Mix & Match! Buy 5 Products, Get 1 Free! Use code B5G1. Get Started!
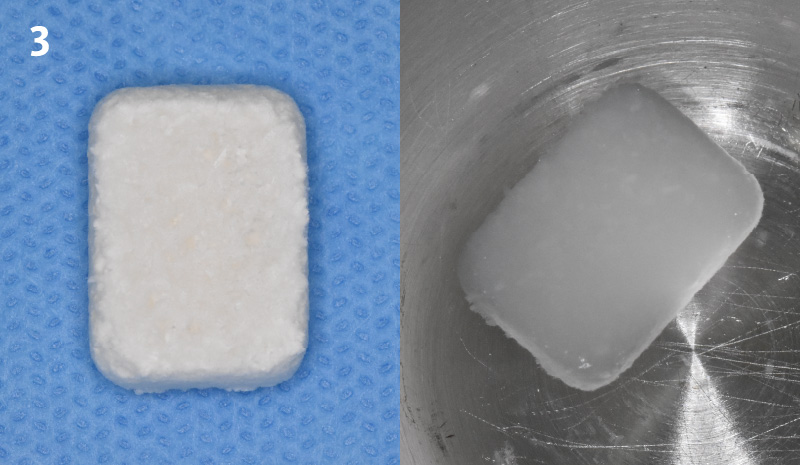
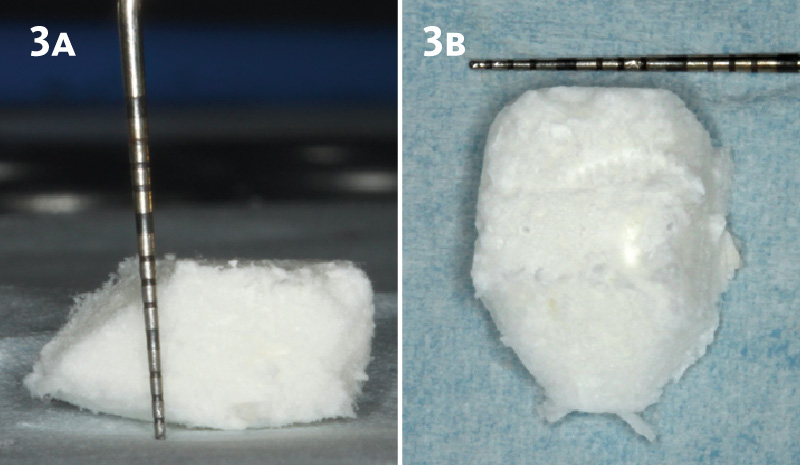
Product: Geistlich Fibro-Gide®

BIOBRIEF
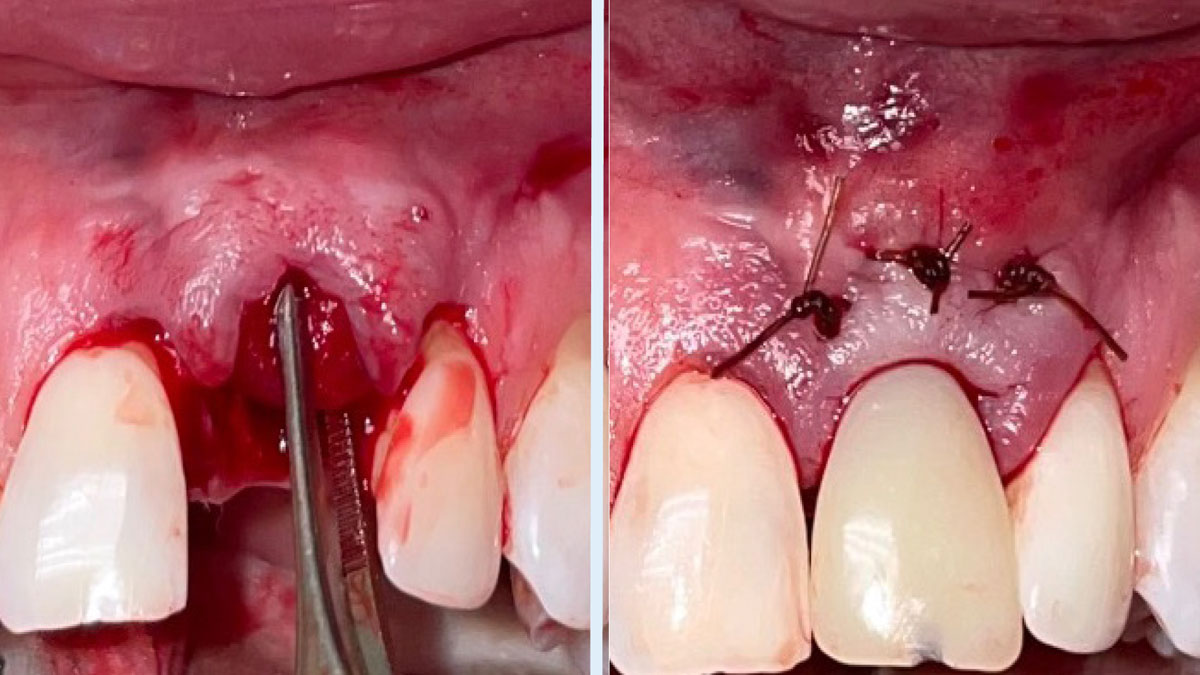
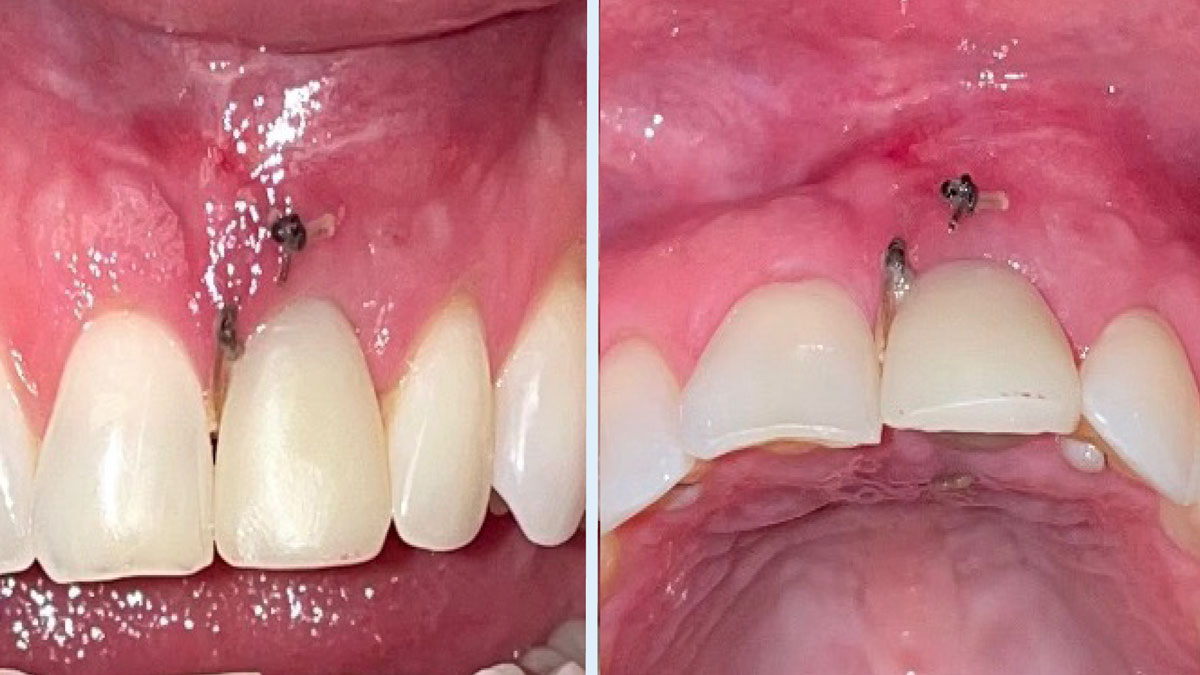
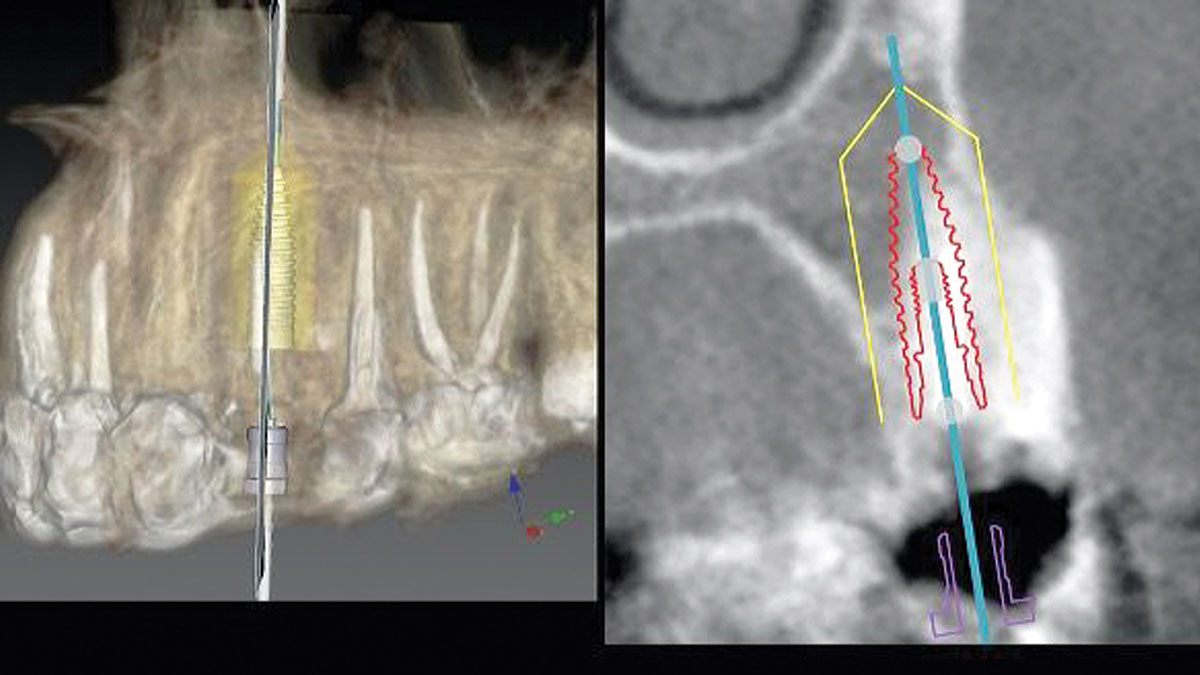
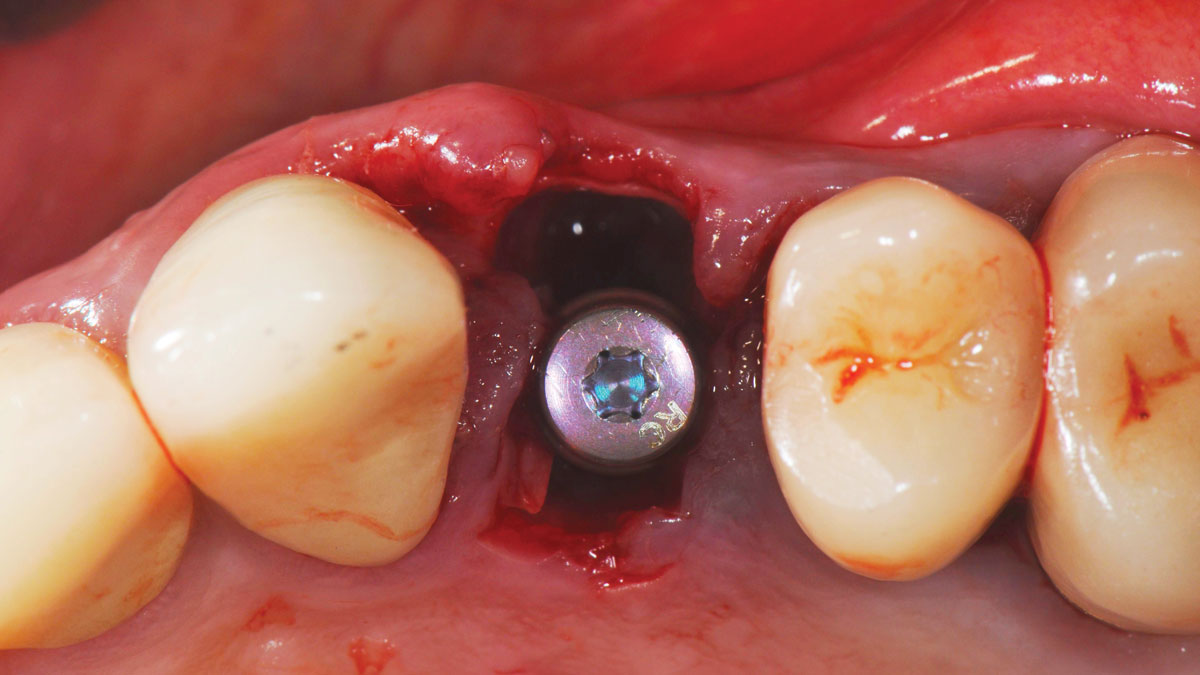
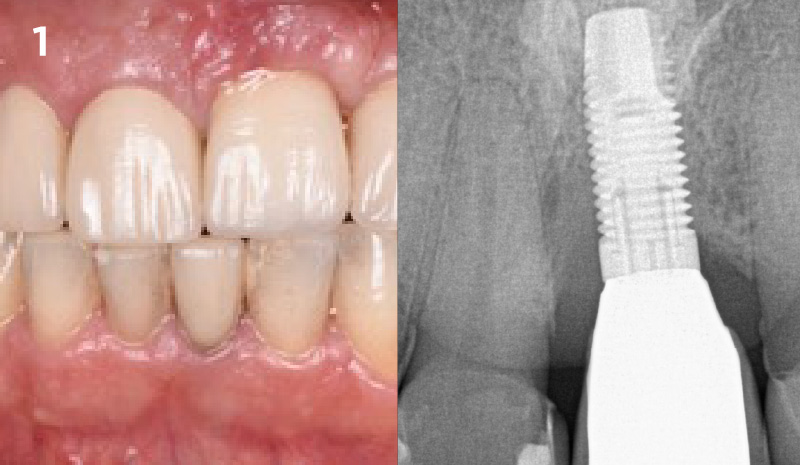
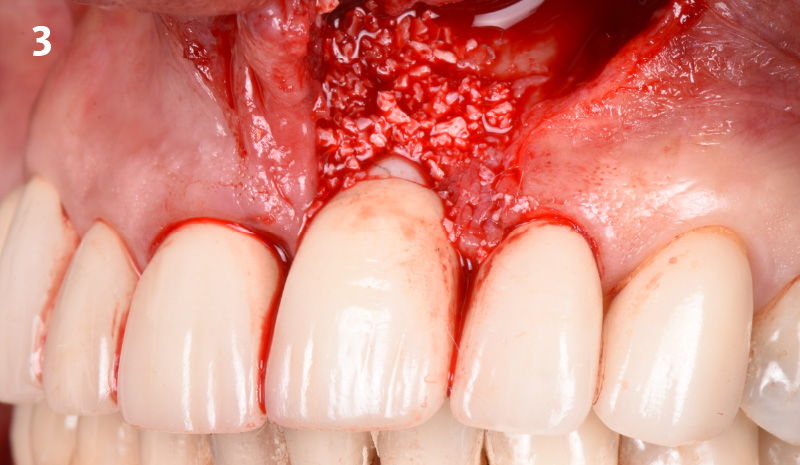
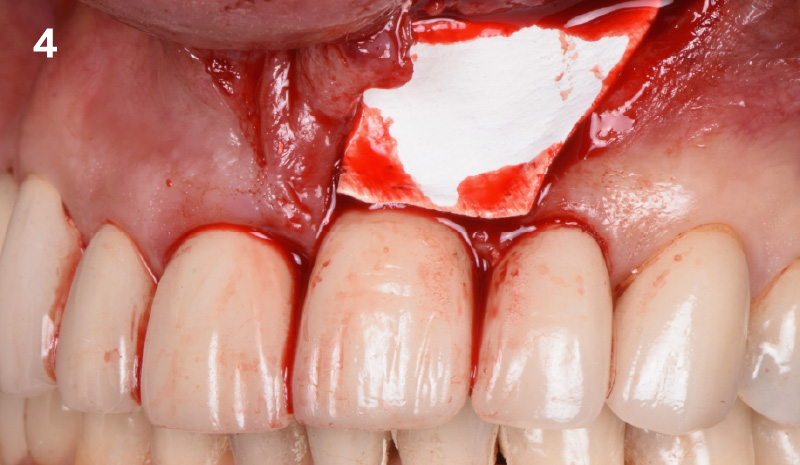
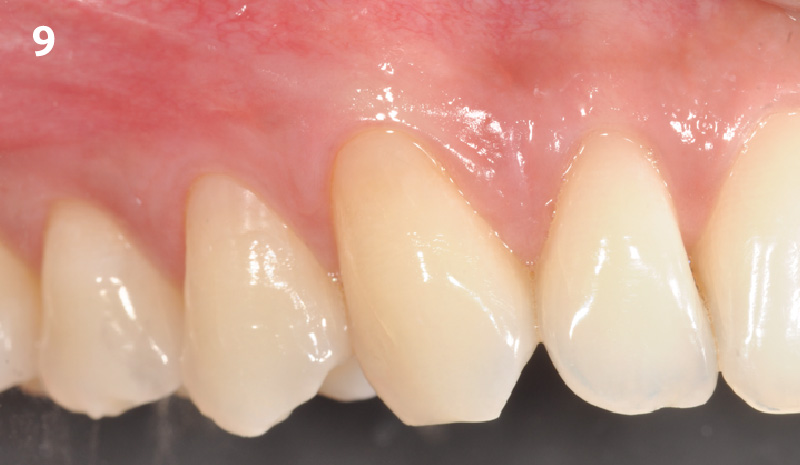
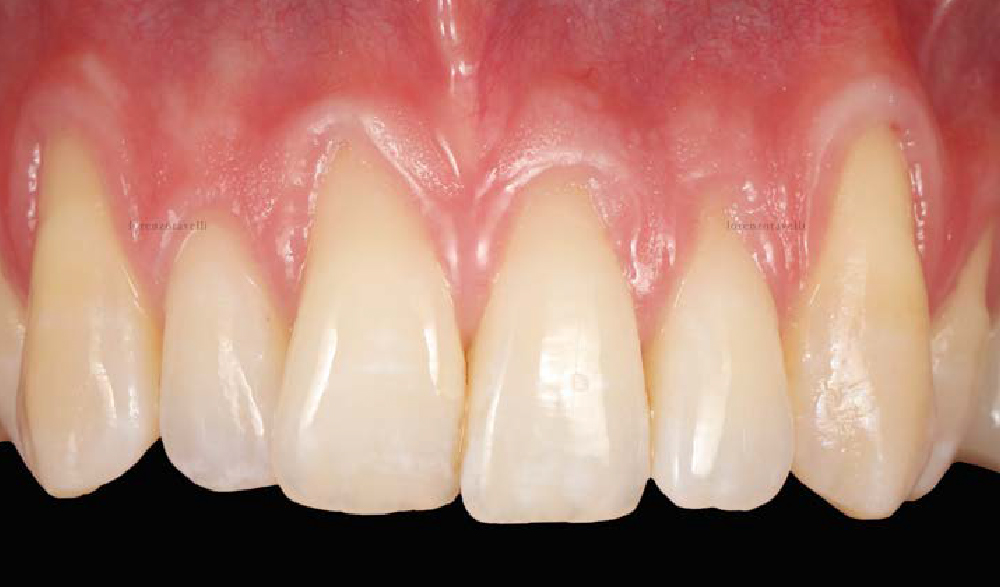
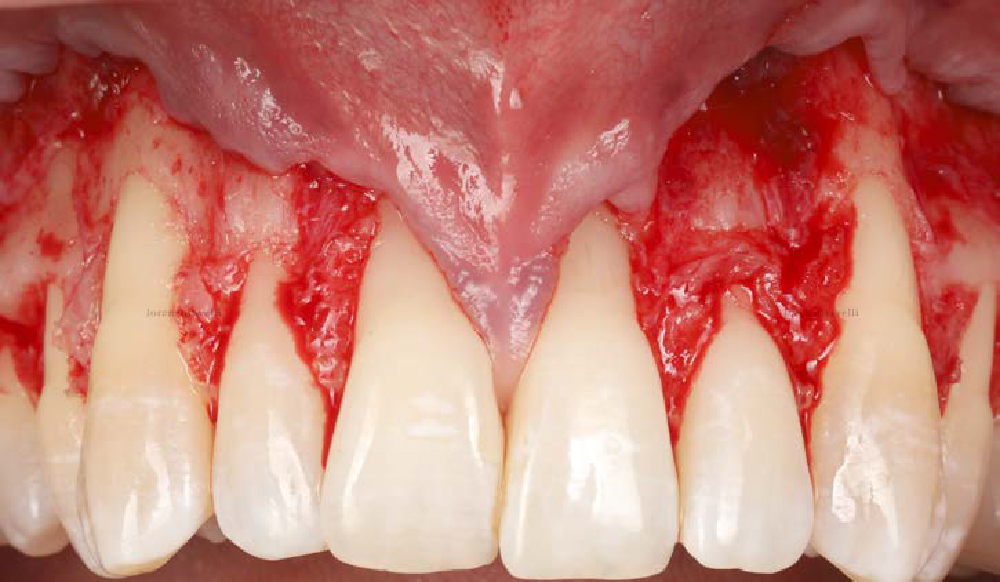
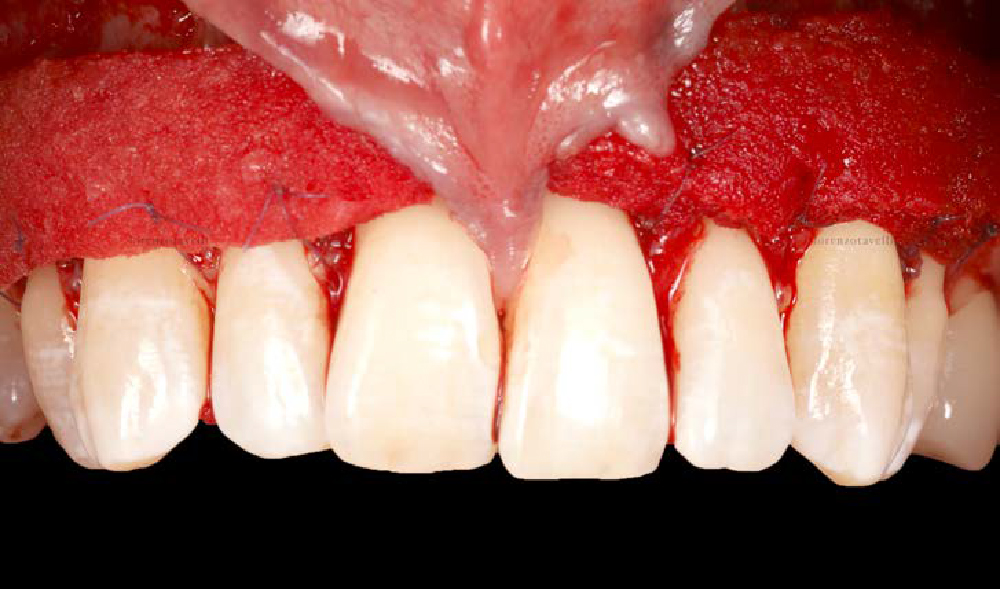
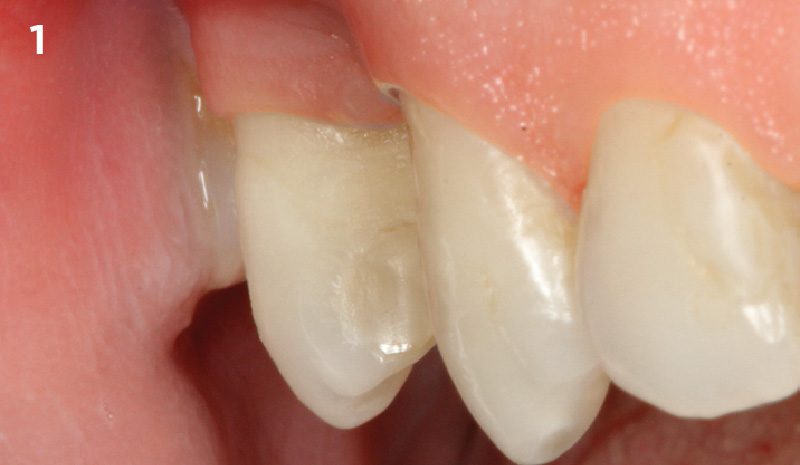
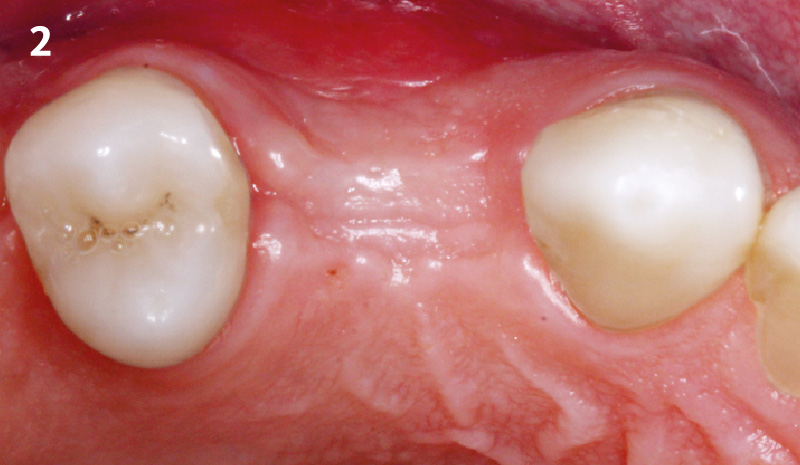
Immediate Implant Placement and Provisionalization for Anterior Esthetics
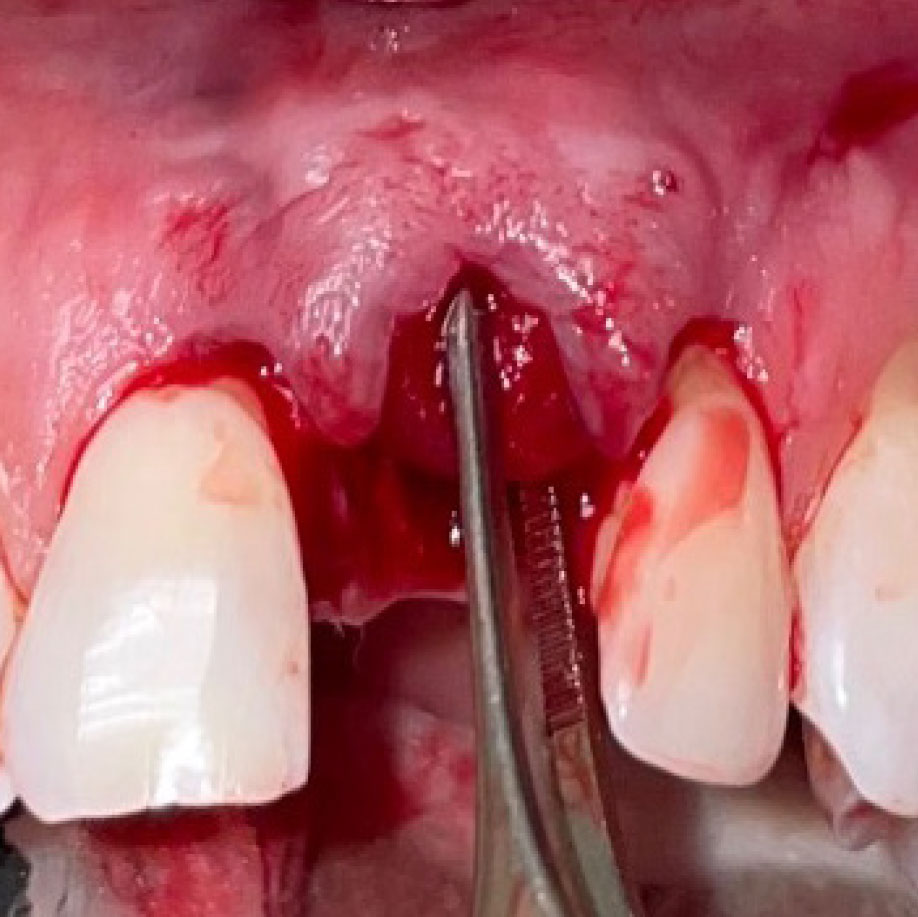

THE SITUATION
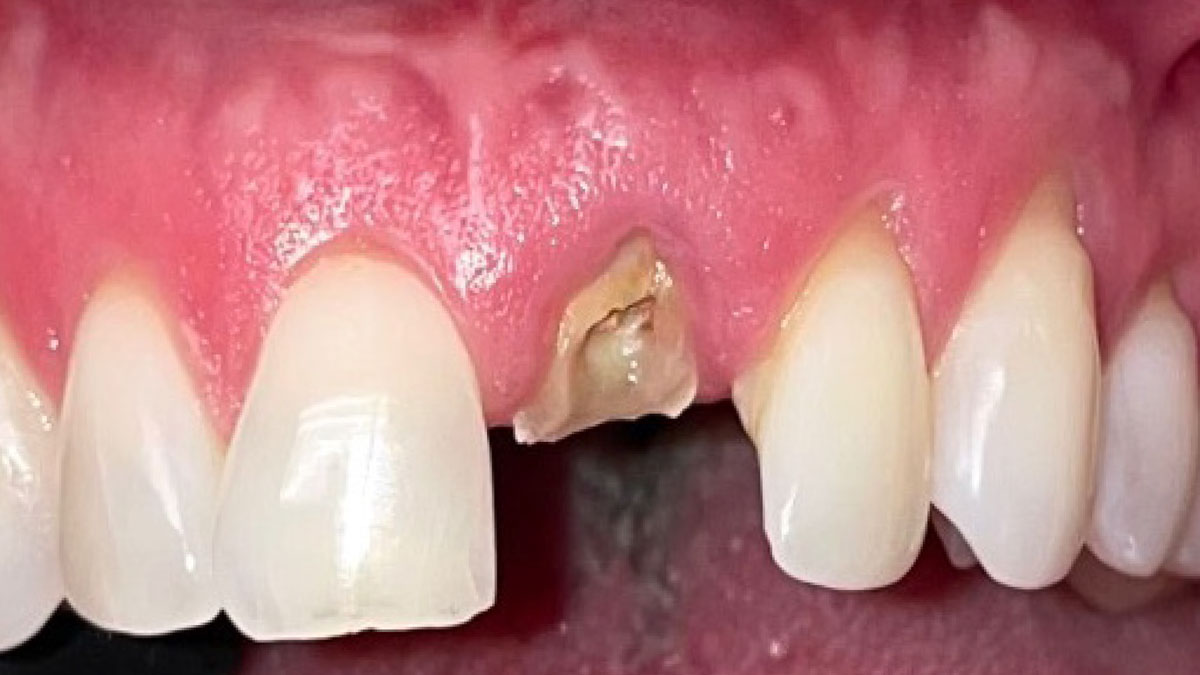
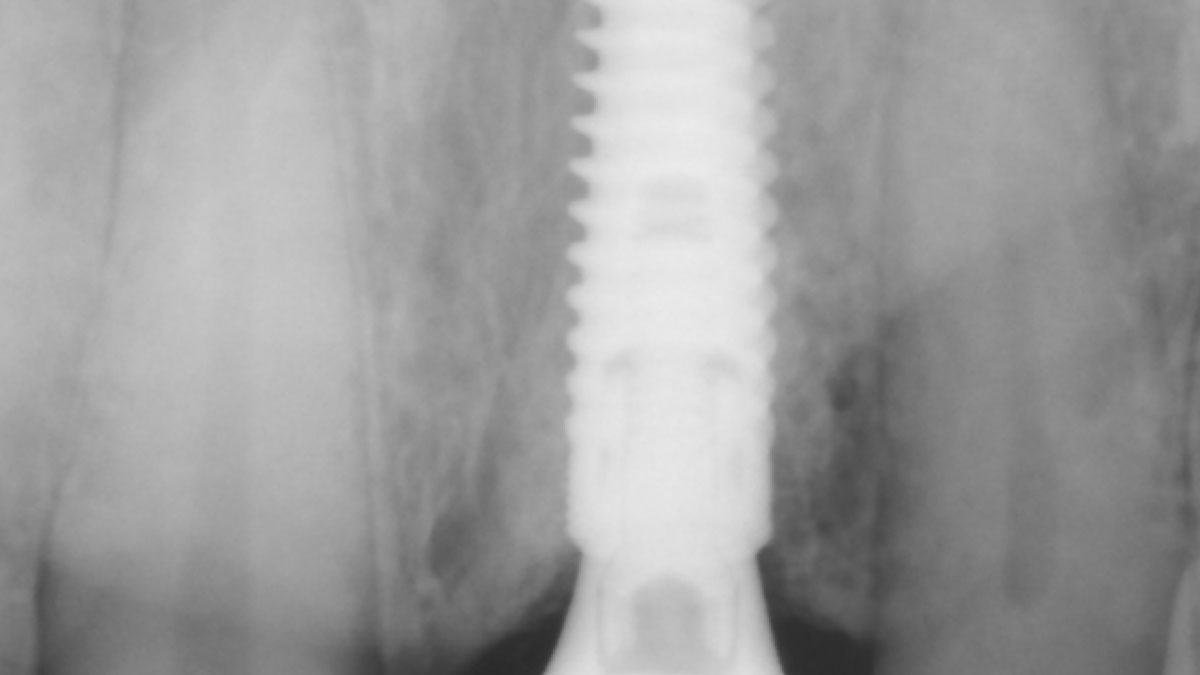
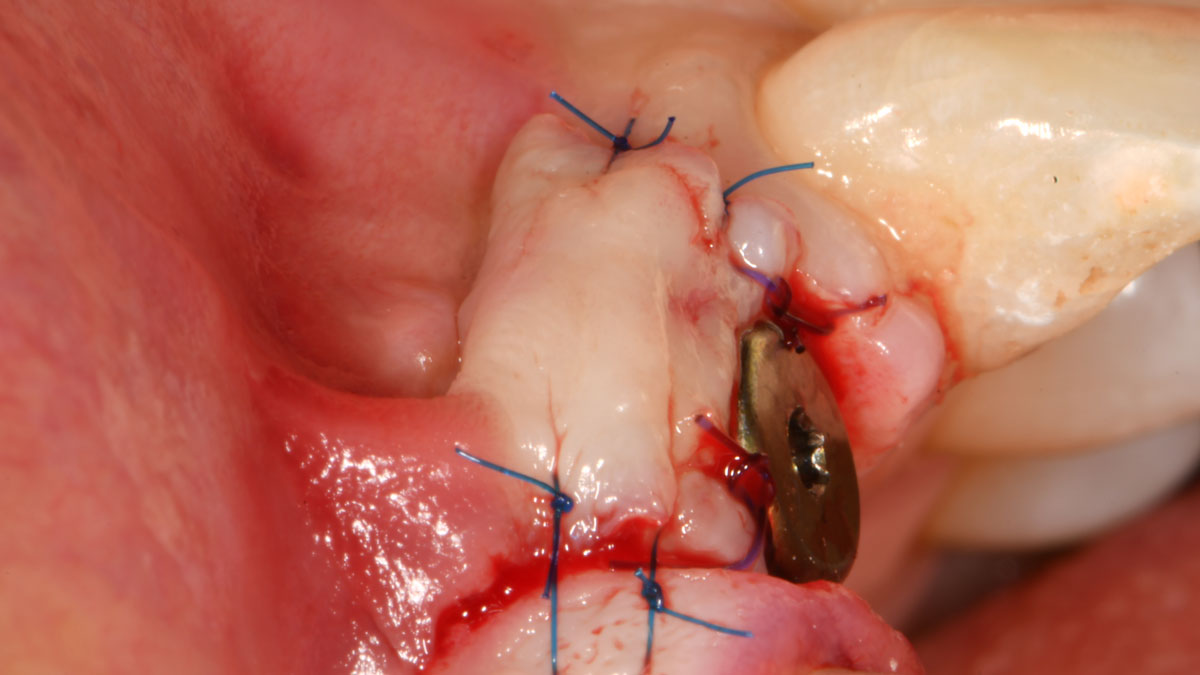
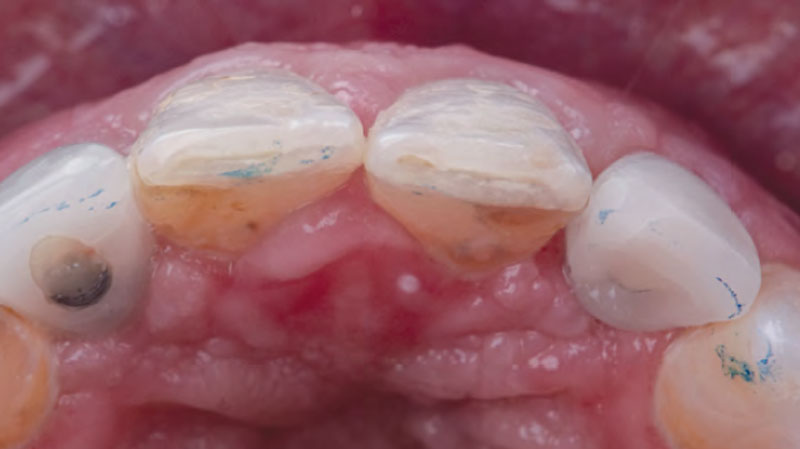
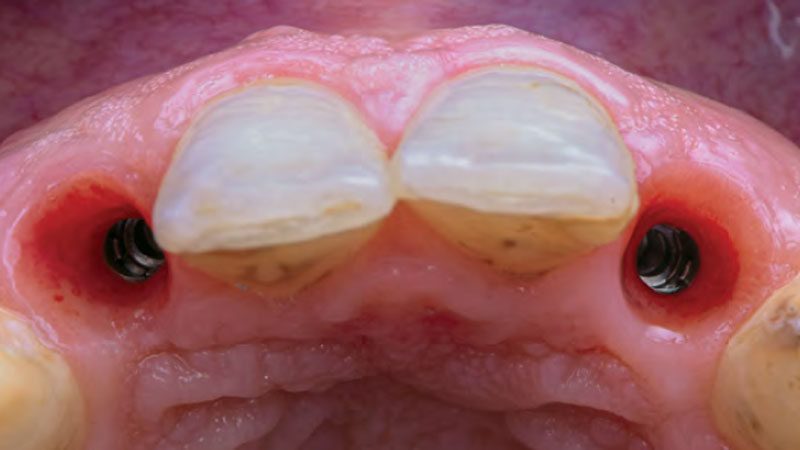
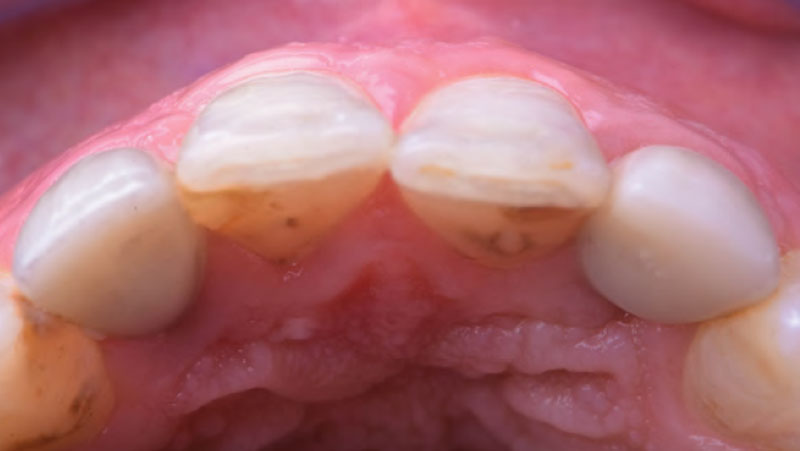
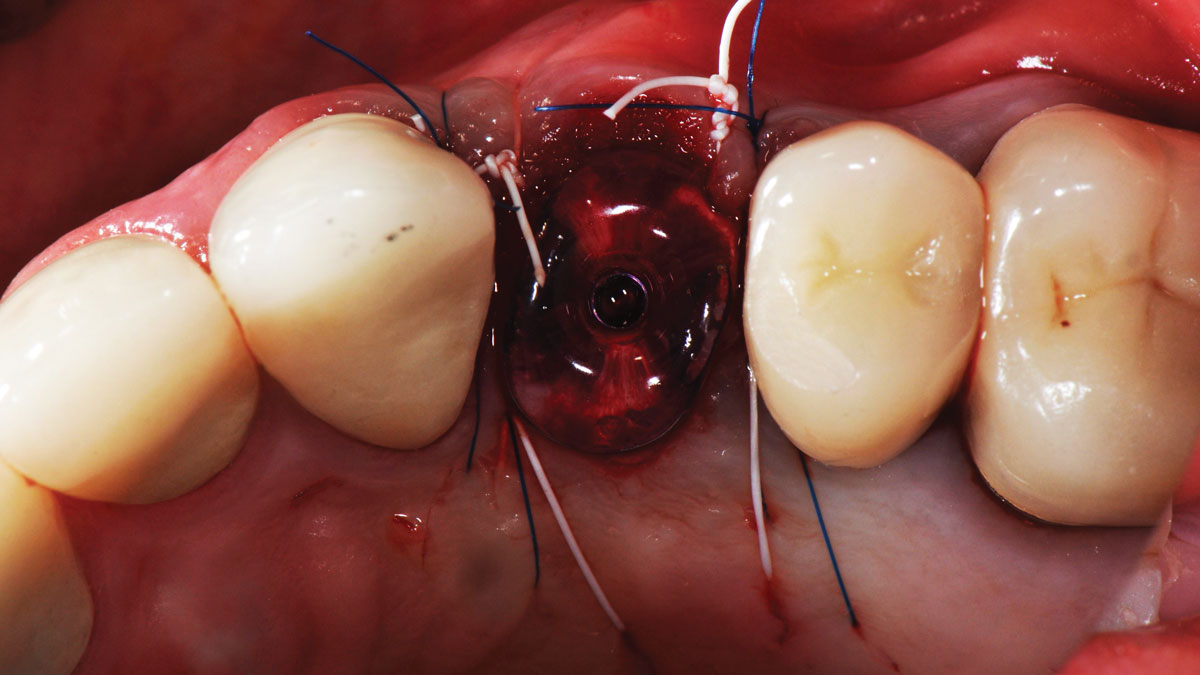
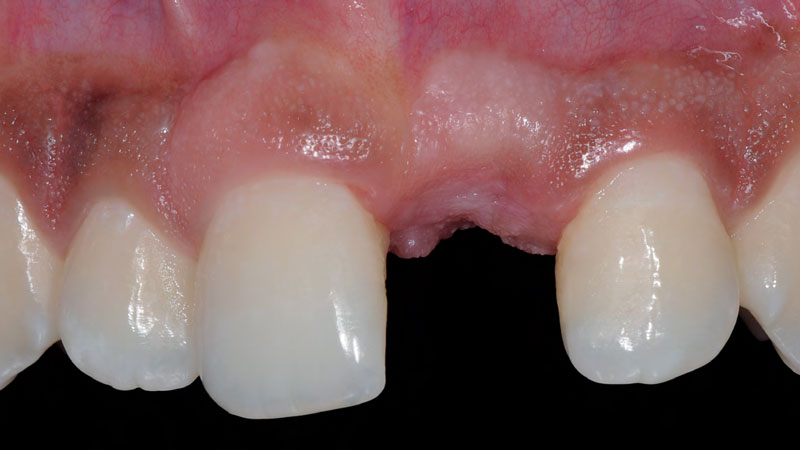
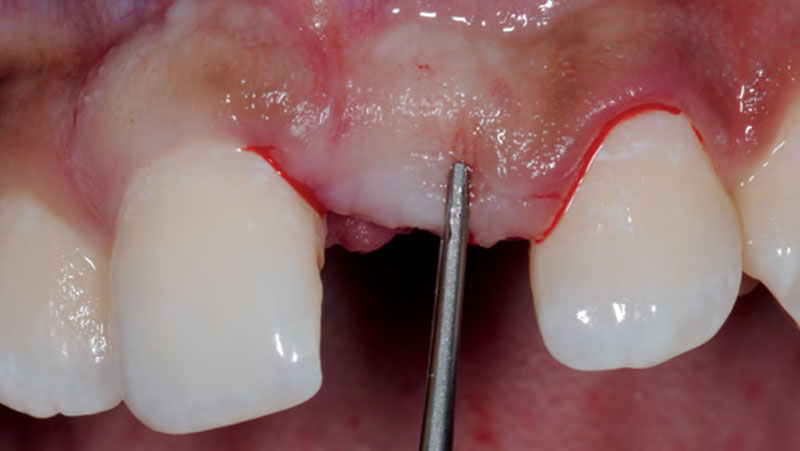
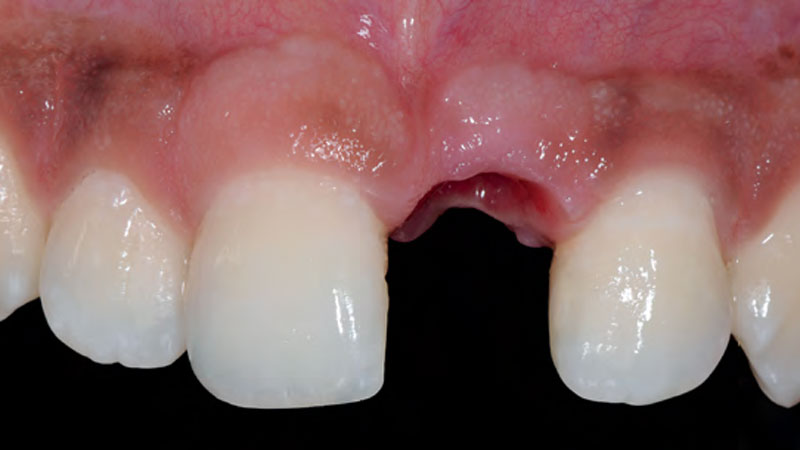
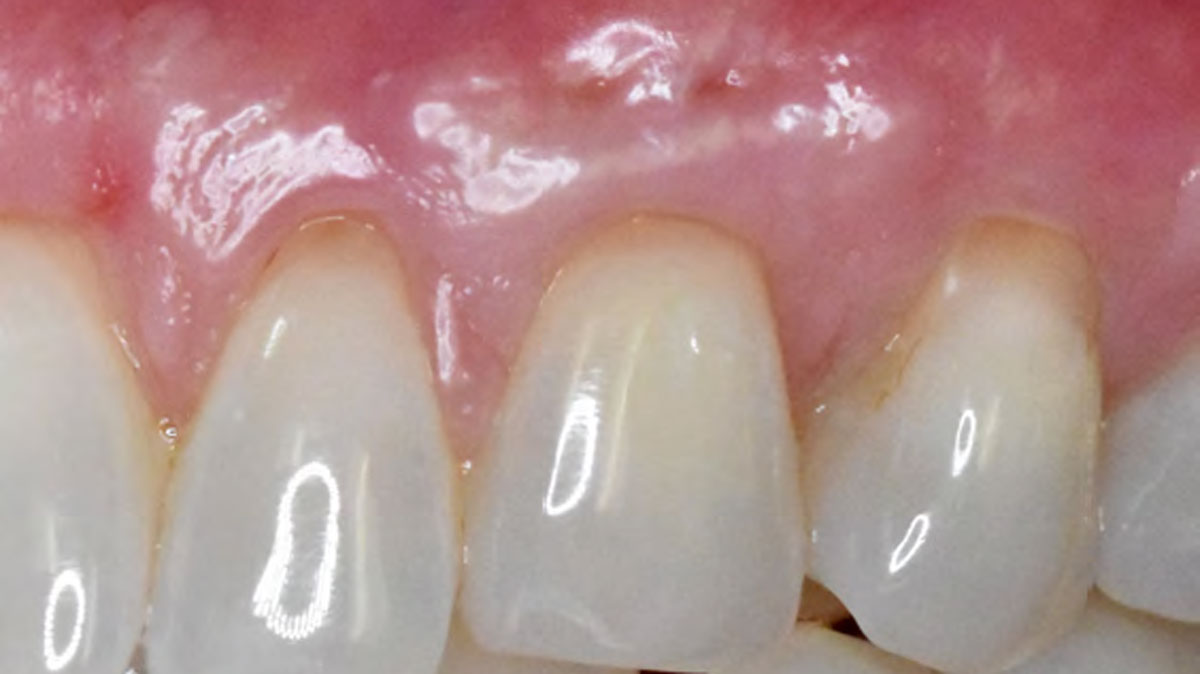
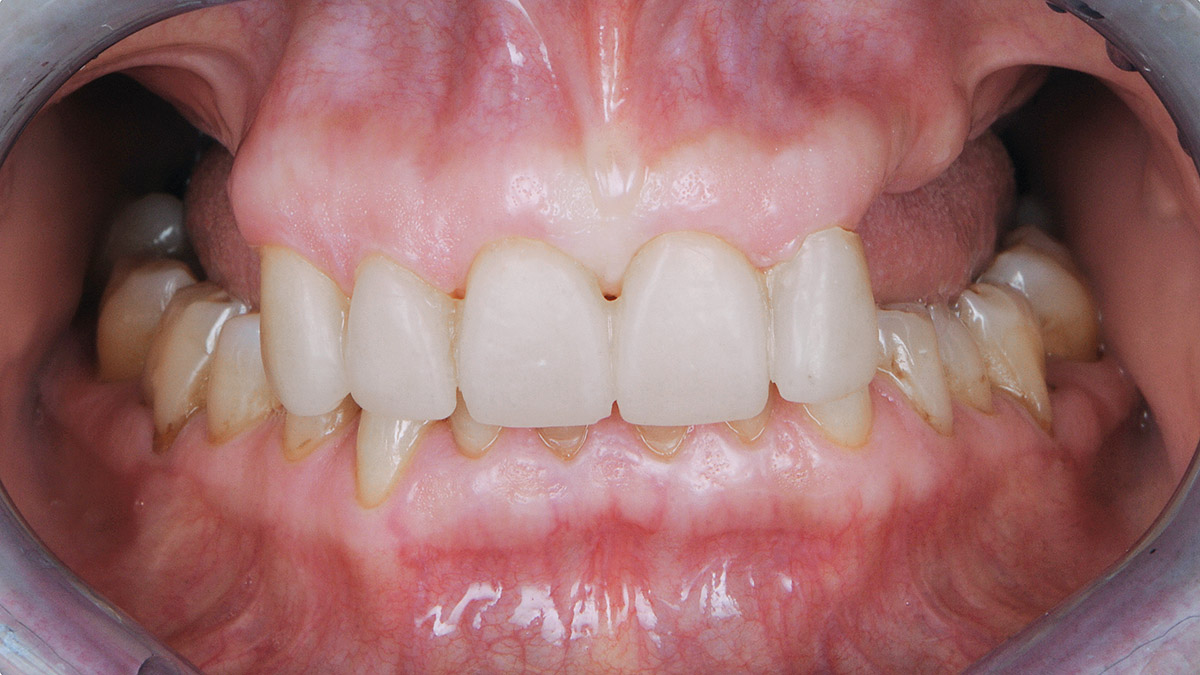
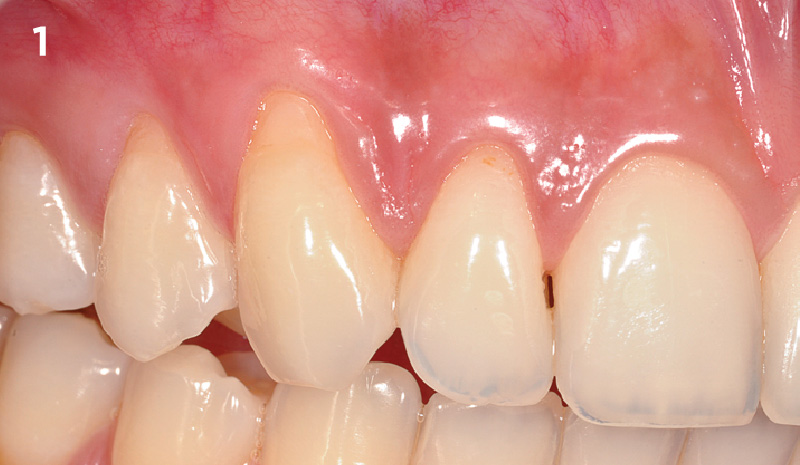
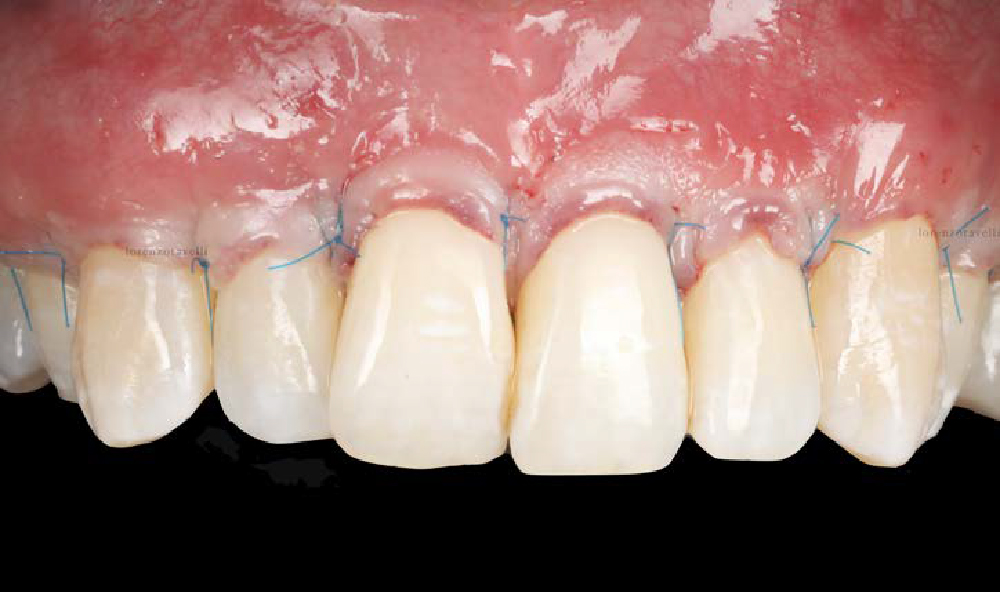
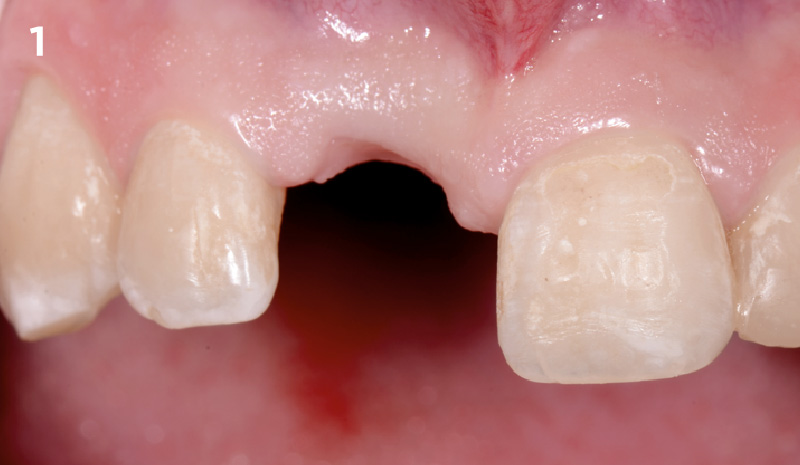
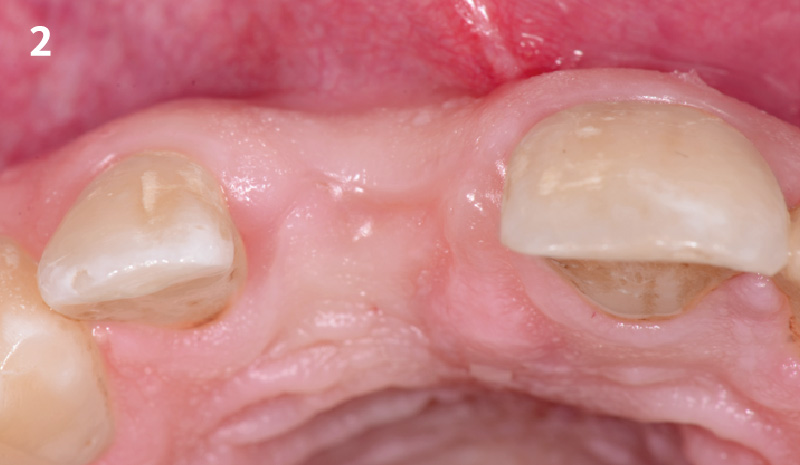
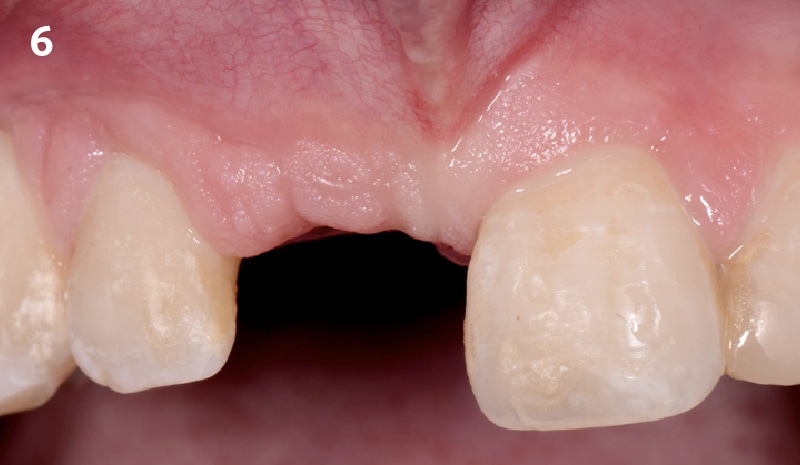
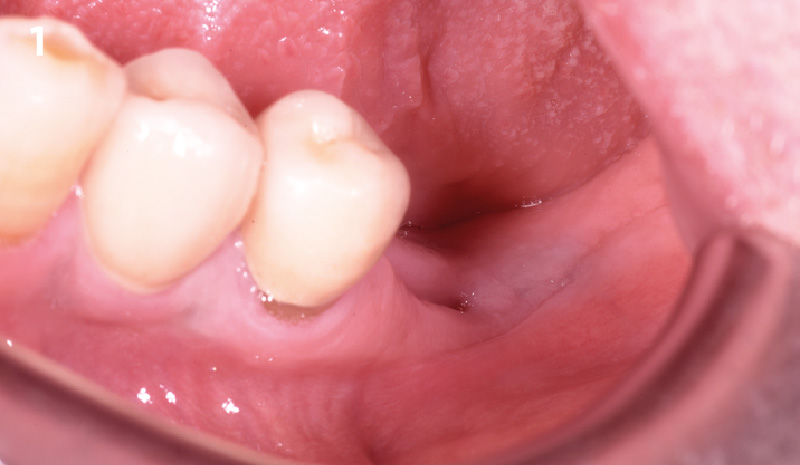
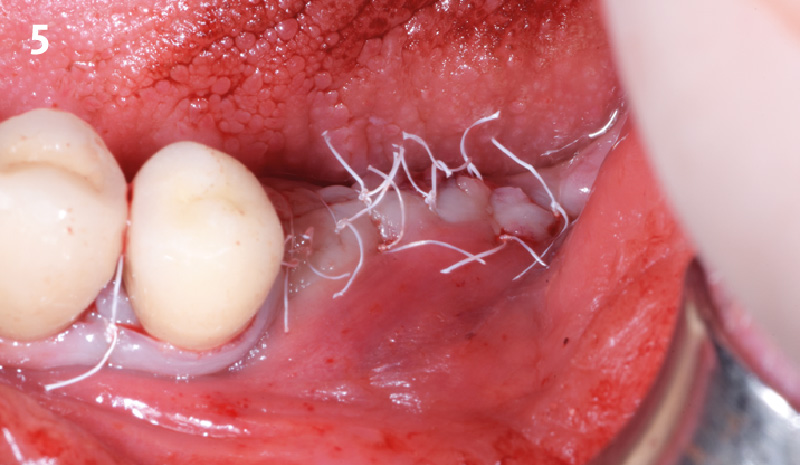
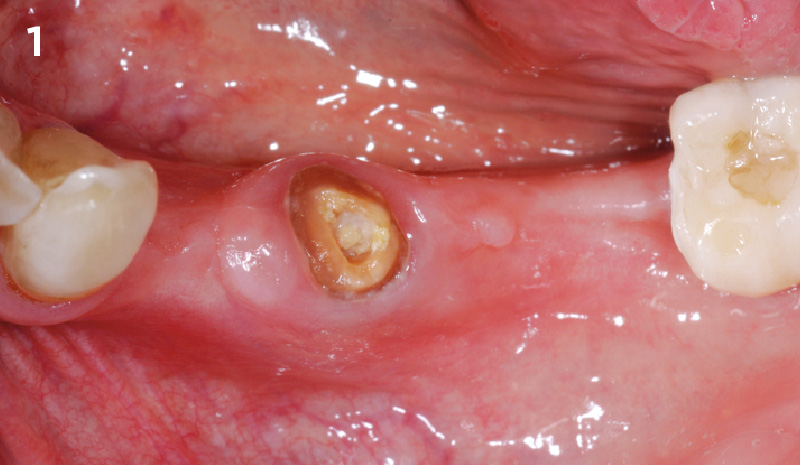
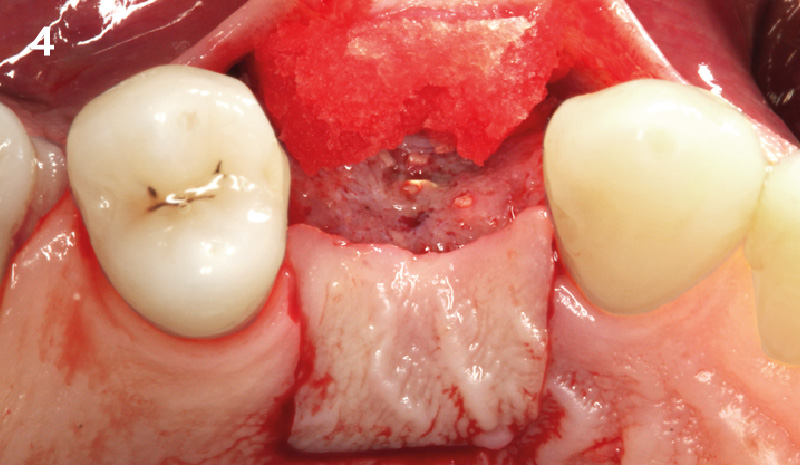
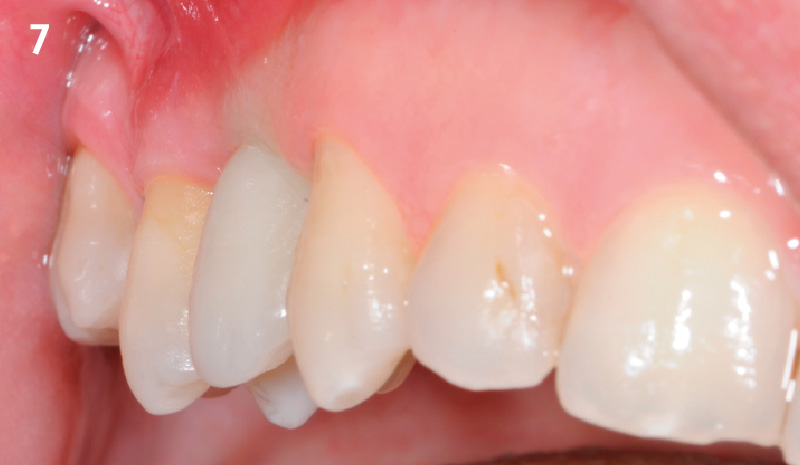
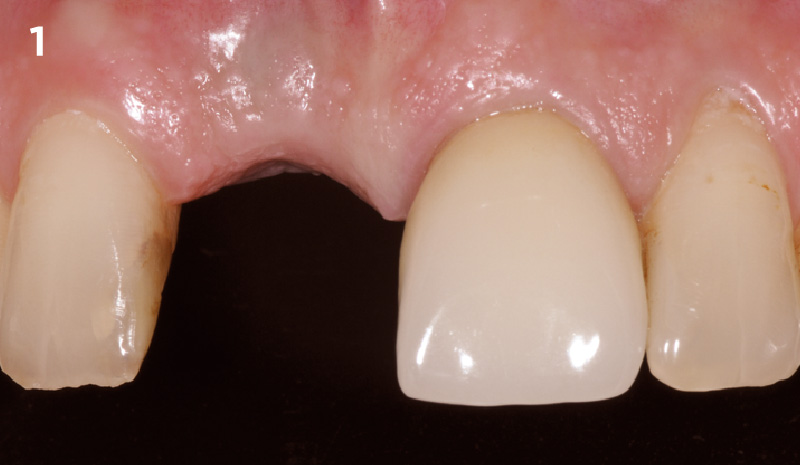
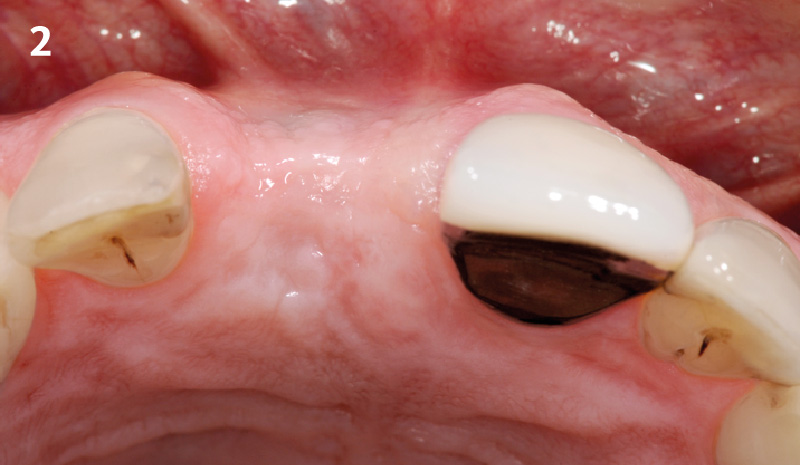
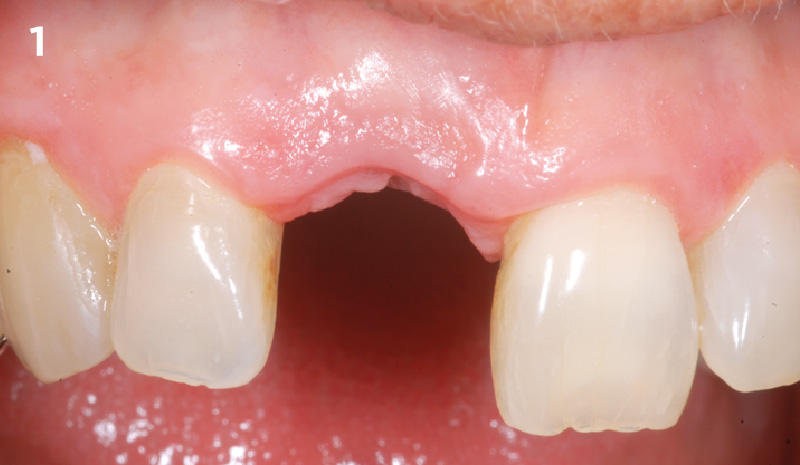
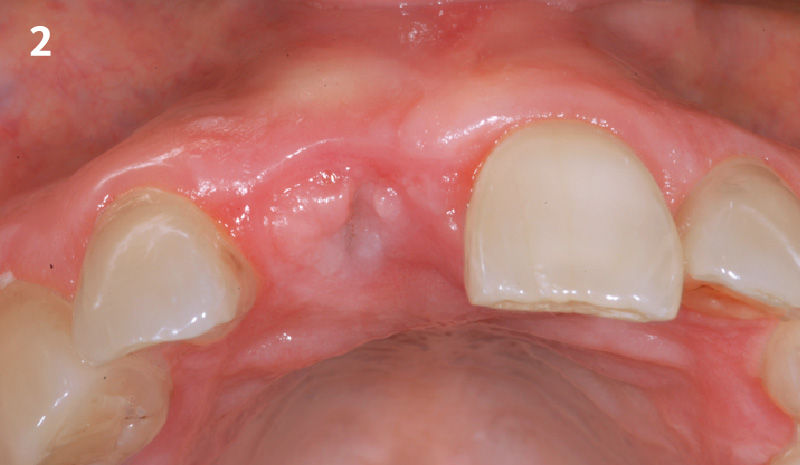
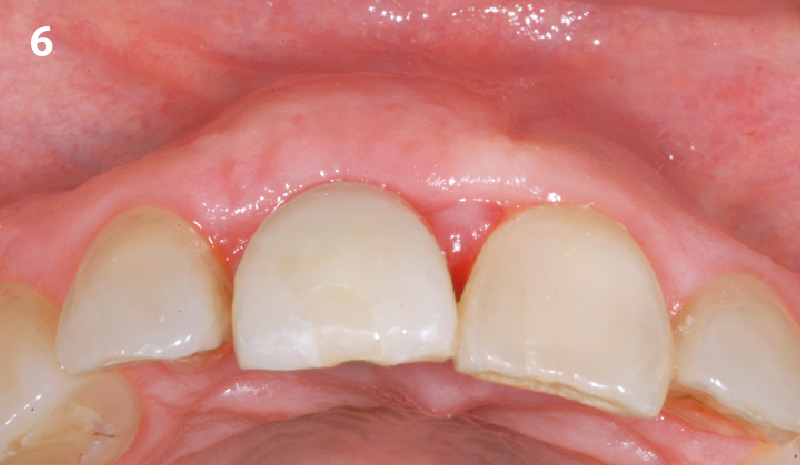
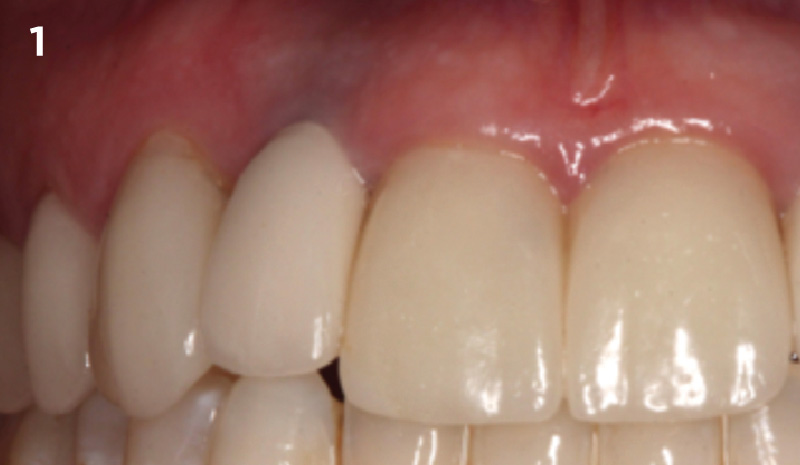
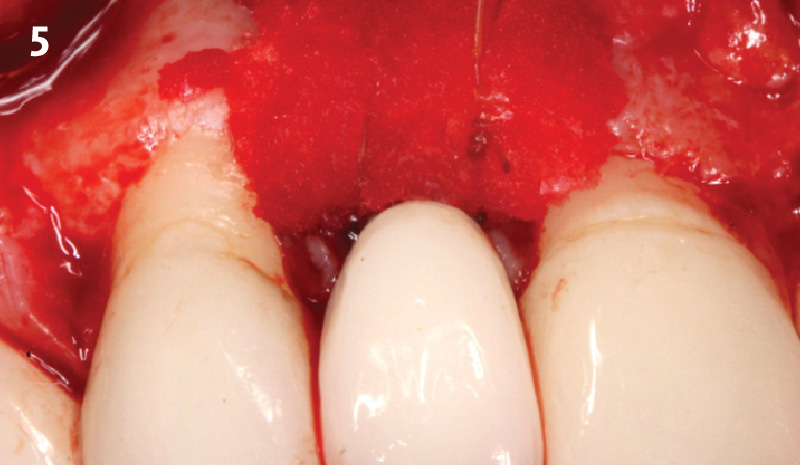
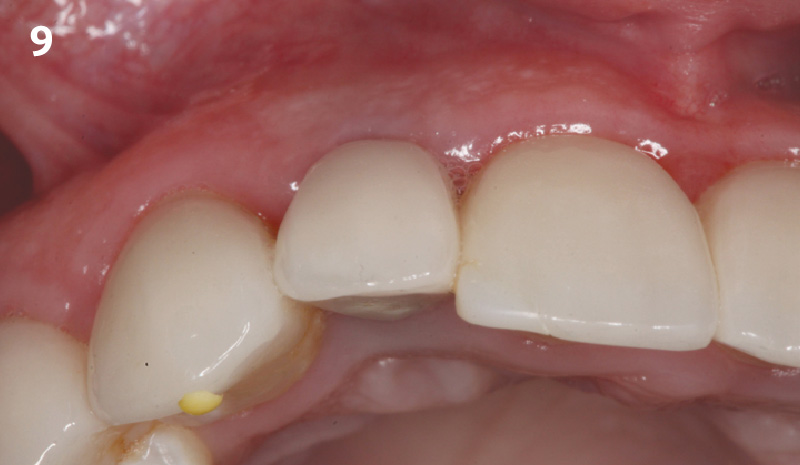
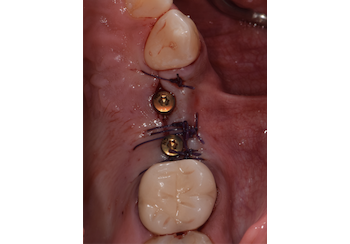
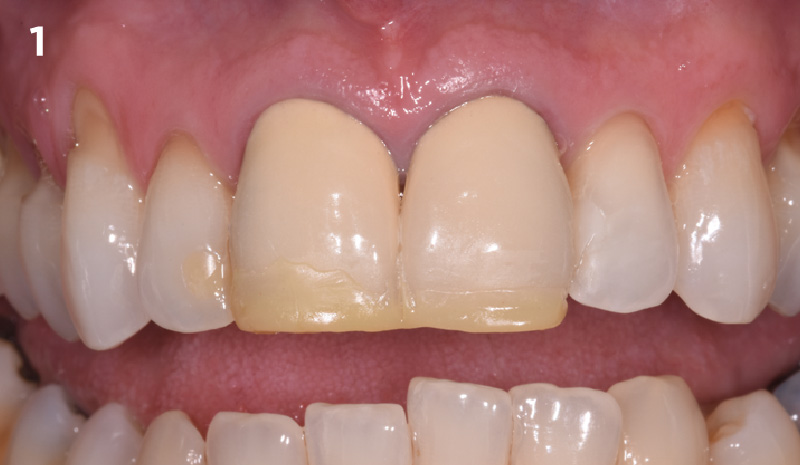
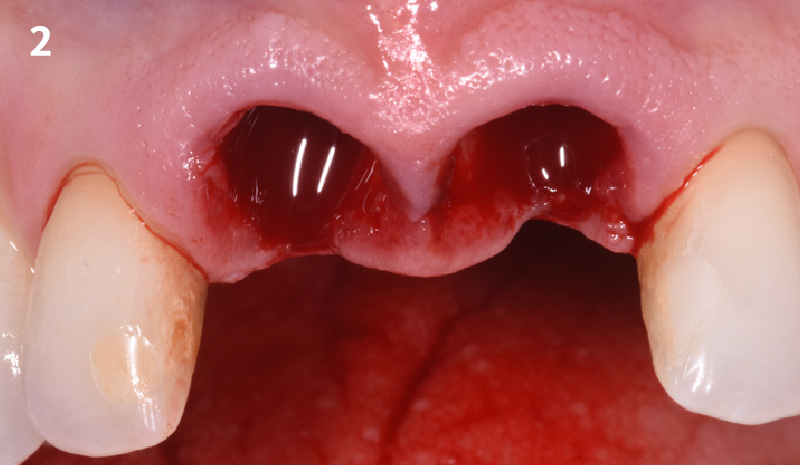
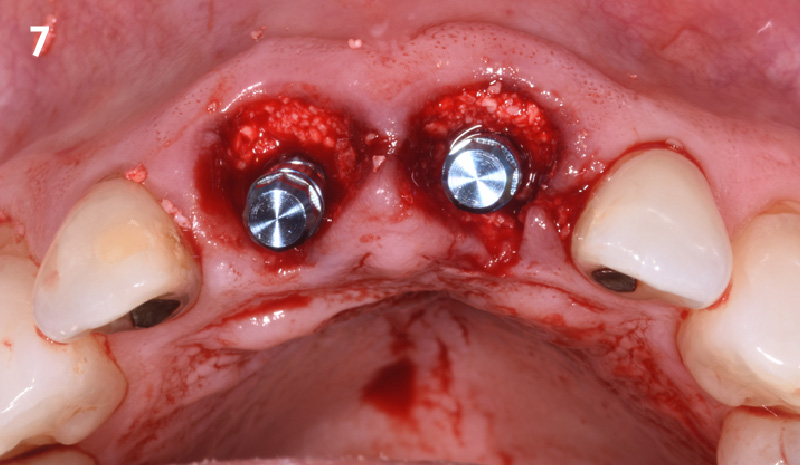
A healthy, 56-year-old female presented with fractured, endodontically treated tooth #9. The tooth was fractured at the gingival level and asymptomatic. Both the patient and the restorative dentist had high esthetic expectations, and preferred immediate implant placement with provisionalization if possible.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system Non-smoker | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of the smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival phenotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
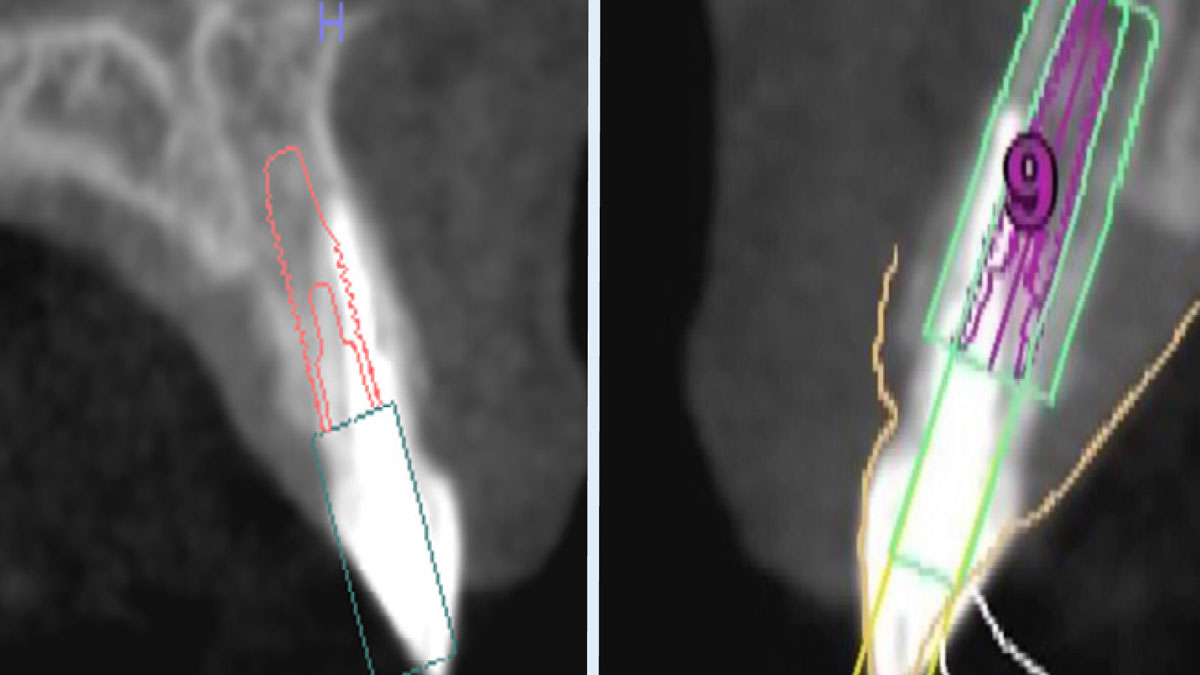
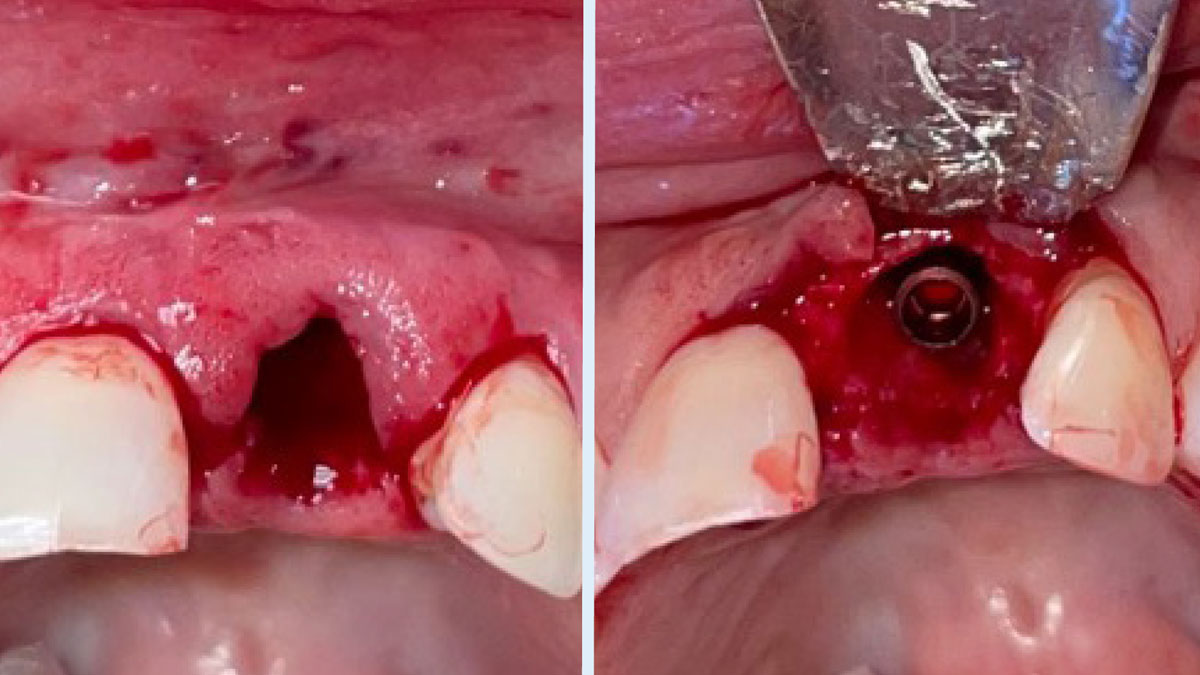
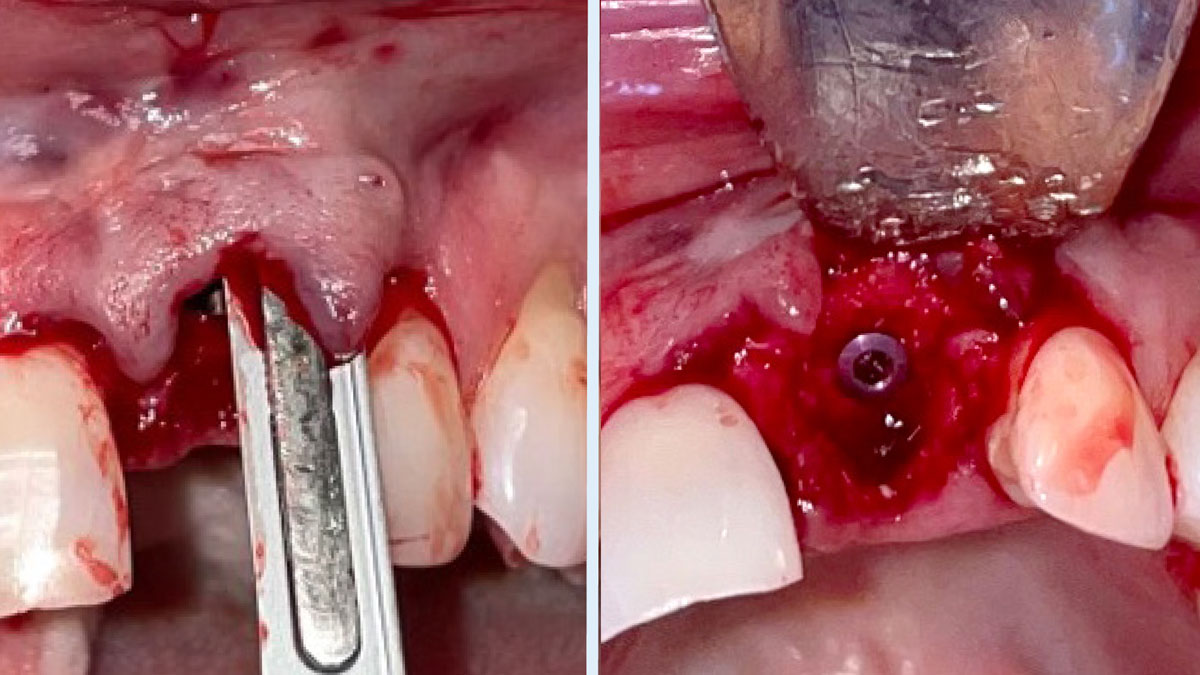
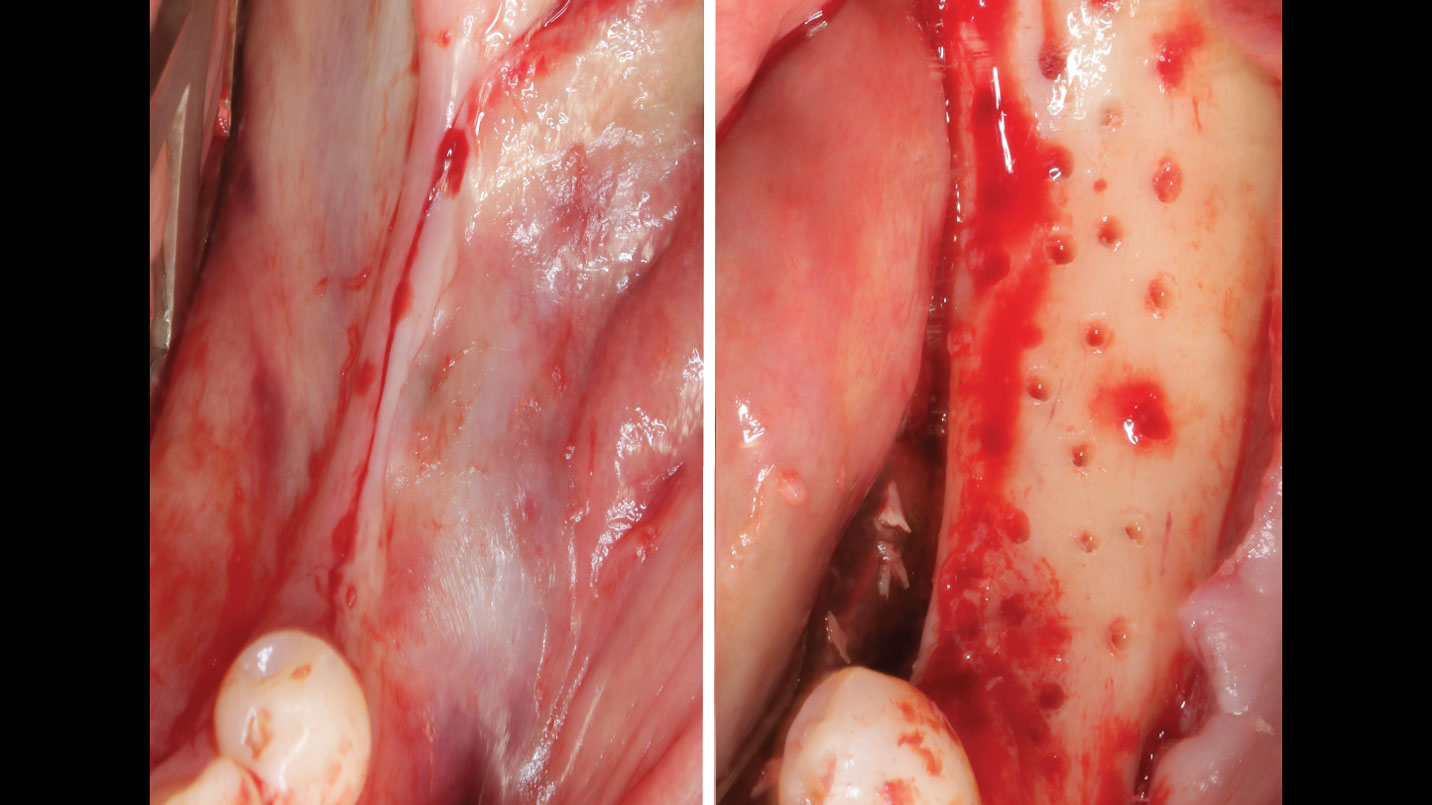
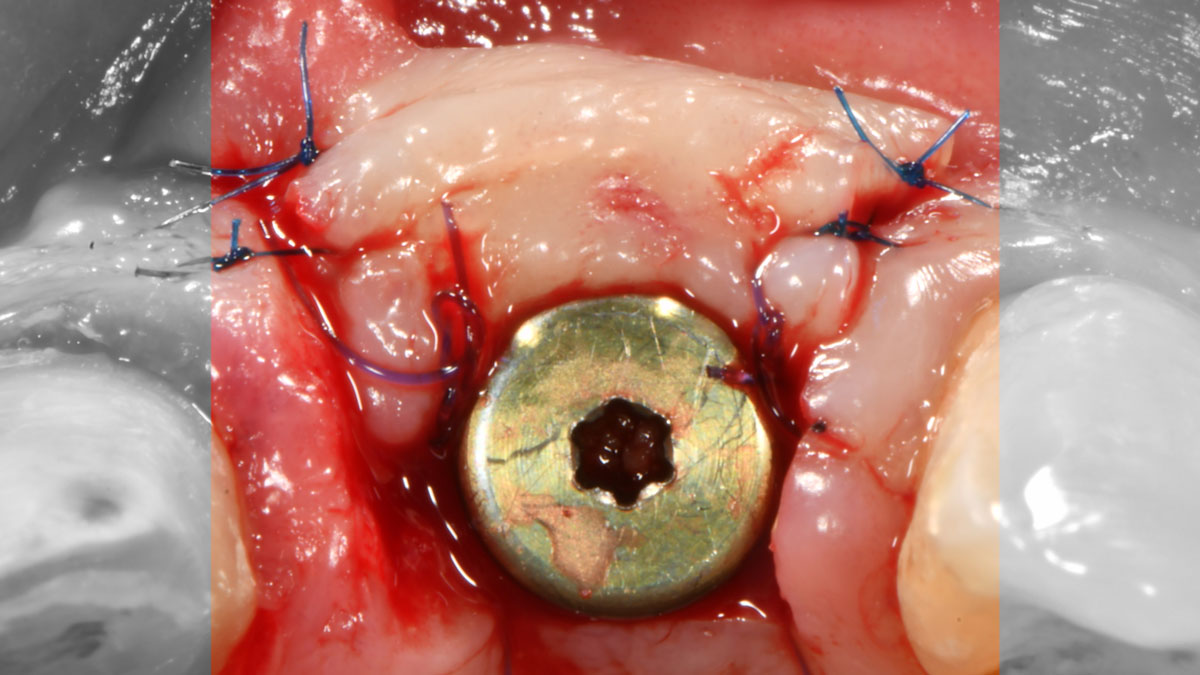
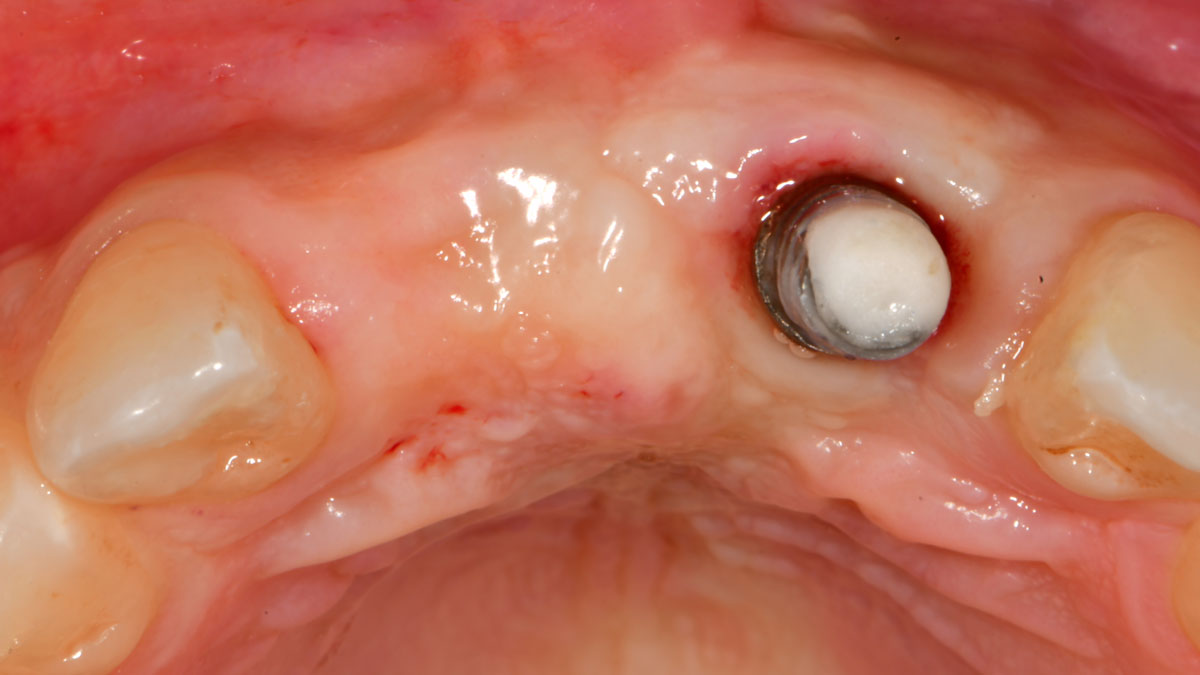
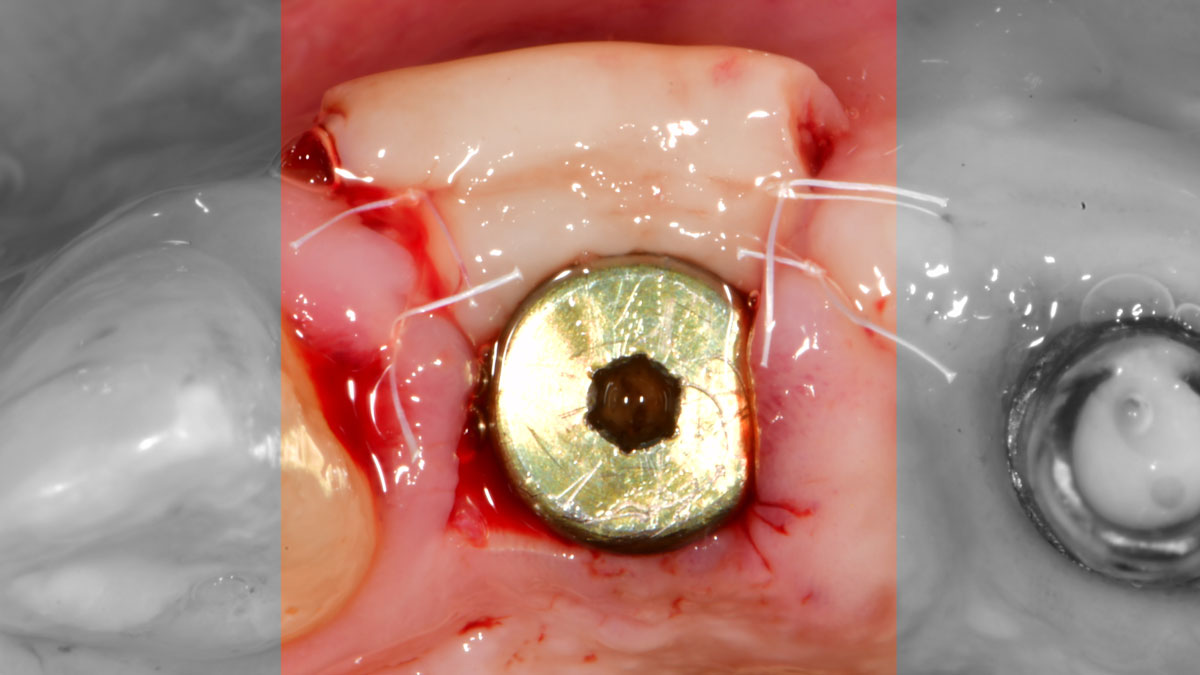
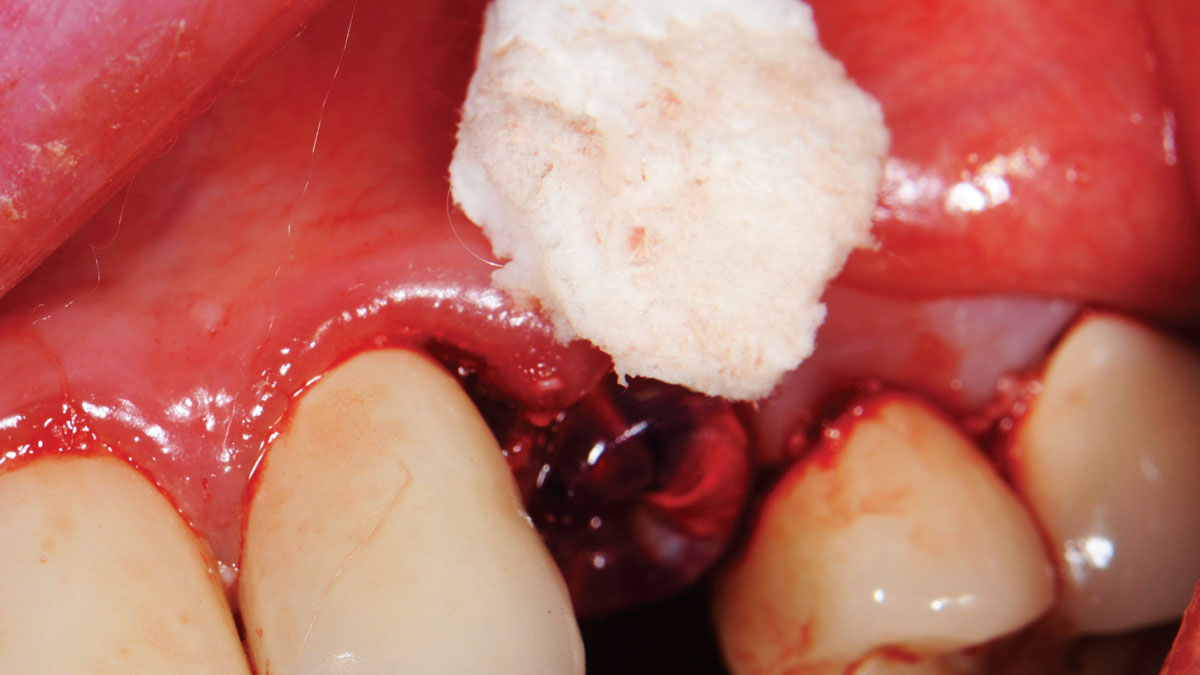
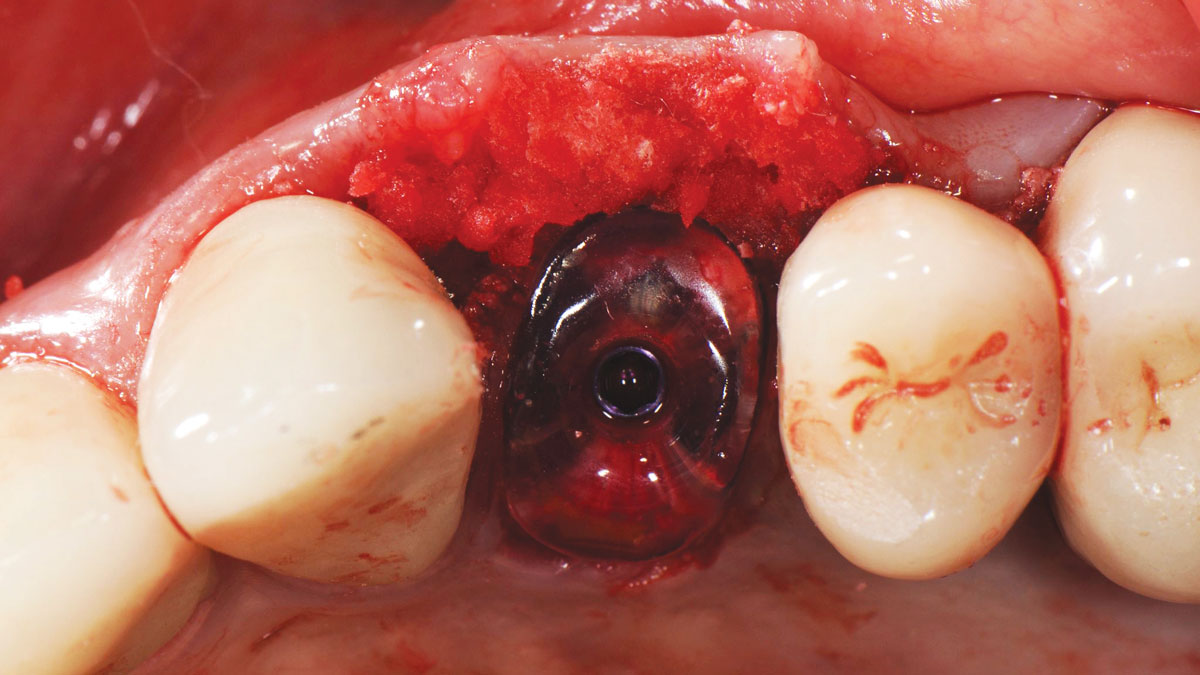
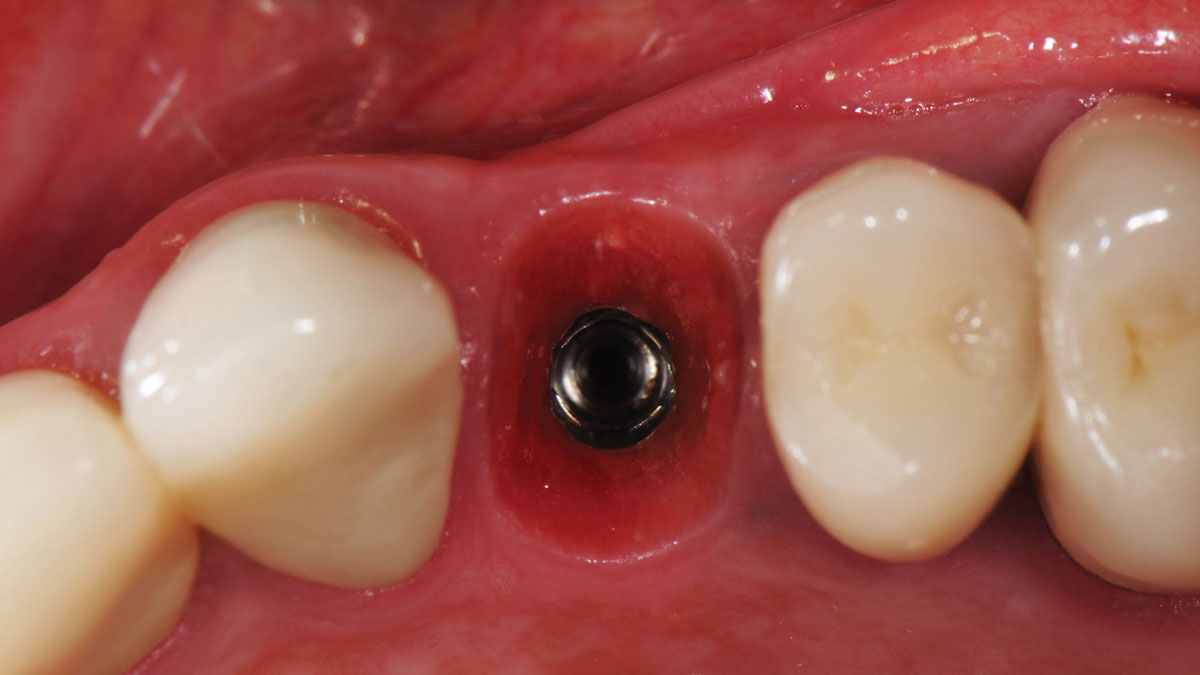
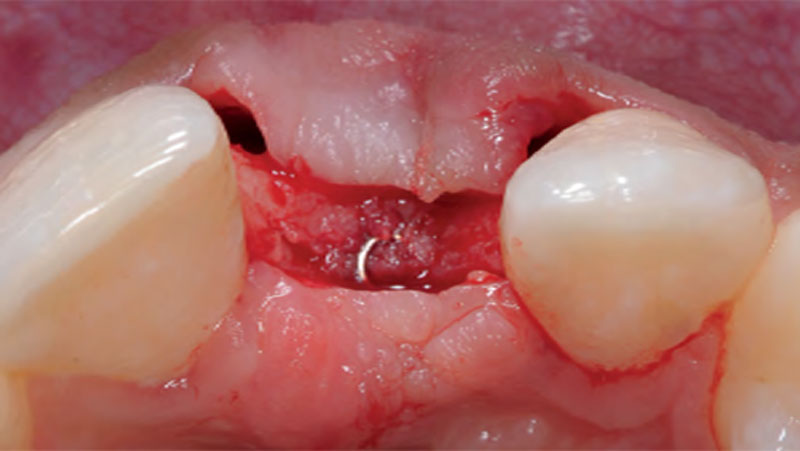
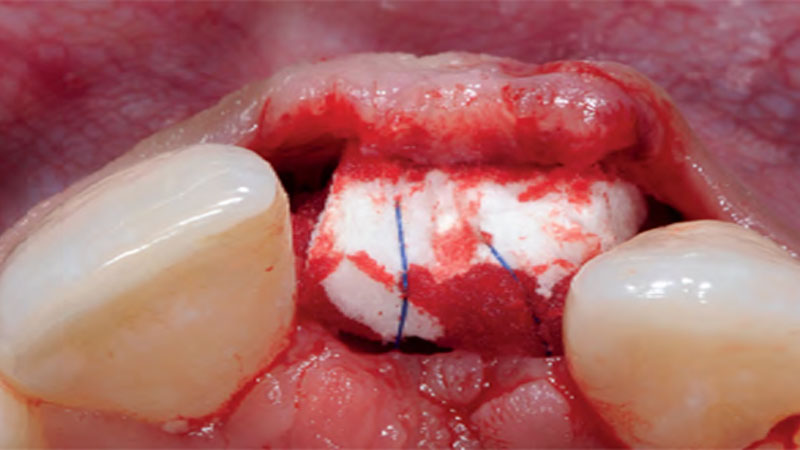
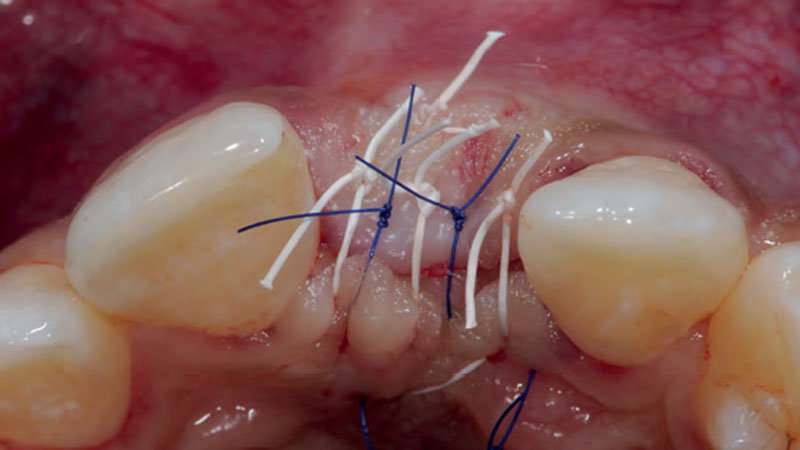
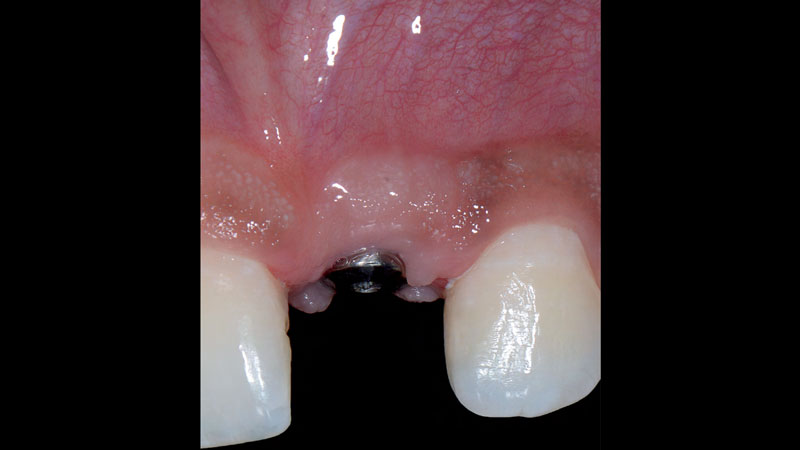
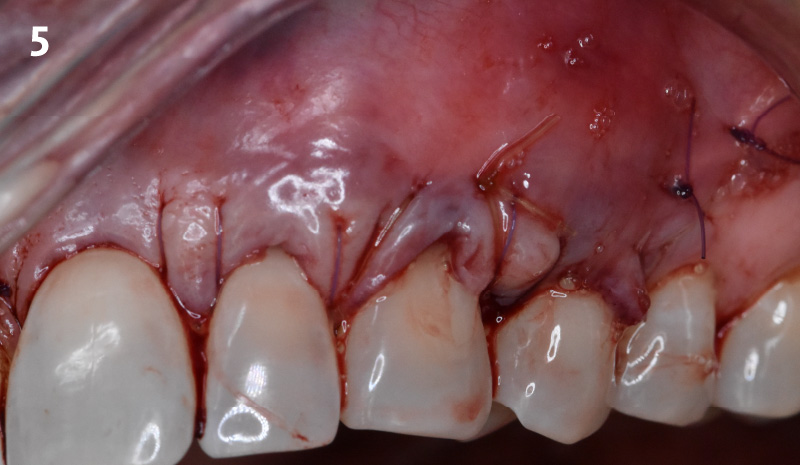
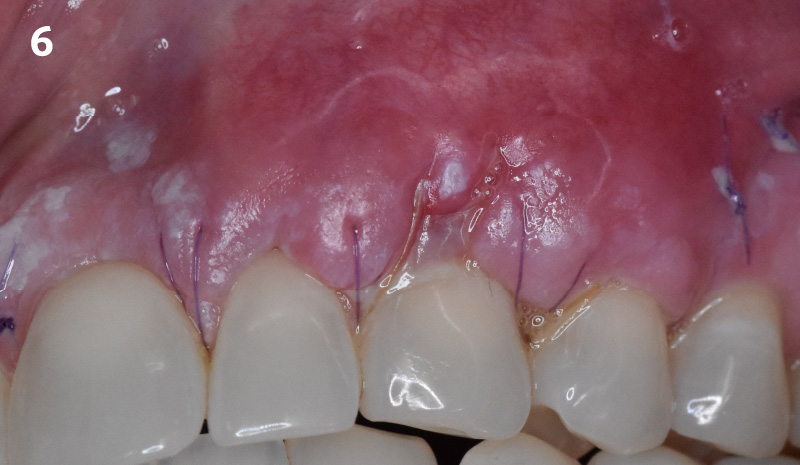
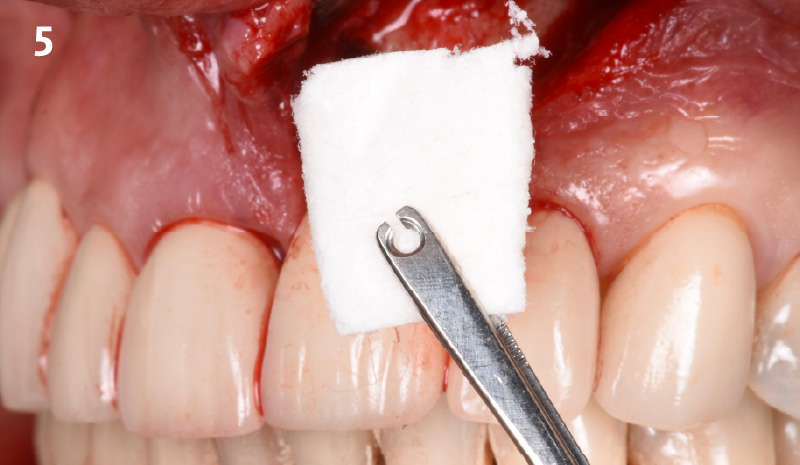
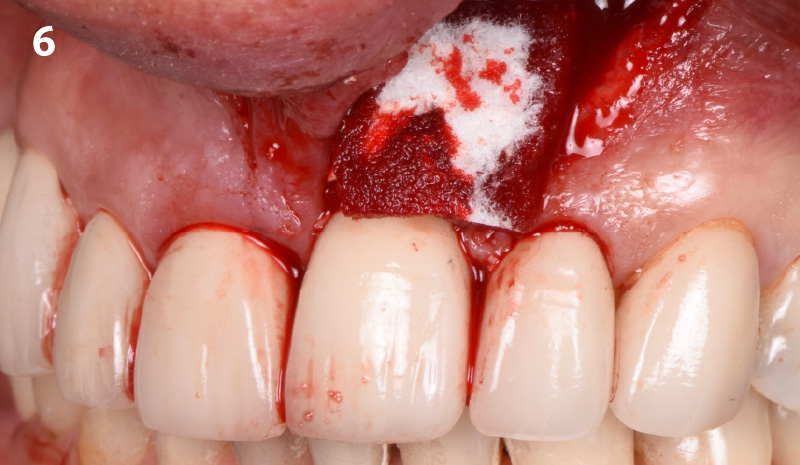
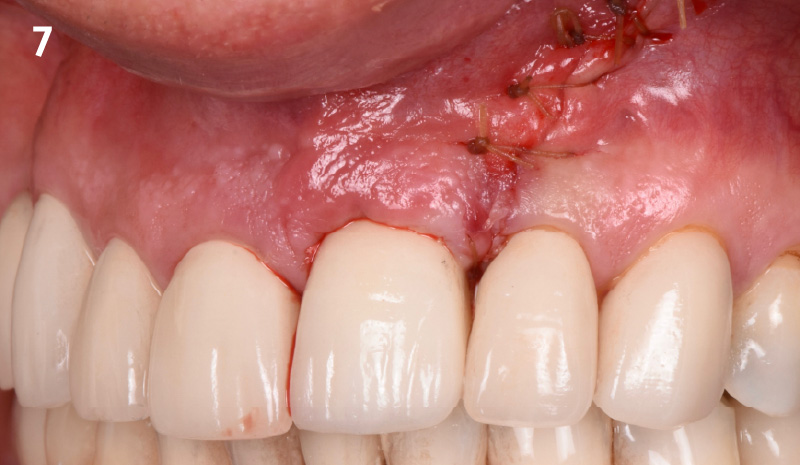
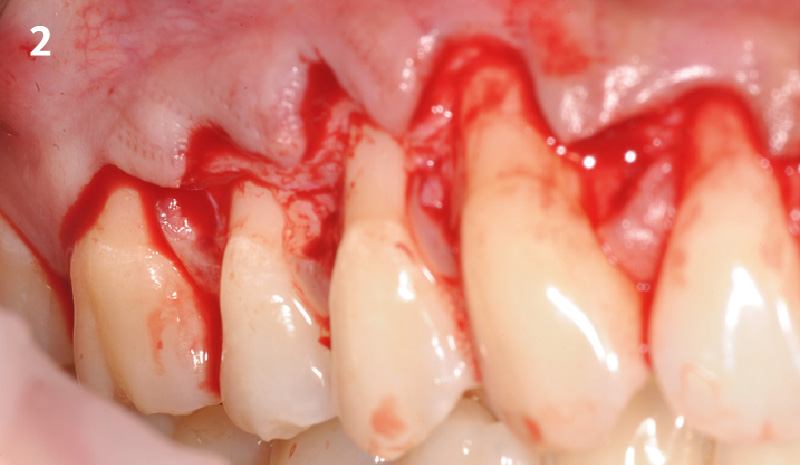
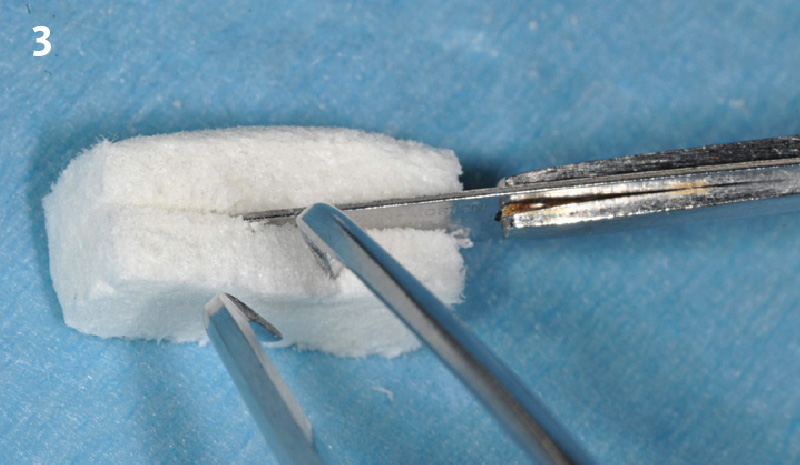
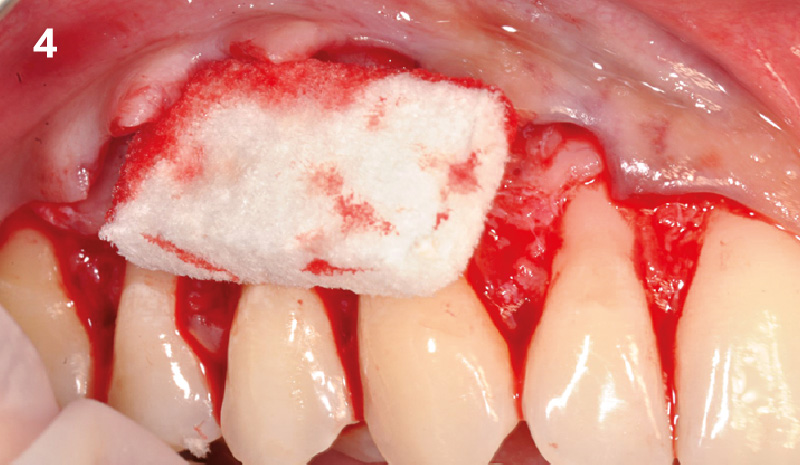
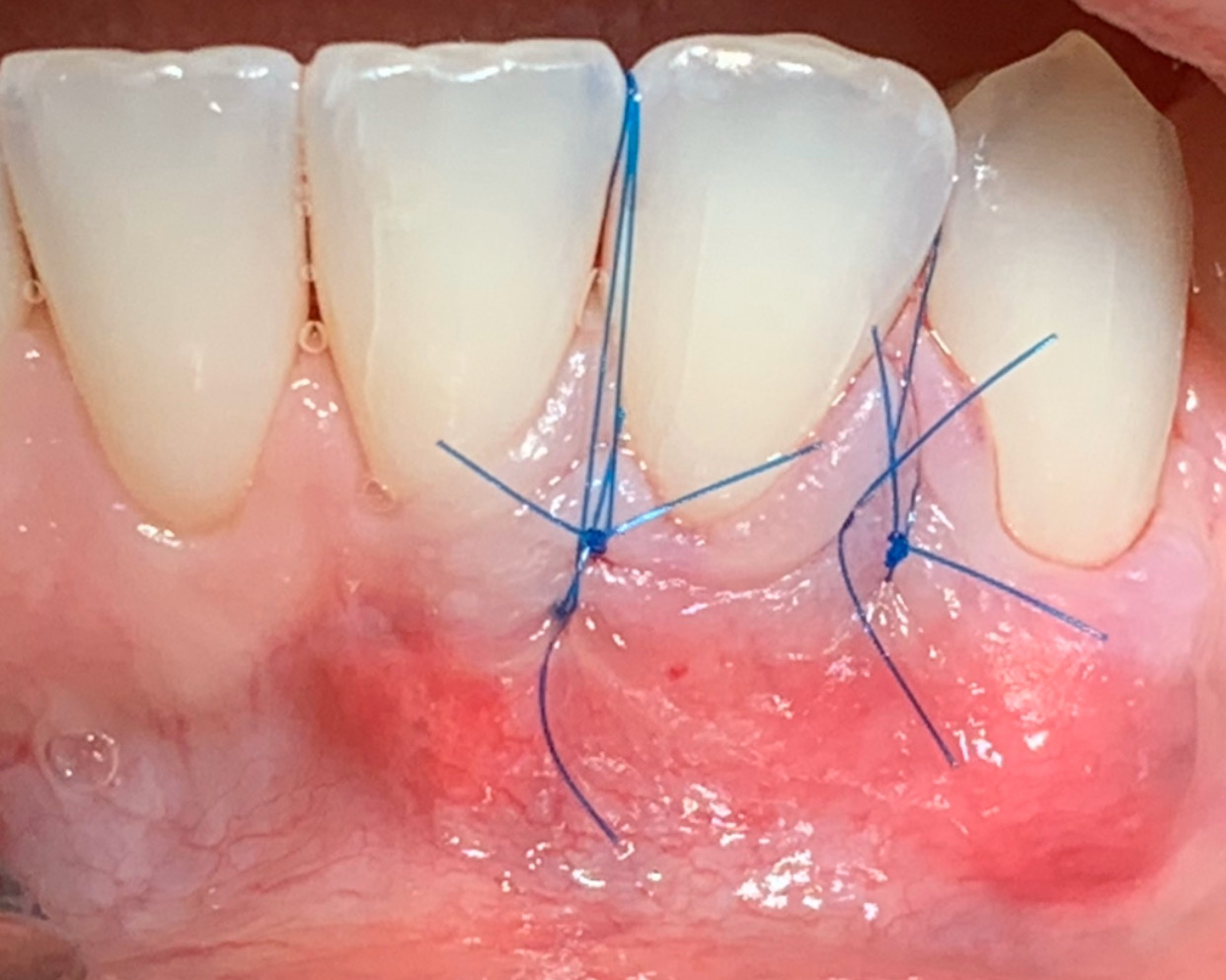
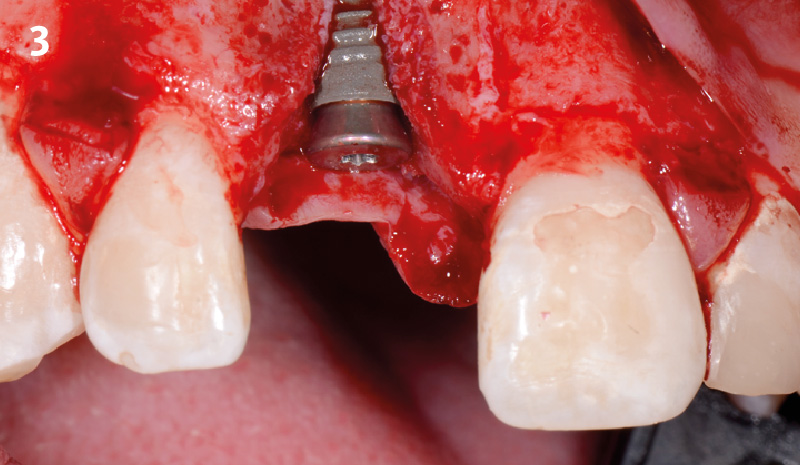
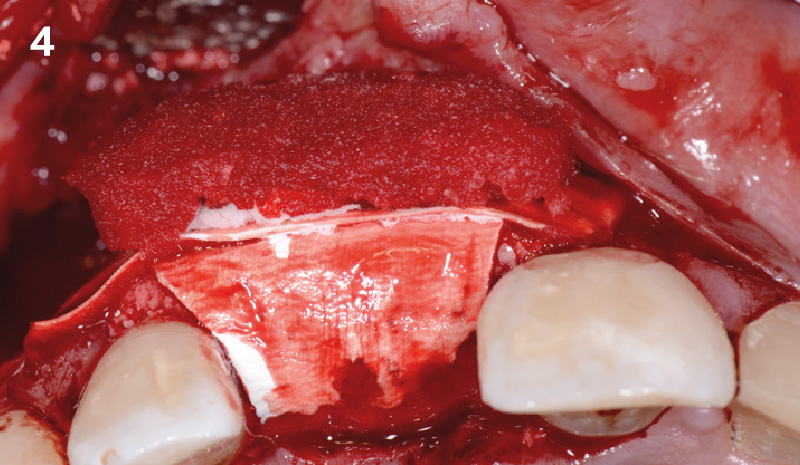
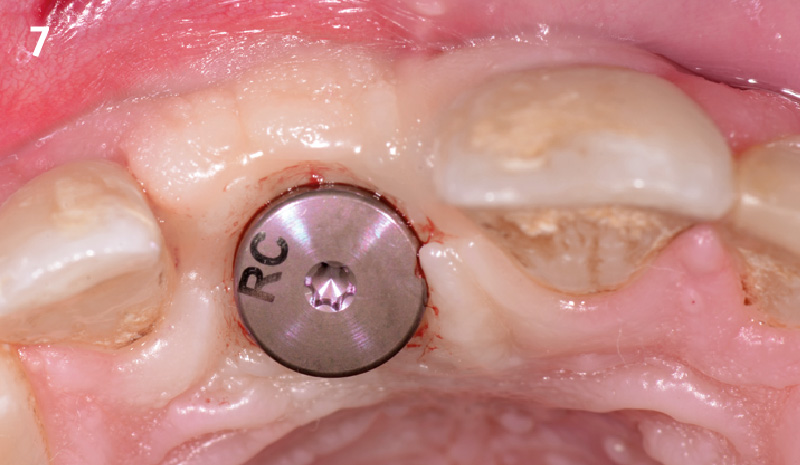
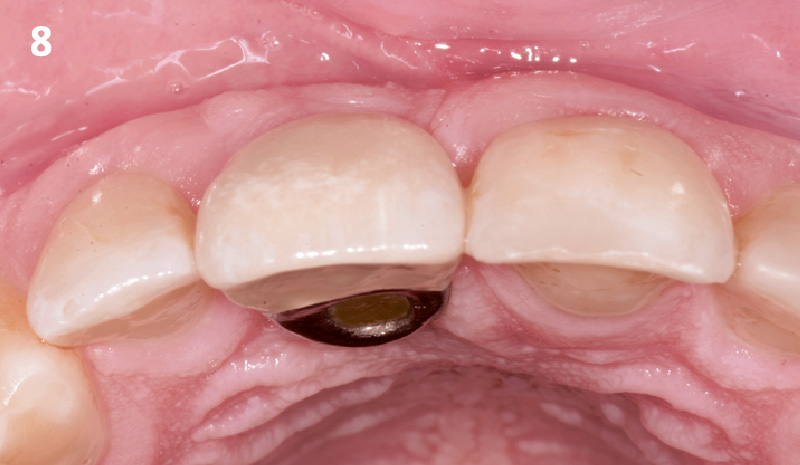
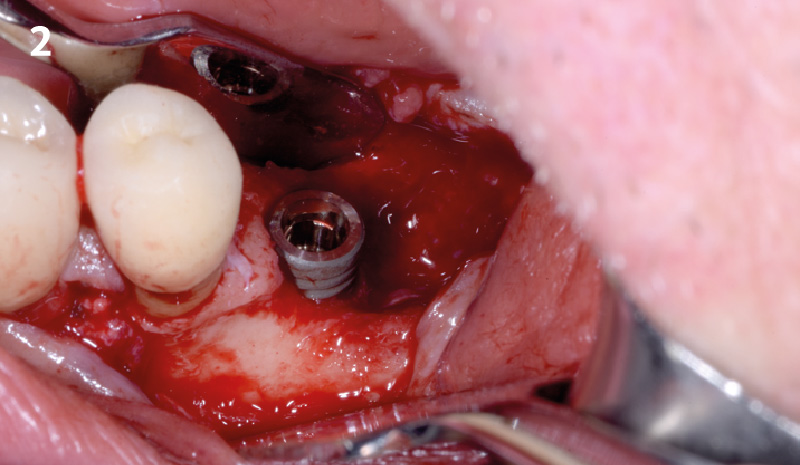
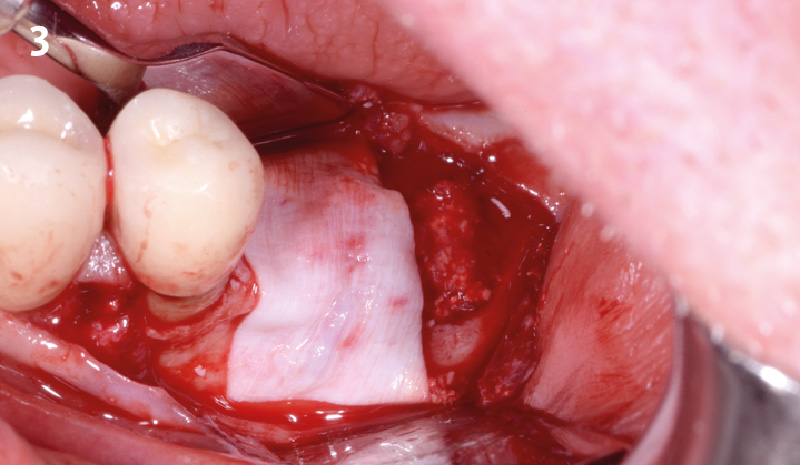
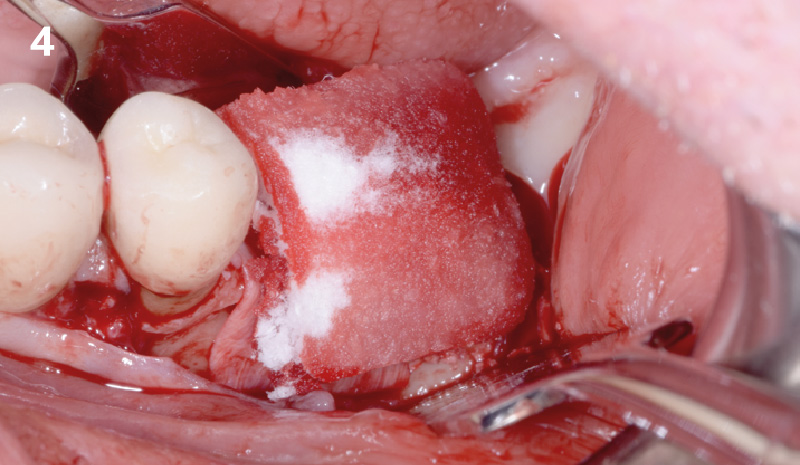
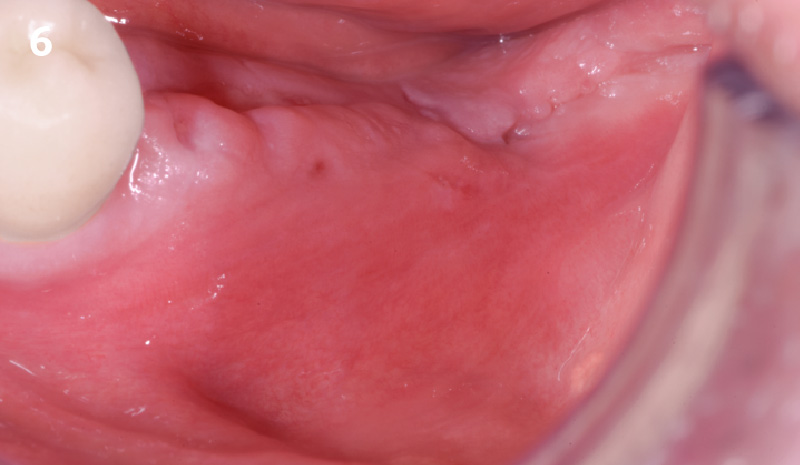
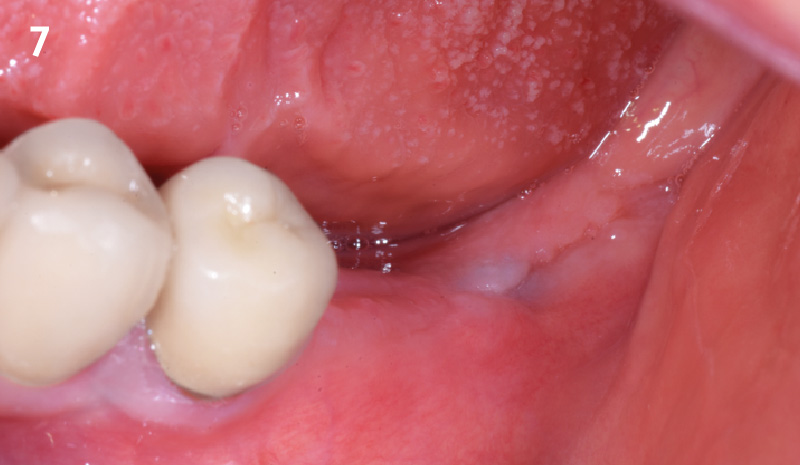
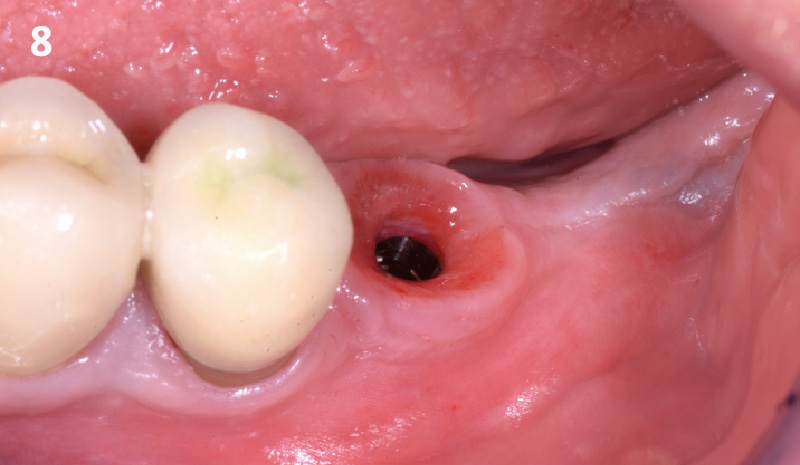
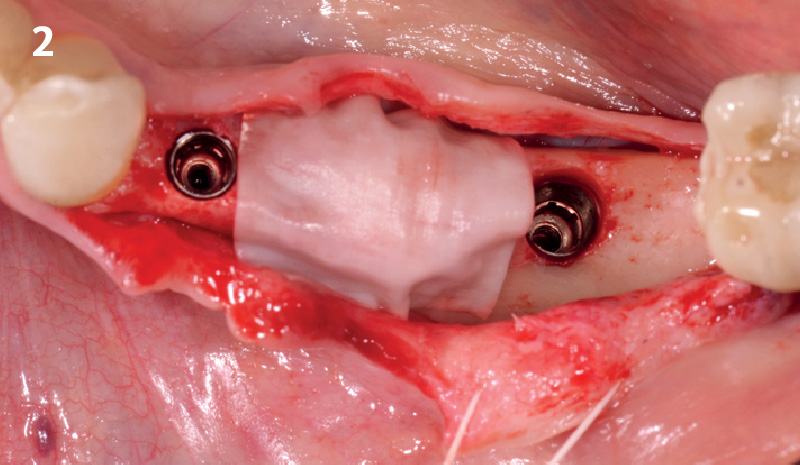
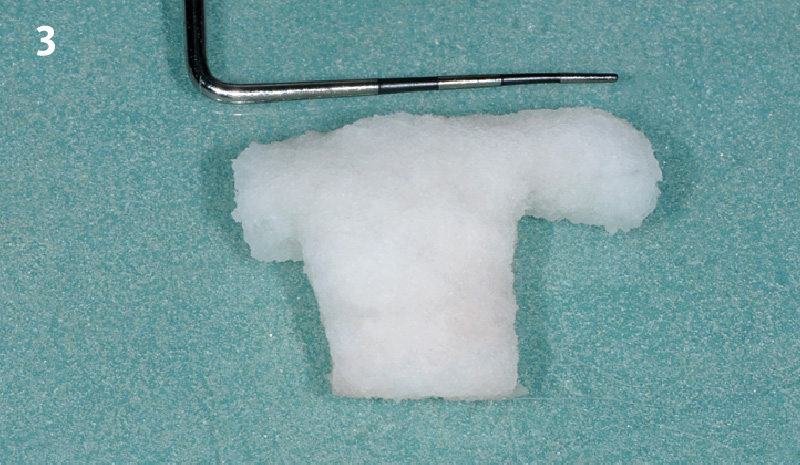
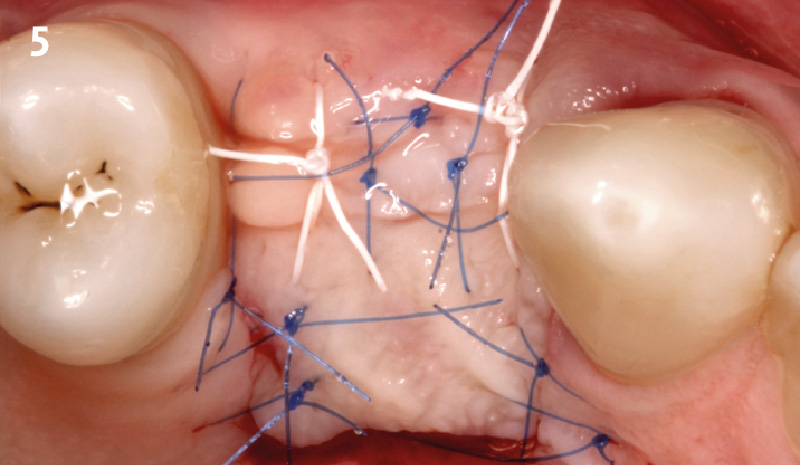
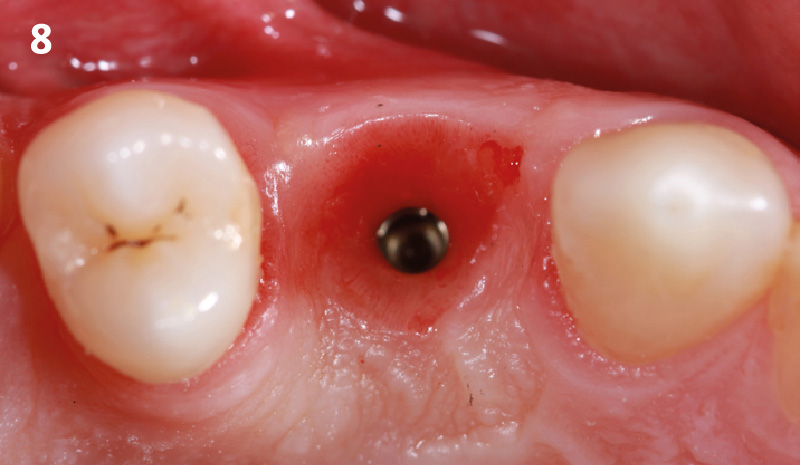
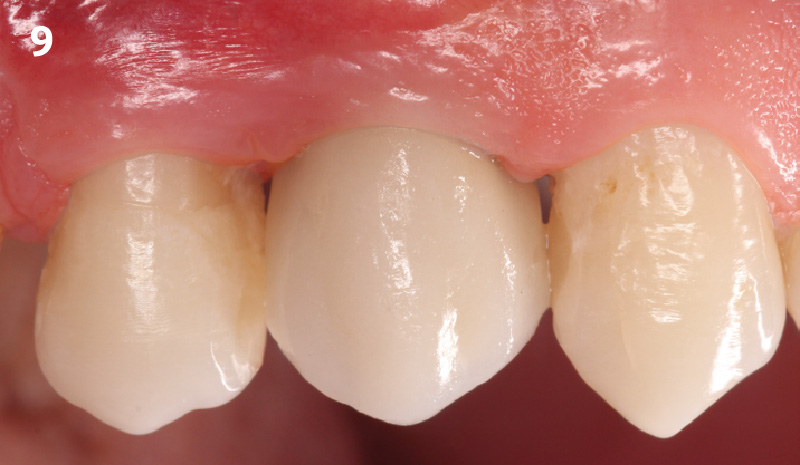
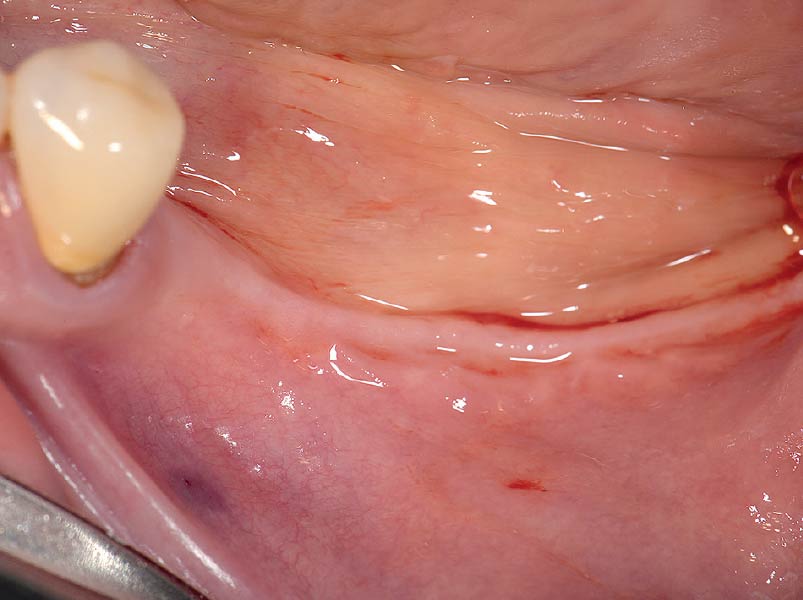
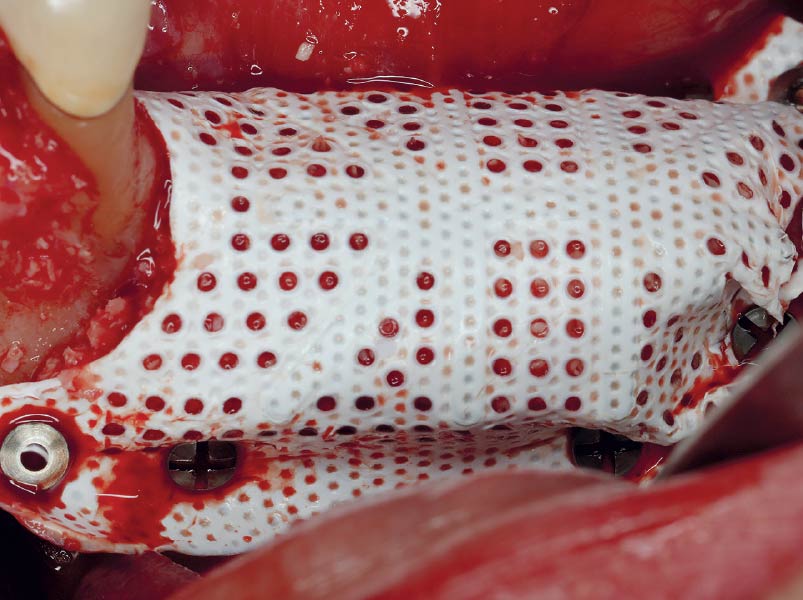
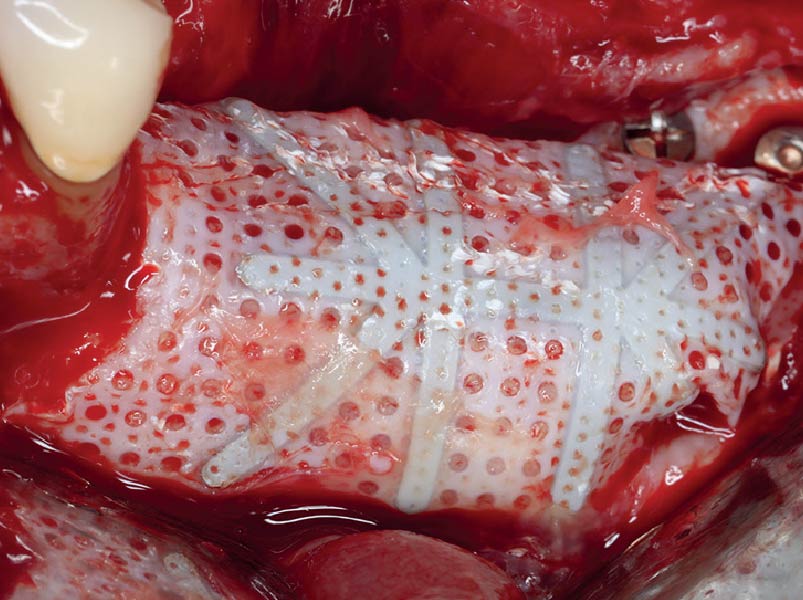
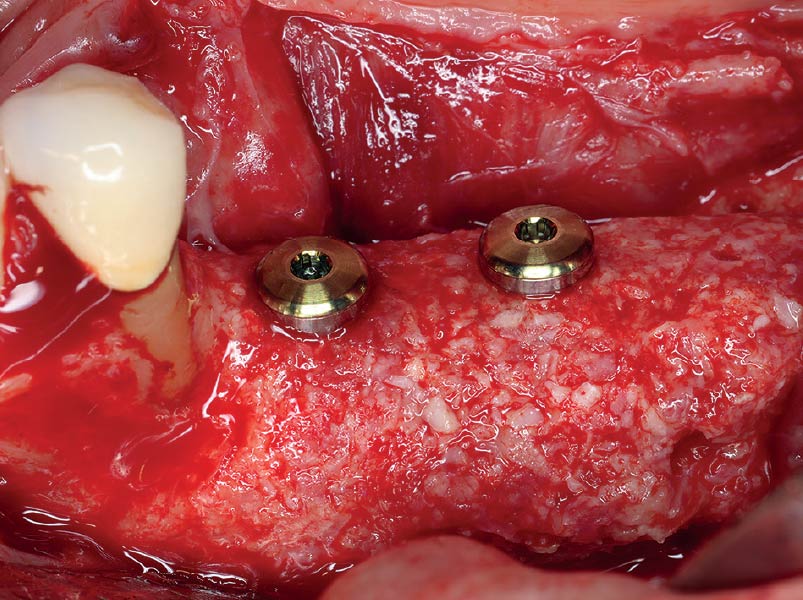
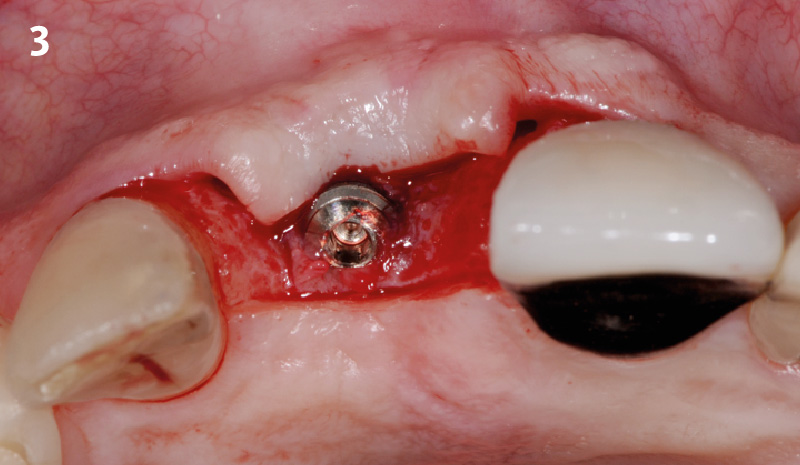
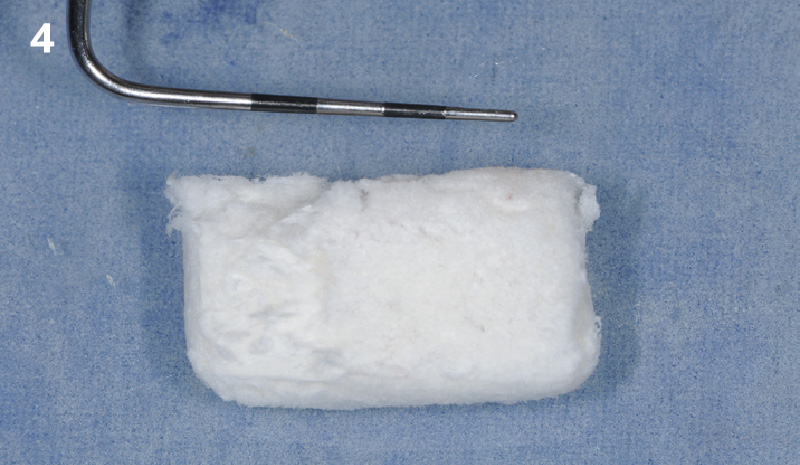
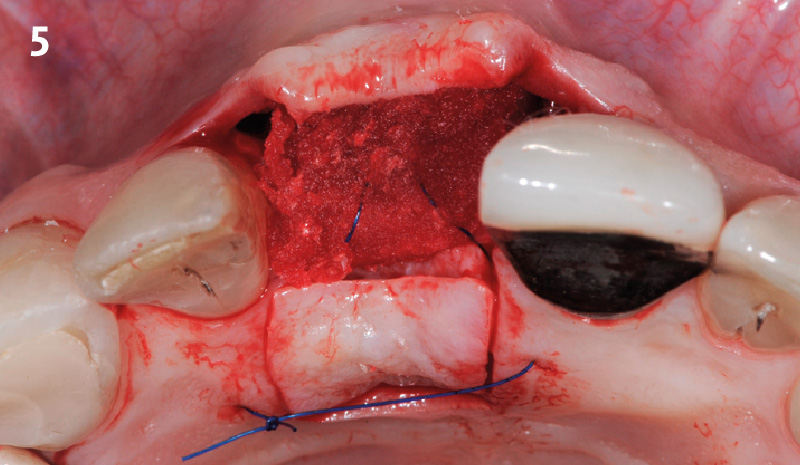
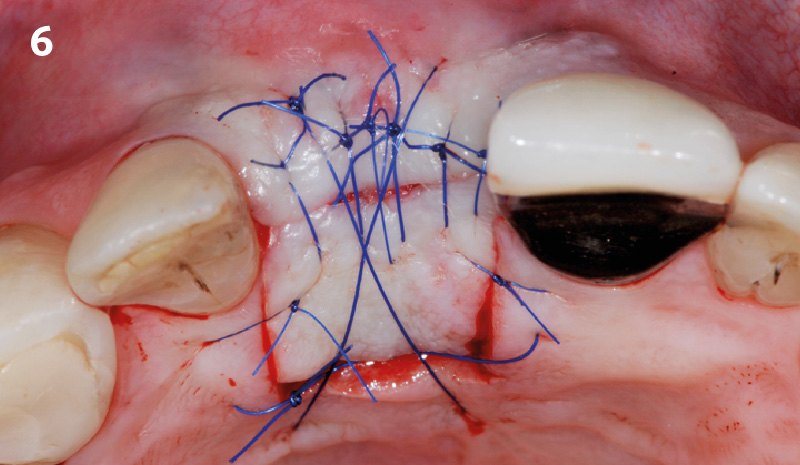
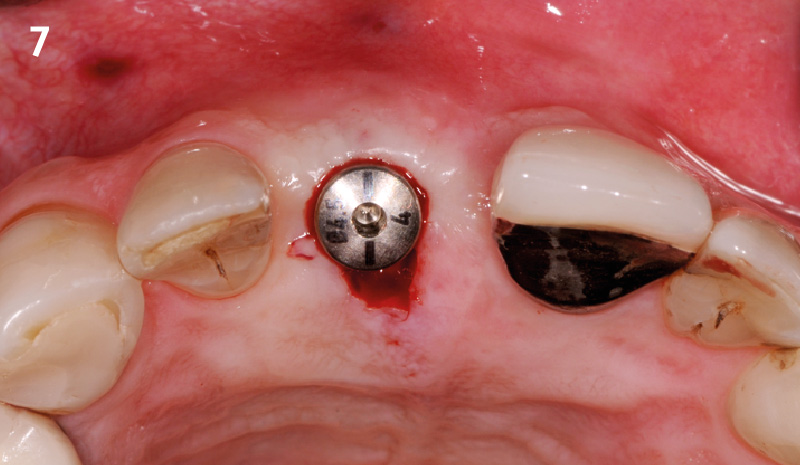
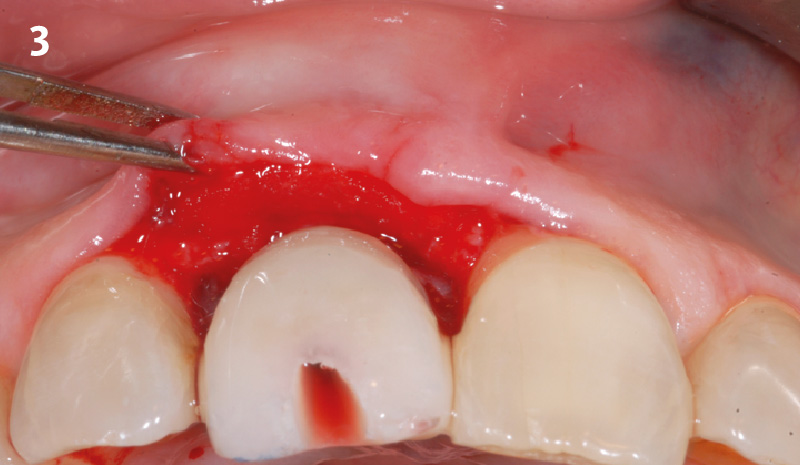
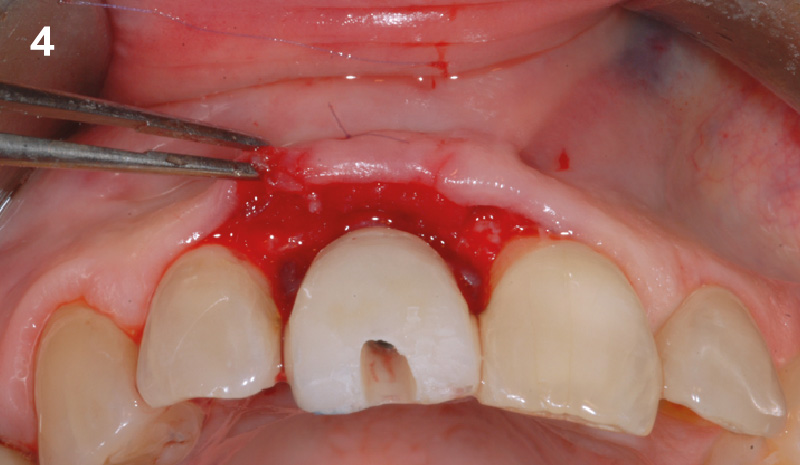
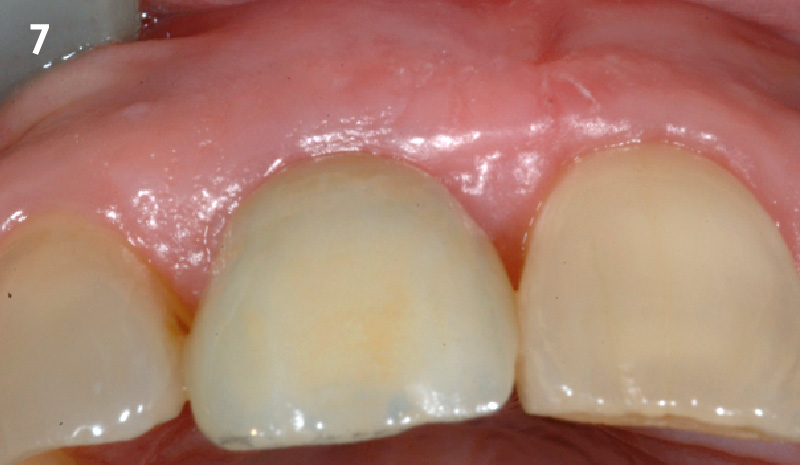
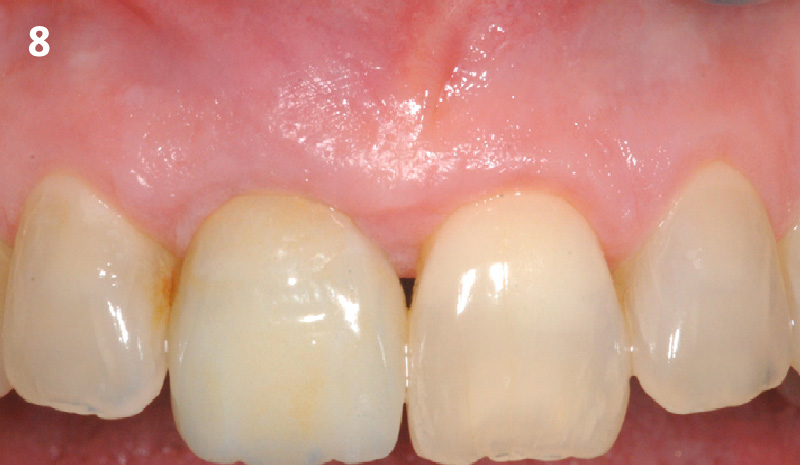
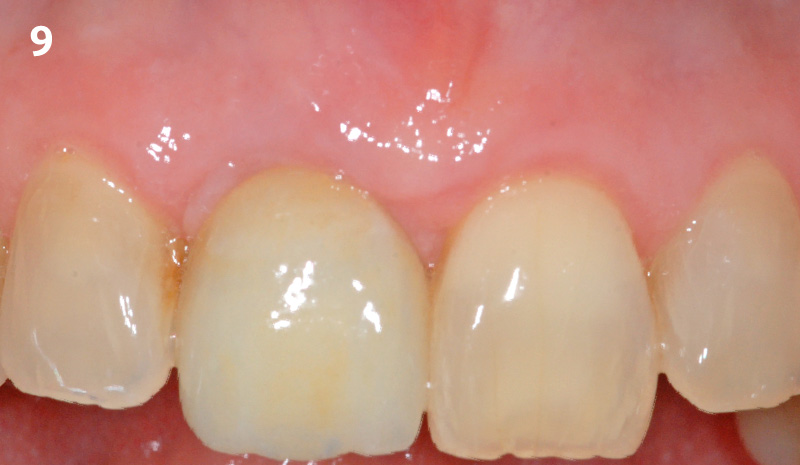
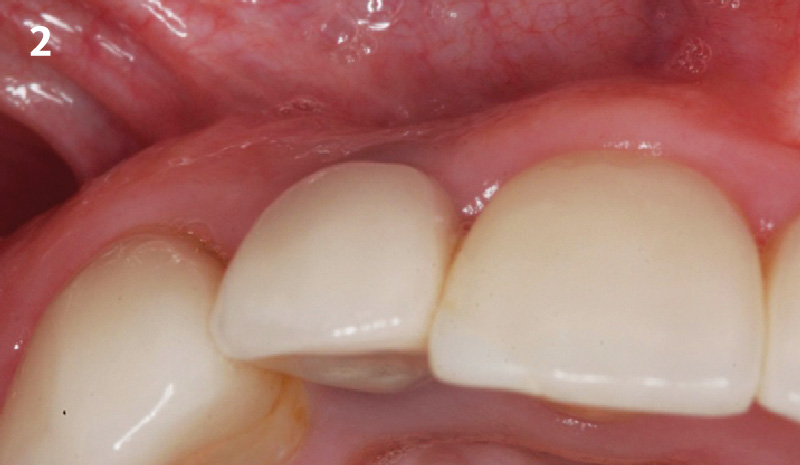
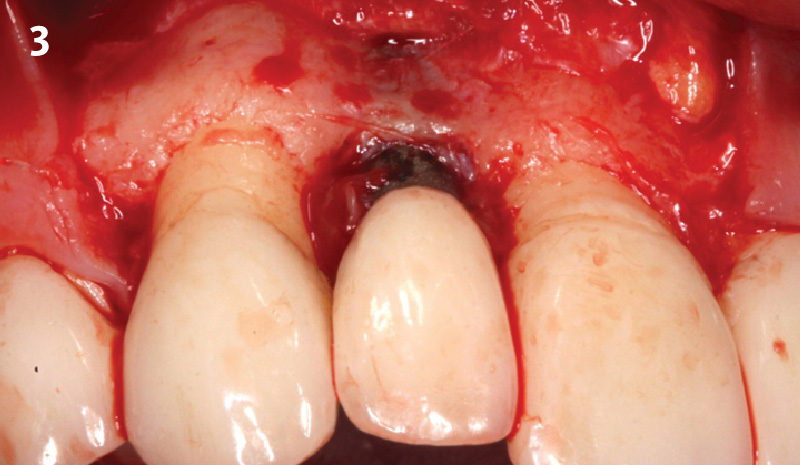
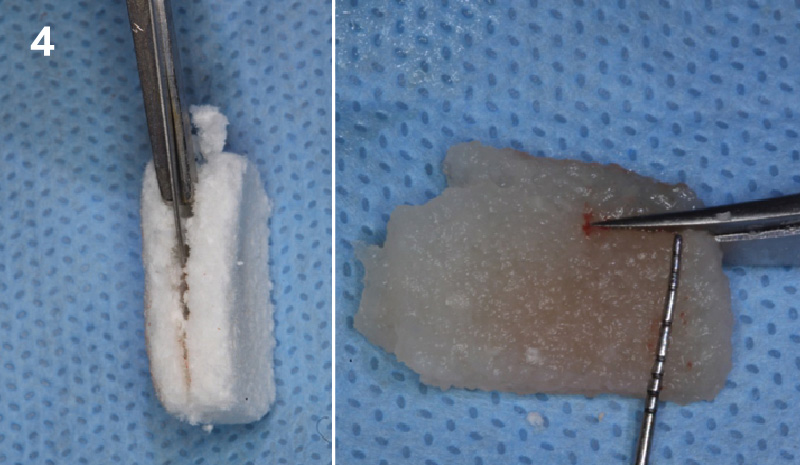
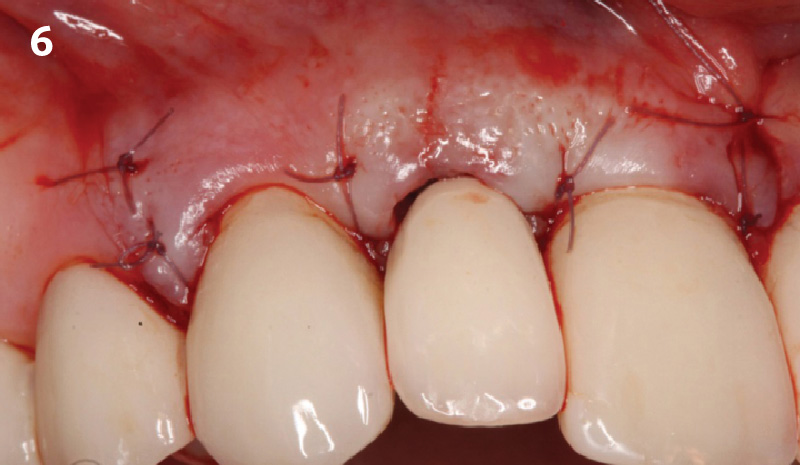
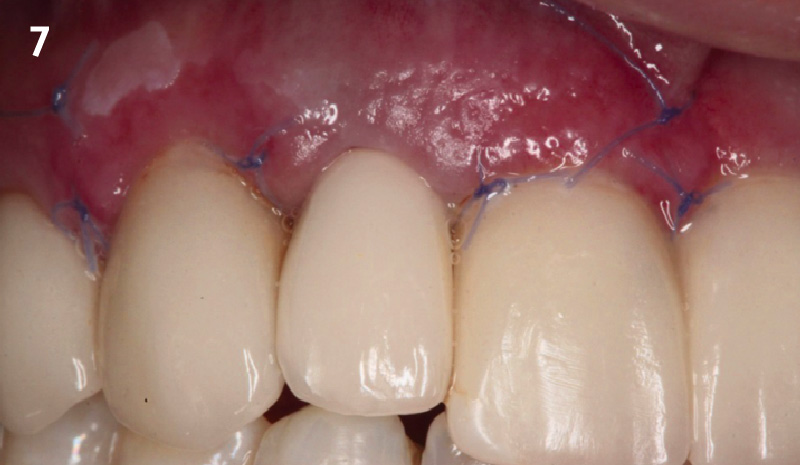
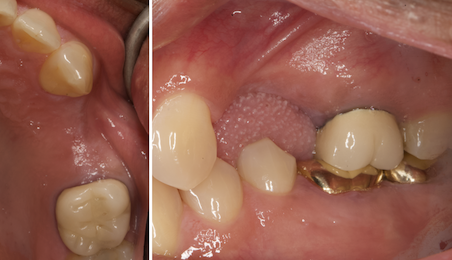
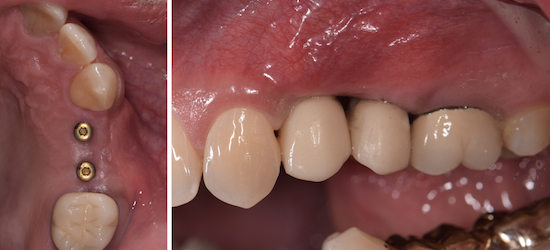
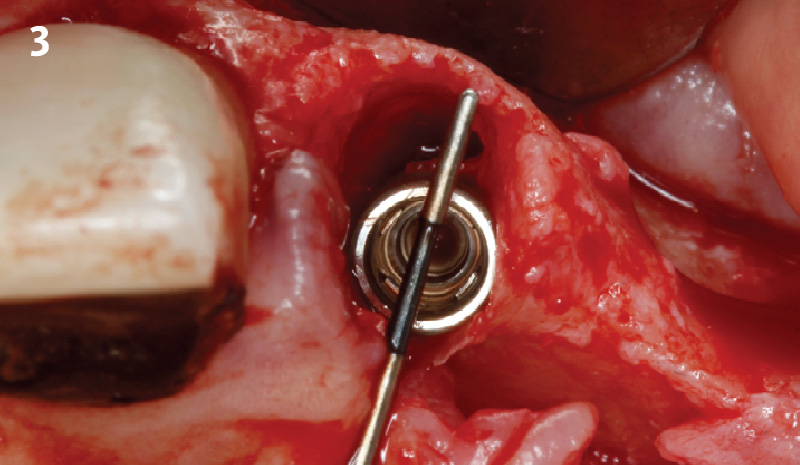
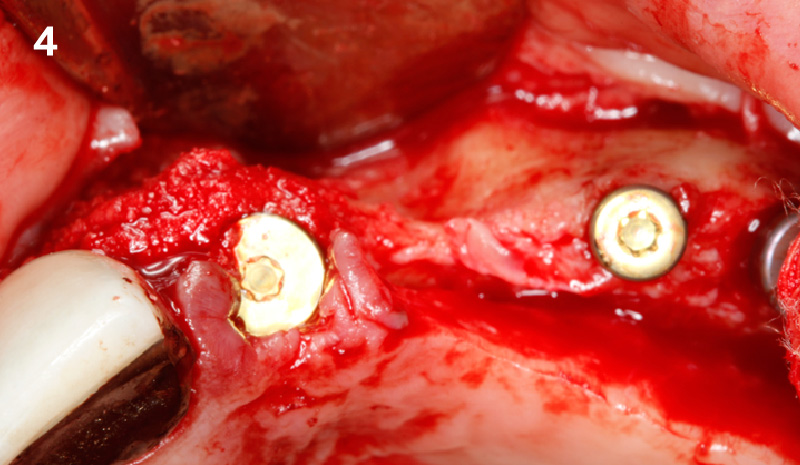
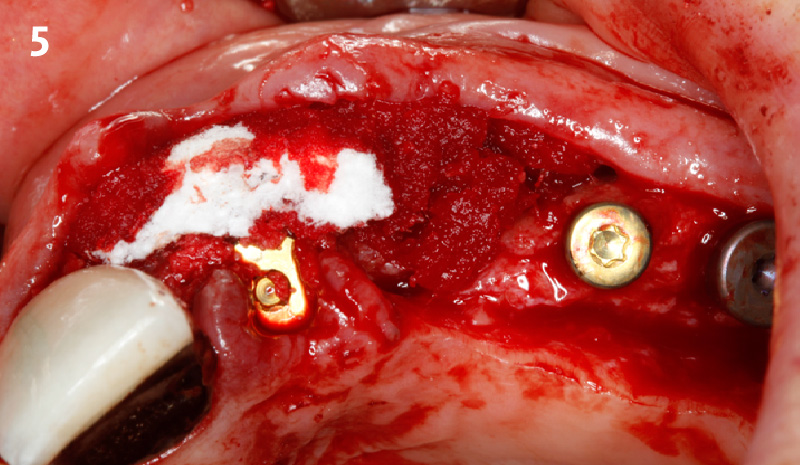
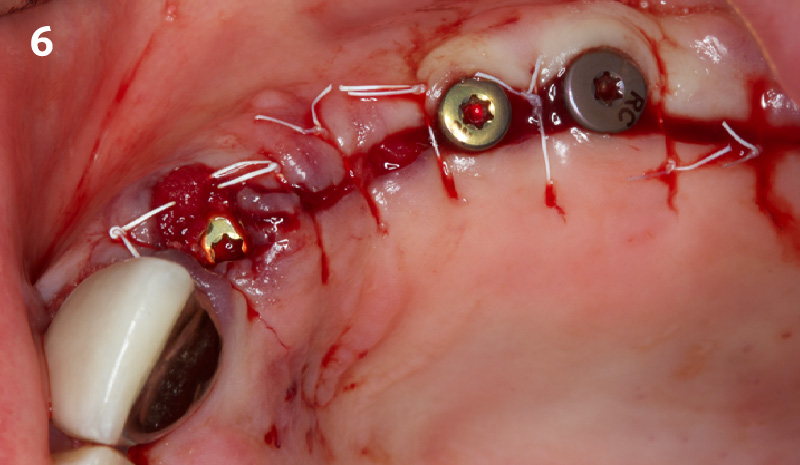
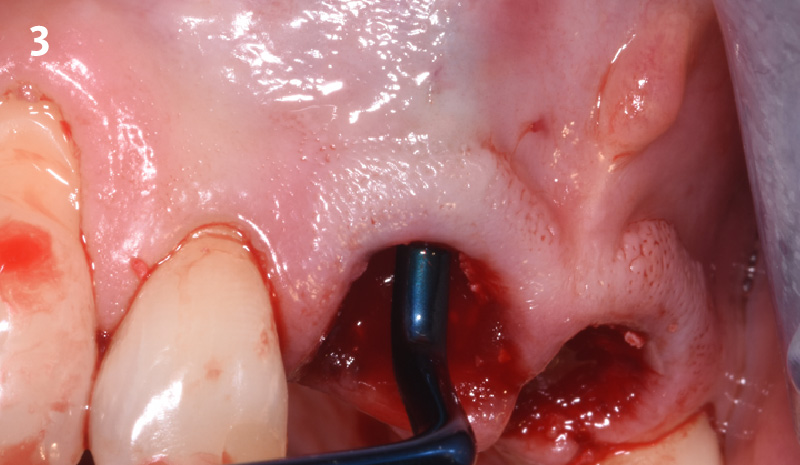
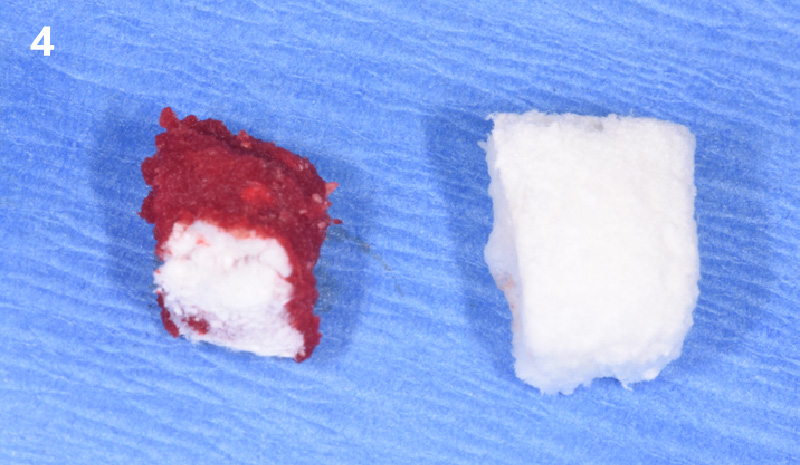
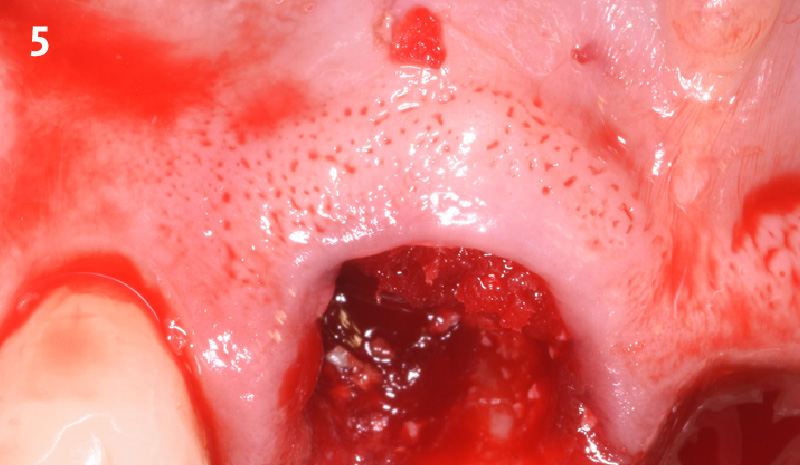
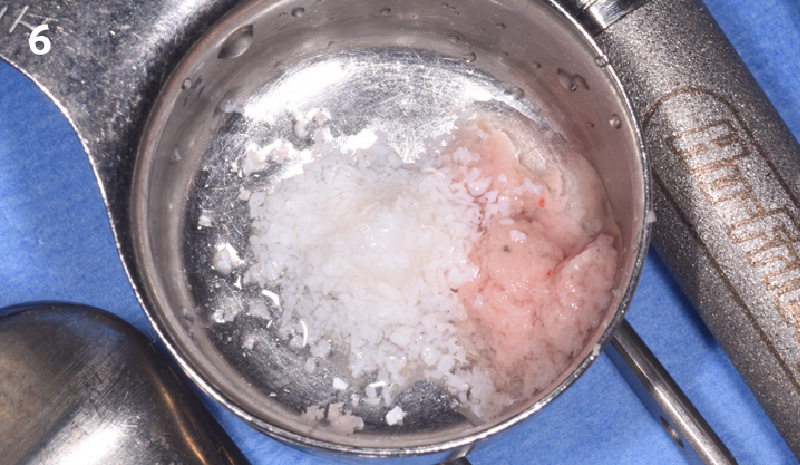
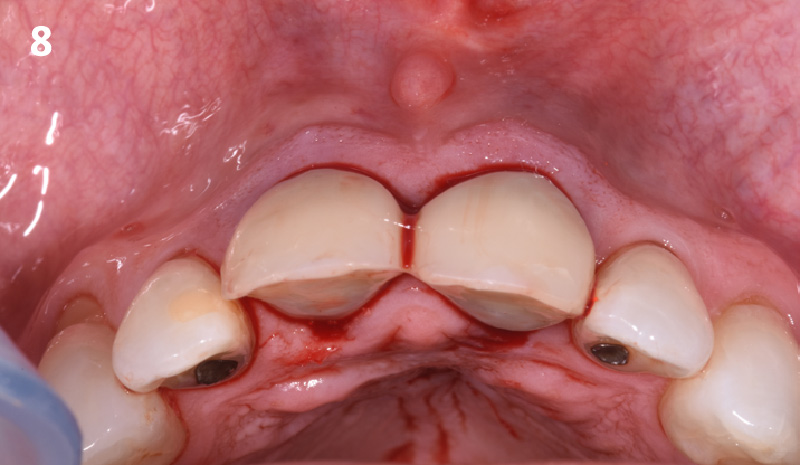
The goals of this case were to: 1) maximize pink and white esthetic scores, 2) preserve the pre-operative soft tissue architecture, 3) minimize hard and soft tissue remodeling over time following tooth extraction, and 4) promote long-term implant health and stability. To achieve these objectives, immediate implant placement with immediate provisionalization was planned. The extraction was performed with minimal flap elevation, and the implant was placed in a guided manner with palatal bias to maximize the facial gap. This gap was then grafted with a slowly resorbing bovine xenograft (Geistlich Bio-Oss Collagen®) to minimize remodeling of the labial bone plate. To further enhance soft tissue volume and contour, the facial soft tissue was augmented after using a Geistlich Fibro-Gide® collagen matrix. Finally, an immediate provisional crown was placed to contain the bone graft and provide support for the soft tissue.
“This was a challenging case in which the patient and her dentist had high esthetic expectations. The goal of this case was to preserve as much of the preoperative anatomy as possible and minimize the inevitable hard and soft tissue remodeling that occurs after a tooth is removed.”
— David E. Urbanek, DMD, MS
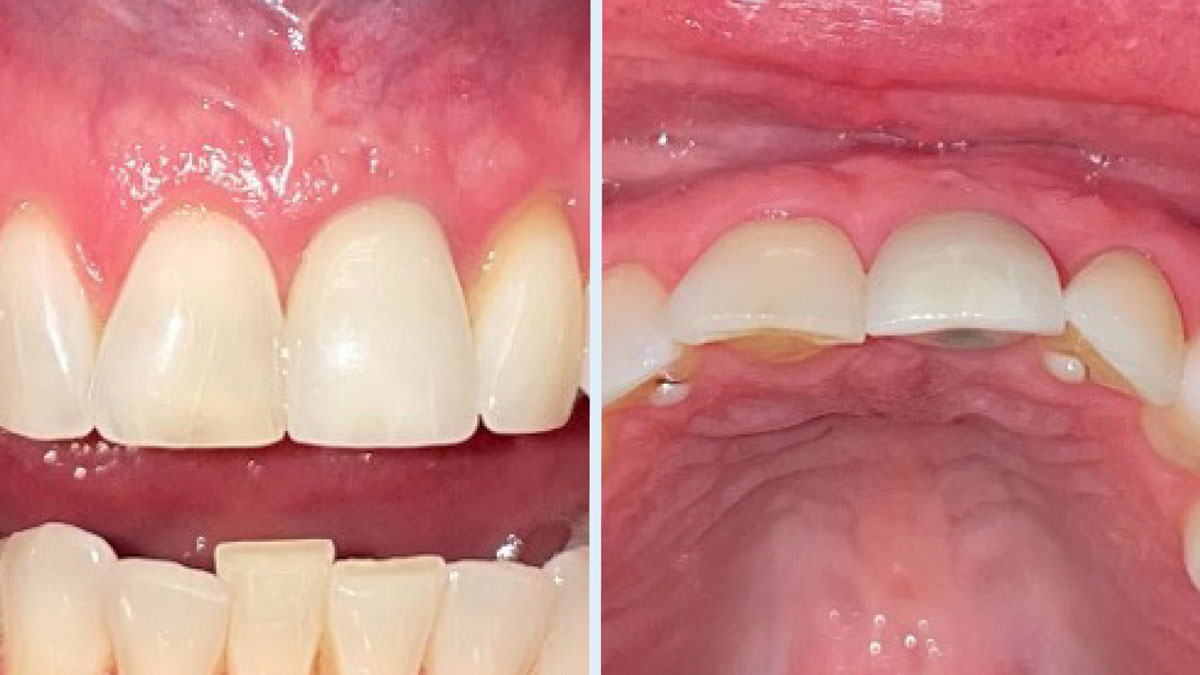
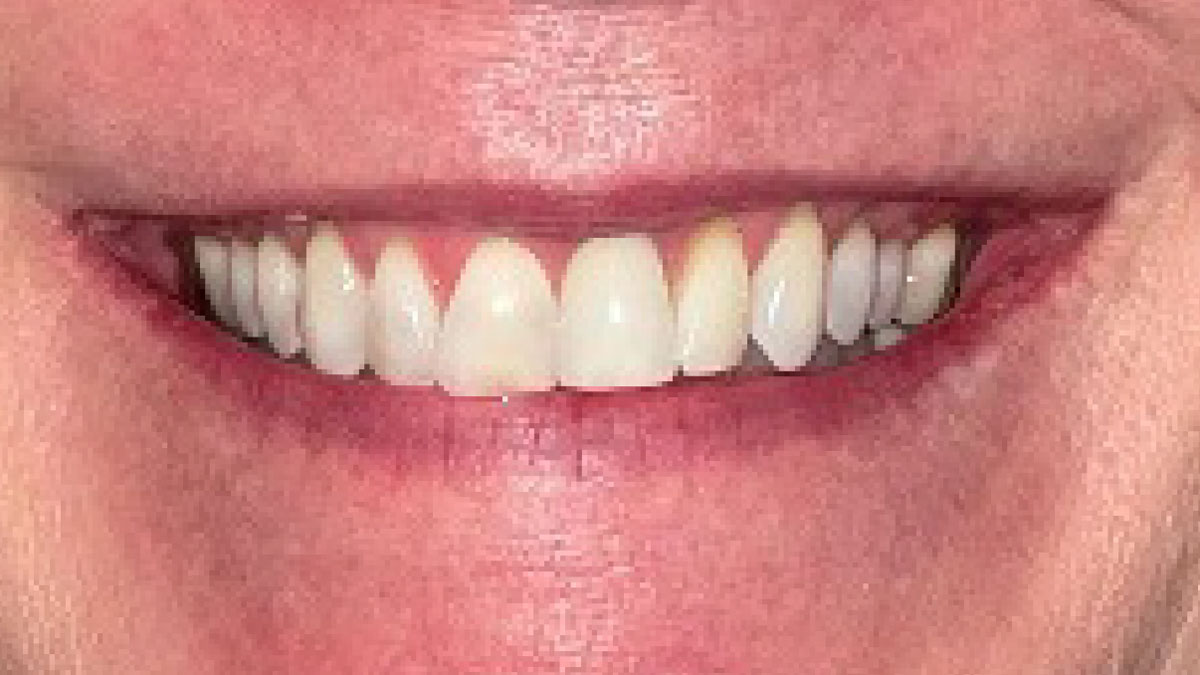
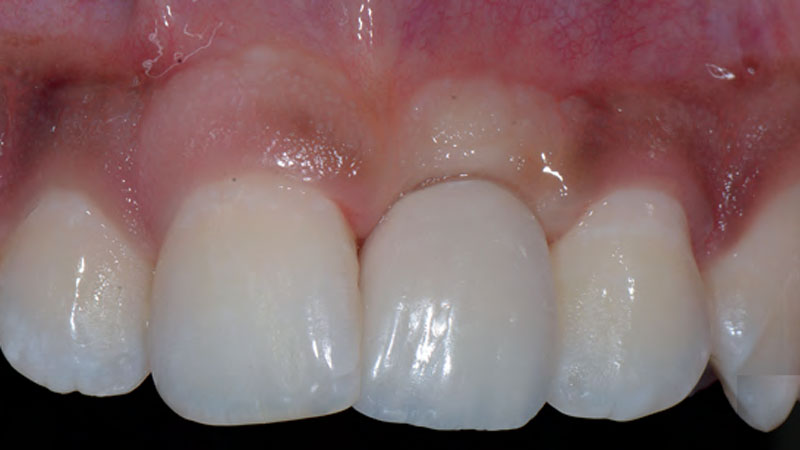
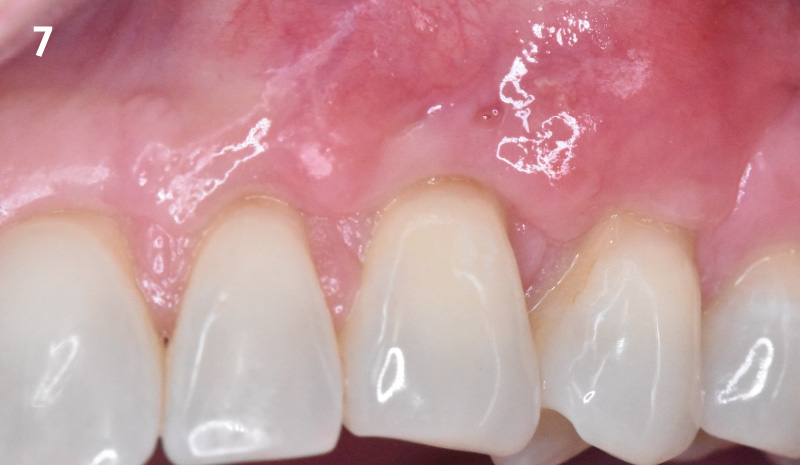
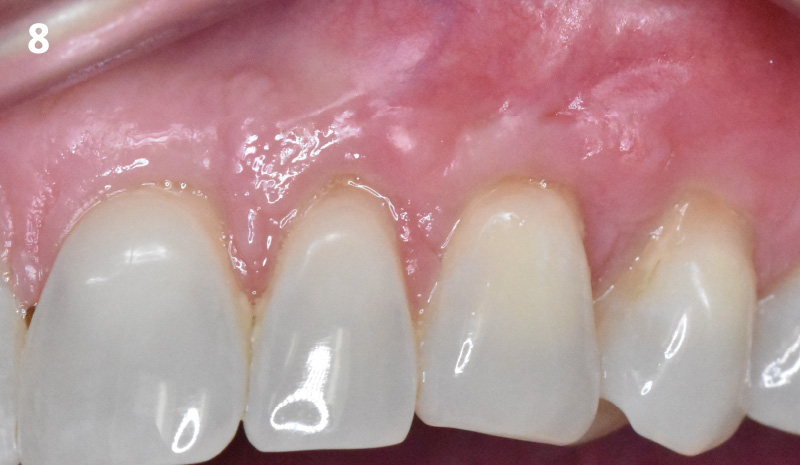
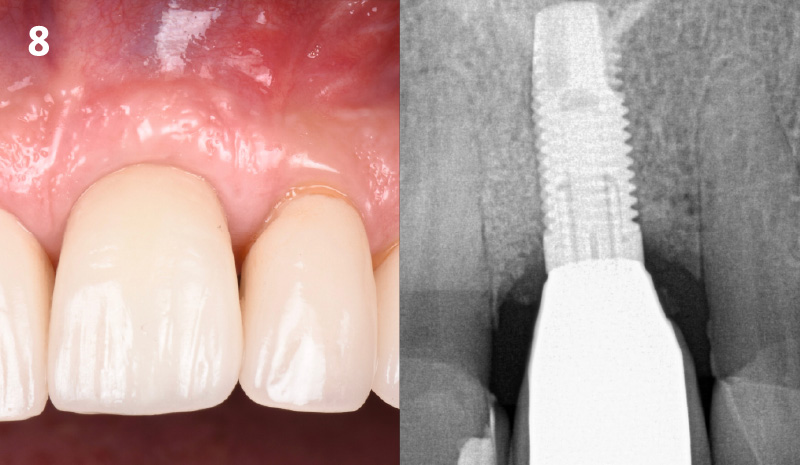
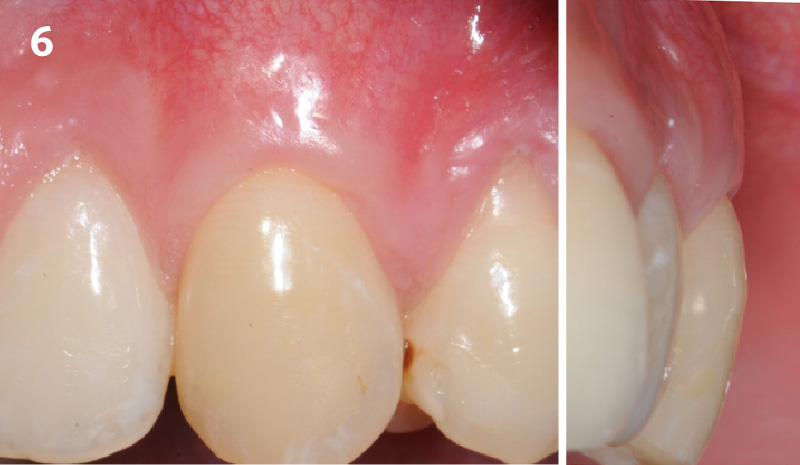
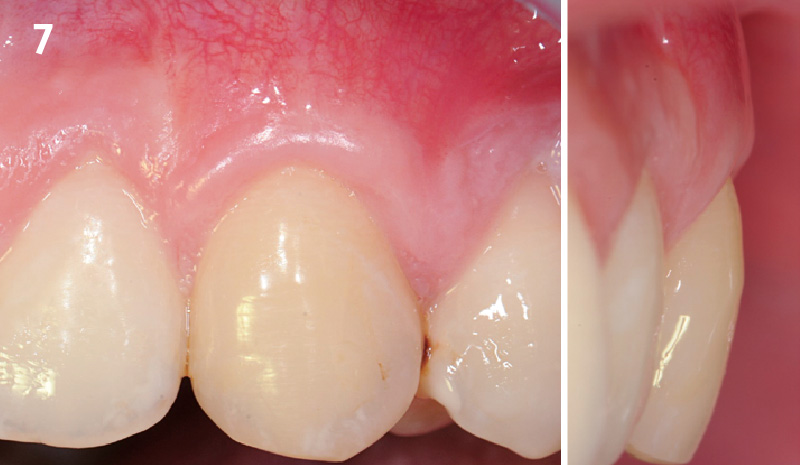
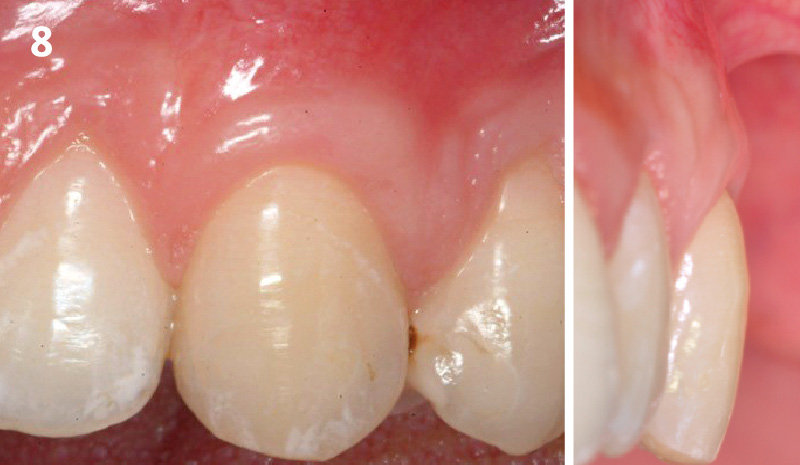
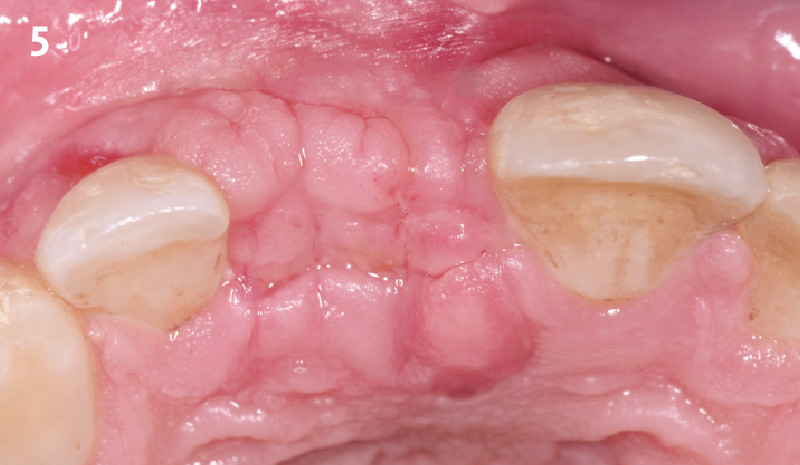
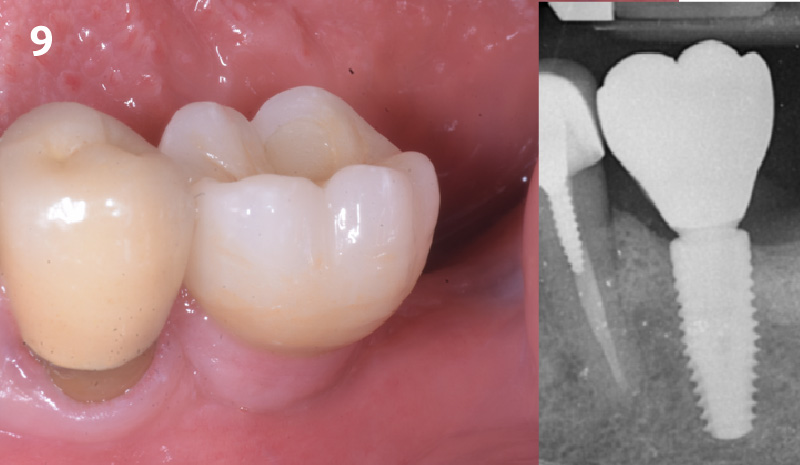
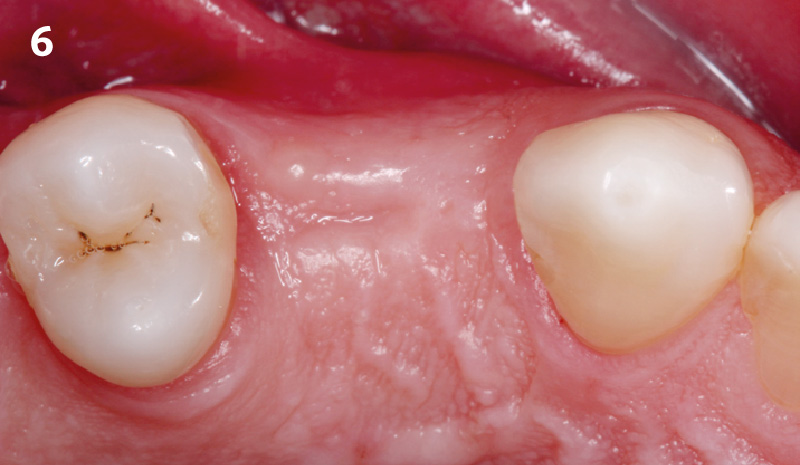
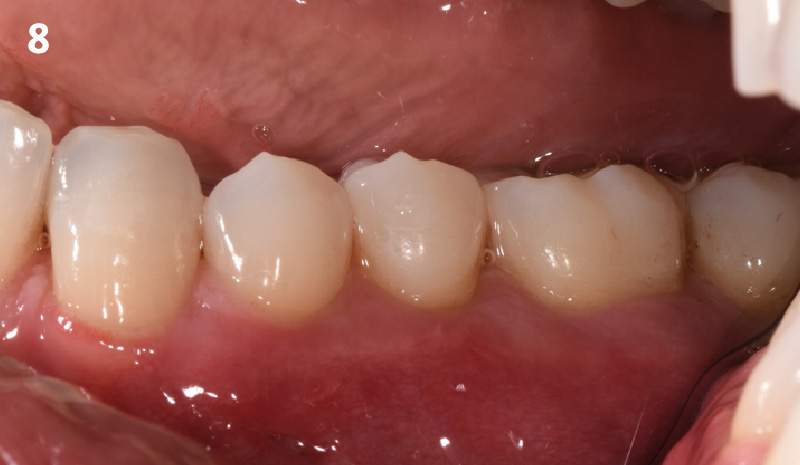
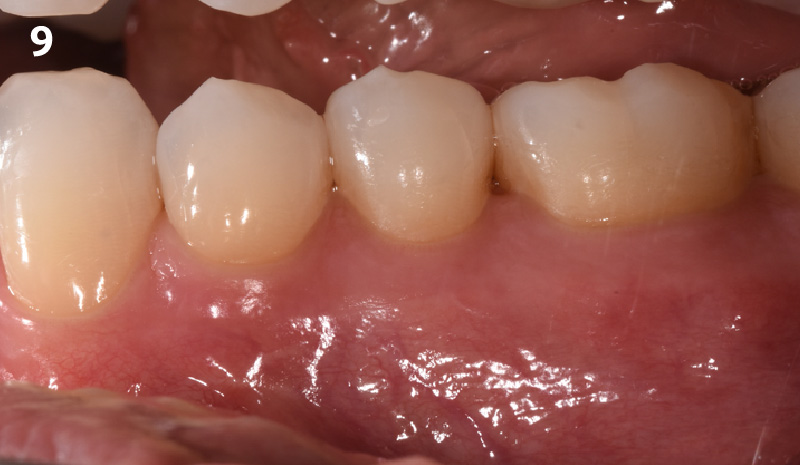
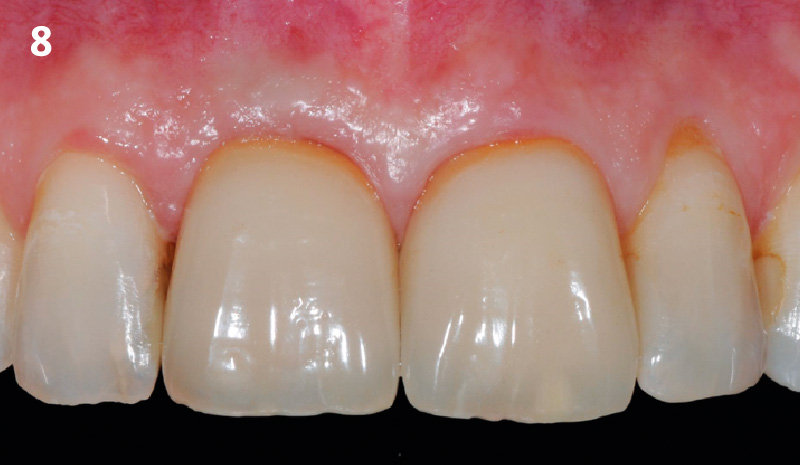
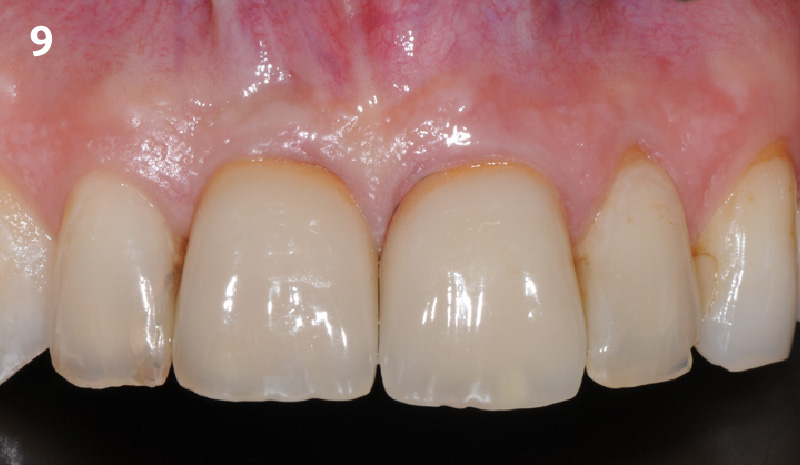
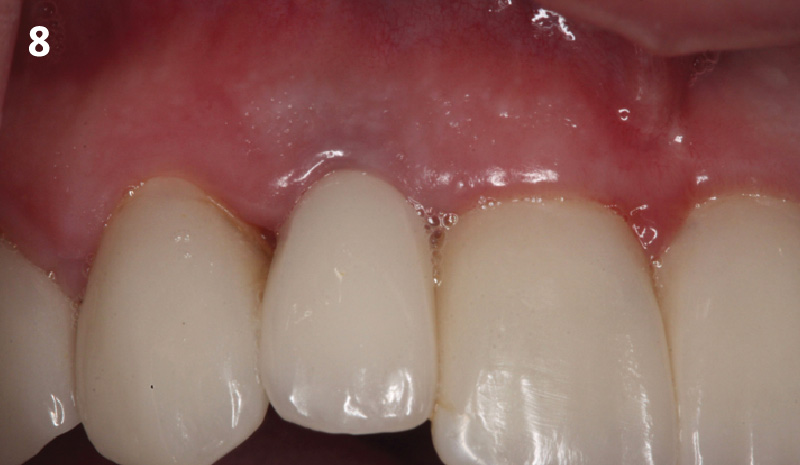
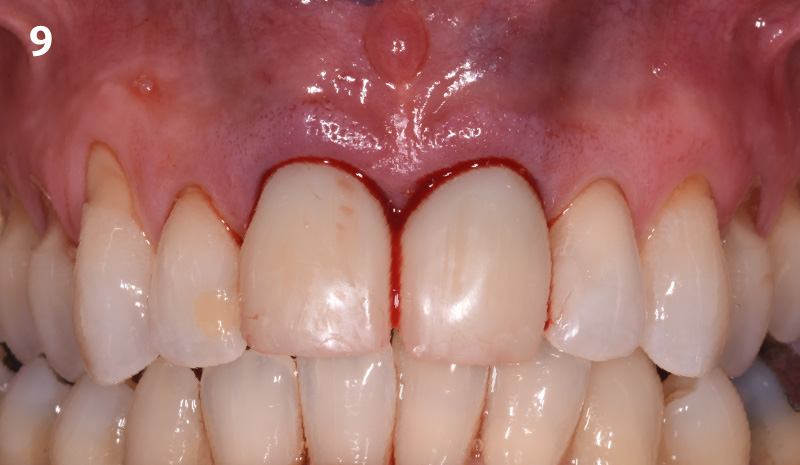
THE OUTCOME
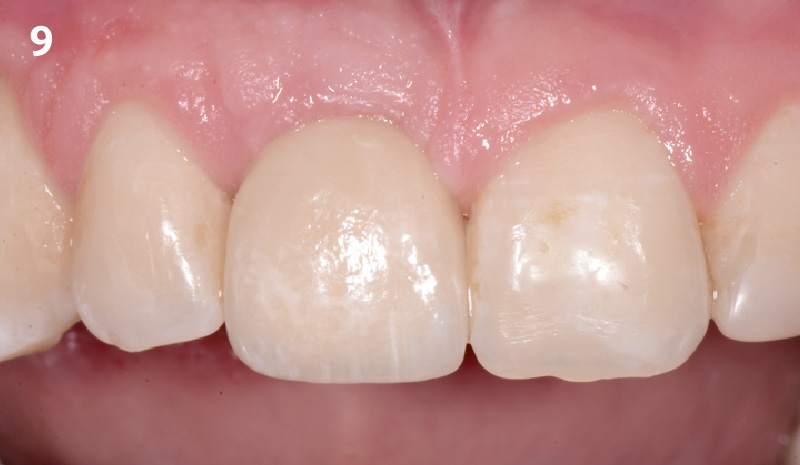
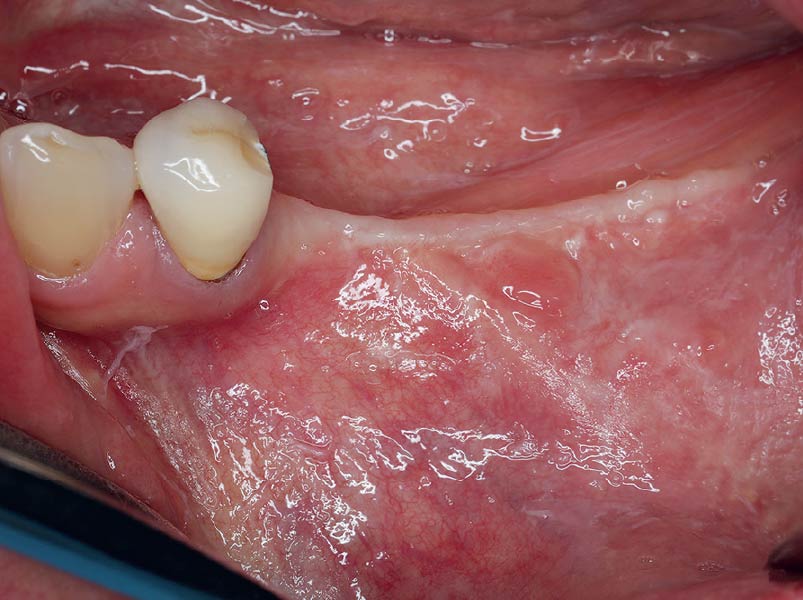
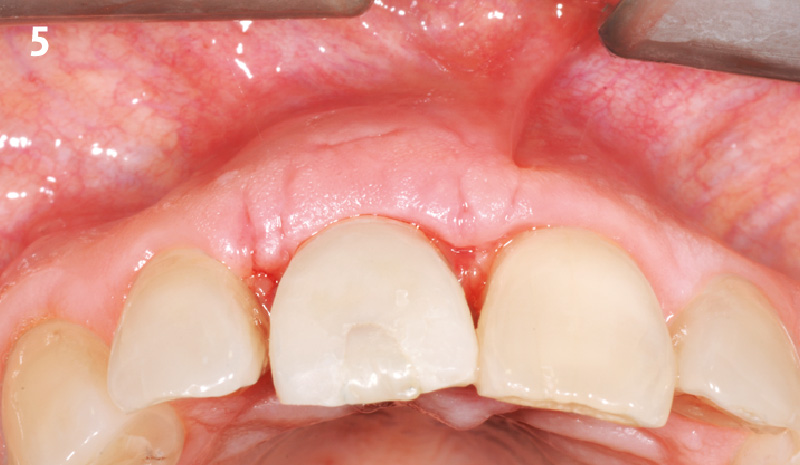
This case finished with excellent pink and white esthetic scores, and the patient and her dentist were very pleased with the results. Most importantly, the implant demonstrated excellent health and stability over one year since placement.

David E. Urbanek, DMD, MS
Dr. Urbanek is a board-certified Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon who practices in St. Louis, Missouri. He completed his OMS training at Carle Foundation Hospital in Champaign/Urbana, Illinois. He earned his Dental Degree from the Case Western Reserve University School of Dental Medicine, and a Master’s Degree with Honors in Applied Anatomy from CWRU. Dr. Urbanek serves as adjunct faculty at Carle Foundation Hospital and the A. T. Still University, Missouri School of Dentistry & Oral Health. In addition he avidly lectures to the dental and OMS community throughout the country.

BIOBRIEF
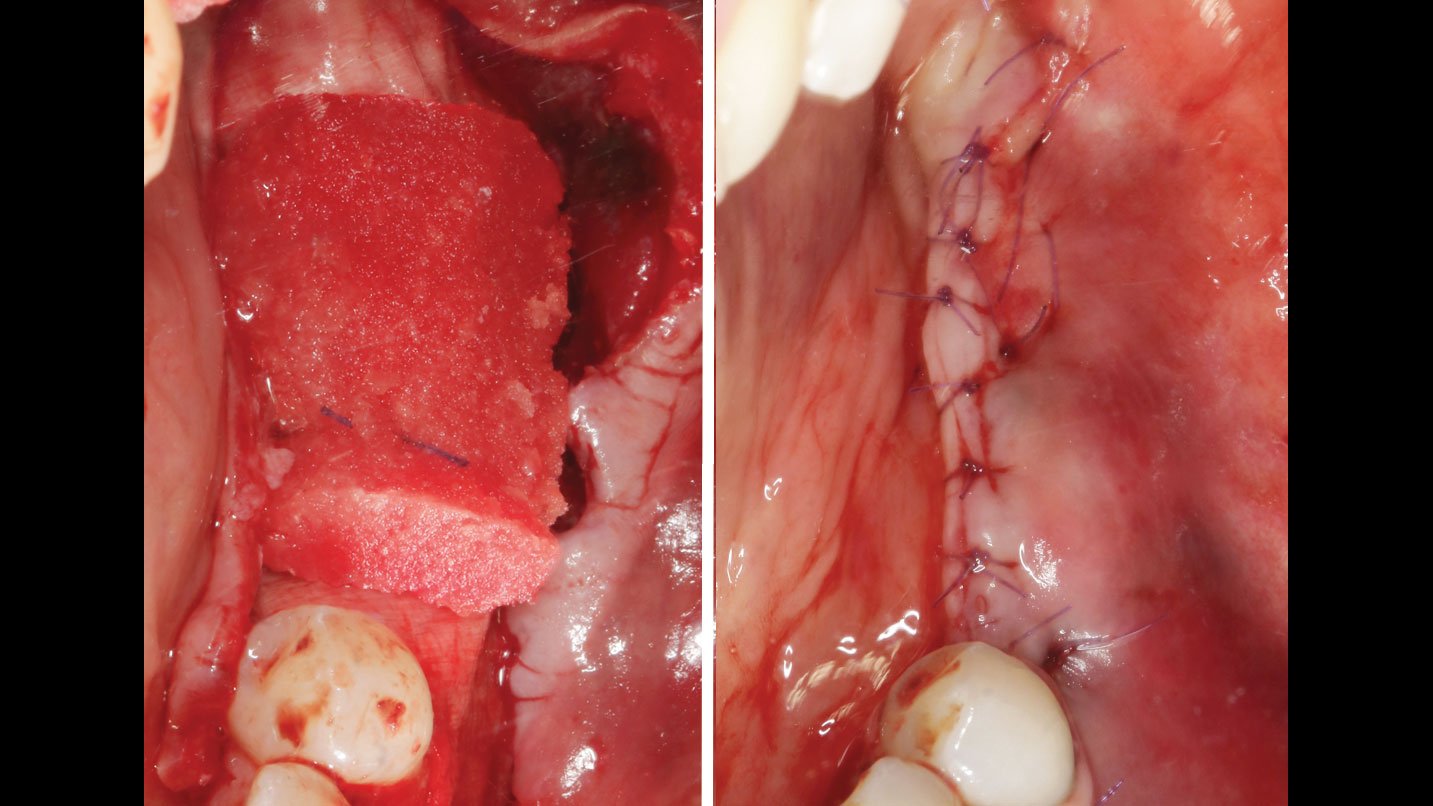
Lateral and Vertical Bone Regeneration with Simultaneous Soft Tissue Augmentation

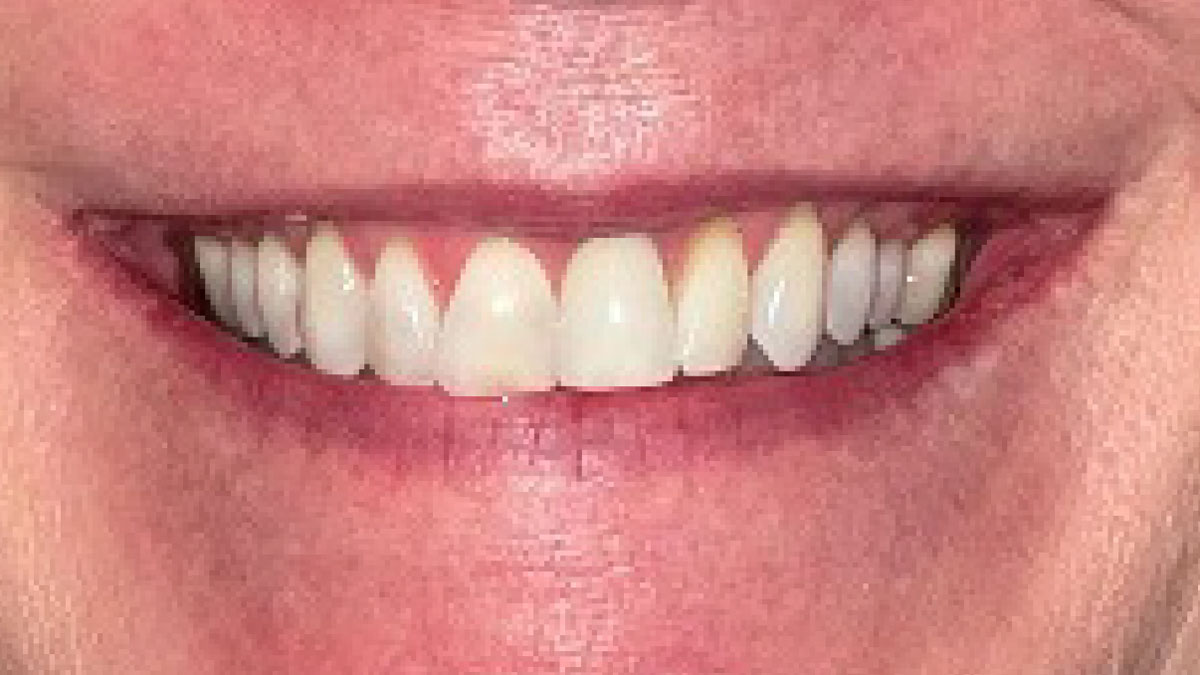
THE SITUATION
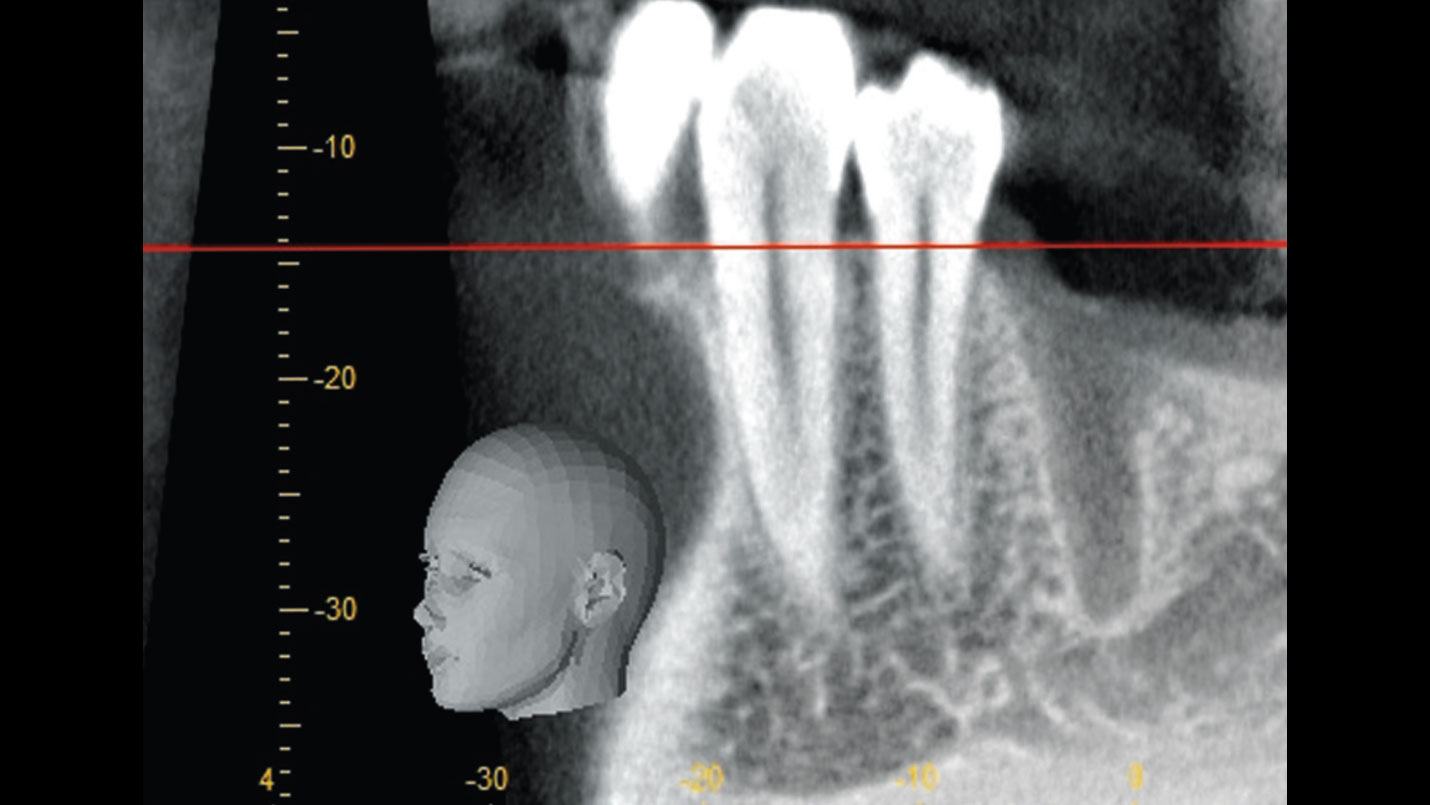
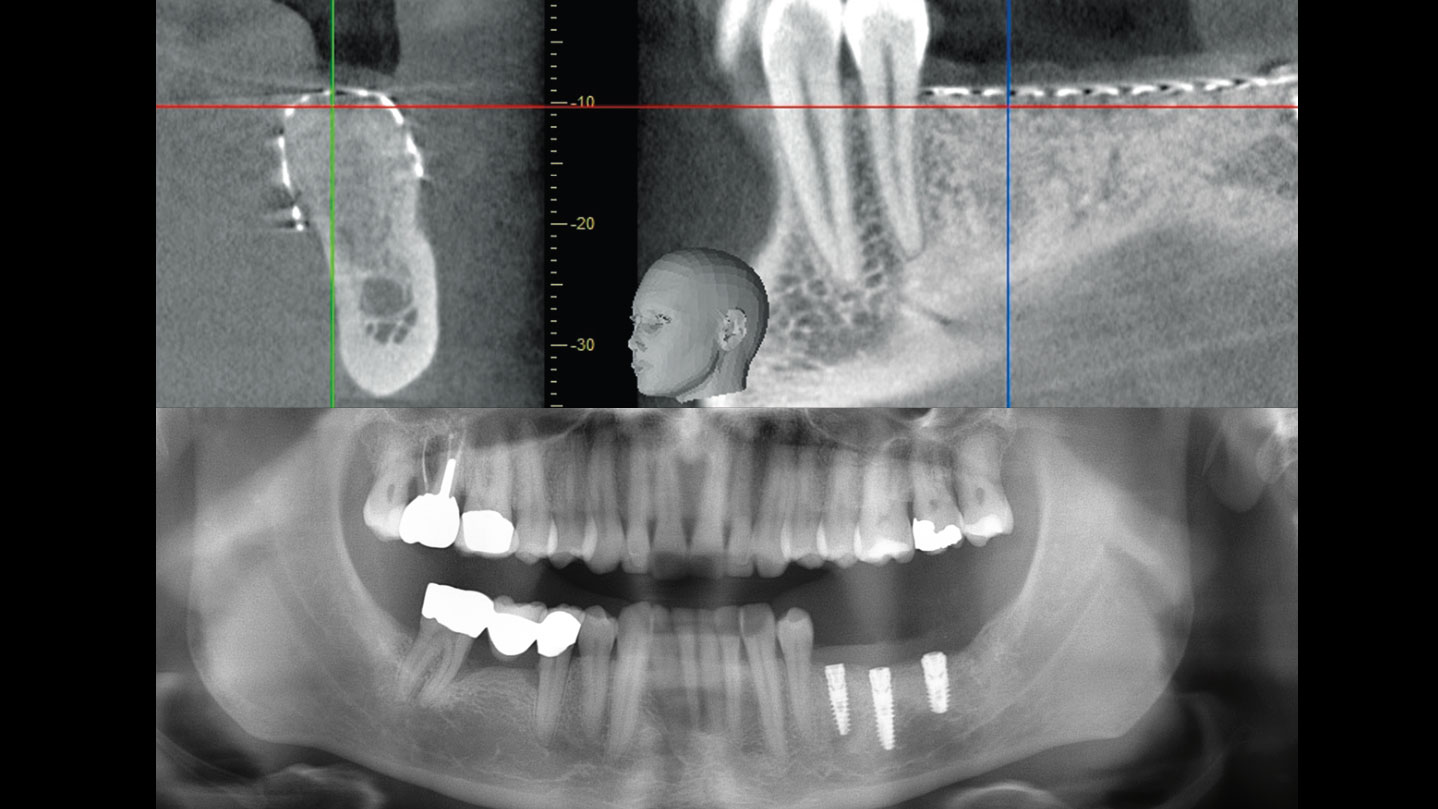
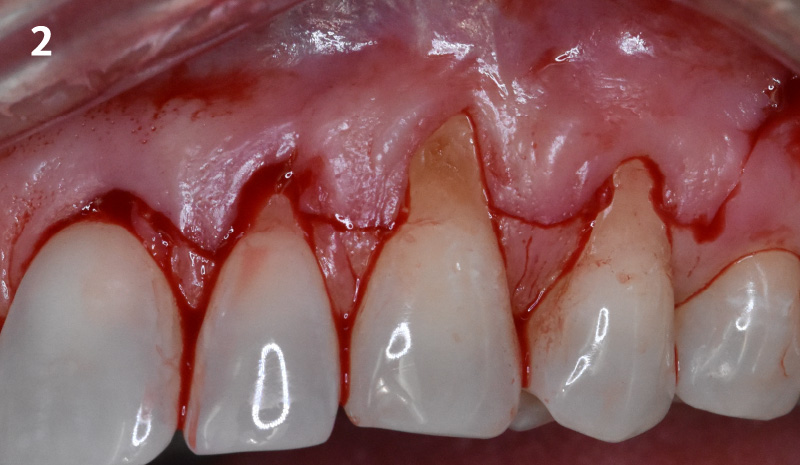
After extraction of the periodontally damaged tooth #20 the preoperative Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) imaging shows reduced vertical bone volume in the area of tooth #s 18 – 20. A lateral and vertical bone regeneration was necessary.
The goal of treatment was a late implant placement after bone regeneration and creation of stable periimplant soft tissue for long-term implant preservation.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
Additional Risk Factors: Roots were divergent, and intra-radicular bone (septal bone) was excellent, with more than 5 mm of remaining apical bone to achieve optimal primary stability.
THE APPROACH
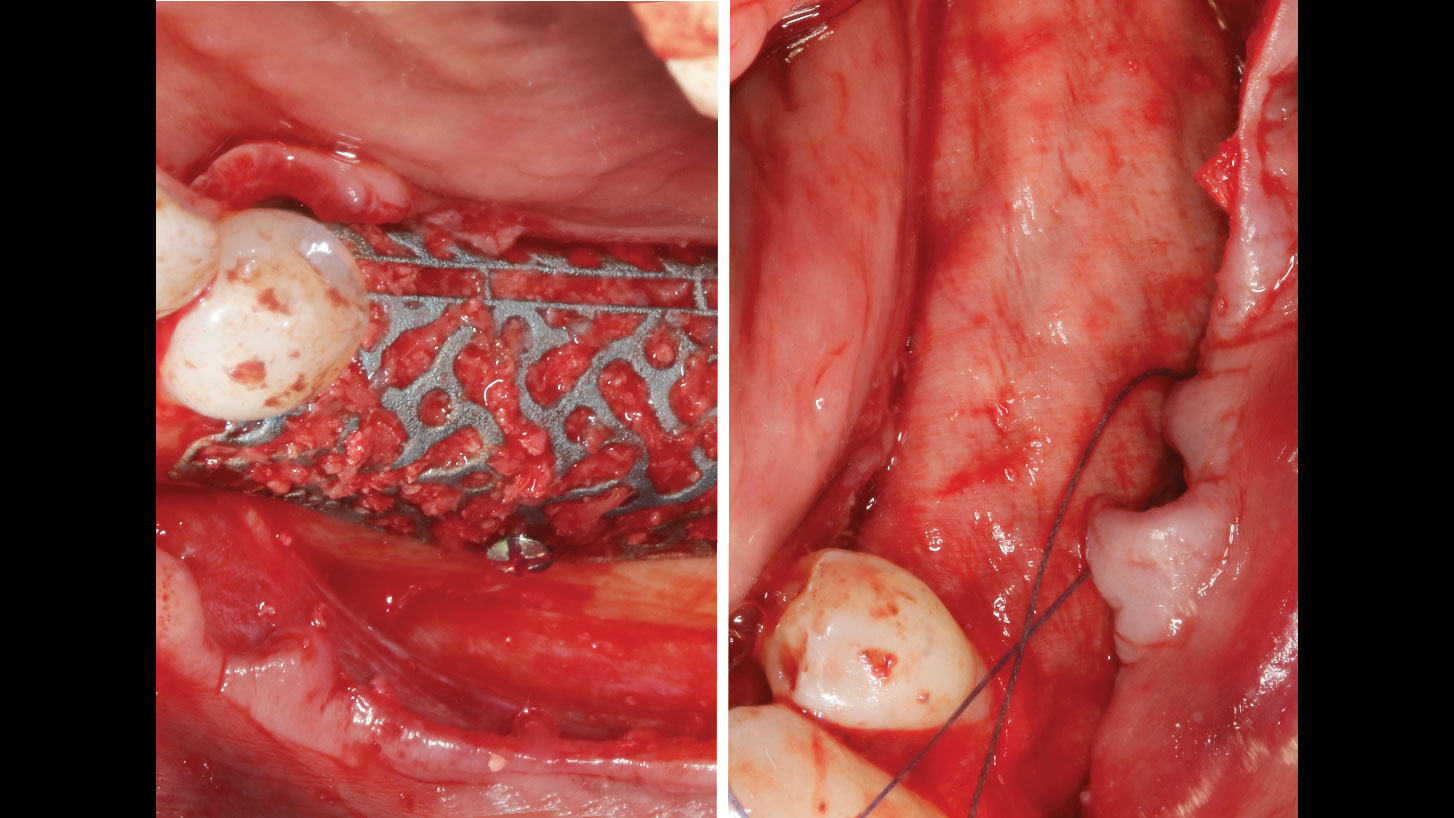
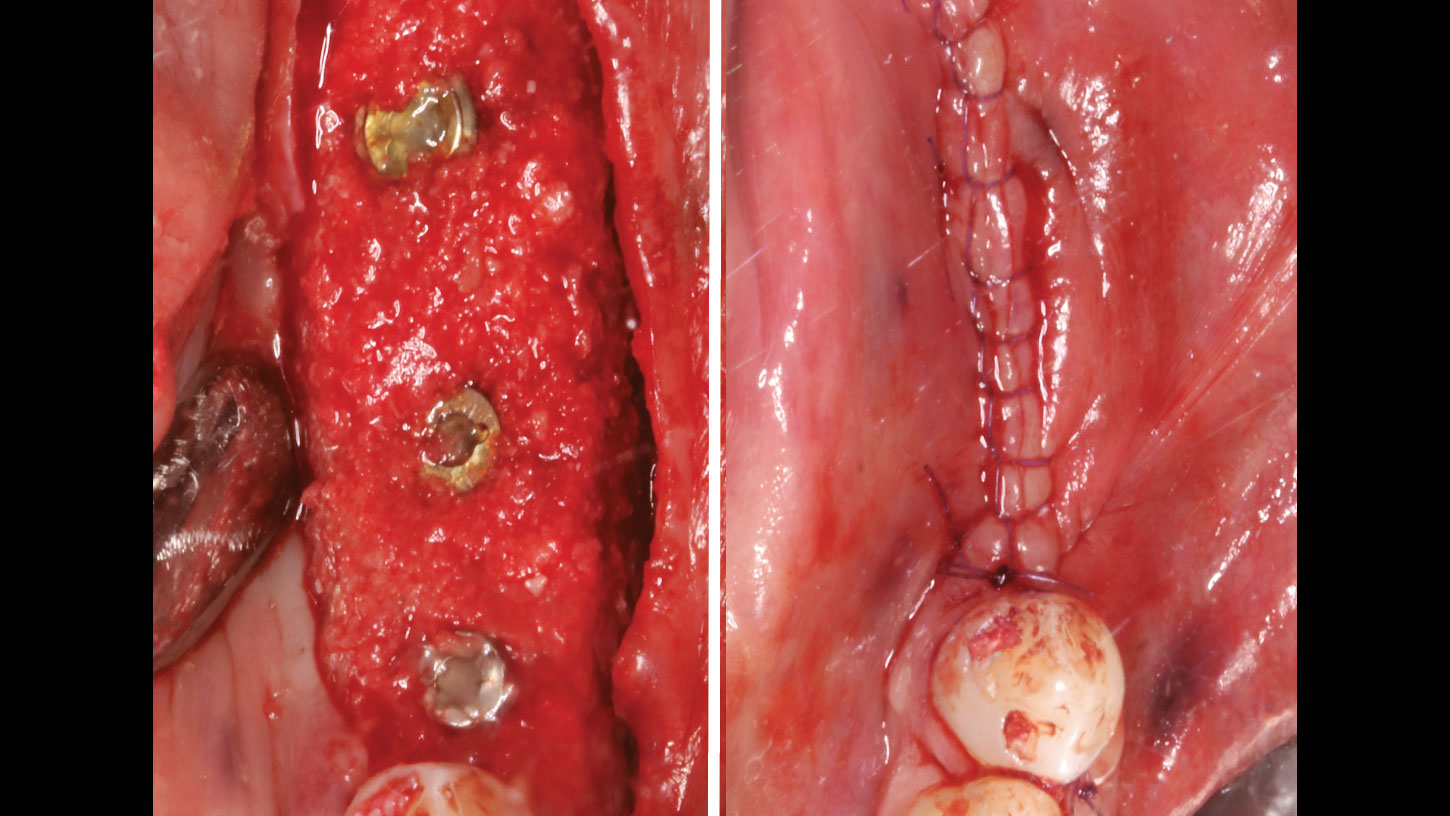
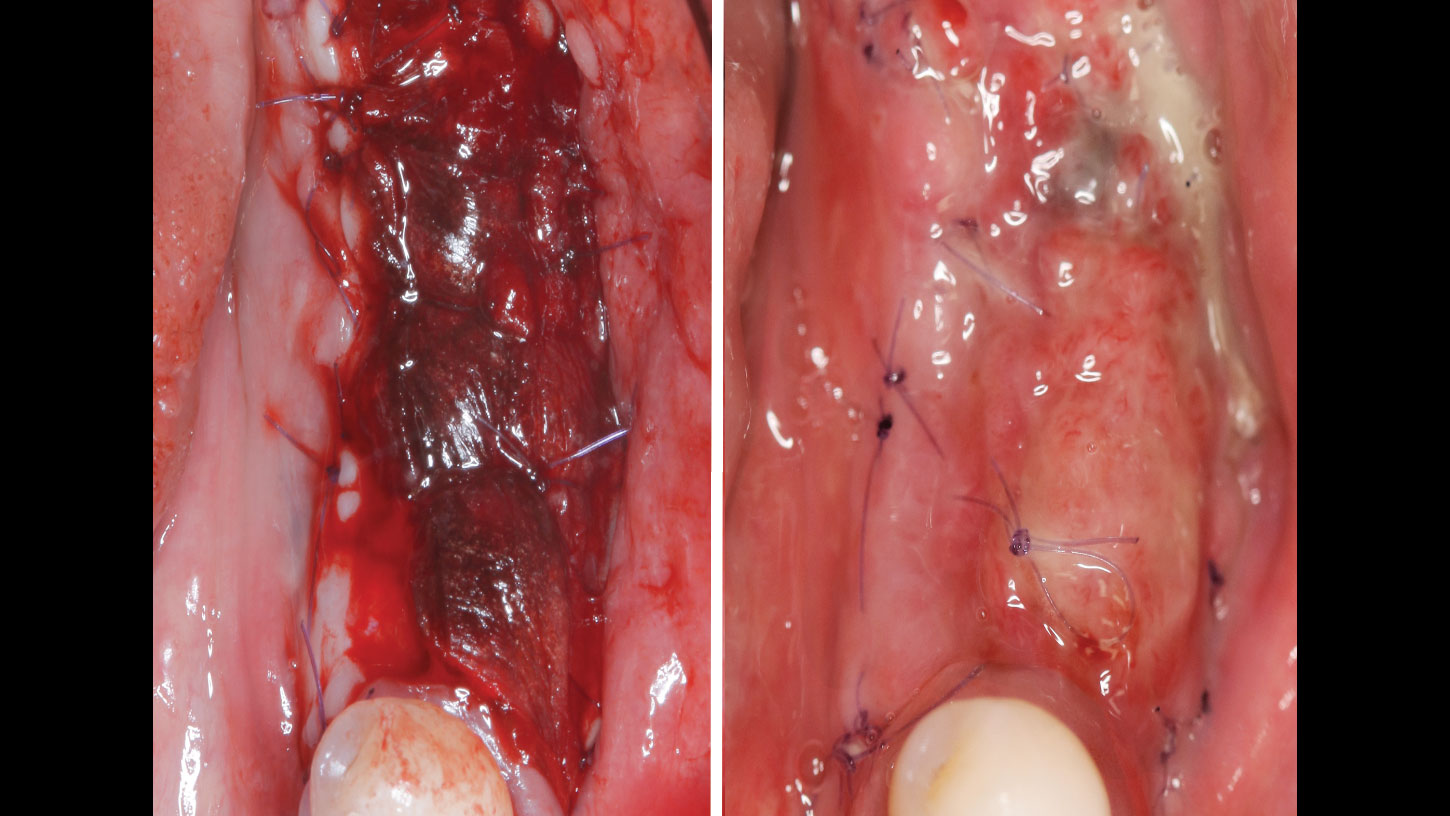
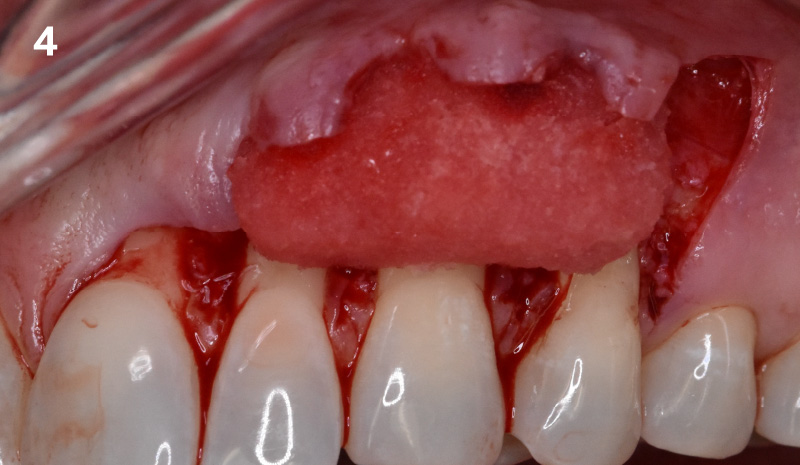
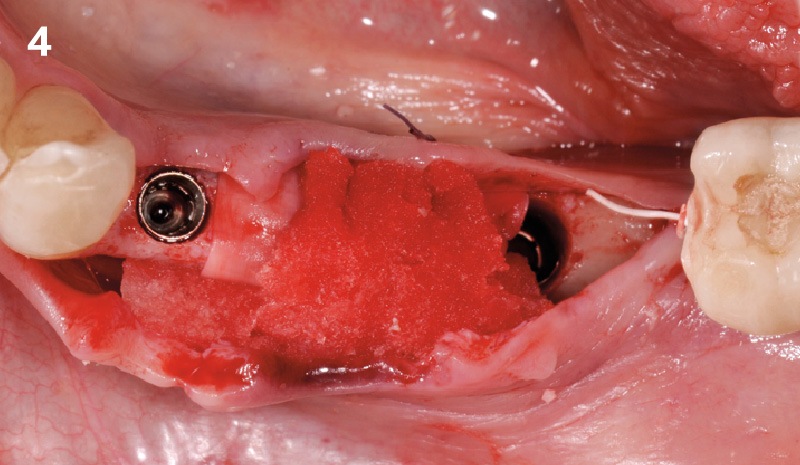
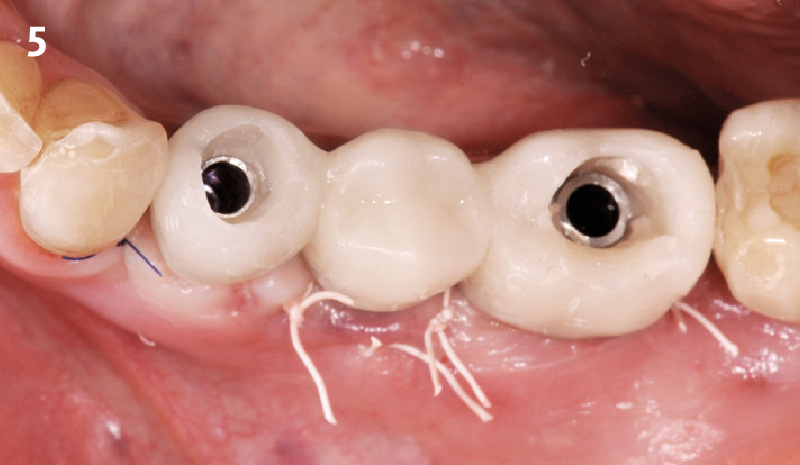
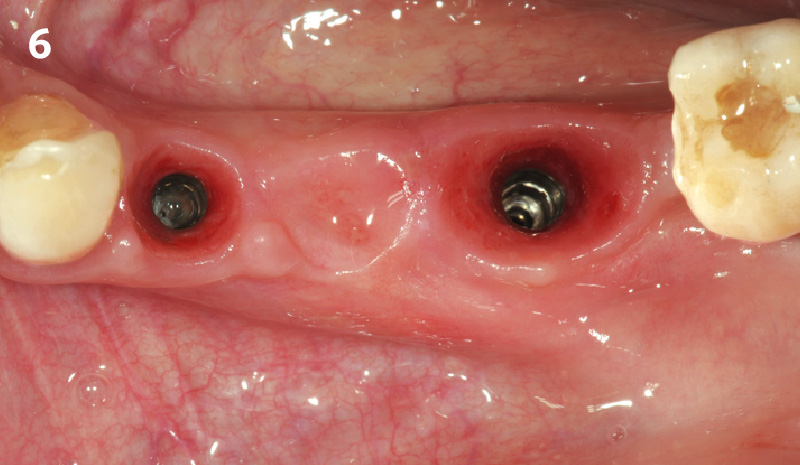
A customized bone regeneration procedure utilizing Yxoss CBR®. Followed by coverage of the graft with Geistlich Bio-Gide® for the purpose of Guided Bone Regeneration (GBR). Soft tissue thickening using Geistlich Fibro-Gide®. Delayed implantation into the augmented tissue. A vestibuloplasty with Geistlich Mucograft® for the regeneration of keratinized mucosa.
“Using the Geistlich Fibro-Gide® matrix enabled concurrent augmentation of hard
— Arnd Lohmann, MSc
and soft tissues without any postoperative complications. At the same time, the soft
tissue thickening facilitated floor of the mouth surgery and vestibuloplasty.”
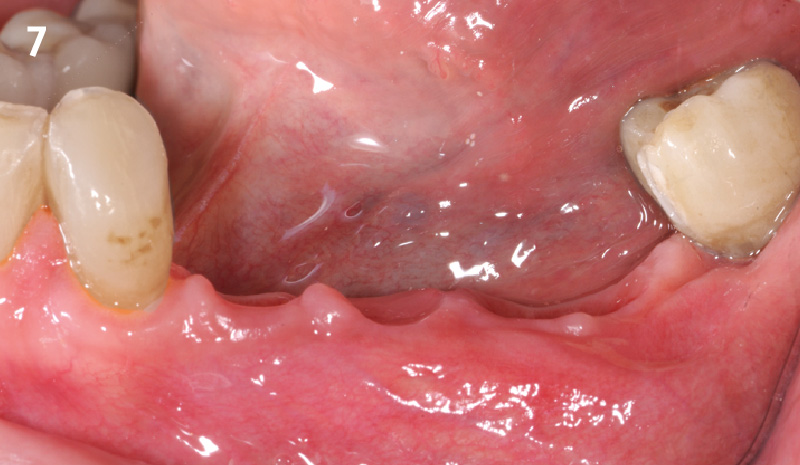
THE OUTCOME
Treatment resulted in approximately 5 mm of vertical bone regeneration. The potential occurrence of a dehiscence associated with a wound opening and exposure of Yxoss CBR® was able to be prevented with Geistlich Fibro-Gide®.
On one hand, the quality of the peri-implant soft tissue was improved by the
soft tissue thickening with Geistlich Fibro‑Gide® and, on the other, by increasing the width of keratinized mucosa with Geistlich Mucograft®. The treatment method chosen resulted in a reduced invasiveness and morbidity by avoiding a donor site for sourcing a transplant.

Arnd Lohmann, MSc
Dr. Arnd Lohmann is a recognized specialist in implantology and periodontology. He earned his dental license in Hamburg in 2002, completed his doctorate in 2003, and has been a partner at a private practice in Bremen since then.
With a Master of Science in Implantology (2007), he specializes in dental implantology and bone augmentation. He is an active speaker at national and international congresses, leads the Bremen study group of the German Society of Oral Implantology (DGOI), and is a member of DGOI, DGZI, and DGI. His practice is equipped with state-of-the-art technology, ensuring high-quality patient care.

WEBINAR

BIOBRIEF
The Buccal Pedicle Flap for Peri-Implant Soft Tissue Volume
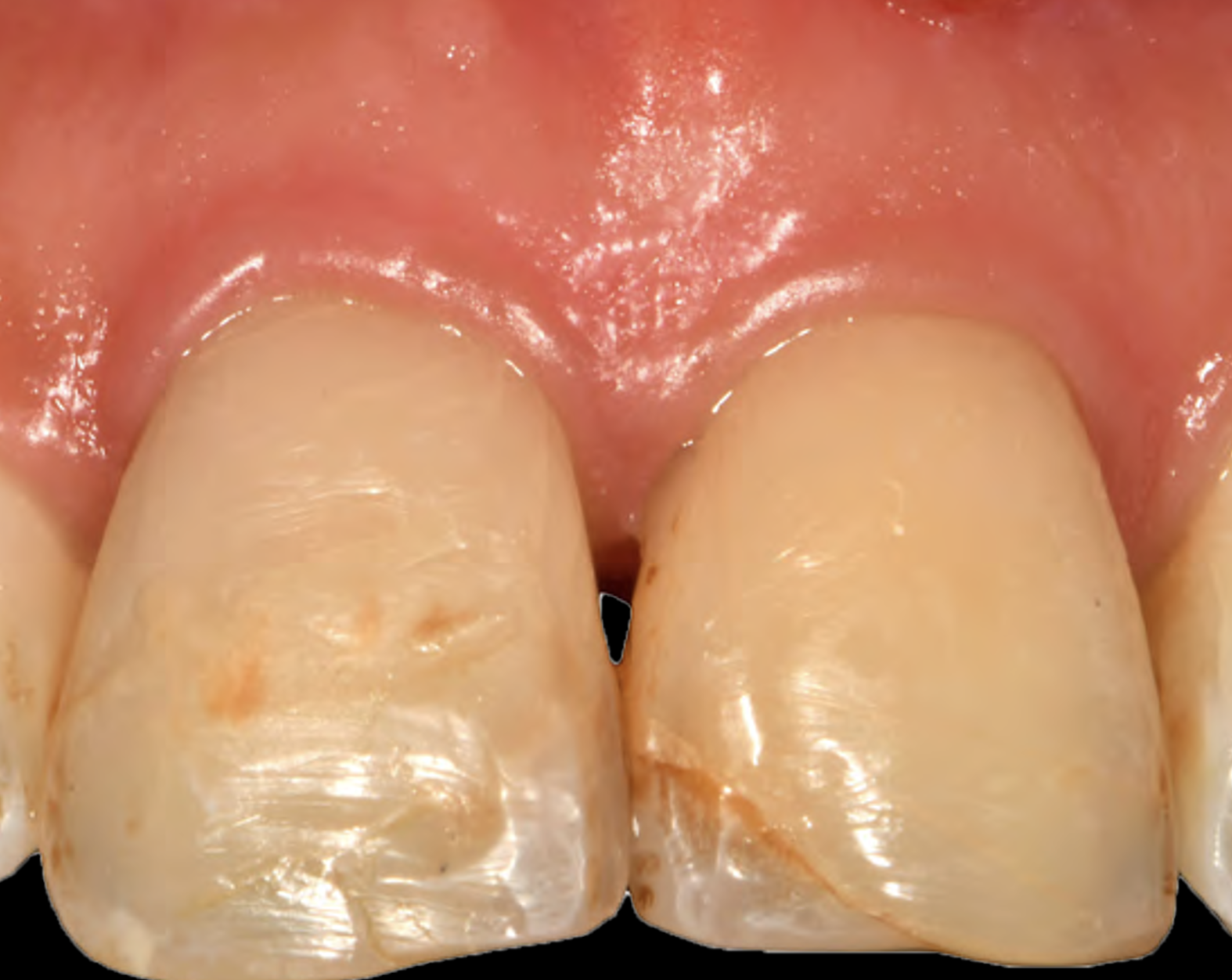

THE SITUATION
Patient presented with a fistula buccal on tooth #9 associated with a chronic peri-apical lesion and external root resorption. Also tooth #8 showed a chronic peri-apical lesion. Her chief complaint was the misalignment of her teeth. The clinical situation revealed the presence of bleeding upon probing and generalized moderate periodontal disease (Stage II, Grade I) as well as multiple endodontic failures.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
The aim of the treatment is to eradicate periodontal disease and restore esthetics and function. Treatment planning: non-surgical and surgical periodontal treatment, orthodontic alignment, extraction of both central incisors, immediate implant placement and Guided Bone Regeneration with Geistlich Bio-Oss®, peri-implant soft tissue boosting with a buccal pedicle flap and full ceramic CAD-CAM restorations.
“Orthodontic treatment must be postponed because of the presence of periodontal disease. A thin biotype and a high smile line needs to be taken into consideration.”
THE OUTCOME
The final outcome at 8 weeks is showing pink esthetics as well as biomimetics and function. The use of the buccal pedicle flap allowed the increased volume of the peri-implant mucosa with a minimally invasive approach. The combination of Geistlich Fibro-Gide® and a buccal pedicle flap had the main advantage of reducing the morbidity generally associated with CT harvesting.
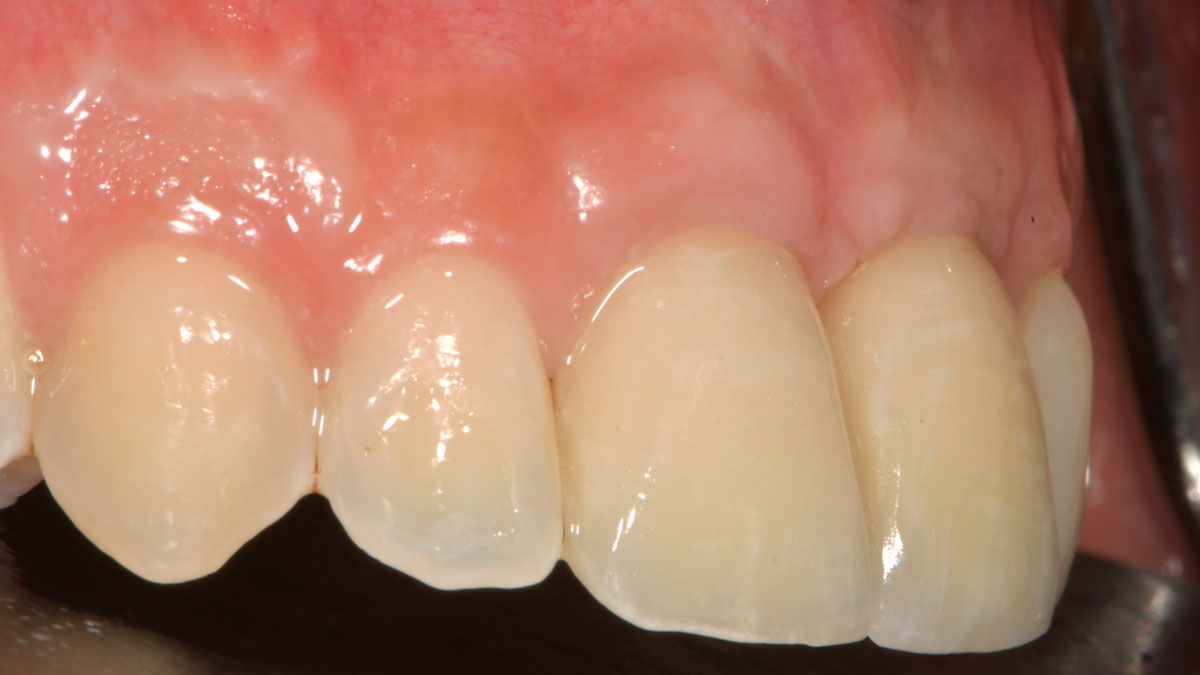

Dr. Giorgio Tabanella
Dr. Tabanella is a Diplomate of the American Board of Periodontology, an Active Member of the Italian Academy of Esthetic Dentistry and author of the book “Retreatment of Failures in Dental Medicine”. He graduated from the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, USA where he obtained his Certificate in Periodontics as well as a Master of Science in Craniofacial Biology. He is Director of O.R.E.C. – Oral Reconstruction and Education Center (www.tabanellaorec.com), reviewer and author of original articles.

BIOBRIEF
Use of Geistlich Fibro-Gide® for Correction of Maxillary Anterior Soft Tissue Peri-implant Ridge Deficiencies
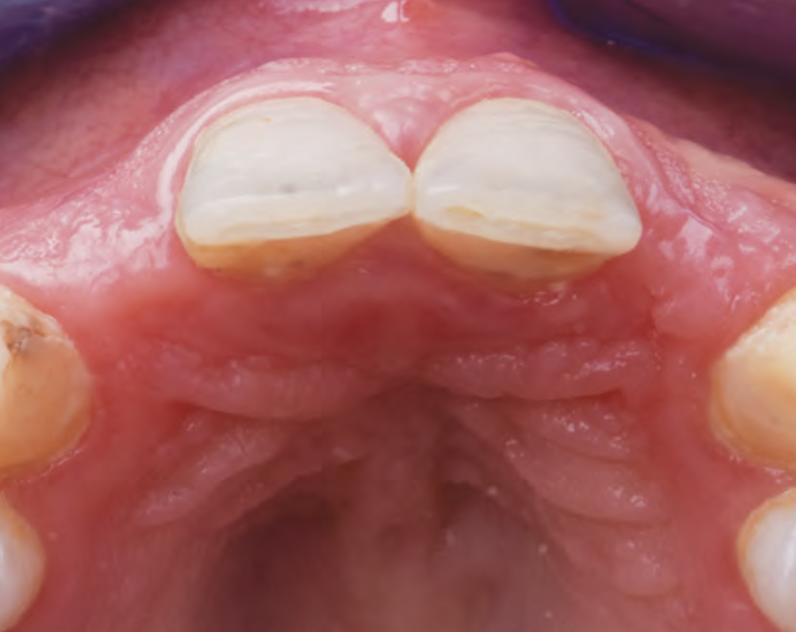

THE SITUATION
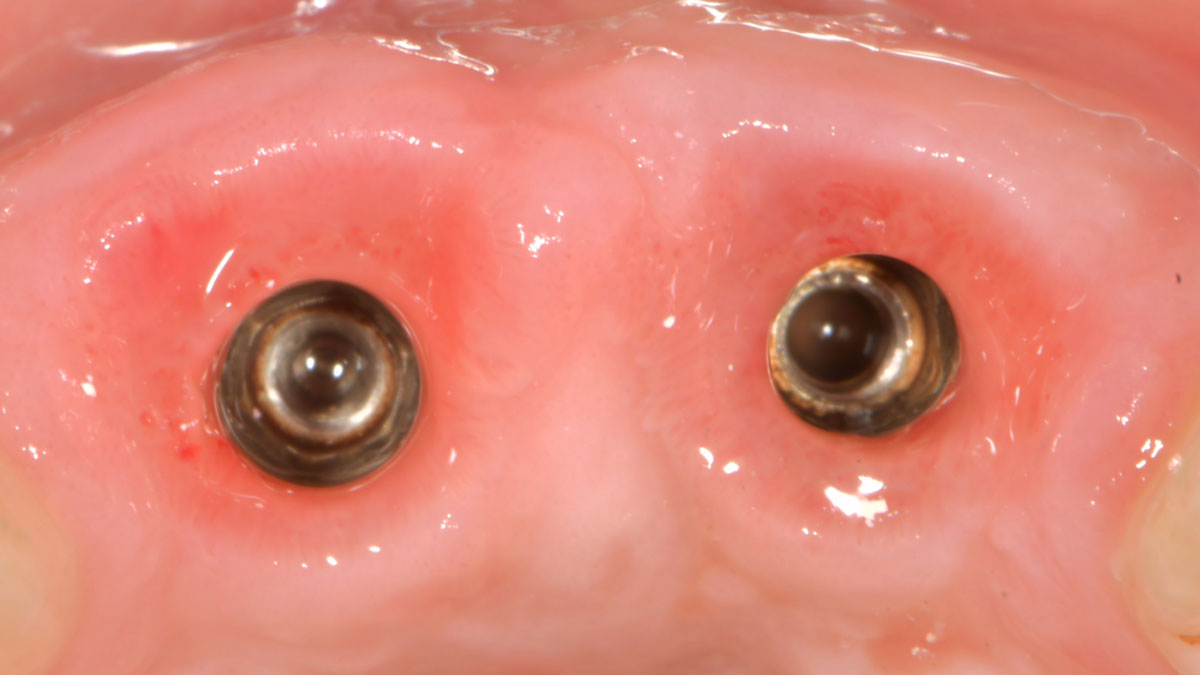
A 27-year-old female with congenitally missing maxillary lateral incisors was referred for implant placement. Following completion of orthodontics, a plan was developed to place dental implants at the #7 and #10 positions. Based on CBCT evaluation, alveolar ridge height and width was deemed sufficient for implant placement. Despite sufficient bone volume, facial ridge volume deficiencies were noted at both edentulous sites, requiring augmentation to allow for optimal esthetics.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
The goal of treatment was to replace missing maxillary lateral incisors with dental implants, while providing an esthetic result with predictable and minimally invasive techniques. Employing a surgical guide for implant placement, implants were placed in precise 3-dimentional positions. The use of xenograft biomaterials (Geistlich Fibro-Gide®) allowed for the augmentation of gingival biotype and elimination of the buccal ridge deficiencies while avoiding the harvesting of autogenous tissue.
“A buccal ridge deficiency with congenitally missing lateral incisors in a high-scallop, high-smile young female patient.”
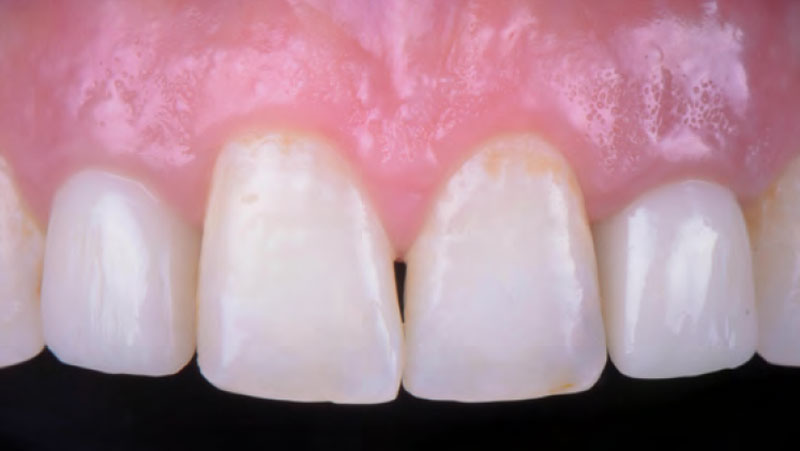
THE OUTCOME
The presented case involves a female patient with congenitally missing maxillary lateral incisors and soft tissue ridge deficiencies. Implants were placed and a volume-stable collagen matrix Geistlich Fibro-Gide® was placed to provide labial soft tissue volume. The tissue emergence was then developed with the use of provisional restorations, one placed at the time of surgery, the other following implant integration. The implants were restored with gingival tissue transformed to mimic convex root emergence.

Dr. Israel Puterman
Dr. Puterman, originally from Montreal Canada, received his DMD from Boston University in 2002 and dual graduate certificates in Implant Dentistry and in Periodontics from Loma Linda University in 2008. He is a published author in various journals including the Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry and the Journal of Prosthodontics. He practices in the Washington, DC area.

BIOBRIEF
Phenotype Conversion Using Geistlich Fibro-Gide® for Immediate Implants in the Esthetic Zone
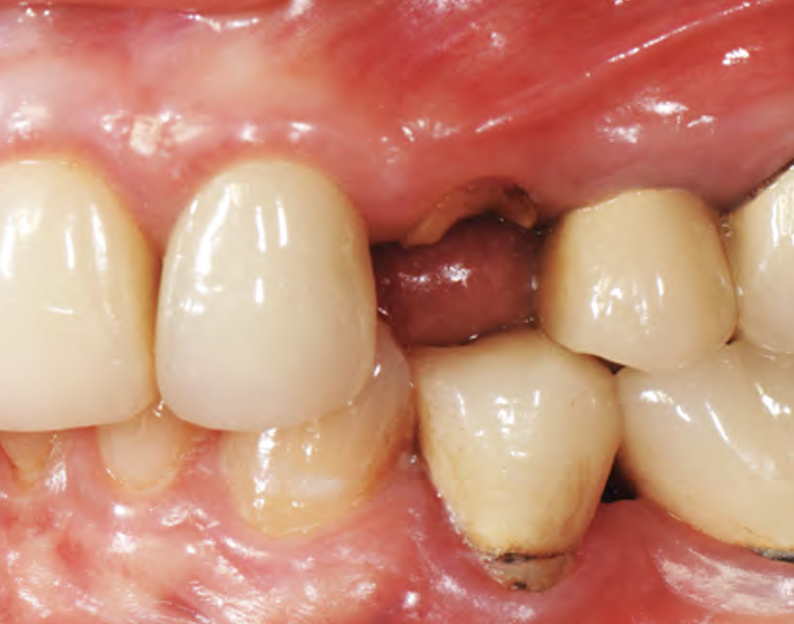

THE SITUATION
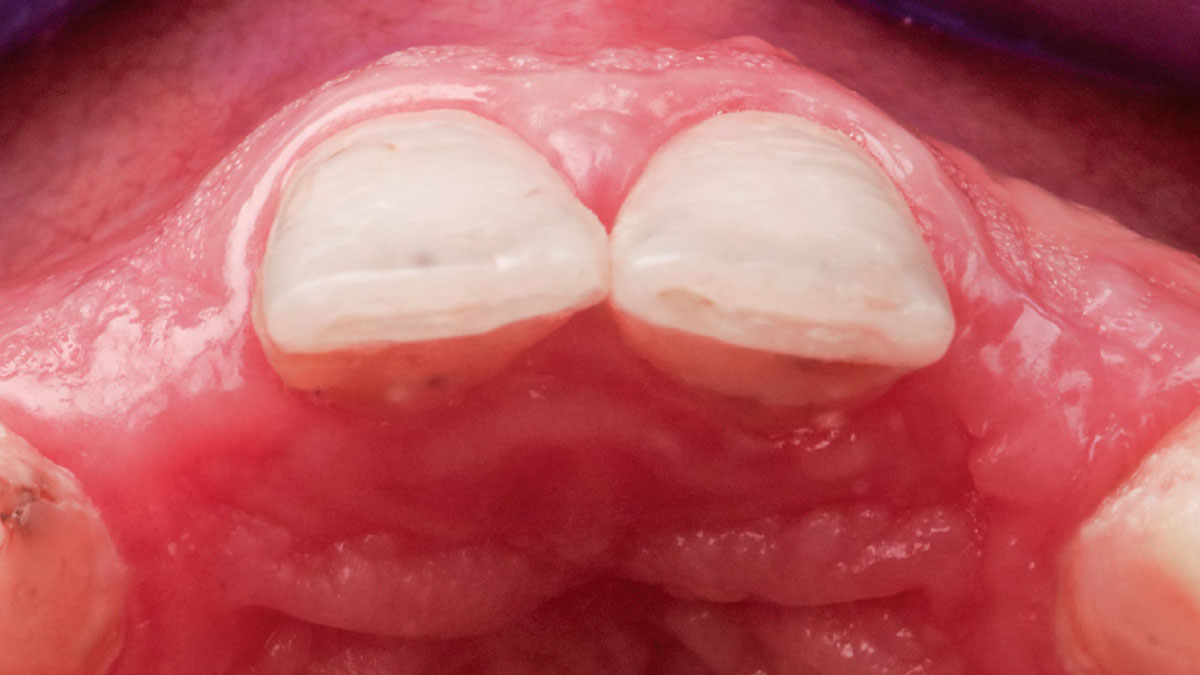
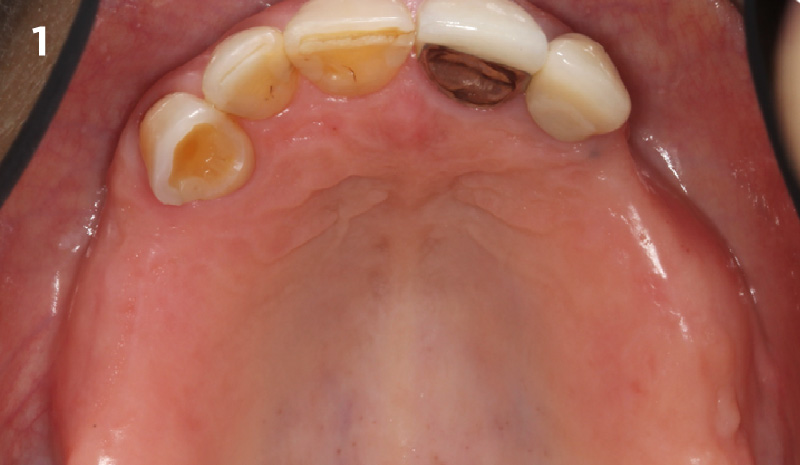
A healthy non-smoking 50-year-old female patient who desires a single tooth solution to replace a non-restorable tooth, #12. A root fracture at the level of the palatal post was diagnosed in a root canaled tooth. Maintaining esthetics of the adjacent teeth is important as they are also restored with single full coverage porcelain crowns. Lastly, treatment time reduction and a minimally invasive surgical technique are desired by the patient for reduced downtime and post-operative morbidity.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
Facial Bone Wall Phenotype: High Risk (<1mm)
Esthetic Risk Profile (ERP) = Medium (summary of above)
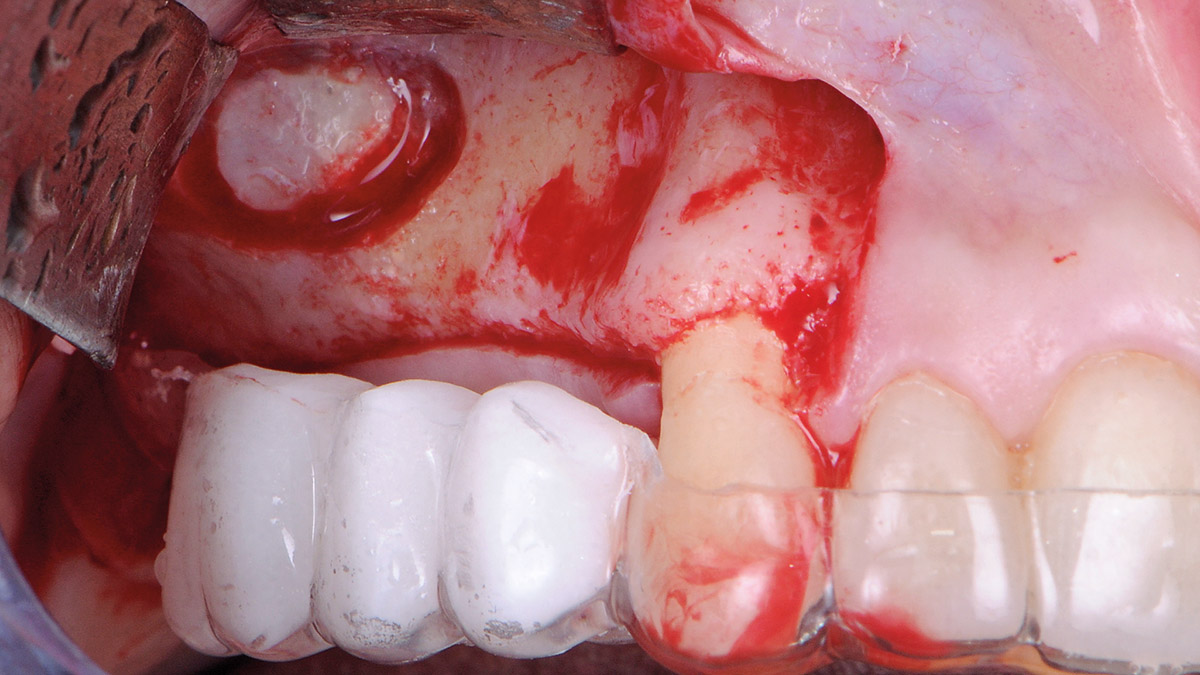
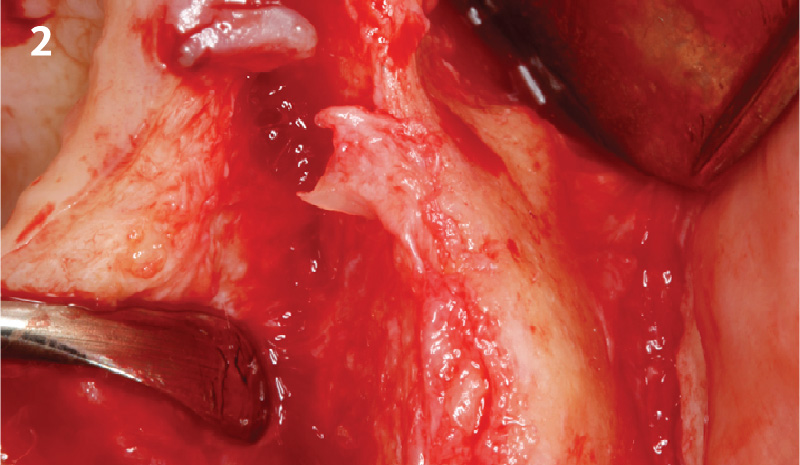
THE APPROACH
A minimally invasive surgical removal of tooth #12 with maintenance of the buccal plate and leaving a 3mm buccal gap. The implant will be placed one mm below the level of the intact buccal plate with an anatomically correct surgical guide template to provide for a screw-retained solution. The gap will be filled with Geistlich Bio-Oss Collagen® to maintain the bone buccal to the implant, and a palate free approach utilizing Geistlich Fibro-Gide® for soft tissue thickening to accomplish “phenotype conversion.” The long-term surgical goal is >2-3mm thickness of both hard and soft tissue buccal to the implant.
“High esthetic demands were the primary concern with this case. They were addressed with the diagnostic tools of clinical photos, a site specific CBCT to evaluate the buccal wall status, and summing the findings with patient expectations gathered using the Esthetic Risk Assessment (knee-to-knee; eye-to-eye) which is used along with our consent agreement to treatment.”
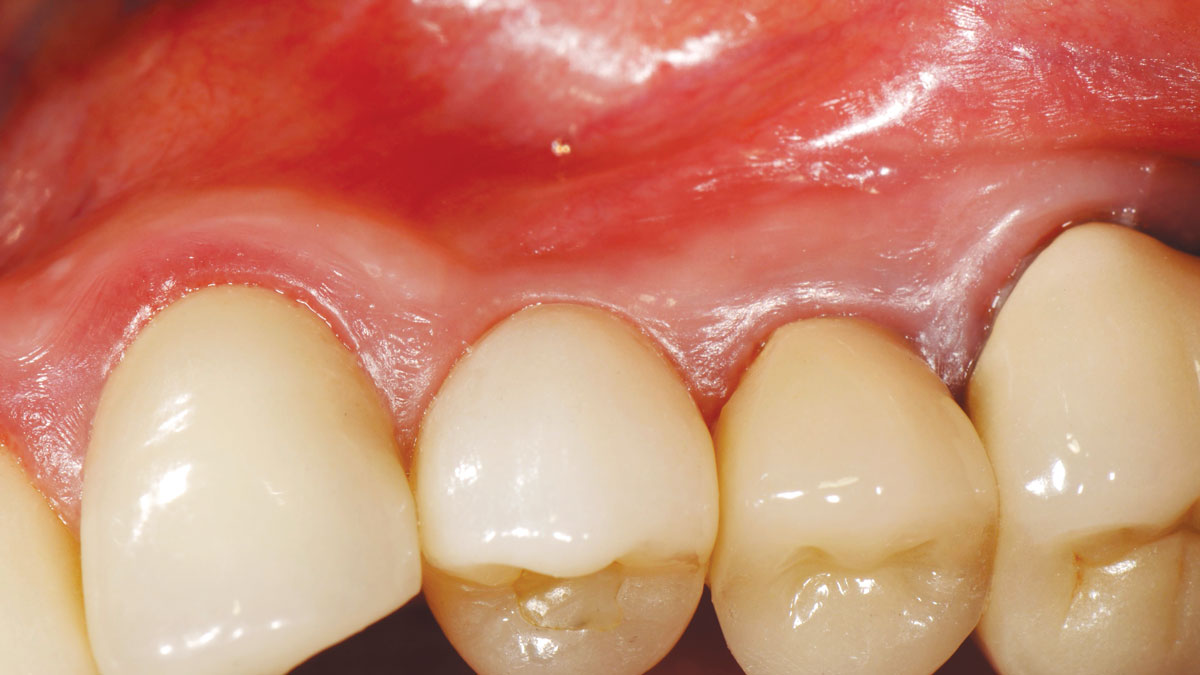
THE OUTCOME
Minimally invasive surgery for buccal wall maintenance, virtually planning the buccal gap and implant width, using a xenograft in the buccal gap with phenotype conversion using a volume stable collagen matrix in conjuction with immediate contour management, allows for the best chance for papillae fill interproximally and maintenance of the mid-buccal gingival margin long-term.

Dr. Robert A. Levine
Robert A. Levine DDS is a board-certified periodontist at the Pennsylvania Center for Dental Implants and Periodontics in Philadelphia. He is a Fellow of the International Team for Dental Implantology (ITI), College of Physicians in Philadelphia, International Society of Periodontal Plastic Surgeons and the Academy of Osseointegration. He has post-graduate periodontology and implantology teaching appointments at Temple University in Philadelphia, UNC in Chapel Hill and UIC in Chicago and has over 80 scientific publications.

BIOBRIEF
Soft-Tissue Augmentation in the Esthetic Zone
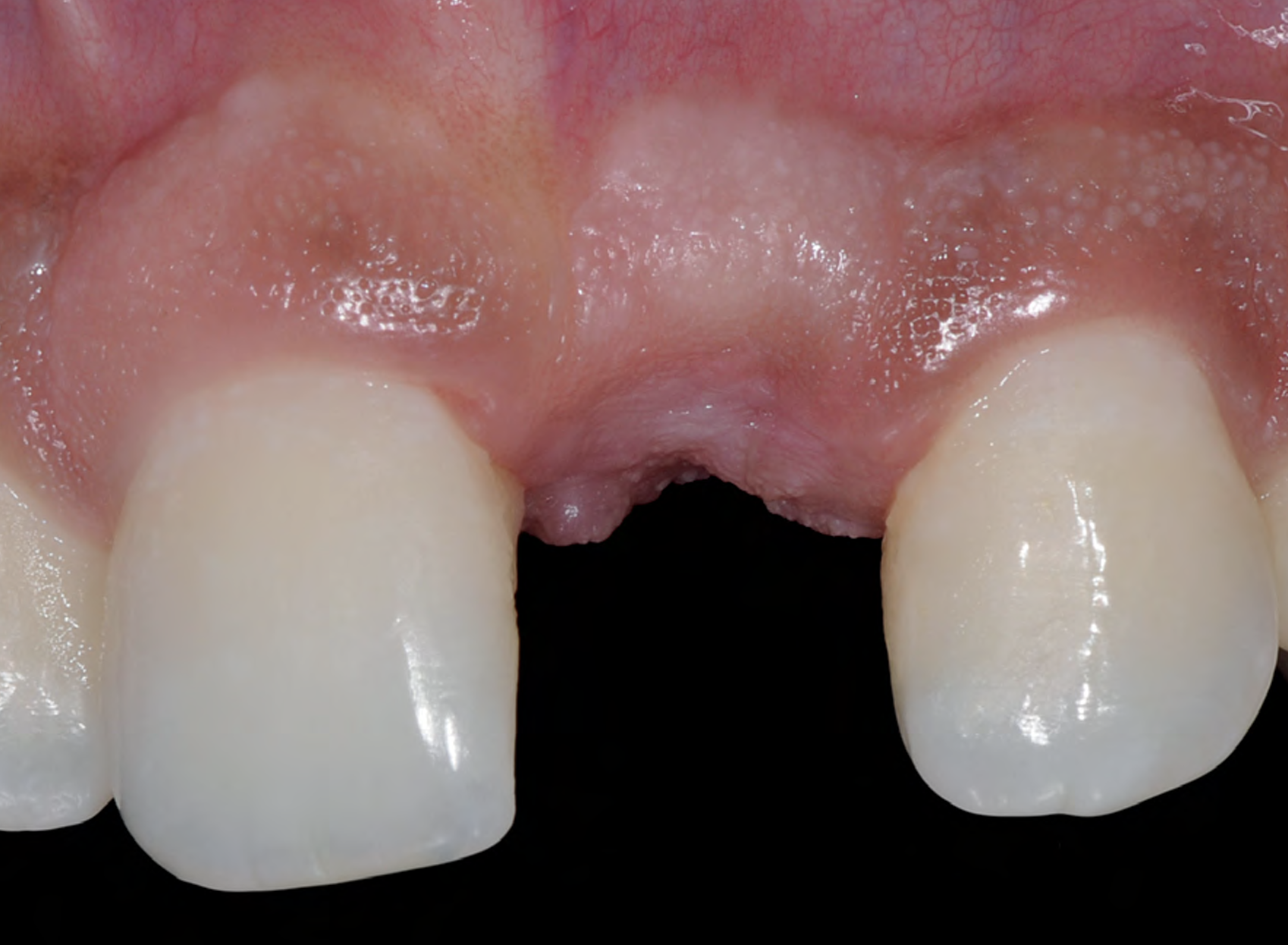

THE SITUATION
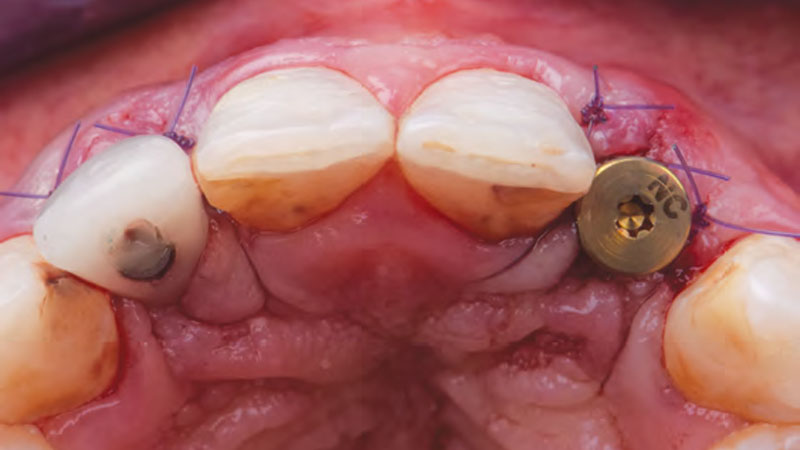
A young male patient was referred to the clinic with a missing central incisor, #9 following trauma. An implant was placed and the patient was referred for an implant-born reconstruction. The patient does not smoke and drinks occasionally. Upon a clinical examination, extensive horizontal and vertical contour deficiencies are present prior to abutment connection.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
The compromized situation with a horizontal and vertical hard and soft-tissue deficit required a soft-tissue volume grafting procedure. A buccal split-thickness flap was prepared and Geistlich Fibro-Gide® shaped and placed. Primary wound closure was obtained. Abutment connection was performed after 8 weeks and the emergence profile created with a provisional reconstruction. The final reconstruction was placed at 3 months.
“The patient presented with severe horizontal and vertical hard and soft-tissue defects. I needed a solution that could increase the soft-tissue anatomy around the implant and prosthesis.”
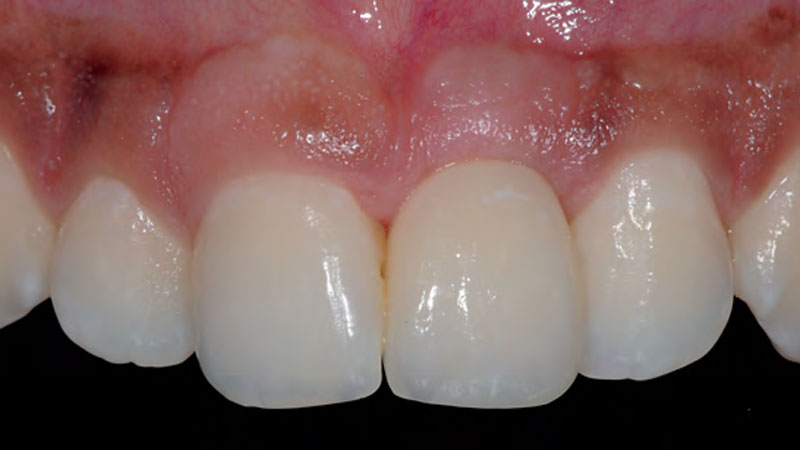
THE OUTCOME
The outcome of the case was very pleasing having fulfilled the patient’s expectations in terms of esthetics and function. The tissues are healthy and volume was obtained through the grafting procedure to match the contour of the neighboring natural tooth.

Prof. Dr. Daniel S. Thoma
Prof. Dr. Daniel Thoma is the head of Reconstructive dentistry and Vice-chairman at the Clinic for Fixed and Removable Prosthodontics and Dental Material Sciences, University of Zurich, Switzerland. He graduated in 2000 at the University of Basel, Switzerland and was trained in implant dentistry and prosthodontics at the clinic for Fixed and Removable Prosthodontics and dental Material Sciences, University of Zurich, Switzerland.

BIOBRIEF
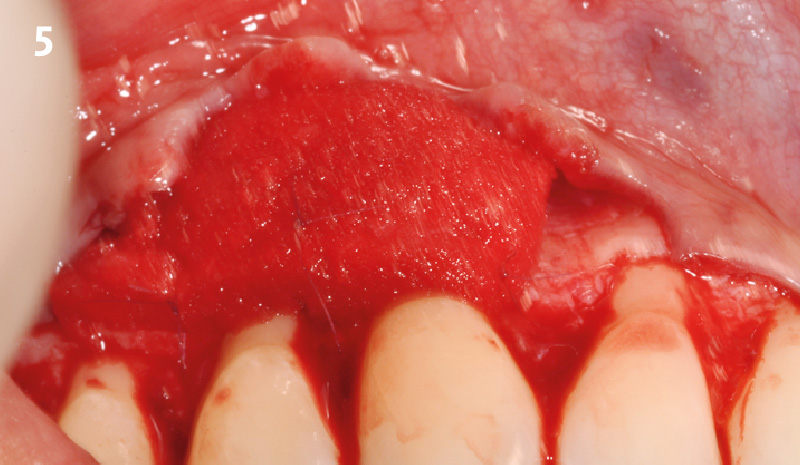
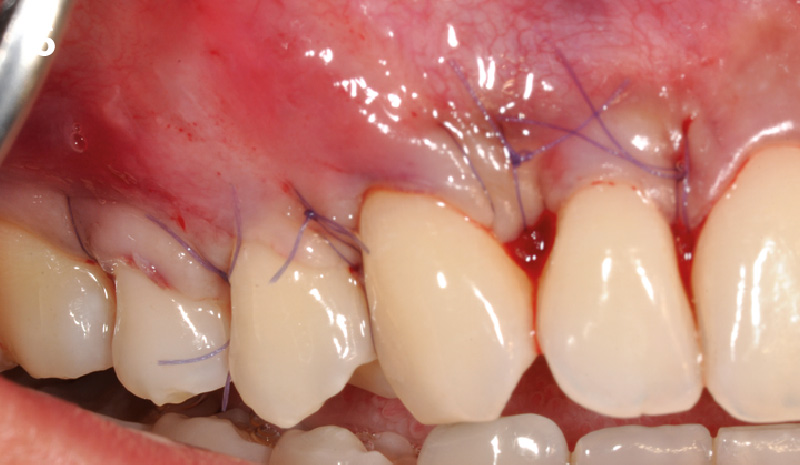
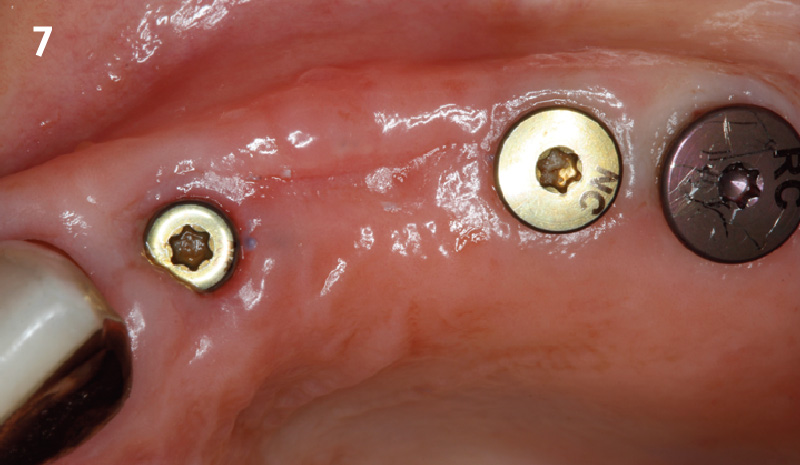
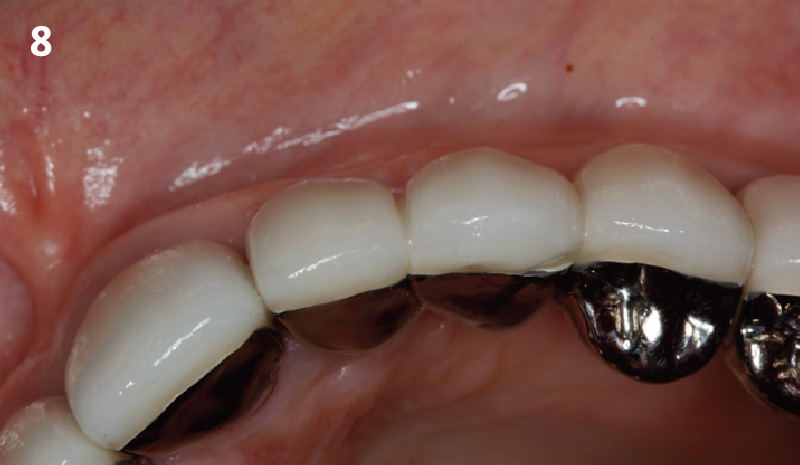
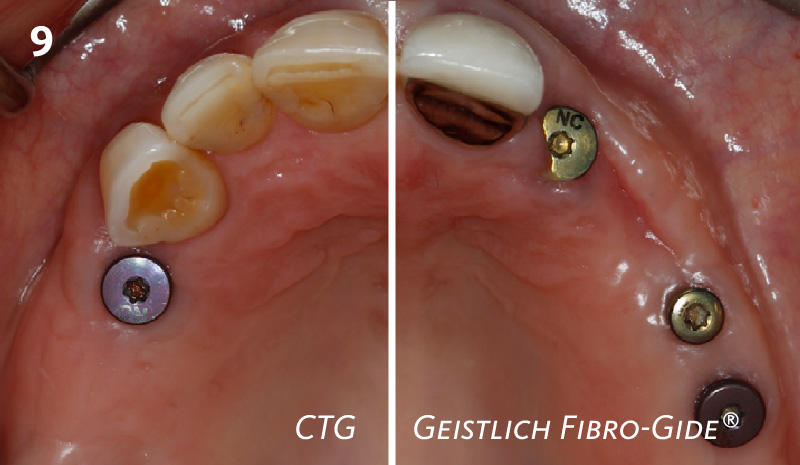
Root Coverage for Multiple Adjacent Teeth in the Maxilla with Geistlich Fibro-Gide® 1.5-Year Follow-Up
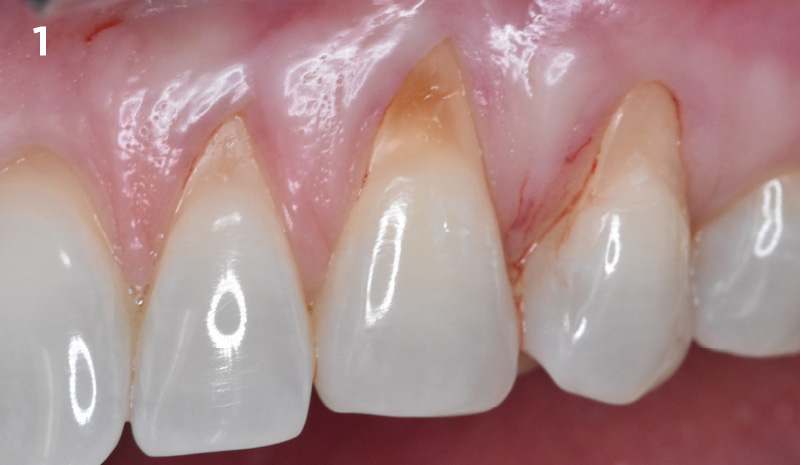

THE SITUATION
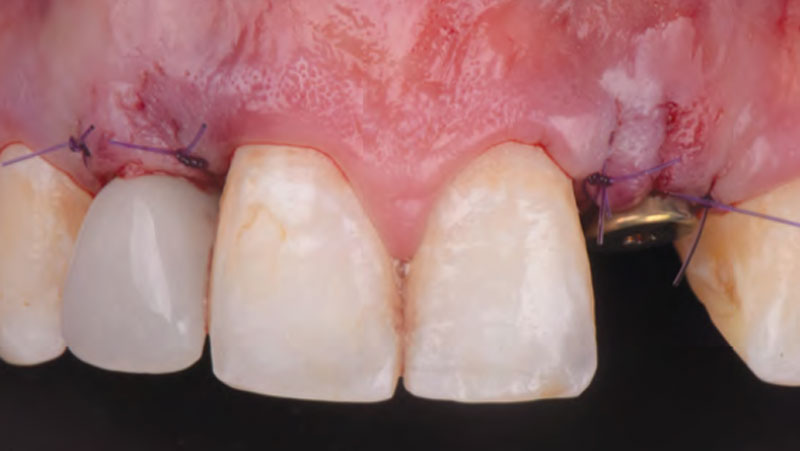
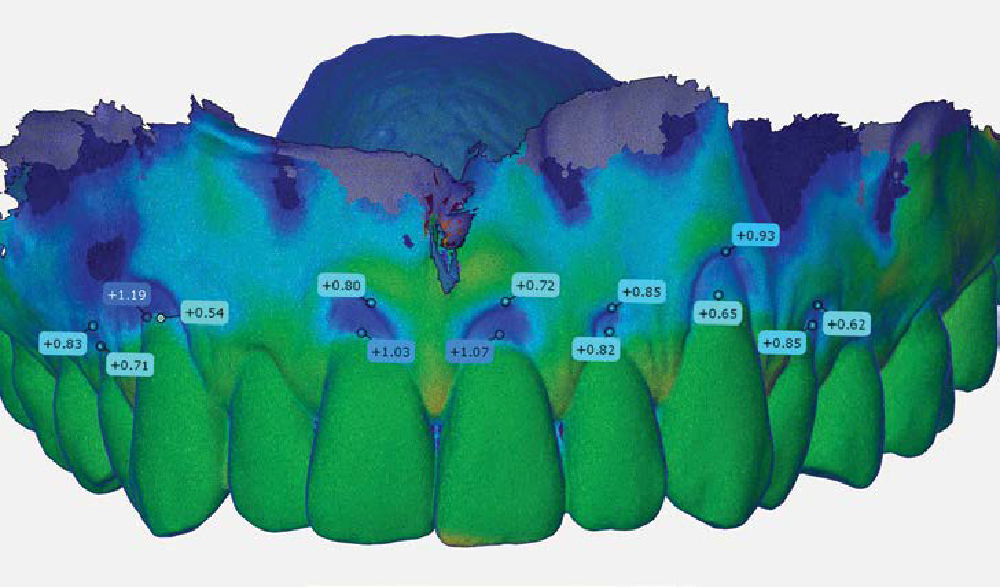
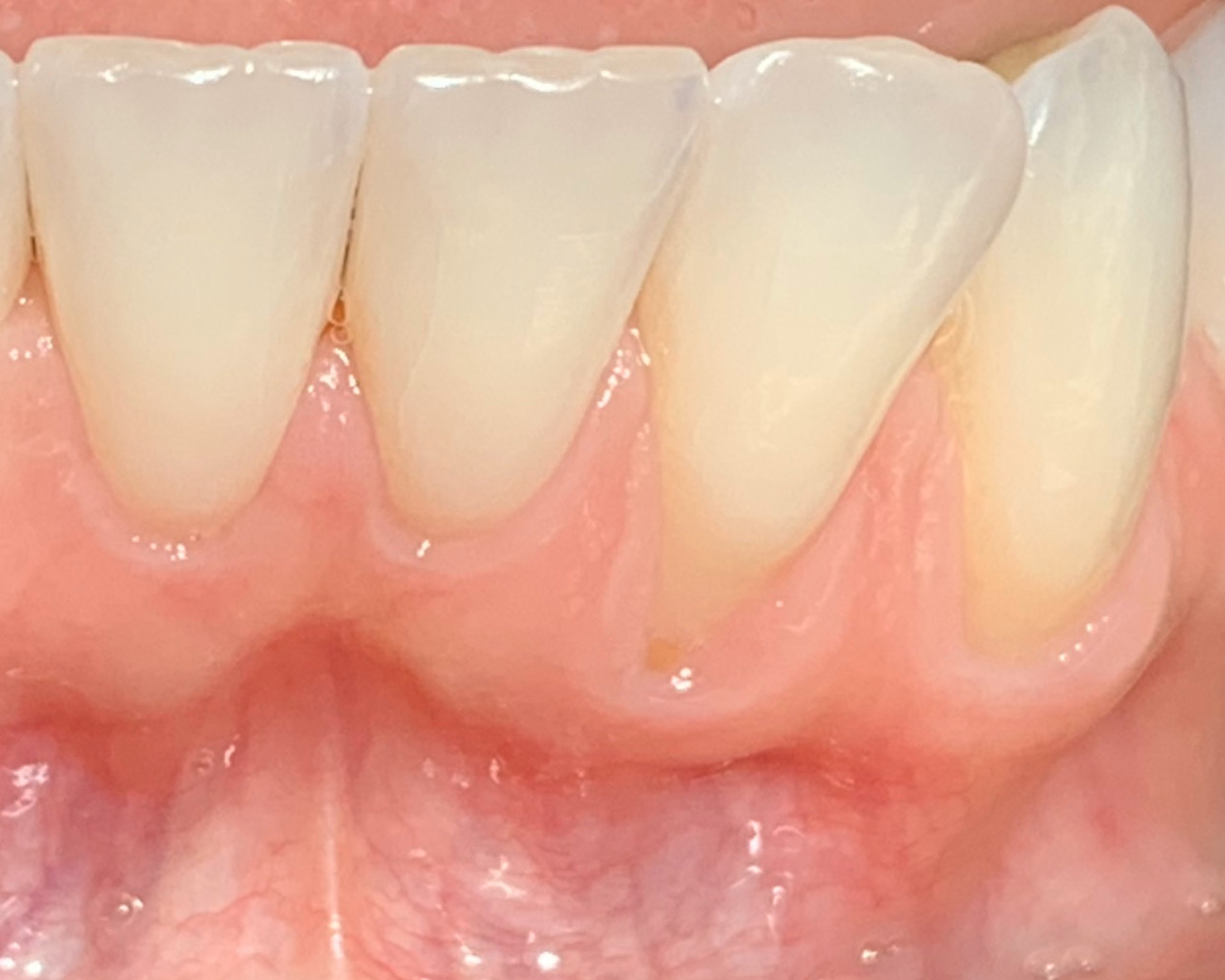
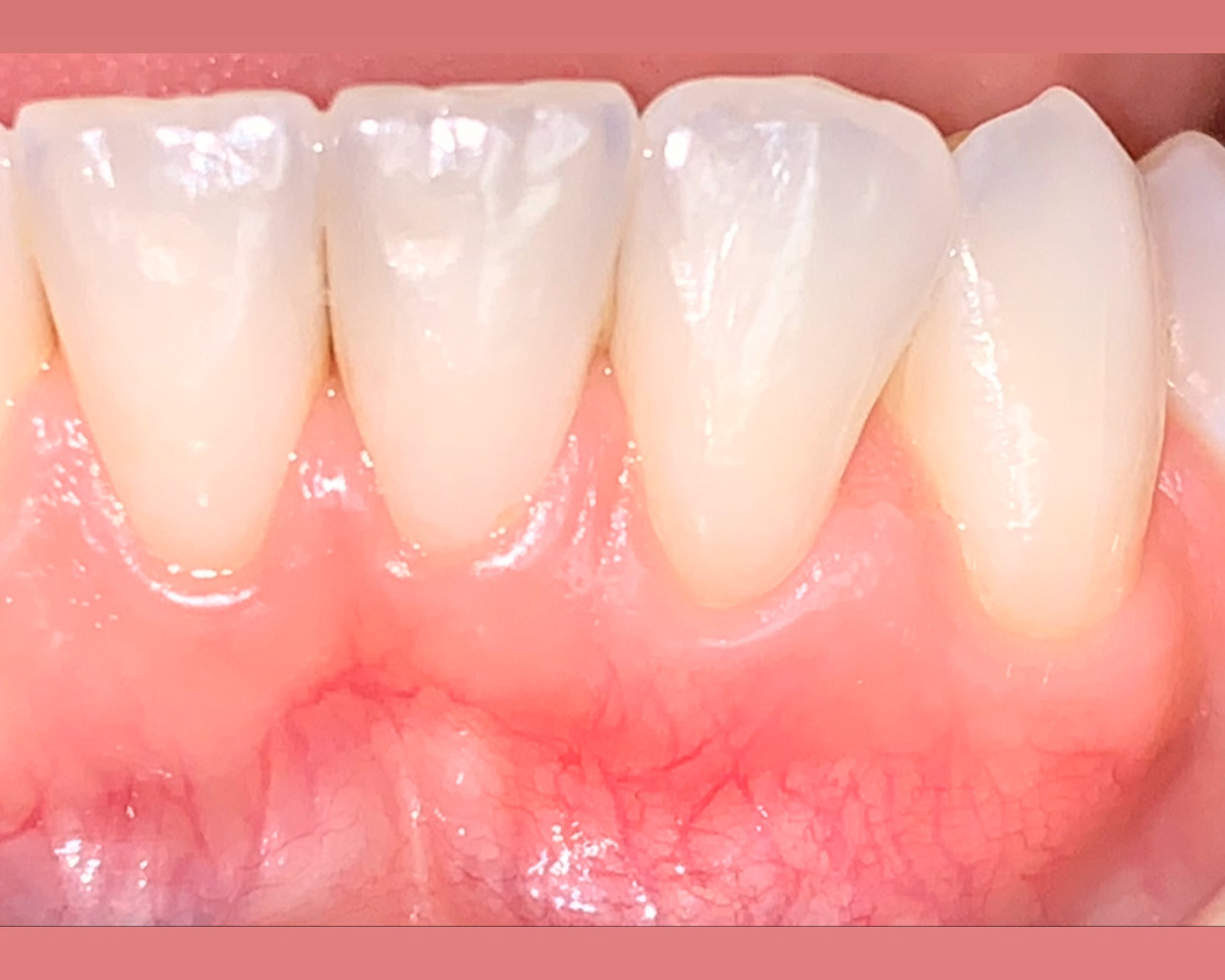
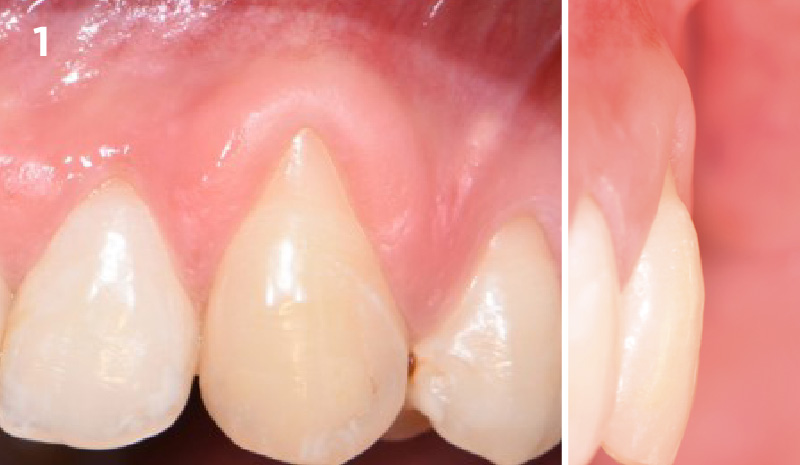
The patient is a healthy, 60-year-old female who presented to our clinic with a chief complaint of progressive gum recession which had led to compromised esthetics and sensitivity involving the maxillary left lateral incisor (#10), canine (#11), and first bicuspid (#12) teeth. The teeth in question had 3-4 mm of gingival recession on the buccal surface with a sufficient zone of keratinized gingiva. These teeth also had obvious cervical abrasion.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
Severity of recession – mild to moderate
Amount of keratinized gingiva – 2 mm or greater for all teeth involved
THE APPROACH
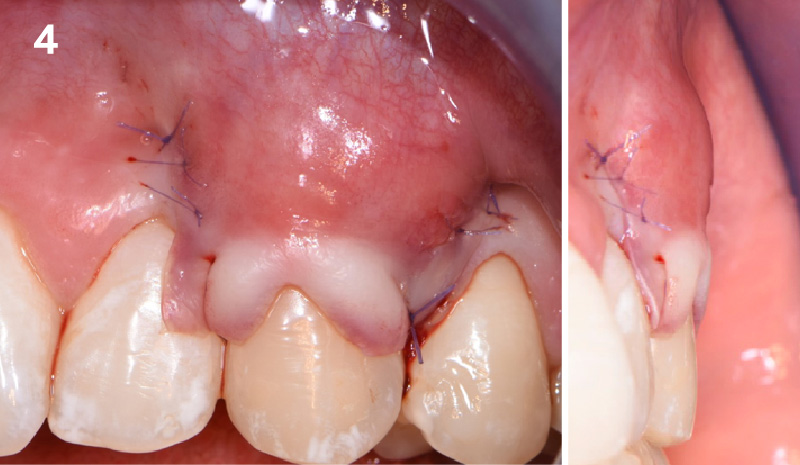
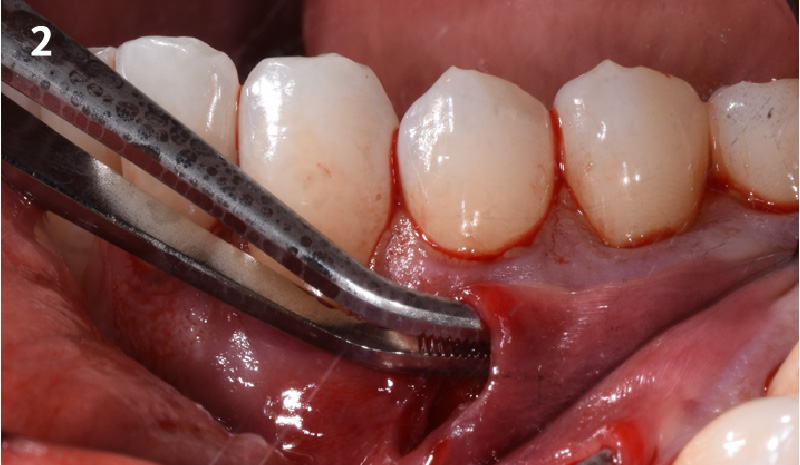
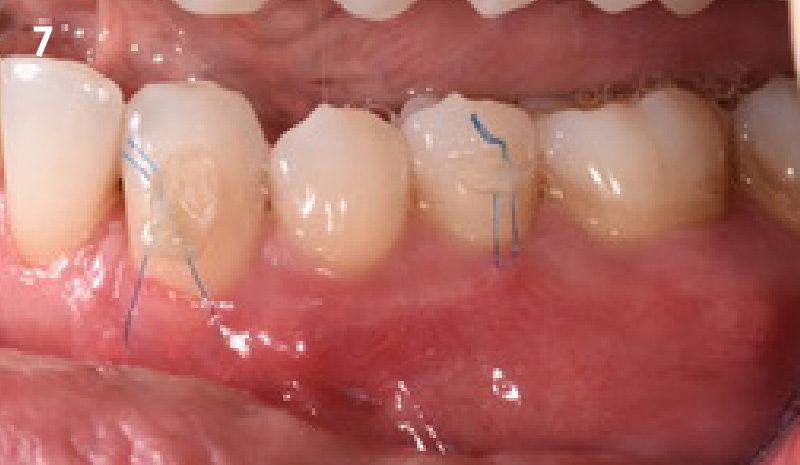
Treatment goals for this case were to obtain complete root coverage, increase soft tissue thickness, and reduce/eliminate cervical sensitivity. A split-thickness envelope flap approach was used. Geistlich Fibro-Gide® was then trimmed, hydrated with saline, and placed over the exposed root surfaces. The flap was coronally advanced in a tension-free manner to completely cover the biomaterial and exposed root surfaces.
“The patient’s main priorities were to improve esthetics and reduce/eliminate root sensitivity. Soft tissue grafting was done with autologous connective tissue in other areas of her mouth many years ago and she was hesitant to undergo surgery again if it involved harvesting tissue from her palate due to the post-operative pain she experienced after these previous procedures.”
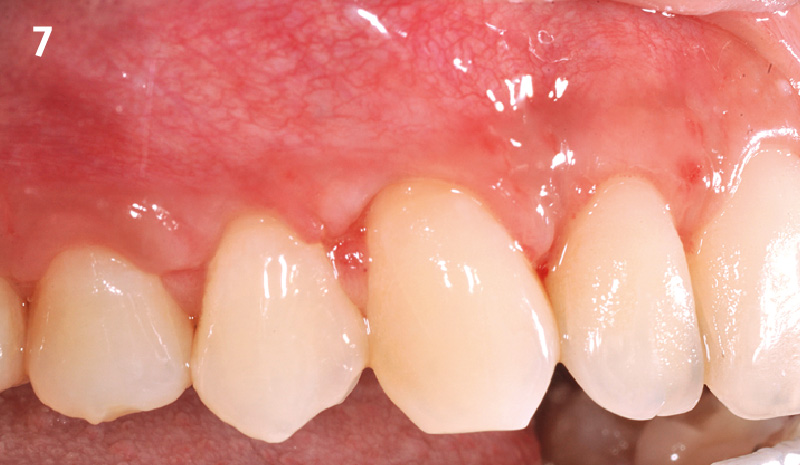
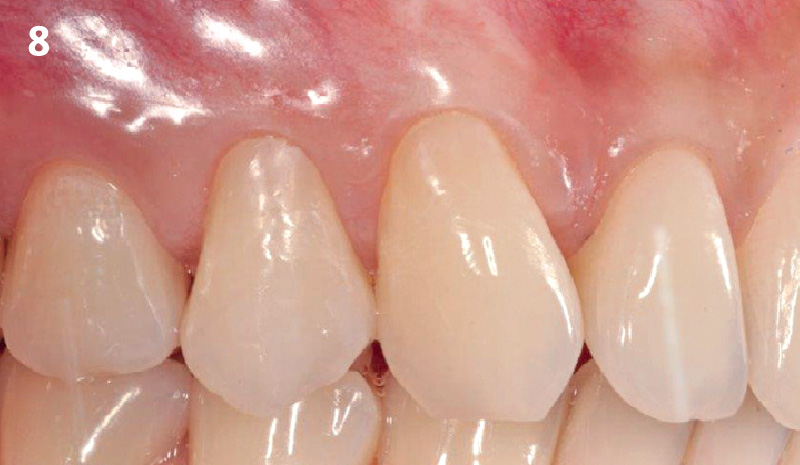
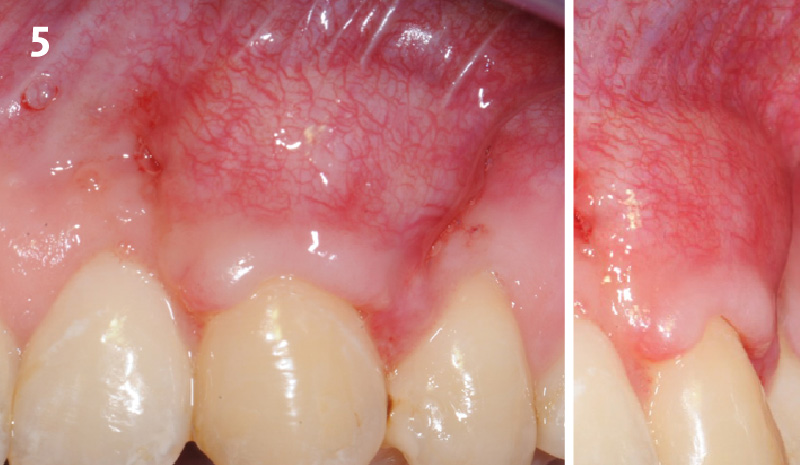
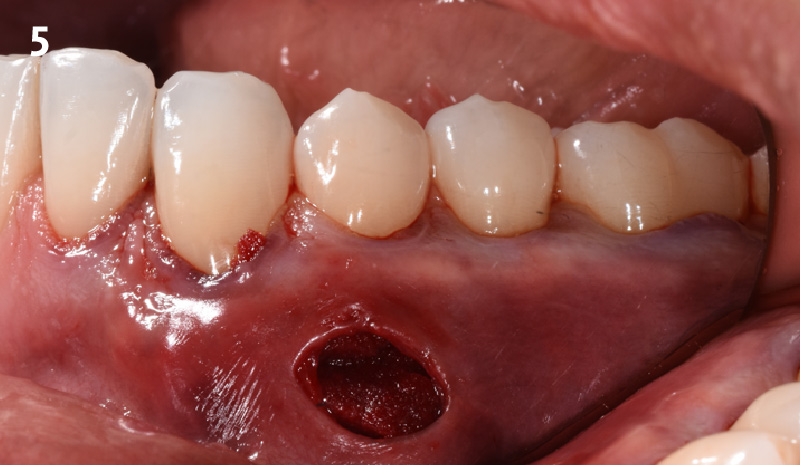
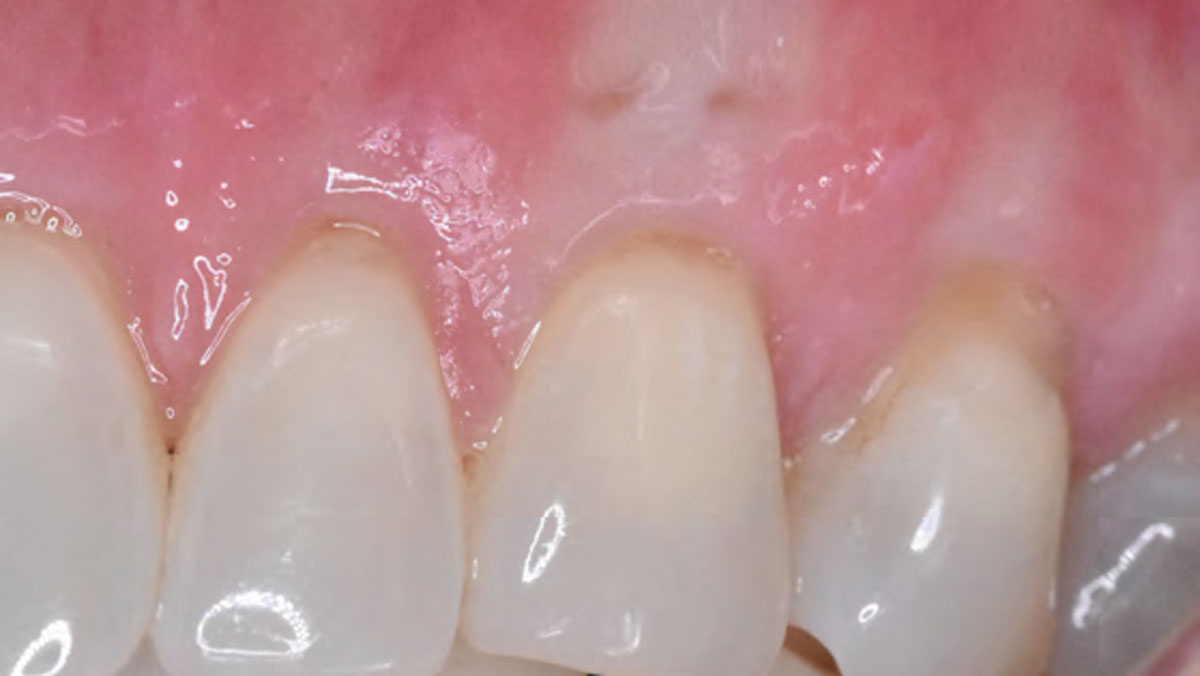
THE OUTCOME
This case nicely shows that the result following root coverage surgery to treat multiple adjacent teeth using a volume-stable collagen matrix is comparable to that seen with autologous connective tissue. At 1.5 years, there is continued stability of the treated site. The tissue appears healthy and firm. The patient‘s chief complaints of esthetics and sensitivity have been addressed and the patient is maintaining excellent oral hygiene and home care.

Dr. Vinay Bhide
Dr. Vinay Bhide is a board certified Periodontist with a special interest in periodontal plastics and reconstructive surgical procedures. Dr. Bhide did his dental and specialty training at the university of Toronto. In addition to private practice, Dr. Bhide is a clinical instructor in the Department of Periodontics at the university of Toronto. He is also a staff periodontist in the Center for Advanced Dental Care and Research at Mount Sinai Hospital, Toronto.

BIOBRIEF
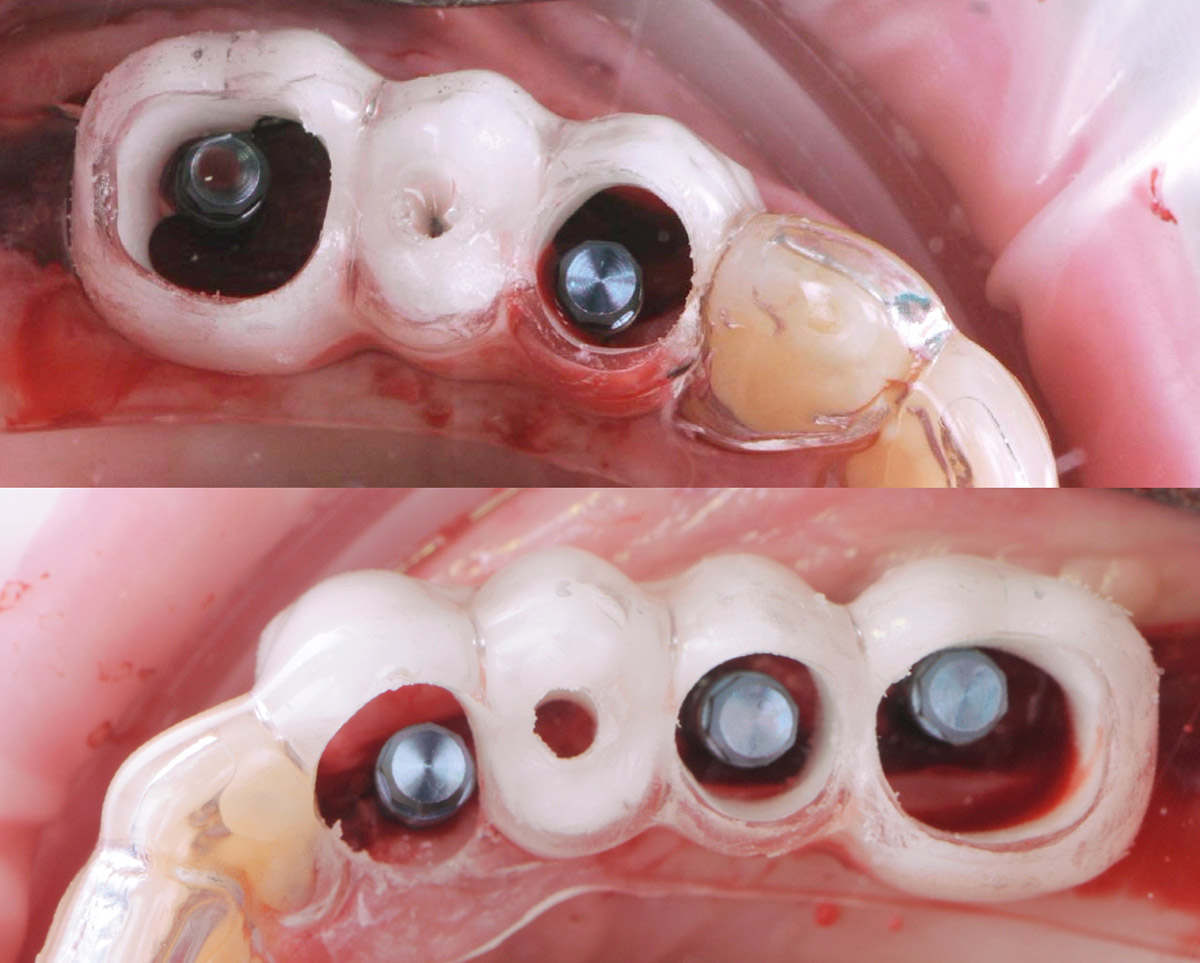
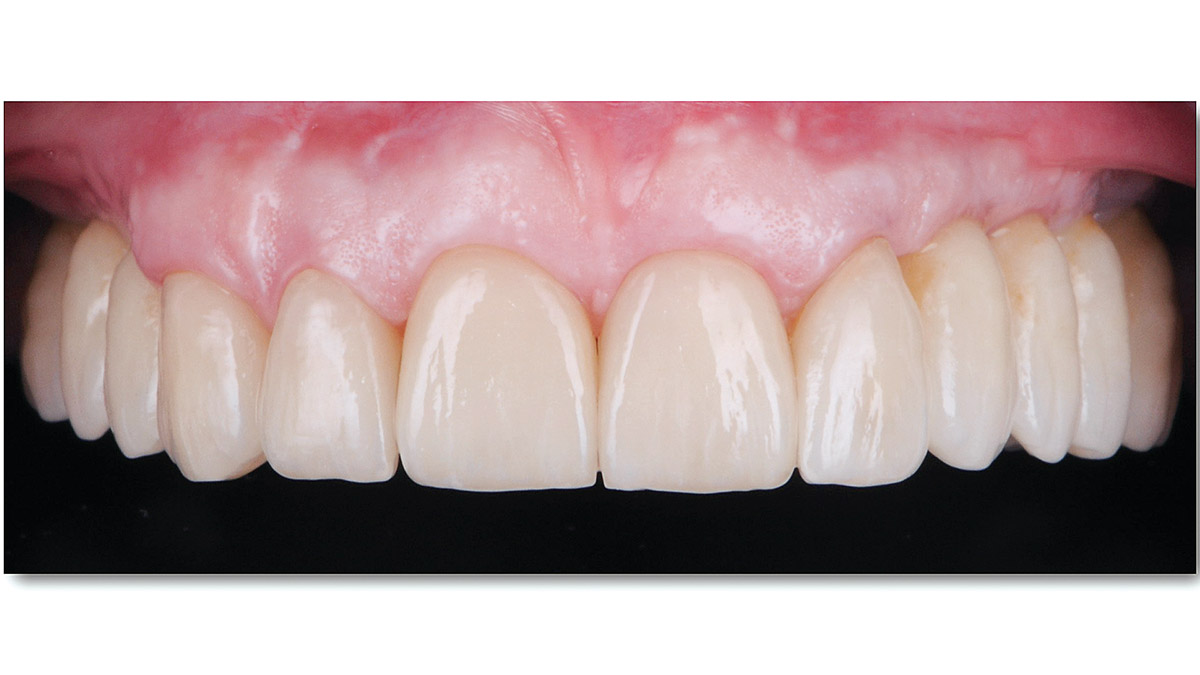
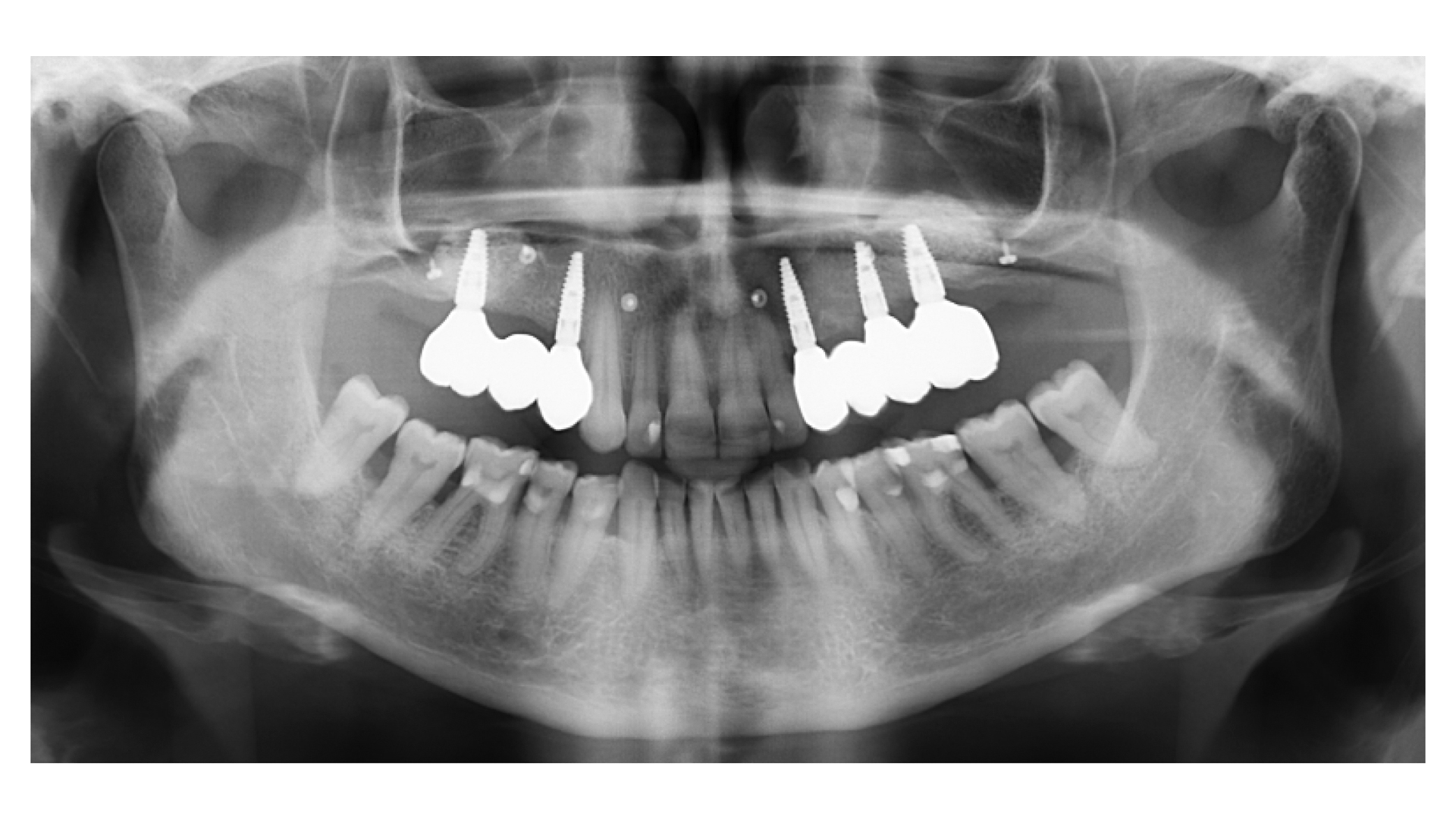
Prosthetically Guided Regeneration (PGR) in the Posterior Maxilla
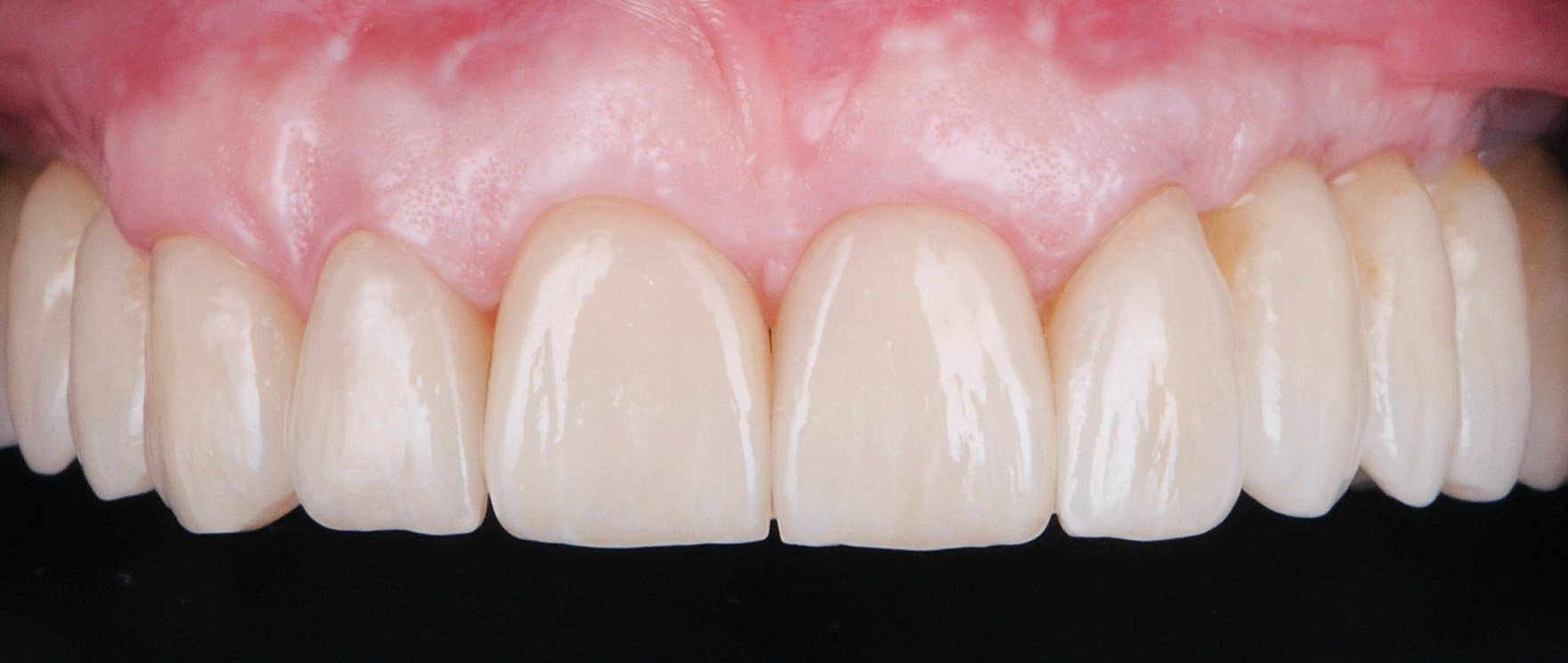

THE SITUATION
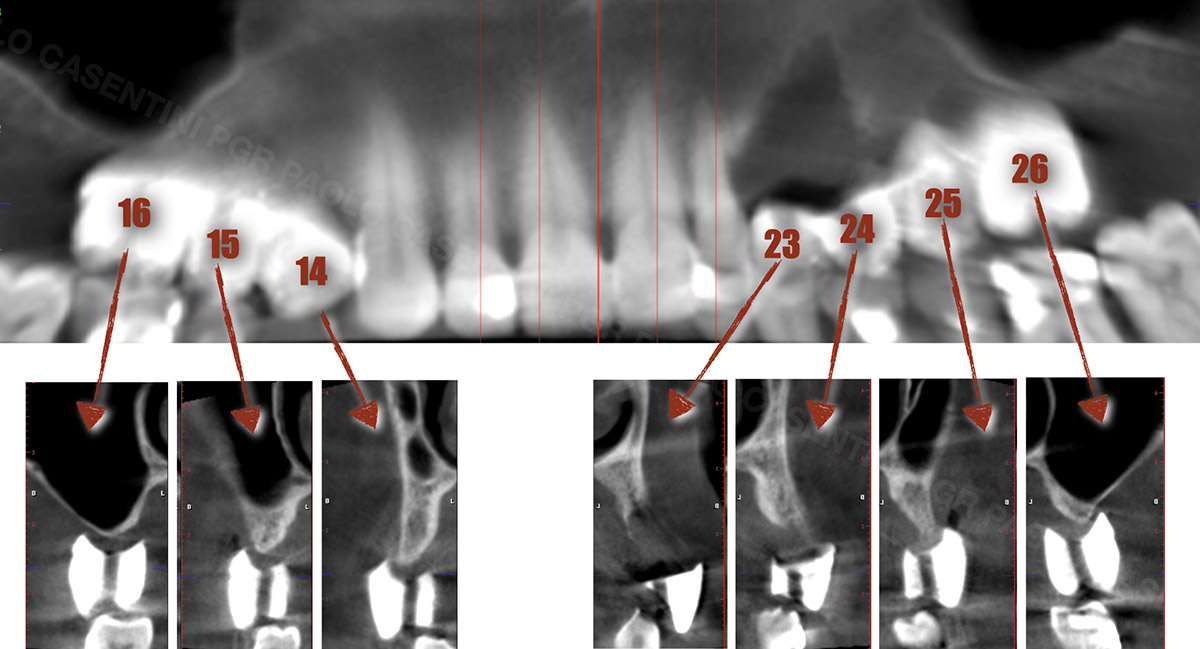
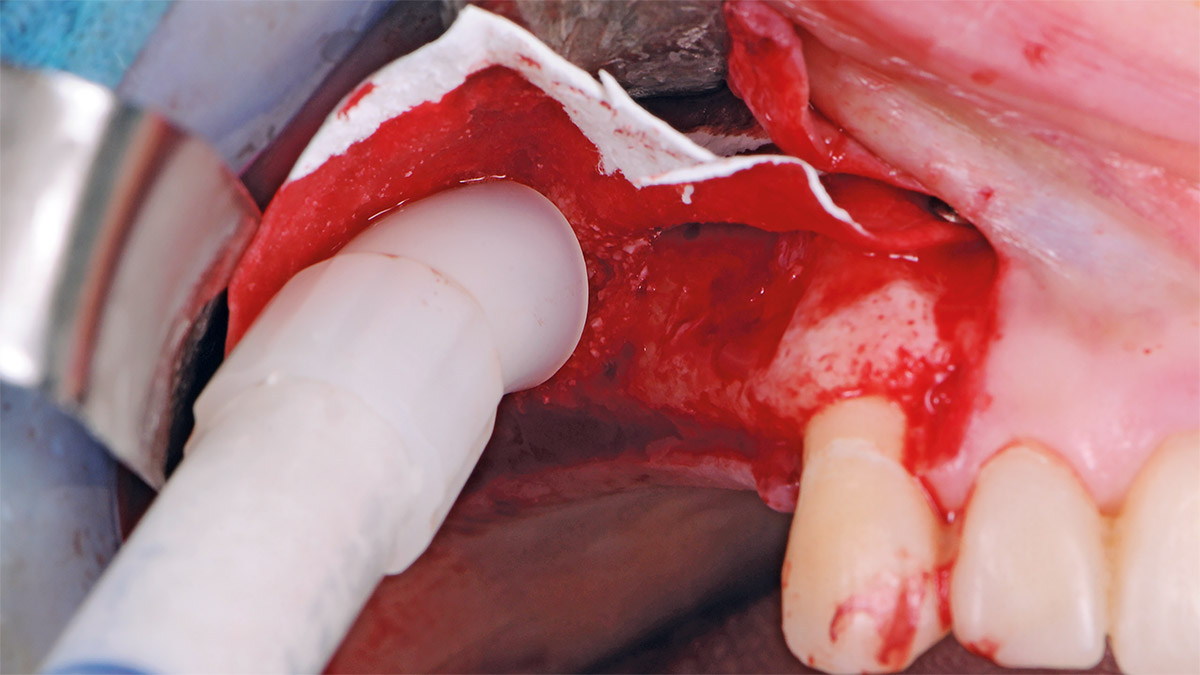
The 60-year-old female patient’s chief complaint was represented by unsatisfactory esthetics and function, related to loss of multiple maxillary teeth. Her request focused on improving esthetics and function by means of a fixed reconstruction.
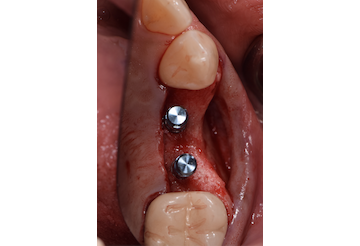
The patient presented five residual anterior maxillary teeth (from 6 to 10) that could be maintained. After preliminary periodontal diagnosis and treatment, specific diagnostic steps for implant treatment demonstrated inadequate bone volume for implant placement.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system Non-smoker | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
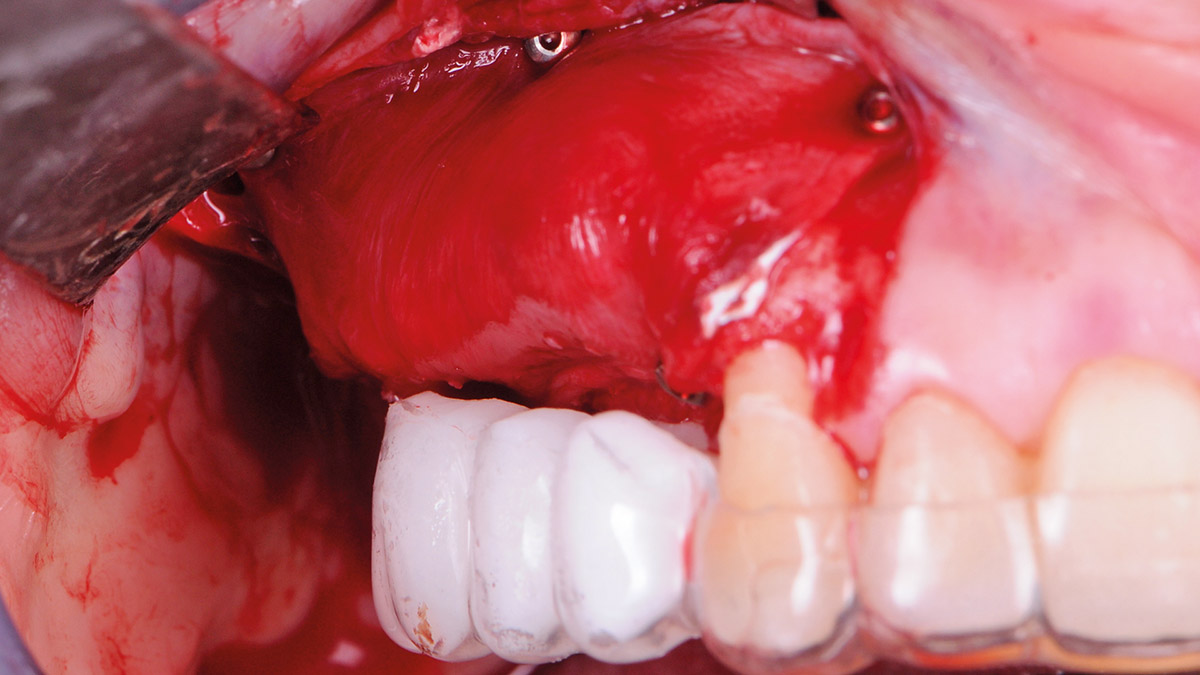
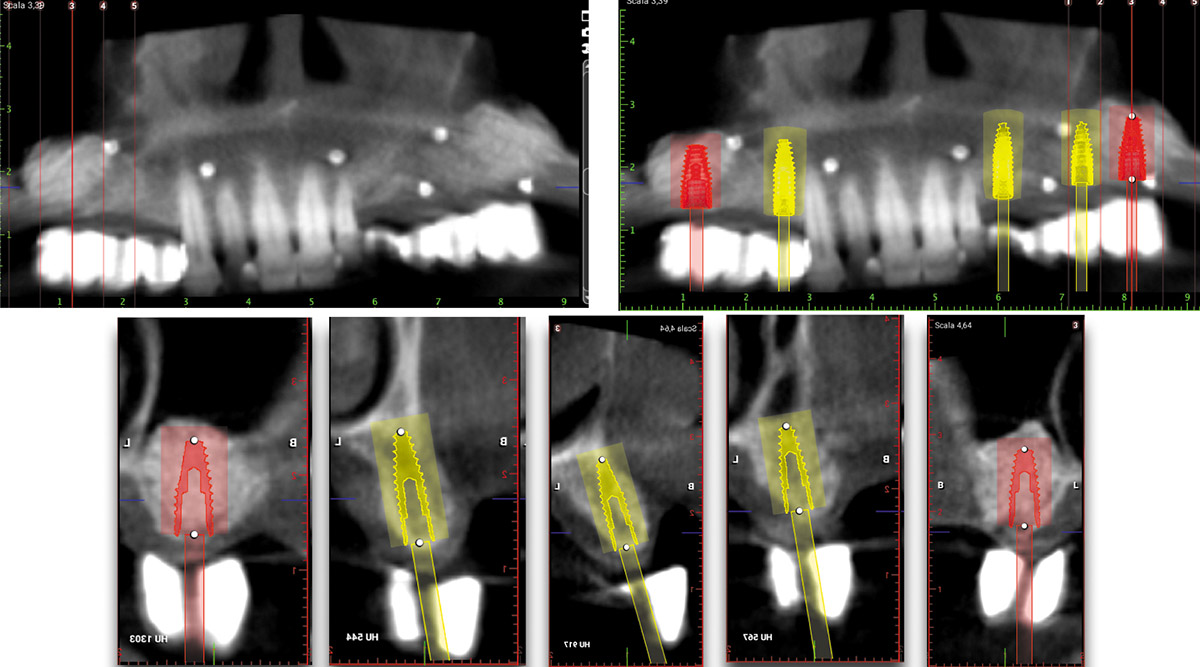
Bi-lateral sinus lift with Geistlich Bio-Oss Pen® and horizontal bone augmentation with a 1:1 mix of autogenous bone and Geistlich Bio-Oss® were performed six months prior to implant placement, following a Prosthetically Guided Regenerative (PGR) approach. The augmented sites were protected with Geistlich Bio-Gide® stabilized with titanium pins. The template utilized for radiographic diagnosis and GBR was then used to guide the implants’ placement.
Using a diagnostic template during the GBR procedure helps to highlight the presence of bone defects in relationship to the restorative plan and future position of implants.
THE OUTCOME
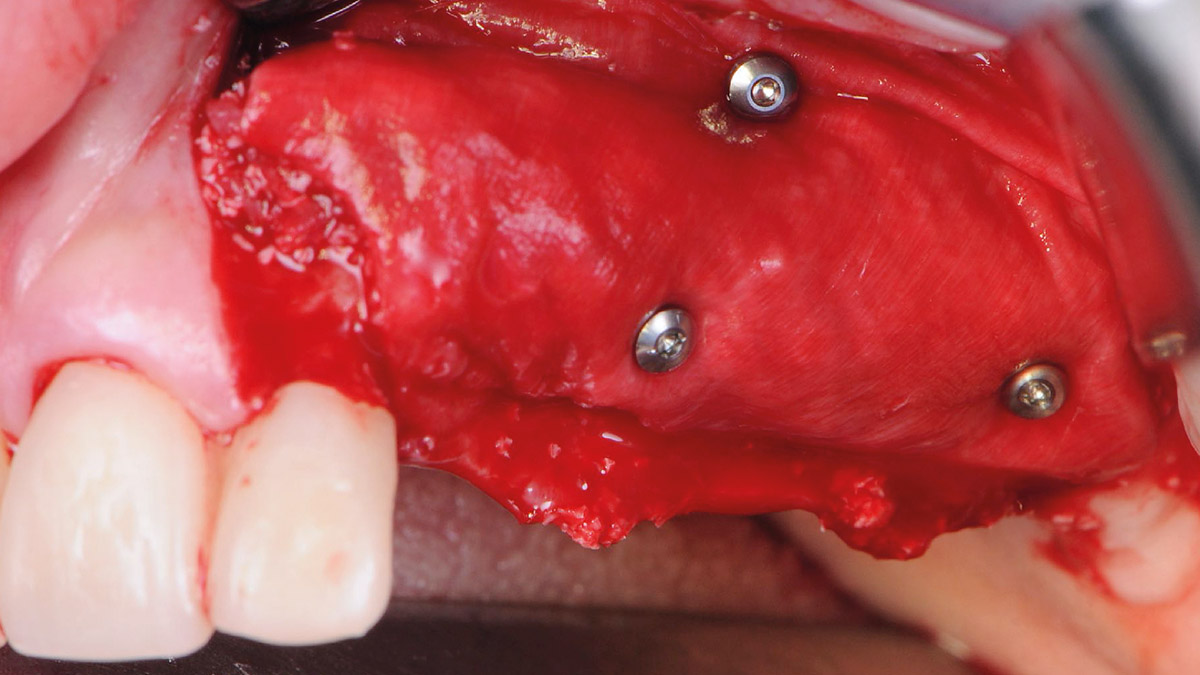
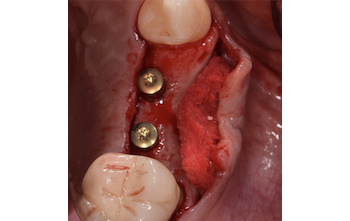
After a healing period of six months, adequate bone volume was achieved for the placement of five implants. Geistlich Fibro-Gide® was also used to optimize soft tissue volume at the buccal aspect of implants.
Implants were early loaded with a temporary screw-retained fixed prostheses six weeks after placement. The final prosthetic reconstruction included ceramic veneers of the frontal residual teeth and zirconium-ceramic screw-retained fixed prostheses on implants.


Paolo Casentini, DDS
Graduated in Dentistry at the University of Milan, Fellow and Past Chairman of the Italian section of ITI, Active member Italian Academy of Osseointegration. Co-author of 10 textbooks including ITI Treatment Guide volume 4, translated in eight languages, and “Pink Esthetic and Soft Tissues in Implant Dentistry” translated in five languages. His field of interest is advanced implantology in complex and esthetically demanding cases. He has extensively lectured in more than 40 countries.

BIOBRIEF
Avoiding Post-Implant Placement and Long Term Crestal Bone Resorption by Thickening Vertical Soft Tissue
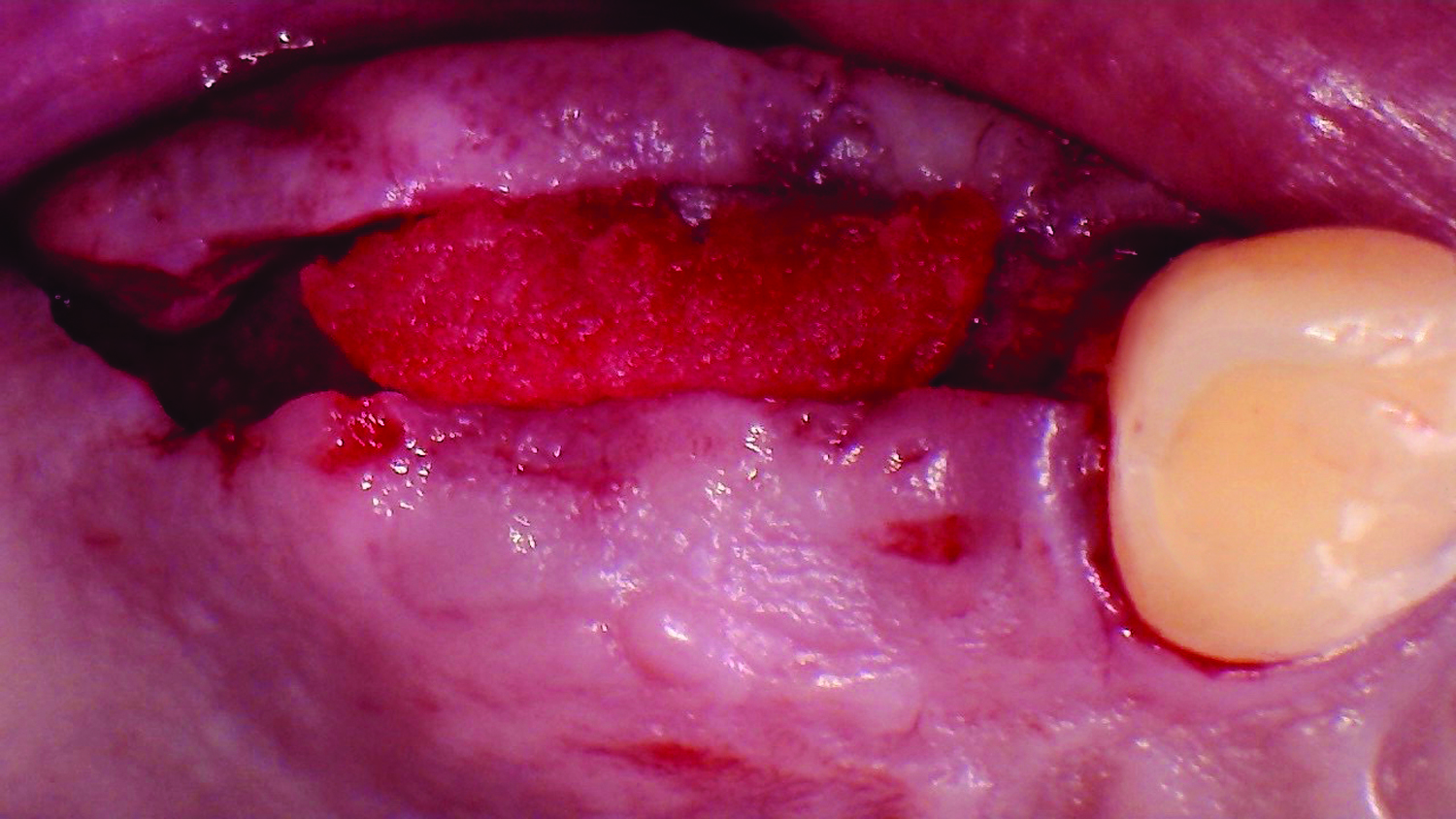

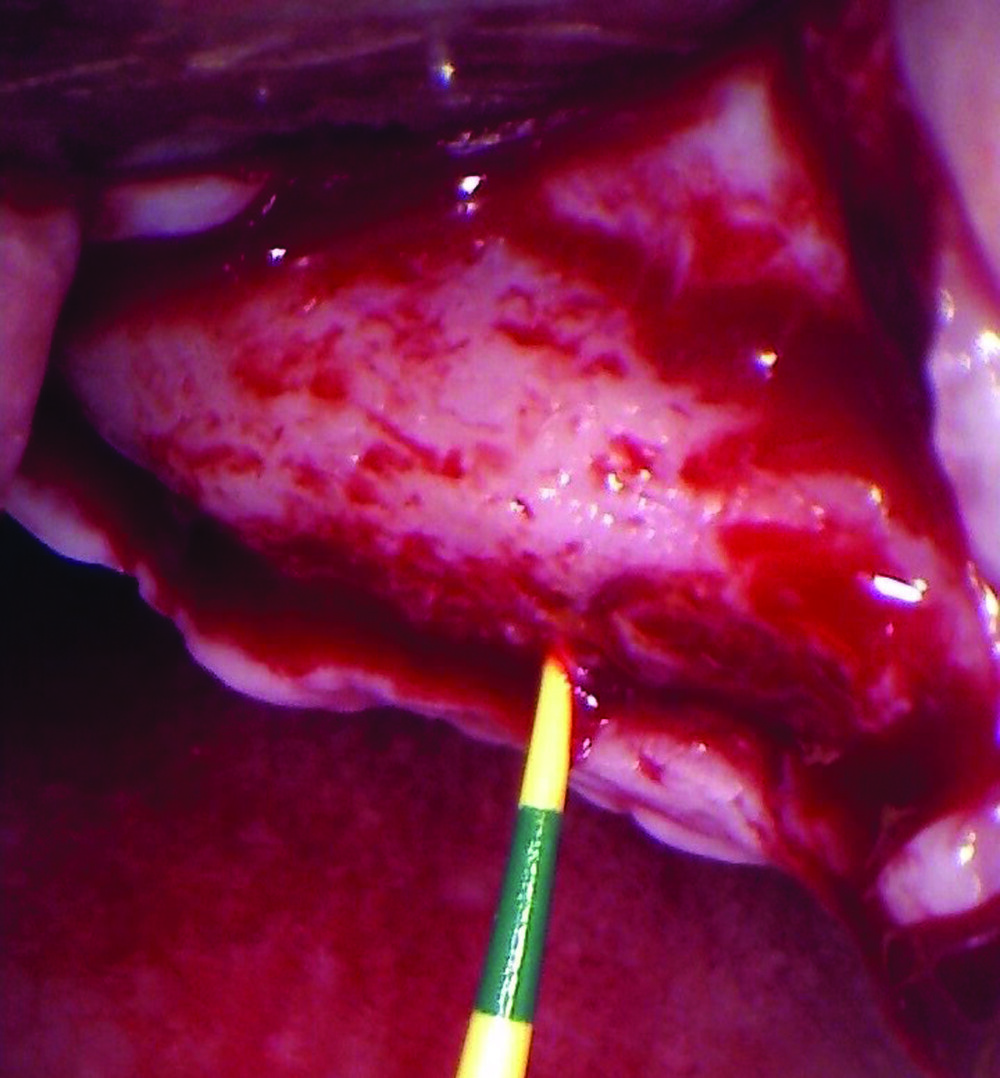
THE SITUATION
Our patient is a 60-year-old caucasian male that had just finished a large ridge augmentation in the area of #4 and #5. We used the sausage technique for the ridge augmentation and yielded excellent bone volume in this area. However, as we began the 2nd stage implant placement procedure, we noticed, as is frequently seen following a large ridge augmentation, very thin vertical soft tissue over the crest of the bone. We know that inadequate soft tissue thickness will lead to compromised vasculature and transfer of oxygen and nutrients to the bone which can absolutely lead to a loss of crestal bone surrounding the implants.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
Note: Bone was augmented prior to this case report due to a severe horizontal defect.
THE APPROACH
Our goal here is to create increased vertical soft tissue thickness over the crest of the implant site. Following implant placement and placement of the cover screws, we used Geistlich Fibro-Gide® over the implants and then layed it over the crest and buccal aspect. Following the placement of Geistlich Fibro-Gide®, we gently released the full thickness flap so that we can achieve tension-free primary closure over the site.
The use of Geistlich Fibro-Gide® is a wonderful alternative to using a connective tissue graft to thicken vertical soft tissue, which will help minimize crestal bone loss around implants.
THE OUTCOME
The soft tissue that will now surround the implant site is thick and healthy due to the use of Geistlich Fibro-Gide® at the time of implant placement. This is a simple technique and only requires a minimal amount of flap release to achieve tension-free primary closure over the site. The results are phenomenal and will be beneficial for the stability of the crestal bone surrounding the implants for years to come.

Tamir Wardany, D.D.S.
Dr. Wardany is a graduate of Meharry Medical College School of Dentistry in Nashville, TN. After completion of a dental implant fellowship through State University of New York Stonybrook, he continues to spend extensive time in Europe training under Dr. Istvan Urban in the field of advanced bone and soft tissue regeneration.
He is a Diplomate of the American Board of Implantology, and lectures extensively on the topic of bone regeneration. He maintains a referral based surgical implant practice in San Francisco and Sacramento, California.

BIOBRIEF
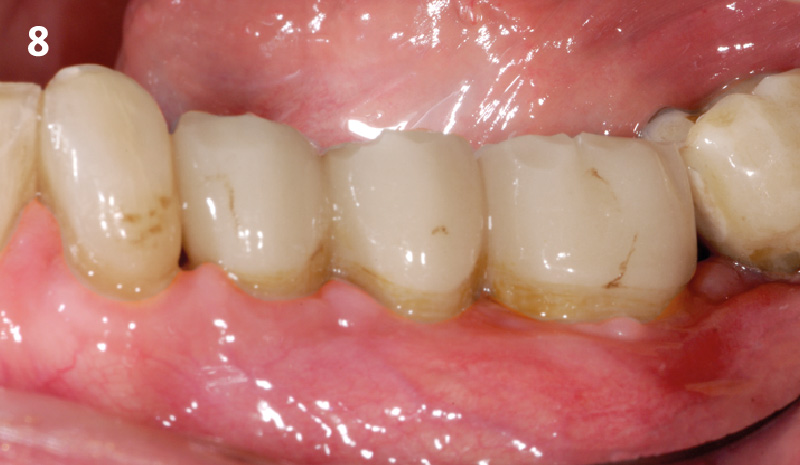
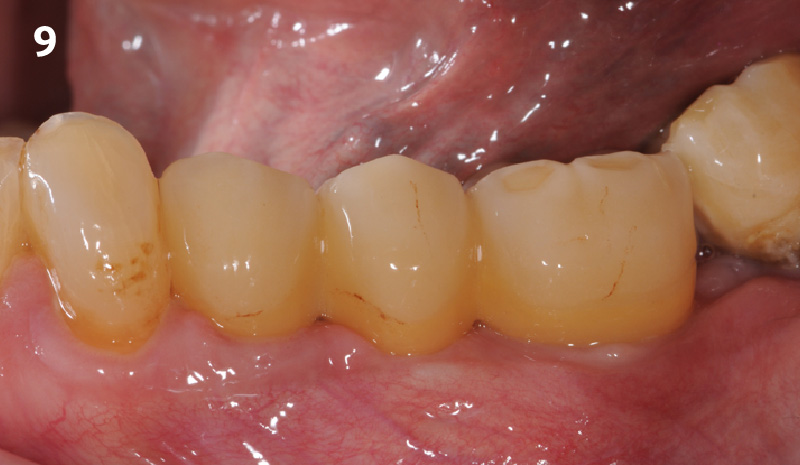
A Regenerative Approach to Peri-implantitis
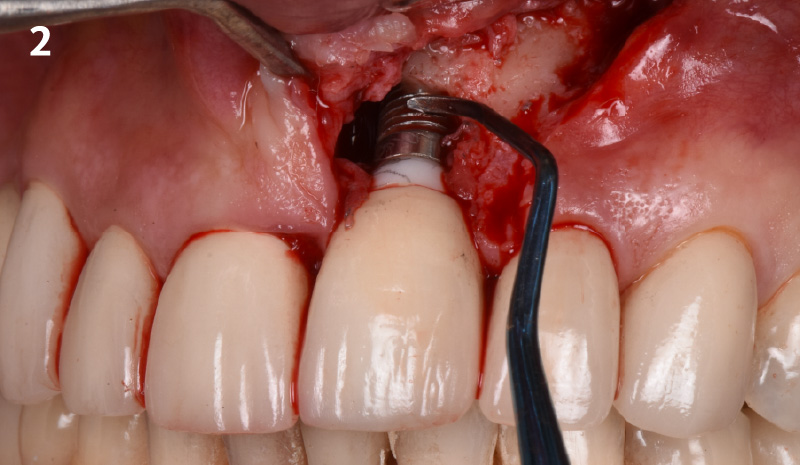

THE SITUATION
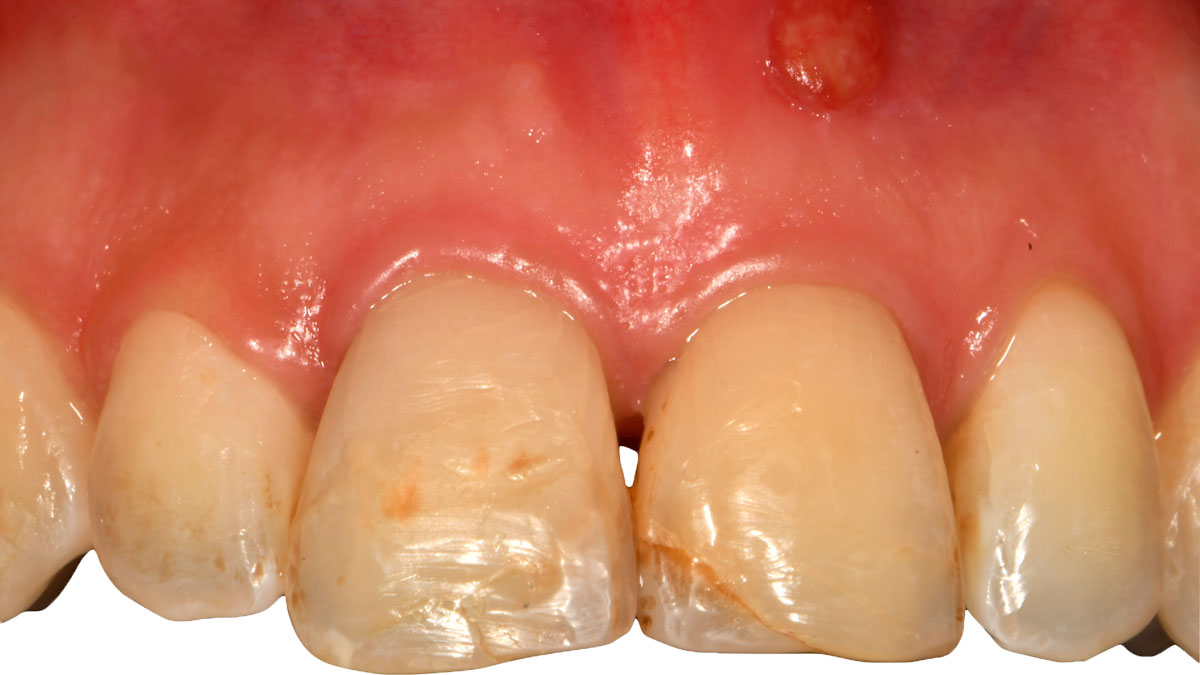
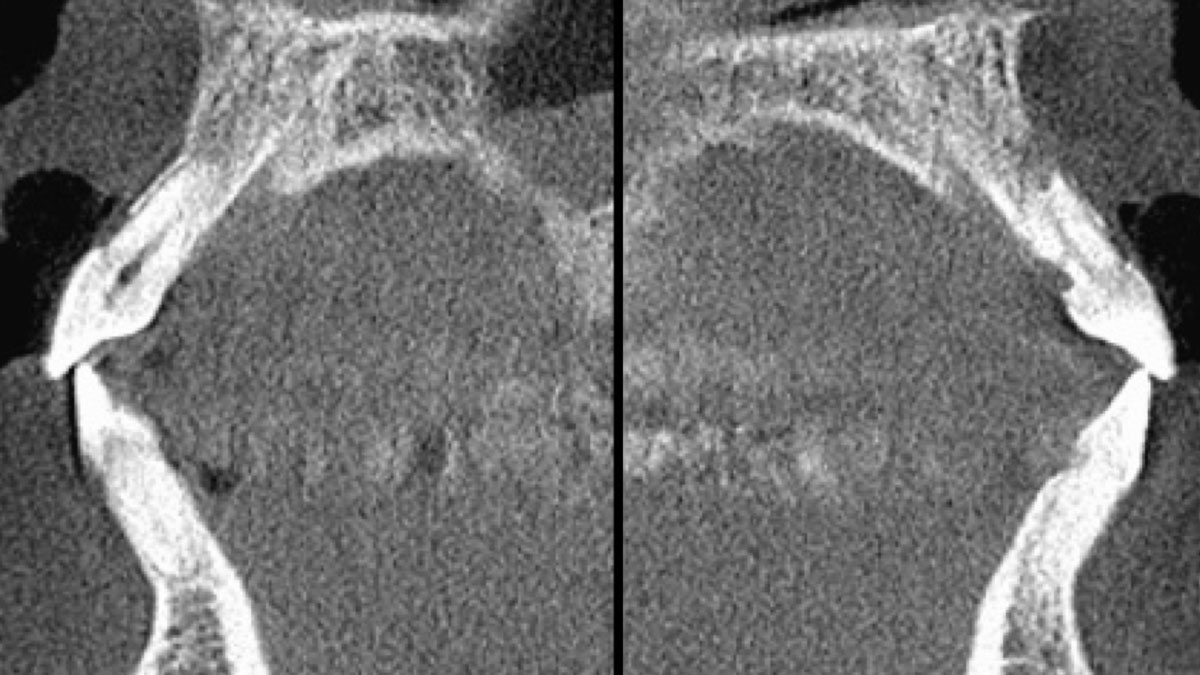
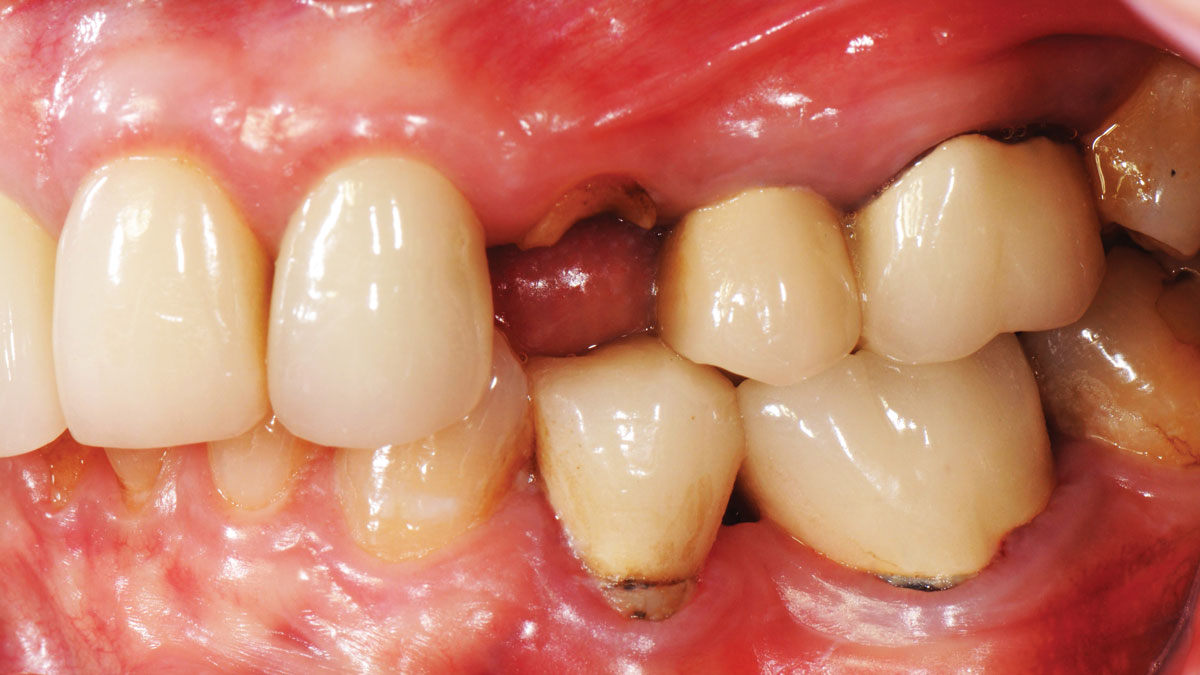
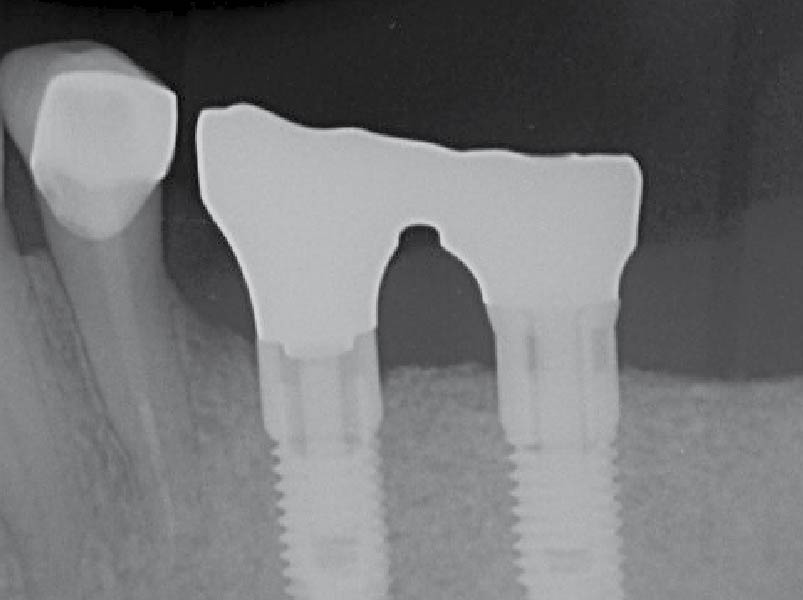
A 55-year-old man was referred to me by his general dentist. Upon initial clinical and radiographic findings, failing implant #9 showed signs of peri-implantitis that included BoP, Suppuration, 9+mm PD and radiographic bone loss affecting both the implant and the natural adjacent tooth. Patient stated that although his gums bleed, he does not have any pain. Gingival erythema was also found.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
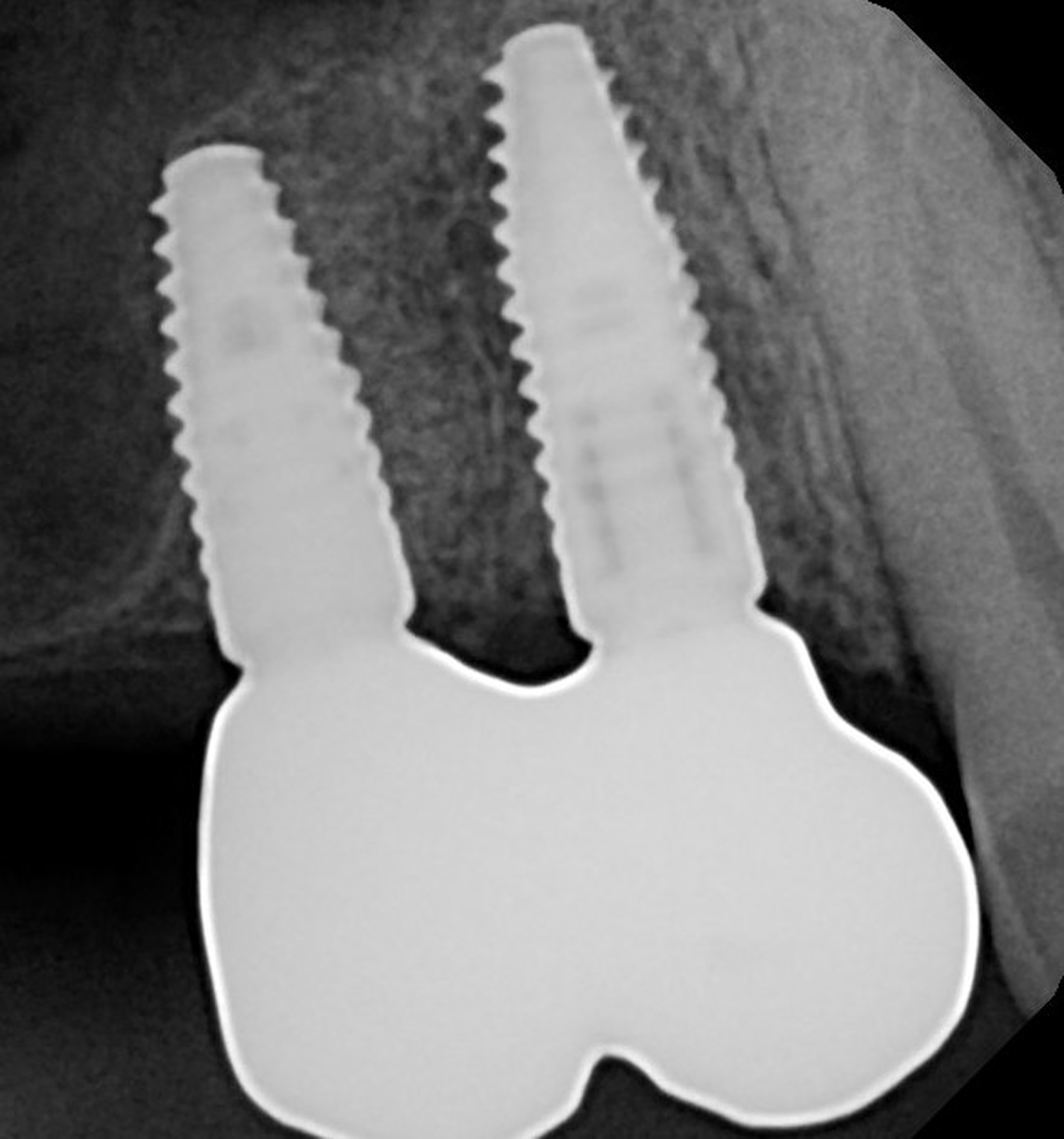
Note: Peri-implantitis on implant #9 migrating to the mesial portion of root #8
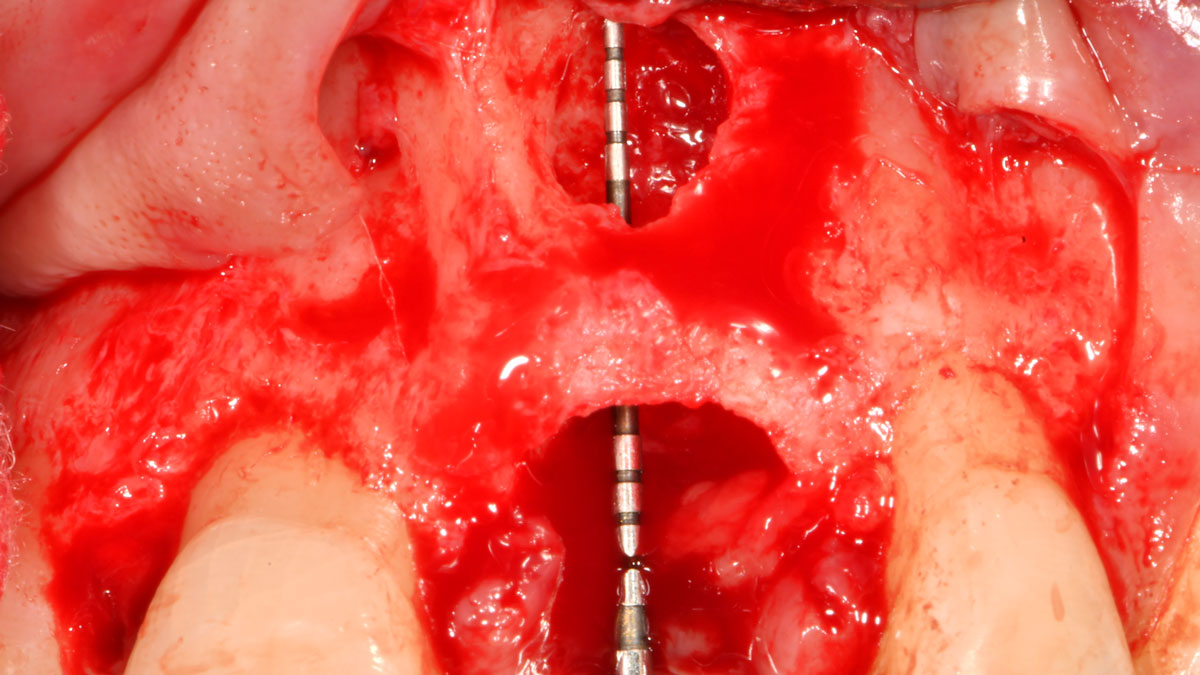
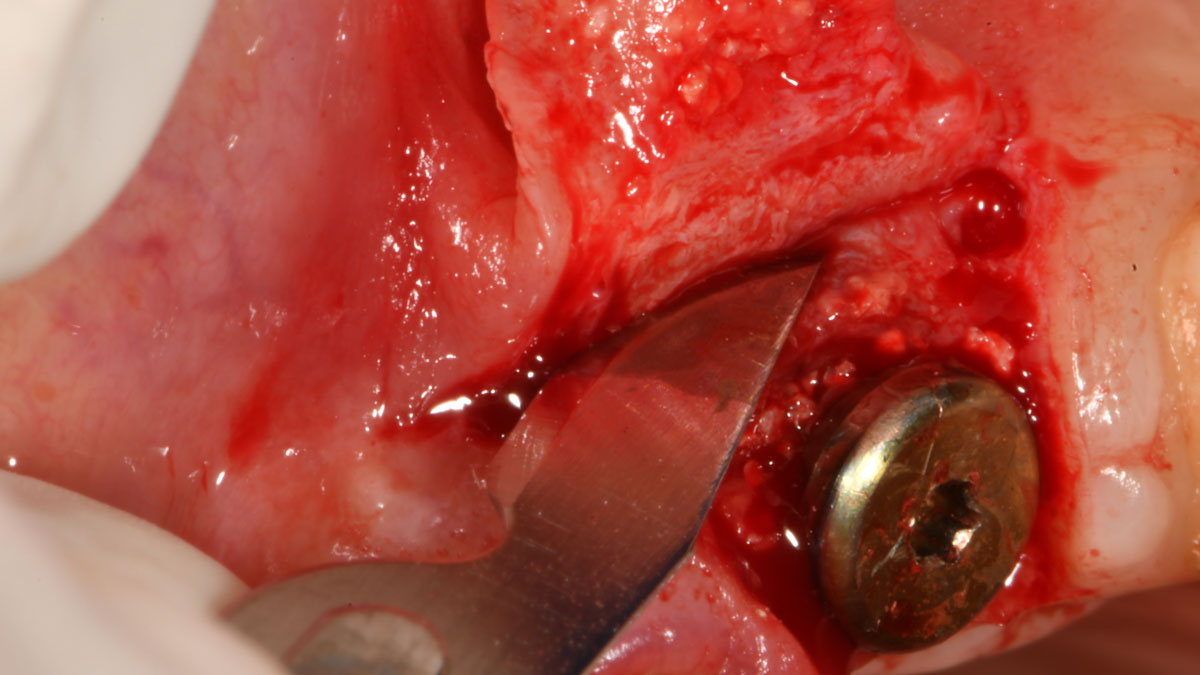
THE APPROACH
The clinical goals were to eliminate the peri-implant infection, restore hard and soft-tissues and have long-term success. The technique utilized was a systematic regenerative approach to eliminate the underlying cause of the peri-implantitis infection and restore hard and soft-tissues to prior health.
Geistlich Fibro-Gide® has the capacity to enhance the soft-tissue during a bone regenerative approach.
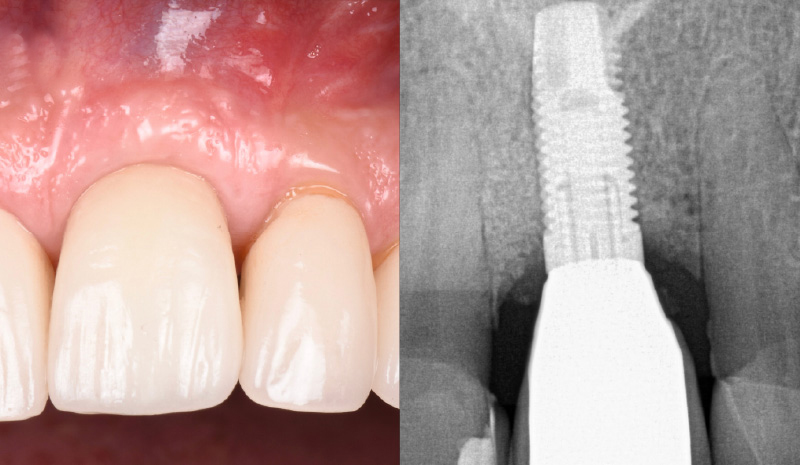
THE OUTCOME
My observation at the 1.5 year follow-up shows the elimination of peri-implantitis and complete peri-implant health was achieved showing a reduction in BOP, PD and most importantly soft tissue thickness stability. Radiographically, crestal bone shows no signs of progressive pathological loss and has maintained adequate volume.

Hector L. Sarmiento, D.M.D., MSc.
Dr. Hector Sarmiento was awarded his D.M.D. degree by the University of Rochester. He is uniquely trained in both maxillofacial surgery and periodontics. He is a professor in the maxillofacial surgery department of trauma and reconstructive unit at the Regional Hospital in Mexico and is an Assistant Clinical Professor in periodontics at the University of Pennsylvania. Along with his periodontal degree, he also received his masters in oral biology from the University of Pennsylvania. Dr. Sarmiento is an international and national lecturer and has published numerous articles in peer reviewed journals and textbooks. His research focus includes infected dental implants such as peri-implantitis, sinus complications as well as bone biology. Dr. Sarmiento maintains his private practice in the upper east side of Manhattan in NYC.

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE