BIOBRIEF
Prosthetic-Surgical Approach to Regenerative Treatment for Peri-Implantitis


THE SITUATION
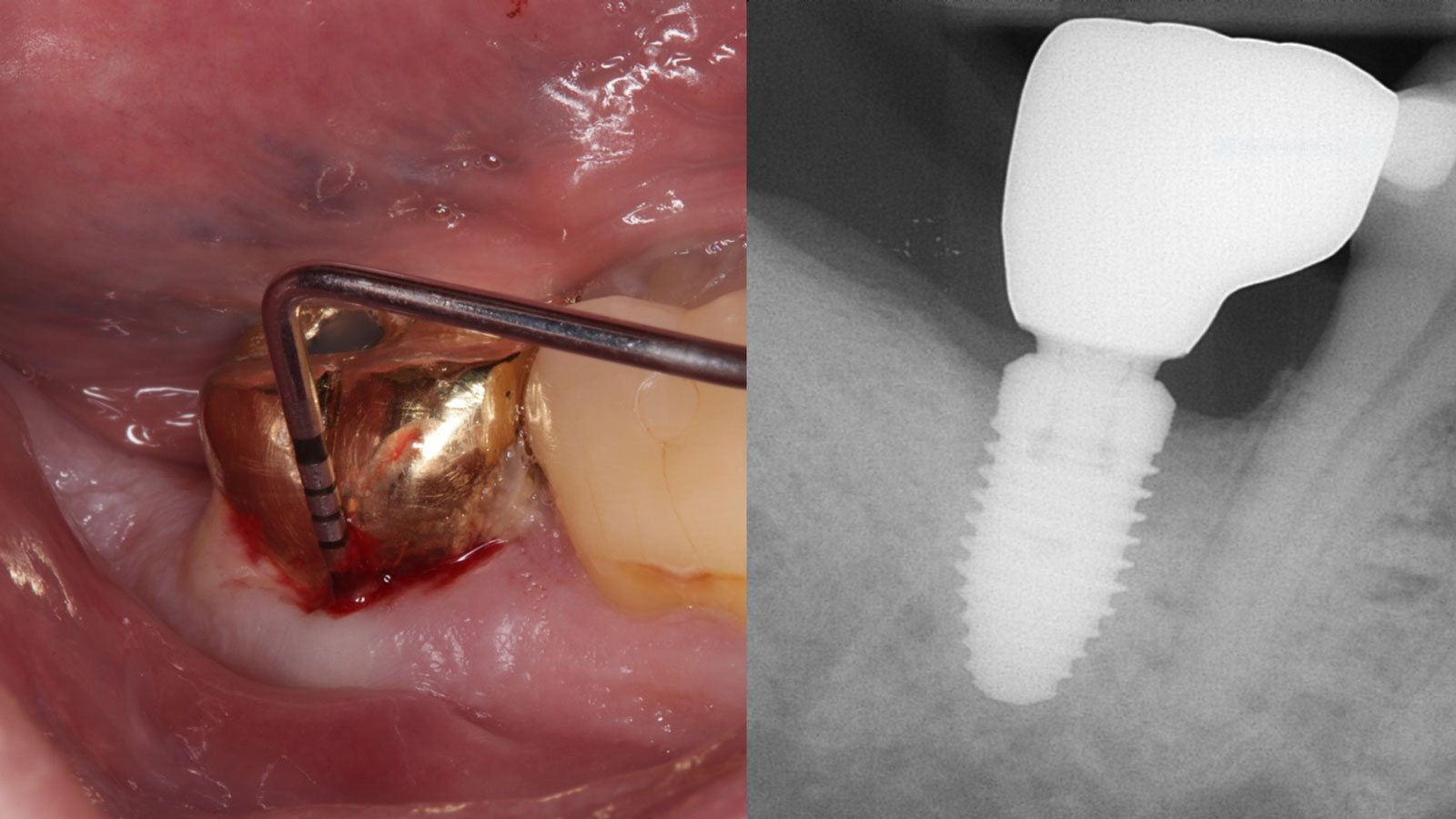
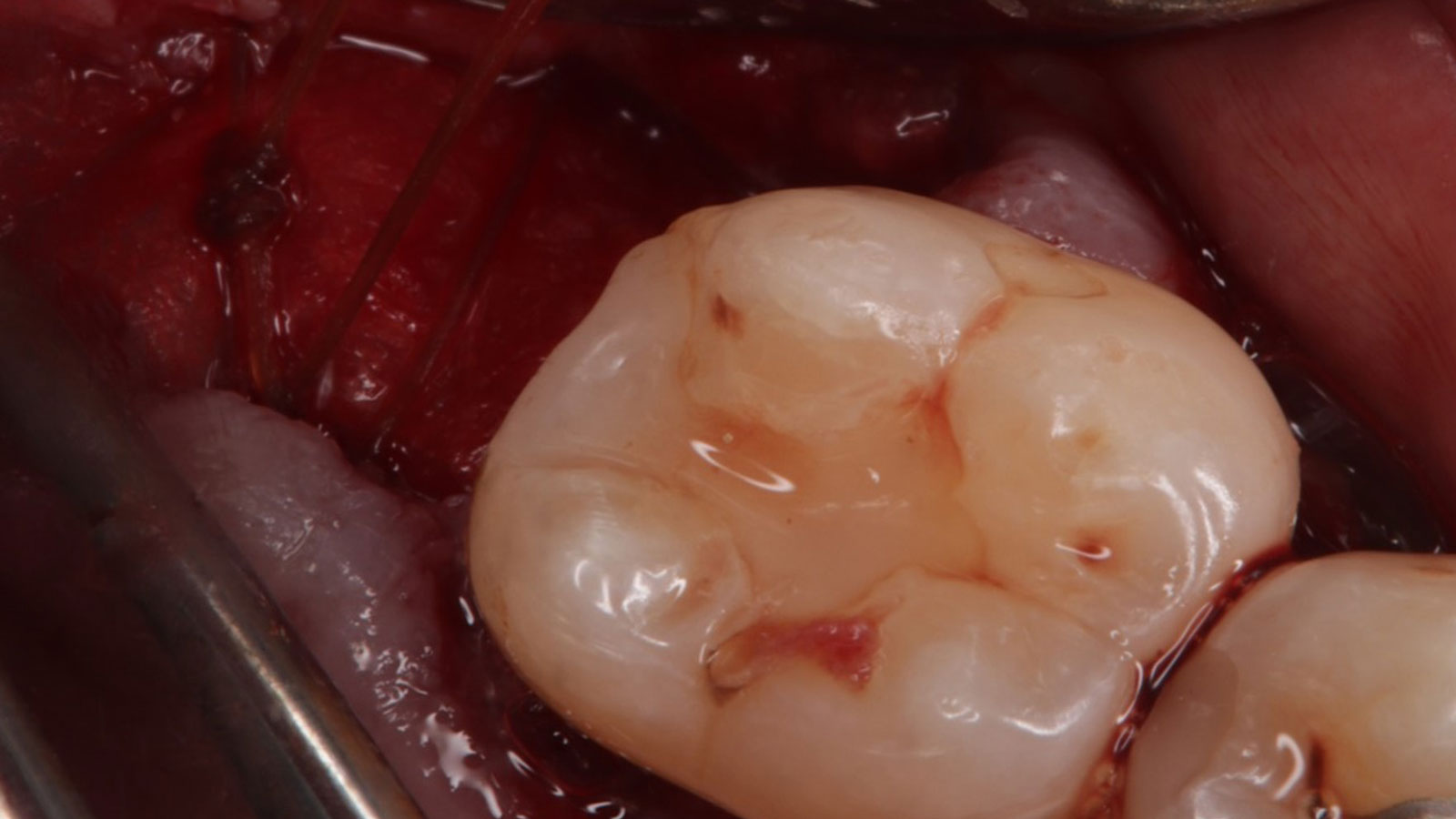
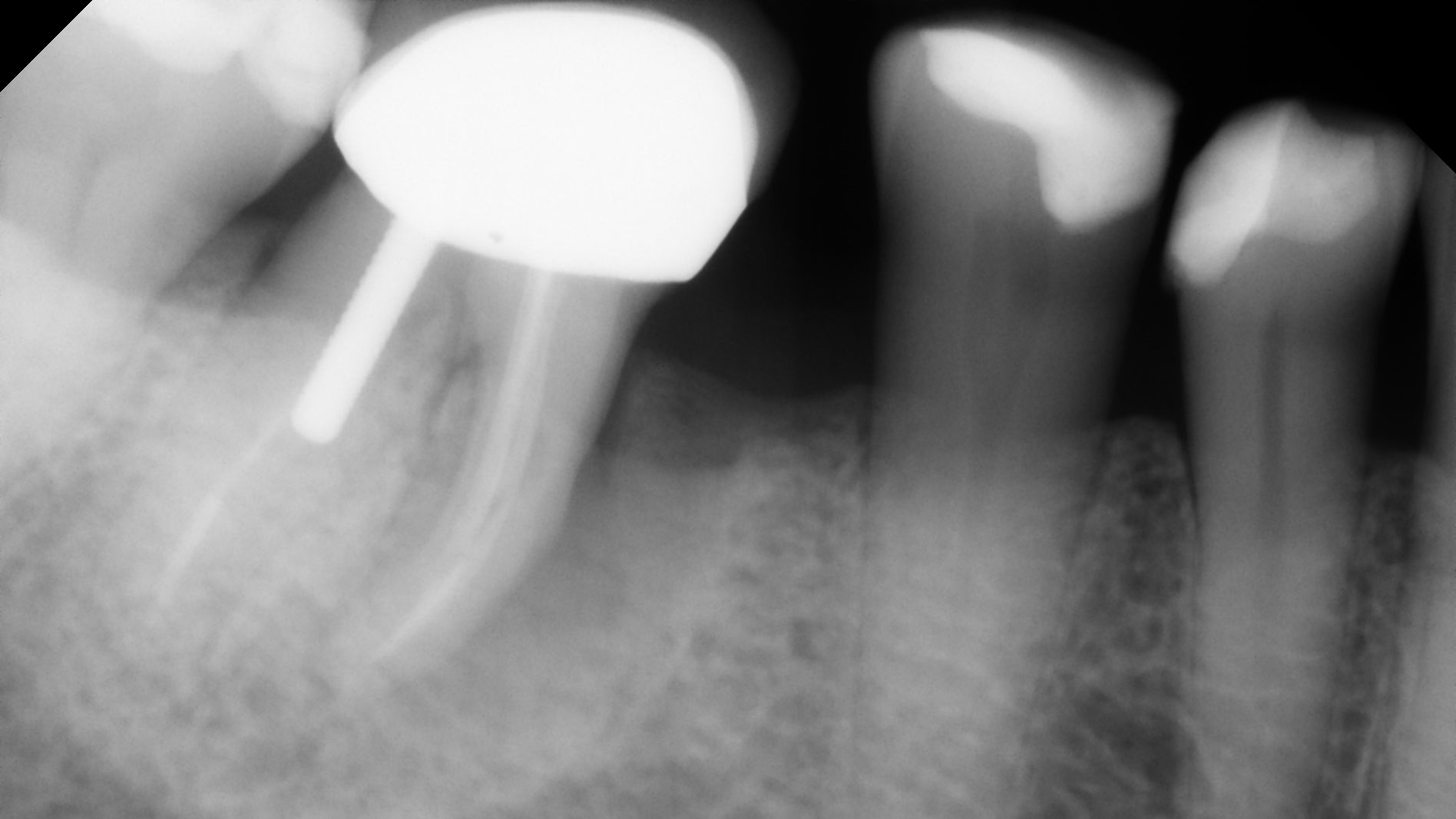
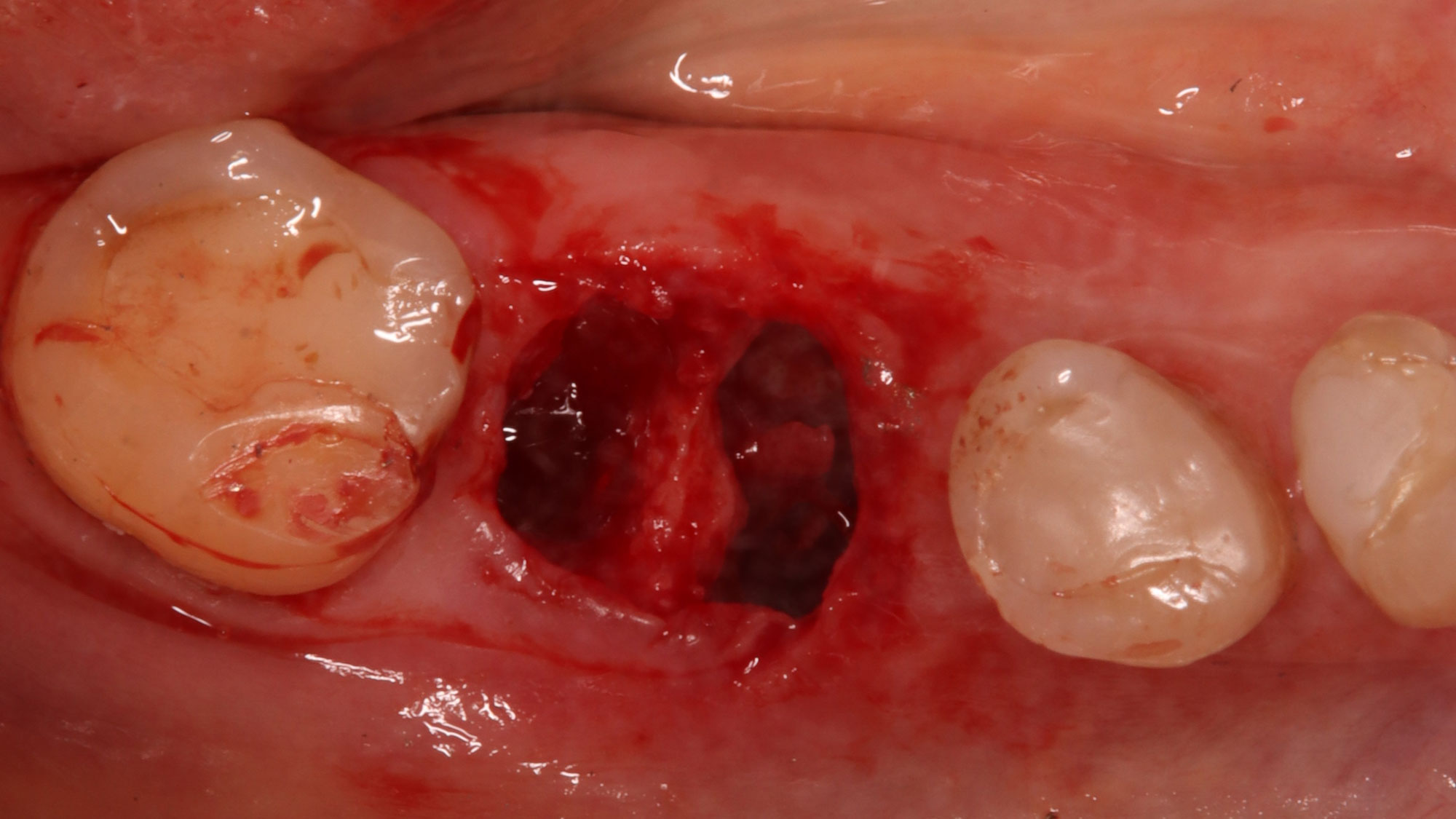
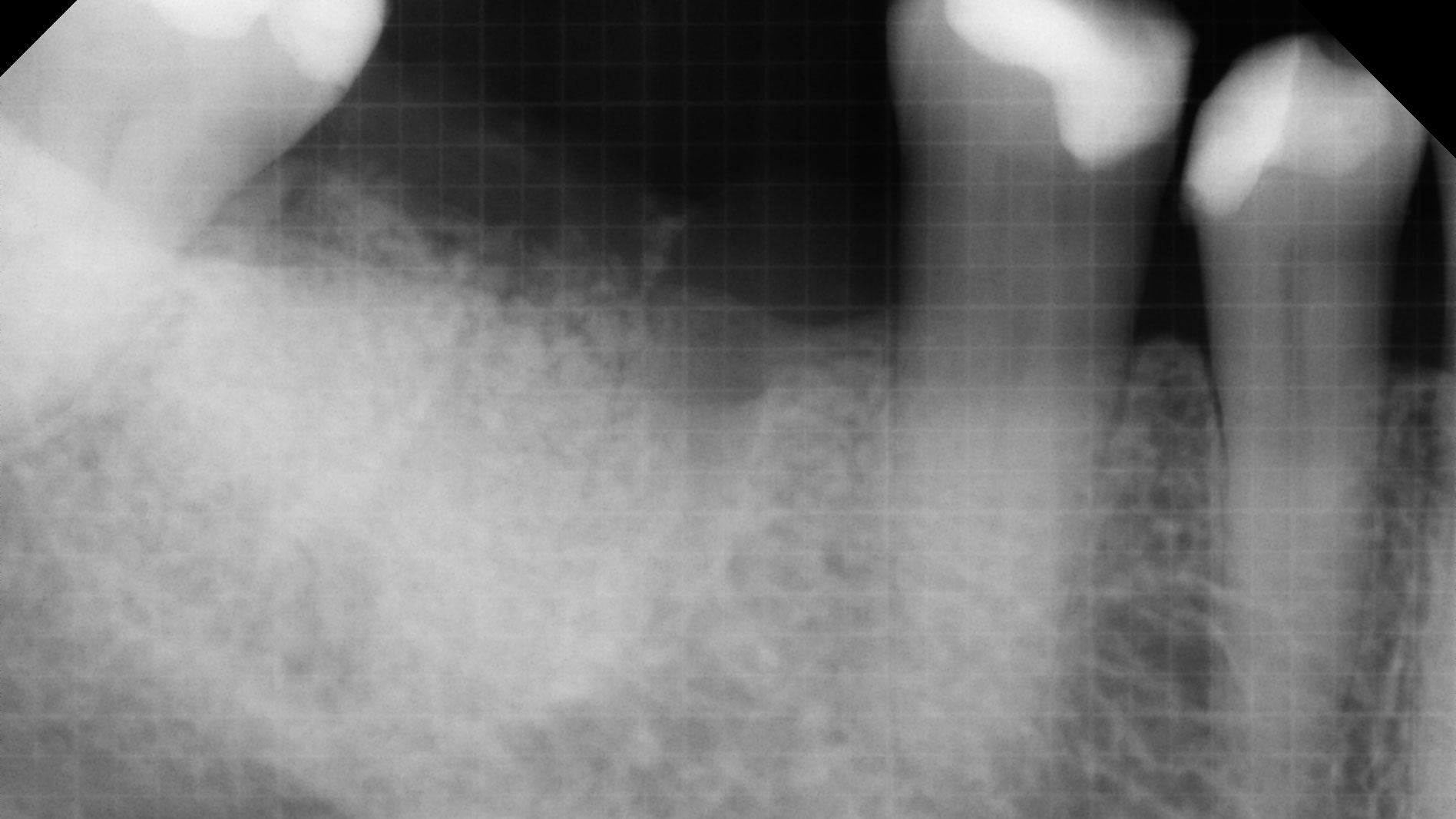
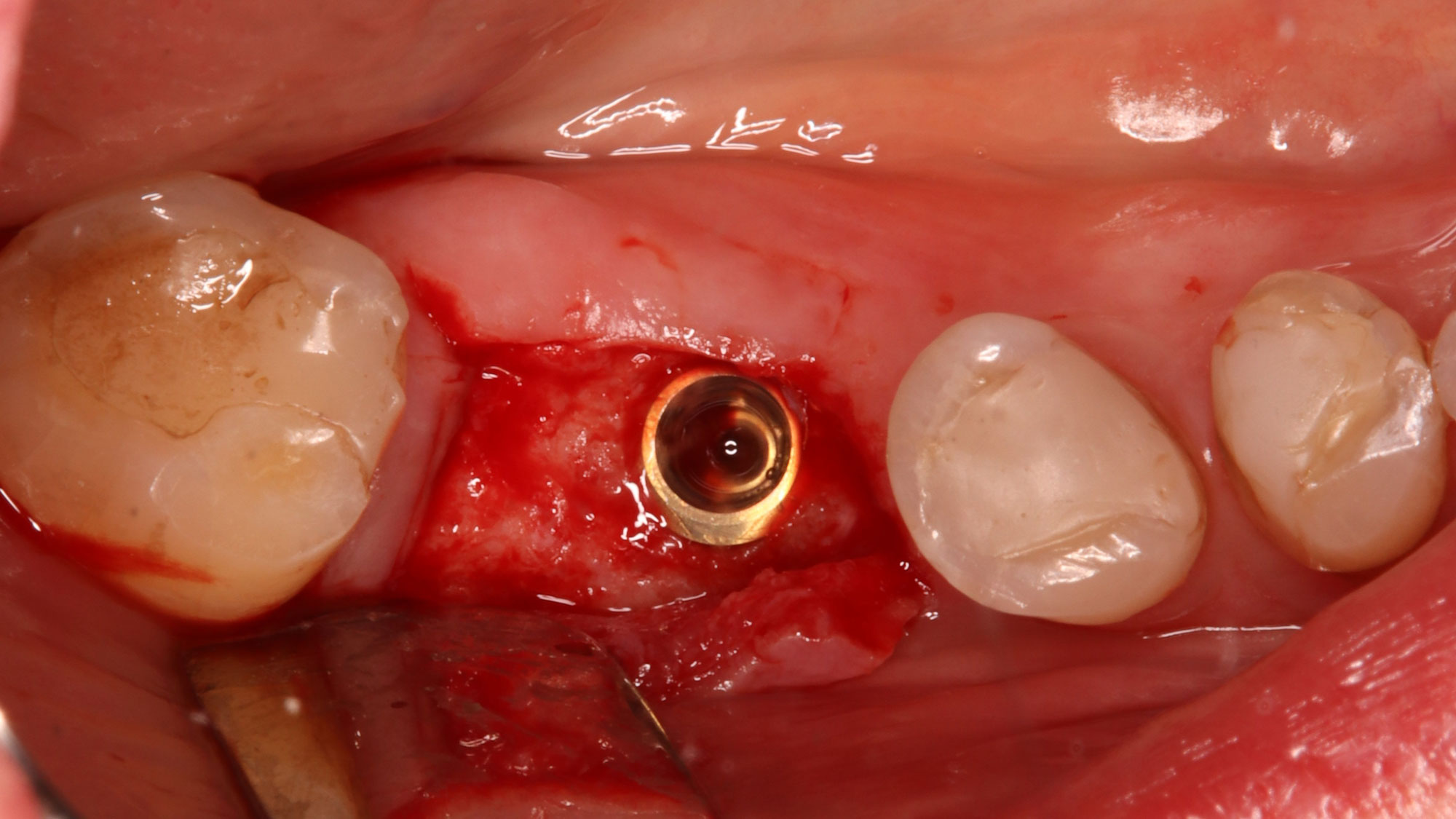
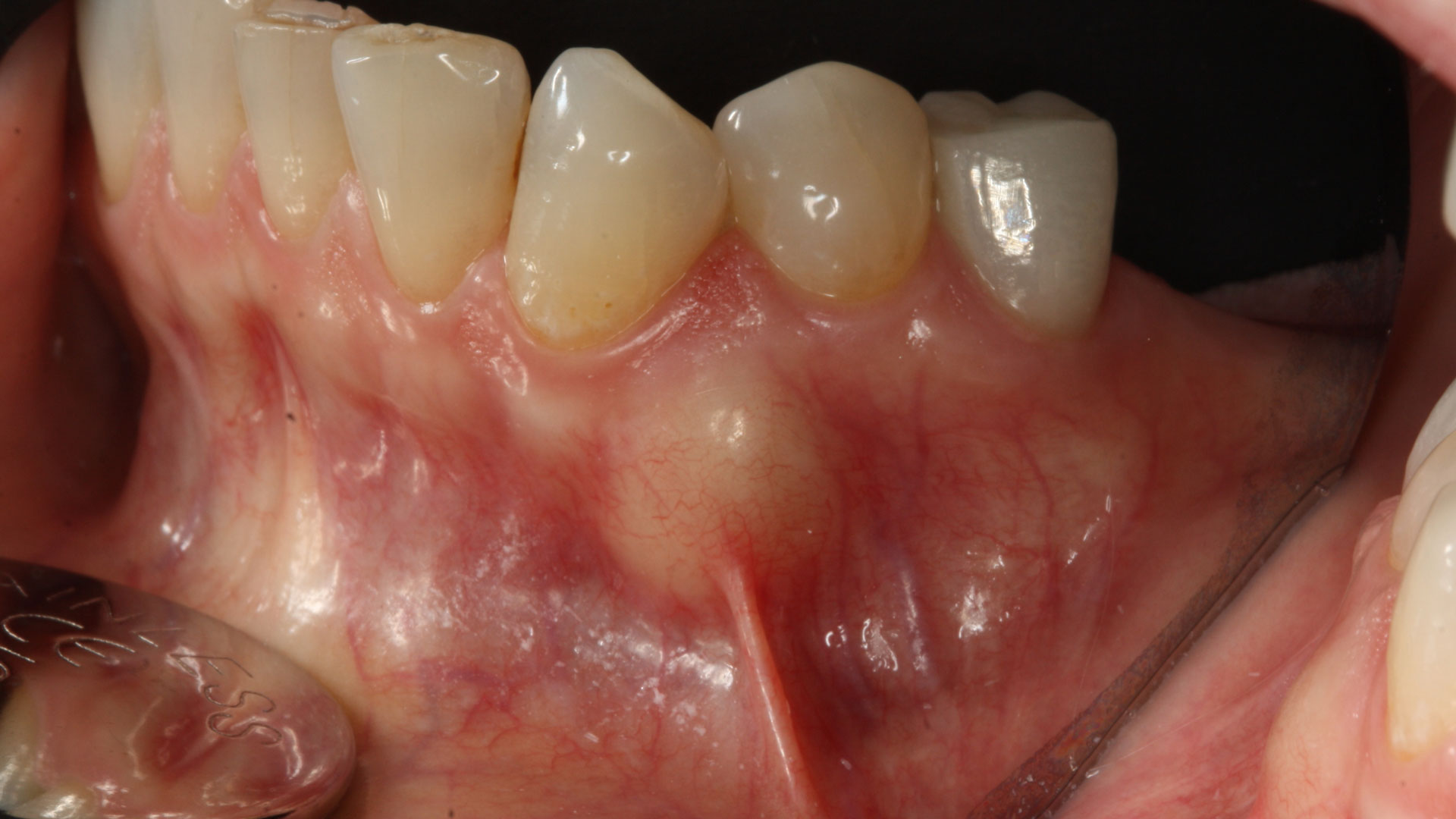
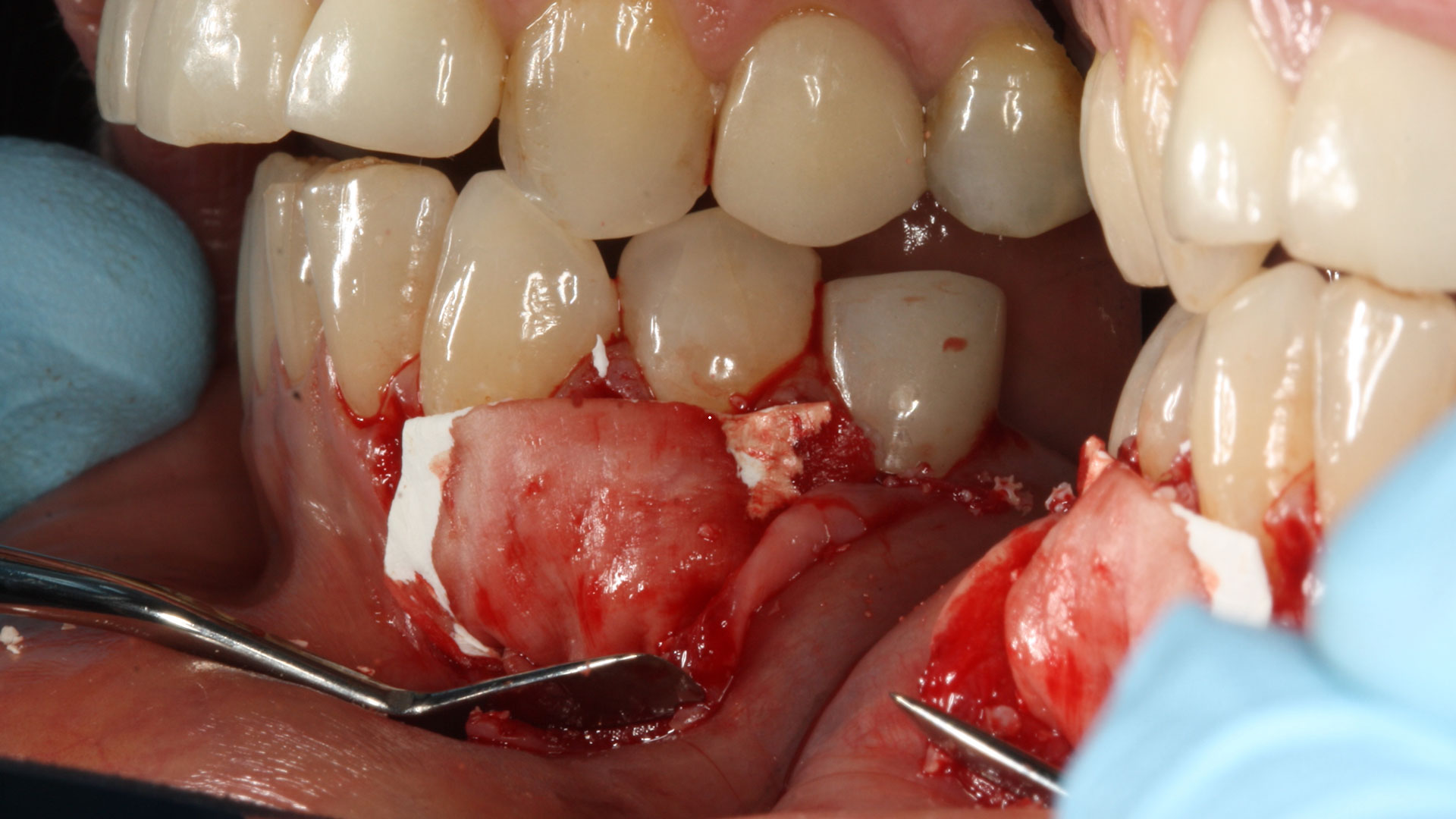
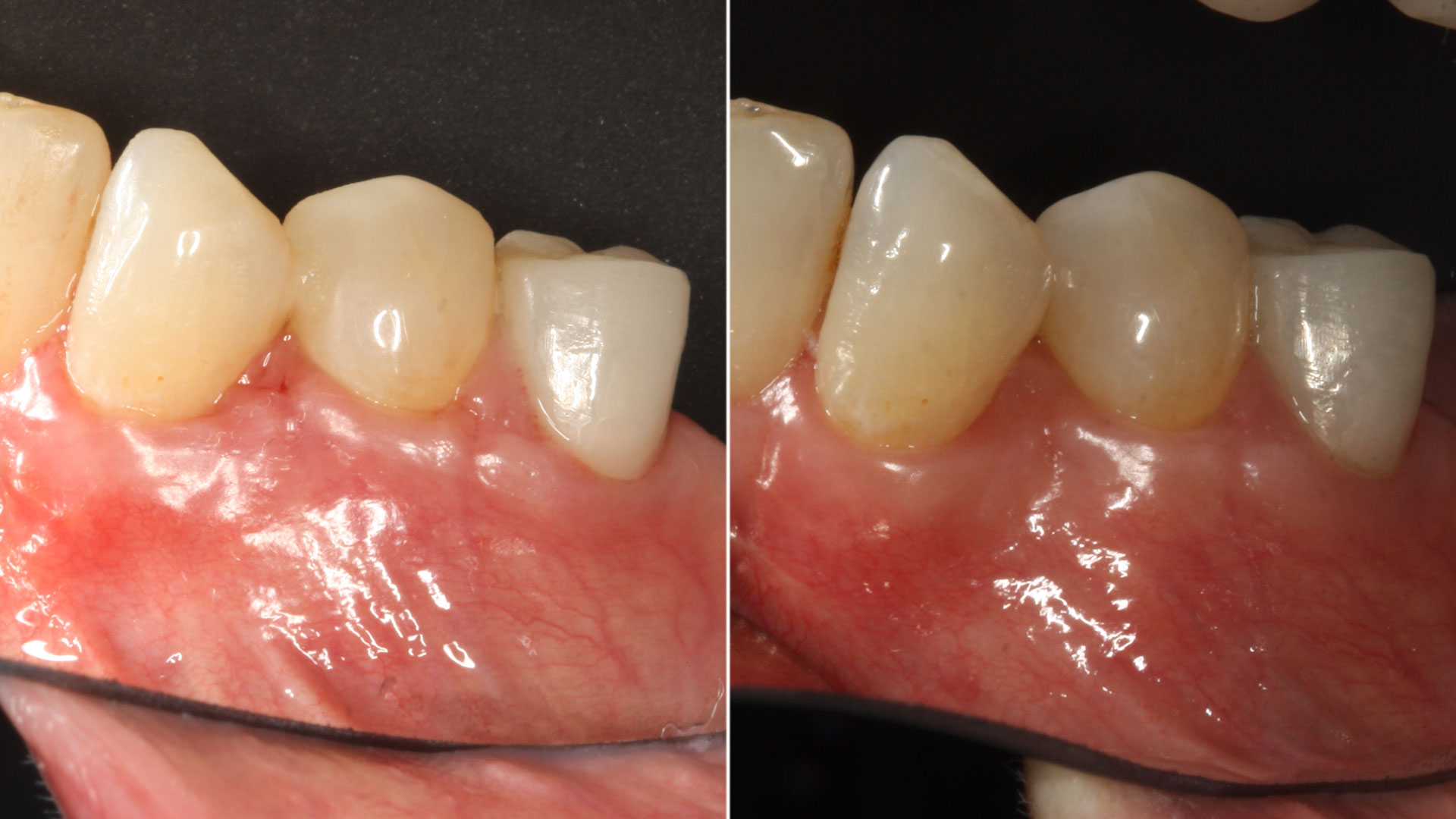
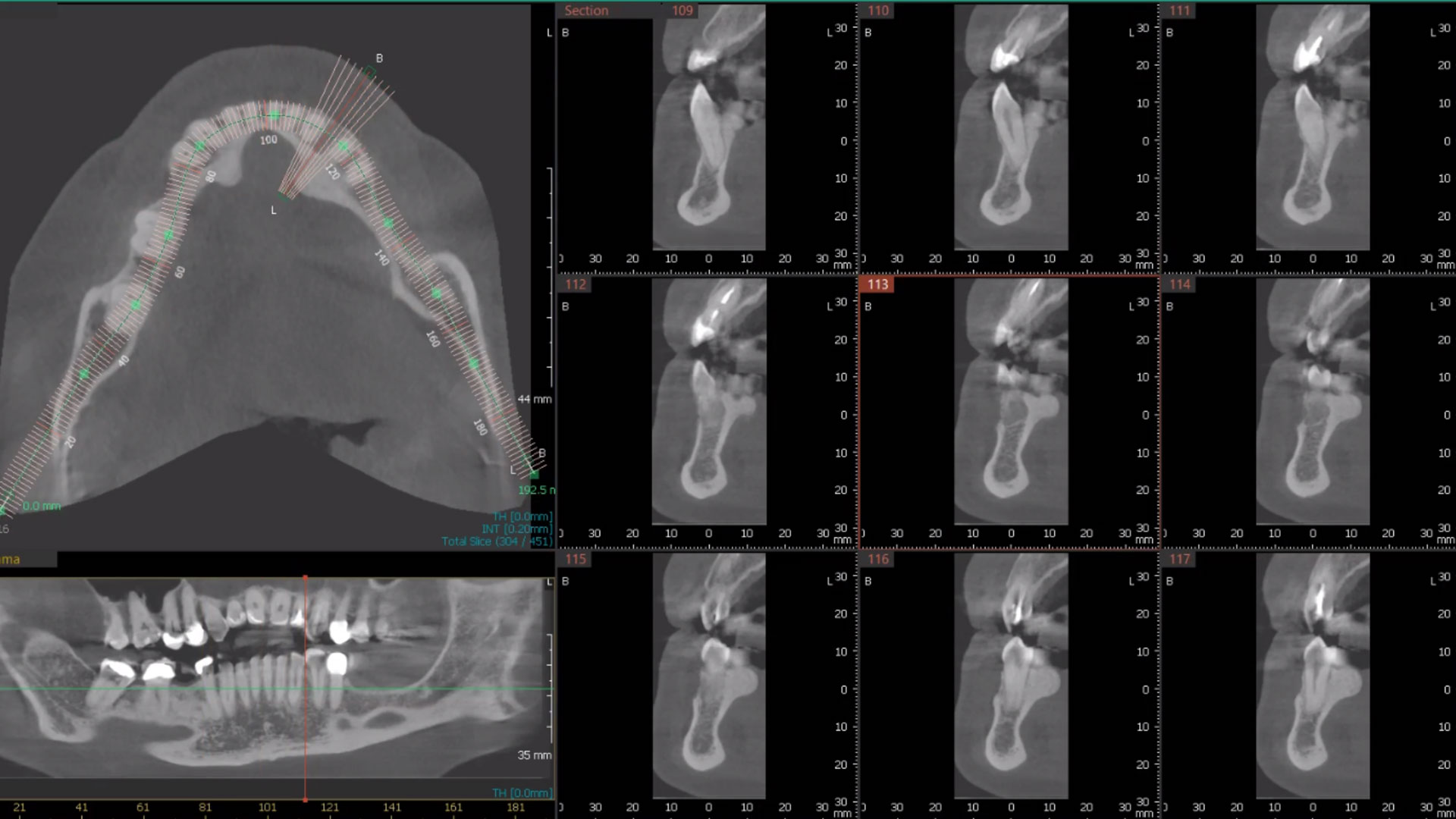
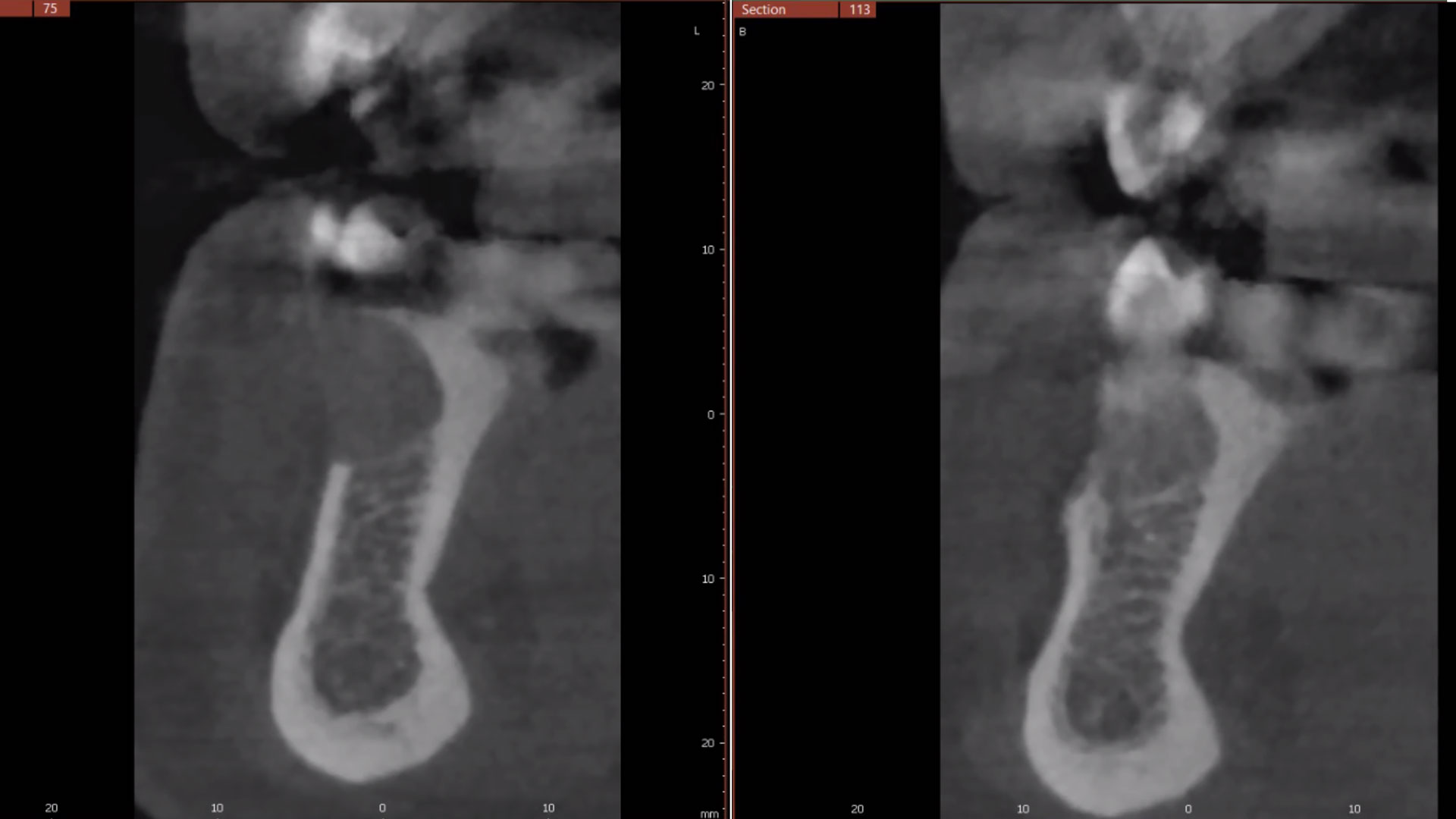
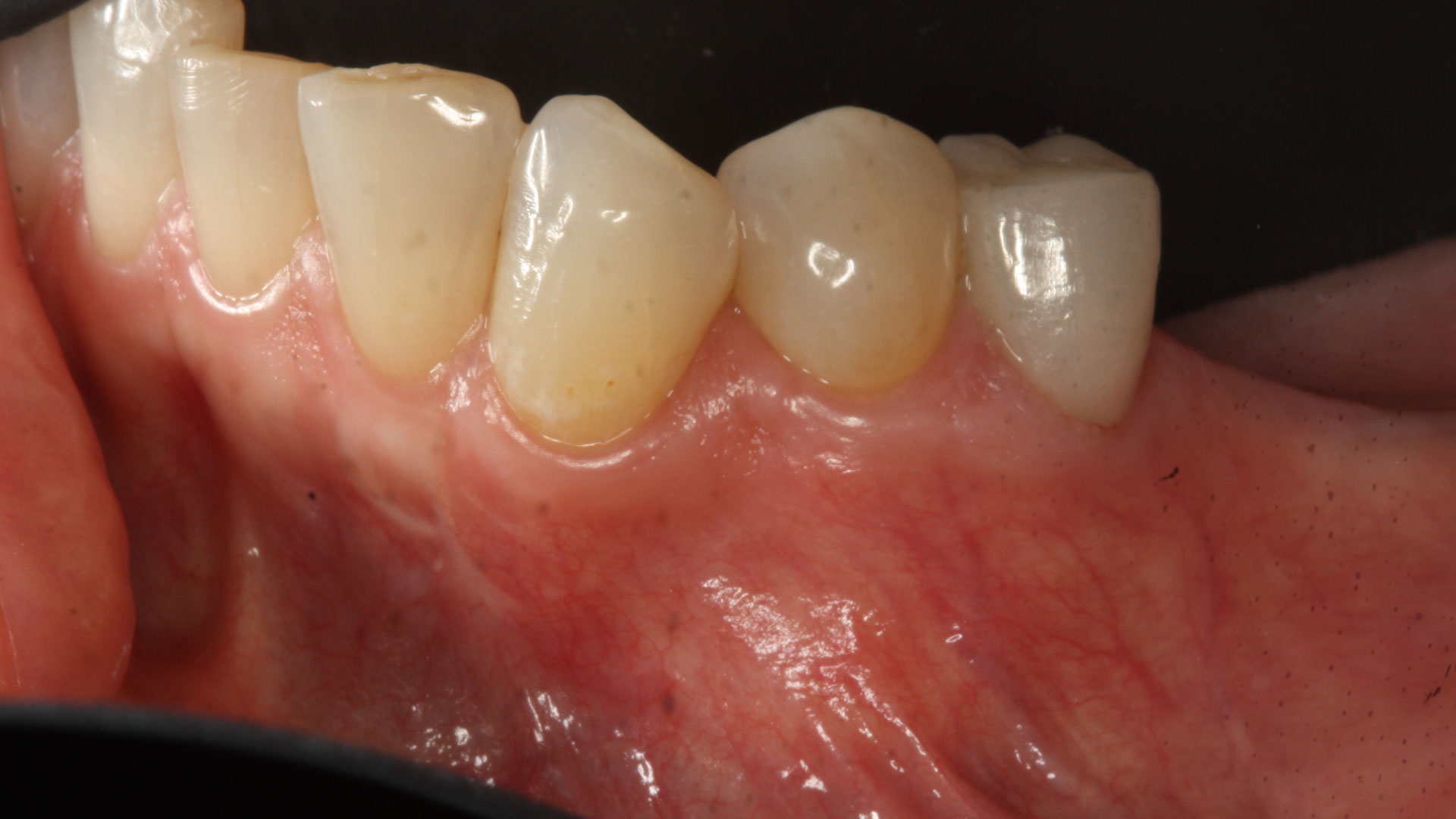
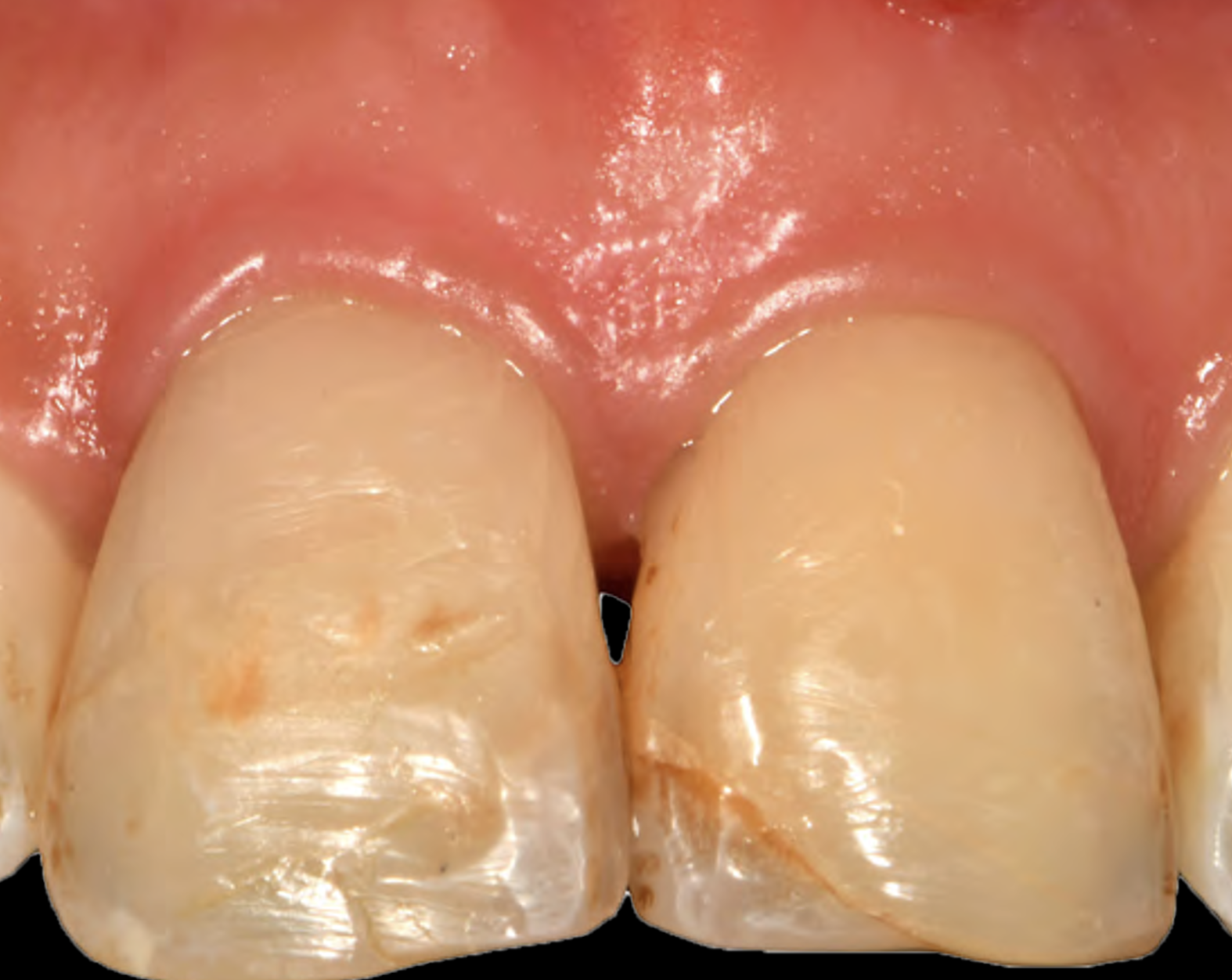
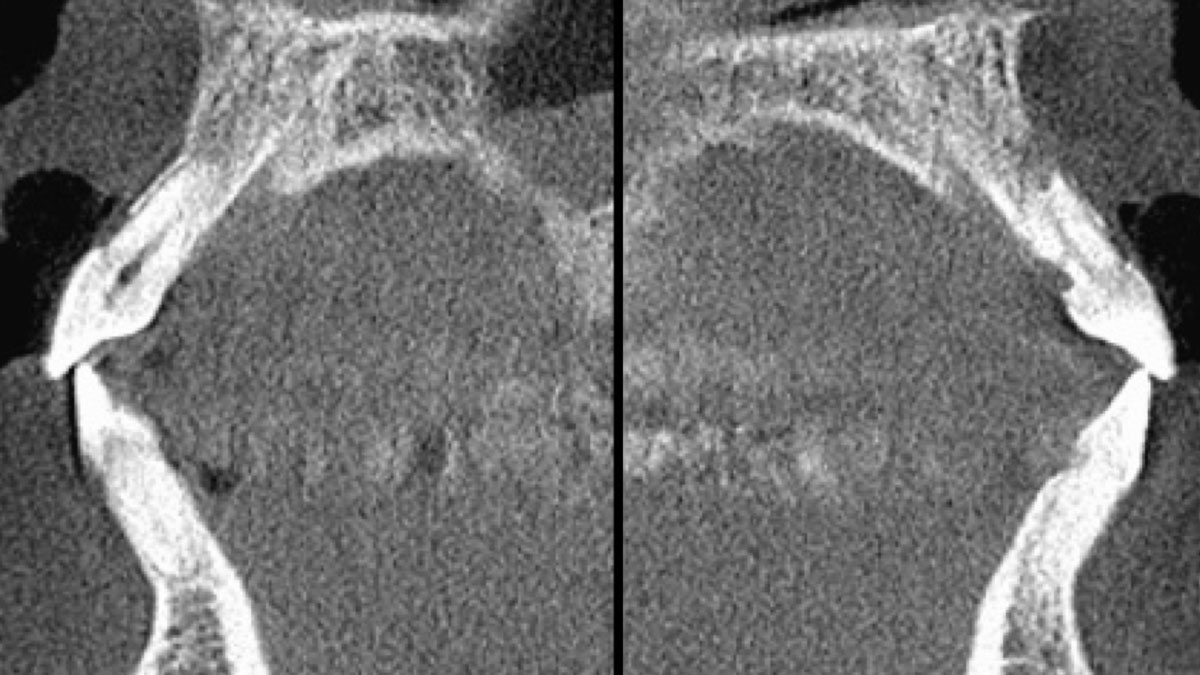
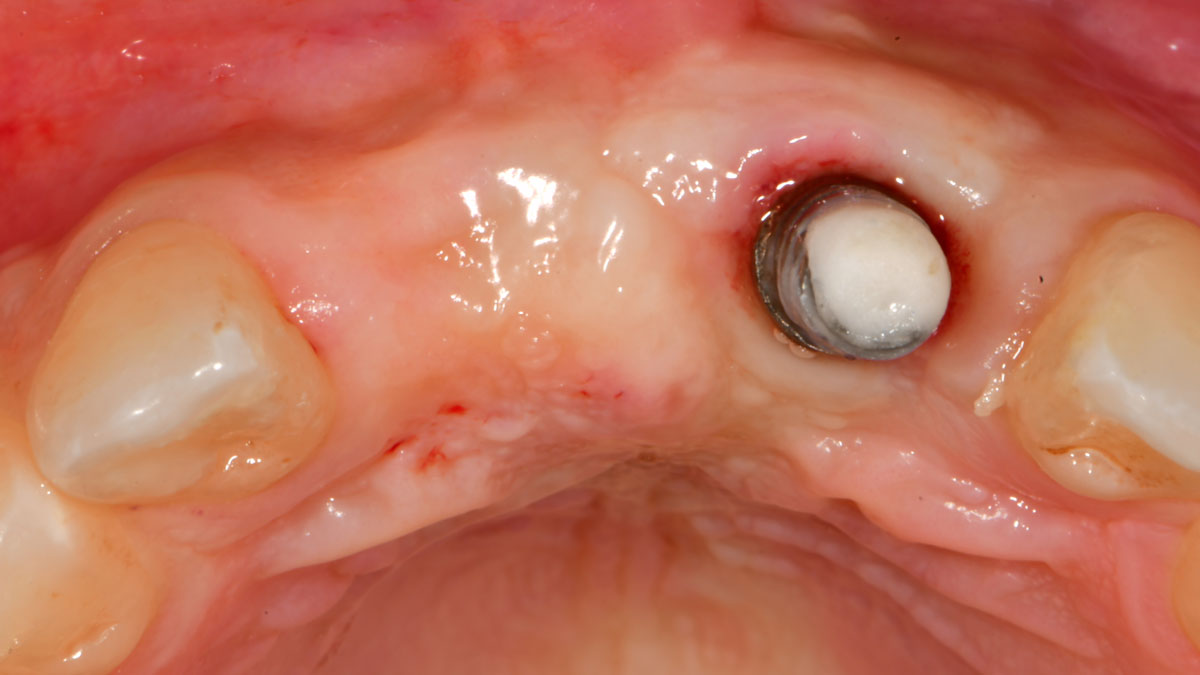
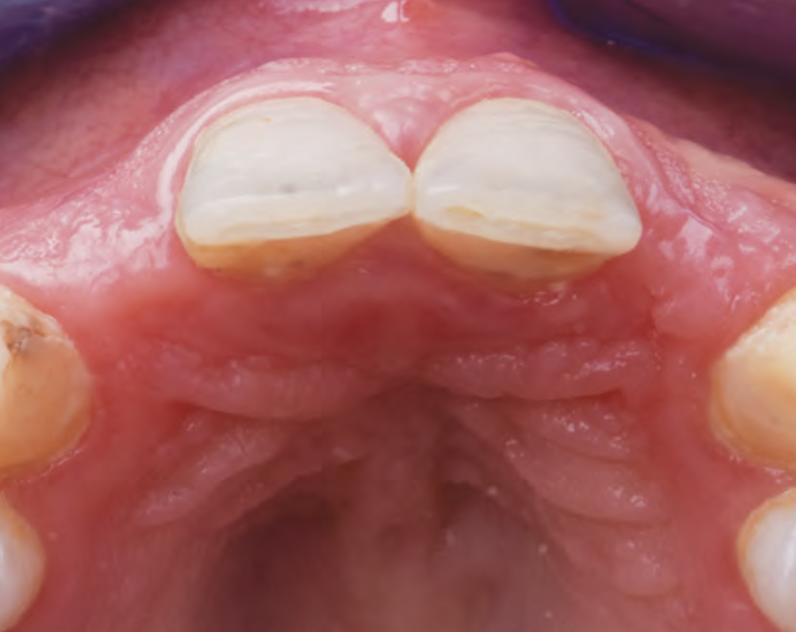
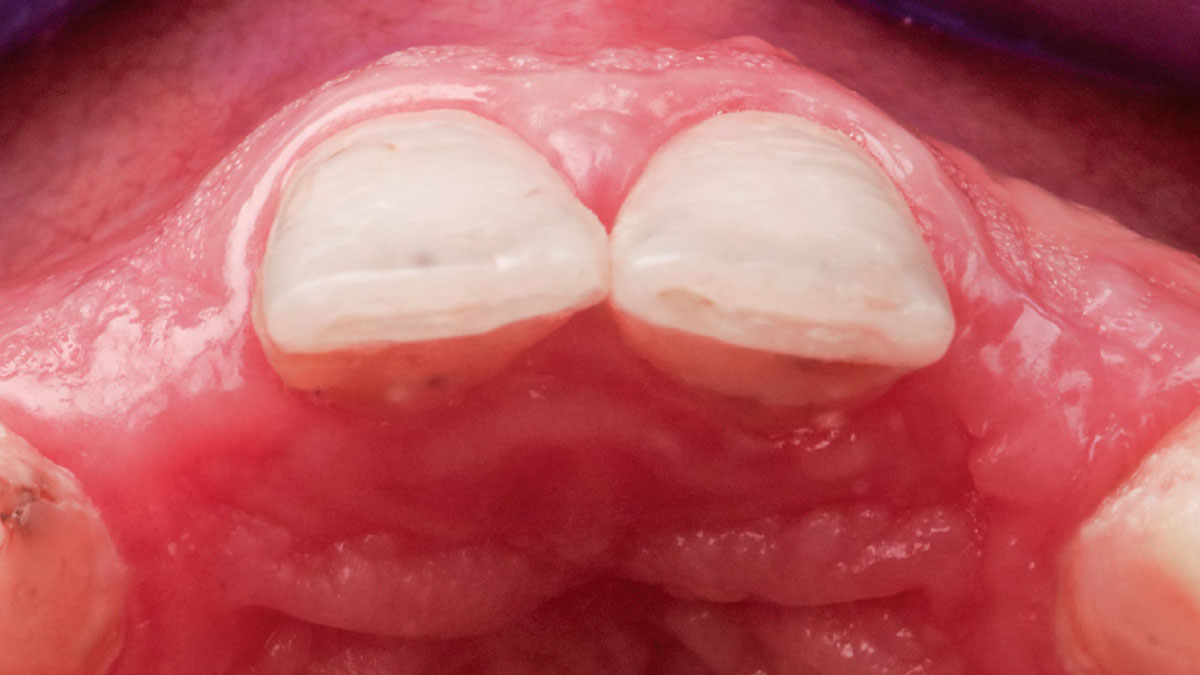
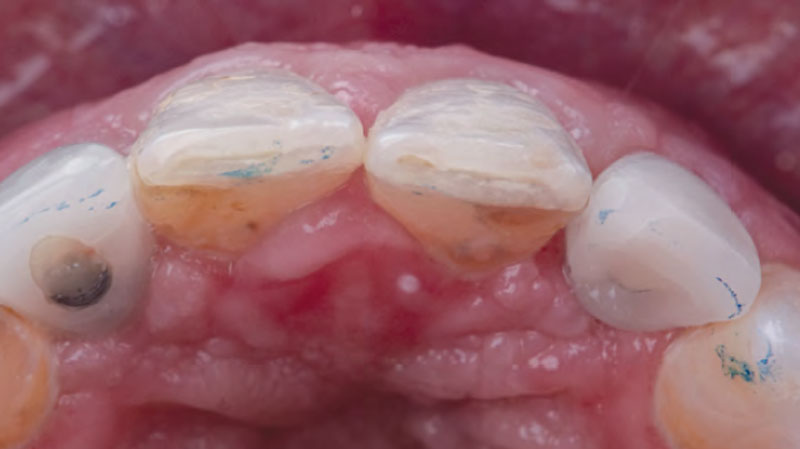
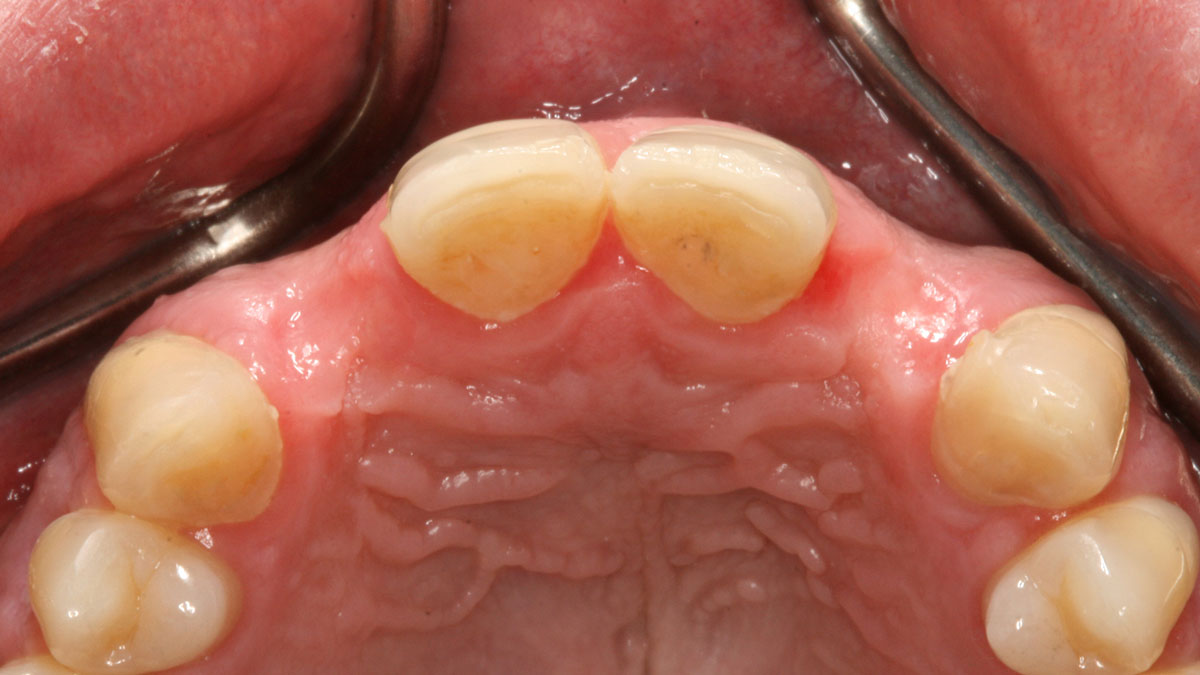
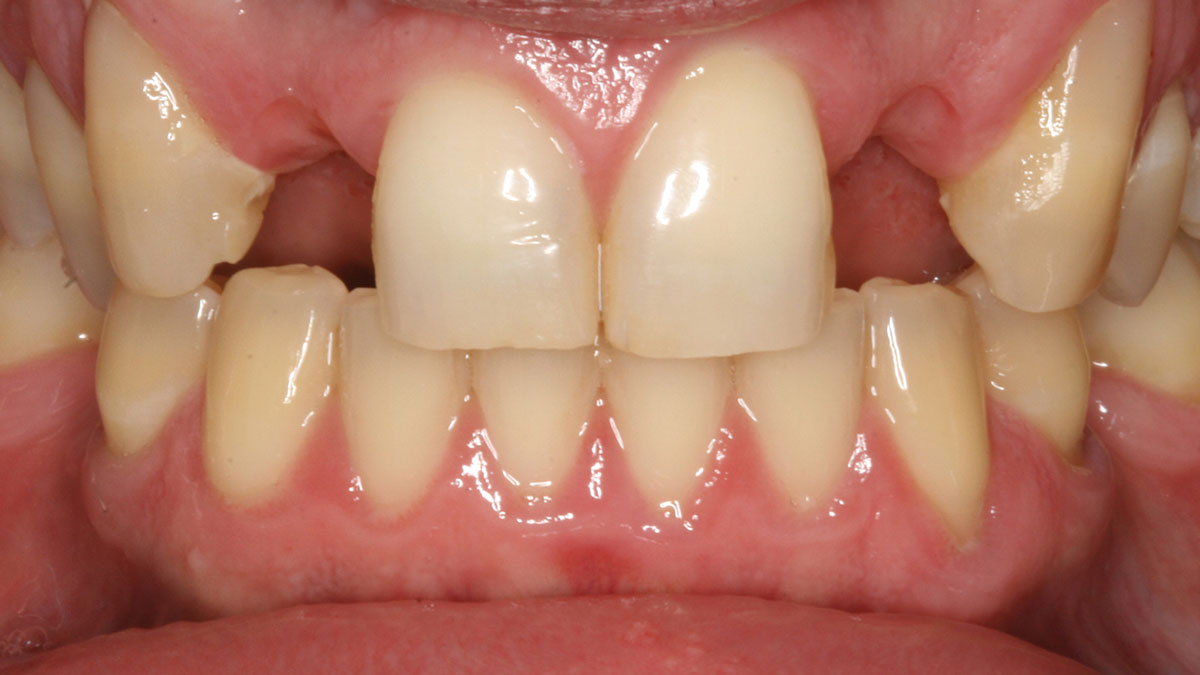
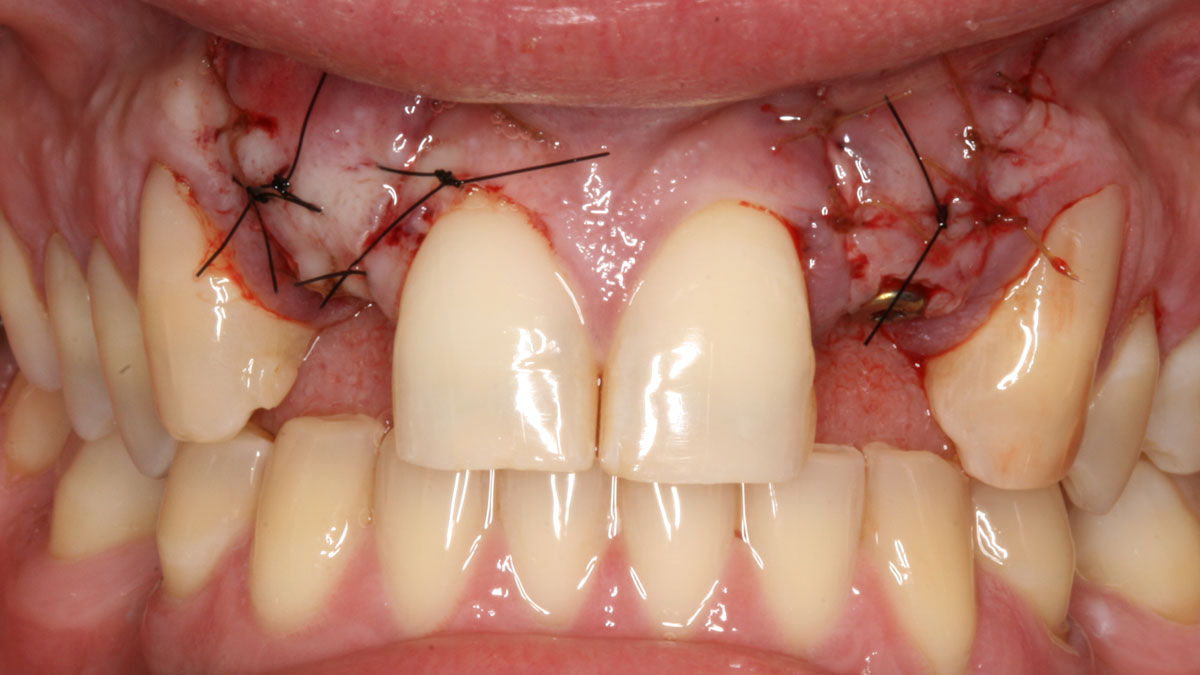
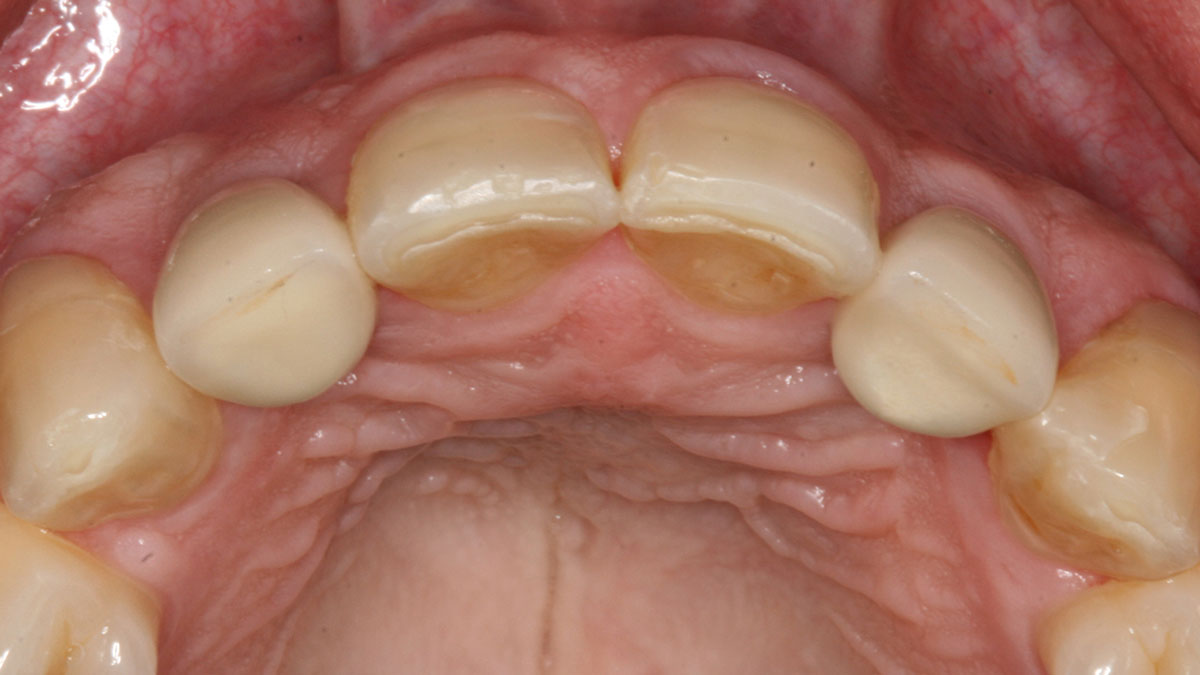
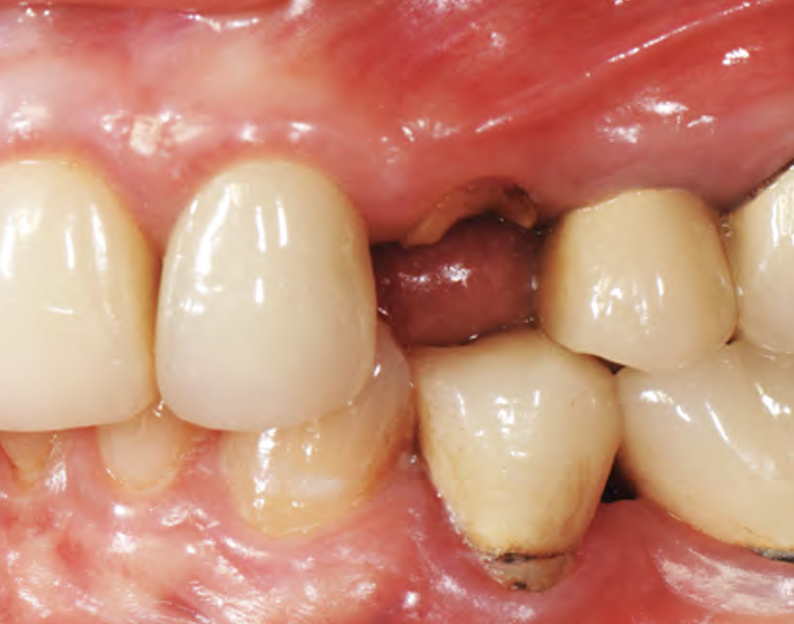
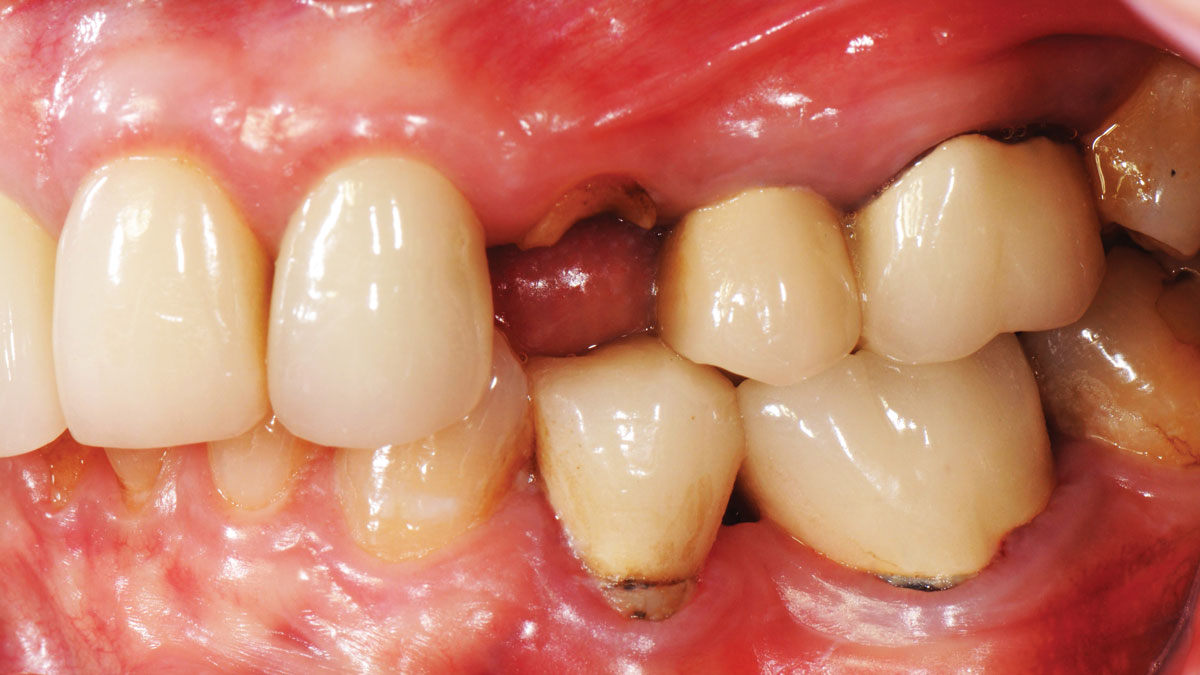
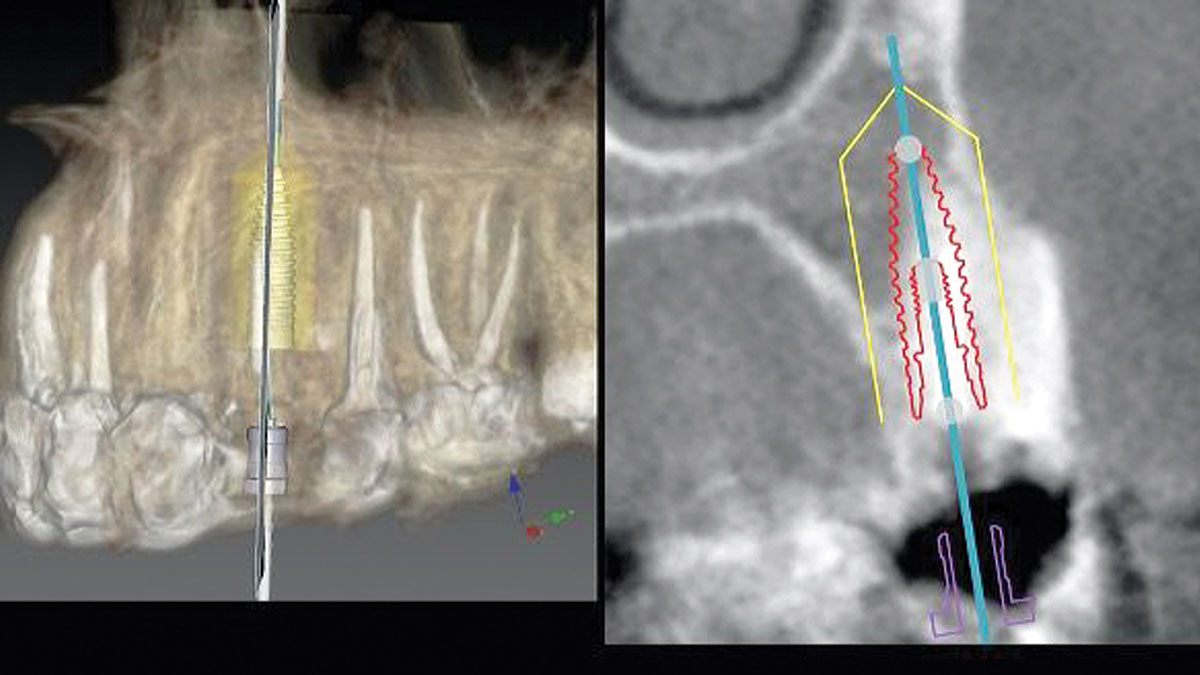
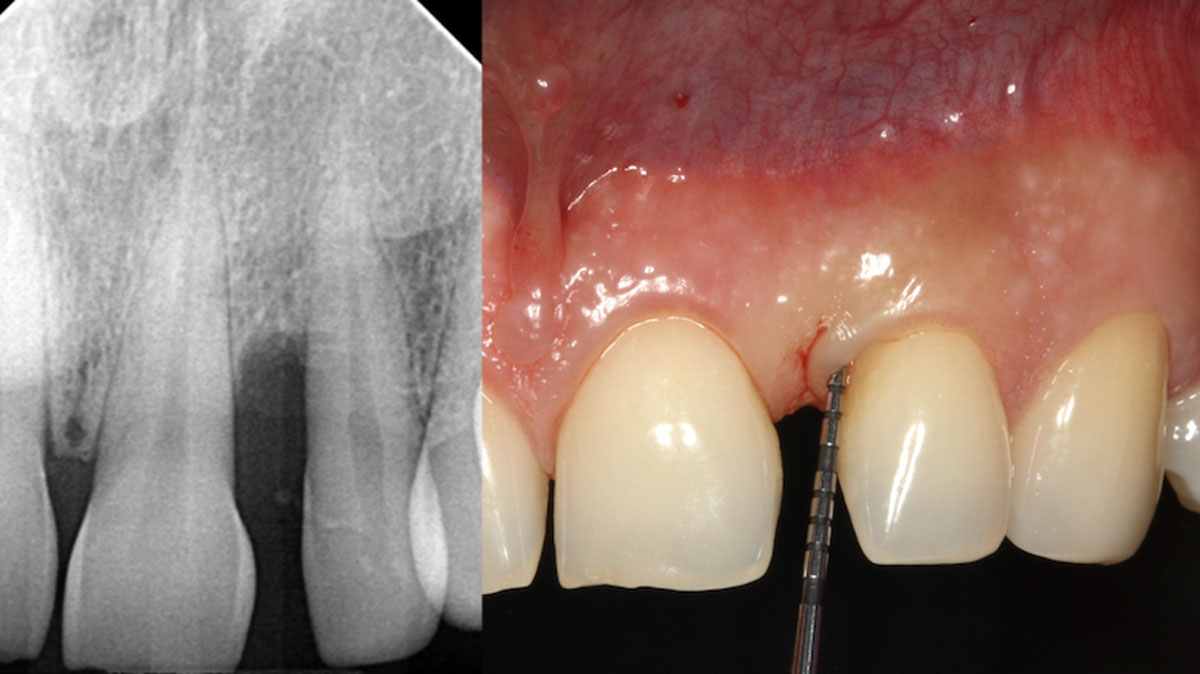
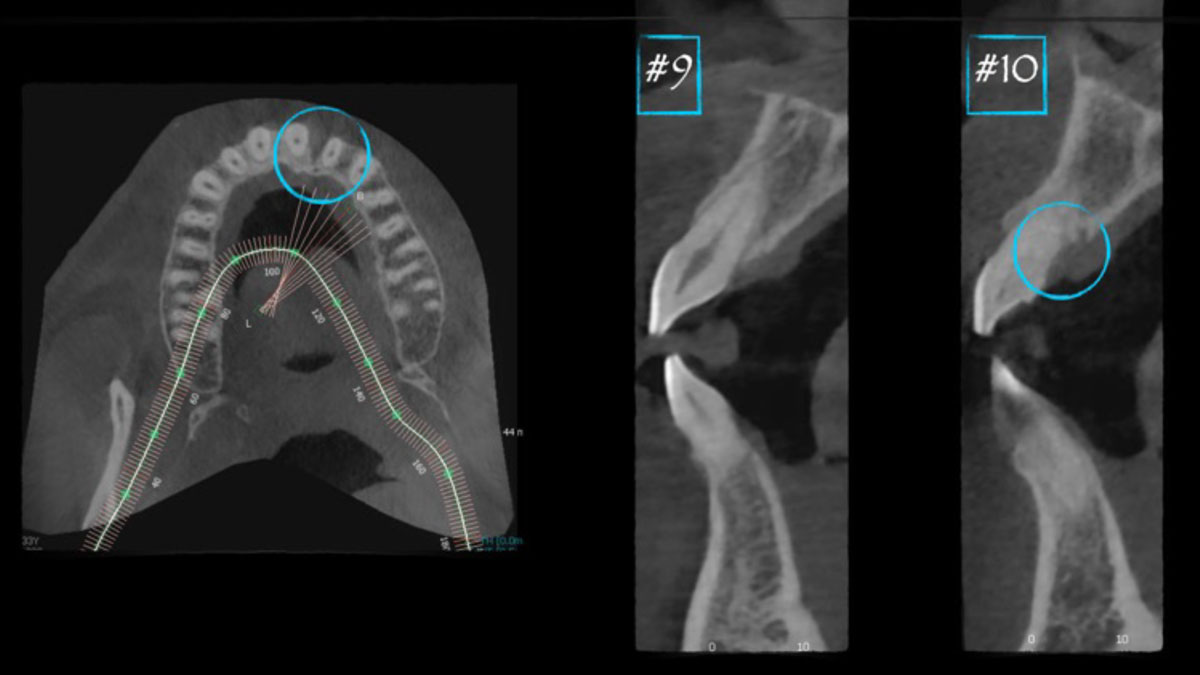
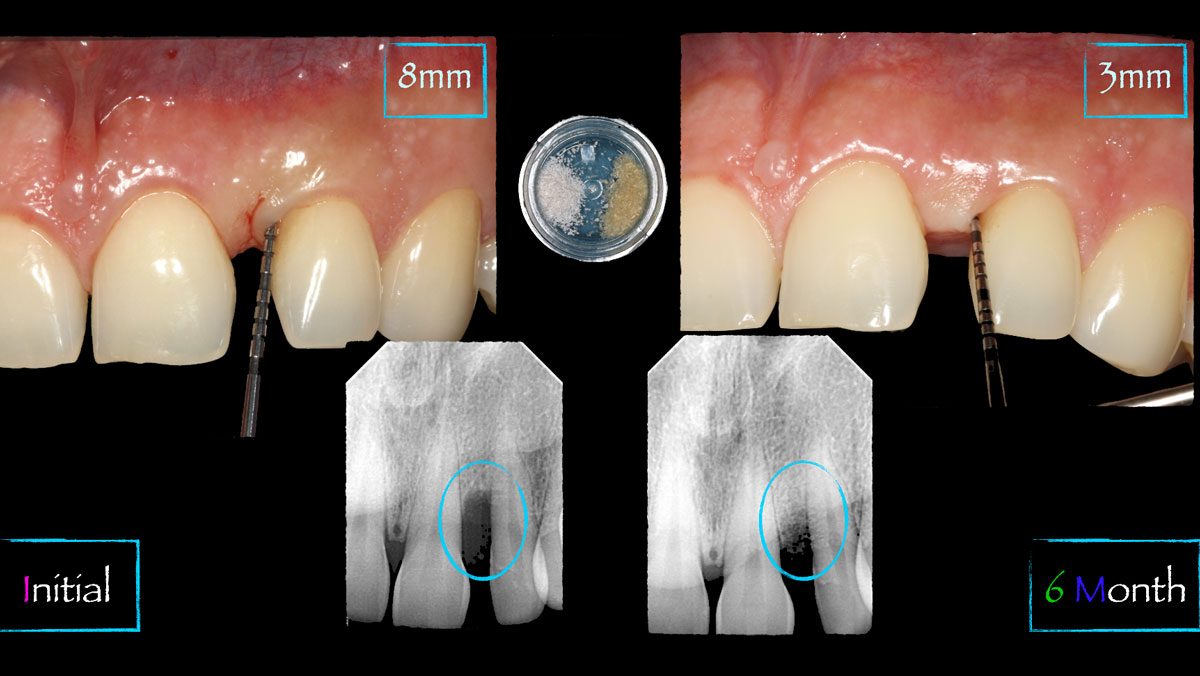
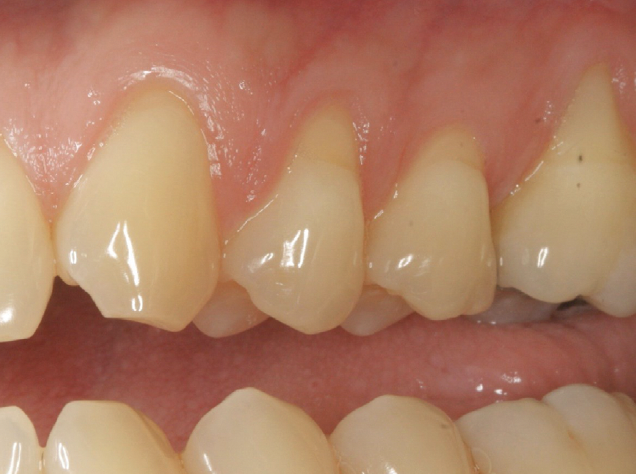
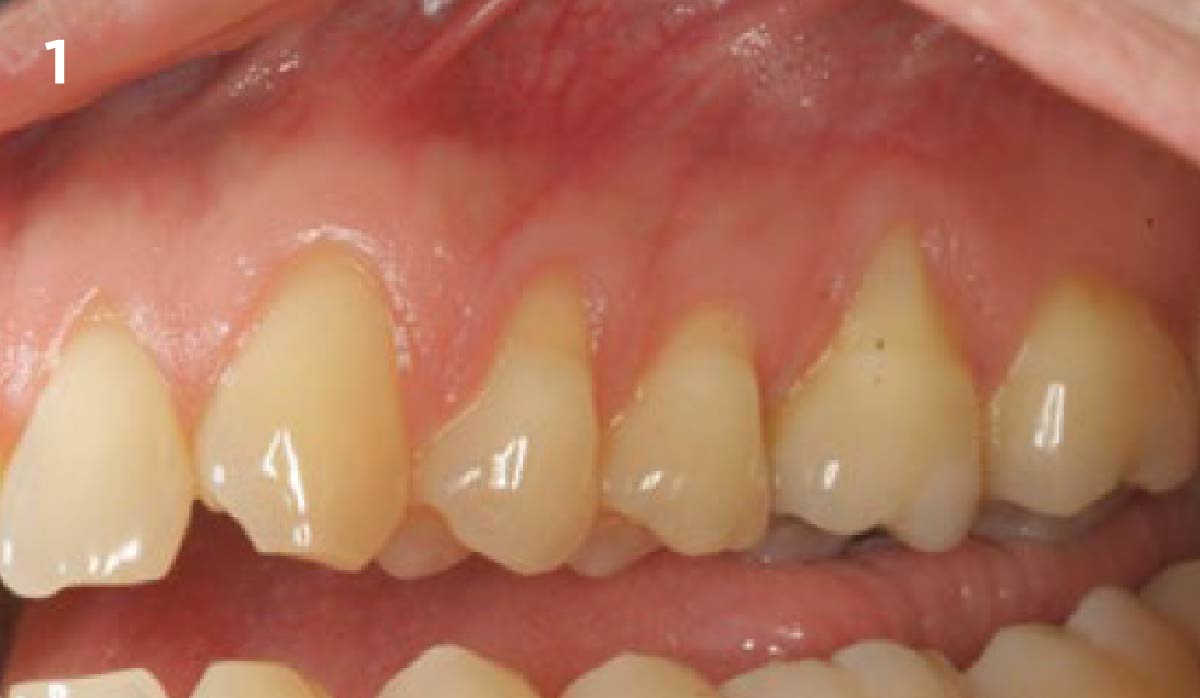
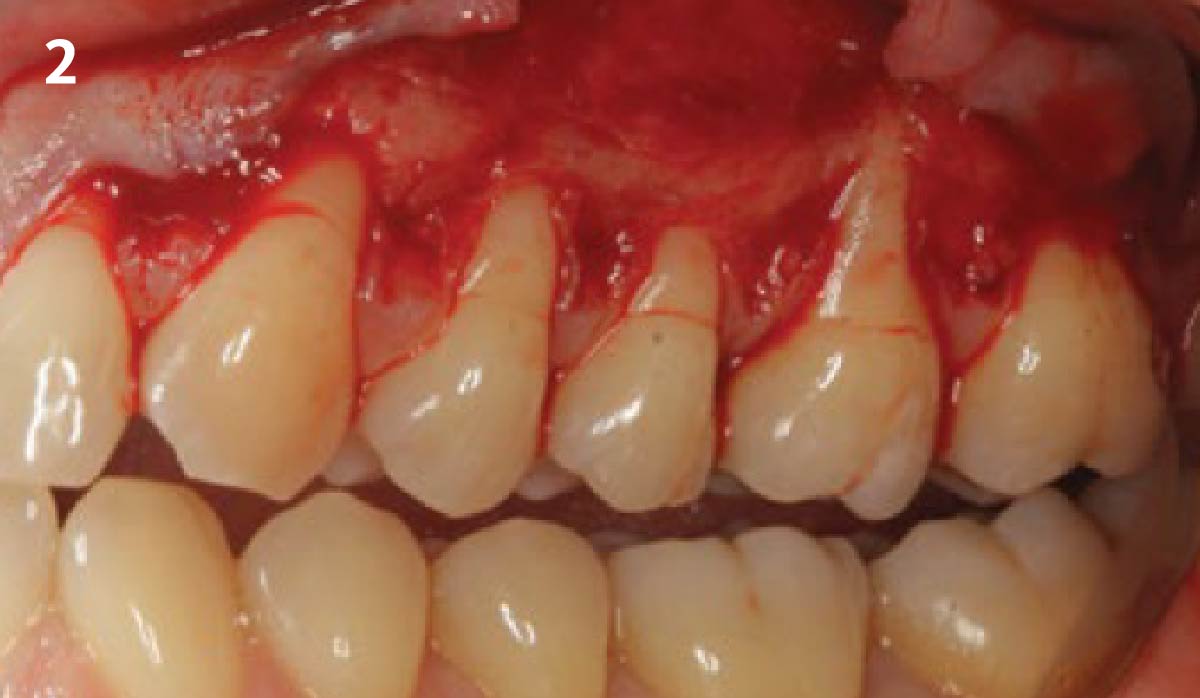
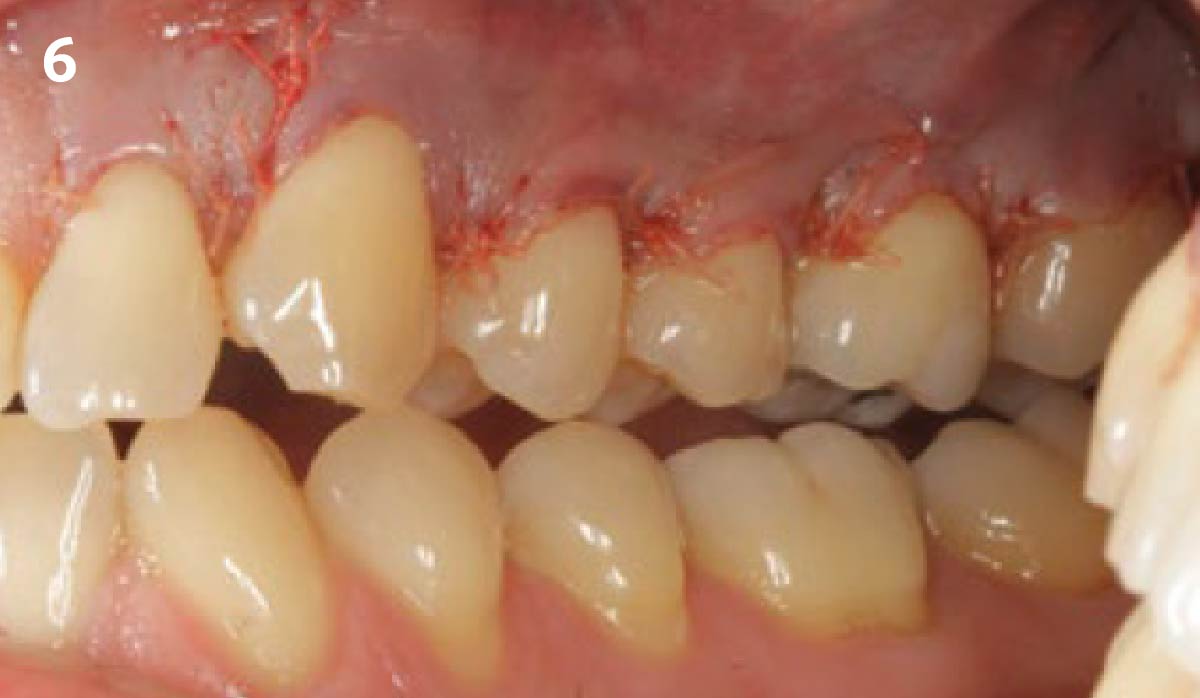
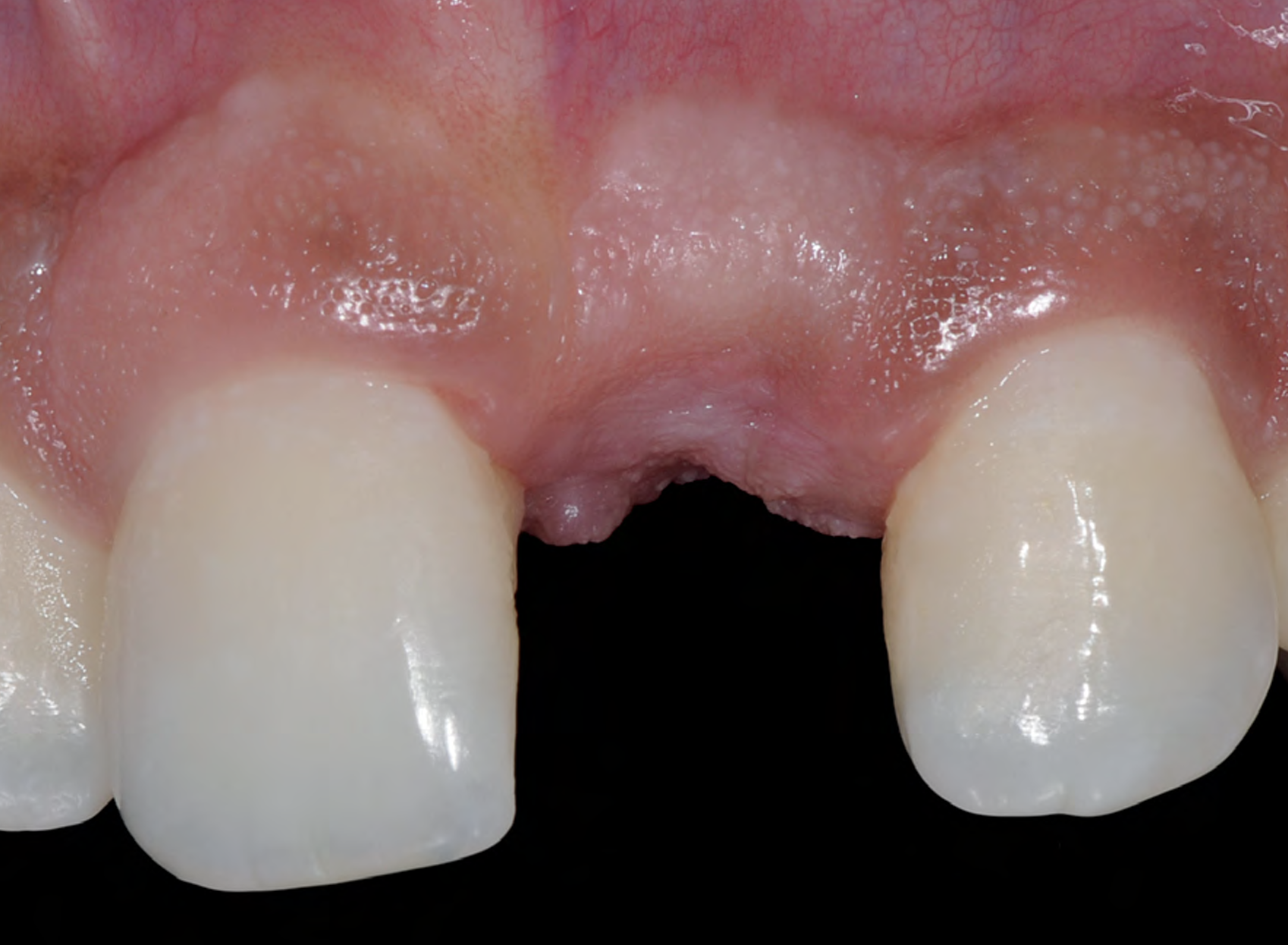
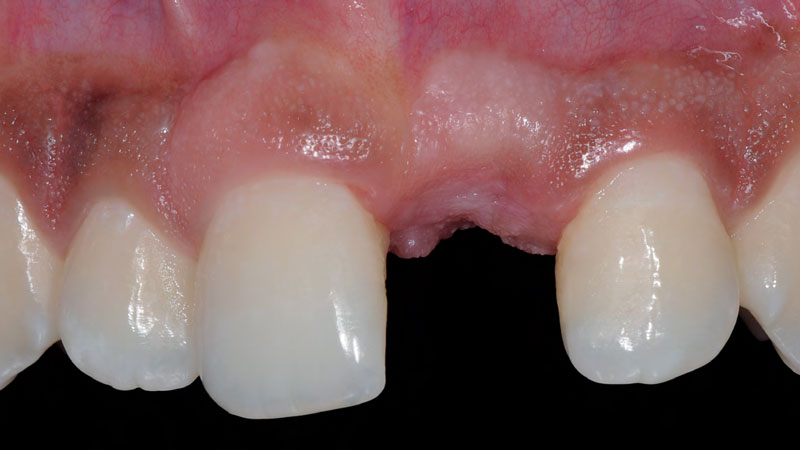
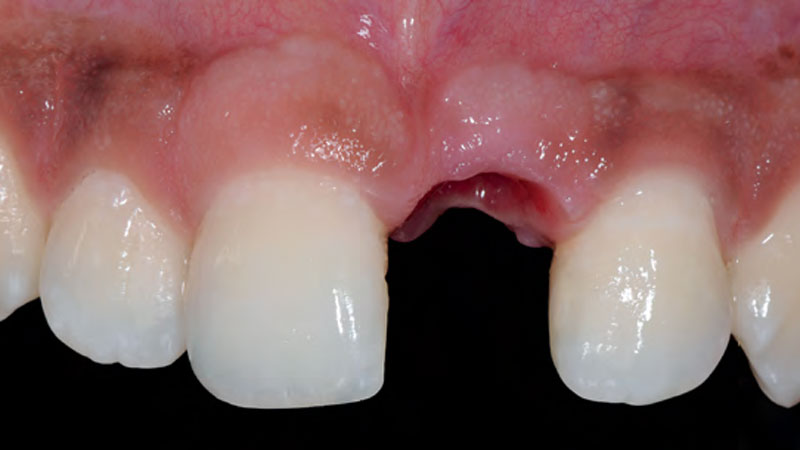
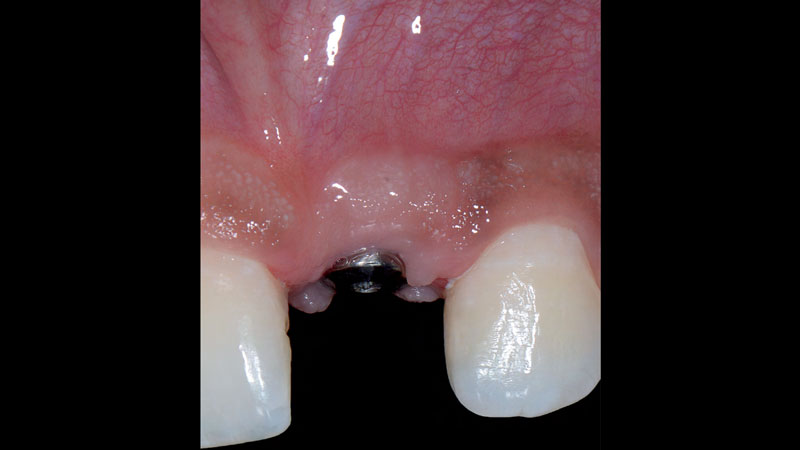
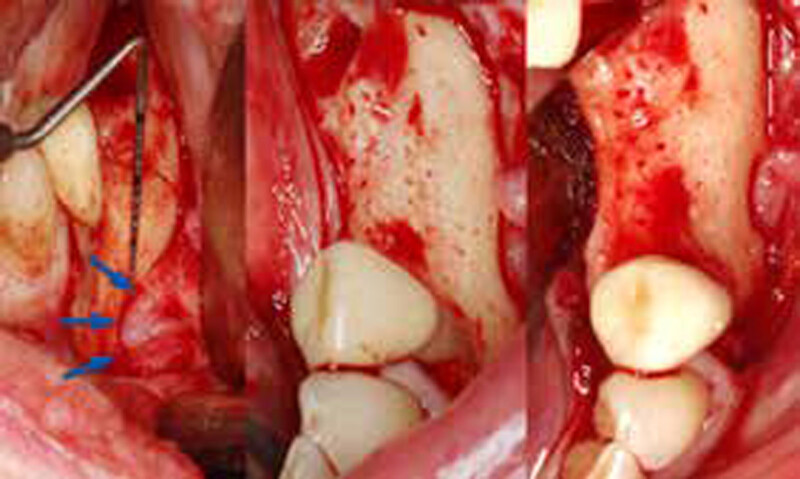
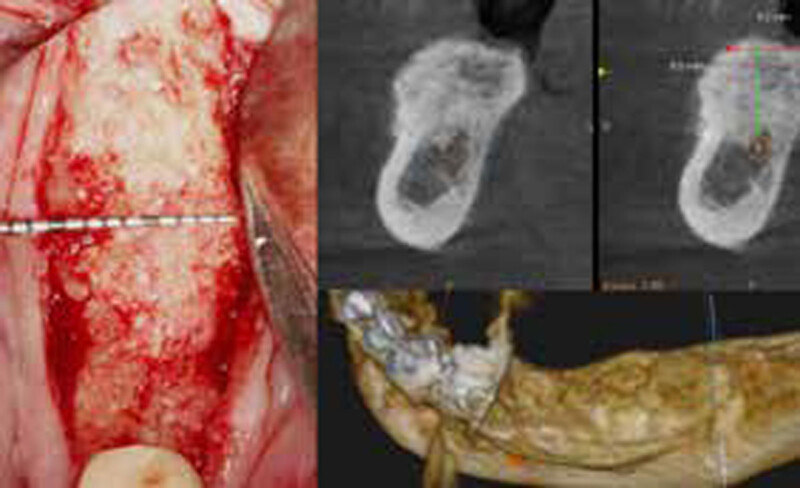
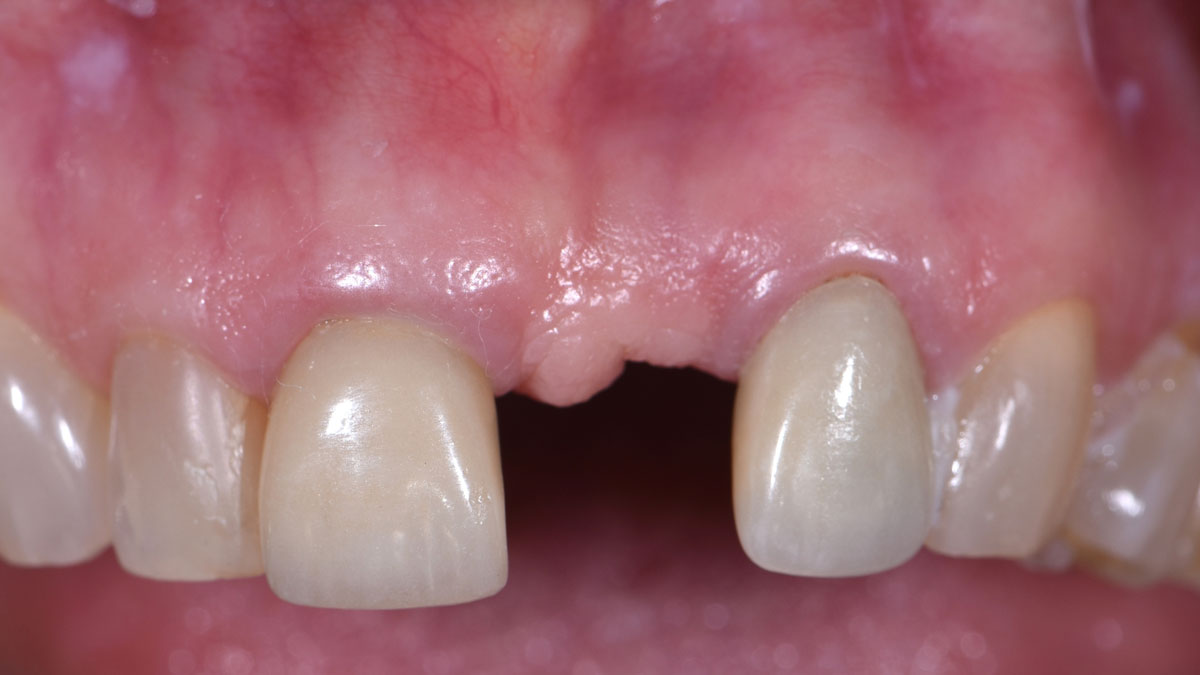
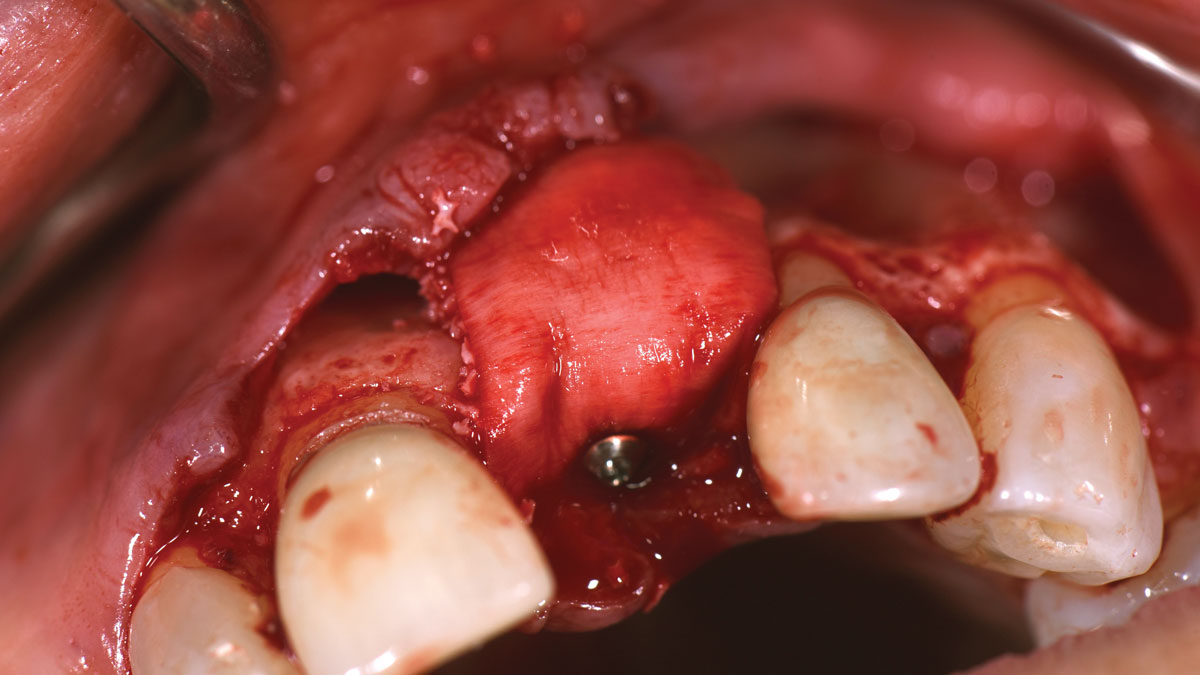
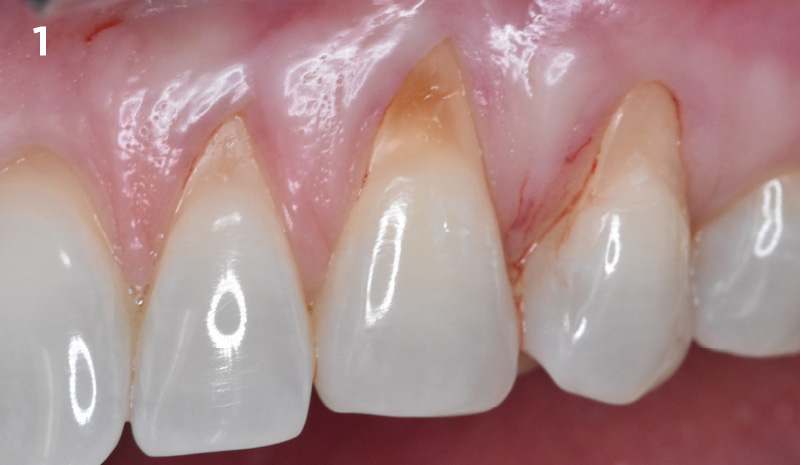
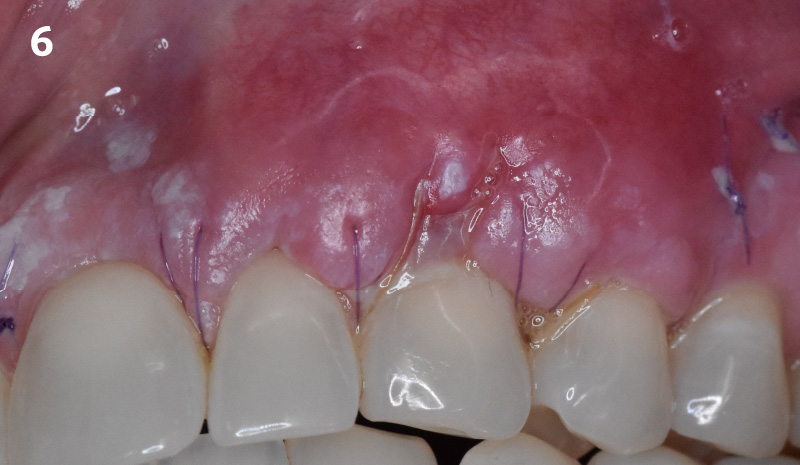
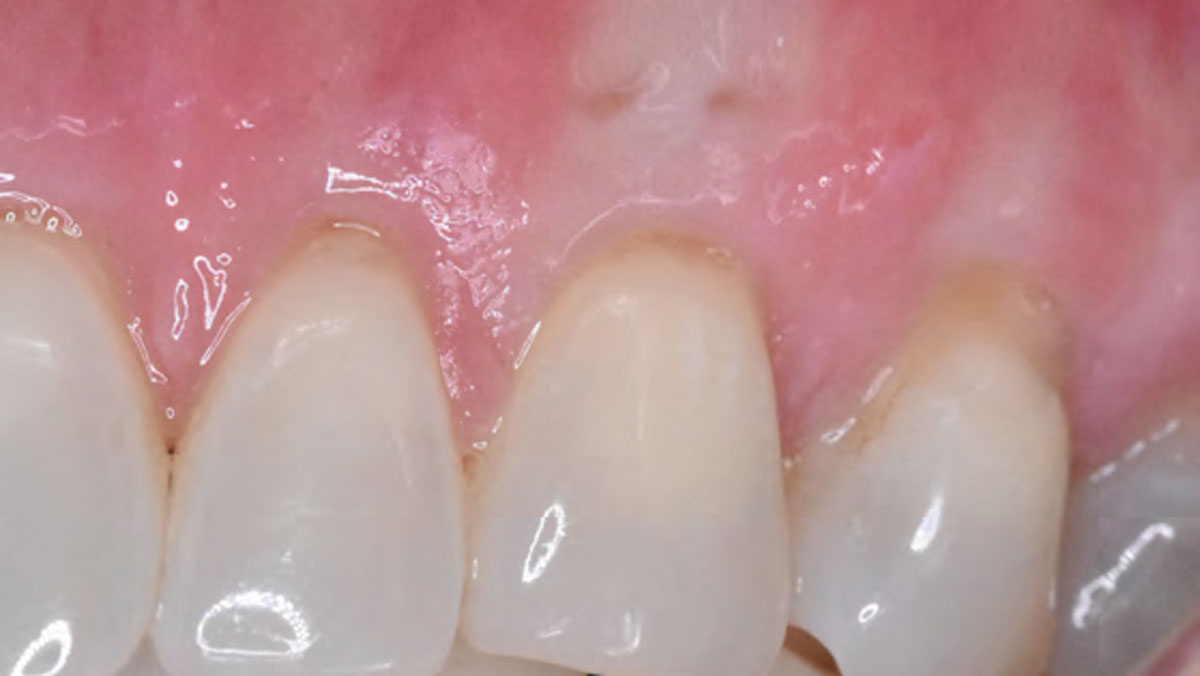
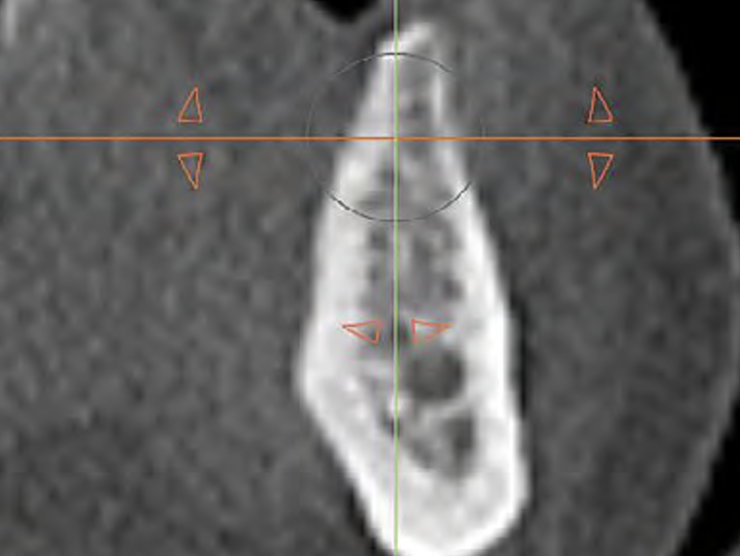
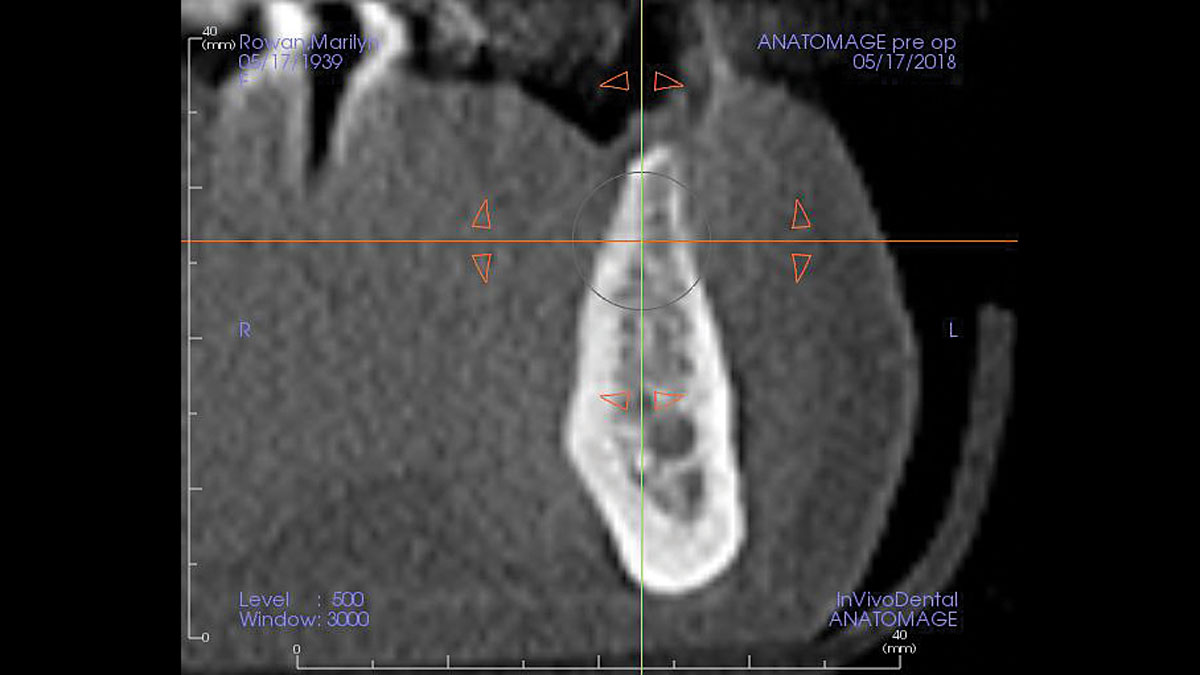
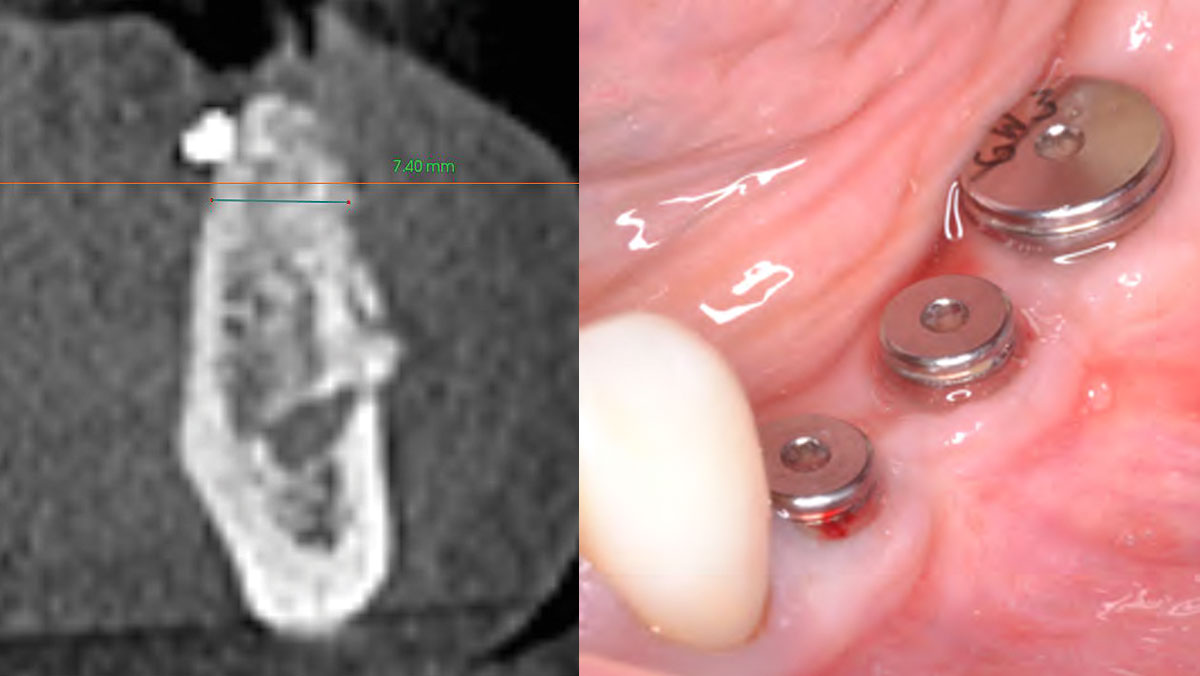
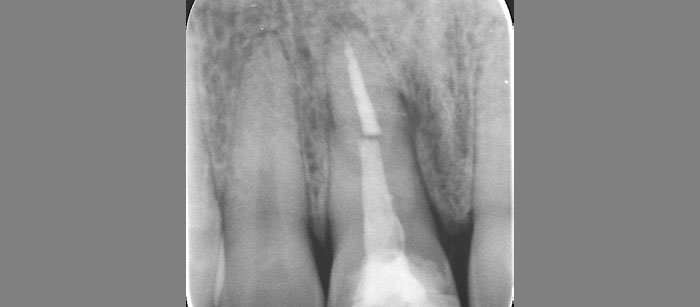
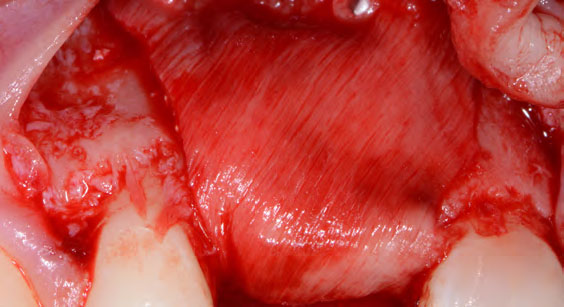
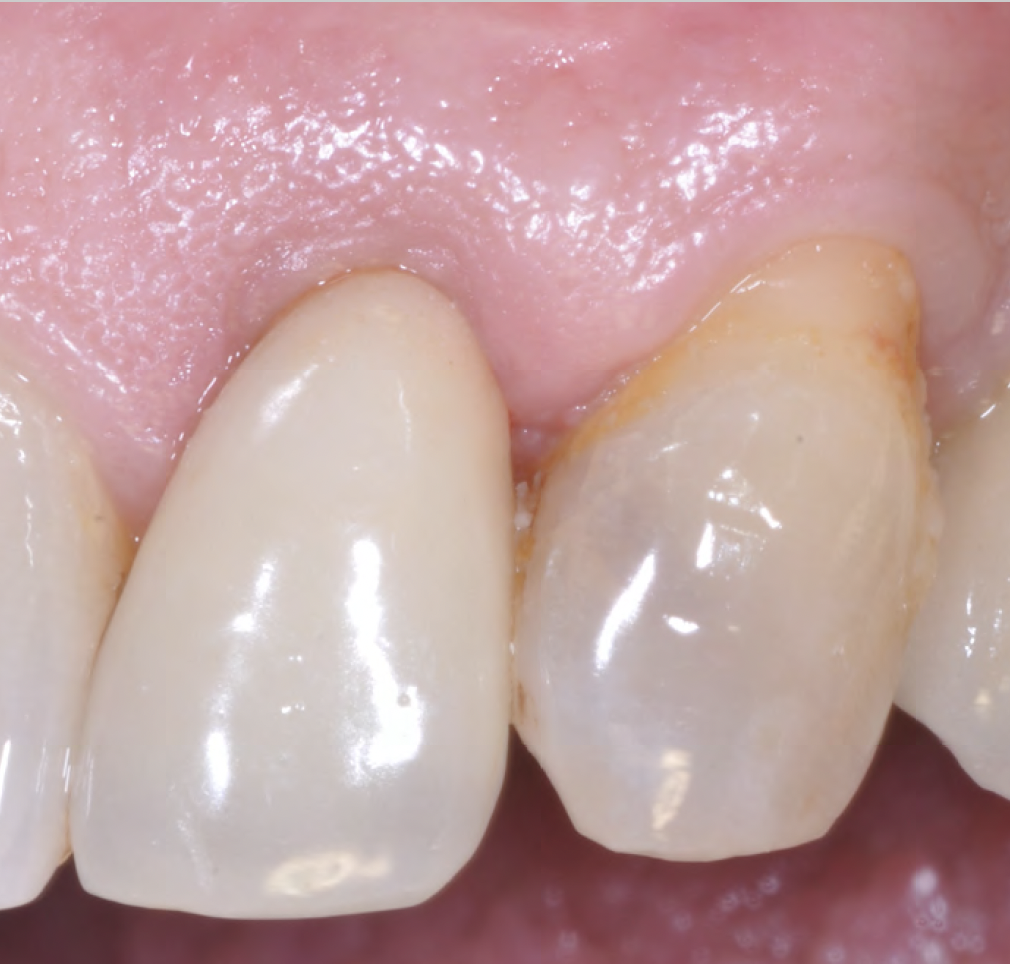
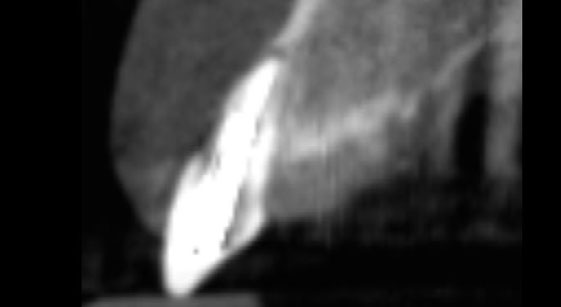
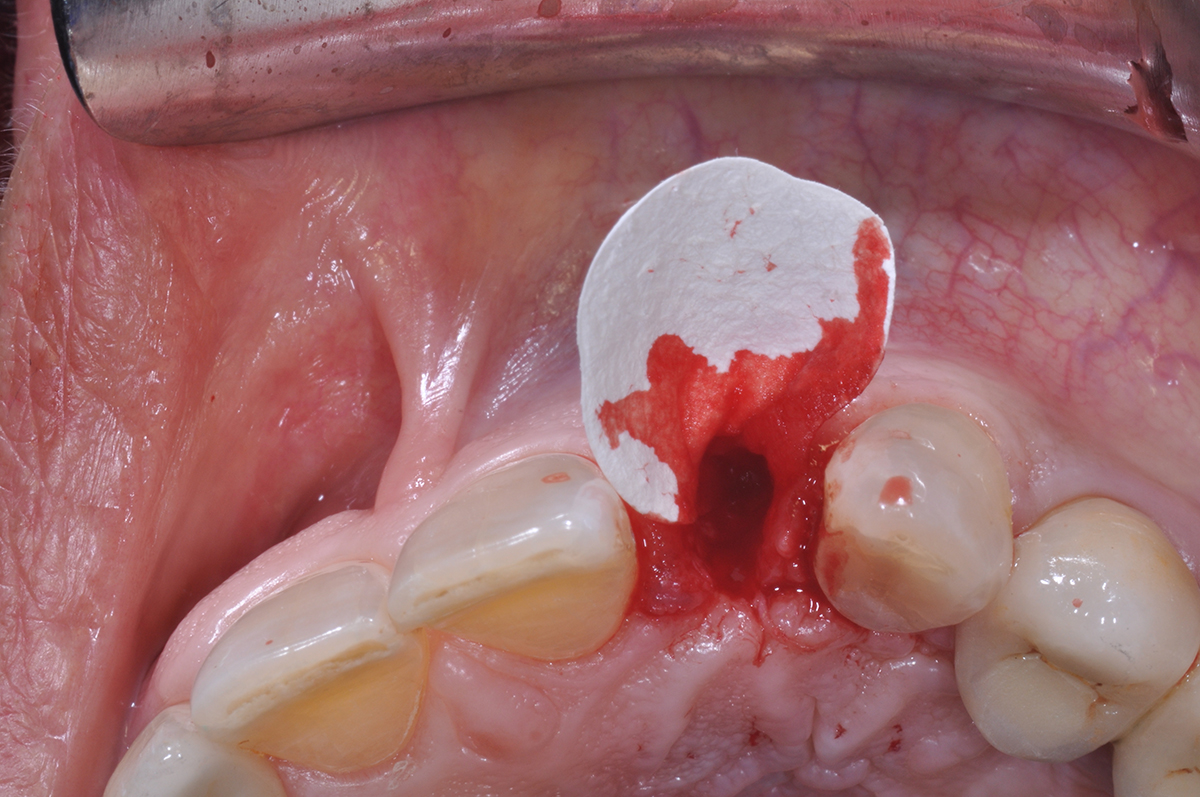
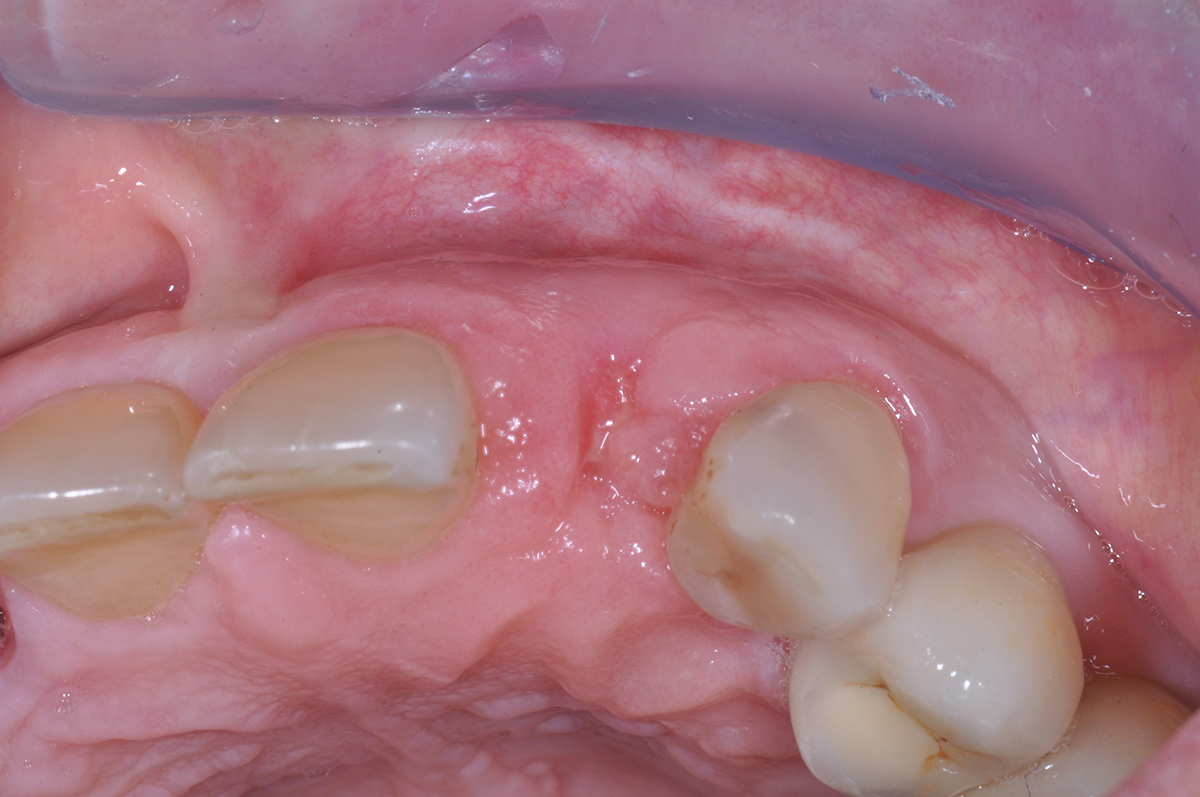
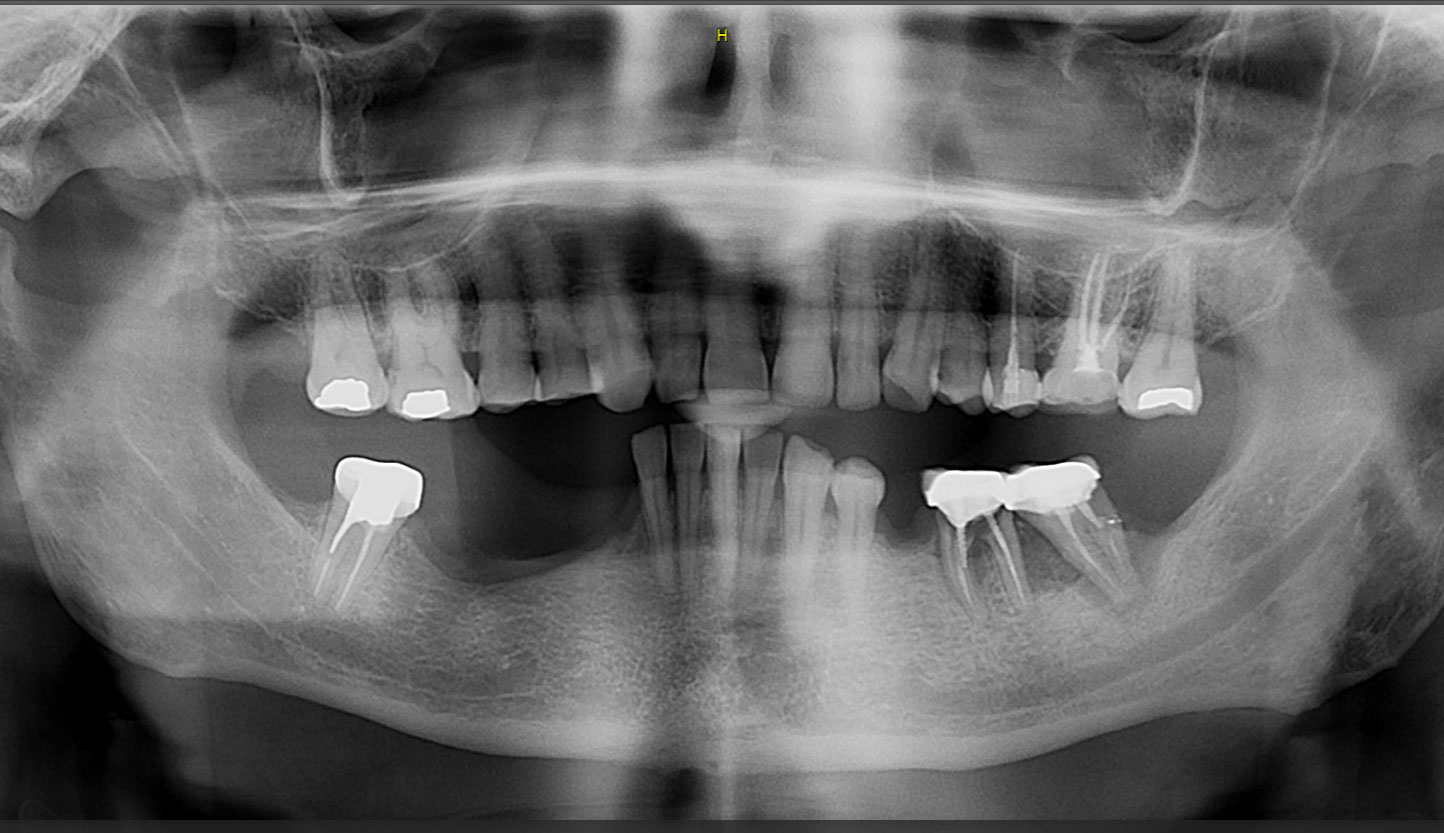
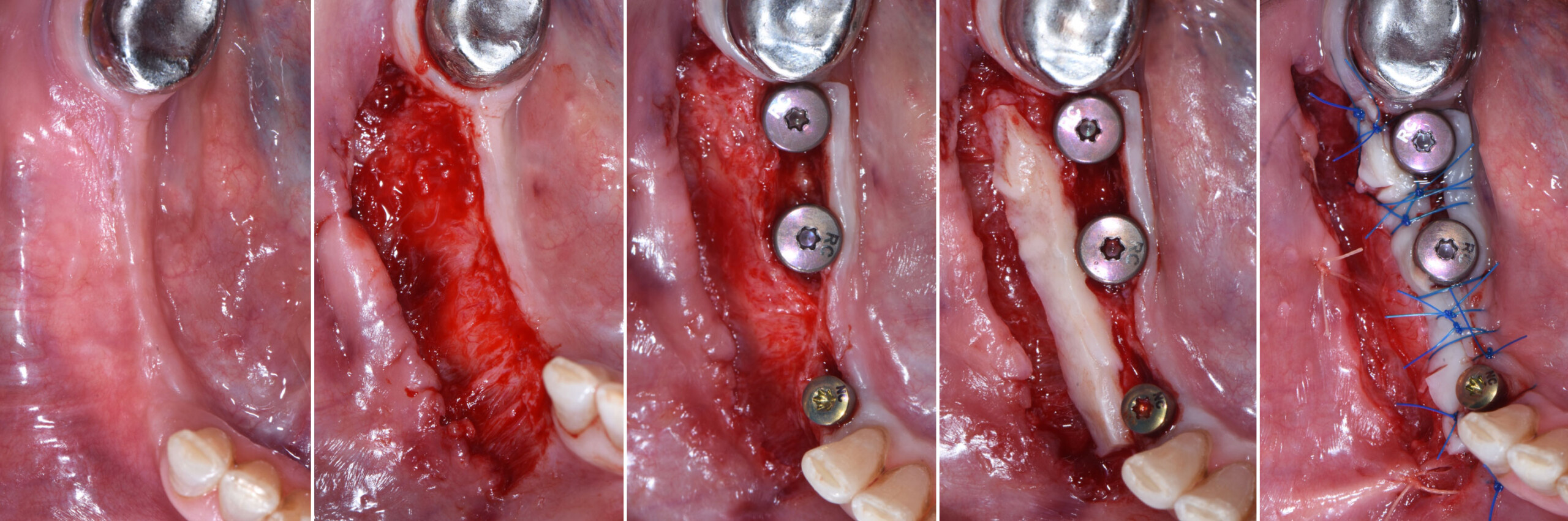
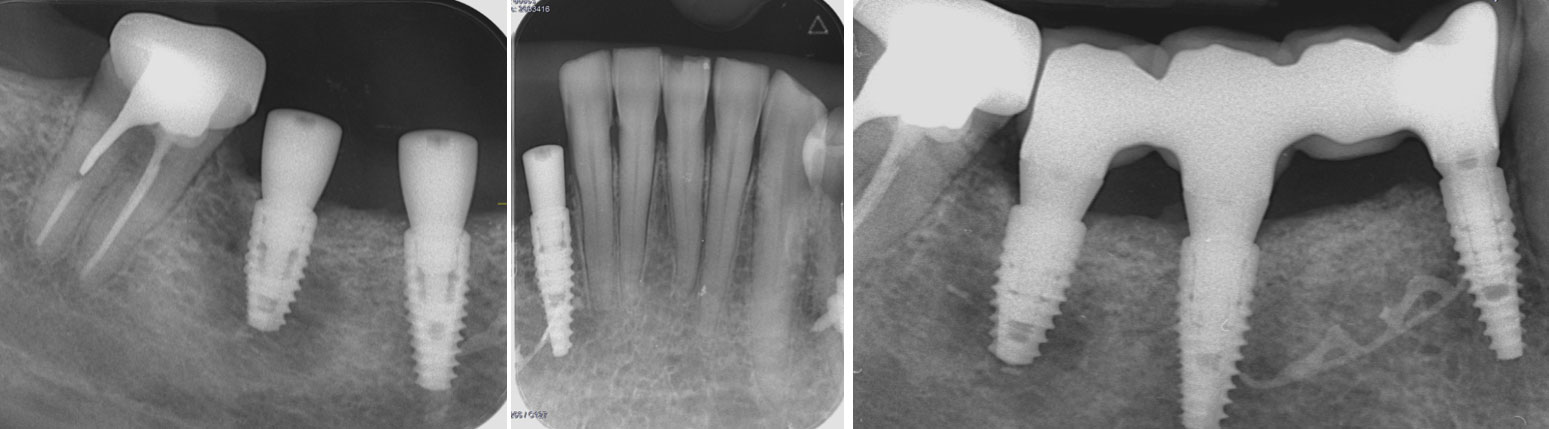
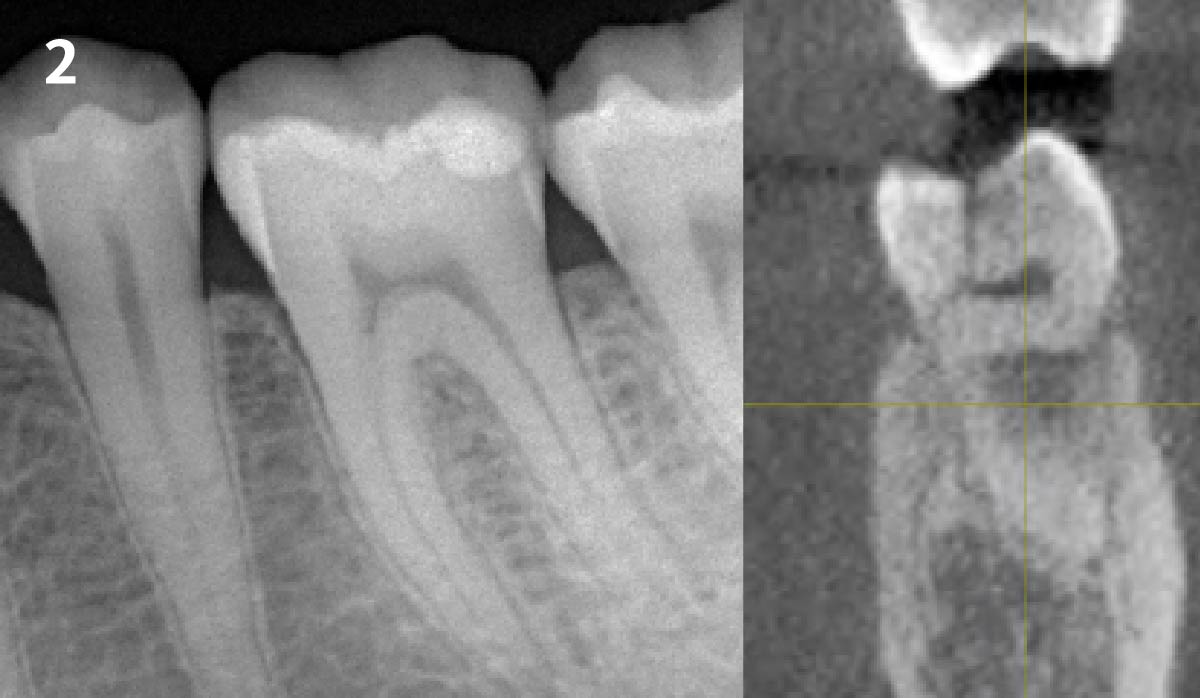
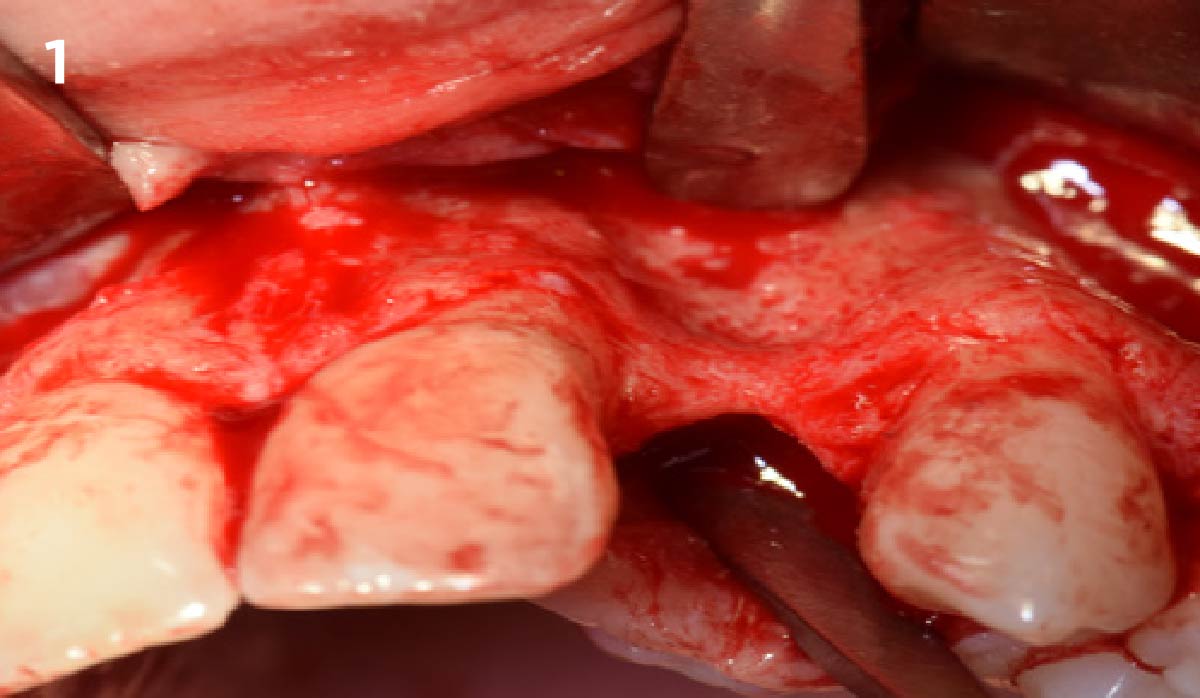
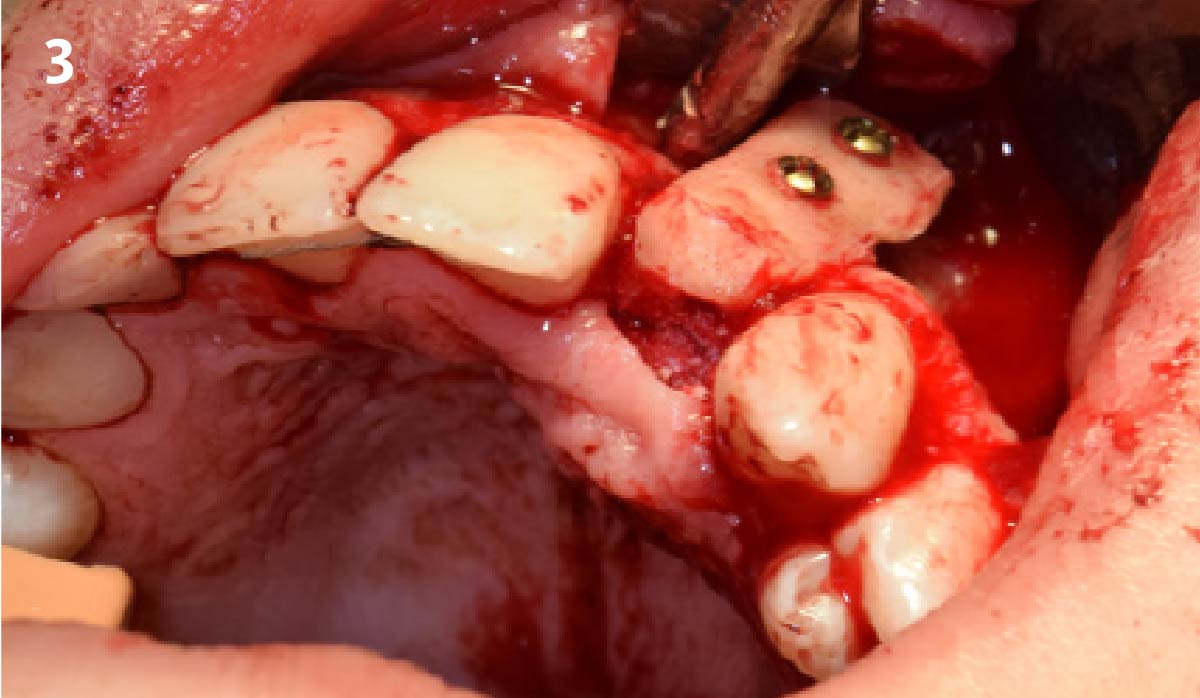
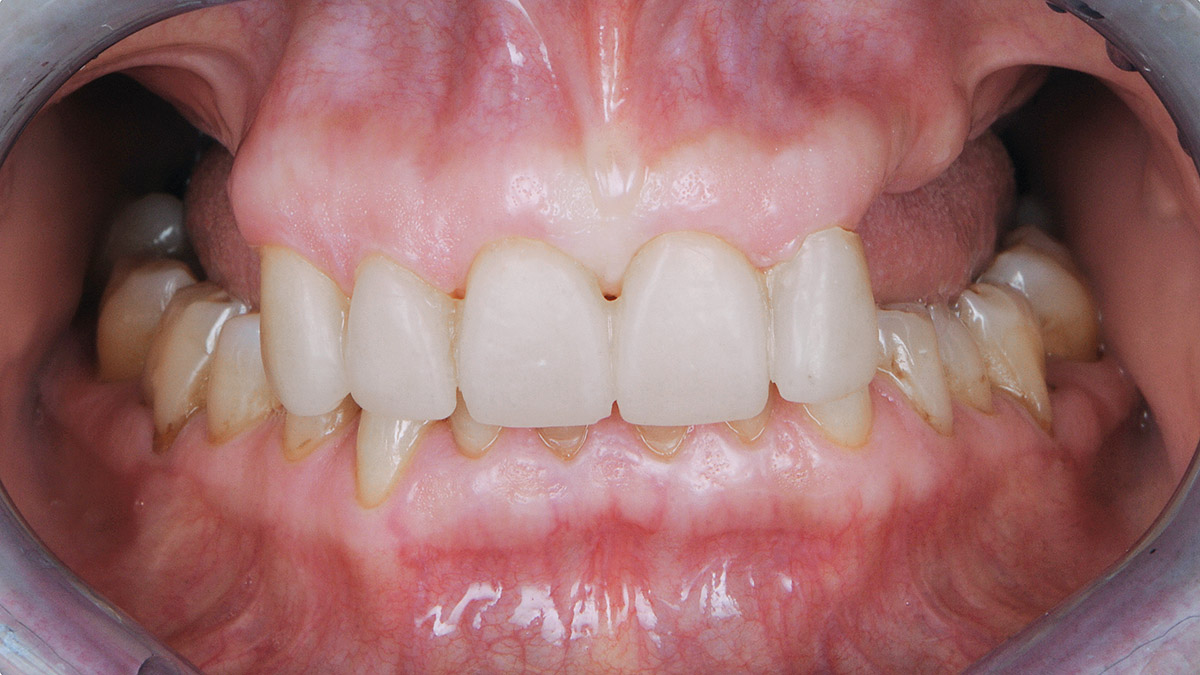
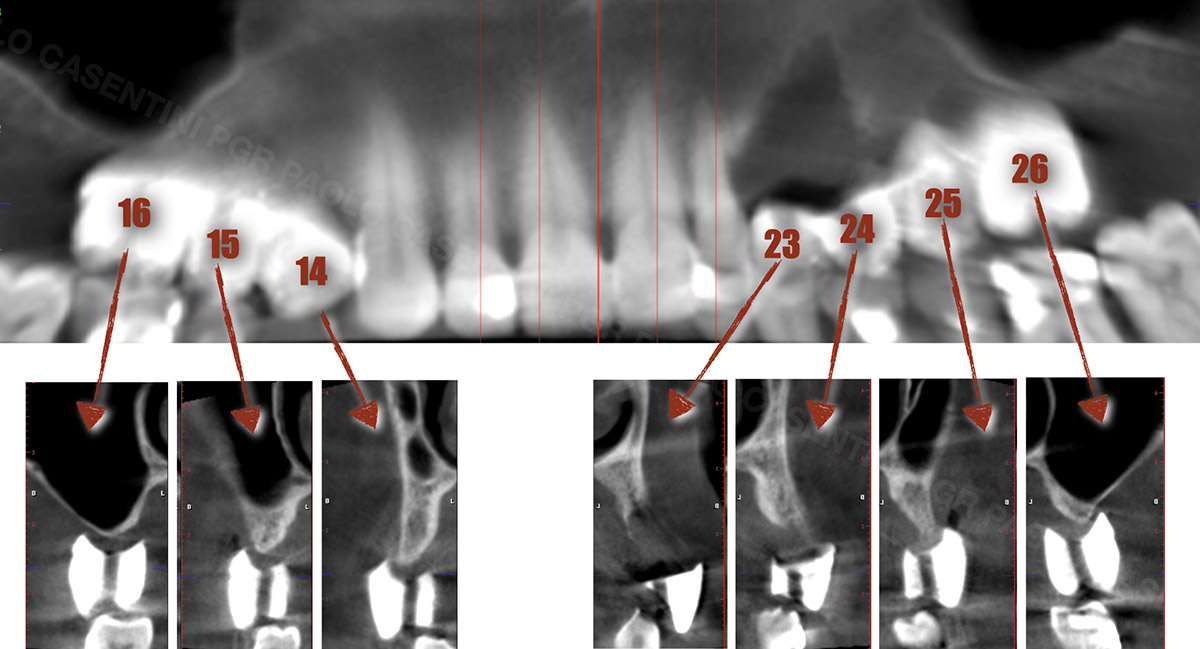
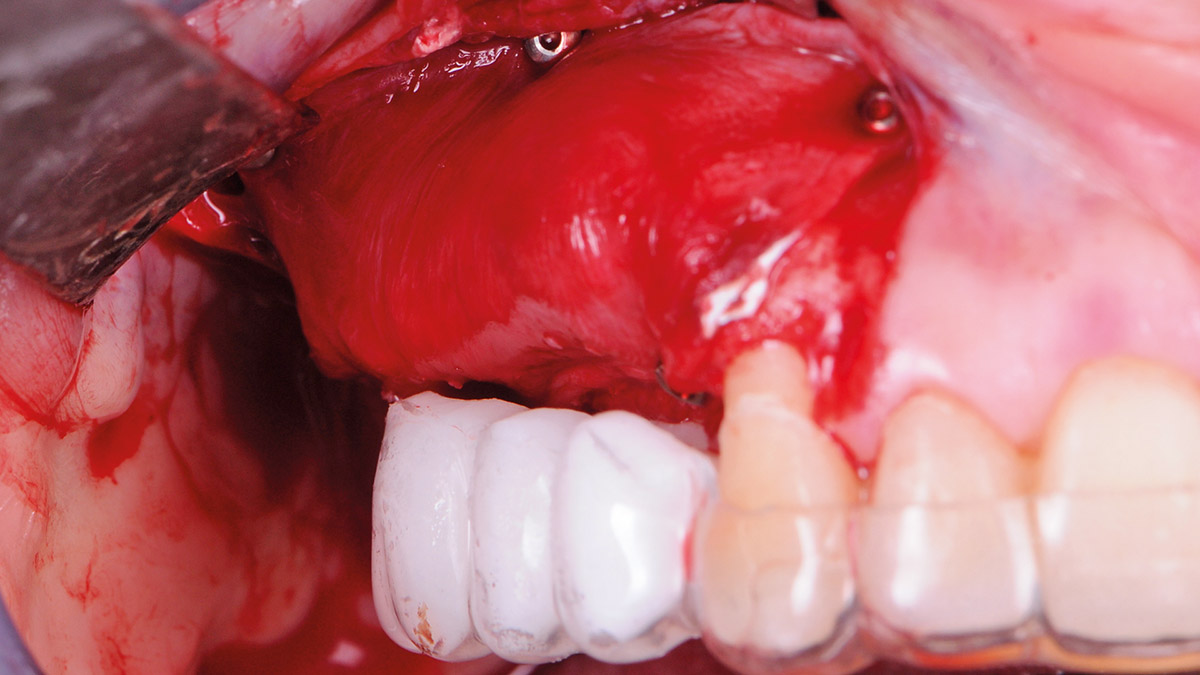
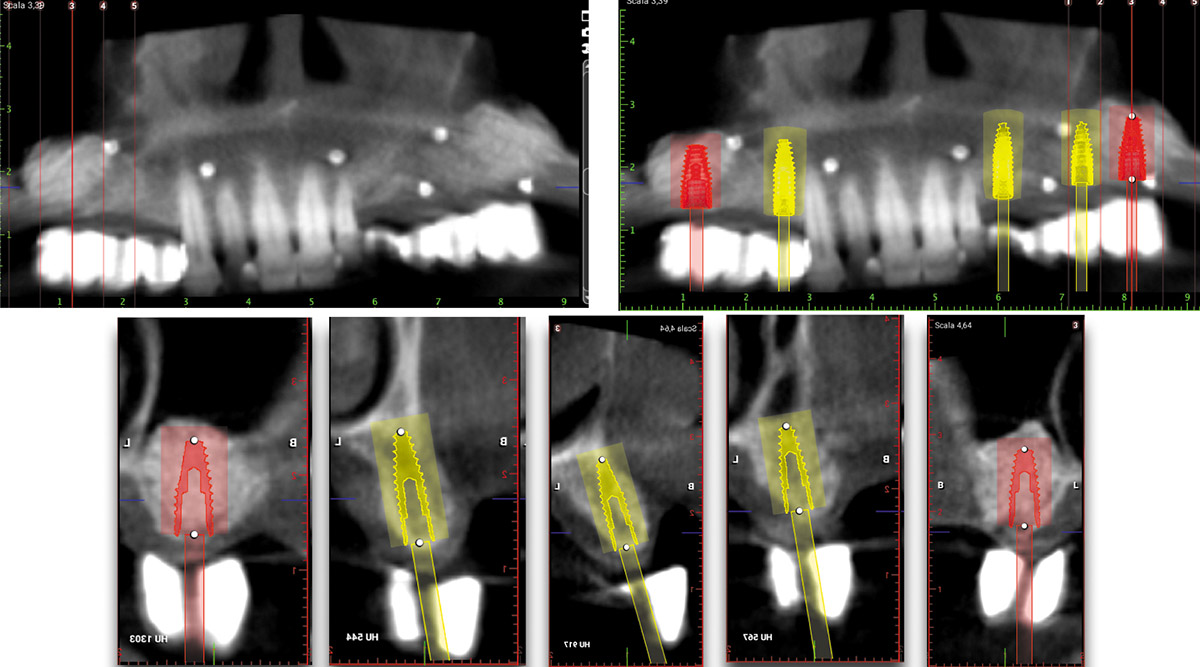
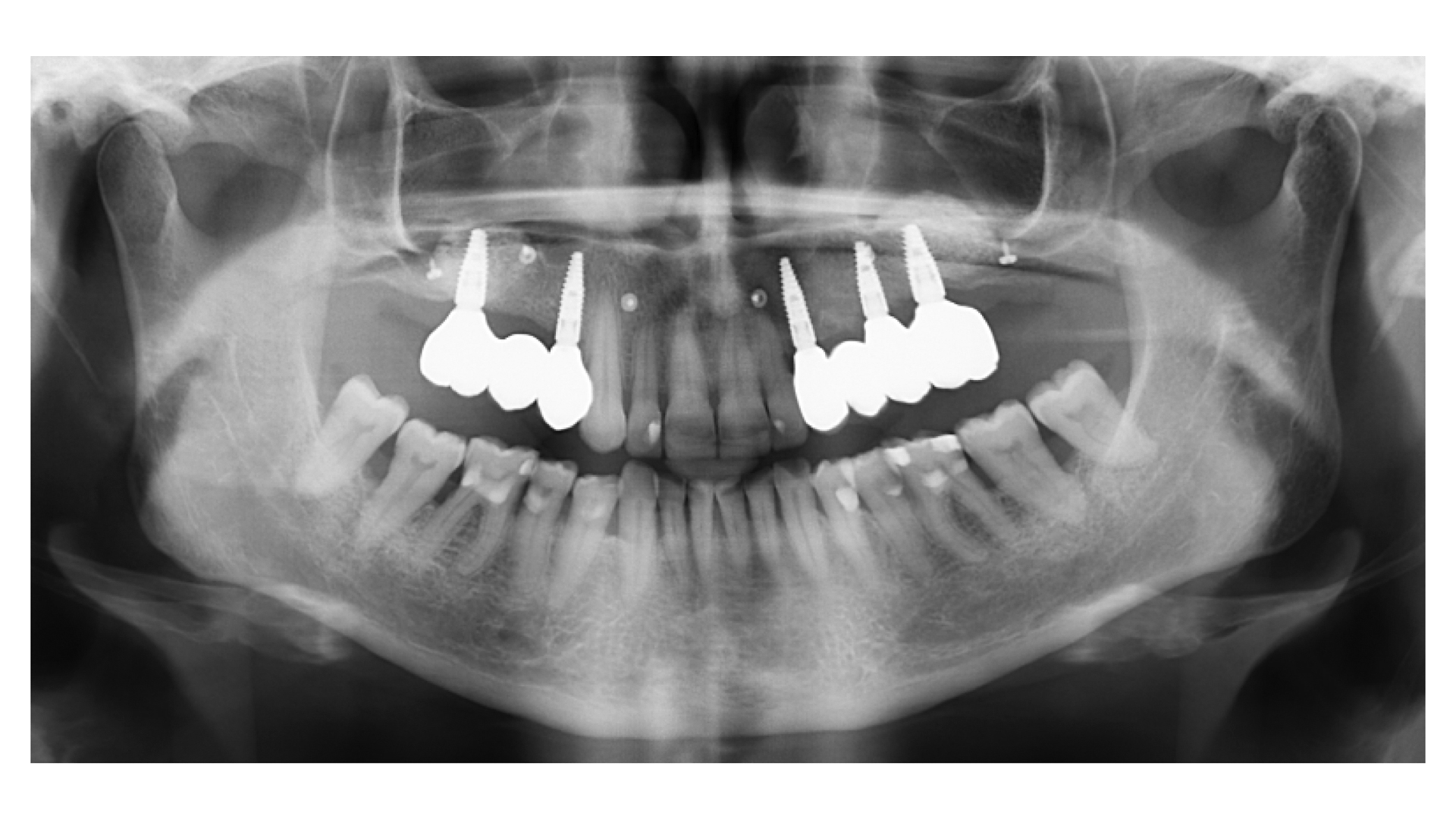
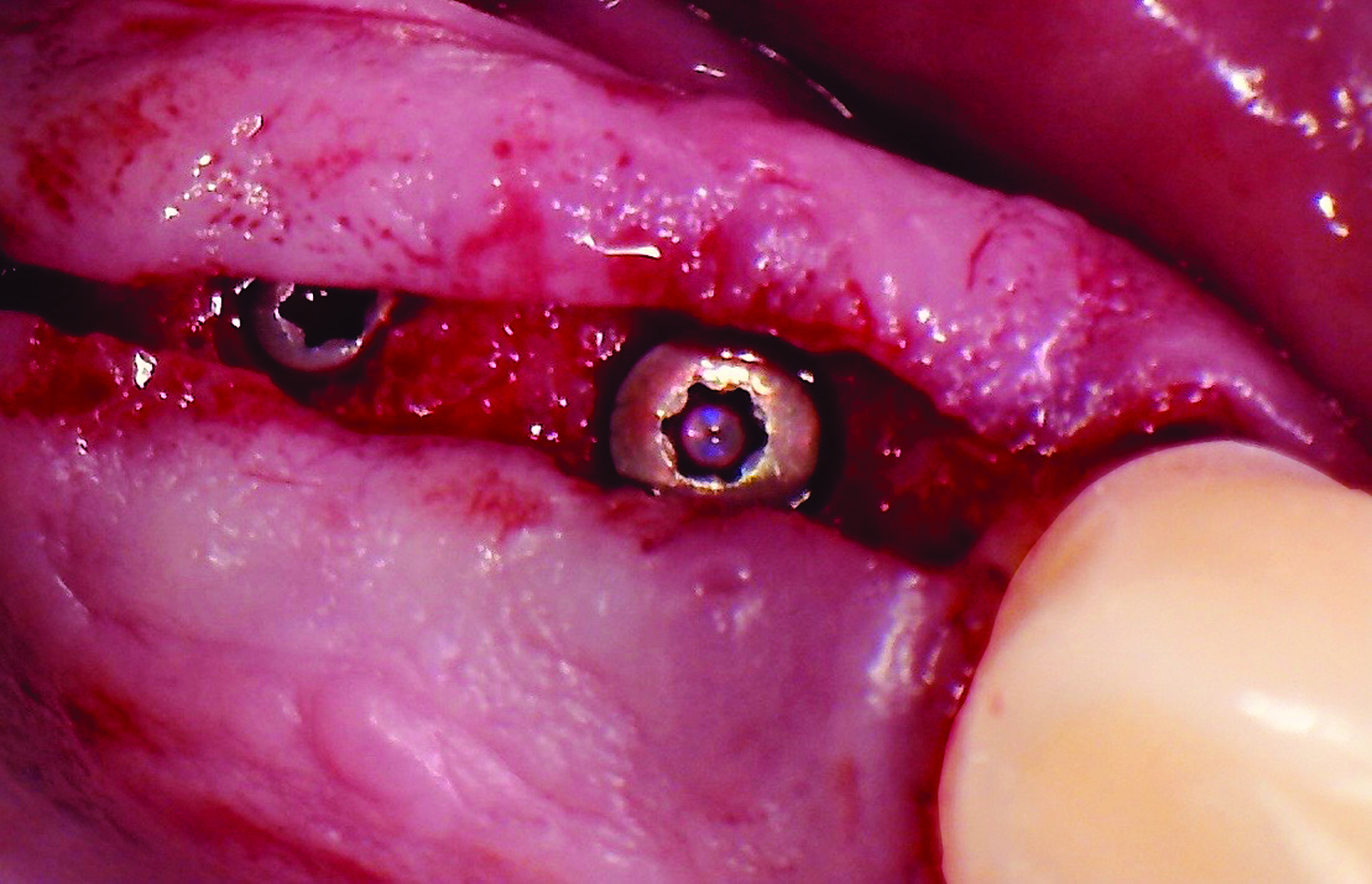
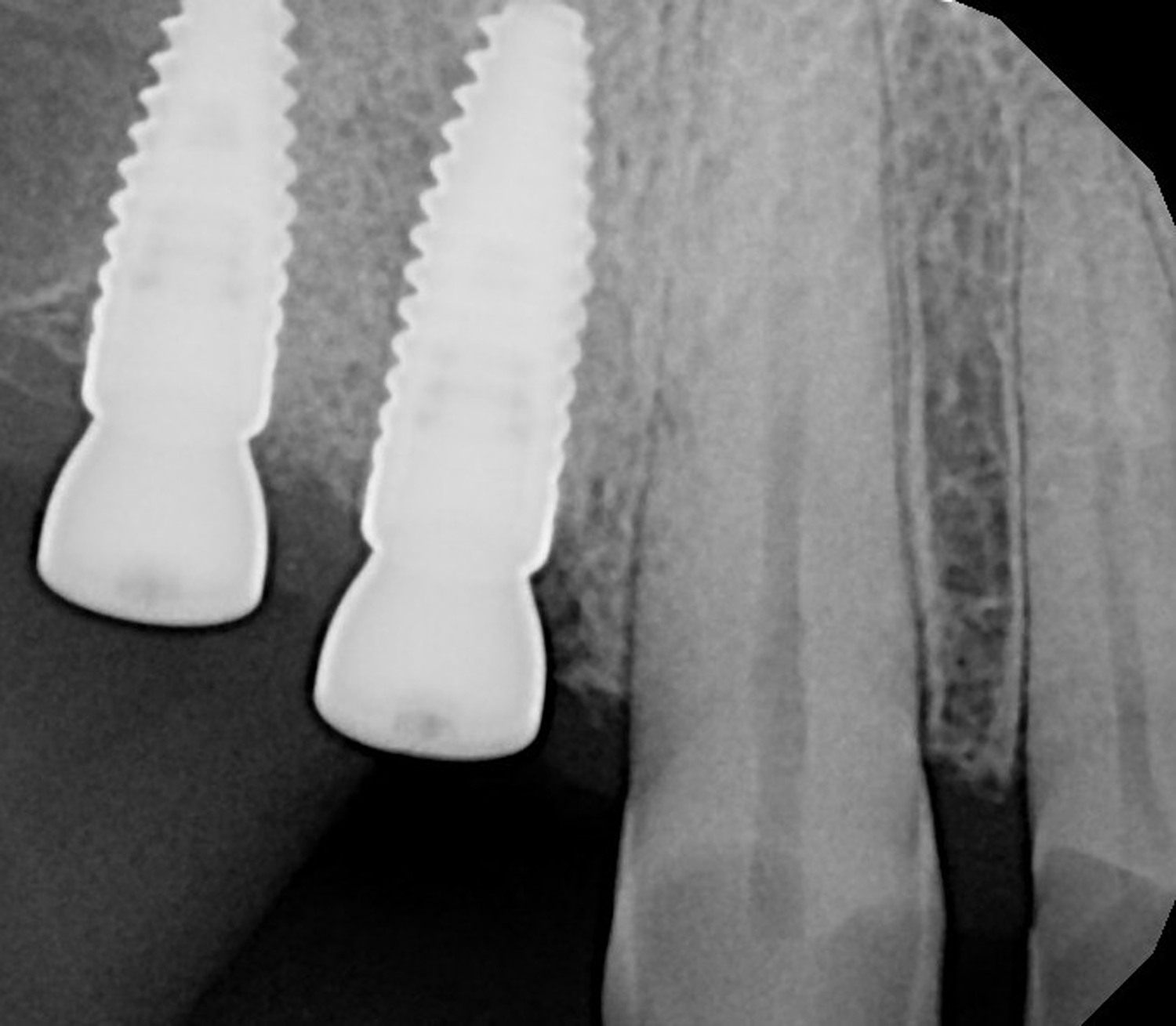
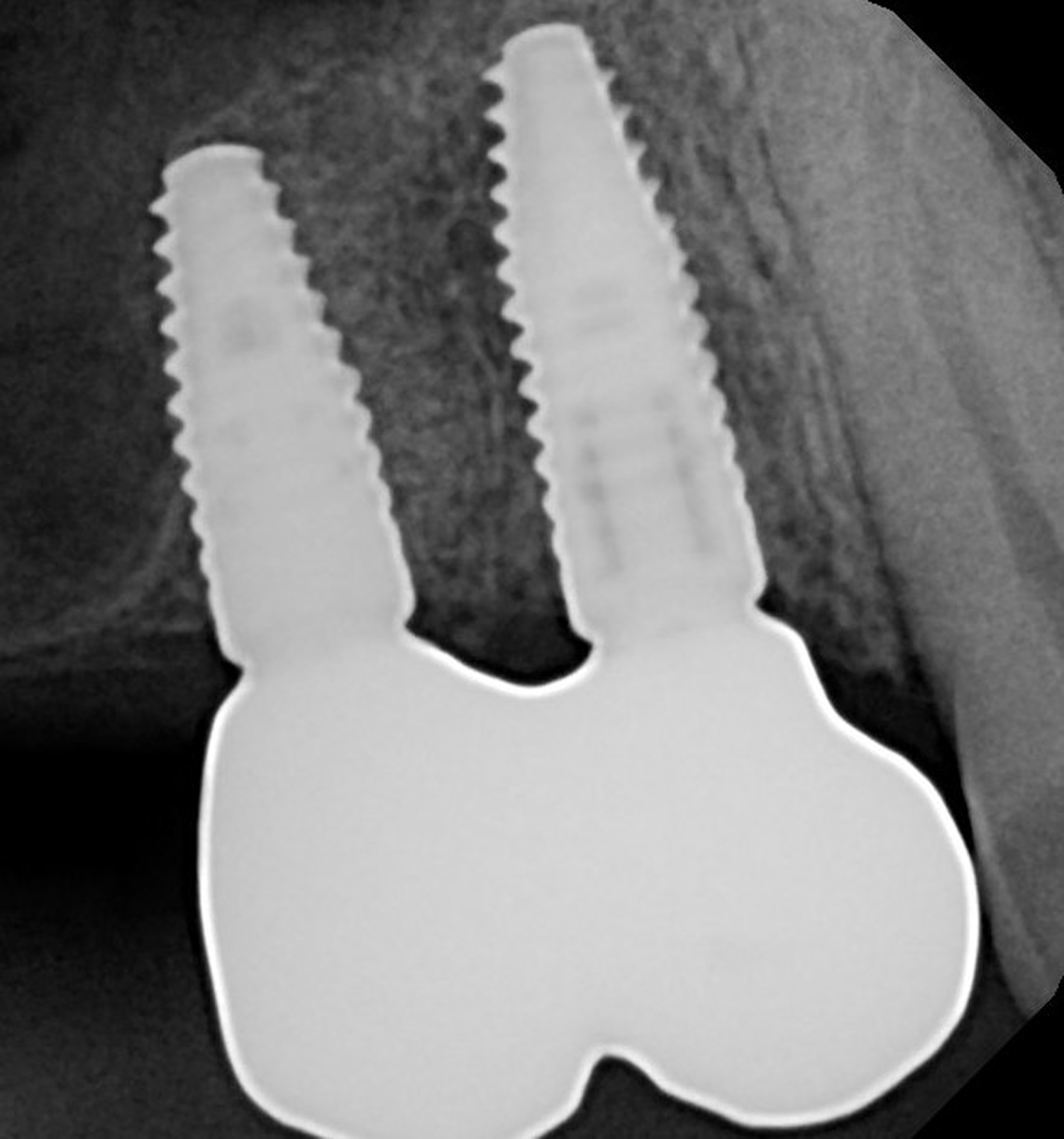
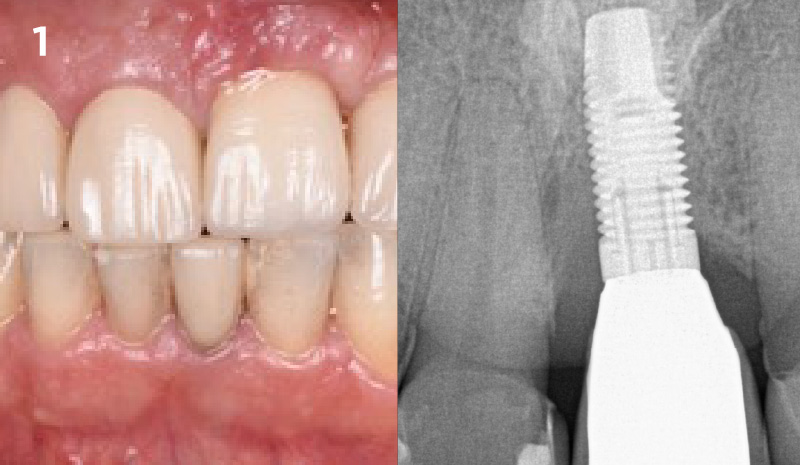
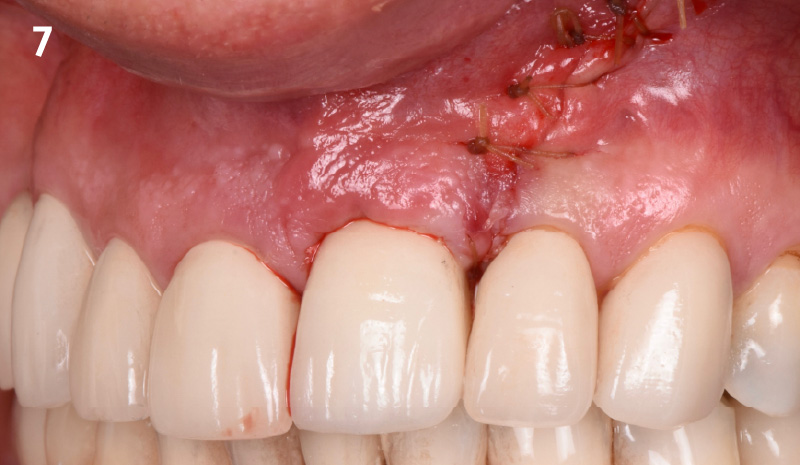
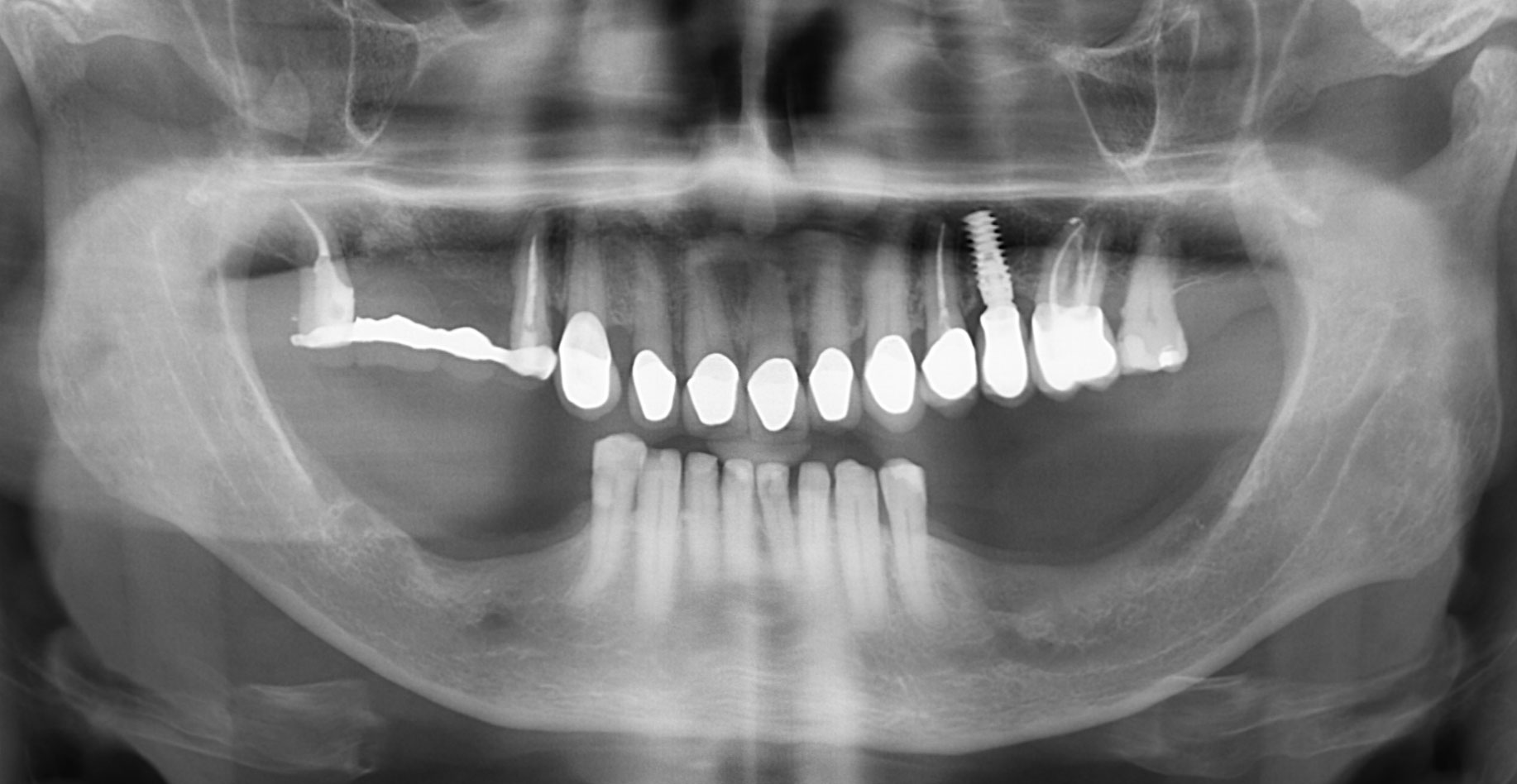
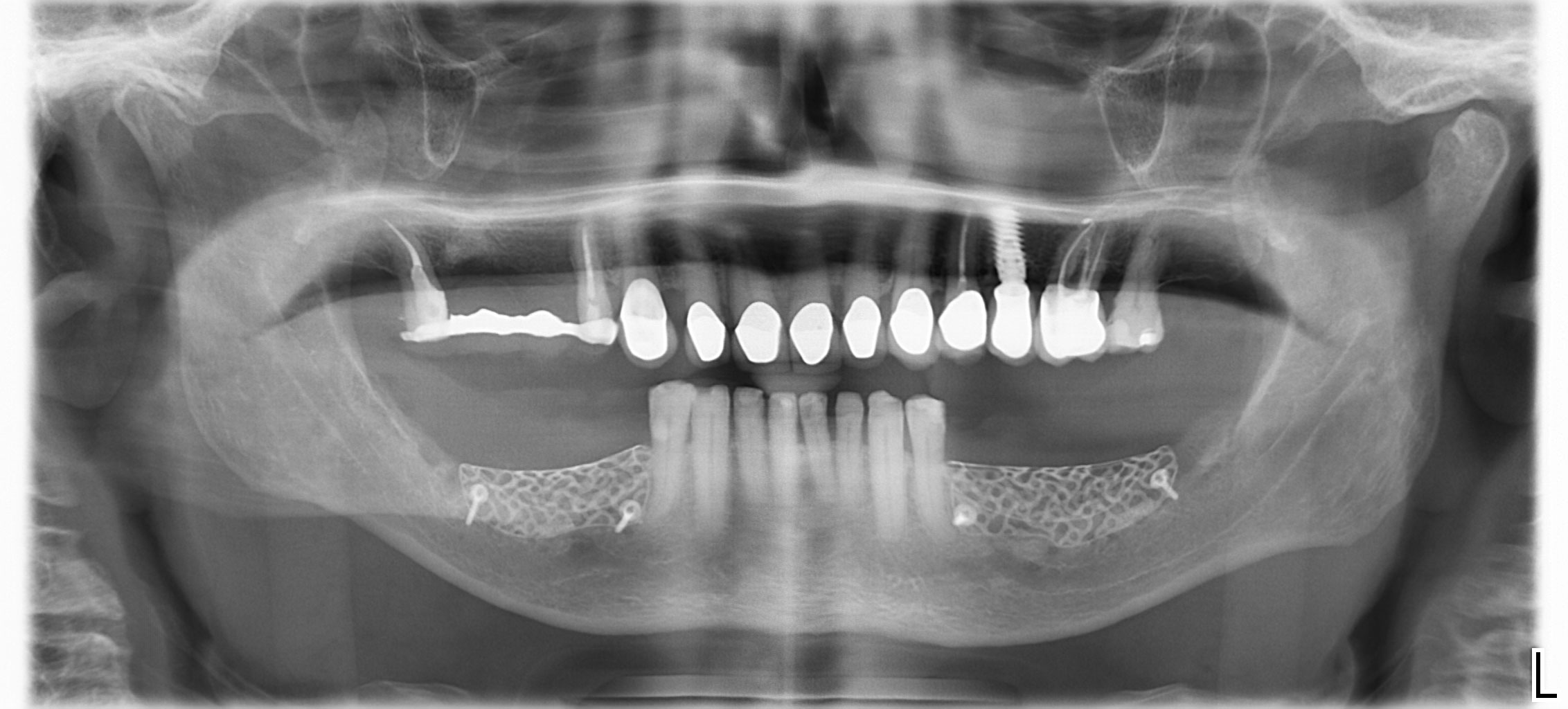
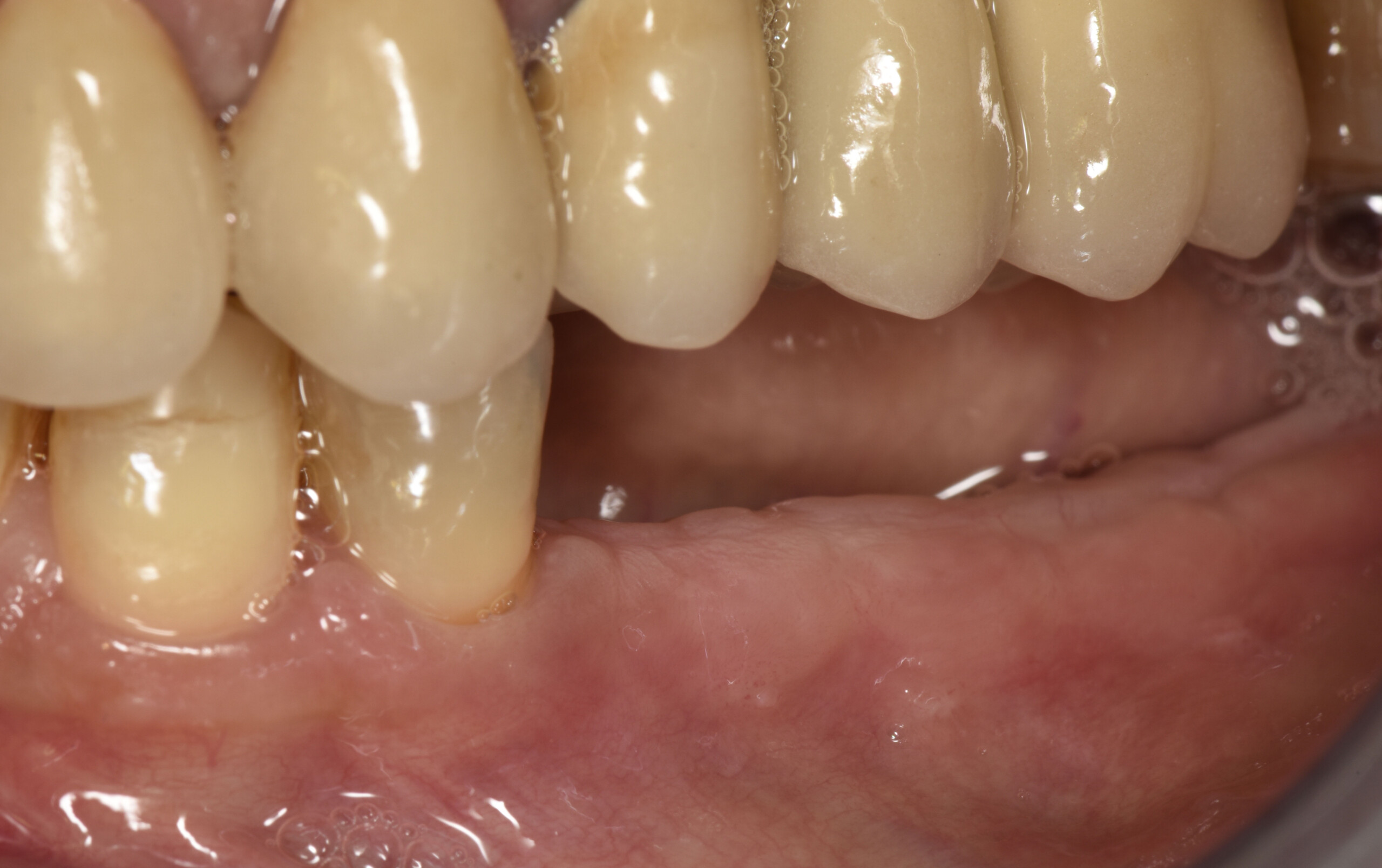
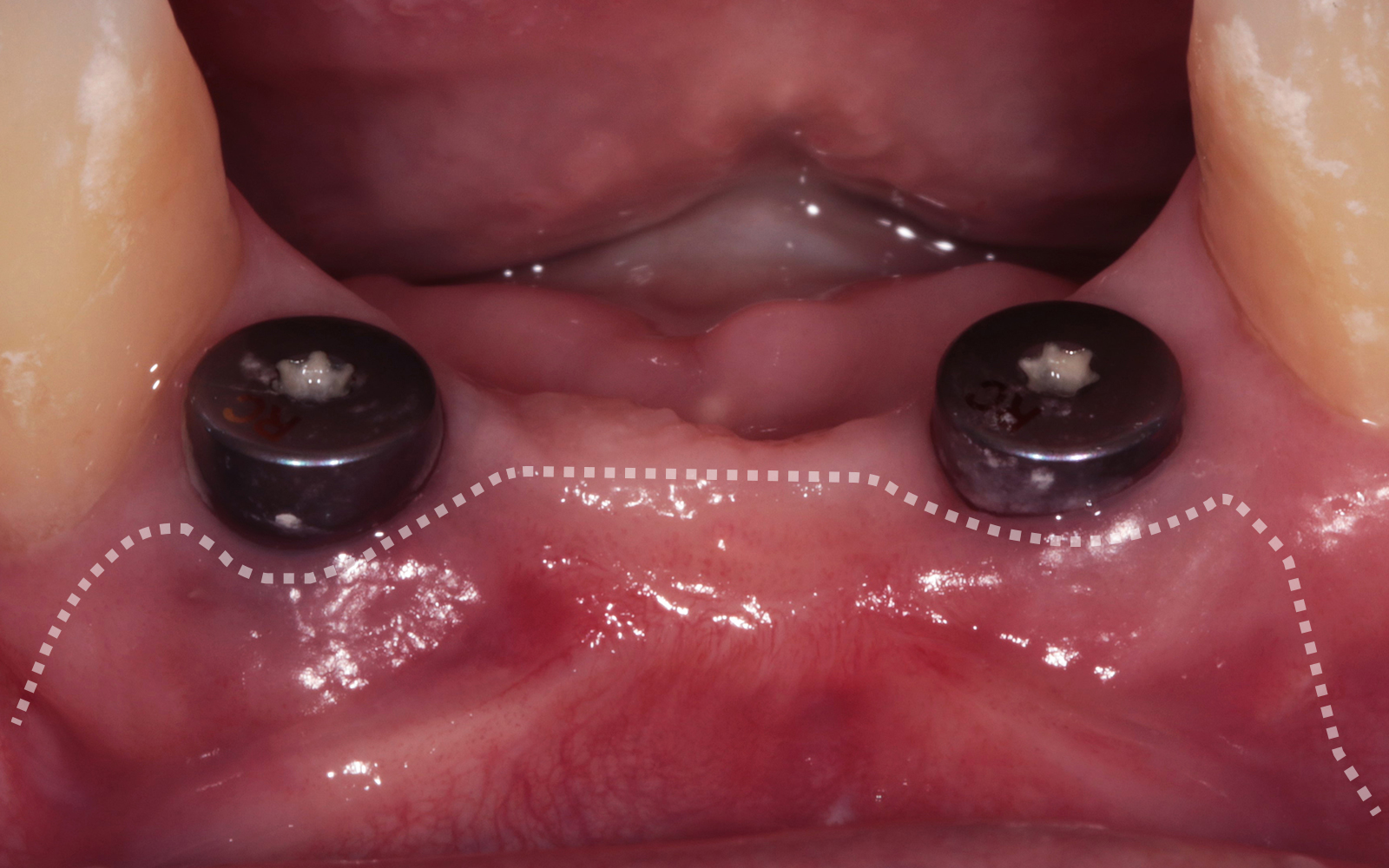
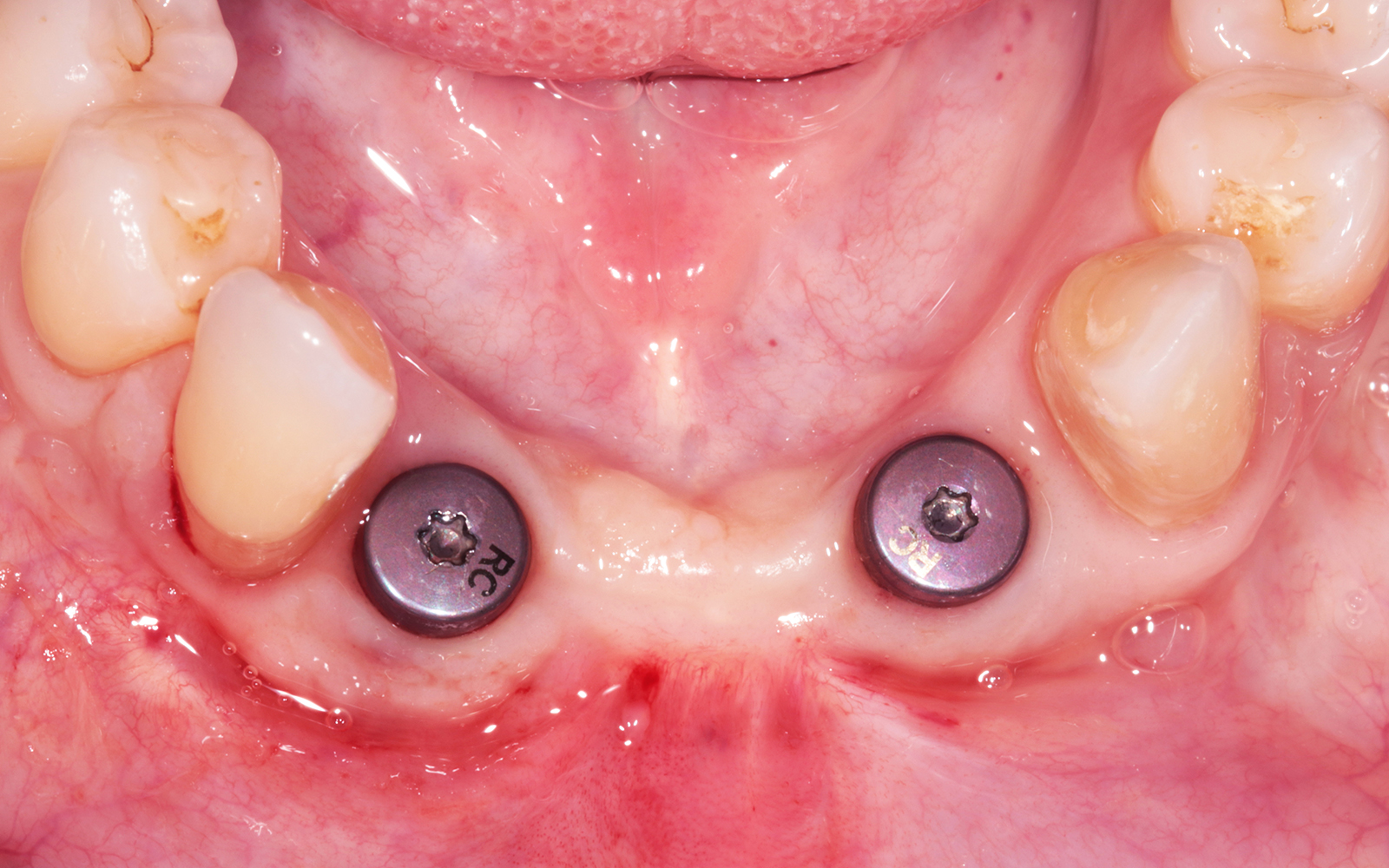
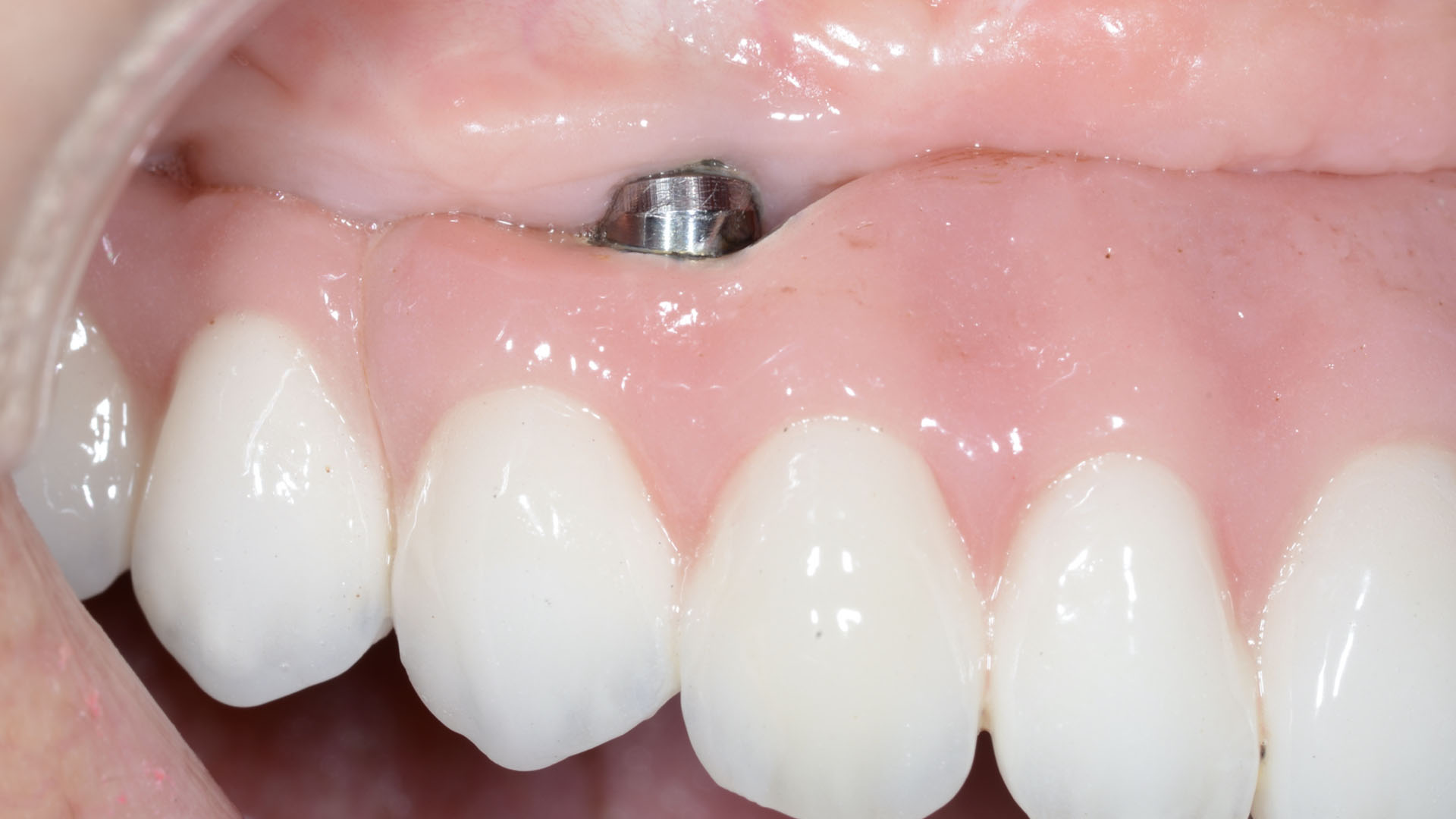
A 68-year-old male patient, who received an implant in tooth position #31 about 8 years prior, presented for an examination. He reports bleeding during brushing around the implant and some discomfort. Clinically, there was severe vertical bone loss, profuse bleeding on probing, and deep probing depths, but no pain. The condition was diagnosed as peri-implantitis according to the 2018 classification.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
Additional Risk Factors: The patient exhibited bleeding on probing and deep pocket depths. He also reported occasional marijuana use and was inconsistent with periodontal maintenance and oral hygiene visits.
THE APPROACH
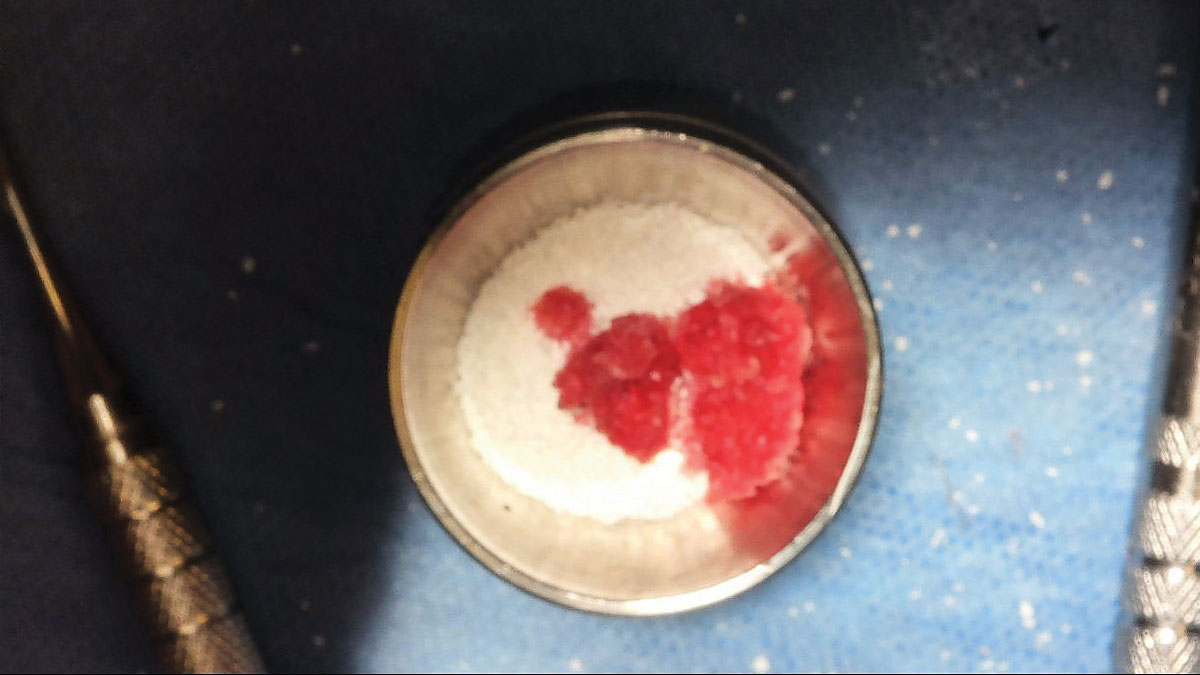
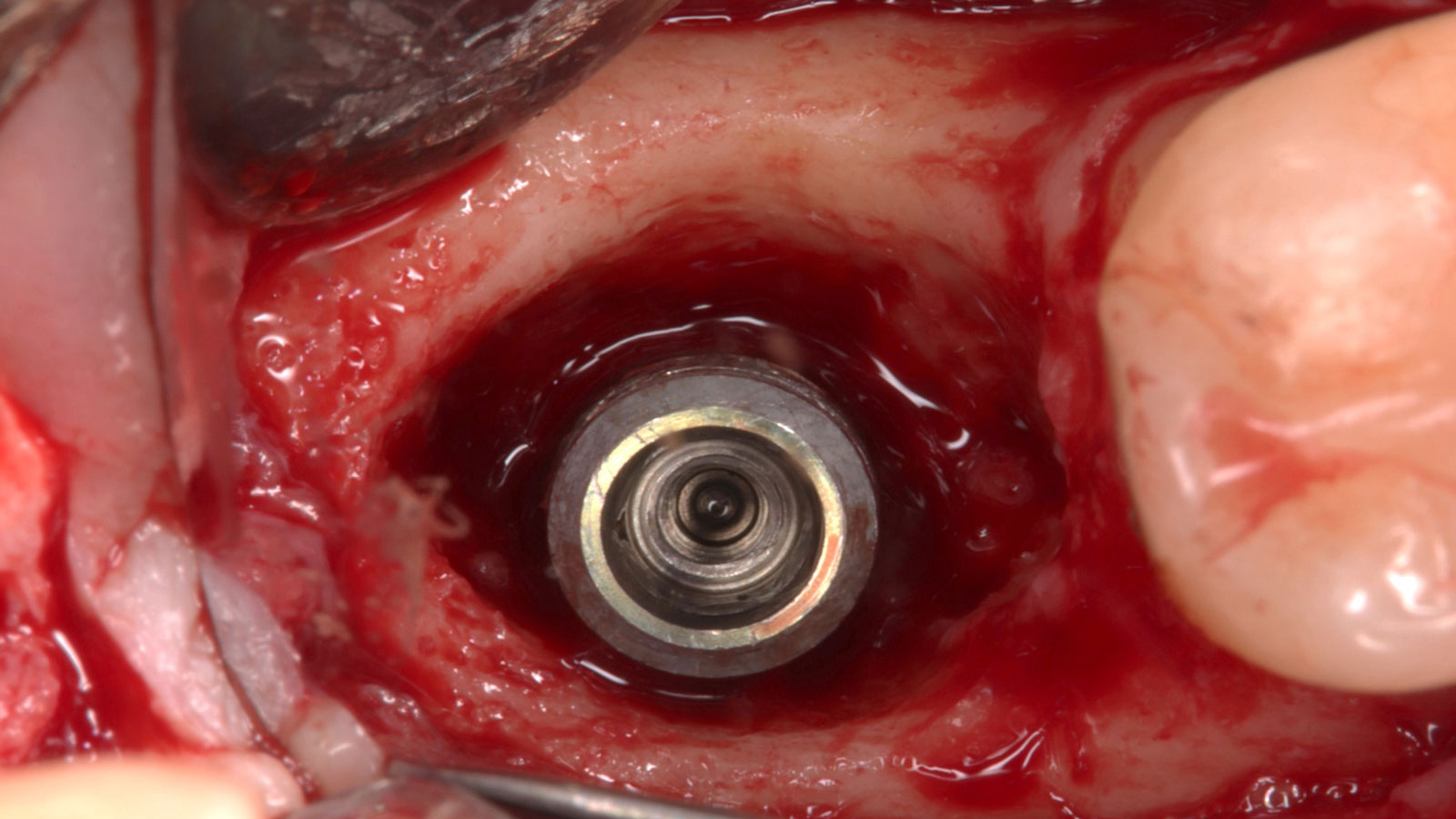
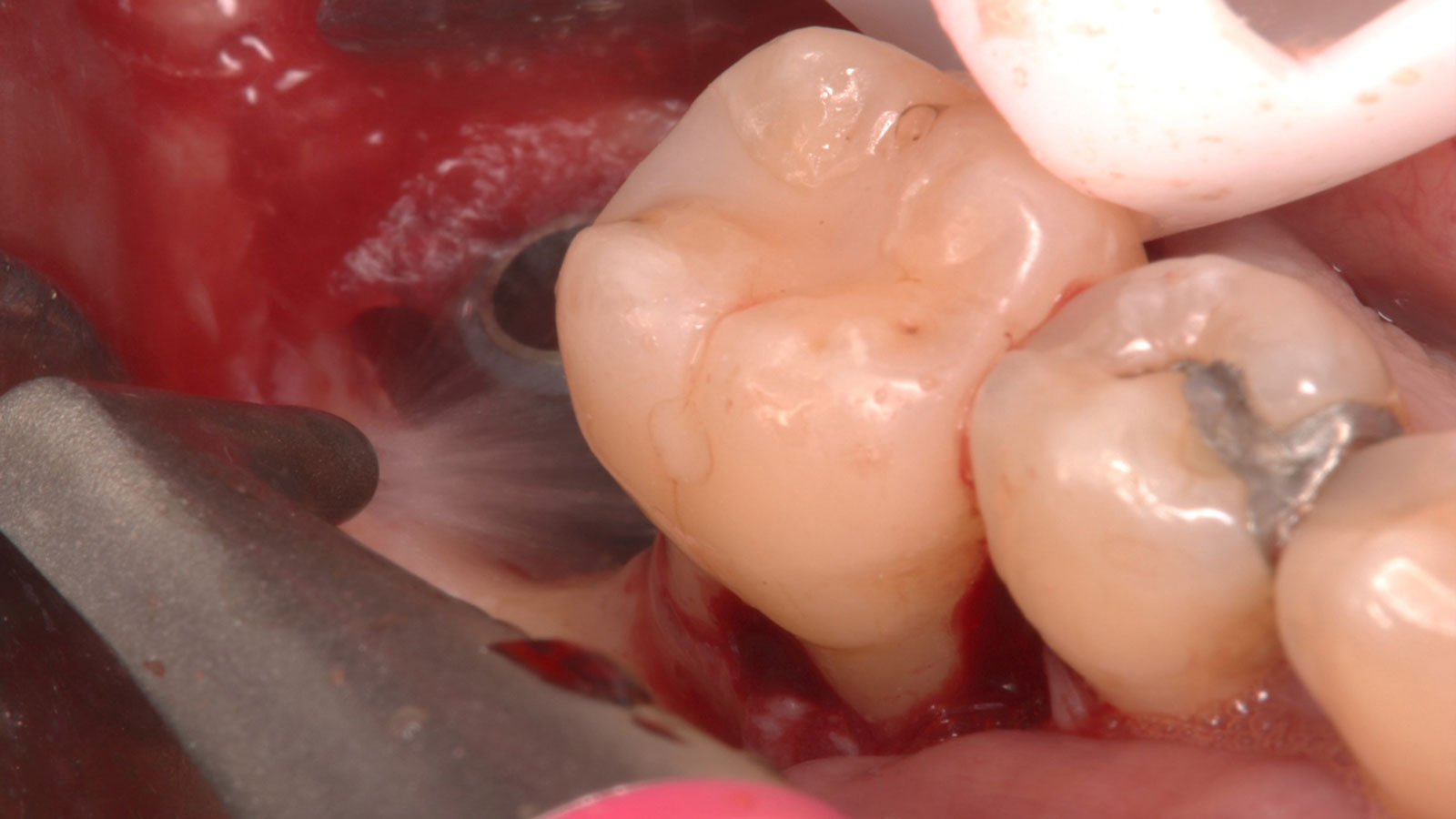
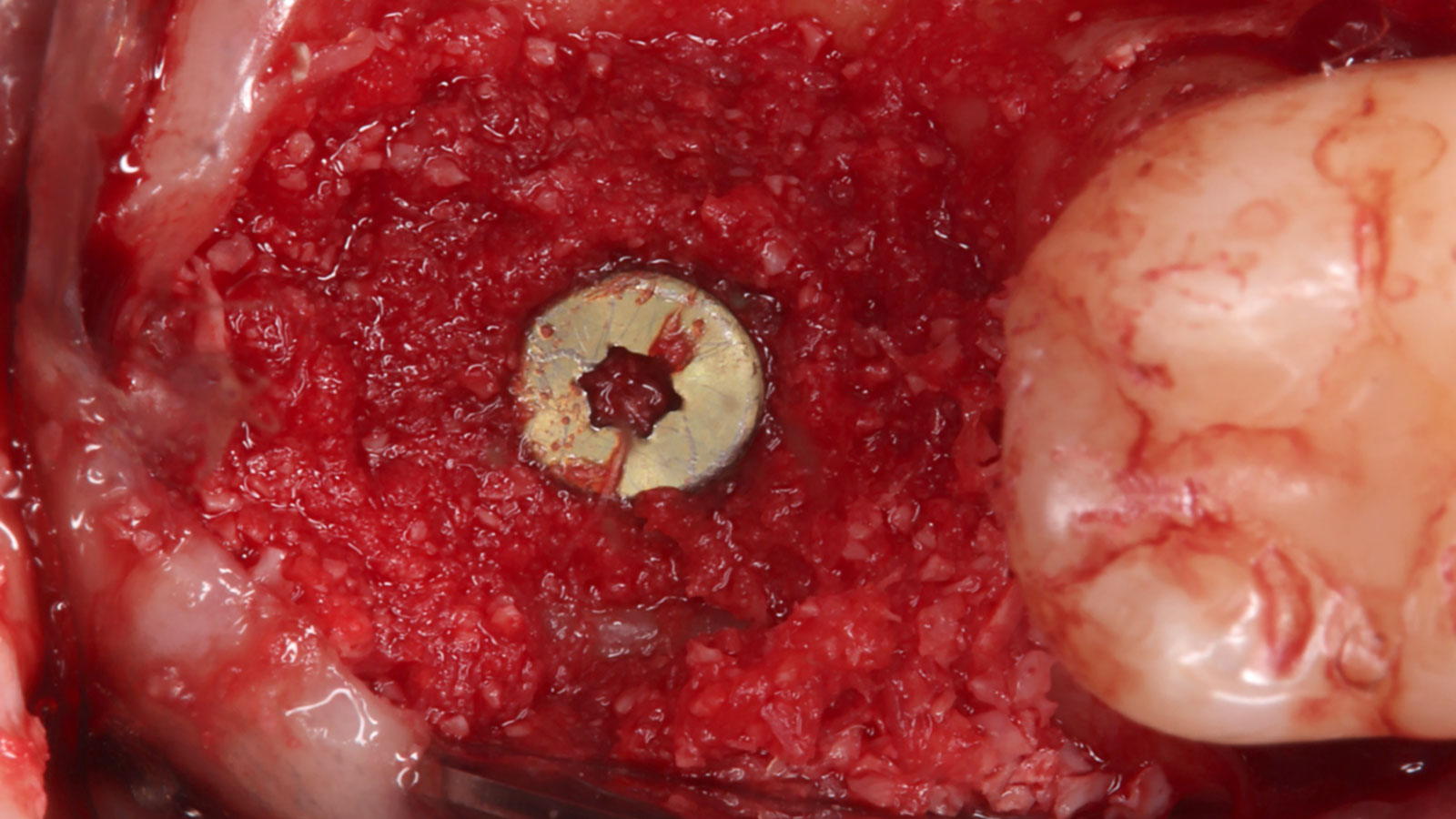
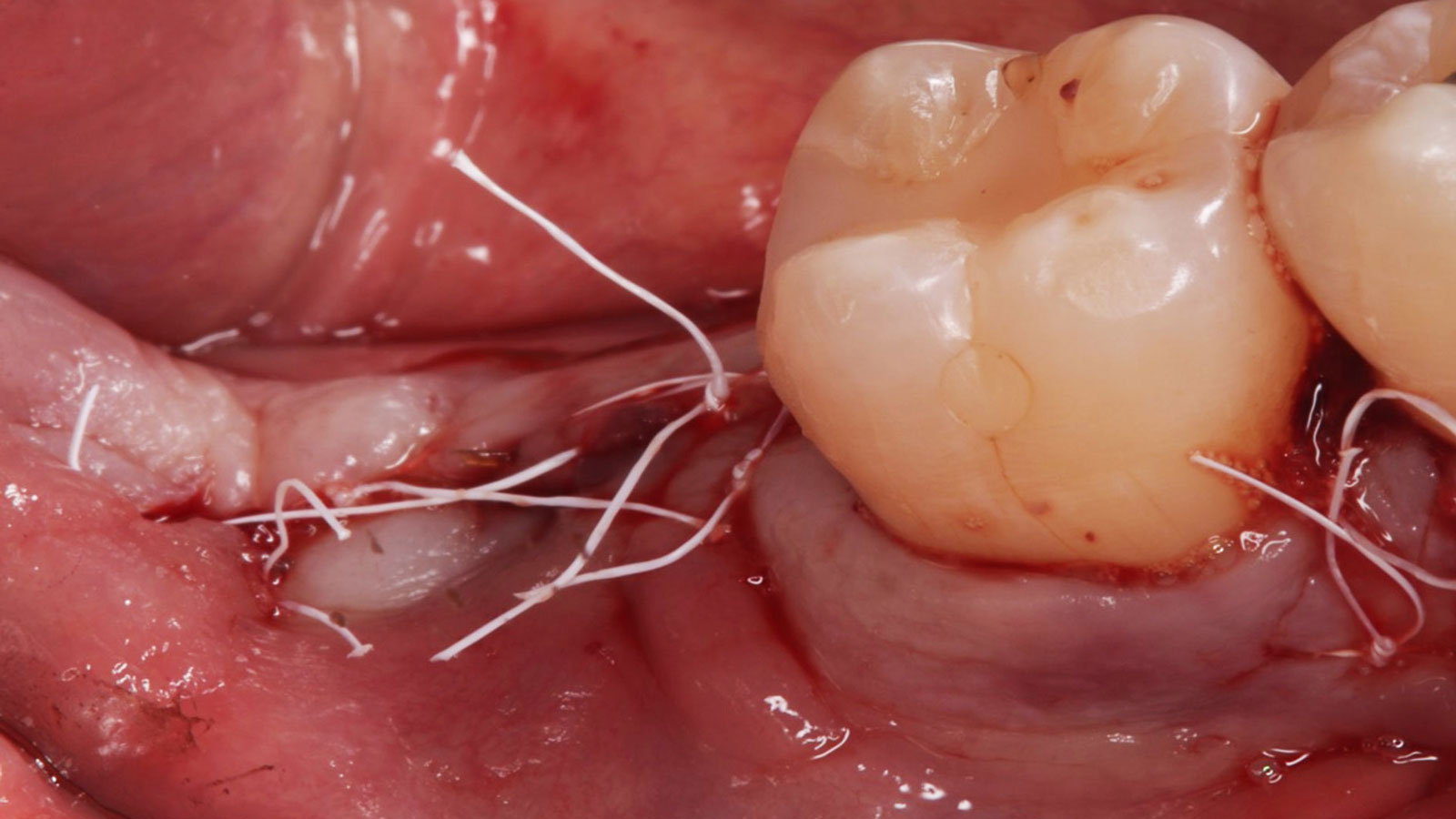
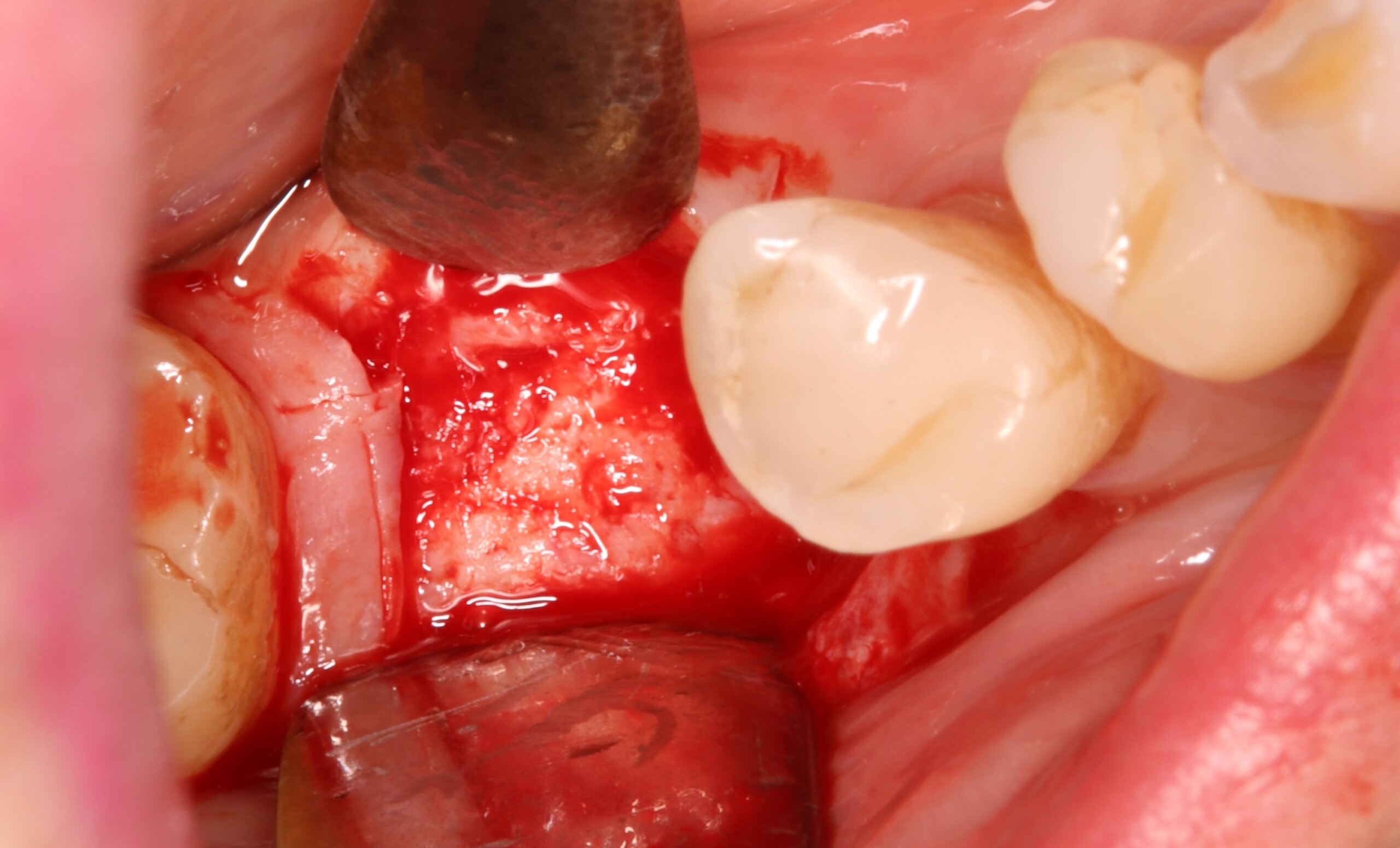
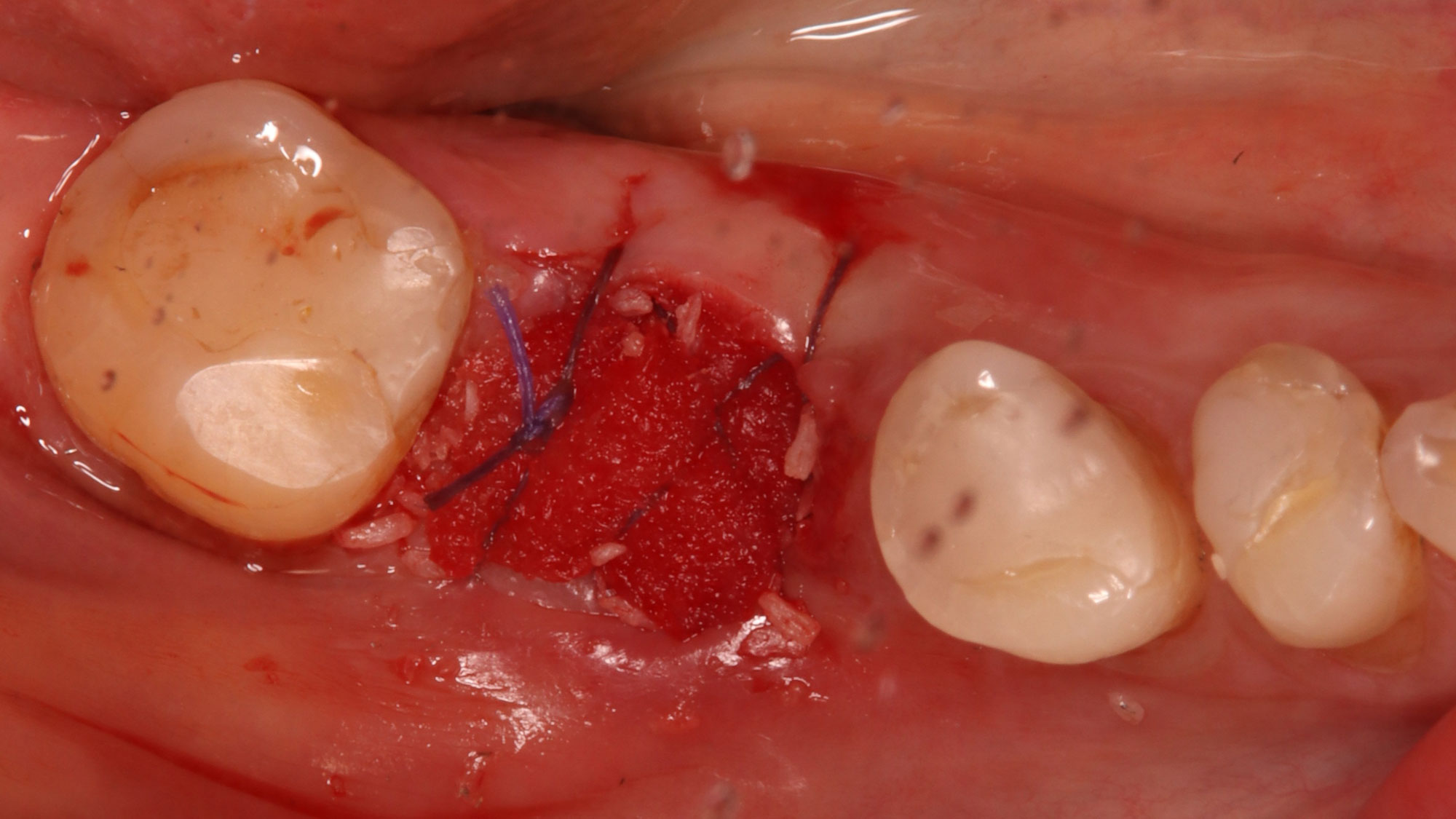
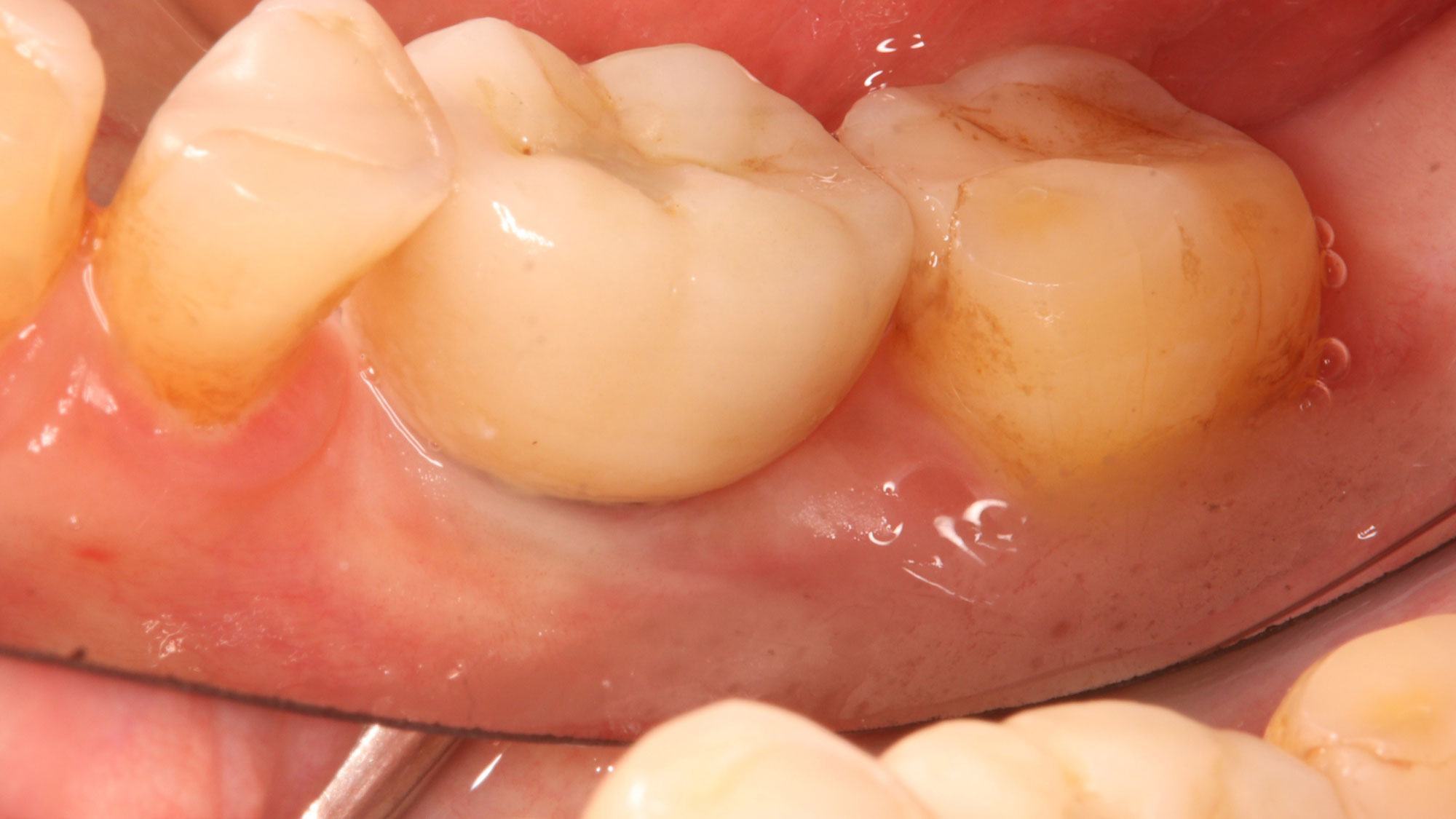
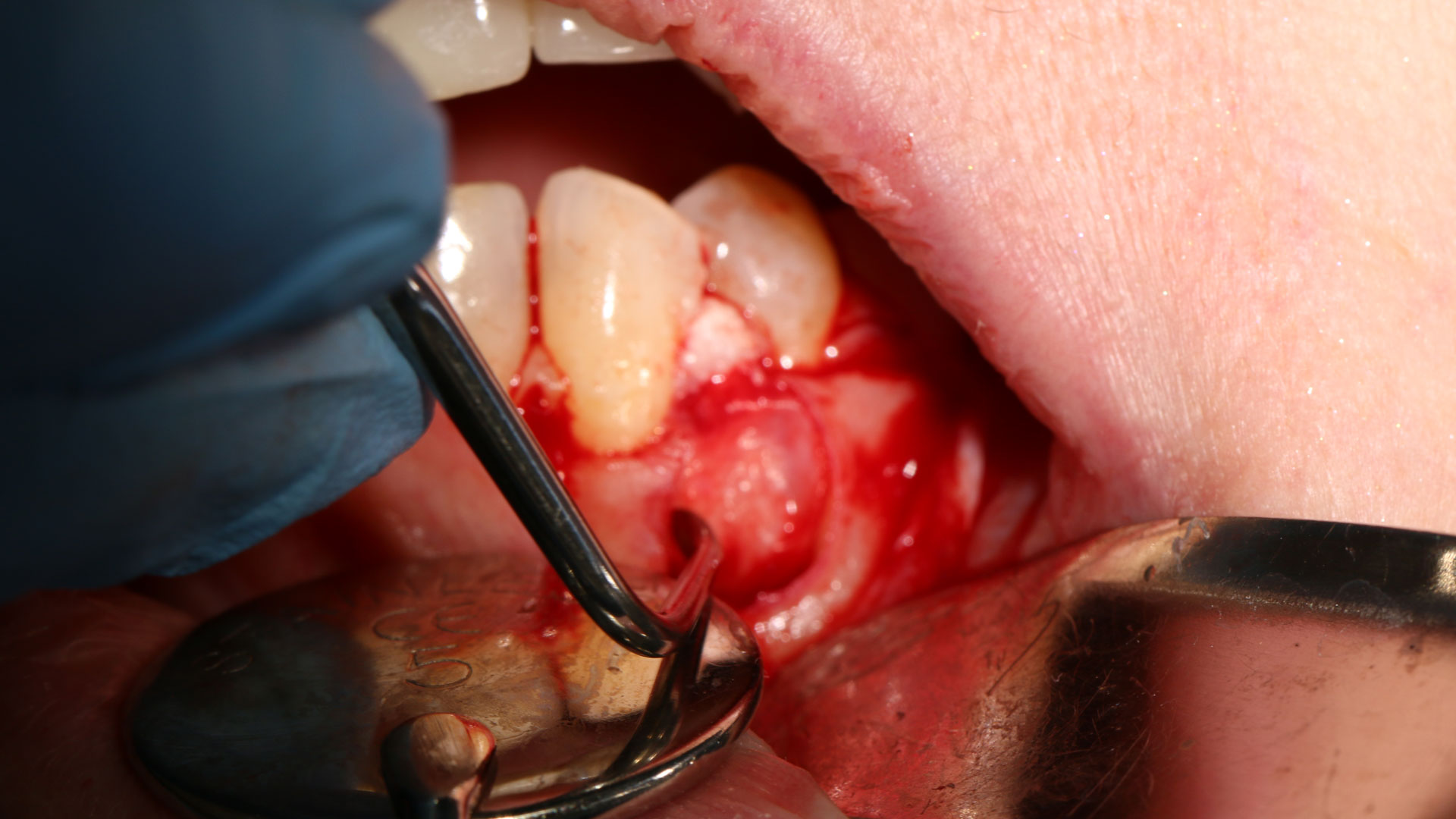
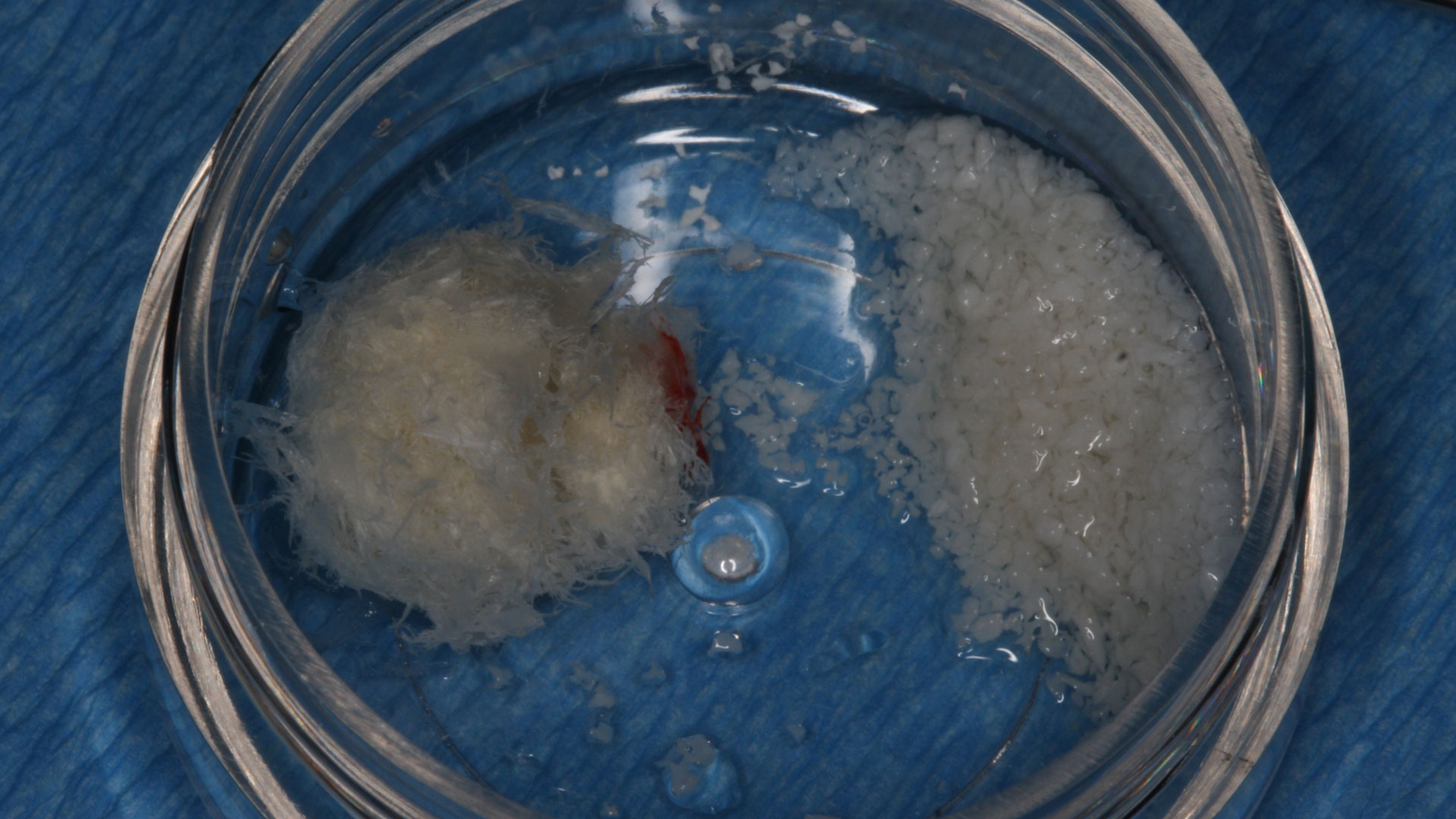
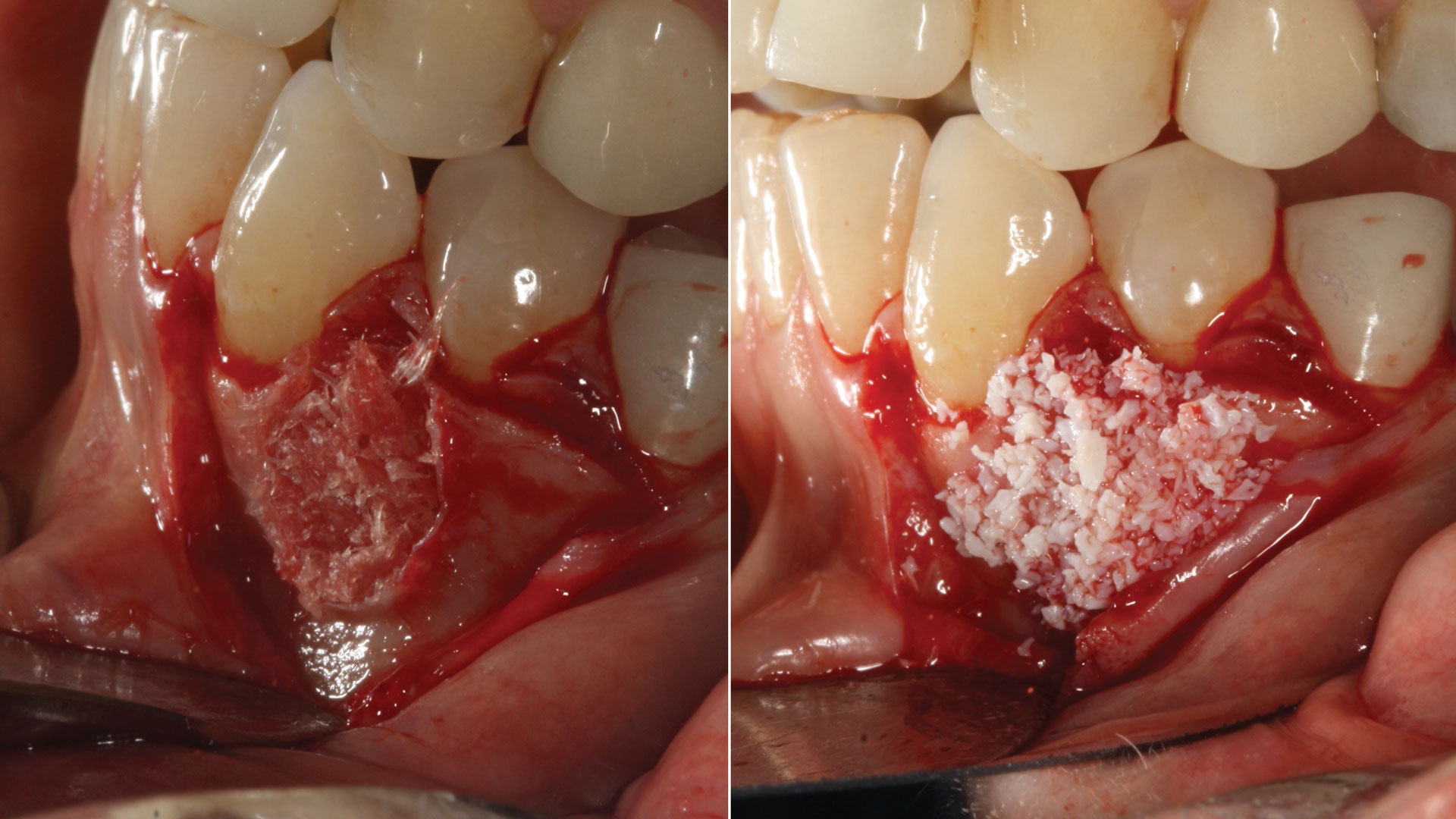
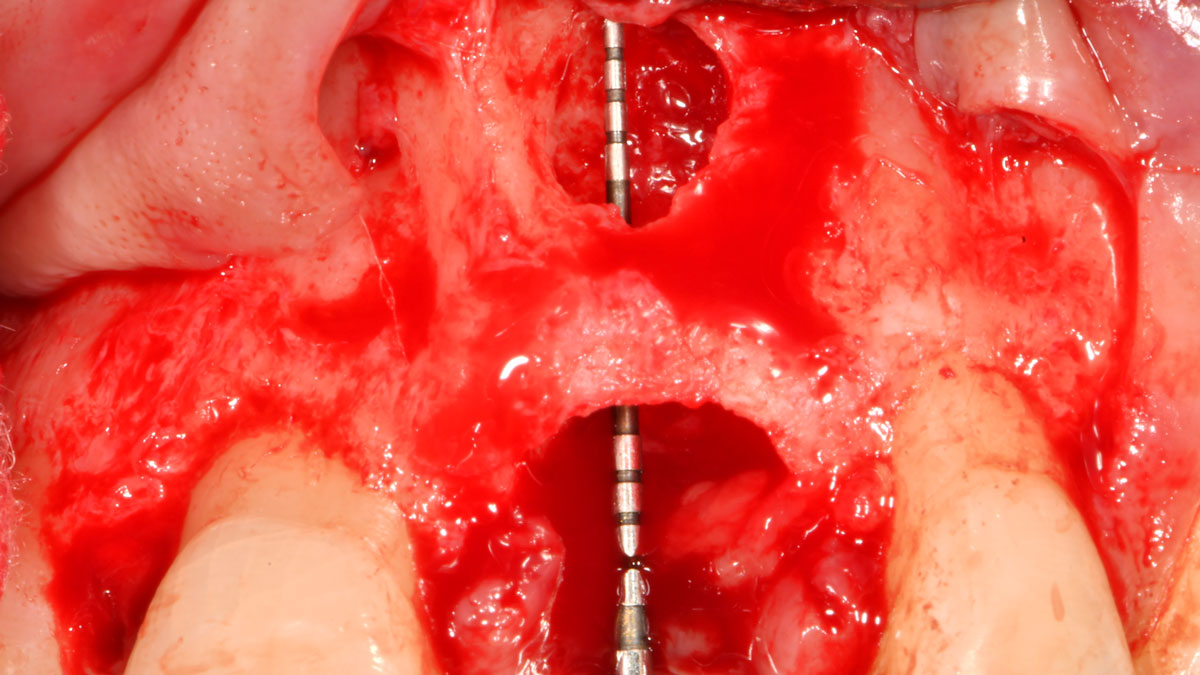
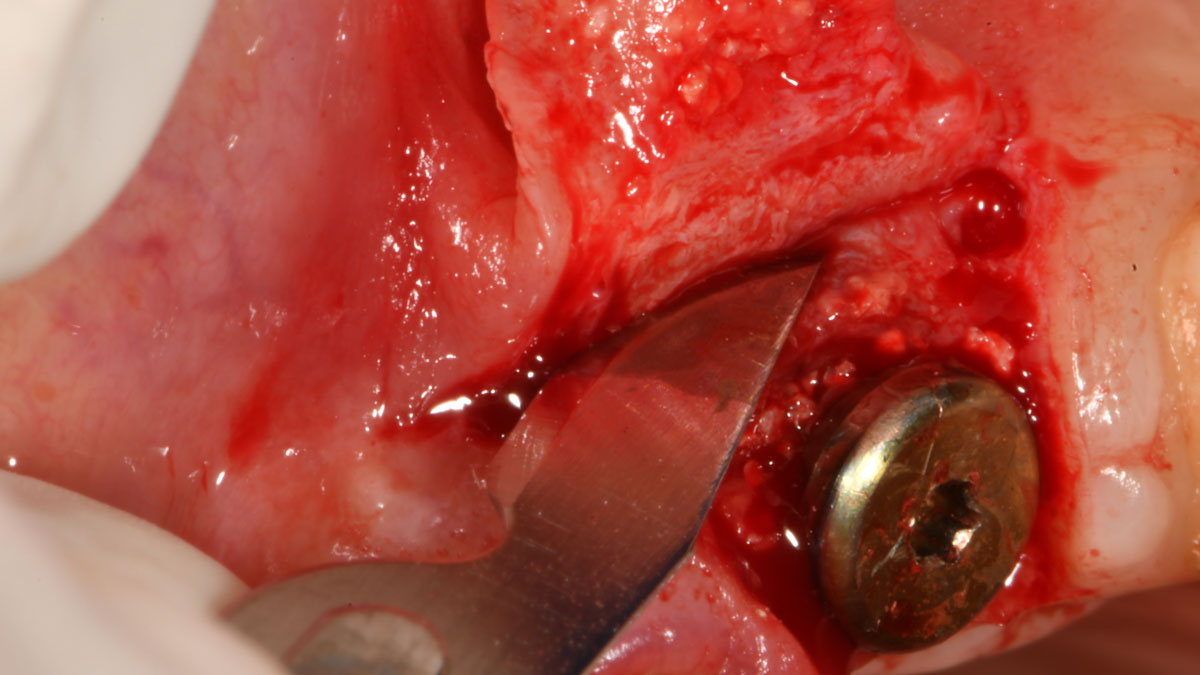
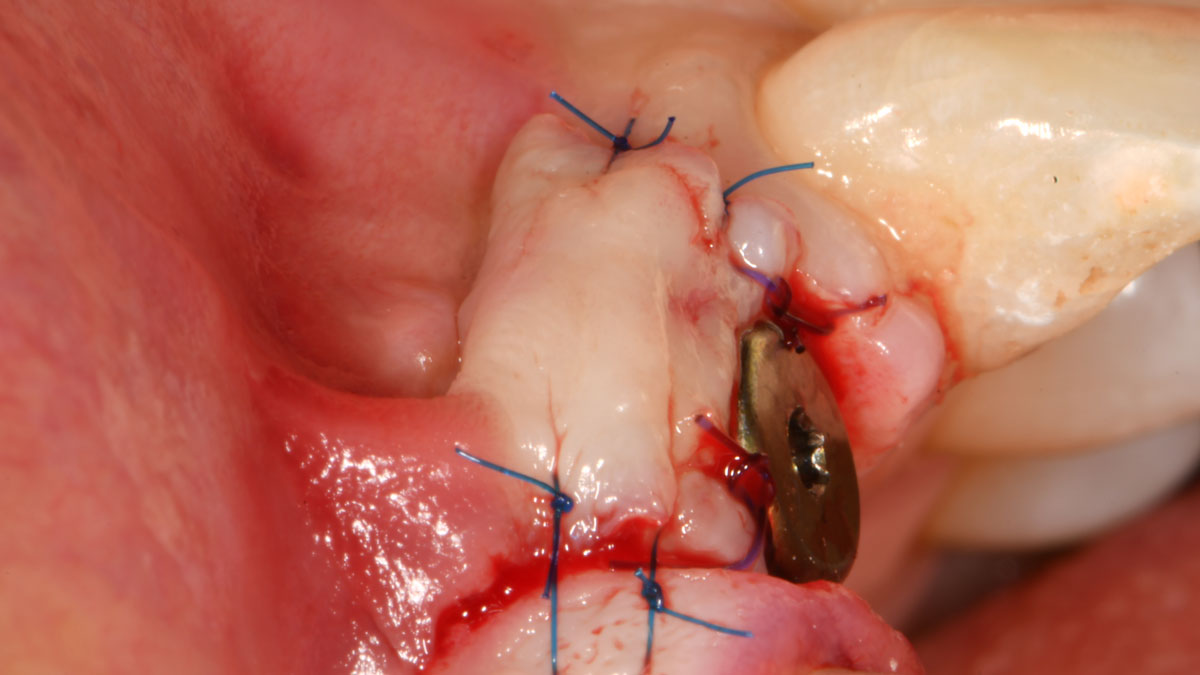
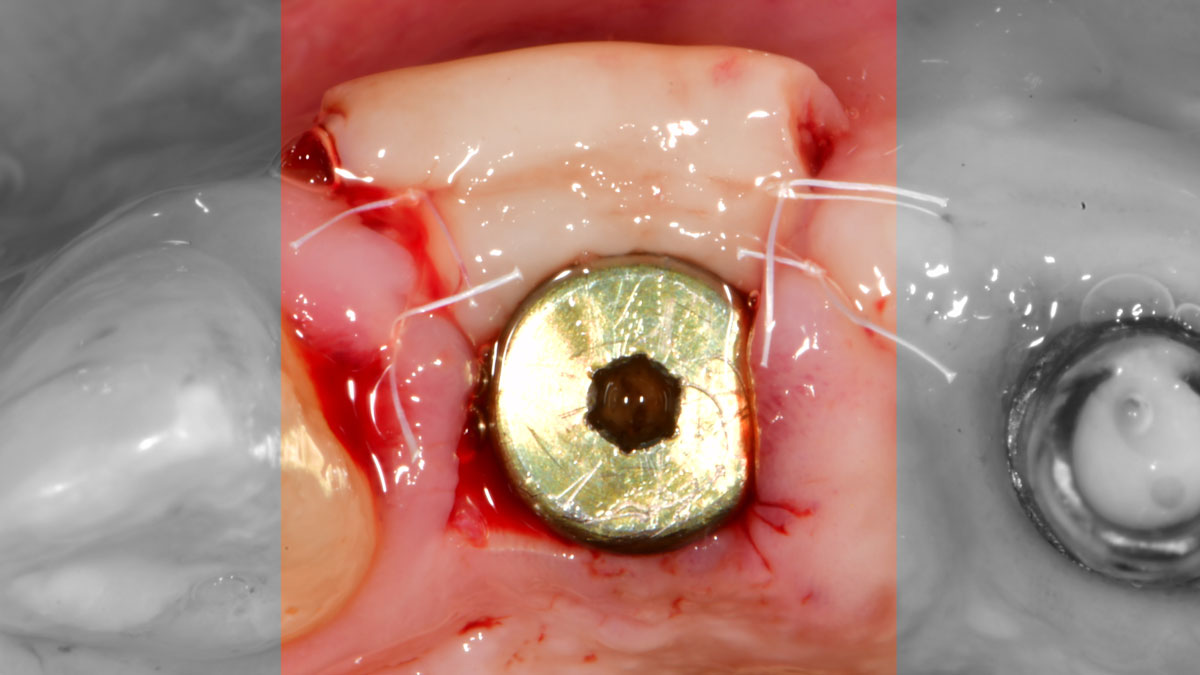
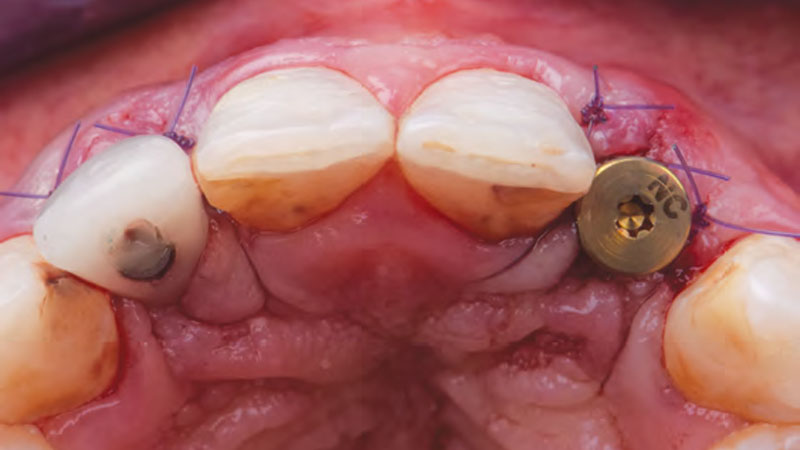
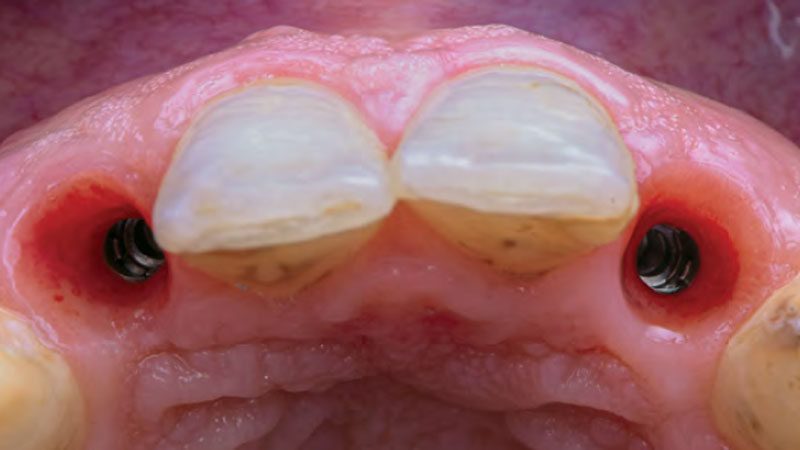
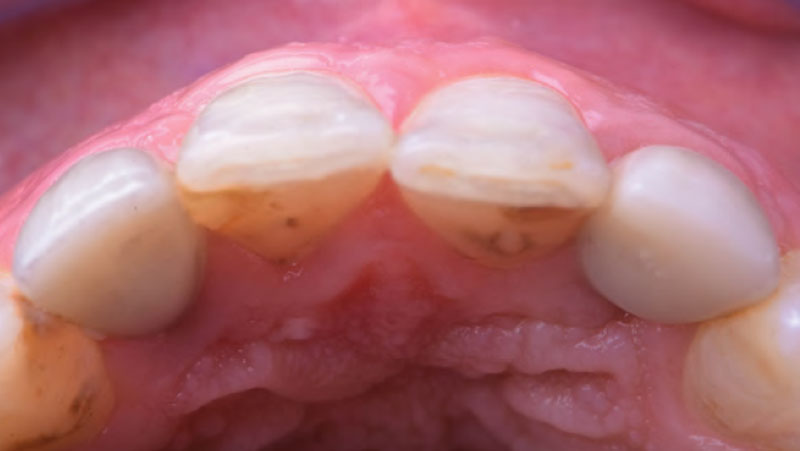
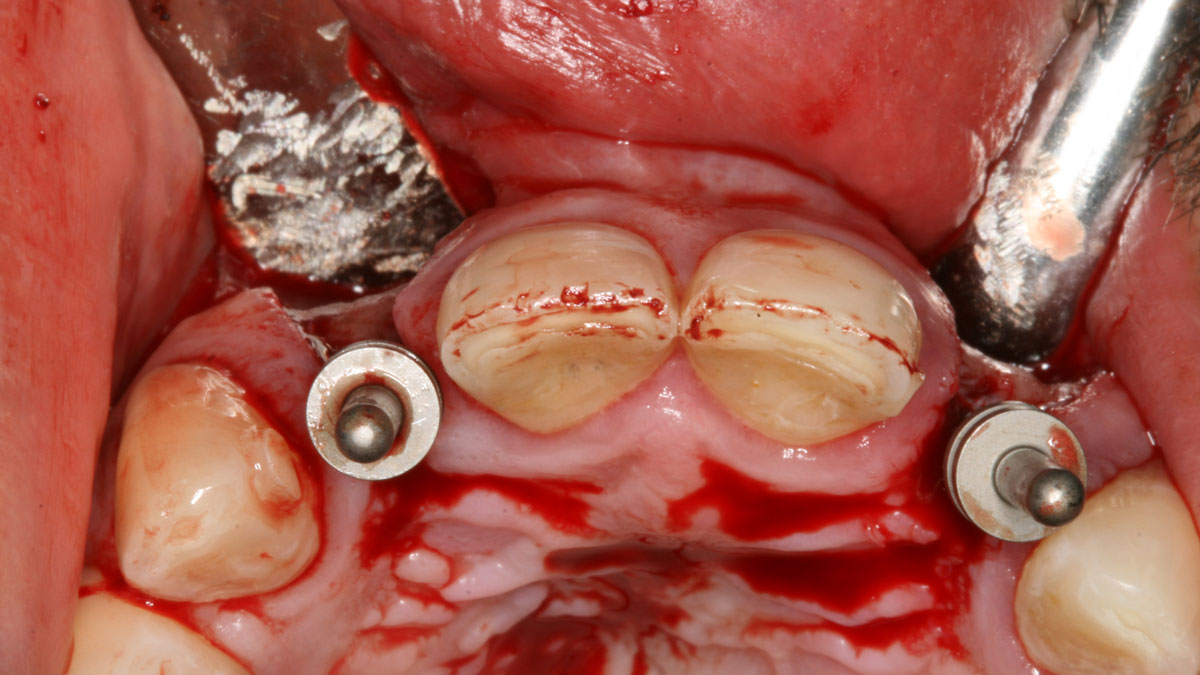
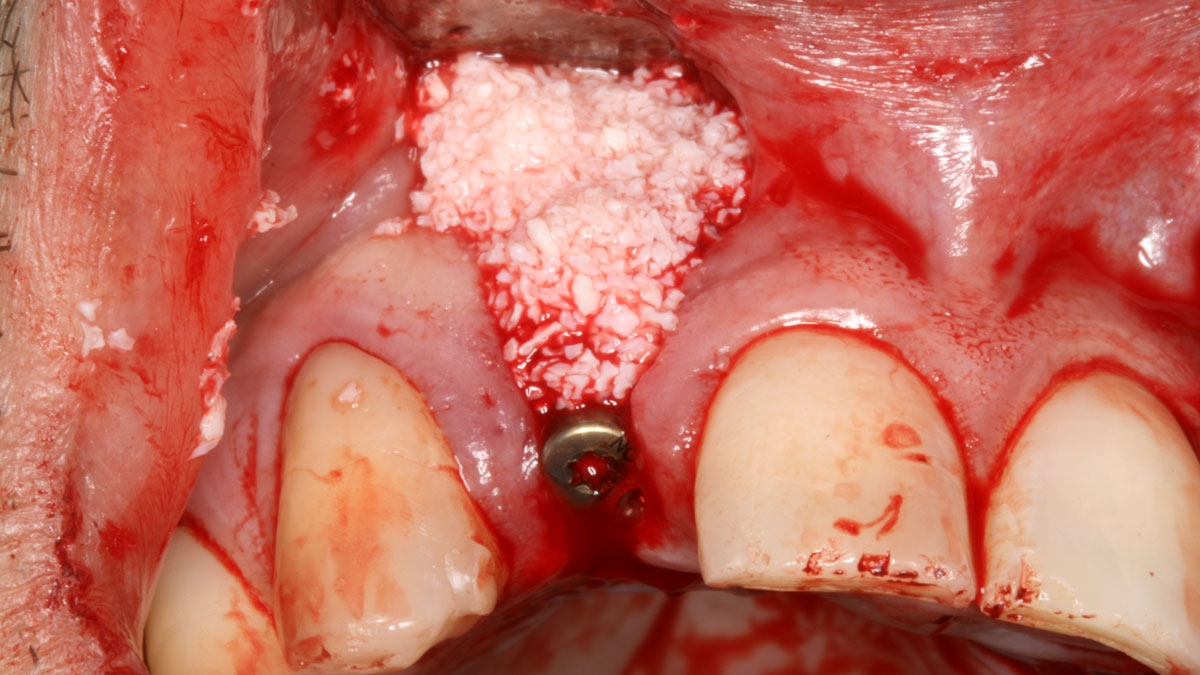
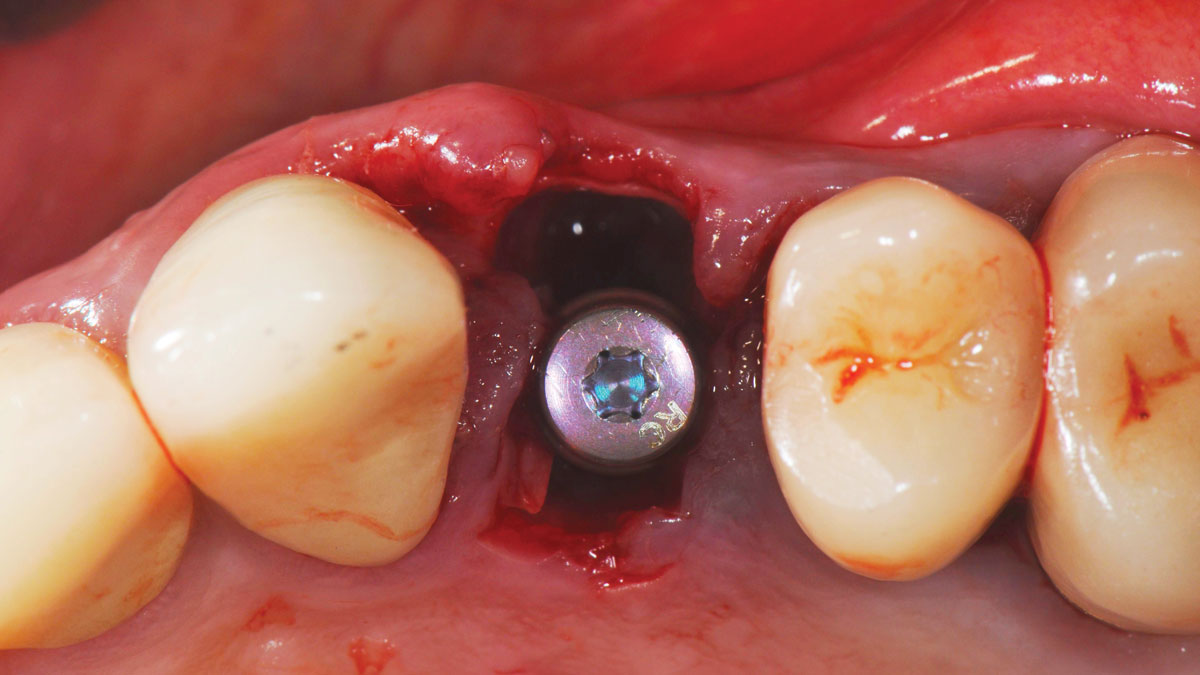
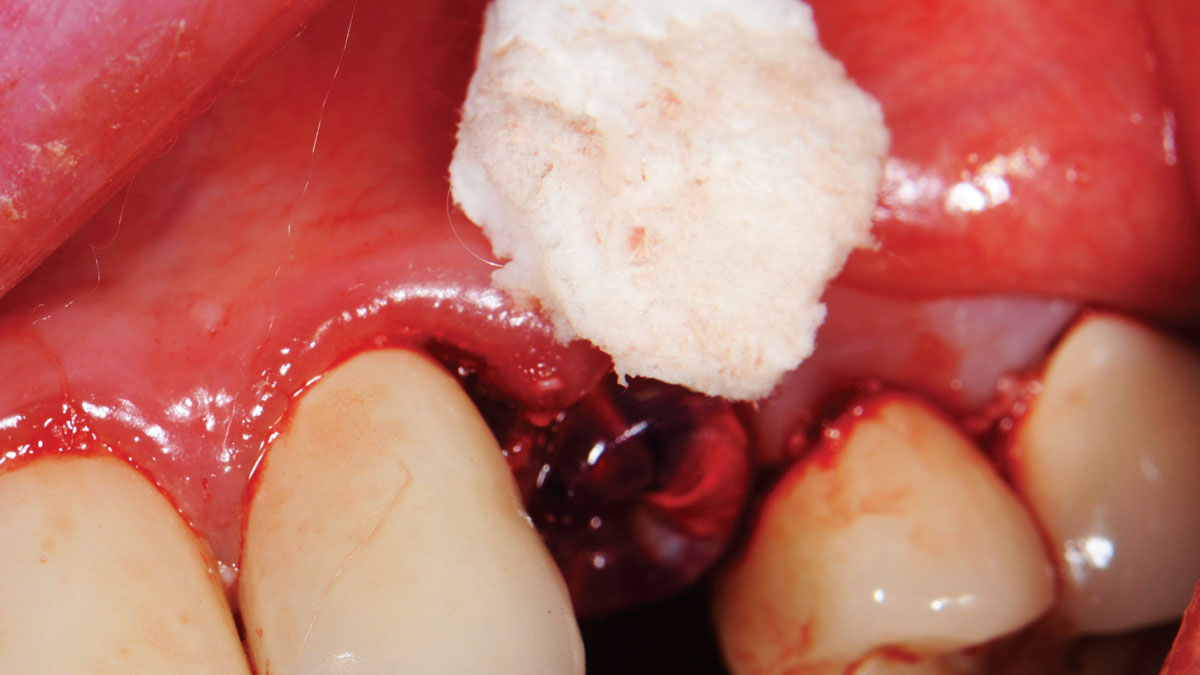
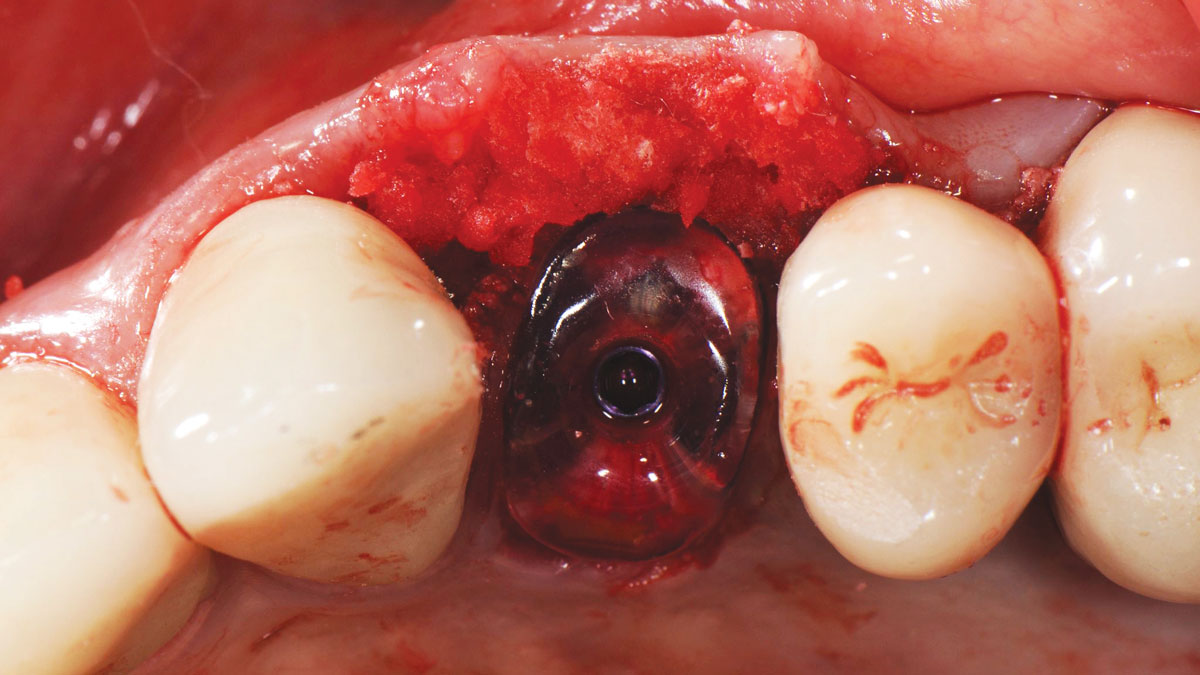
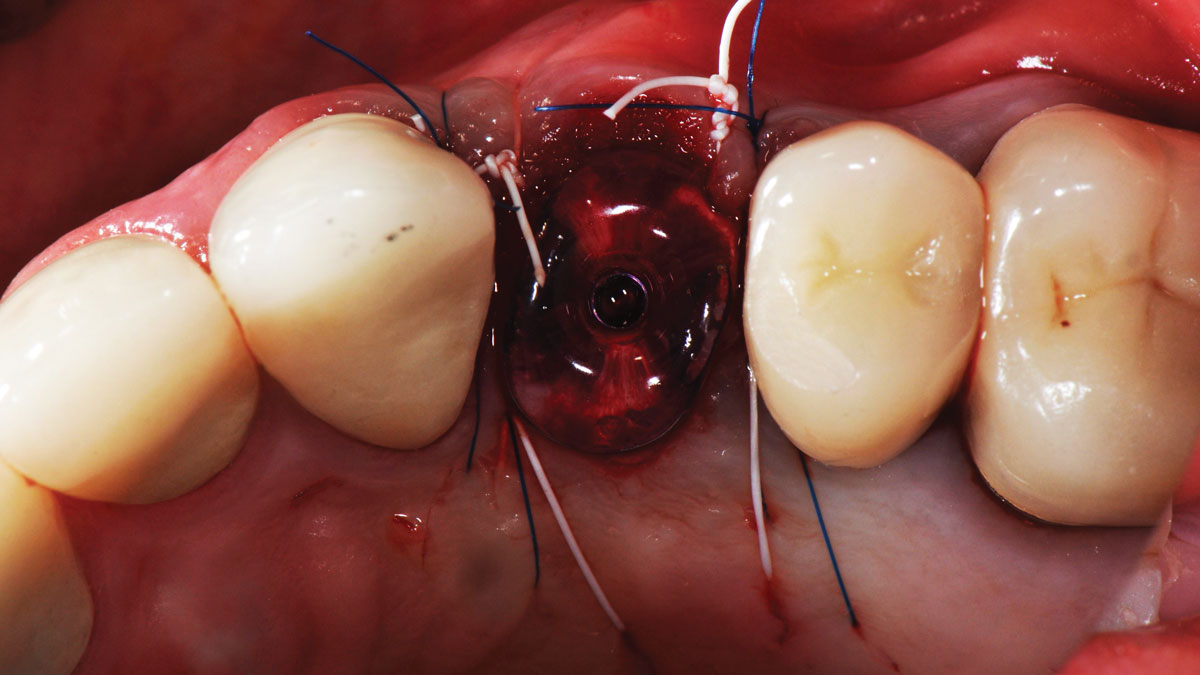
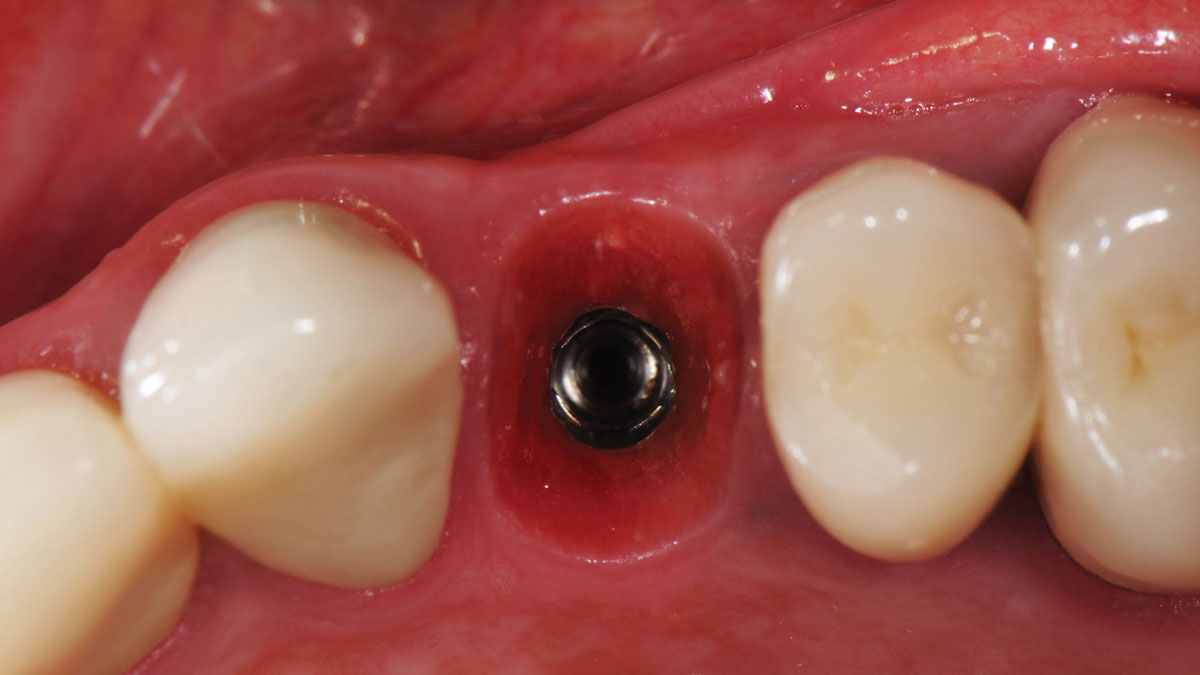
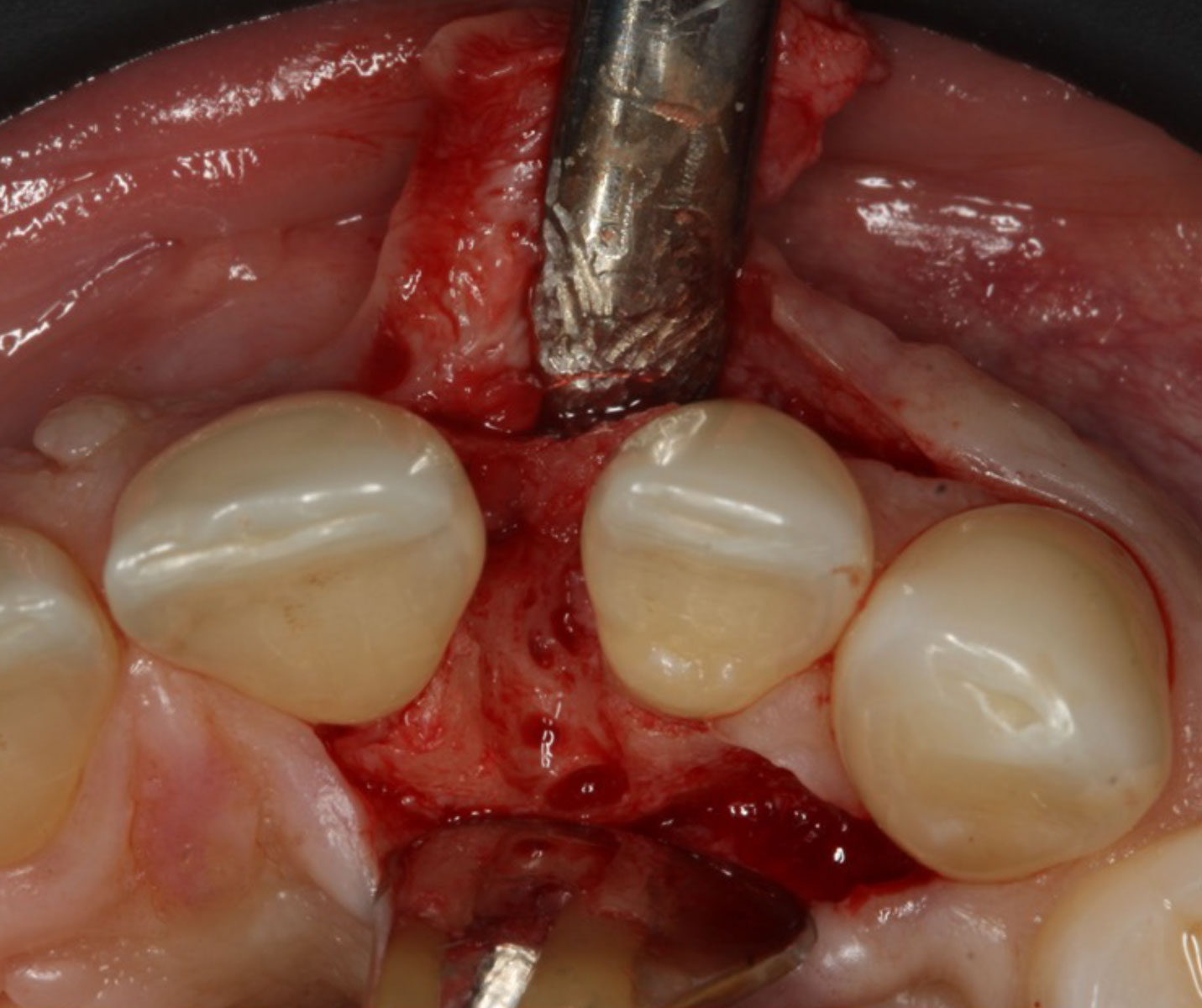
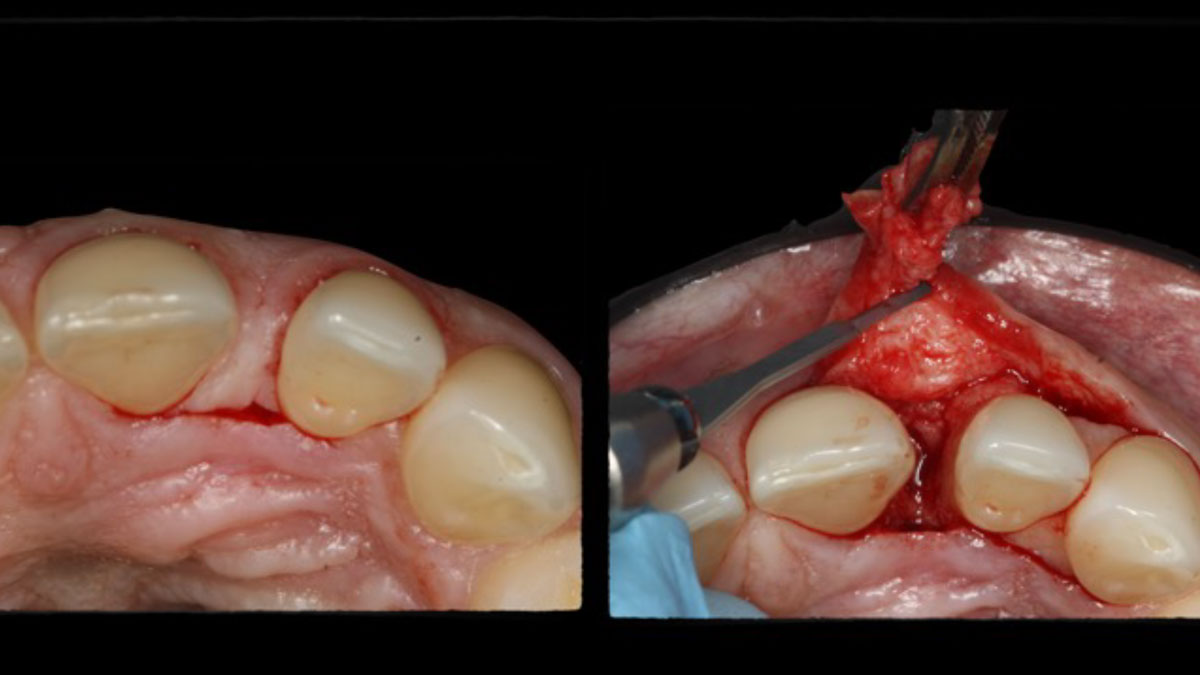
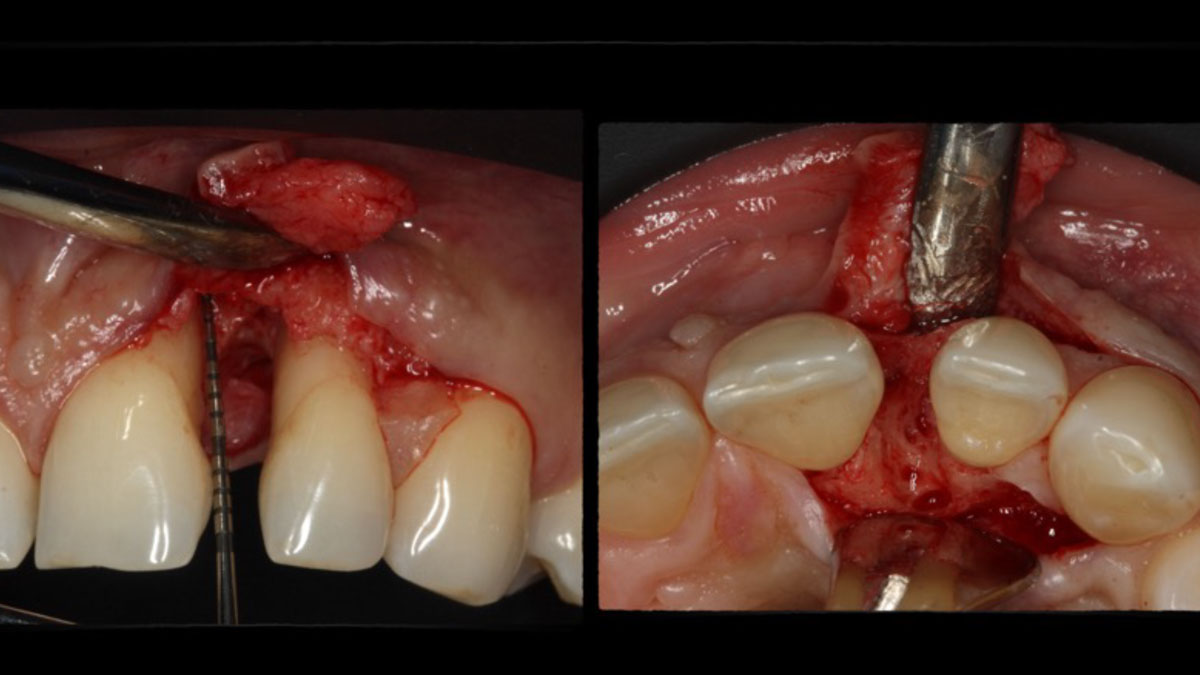
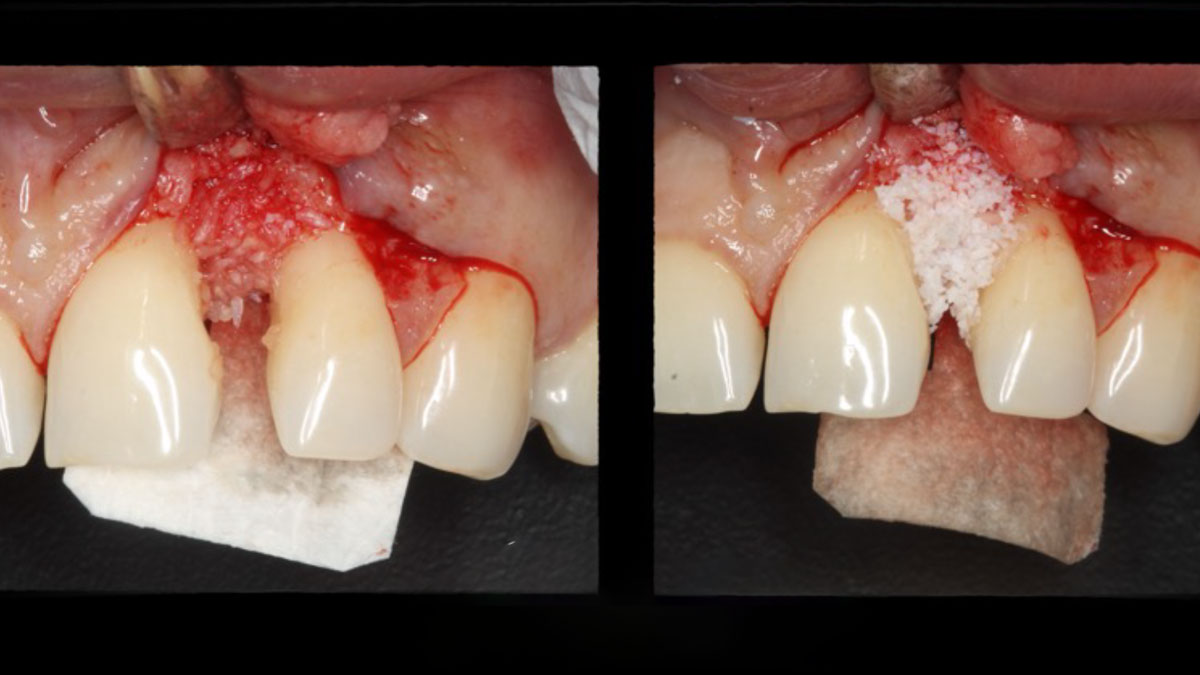
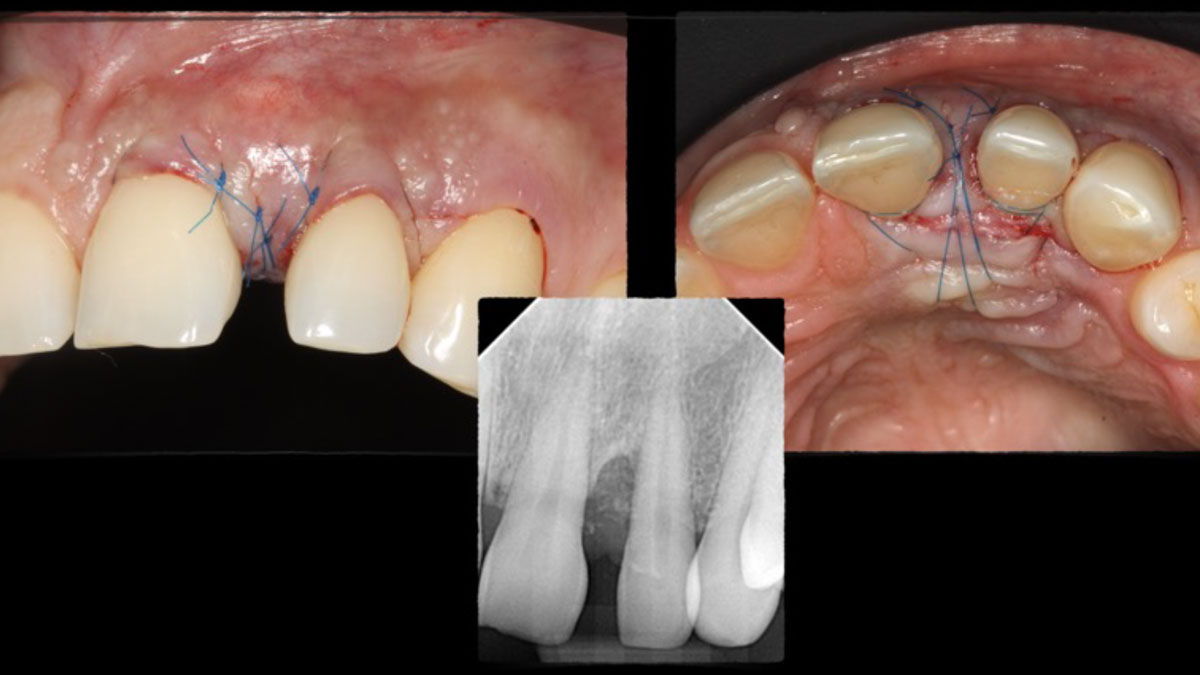
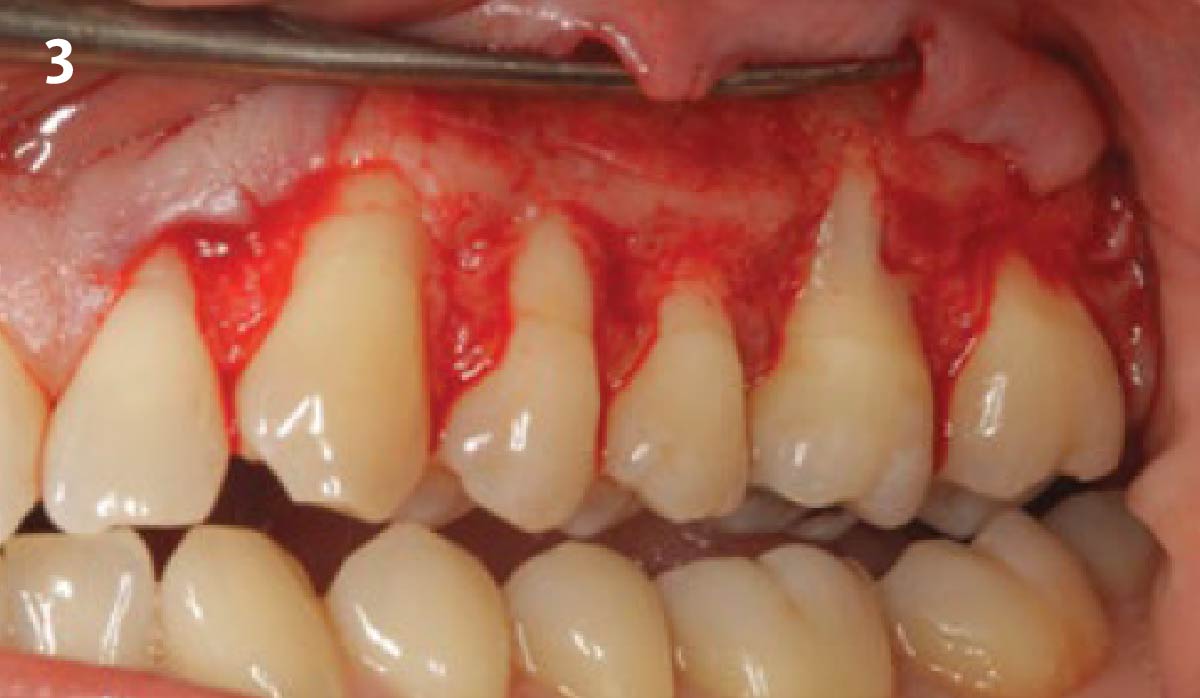
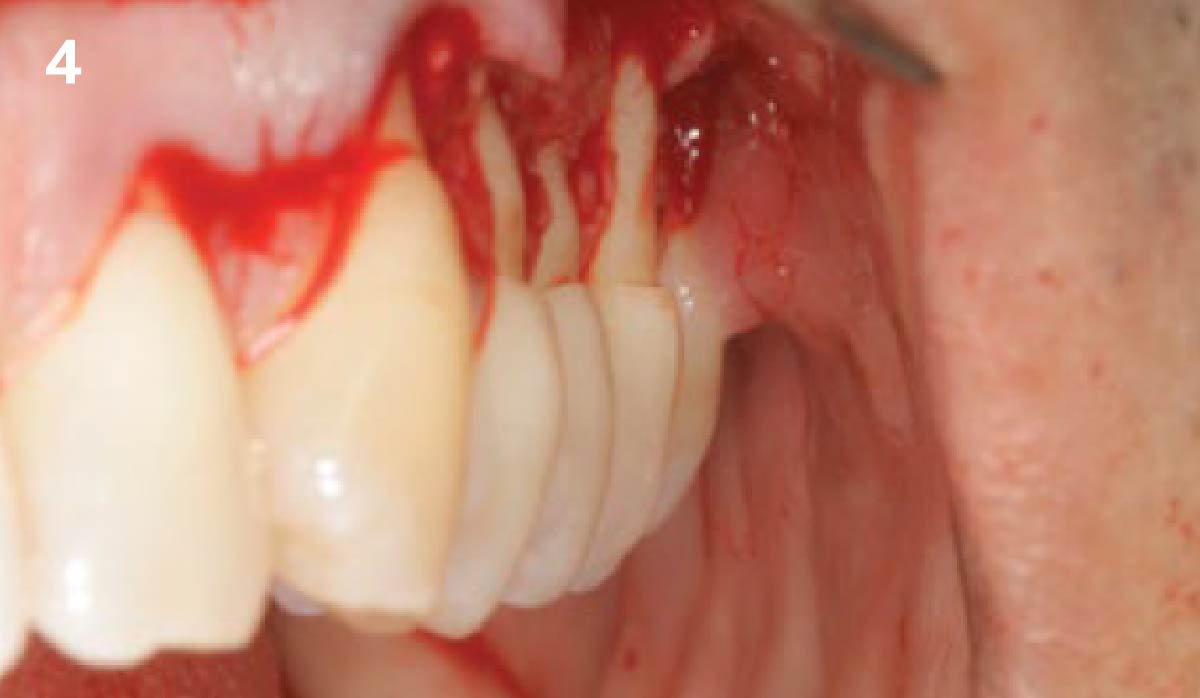
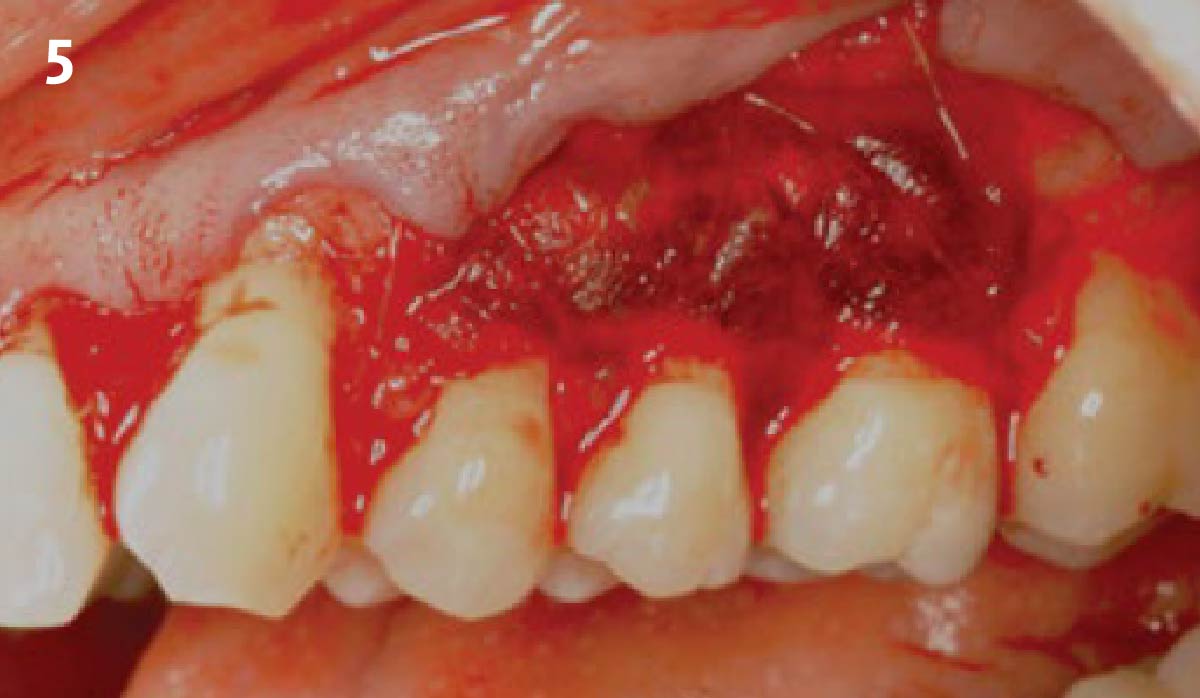
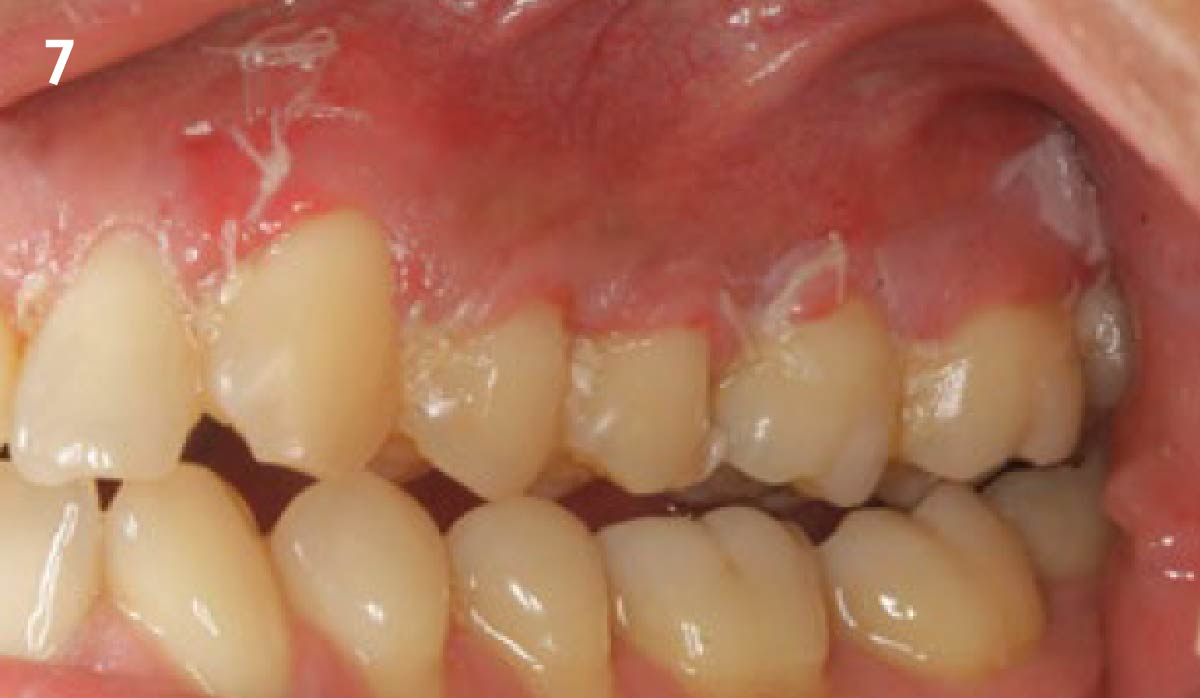
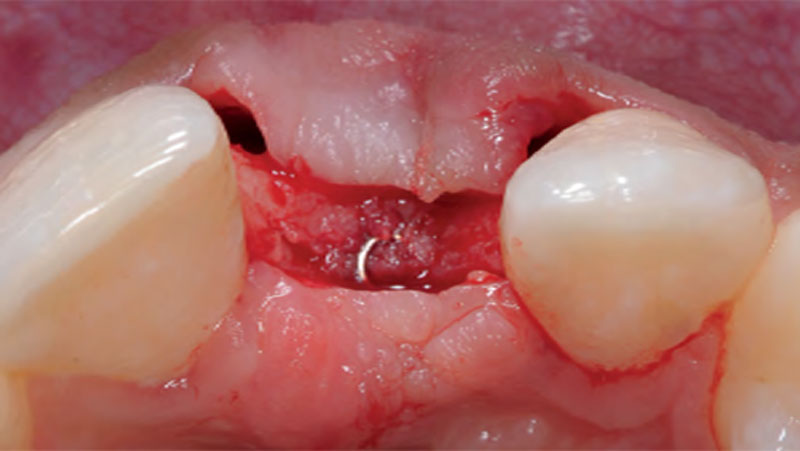
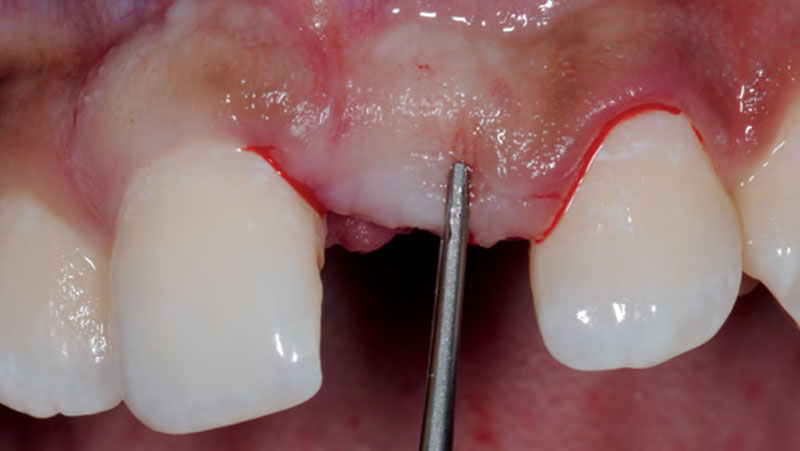
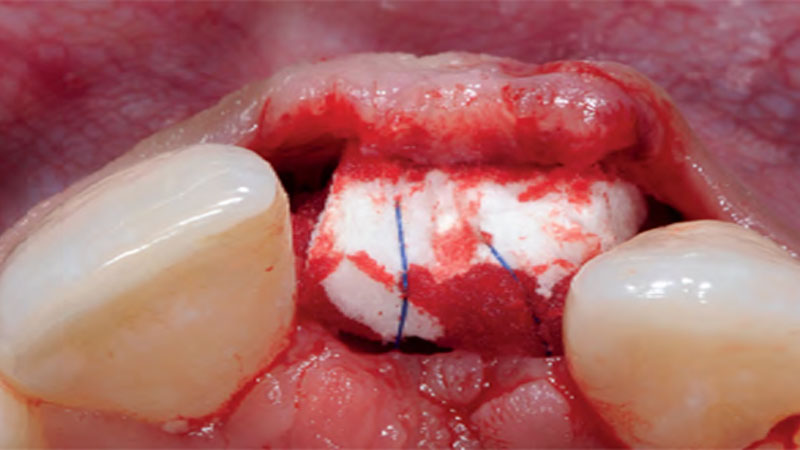
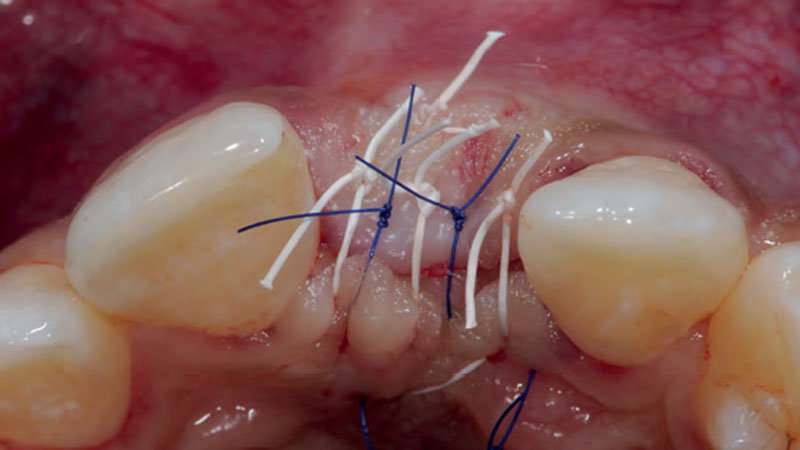
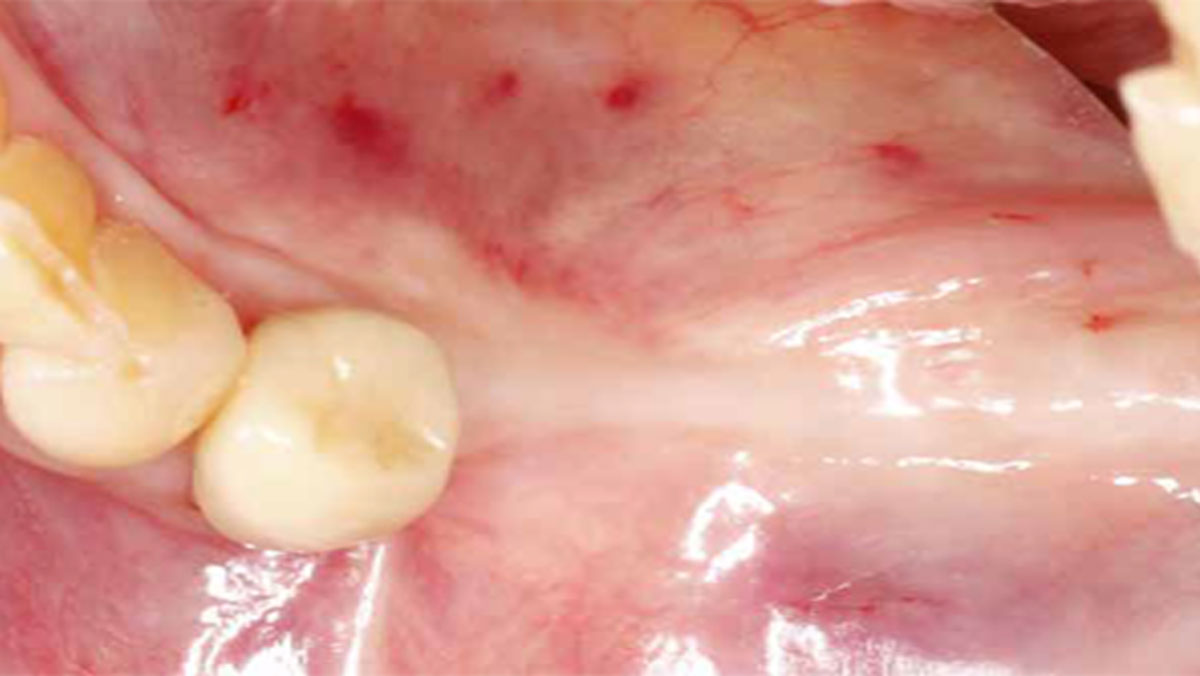
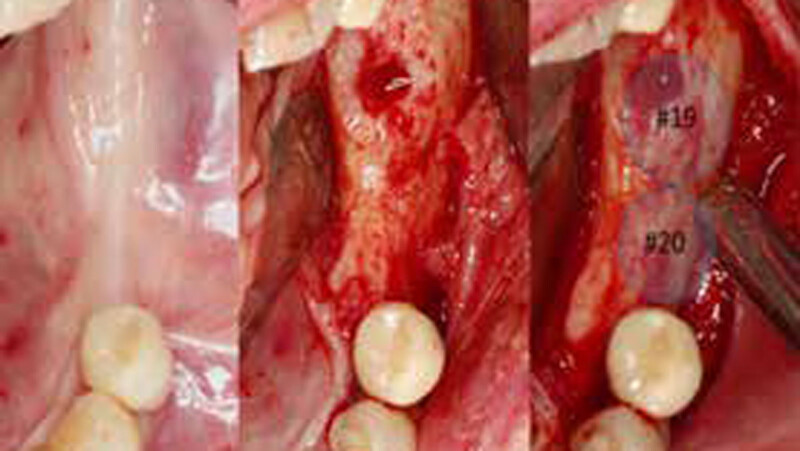
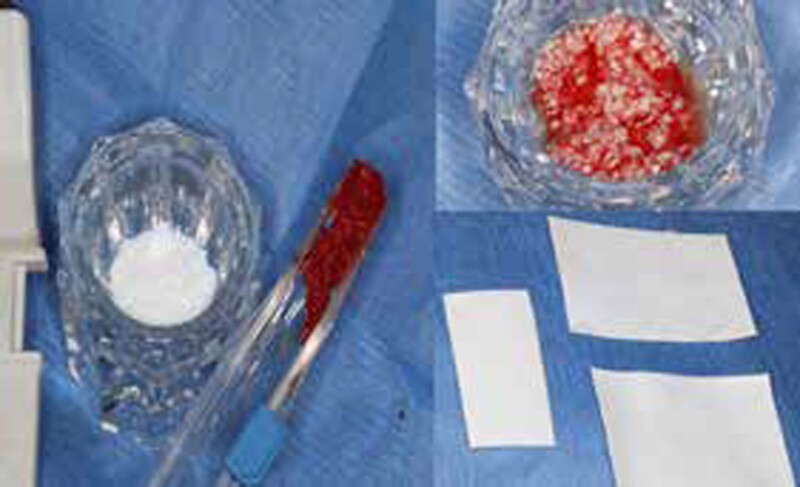
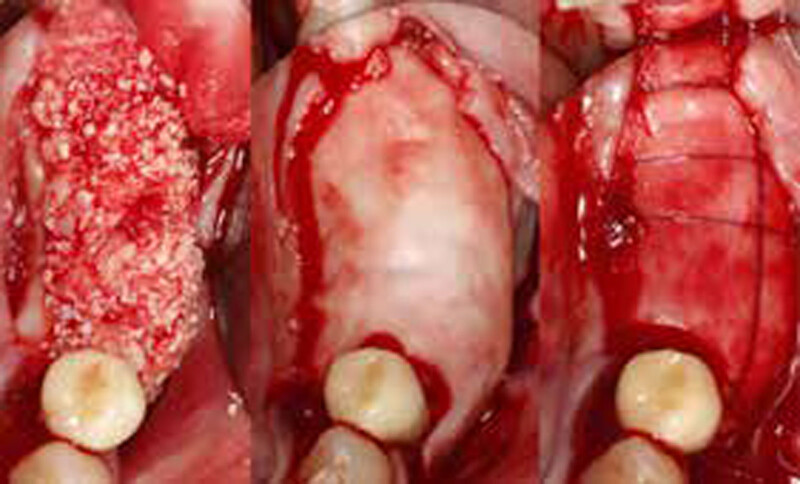
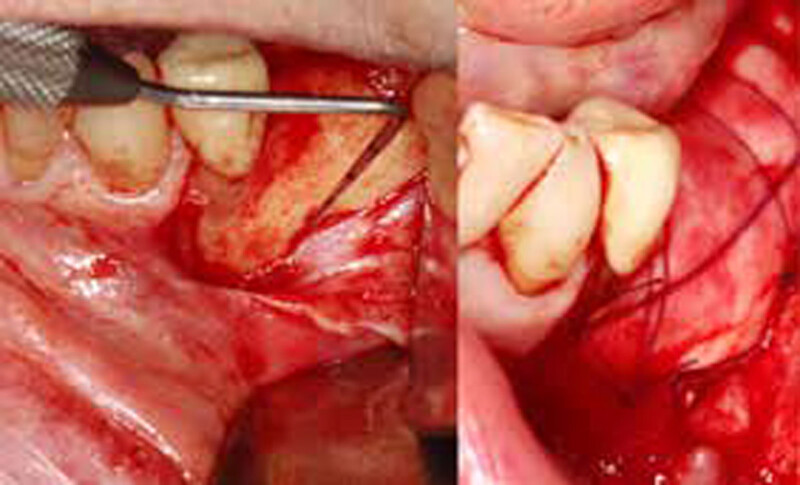
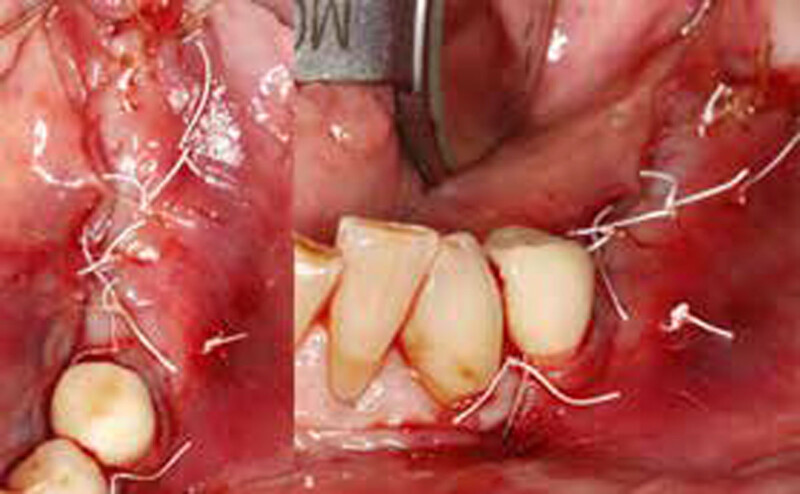
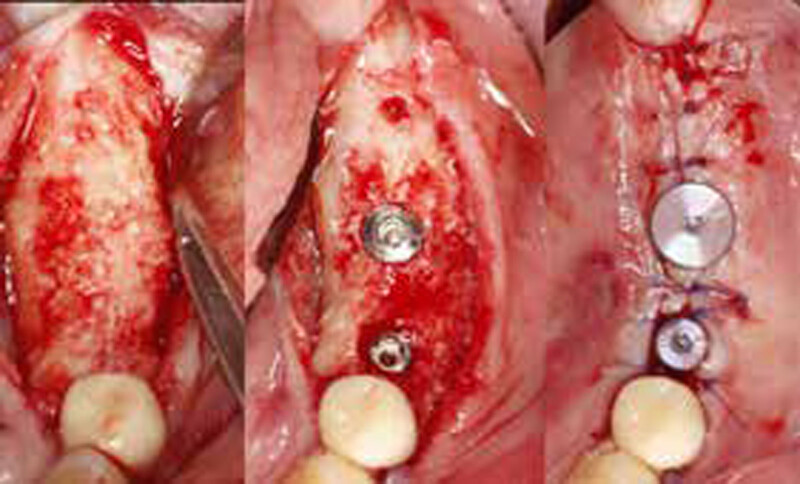
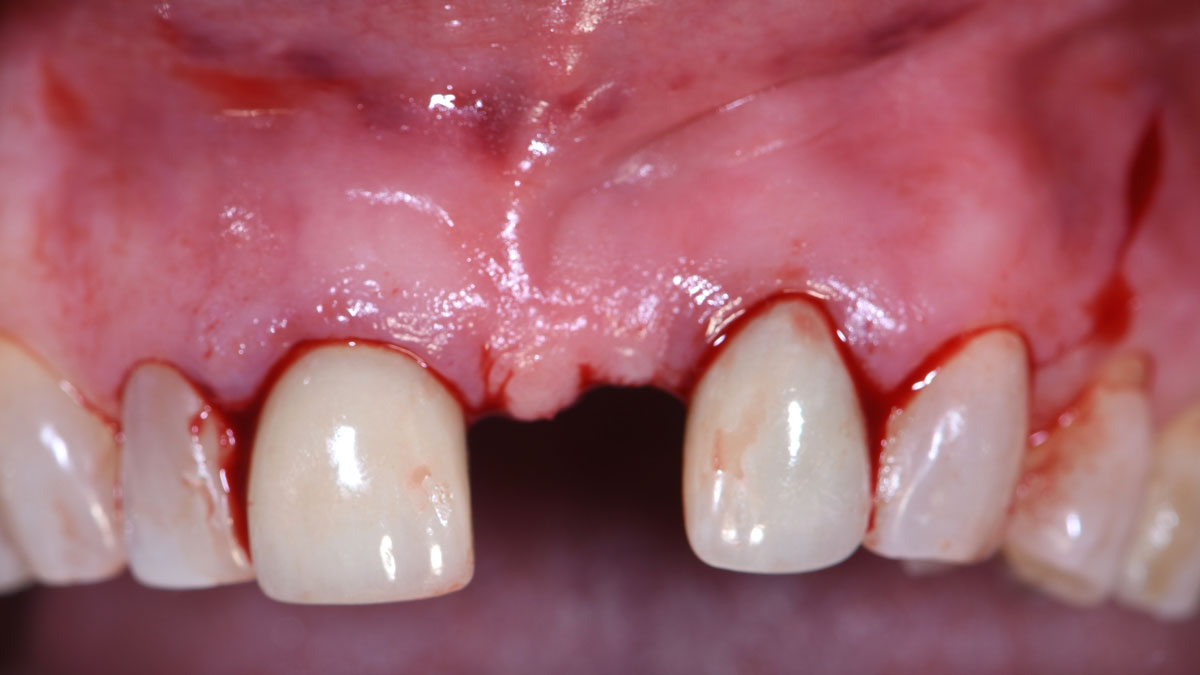
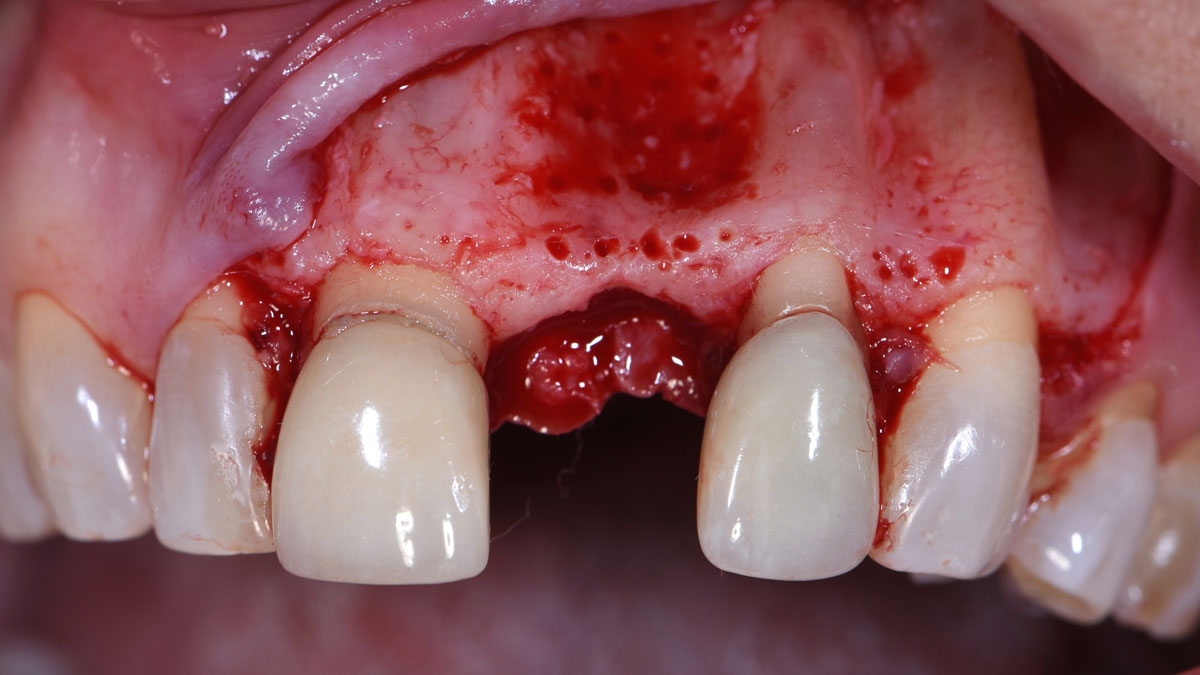
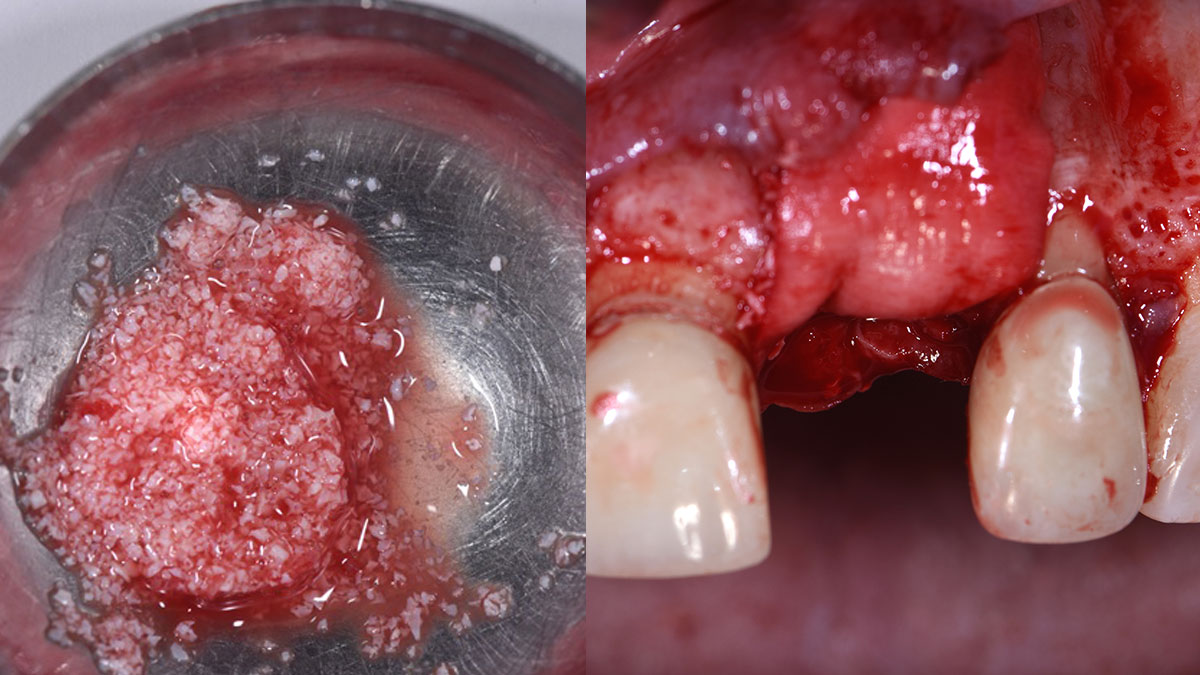
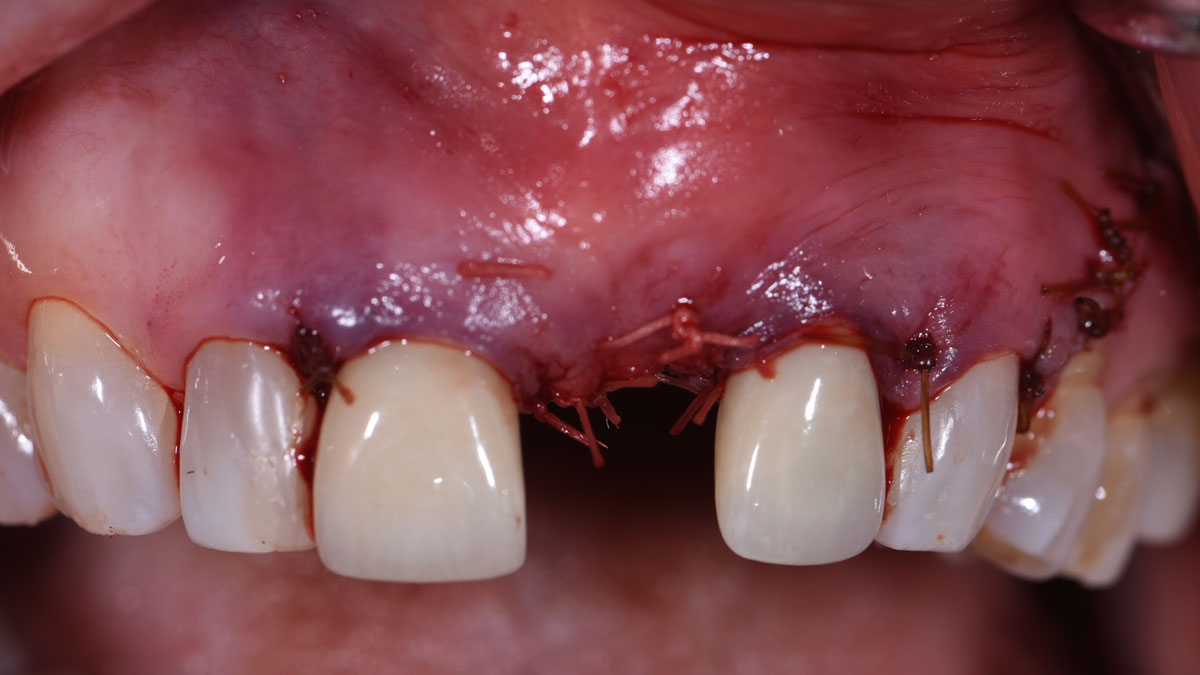
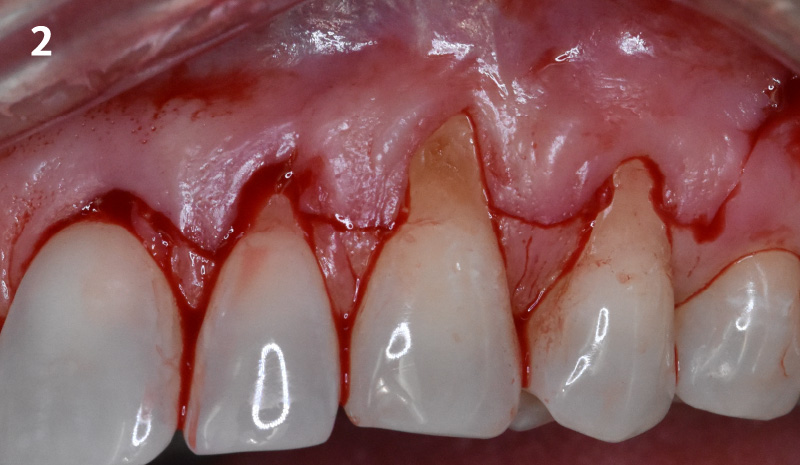
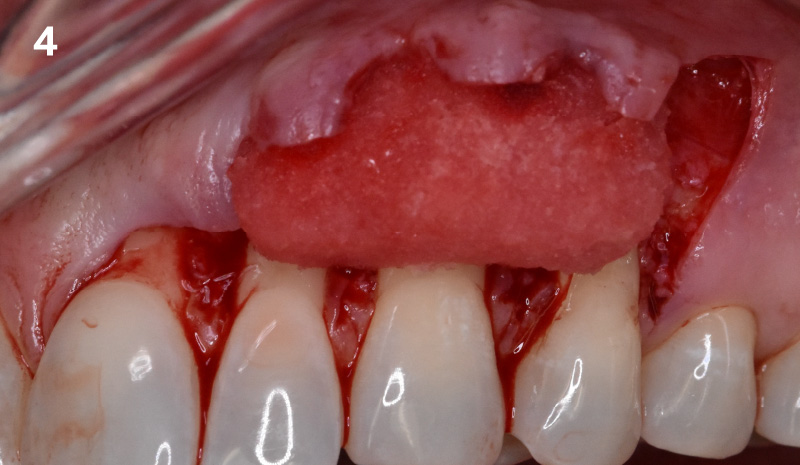
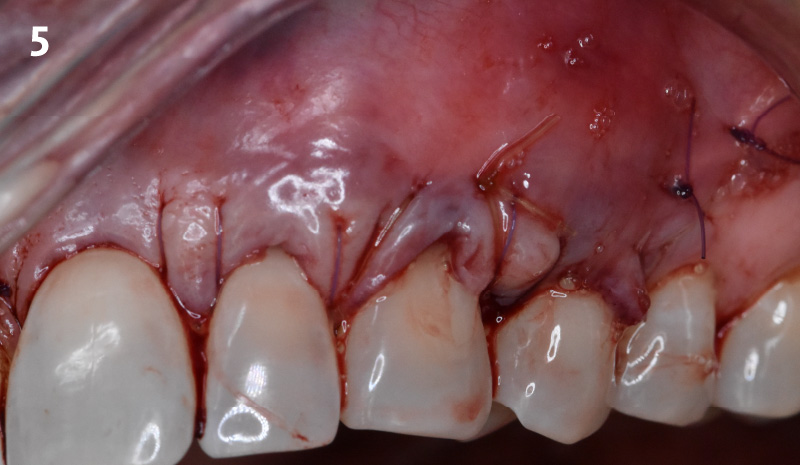
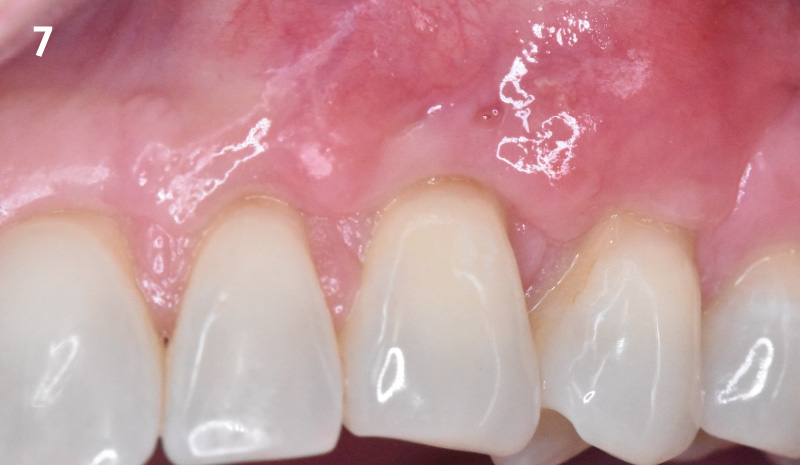
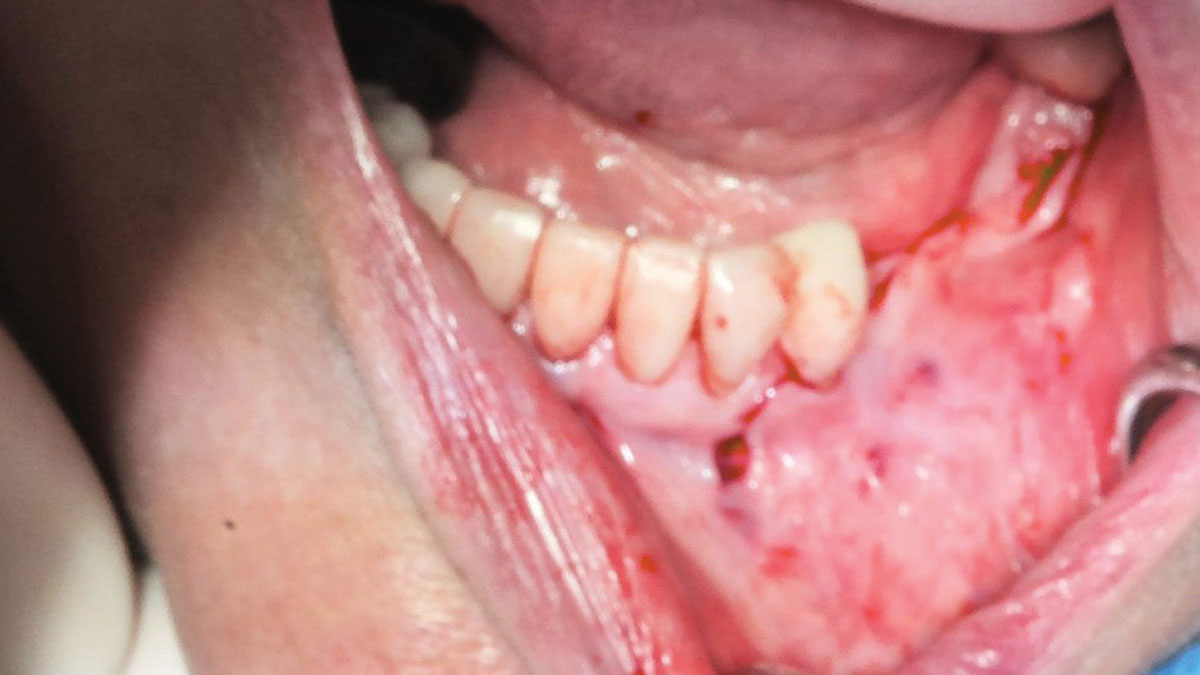
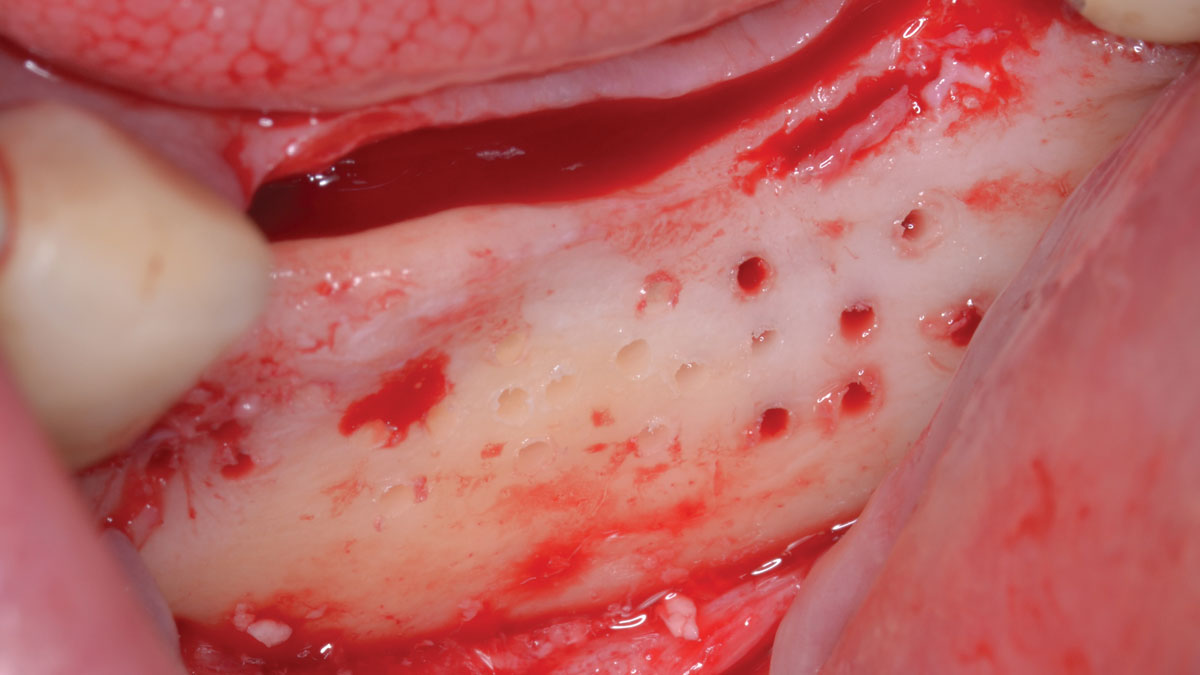
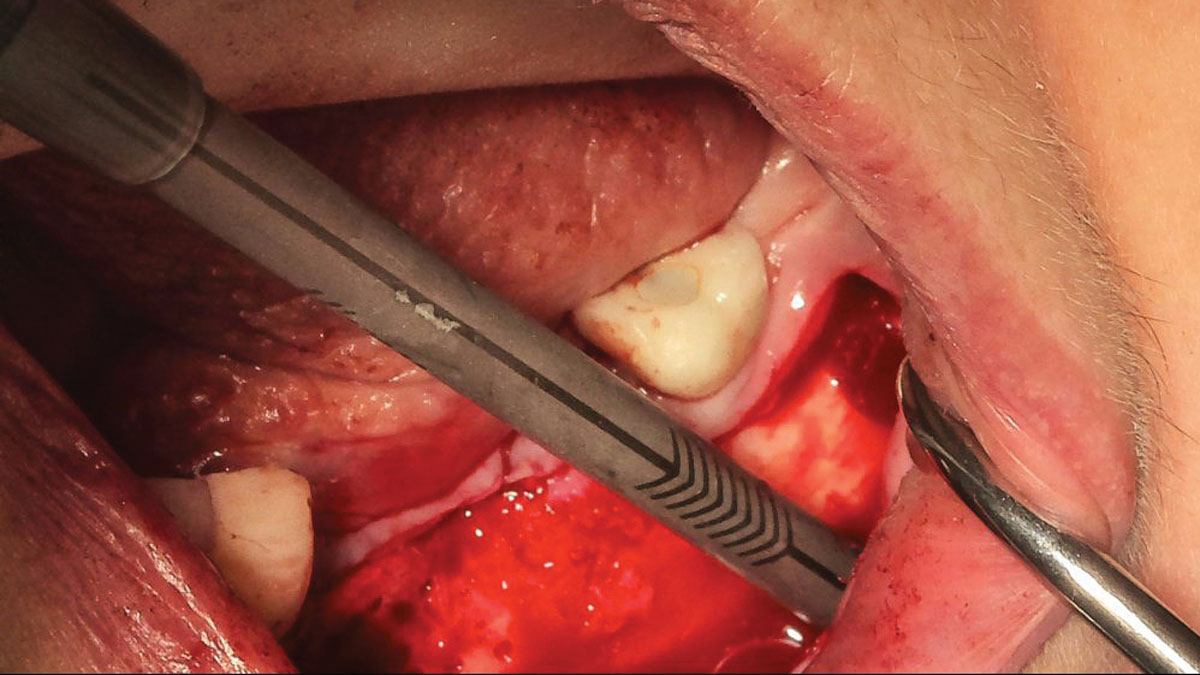
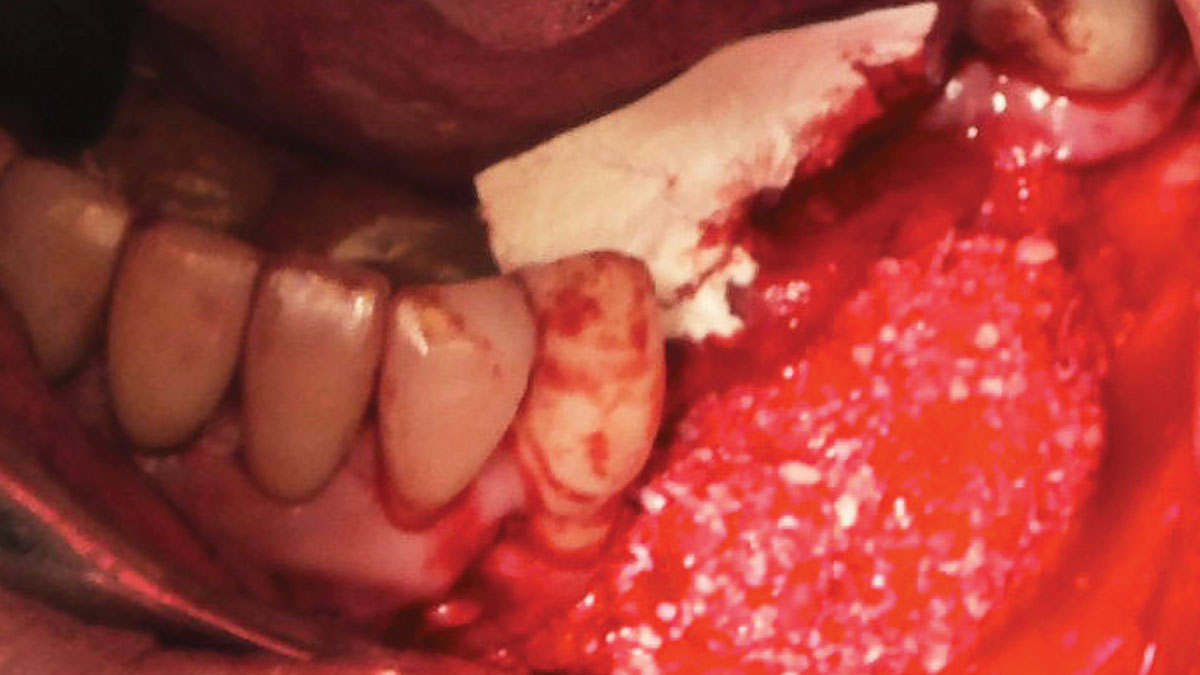
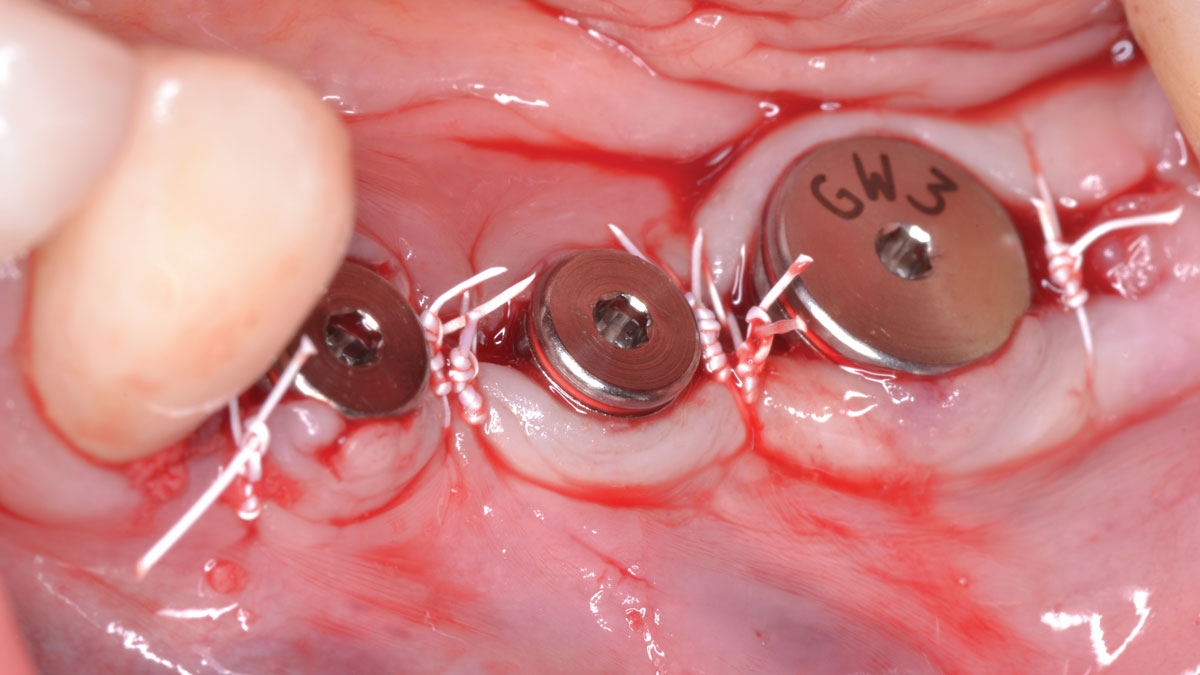
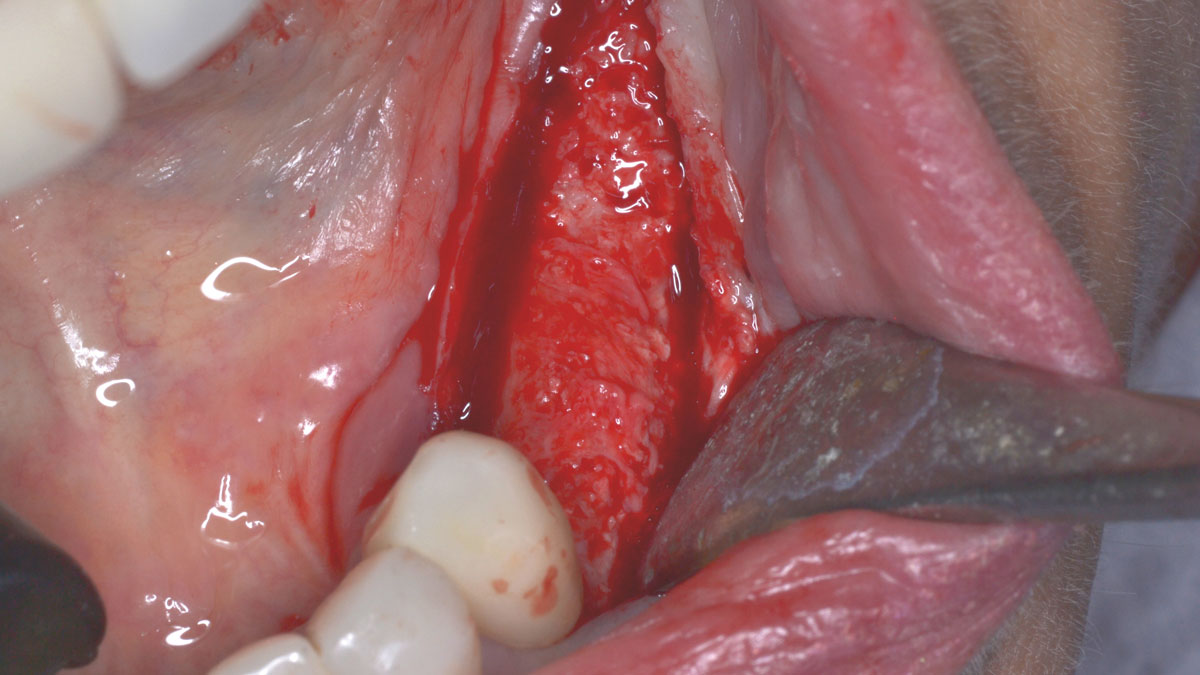
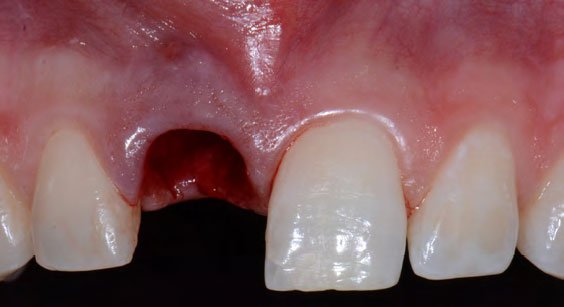
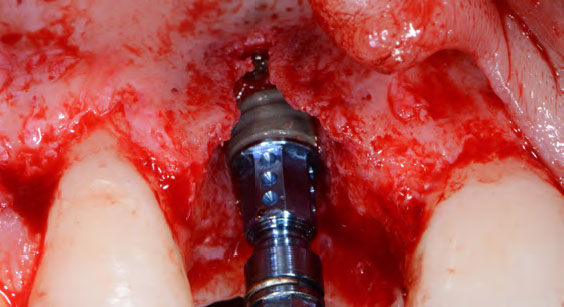
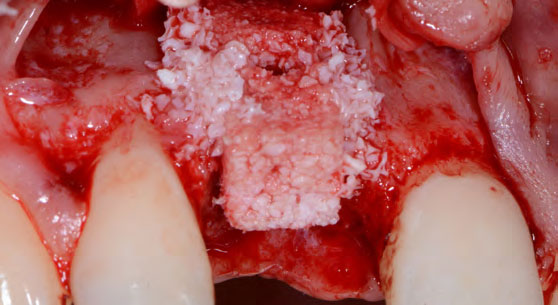
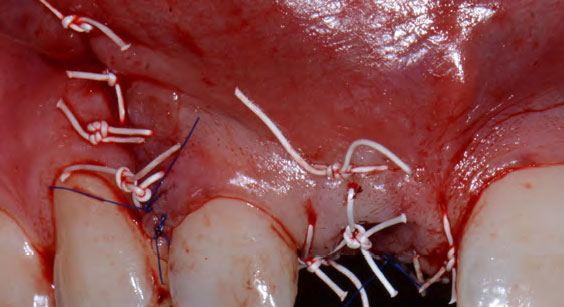
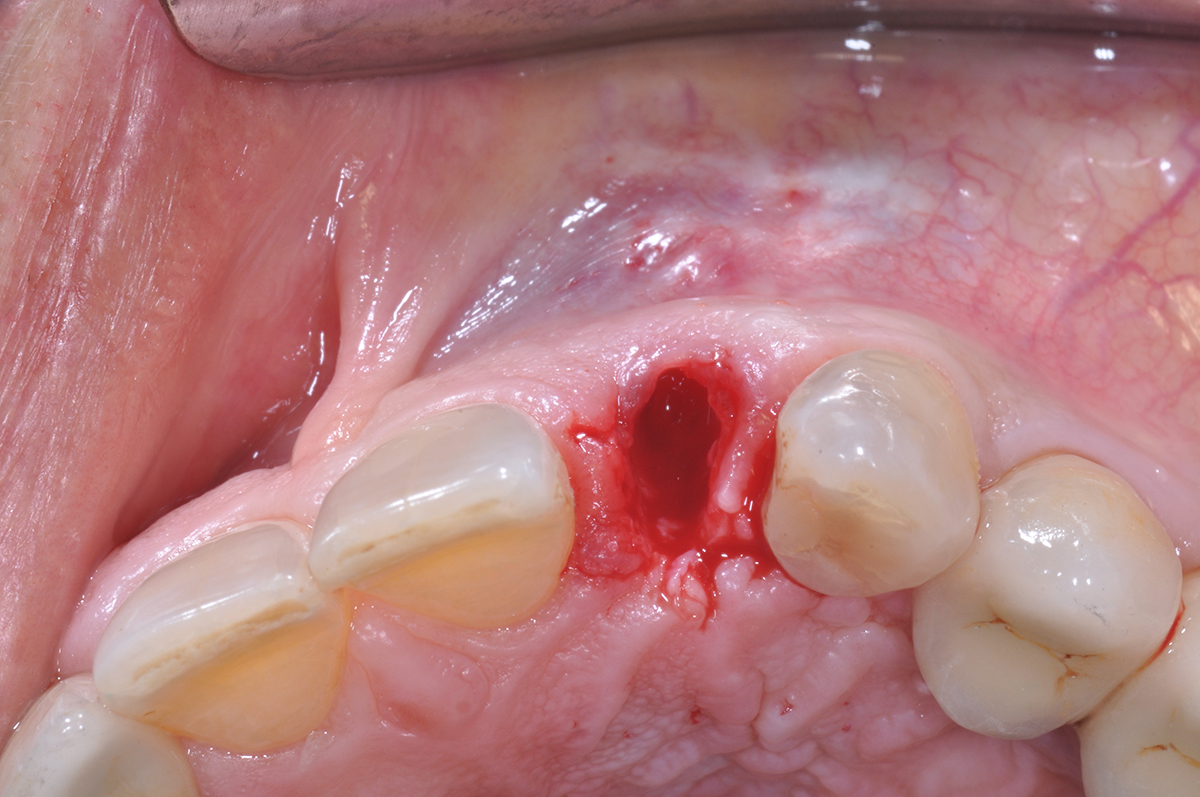
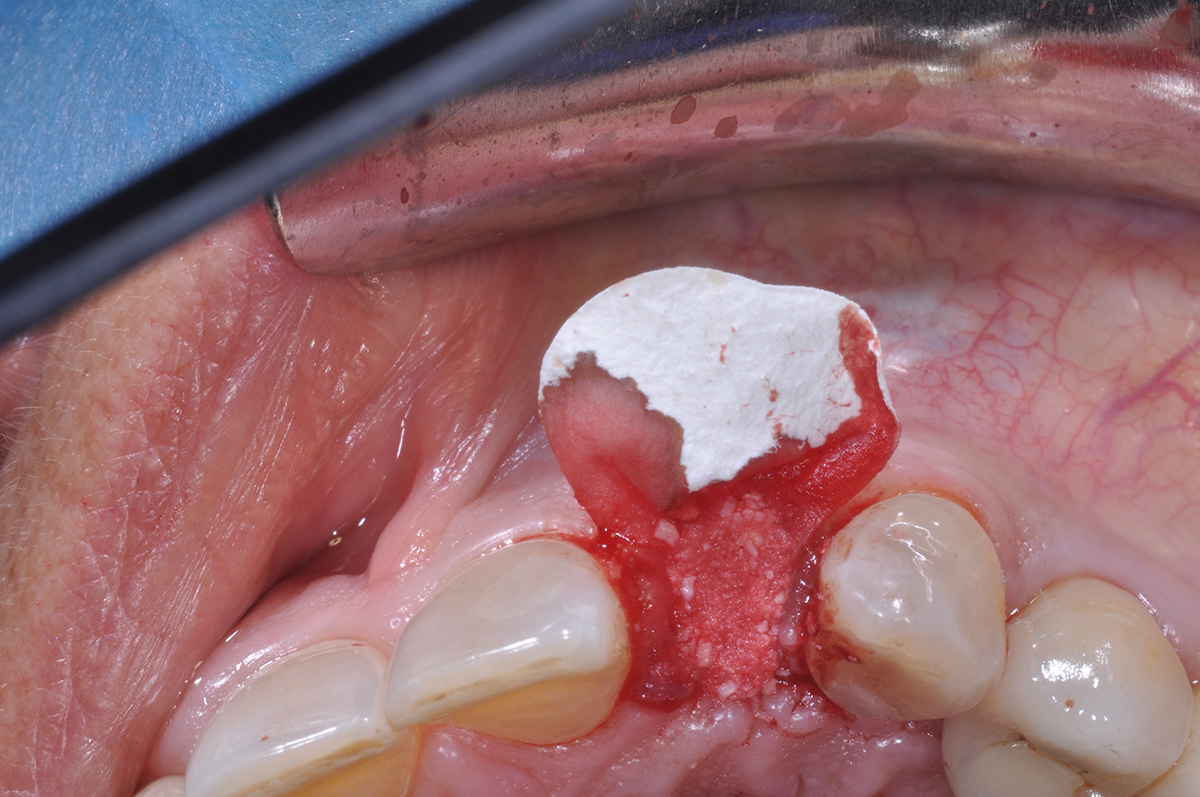
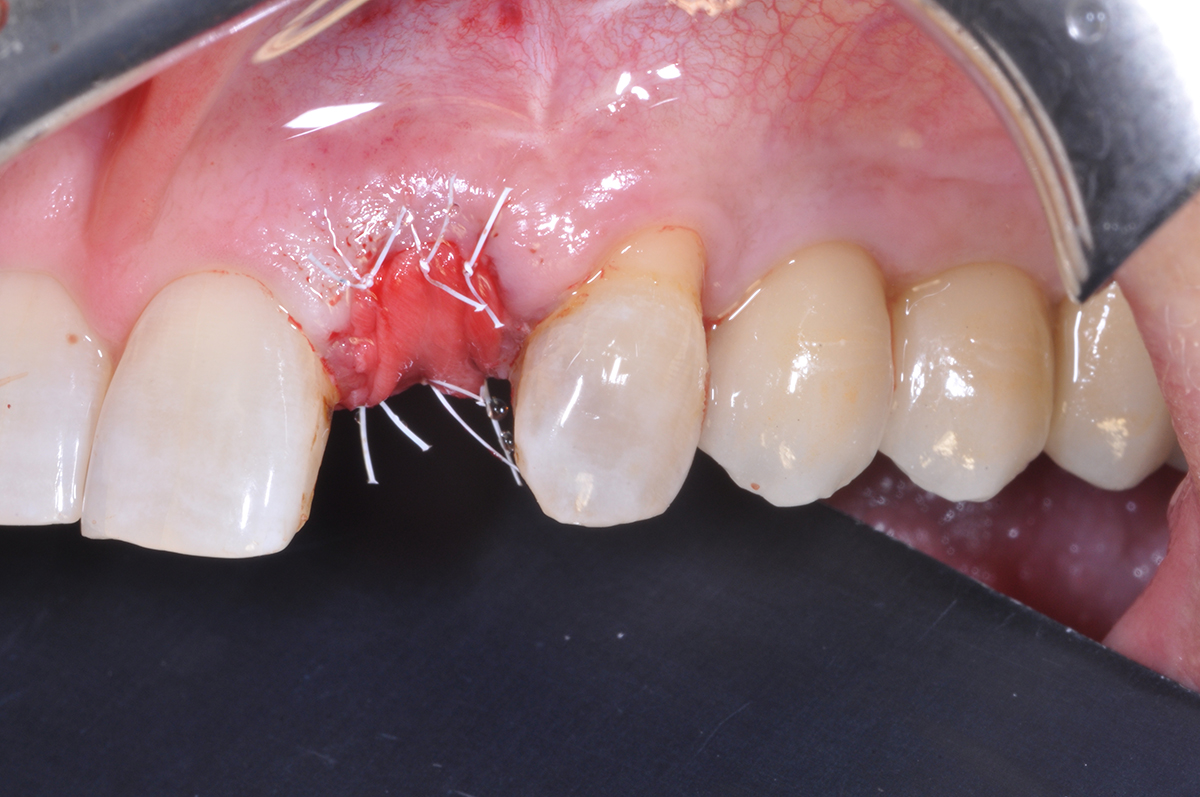
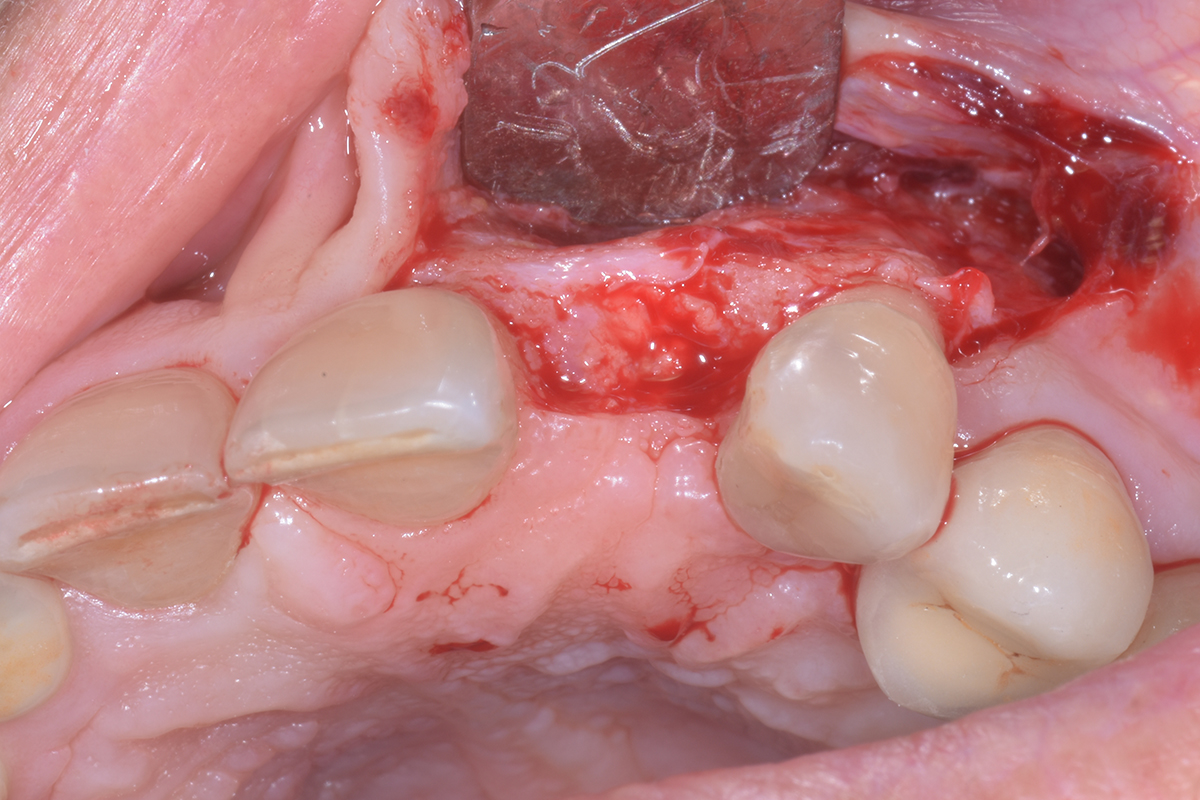
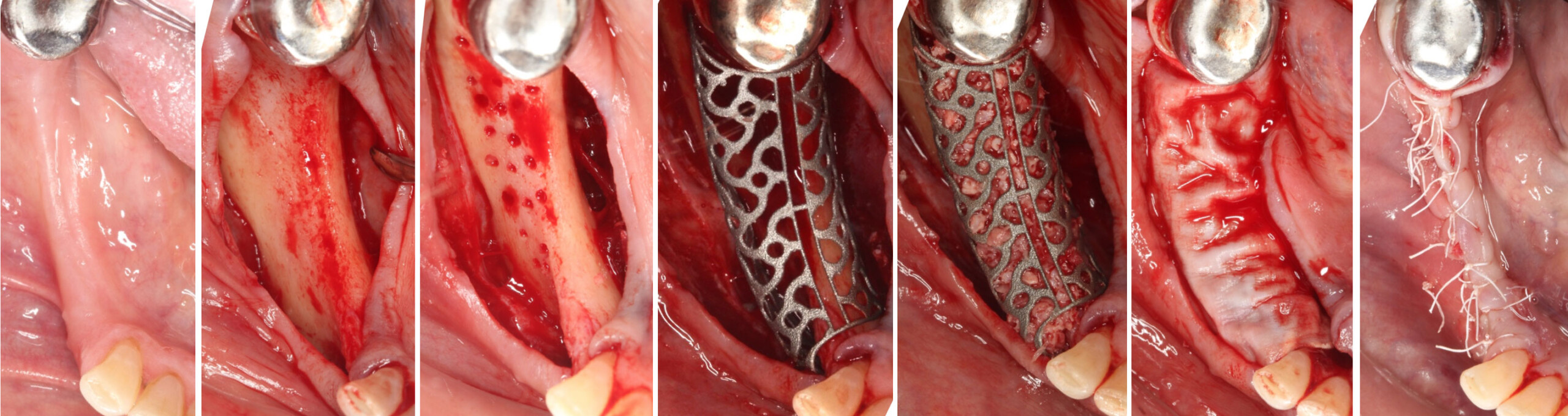
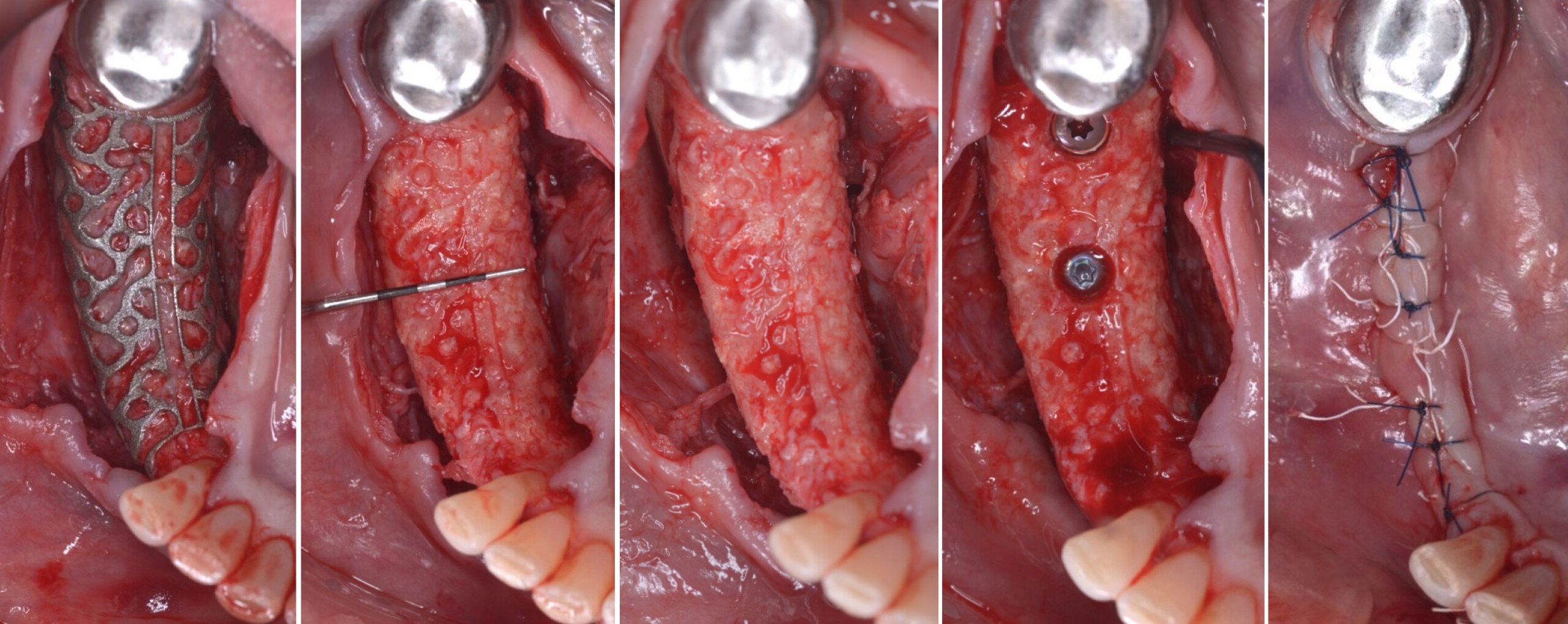
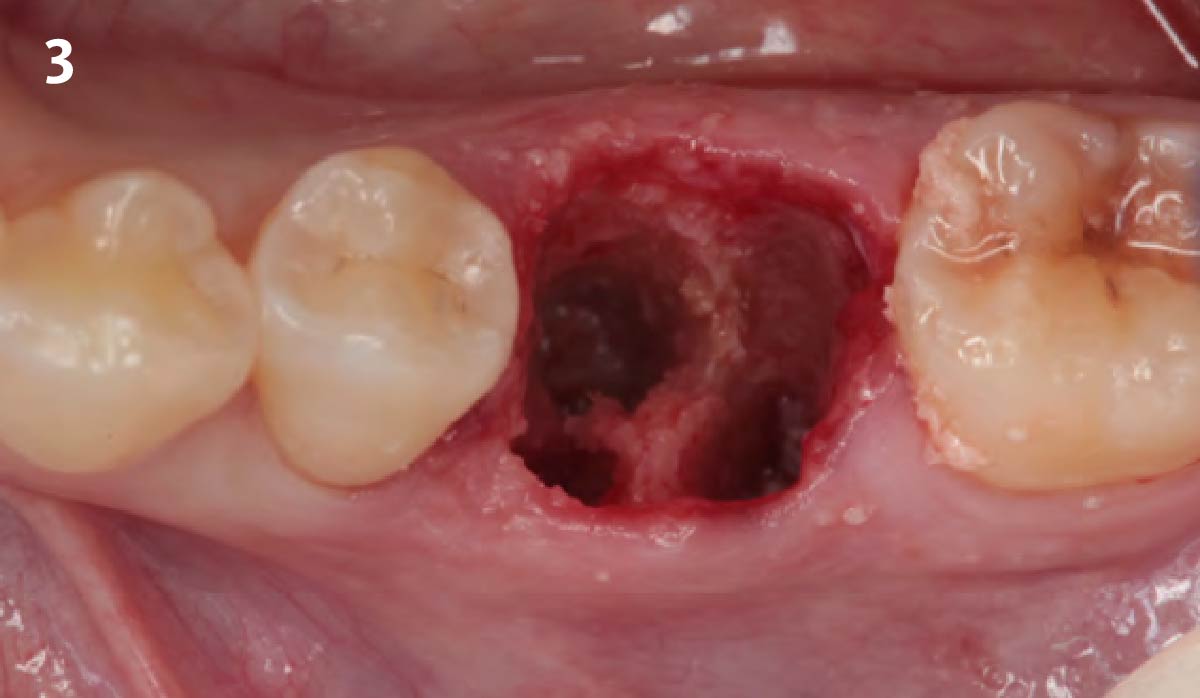
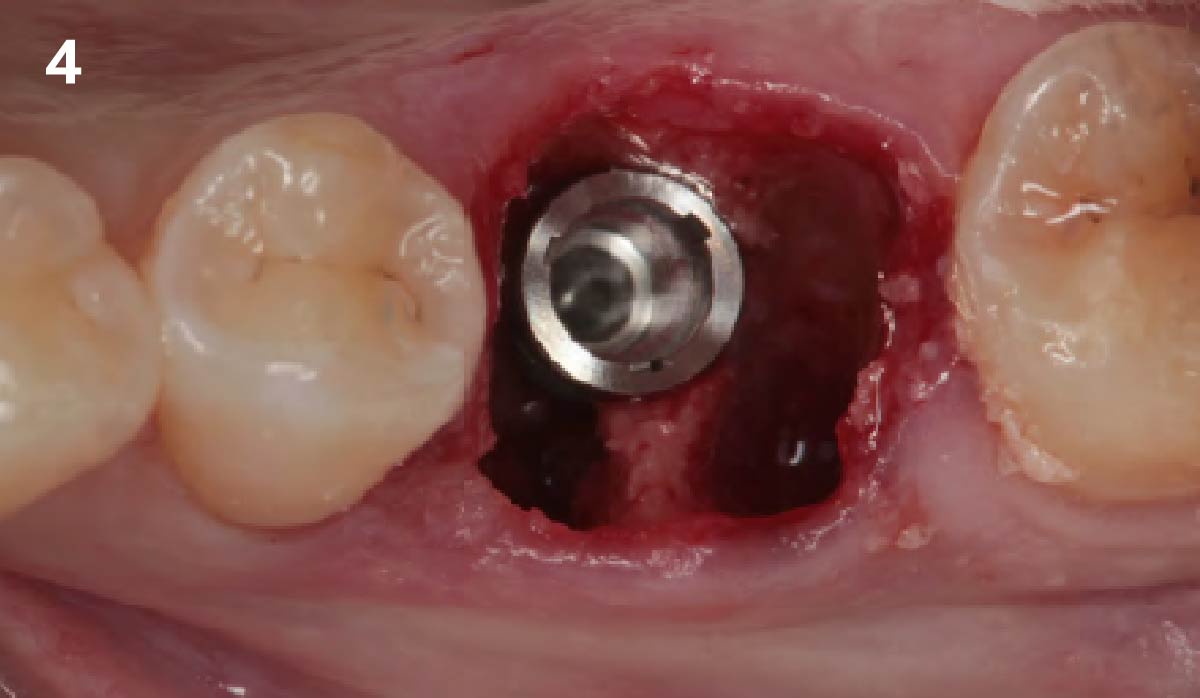
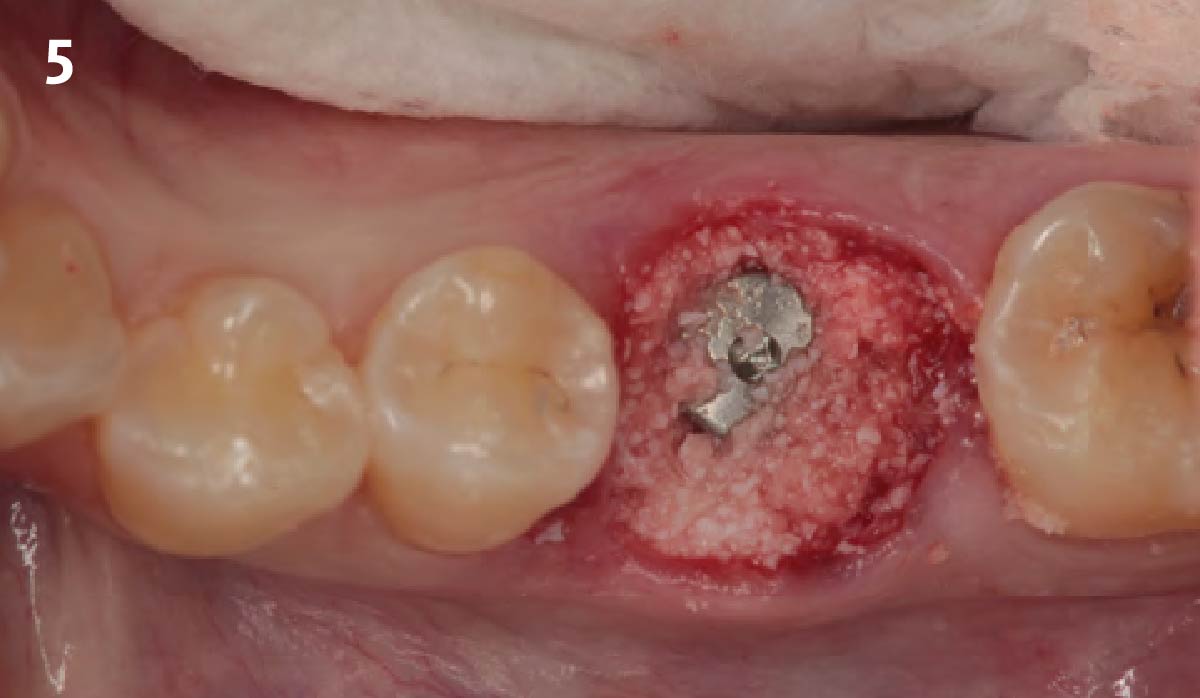
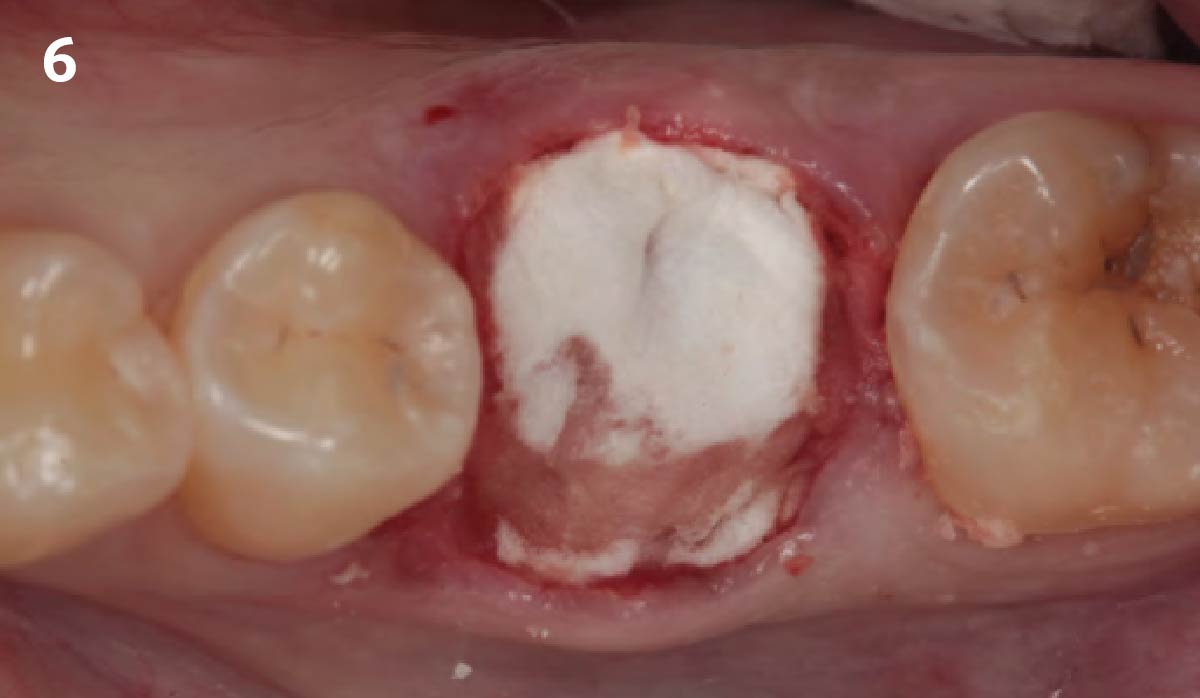
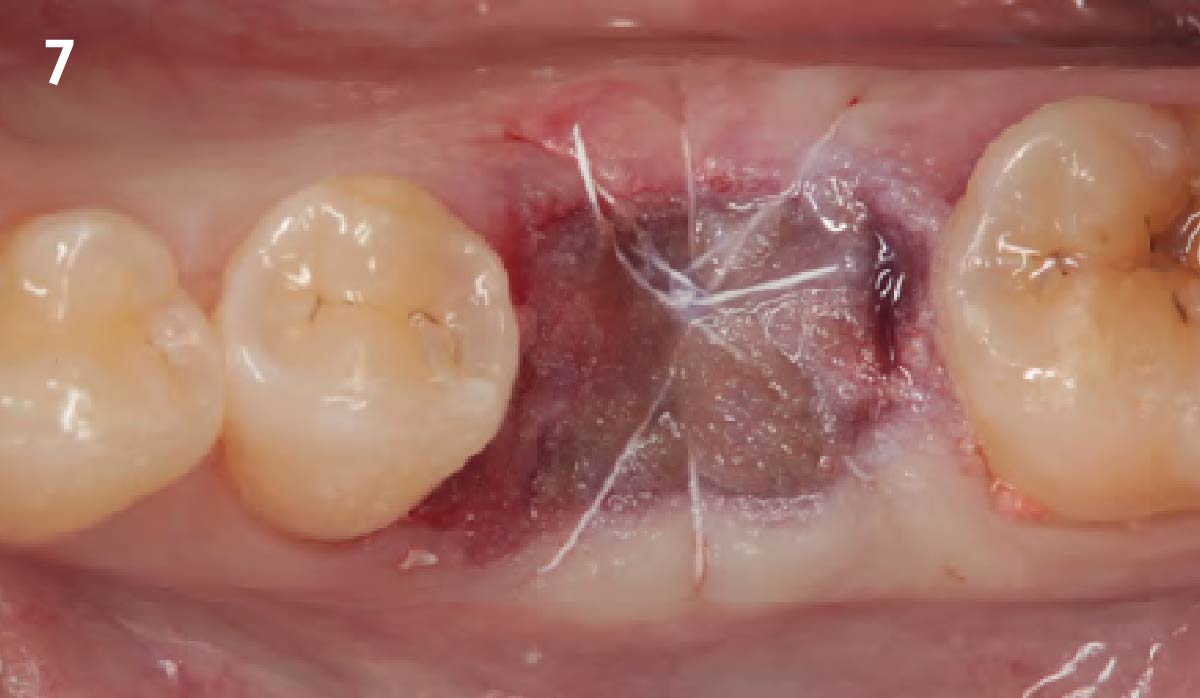
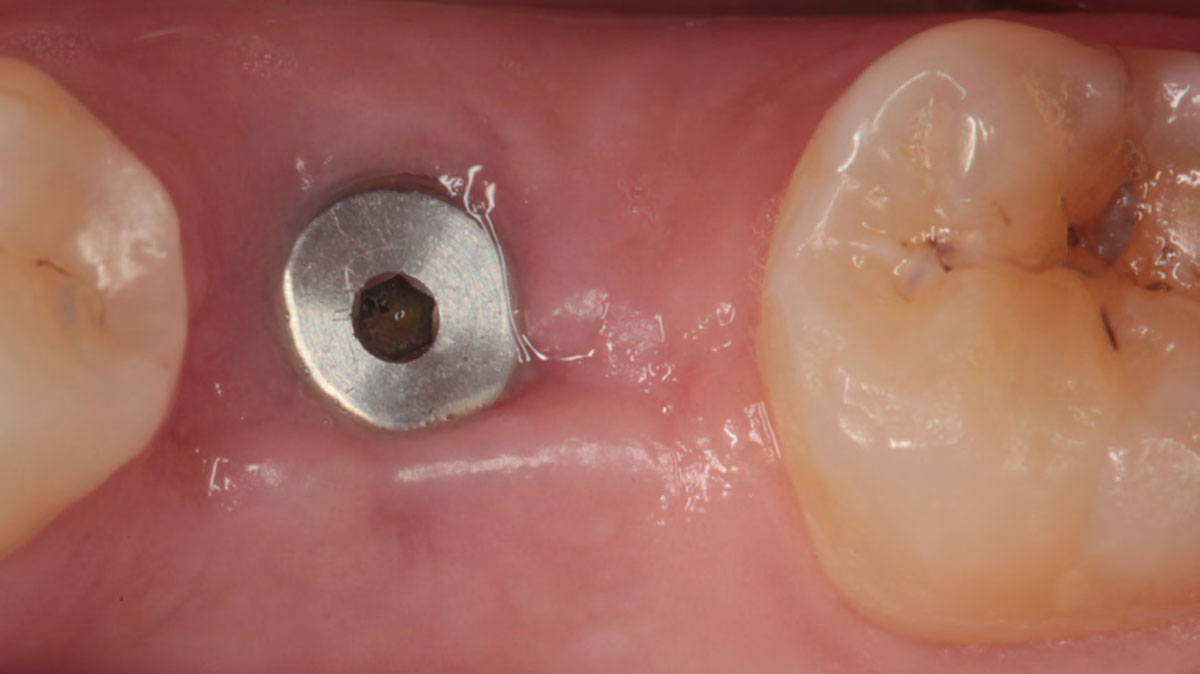
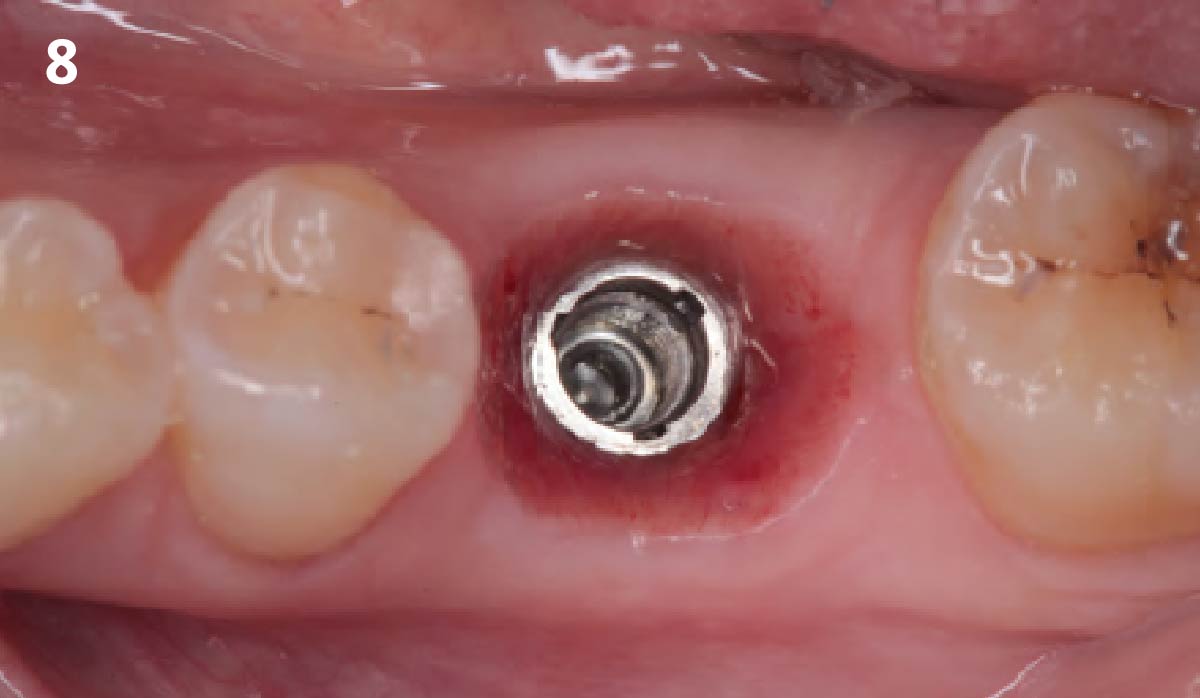
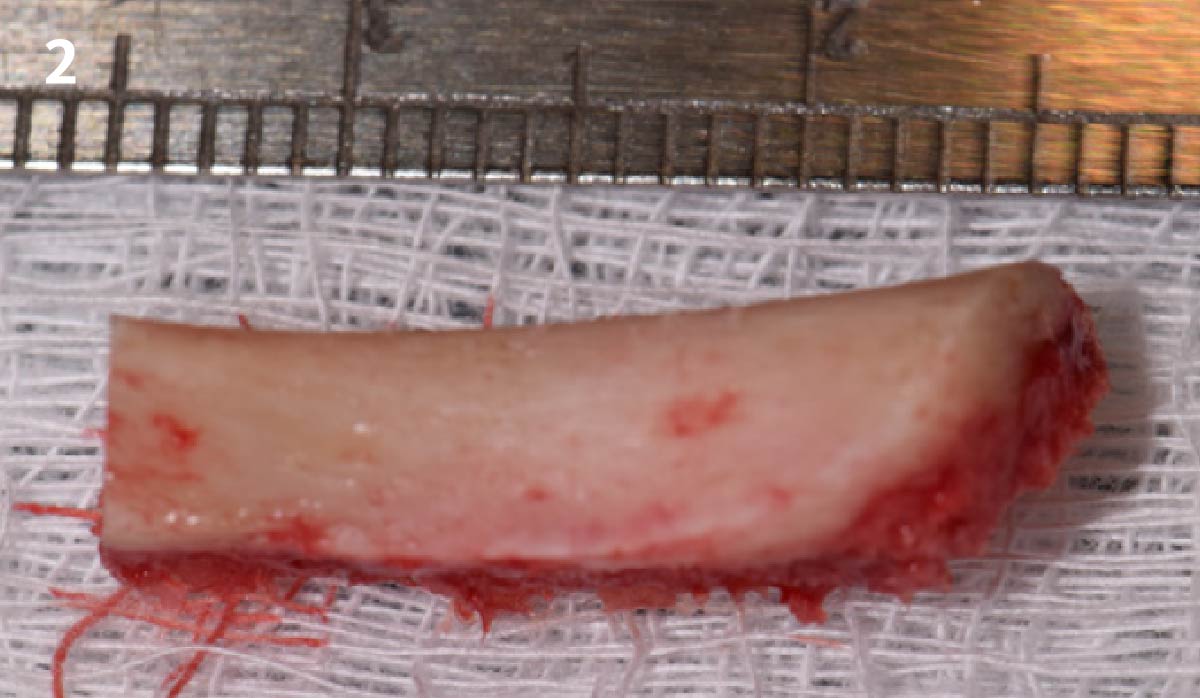
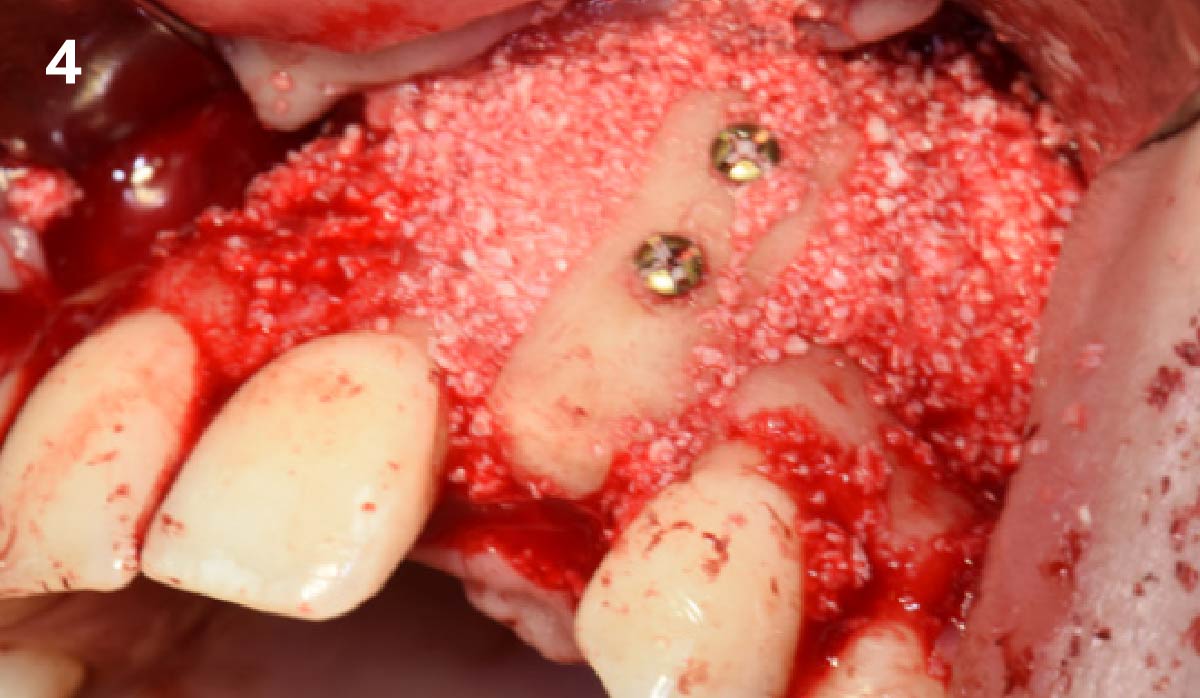
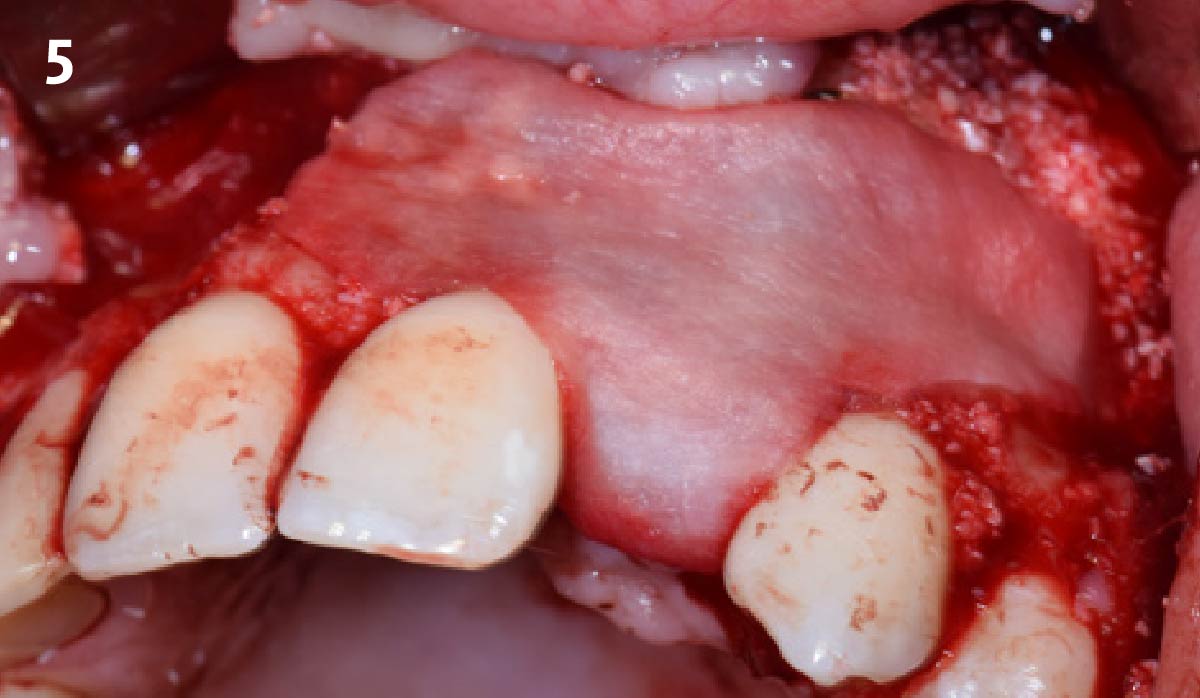
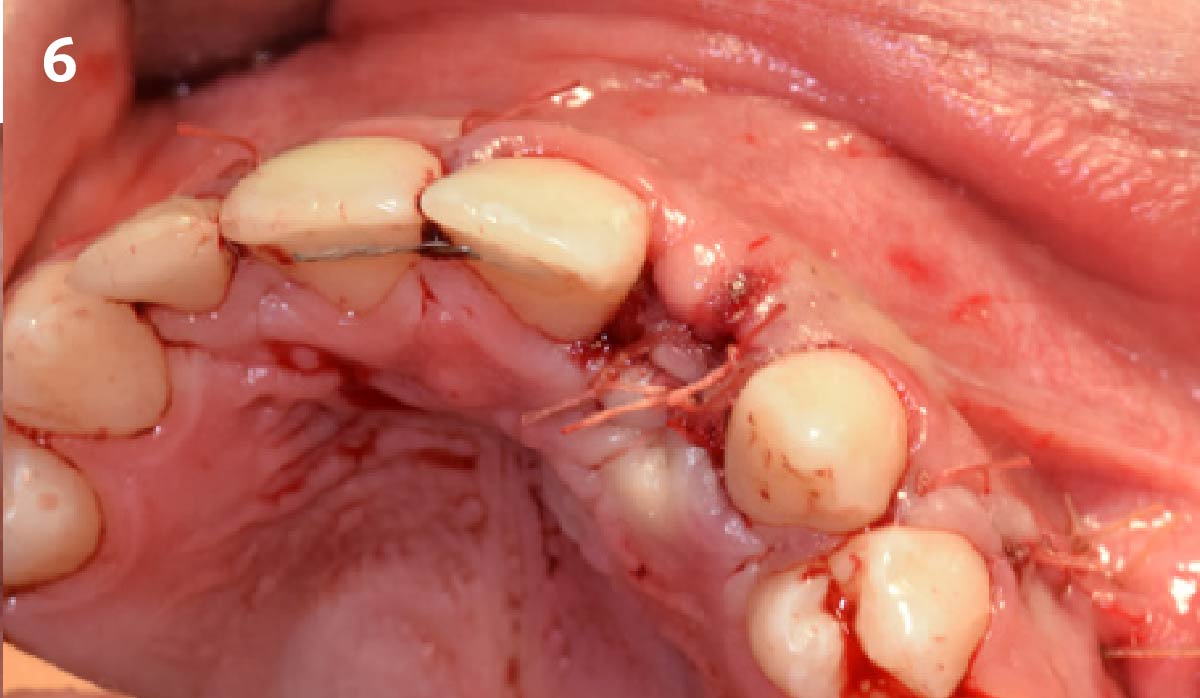
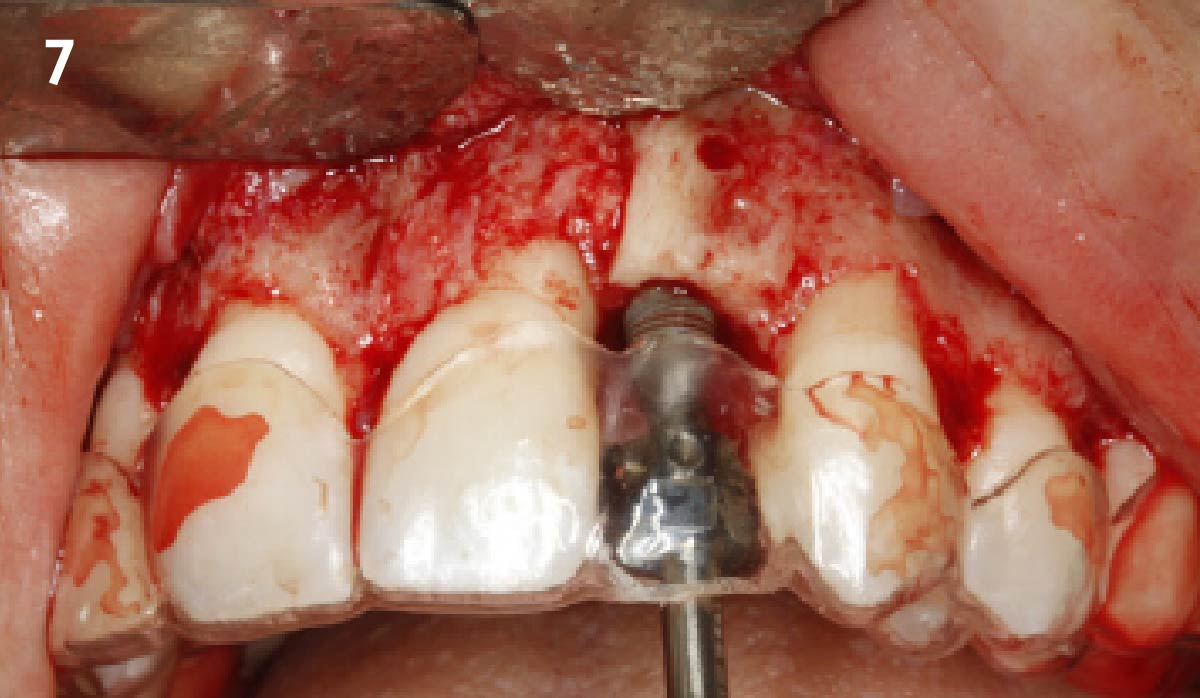
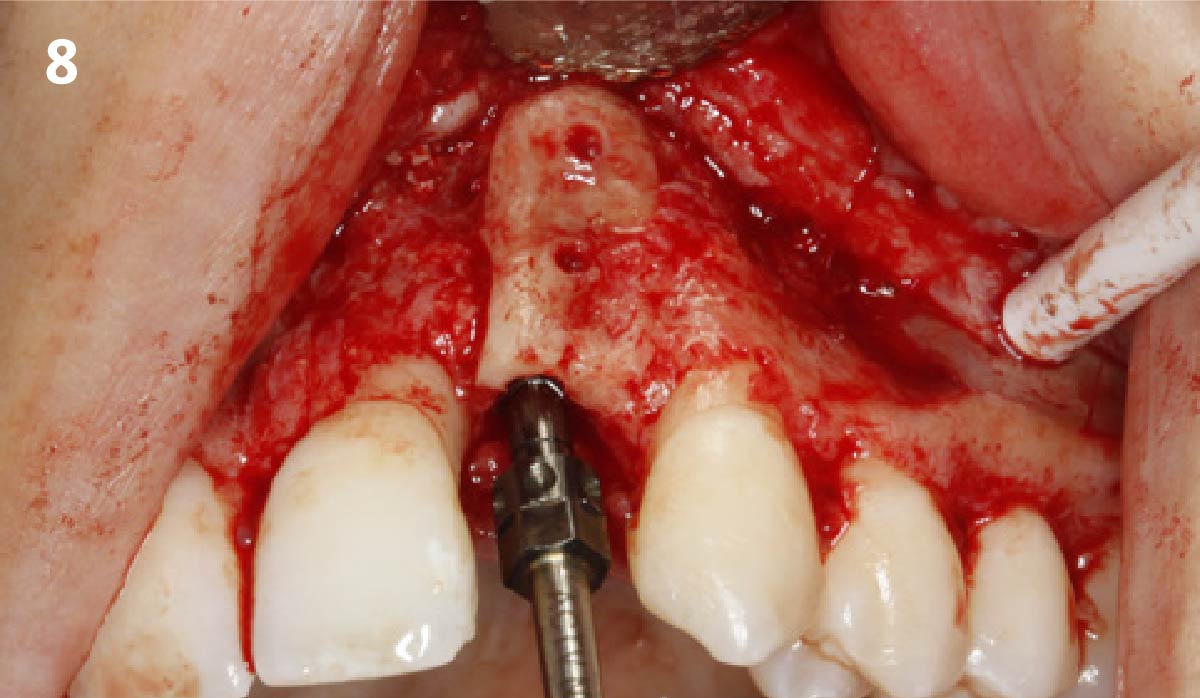
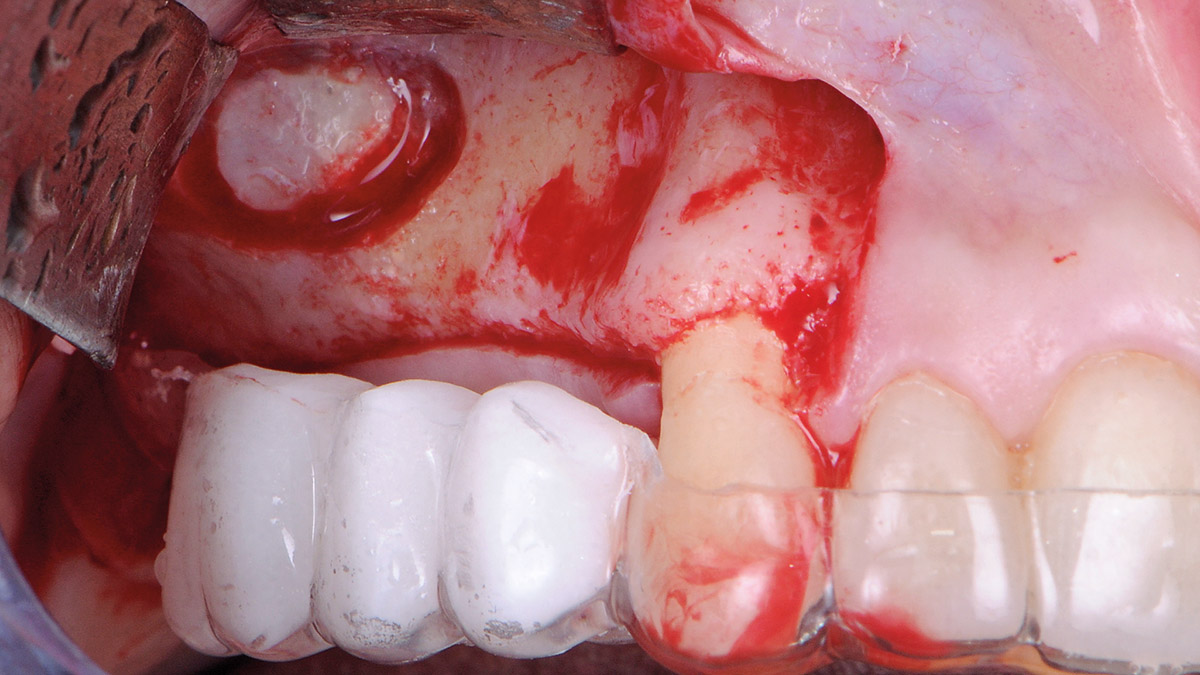
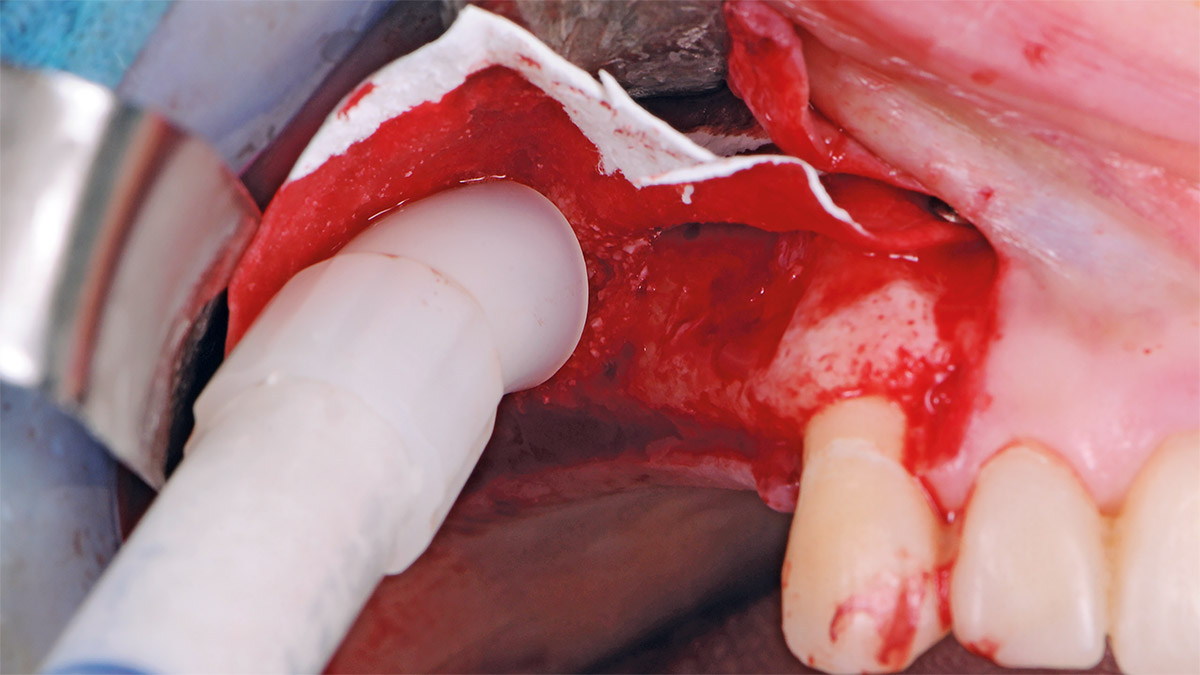
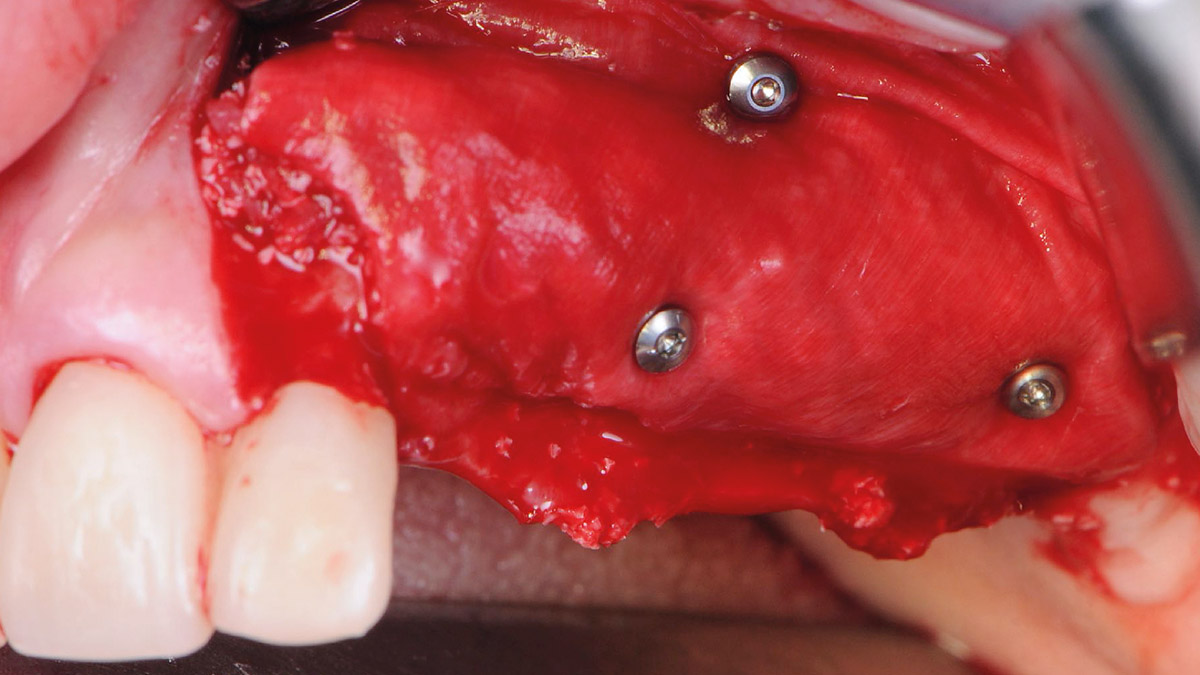
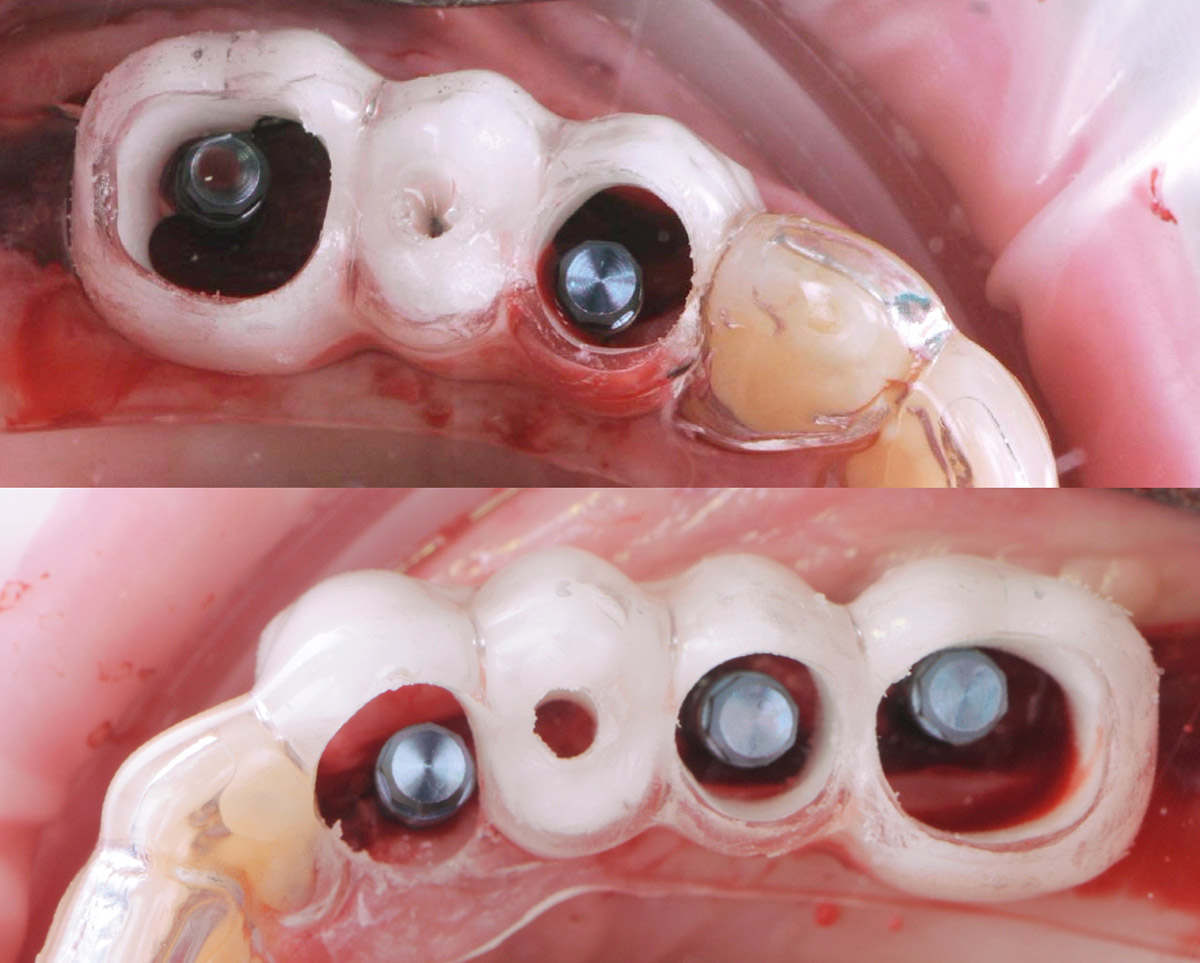
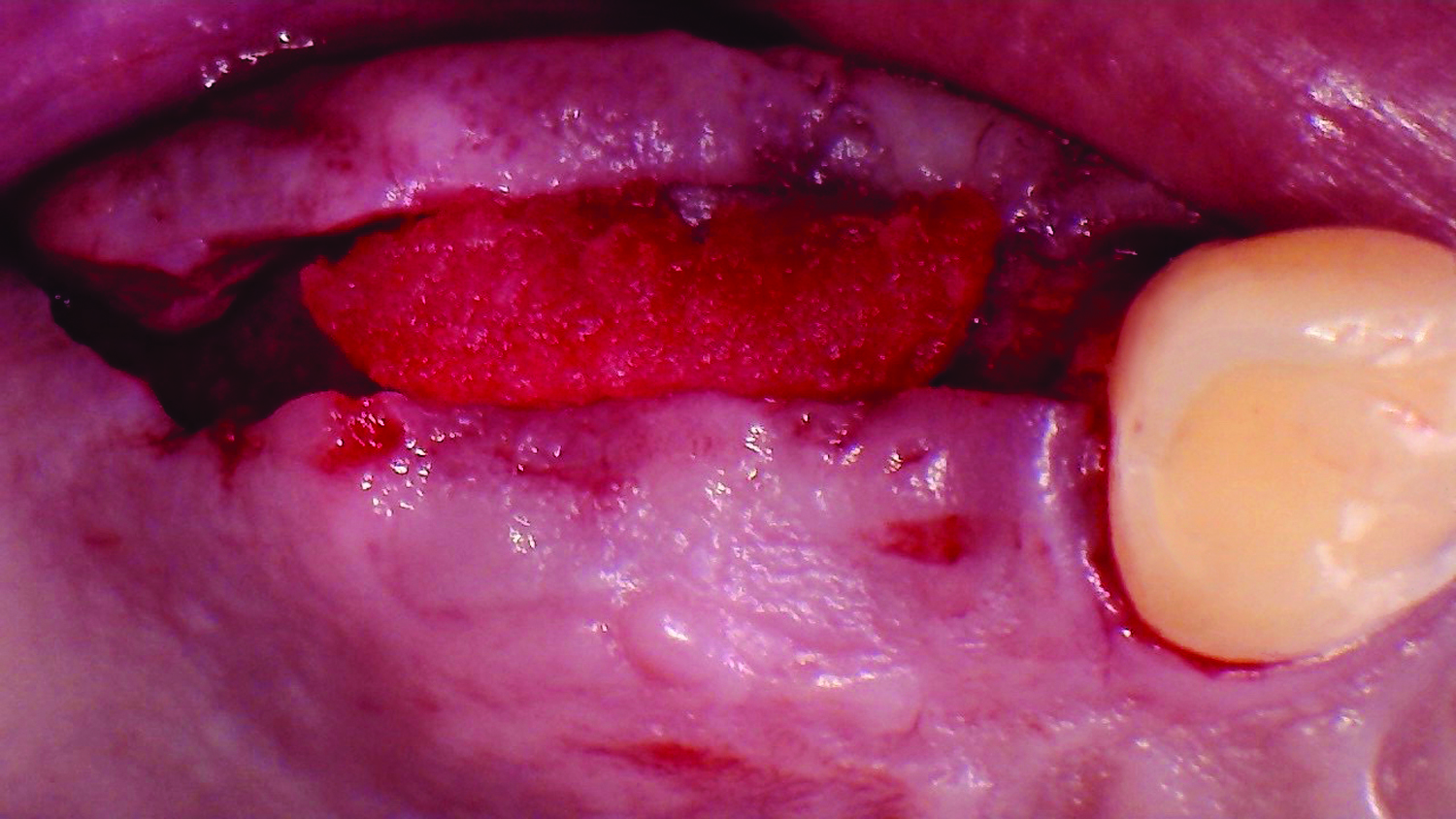
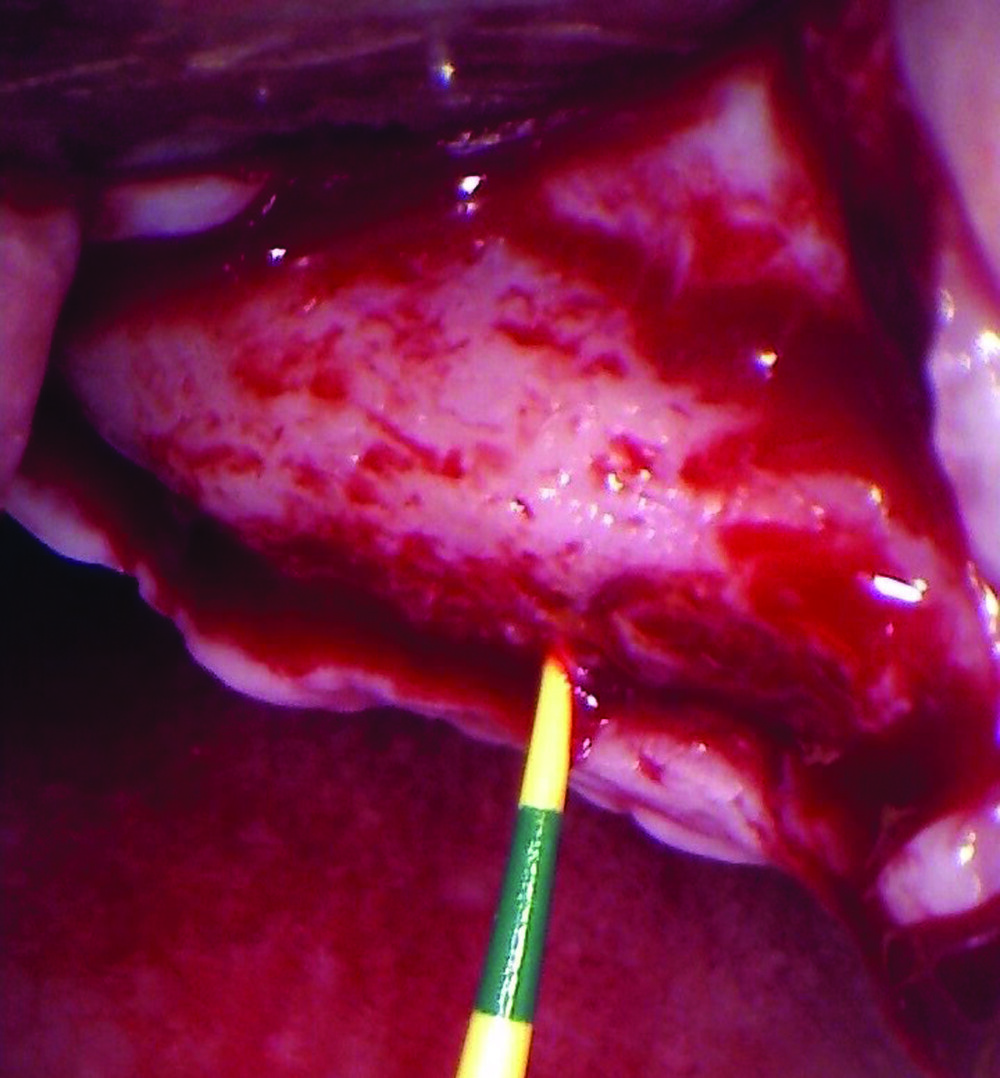
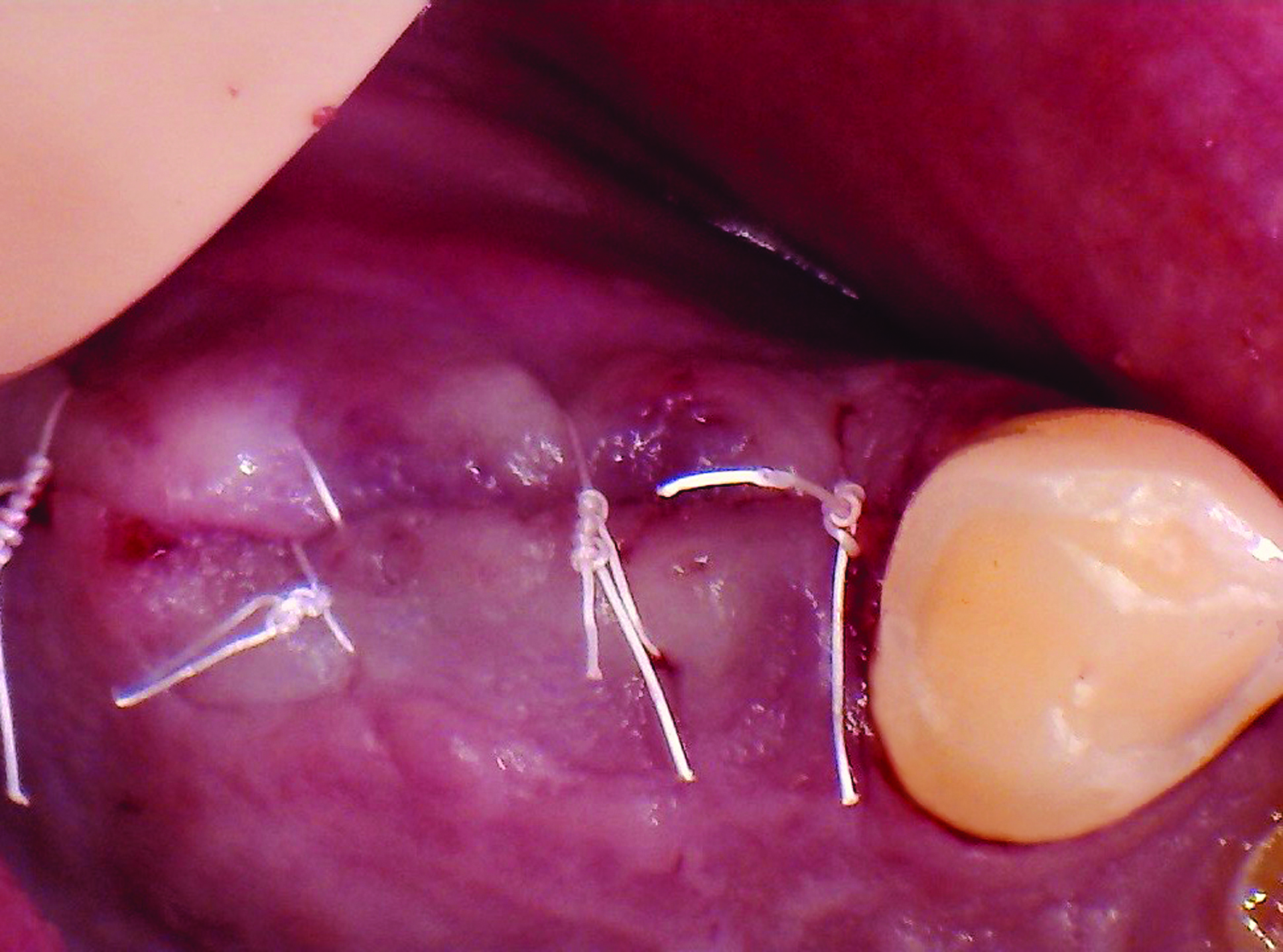
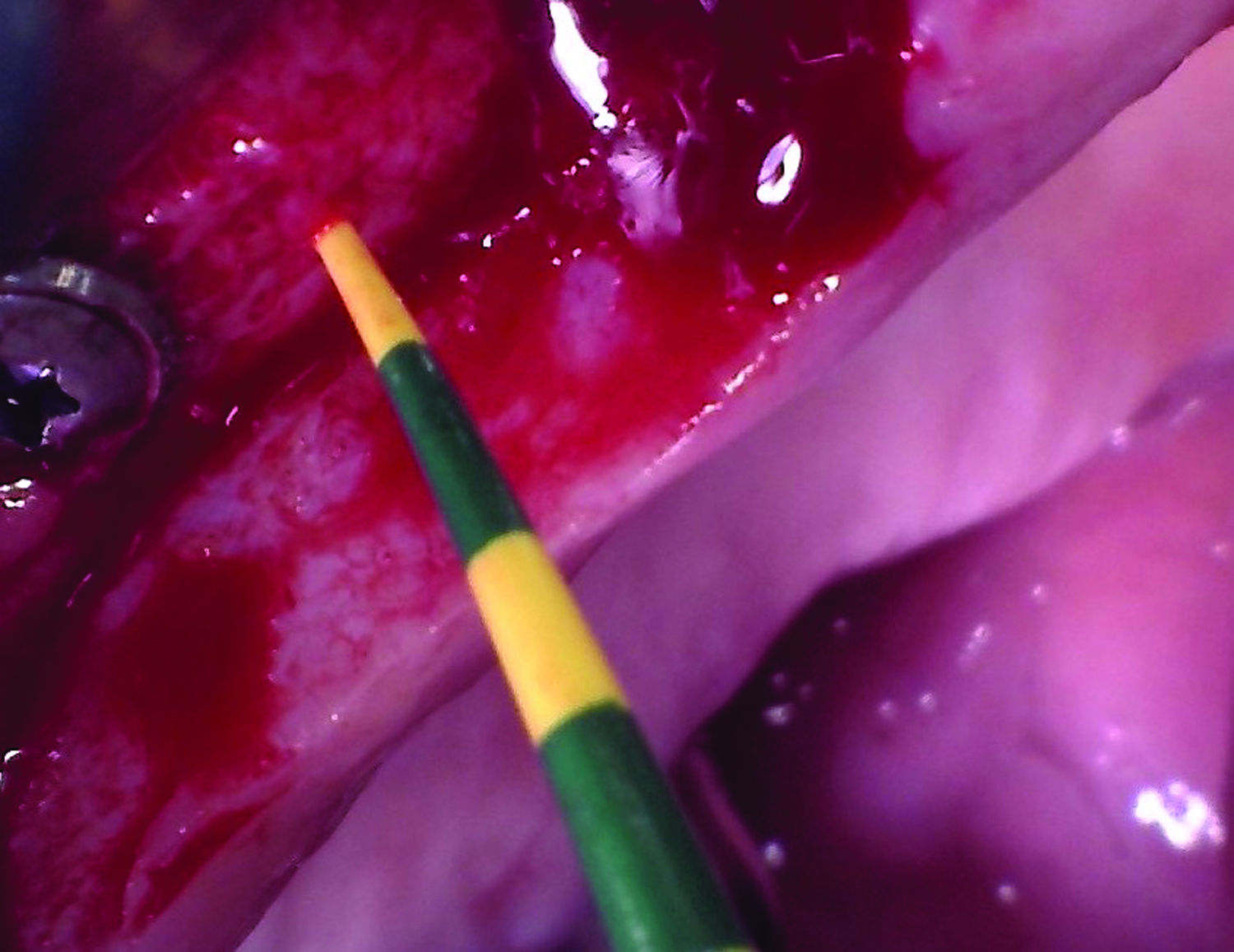
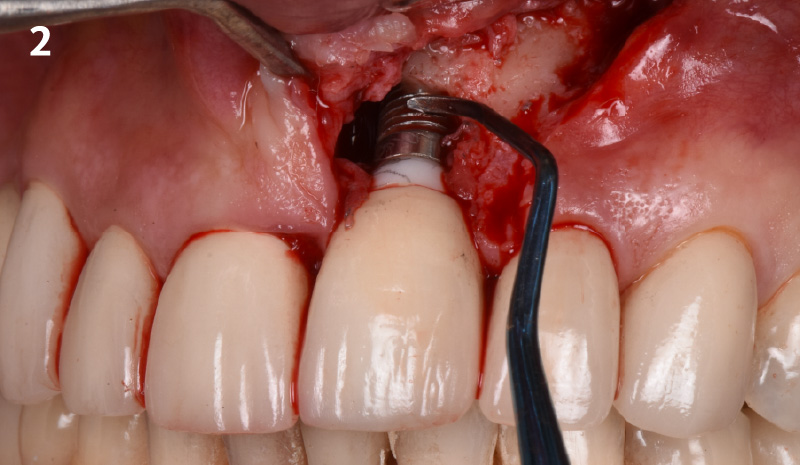
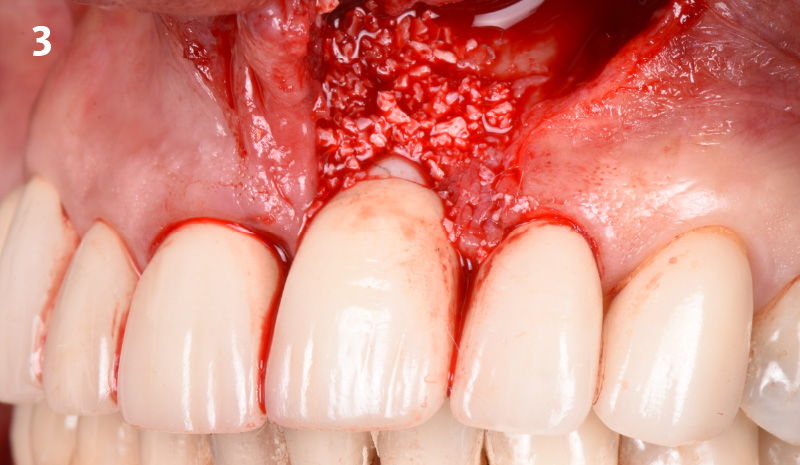
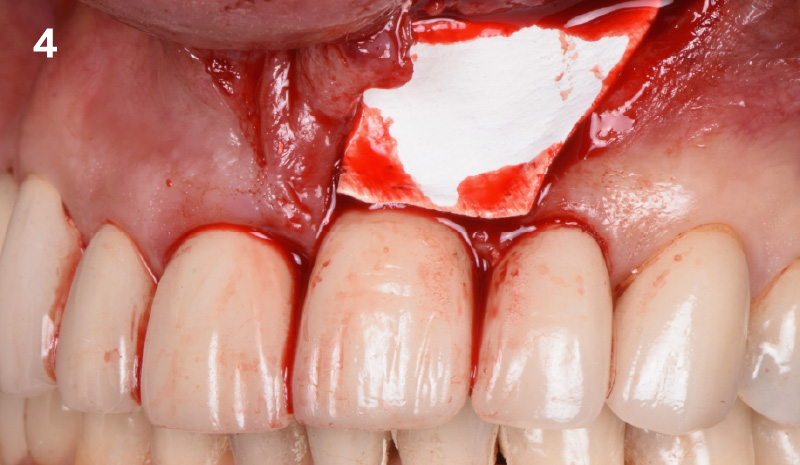
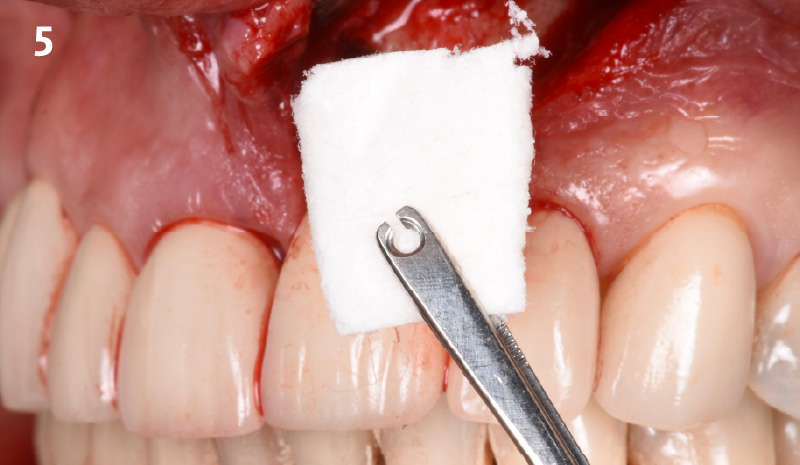
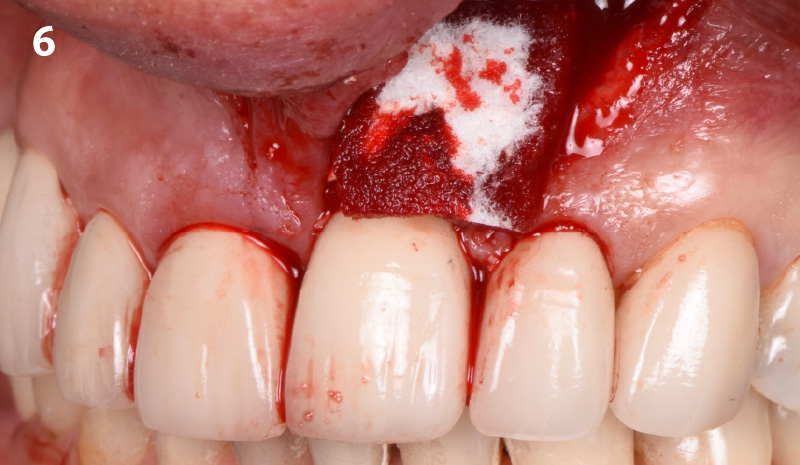
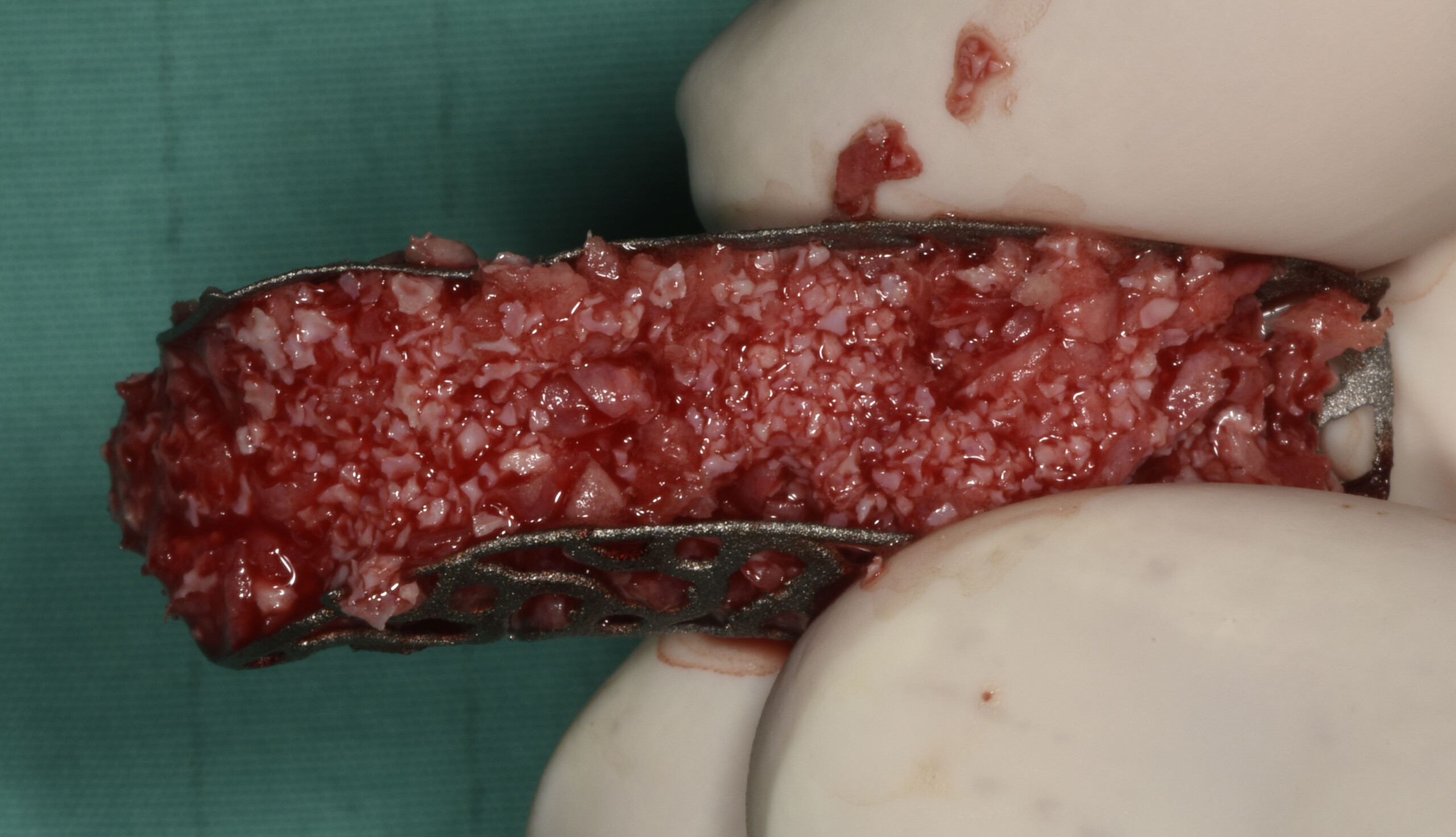
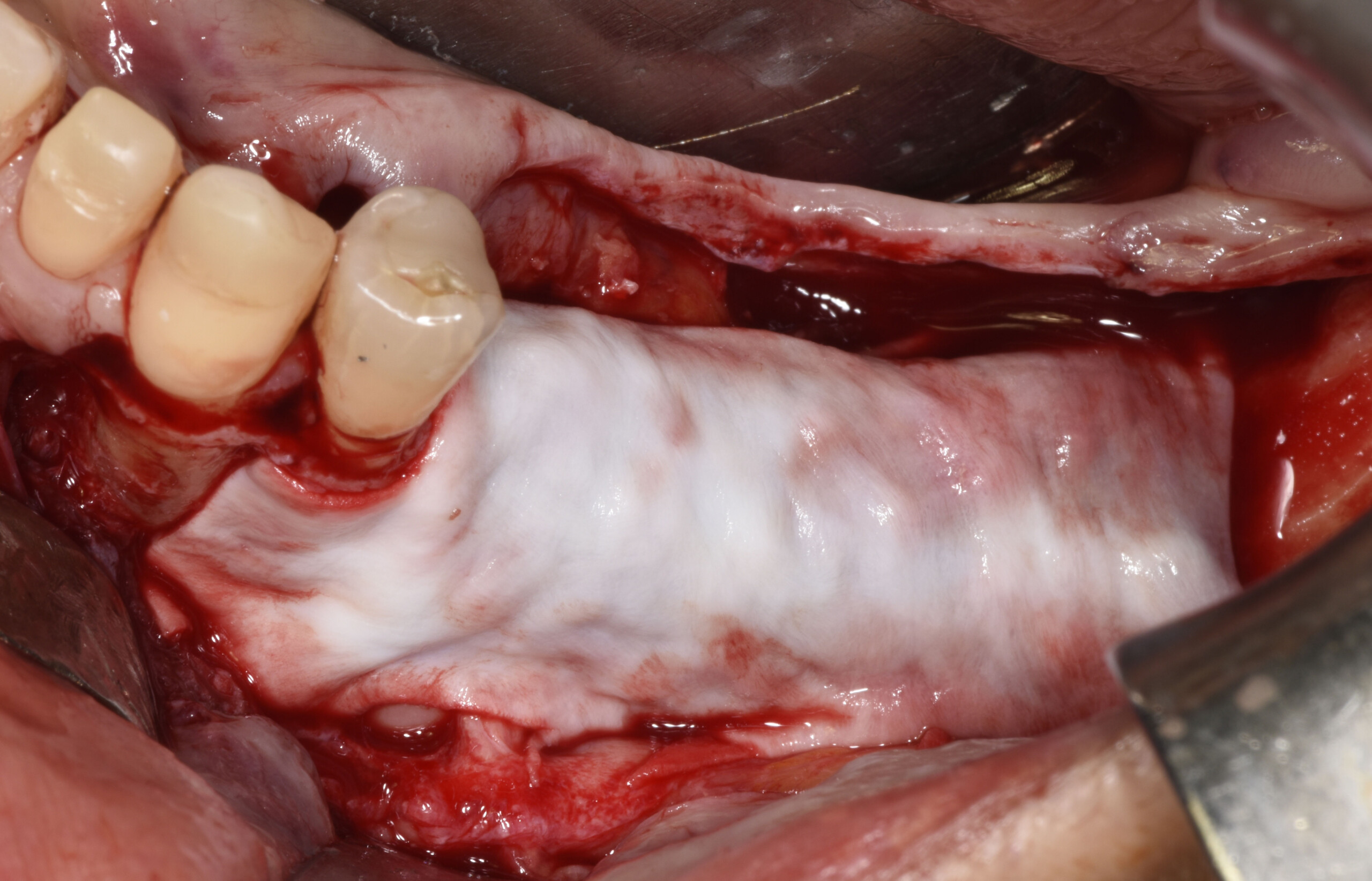
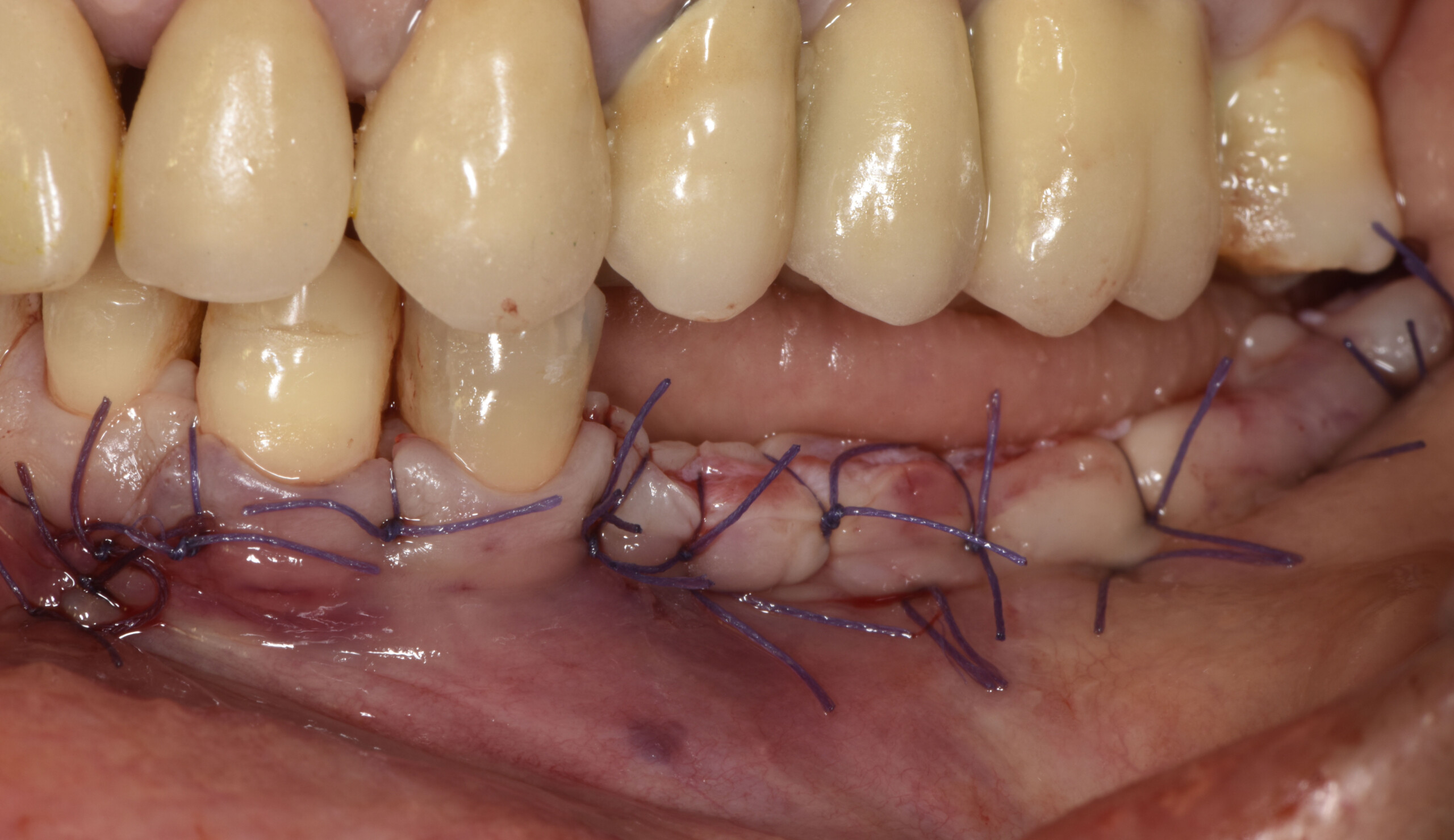
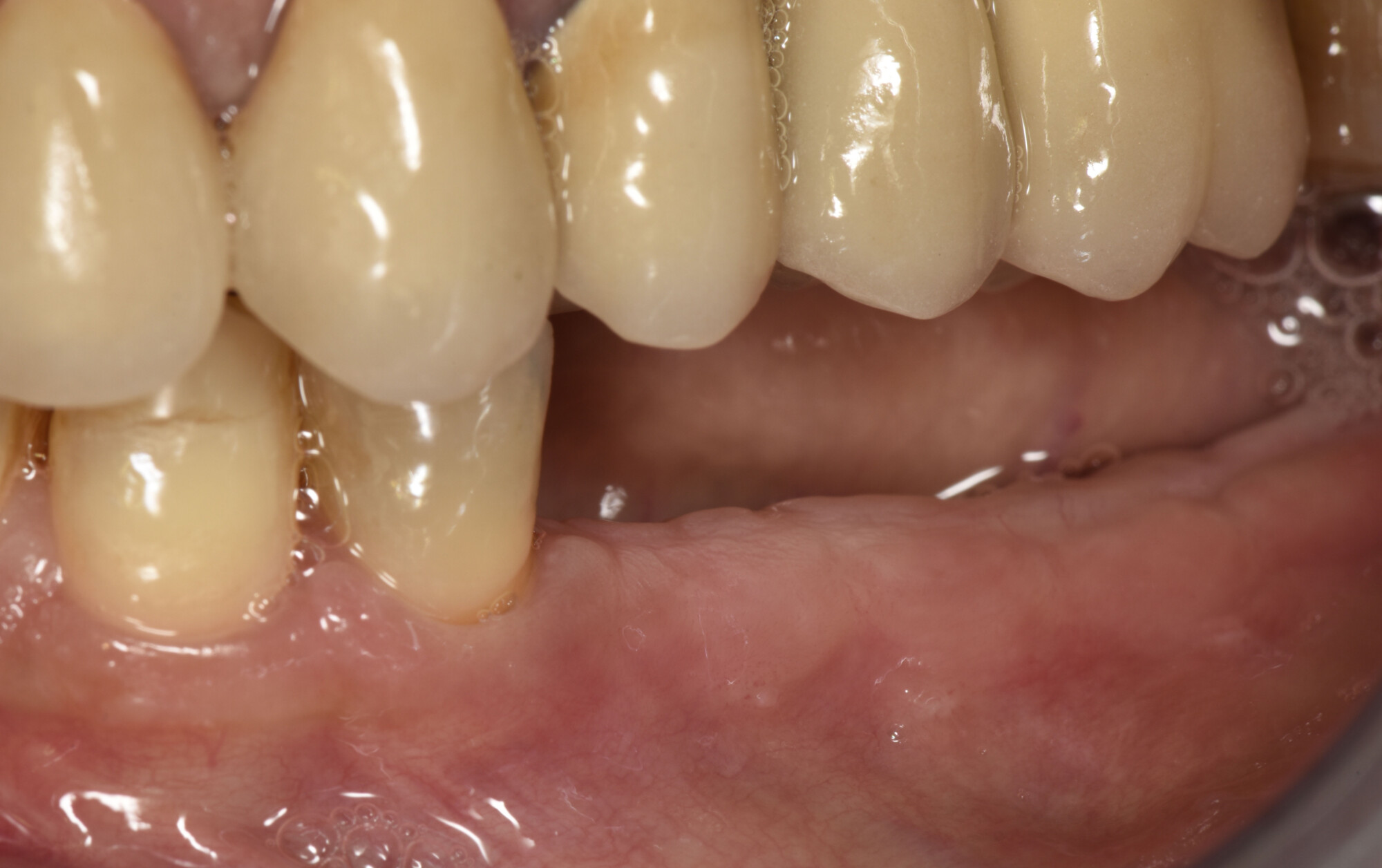
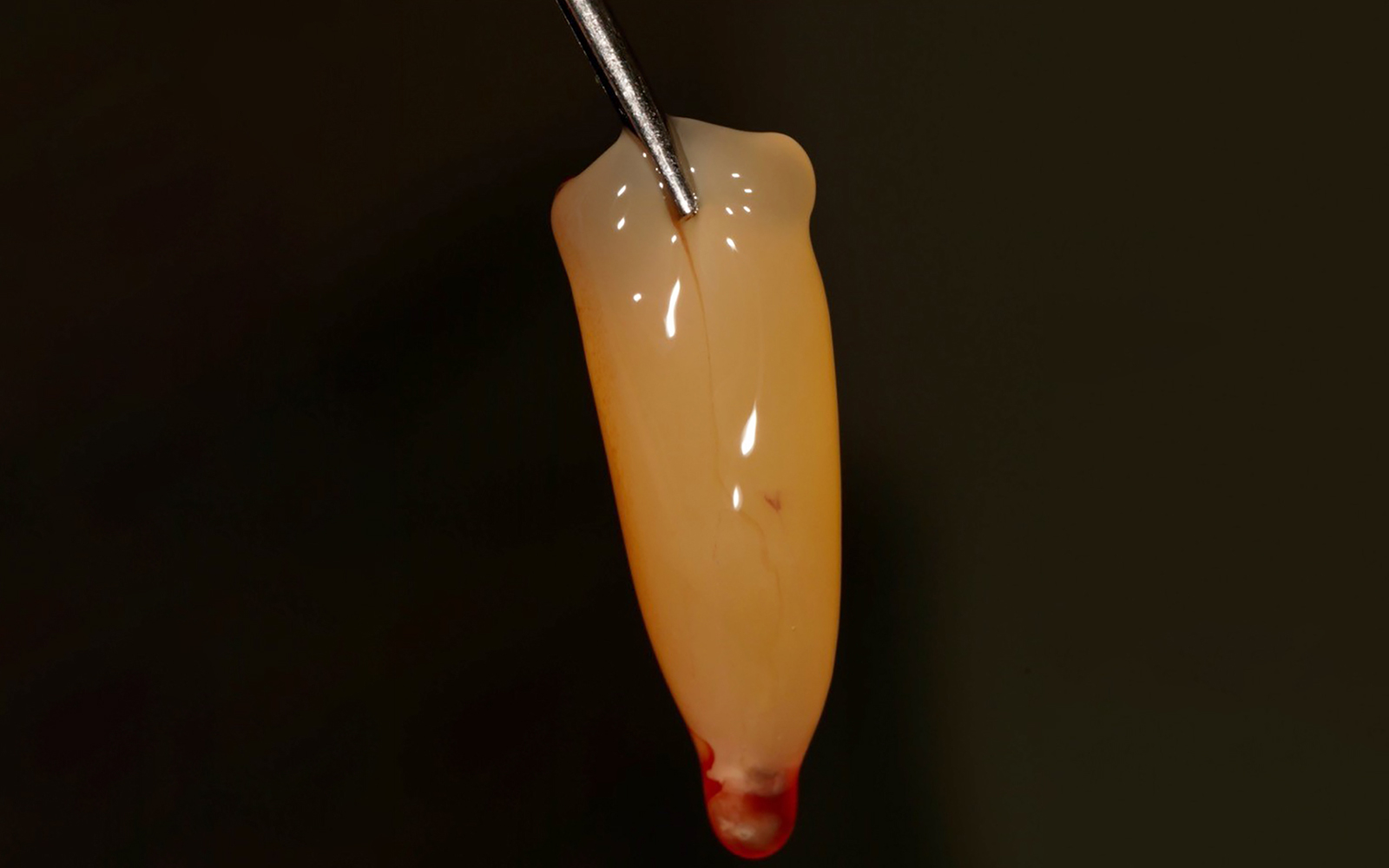
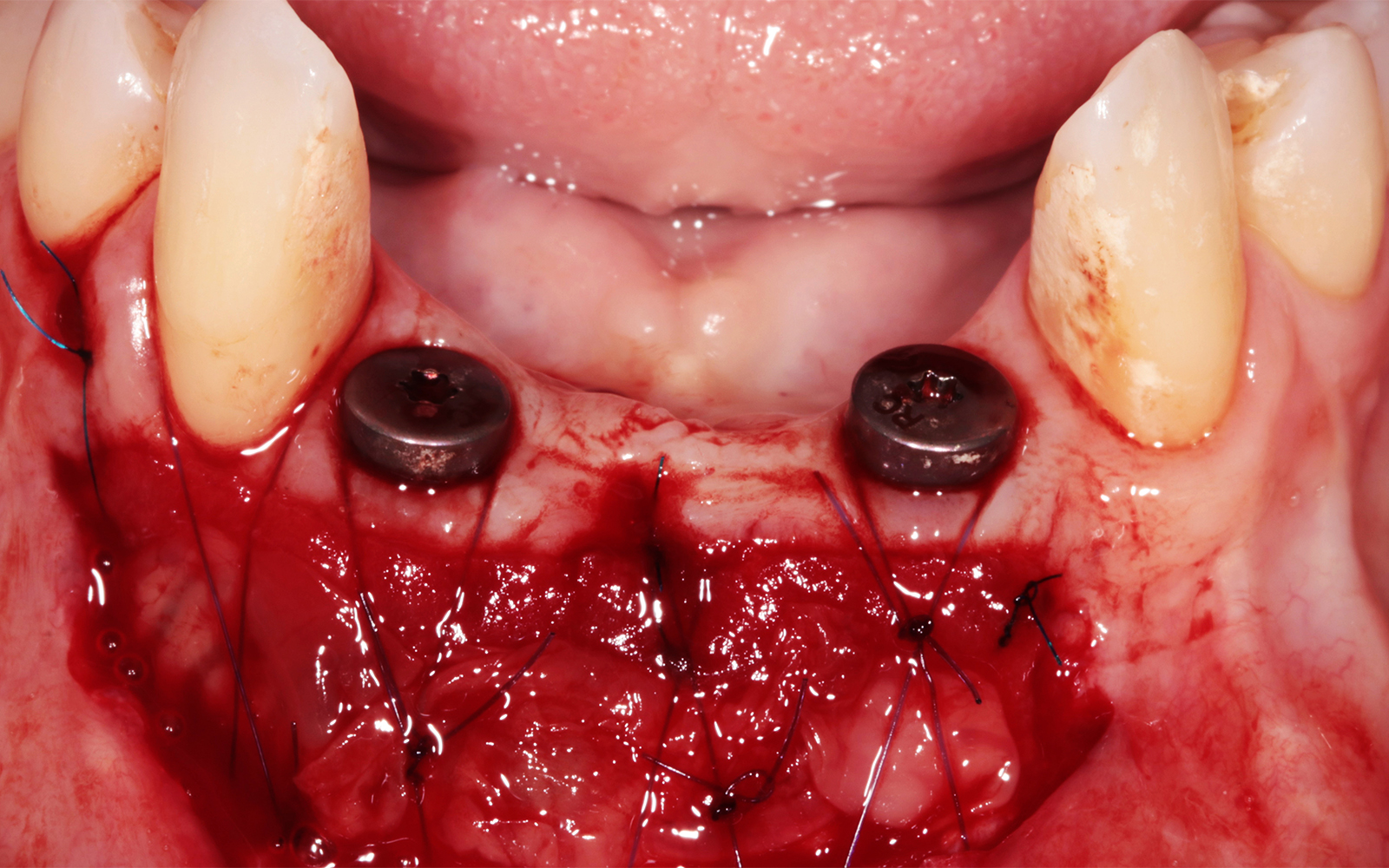
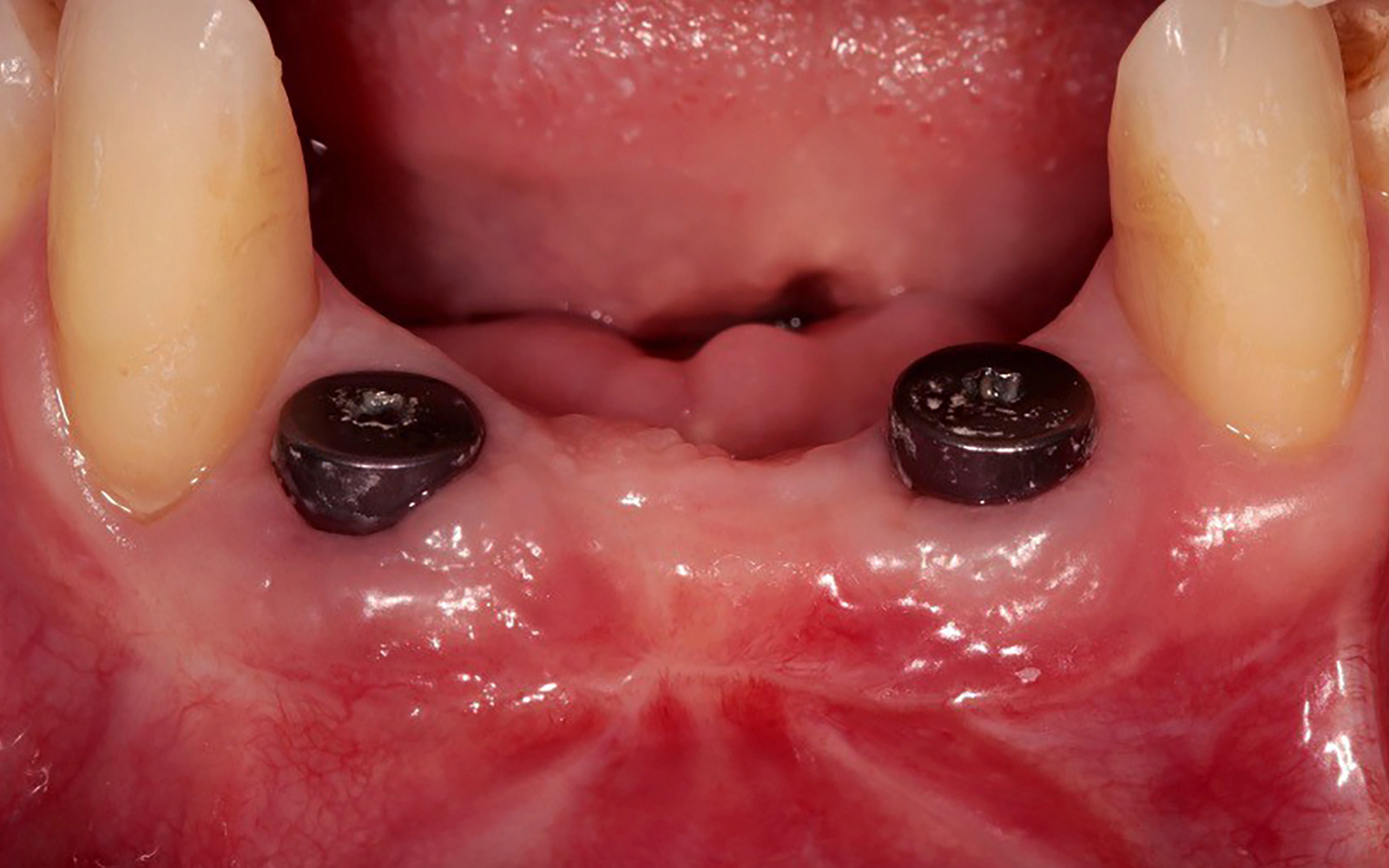
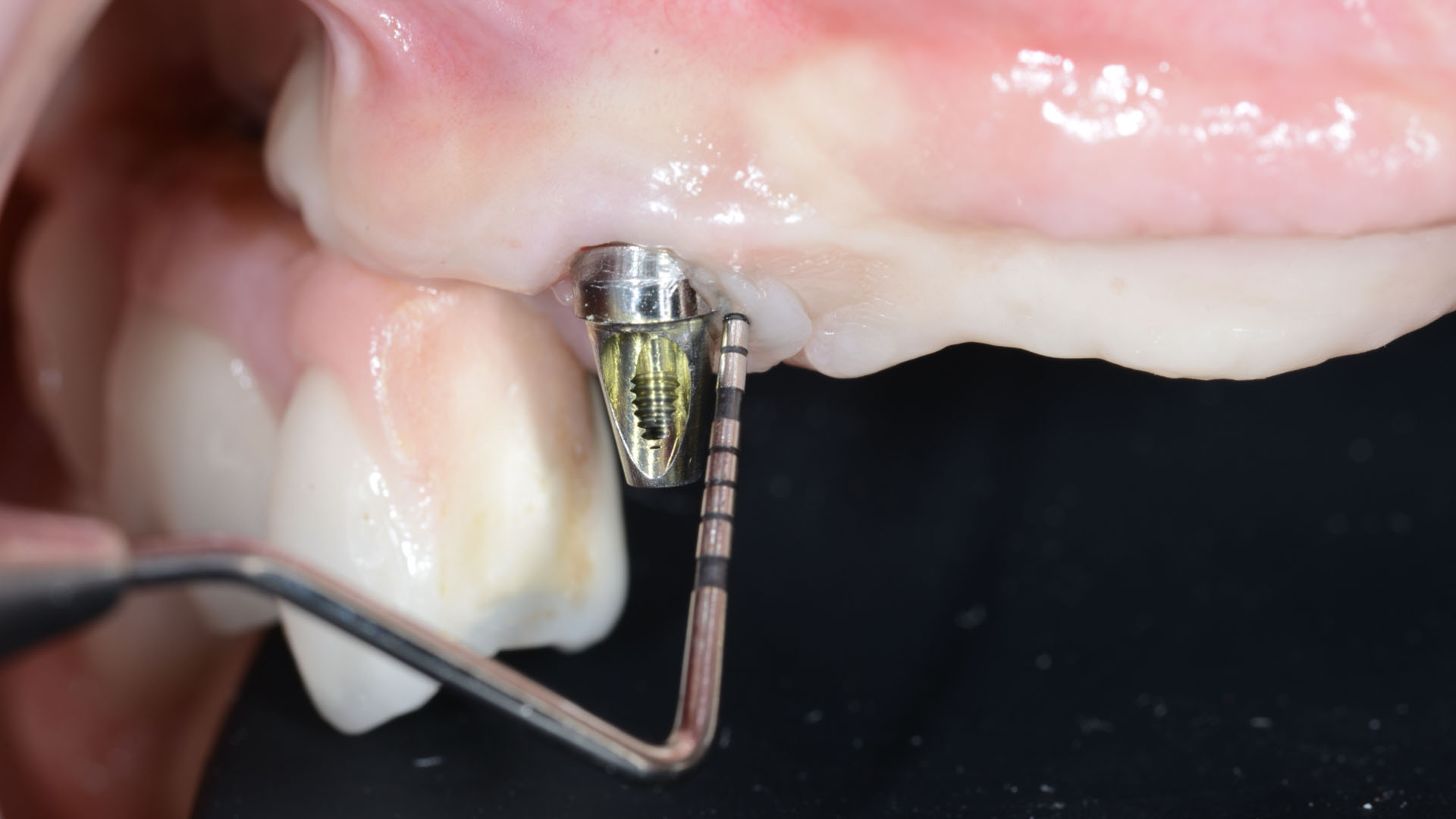
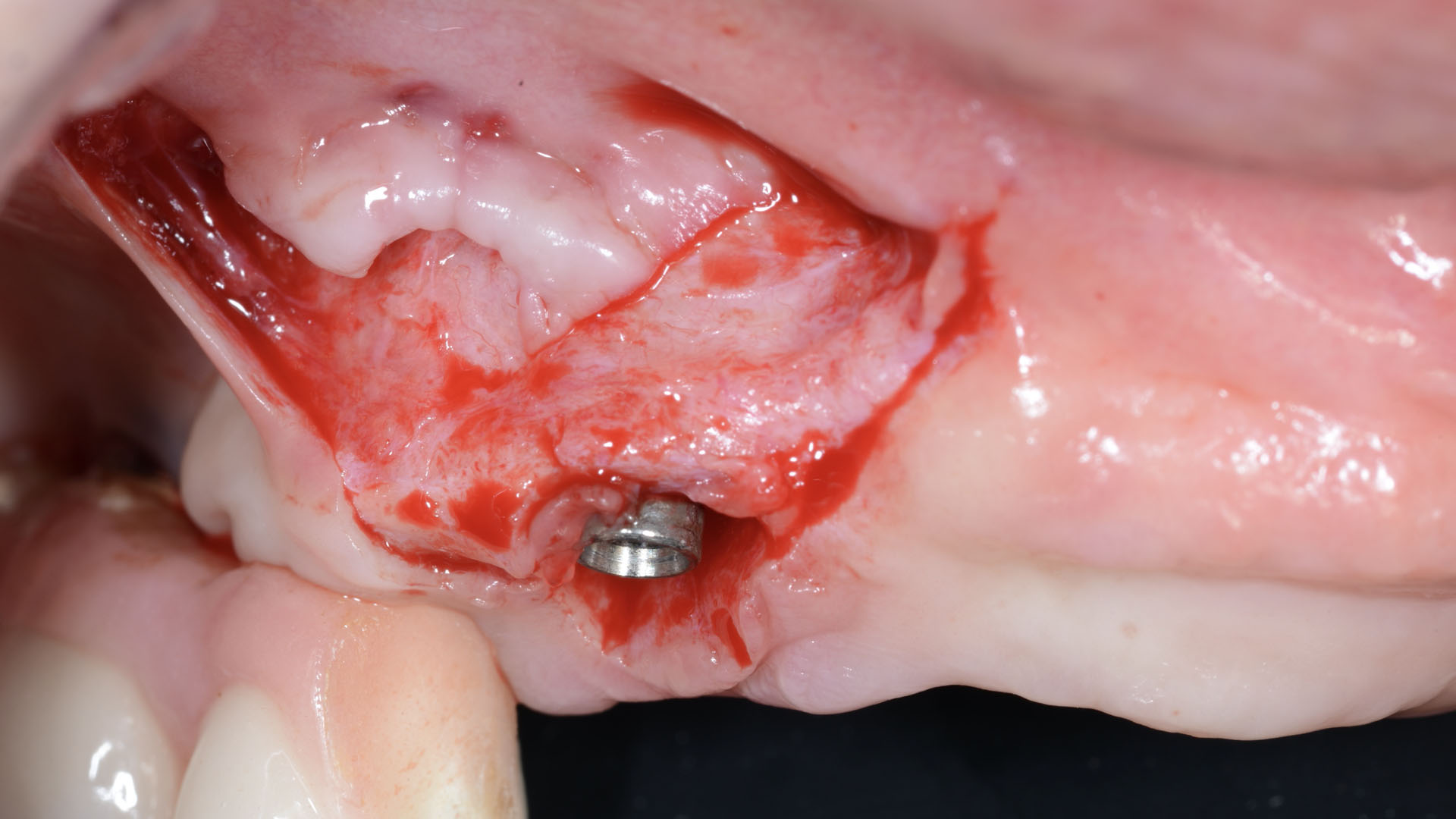
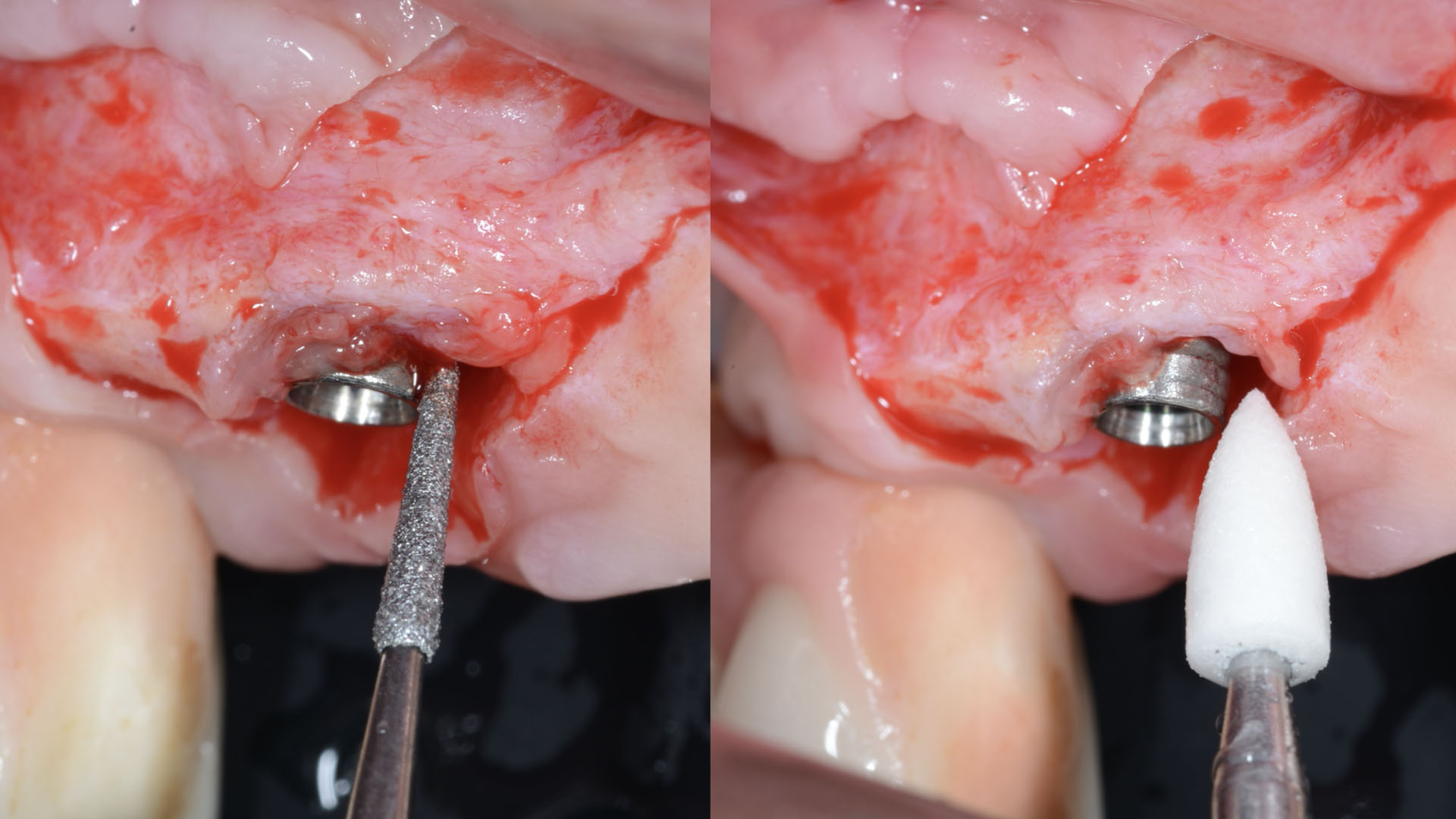
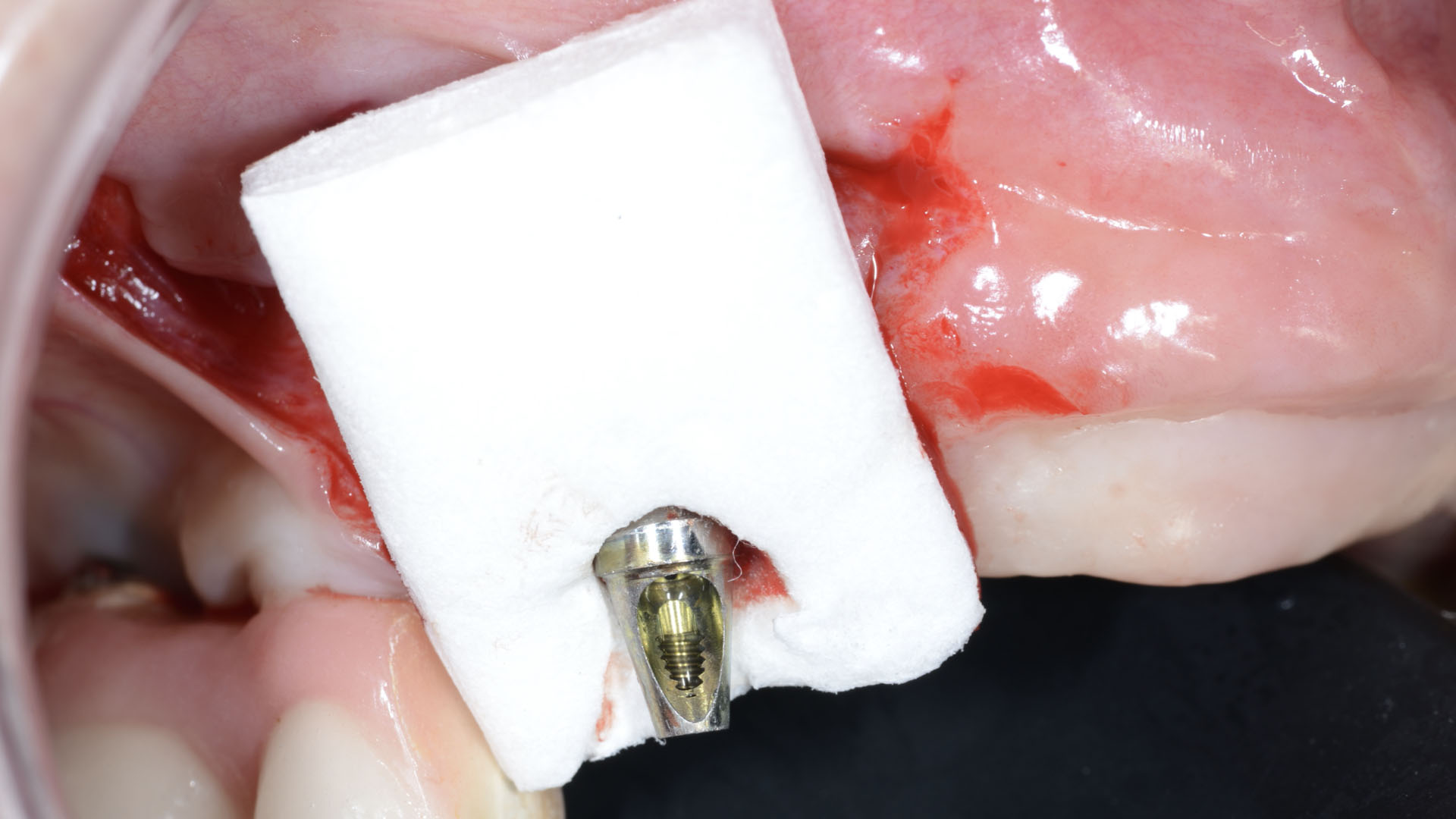
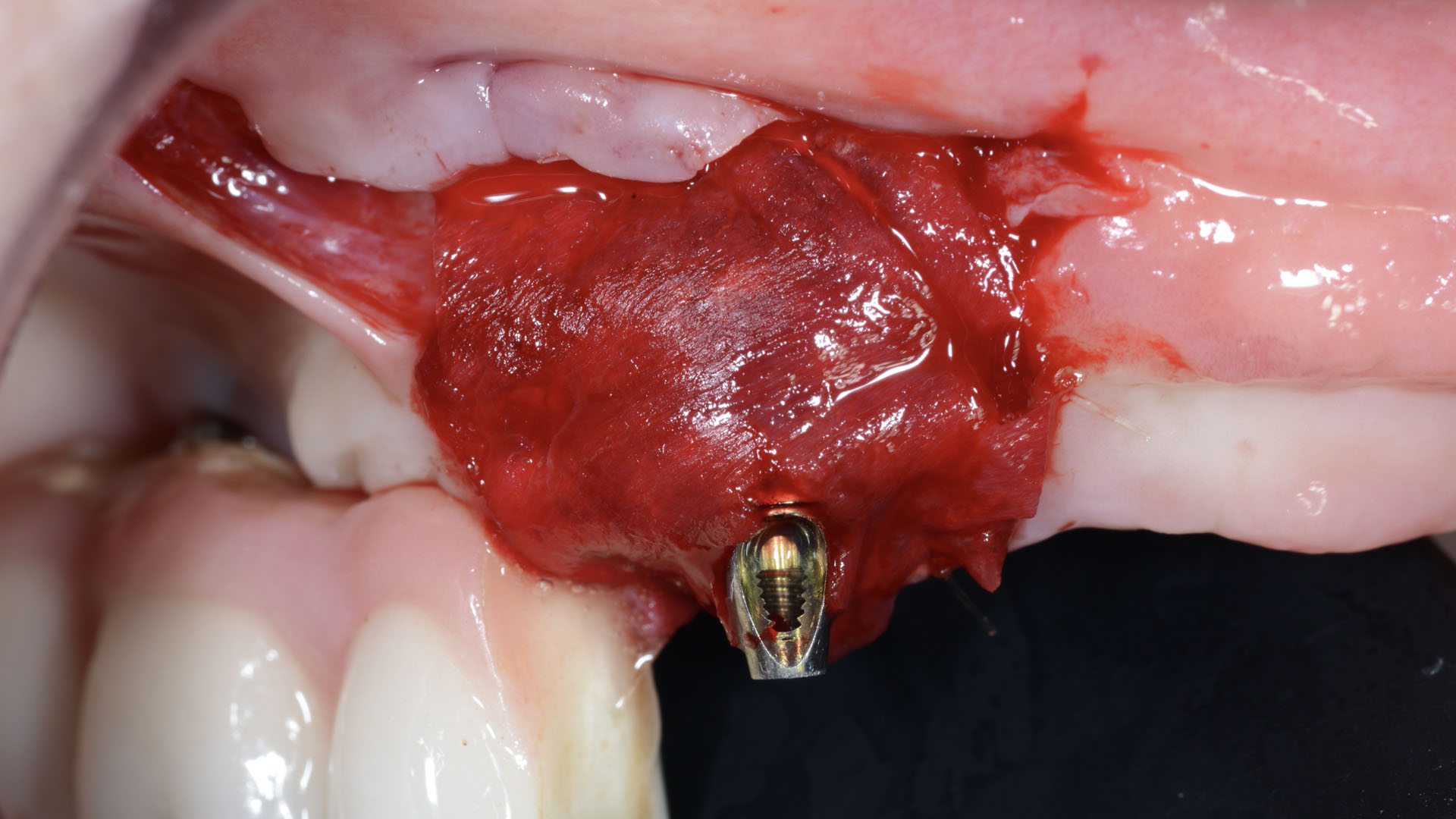
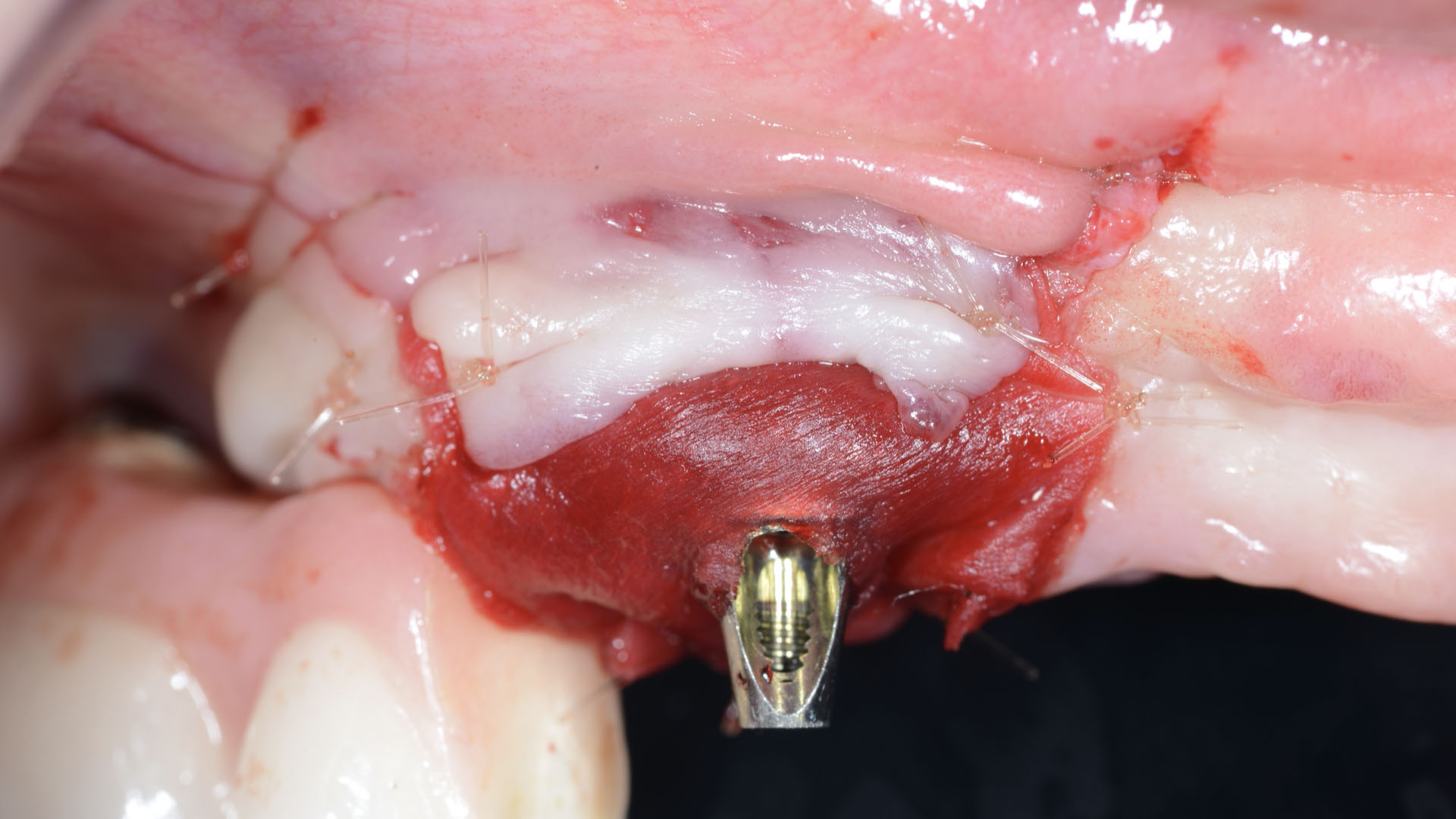
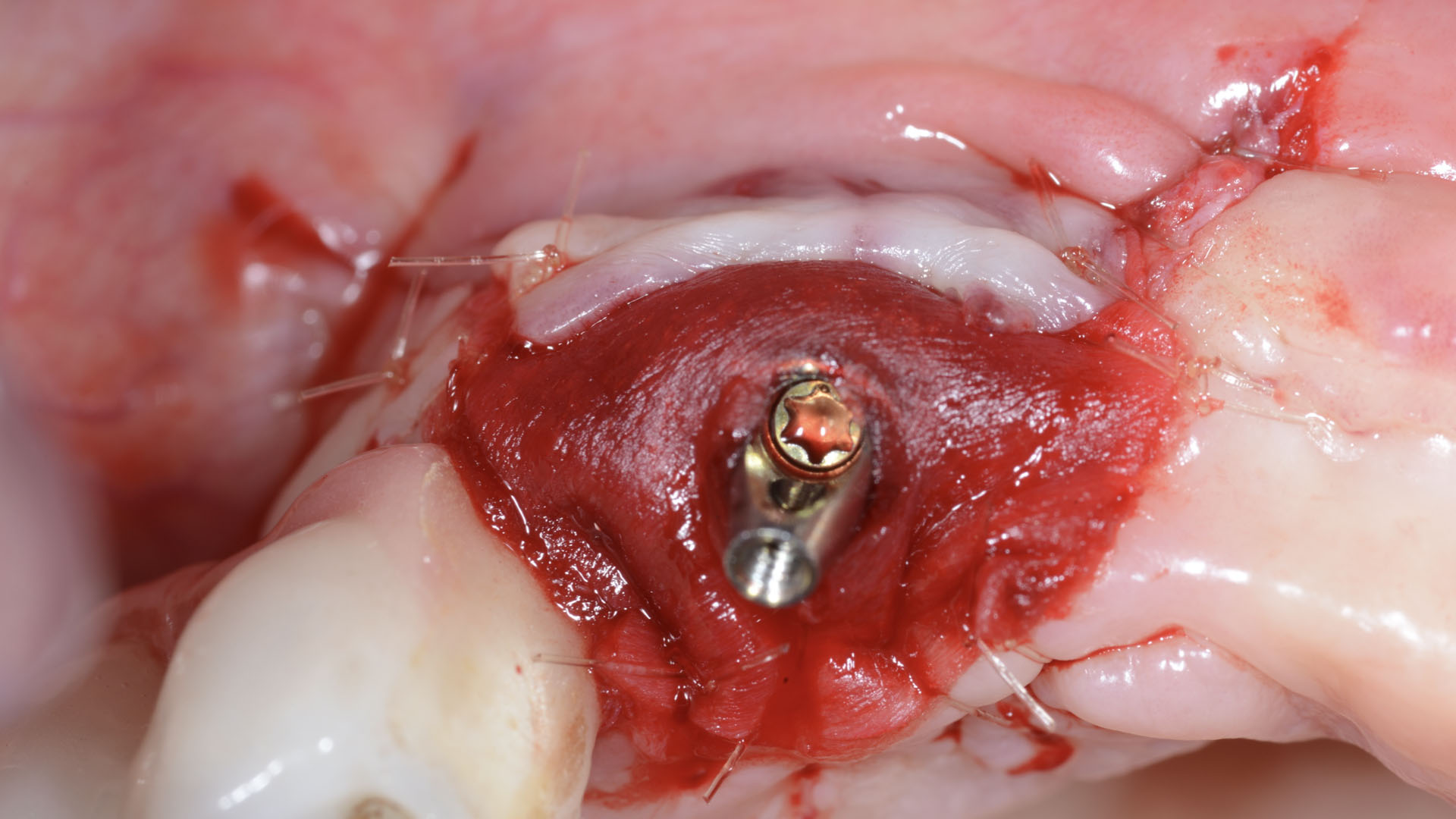
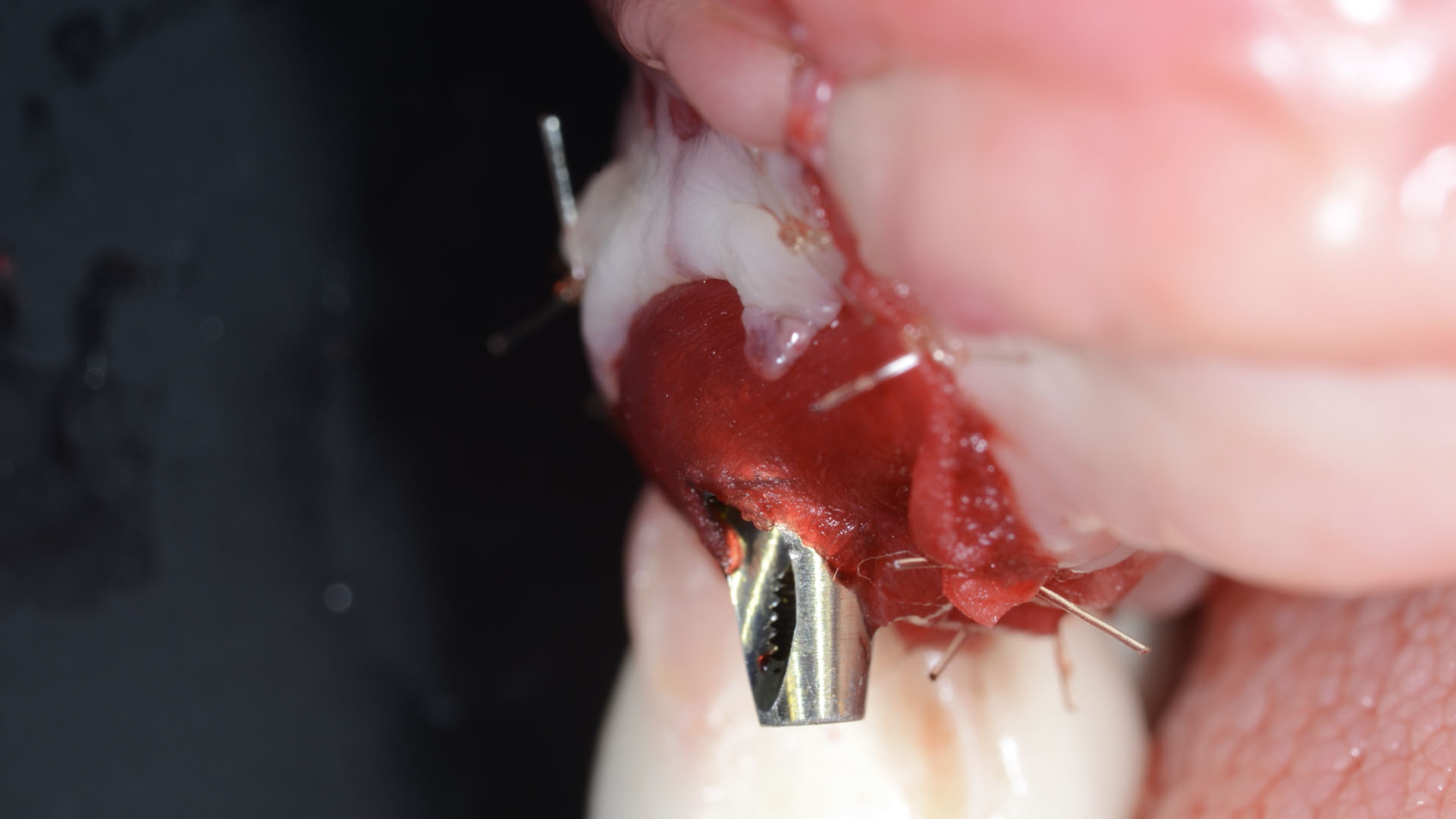
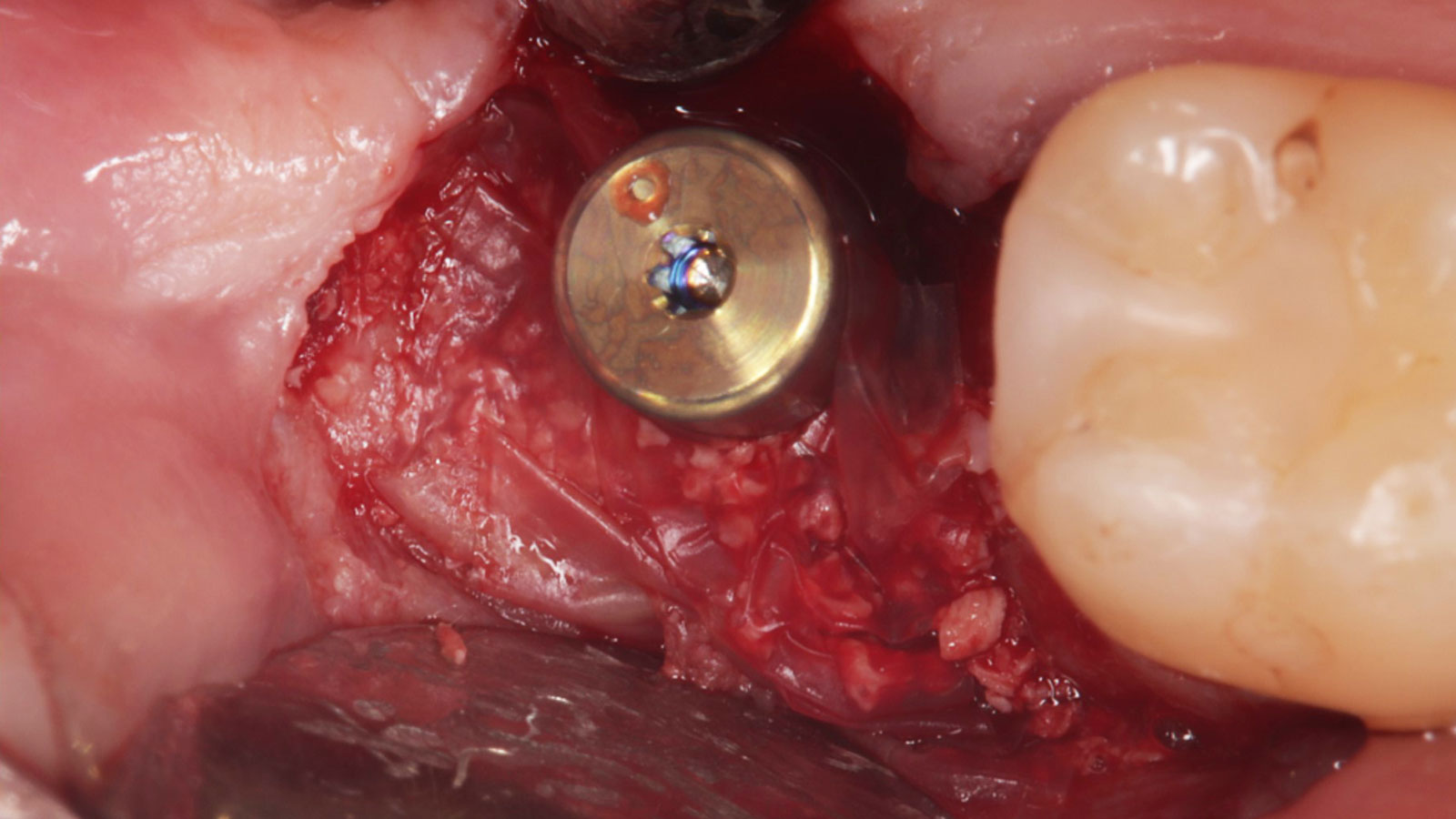
The treatment goals were to eliminate peri-implant infection, regenerate lost hard and soft tissues, and ensure long-term implant stability. A closed regenerative approach was utilized, including crown removal, thorough implant decontamination with Perioflow®, an airpolishing technology, application of the correct bone grafting materials (Geistlich Bio-Oss®, vallos® and GEM 21S®), enclosed healing, and fabrication of a new crown to facilitate hygiene.
“The implant presented with significant bone loss, deep probing depths, and bleeding on probing, placing it at risk of failure and requiring intervention to preserve function and longevity.”
— Andrea Ravidà, DDS, MS, PhD
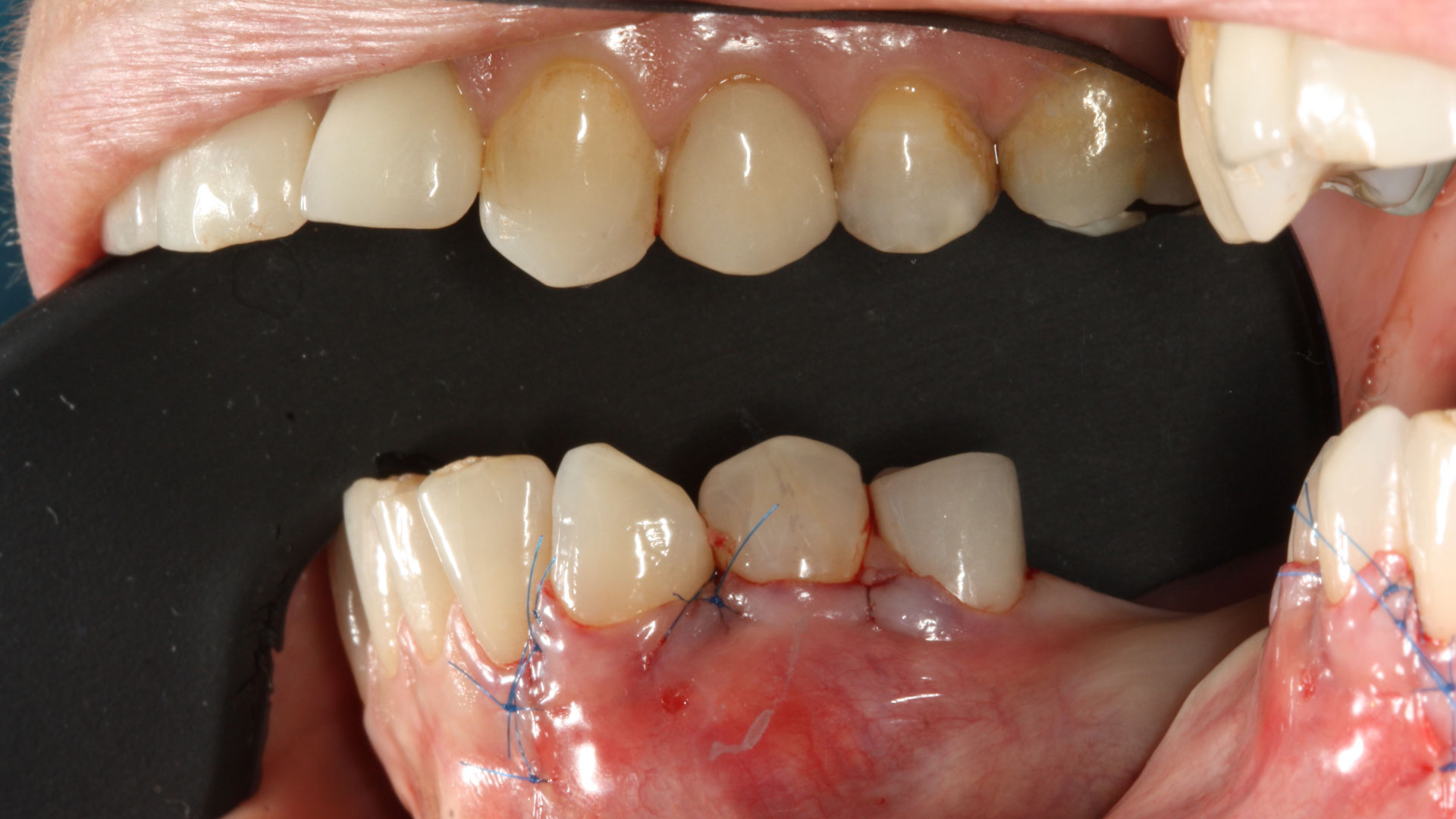
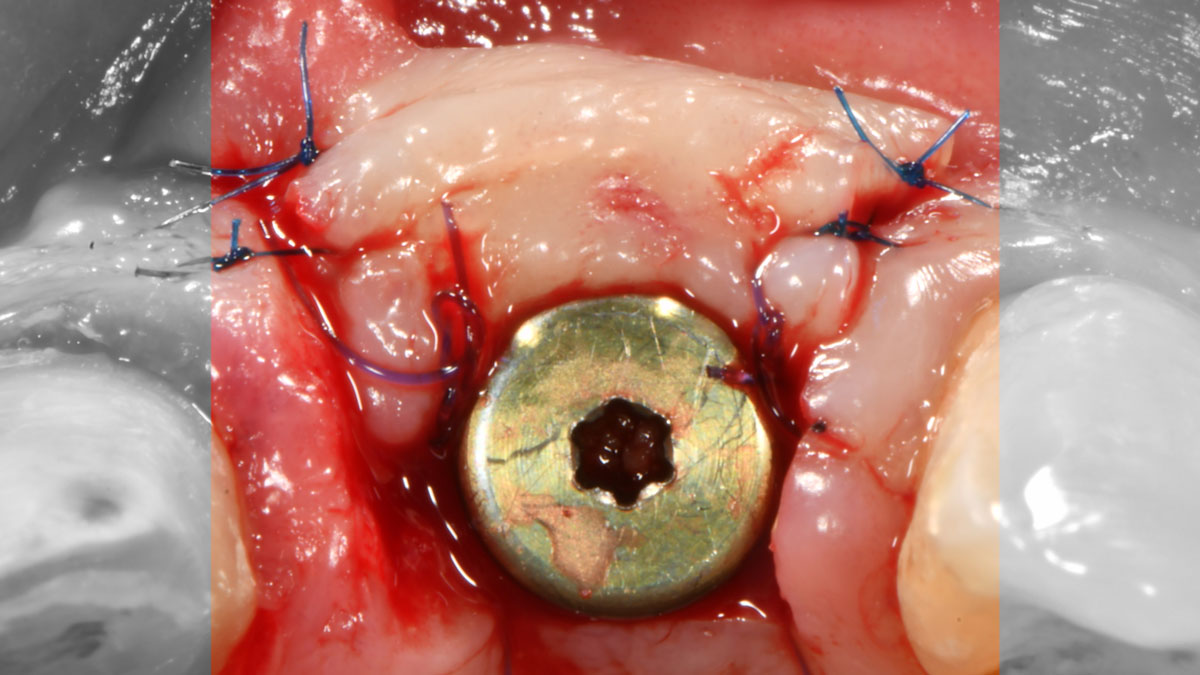
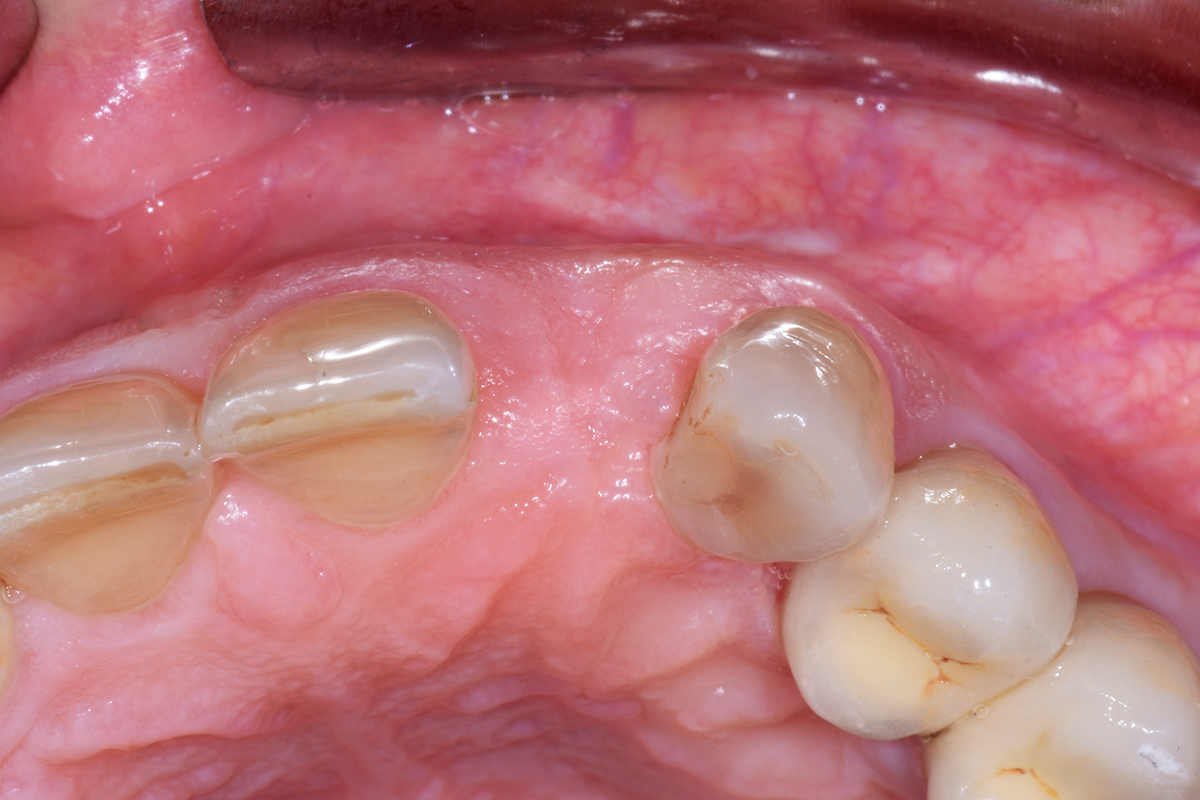
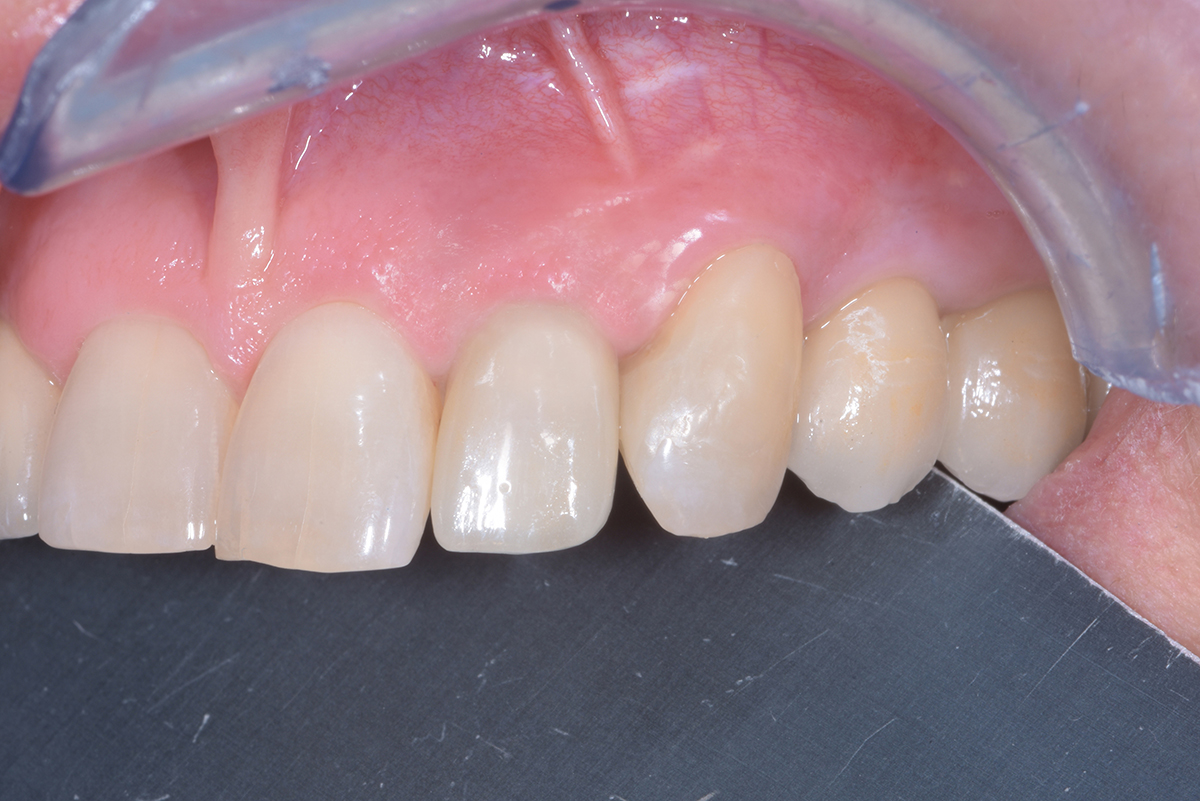
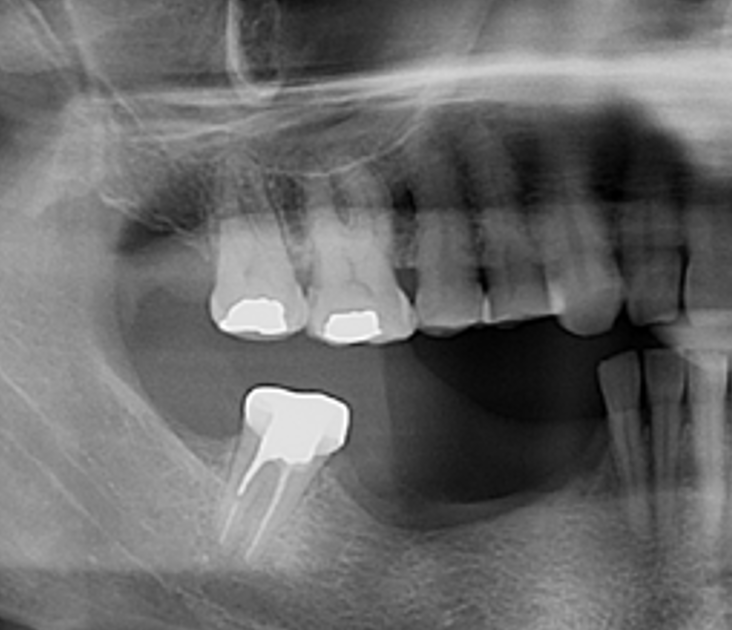
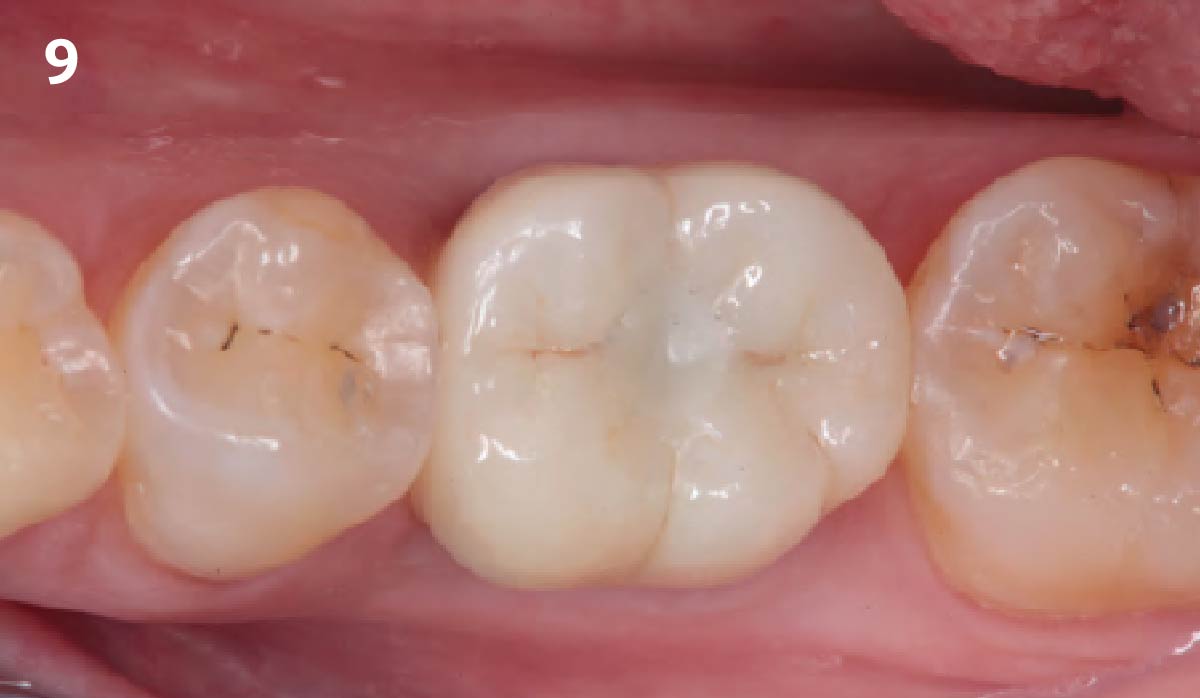
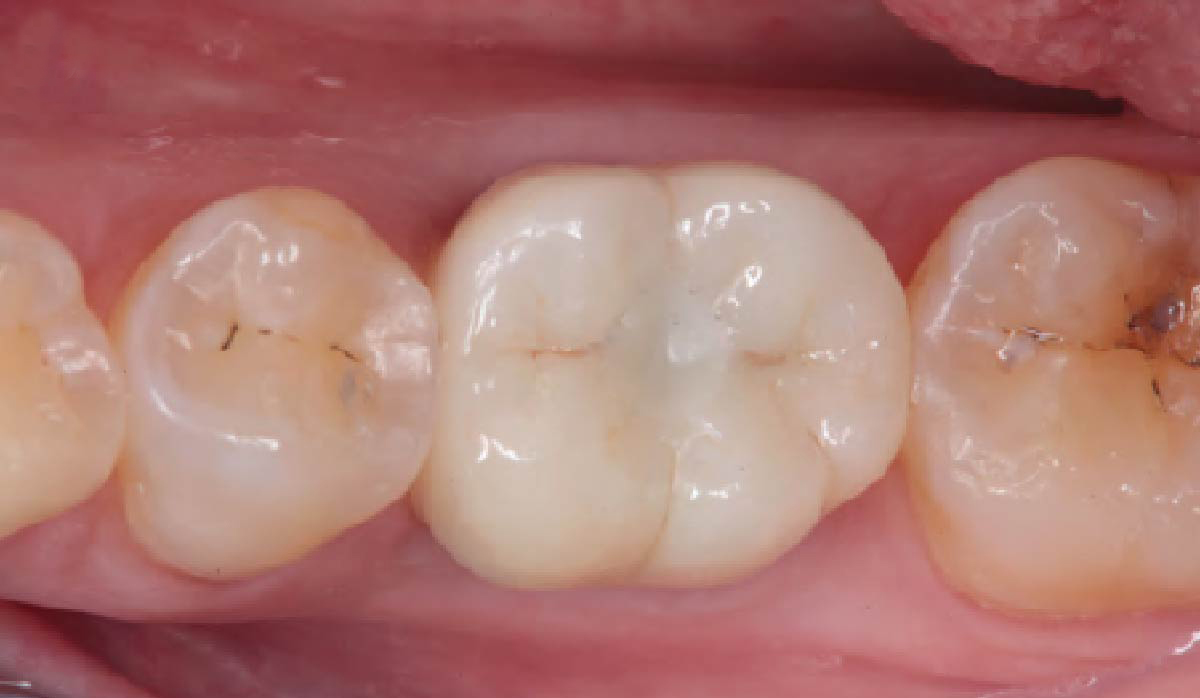
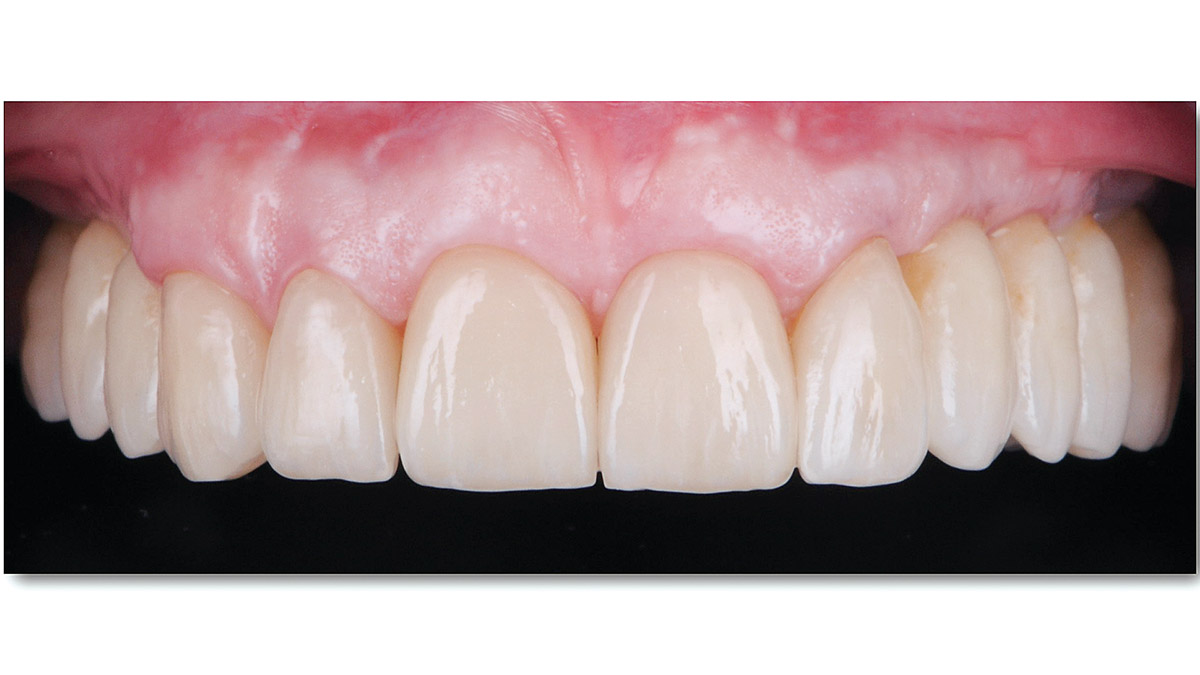
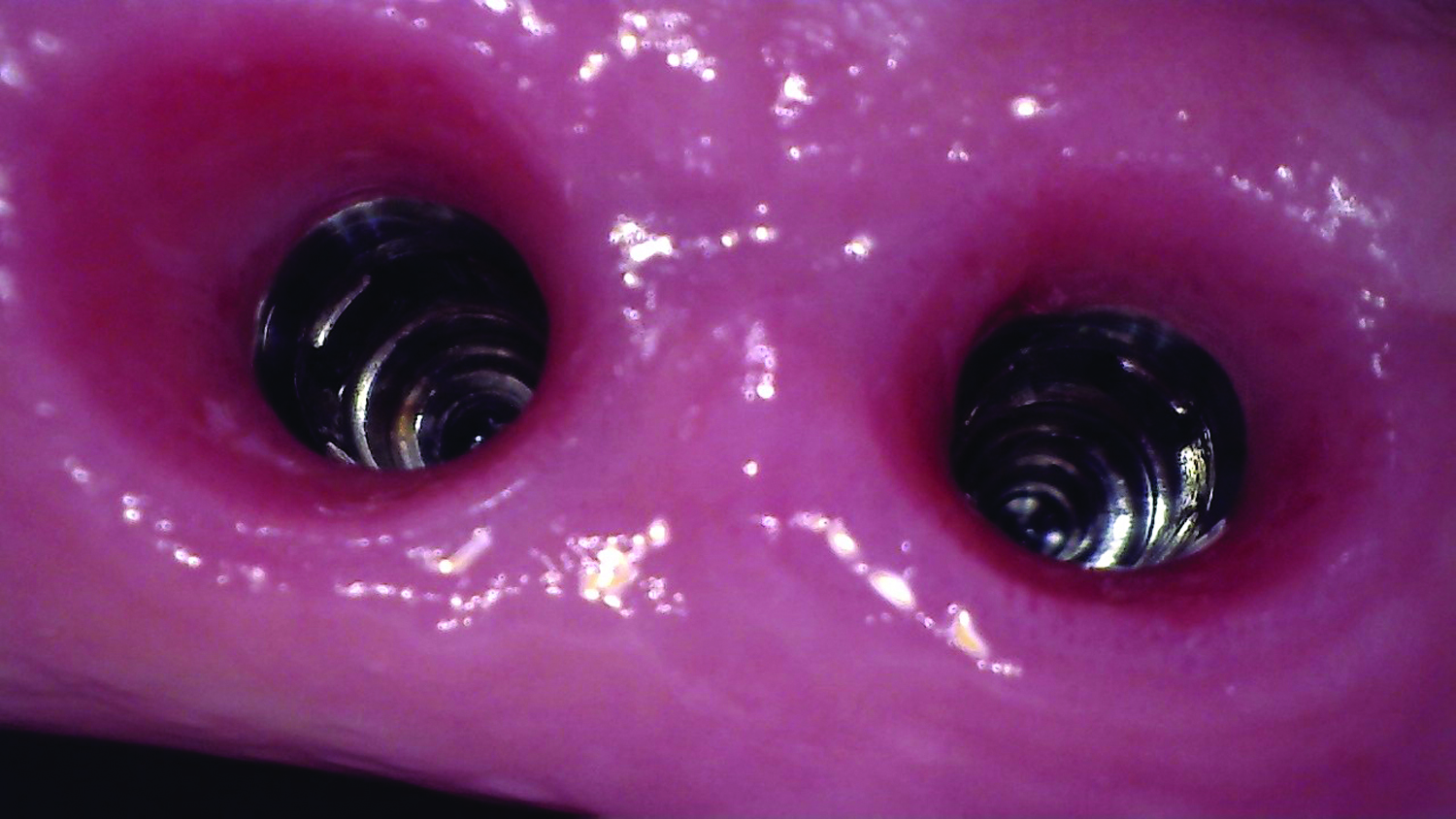
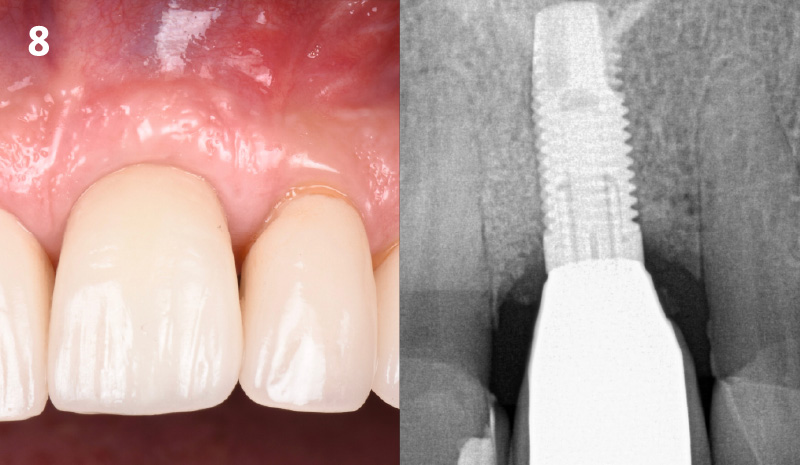
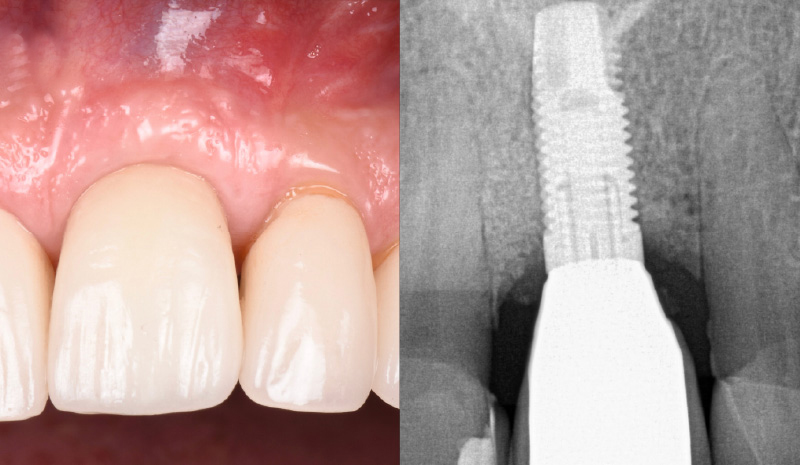
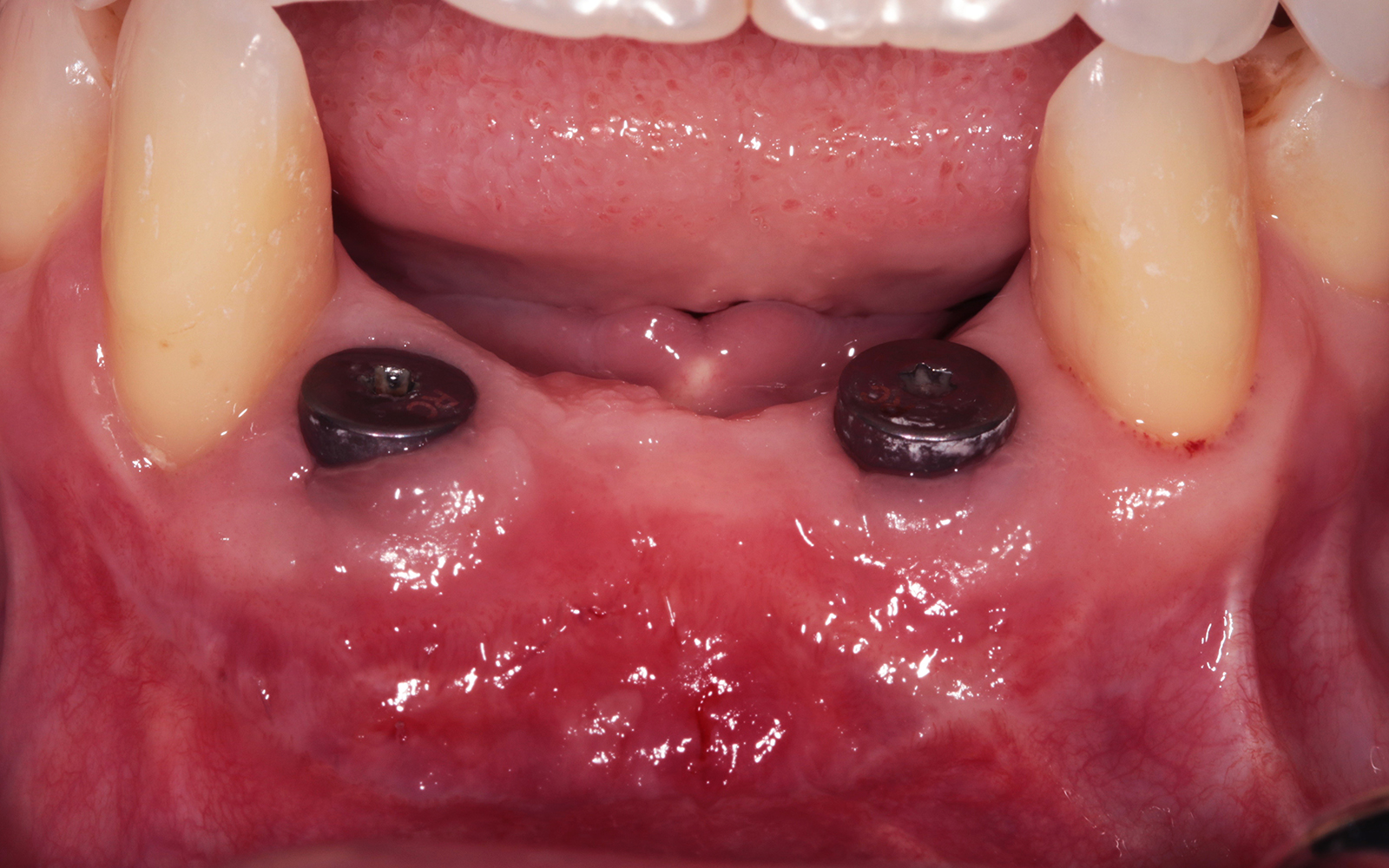
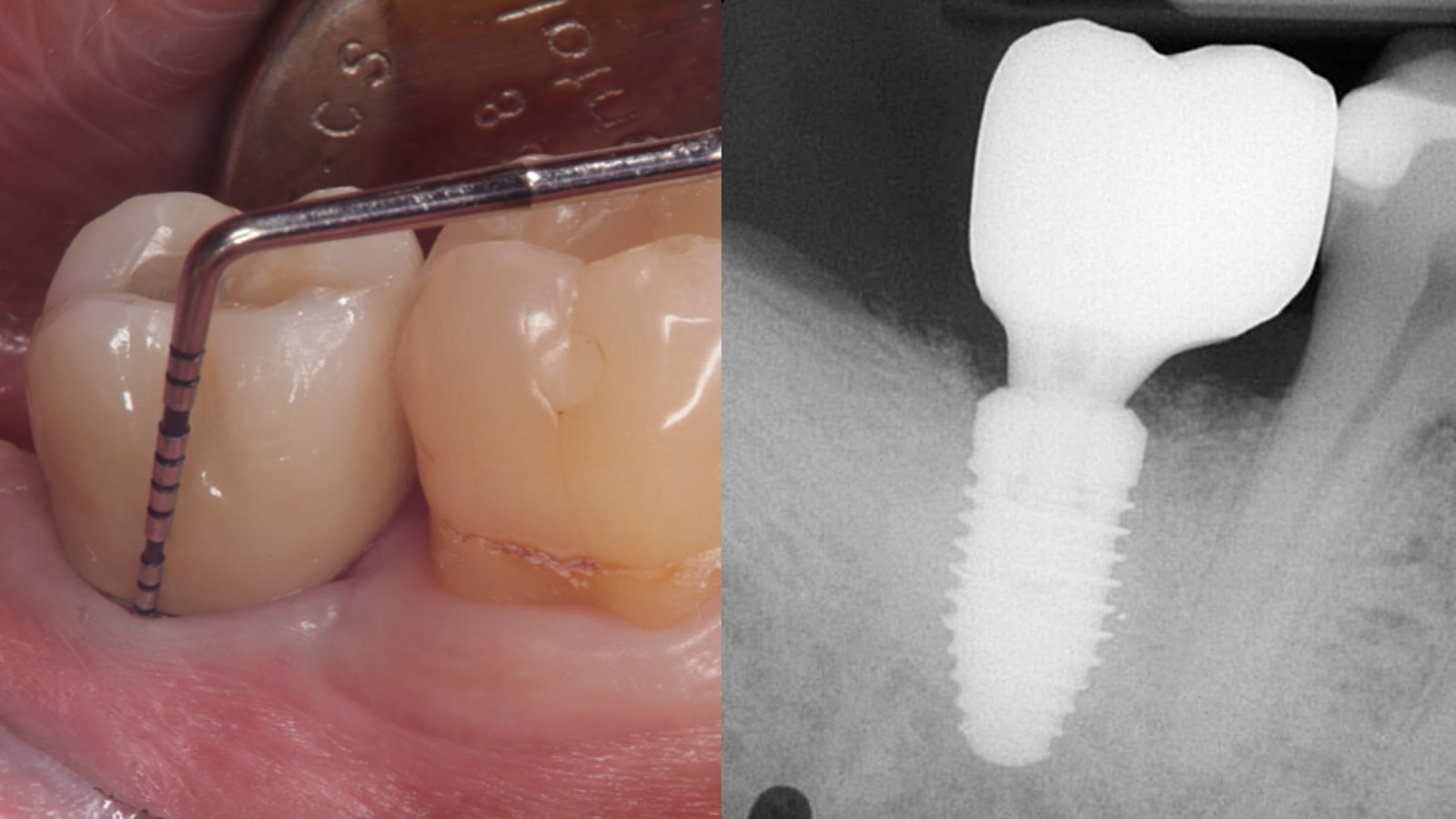
THE OUTCOME
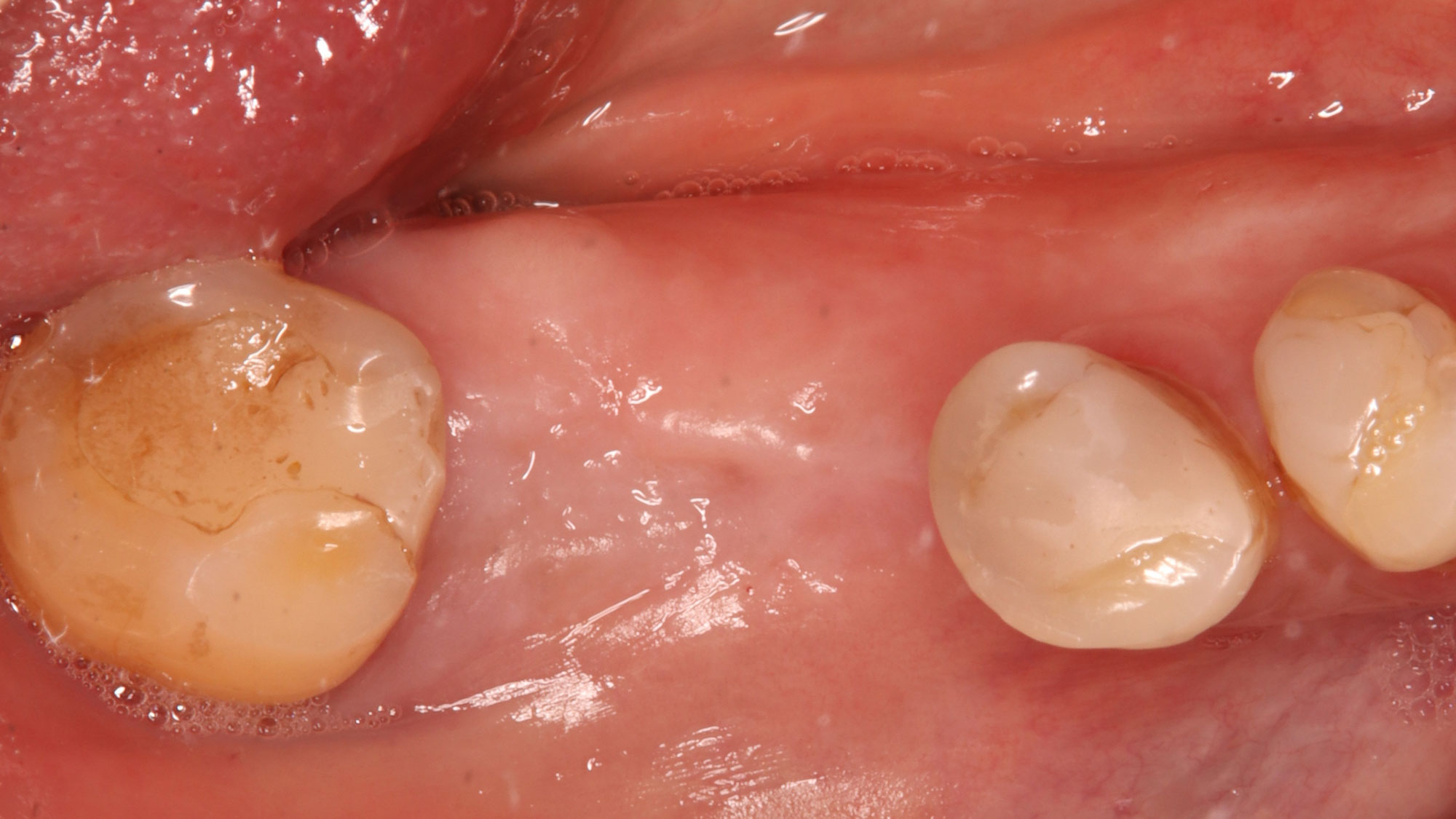
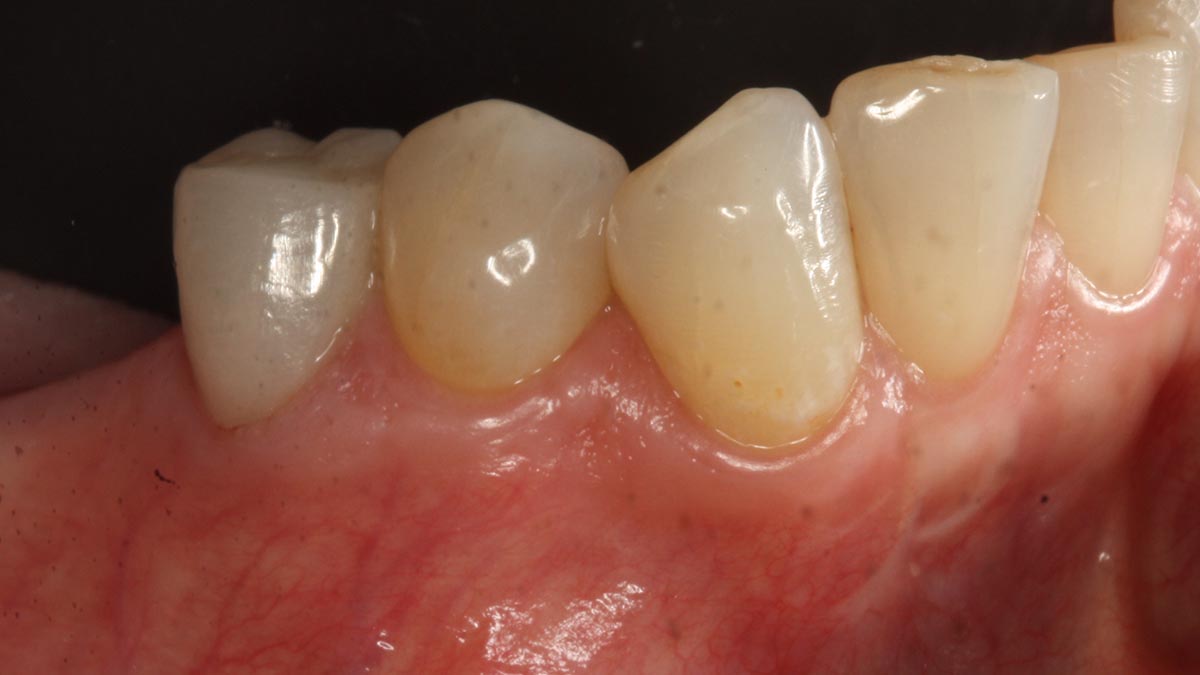
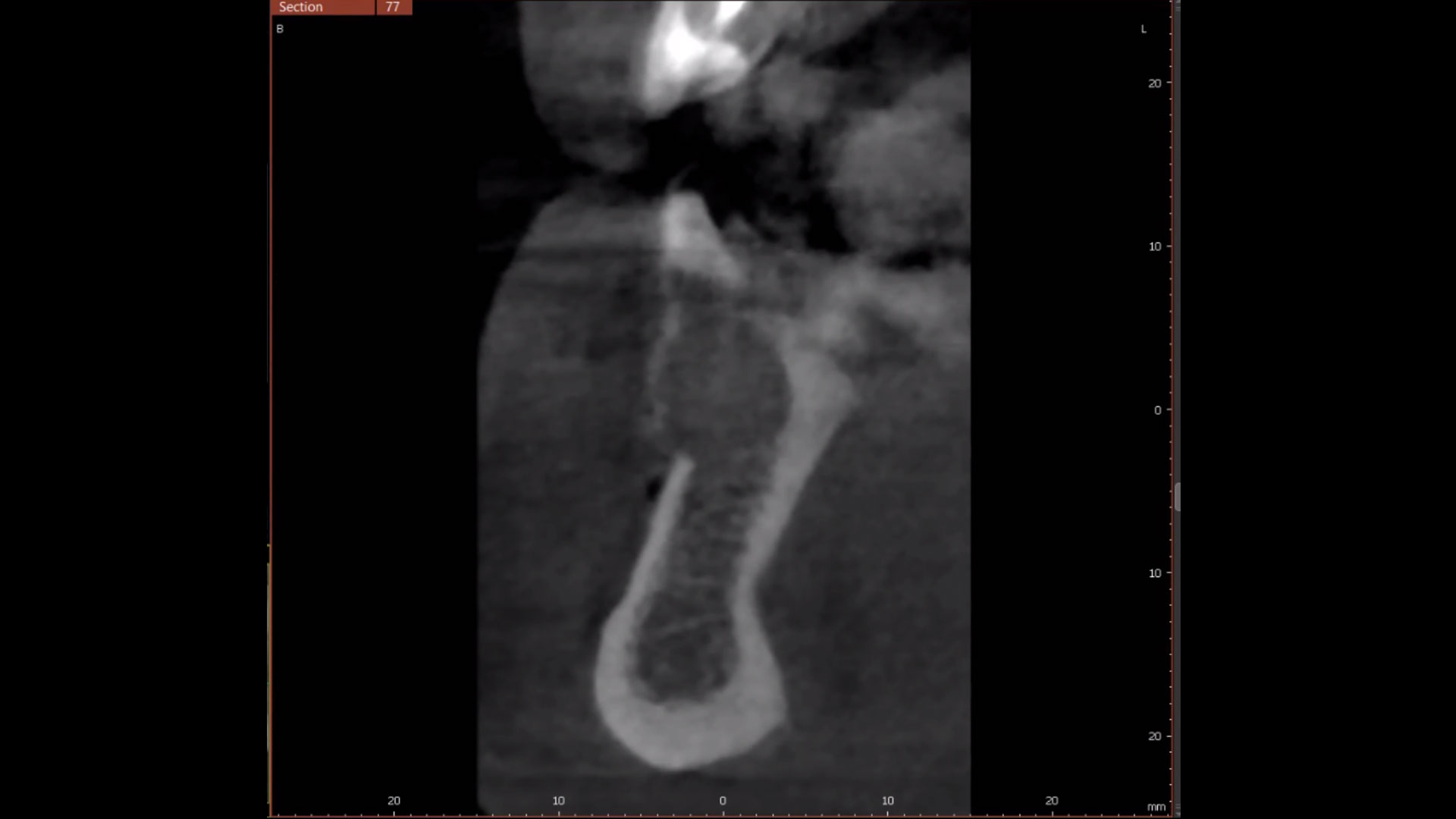
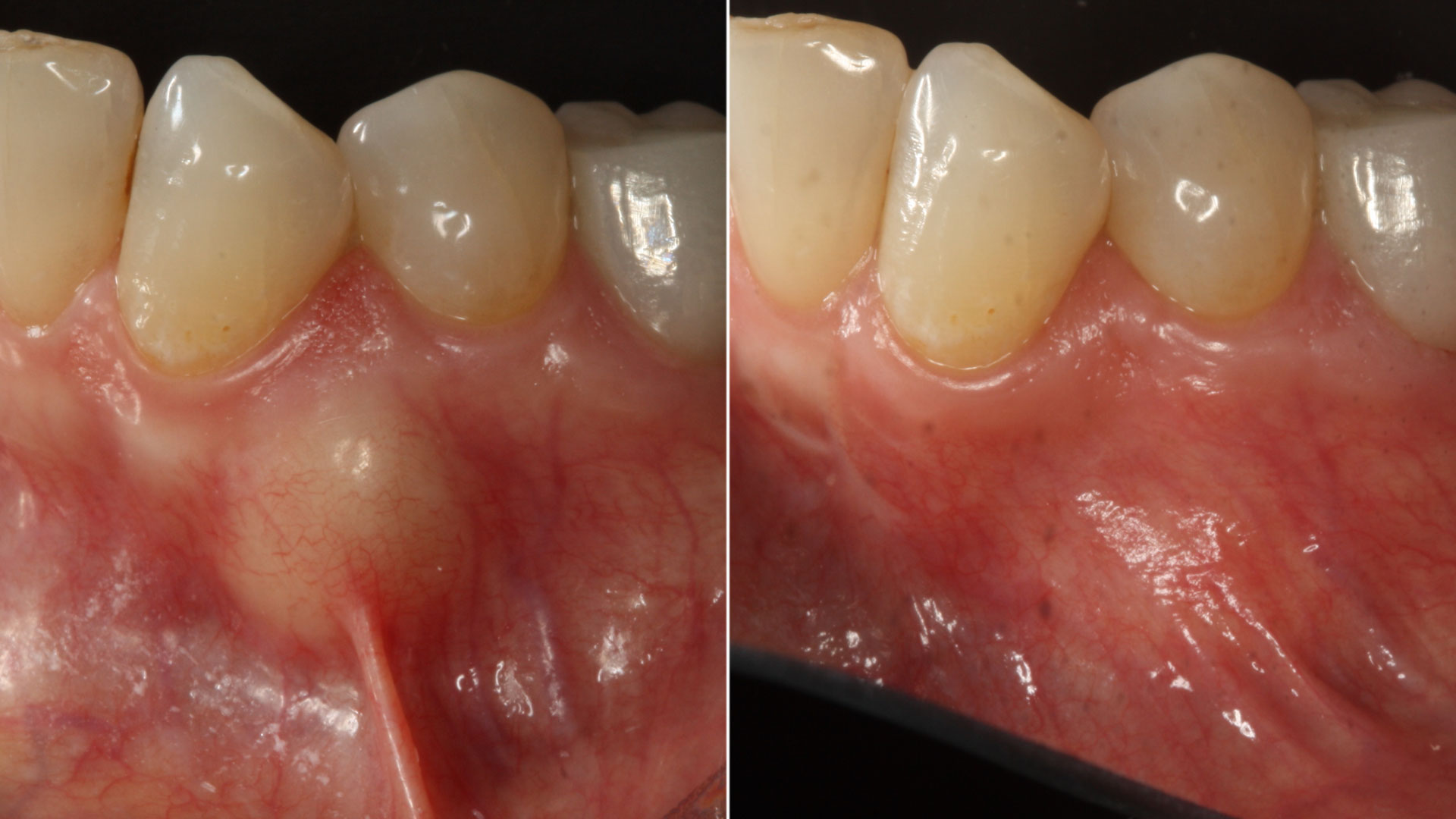
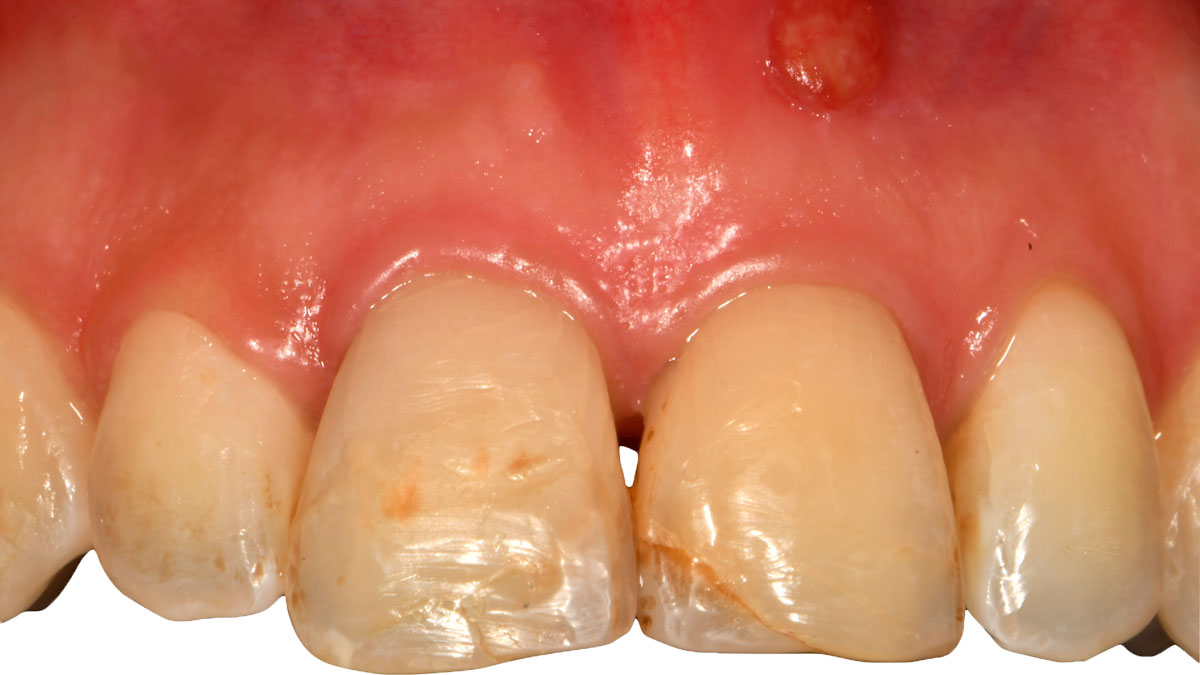
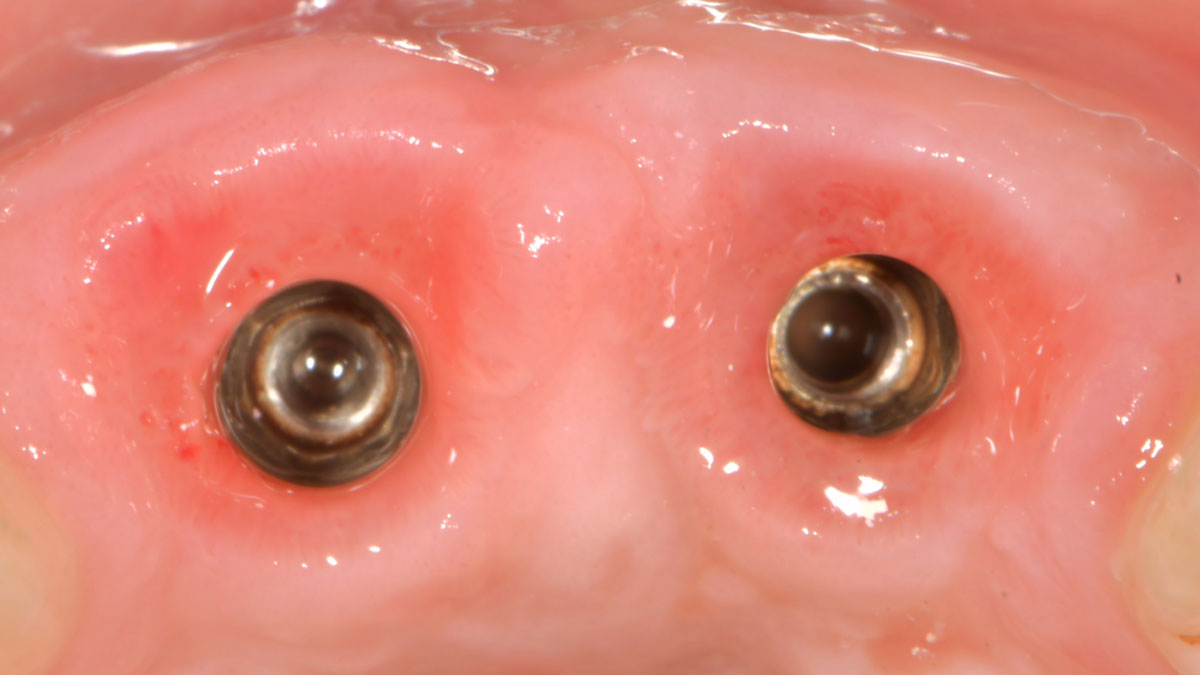
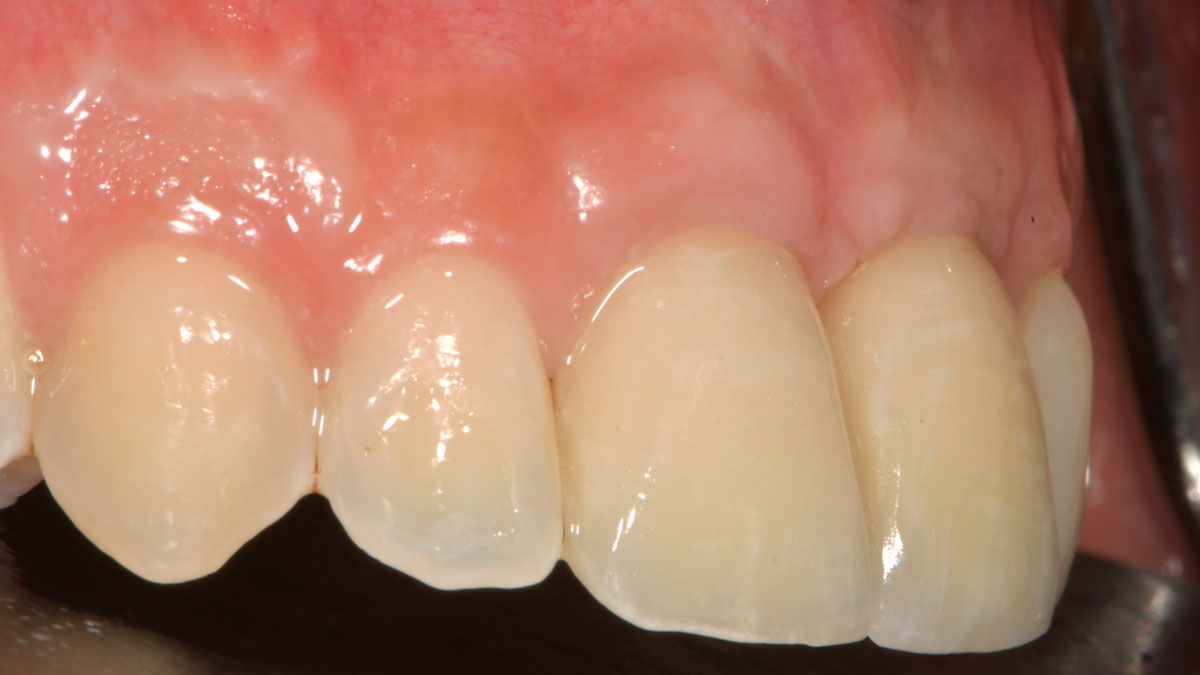
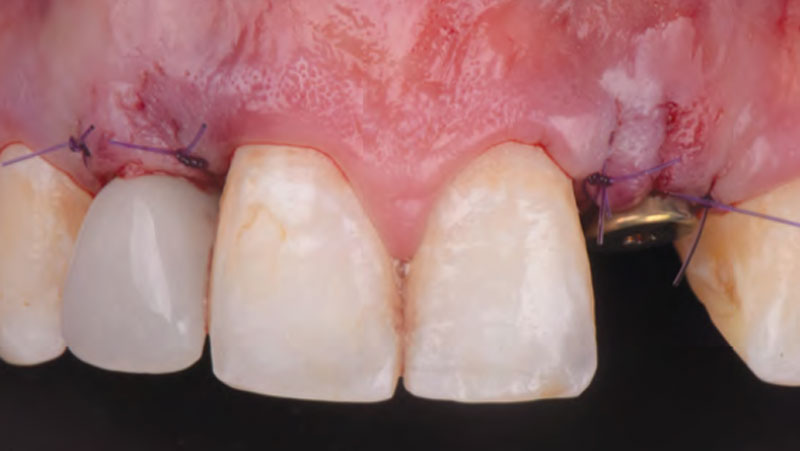
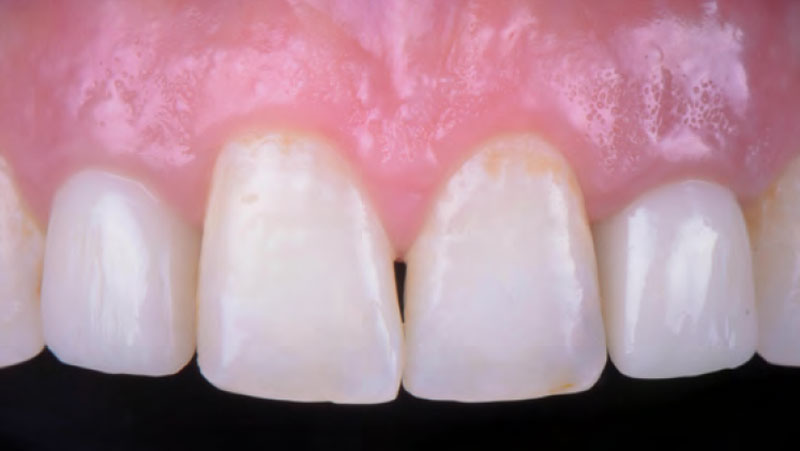
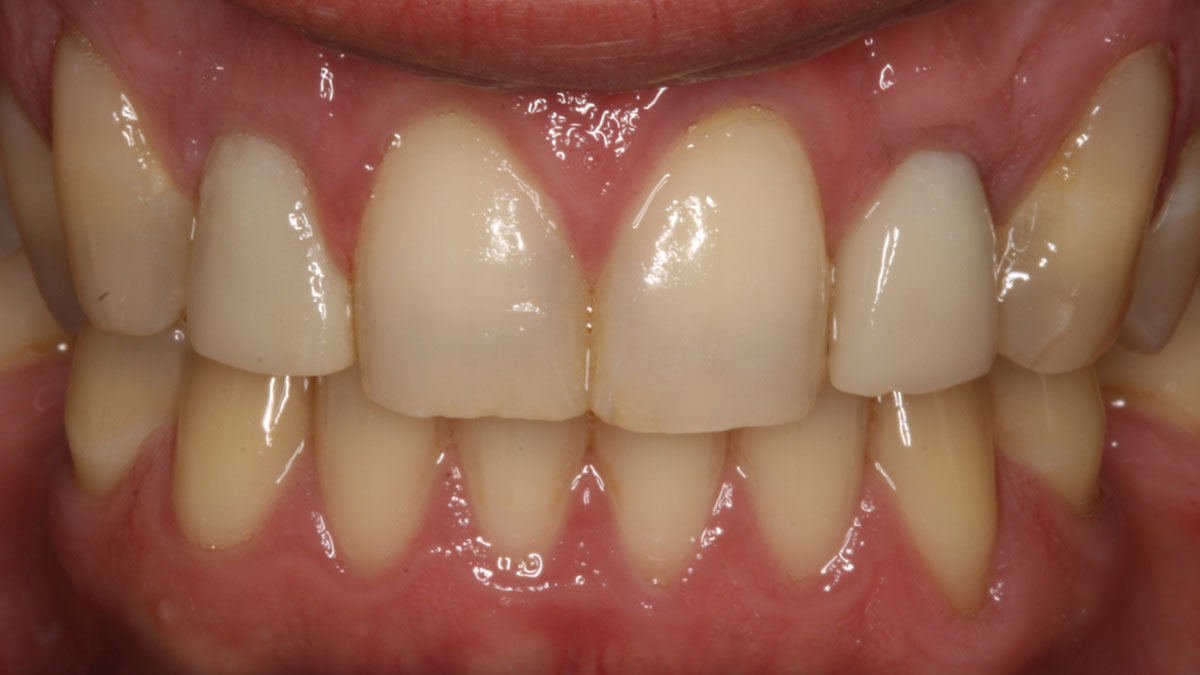
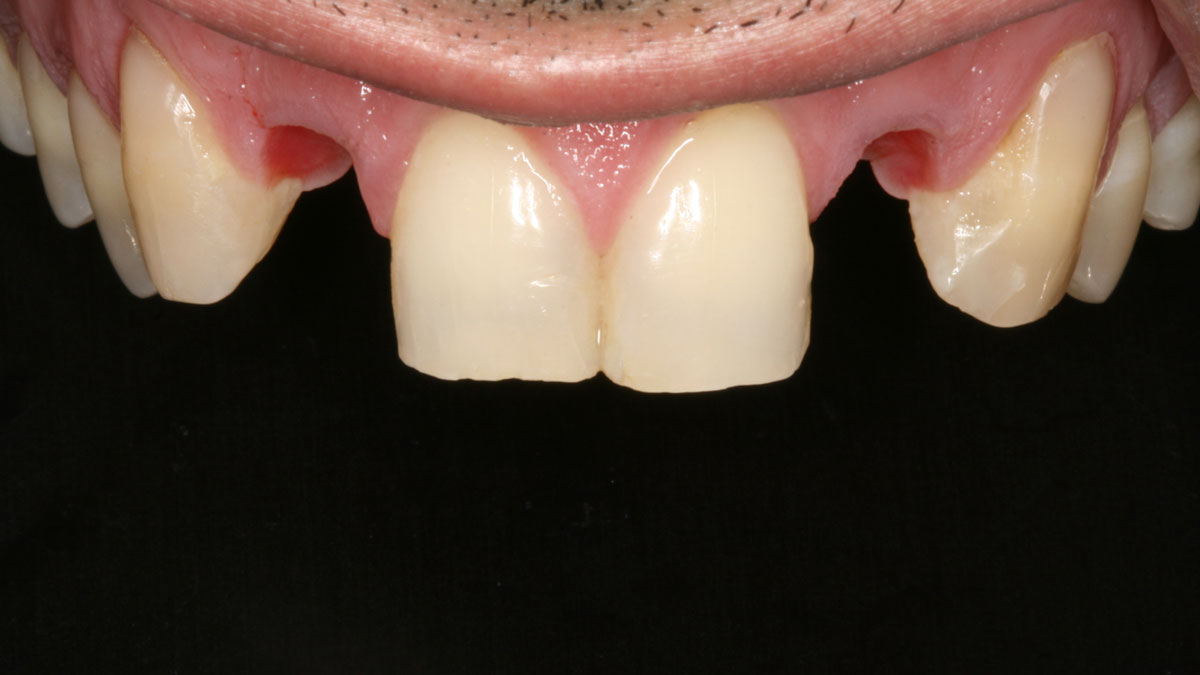
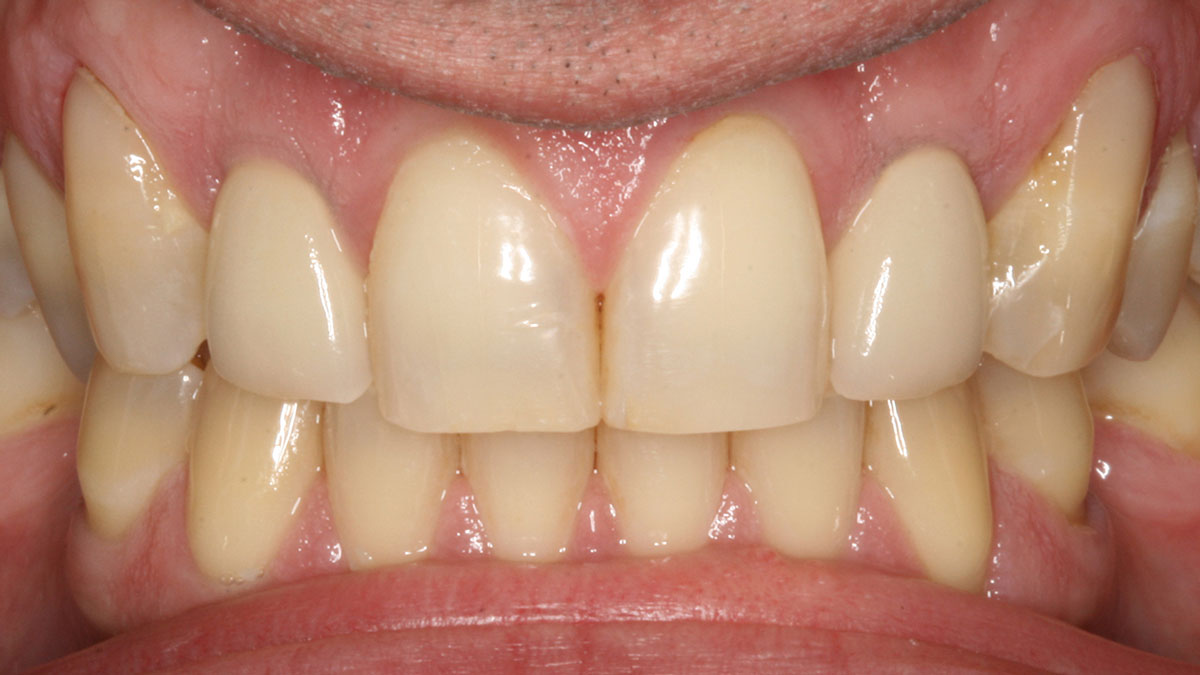
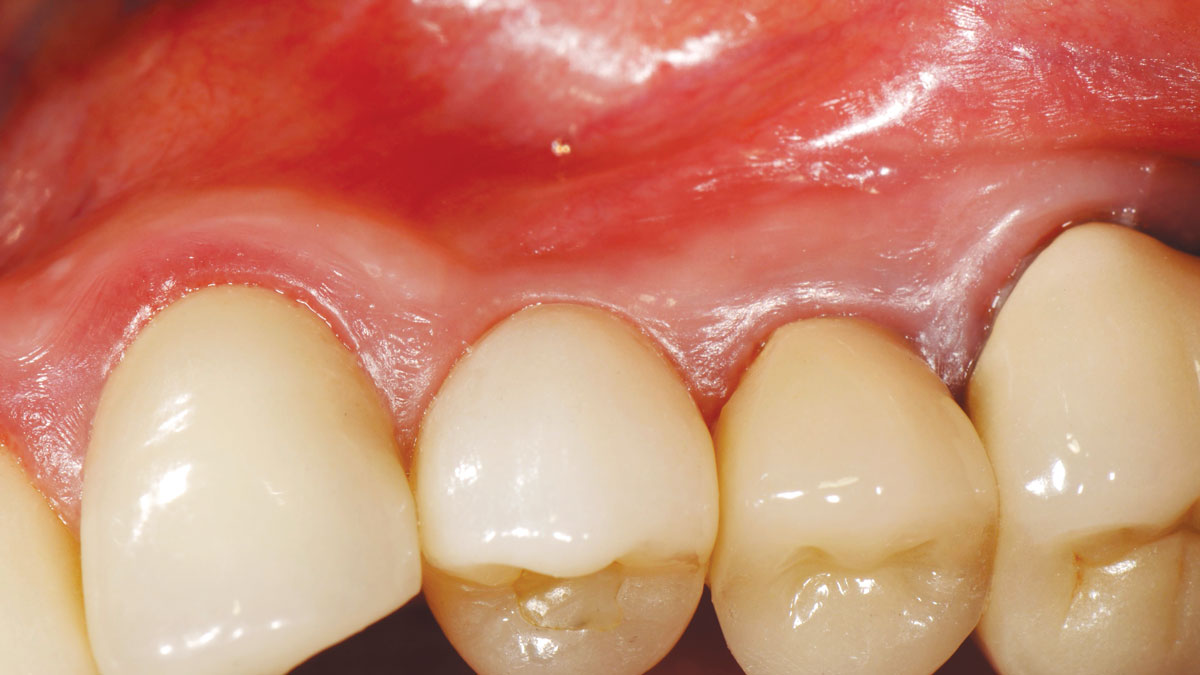
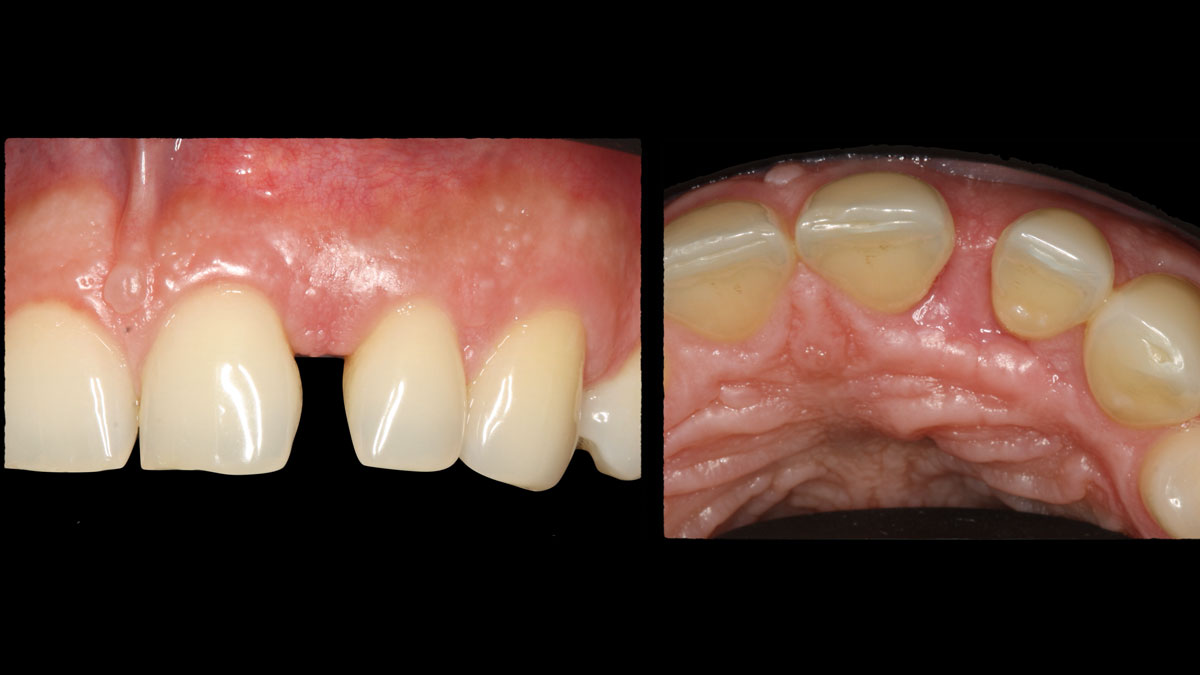
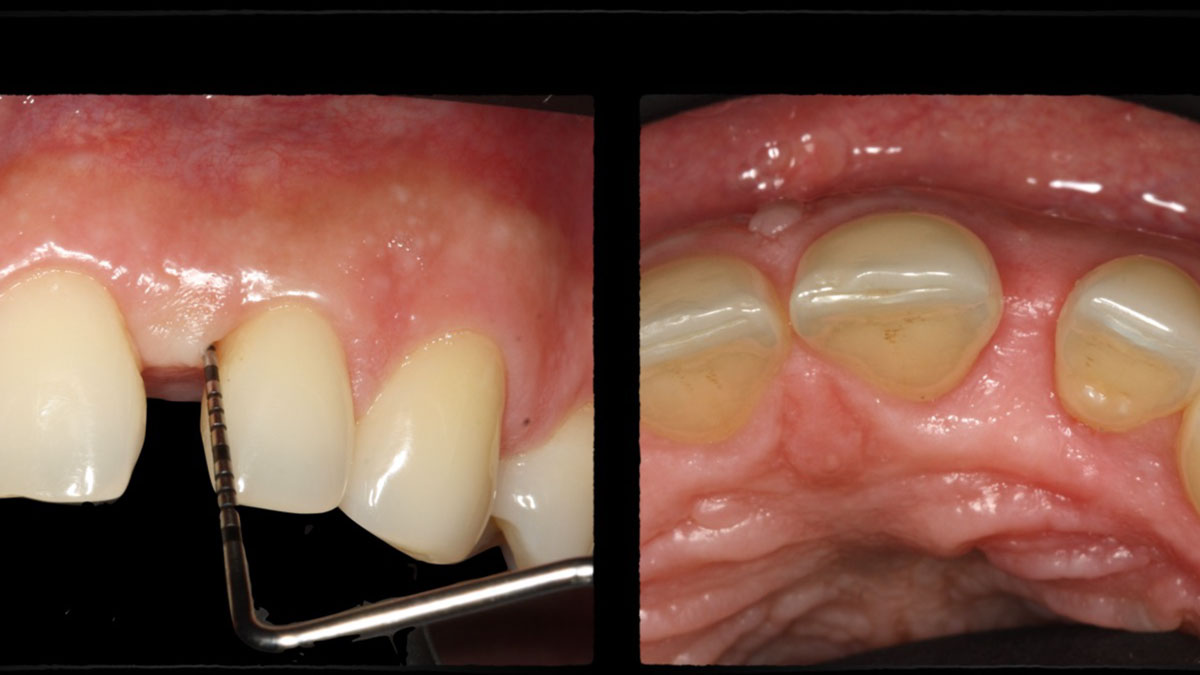
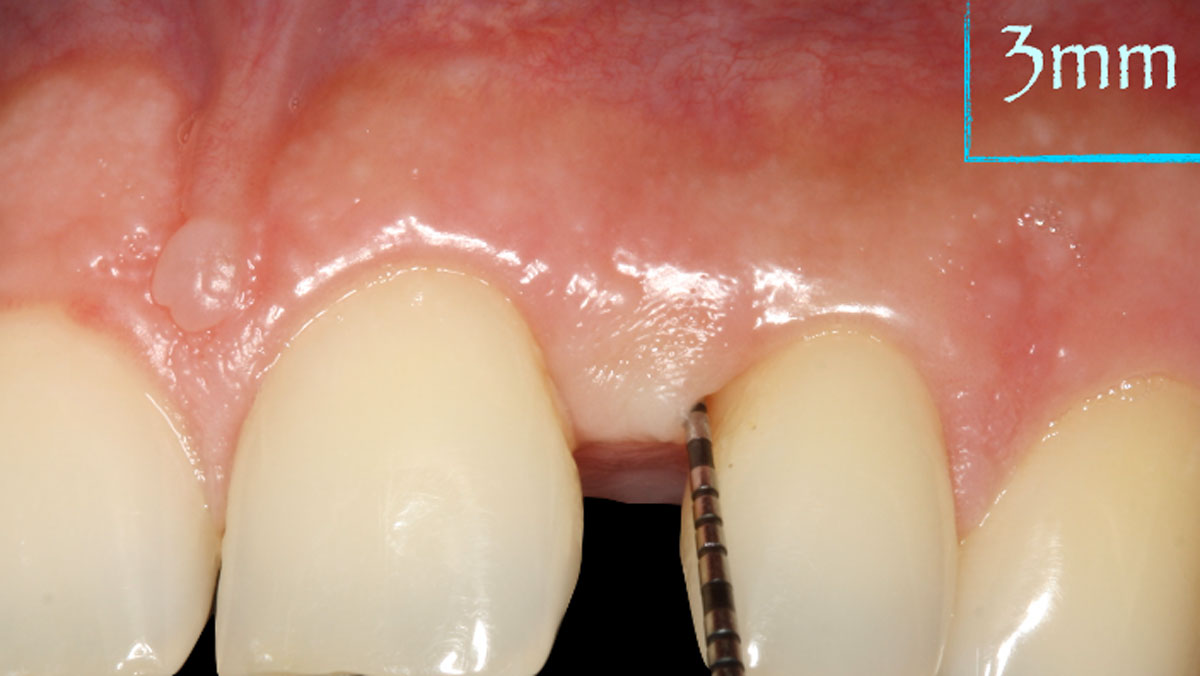
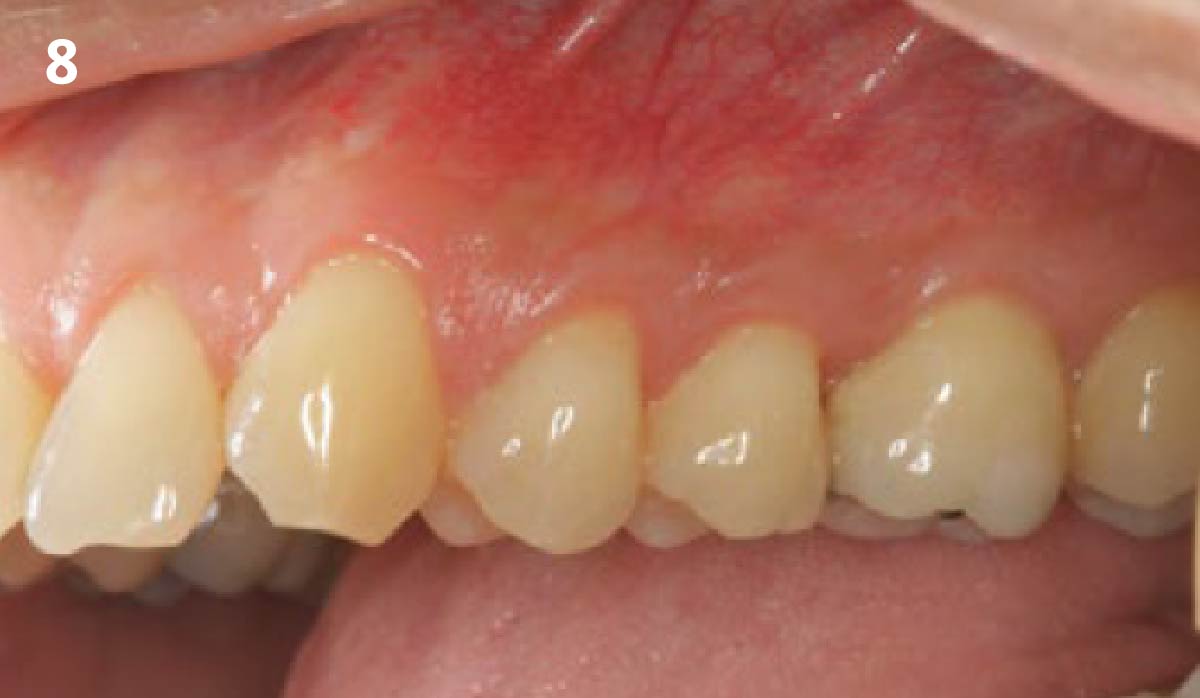
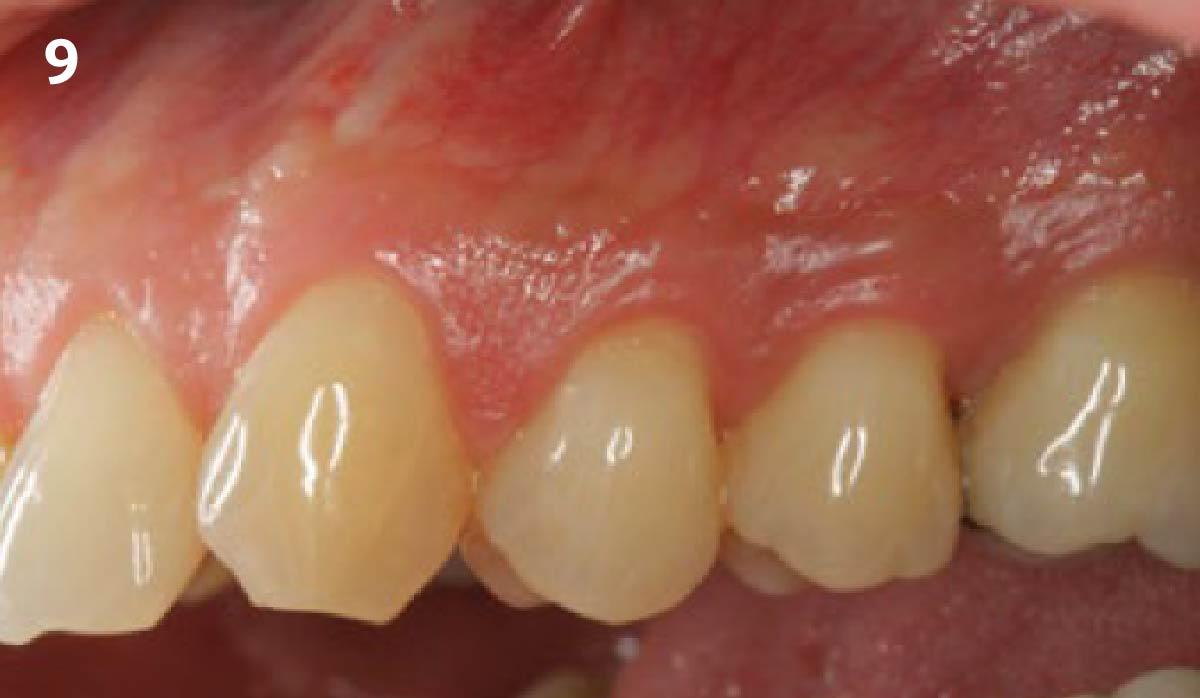
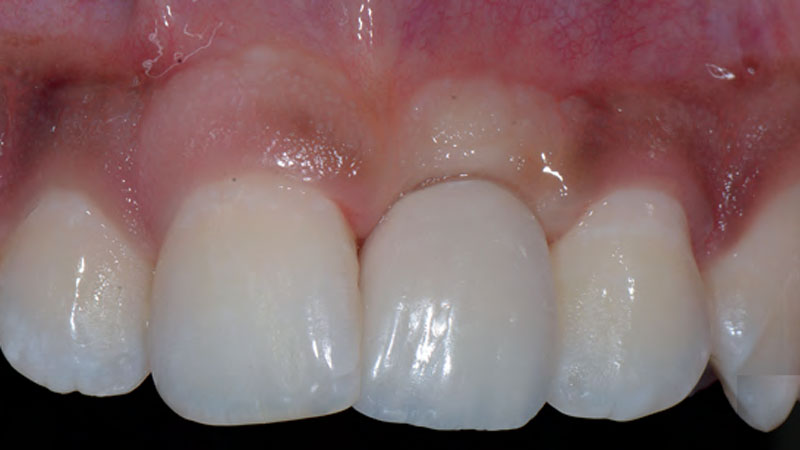
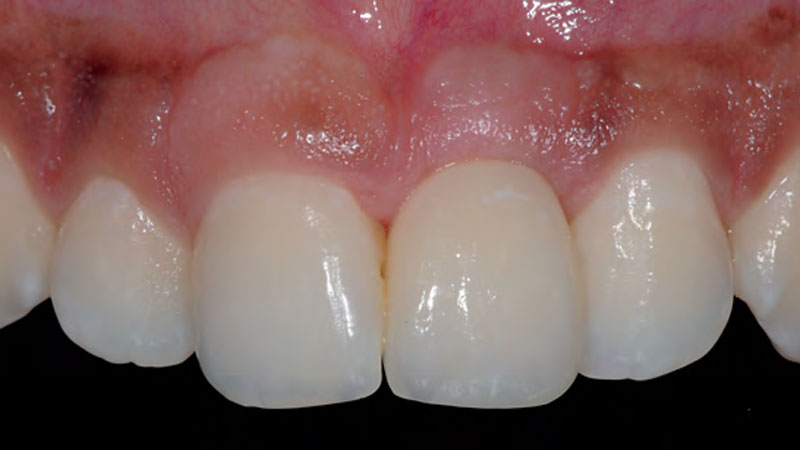
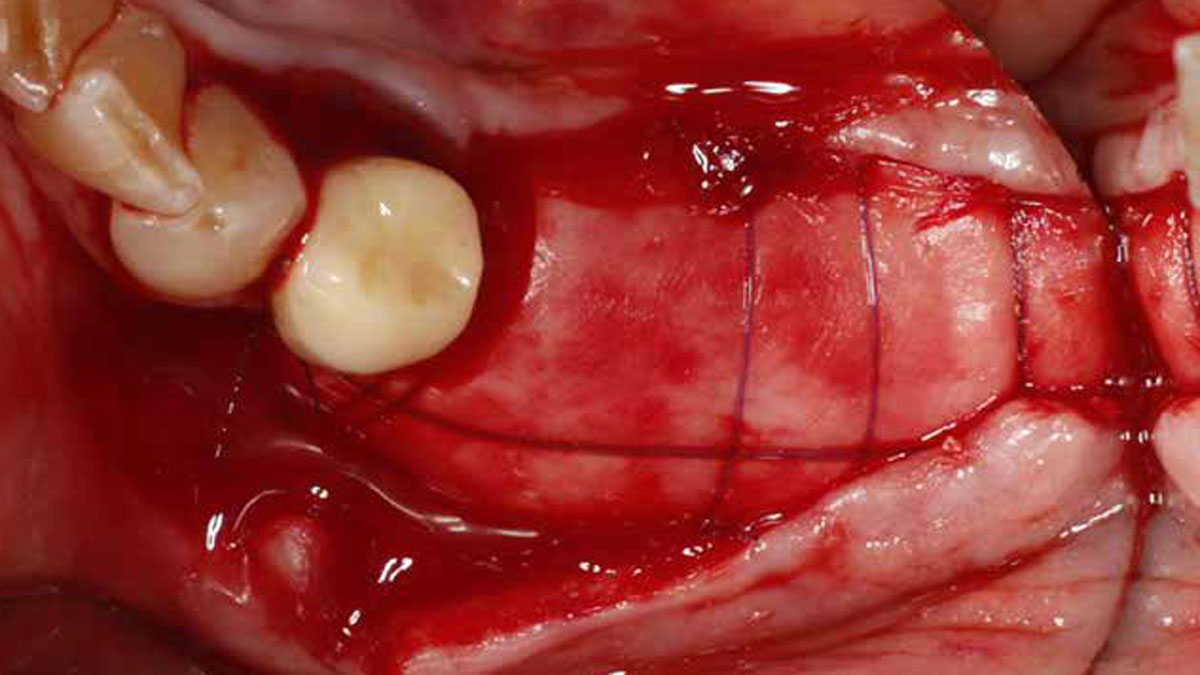
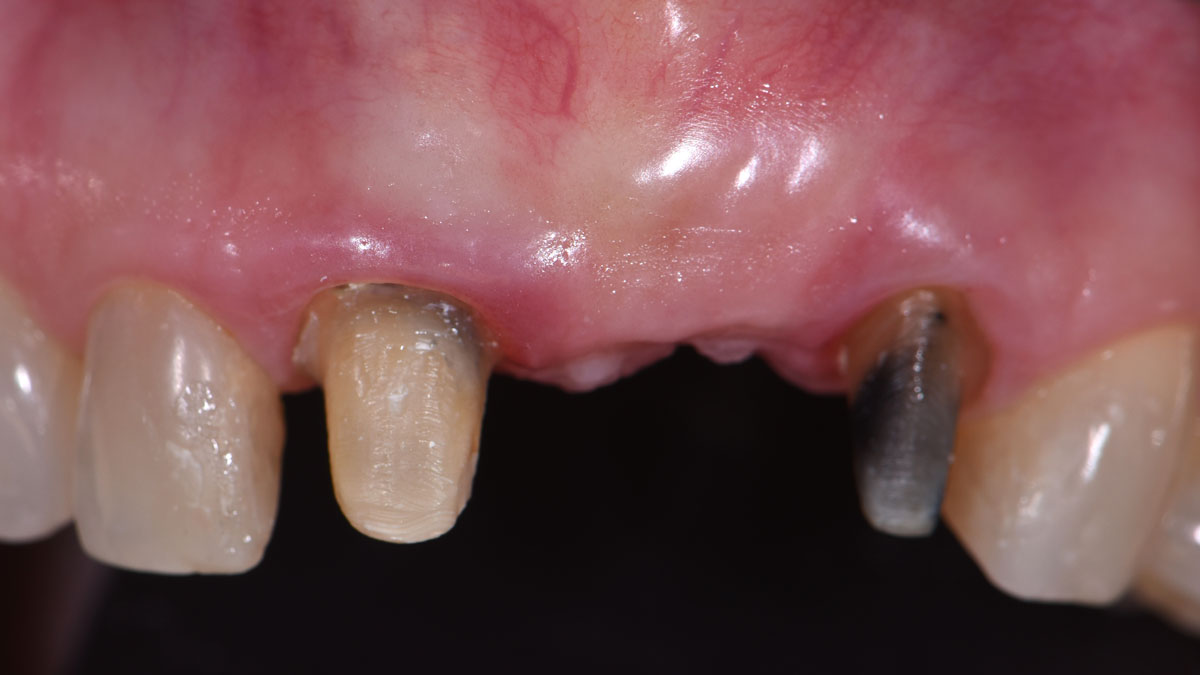
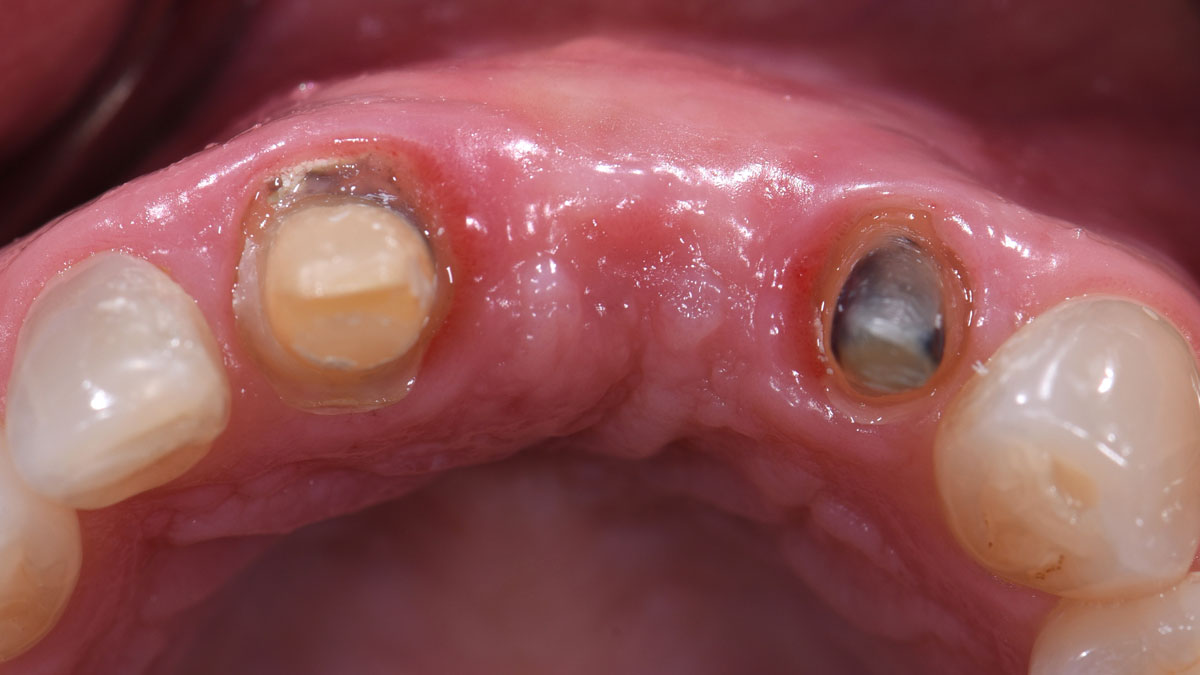
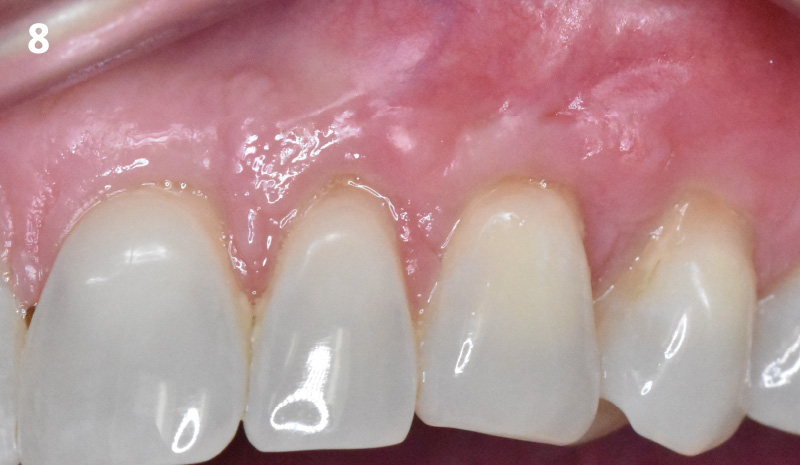
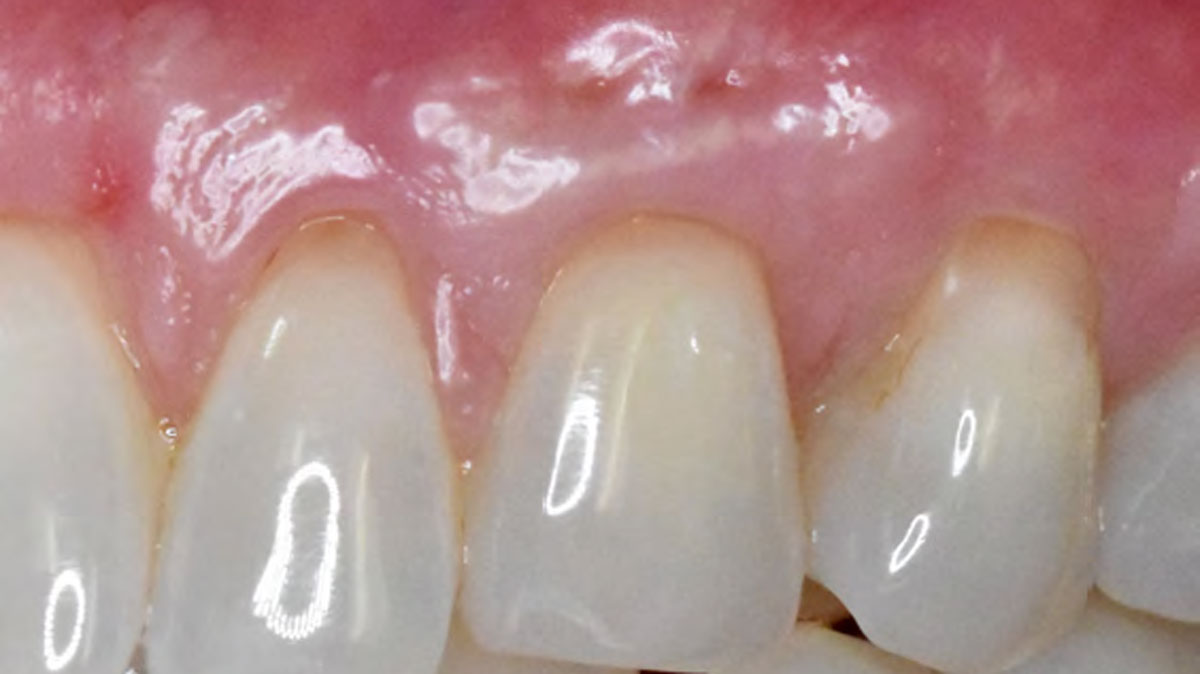
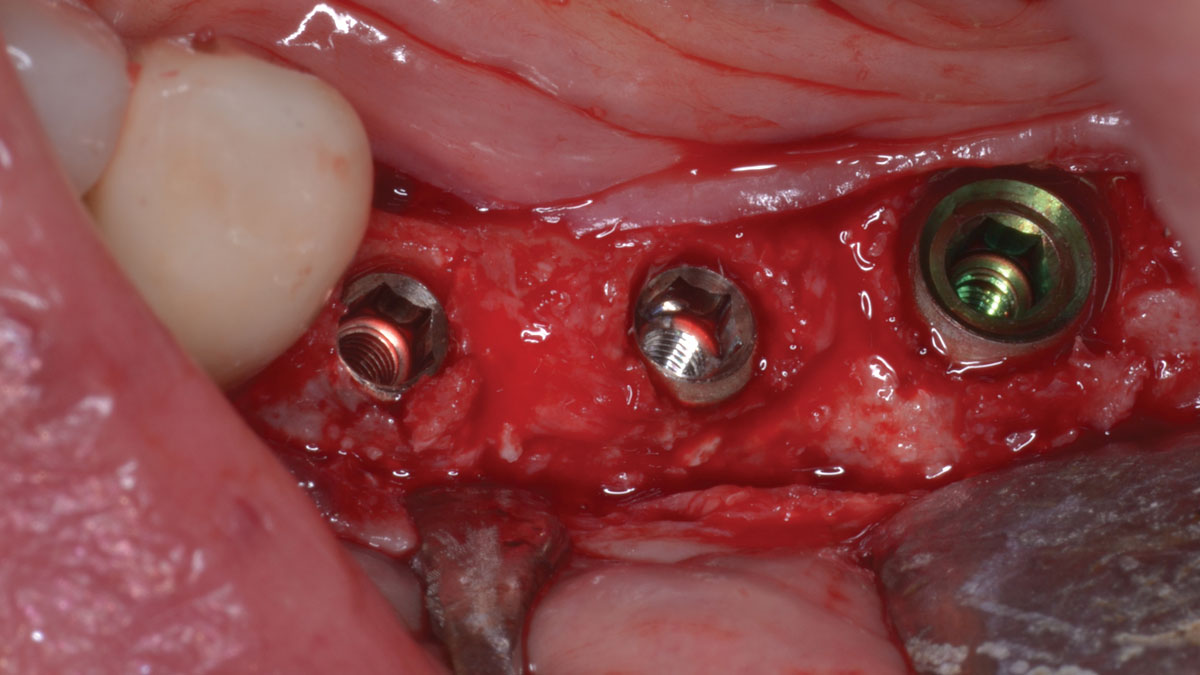
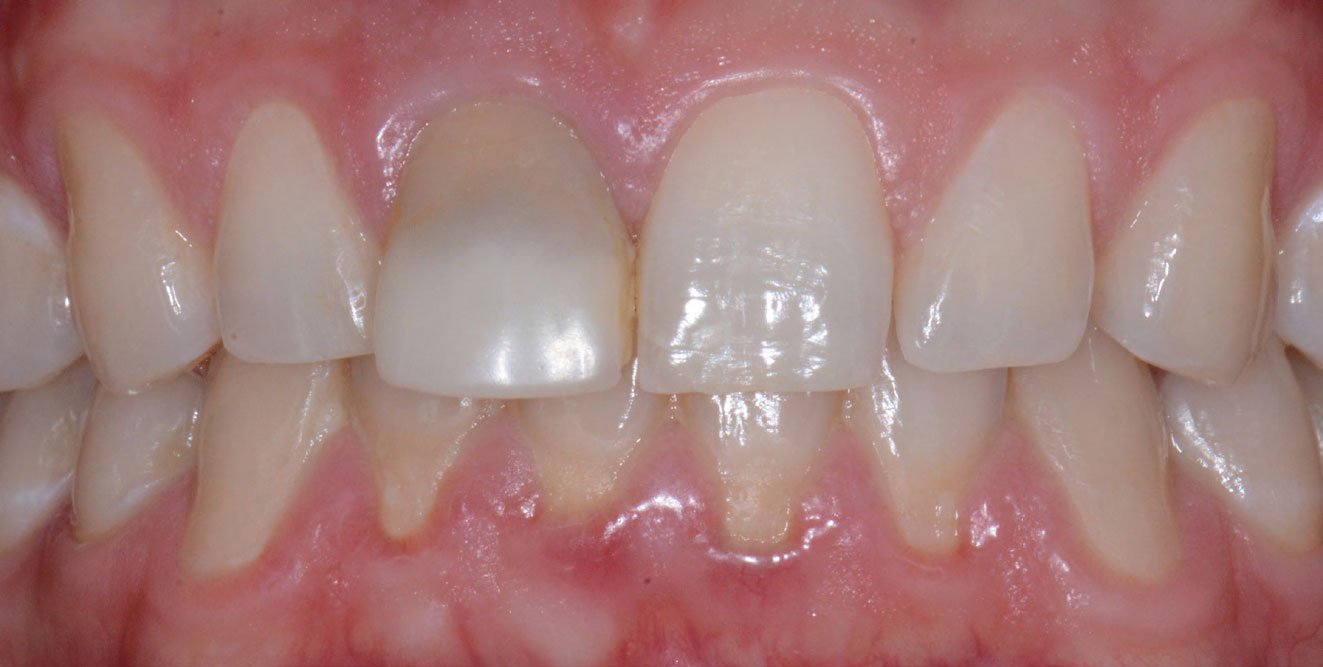
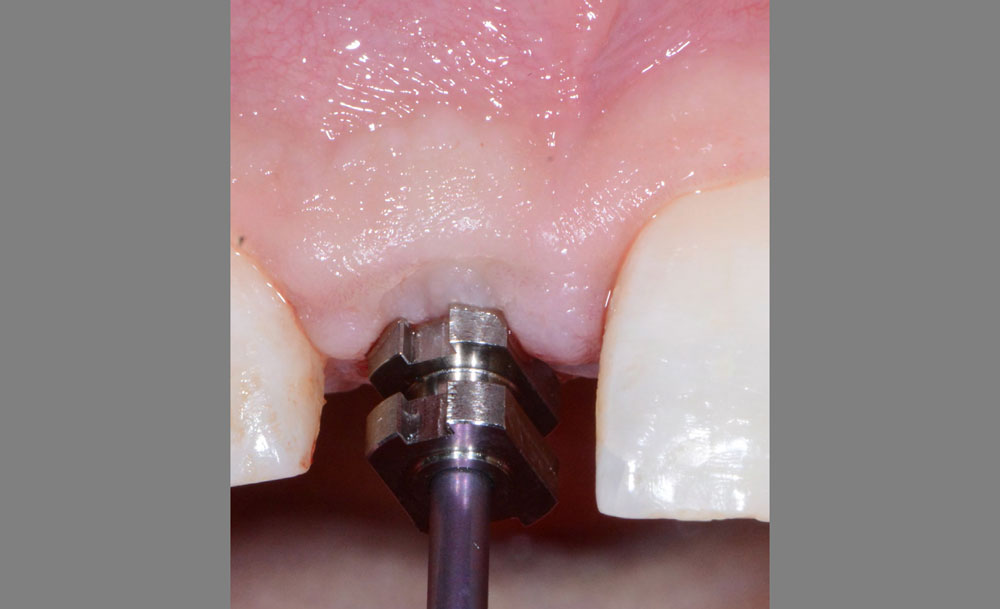
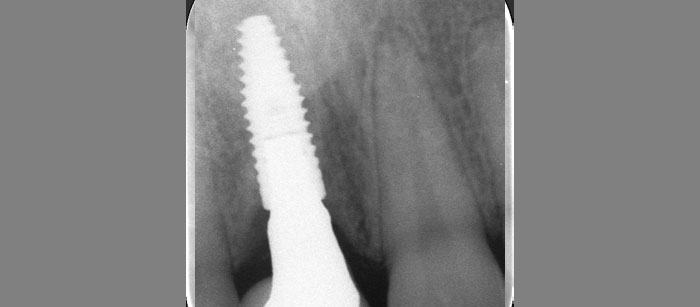
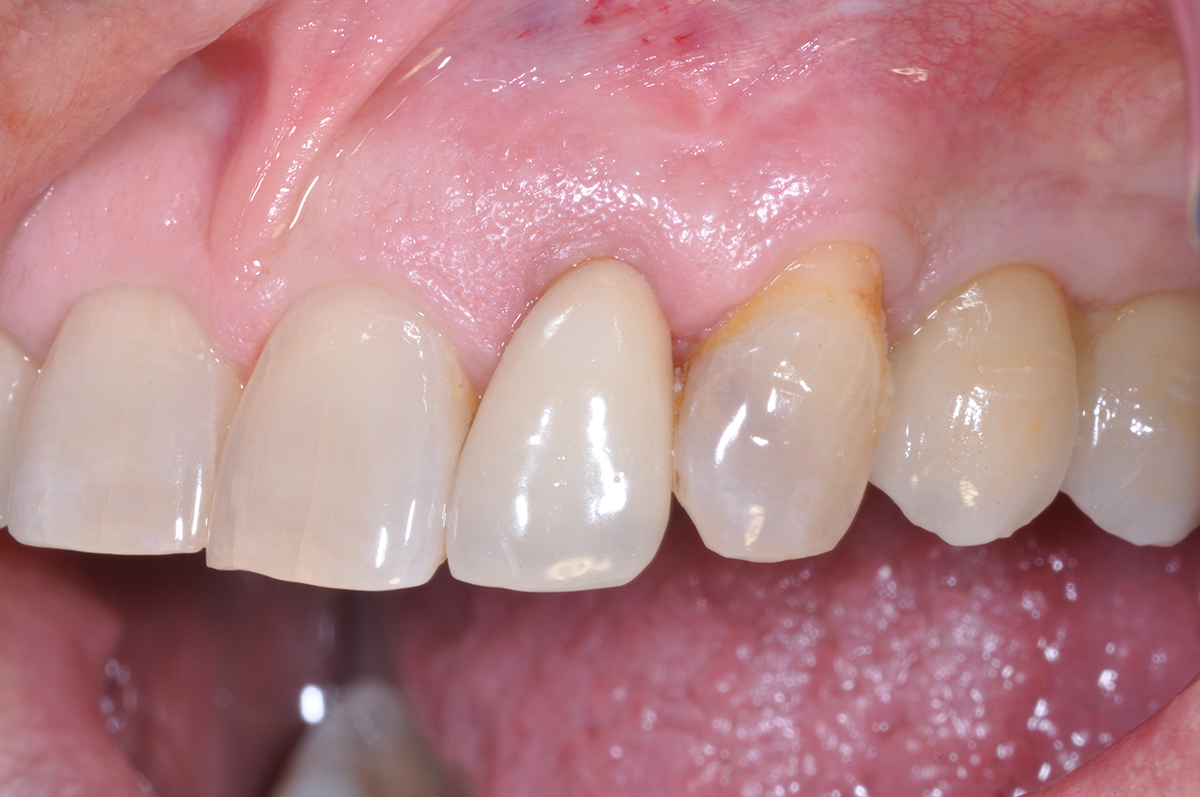
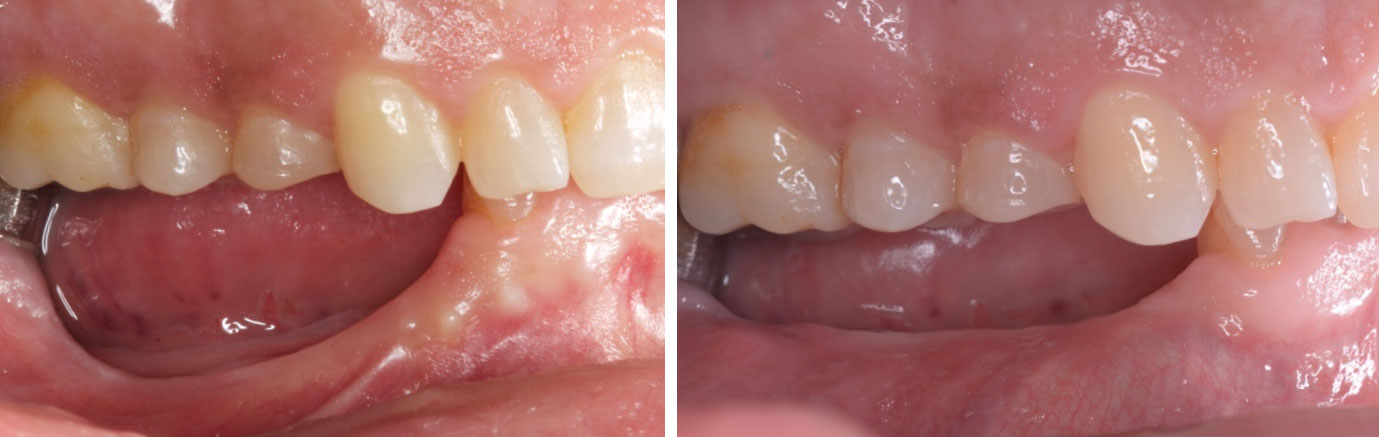
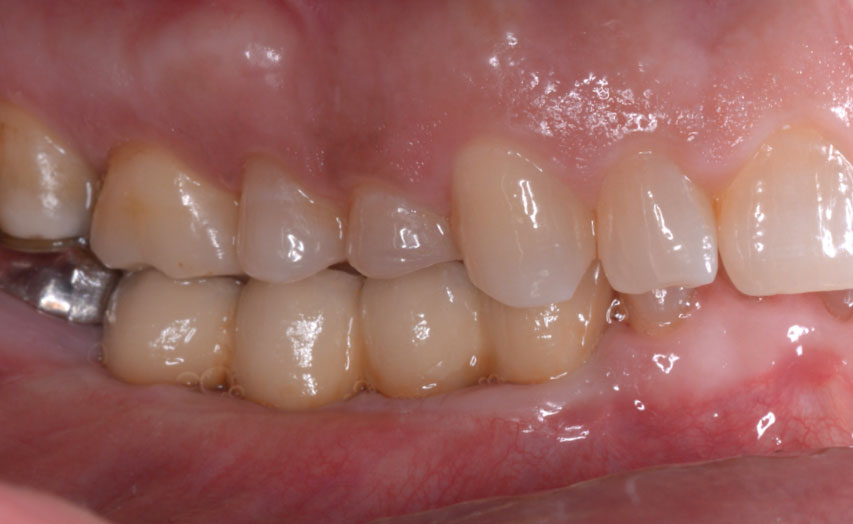
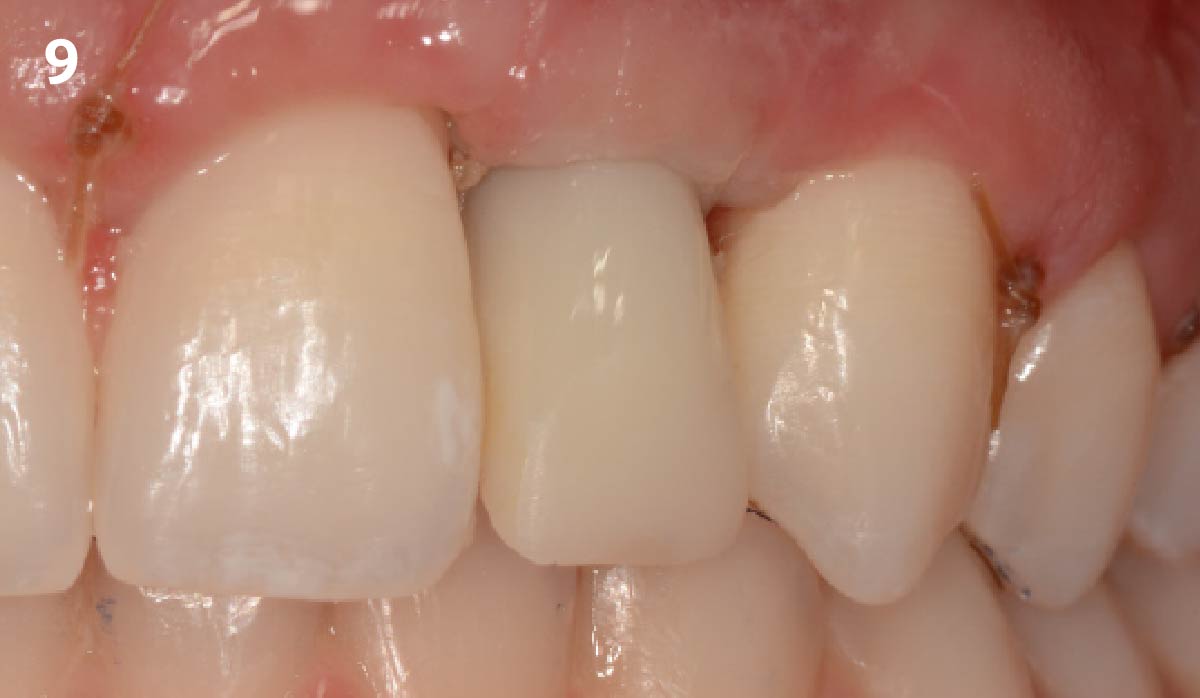
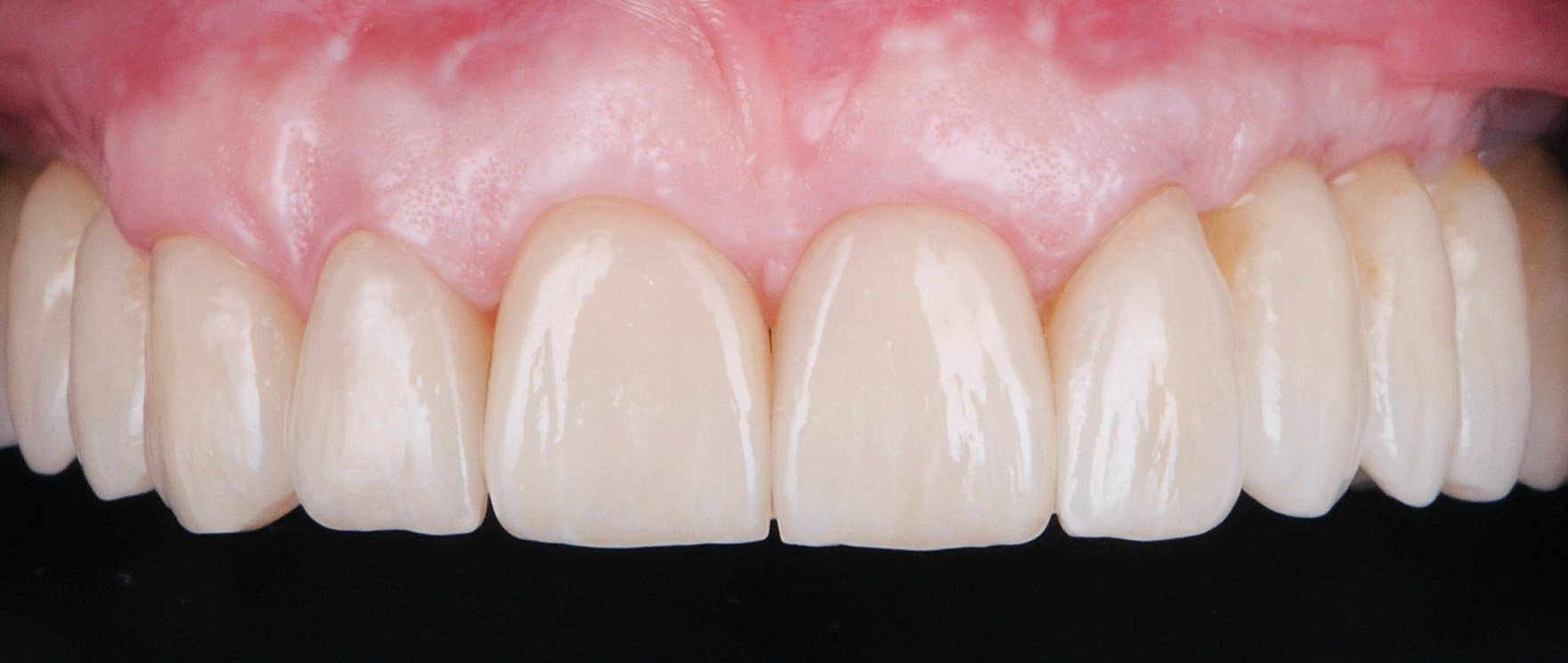
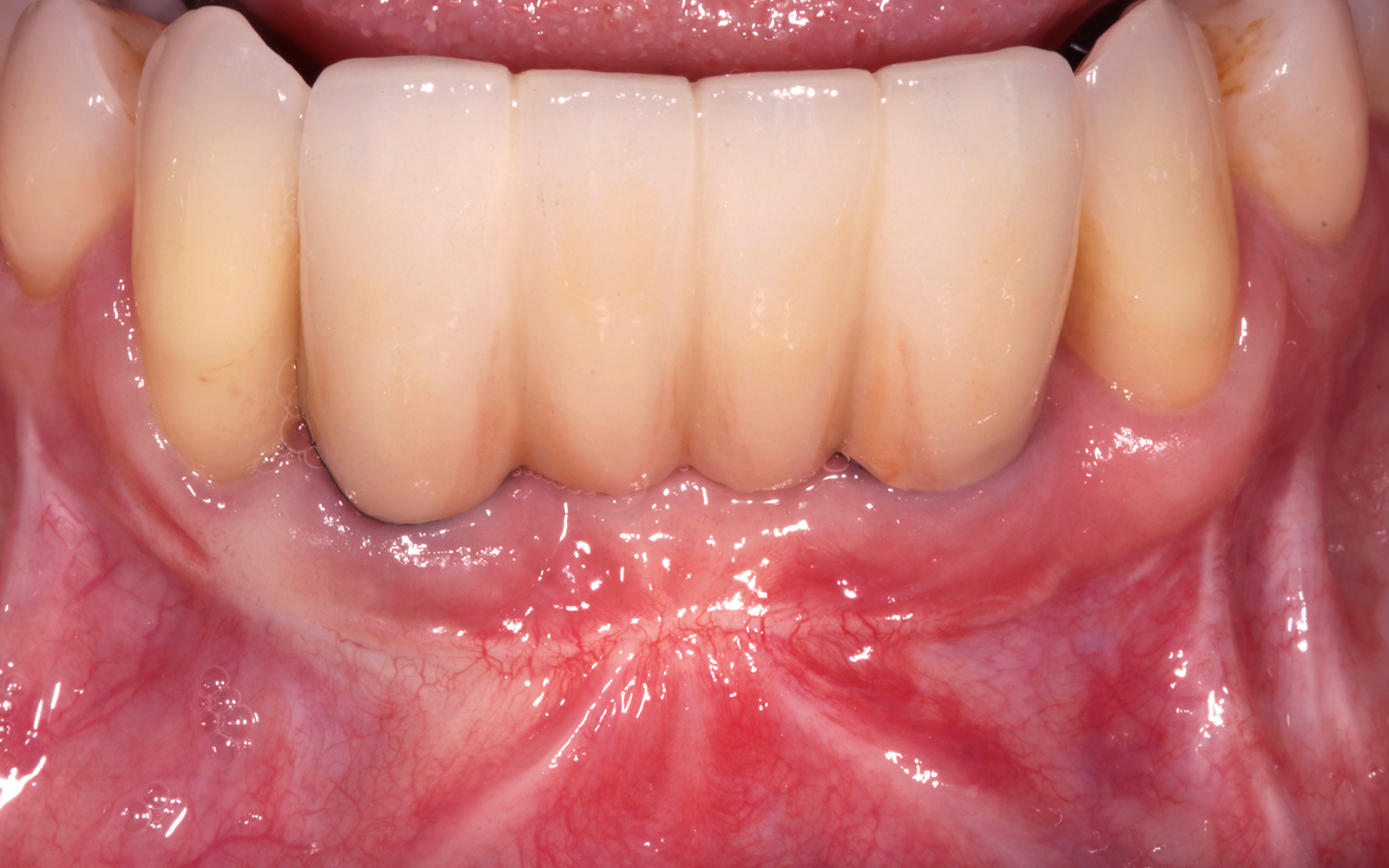
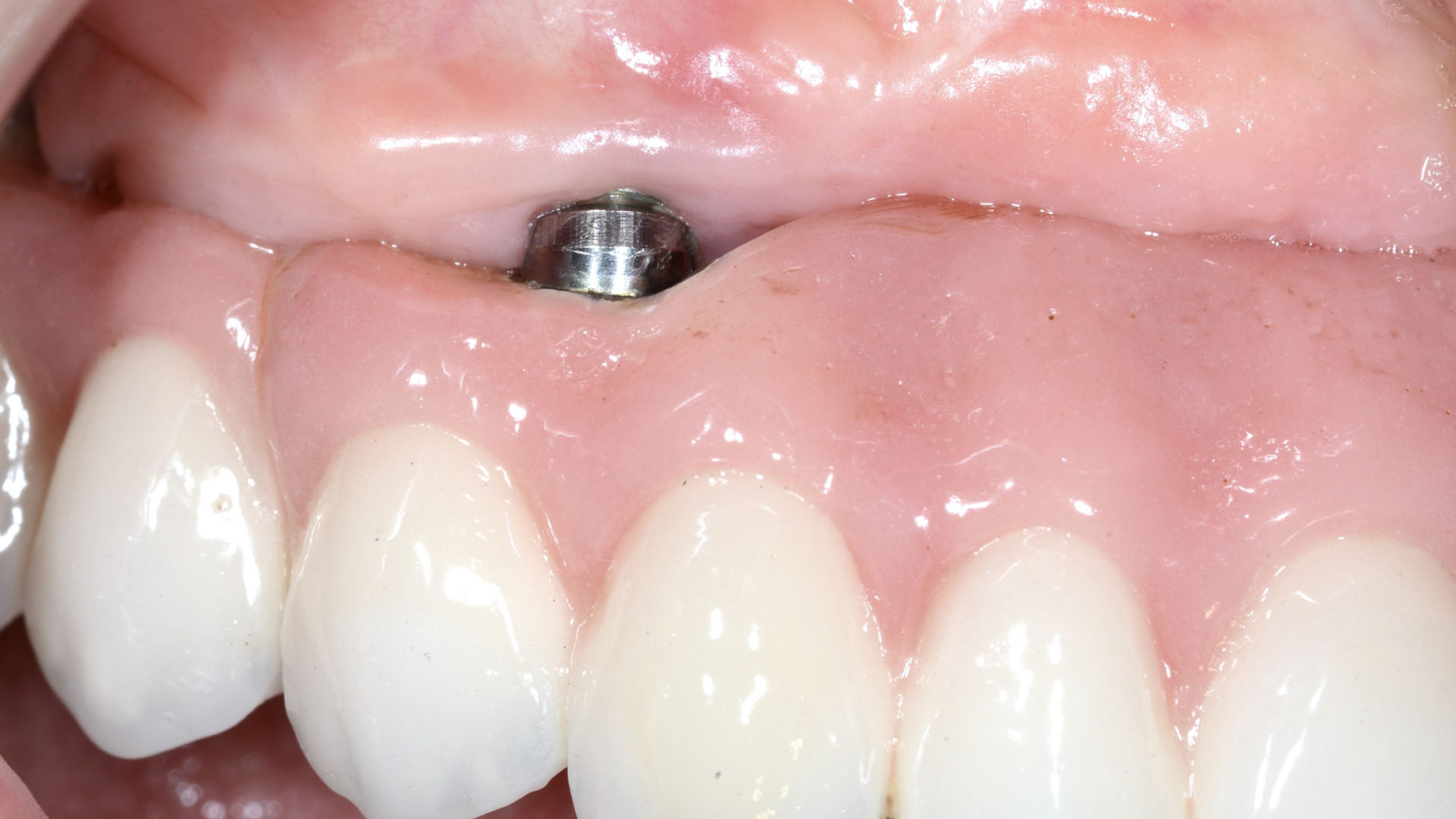
At the two-year follow-up, clinical and radiographic assessments showed disease resolution, complete bone gain, and stable peri-implant tissues. Probing depths were within healthy ranges, and no bleeding on probing was observed, confirming the long-term success of the treatment.

Andrea Ravidà, DDS, MS, PhD
Dr. Andrea Ravidà is the Director of the Graduate Periodontics Program in the department of Periodontics at the University of Pittsburgh. He conducts clinical research focusing on peri-implantitis, periodontitis and short implants. He has published more than 70 peer-reviewed articles and conference abstracts/presentations related to periodontics and implant therapy. He is section editor of the International Journal of Oral Implantology and the Journal of Translational Medicine.

Anu Viswanathan DDS, MDS
Dr. Anu Viswanathan is a Diplomate of the American Board of Periodontology and Implant Dentistry. She earned her Doctor of Dental Surgery degree from the University of Colorado School of Dental Medicine in 2019. Dr. Viswanathan completed a Certificate in Periodontics and earned a Master of Dental Science at the University of Pittsburgh School of Dental Medicine. She also obtained a Certificate in IV Sedation. Dr. Viswanathan is currently in private practice in Shoreline, Connecticut.