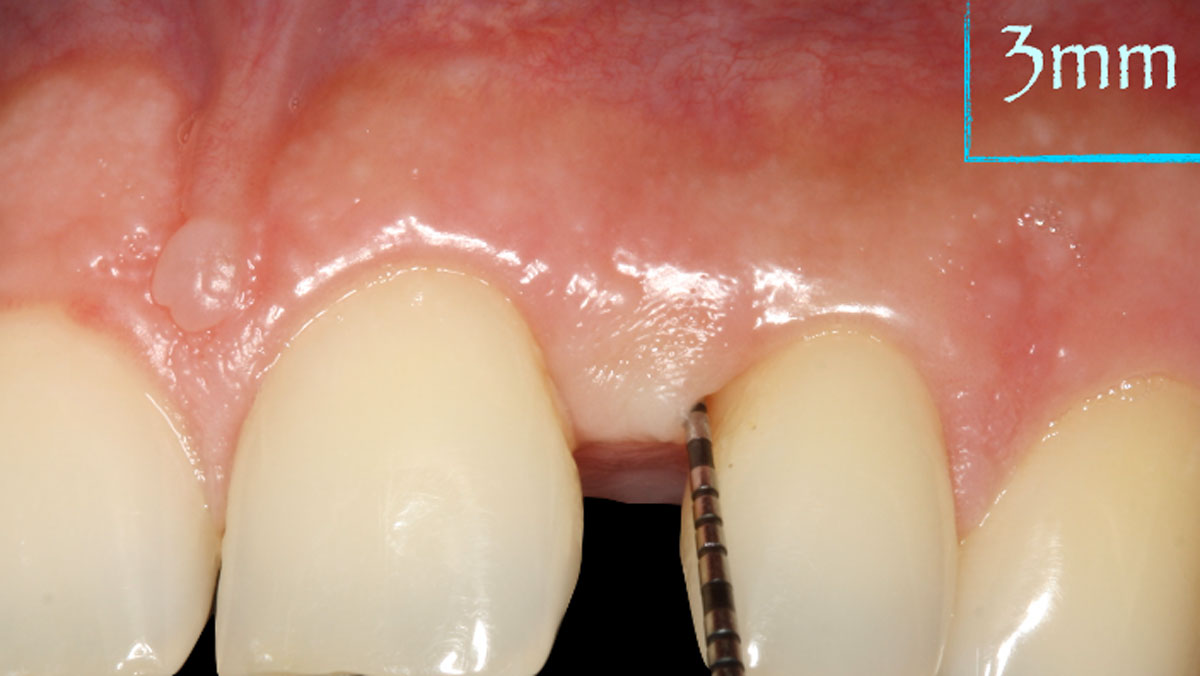
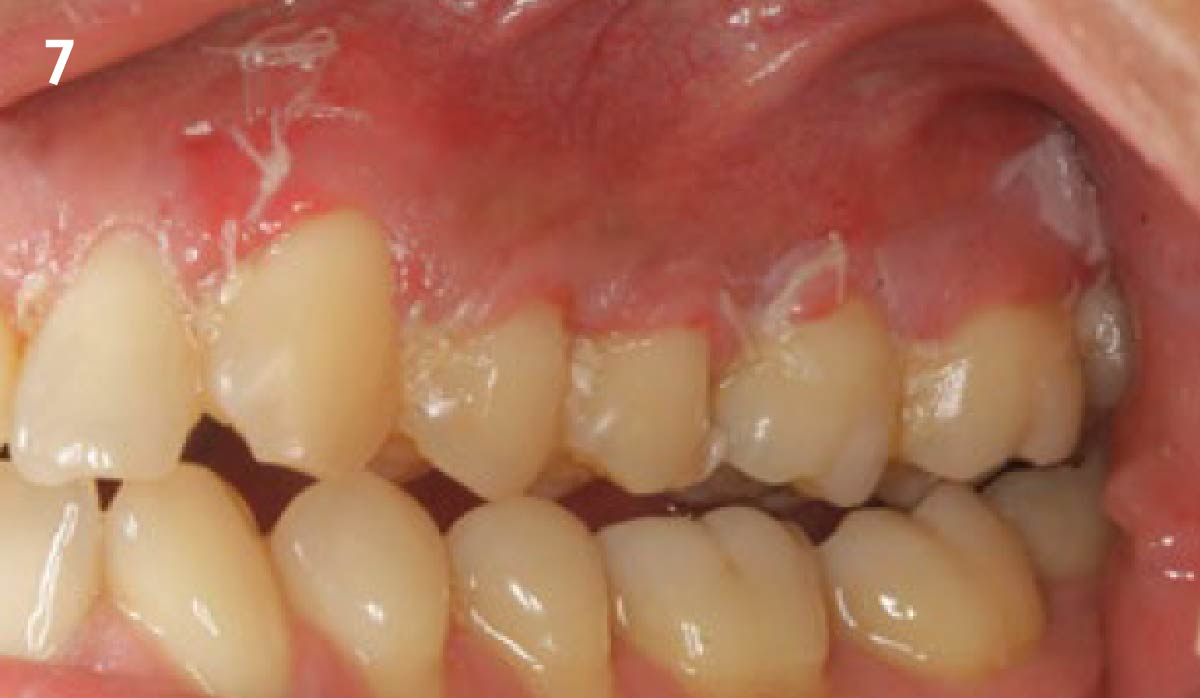
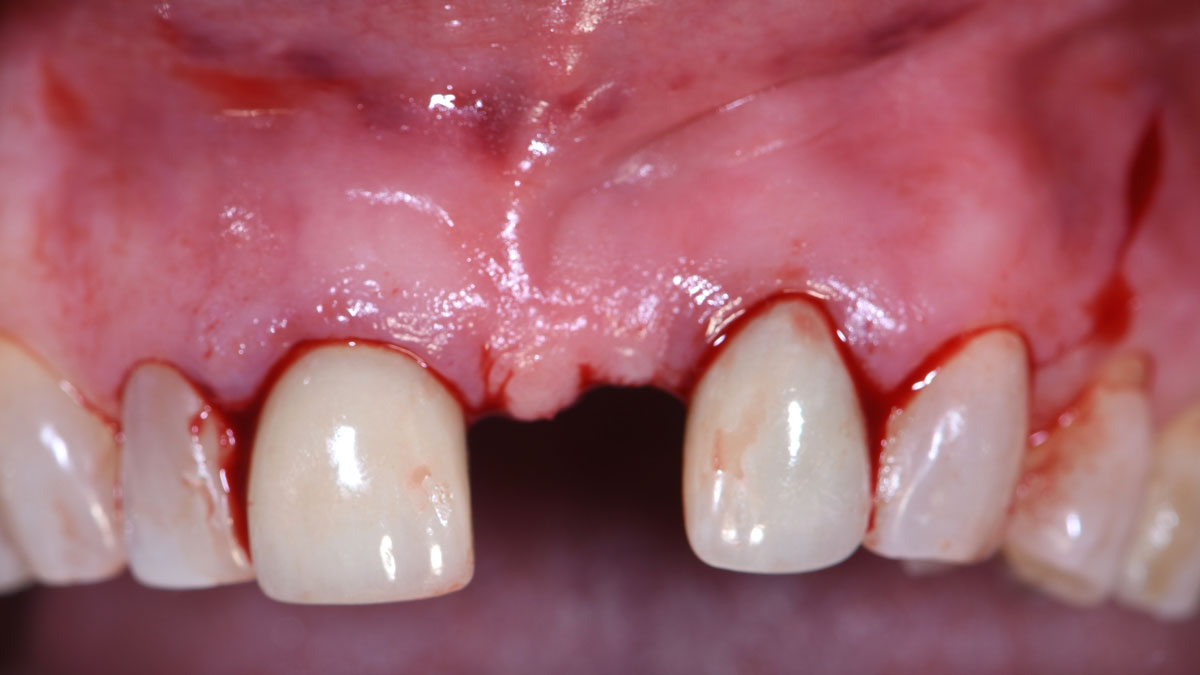
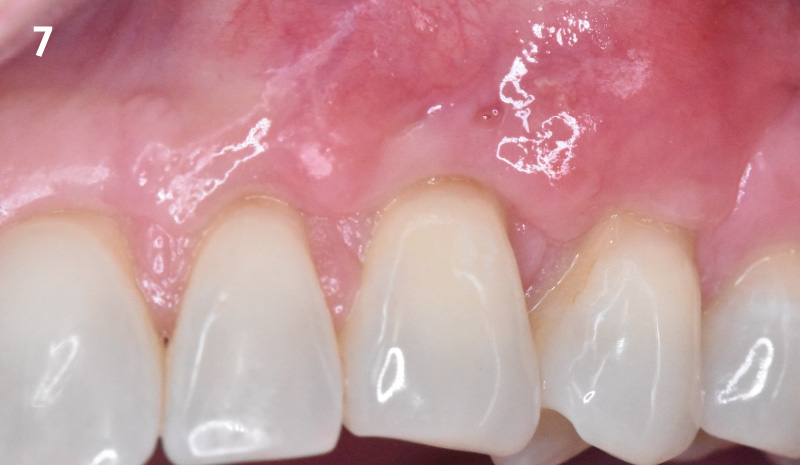
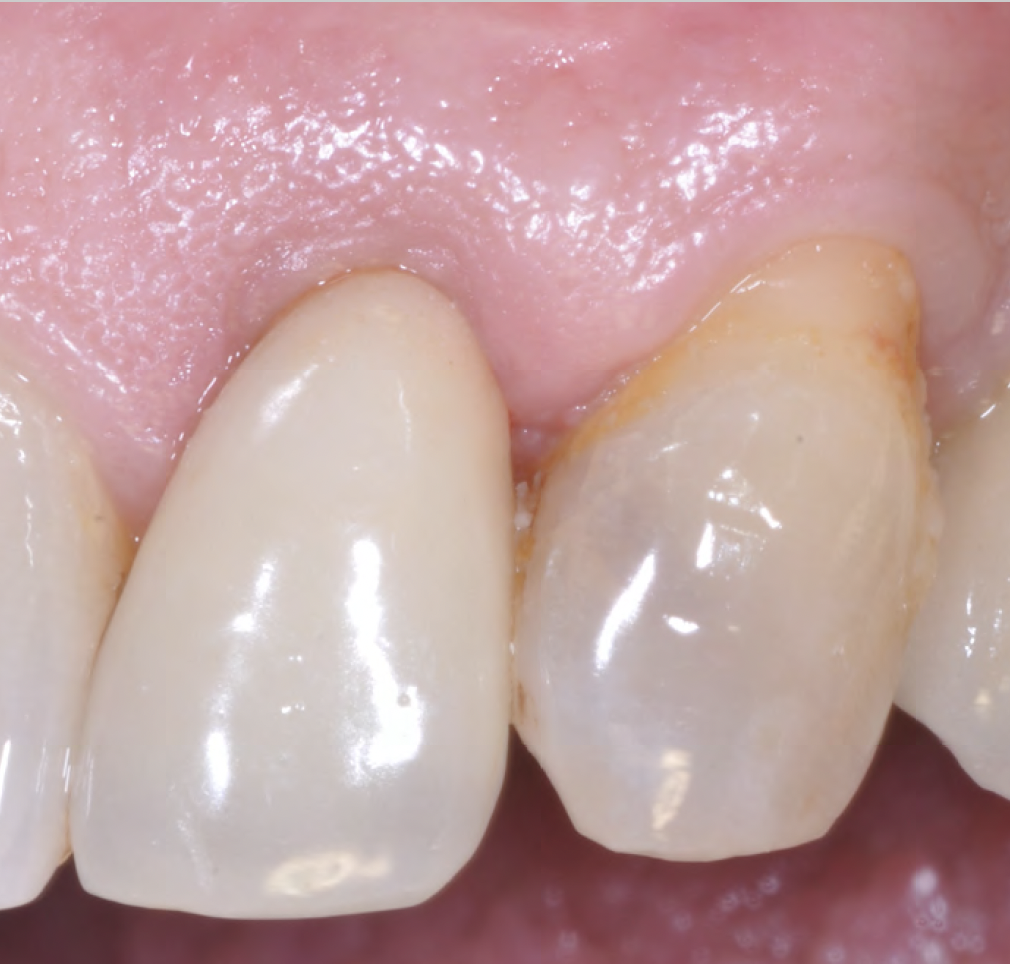
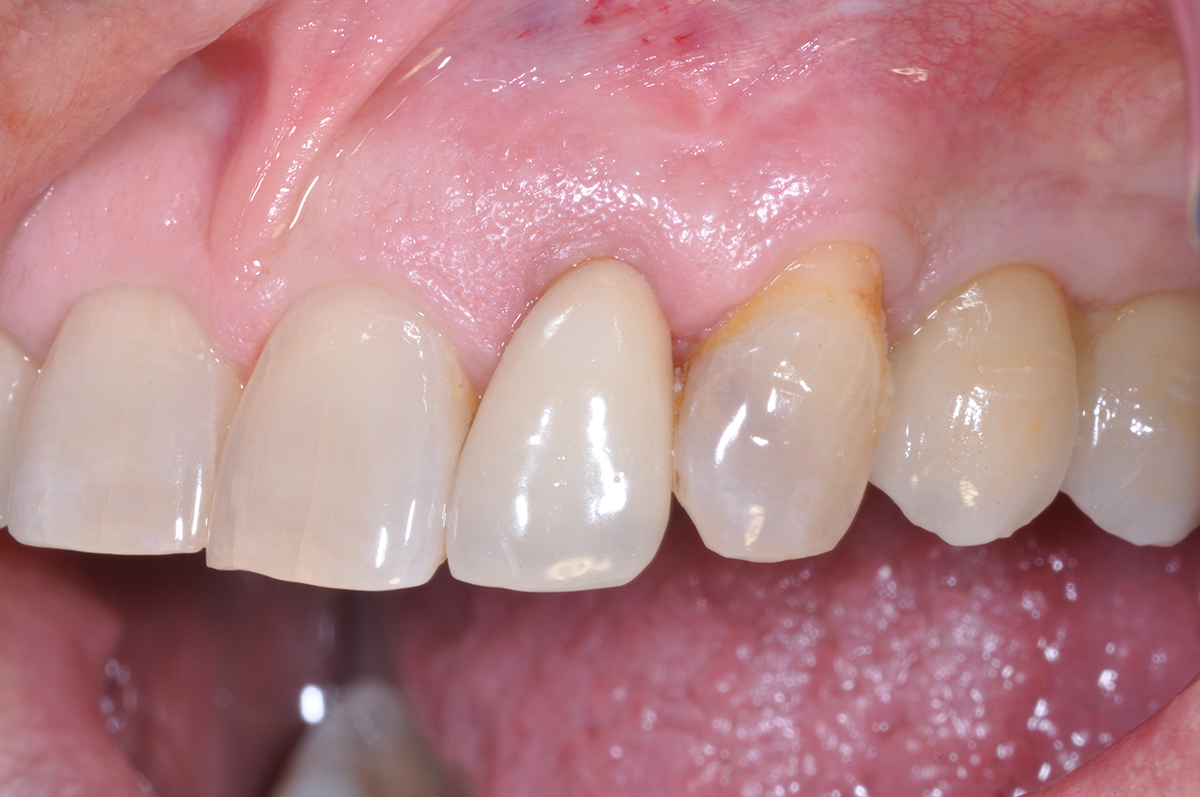
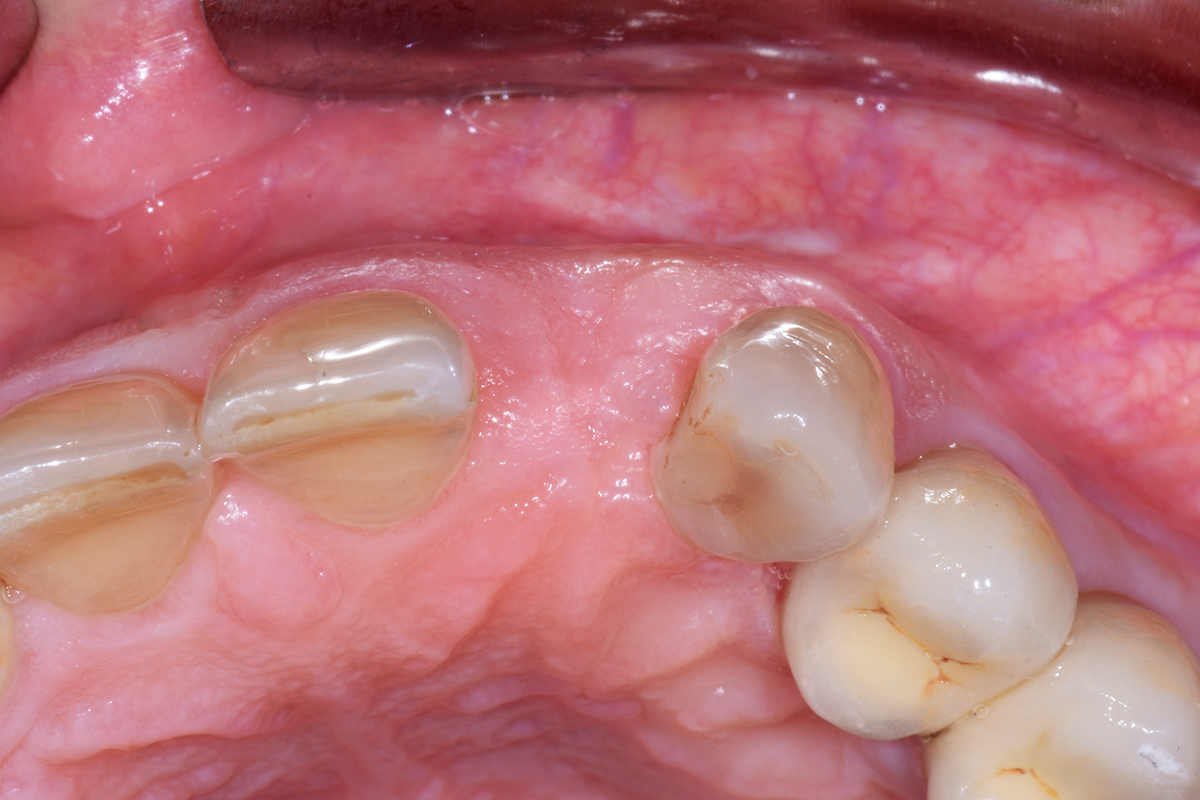
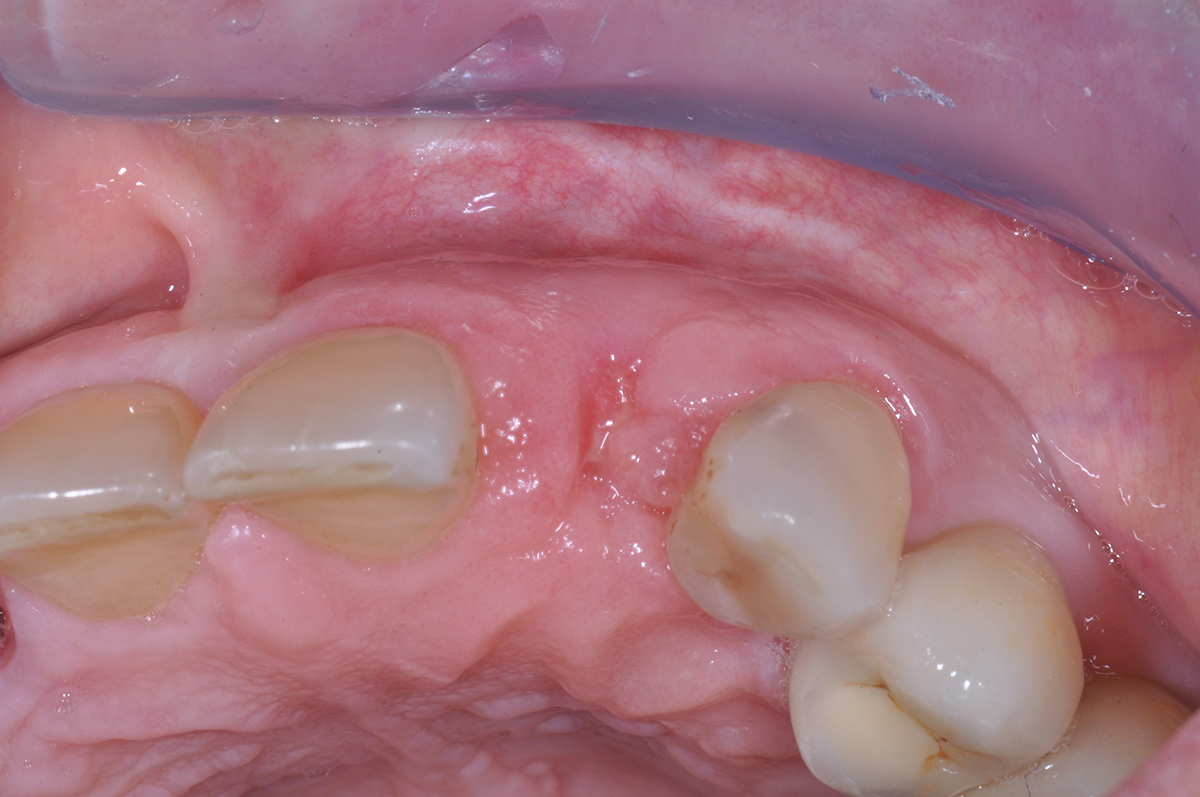
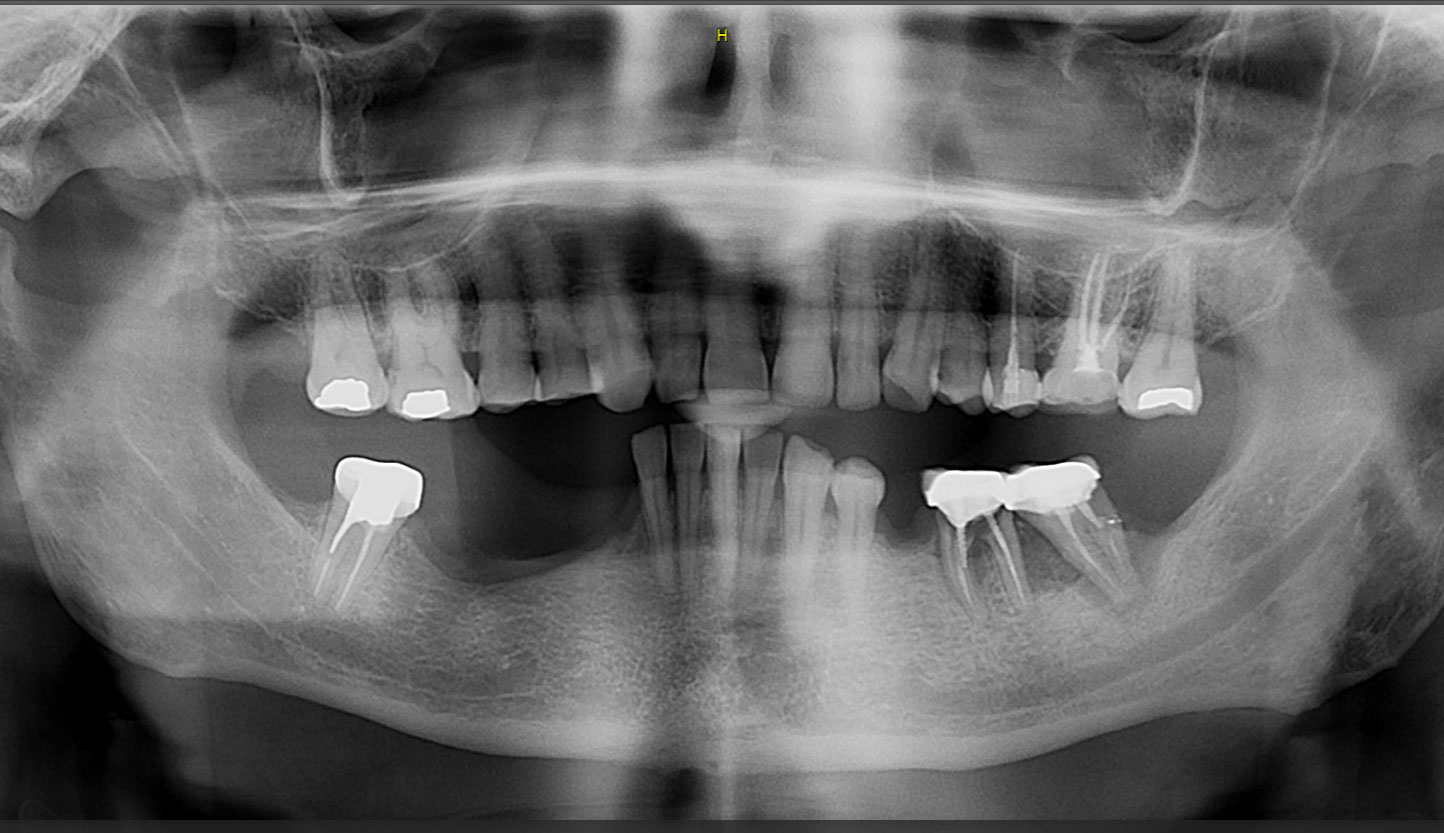
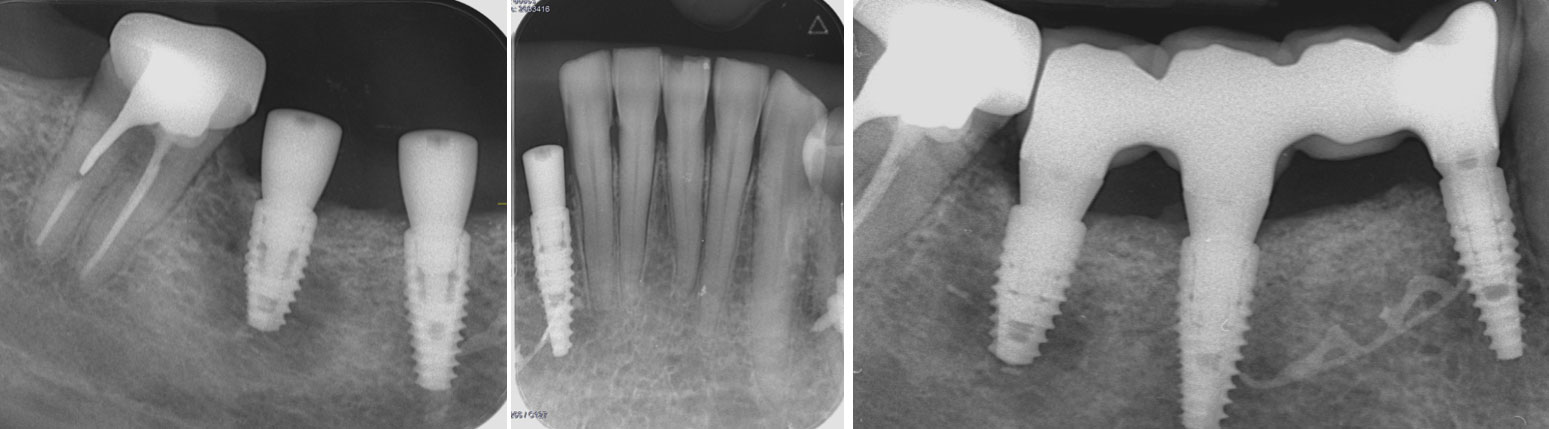
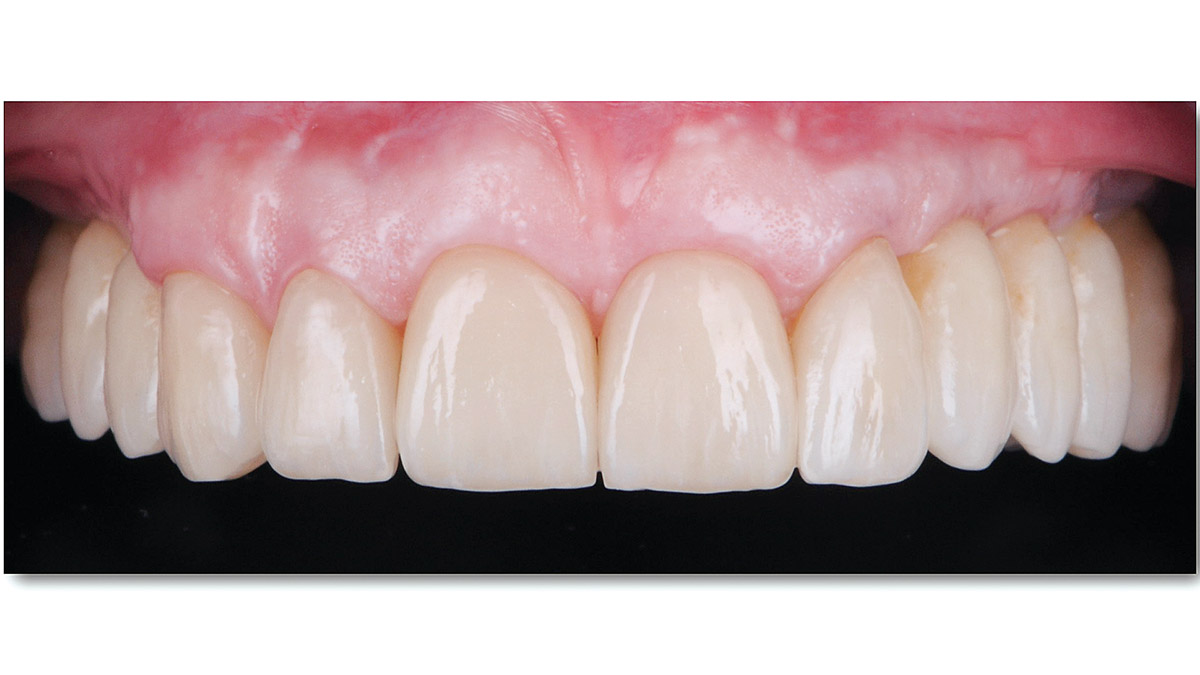
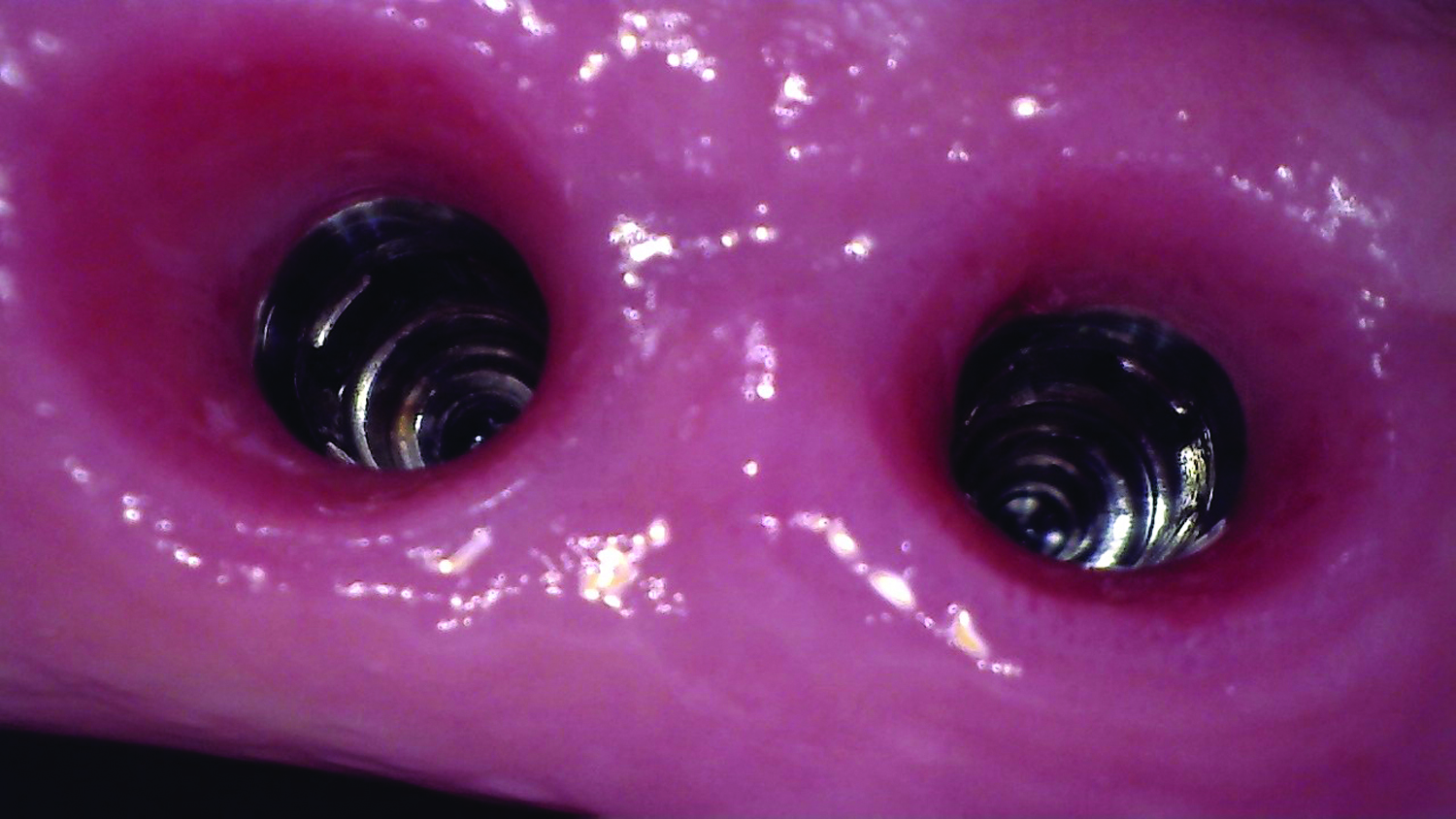
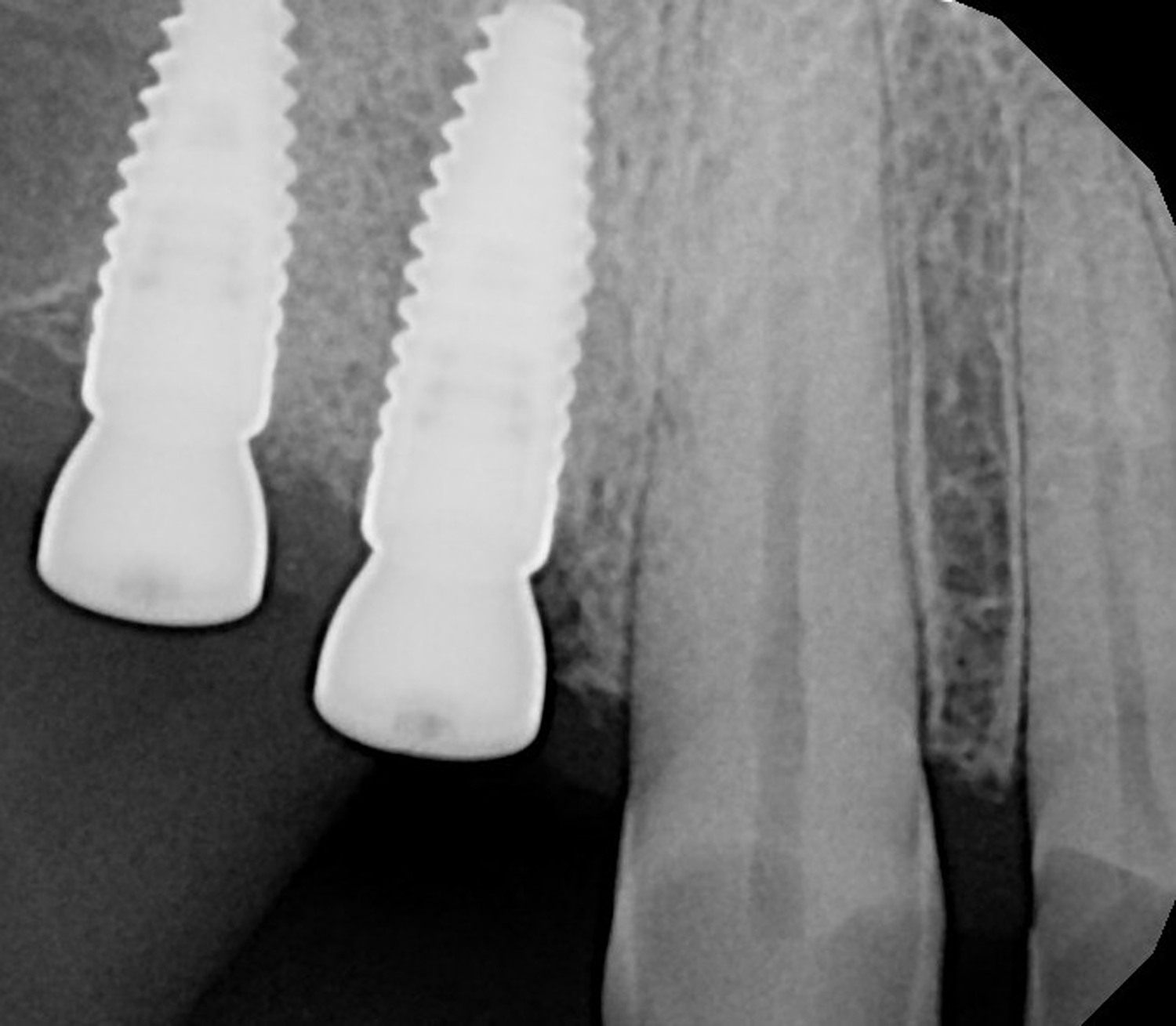
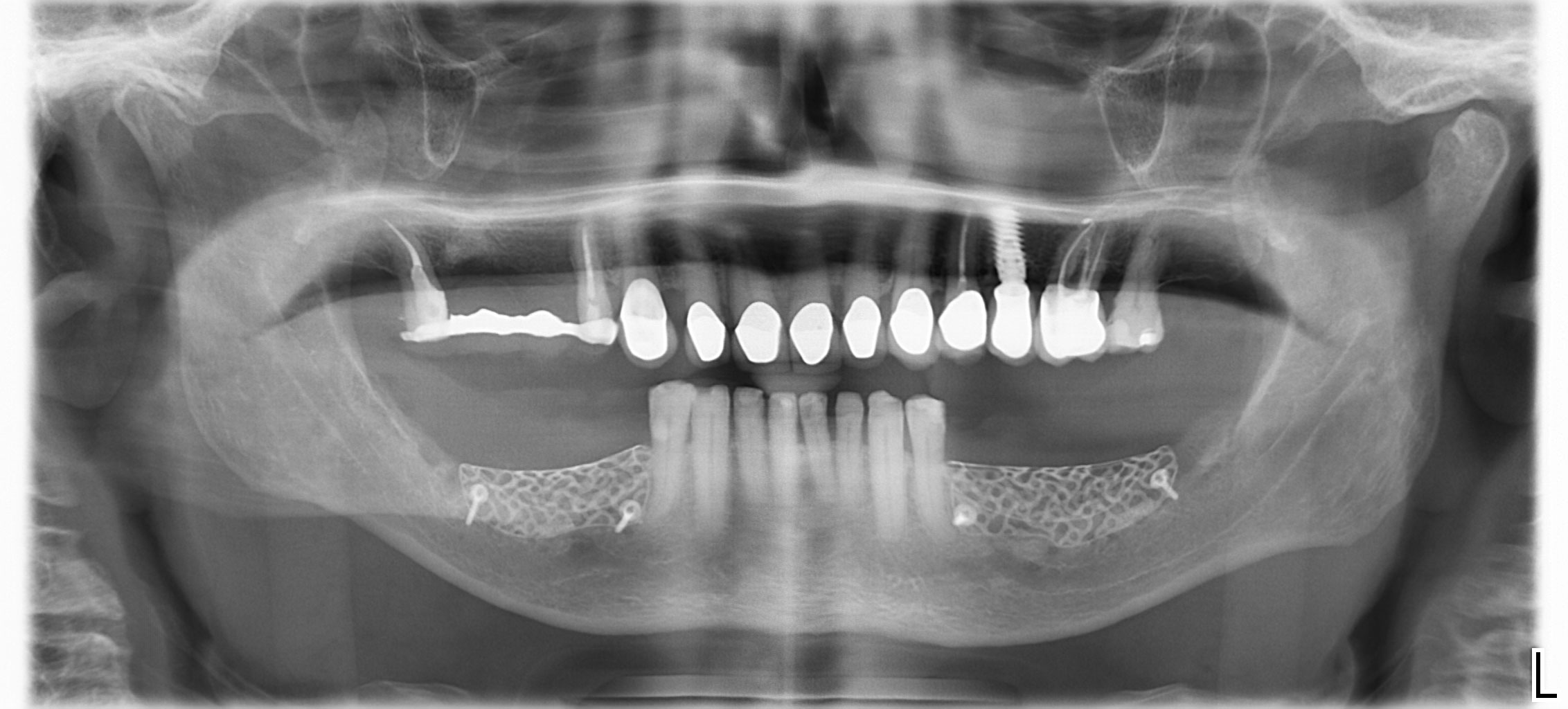
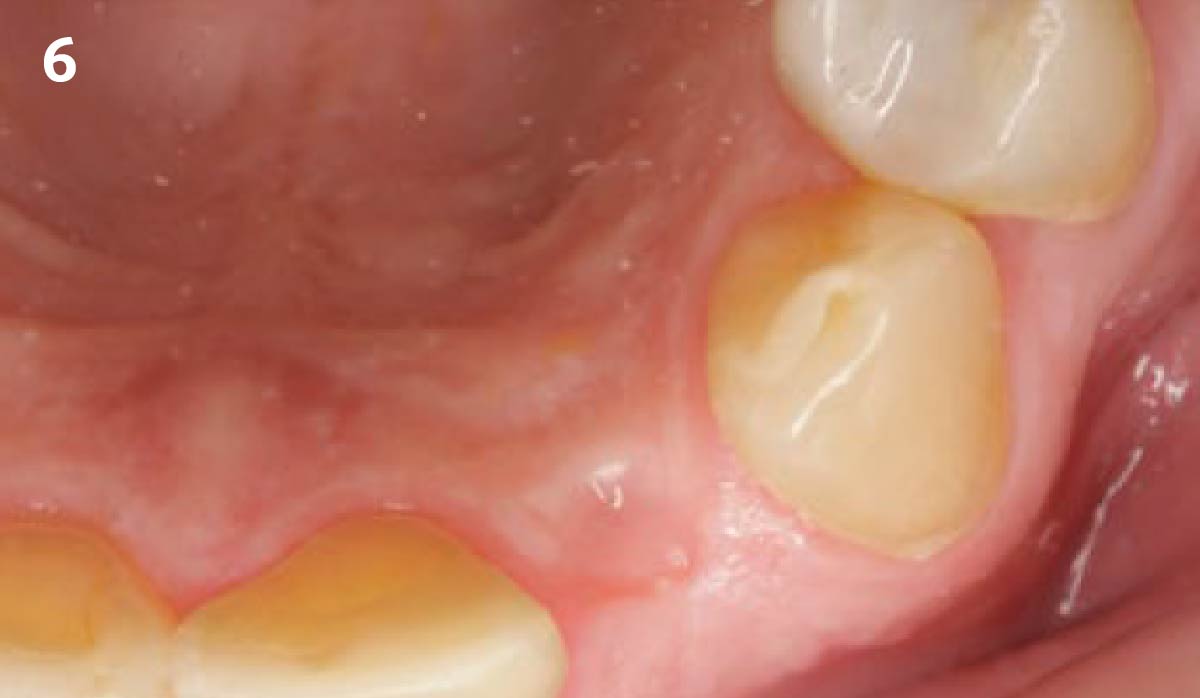
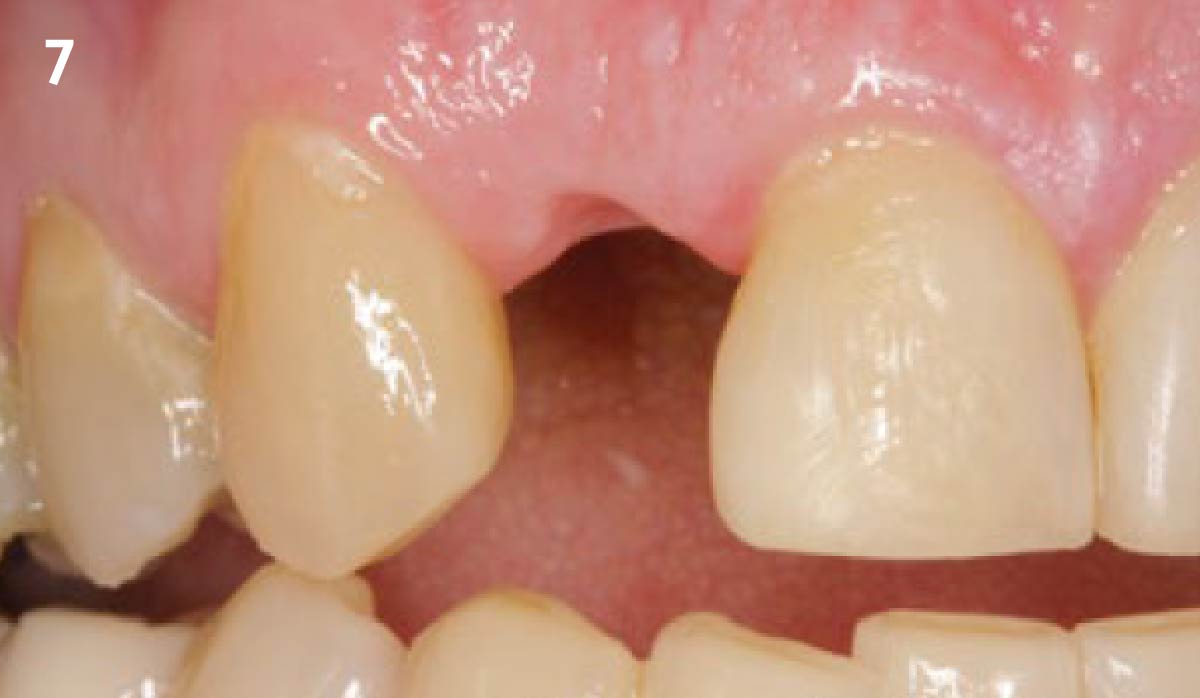
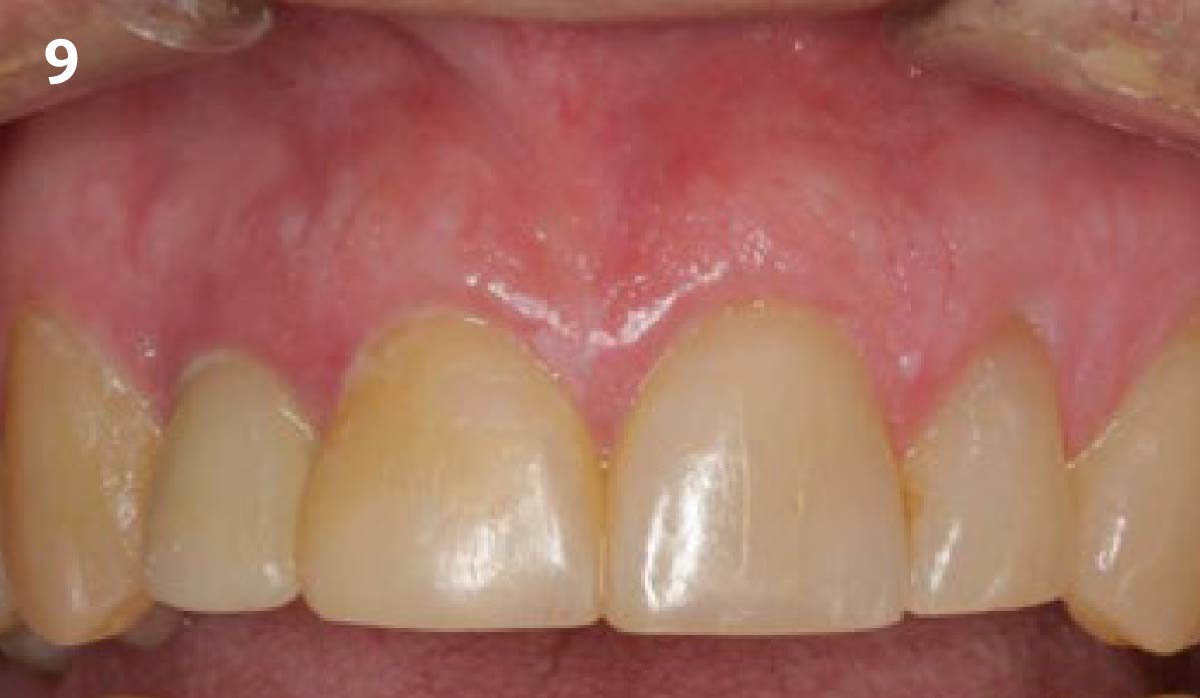
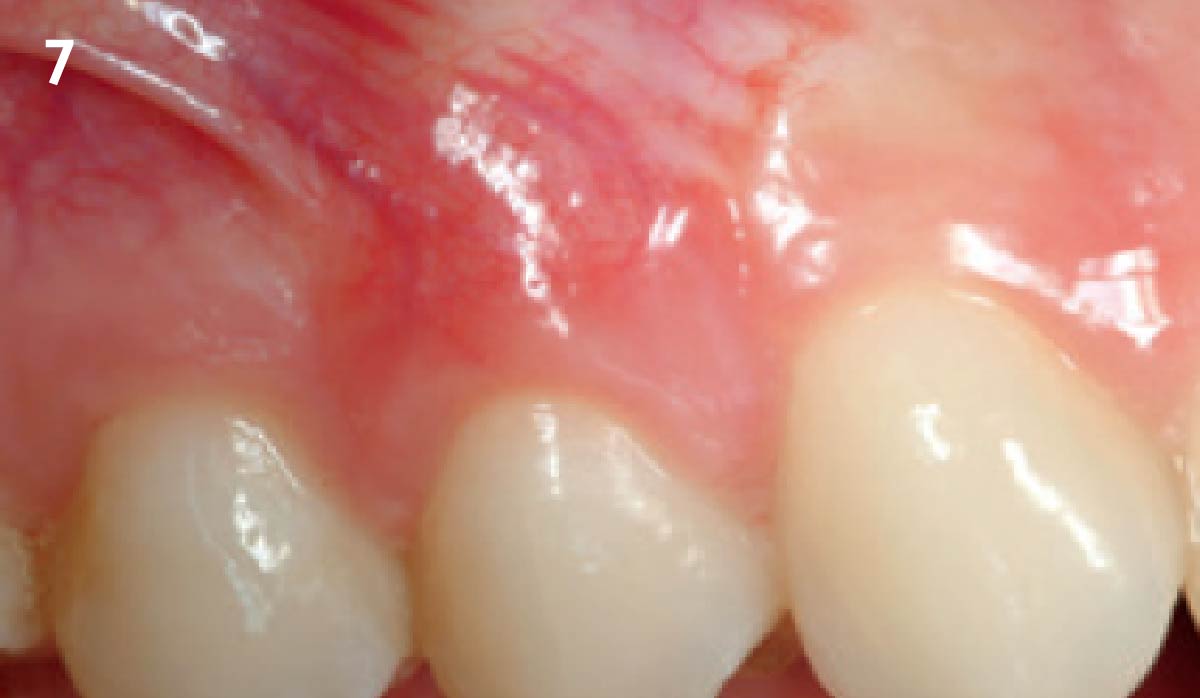
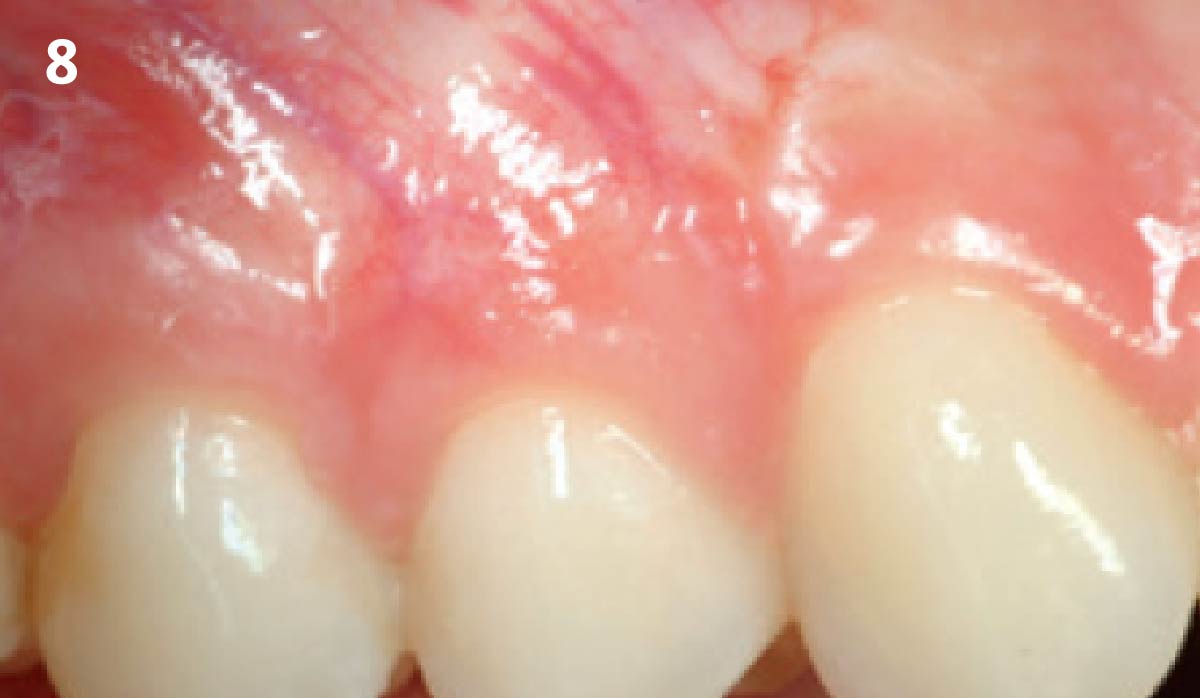
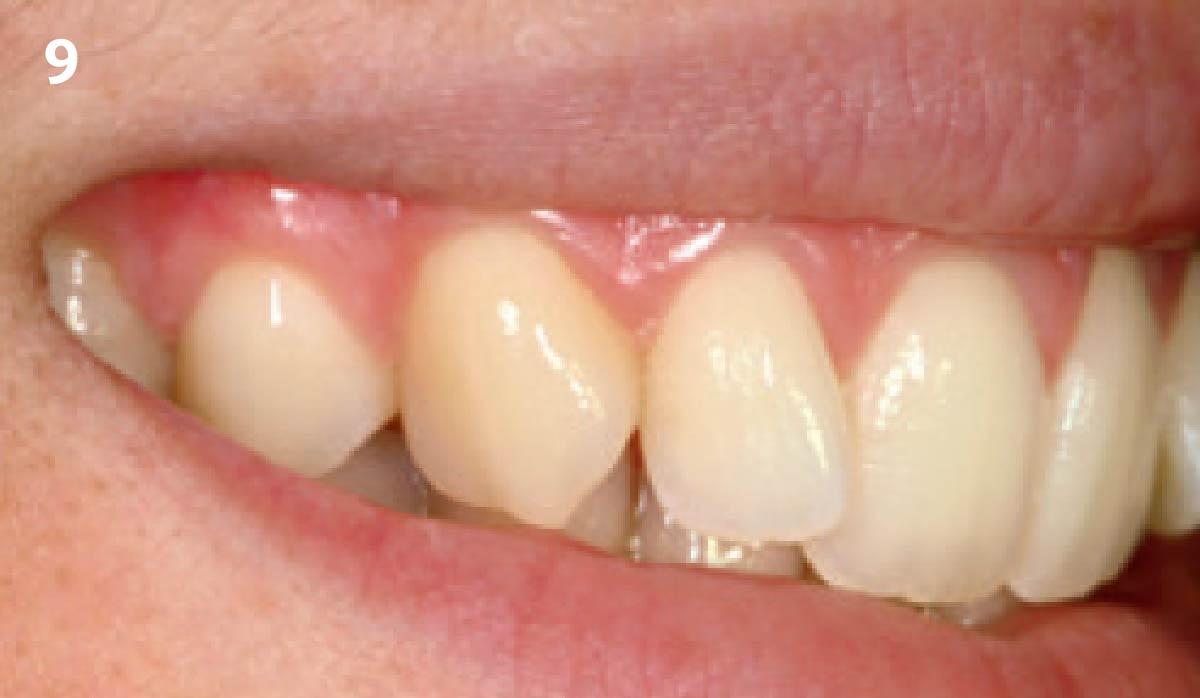
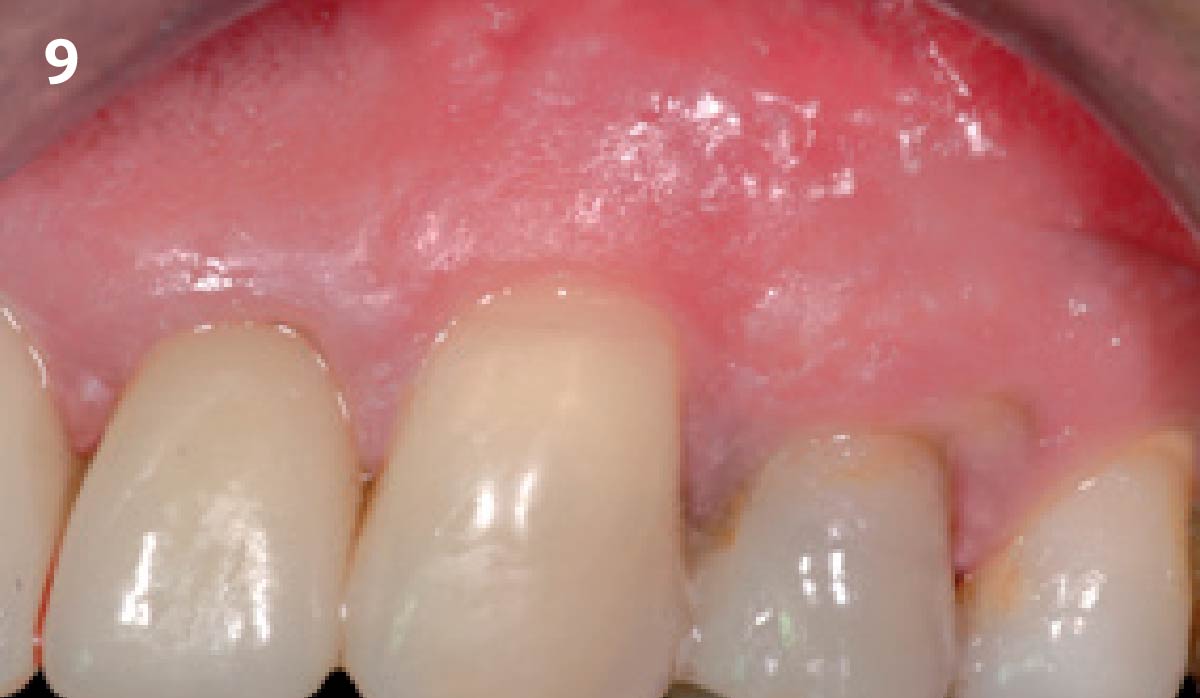
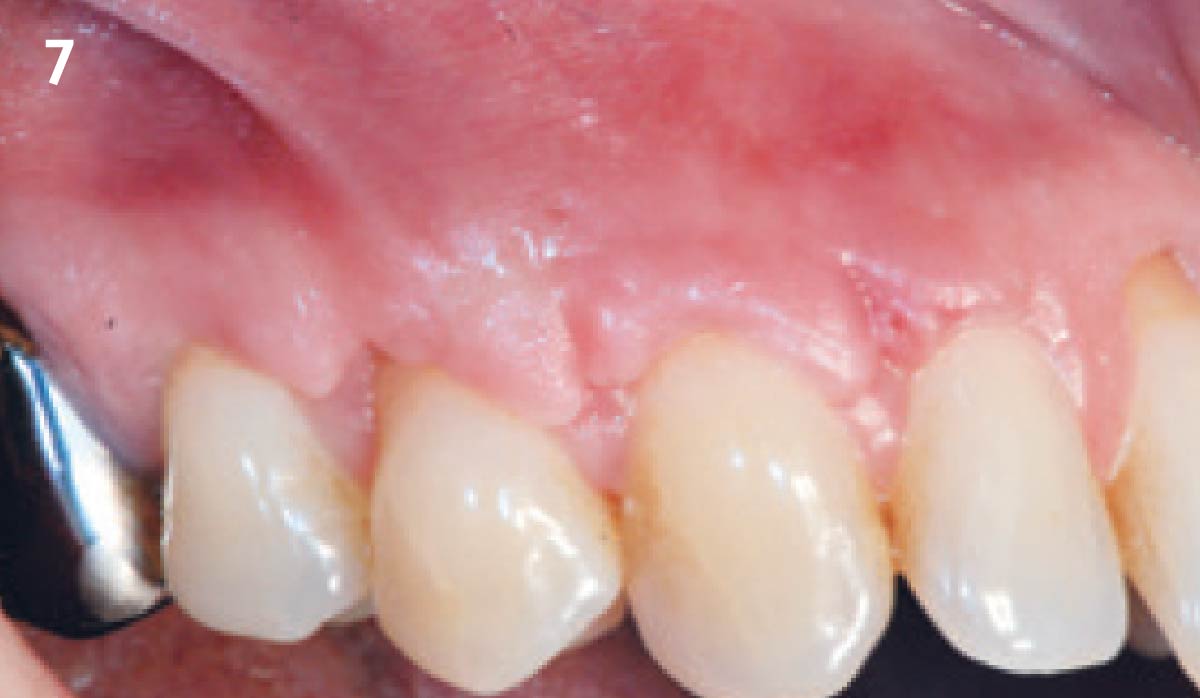
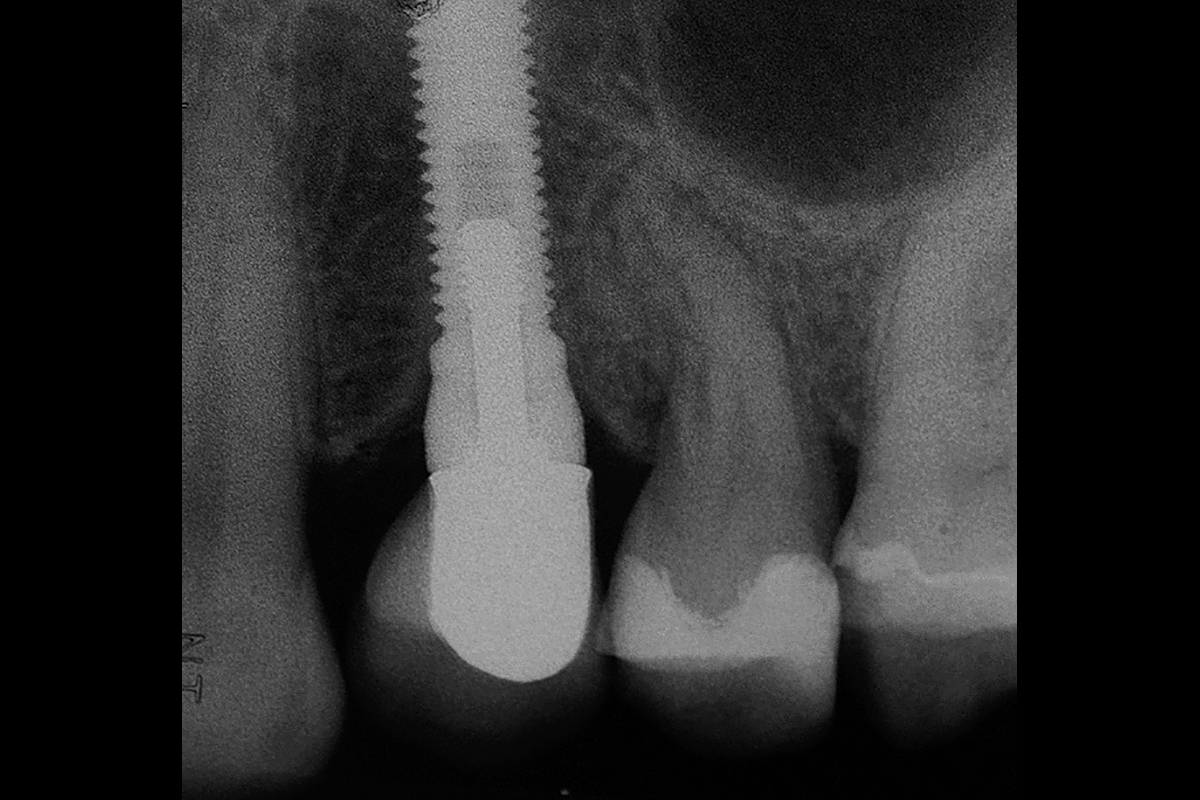
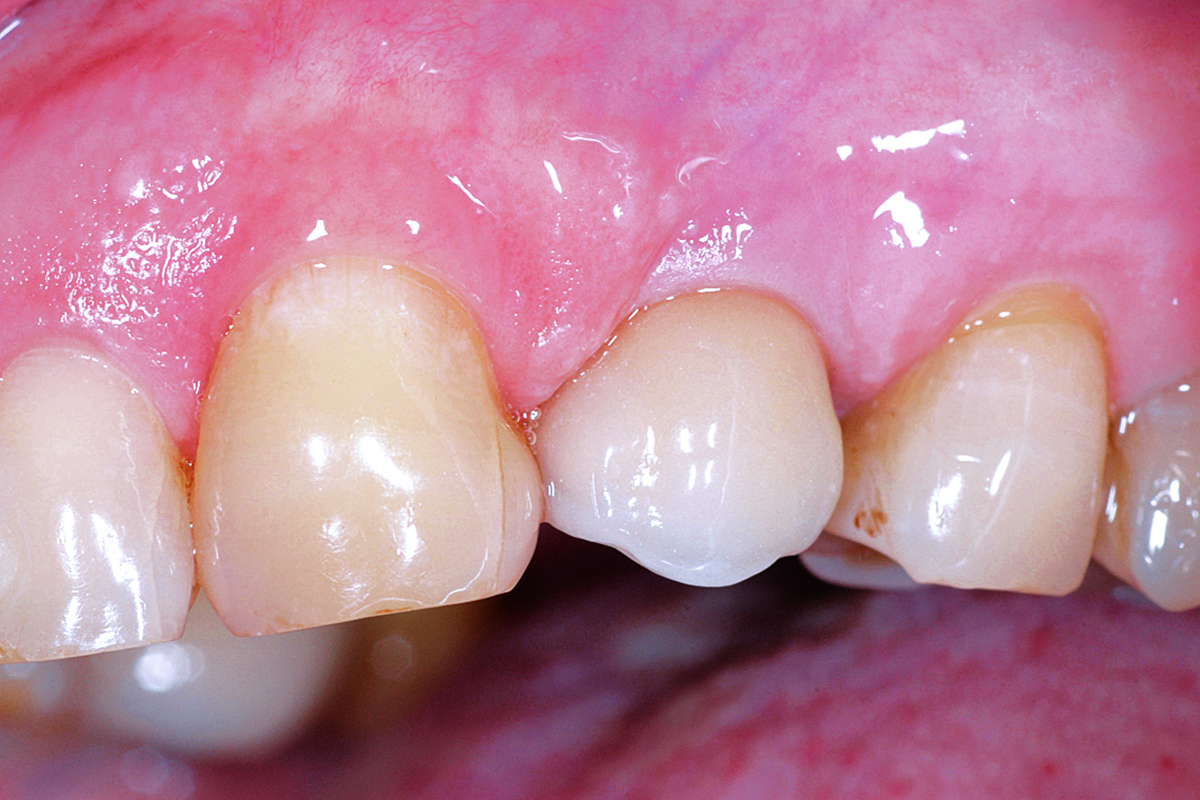
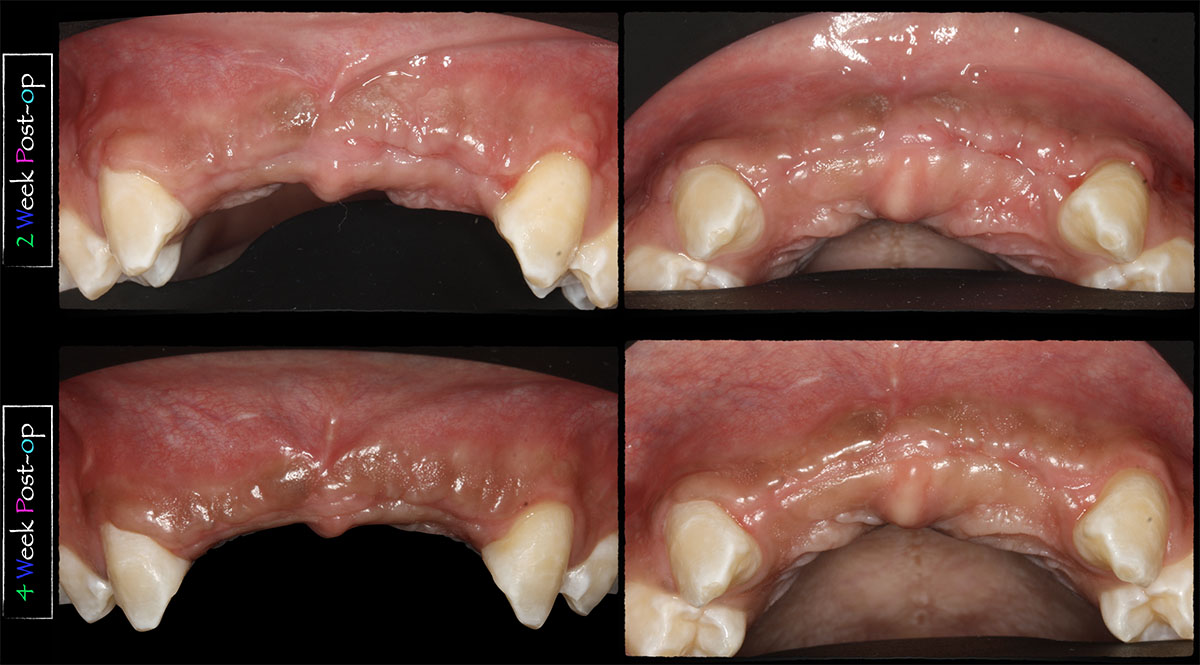
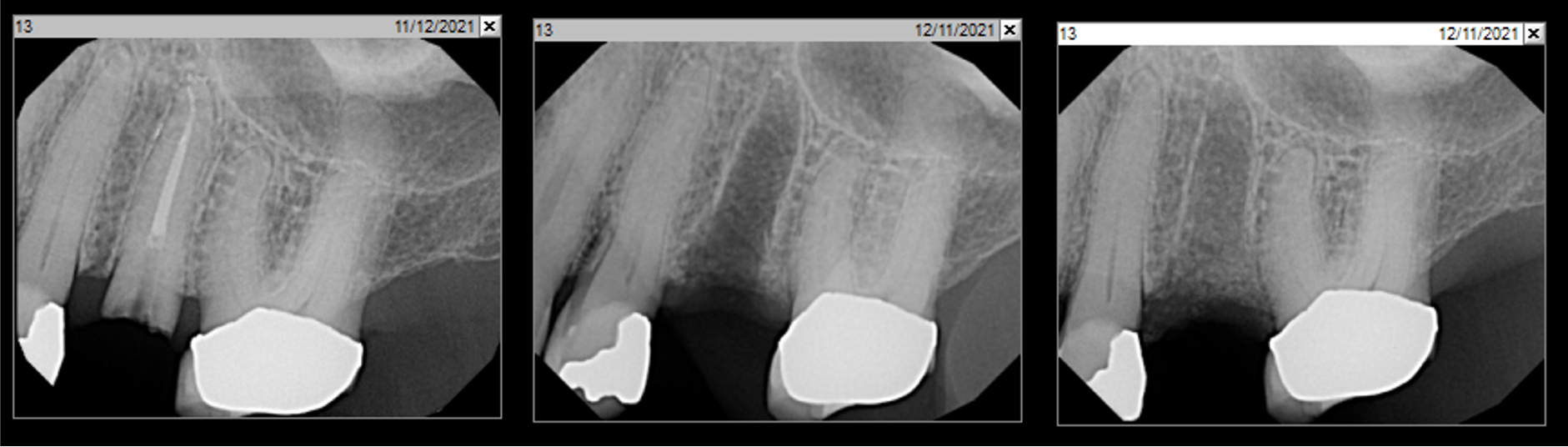
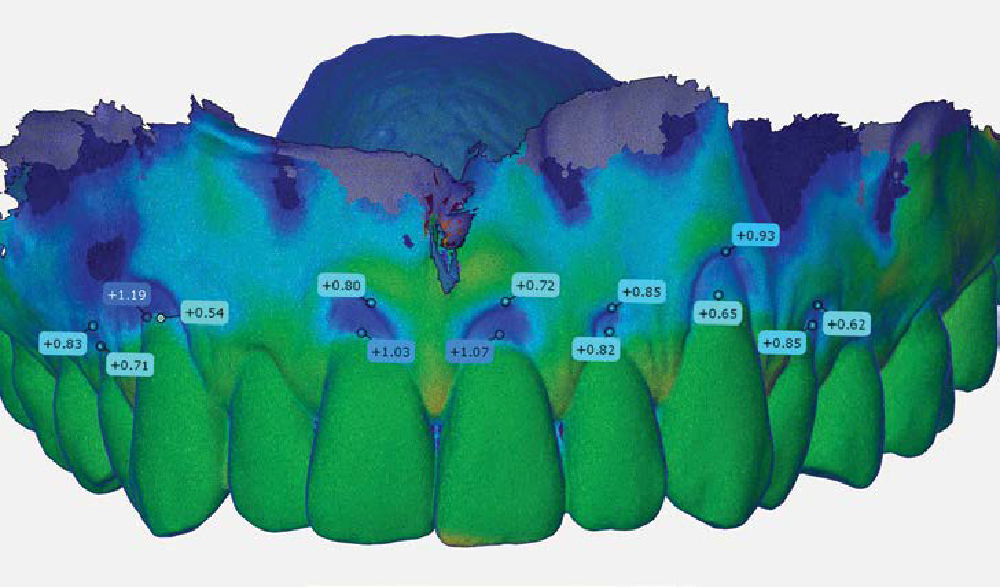
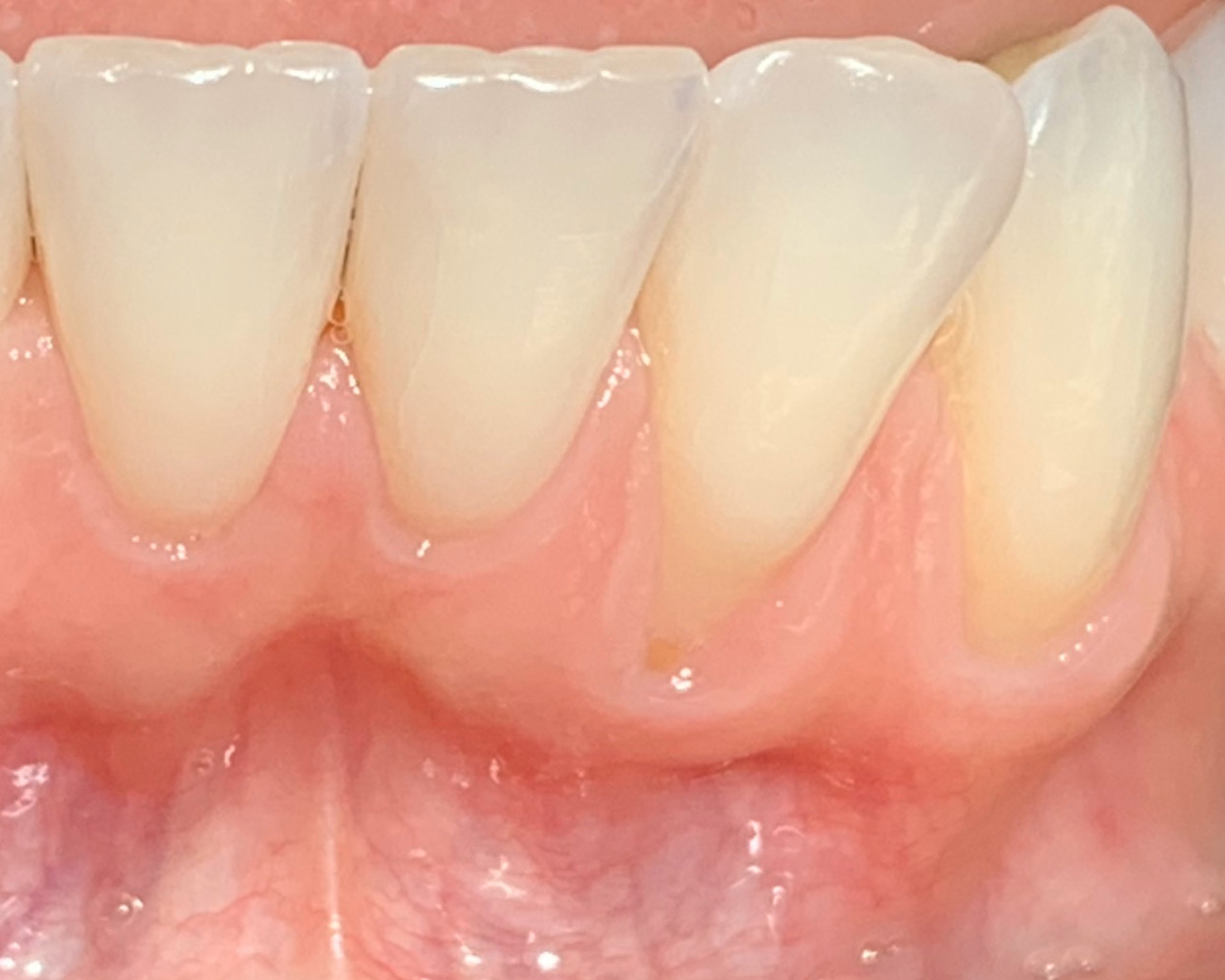
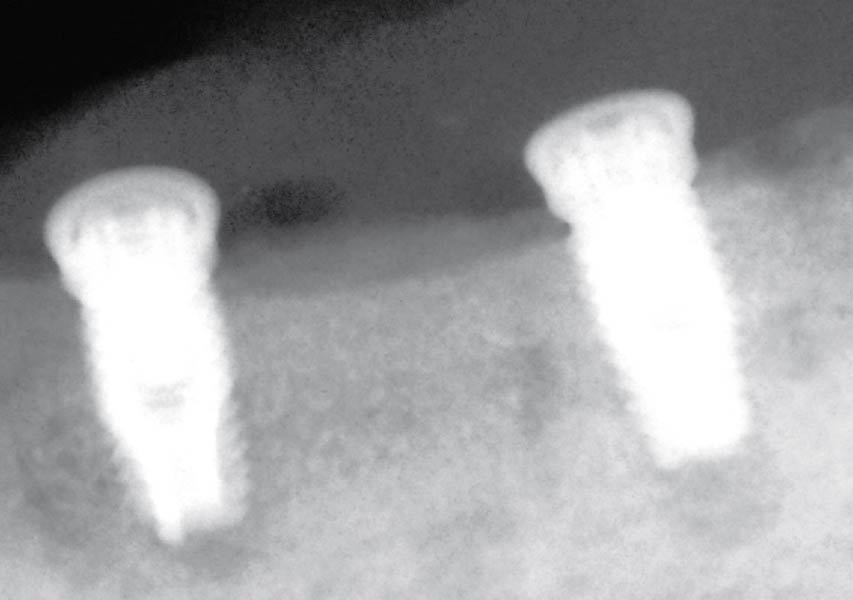
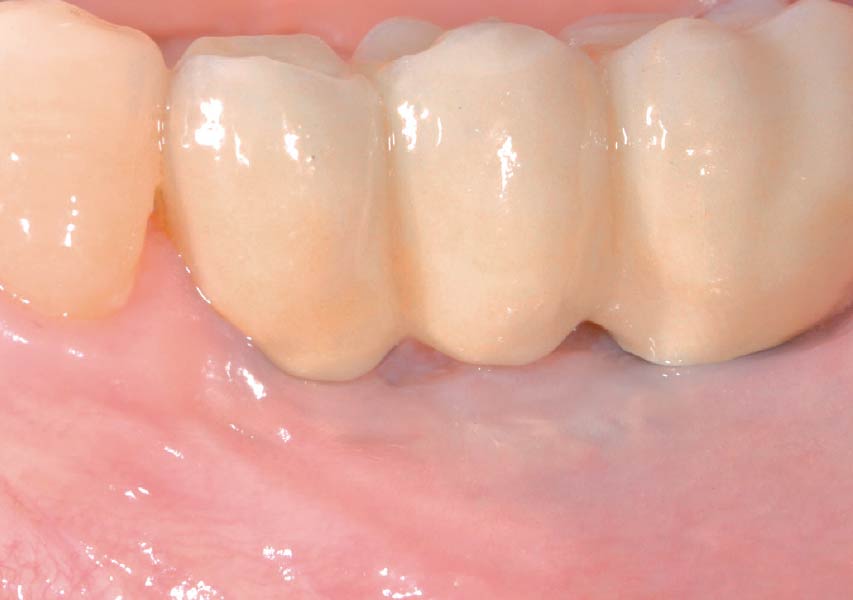
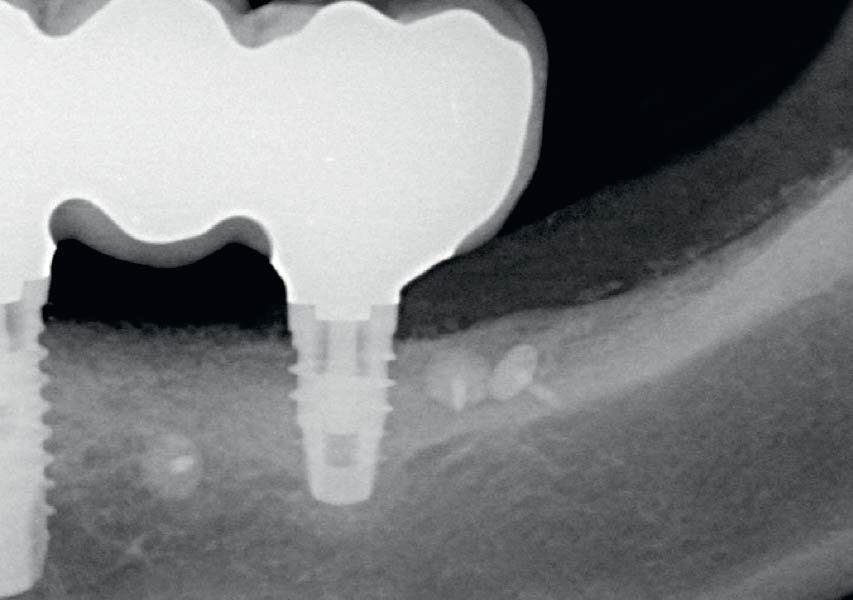
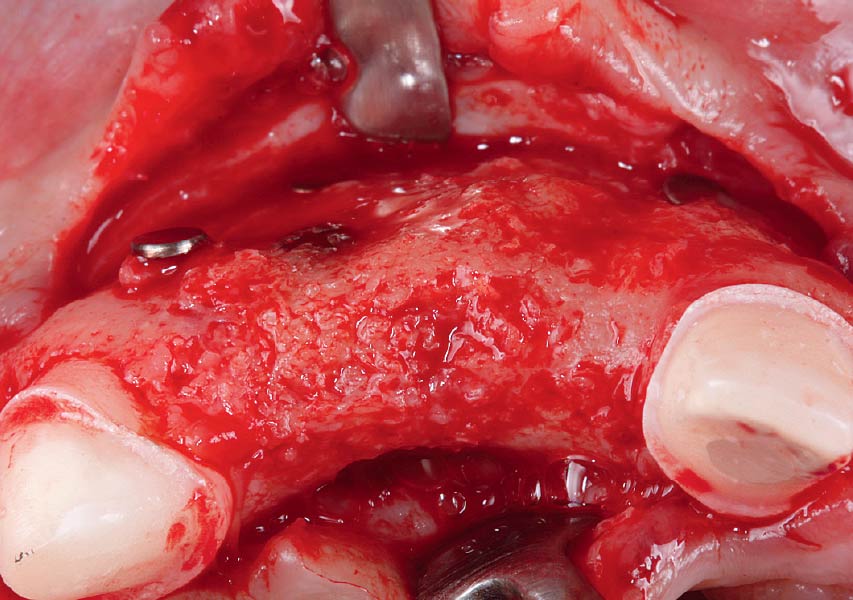
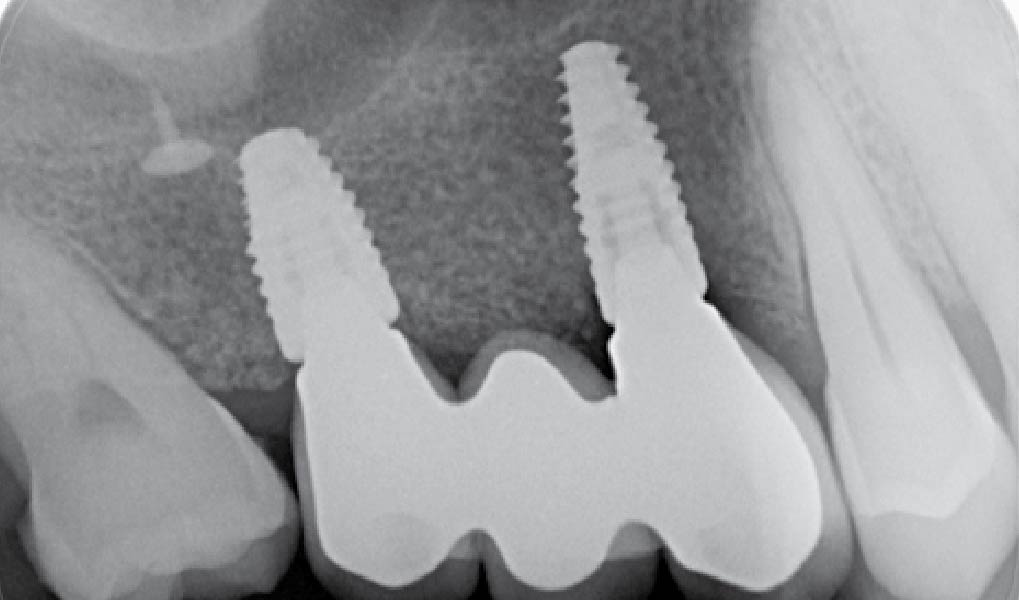
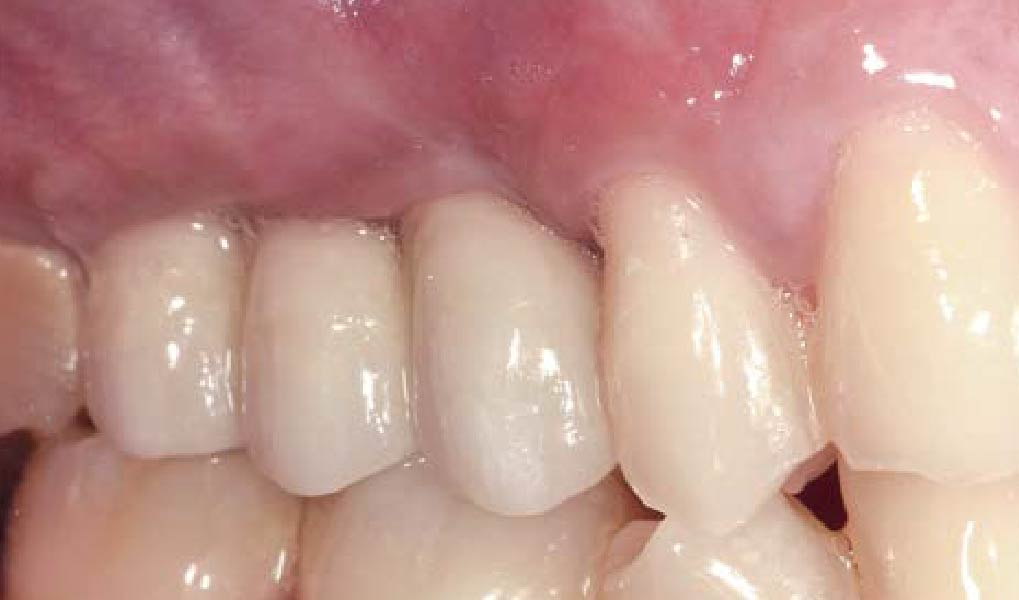
This case finished with excellent pink and white esthetic scores, and the patient and her dentist were very pleased with the results. Most importantly, the implant demonstrated excellent health and stability over one year since placement.

David E. Urbanek, DMD, MS
Dr. Urbanek is a board-certified Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon who practices in St. Louis, Missouri. He completed his OMS training at Carle Foundation Hospital in Champaign/Urbana, Illinois. He earned his Dental Degree from the Case Western Reserve University School of Dental Medicine, and a Master’s Degree with Honors in Applied Anatomy from CWRU. Dr. Urbanek serves as adjunct faculty at Carle Foundation Hospital and the A. T. Still University, Missouri School of Dentistry & Oral Health. In addition he avidly lectures to the dental and OMS community throughout the country.