Mix & Match! Buy 5 Products, Get 1 Free! Use code B5G1. Get Started!
Product: Geistlich Bio-Gide®

BIOBRIEF
Horizontal Ridge Augmentation with a Layered Allograft-Xenograft Approach


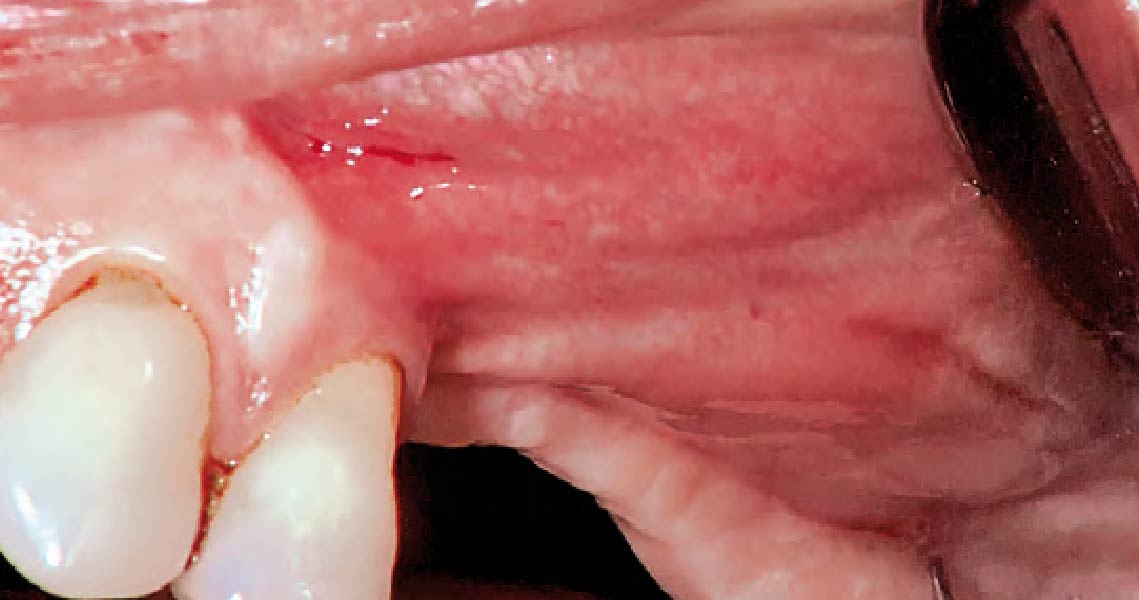
THE SITUATION
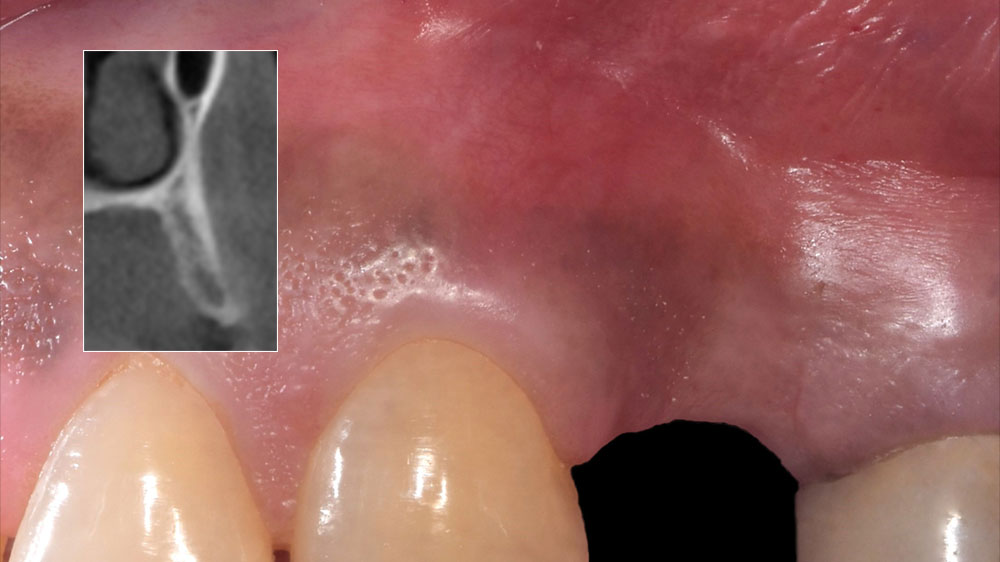
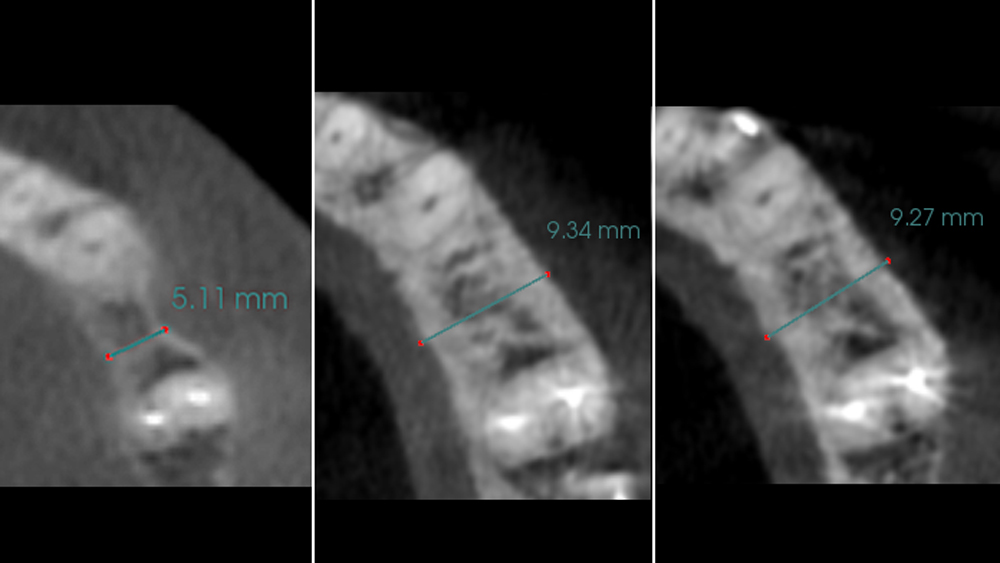
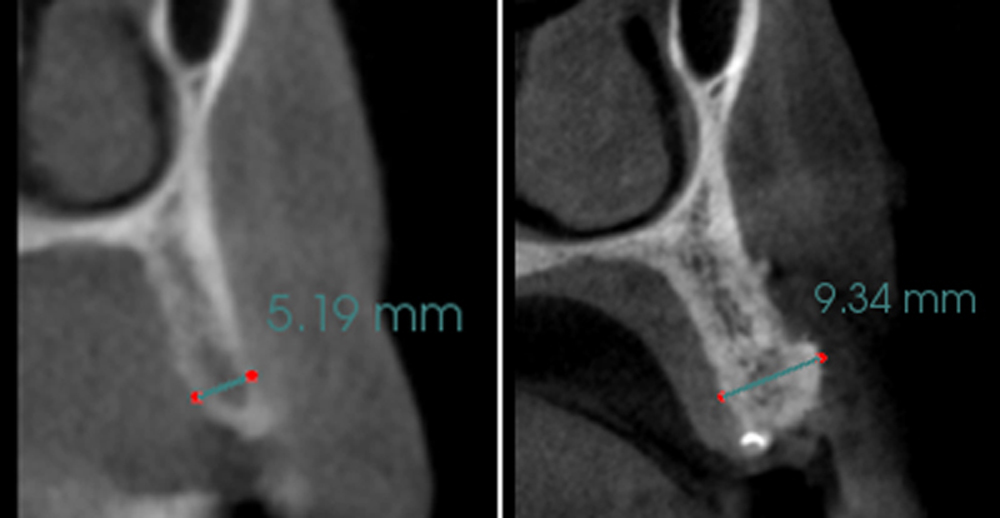
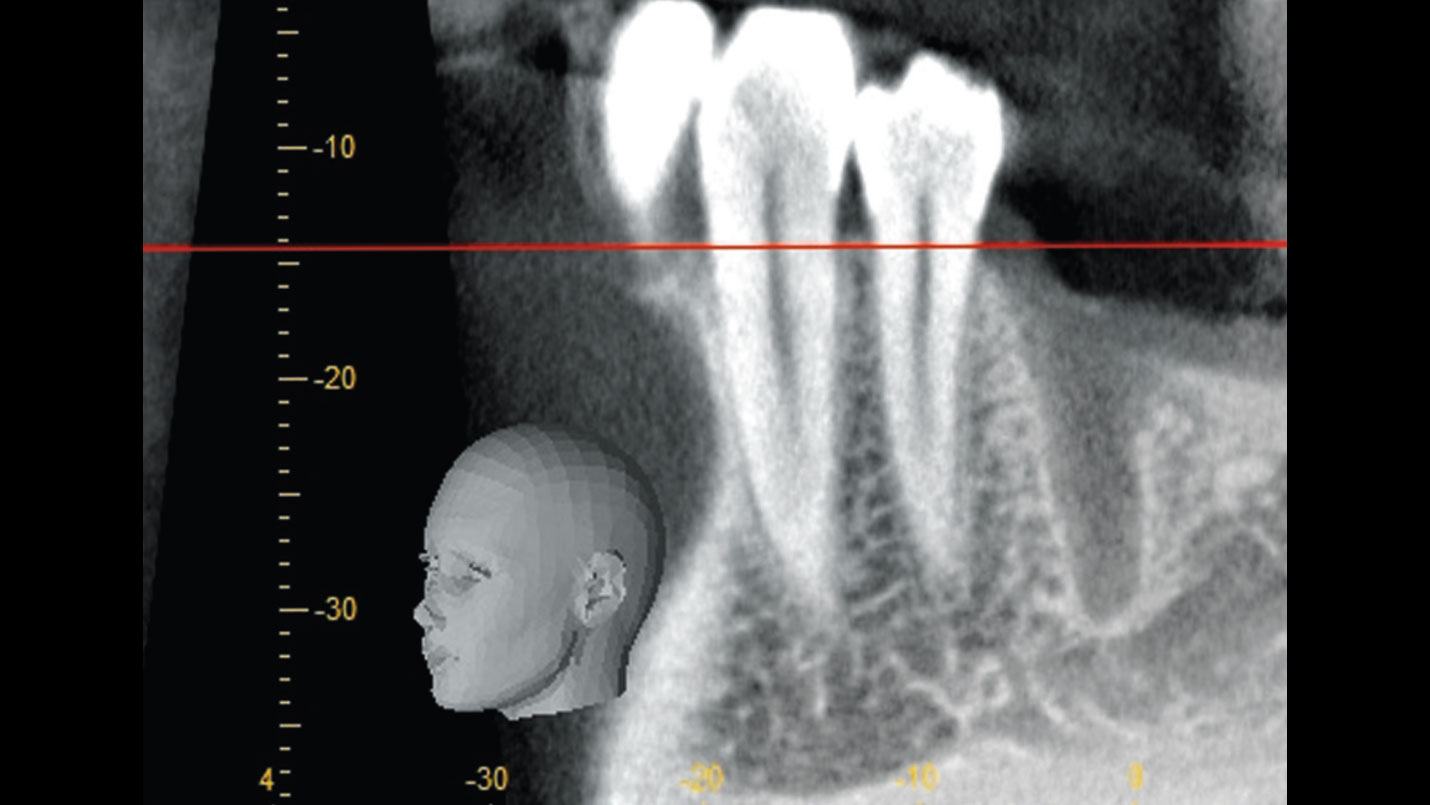
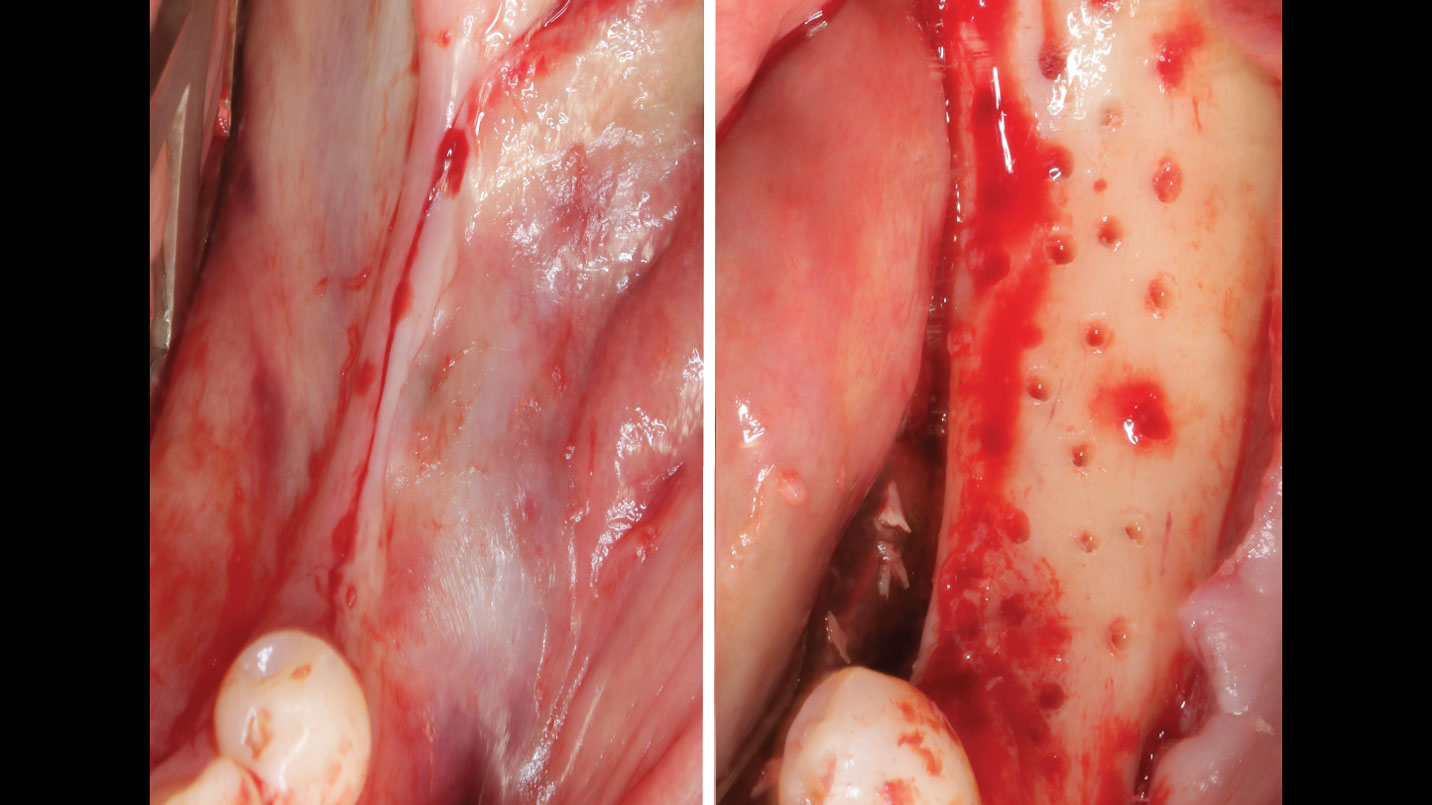
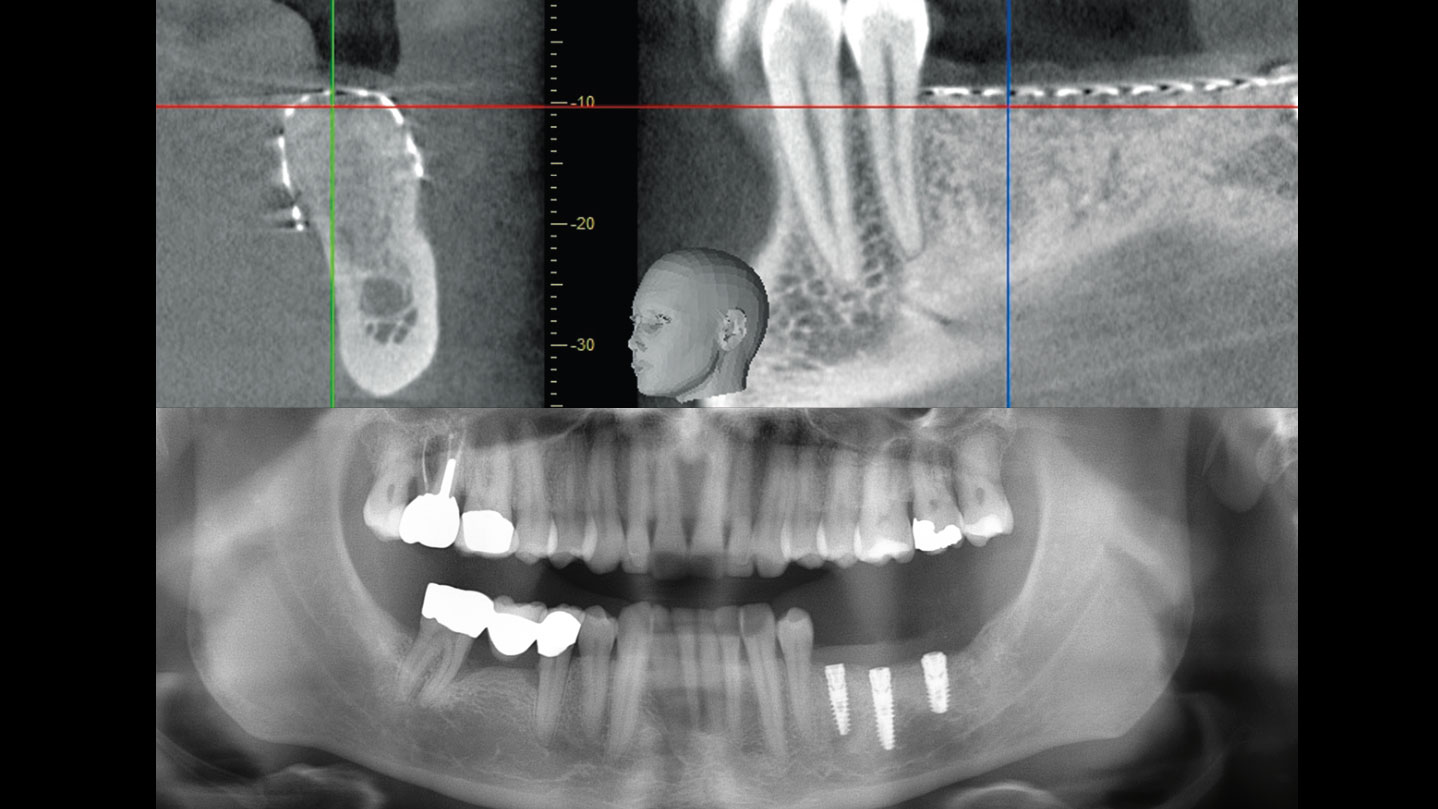
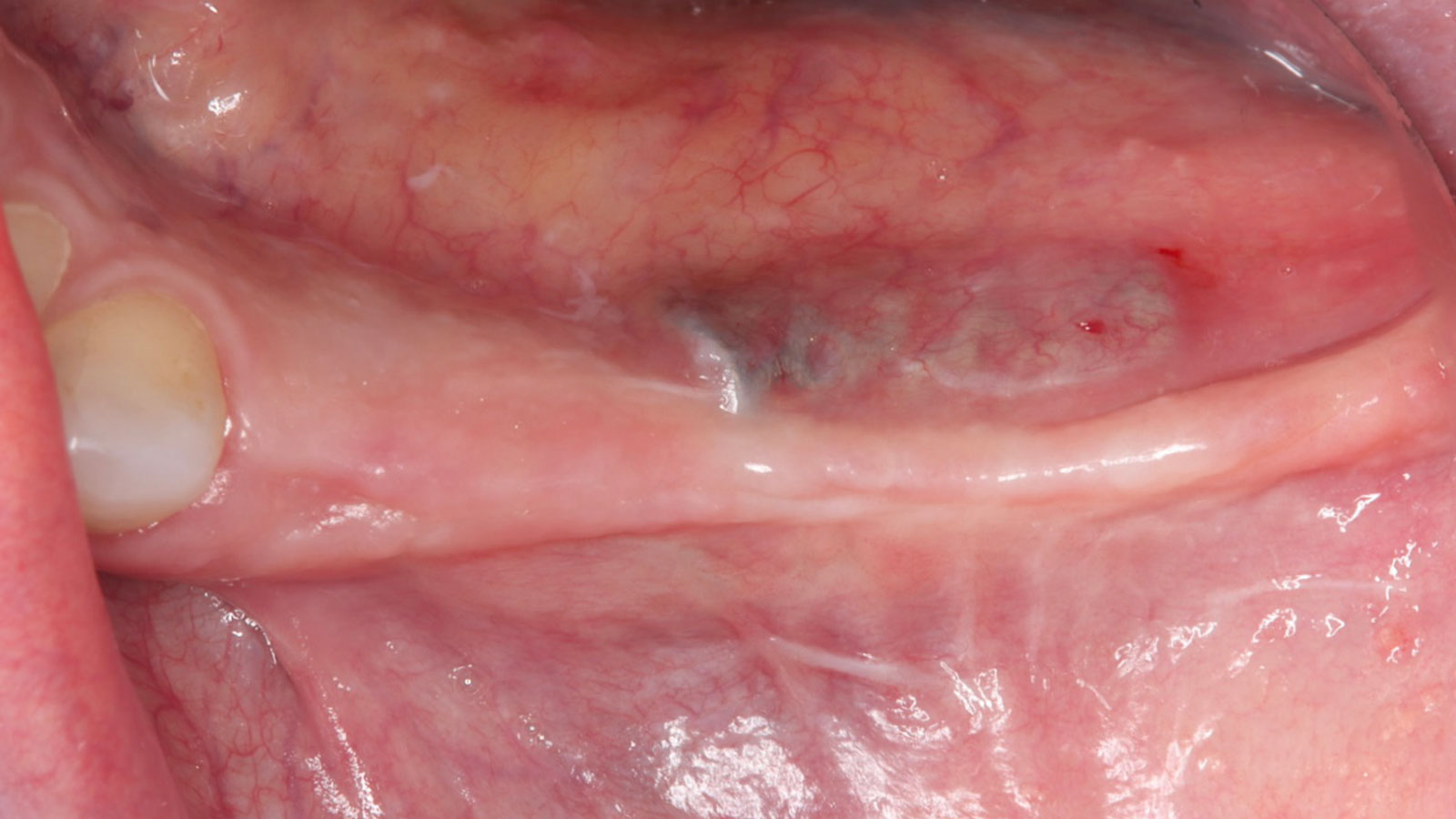
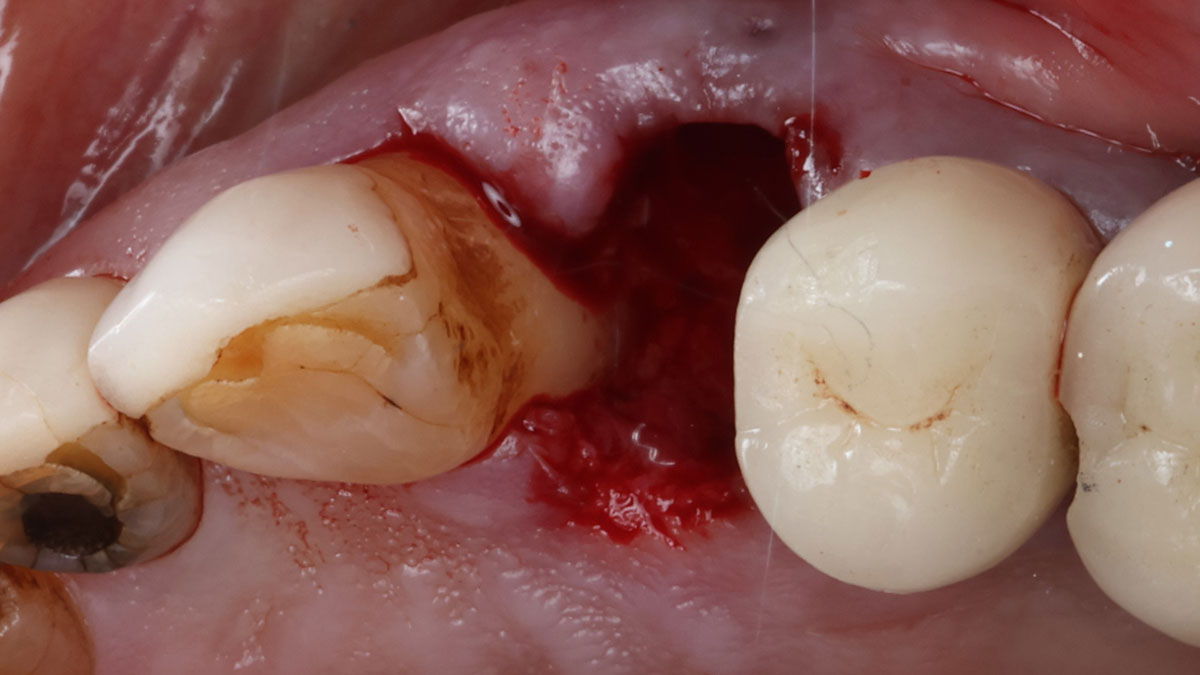
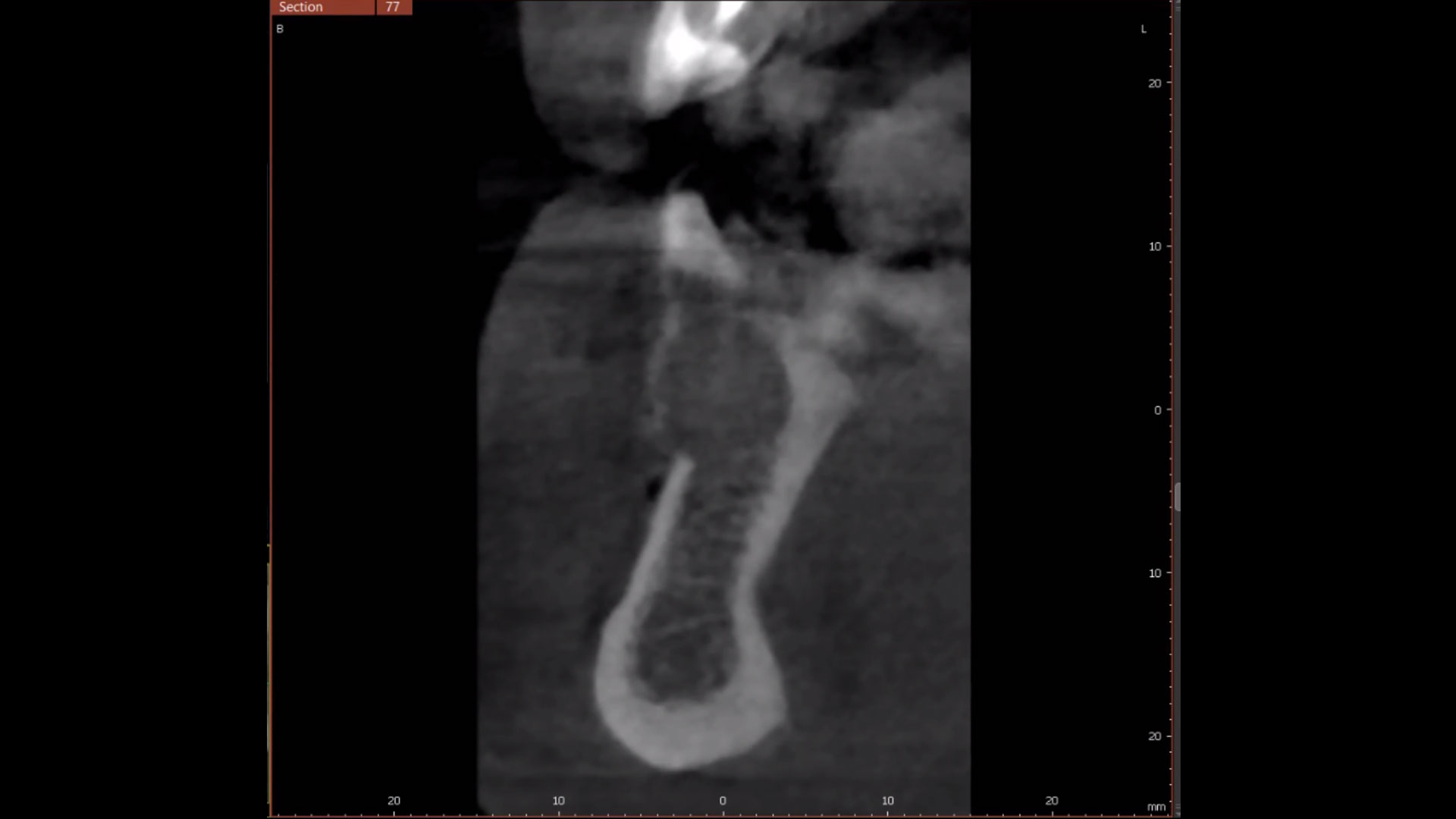
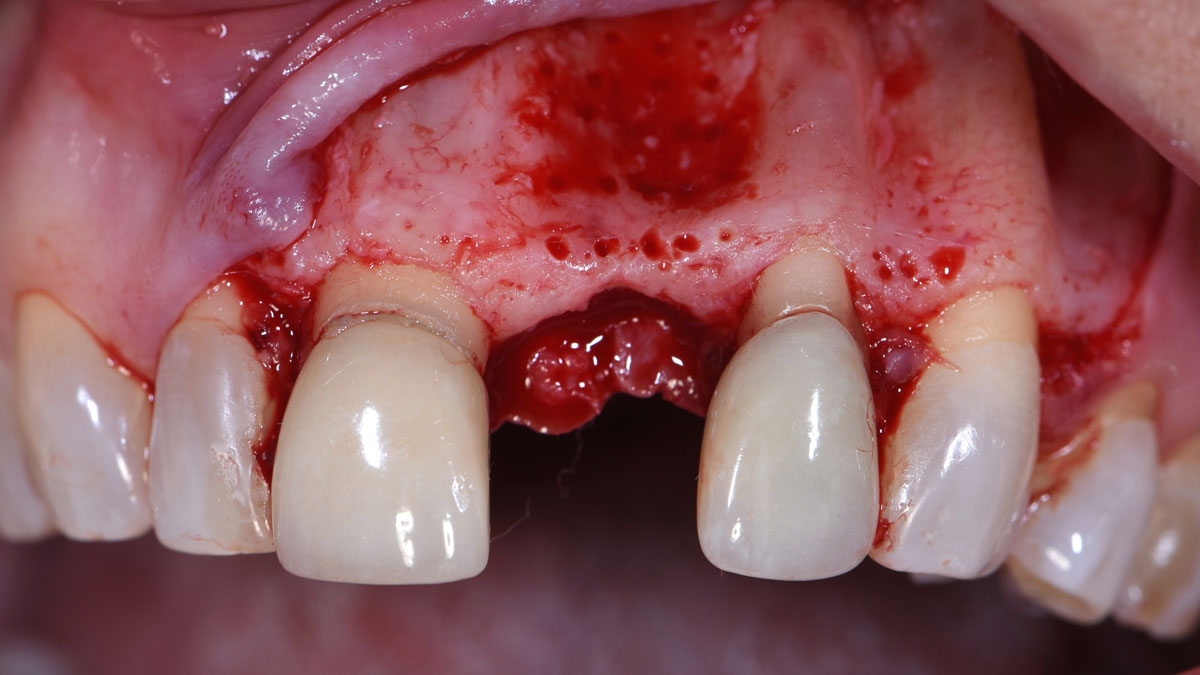
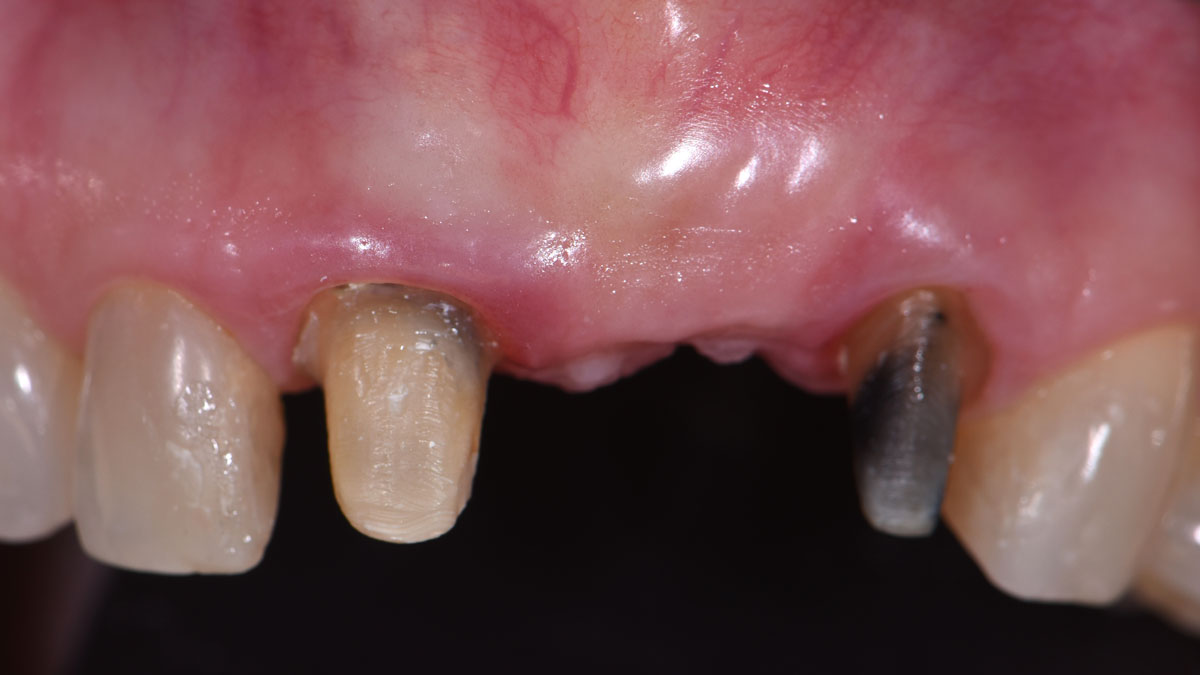
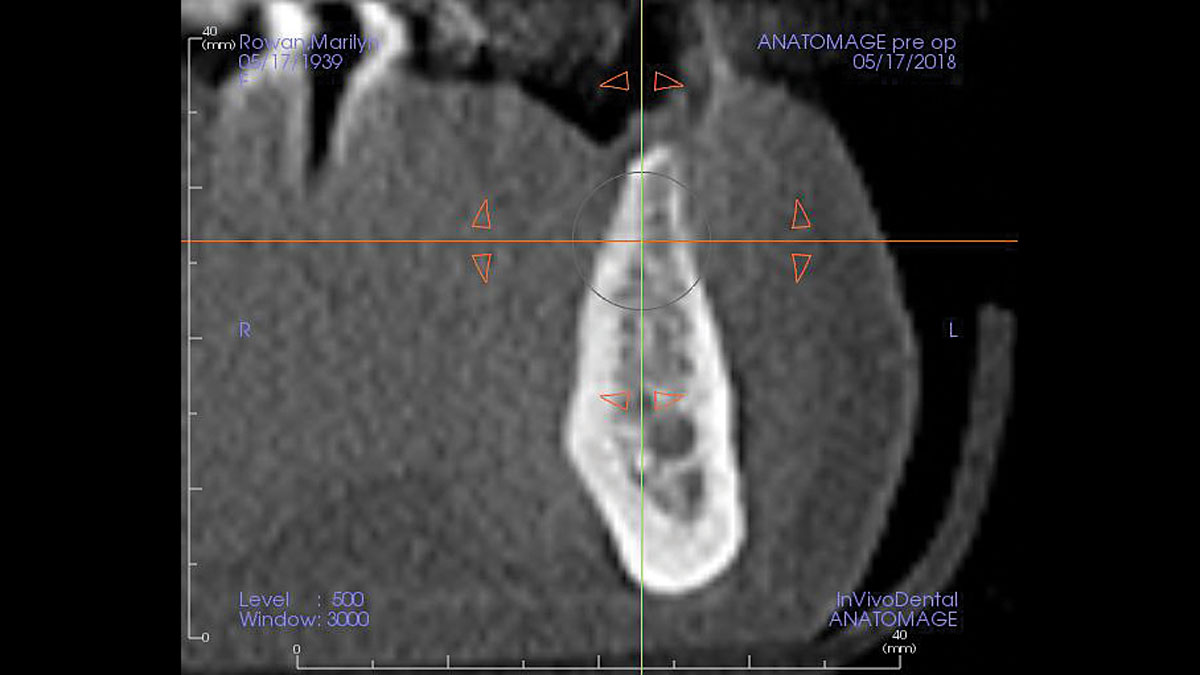
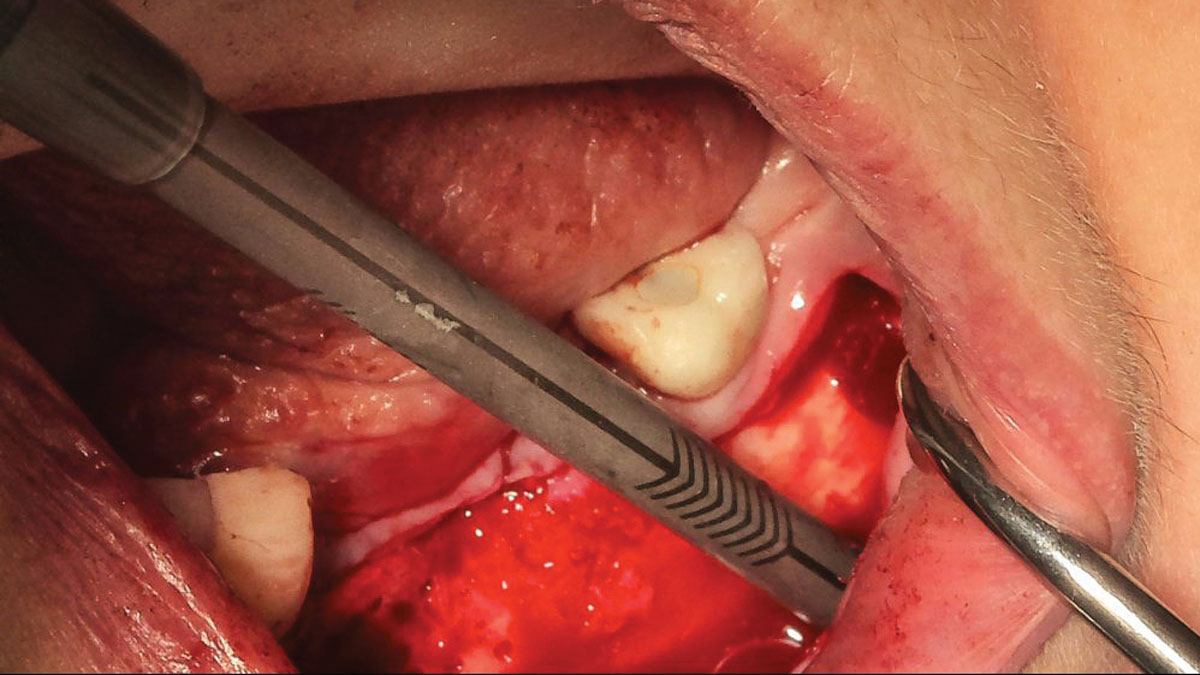
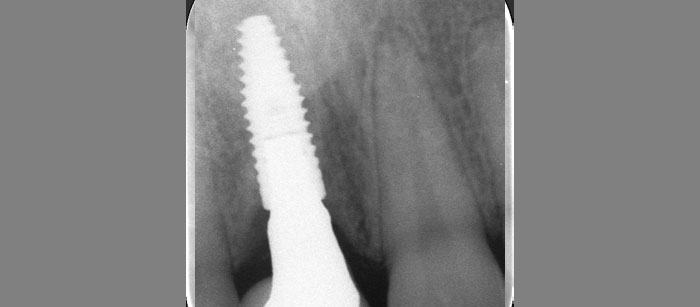
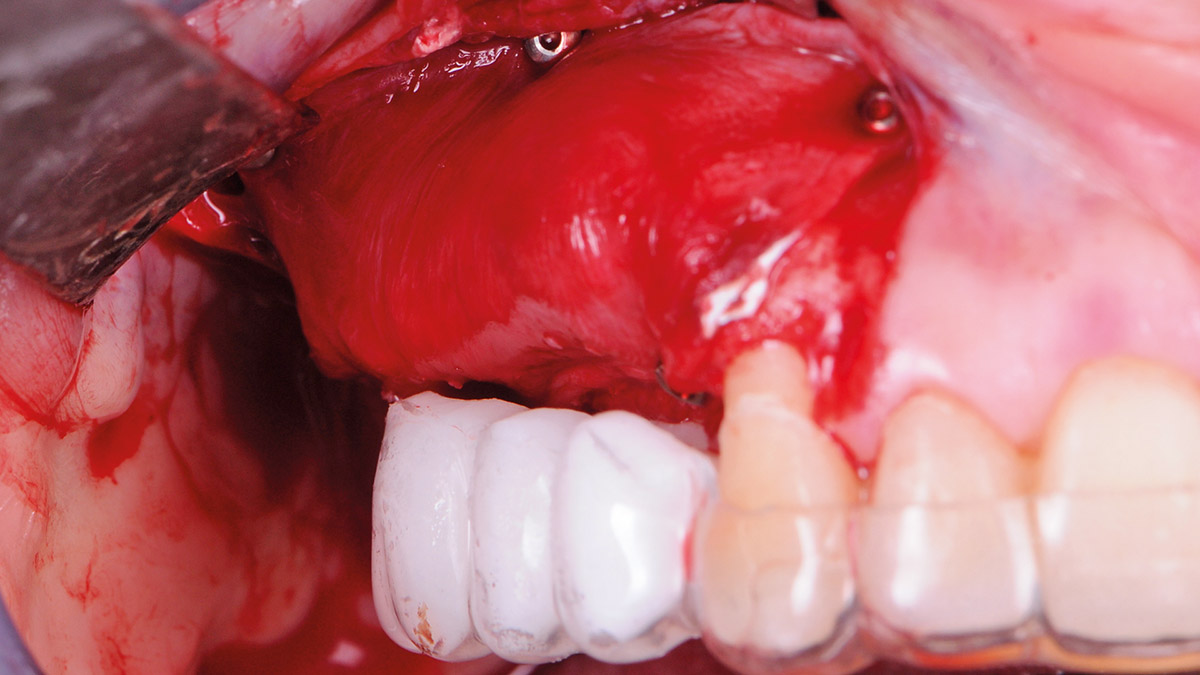
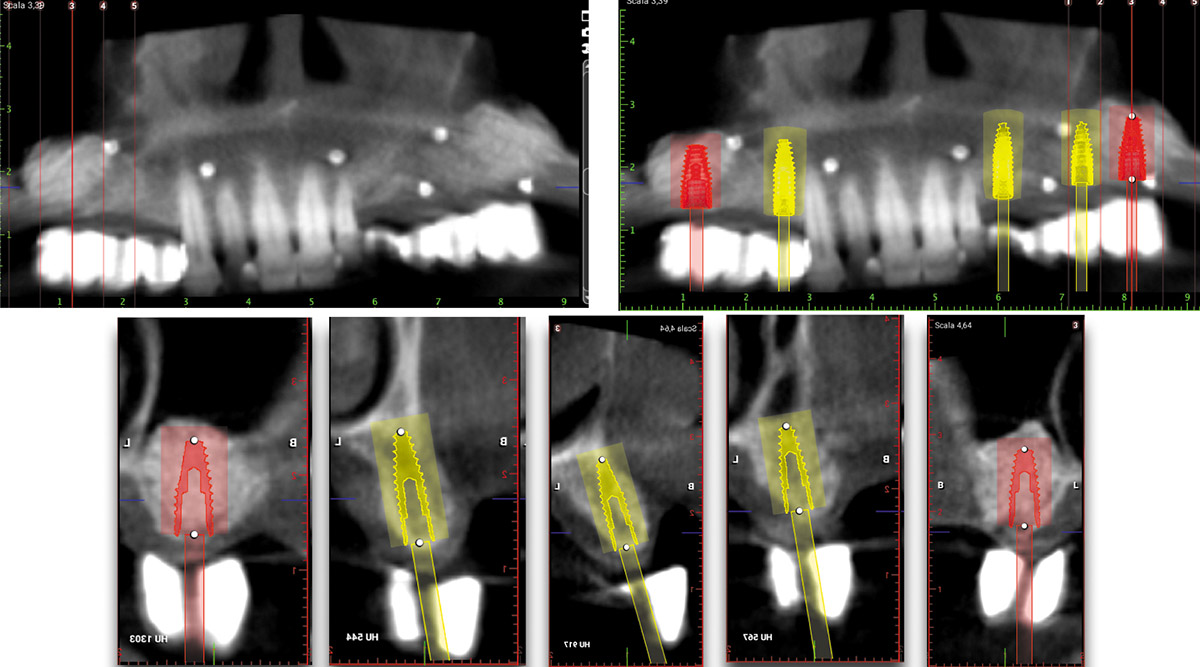
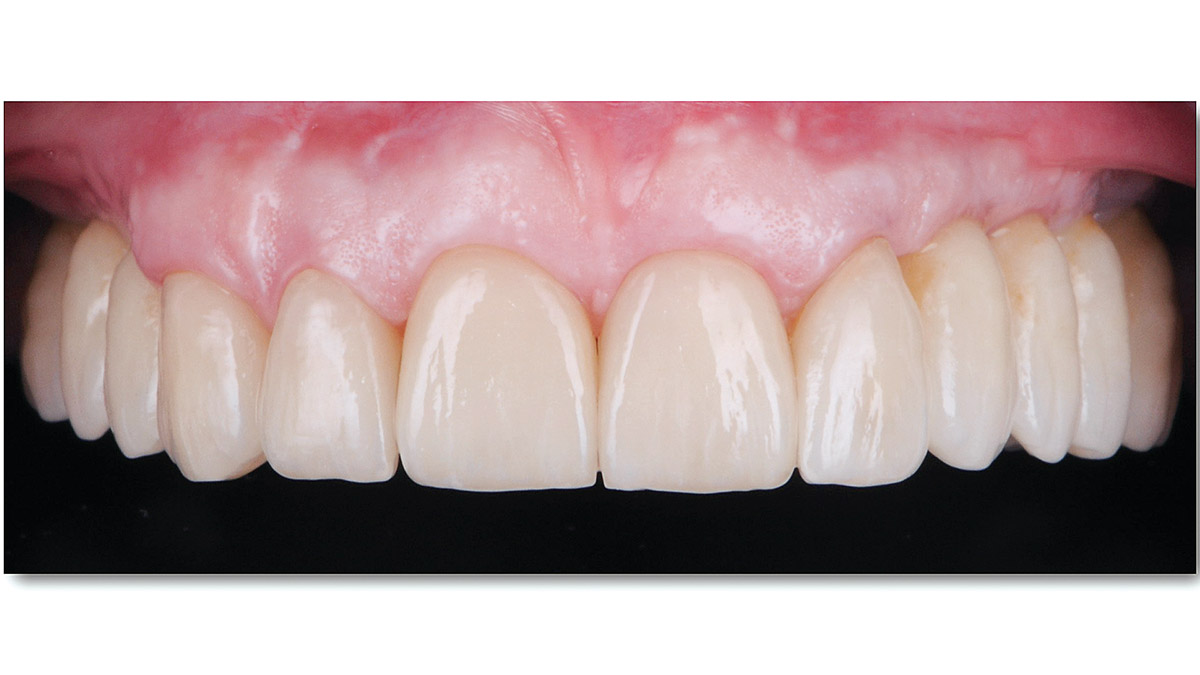
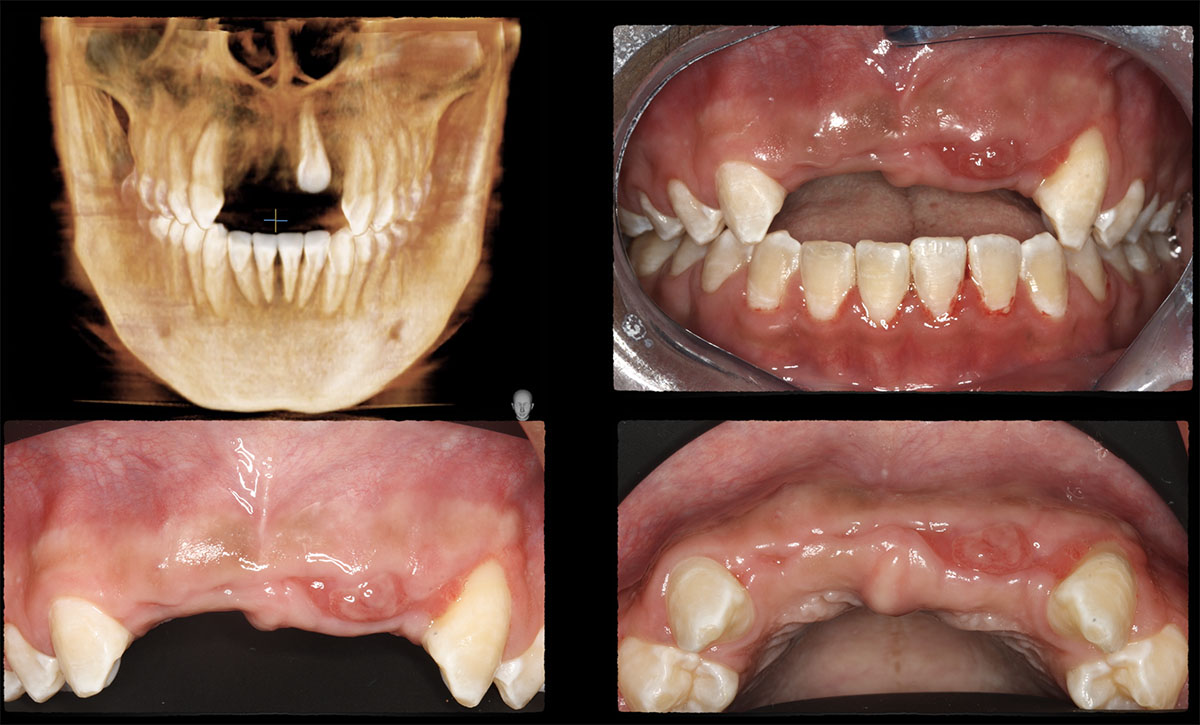
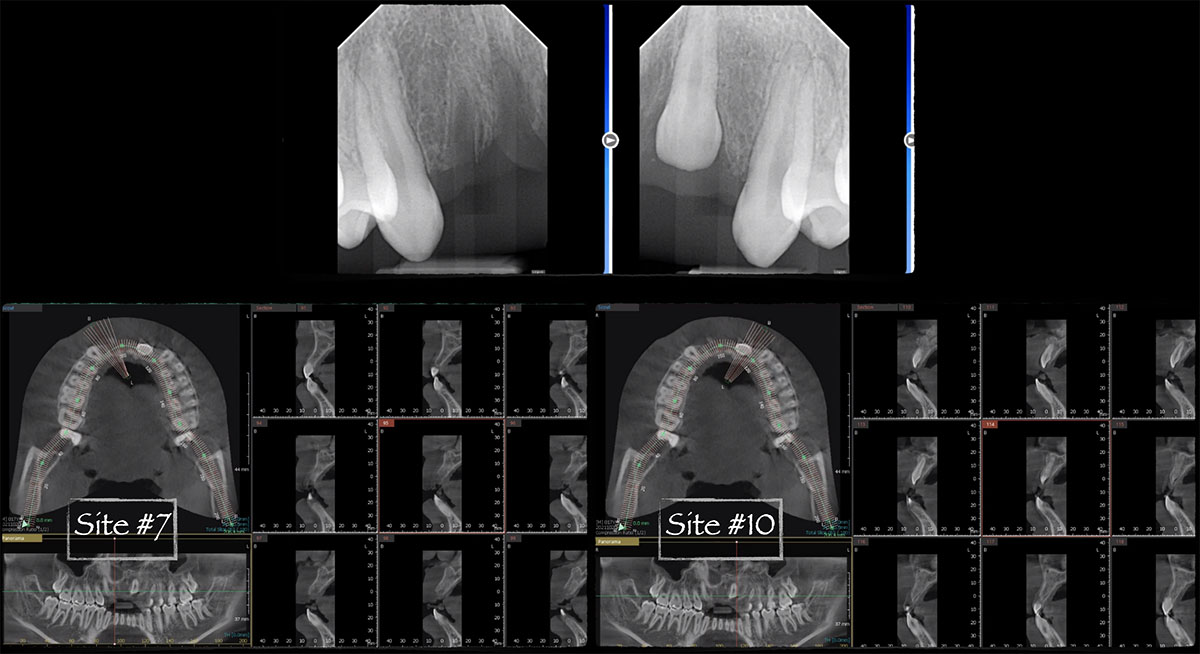
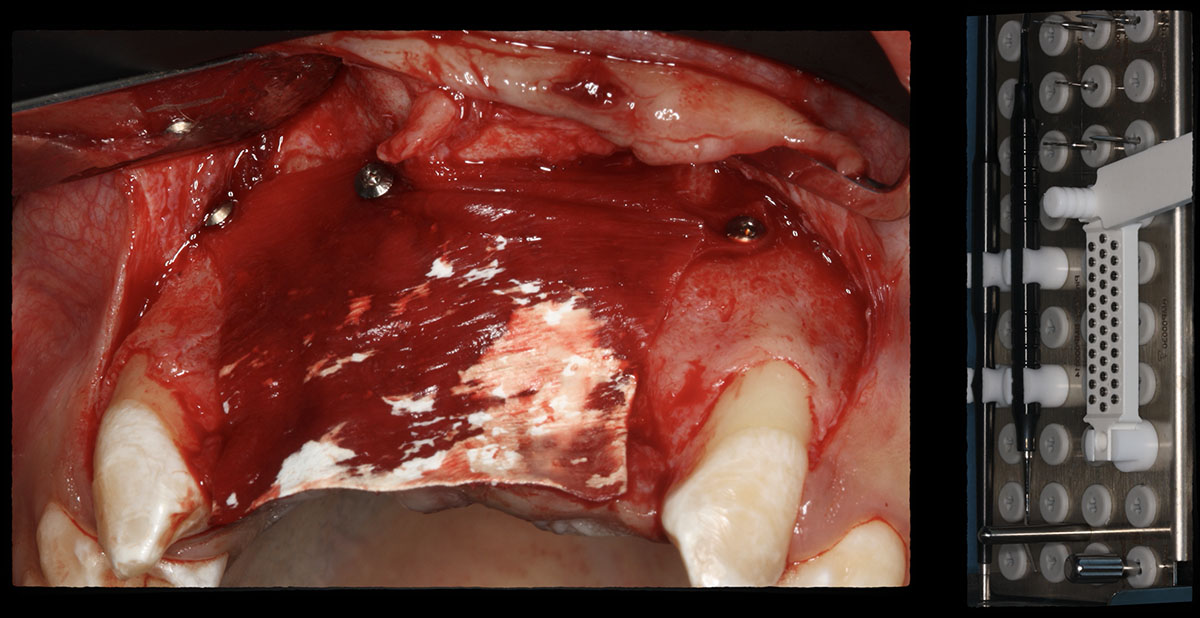
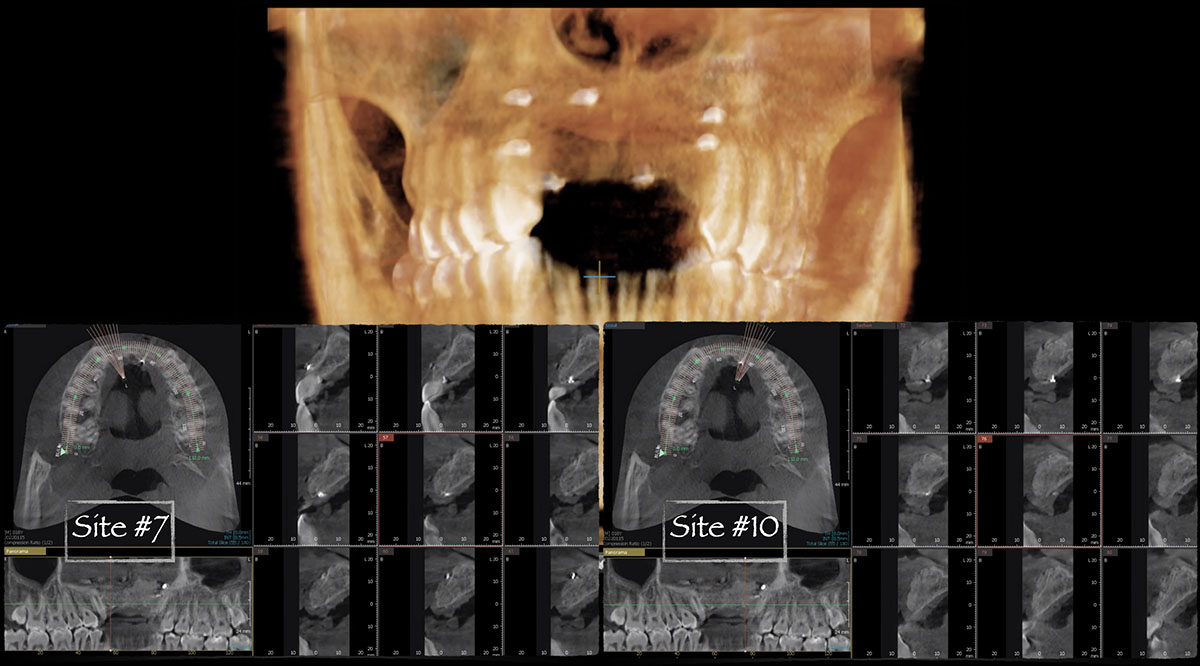
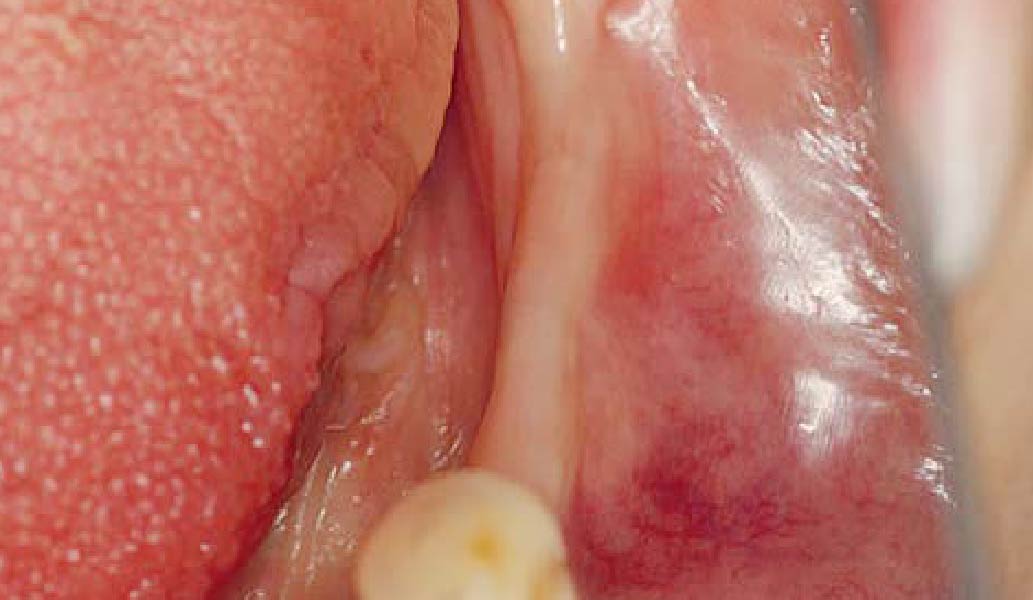
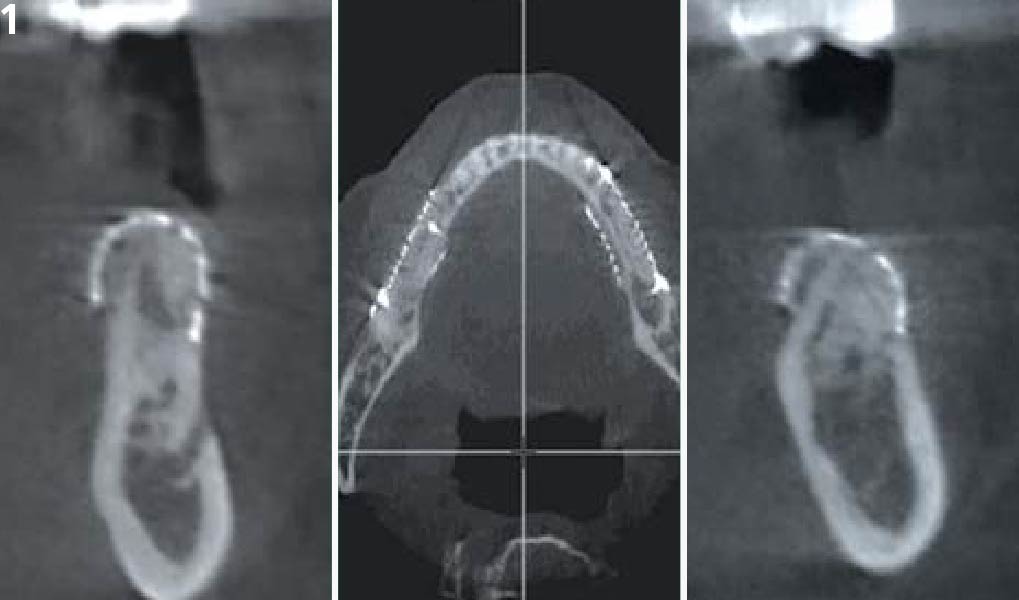
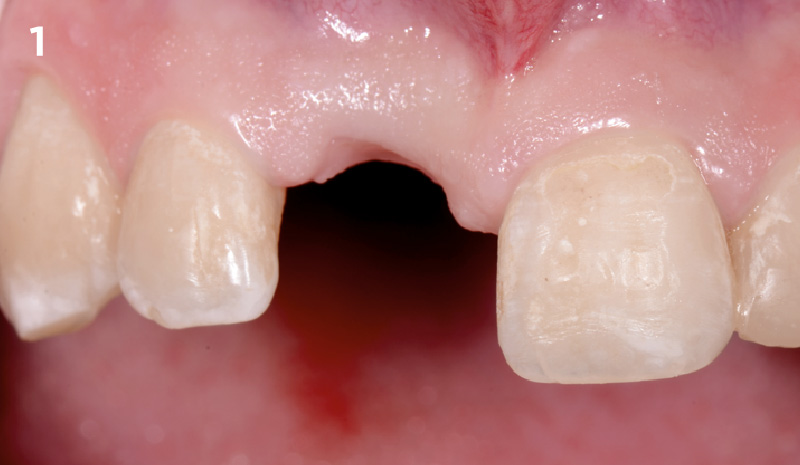
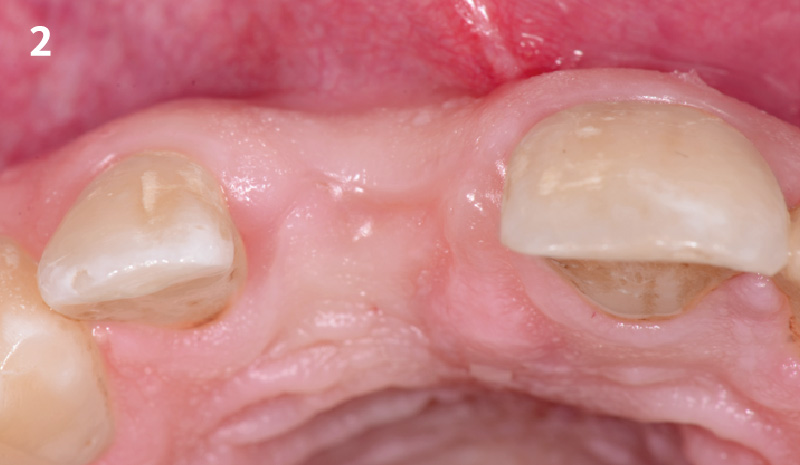
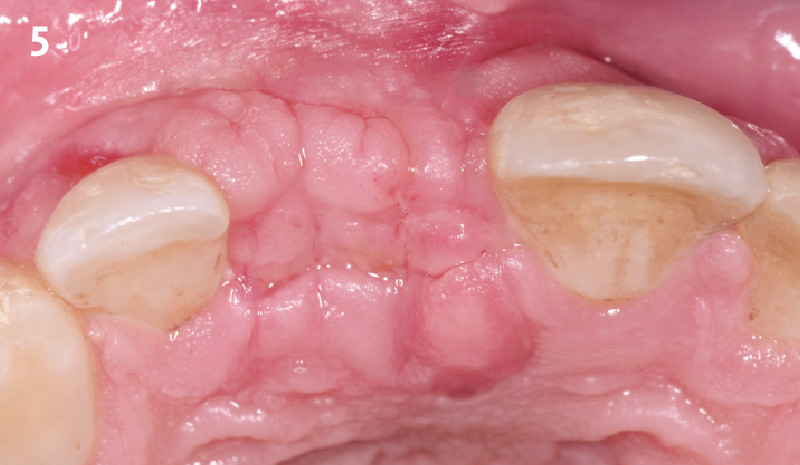
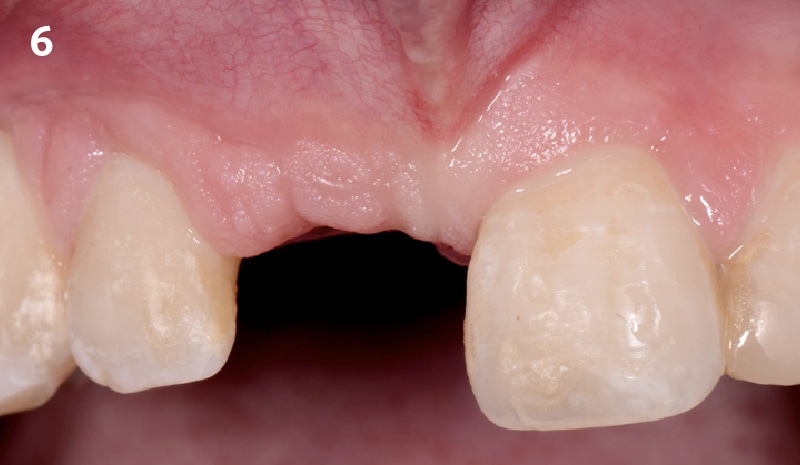
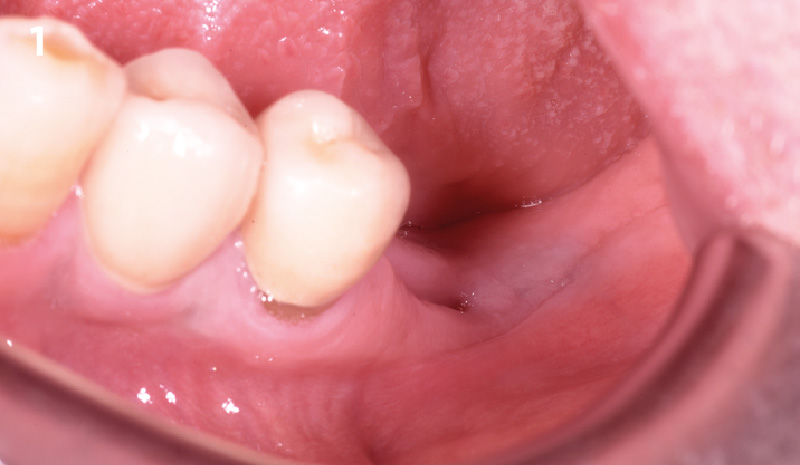
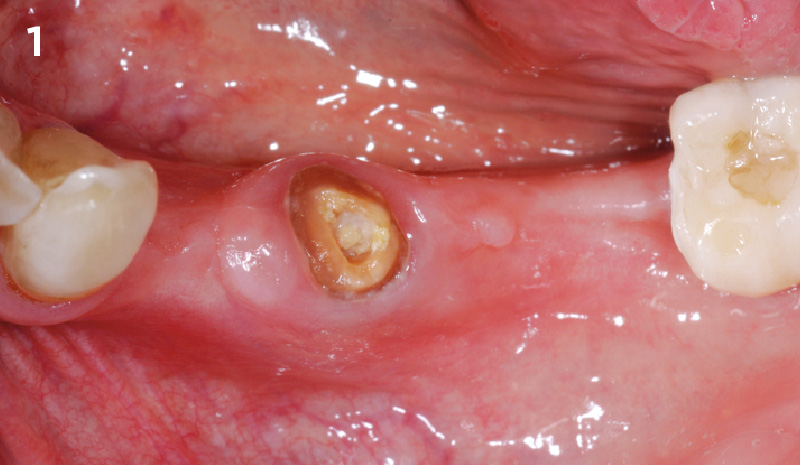
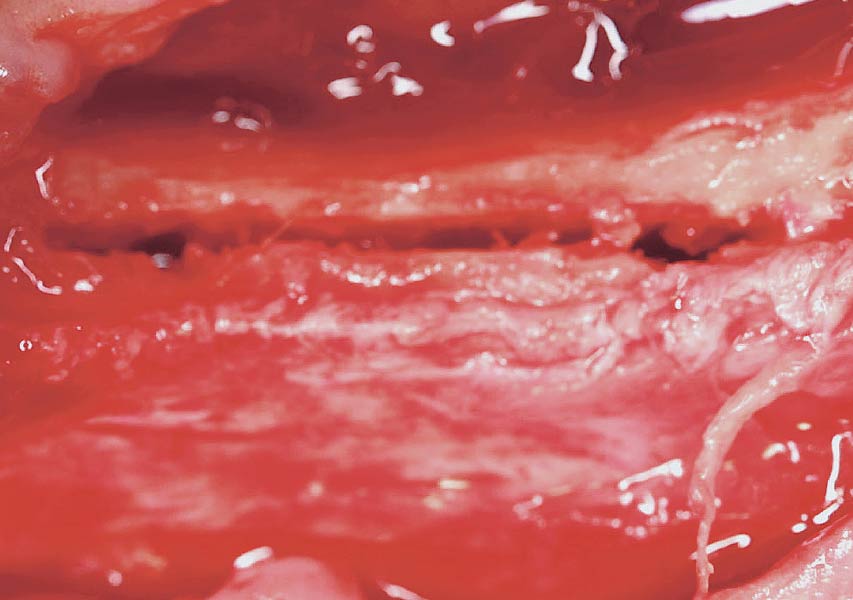
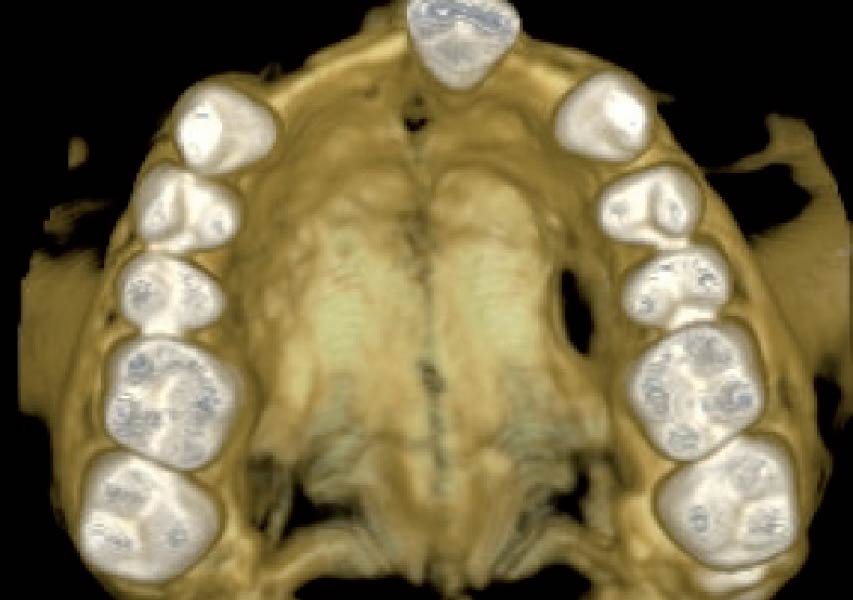
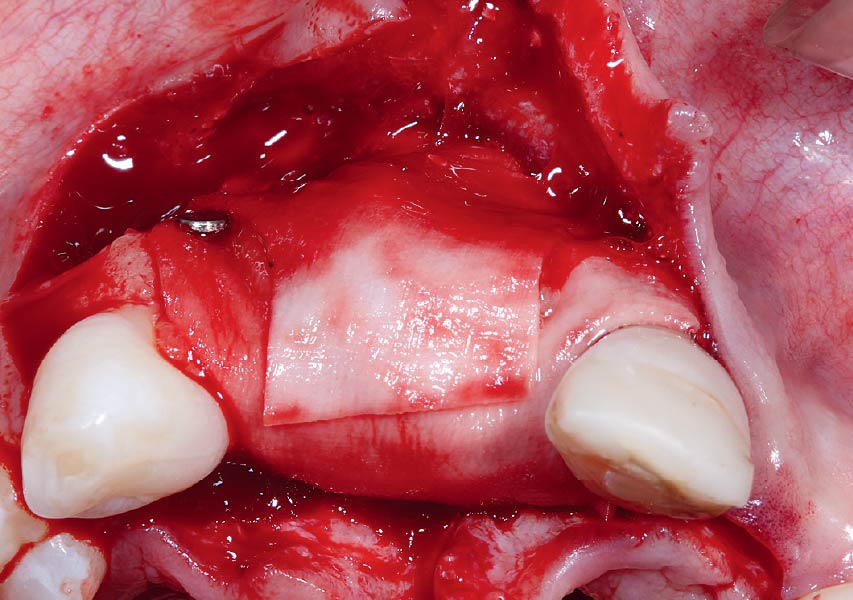
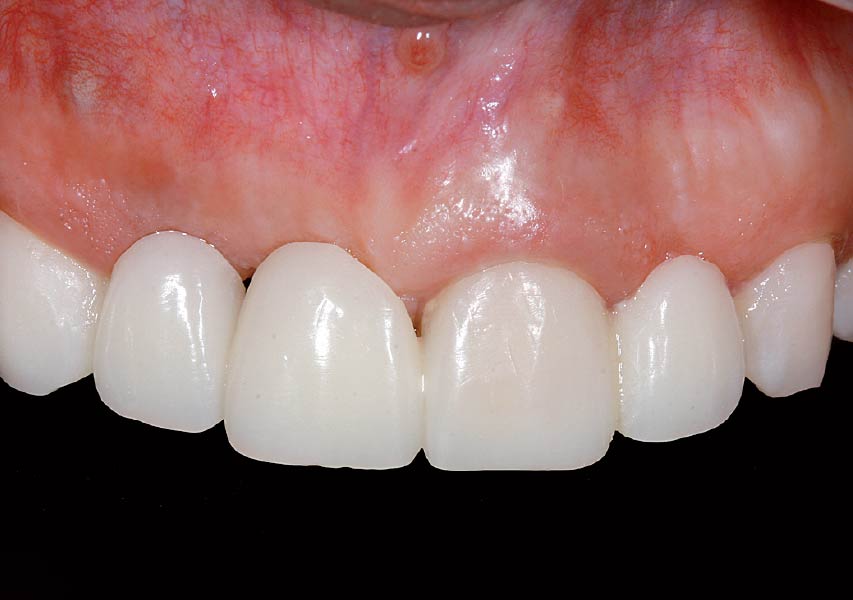
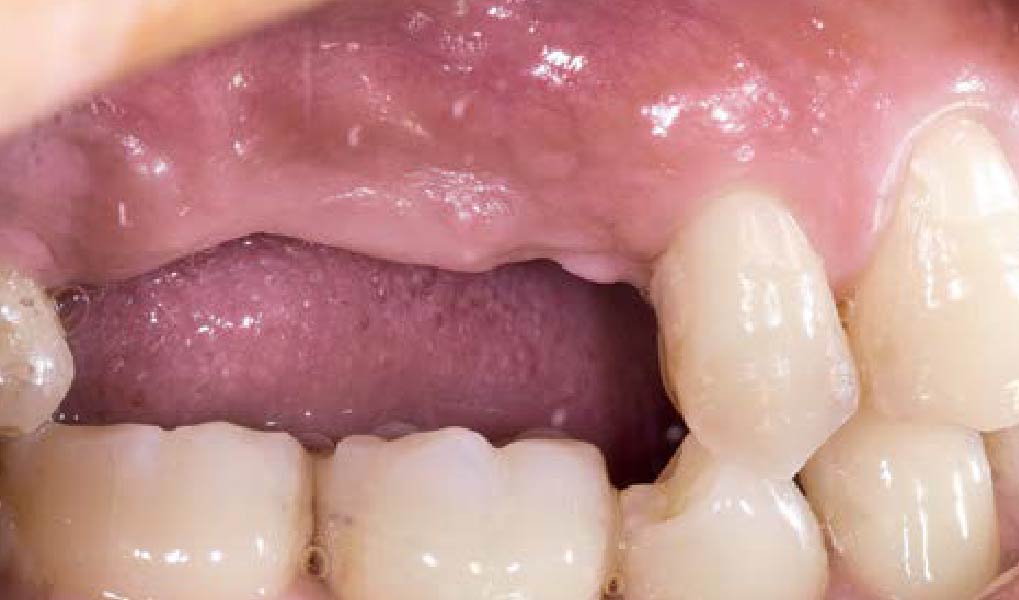
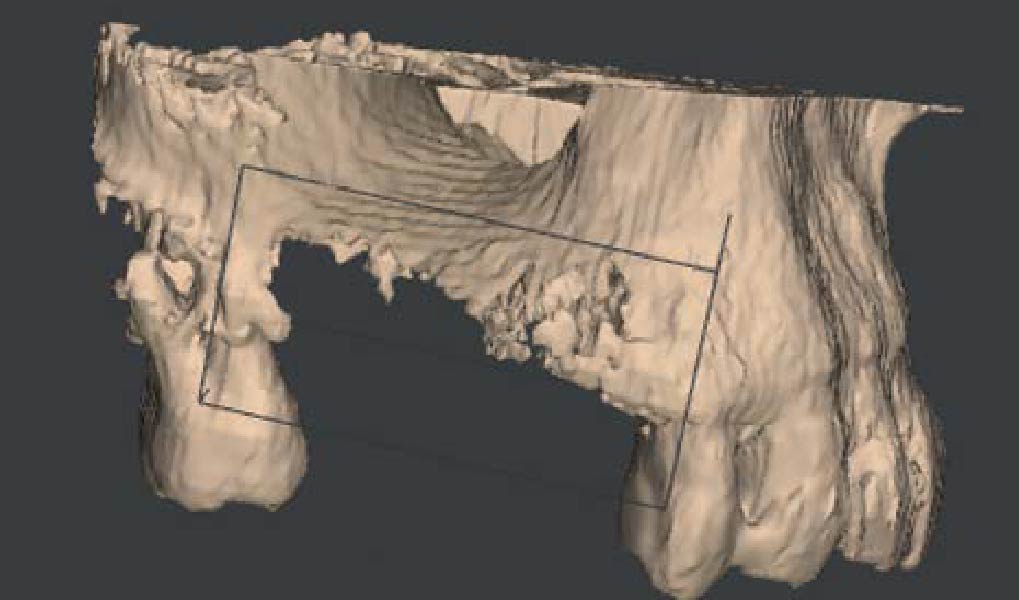
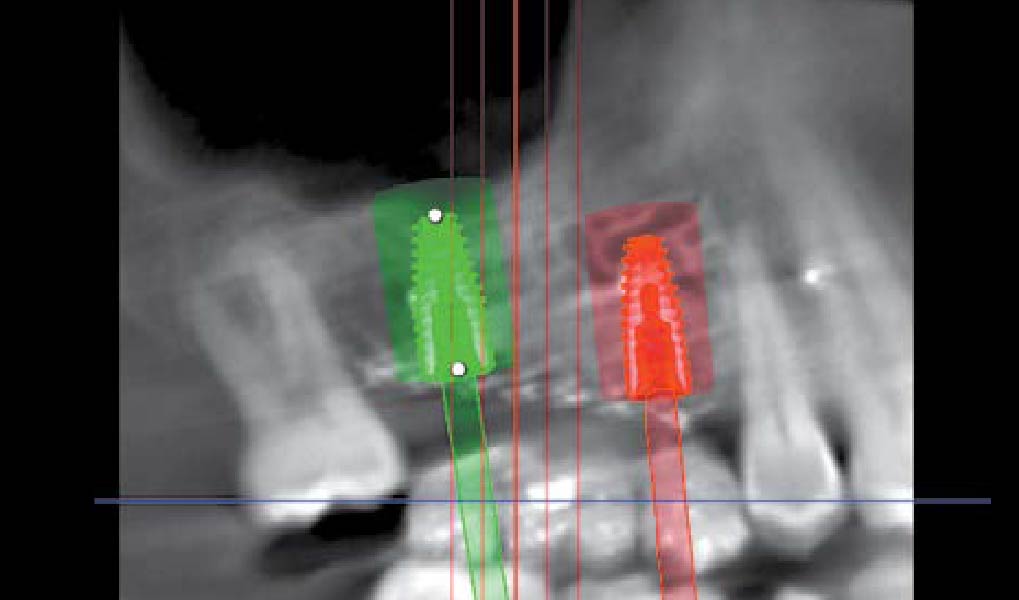
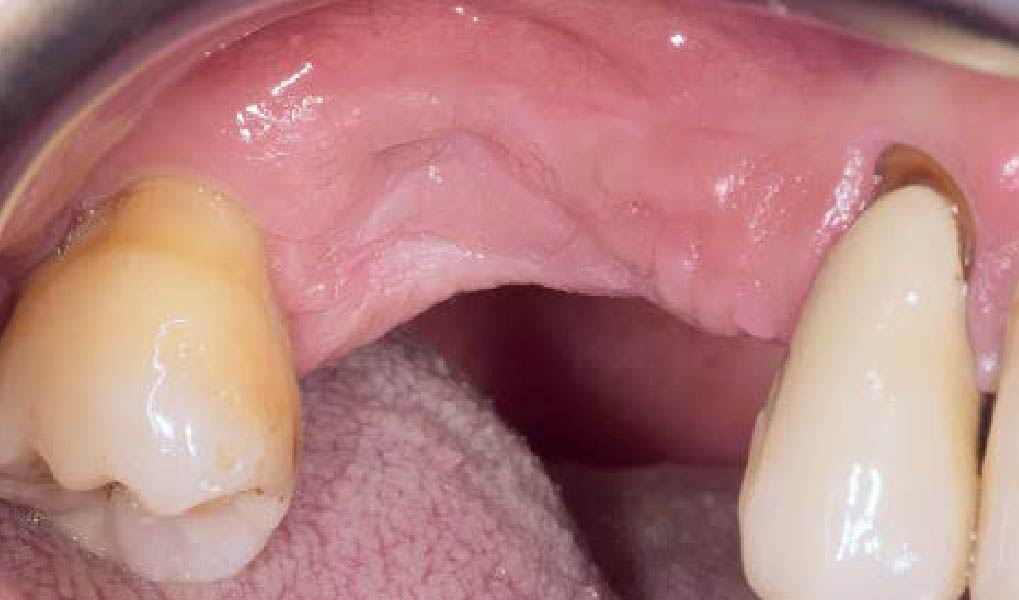
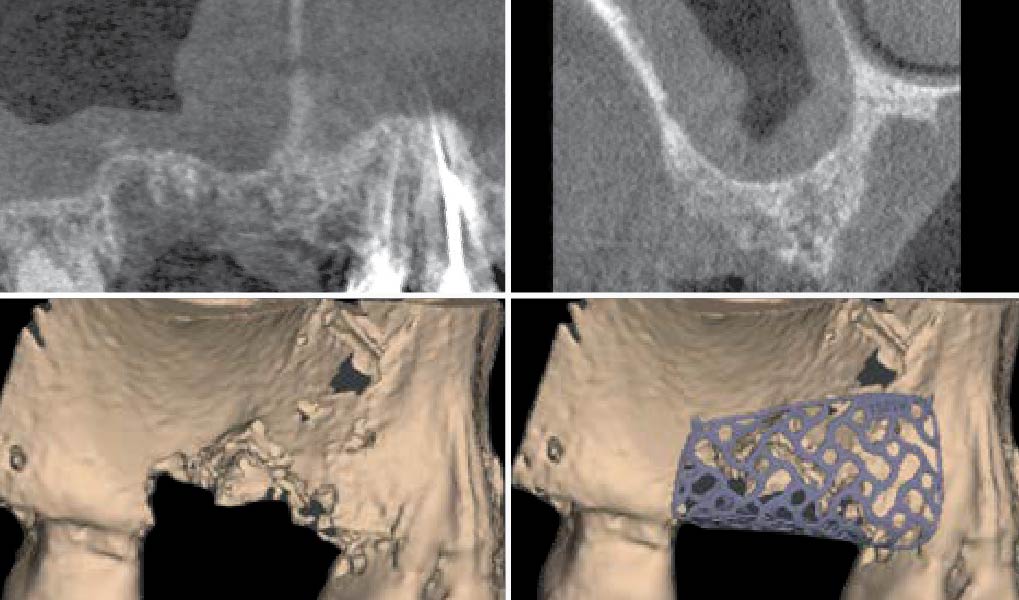
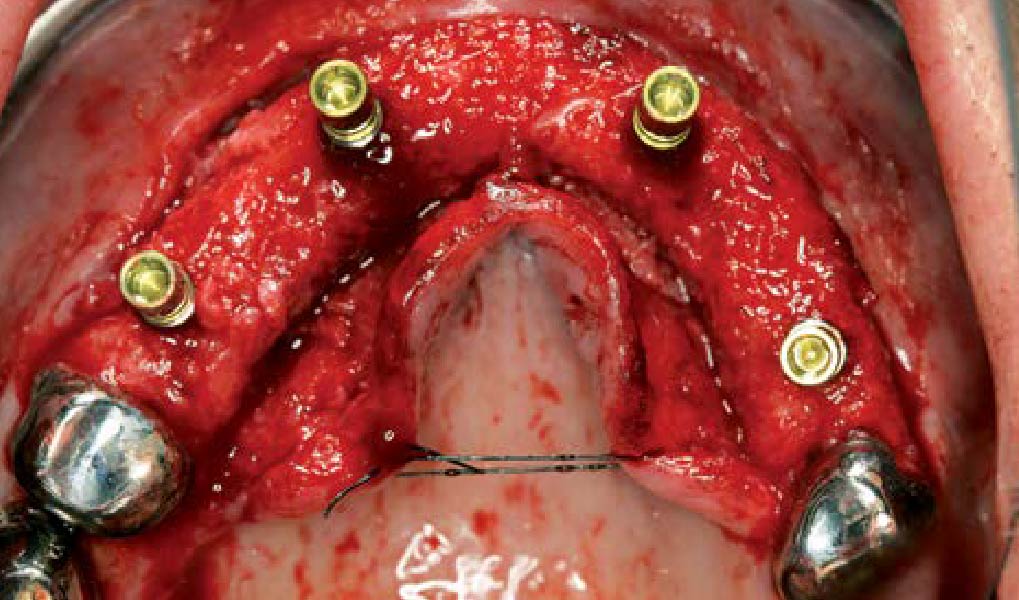
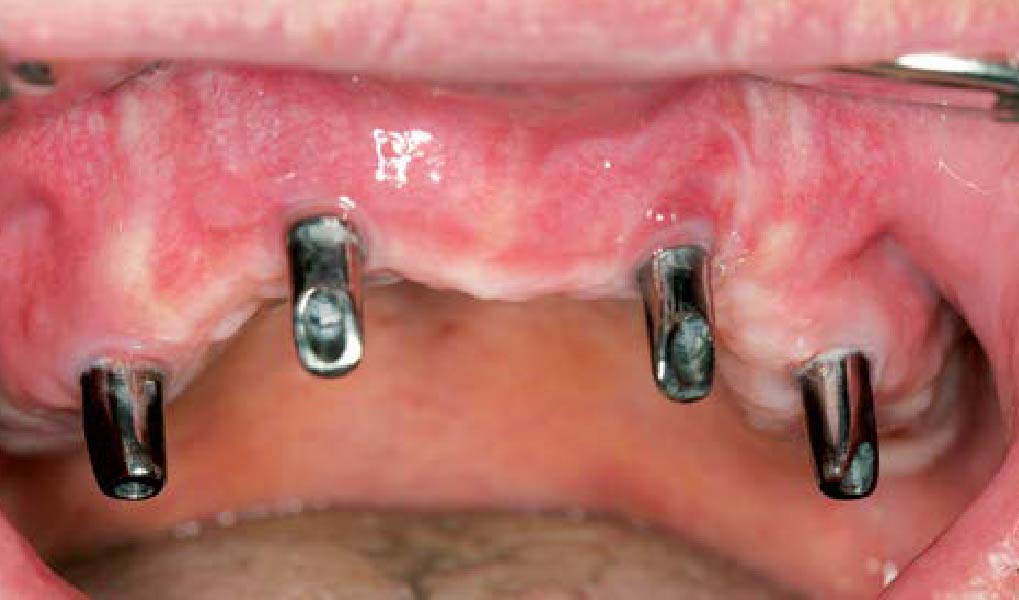
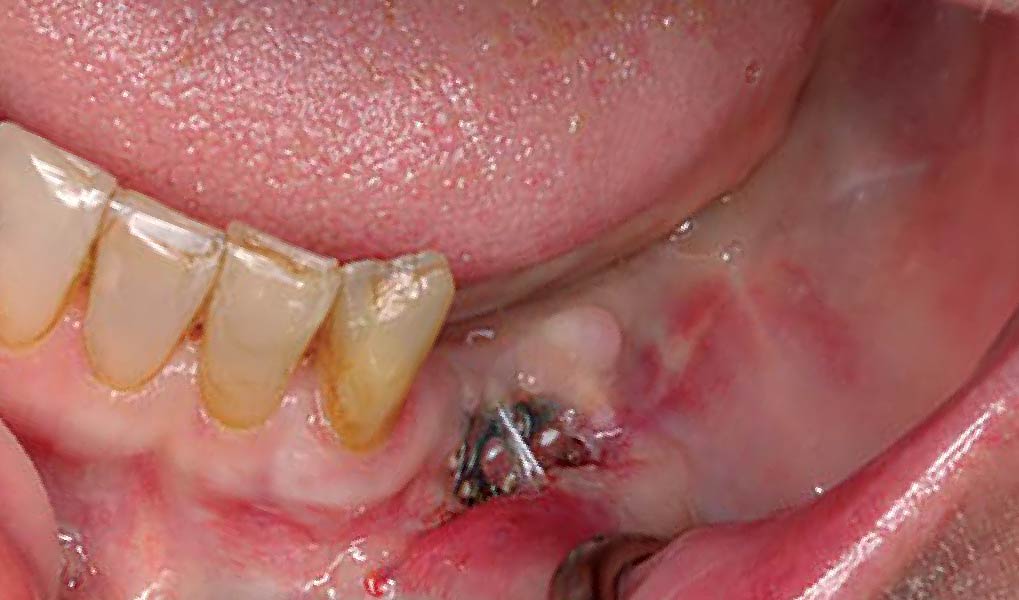
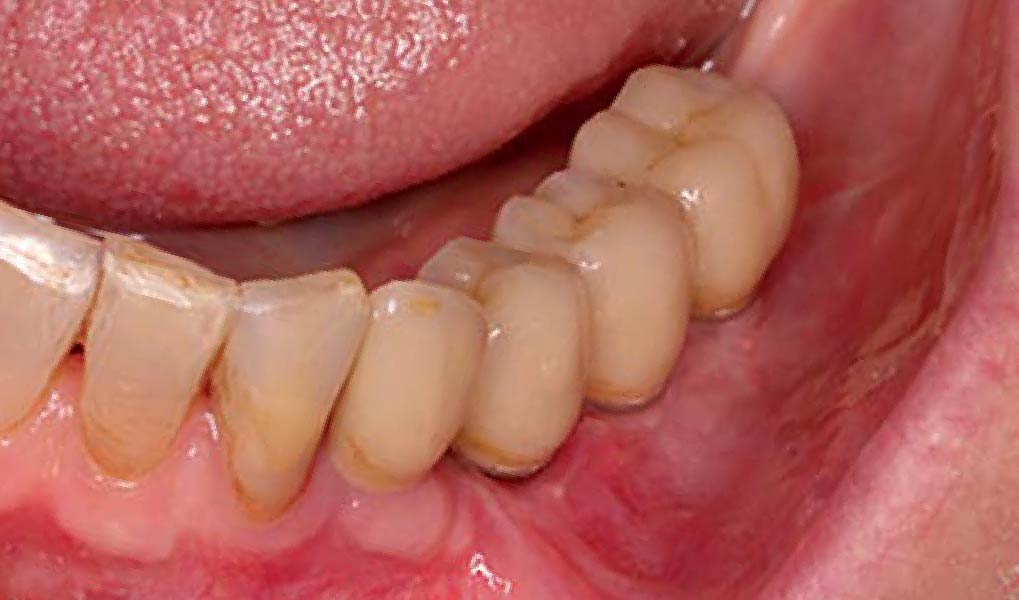
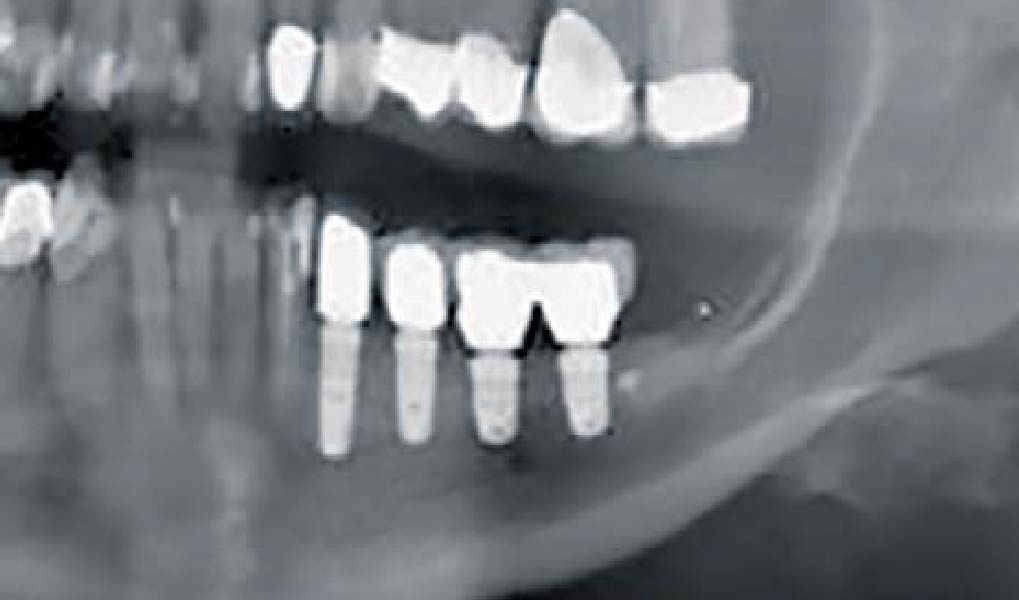
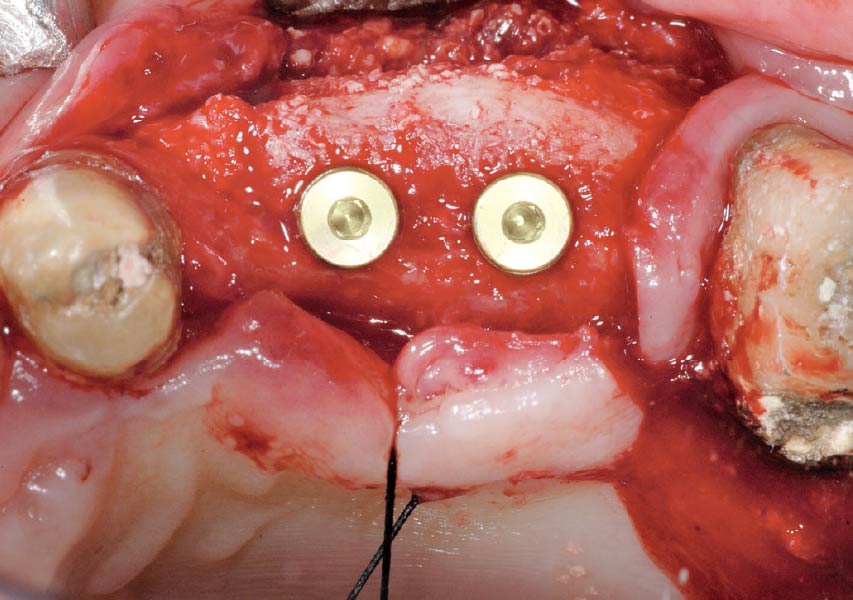
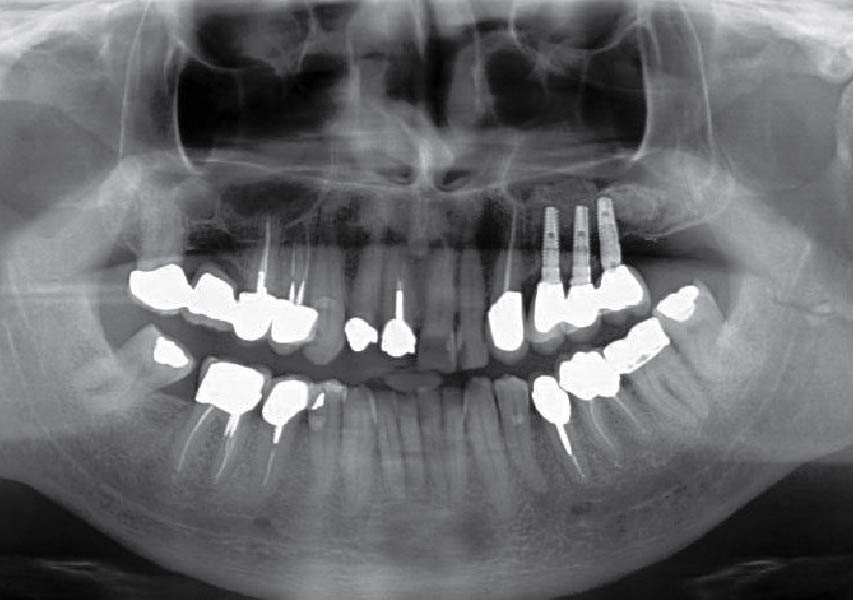
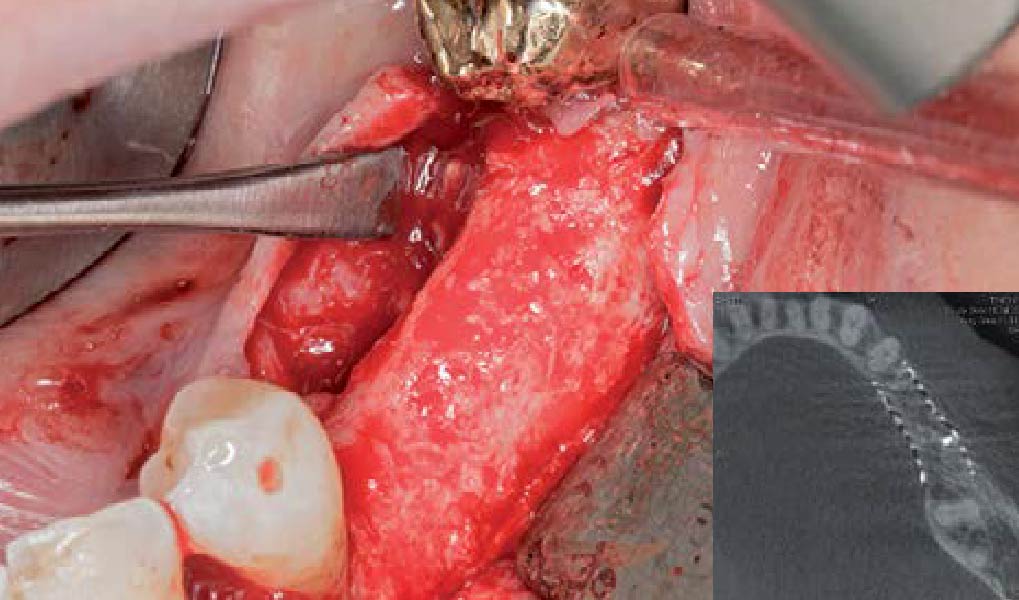
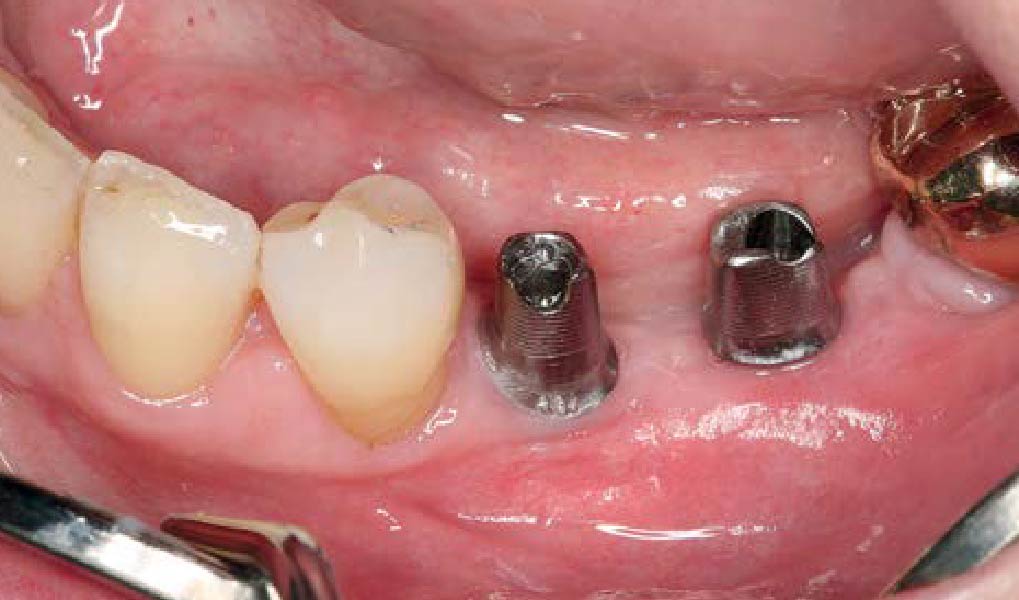
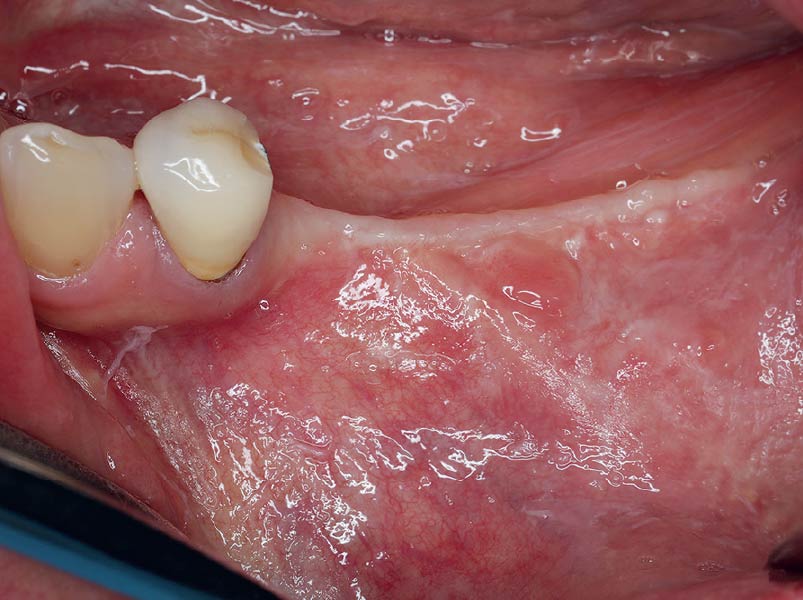
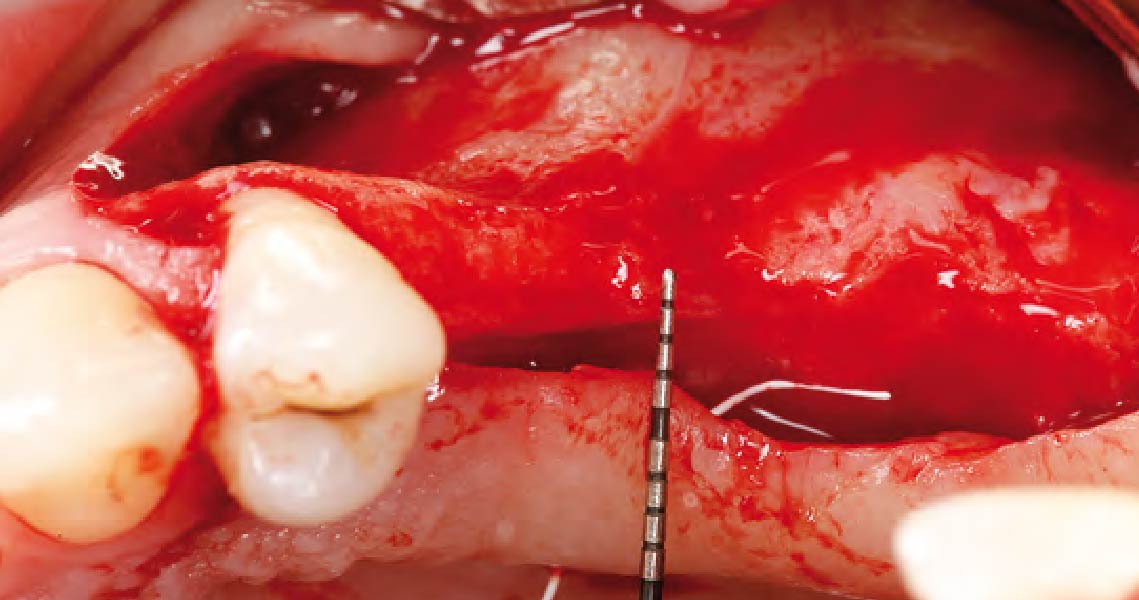
The patient presented to the clinic for a dental implant in the tooth #12 location. Clinical evaluation revealed a ridge deficiency. A Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) scan was taken, confirming insufficient ridge width for implant placement. As a result, the site was treatment planned for horizontal ridge augmentation.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
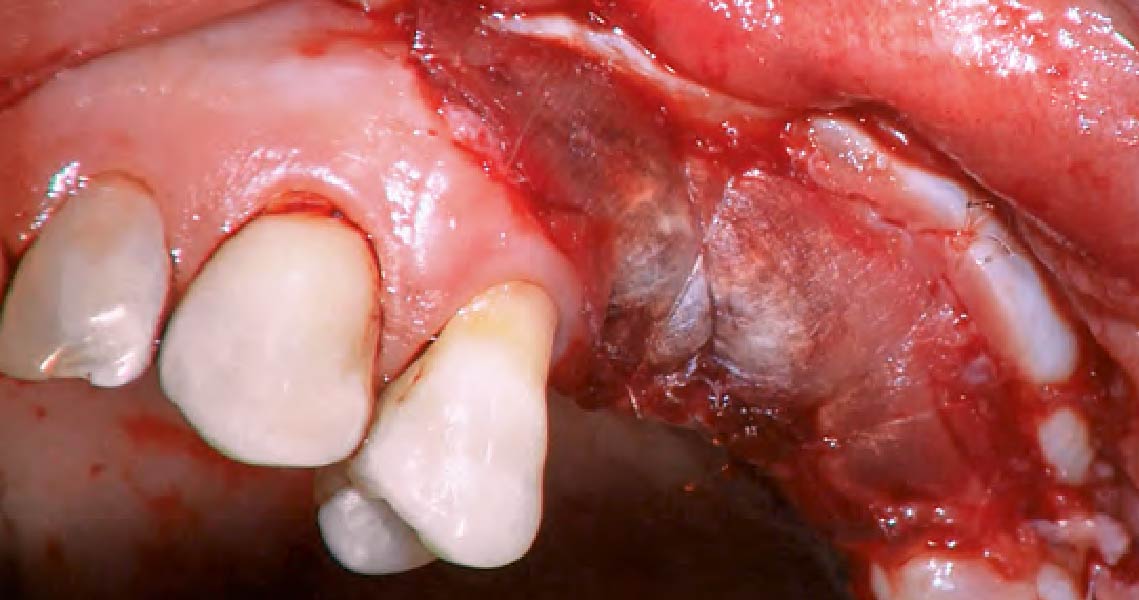
THE APPROACH
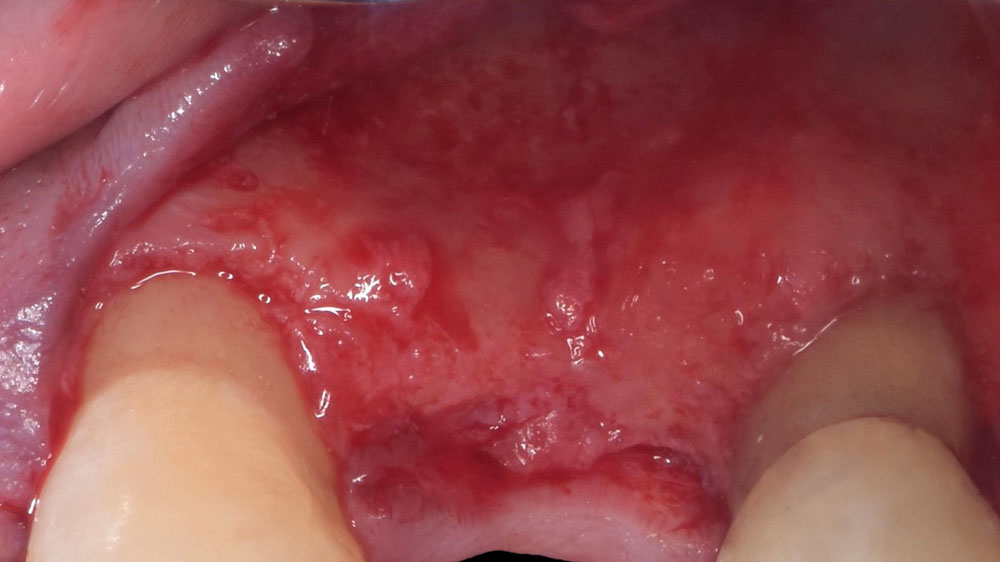
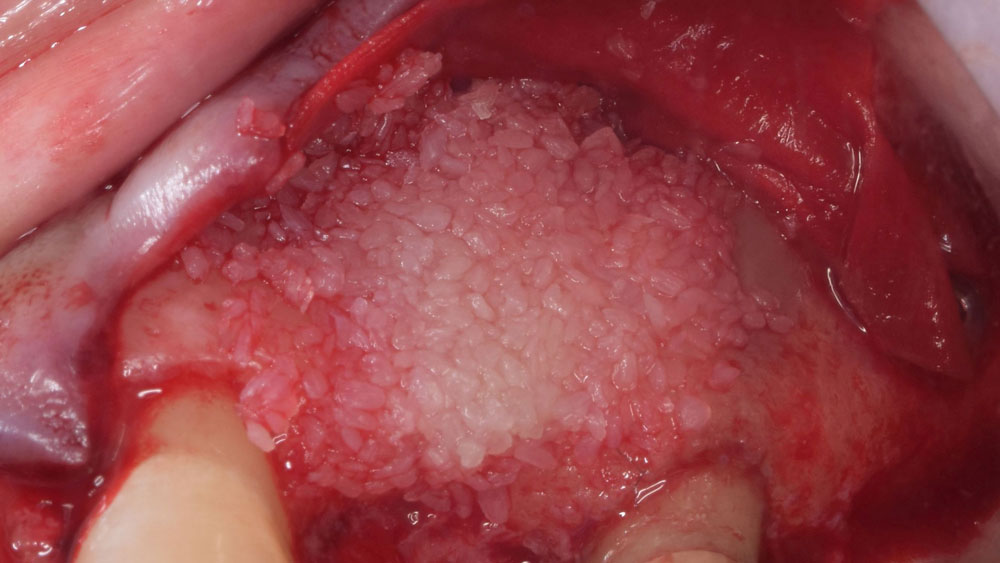
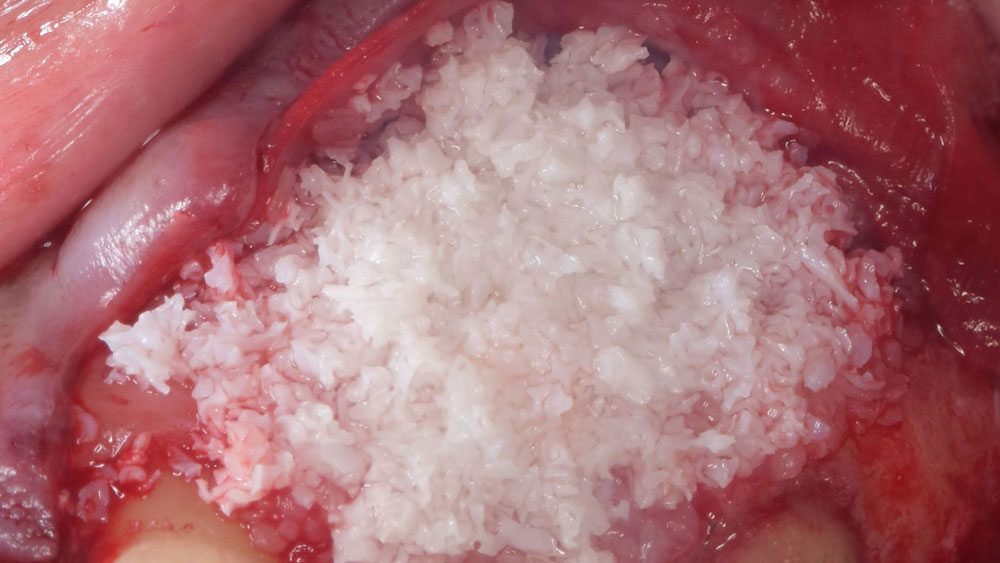
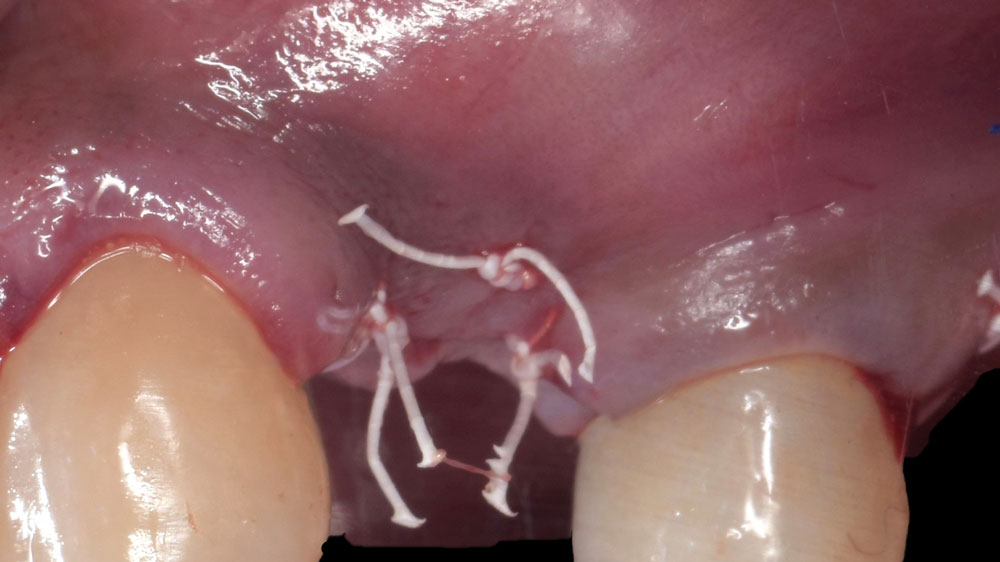
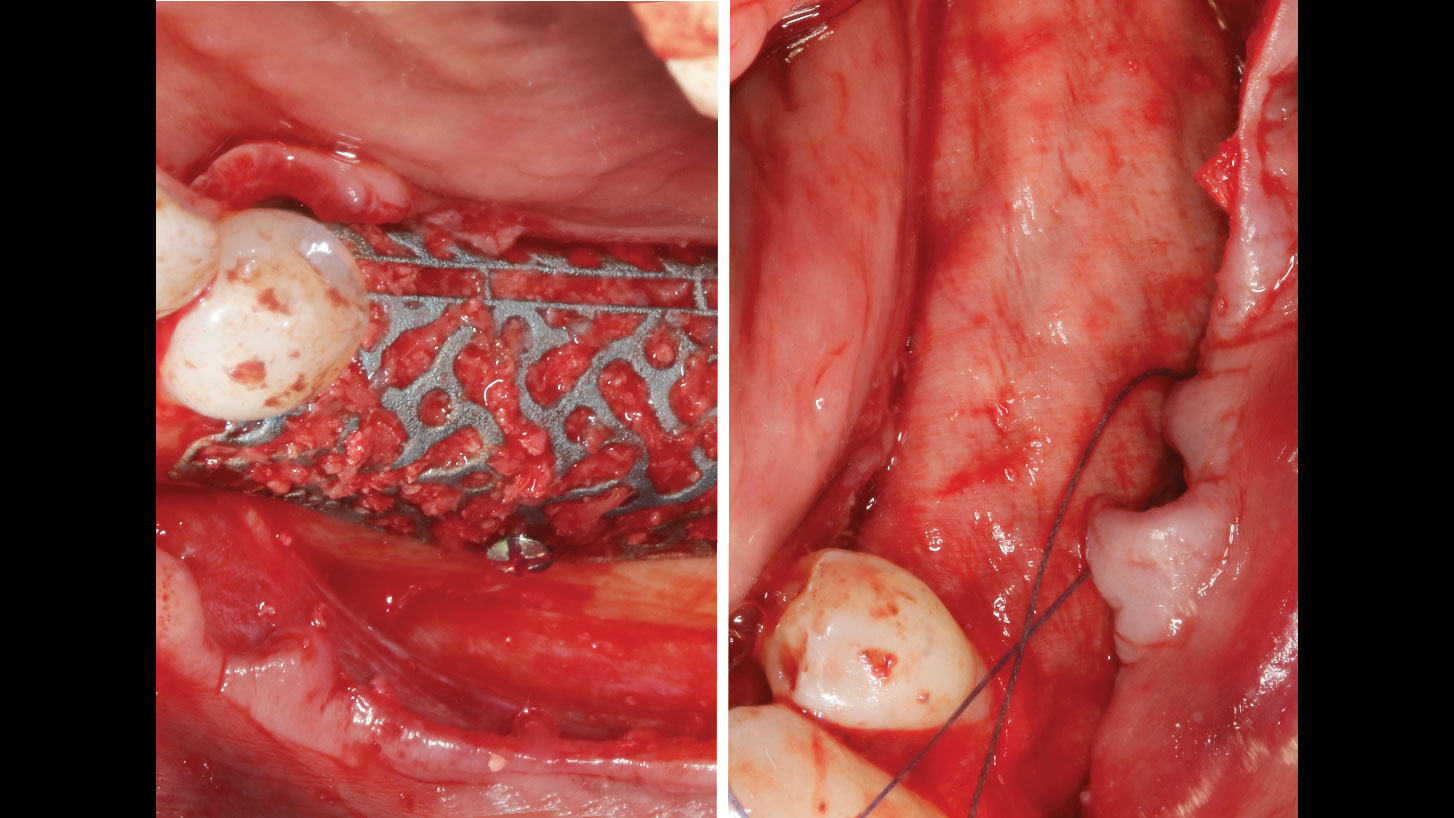
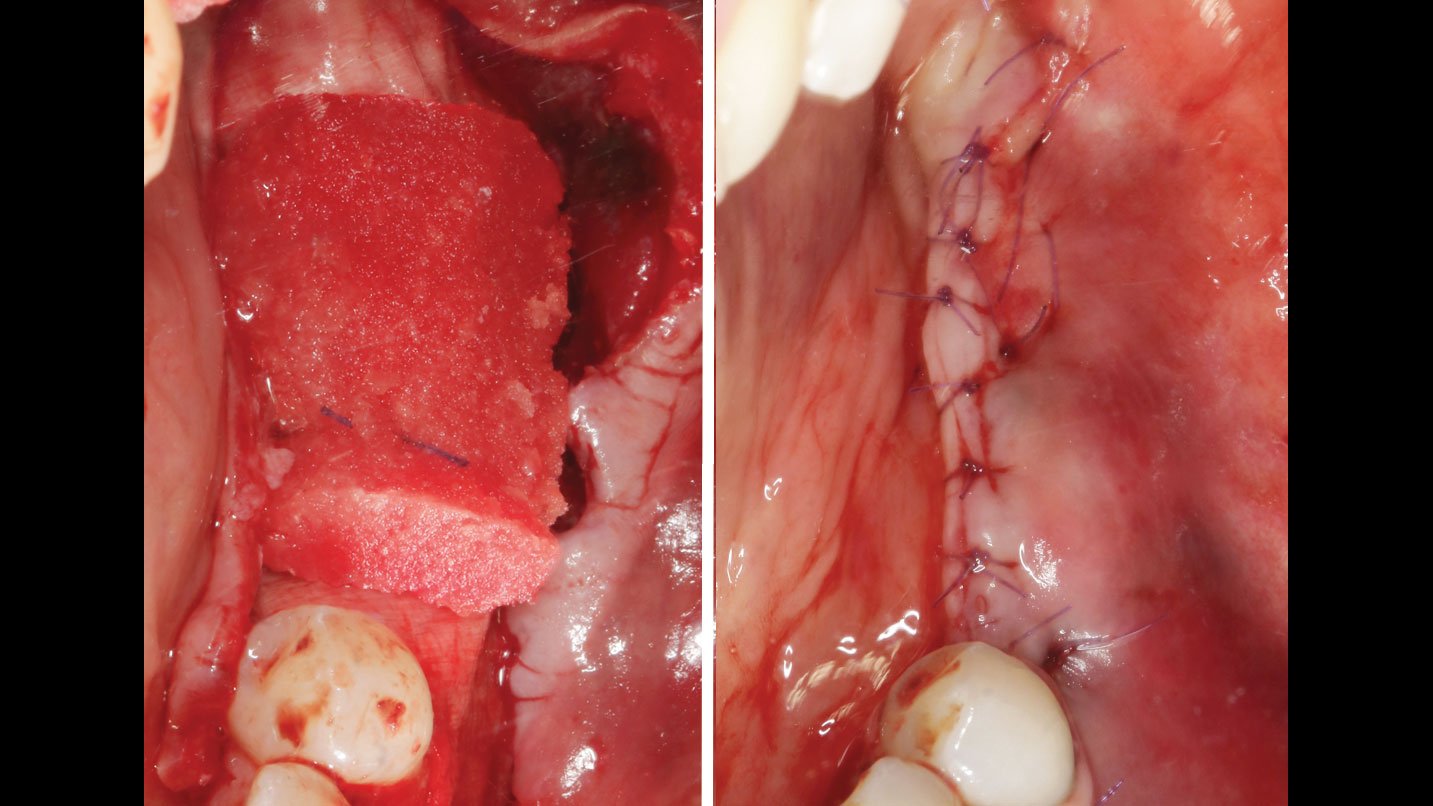
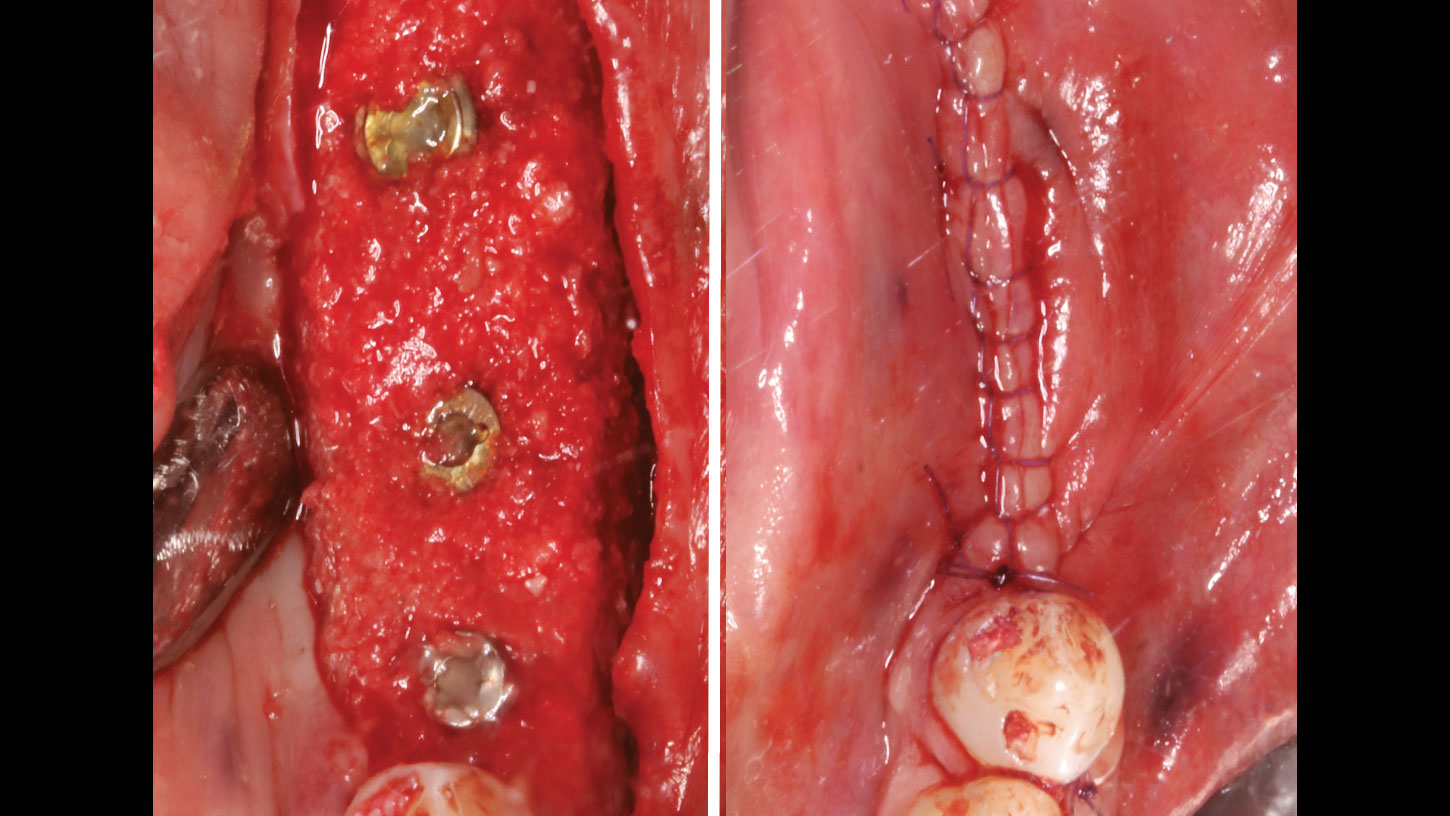
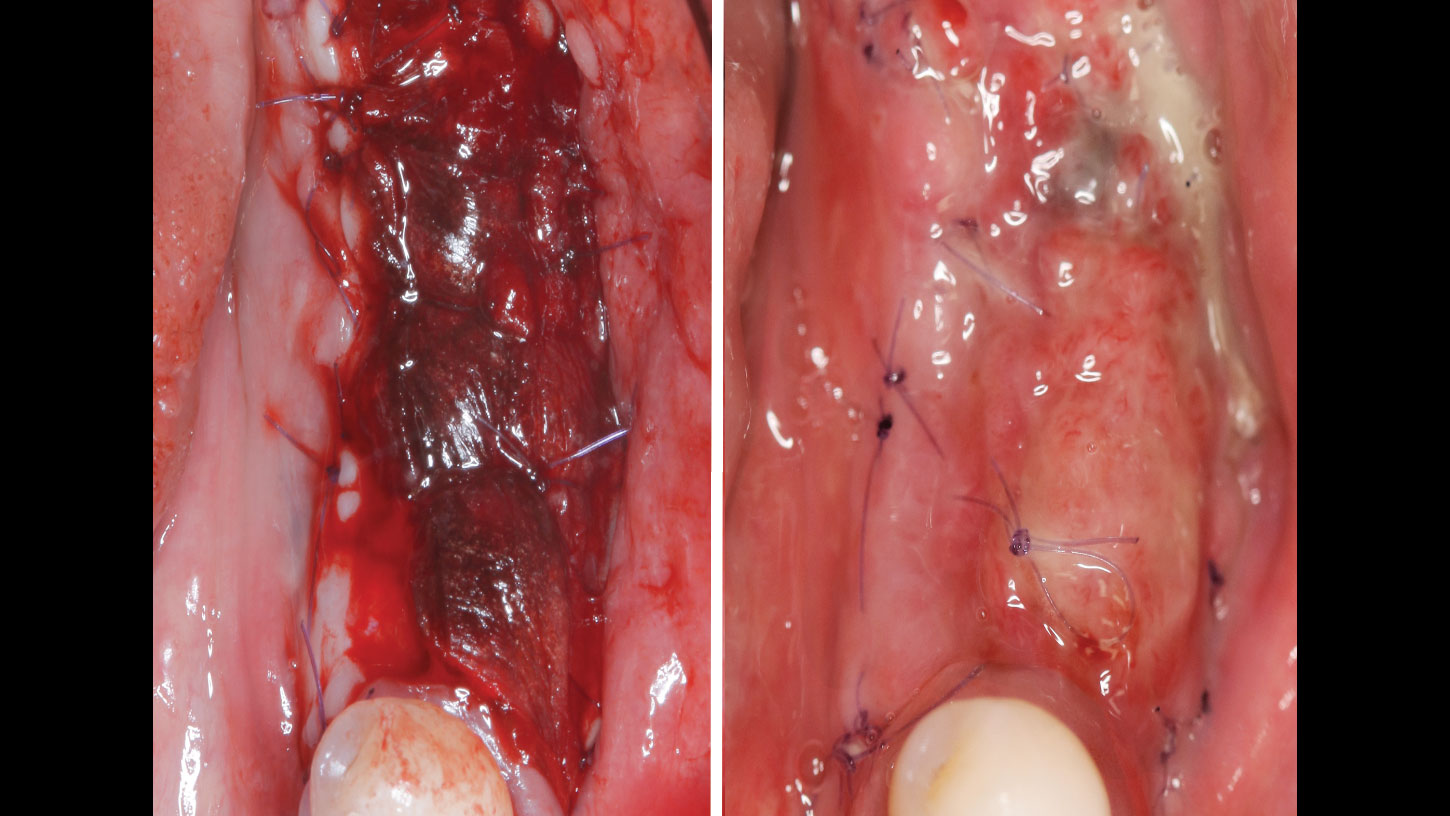
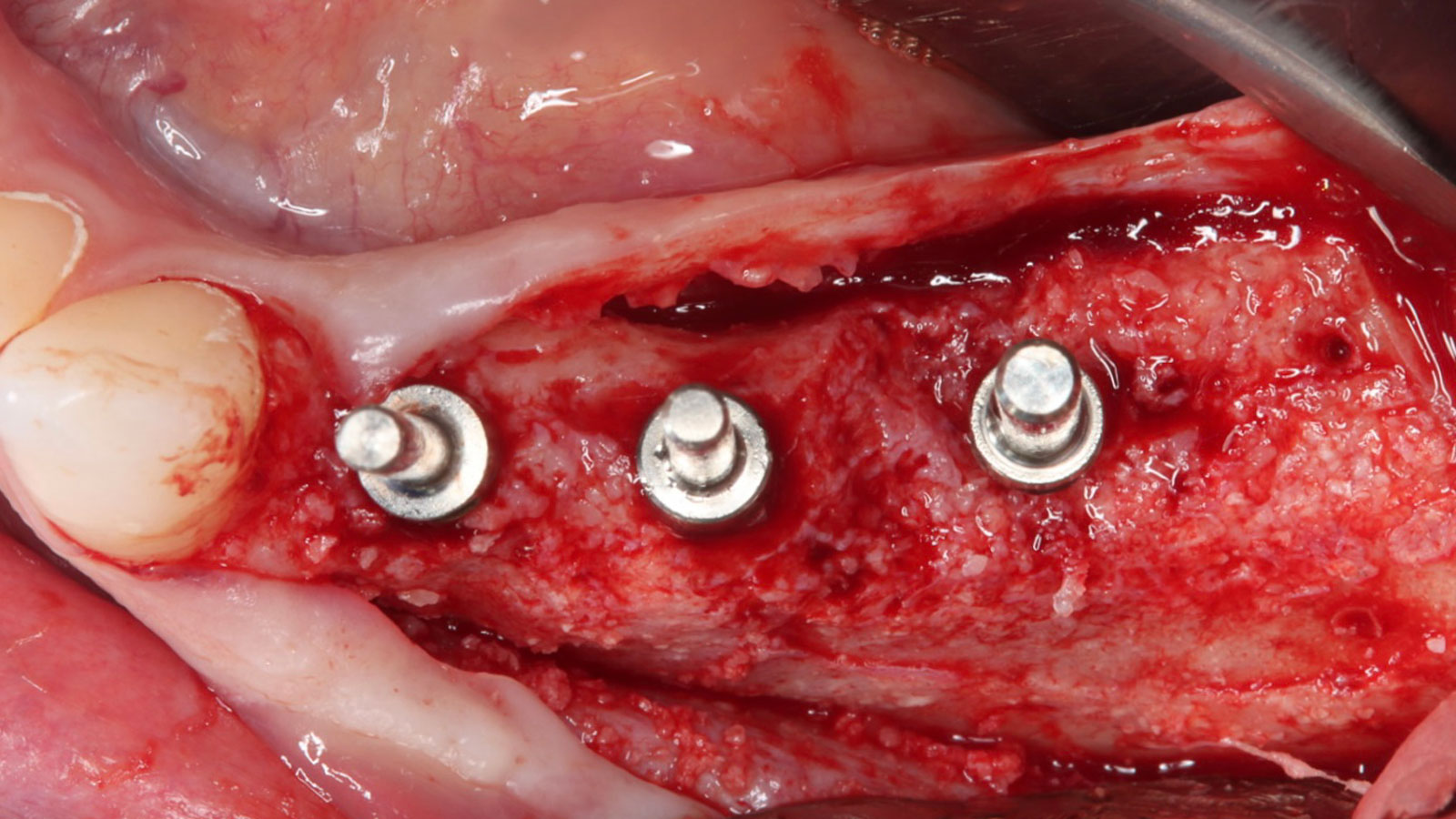
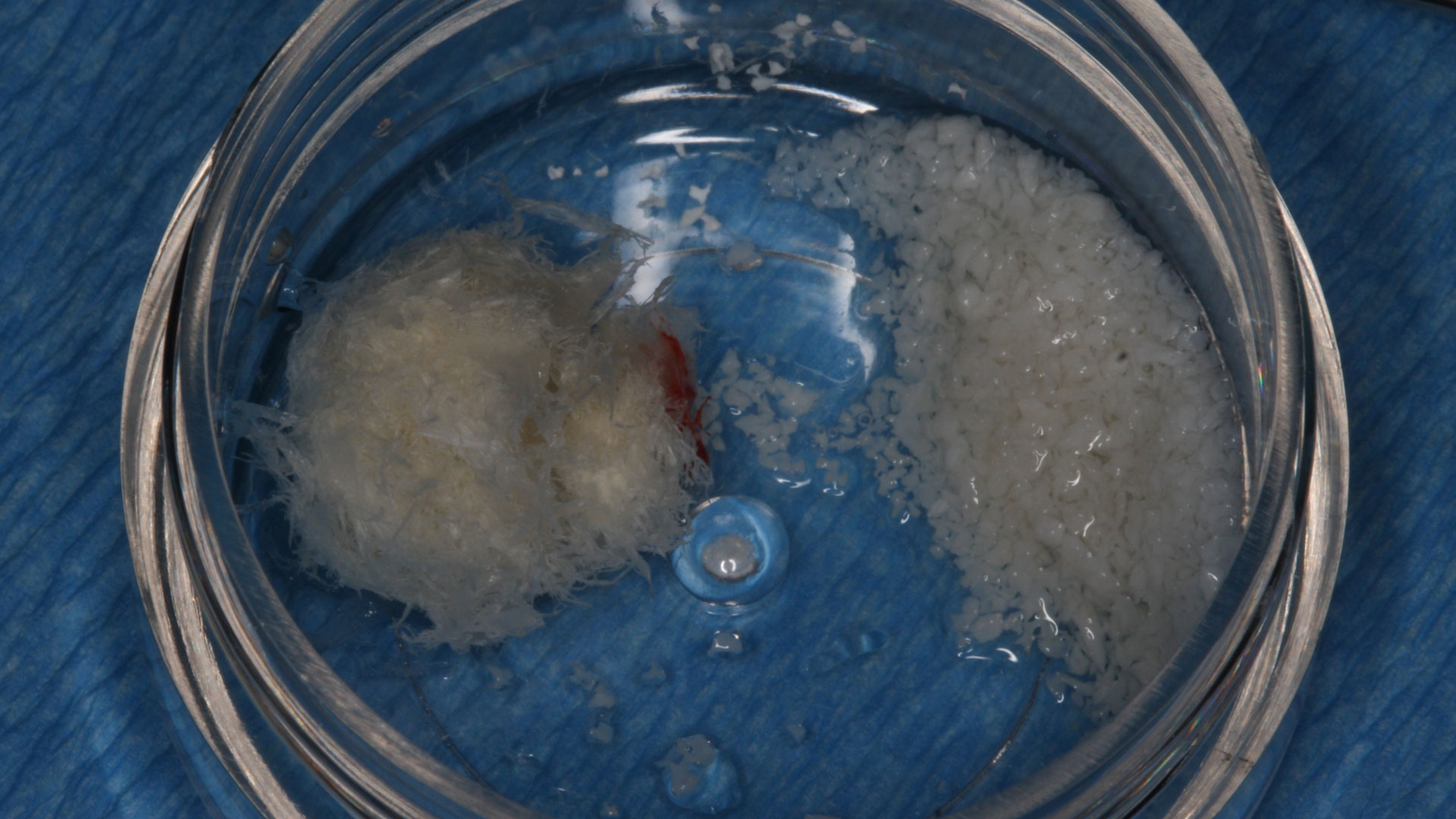
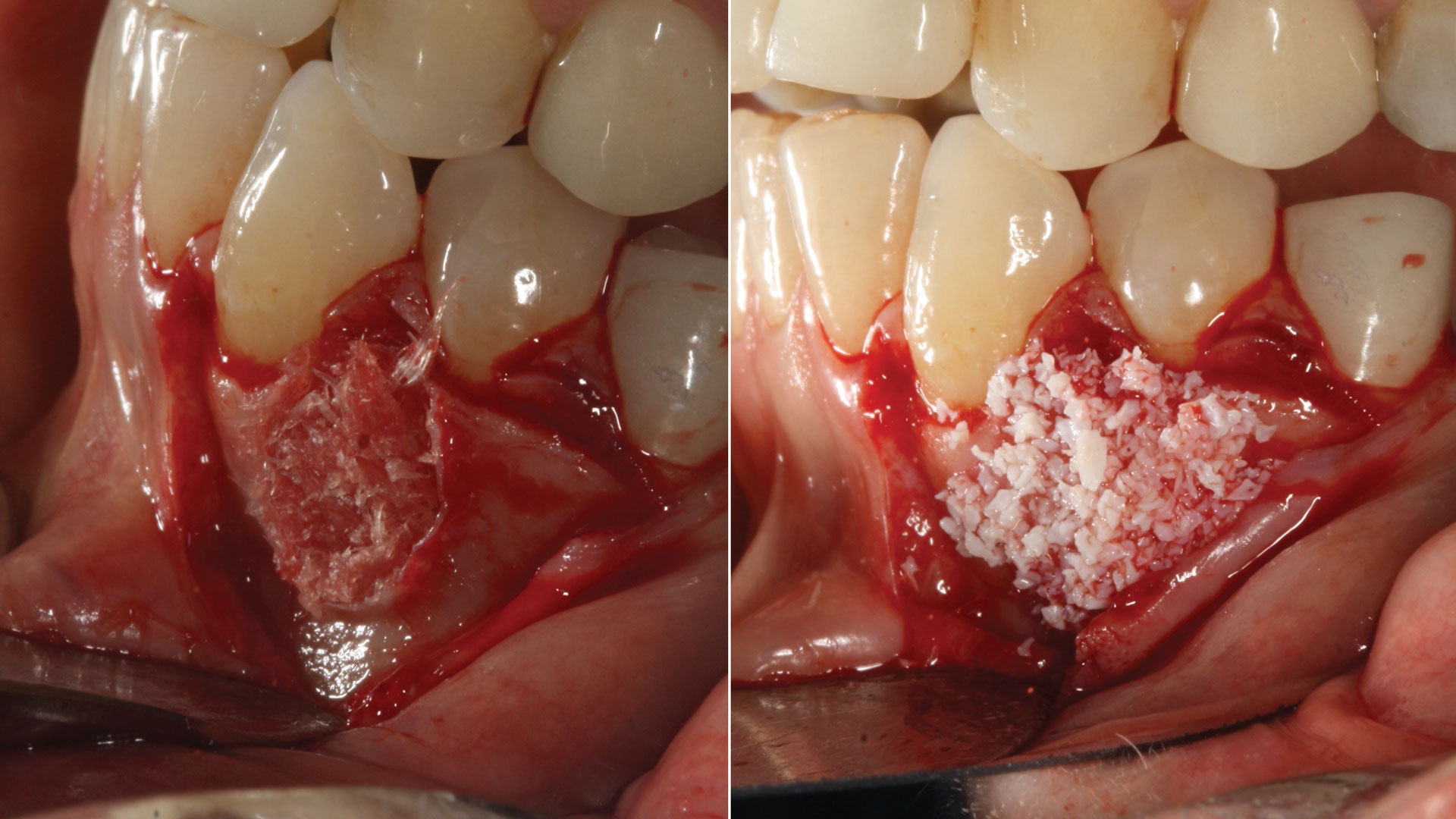
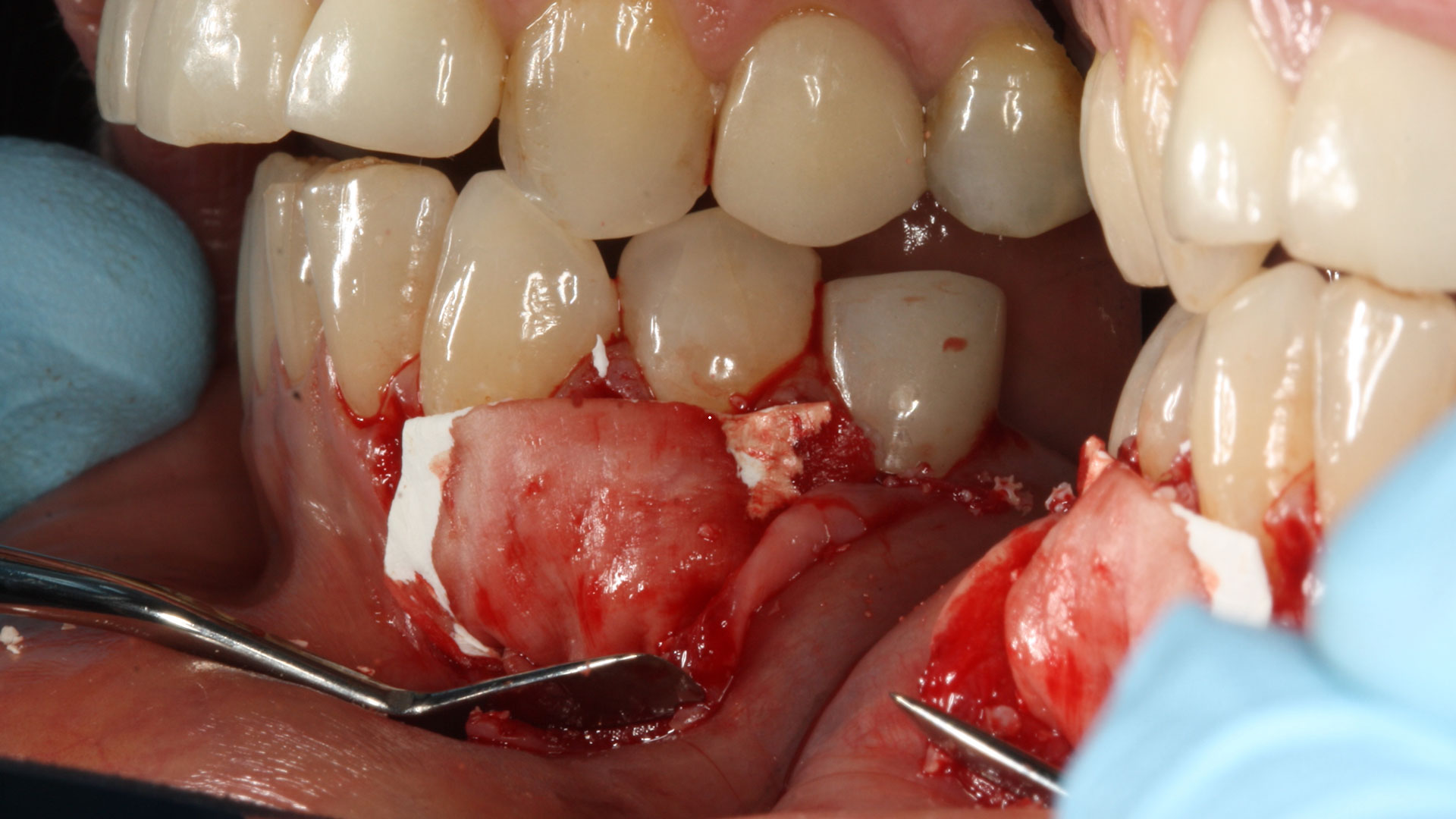
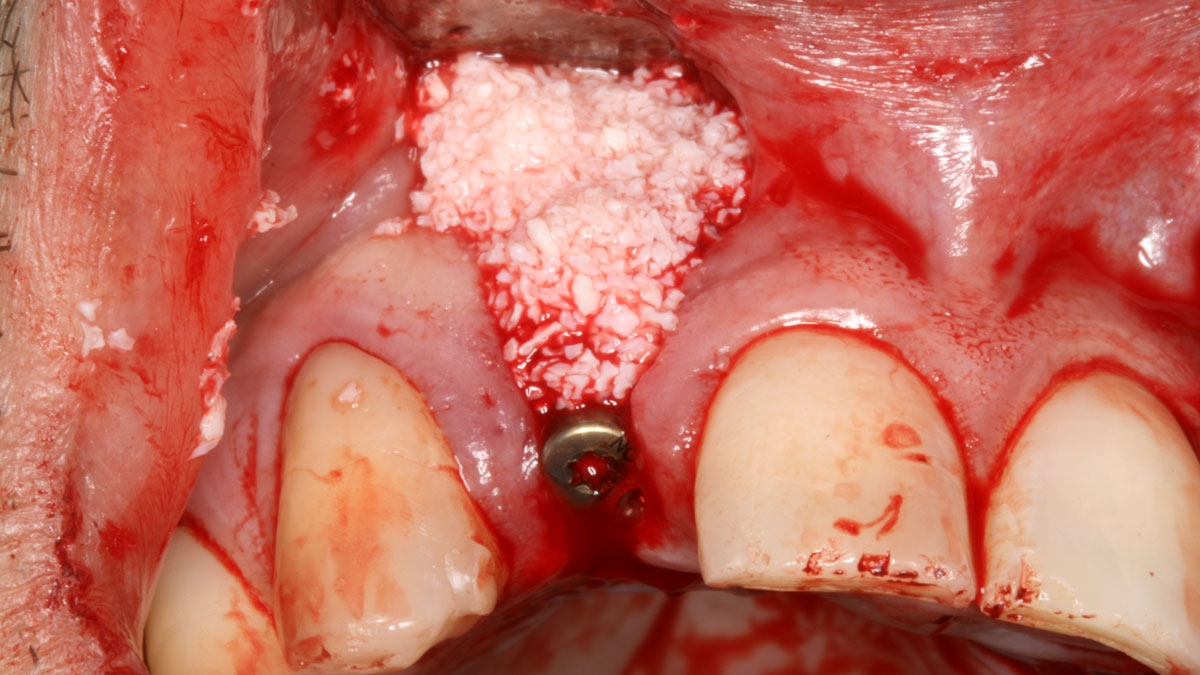
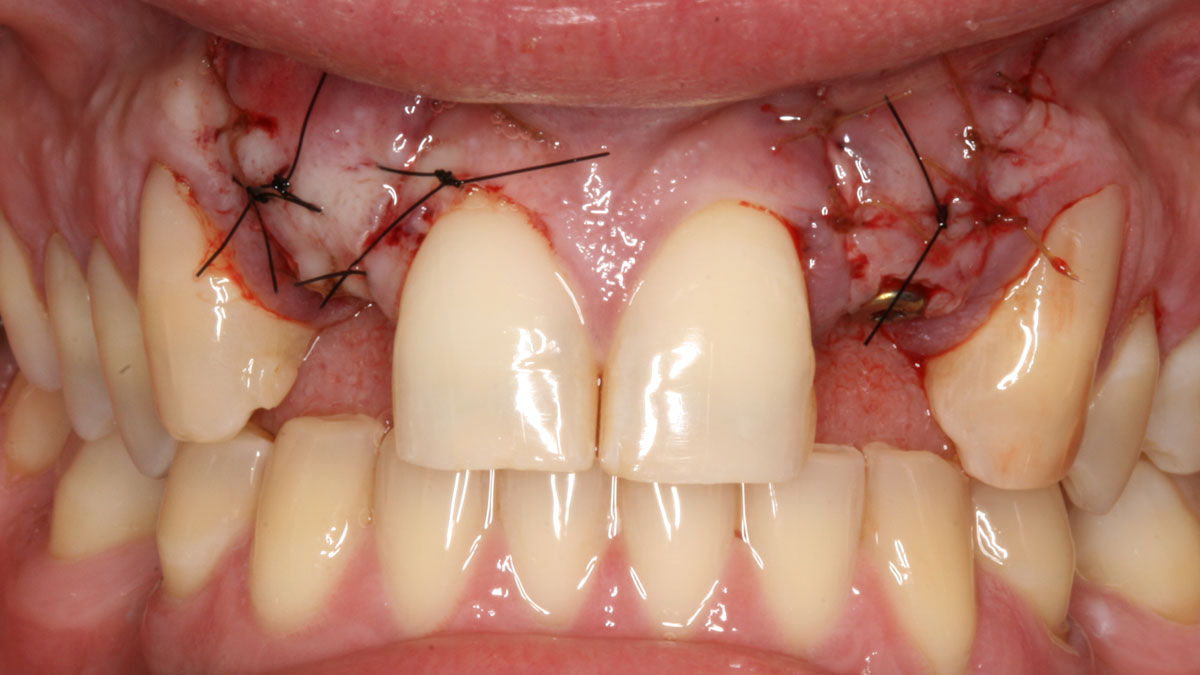
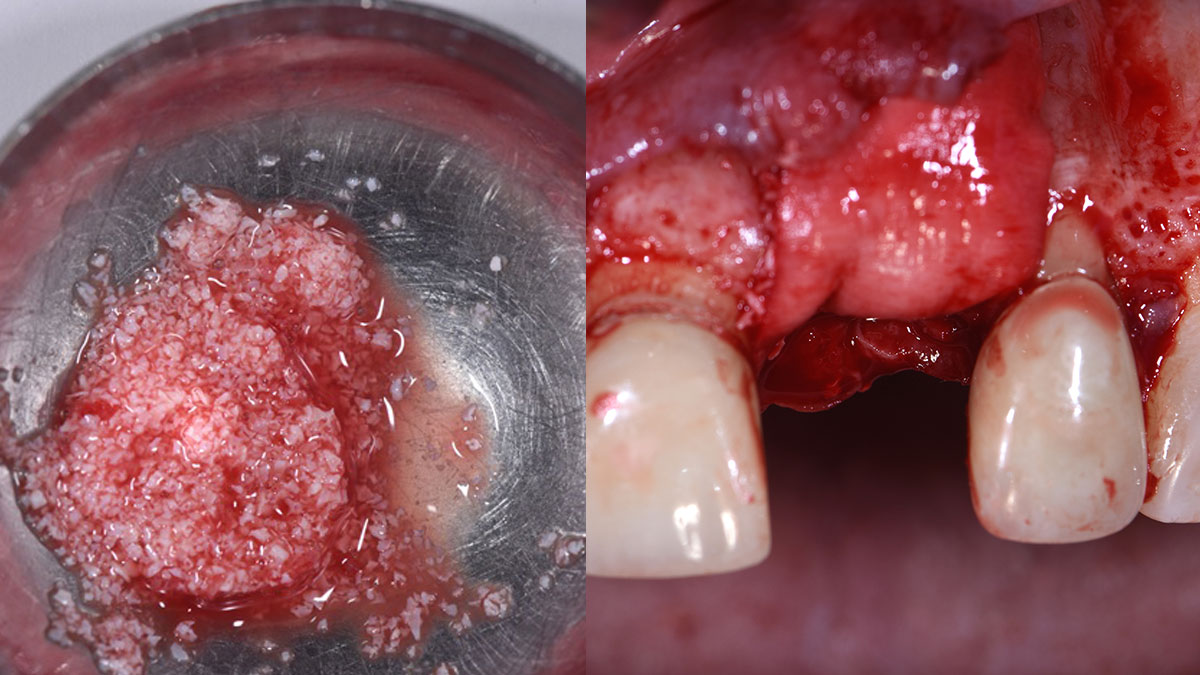
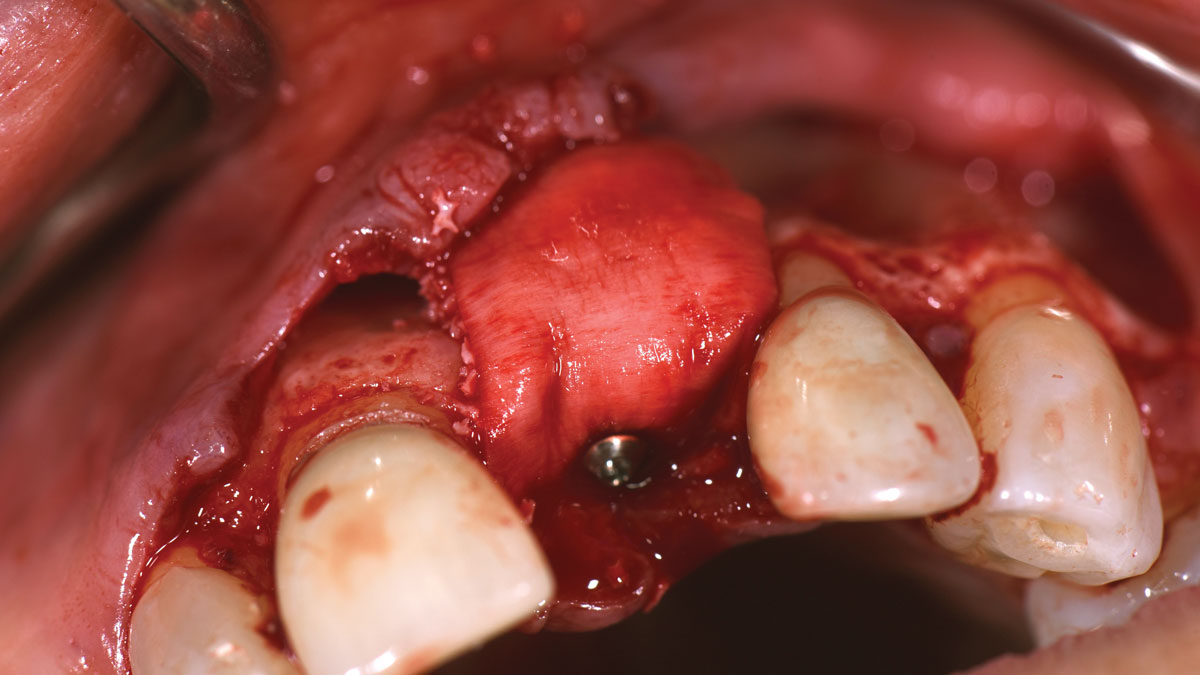
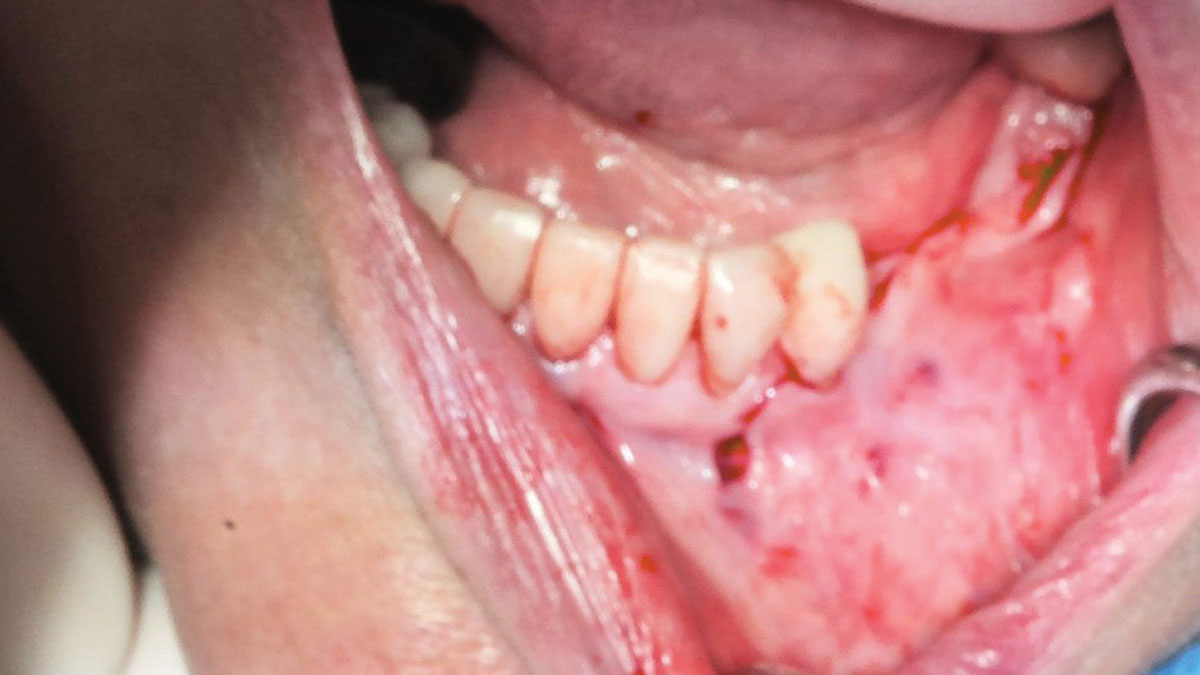
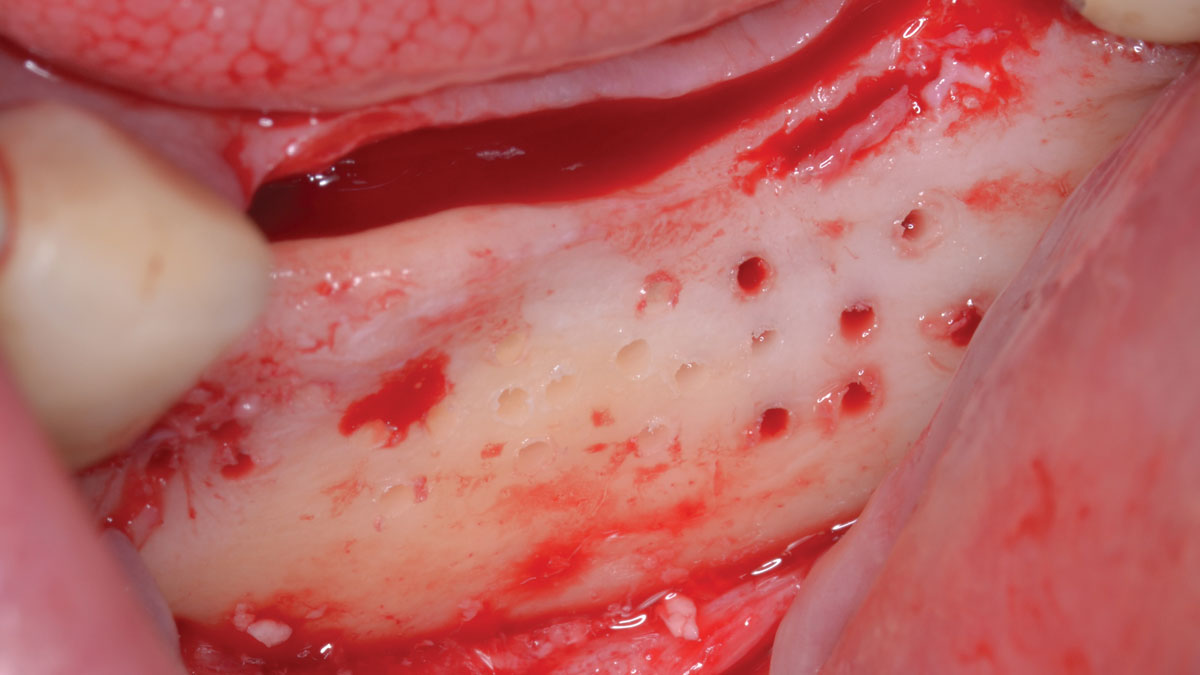
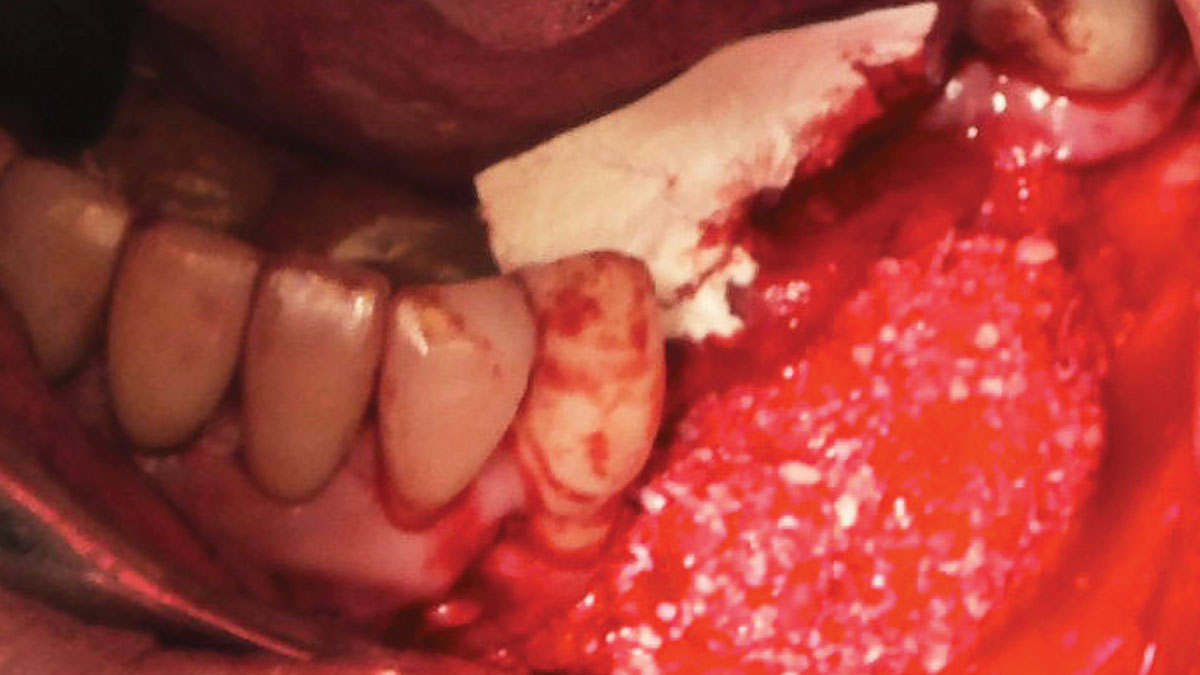
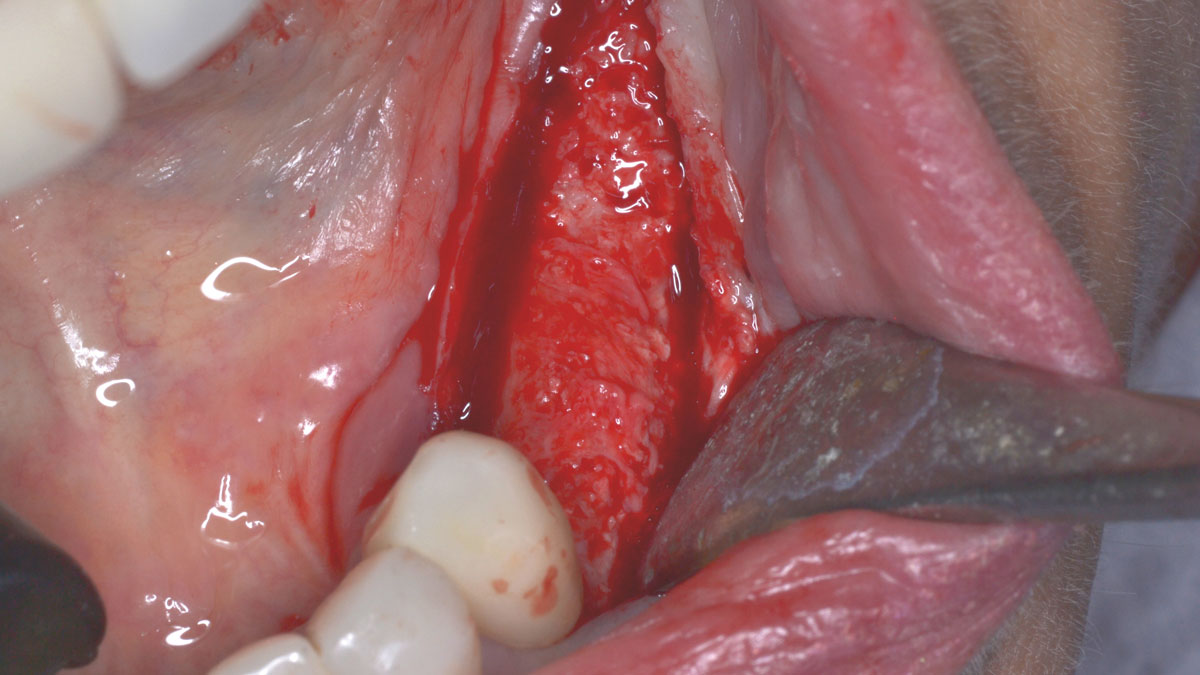
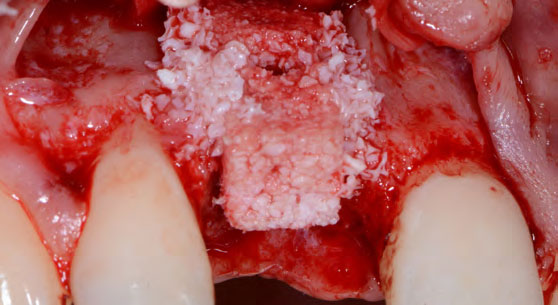
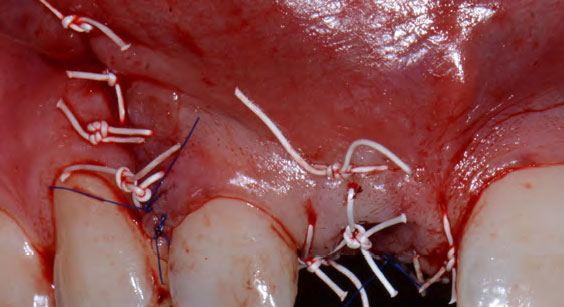
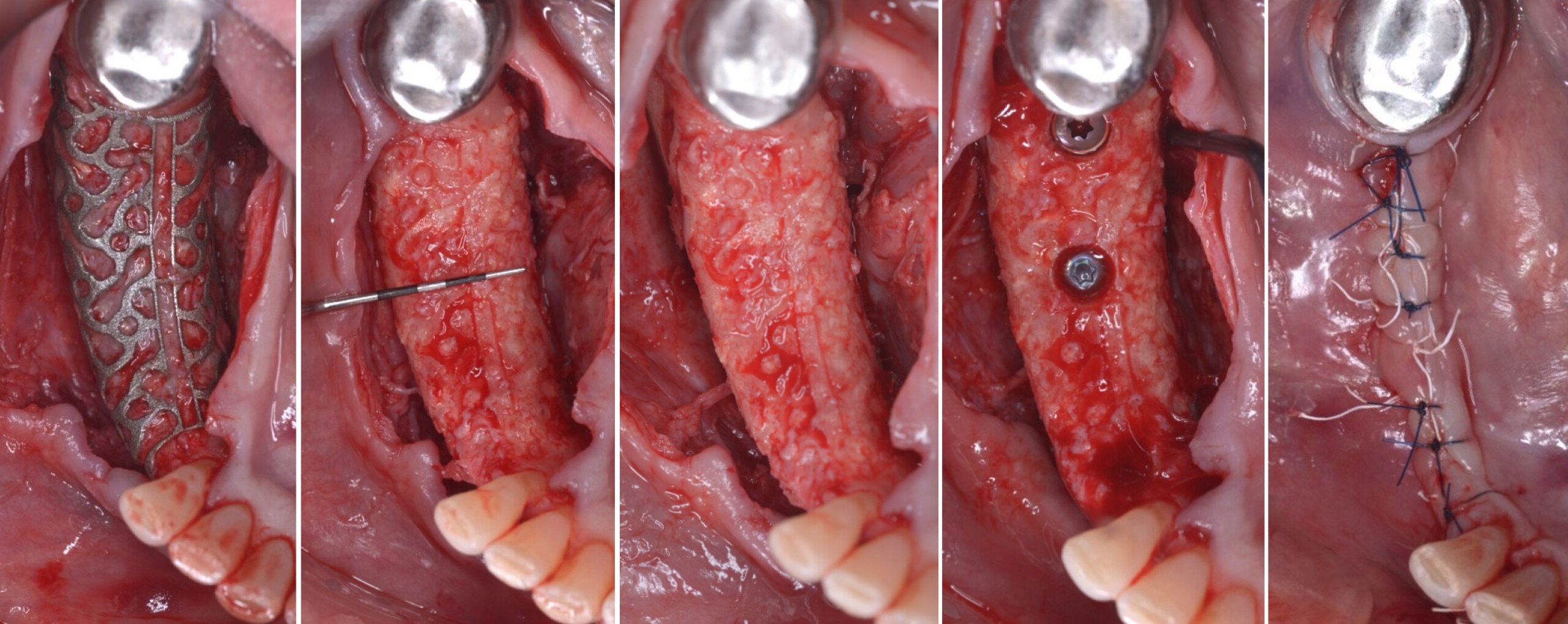
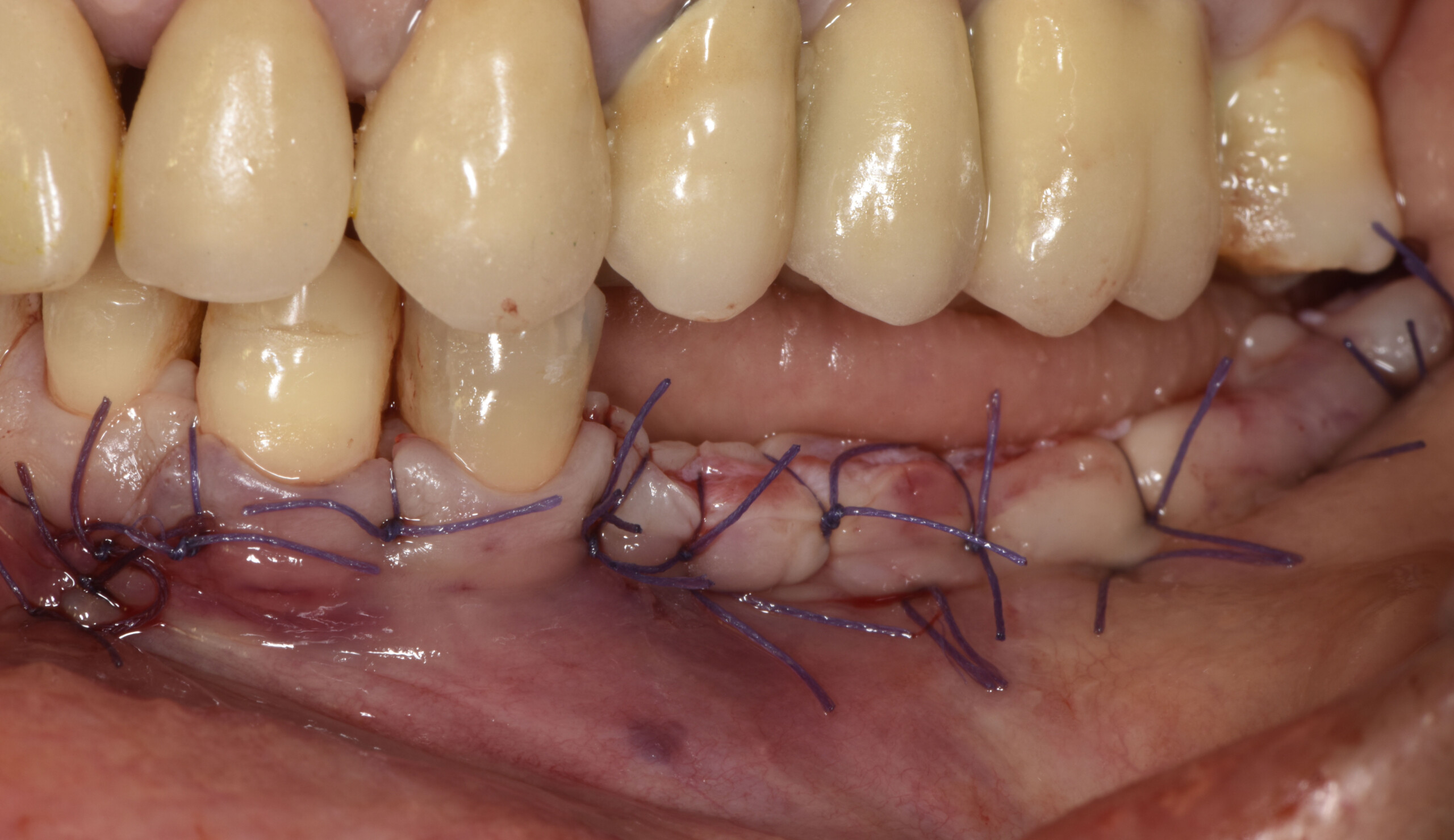
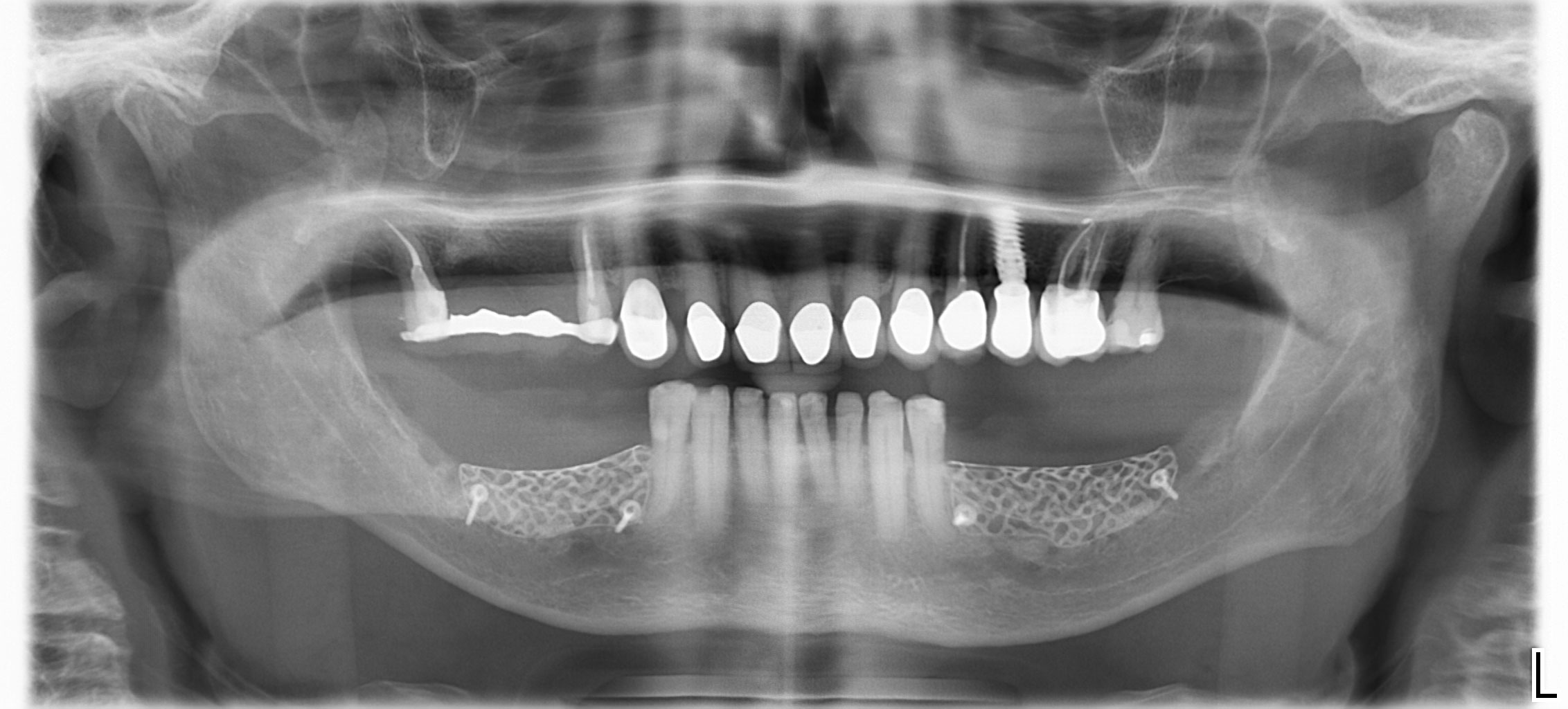
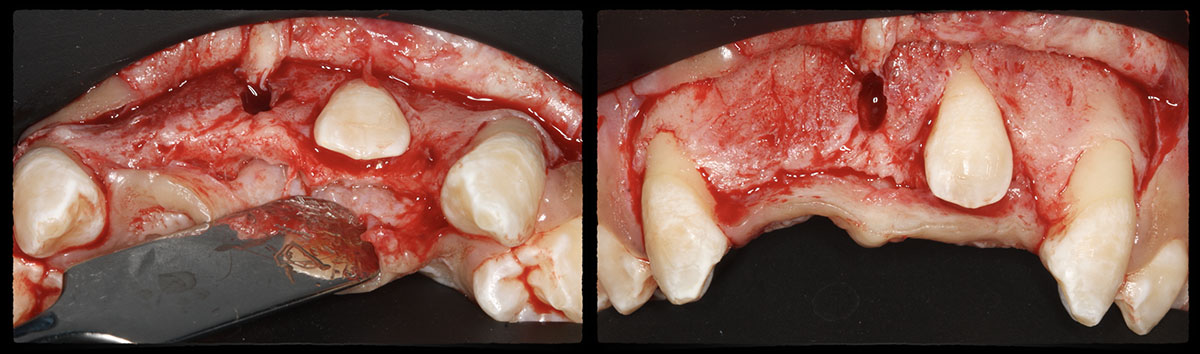
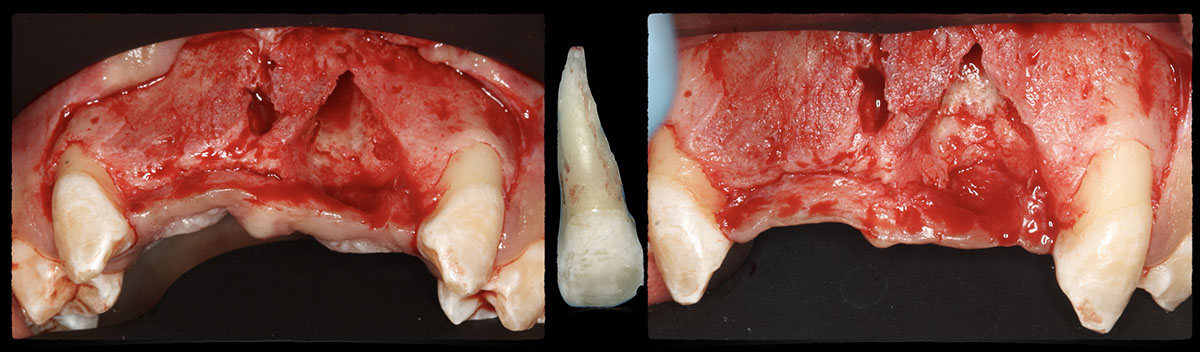
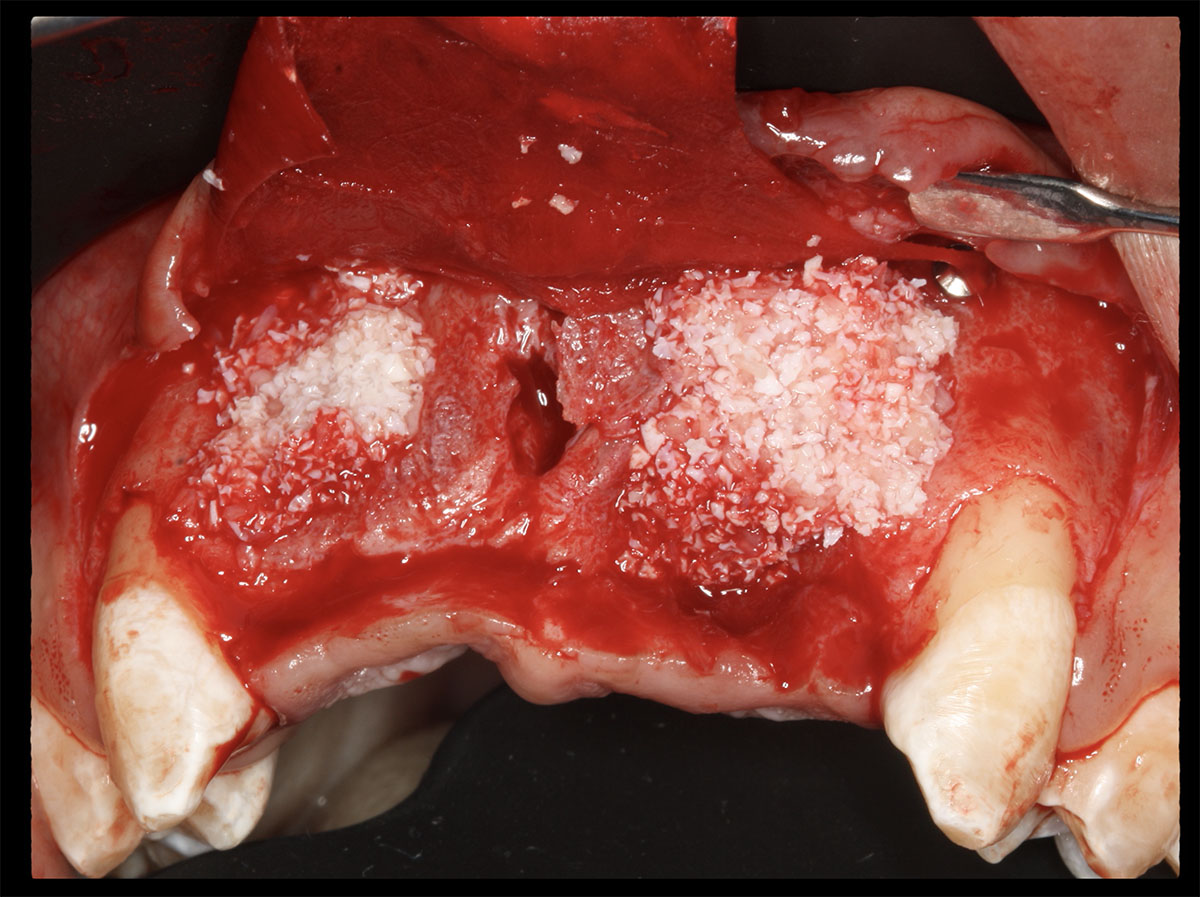
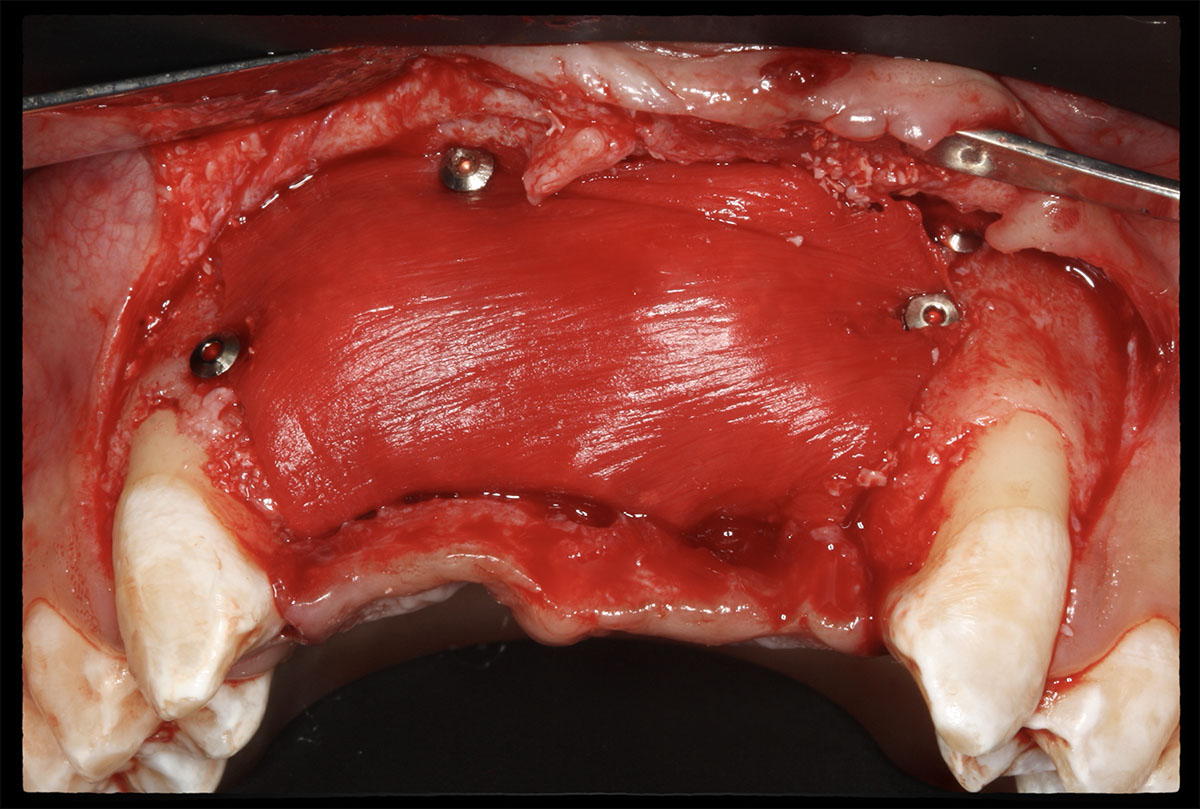
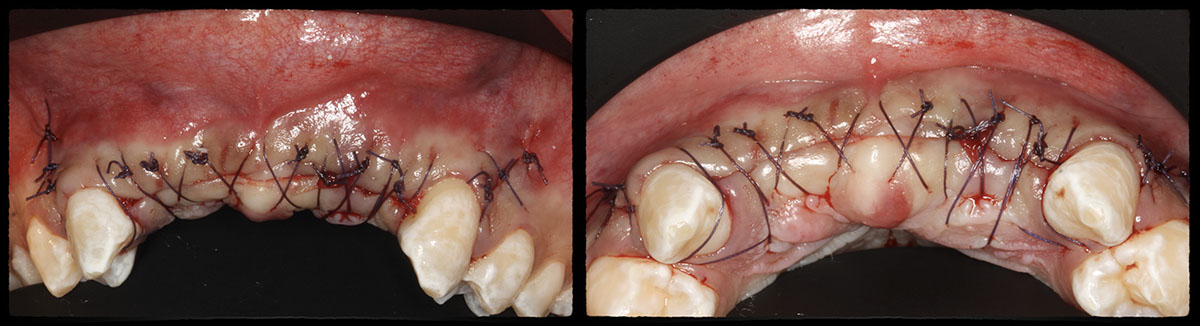
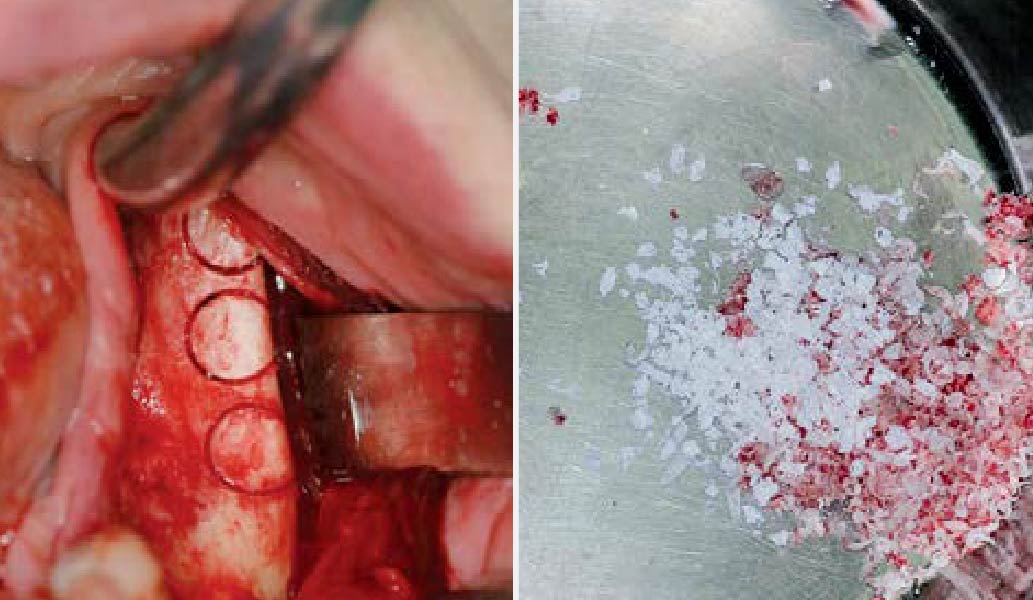
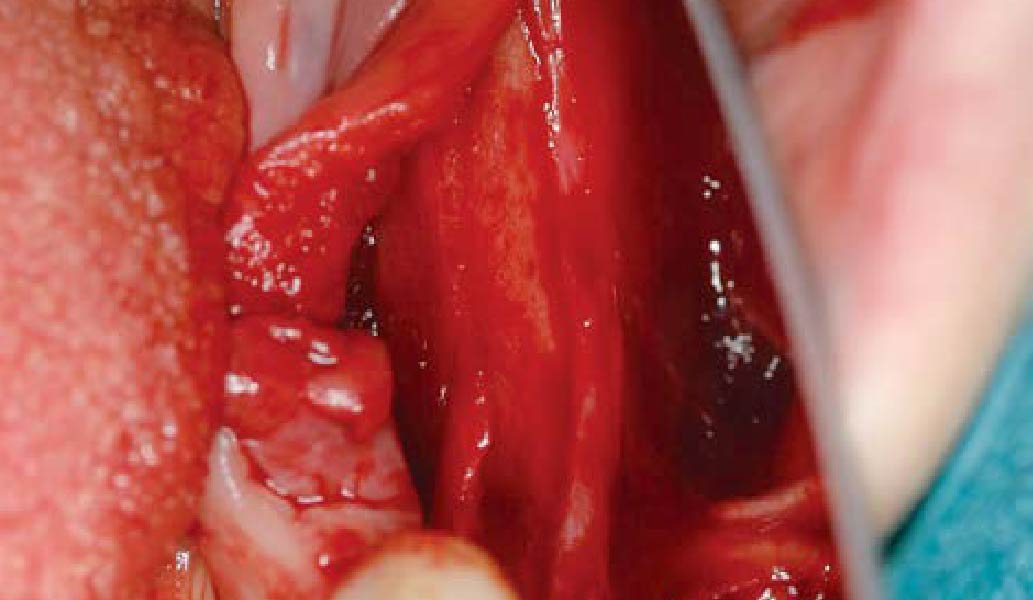
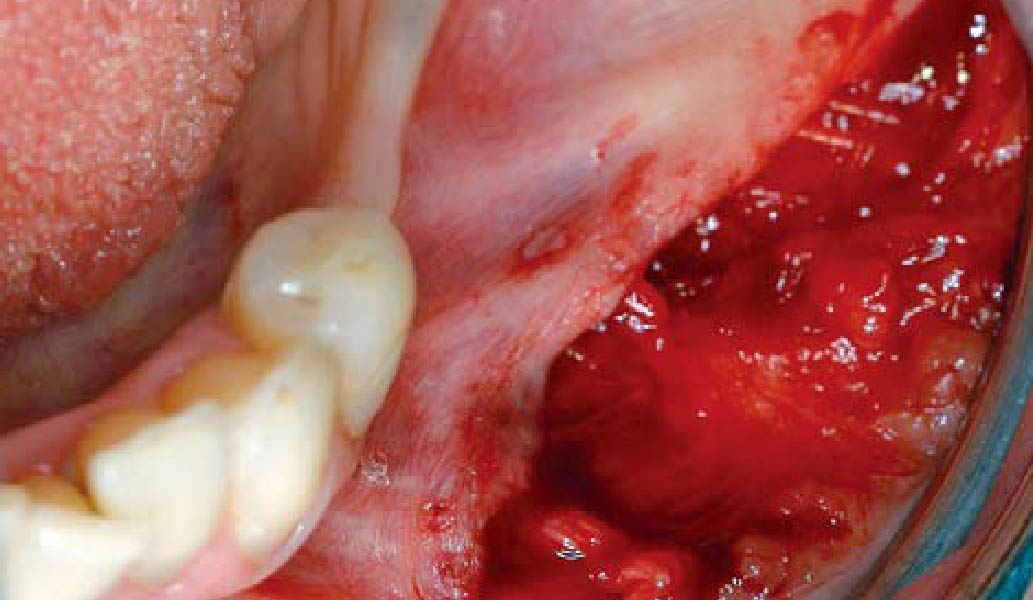
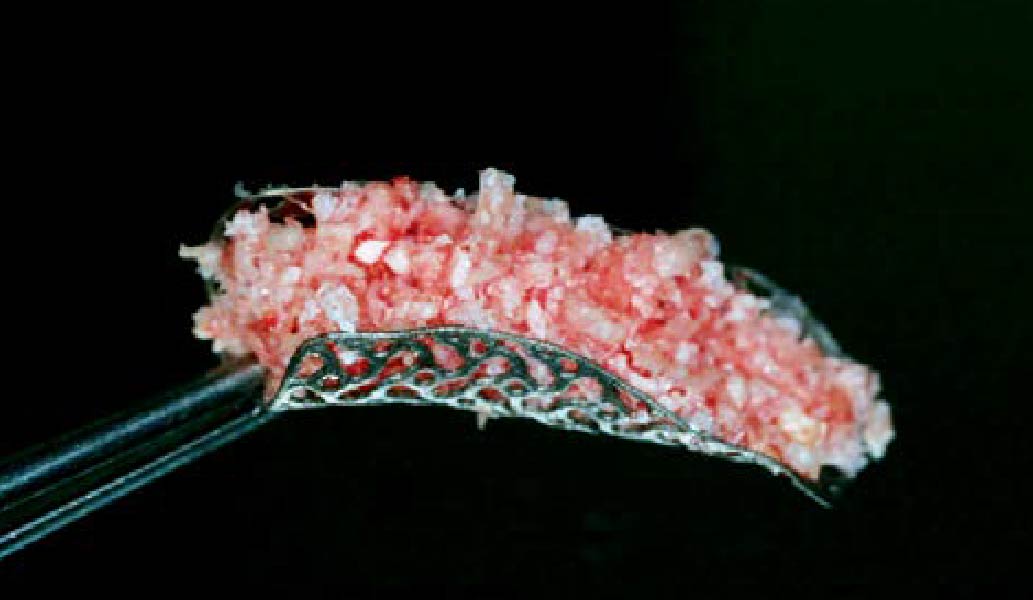
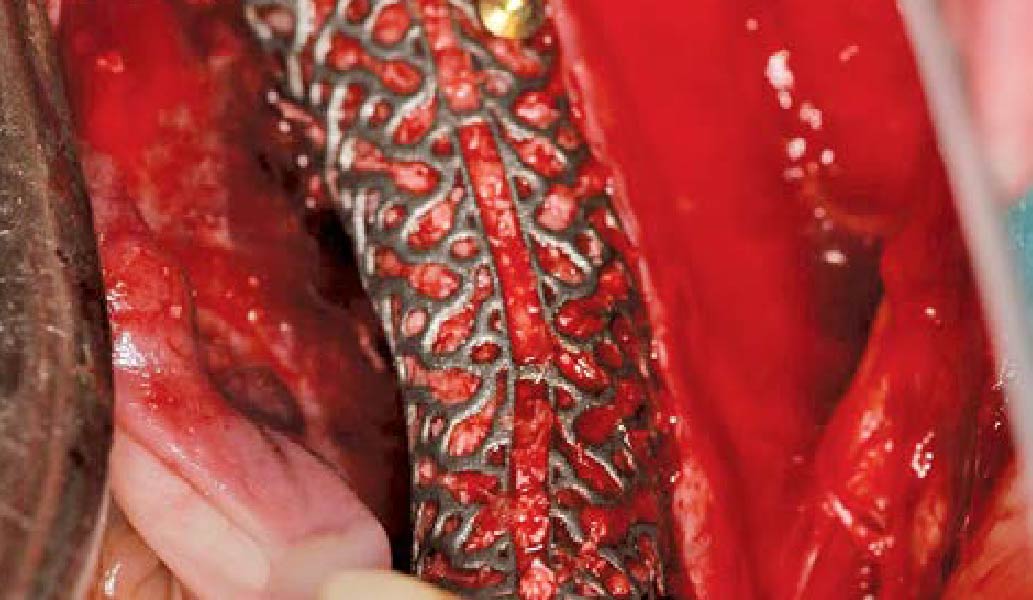
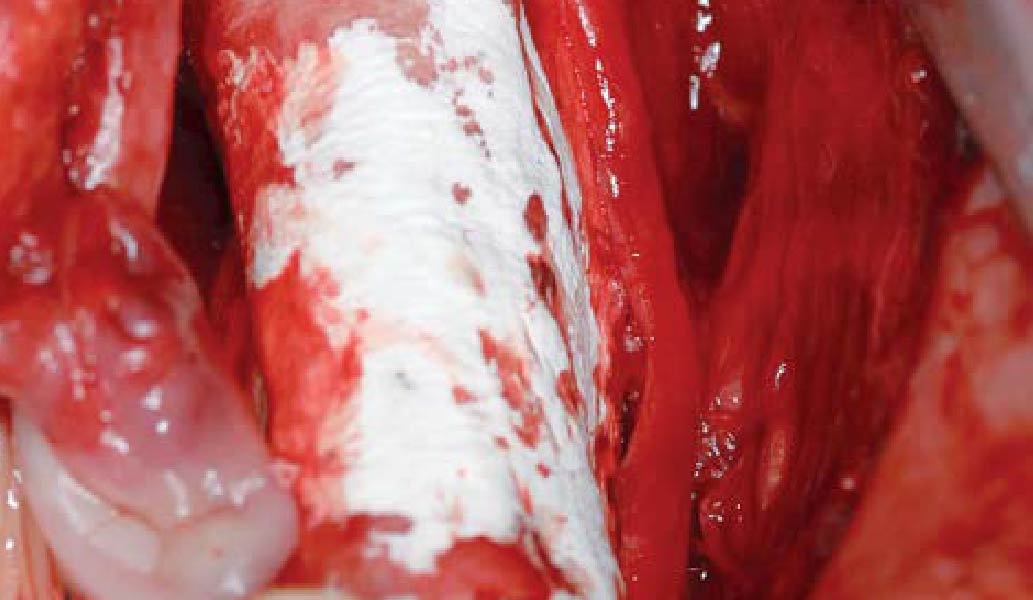
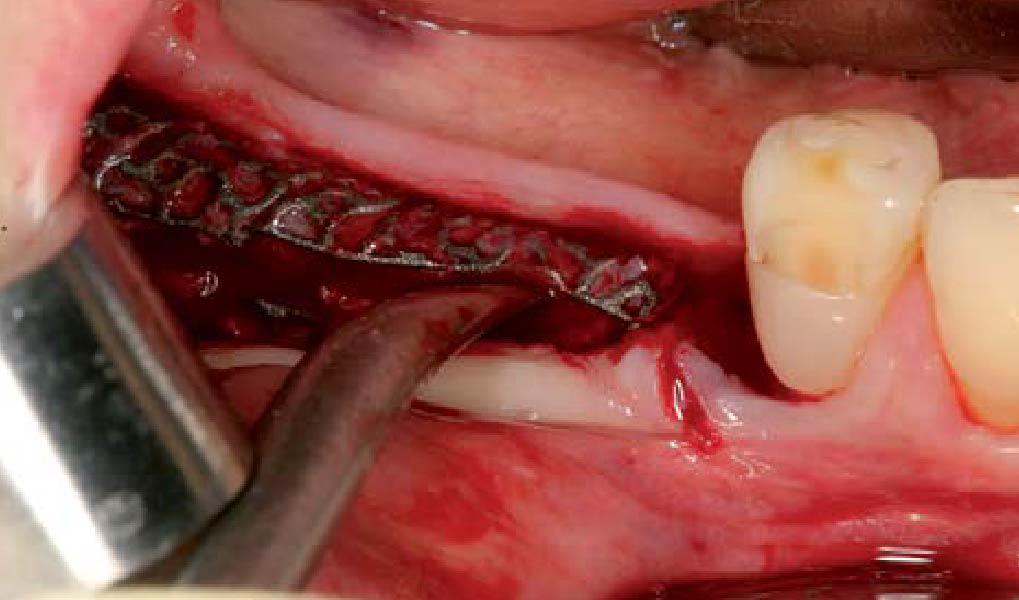
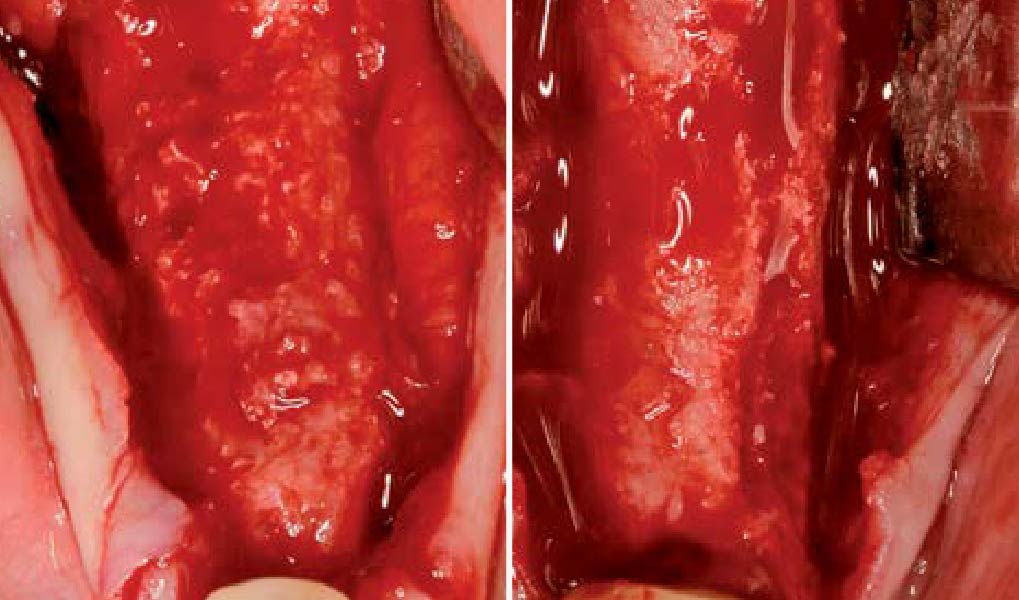
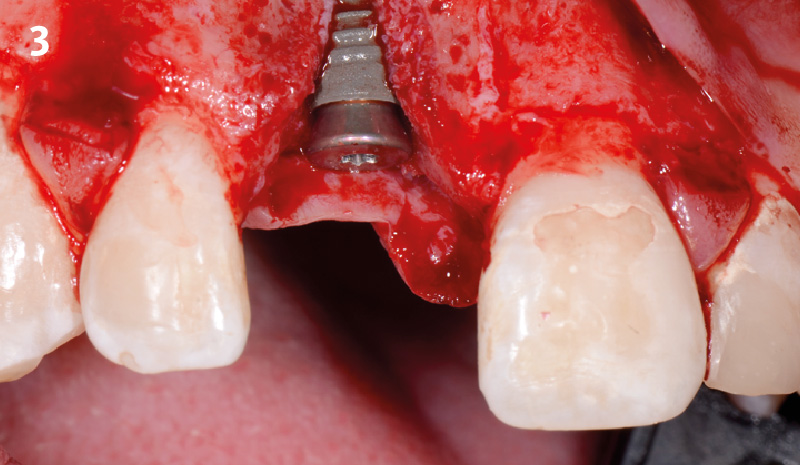
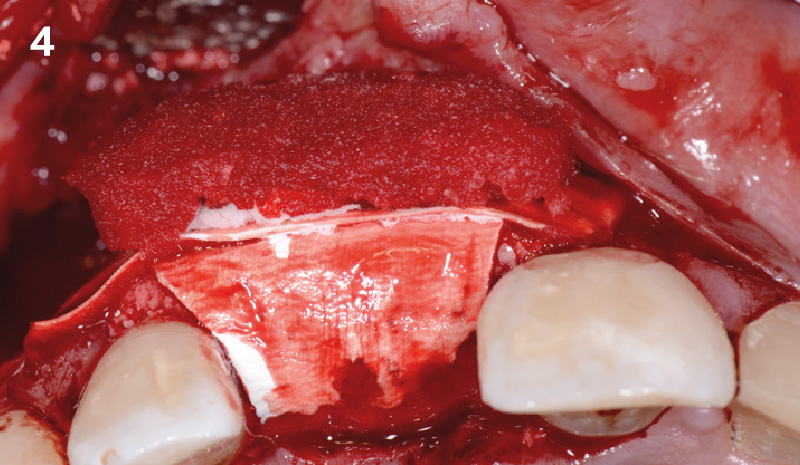
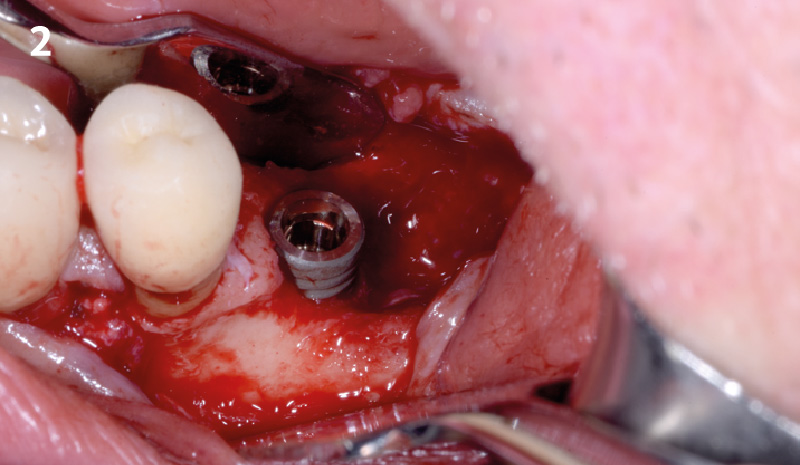
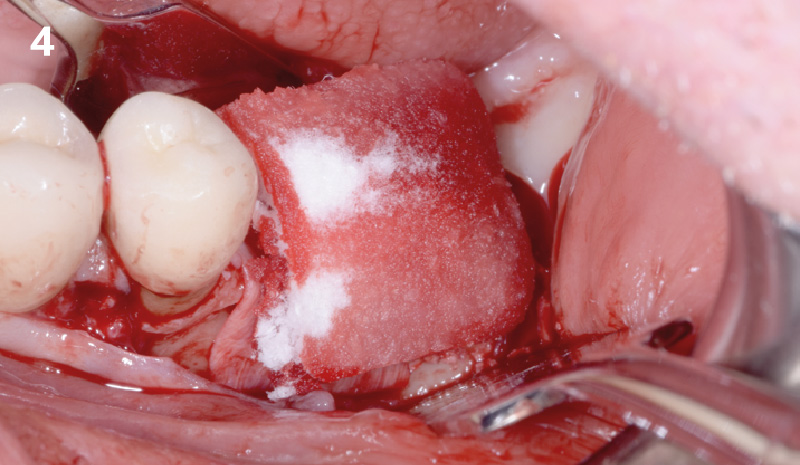
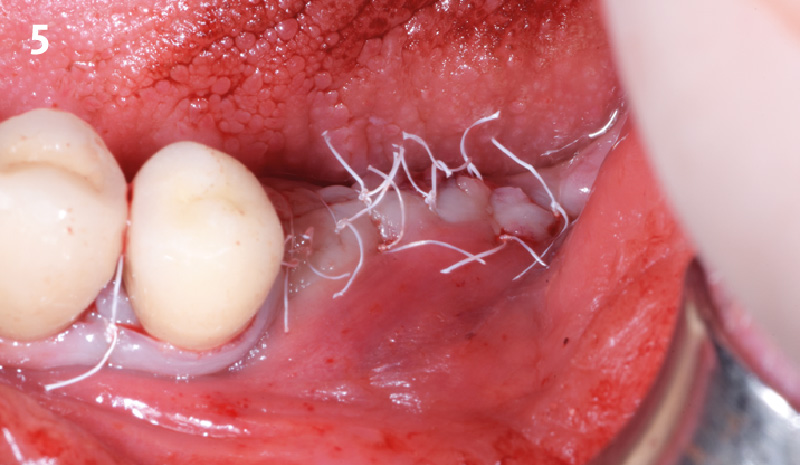
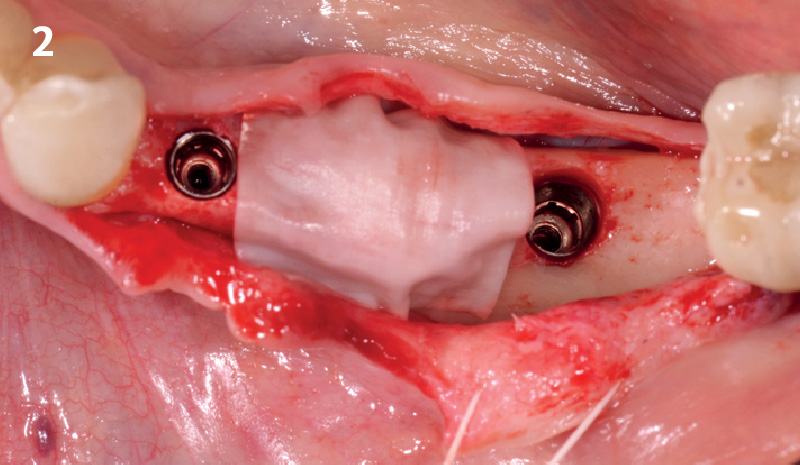
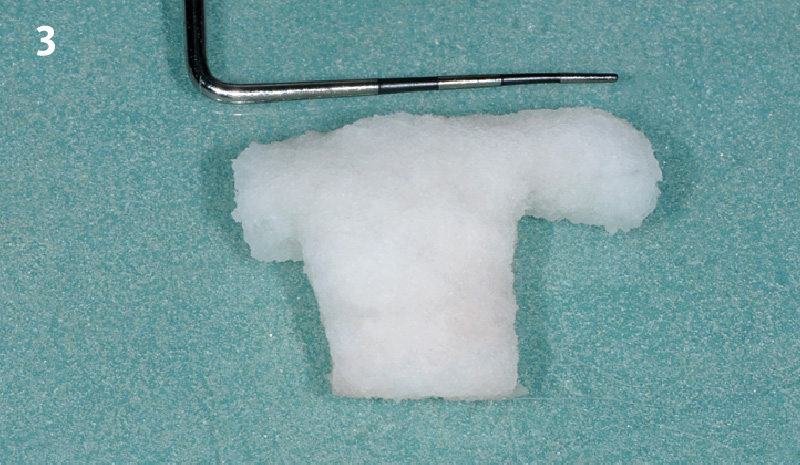
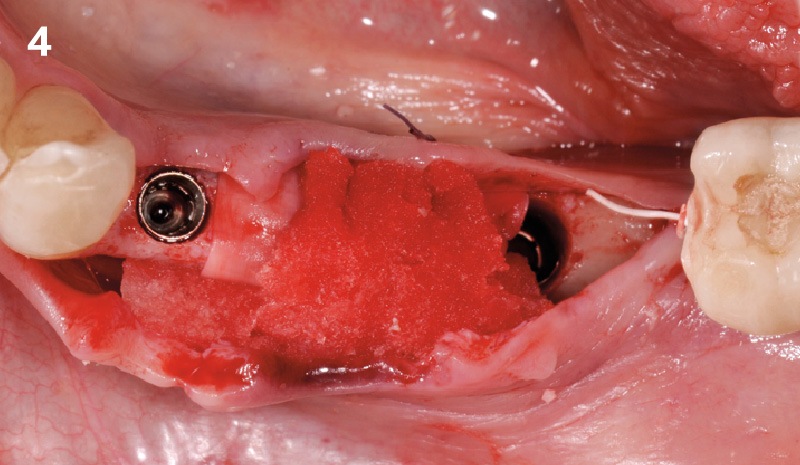
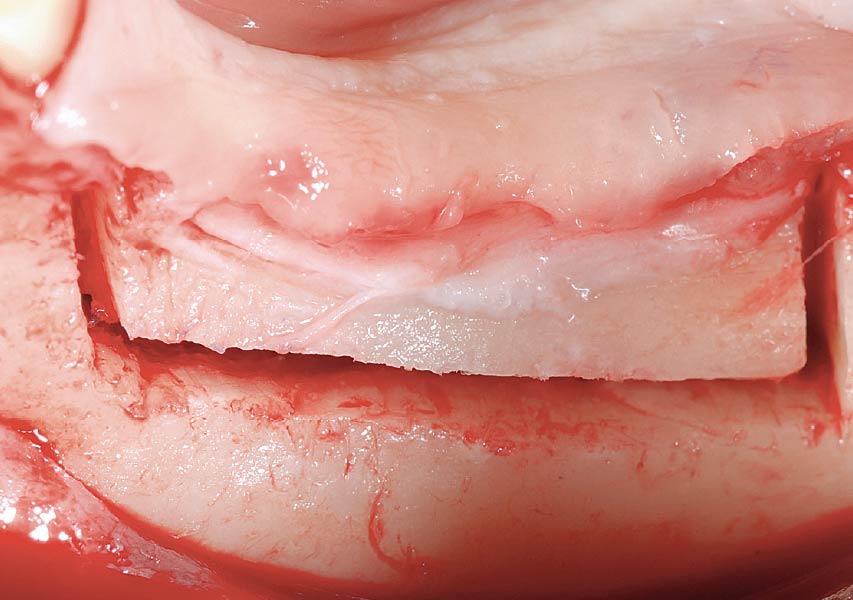
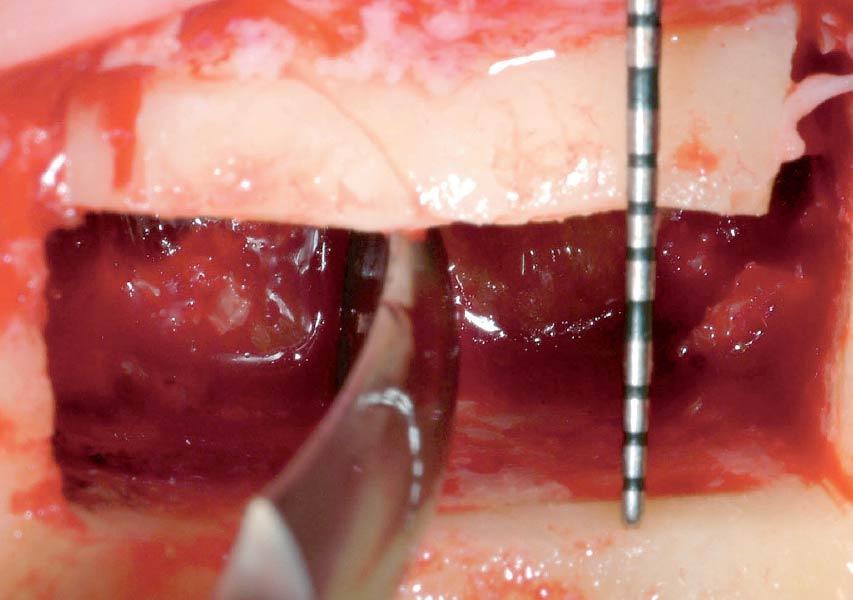
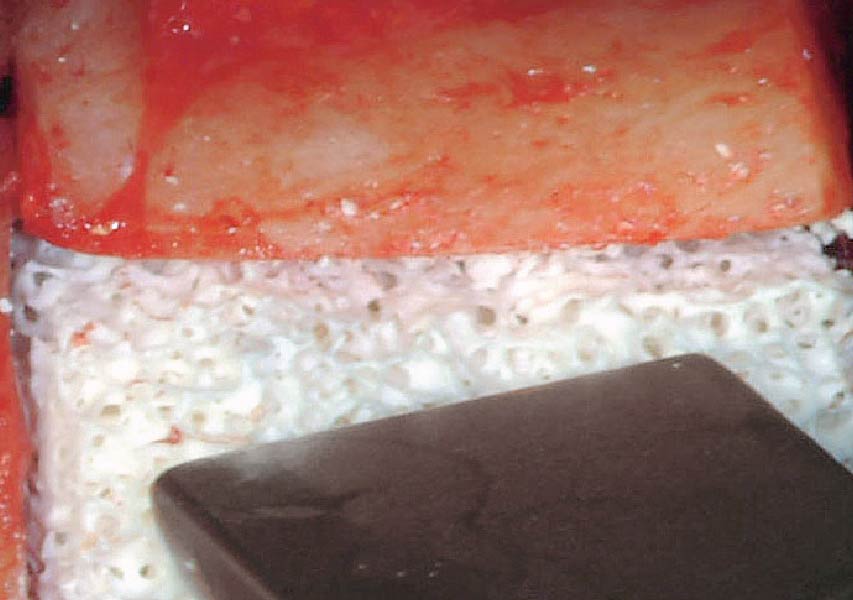
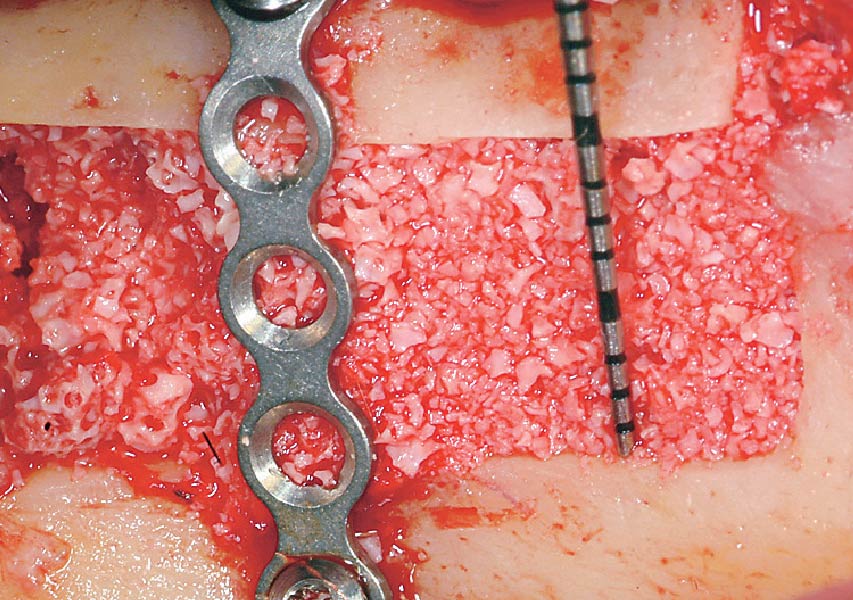
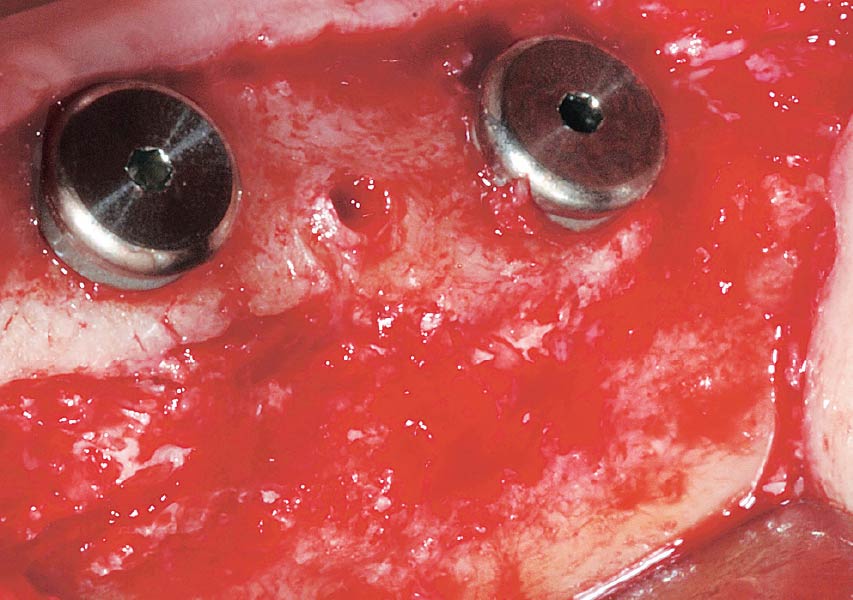
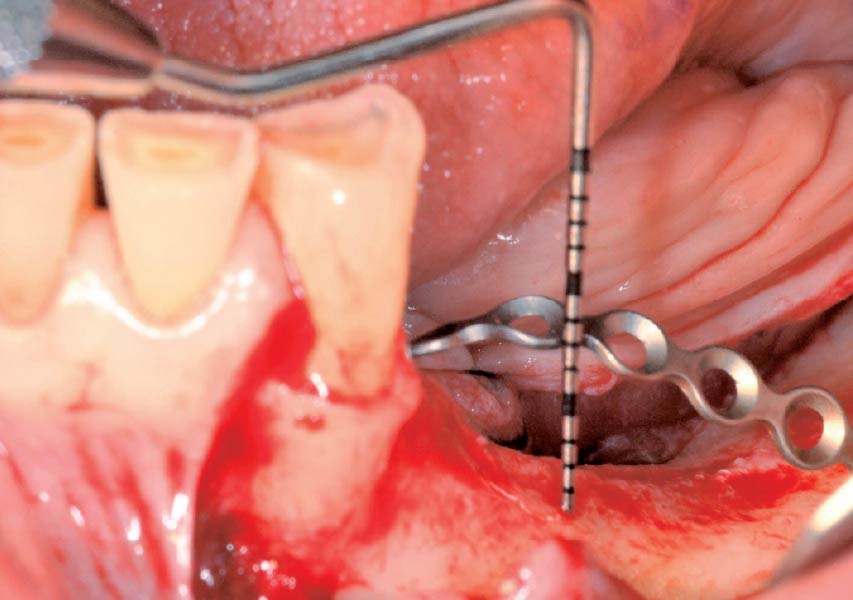
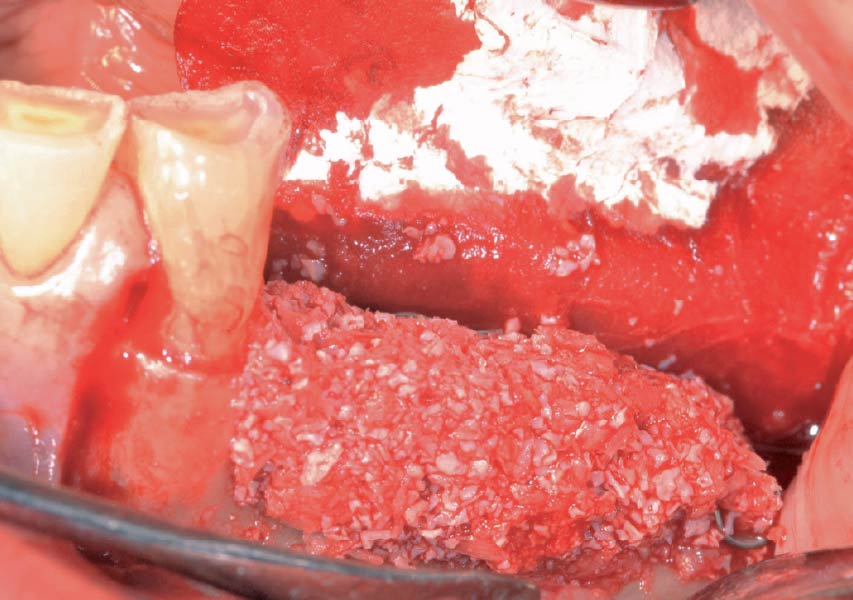
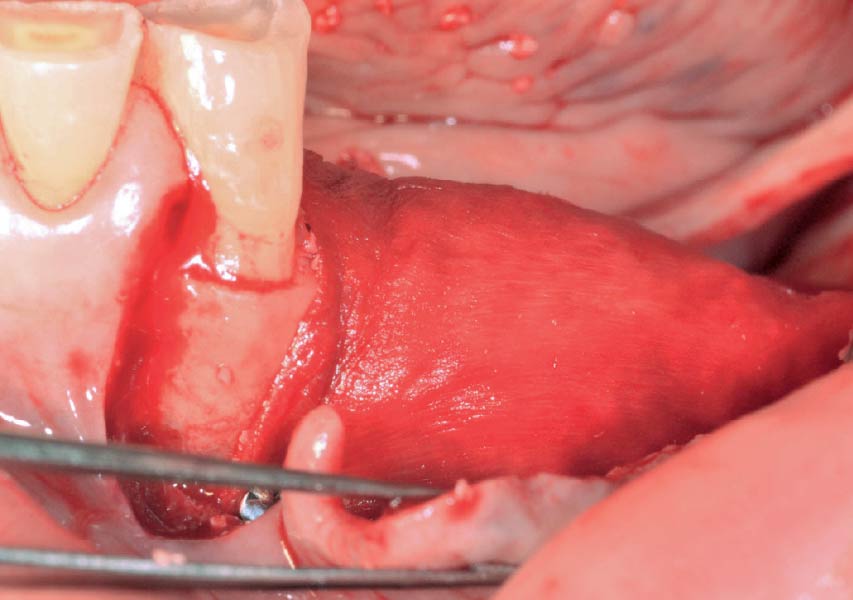
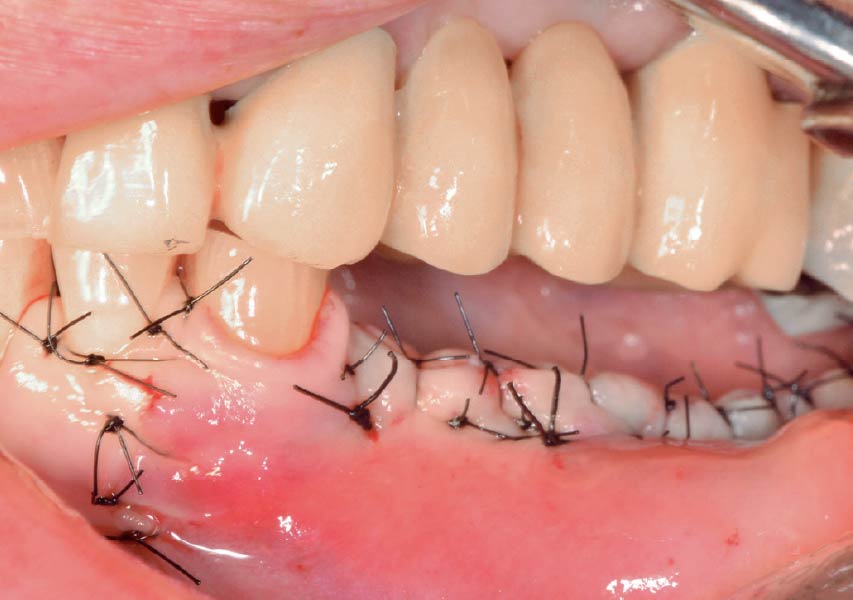
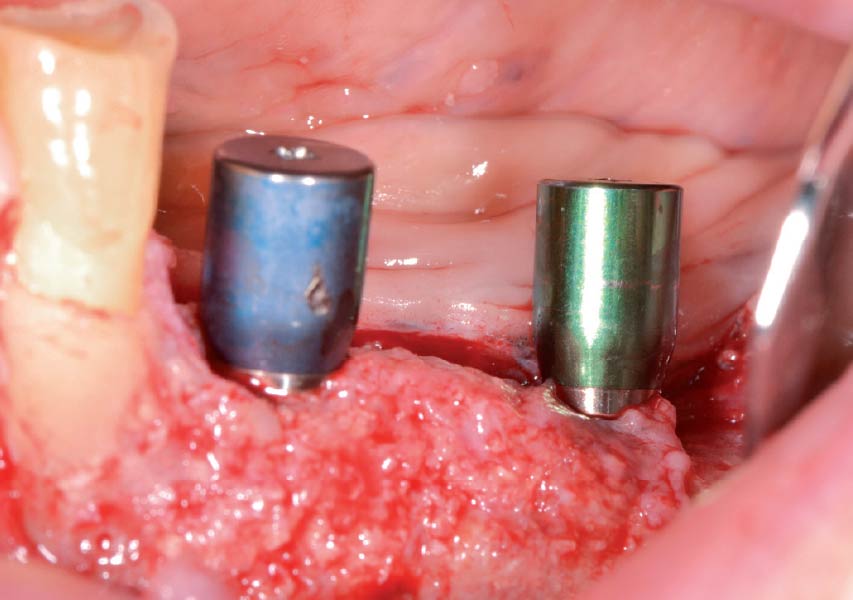
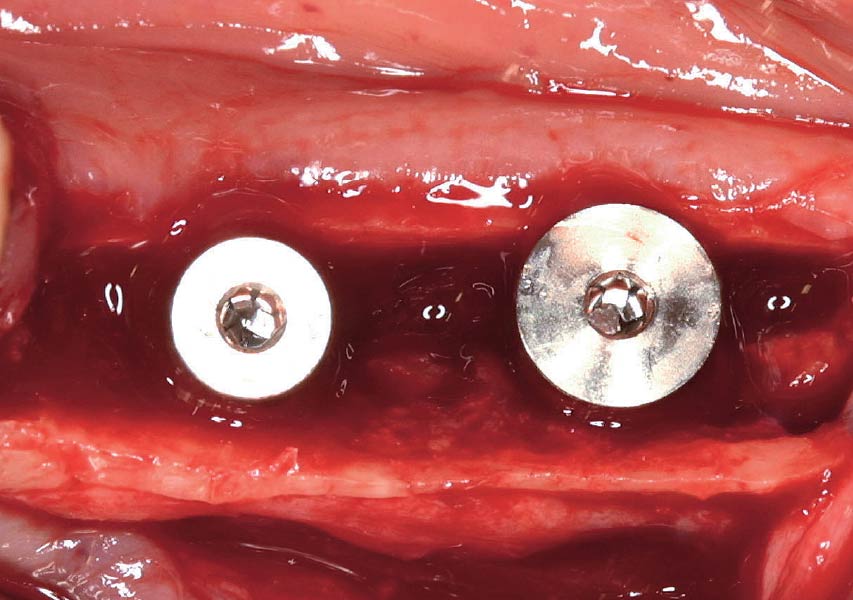
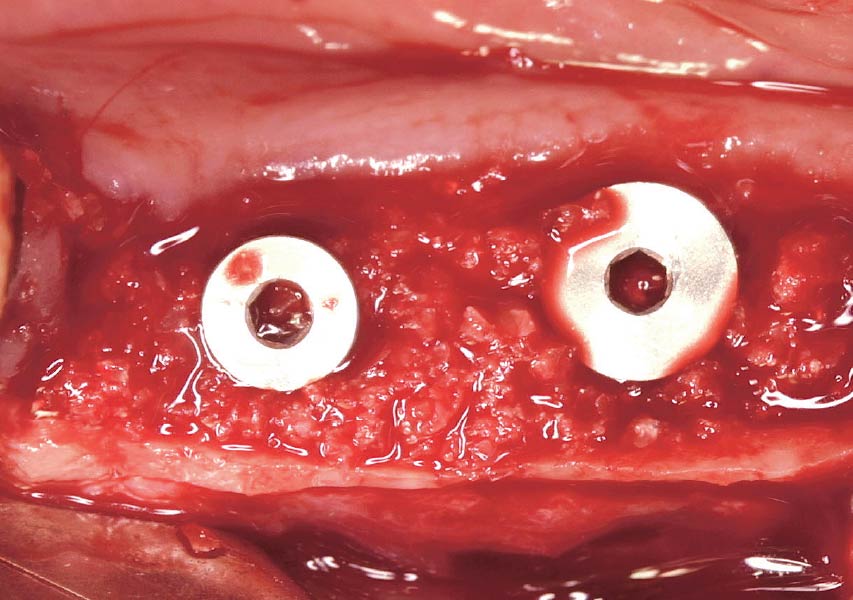
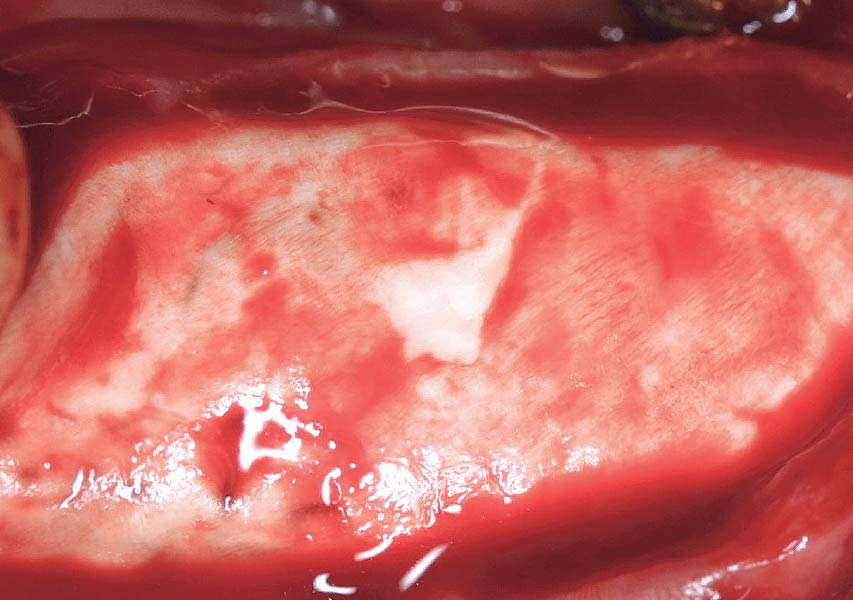
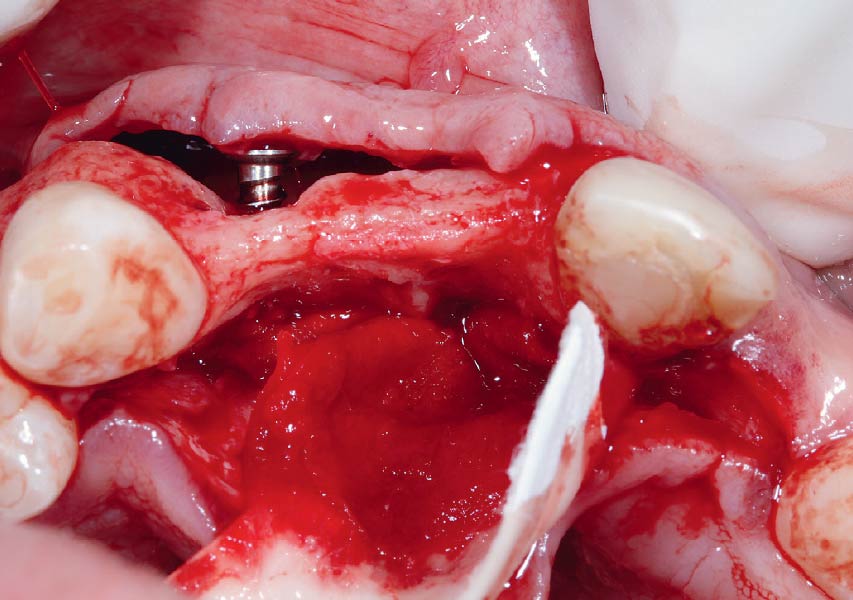
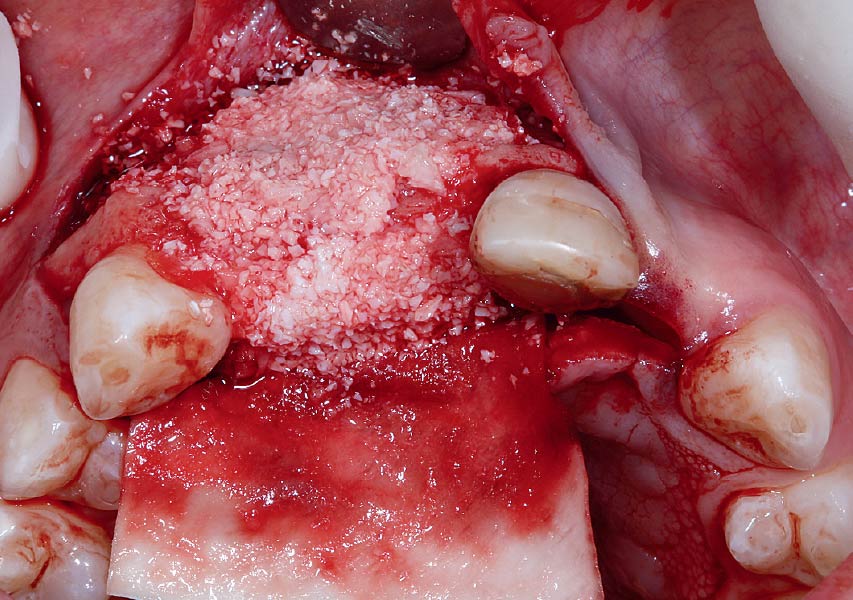
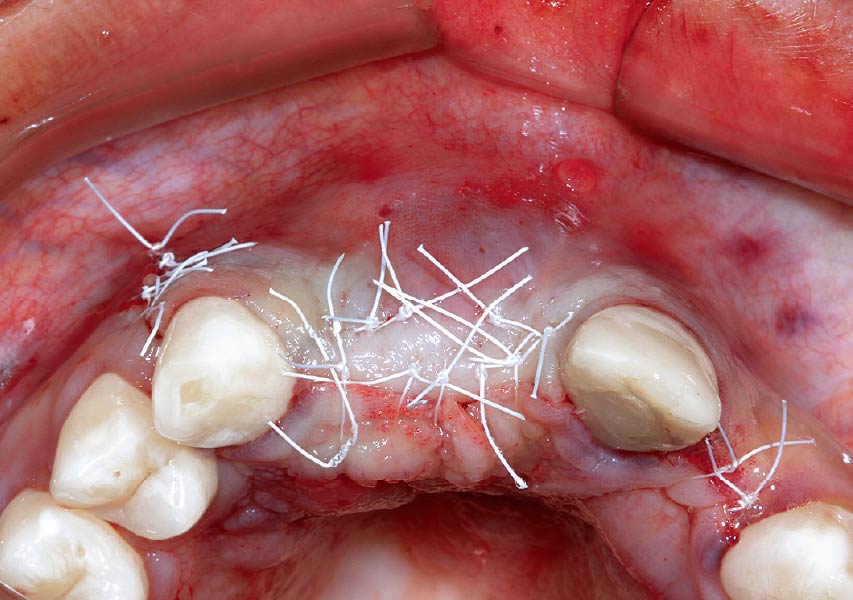
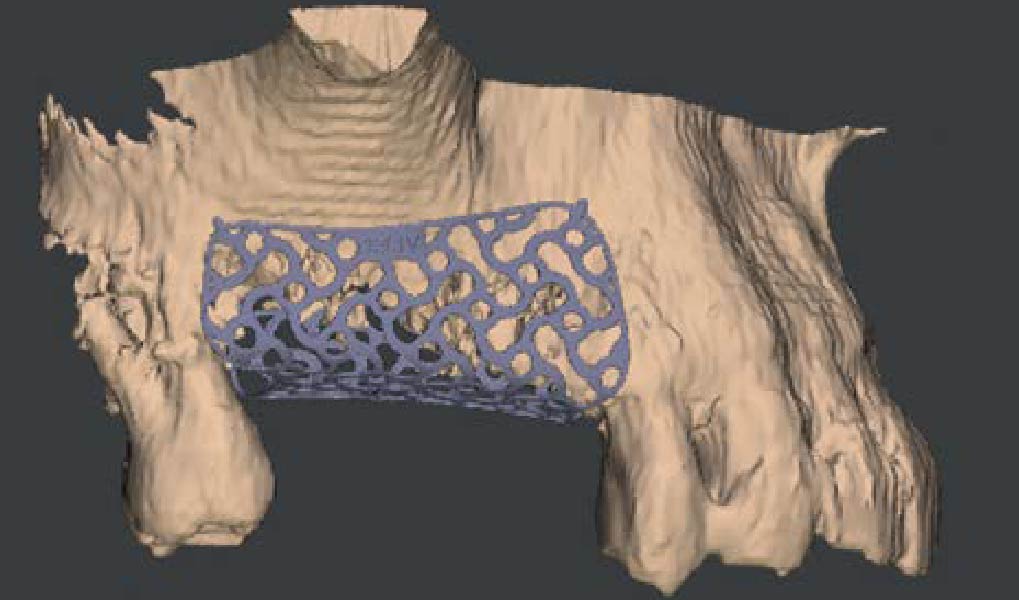
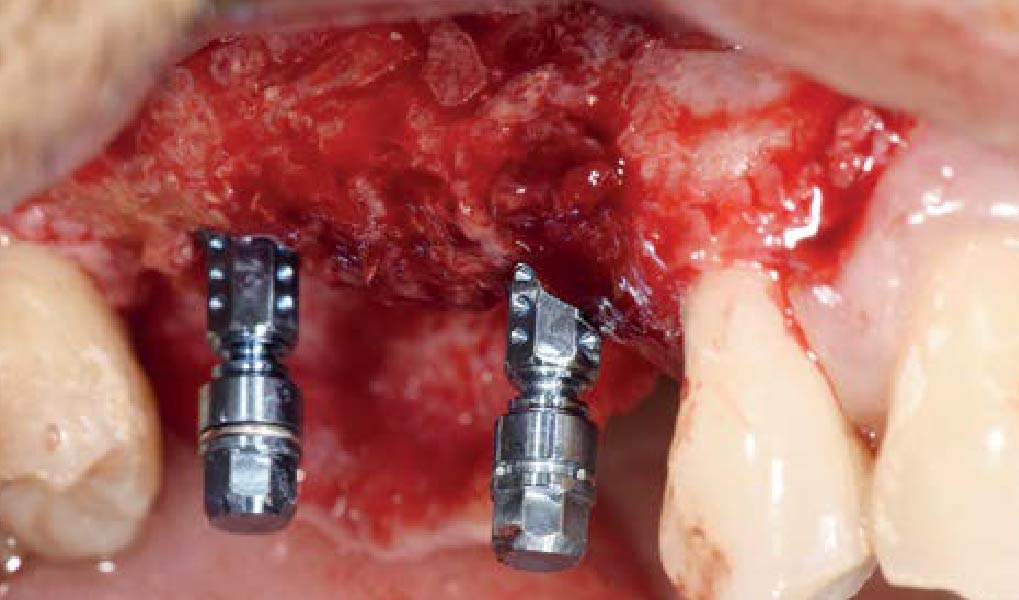
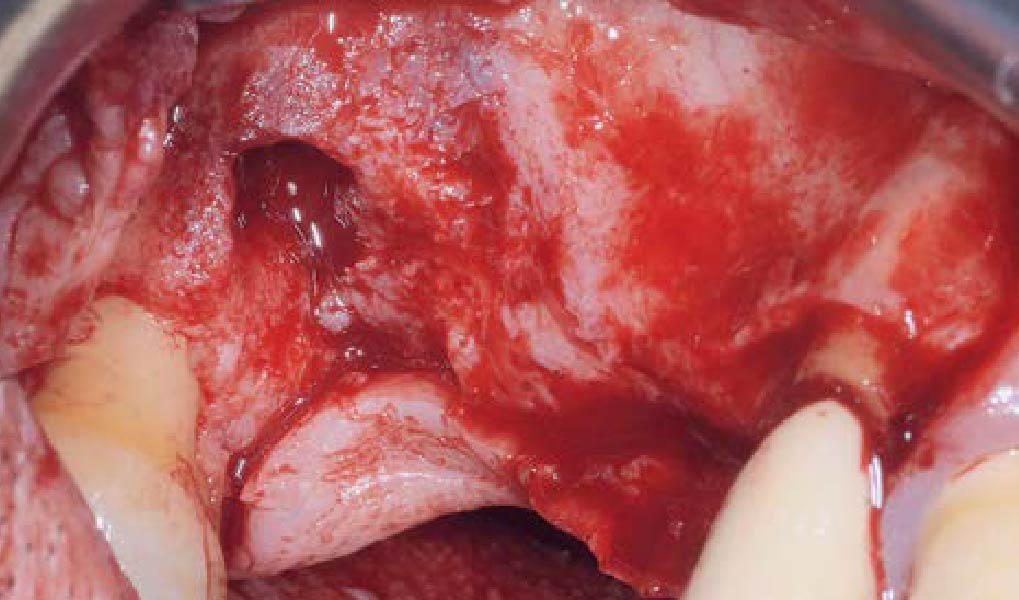
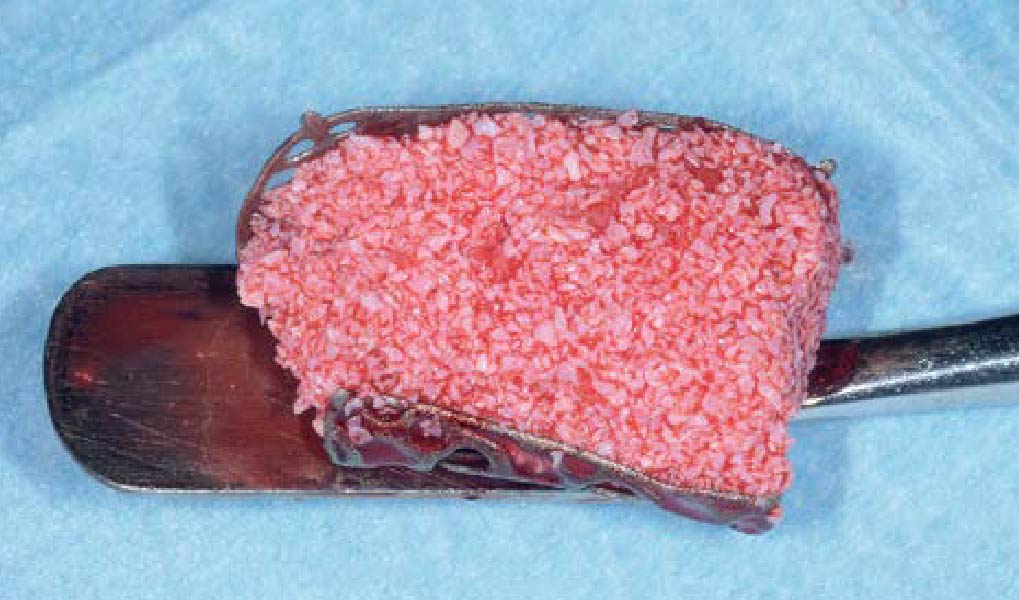
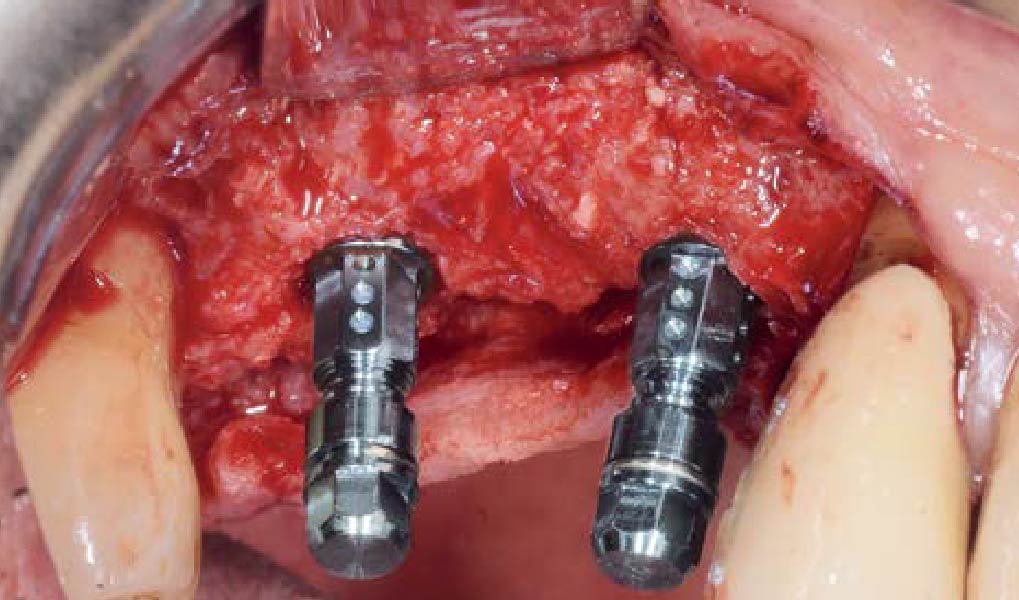
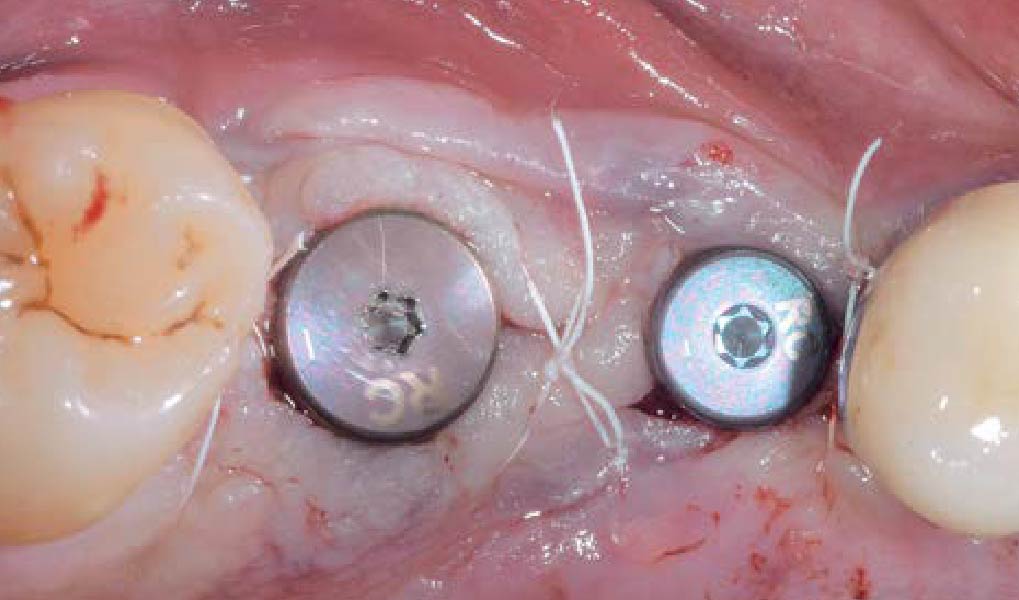
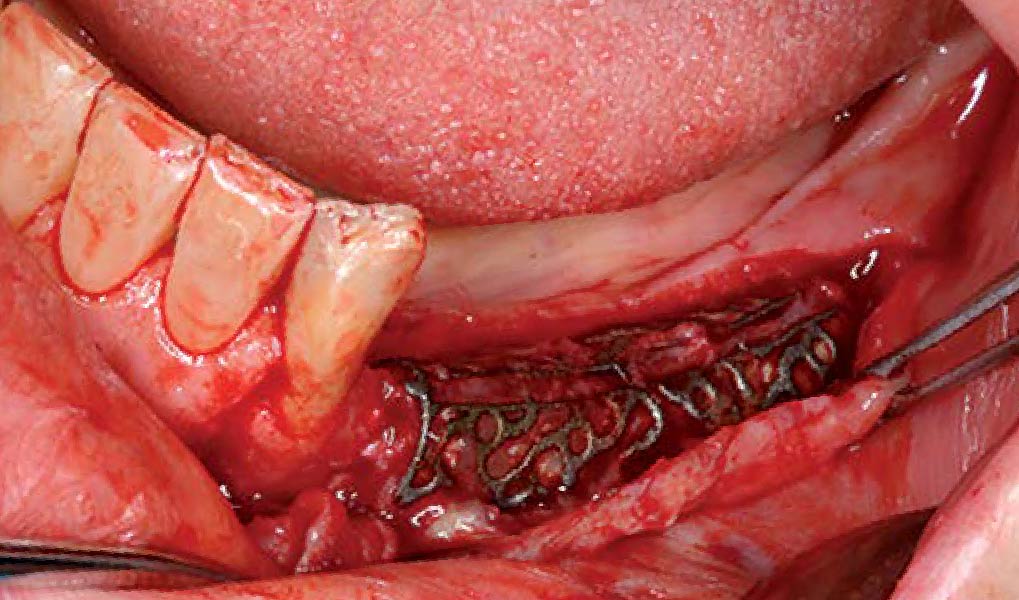
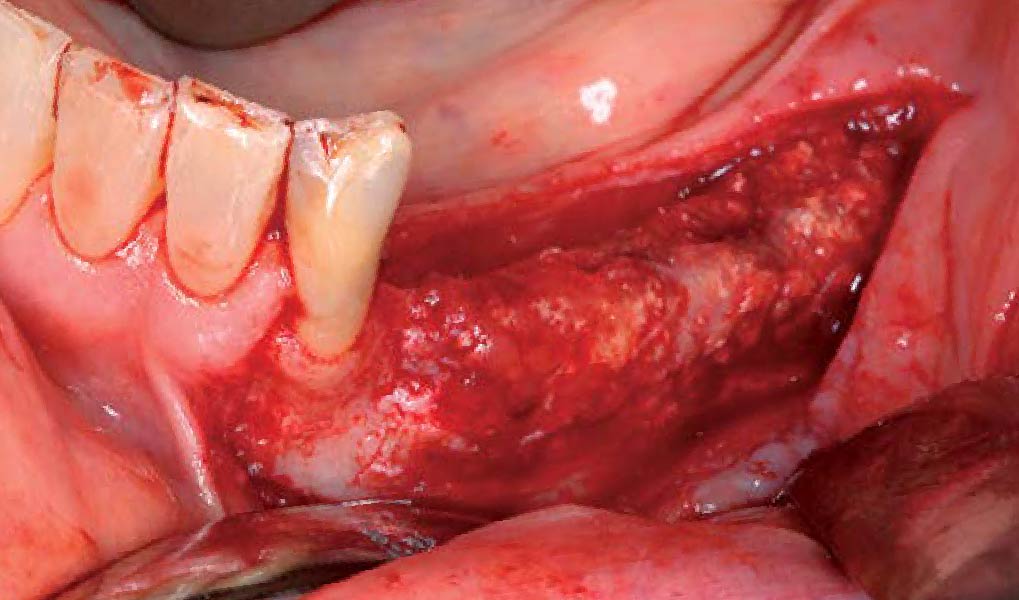
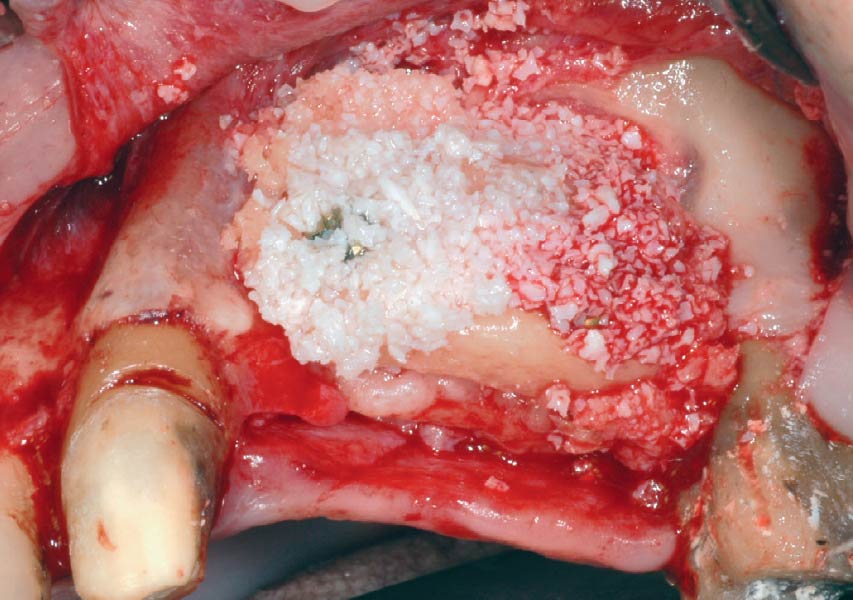
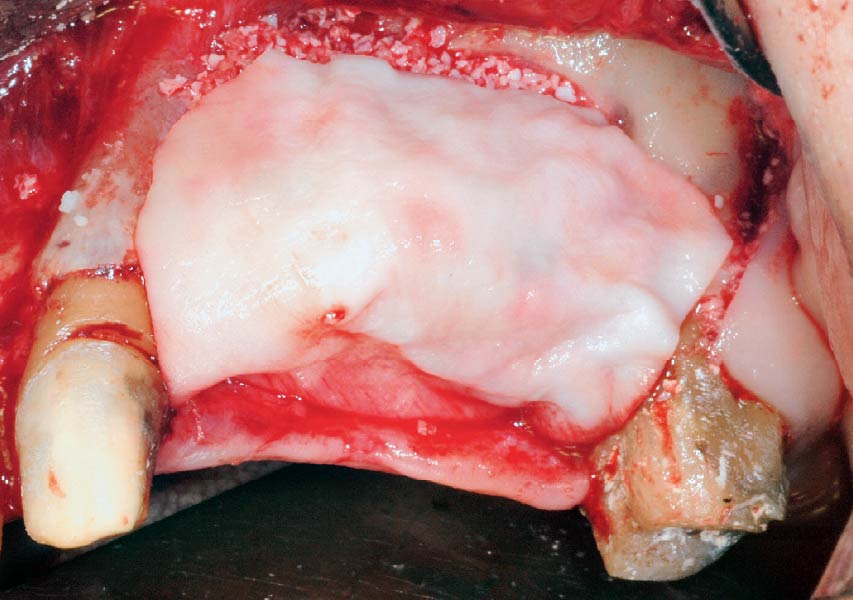
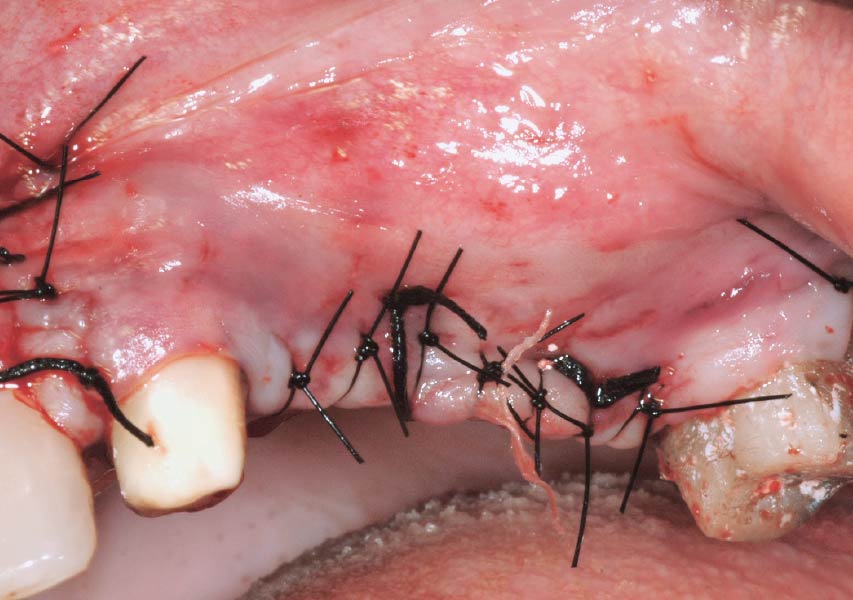
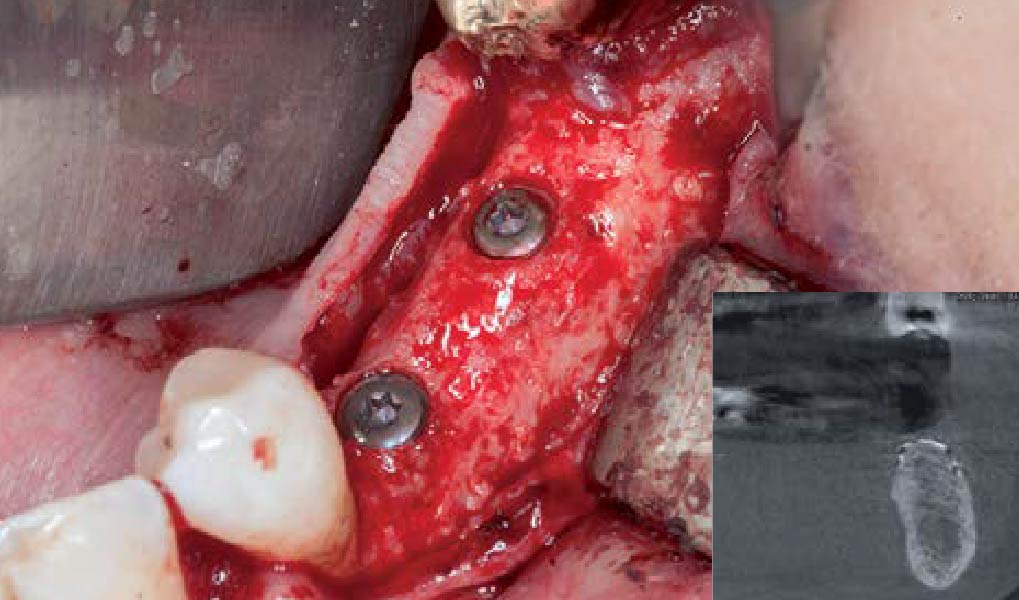
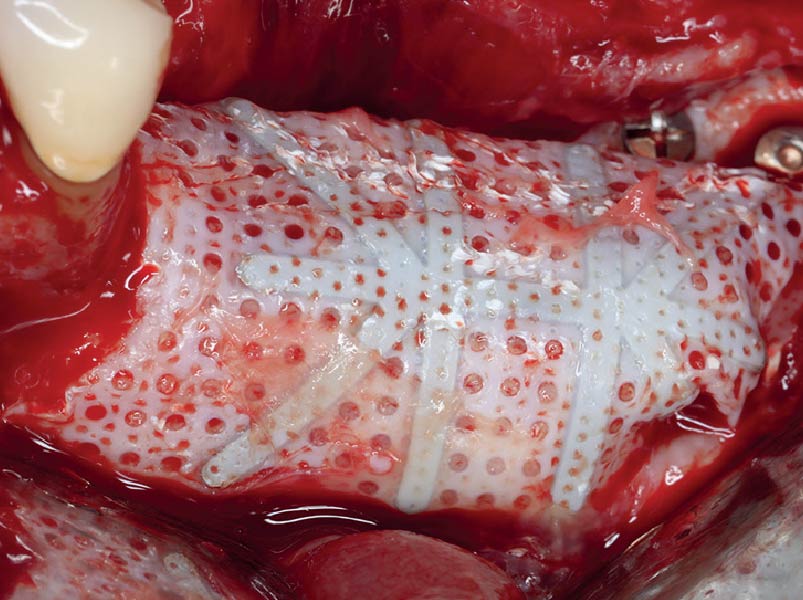
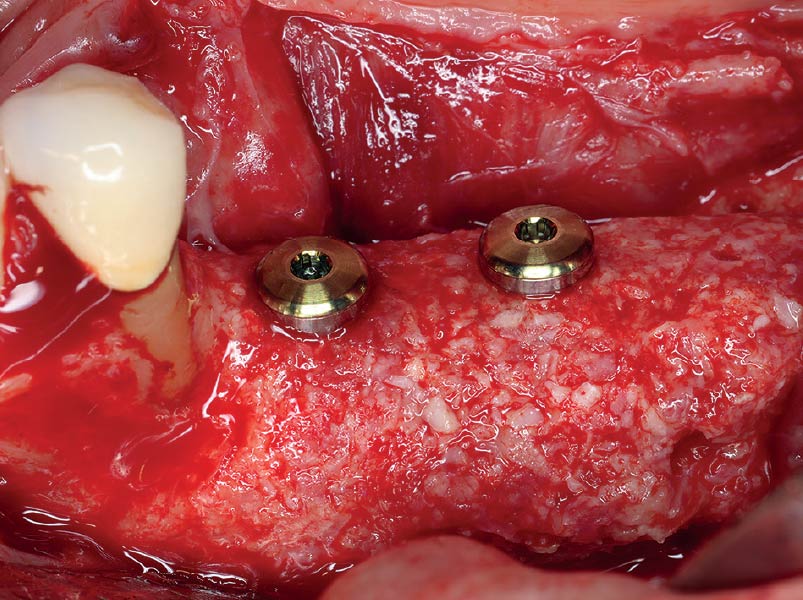
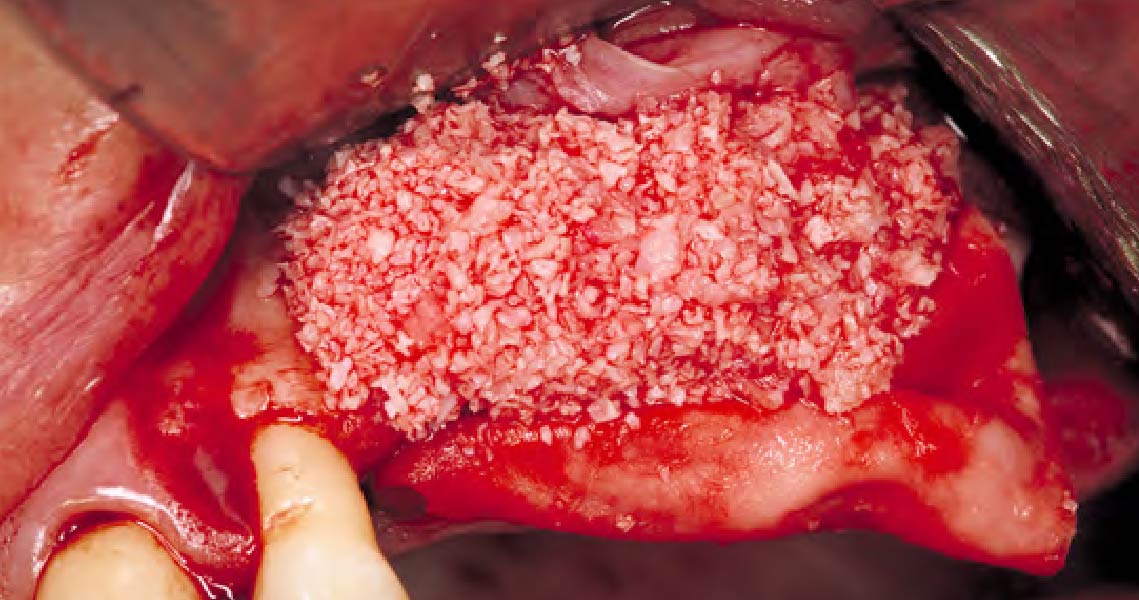
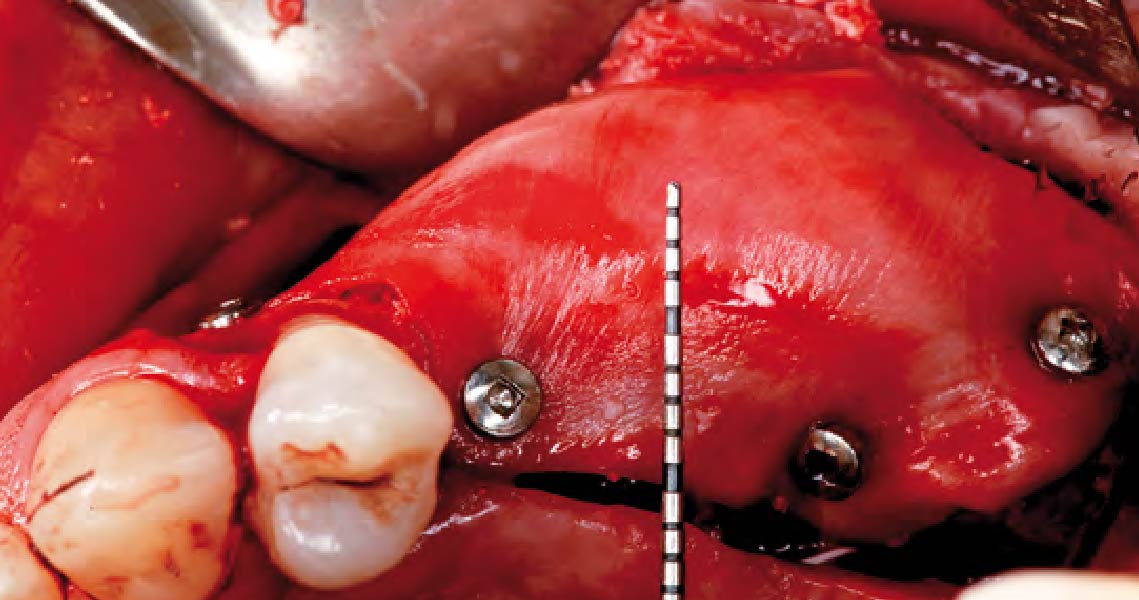
Horizontal ridge augmentation was performed using a horizontal layering technique. An inner layer of demineralized freeze-dried bone allograft (DFDBA), featuring vallos® demineralized cortical particles (to promote osteoinduction), was followed by an outer layer of deproteinized bovine bone, Geistlich Bio-Oss® (to maintain space and volume). The graft was contained with a native bilayer collagen membrane, Geistlich Bio-Gide®, and secured with titanium pins (tacks).
“By horizontally layering two distinct bone graft materials—Geistlich Bio-Oss® and vallos®—this approach was designed to tailor the regenerative environment, harnessing the unique osteoinductive potential of the allograft and the long-term space-maintaining properties of the xenograft to optimize both early bone formation and dimensional stability.”
— Eswar Kandaswamy, BDS, MS
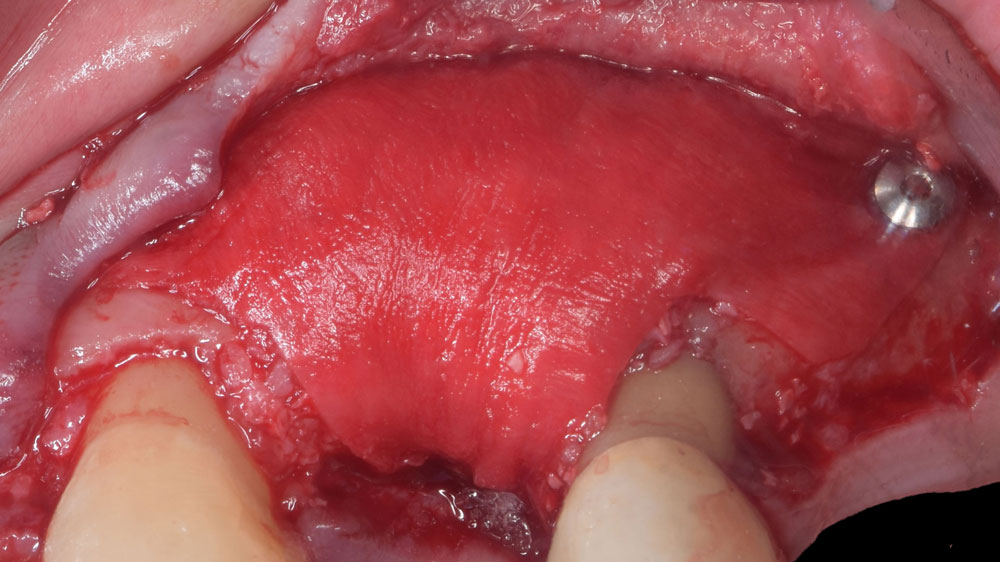
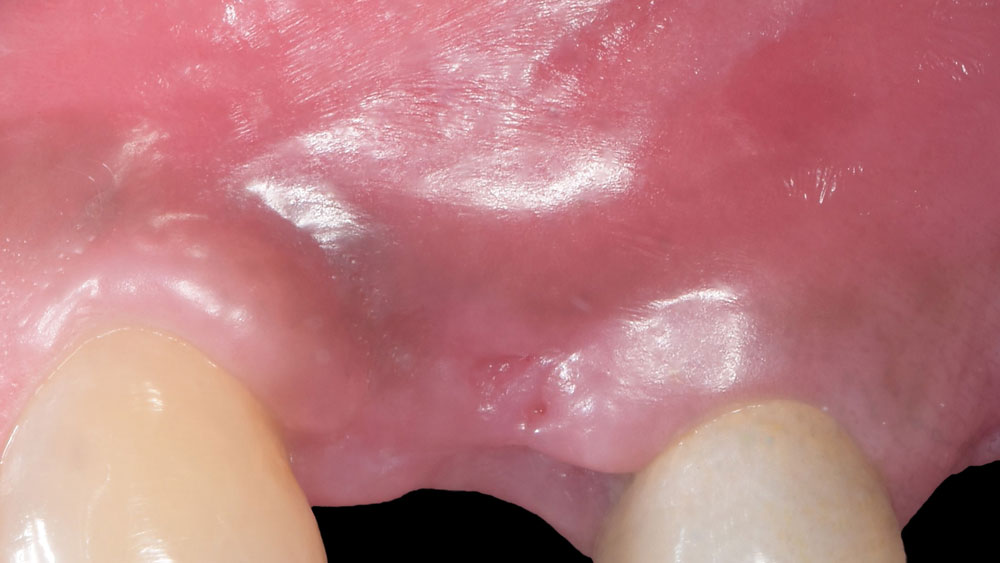
THE OUTCOME
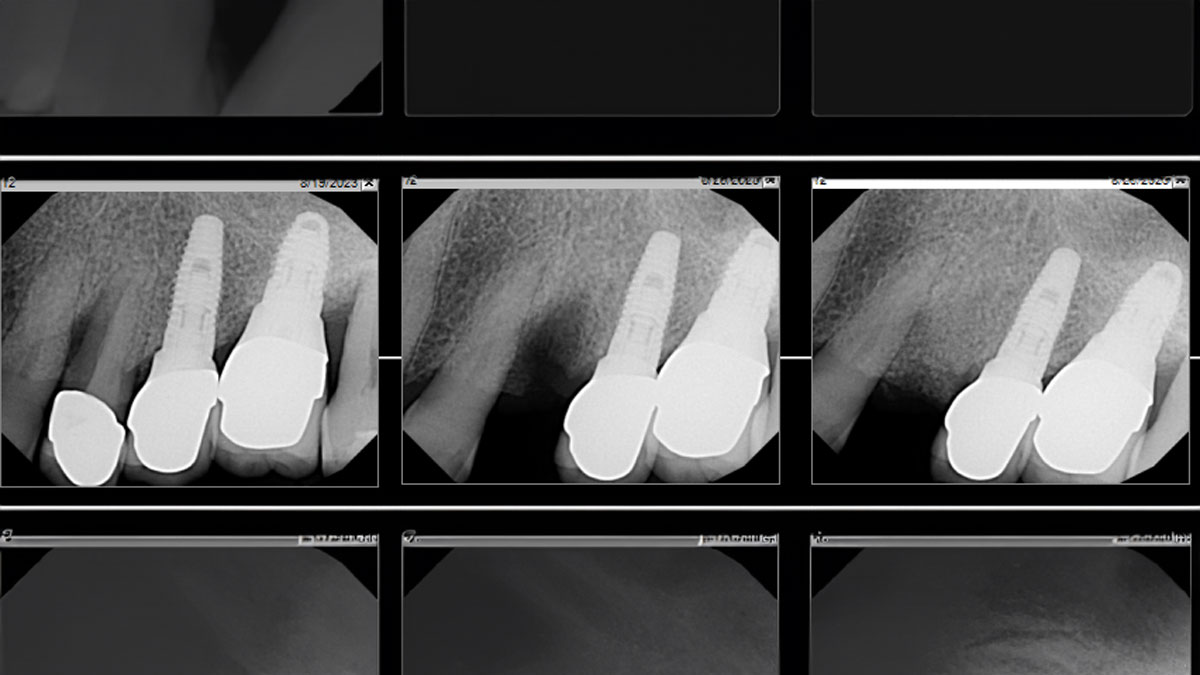
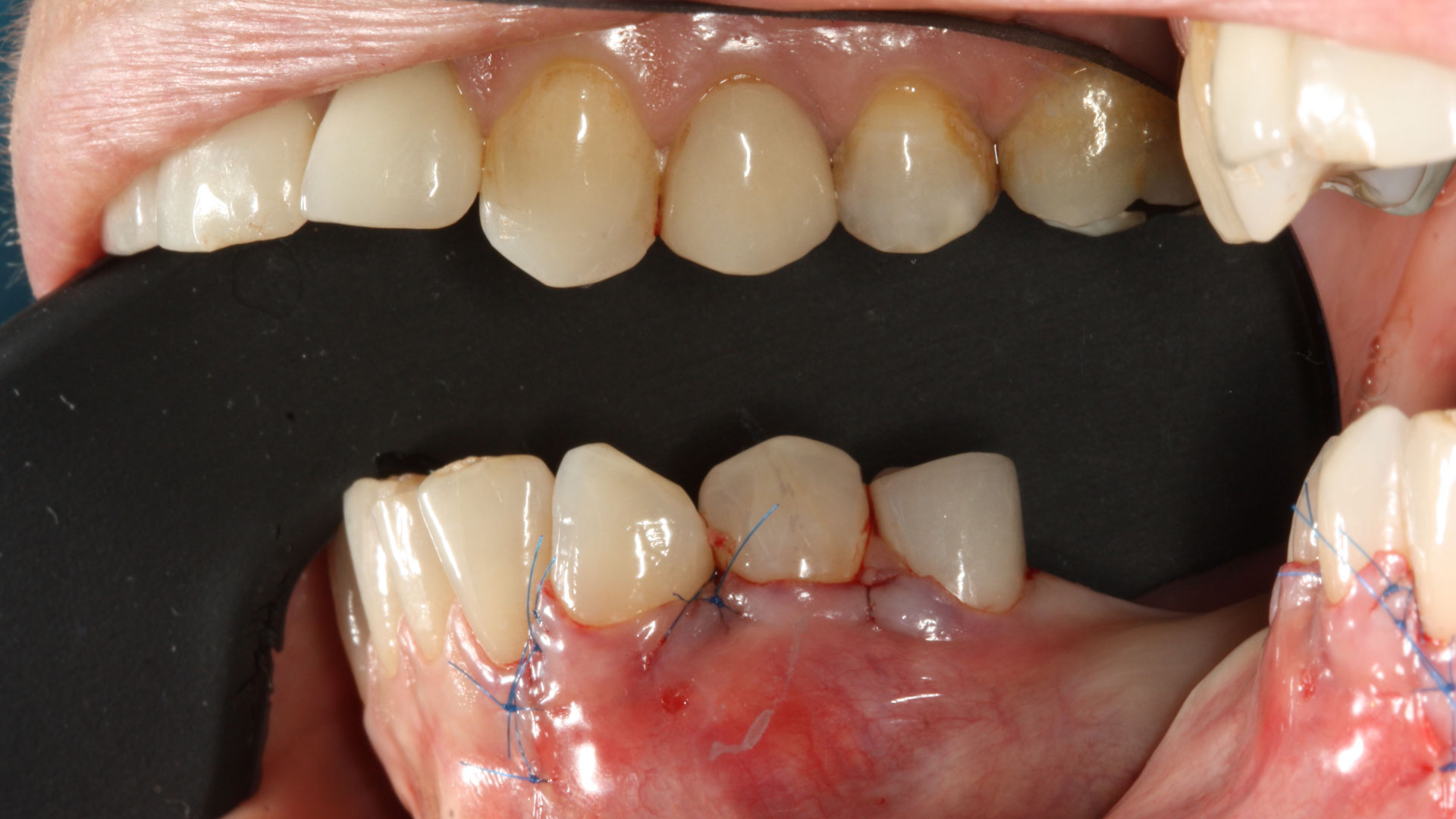
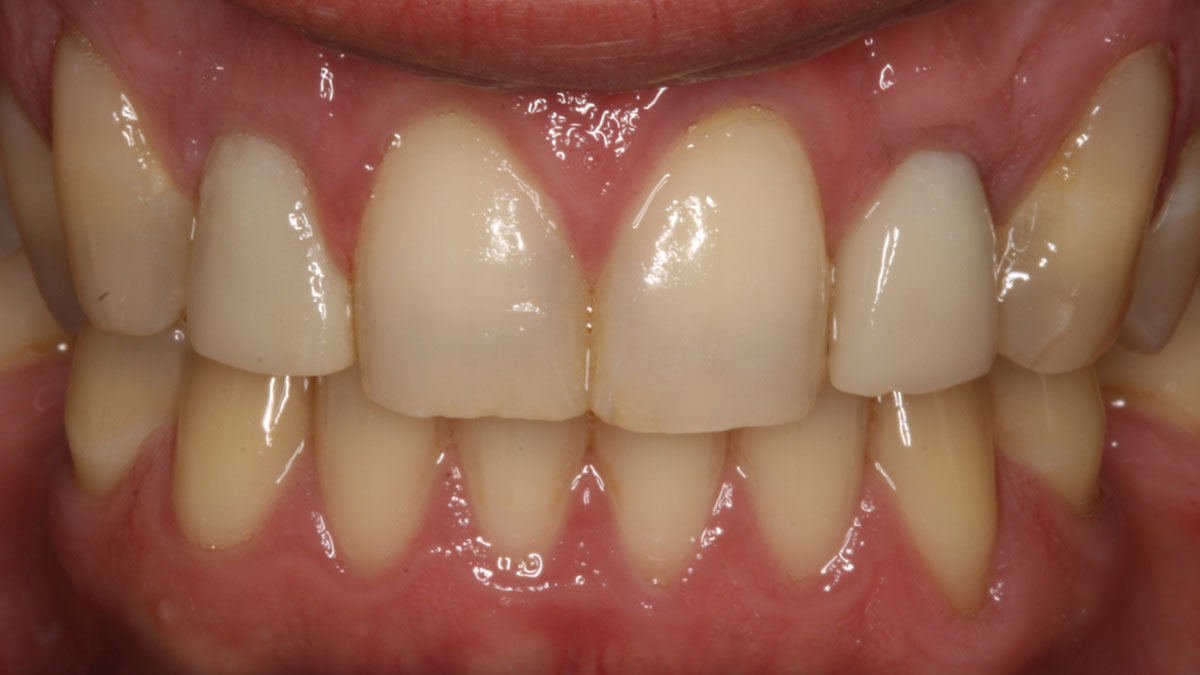
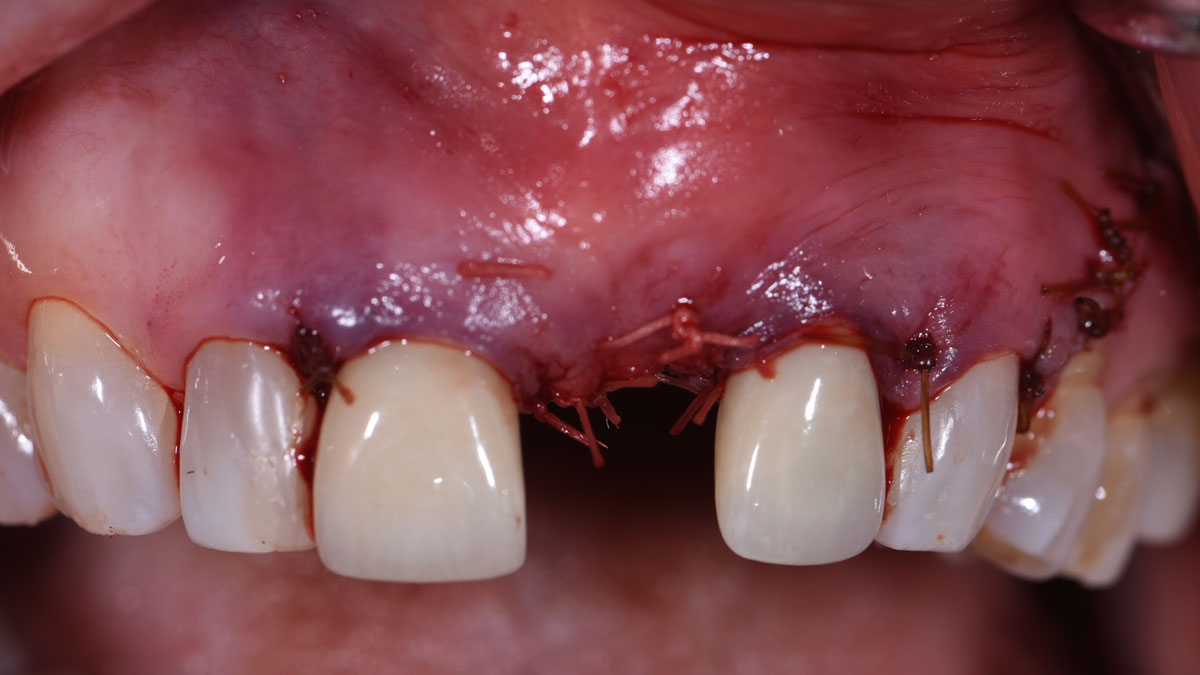
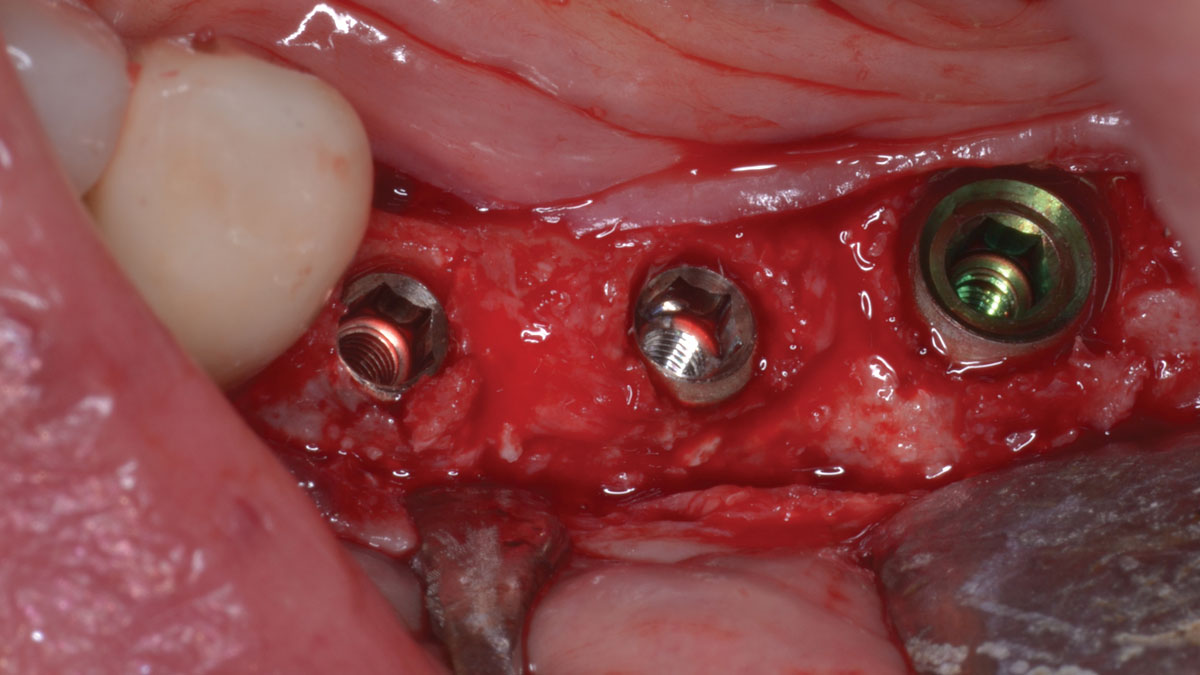
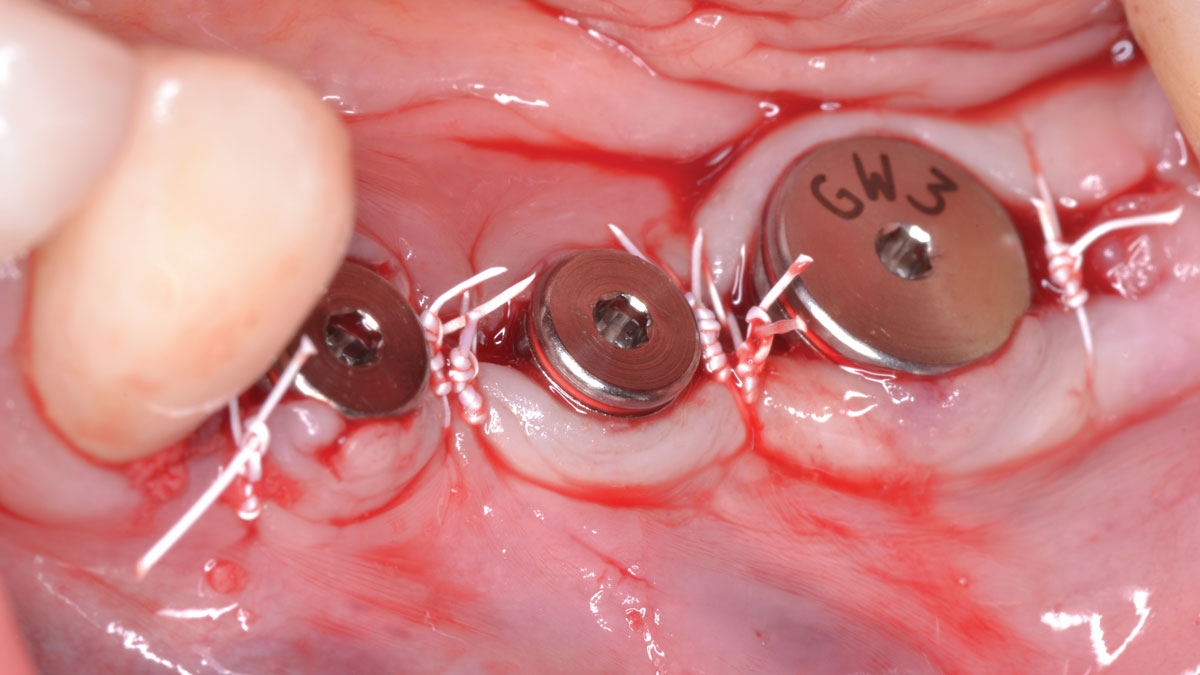
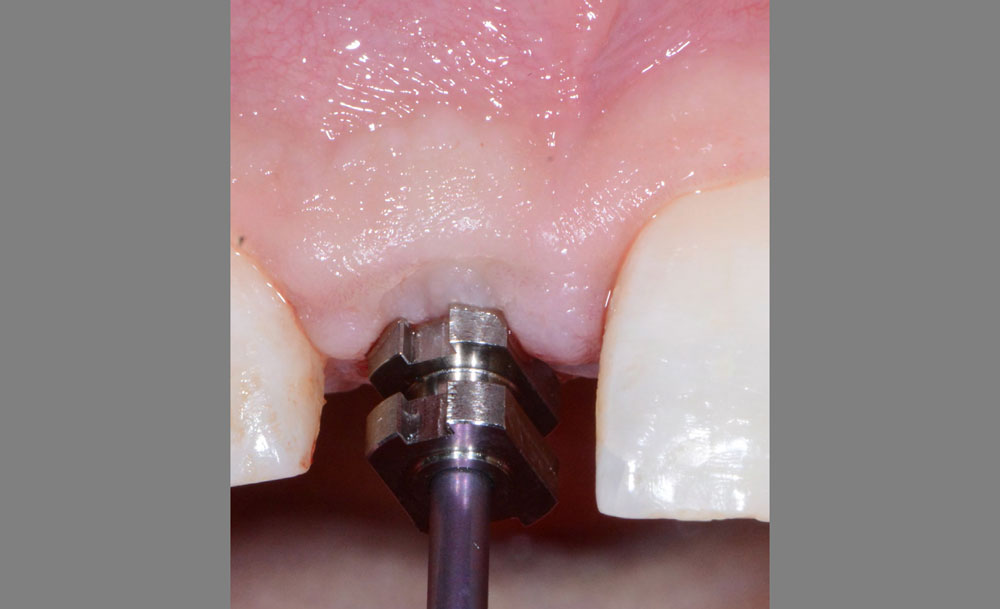
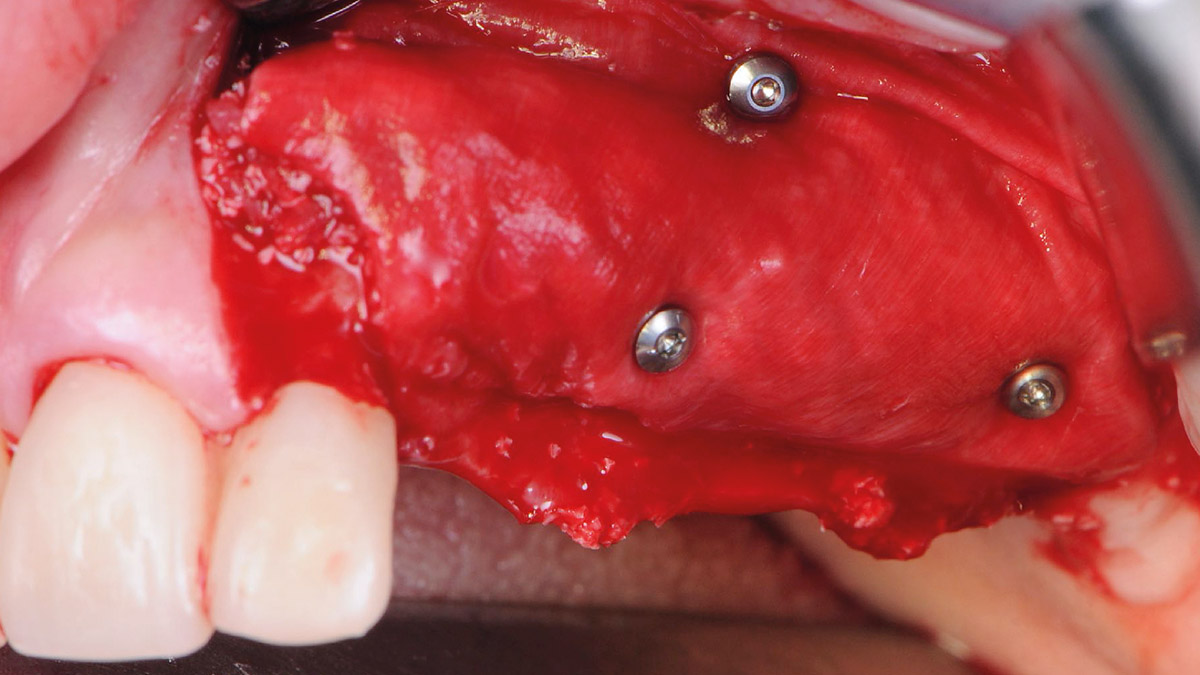
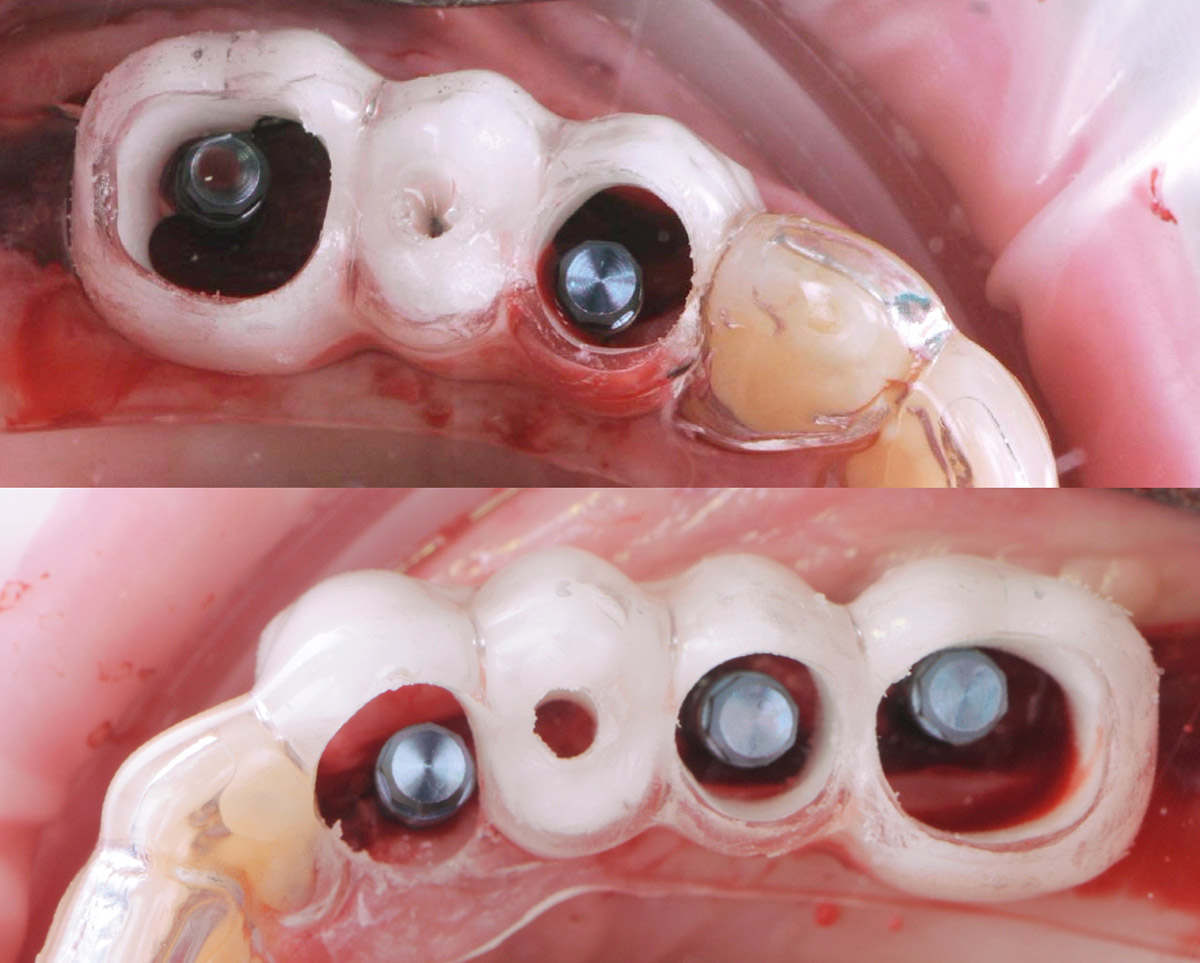
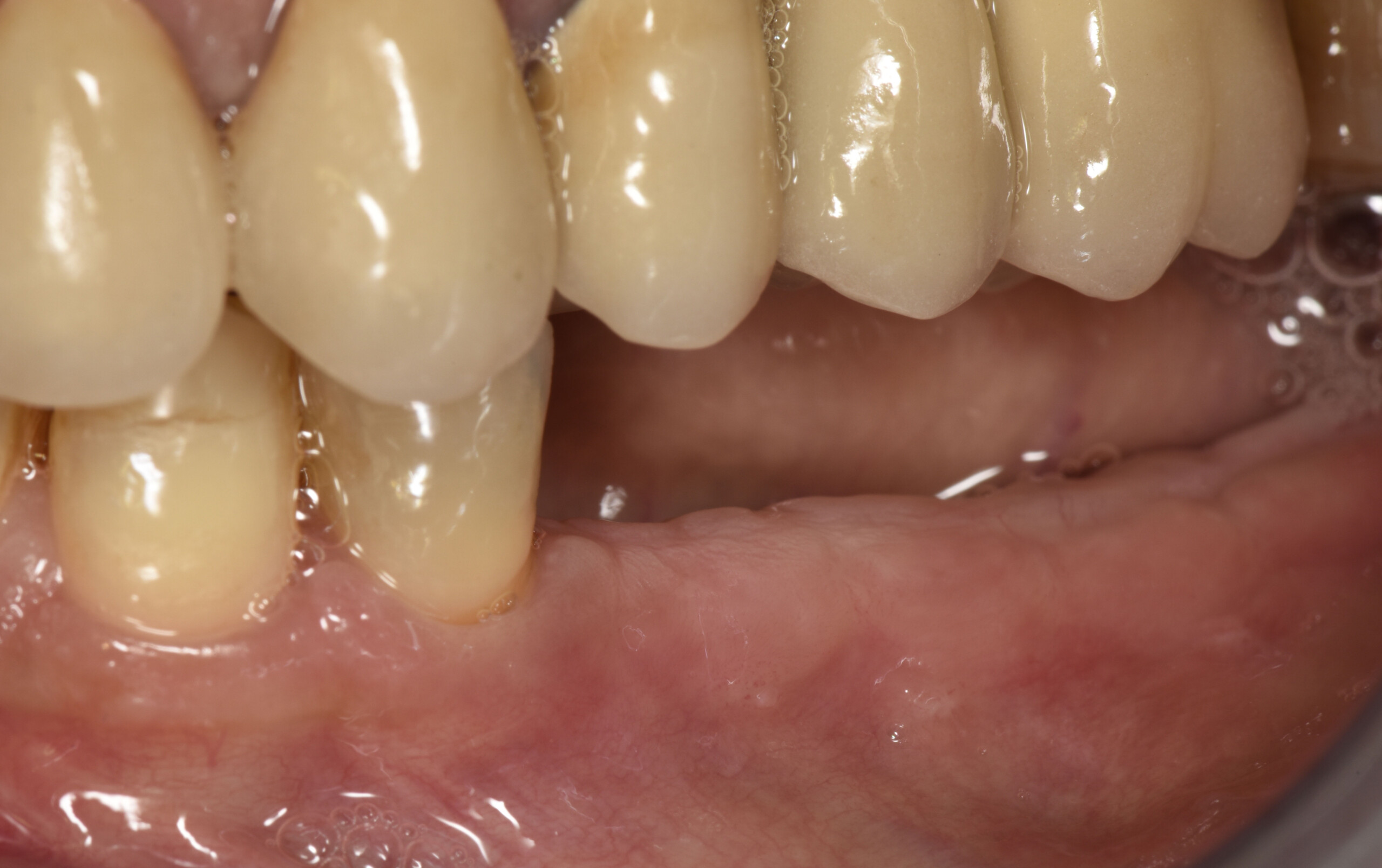
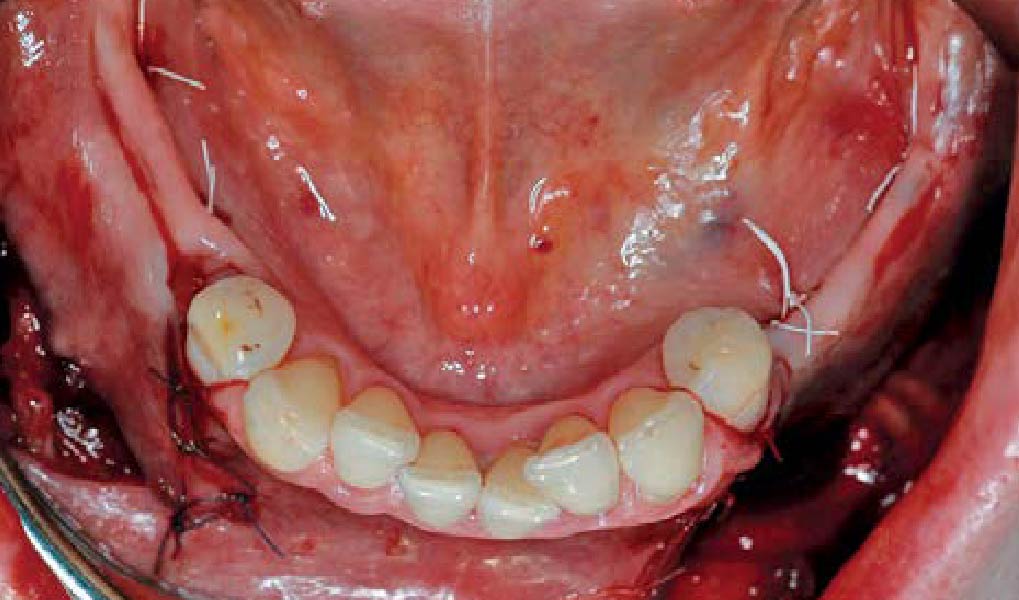
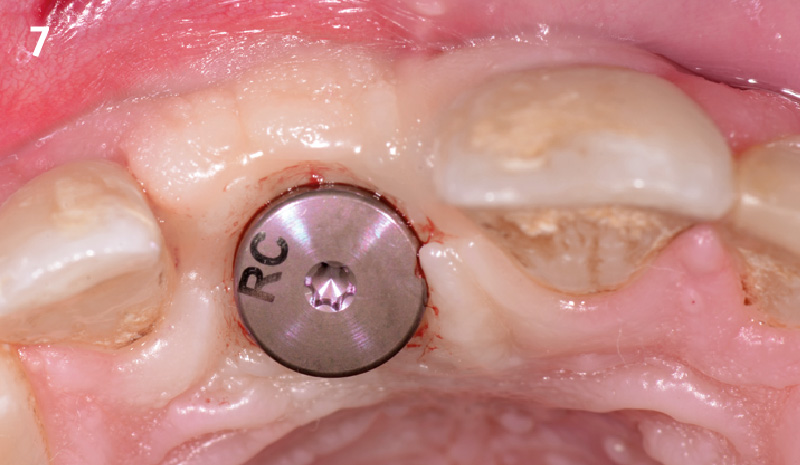
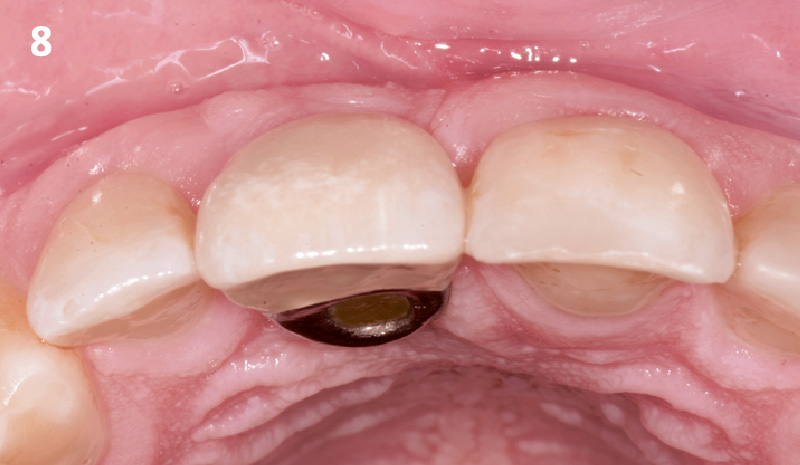
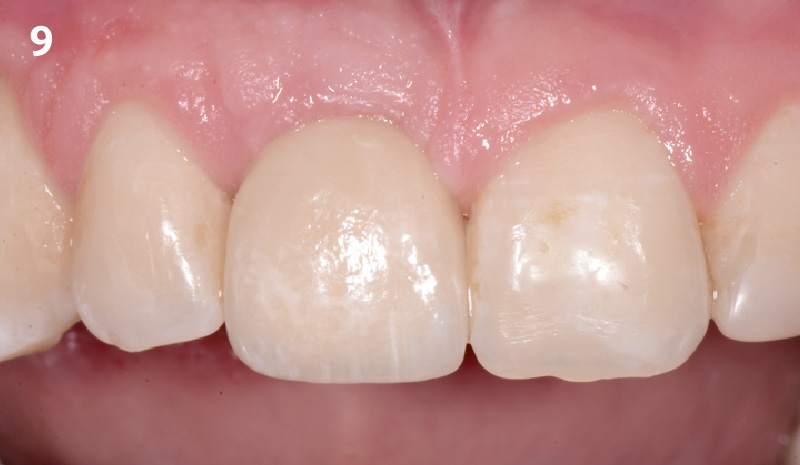
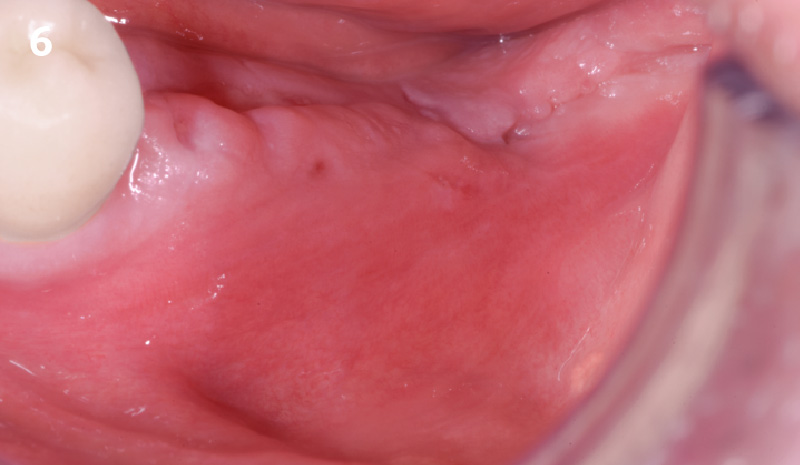
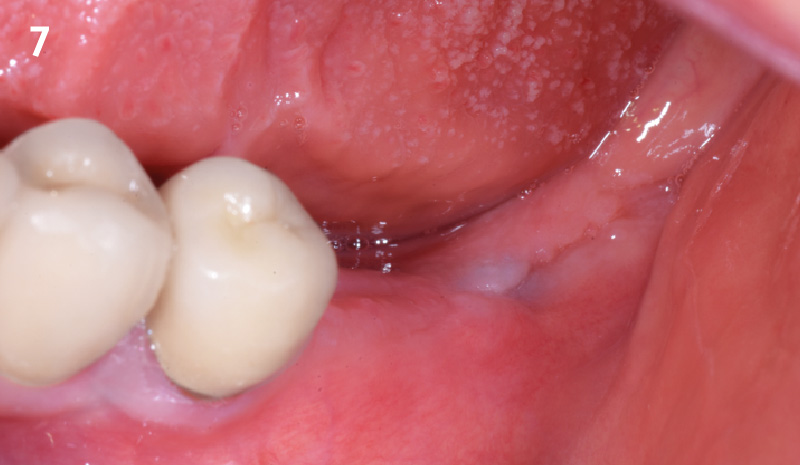
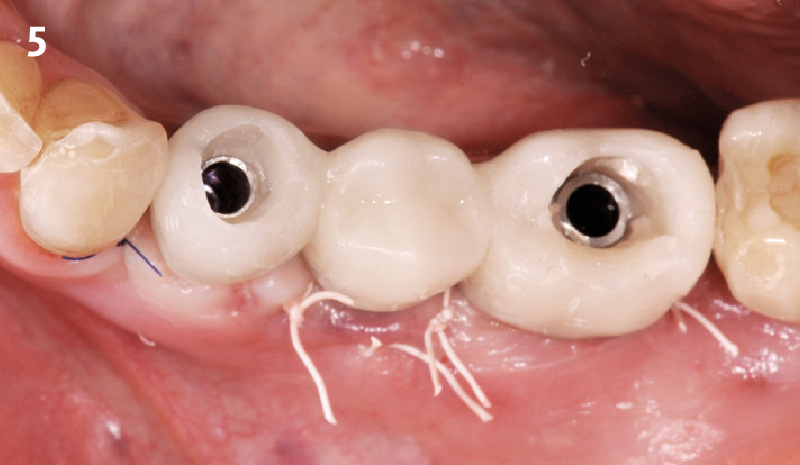
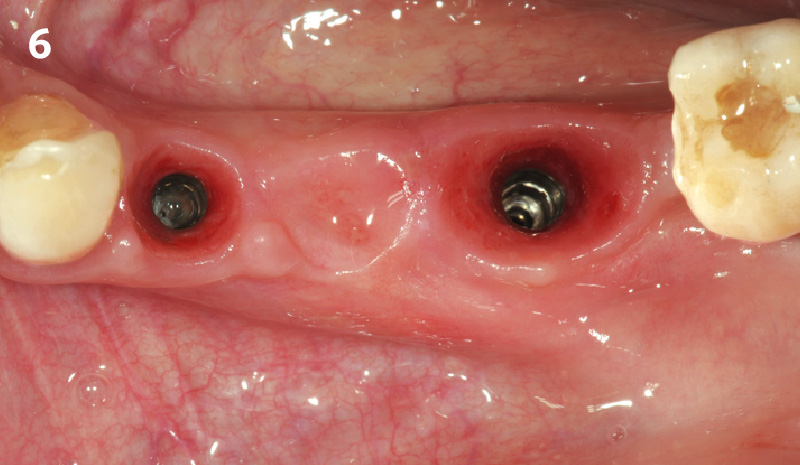
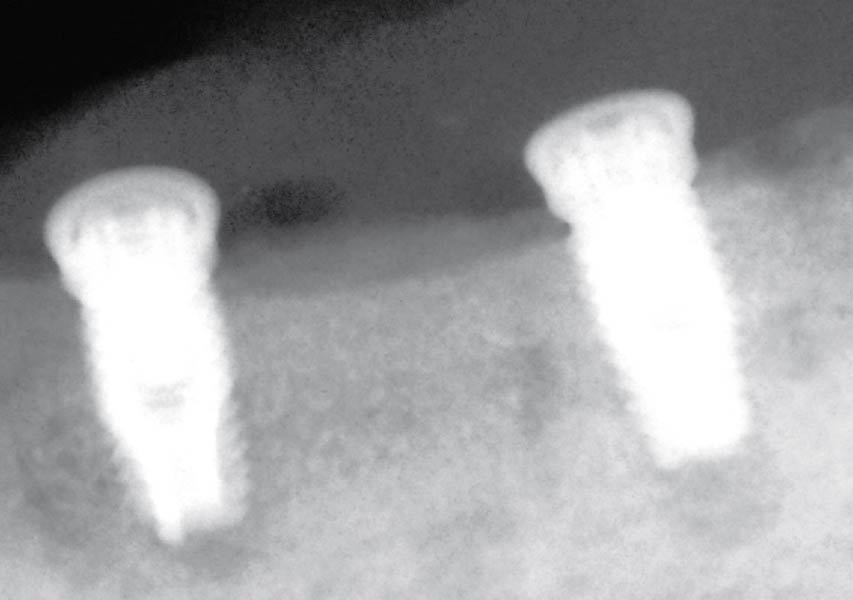
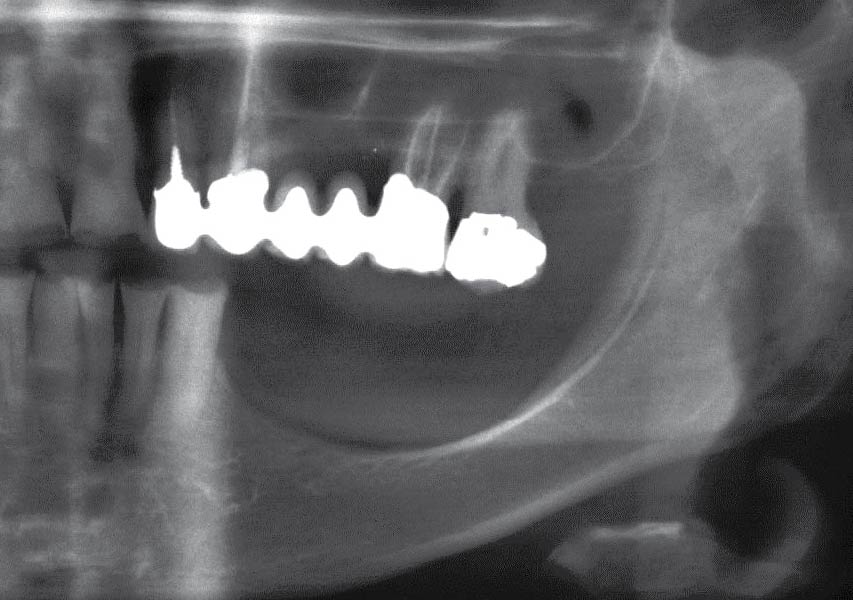
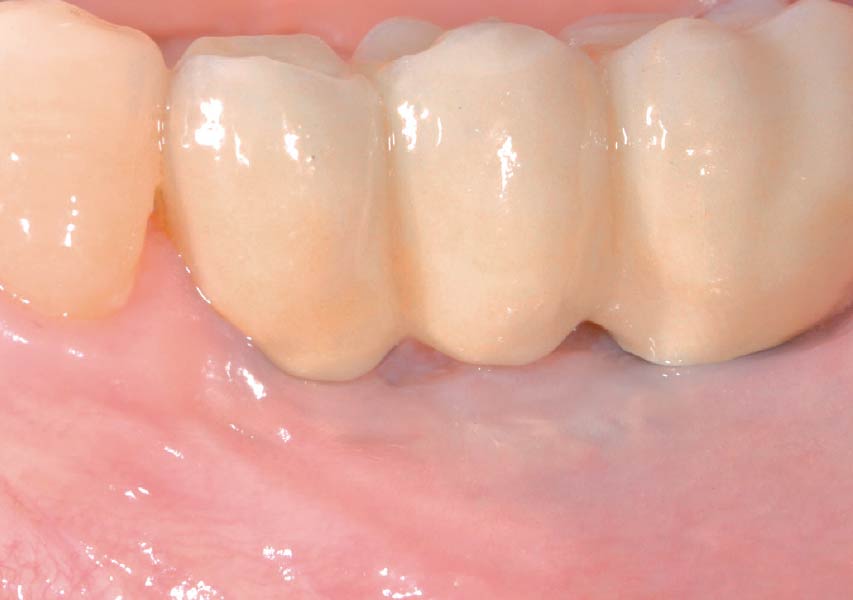
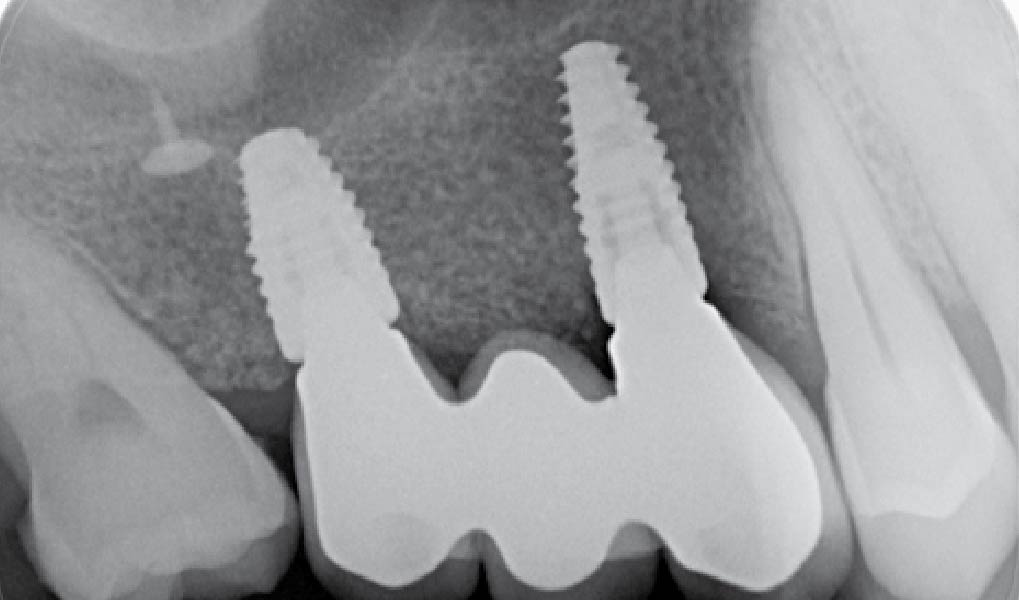
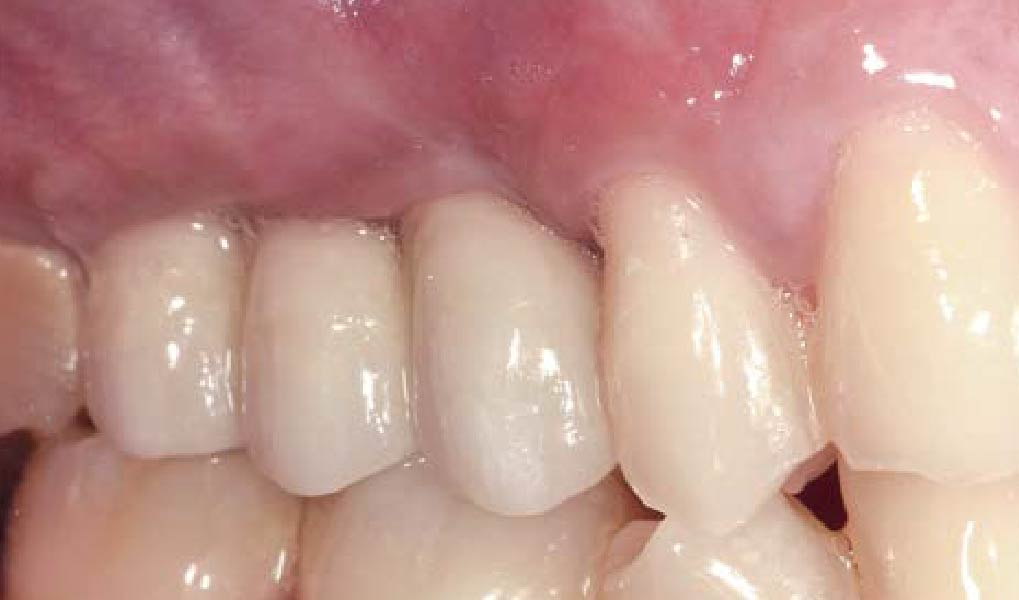
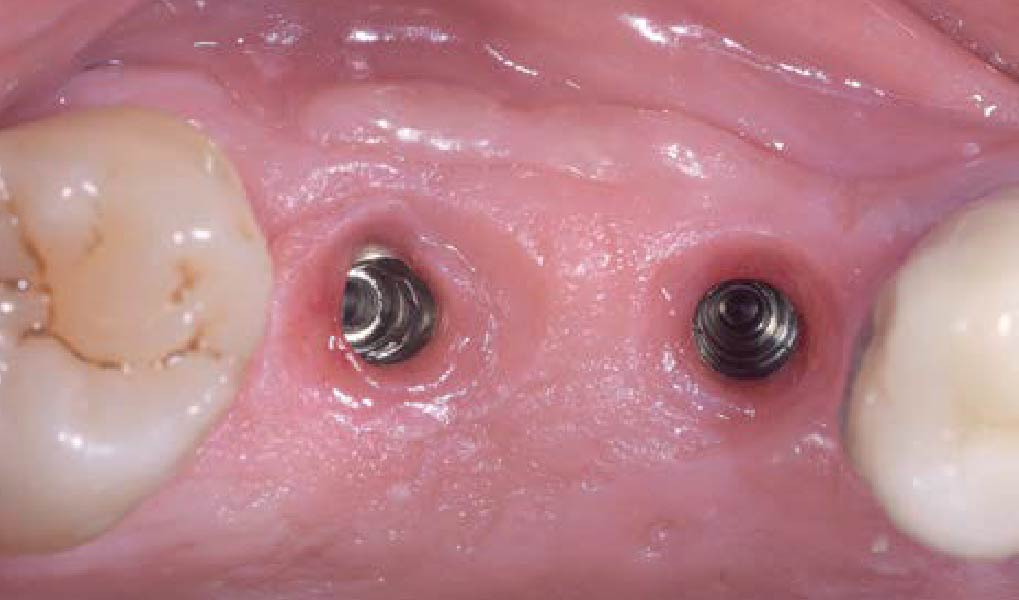
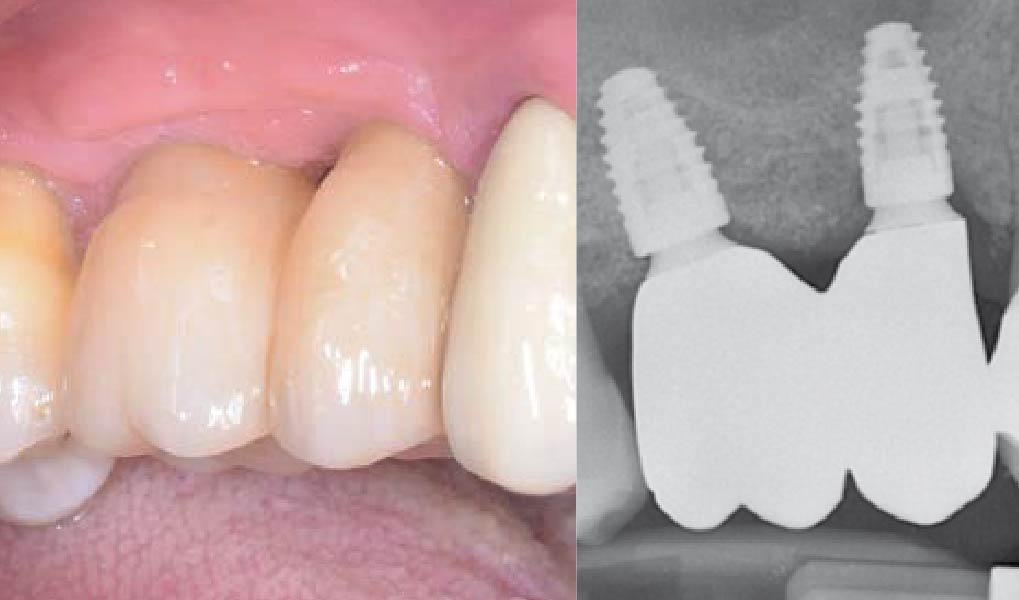
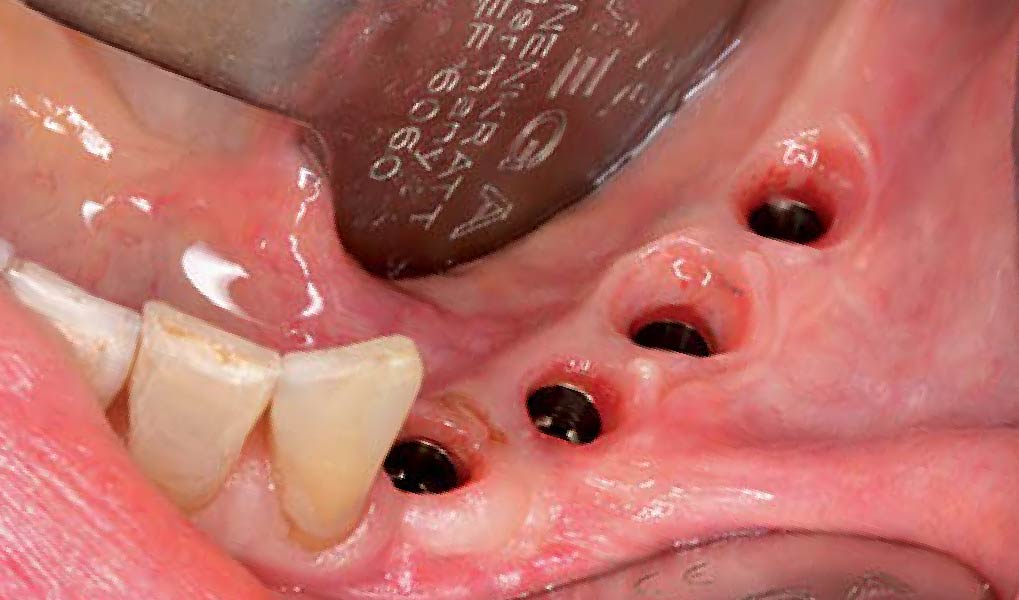
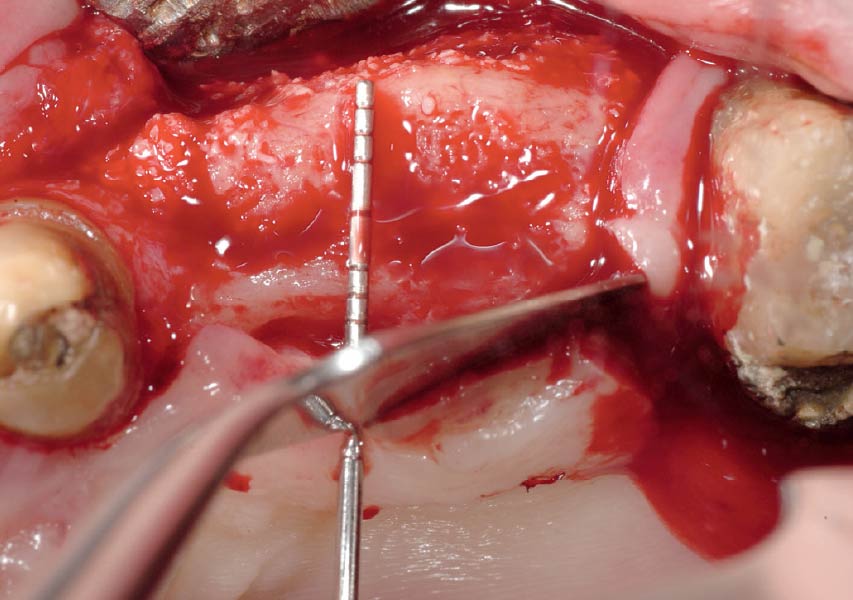
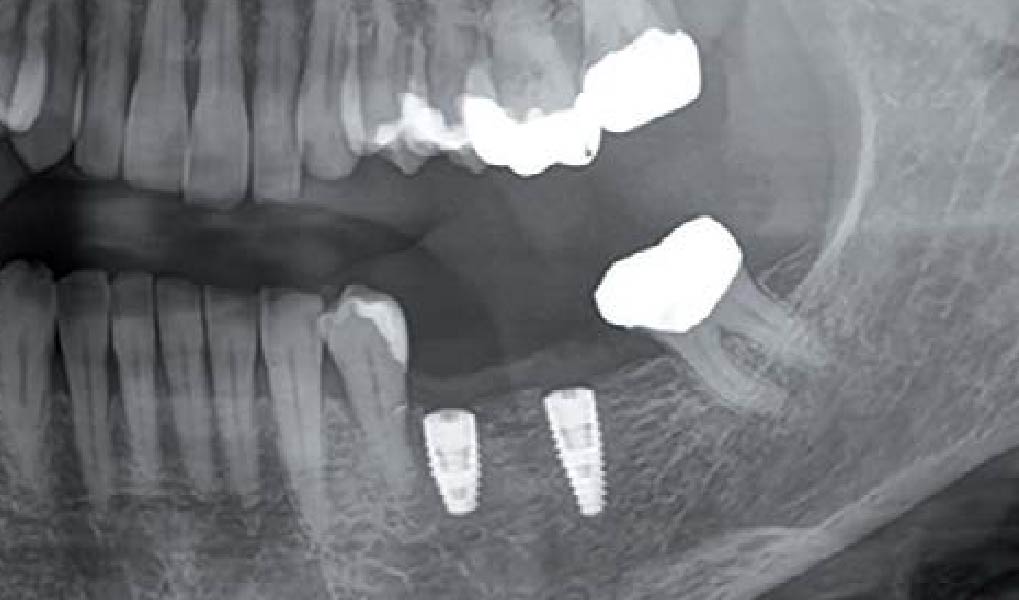
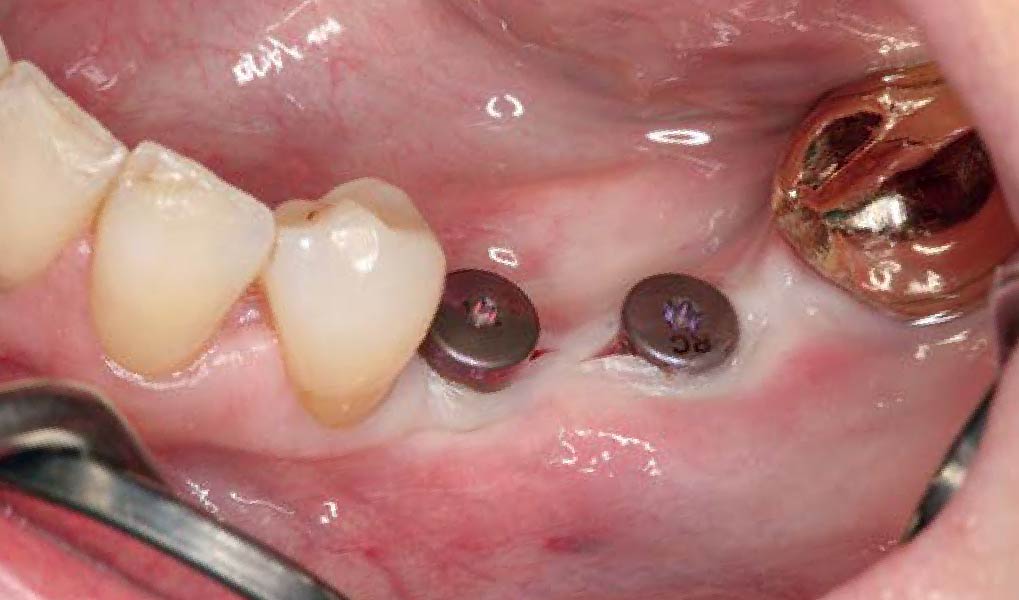
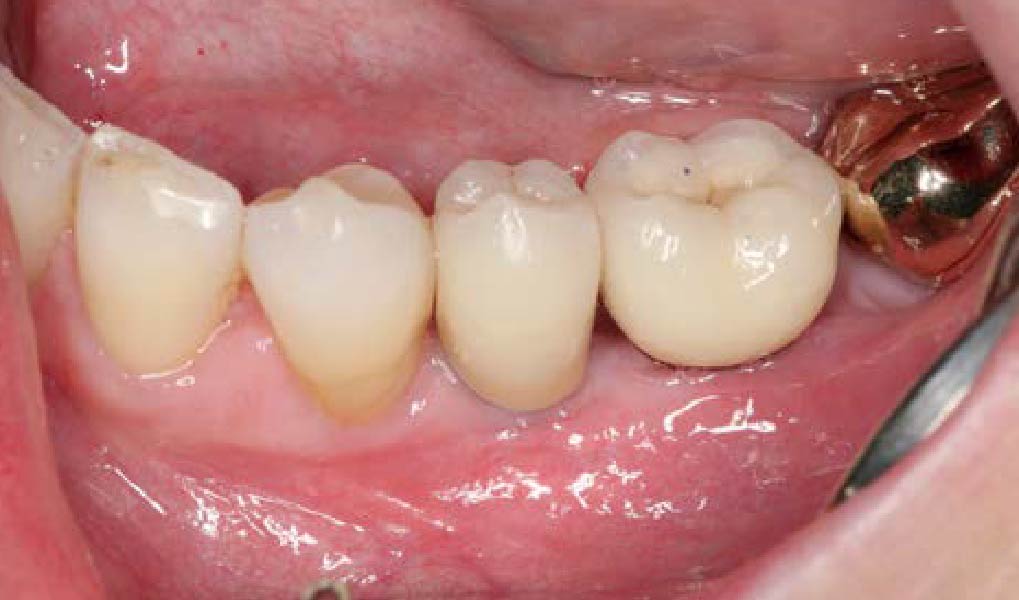
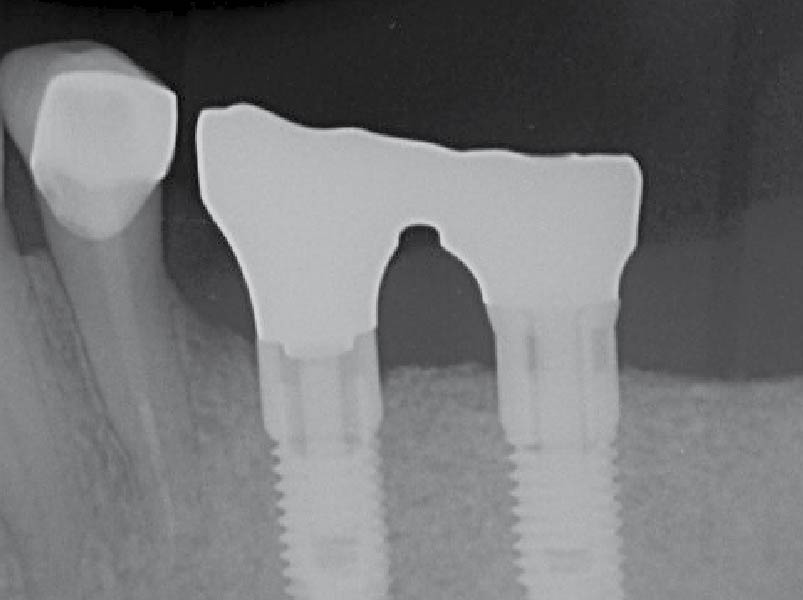
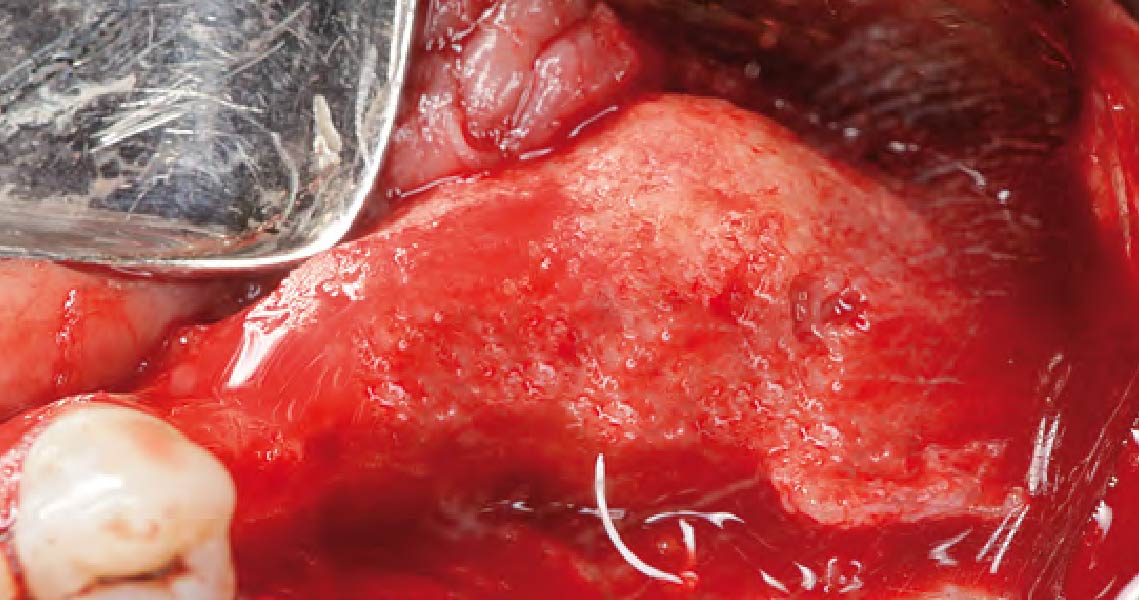
The 6-month post-operative CBCT evaluation demonstrated sufficient ridge width for restoratively driven implant placement, a result achieved through the utilization of vallos® and Geistlich Bio-Oss® bone graft materials.

Eswar Kandaswamy, BDS, MS
Dr. Eswar Kandaswamy, BDS MS, is an Assistant Professor at Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center, School of Dentistry. He earned his Dental Degree from Sri Ramachandra University, India, and practiced general dentistry for two years. He then completed his specialty training in Periodontics and a Master of Science at The Ohio State University.

Amber Kreko, DDS
Dr. Amber Kreko, DDS is a third-year Periodontics resident at Louisiana State University School of Dentistry, soon to earn her Master of Science. With a foundation in dental hygiene and six years of clinical practice in Southeast Louisiana,she returned to LSU for her DDS. Her comprehensive background enriches her approach to periodontal care. Upon graduation, she will transition to private practice.

BIOBRIEF
Lateral and Vertical Bone Regeneration with Simultaneous Soft Tissue Augmentation
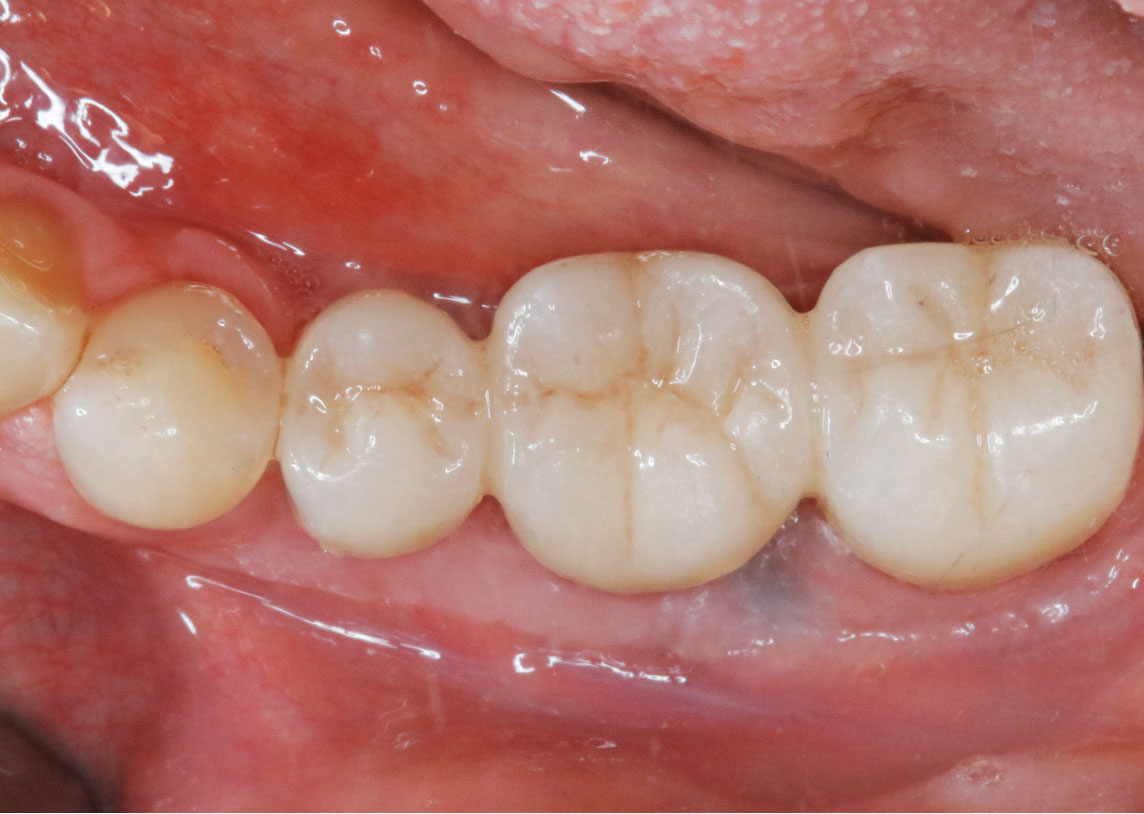

THE SITUATION
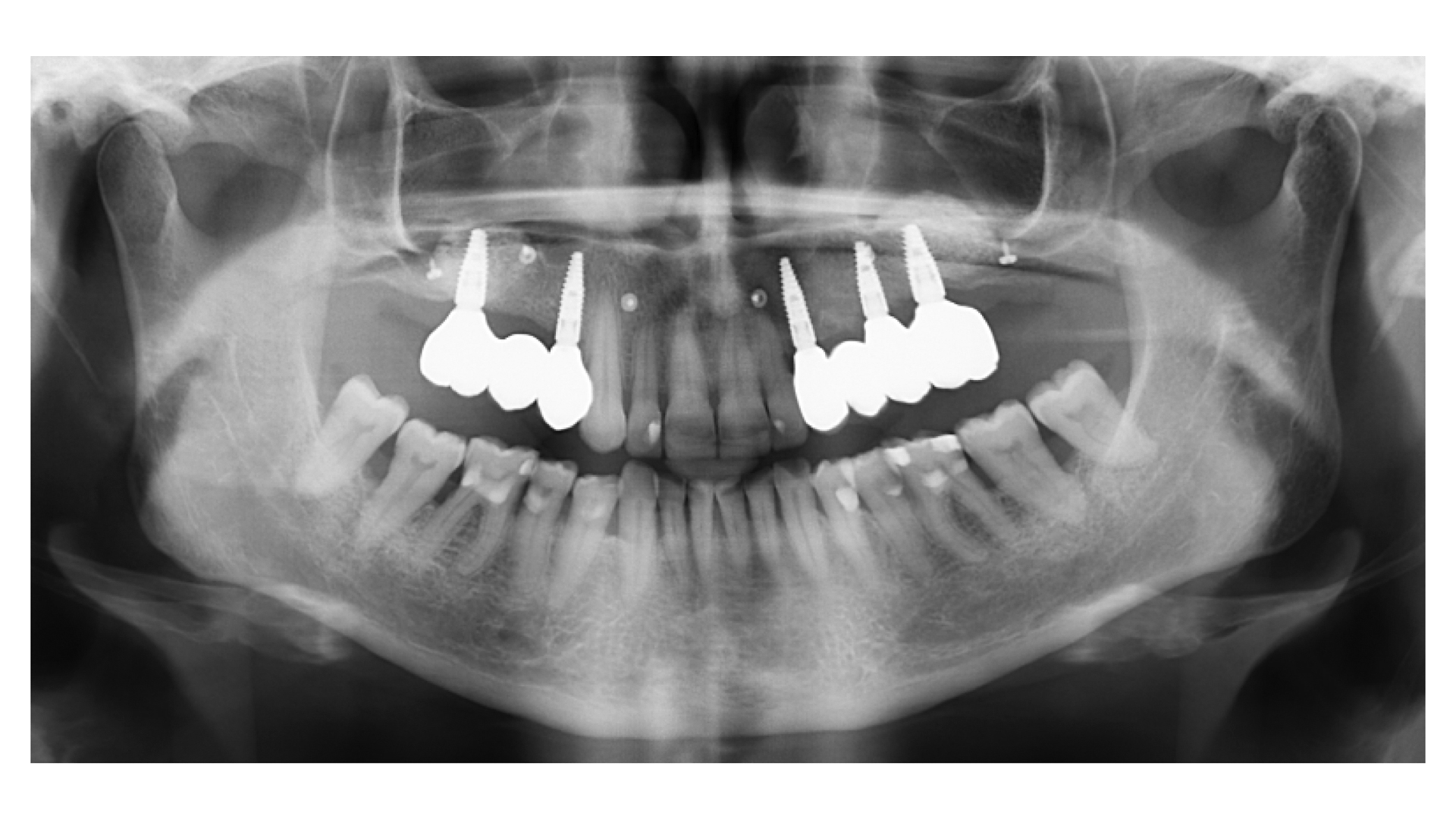
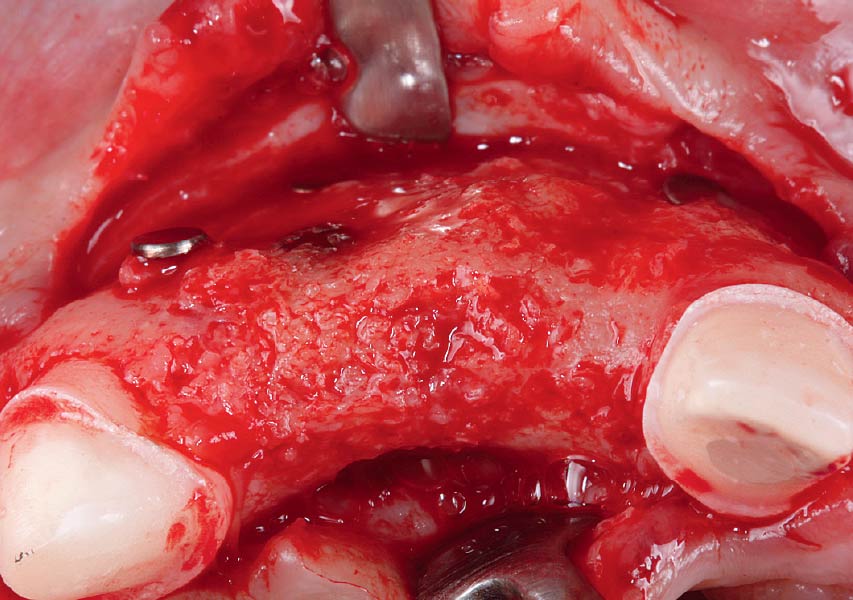
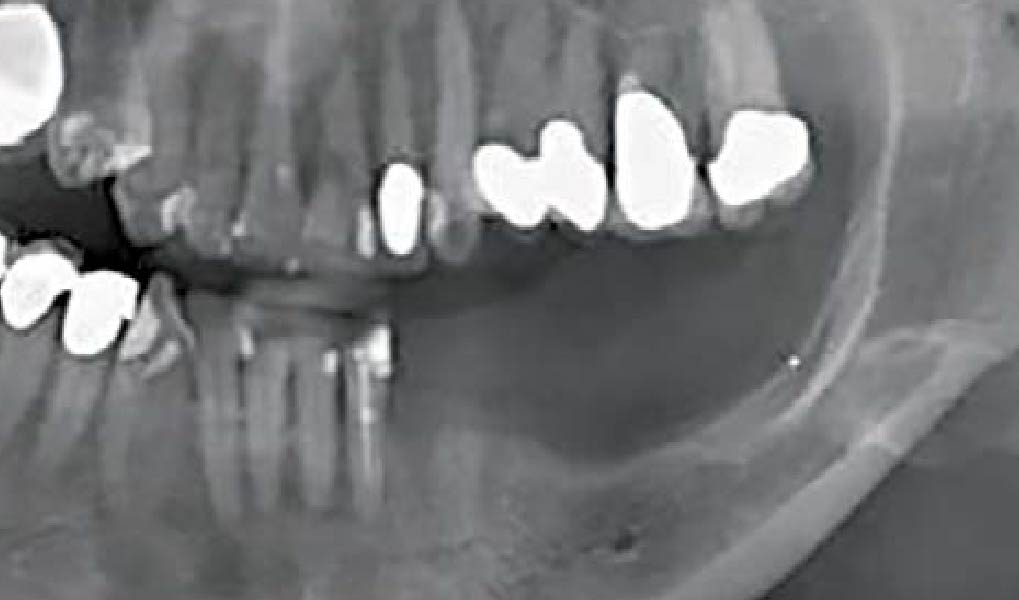
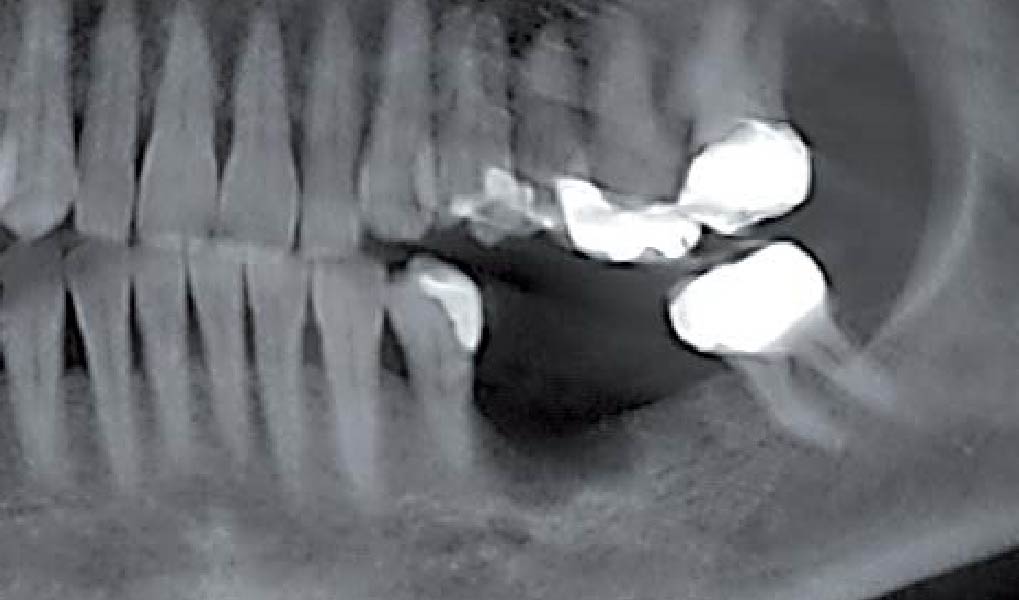
After extraction of the periodontally damaged tooth #20 the preoperative Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) imaging shows reduced vertical bone volume in the area of tooth #s 18 – 20. A lateral and vertical bone regeneration was necessary.
The goal of treatment was a late implant placement after bone regeneration and creation of stable periimplant soft tissue for long-term implant preservation.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
Additional Risk Factors: Roots were divergent, and intra-radicular bone (septal bone) was excellent, with more than 5 mm of remaining apical bone to achieve optimal primary stability.
THE APPROACH
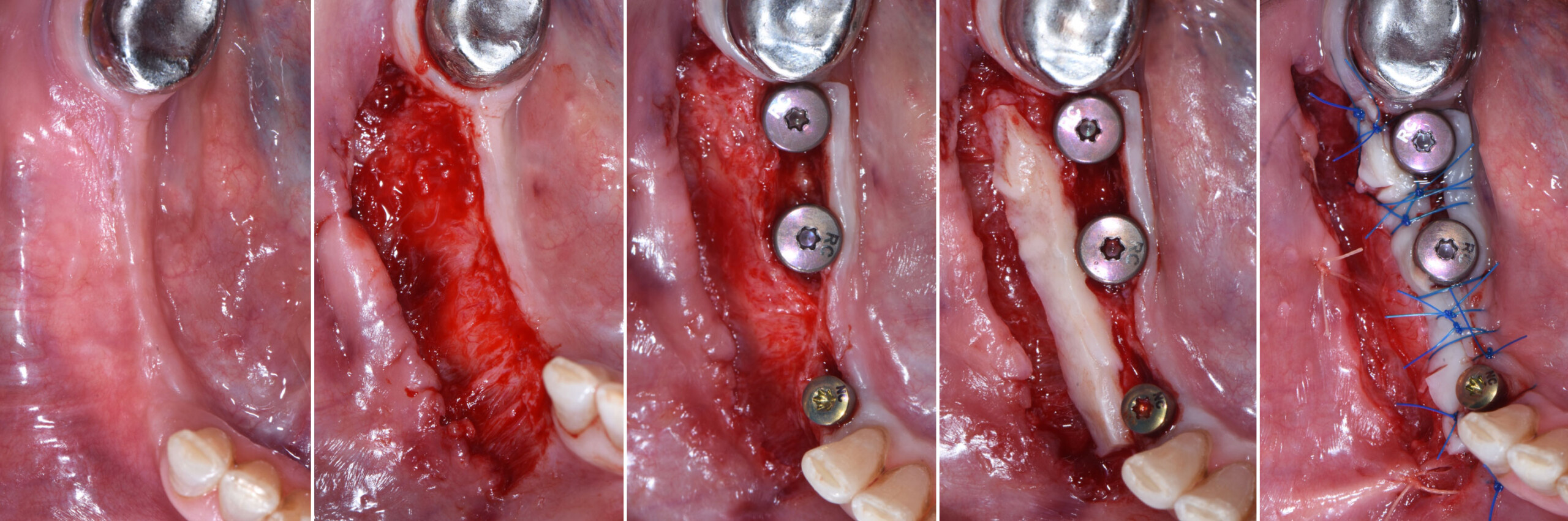
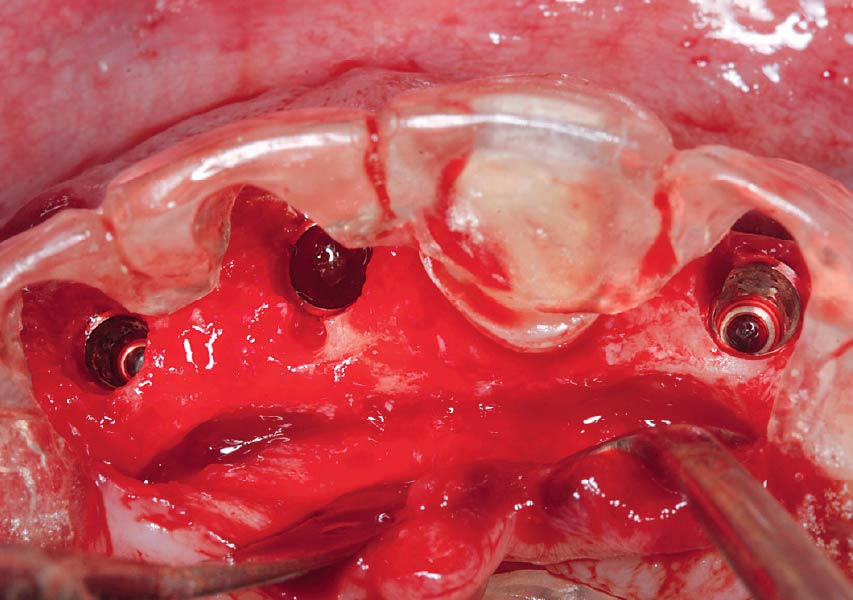
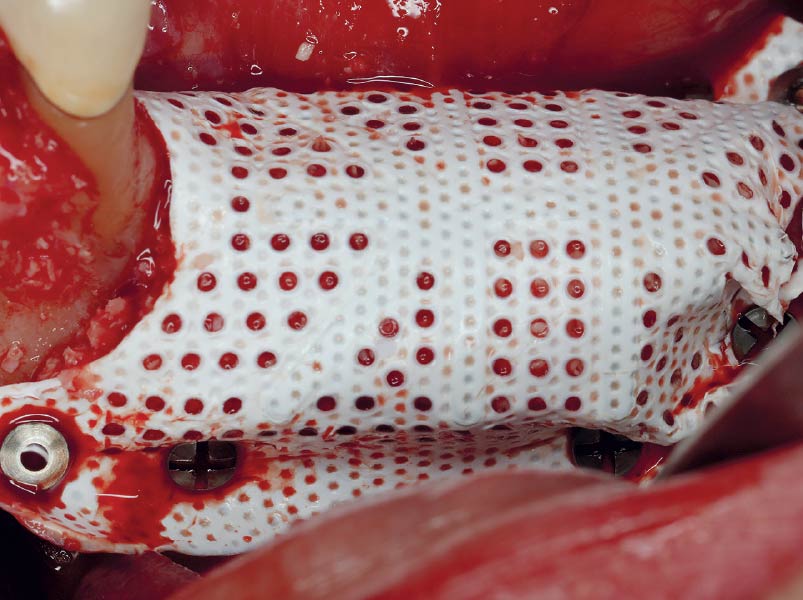
A customized bone regeneration procedure utilizing Yxoss CBR®. Followed by coverage of the graft with Geistlich Bio-Gide® for the purpose of Guided Bone Regeneration (GBR). Soft tissue thickening using Geistlich Fibro-Gide®. Delayed implantation into the augmented tissue. A vestibuloplasty with Geistlich Mucograft® for the regeneration of keratinized mucosa.
“Using the Geistlich Fibro-Gide® matrix enabled concurrent augmentation of hard
— Arnd Lohmann, MSc
and soft tissues without any postoperative complications. At the same time, the soft
tissue thickening facilitated floor of the mouth surgery and vestibuloplasty.”
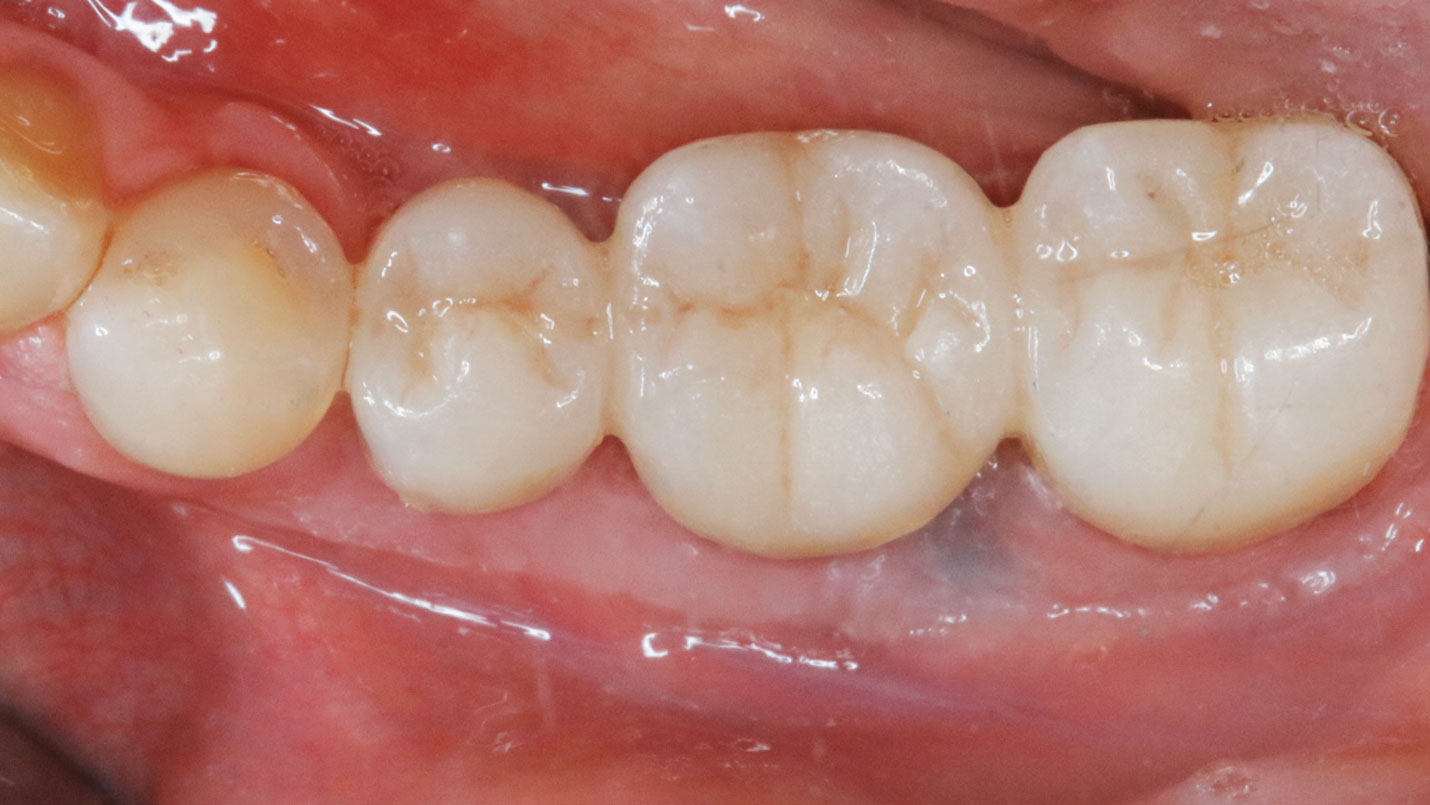
THE OUTCOME
Treatment resulted in approximately 5 mm of vertical bone regeneration. The potential occurrence of a dehiscence associated with a wound opening and exposure of Yxoss CBR® was able to be prevented with Geistlich Fibro-Gide®.
On one hand, the quality of the peri-implant soft tissue was improved by the
soft tissue thickening with Geistlich Fibro‑Gide® and, on the other, by increasing the width of keratinized mucosa with Geistlich Mucograft®. The treatment method chosen resulted in a reduced invasiveness and morbidity by avoiding a donor site for sourcing a transplant.

Arnd Lohmann, MSc
Dr. Arnd Lohmann is a recognized specialist in implantology and periodontology. He earned his dental license in Hamburg in 2002, completed his doctorate in 2003, and has been a partner at a private practice in Bremen since then.
With a Master of Science in Implantology (2007), he specializes in dental implantology and bone augmentation. He is an active speaker at national and international congresses, leads the Bremen study group of the German Society of Oral Implantology (DGOI), and is a member of DGOI, DGZI, and DGI. His practice is equipped with state-of-the-art technology, ensuring high-quality patient care.

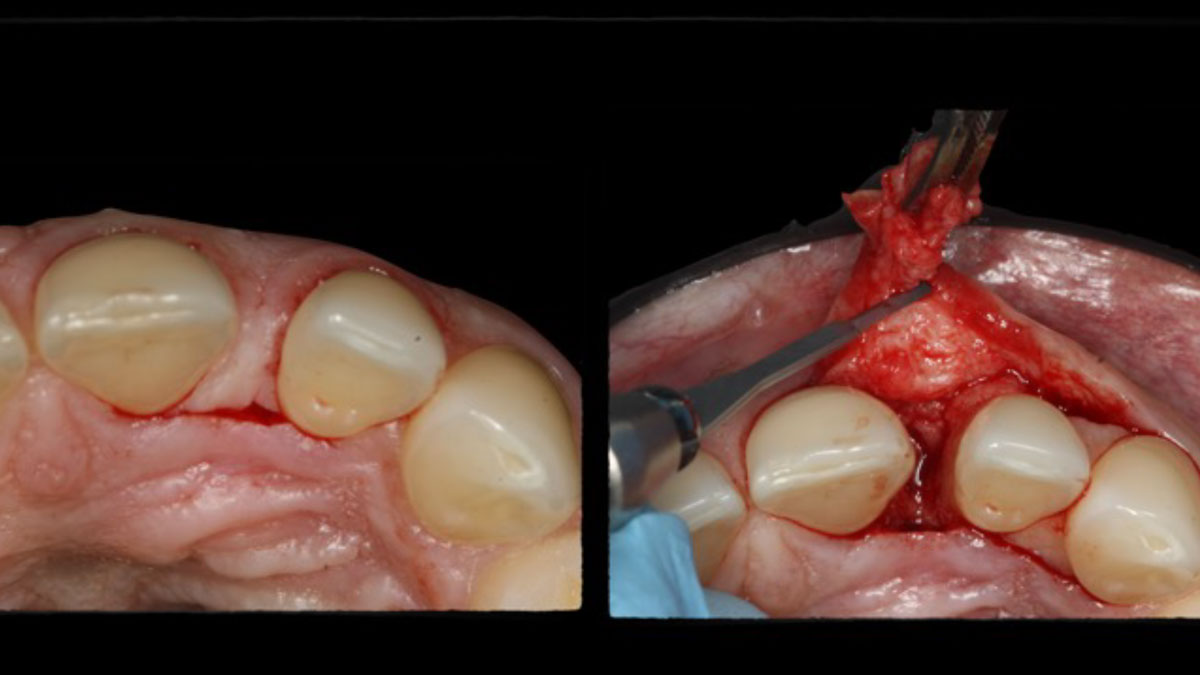
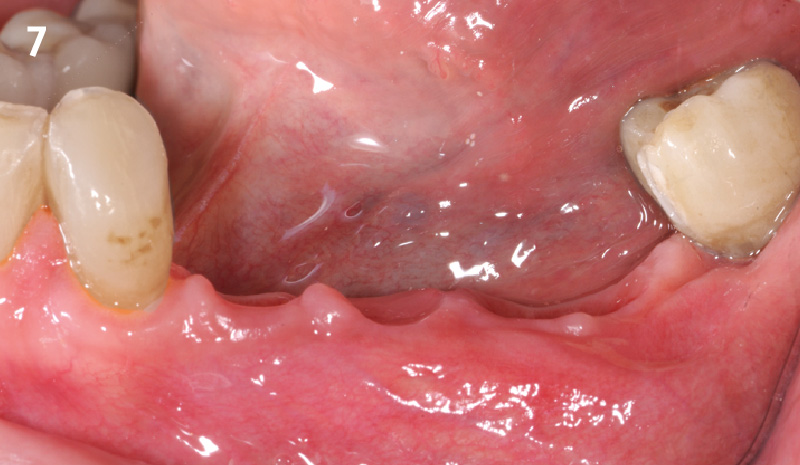
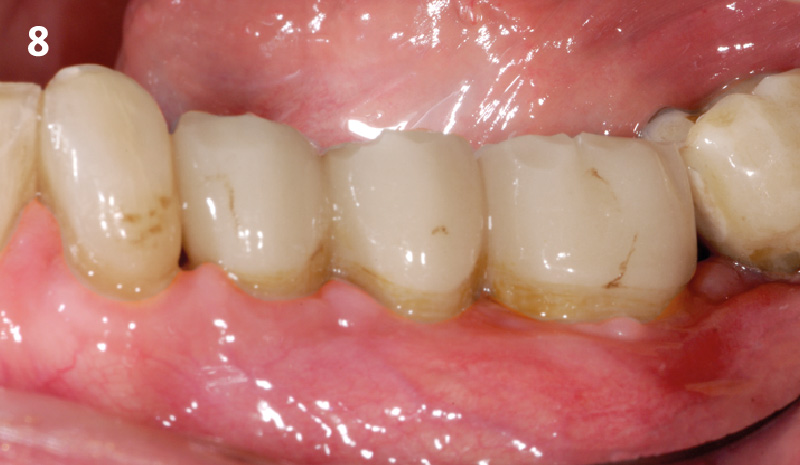
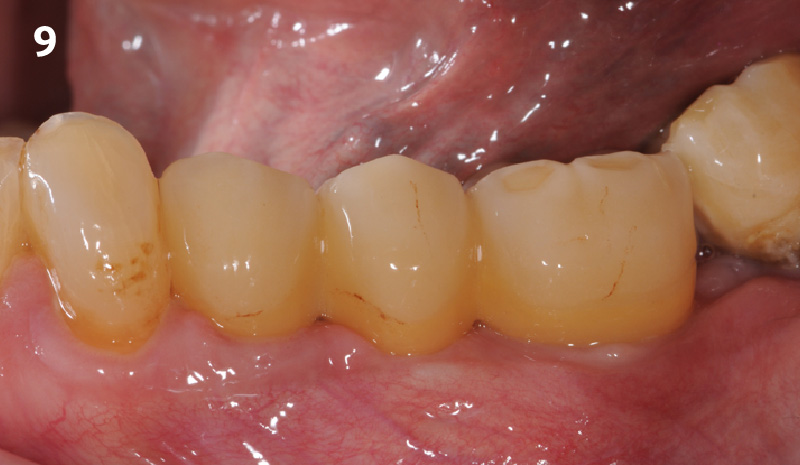
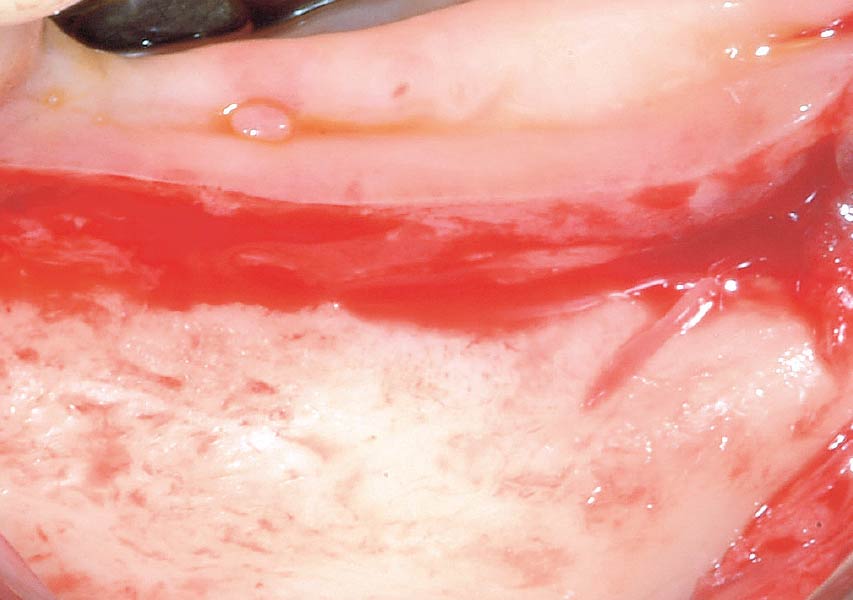
CLINICAL CASE
THE APPROACH
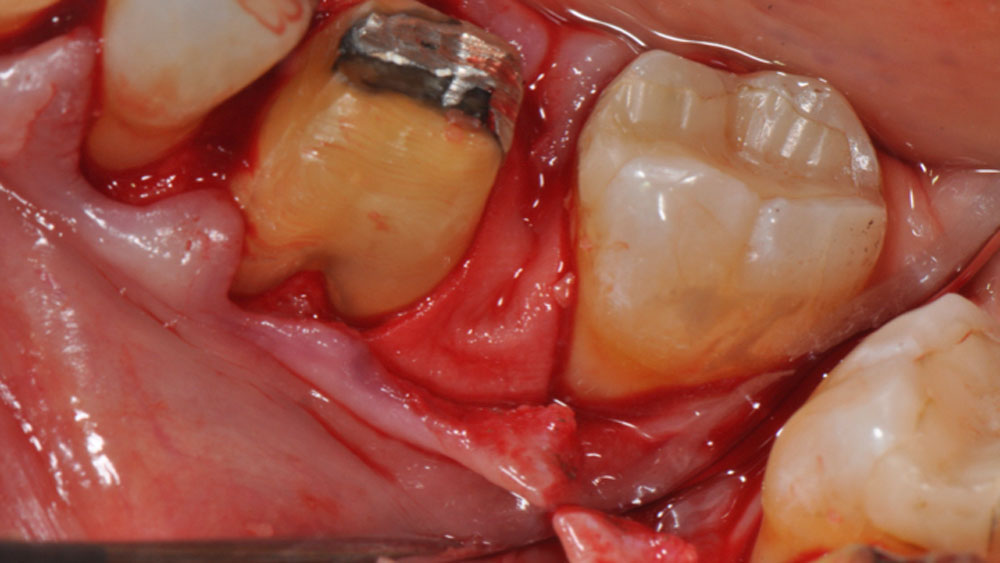
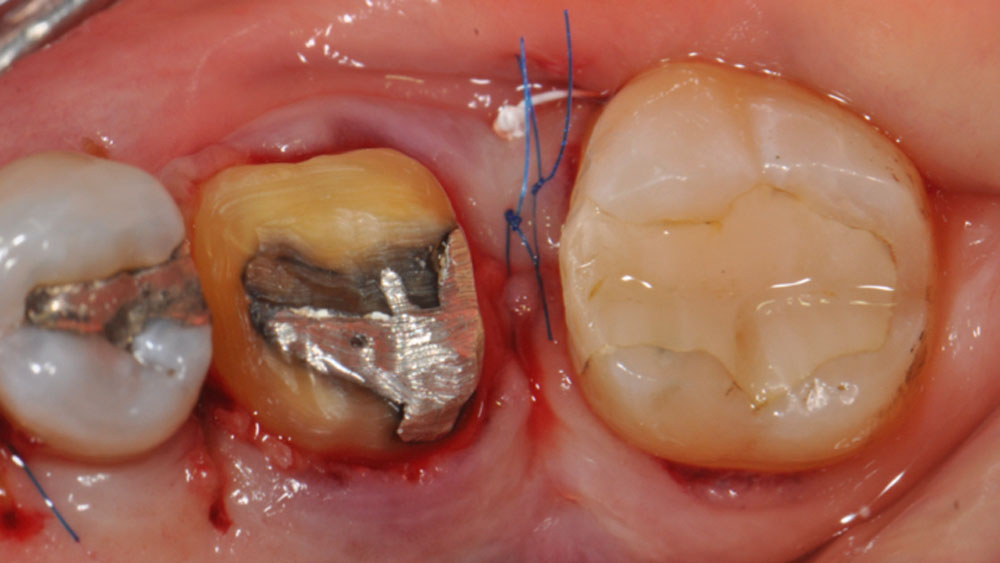
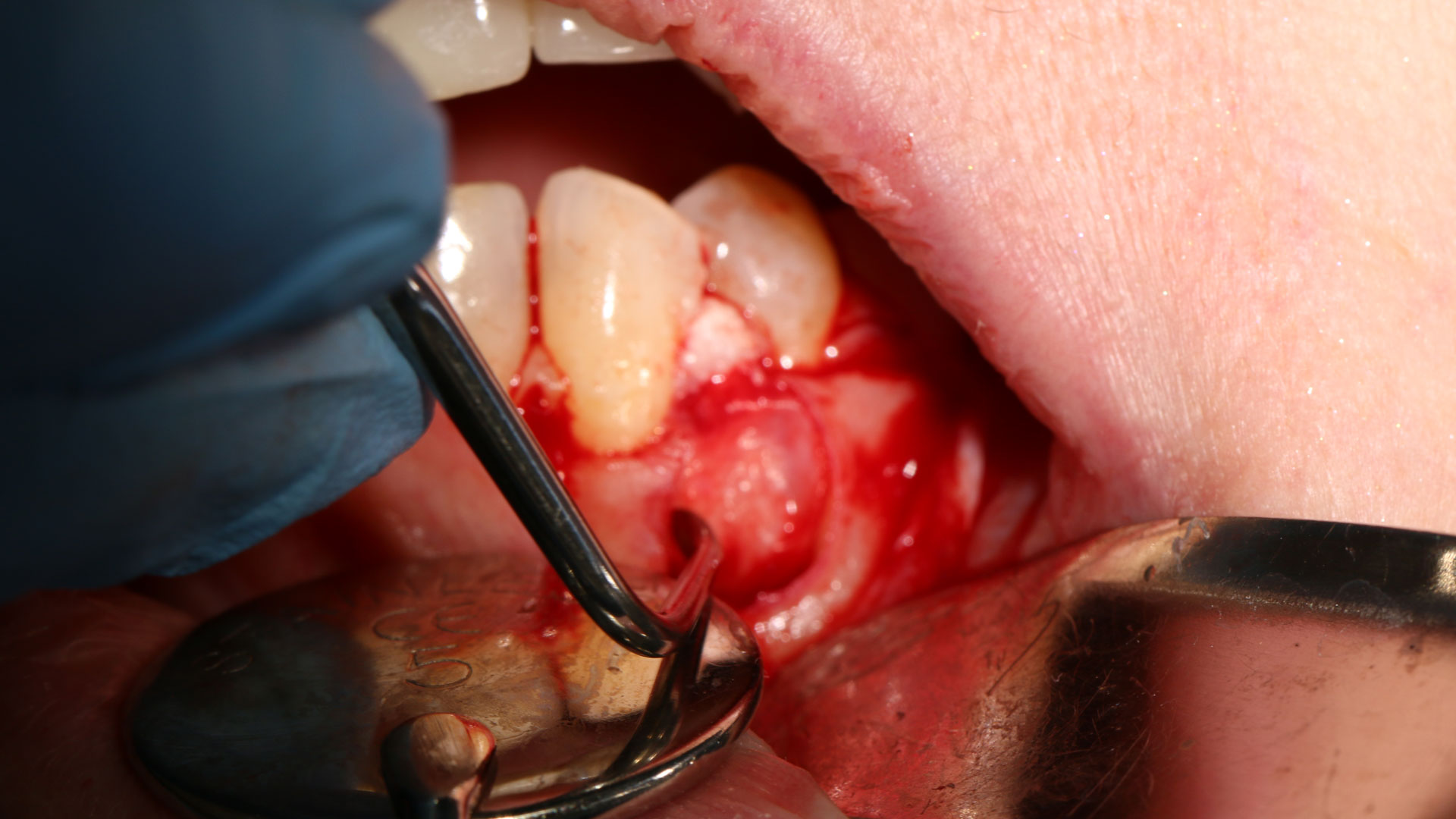
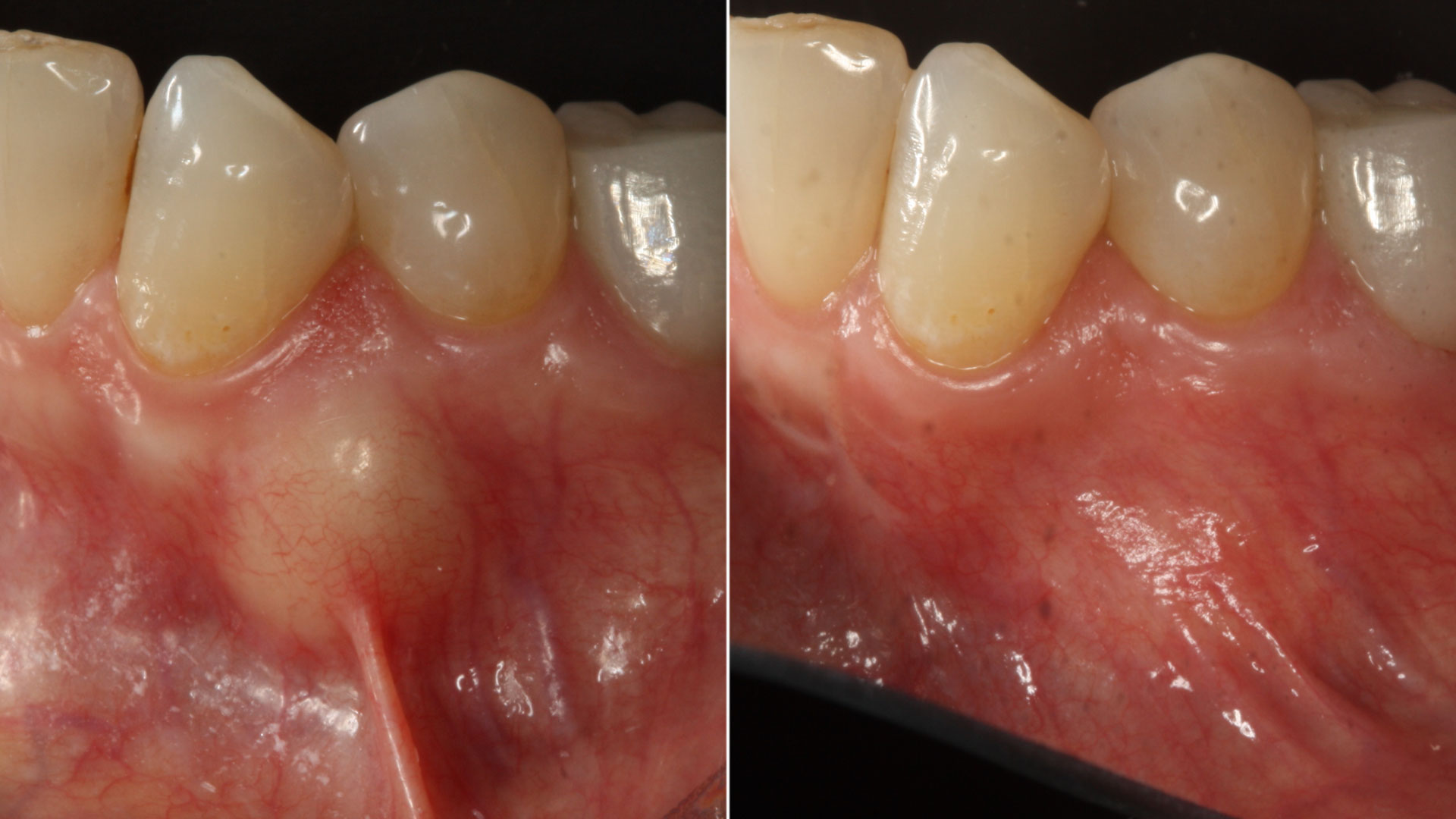
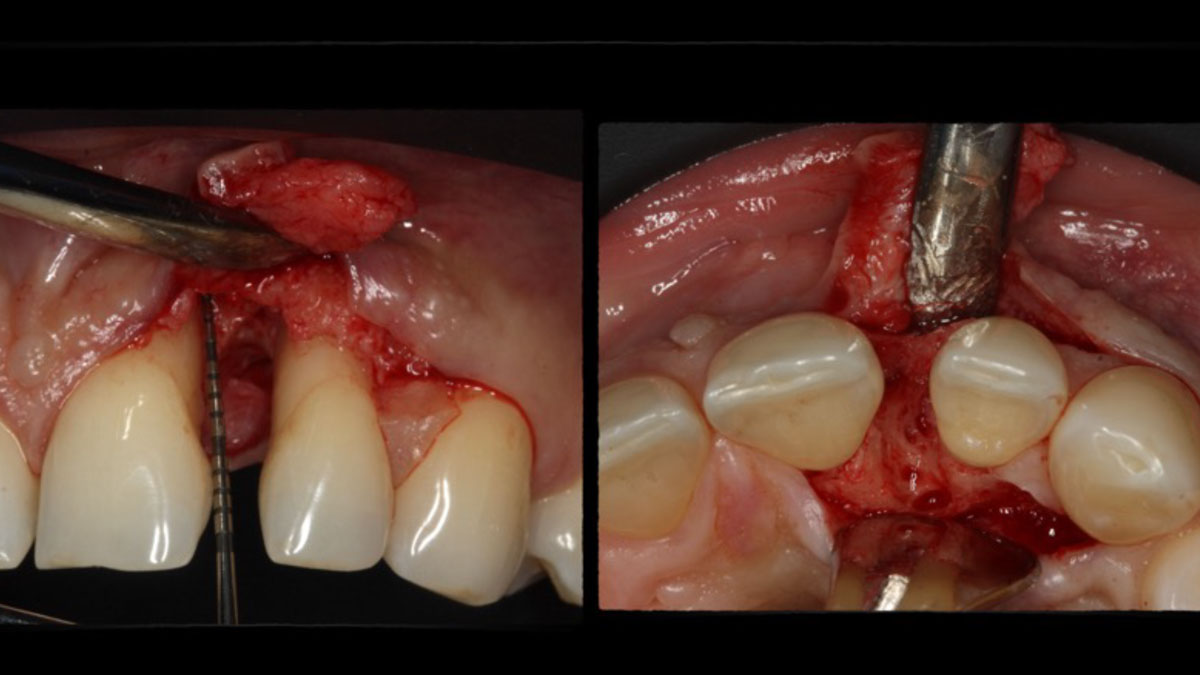
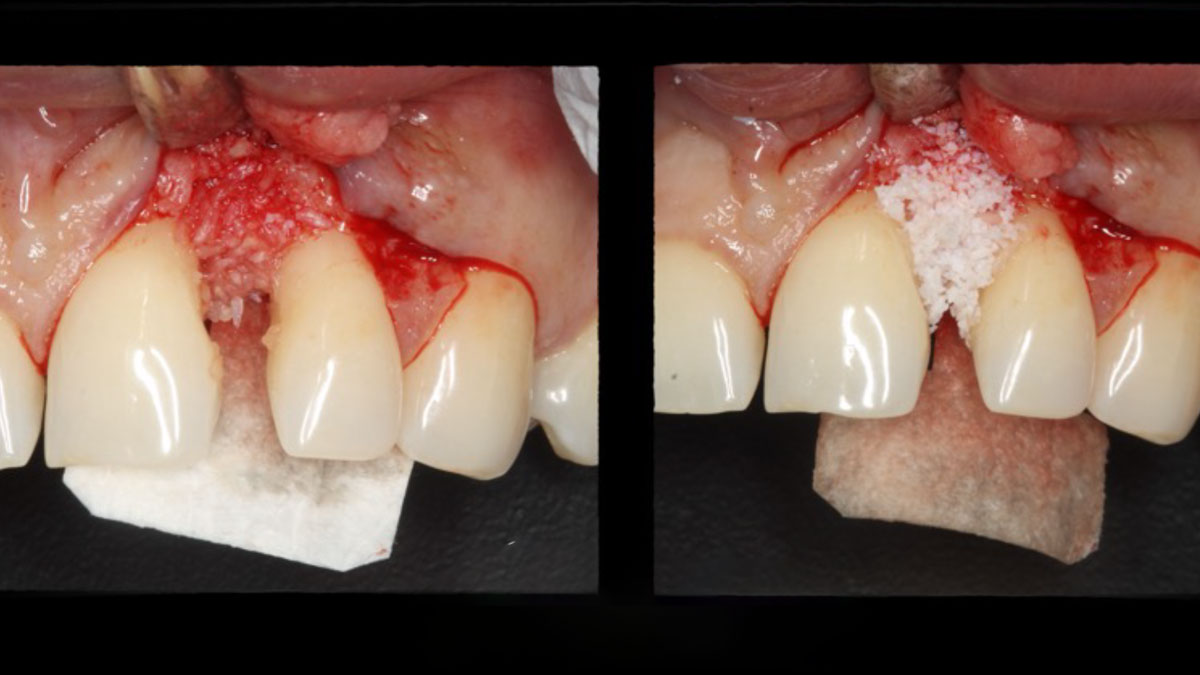
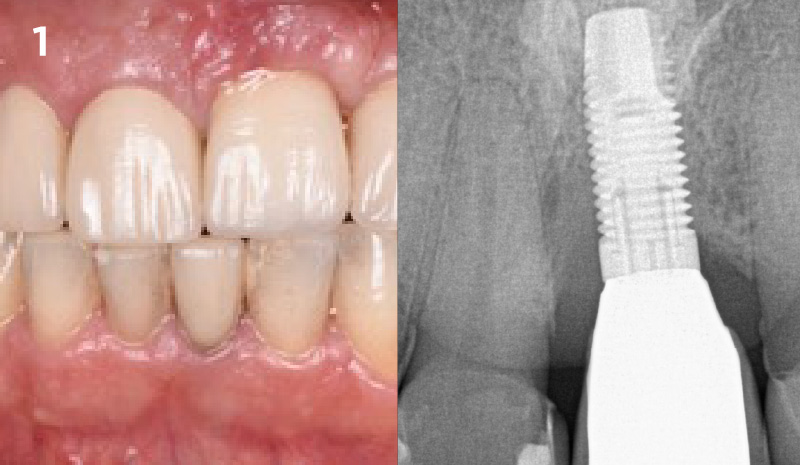
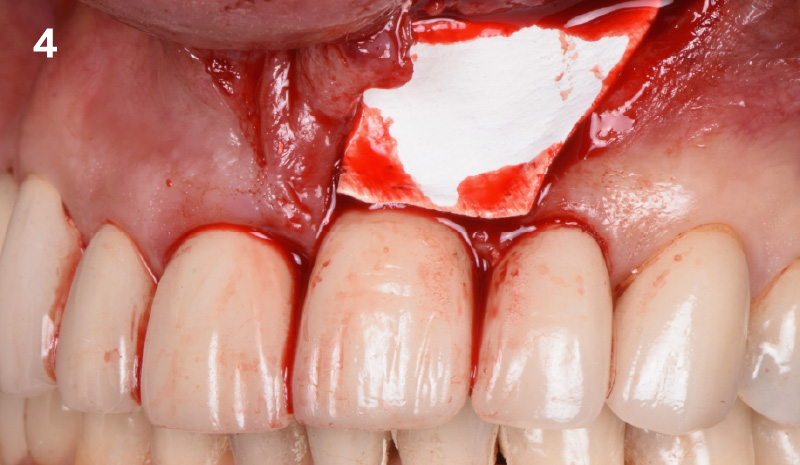
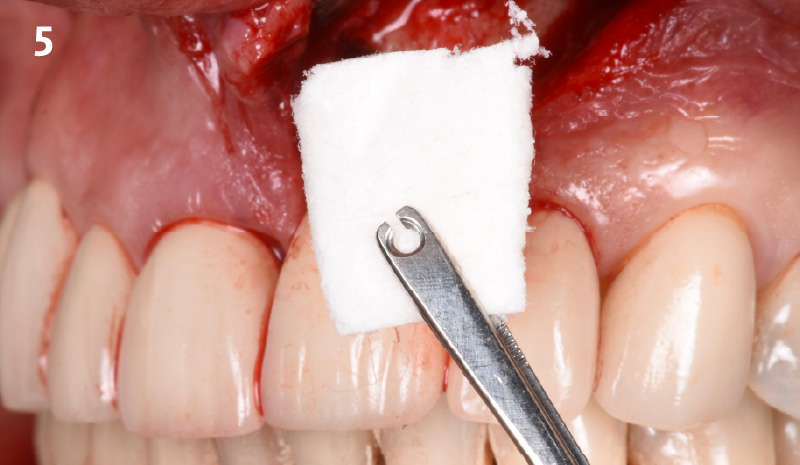
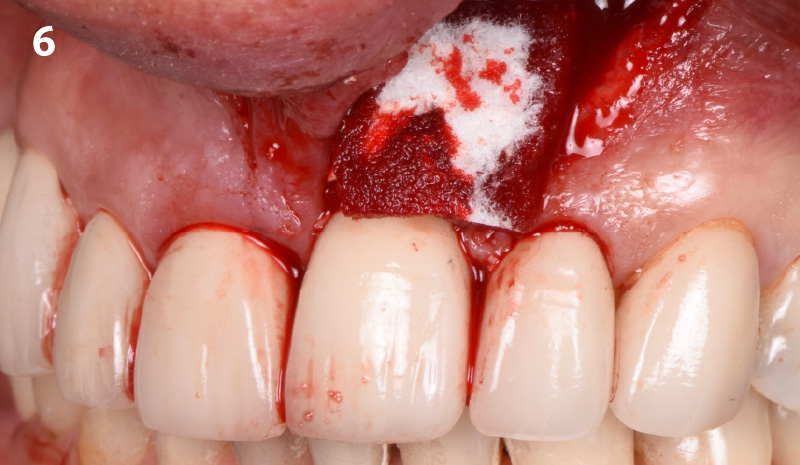
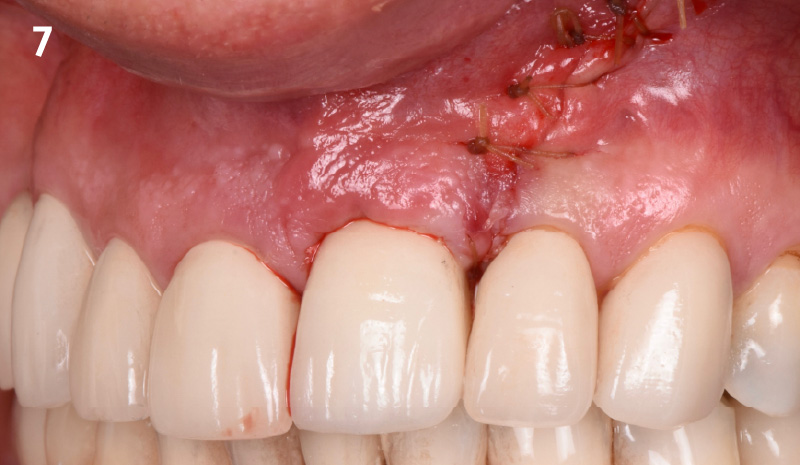
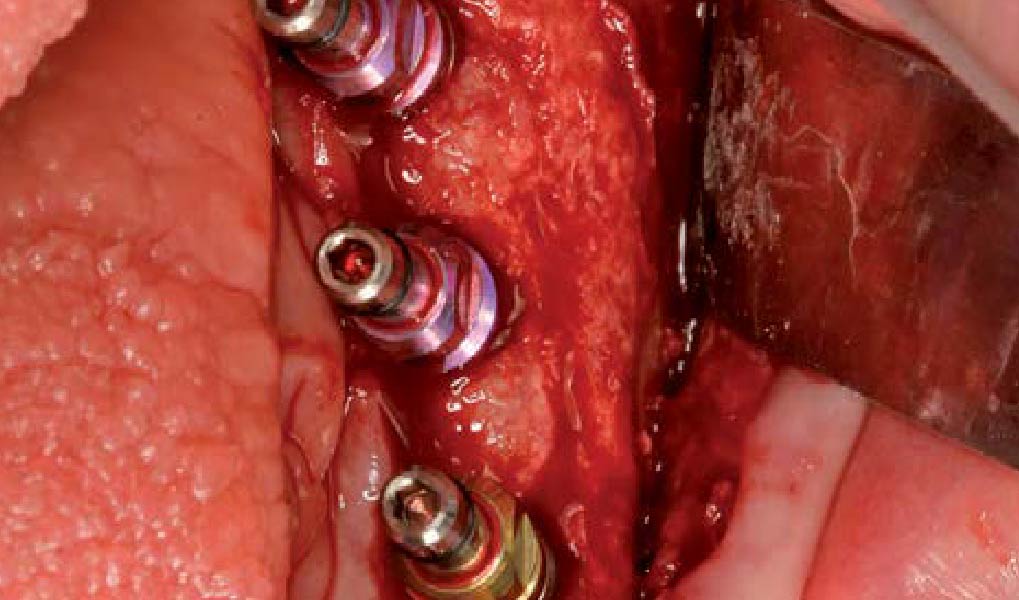
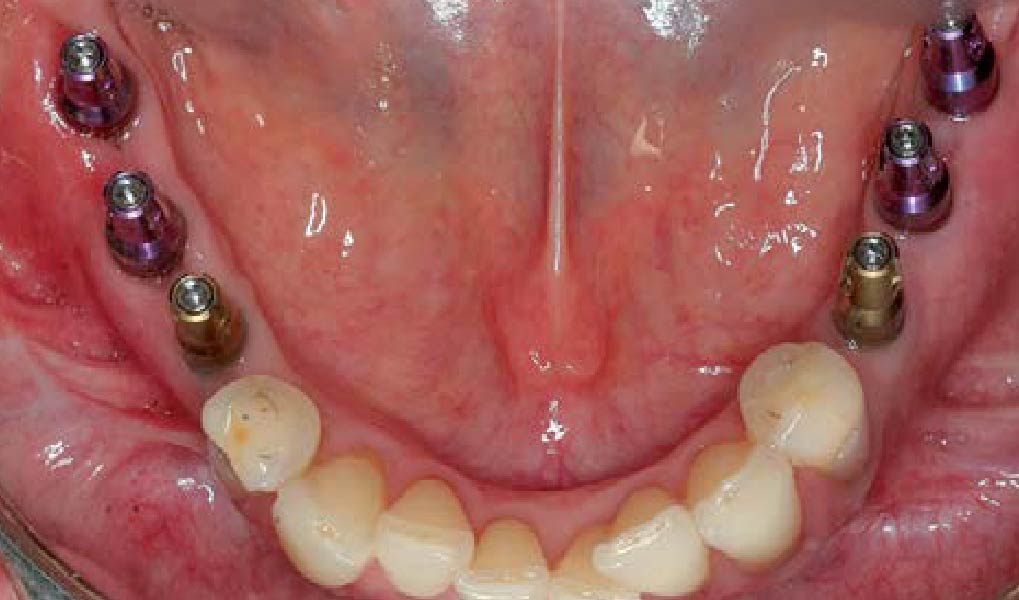
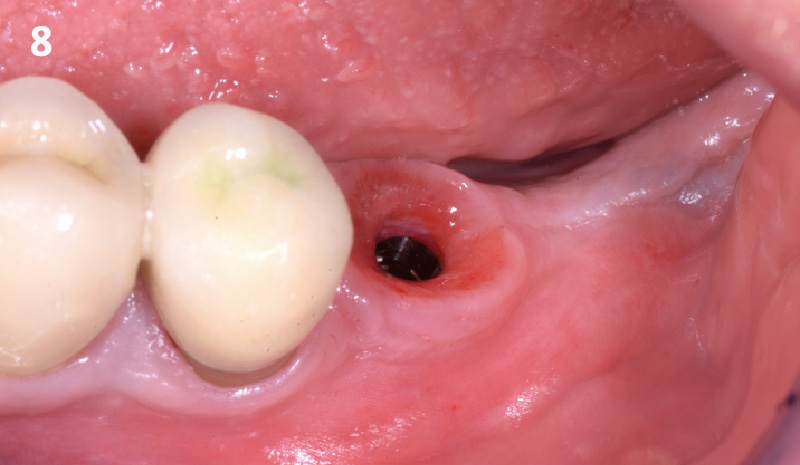
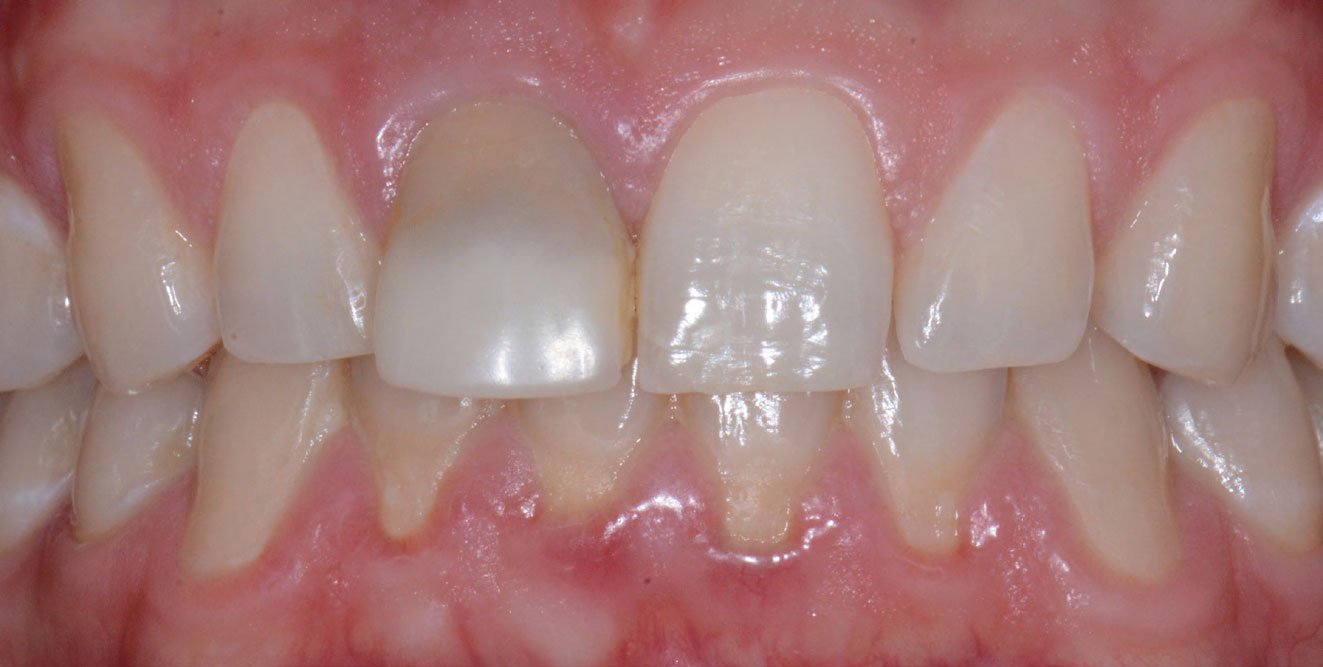
The crown was biologically shaped, and the root surface was detoxified using Ellman burs. Following flap elevation and thorough defect debridement, an allograft mixed with GEM 21S® was used to fill the defect. The graft was then covered with Geistlich Bio-Gide®.
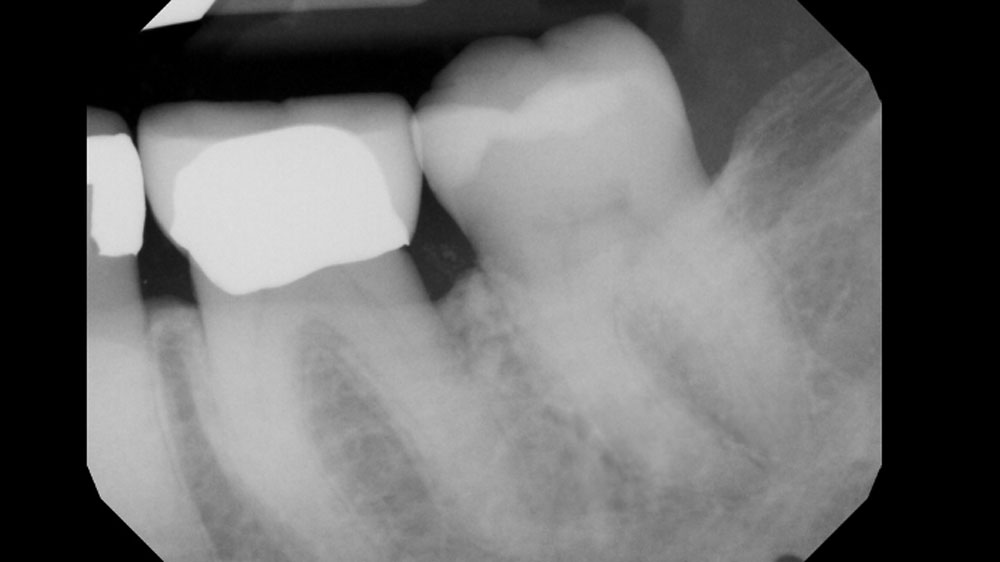
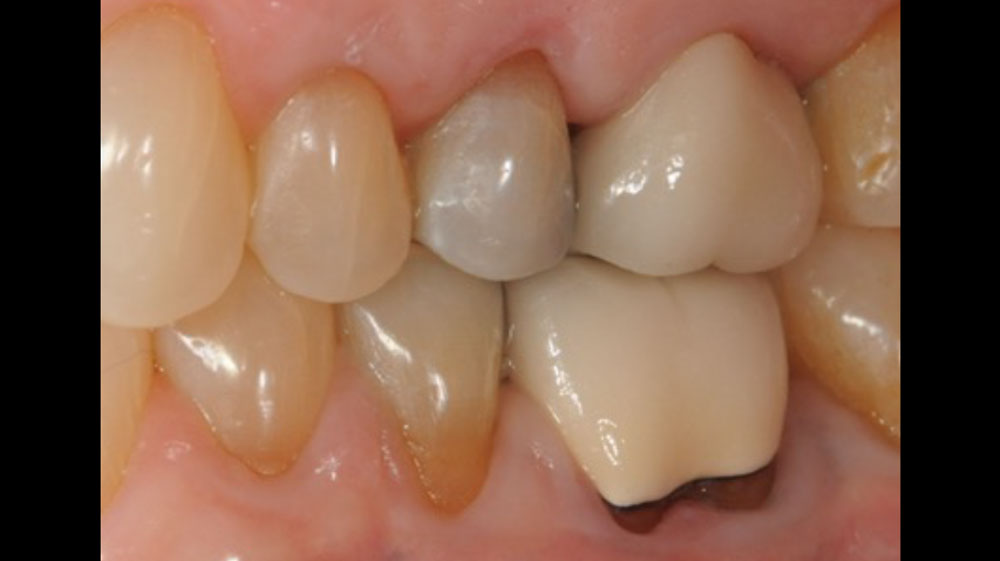
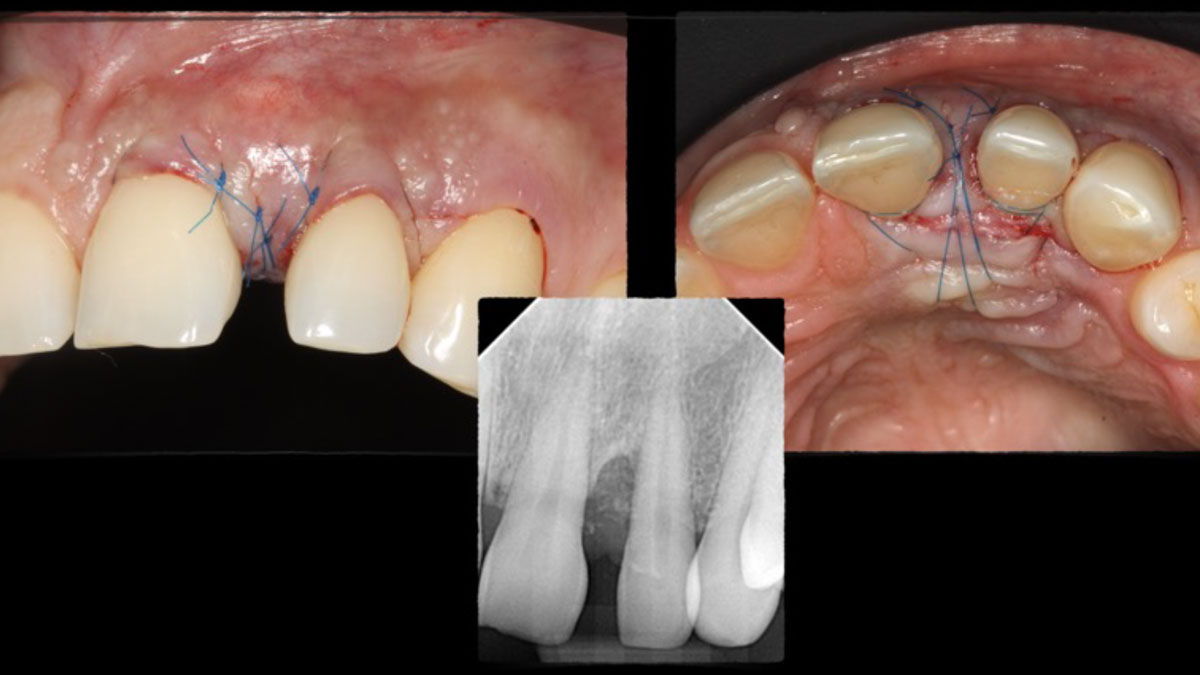
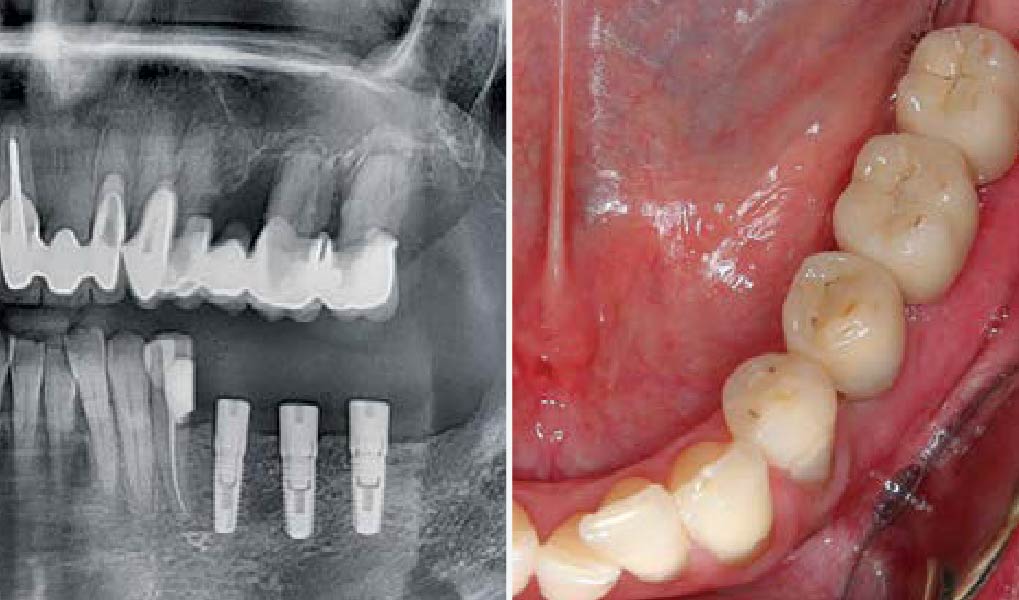
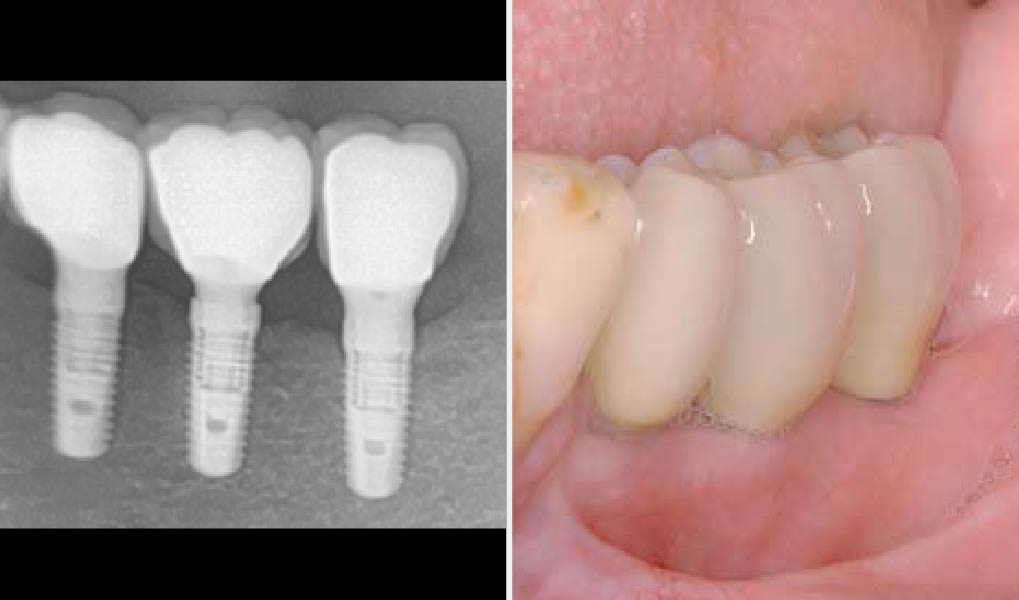
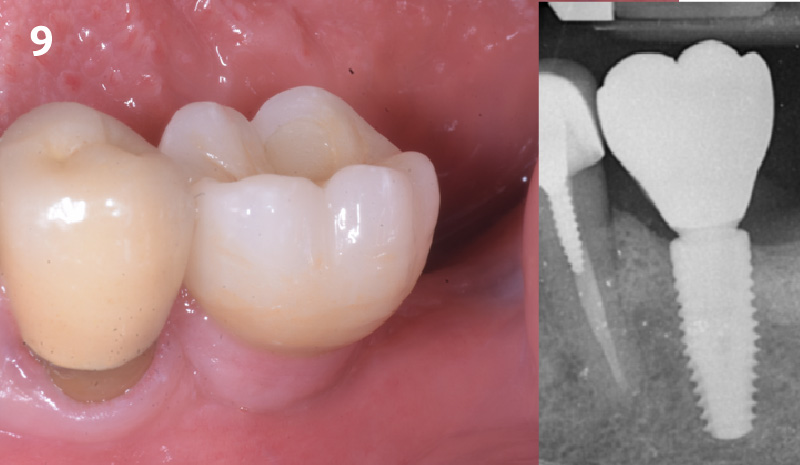
THE OUTCOME
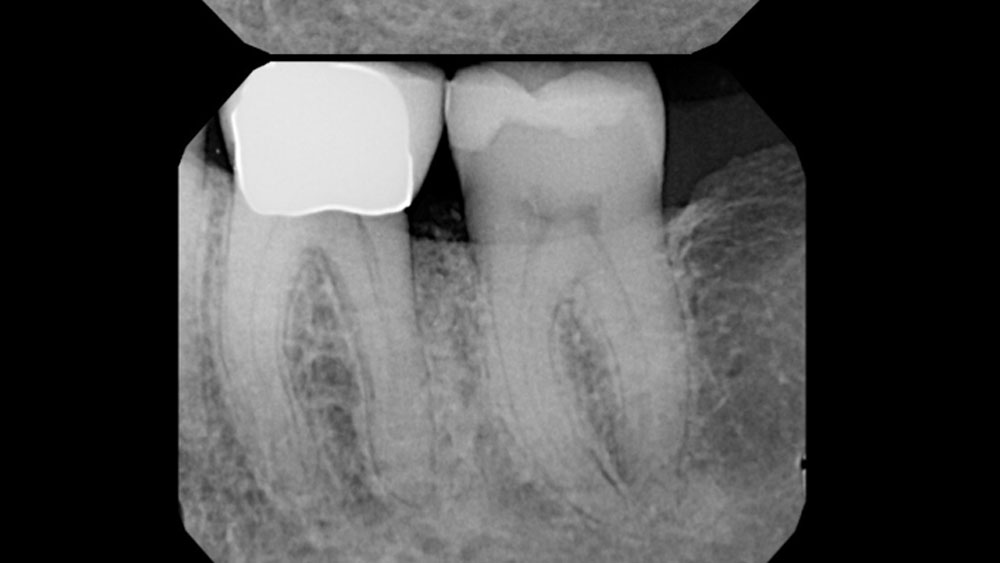
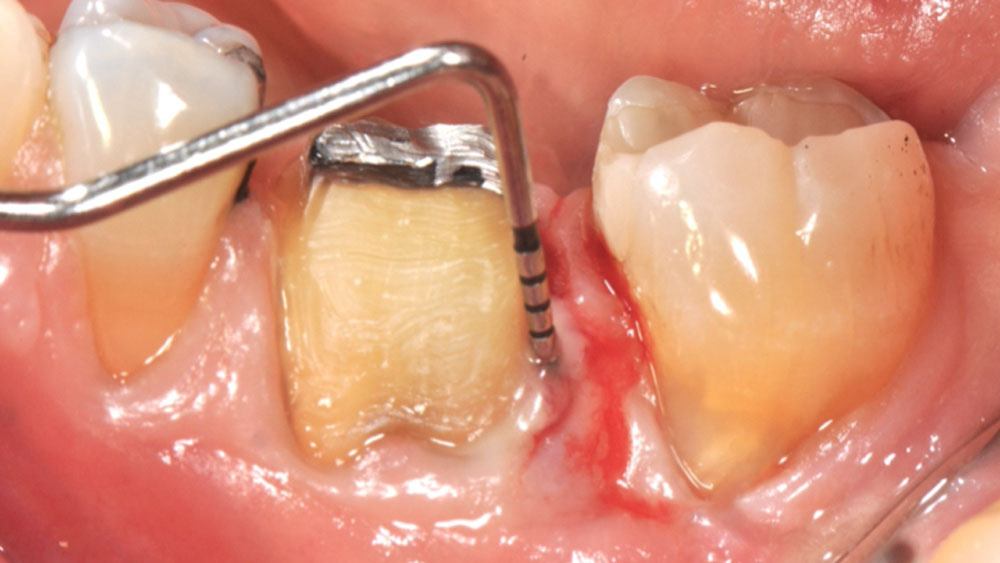
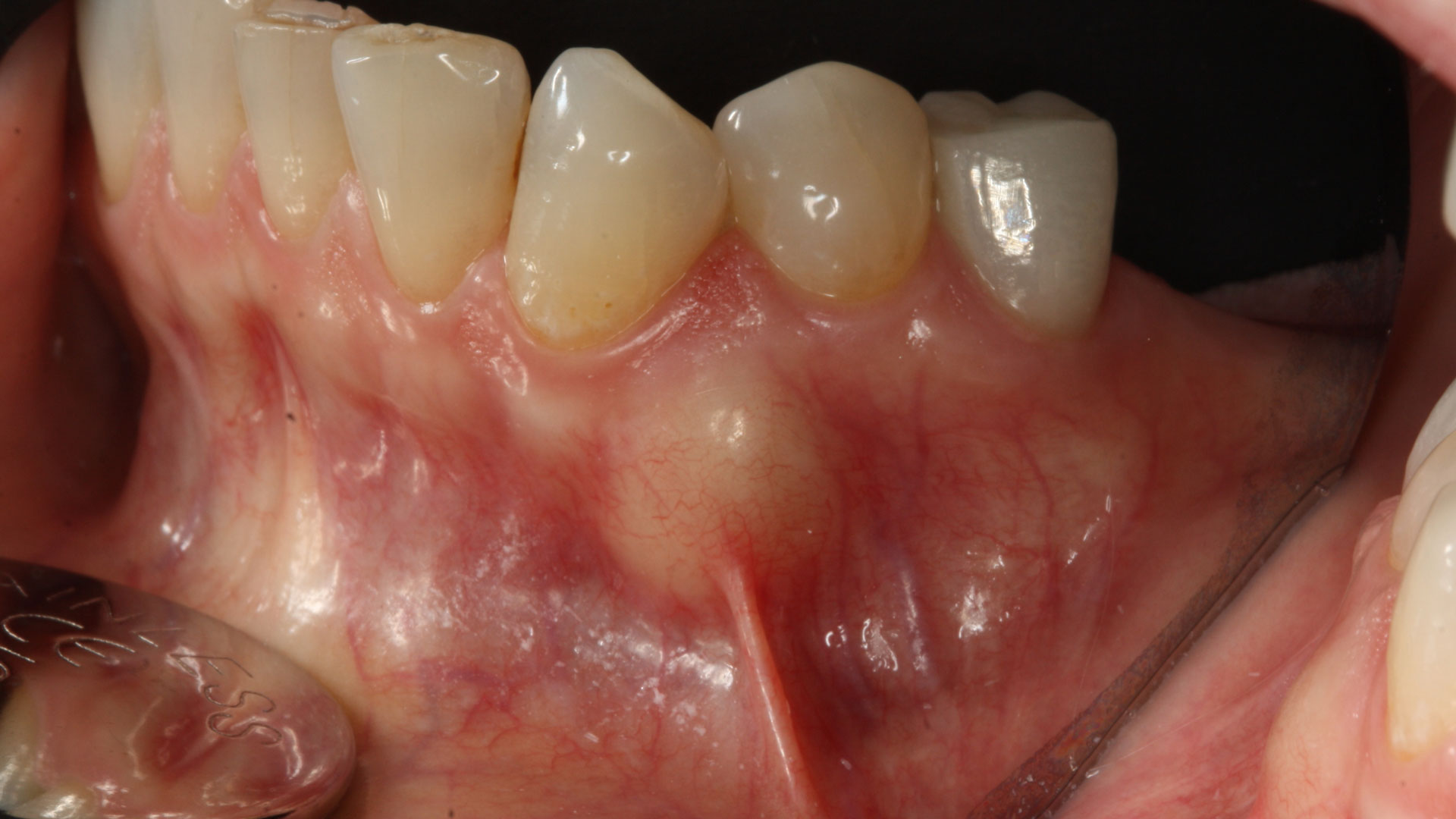
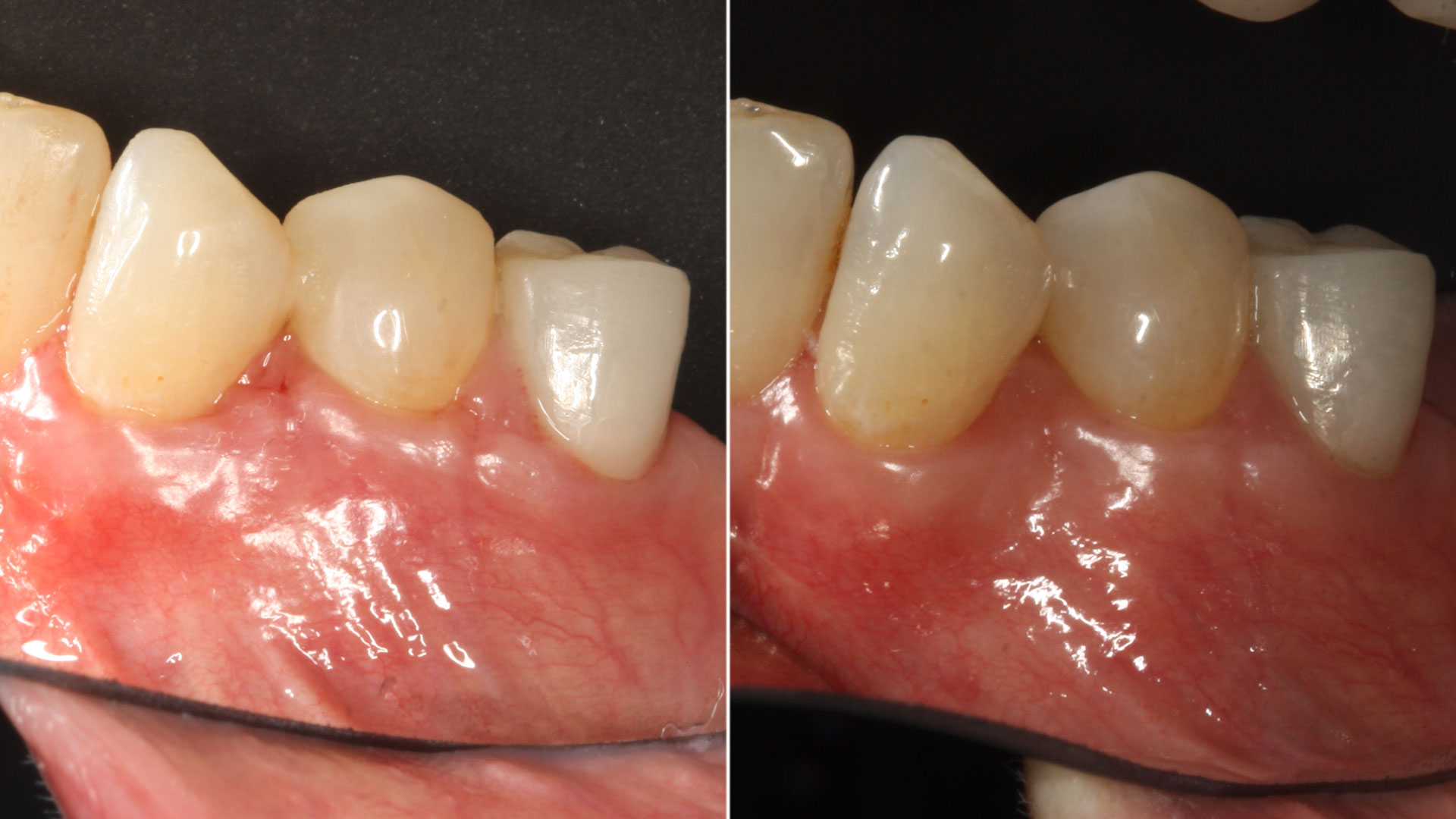
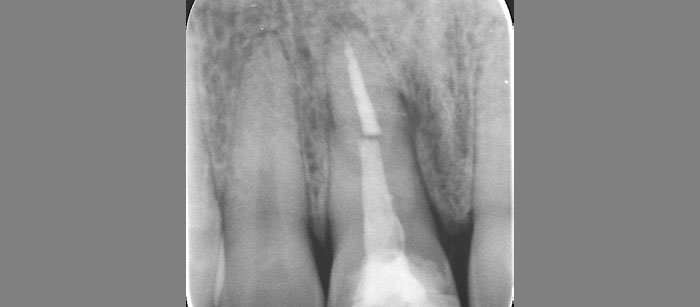
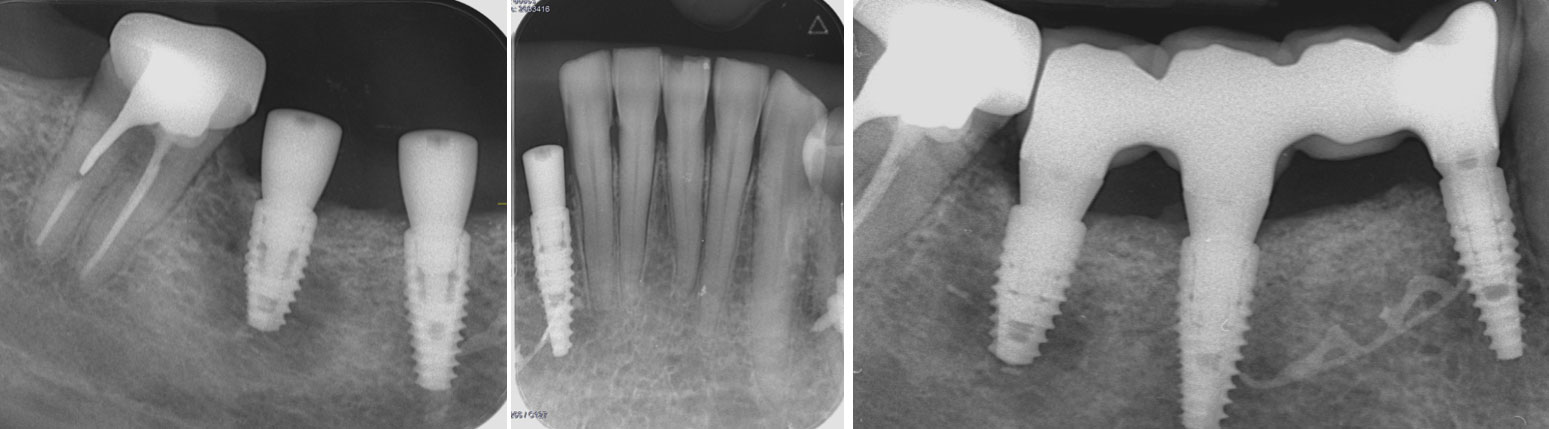
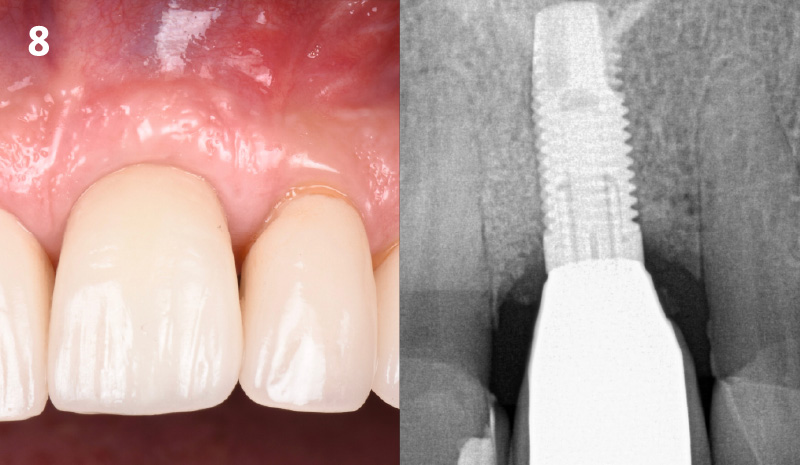
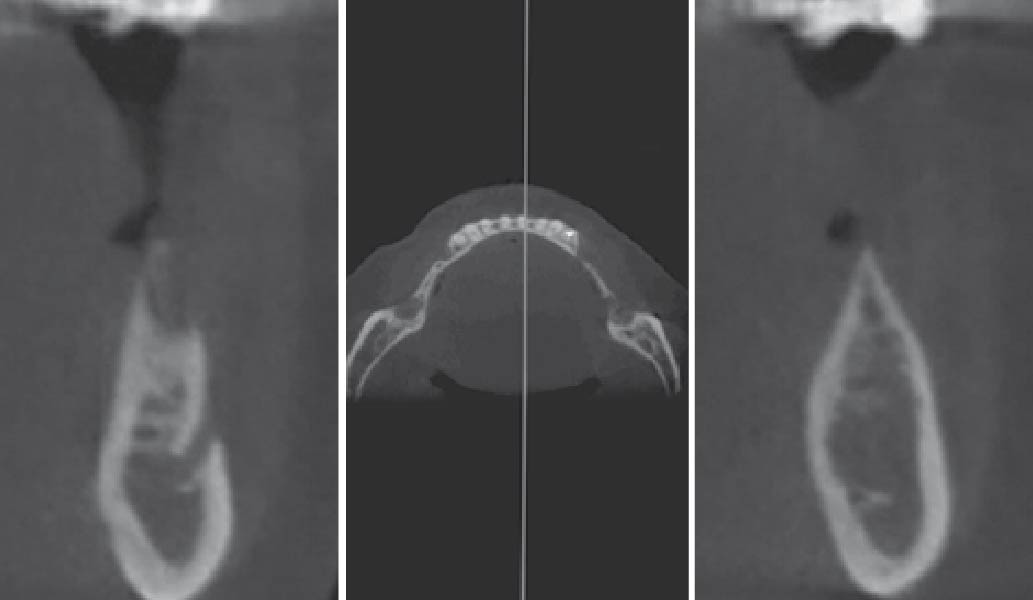
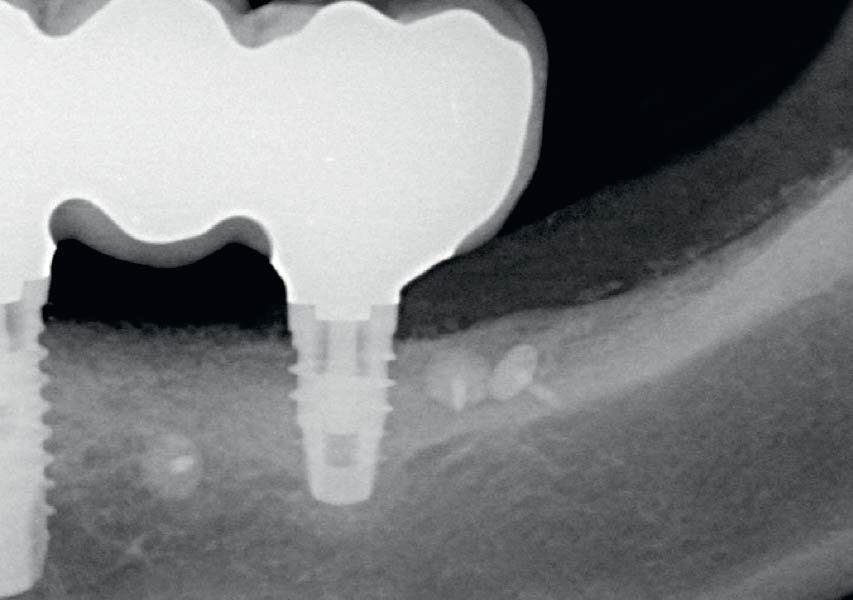
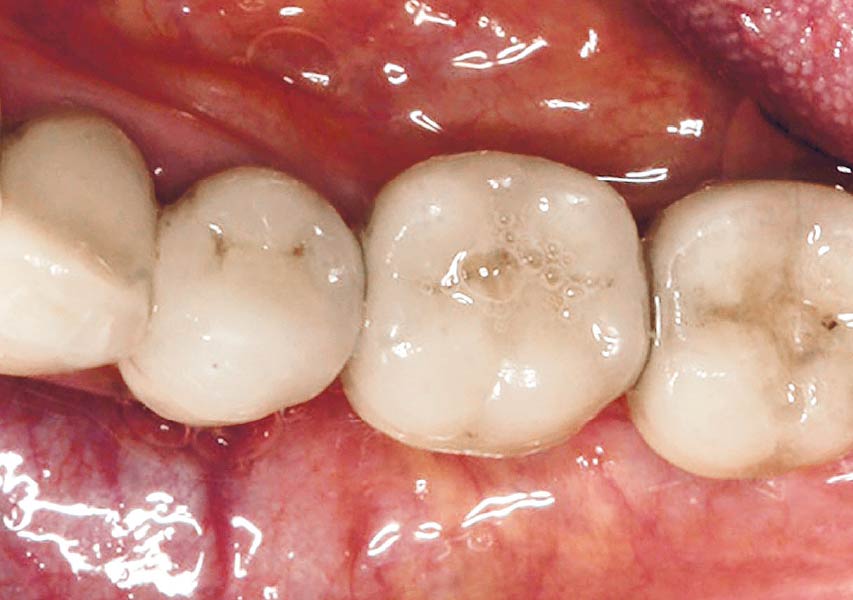
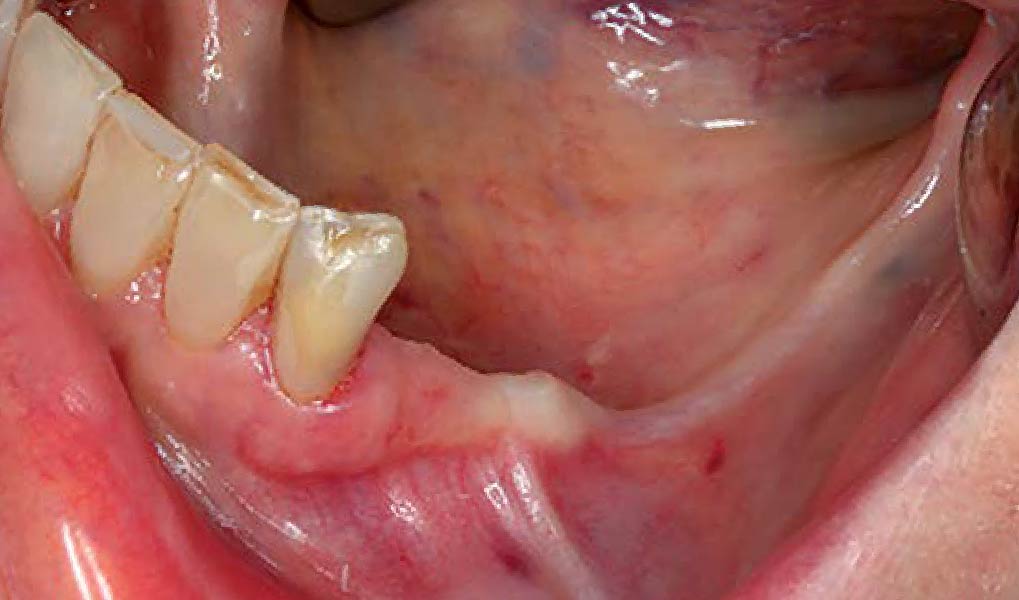
At the 10-month follow-up, radiographs revealed evidence of bone fill, and clinically, the interdental tissue showed signs of maturation. At the 9-year follow-up, clinical photos demonstrated long-term stability, with maintained bone levels, minimal interproximal recession, and lack of facial recession. Radiographic analysis further confirmed the sustained stability of the bone.
Disclaimer: These results are not guaranteed; individual outcomes may vary depending on patient circumstances. This information is for informational purposes only and may not reflect Geistlich’s official position, opinion, or recommendation. Treatment decisions are made at the physician’s discretion, based on the unique needs of each patient.

BIOBRIEF
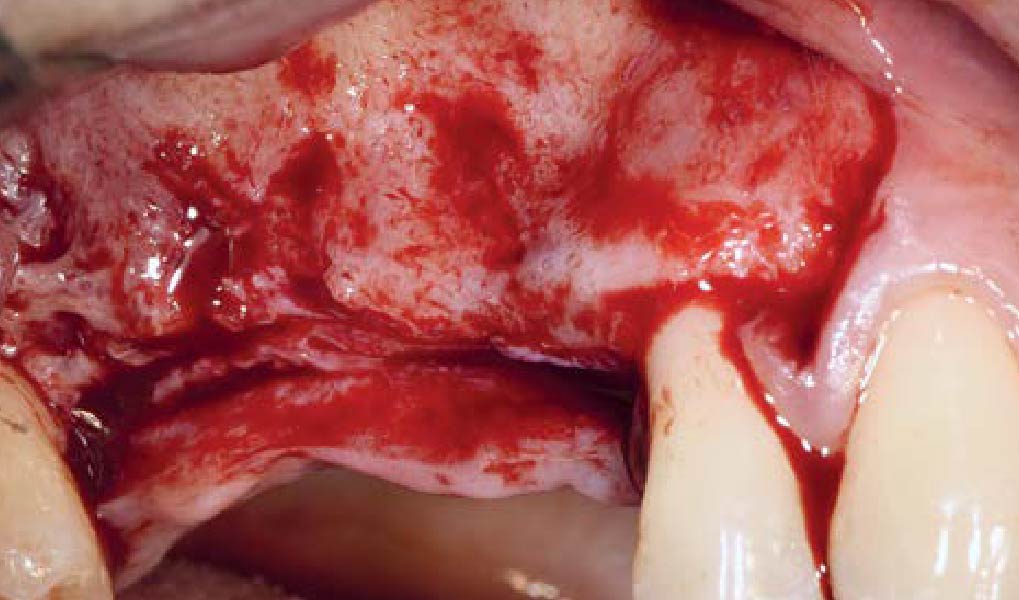
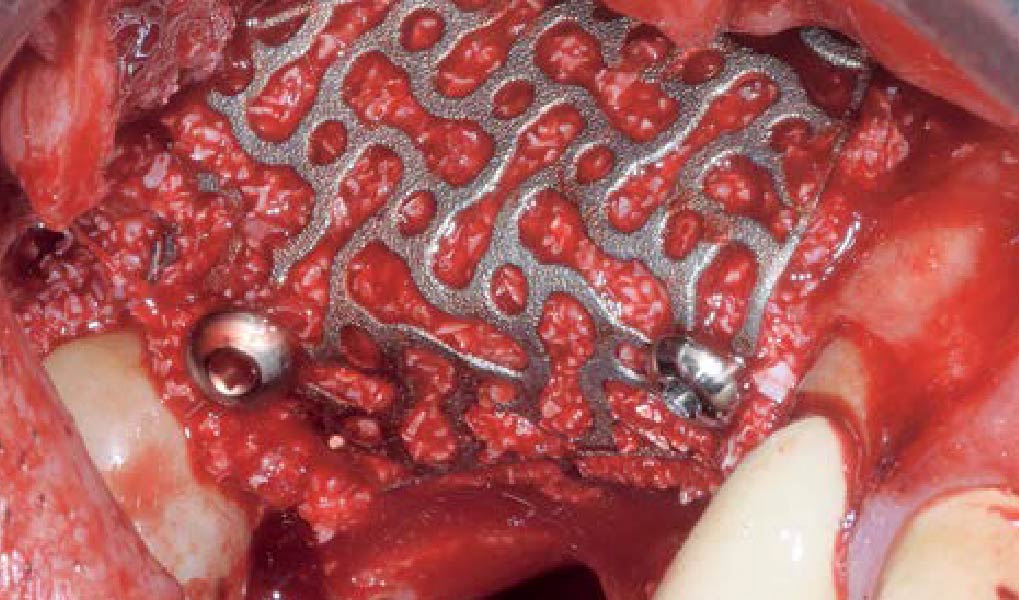
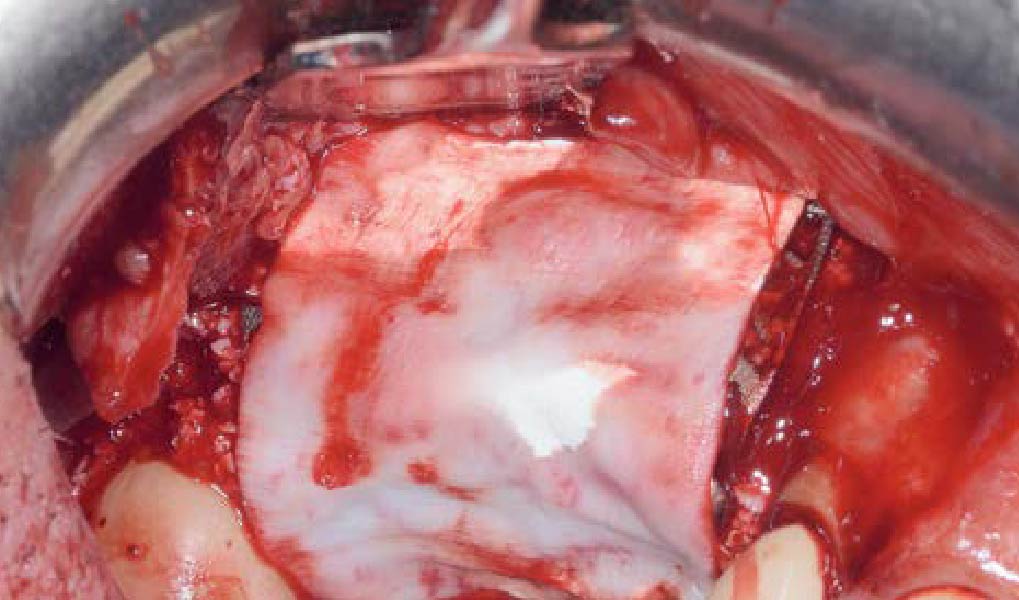
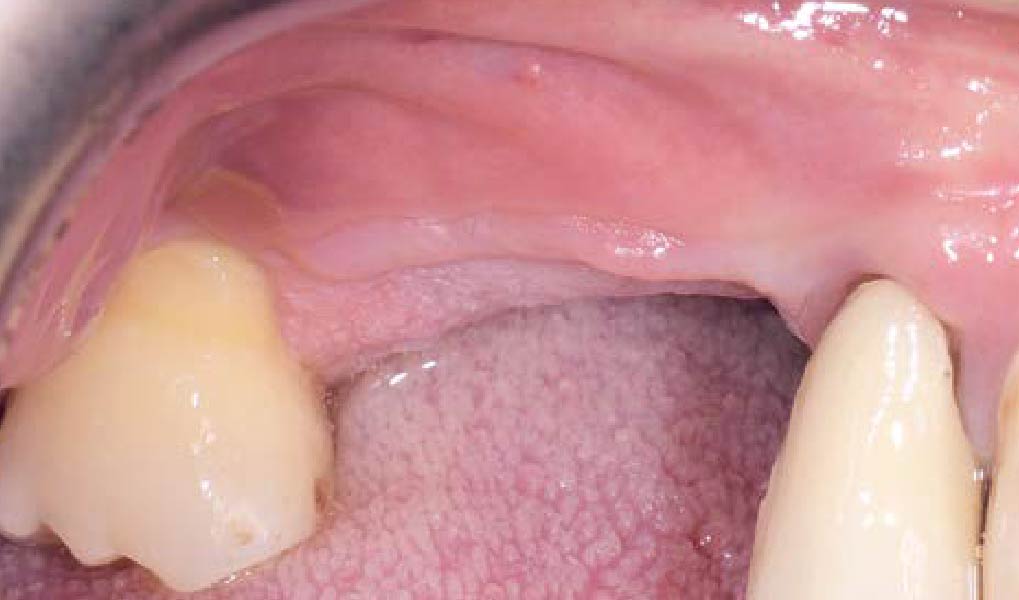
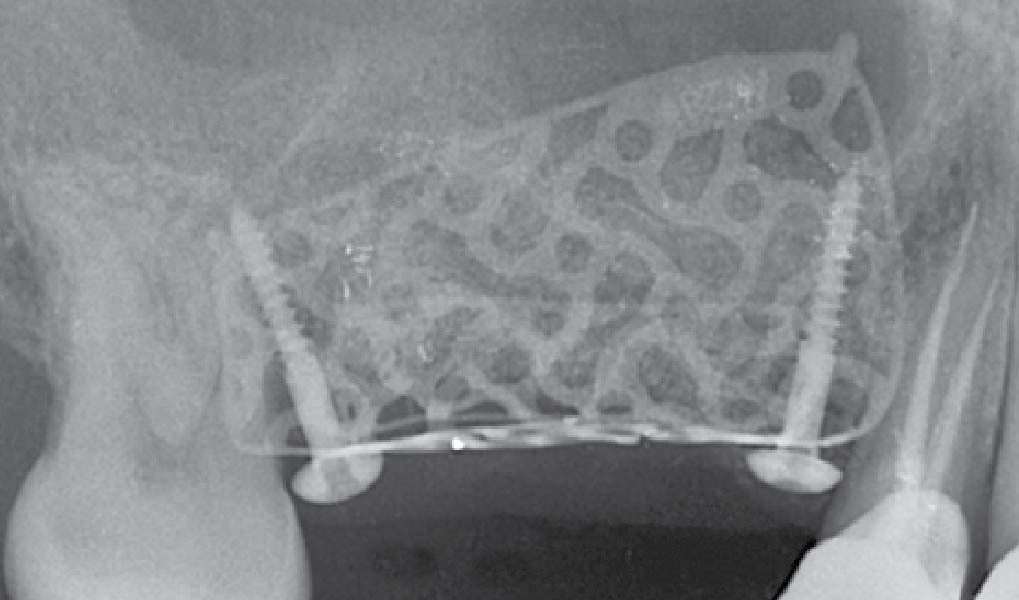
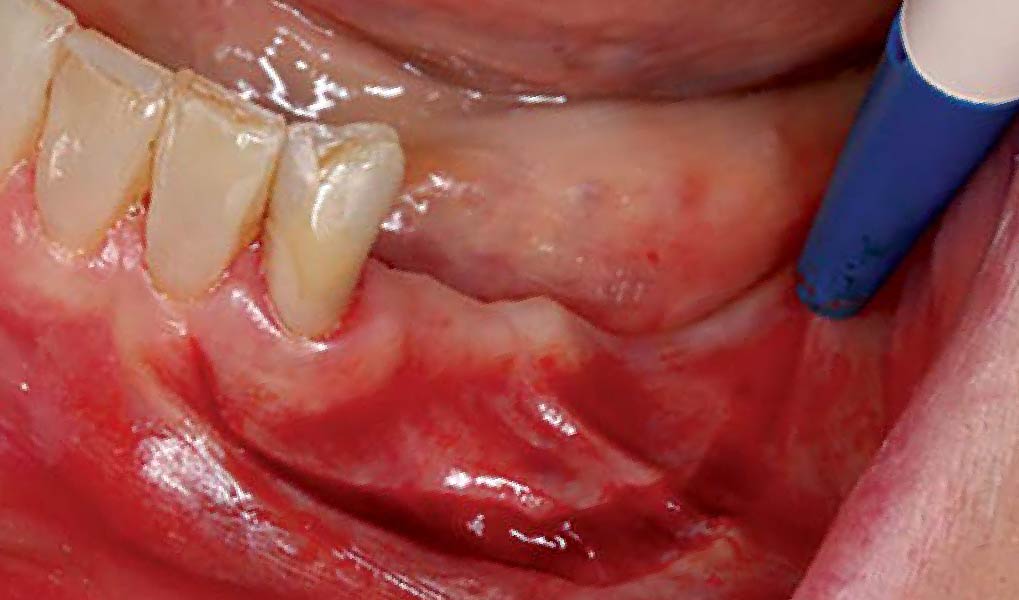
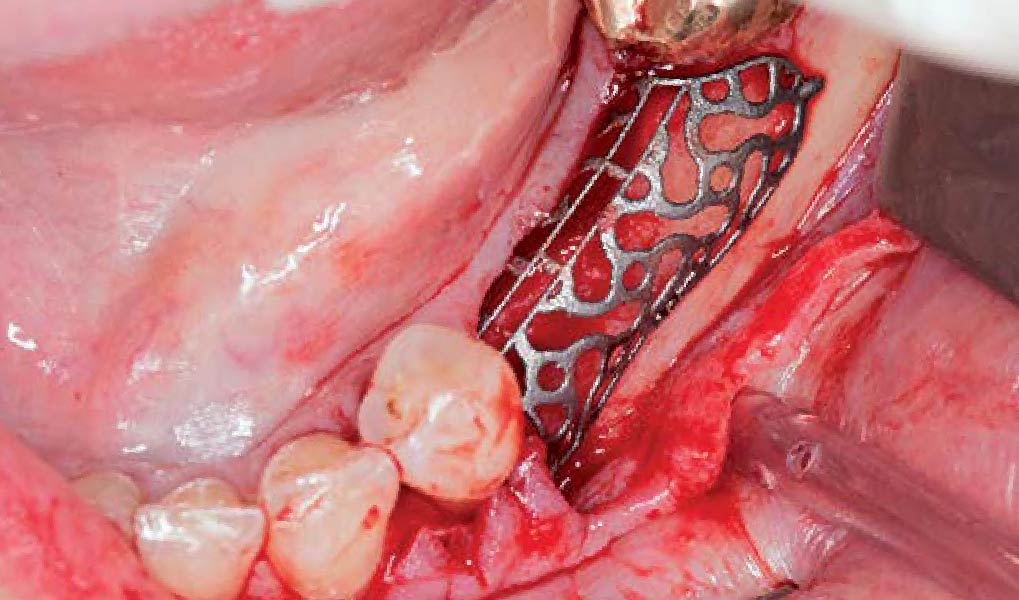
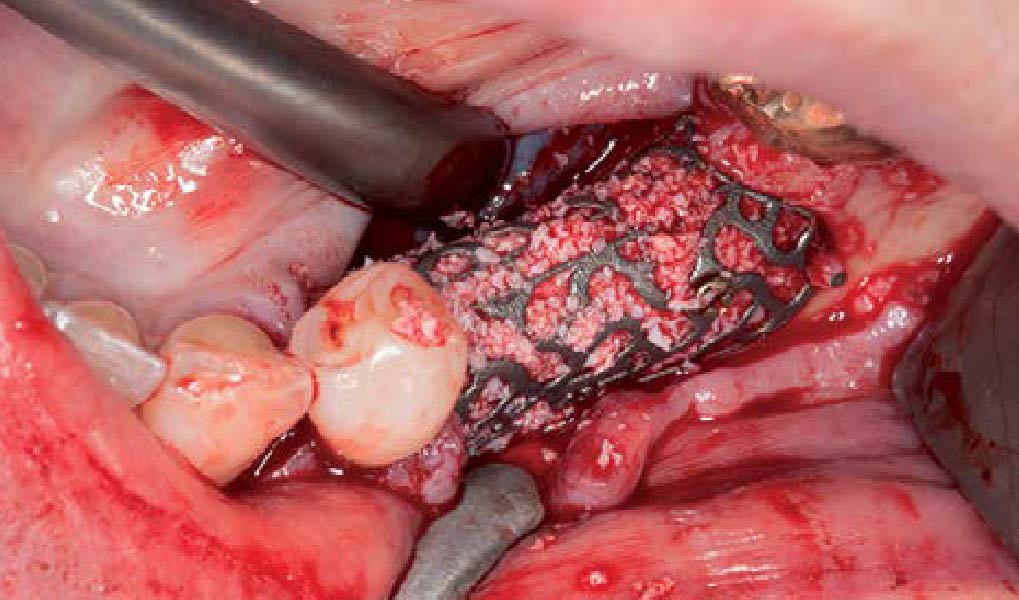
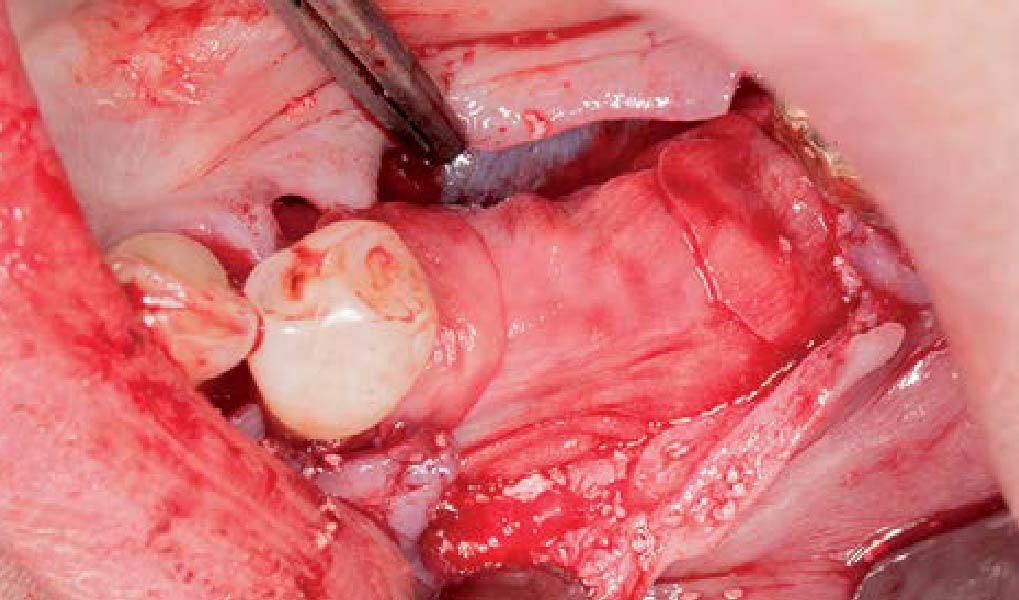
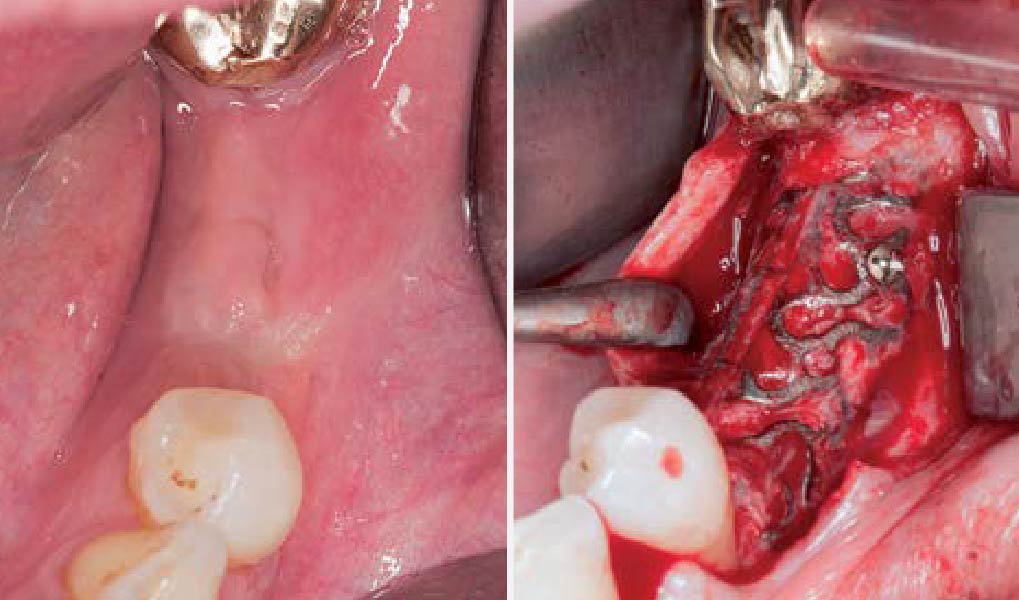
Mandibular Ridge Augmentation Using Customized Titanium Mesh
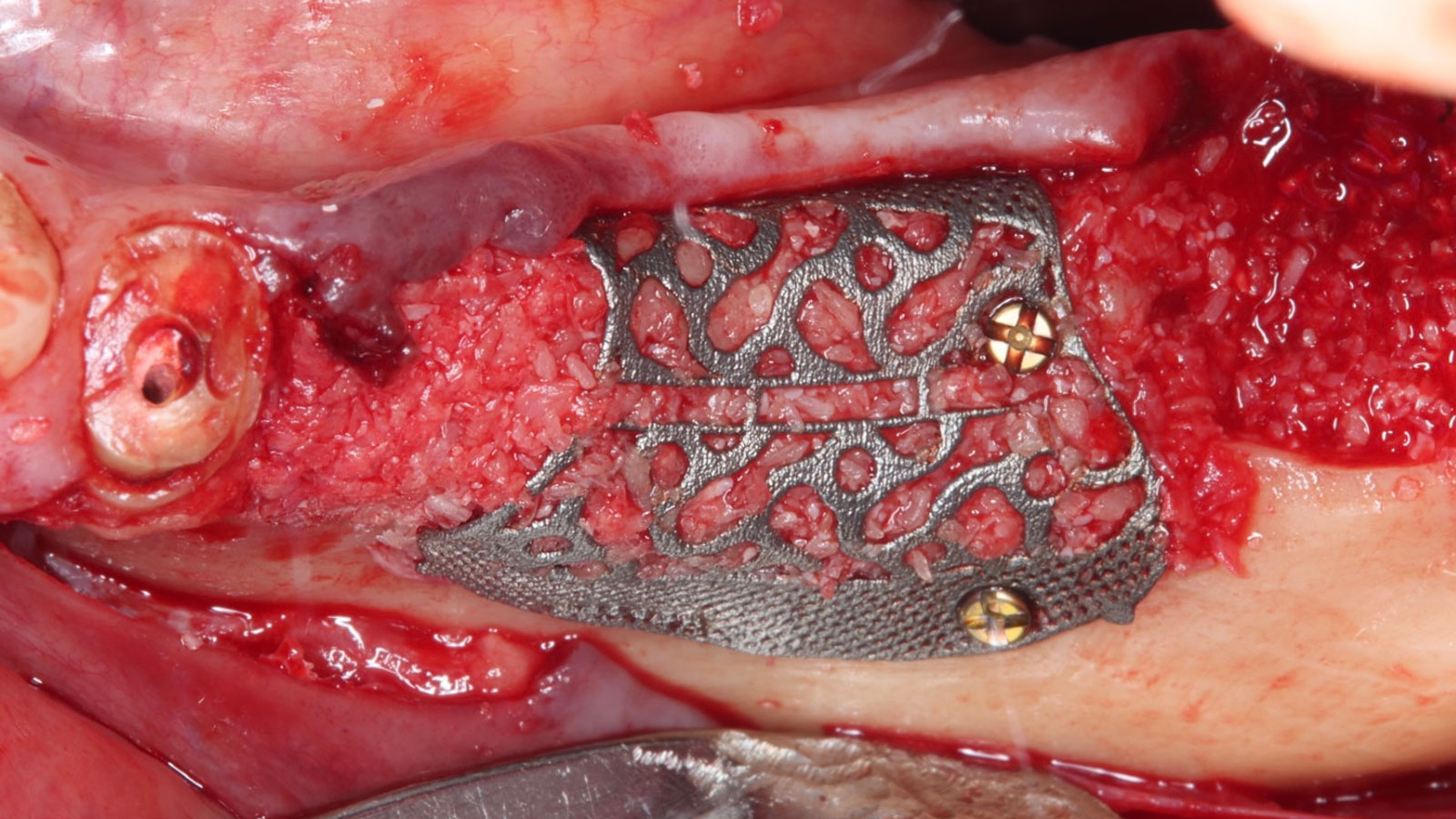

THE SITUATION
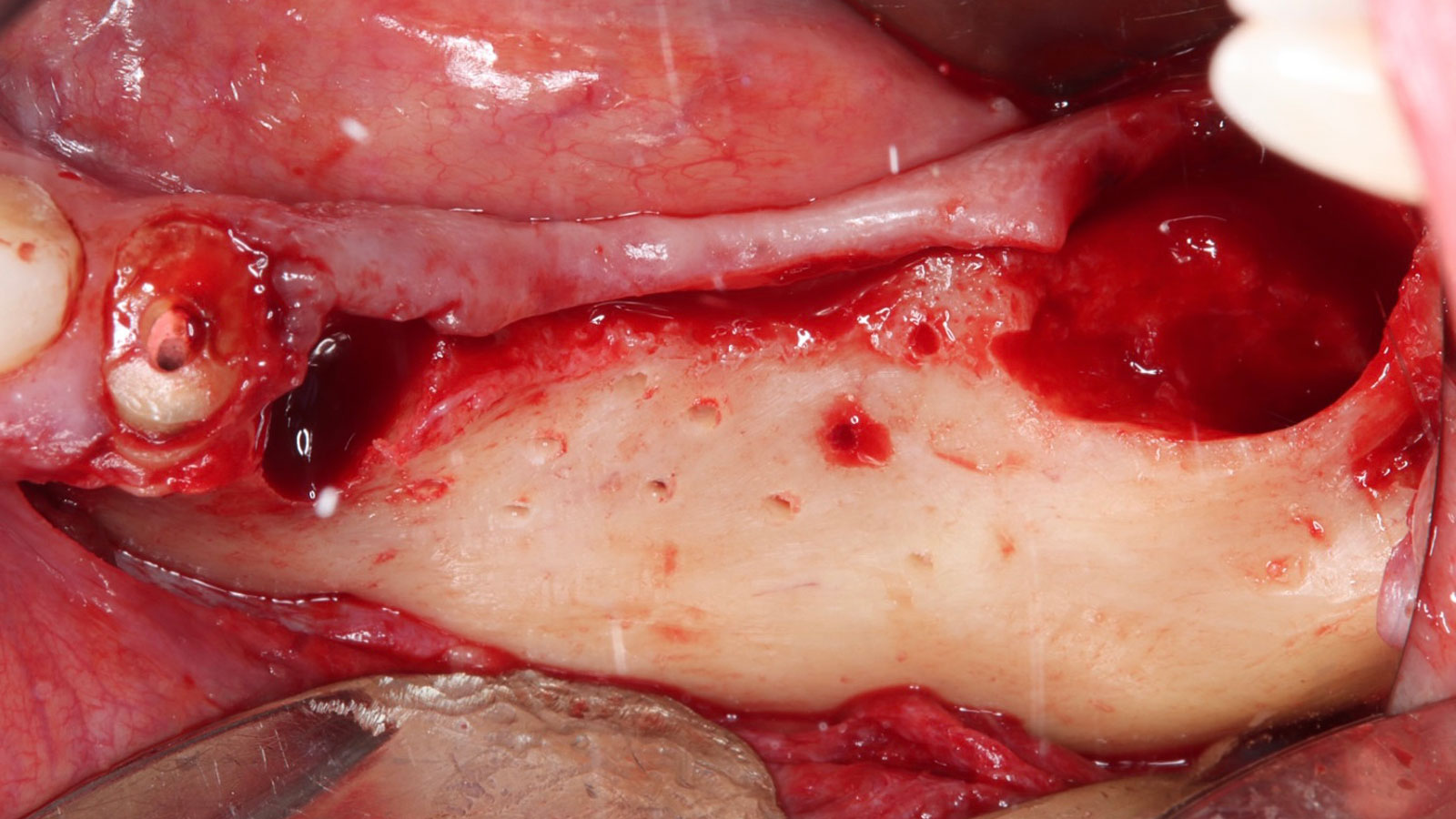
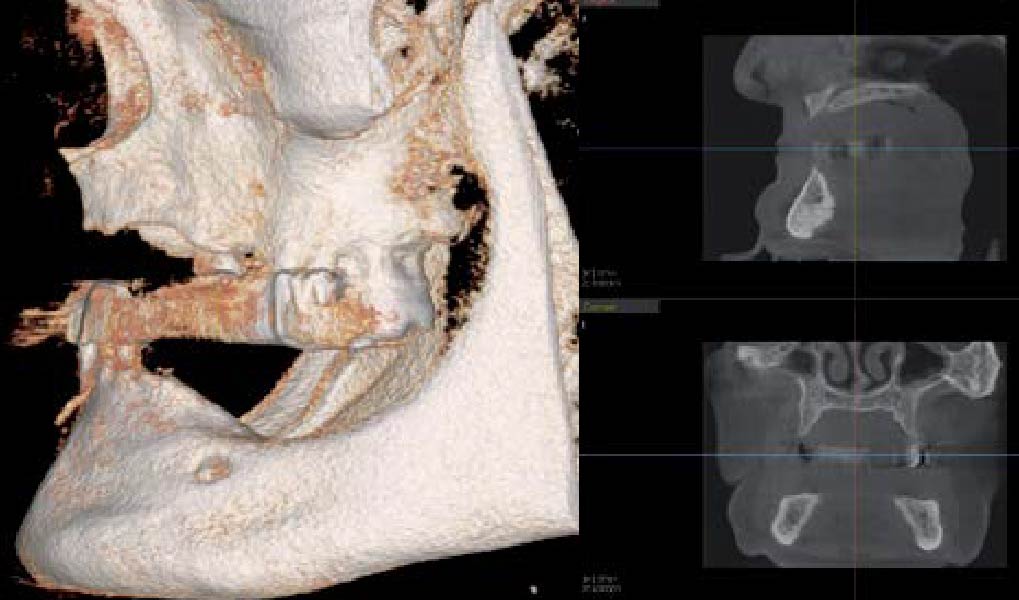
A 60-year-old healthy male presented with a failing lower left bridge. Due to a long history of missing teeth, he had a significantly atrophic mandibular ridge. We decided to use a customized titanium mesh to achieve the necessary vertical and horizontal bone augmentation for dental implant rehabilitation.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
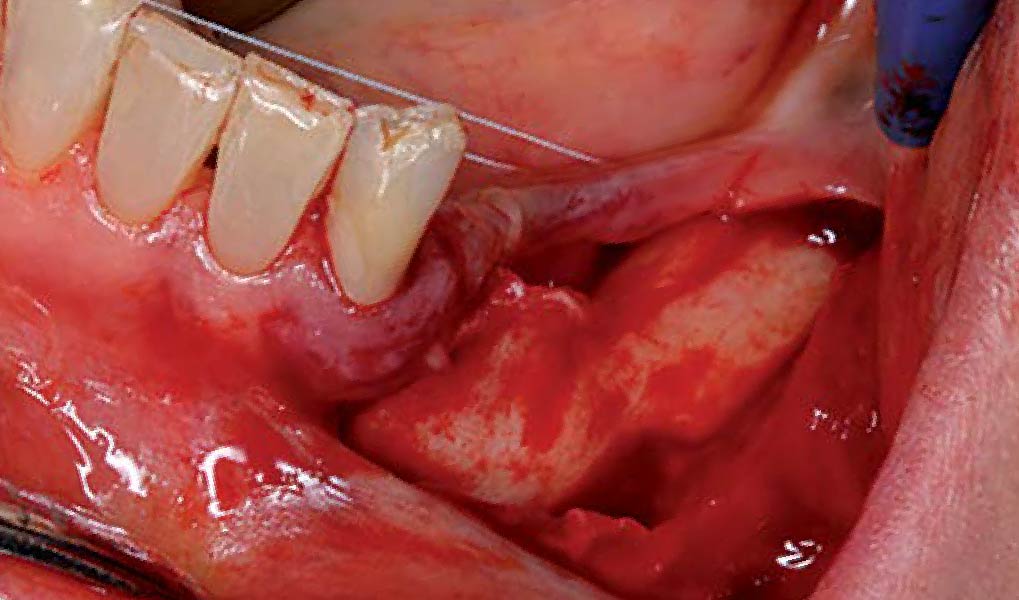
THE APPROACH
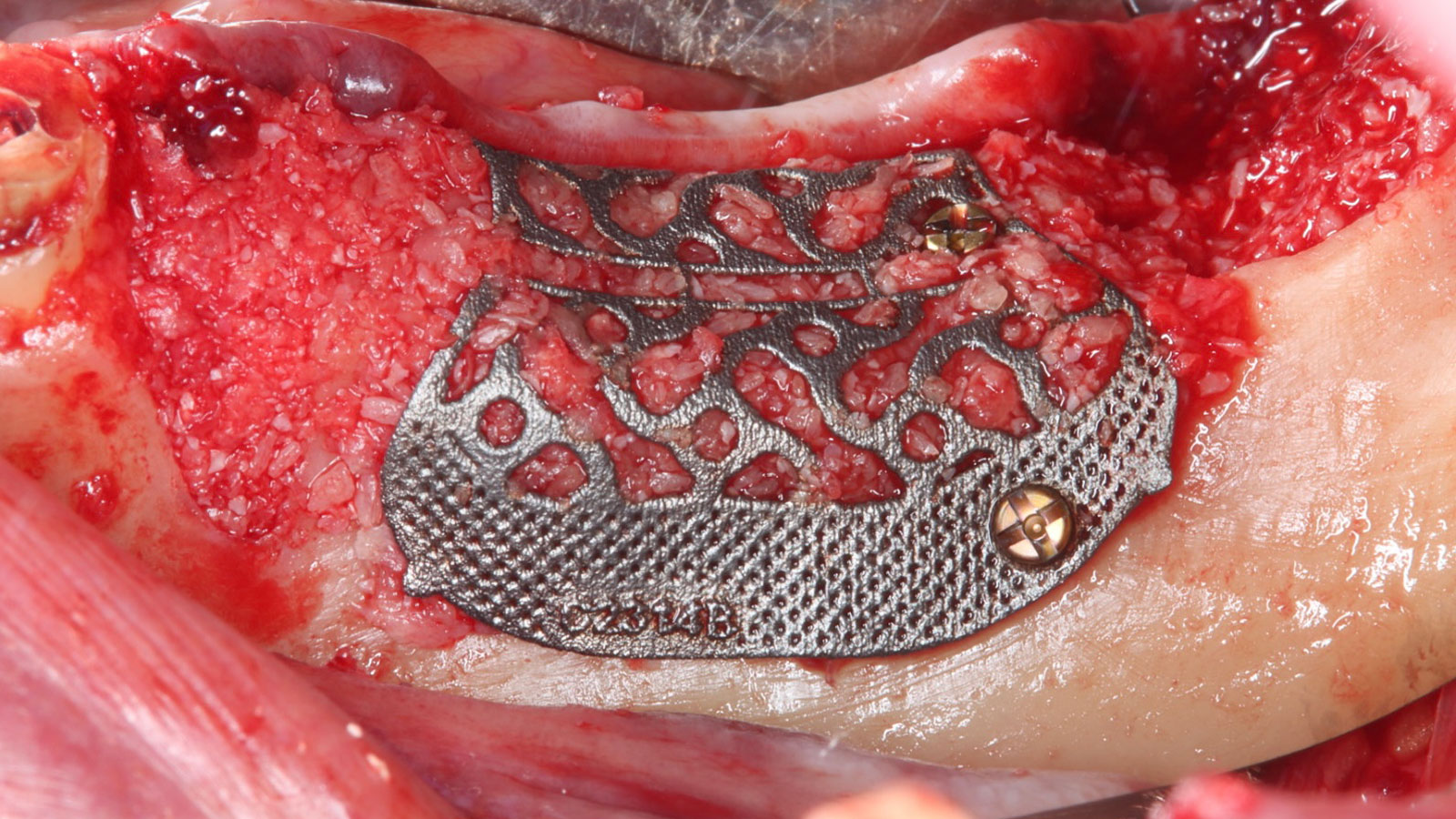
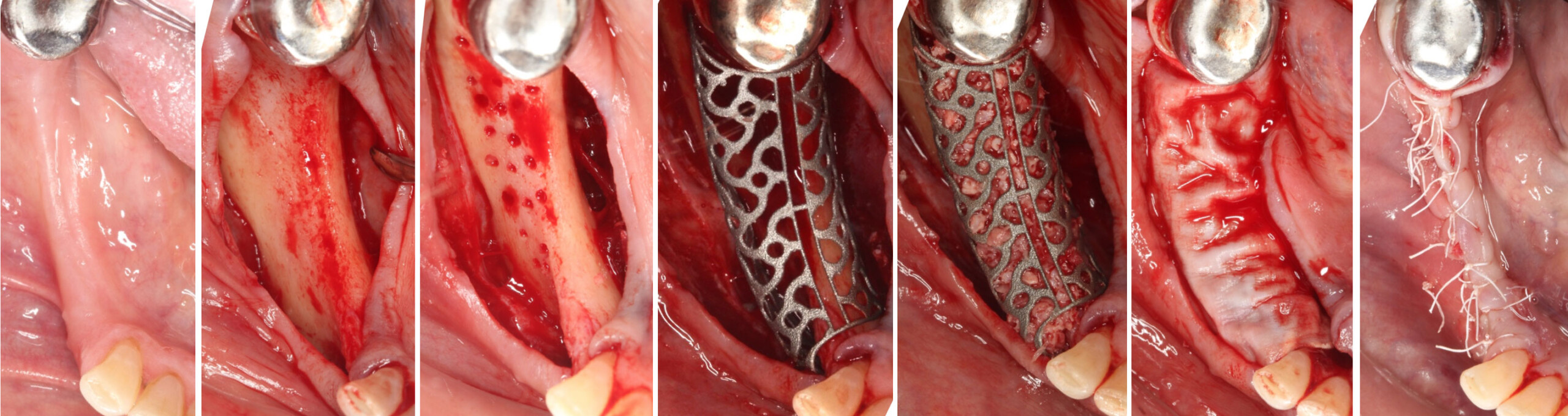
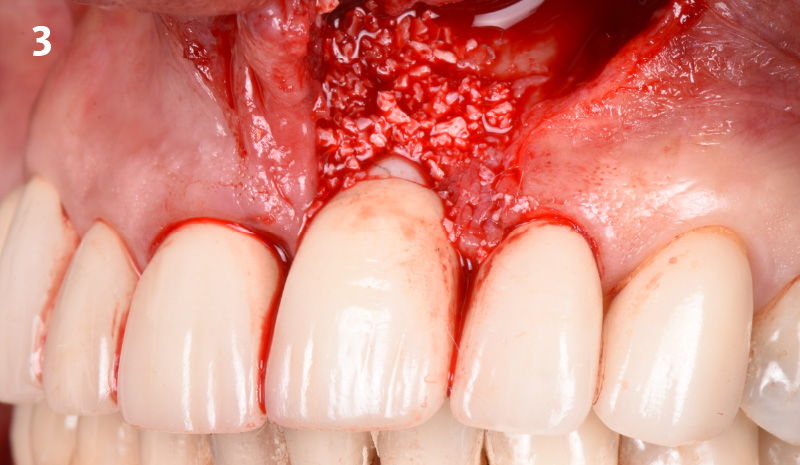
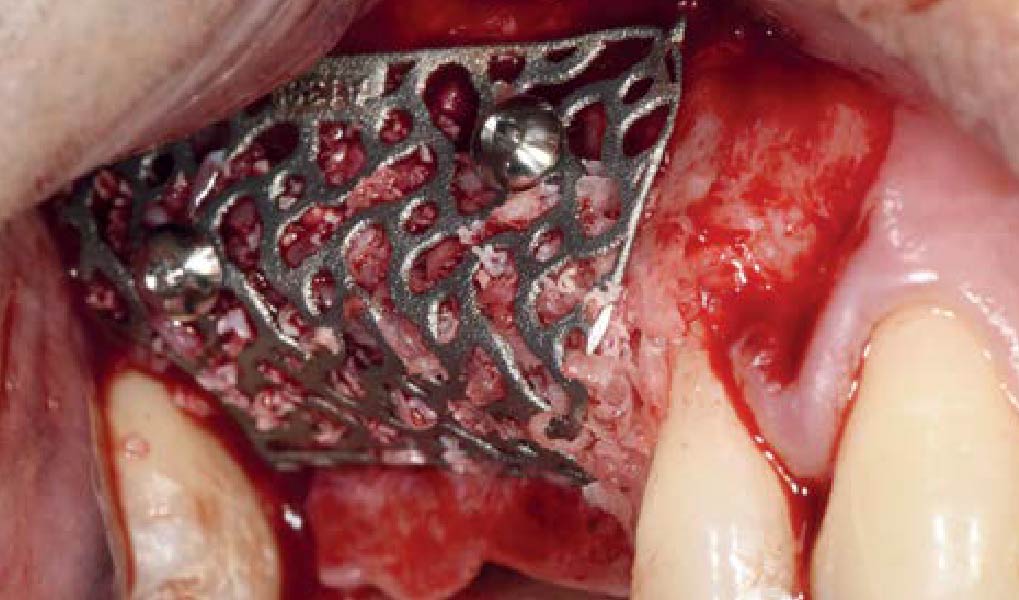
The goal of this procedure was to regenerate sufficient bone to place restoratively driven dental implants. Due to the horizontal and vertical ridge deficiency, we used a customized titanium mesh to predictably achieve this outcome.
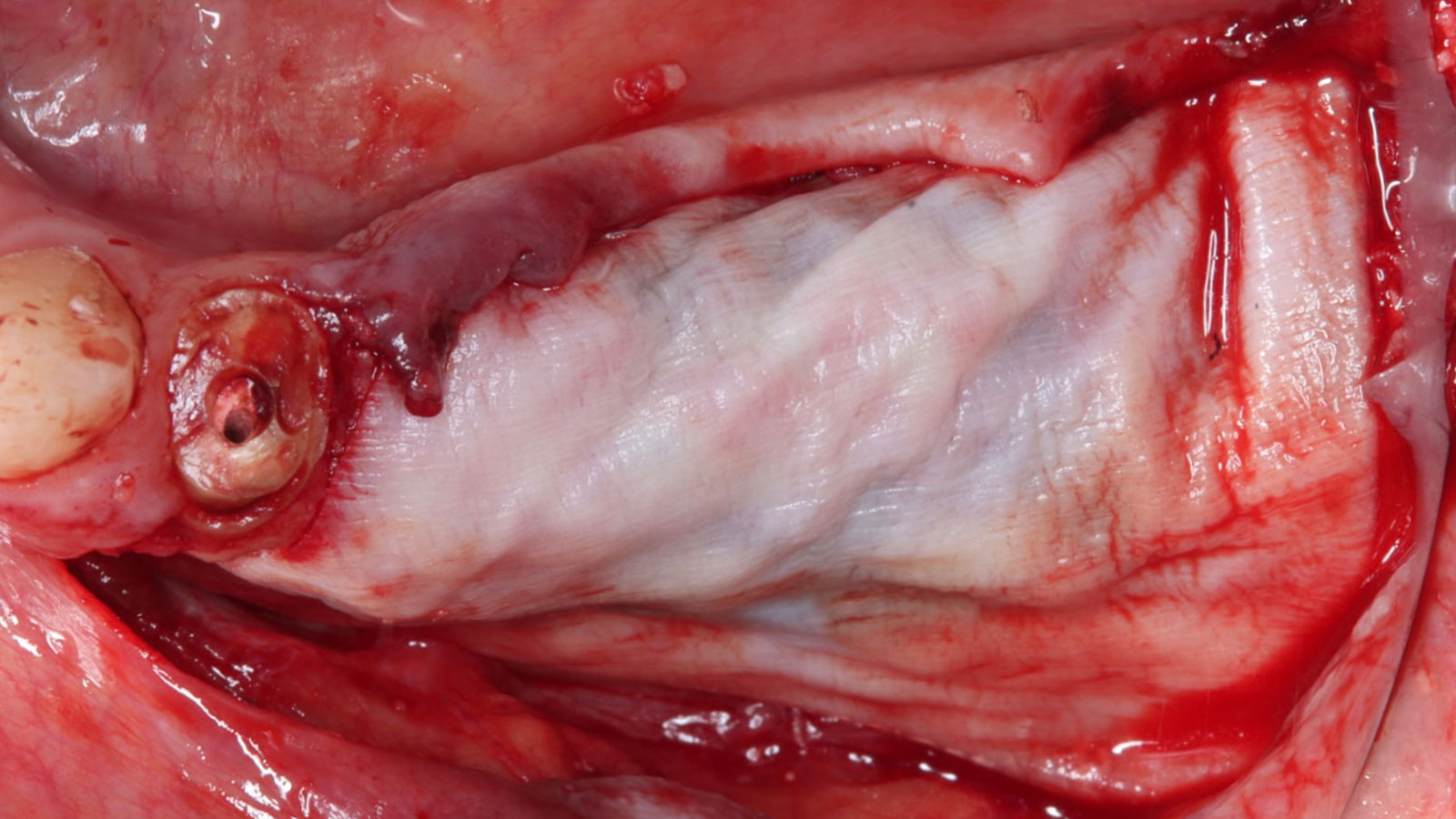
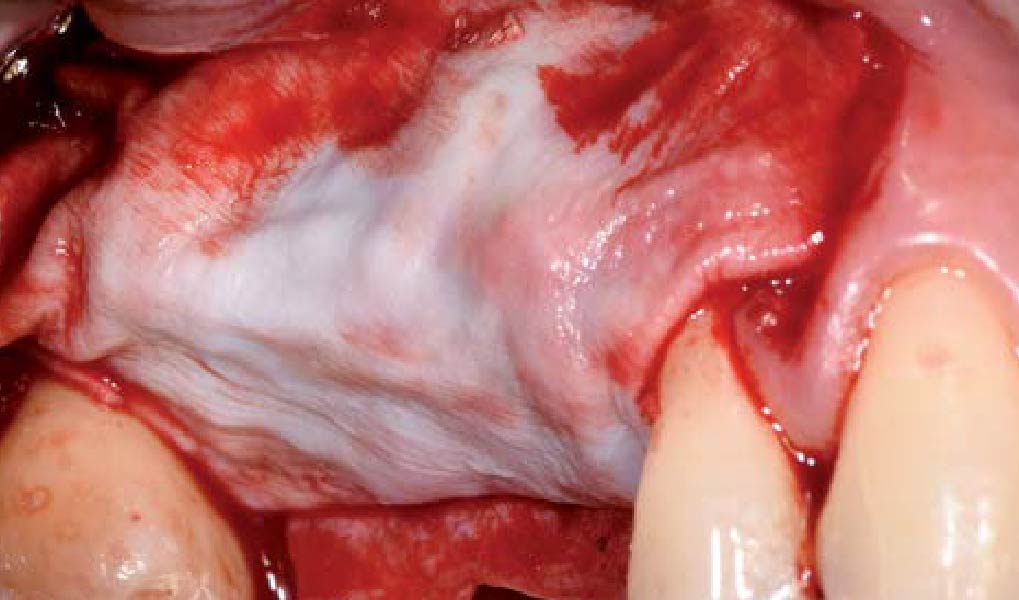
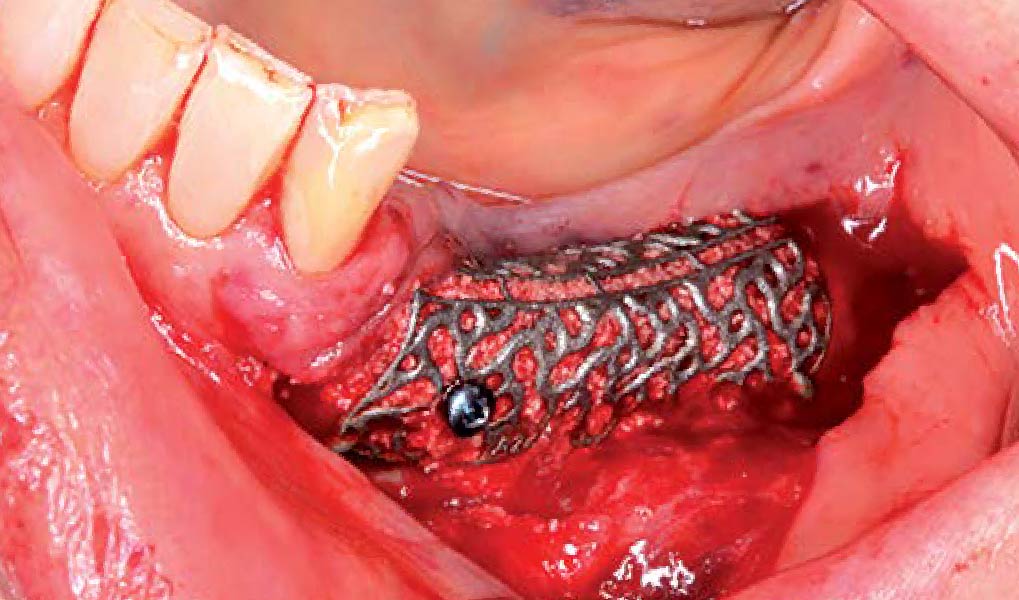
Autogenous bone collected with SafeScraper Twist and Geistlich Bio-Oss® filled the Yxoss CBR® Protect and a Geistlich Bio-Gide® collagen membrane covered the mesh.
.
“Success in these cases primarily depends on proper mesh design and careful handling of soft tissue to ensure zero-tension primary closure.”
— Shaun R. Young, DMD
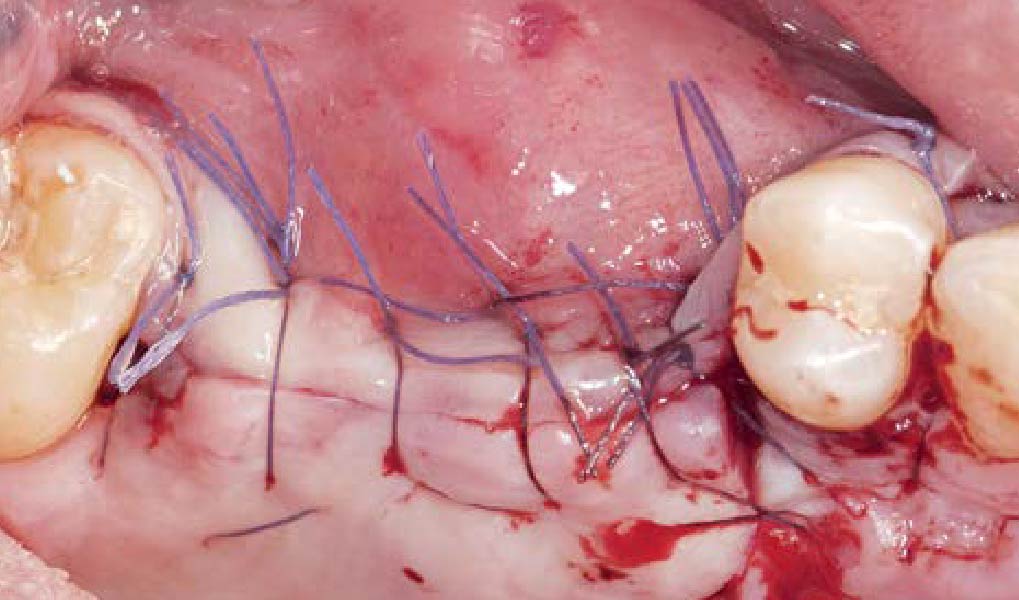
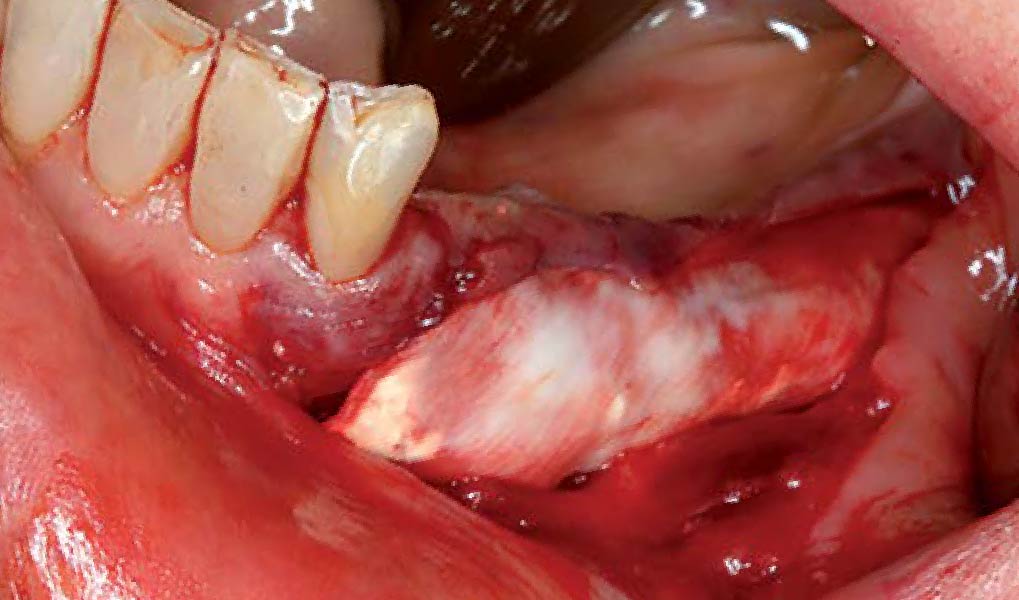
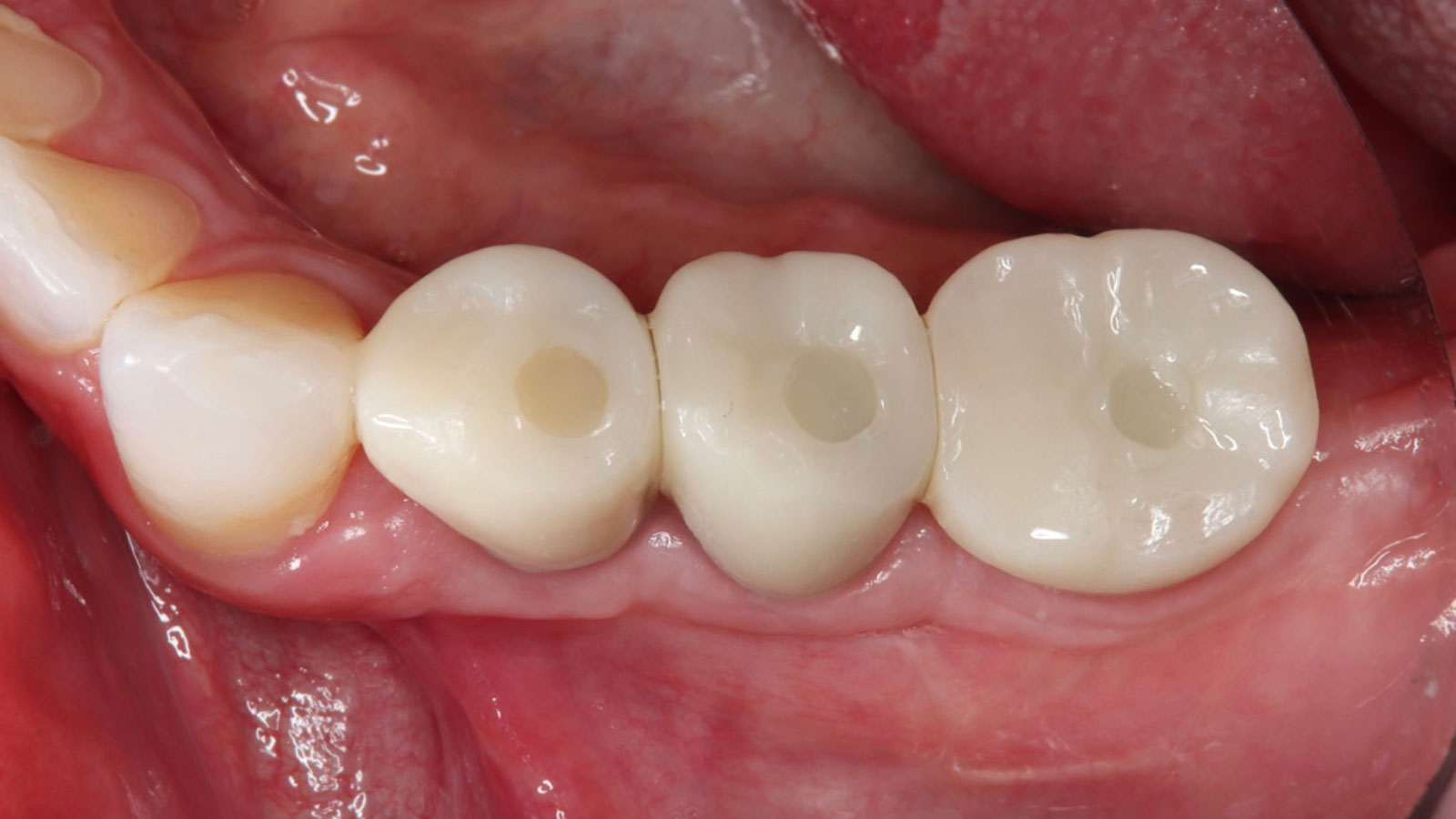
THE OUTCOME
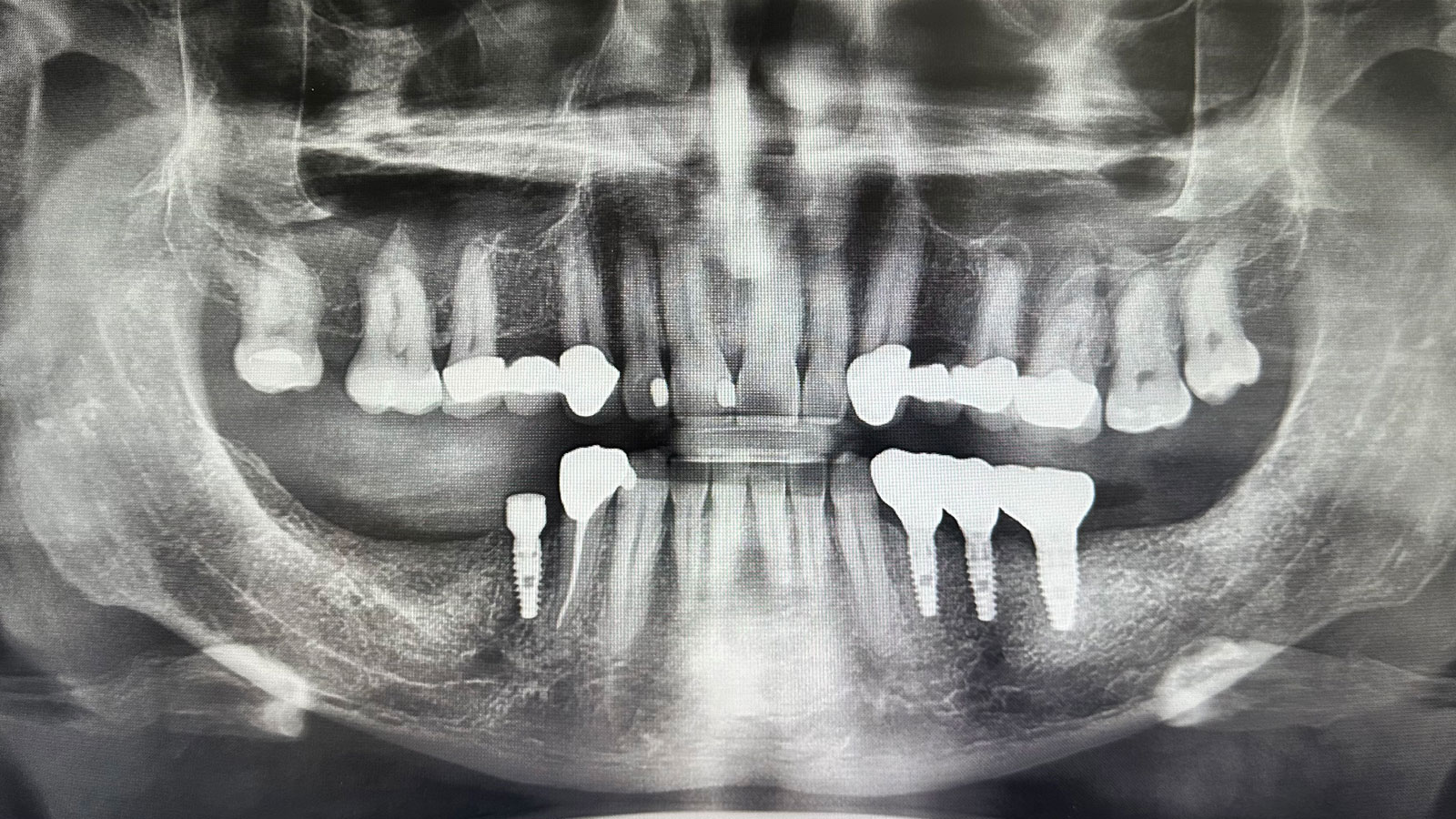
A left mandibular ridge deficiency was corrected using a Yxoss CBR® Protect Customized Bone Regeneration Titanium Mesh, designed from the patient’s CBCT scan.

Shaun R. Young, DMD
Dr. Shaun Young, an Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon based in Tampa, Florida, specializes in complex ridge augmentation, immediate implants, and All-on-X full arch rehabilitation. He earned his Doctor of Dental Medicine degree from the University of Florida and completed his OMFS residency at Emory University in Atlanta, Georgia, where he served as Administrative Chief Resident. Dr. Young brings his expertise to a full-scope group practice, serving Tampa, Clearwater, and New Port Richey, Florida.

BIOBRIEF
Selecting Biomaterials for Combined Complex Defects


THE SITUATION
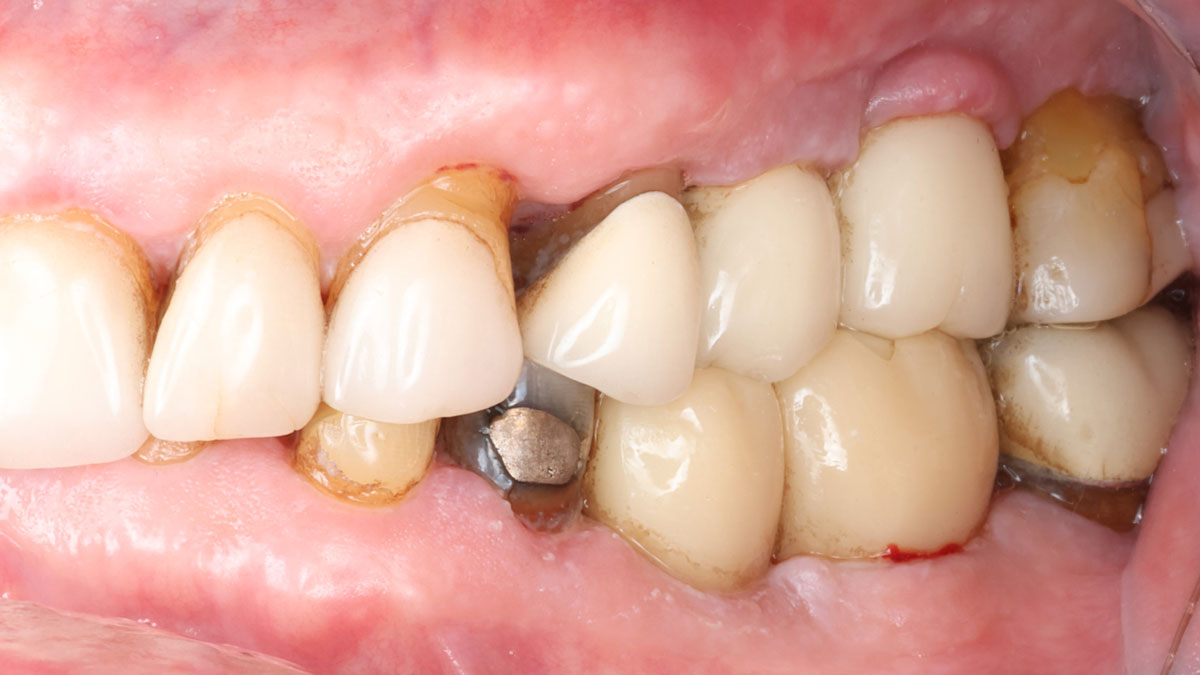
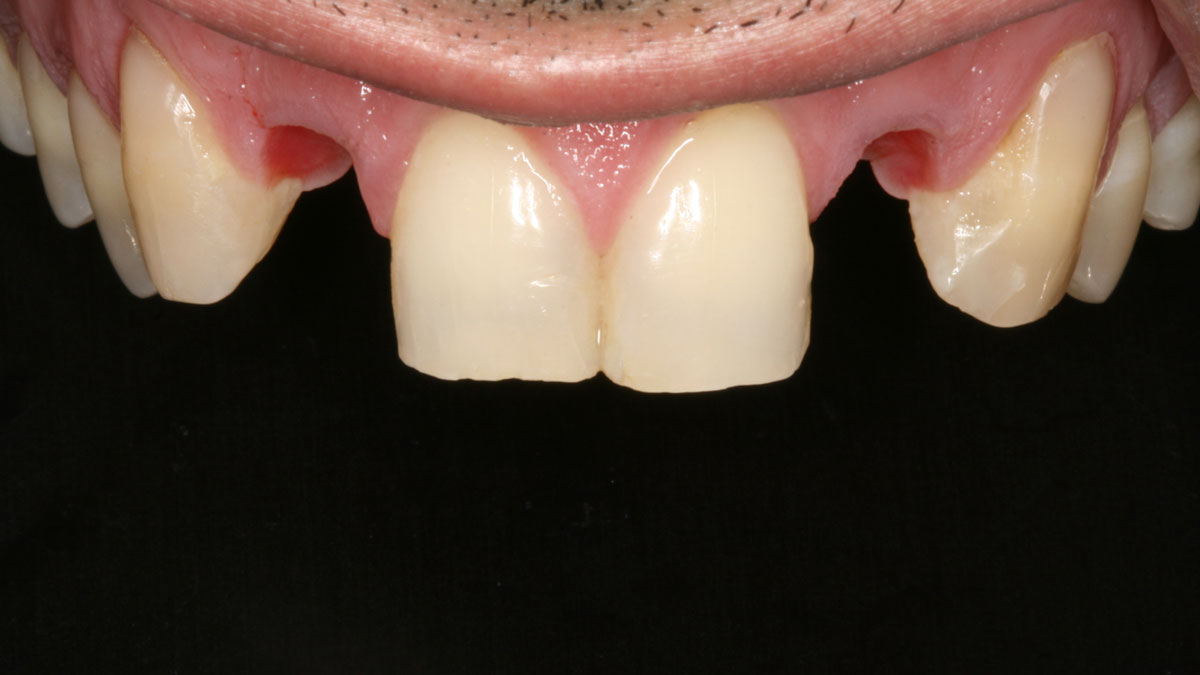
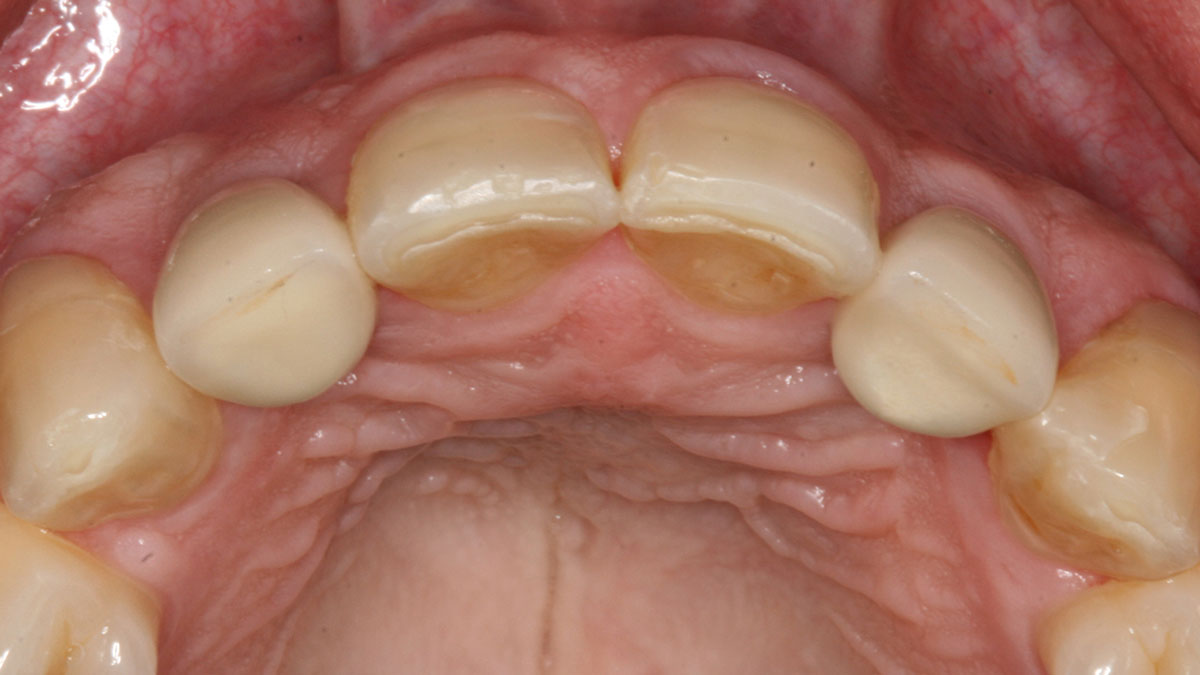
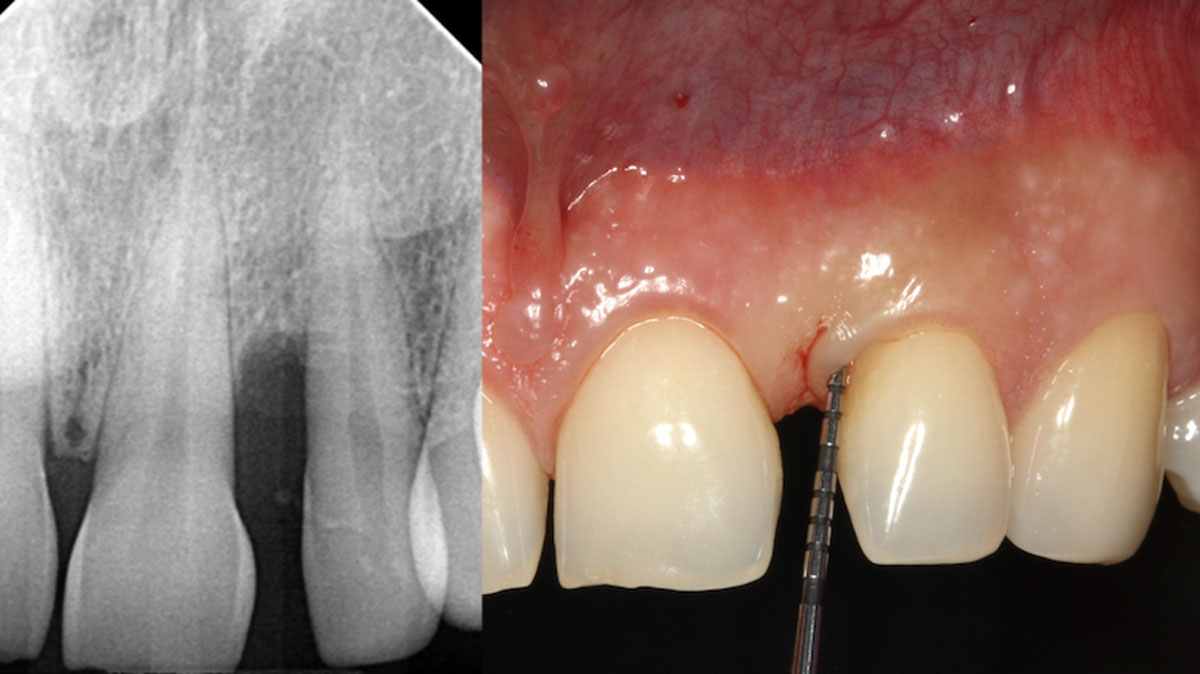
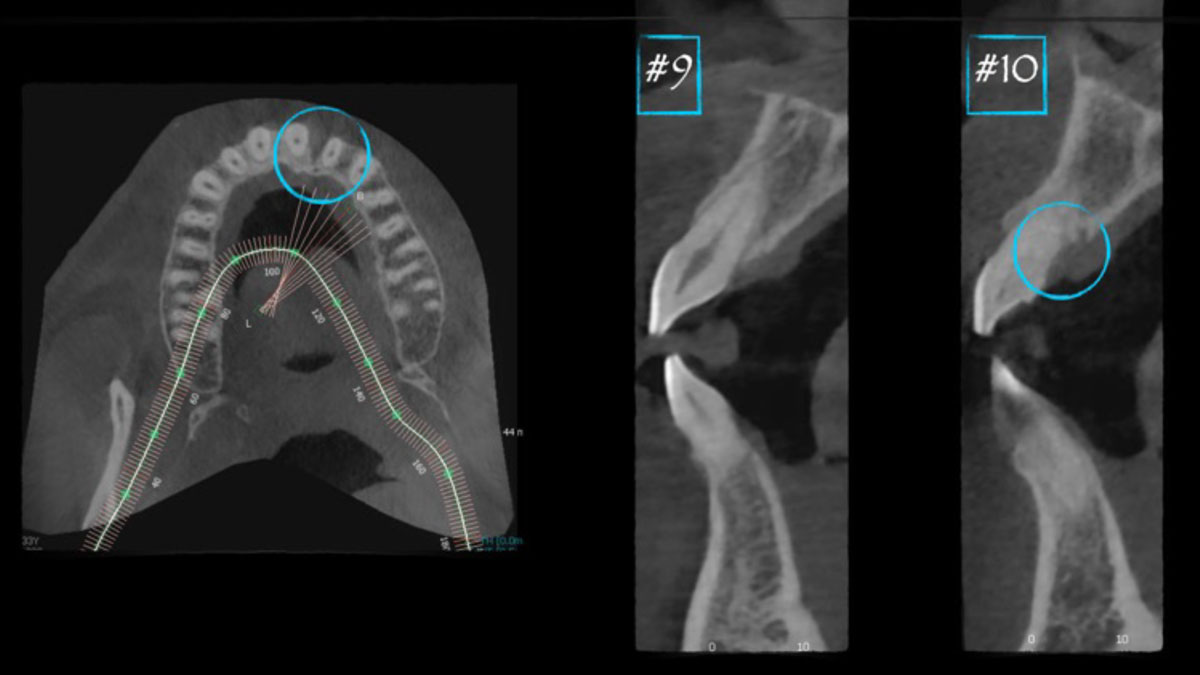
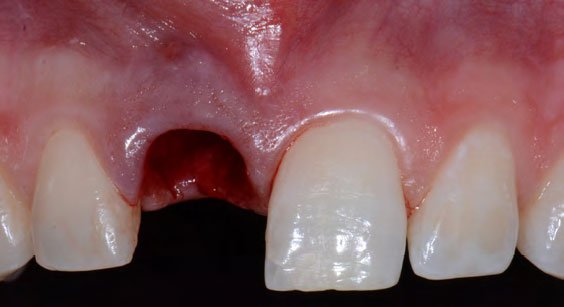
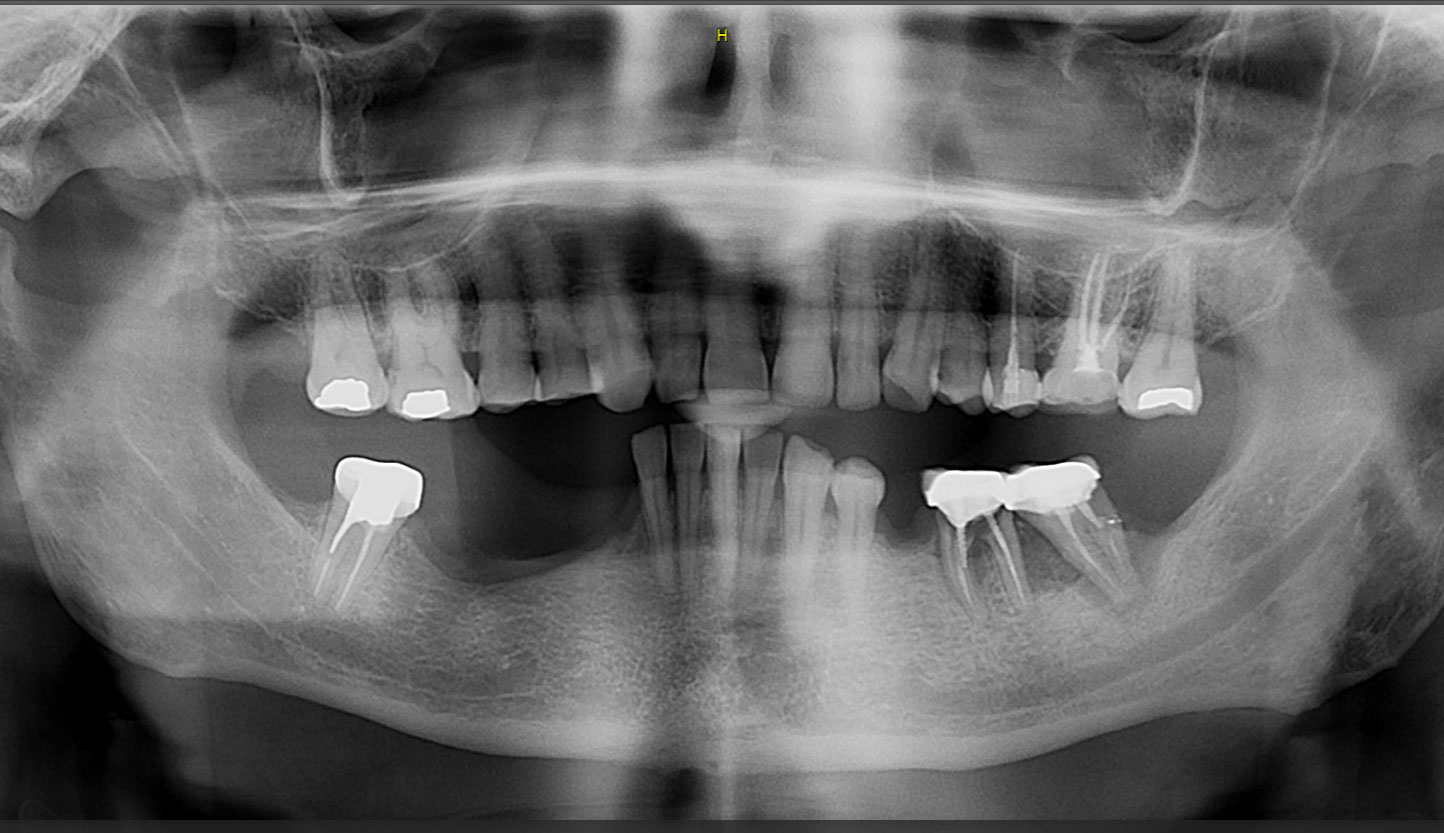
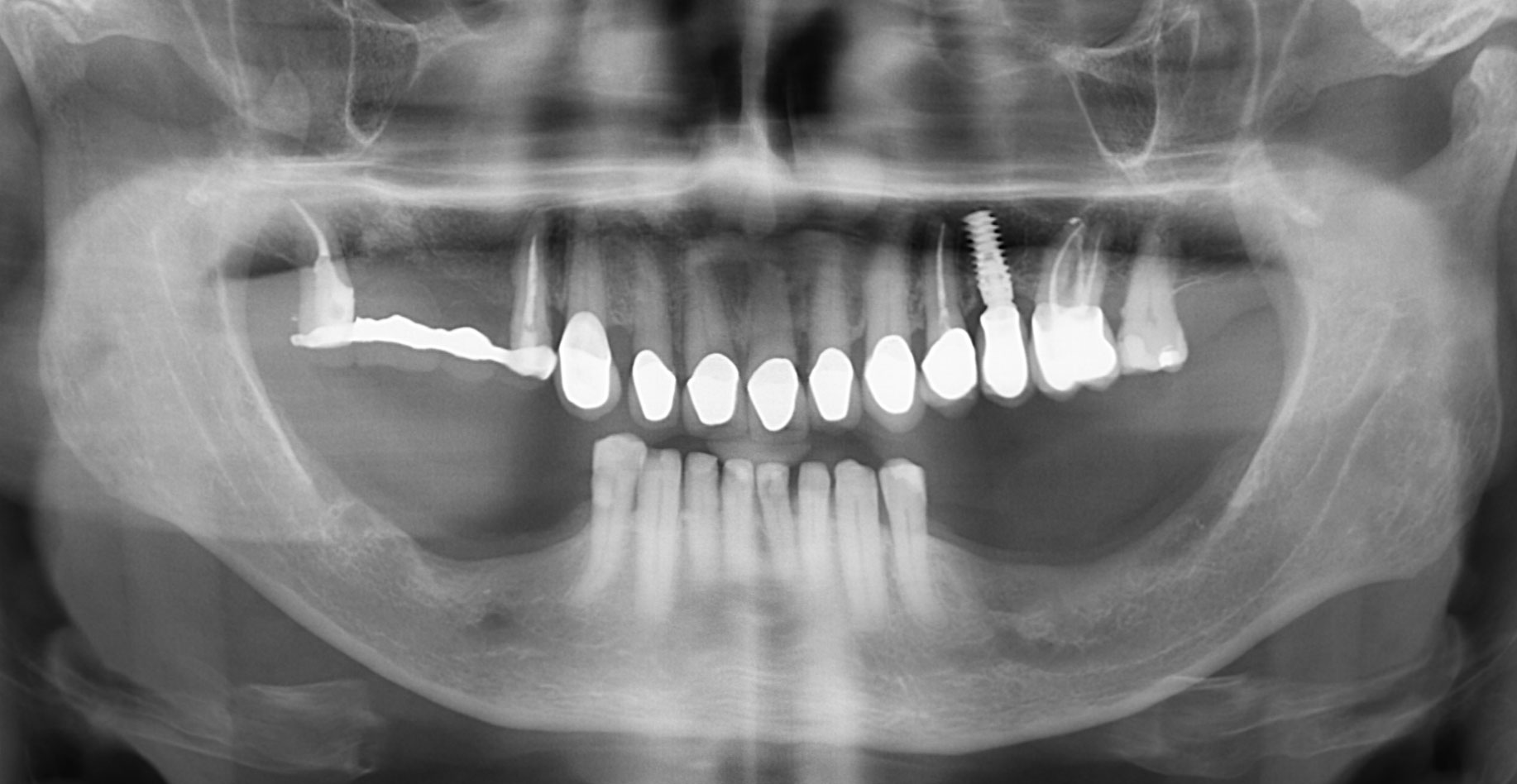
The patient called the office complaining of sensitivity and swelling in the maxillary left quadrant. He was seen and prescribed an antibiotic. Tooth #12 was deemed hopeless, and the peri-apical and radicular lesion presented on the radiograph extended significantly on the mesial aspect, impacting the interproximal bone level for tooth #11. Patient presents with implant supported restorations distal to the affected area and was concerned about the infection spreading to that area as well. The area was treated successfully, and the patient was pleased with the outcome, allowing him to preserve the tooth, on the mesial aspect of the lesion and the implant distally.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system/Non-smoker | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
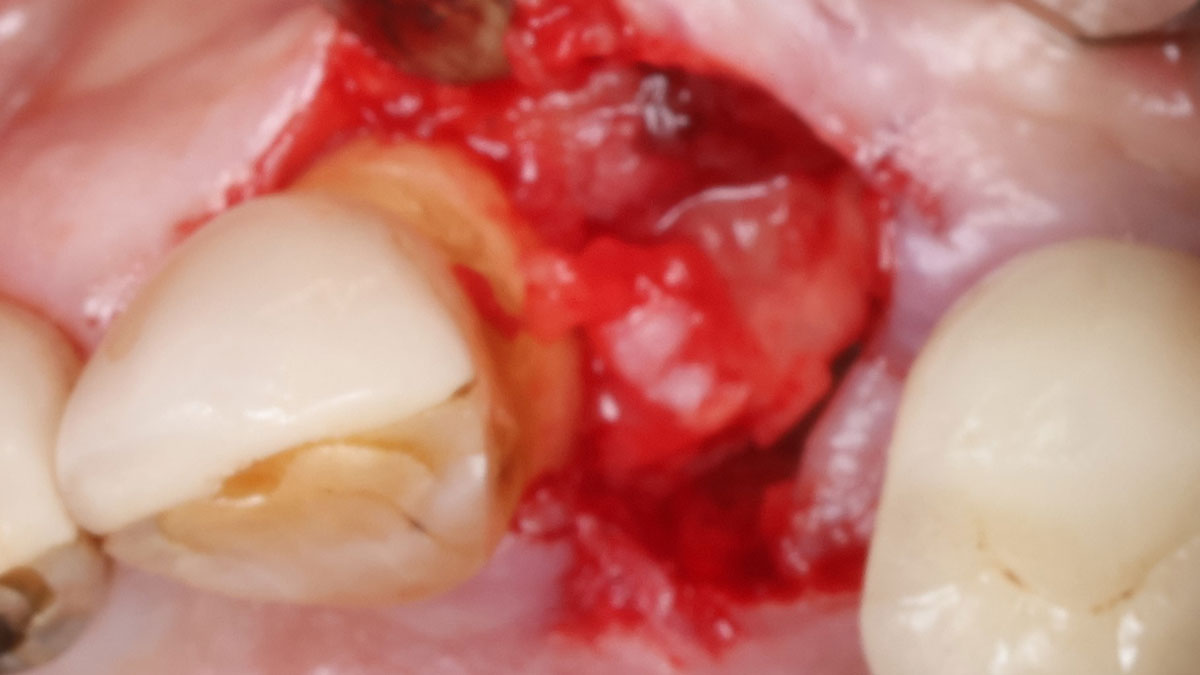
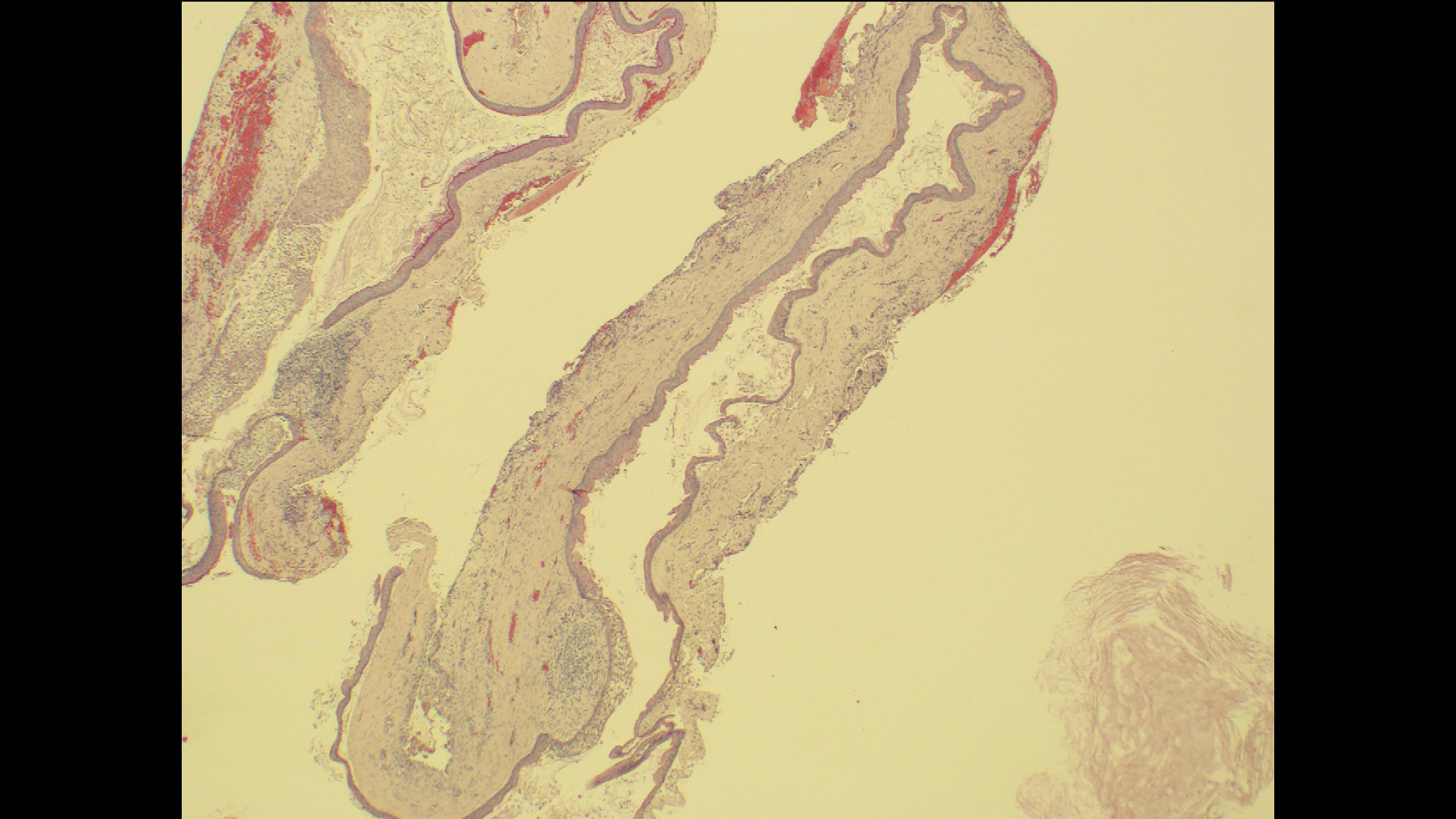
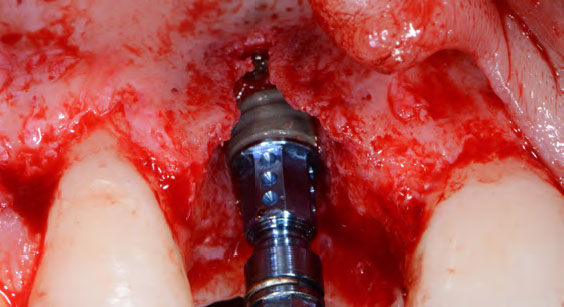
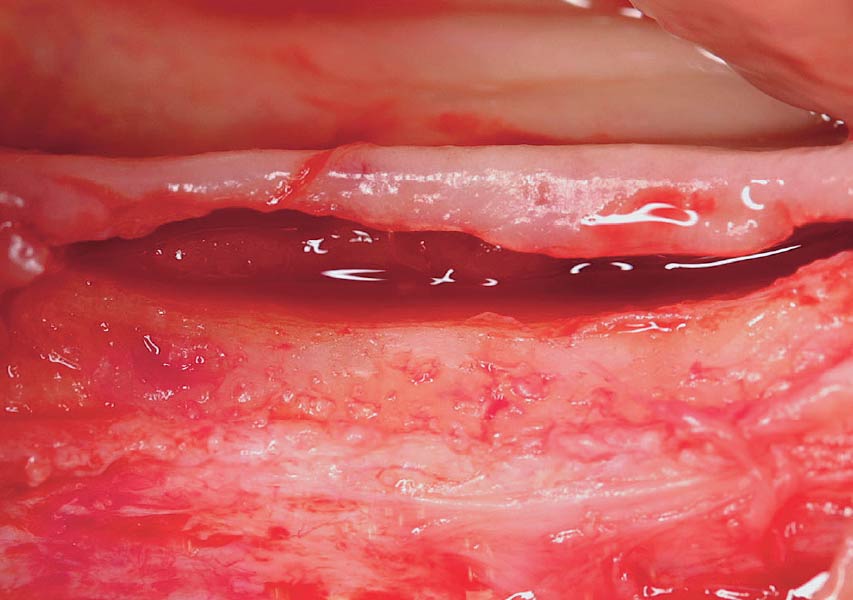
The goals of the procedure were to eliminate infection, the source of pain, and reduce periodontal problems to the adjacent tooth and implant. Full thickness flap was reflected, #12 was removed and the socket was debrided and irrigated. A peri-radicular lesion was removed and submitted for histopathological exam.
“A localized infection can easily spread and impact adjacent teeth and implants. It is critical for clinicians to intervene as soon as possible to prevent further complications. Patient education and motivation is key to successfully treat these types of clinical situations encountered in a daily practice.”
— Dr. Irina Dragan
THE OUTCOME
The combined defect: #11 distal guided tissue regeneration and #12 alveolar ridge preservation for #12. This area was treated with vallos®, Geistlich Bio-Oss Collagen®, and Geistlich Bio-Gide®. The xenograft was placed in the apical portion of the socket and the allograft towards the coronal surface.


Irina F. Dragan, DDS, DMD, MS, eMBA
Periodontology and Implant Dentistry
Dr. Irina Dragan is board certified and an examiner for the American Board of Periodontology and Implant Dentistry. She is part-time faculty in postgraduate periodontics at Harvard School of Dental Medicine and an adjunct associate professor of periodontology at Tufts University School of Dental Medicine. She is a periodontist and clinical researcher at The Perio Studio, a practice limited to periodontology and implant dentistry in Boston, MA.

BIOBRIEF
Odontogenic Keratocyst Management
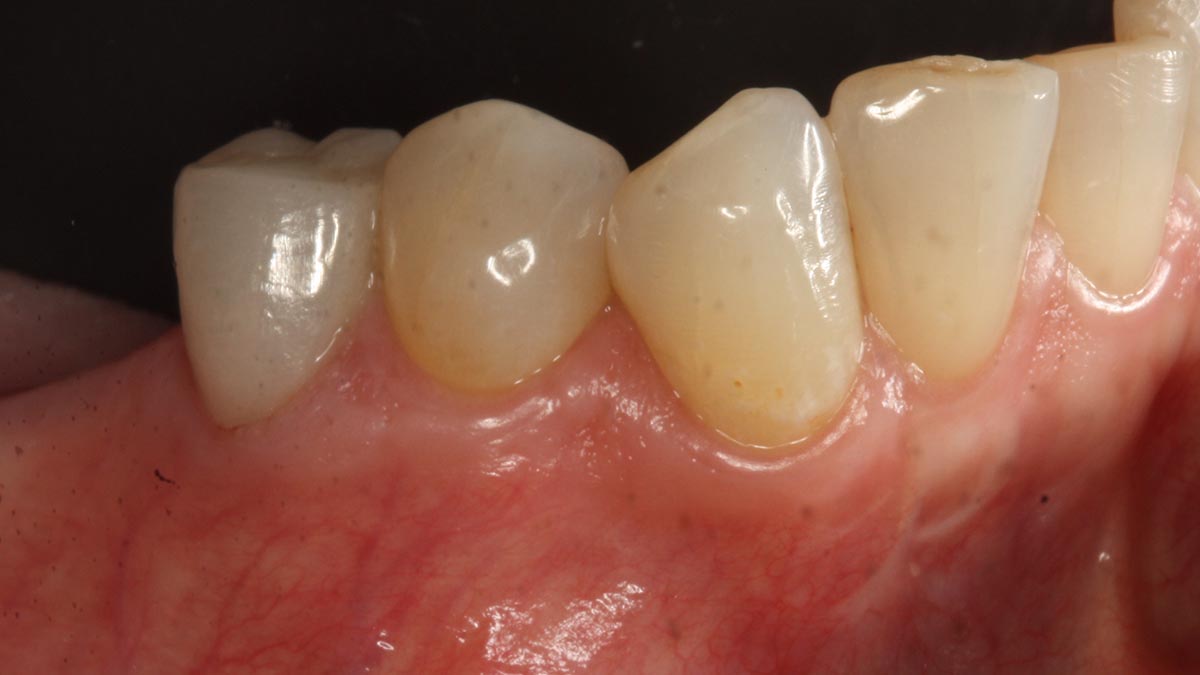

THE SITUATION
A 60-year-old-heathy Caucasian female presented with the chief complaint: “I noticed a bump on my lower left teeth since last year.” An examination revealed a stable periodontium except for enlarged gingival tissue between #21-22 measuring 10x8x5mm, well-defined borders, depressible, non-painful, and vital teeth without displacement. The treatment plan included flap surgery, excisional biopsy, GTR #21-22 (Diff Dx: Lateral periodontal cyst (LPC), Odontogenic Keratocyst (OKC), Benign Fibro-Osseous lesion (BFOL).
Guided Tissue Regeneration (GTR) using Geistlich Bio-Oss® and vallos®f was performed and covered with a resorbable collagen membrane (Geistlich Bio-Gide®).
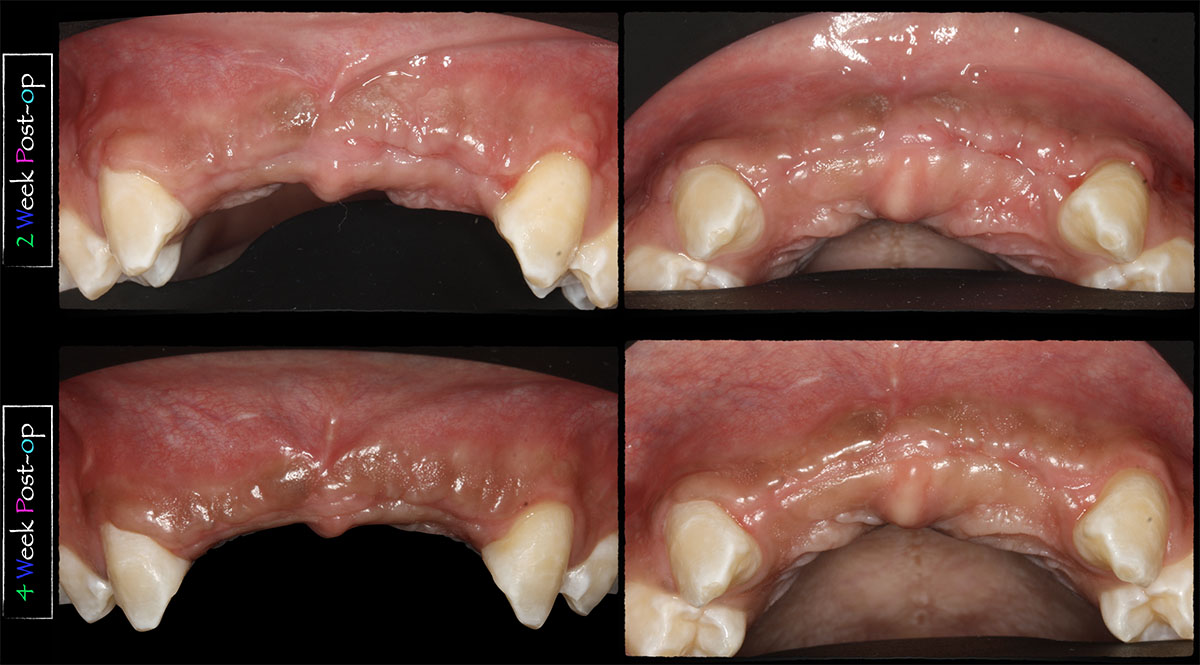
Primary closure was completed using non-resorbable sutures. Follow-up at 2, 4 weeks, 3, 6 months showed stable periodontium without re-occurrence. The pathology report indicated OKC and the area is monitored annually.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
The treatment goal was to excise the lesion around #21-22 and stabilize the periodontium. Sulcular incisions #20-22 with vertical incision #22 MF were performed. Upon full thickness flap reflection, the lesion was removed (excisional biopsy). The defect extended #21M-#22D with complete facial bone loss. It was a wide 1-2 bony wall defect measuring 10x8x5mm. GTR procedure using Geistlich Bio-Oss® and vallos®f and Geistlich Bio-Gide® for the collagen membrane were employed. Primary closure was obtained using 6-0 prolene suture.
“Excisional biopsy and guided tissue regeneration is indicated to treat the pathology (#21-22 area) and stabilize the periodontium.”
— Dr. Bassam Kinaia
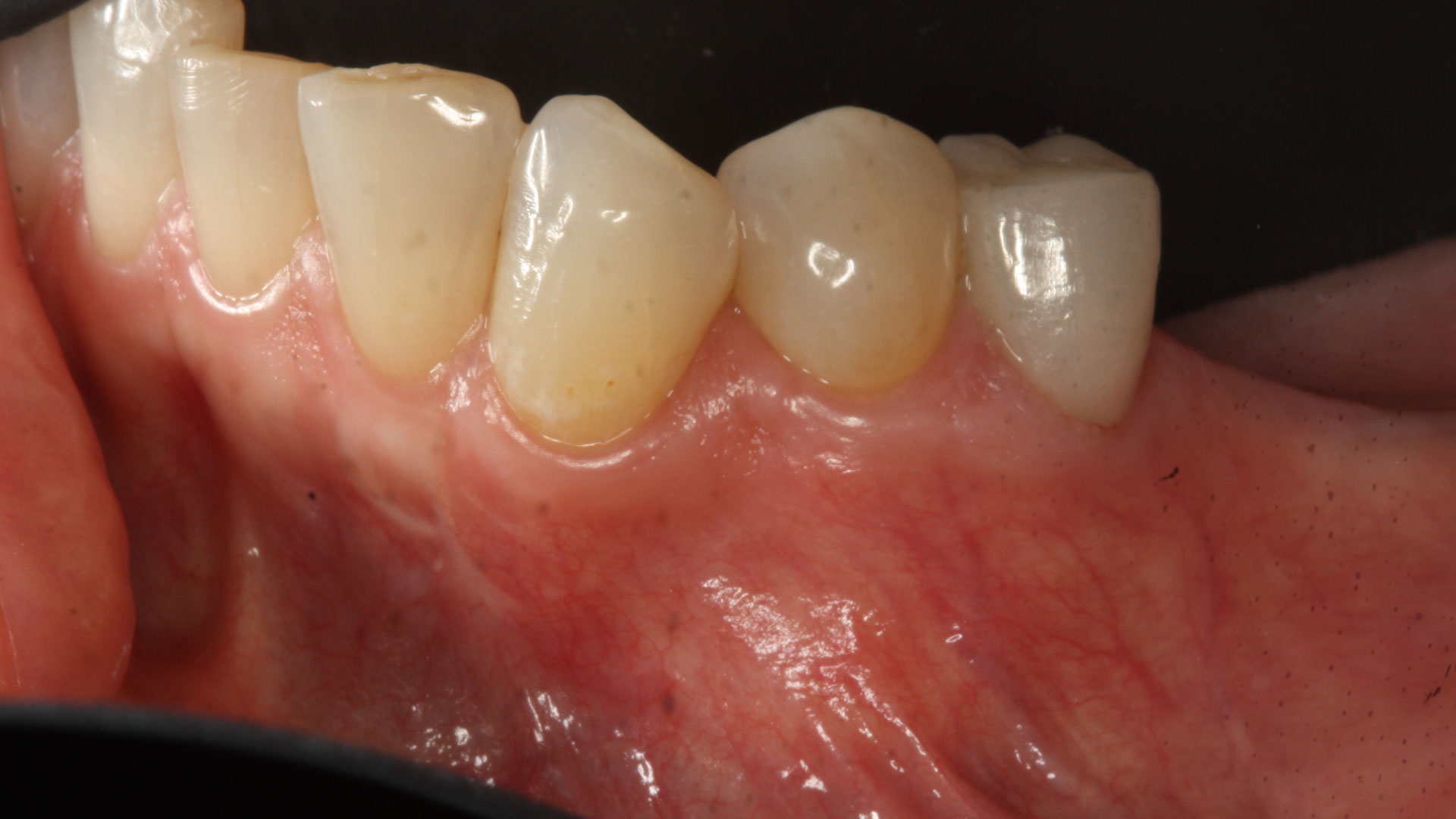
THE OUTCOME
Complete excision of pathology and biopsy followed by GTR using vallos®f internally for maximum osteogenic/osteoinductive potential and Geistlich BioOss® externally for space maintenance showed excellent radiographic bone fill and stable periodontium.

Bassam Kinaia, DDS, MS, DICOI
Dr. Kinaia is the Associate Director of the Graduate Periodontology Program at the University of Detroit Mercy (UDM). He is also the former Director of the Periodontology Program at UDM in Michigan and Boston University Institute for Dental Research and Education in Dubai. He is a Diplomate of the American Academy of Periodontology (AAP) and International Congress of Oral Implantology (ICOI). He received a certificate of Excellence from the AAP in recognition of teaching-research fellowship.

BIOBRIEF
Successful Implant Placement and Horizontal Augmentation for Bilateral Congenitally Missing Maxillary Incisors
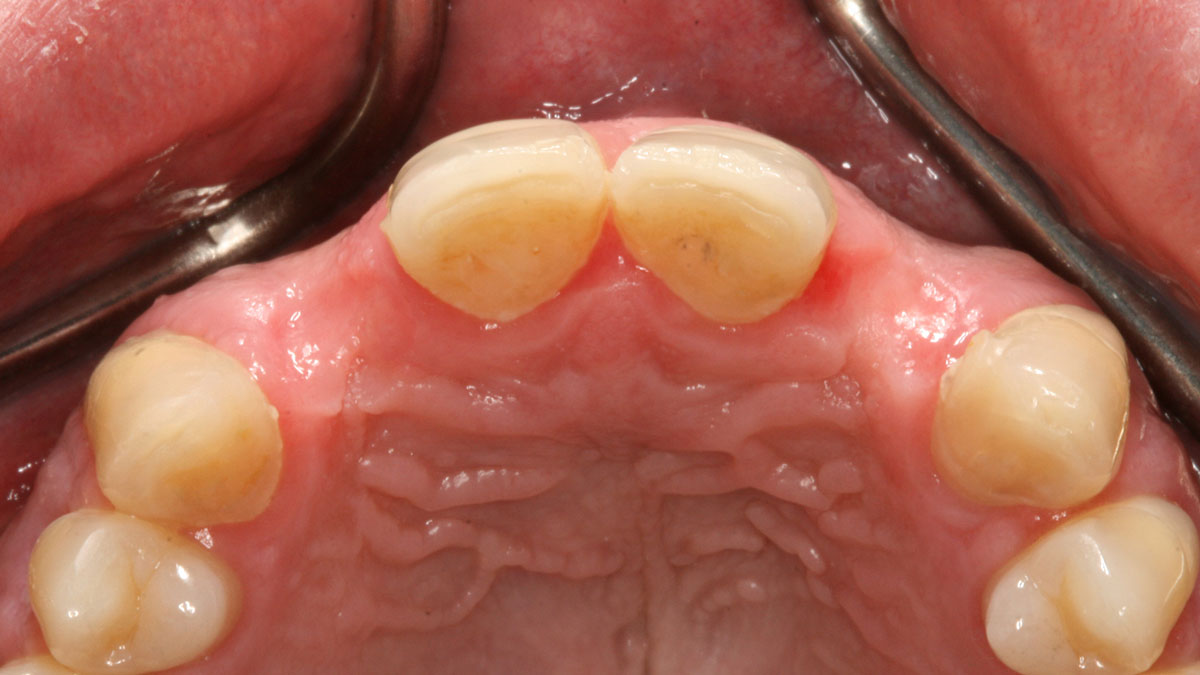

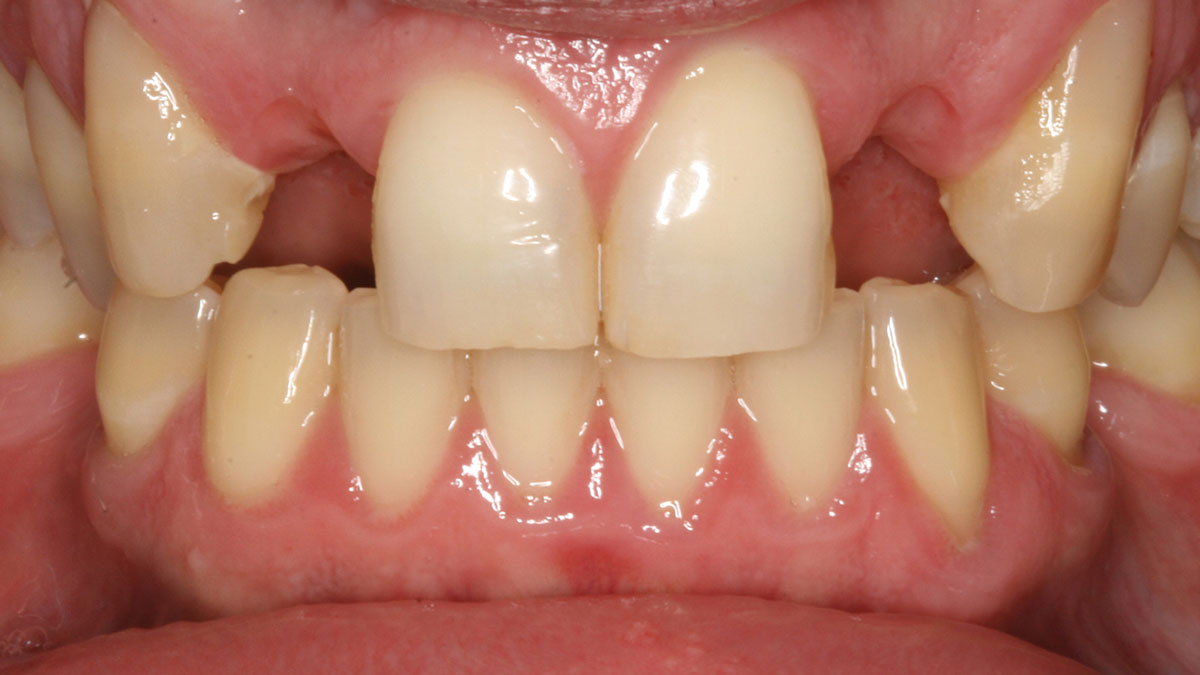
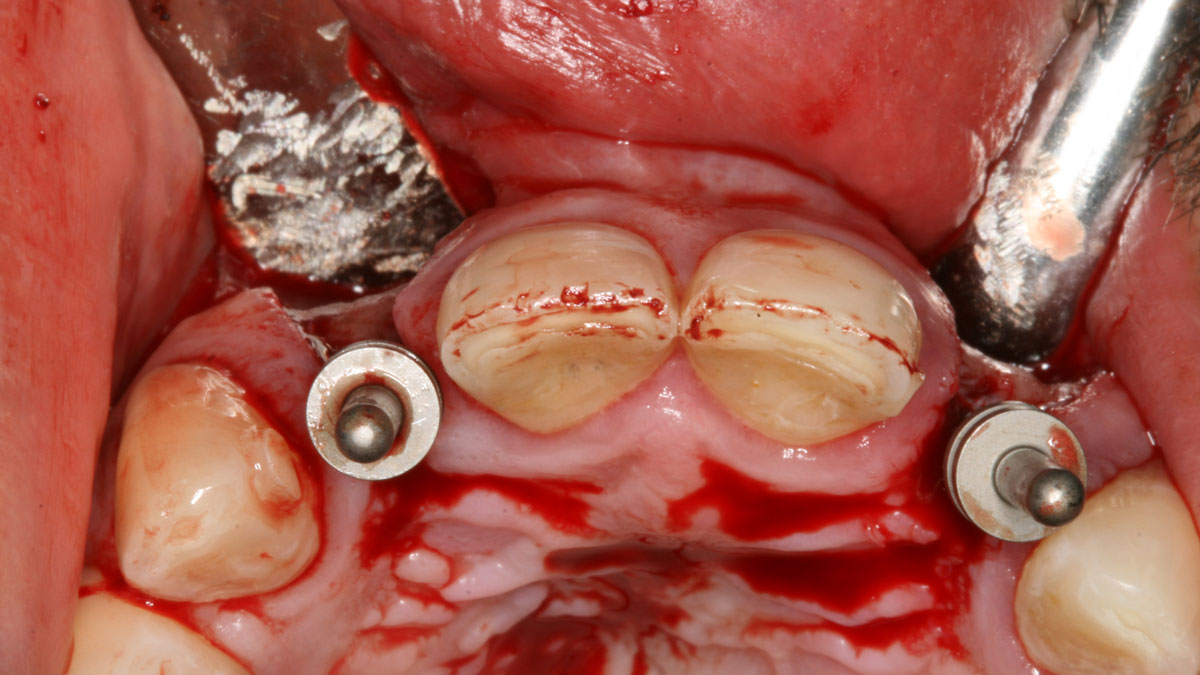
THE SITUATION
A 30-year-old male patient was referred to me with bilateral congenitally missing lateral incisors in the maxilla. The referring general dentist had previously made a resin-bonded bridge which was successful for a few years but had frequent debondings. Clinical examination revealed lack of ridge contour but the CBCT revealed existence of adequate width for placement of narrow-diameter implants with additional bone grafting and contour augmentation. The existing bone anatomy precluded placement of implants for screw-retained restorations without a pre-surgical lateral ridge augmentation procedure. The patient accepted a treatment plan for placement of two narrow-diameter implants and simultaneous bone grafting and contour augmentation followed by restoration with zirconia cement-retained crowns.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Compromised | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
My treatment goals were to preserve the existing soft-tissue architecture, especially the interdental papilla, mesial and distal to the lateral incisors, improve the facial contour at the lateral incisor sites by bone grafting with a low substitution biomaterial, and harmonize esthetics and function with optimal implant-supported restorations.
“The patient had failed resin-bonded bridges with deficient contours for bilateral congenitally missing lateral incisors.”
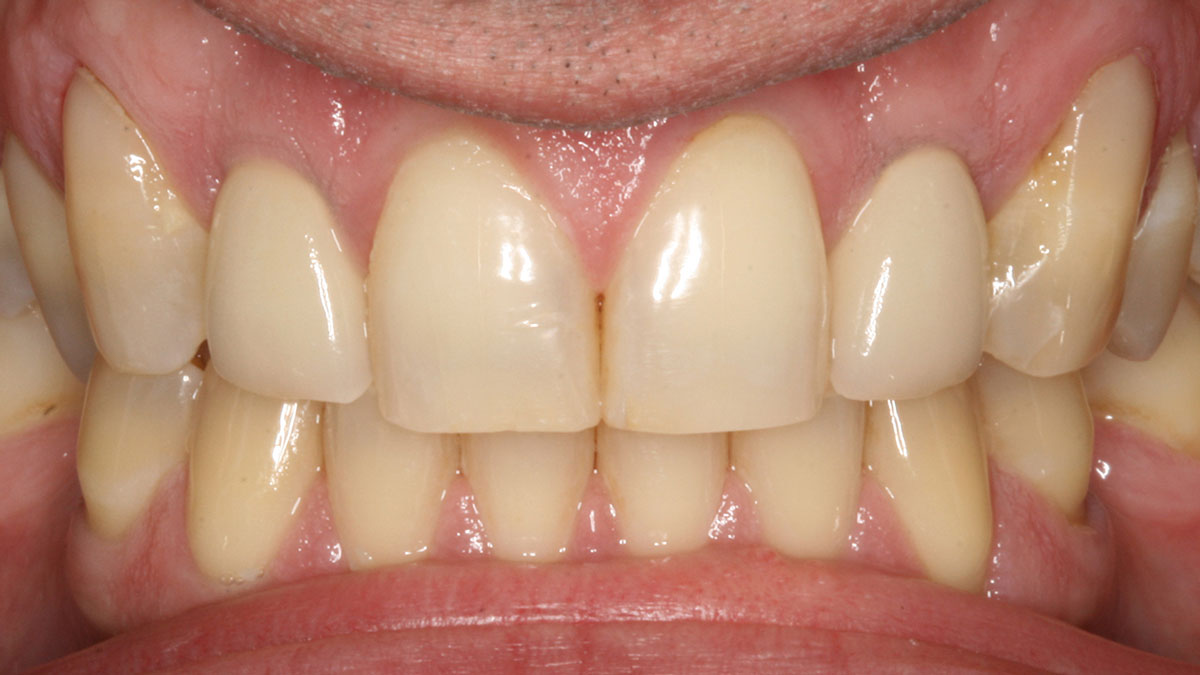
THE OUTCOME
Single-stage implant placement with bilateral papilla-sparing incision design and simultaneous contour augmentation using a mixture of Geistlich Bio-Oss® autologous bone chips and Geistlich Bio-Gide®.

Dr. Avinash Bidra
Dr. Bidra is a Board Certified Maxillofacial Prosthodontist and Director of the Prosthodontics Residency Program at UCONN School of Dental Medicine. He has extensive surgical experience and maintains a part-time private practice restricted to Implant Surgery and Prosthodontics in Meriden, CT. He has lectured at national and international meetings, as well as published extensively in international scientific journals. He has invented prosthetic components and is a co-inventor of a new implant design.

BIOBRIEF
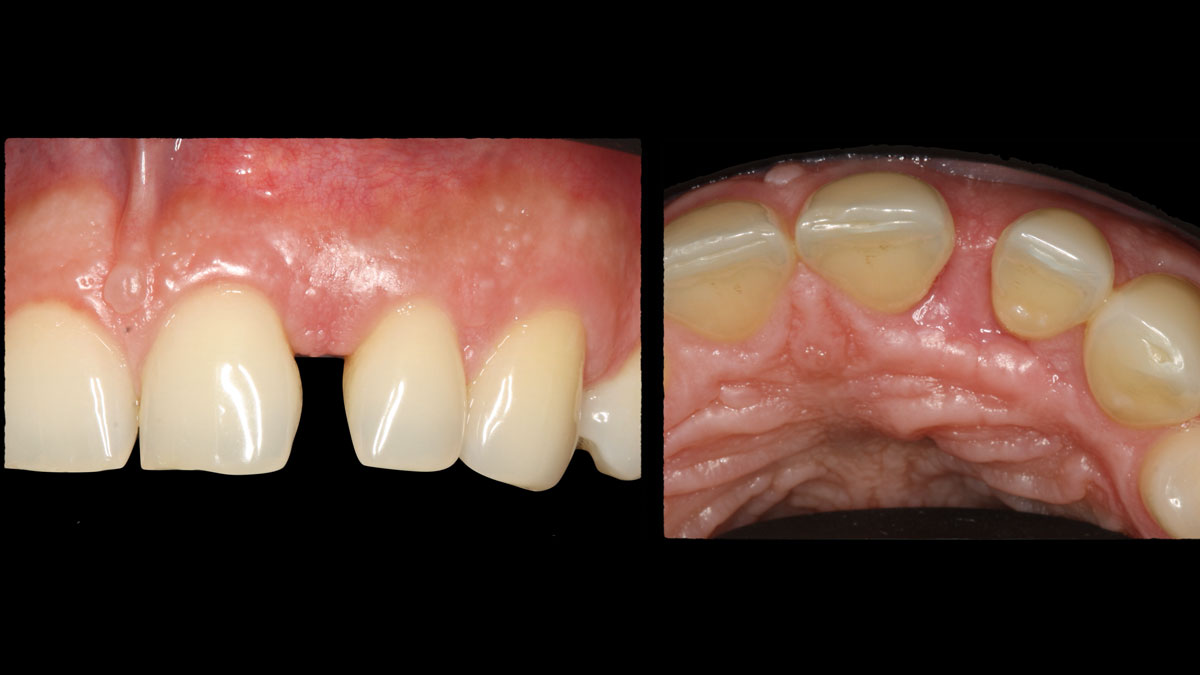
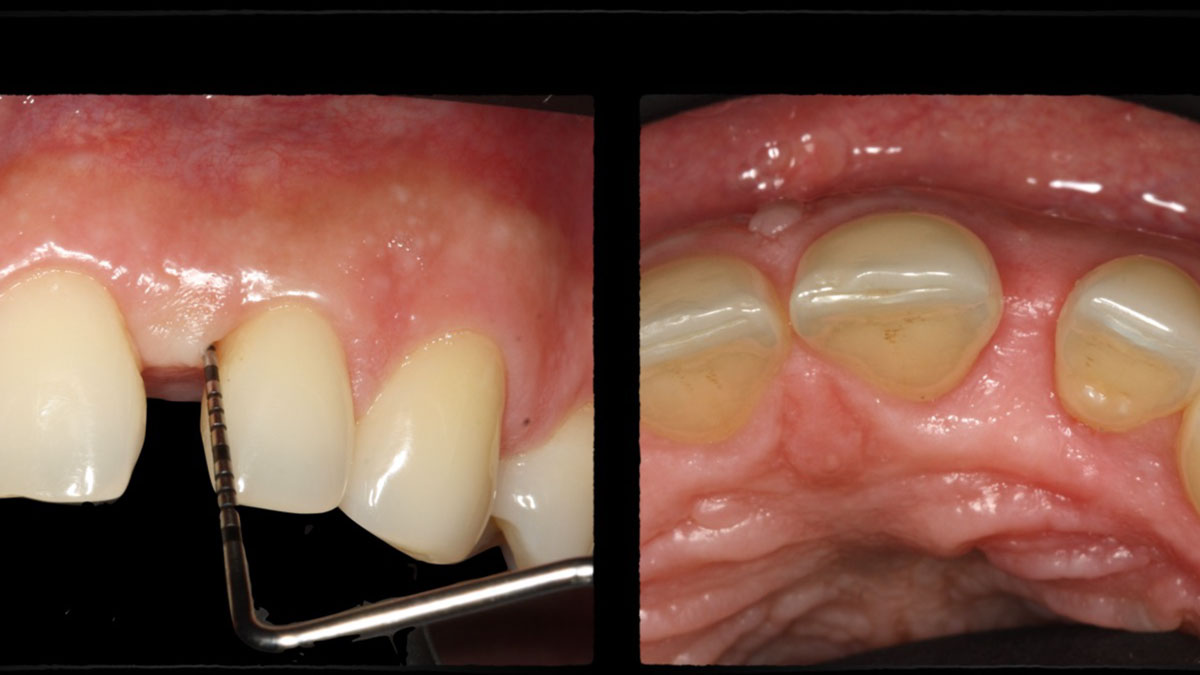
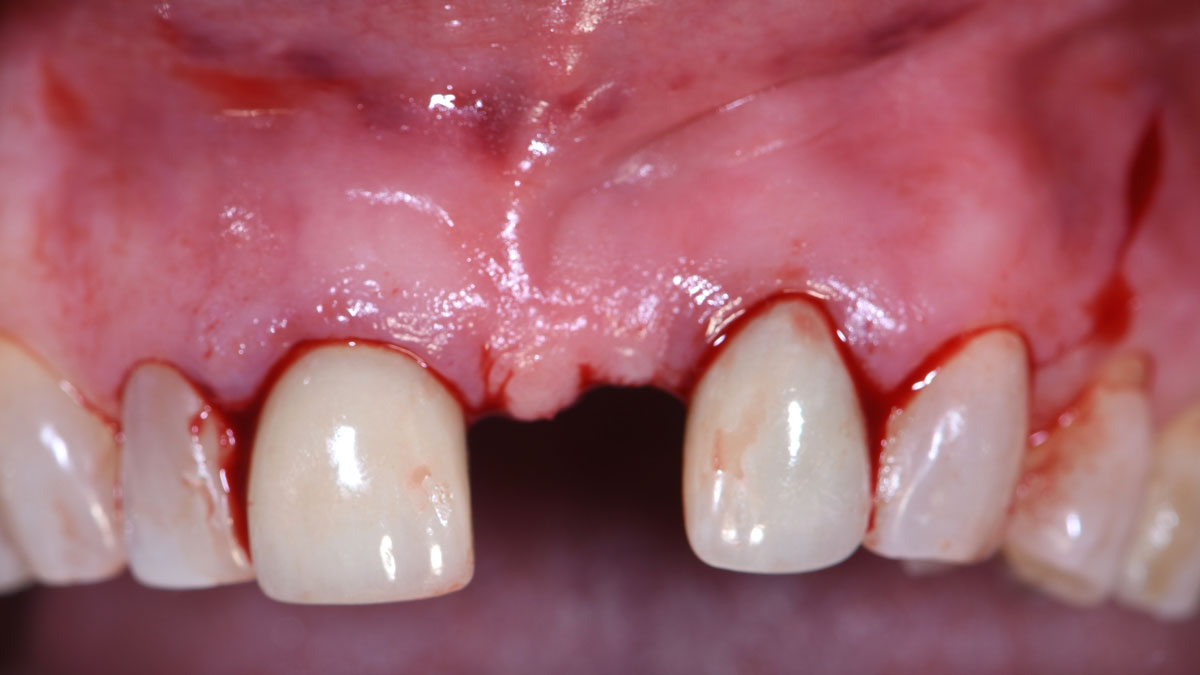
Guided Tissue Regeneration in the Esthetic Zone of a 34-Year-Old Male
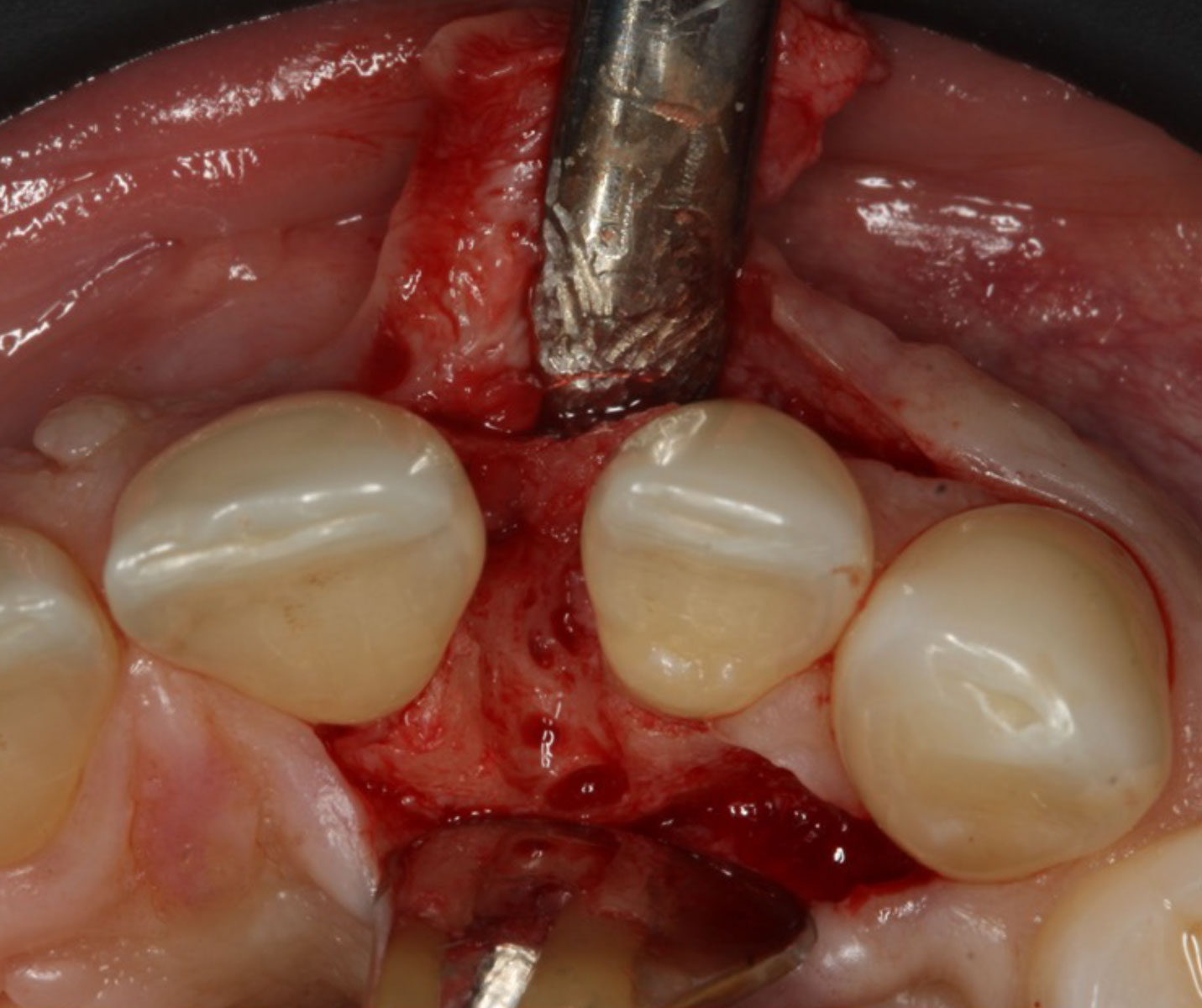

THE SITUATION
A 34-year-old healthy male presented with increased spacing between maxillary left central and lateral incisors. Clinical examination showed deep probing depths between #9-10 area. Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) showed vertical bone loss #9-10 wrapping around the palatal surfaces. Treatment recommendation included guided tissue regeneration (GTR) to stabilize the periodontium.
Area #9-10 was debrided and showed a wide 1-2 wall defect measuring ~7mm vertical bone loss. GTR procedure using Geistlich vallomix™ bone graft (allograft + xenograft) and a collagen membrane were employed and primary closure obtained. Healing at 2 and 4 weeks and 6 months showed proper bone fill with stable periodontium.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
Correct the vertical bone loss around #9-10 and save the dentition. Sulcular incisions with a paracrestal incision around #9-10 were performed. The area was debrided showing a wide 1-2 bony wall defect (measuring ~7mm vertical bone loss). Primary closure was obtained using 6-0 prolene sutures.
“Guided tissue regeneration is indicated to correct the vertical bone loss around the #9-10 area and stabilize the periodontium.”
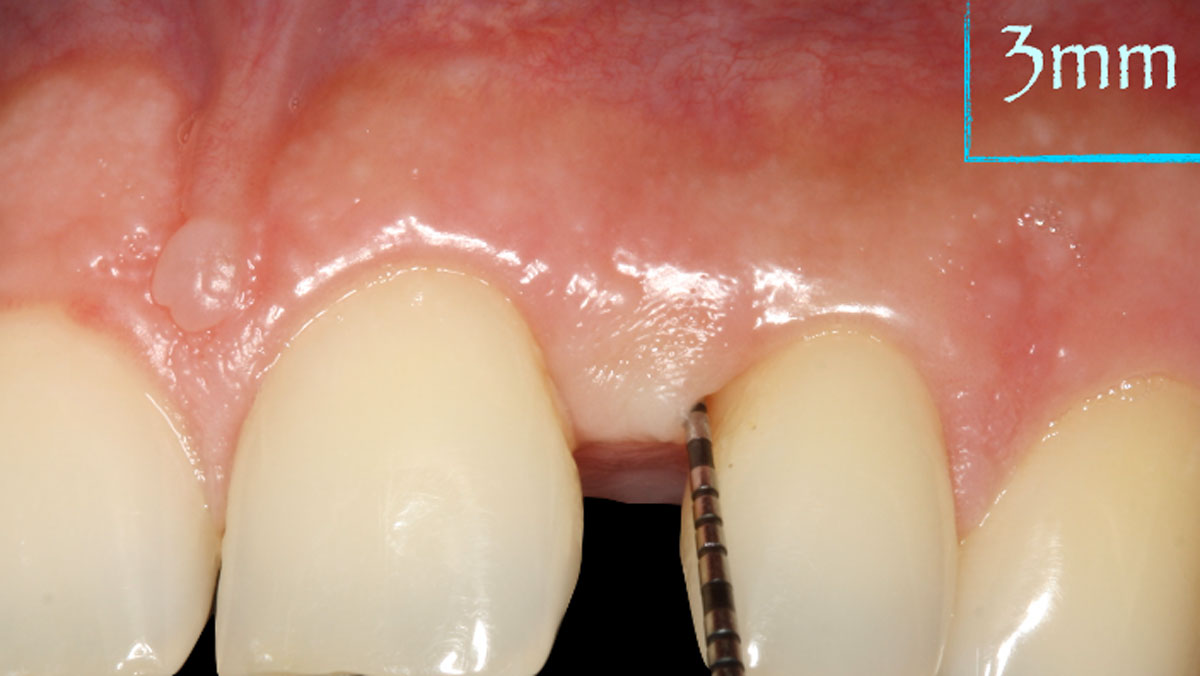
THE OUTCOME
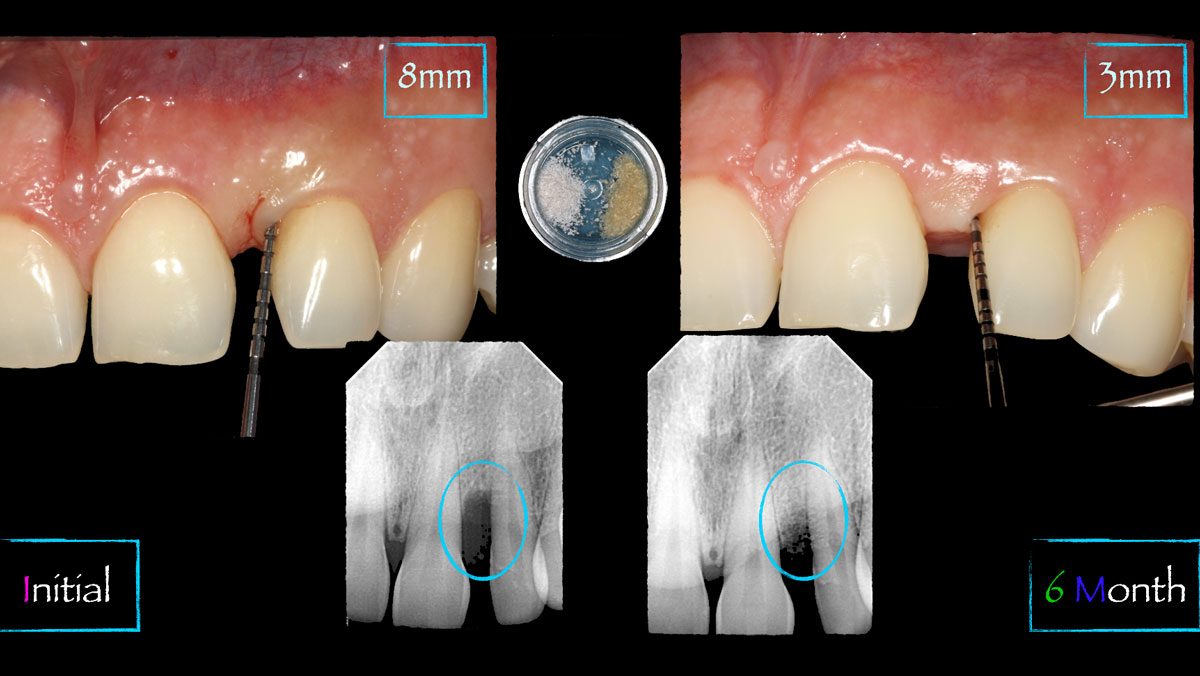
The use of a minimally invasive surgical GTR approach showed excellent radiographic bone fill and reduction in probing depths from 8mm to 3mm at 6 months follow-up. Treatment outcome revealed stable periodontium and the patient was happy with the healthy stable teeth.

Bassam Kinaia, DDS, MS, DICOI
Dr. Kinaia is the Associate Director of the Graduate Periodontology Program at the University of Detroit Mercy (UDM). He is also the former Director of the Periodontology Program at UDM in Michigan and Boston University Institute for Dental Research and Education in Dubai. He is a Diplomate of the American Acade- my of Periodontology (AAP) and International Congress of Oral Implantology (ICOI). He received a certificate of Excellence from the AAP in recognition of teaching-research fellowship.

BIOBRIEF
Horizontal Ridge Augmentation in the Esthetic Zone
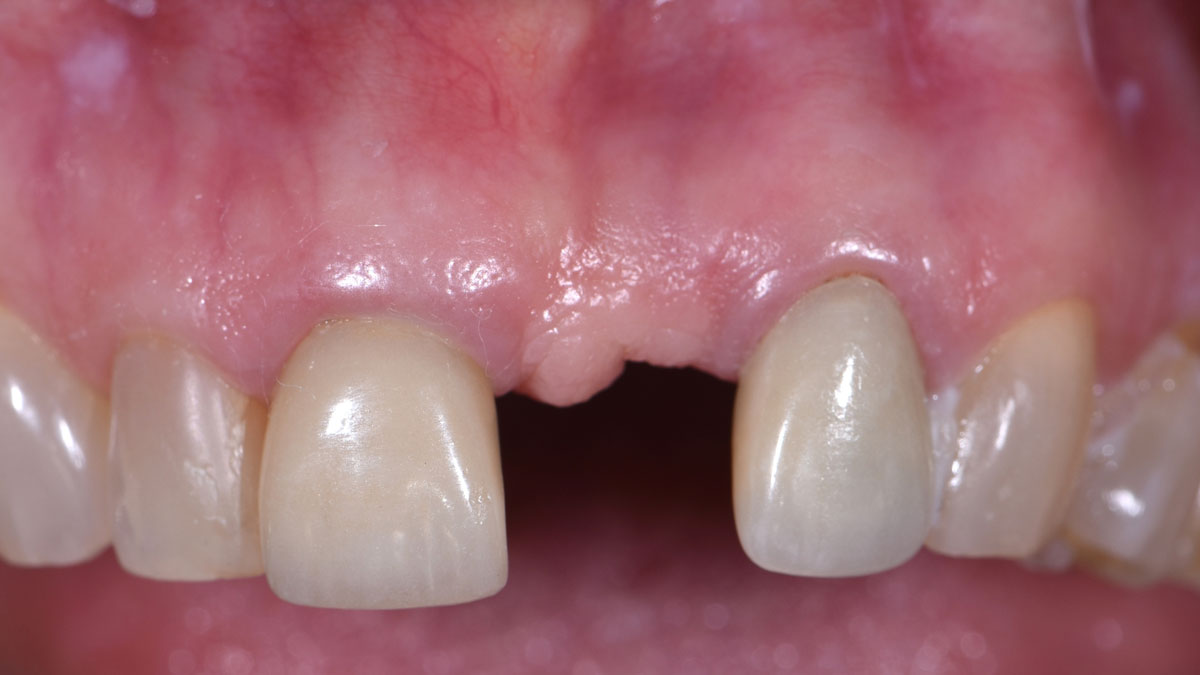

THE SITUATION
An adult female patient presented with a long history of edentulism at site #9. Patient was interested in replacing her missing tooth with a dental implant, and was wearing a Nesbit appliance. The irritation from the ill-fitting Nesbit appliance resulted in irregular and friable soft-tissue at site #9.
Pre-operative CBCT demonstrated a hard-tissue concavity apical to the crest of the bone. The primary goal of therapy was to regain horizontal dimension of hard and soft-tissue to achieve prosthetically-driven placement of a dental implant to replace the patient‘s left central incisor.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
The treatment goal was to regain the horizontal dimension of hard and soft-tissue through guided bone regeneration. In coordination with the restoring dentist, a diagnostic wax up was completed to determine the ideal tooth position and to regain mutually protected occlusion on the patient’s left side. The combination of Geistlich Bio-Oss® and autologous bone chips was used along with Geistlich Bio-Gide® to regenerate the horizontal dimension for prosthetically-driven implant placement.
“Patient with a long history of partial edentulism was seeking a long-term, predictable restorative option to replace her missing left central incisor.”
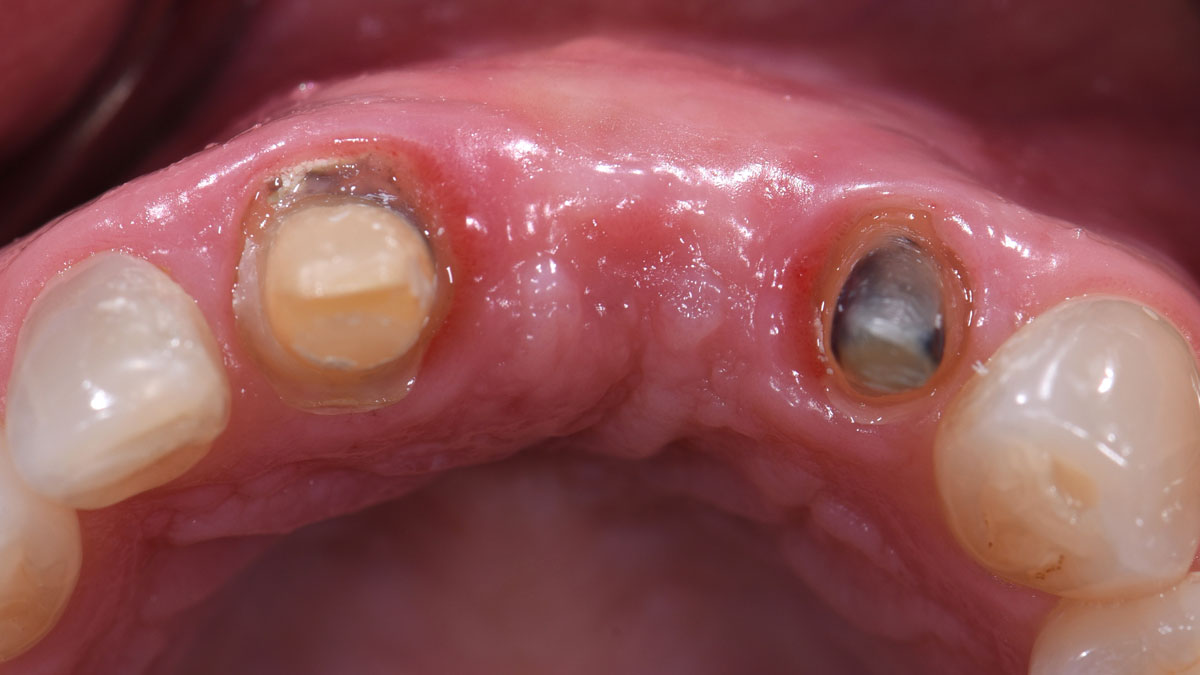
THE OUTCOME
Adequate hard and soft-tissue architecture was restored with the use of Geistlich Bio-Oss® and Geistlich Bio-Gide® for predictable, prosthetically-driven implant placement. The combination of Geistlich Bio-Oss® and autologous bone chips provides the best chance for regeneration while maintaining the hard and soft-tissue contours.

Dr. Justin Kang
Dr. Justin Kang received his Doctor of Dental Medicine degree from University of Pennsylvania School of Dental Medicine. He completed his residency and received his Masters of Science in Periodontics at Columbia University College of Dental Medicine. Dr. Kang is a Diplomate of the American Board of Periodontology and a member of numerous professional associations including the Academy of Osseointegration, American Dental Association and the New Jersey Dental Association.

BIOBRIEF
Lateral Ridge Augmentation in the Posterior Mandible
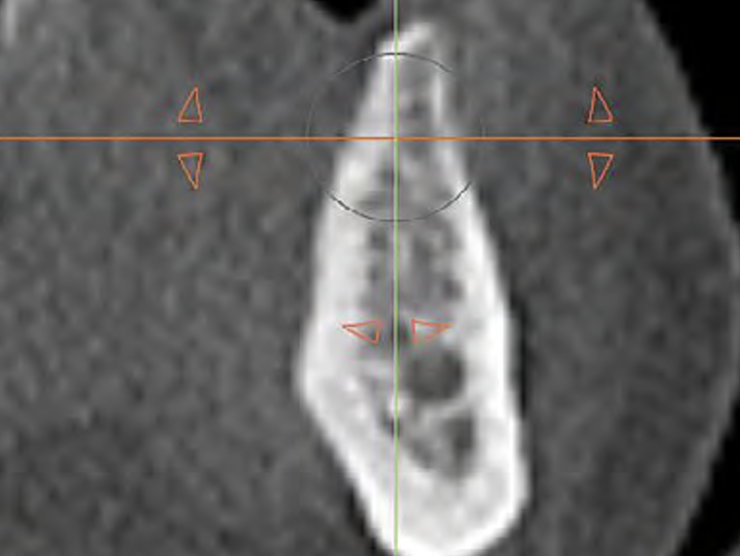

THE SITUATION
A 70-year-old female in good health presented with a fracture of tooth #19 which is the distal abutment for a four-unit bridge tooth #19-22, with pontics in the #20 and #21 positions. With the loss of the bridge, the patient desired a fixed prosthetic replacement. A bridge from tooth #22 to an implant placed at the #18 position was not deemed mechanically sound. She opted for implant placement at positions #19, #20 and #21 following lateral ridge augmentation with autogenous bone and Geistlich Bio-Oss® contained with a Geistlich Bio-Gide® membrane.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Compromised | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
A subperiosteal flap with a mid-ridge incision was performed with anterior and posterior releasing incisions which were placed the distance of one tooth mesial and one tooth distal from the graft site. The posterior releasing incision allowed for exposure of the ramus for harvesting of the autologous bone. The grafted site was allowed to heal for a period of 8 months at which time the implants were placed. Abutment connection occurred 4 months following implant placement.
“A bone graft was required to augment the ridge, a CBCT scan was performed prior to surgery to determine bone volume and the amount of bone required to graft.”
THE OUTCOME
Following 8 months of healing, the augmented site showed sufficient bone width that was assessed with a CT scan. After examination, it was determined that the bone width was adequate for implant placement in the desired position to allow an esthetically pleasing and functional outcome for the patient.

Dr. John M. Sisto
Dr. John M. Sisto received his Doctorate in Dental Surgery degree from Loyola University and completed his residency and certification in Oral and Maxilofacial Surgery at the Cook County Hospital in Chicago. Dr. Sisto was the Director of Residency Education at Cook County Hospital from 1985 to 2010 and started the residency program in oral and maxillofacial surgery in 1990. He held teaching positions at both Northwestern and University of Illinois Dental schools as a clinical assistant professor, and also at Northwestern Medical School. He was the Division Chief of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery at Cook County Hospital and Chairman of Dentistry at Resurrection Medical Center. Dr. Sisto has published papers on dental implant surgery, trauma surgery, orthognathic surgery and maxillofacial infections. He has lectured both locally and nationally at various educational forums.

BIOBRIEF
Bone Augmentation L-Shape Technique with Early Implant Placement

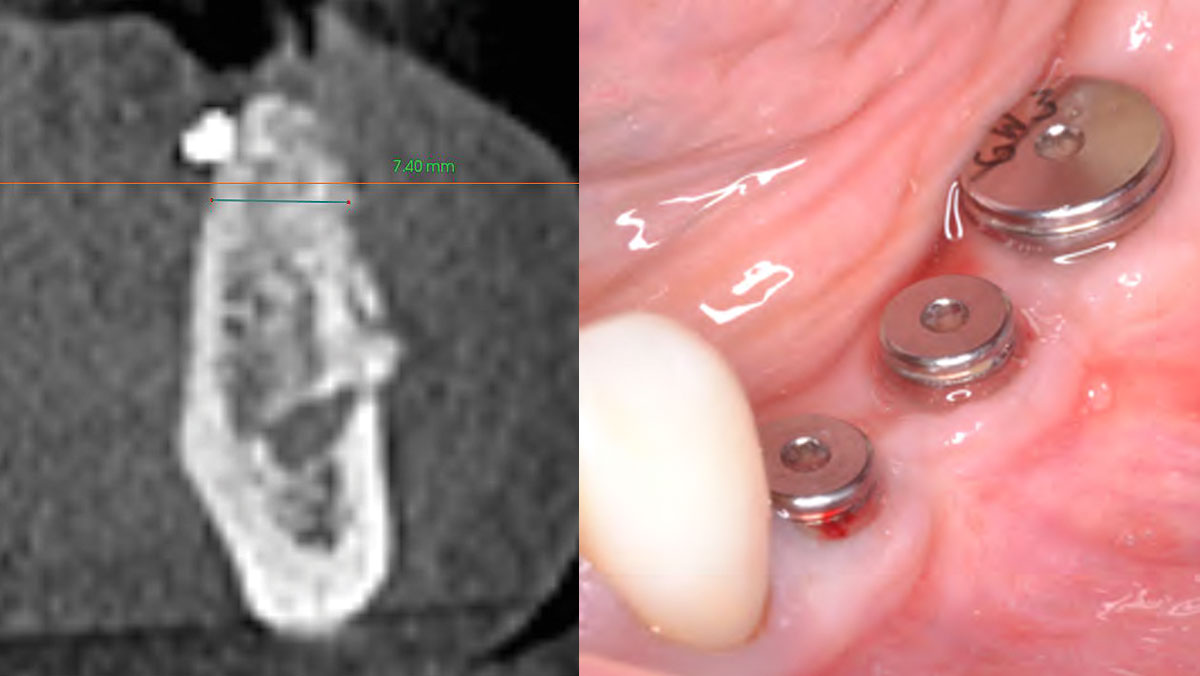
THE SITUATION
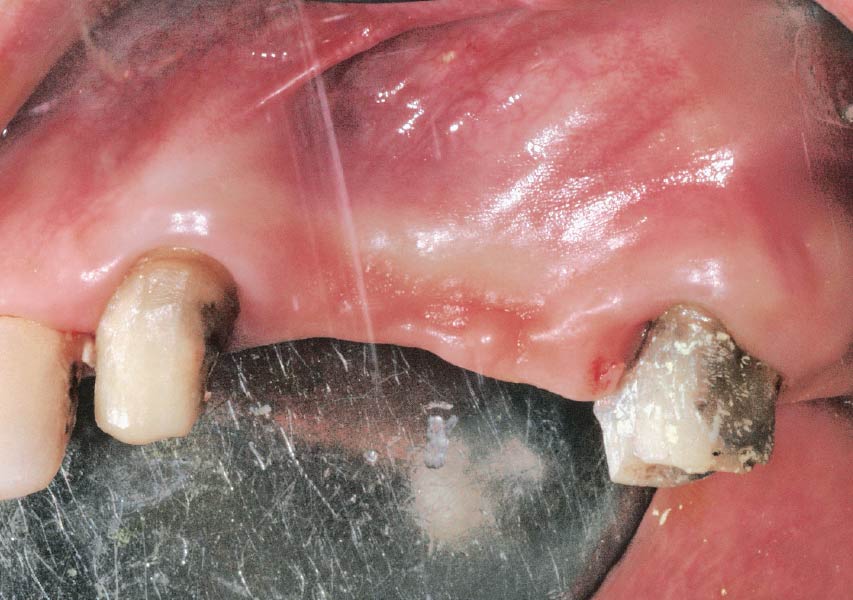
The patient presented to the clinic with a discolored tooth #8, with mobility and a history of trauma. The tooth has a horizontal fracture in the apical third of the root and has recurrent infection after the root canal treatment. The patient feels discomfort and dislikes his esthetic appearance. He would like the fractured tooth #8 removed and replaced with a fixed solution.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
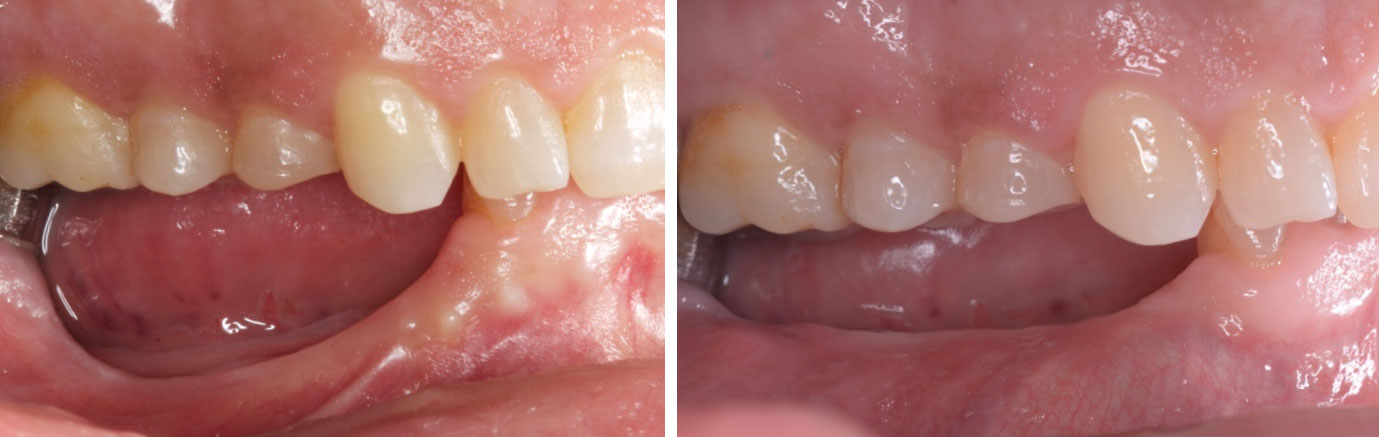
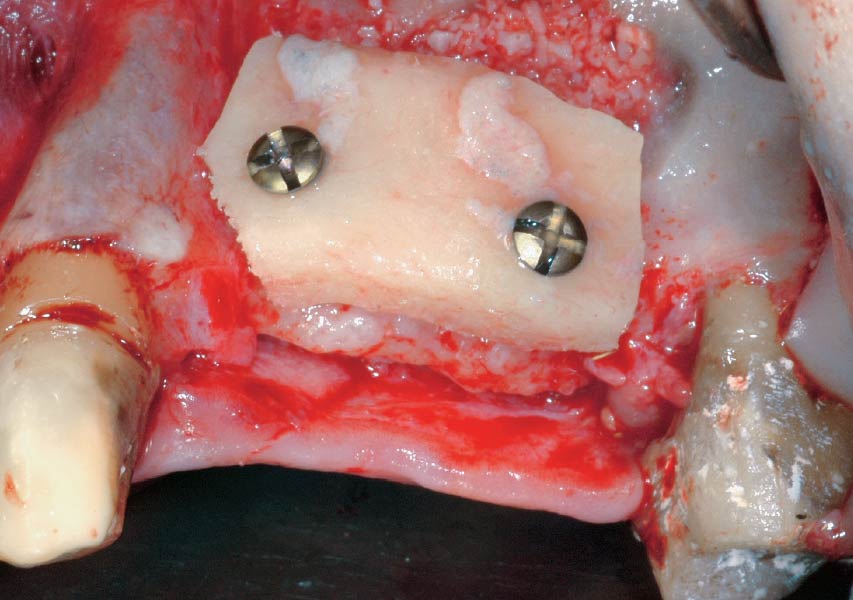
To carefully extract tooth #8 and to replace it with an early-stage implant placed with simultaneous guided bone regeneration through the use of Geistlich Bio-Oss Collagen® trimmed in an “L-Shape” under the protection of a Geistlich Bio-Gide® membrane. To augment the peri-implant soft-tissue with the use of a connective tissue graft during implant healing time, increasing the overall volume of site #8. To provisionalize the implant for the development of a proper emergence profile. To deliver a definitive reconstruction which is functional and esthetic for the patient.
“A fractured anterior tooth needs to be replaced with an implant-supported reconstruction.”
THE OUTCOME
The implant and its prosthetic reconstruction were successful because they provided the patient with a fixed solution with adequate function and esthetics. The implant shows stable marginal bone levels due to the proper implant placement together with the guided bone regeneration procedure. The peri-implant soft-tissue is healthy and stable with sufficient volume created by the soft-tissue augmentation. The definitive reconstruction meets the patient’s esthetic demands and is functional in occlusion.


Prof. Dr. Ronald E. Jung
Prof. Dr. Jung is currently Head of the Division of Implantology, Clinic for Fixed and Removable Prosthodontics and Dental Material Science, Center of Dental Medicine at the University of Zürich. In 2006 he worked as Visiting Associate Professor at the Department of Periodontics at the University of Texas Heath Science center at San Antonio, USA (Chairman: Prof. D. Cochran). In 2008 he finalized his “Habilitation” (venia legendi) in dental medicine and was appointed associate professor at the University of Zürich. In 2011 he received his PhD degree from the University of Amsterdam, ACTA dental school, The Netherlands. He is an accomplished and internationally renowned lecturer and researcher, best known for his work in the field of hard- and soft-tissue management and his research on new technologies in implant dentistry.

BIOBRIEF
Combined Horizontal and Vertical Regeneration Using a CAD-CAM Titanium Scaffold
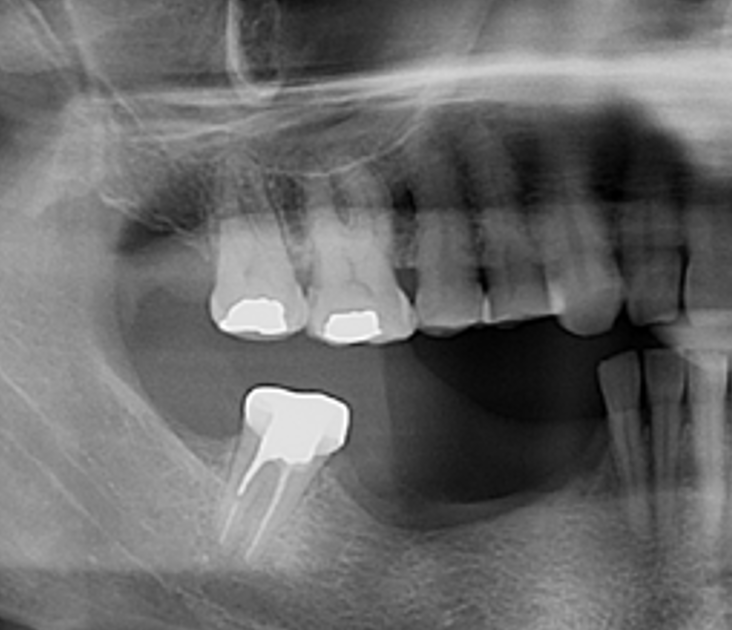


THE SITUATION
A 54-year-old, systematically healthy male patient (*ASA) came to our attention presenting with partial edentulism in the lower jaw and requiring a fixed and esthetic rehabilitation, refusing any removable solution. The clinical and radiographic evaluation resulted in significant bone atrophy both in the vertical and horizontal components; which makes it impossible to place both conventional implants and short or narrow implants.
*American Society of Anesthesiologists Physical Status Classification System
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system Non-smoker | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
Solving the case was developed in two steps: first bone reconstruction to restore the ideal anatomy, second positioning of the prosthetically guided implants. An individualized regeneration technique was chosen using a CAD-CAM titanium scaffold (Yxoss CBR®) in conjunction with a mix of 60% autogenous bone and 40% Geistlich Bio-Oss®, covered by Geistlich Bio-Gide®. At 9 months, the titanium scaffold was easily removed and 3 prosthetically guided implants were placed, completely surrounded by bone. At 12 months, a free gingival graft was performed to re-establish the missing amount of keratinized mucosa. Finally, at 16 months, the final rehabilitation was carried out with a fixed prosthesis on implants.
“Combined horizontal and vertical bone augmentation utilizing a CAD CAM titanium scaffold can be achieved with less surgical time and less complications.”
THE OUTCOME
The final resolution of the case was very satisfactory. There were no complications during all the procedures performed. The Yxoss CBR® allowed for easier reconstructive surgery and a significant reduction in surgical times, thanks to the precise dimensions of the scaffold. This resulted in a favorable post- operative situation for the patient and complications were prevented.

Dr. Gian Maria Ragucci
Universitat Internacional de Catalunya (UIC), Barcelona Dental degree at Universidad Europea de Madrid 2015
International Master in oral surgery at UIC, Barcelona 2018
PhD student at UIC, Barcelona 2018
EAO Certification program in implant dentistry 2018
EAO European prize in implant dentistry 2019

Prof. Federico Hernández-Alfaro
Full professor & Chairman, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, UIC, Barcelona
Institute of Maxillofacial Surgery, Teknon Medical Center, Barcelona

BIOBRIEF
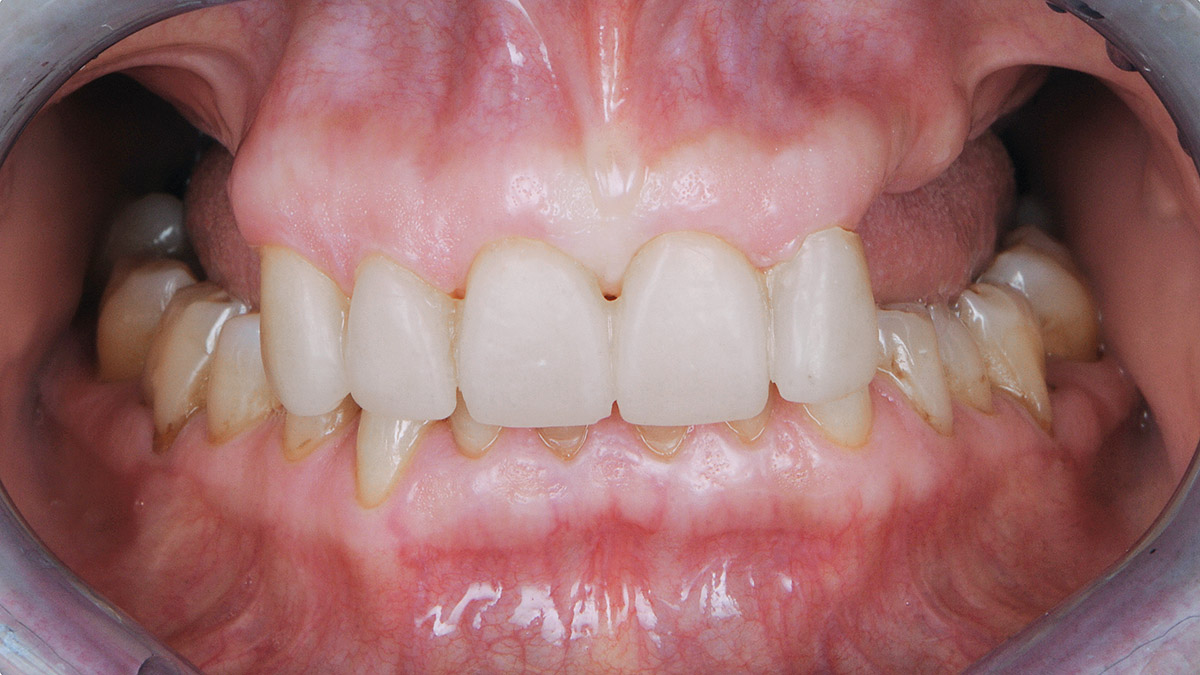
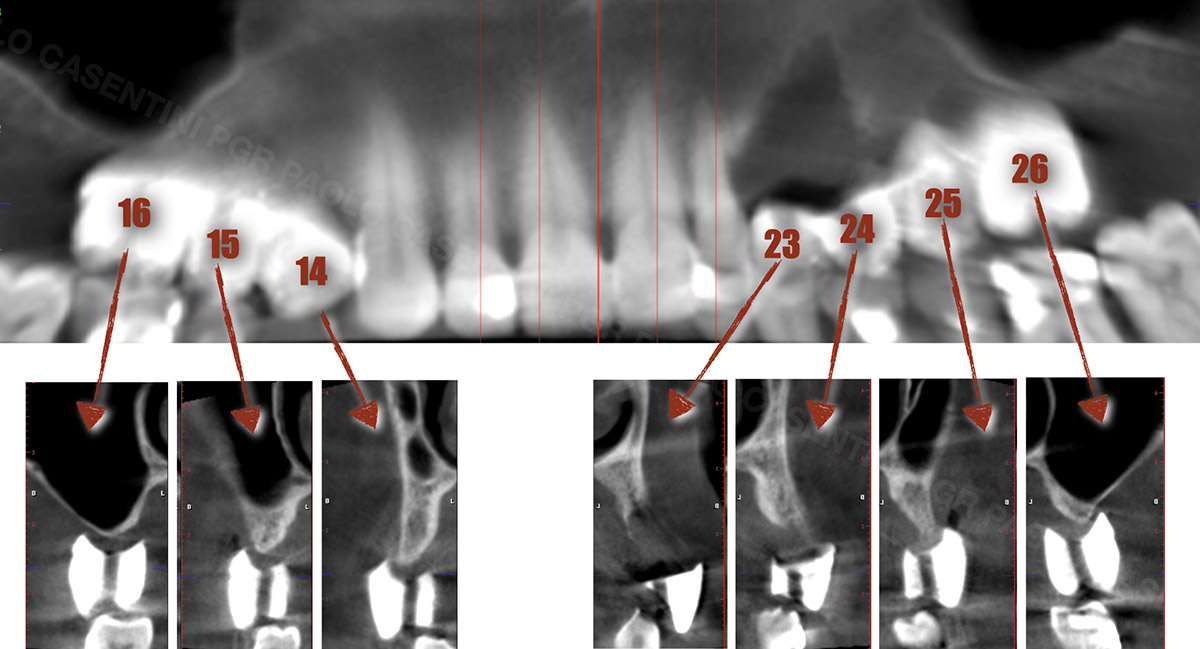
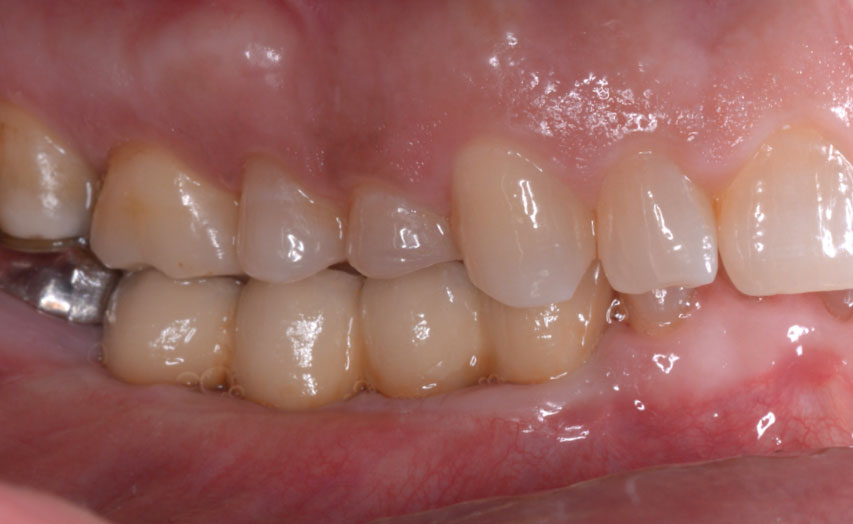
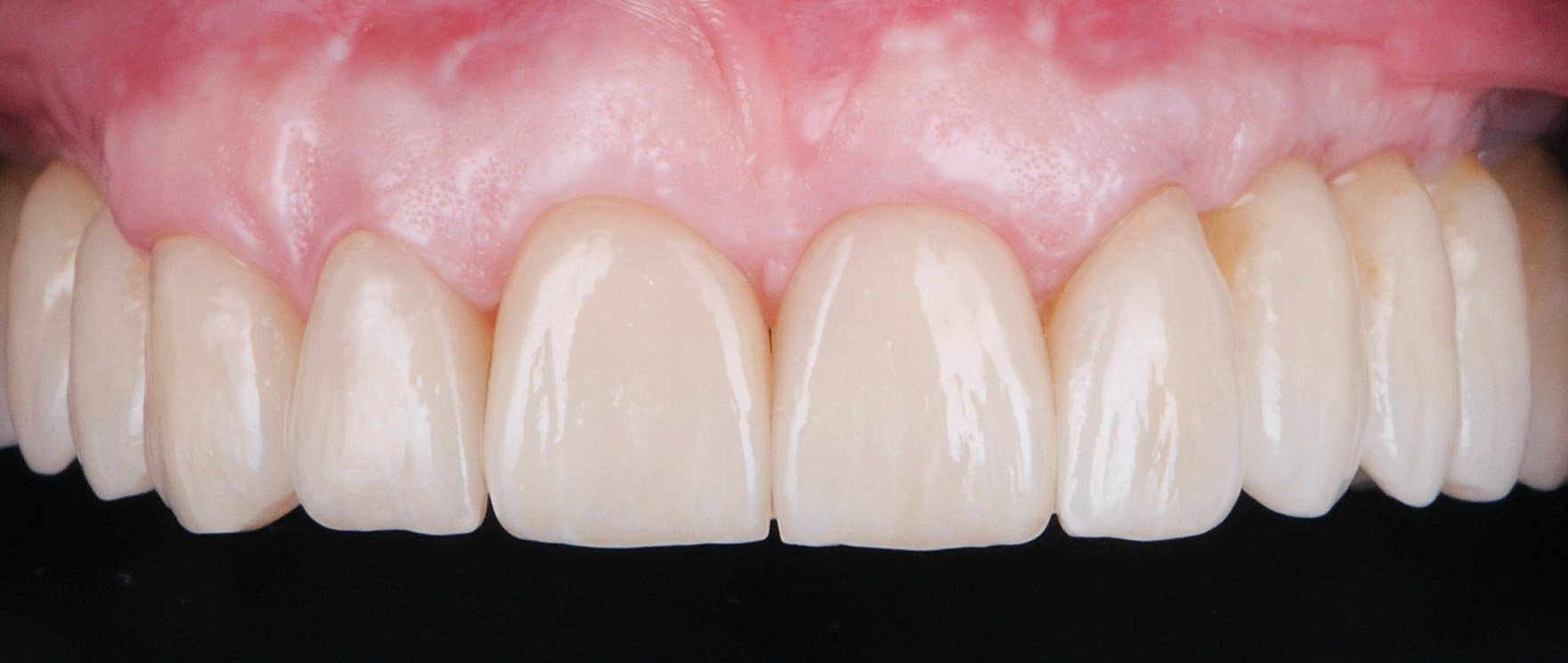
Prosthetically Guided Regeneration (PGR) in the Posterior Maxilla

THE SITUATION
The 60-year-old female patient’s chief complaint was represented by unsatisfactory esthetics and function, related to loss of multiple maxillary teeth. Her request focused on improving esthetics and function by means of a fixed reconstruction.
The patient presented five residual anterior maxillary teeth (from 6 to 10) that could be maintained. After preliminary periodontal diagnosis and treatment, specific diagnostic steps for implant treatment demonstrated inadequate bone volume for implant placement.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system Non-smoker | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
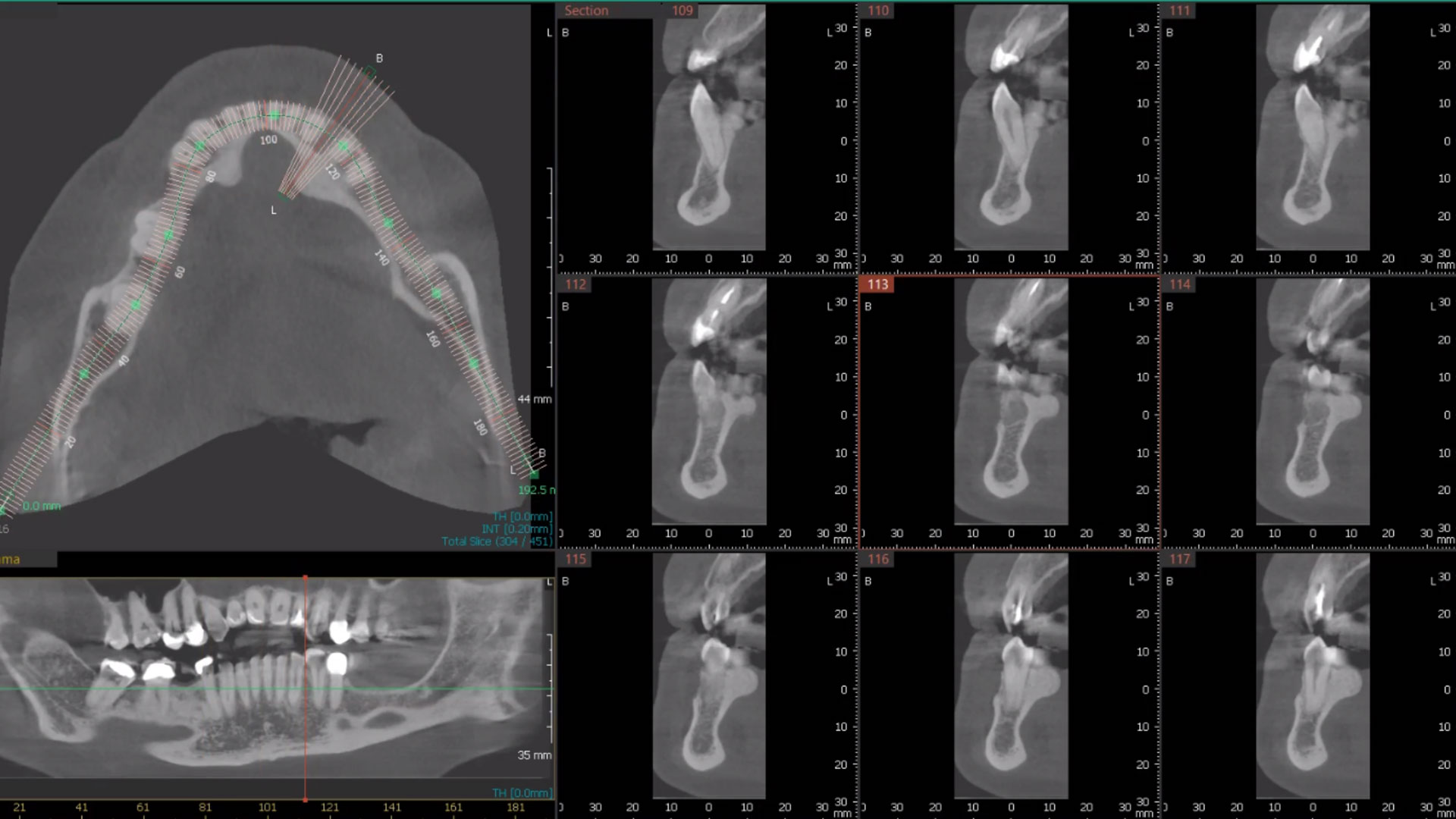
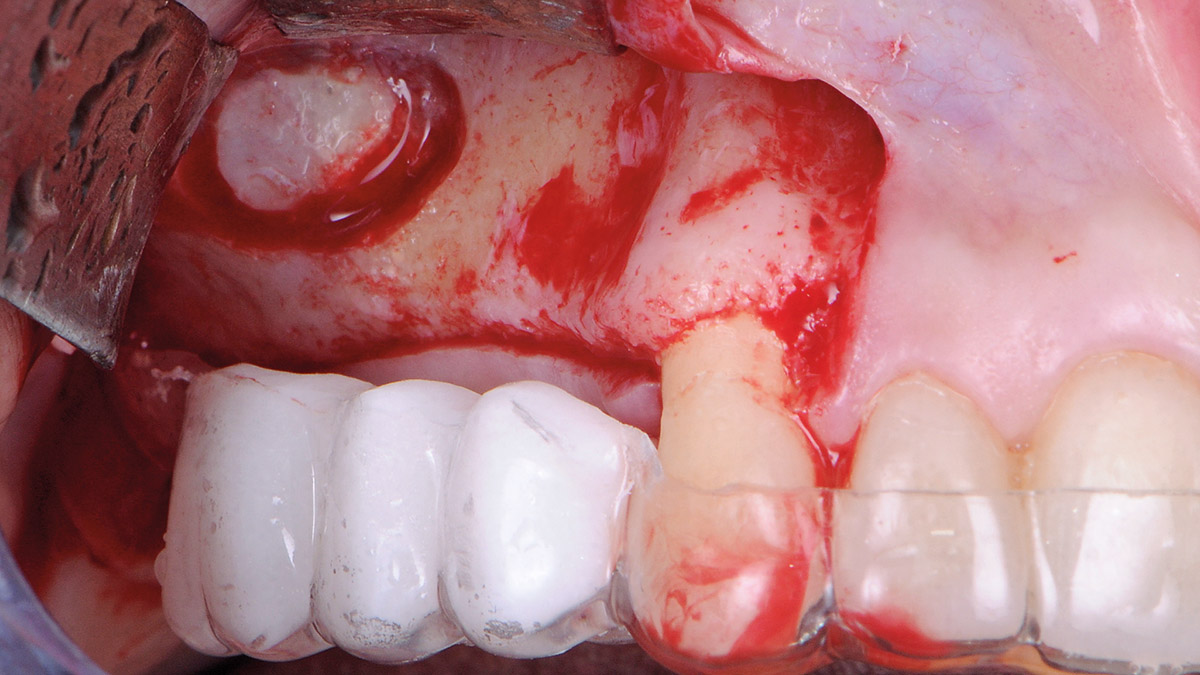
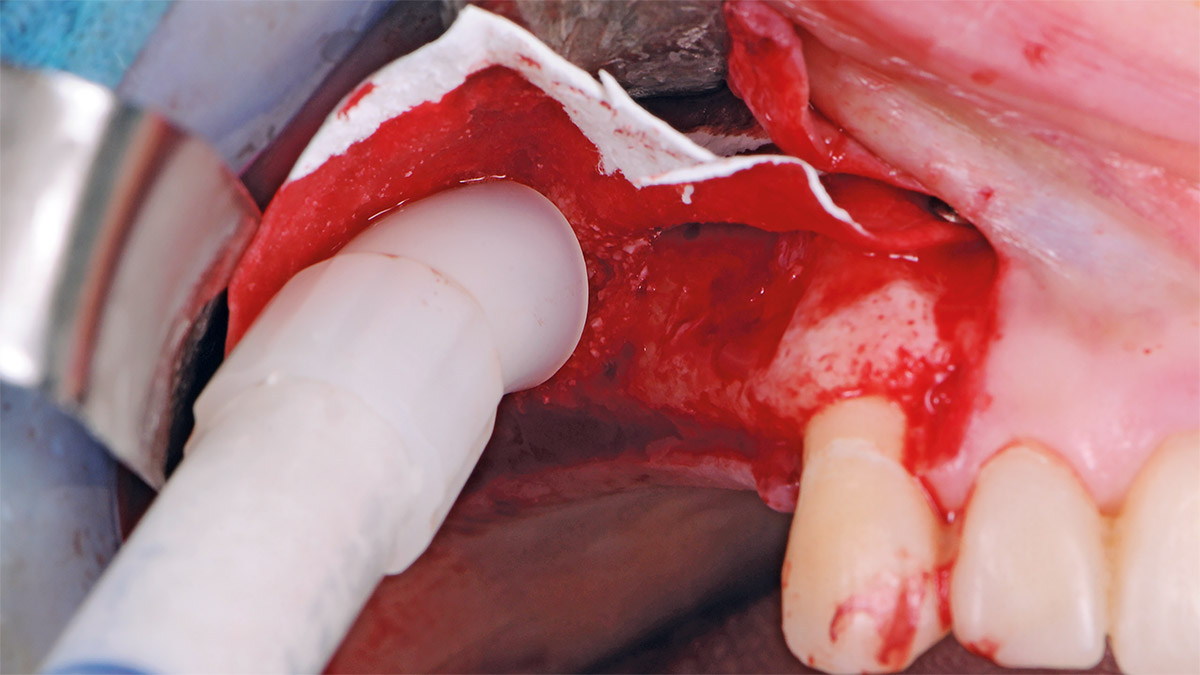
Bi-lateral sinus lift with Geistlich Bio-Oss Pen® and horizontal bone augmentation with a 1:1 mix of autogenous bone and Geistlich Bio-Oss® were performed six months prior to implant placement, following a Prosthetically Guided Regenerative (PGR) approach. The augmented sites were protected with Geistlich Bio-Gide® stabilized with titanium pins. The template utilized for radiographic diagnosis and GBR was then used to guide the implants’ placement.
Using a diagnostic template during the GBR procedure helps to highlight the presence of bone defects in relationship to the restorative plan and future position of implants.
THE OUTCOME
After a healing period of six months, adequate bone volume was achieved for the placement of five implants. Geistlich Fibro-Gide® was also used to optimize soft tissue volume at the buccal aspect of implants.
Implants were early loaded with a temporary screw-retained fixed prostheses six weeks after placement. The final prosthetic reconstruction included ceramic veneers of the frontal residual teeth and zirconium-ceramic screw-retained fixed prostheses on implants.


Paolo Casentini, DDS
Graduated in Dentistry at the University of Milan, Fellow and Past Chairman of the Italian section of ITI, Active member Italian Academy of Osseointegration. Co-author of 10 textbooks including ITI Treatment Guide volume 4, translated in eight languages, and “Pink Esthetic and Soft Tissues in Implant Dentistry” translated in five languages. His field of interest is advanced implantology in complex and esthetically demanding cases. He has extensively lectured in more than 40 countries.

BIOBRIEF
A Regenerative Approach to Peri-implantitis
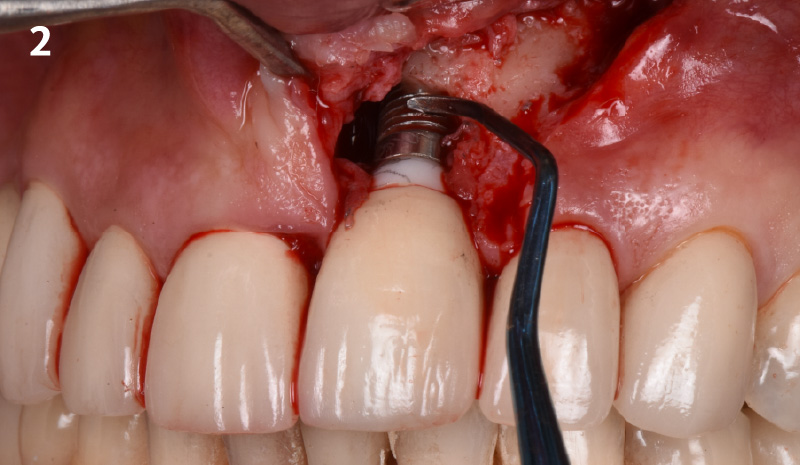

THE SITUATION
A 55-year-old man was referred to me by his general dentist. Upon initial clinical and radiographic findings, failing implant #9 showed signs of peri-implantitis that included BoP, Suppuration, 9+mm PD and radiographic bone loss affecting both the implant and the natural adjacent tooth. Patient stated that although his gums bleed, he does not have any pain. Gingival erythema was also found.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
Note: Peri-implantitis on implant #9 migrating to the mesial portion of root #8
THE APPROACH
The clinical goals were to eliminate the peri-implant infection, restore hard and soft-tissues and have long-term success. The technique utilized was a systematic regenerative approach to eliminate the underlying cause of the peri-implantitis infection and restore hard and soft-tissues to prior health.
Geistlich Fibro-Gide® has the capacity to enhance the soft-tissue during a bone regenerative approach.
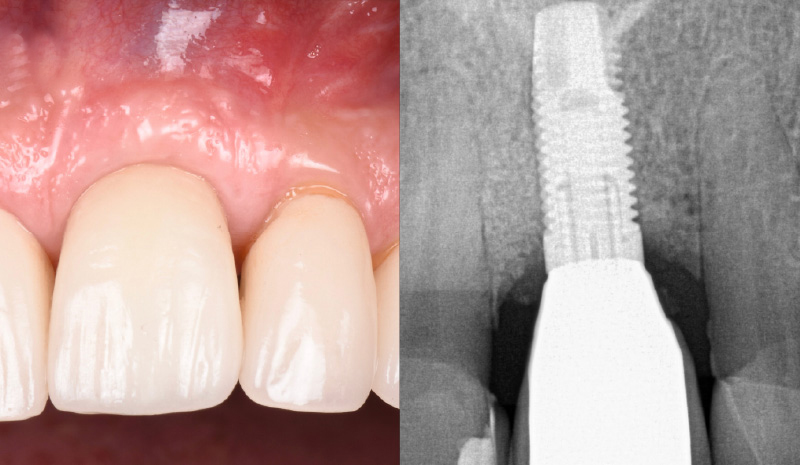
THE OUTCOME
My observation at the 1.5 year follow-up shows the elimination of peri-implantitis and complete peri-implant health was achieved showing a reduction in BOP, PD and most importantly soft tissue thickness stability. Radiographically, crestal bone shows no signs of progressive pathological loss and has maintained adequate volume.

Hector L. Sarmiento, D.M.D., MSc.
Dr. Hector Sarmiento was awarded his D.M.D. degree by the University of Rochester. He is uniquely trained in both maxillofacial surgery and periodontics. He is a professor in the maxillofacial surgery department of trauma and reconstructive unit at the Regional Hospital in Mexico and is an Assistant Clinical Professor in periodontics at the University of Pennsylvania. Along with his periodontal degree, he also received his masters in oral biology from the University of Pennsylvania. Dr. Sarmiento is an international and national lecturer and has published numerous articles in peer reviewed journals and textbooks. His research focus includes infected dental implants such as peri-implantitis, sinus complications as well as bone biology. Dr. Sarmiento maintains his private practice in the upper east side of Manhattan in NYC.

BIOBRIEF
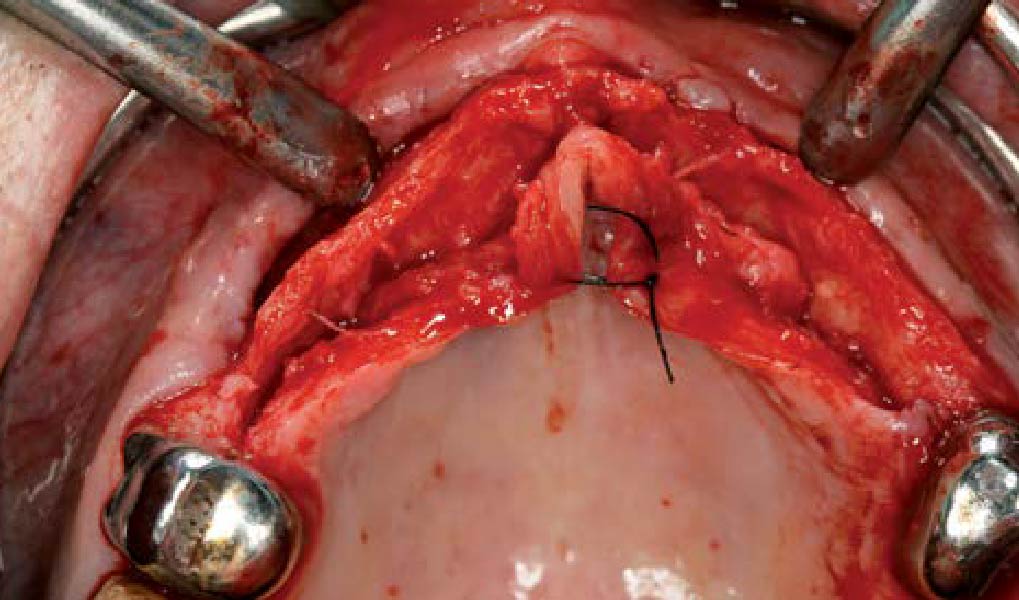
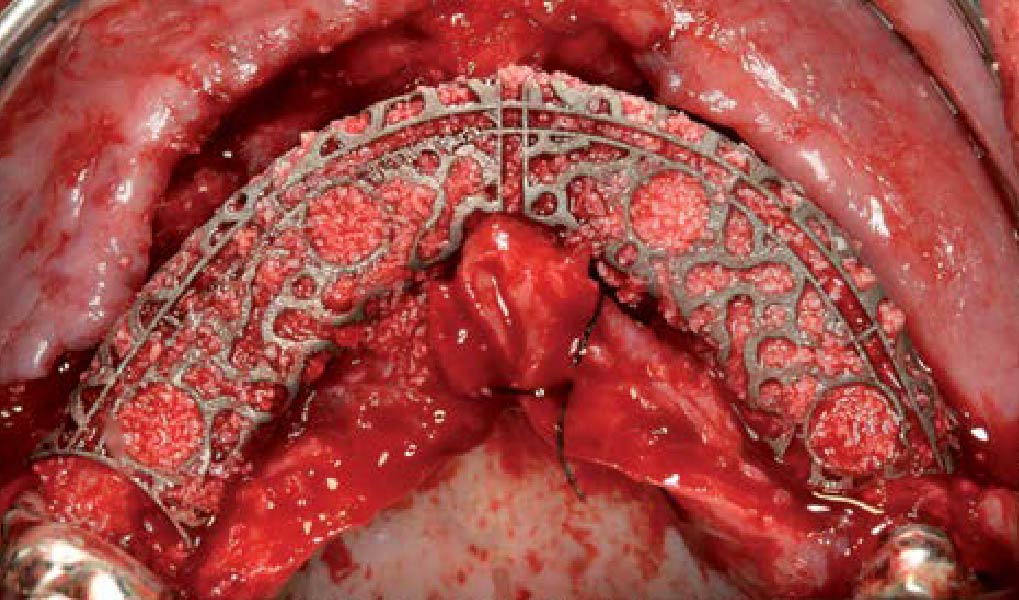
3D Bone Augmentation Using Customized Titanium Mesh in Conjunction with Autogenous Bone and Bovine Bone Material Granules
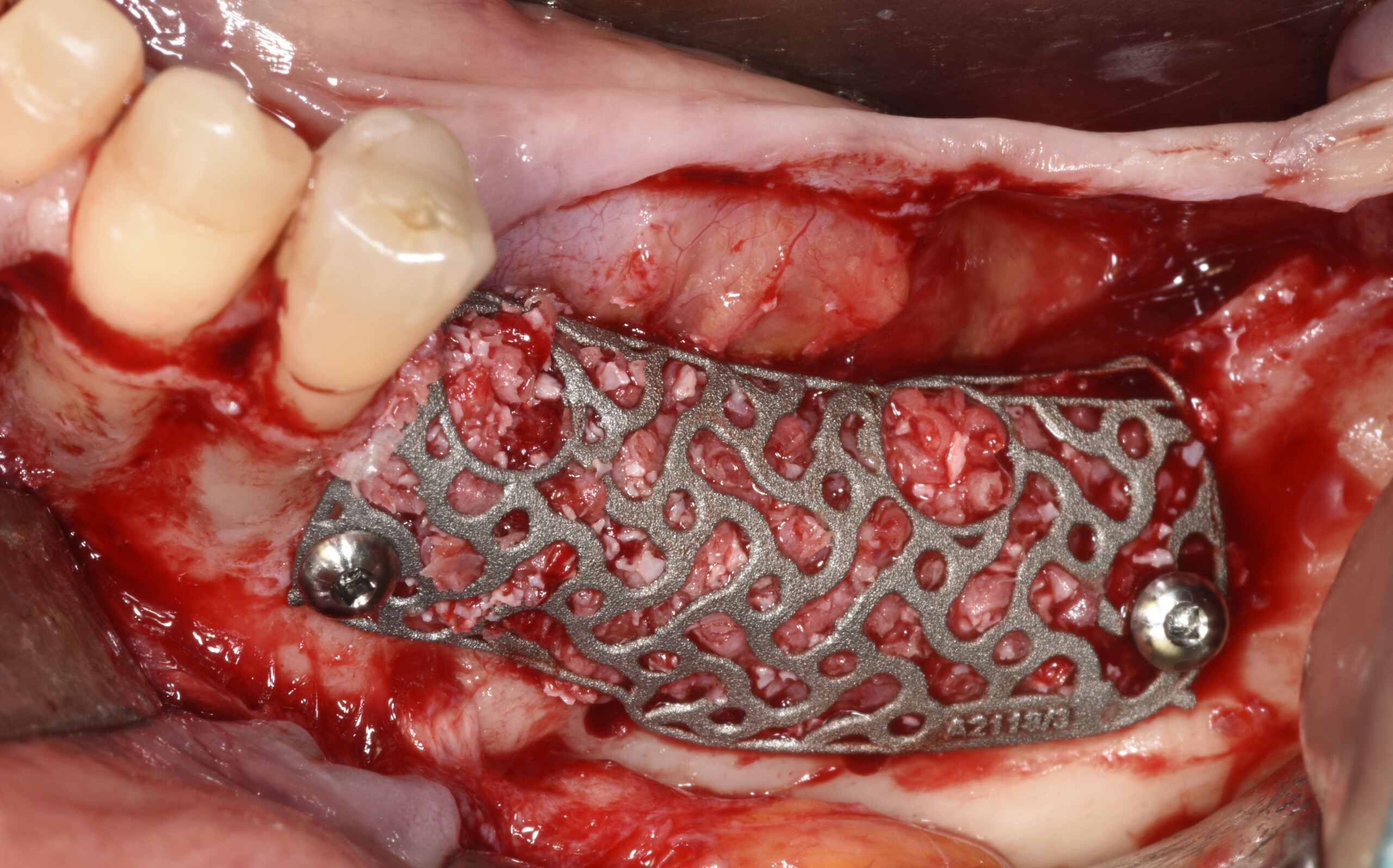


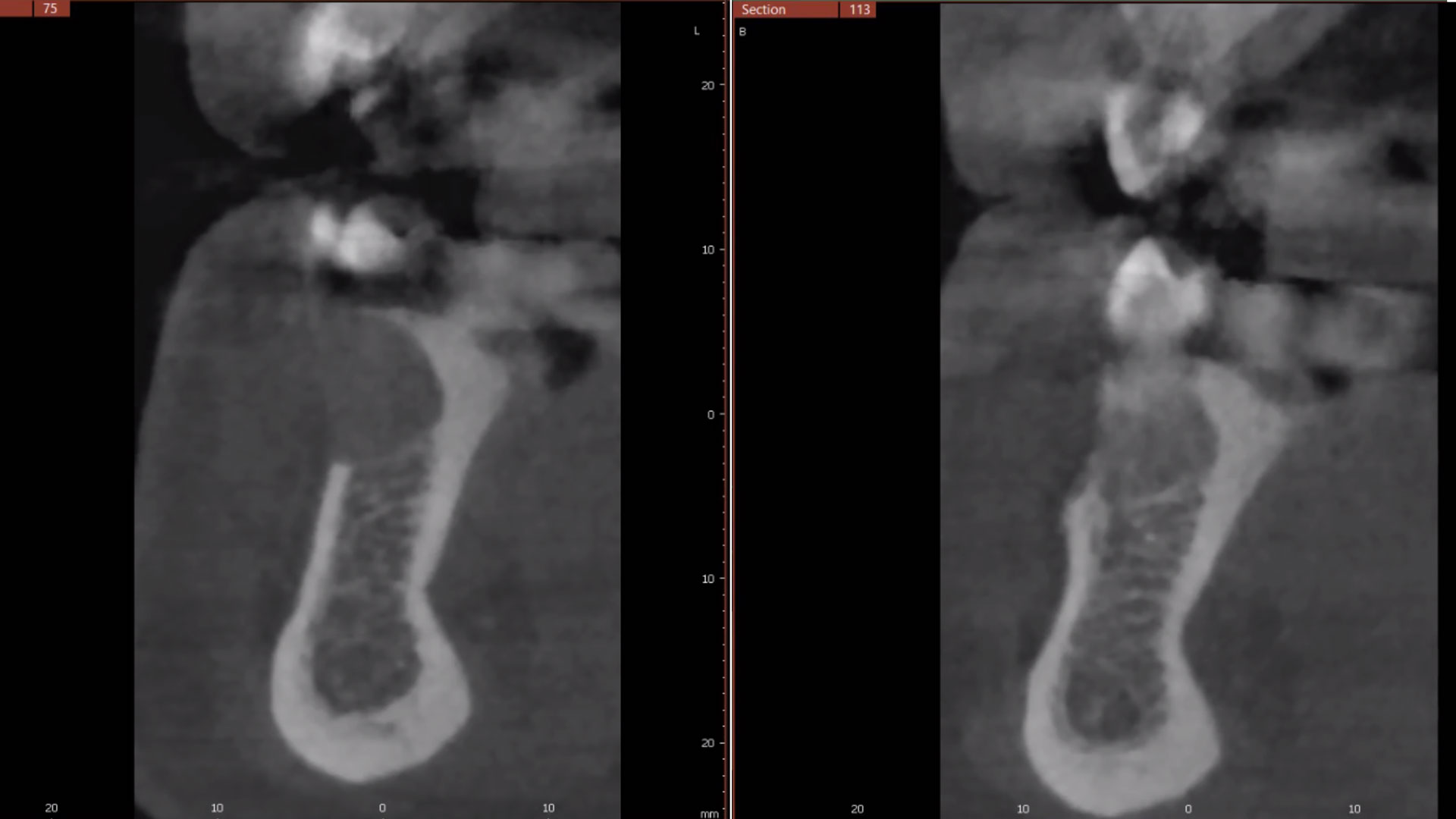
THE SITUATION
A 75-year-old systemically healthy female came to our attention presenting with absent mandibular second bicuspids and molars and requiring a fixed rehabilitation supported by implants as she refused a removable solution. The clinical and radiographic evaluation showed a relevant vertical and horizontal bone atrophy of such an extent that short or narrow implants were not considered a reliable option. The patient smoked <10 cigarettes per day.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
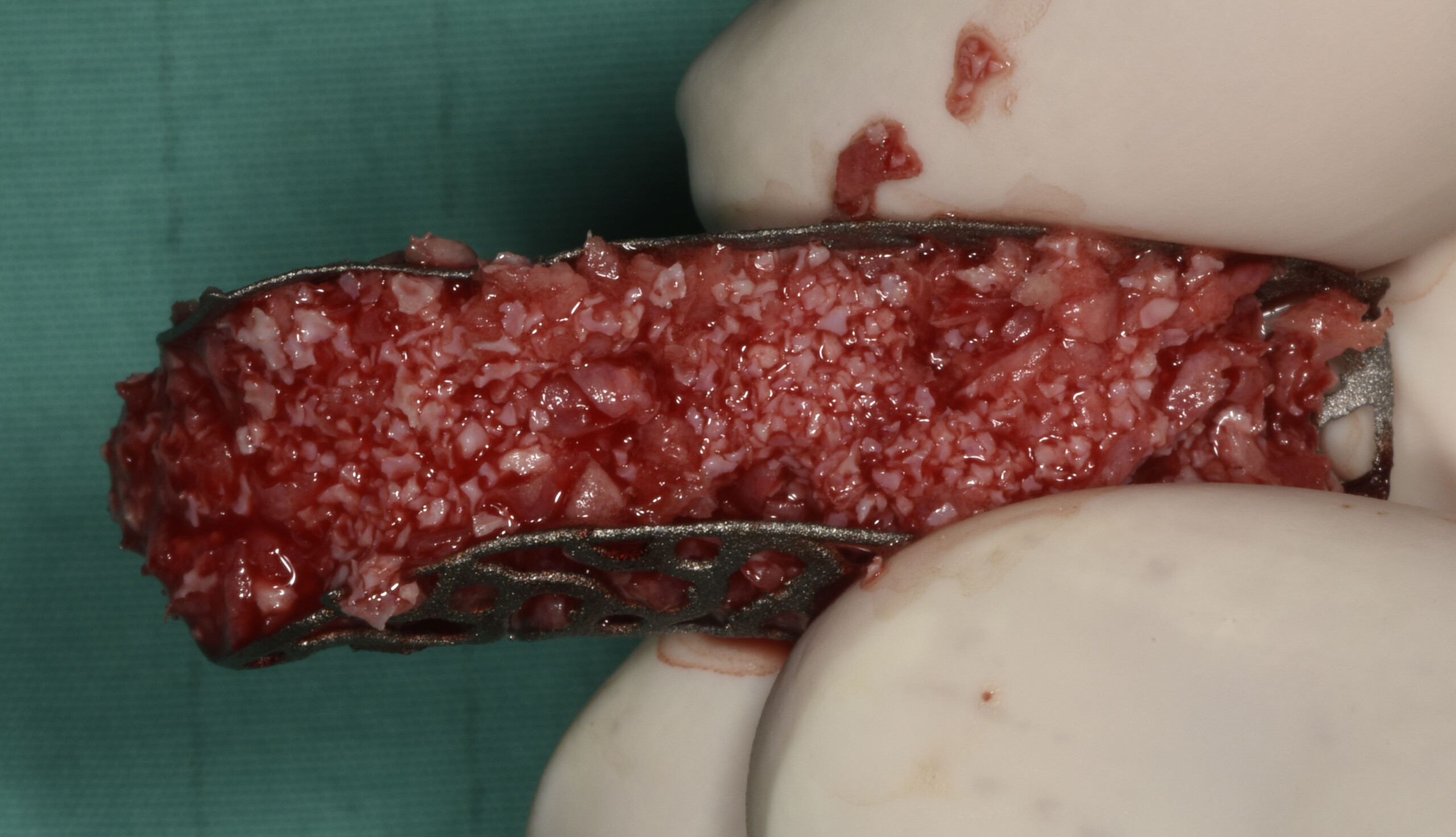
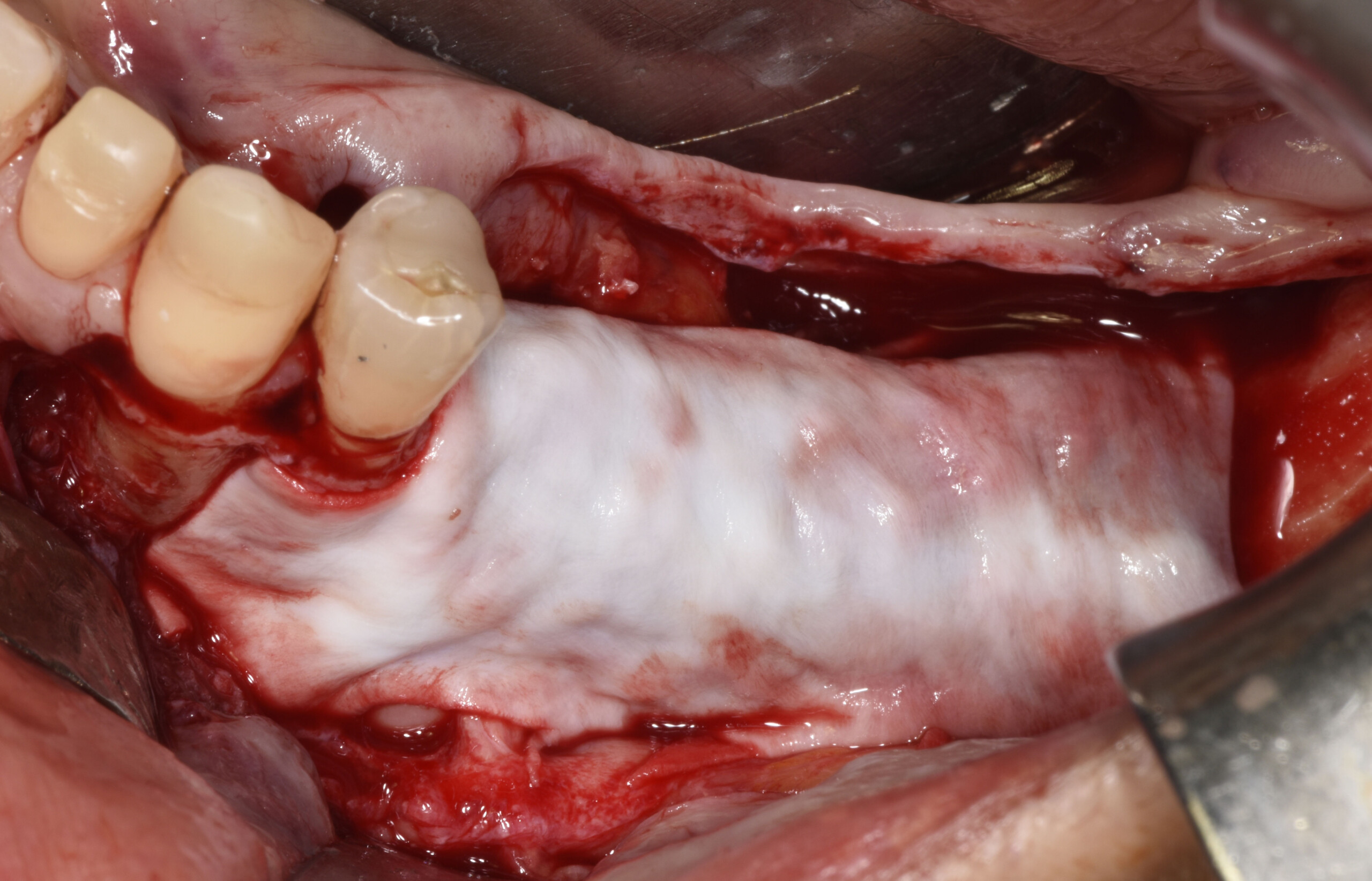
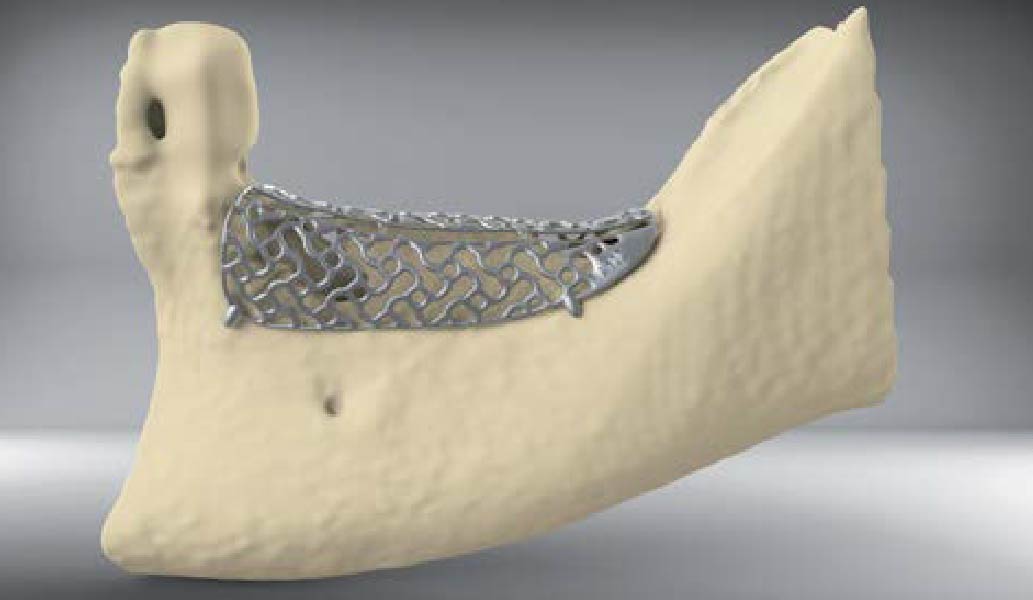
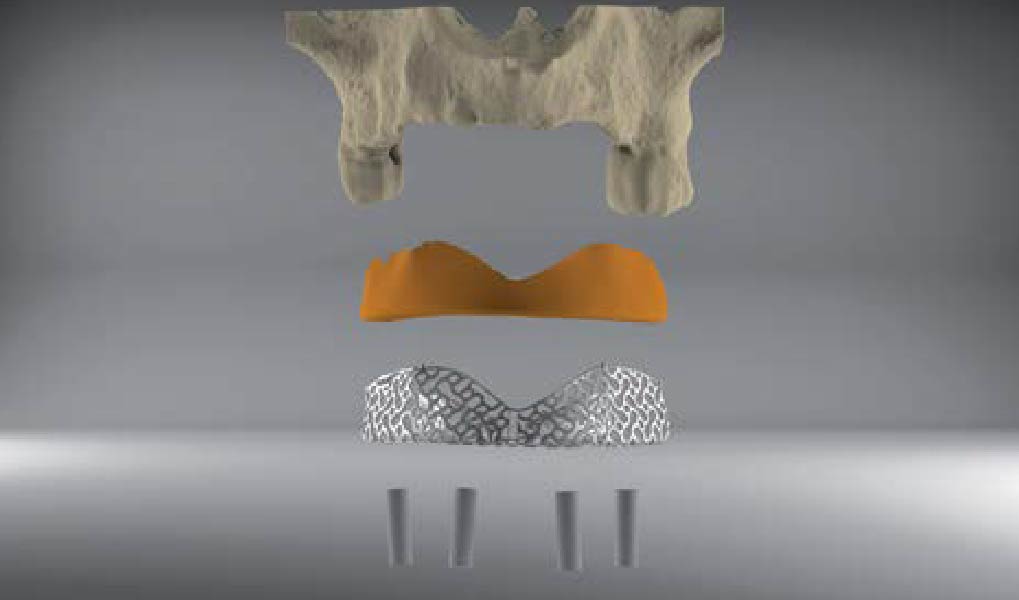
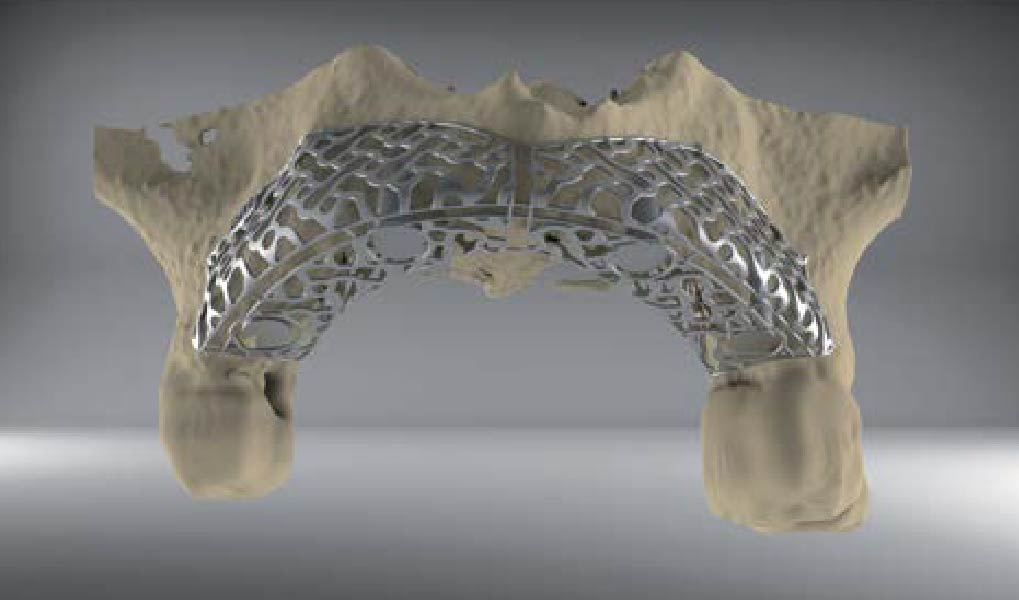
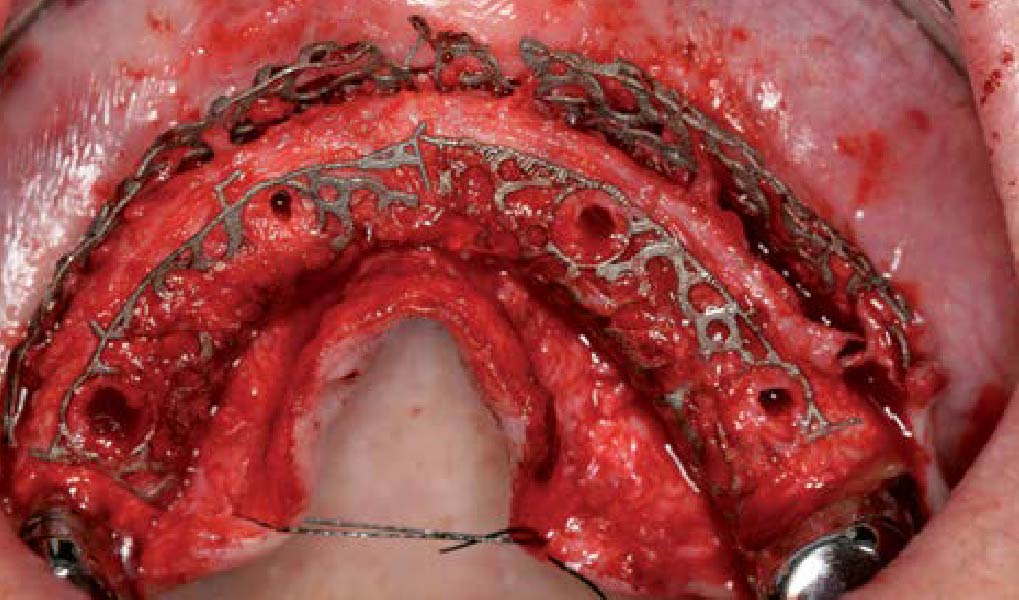
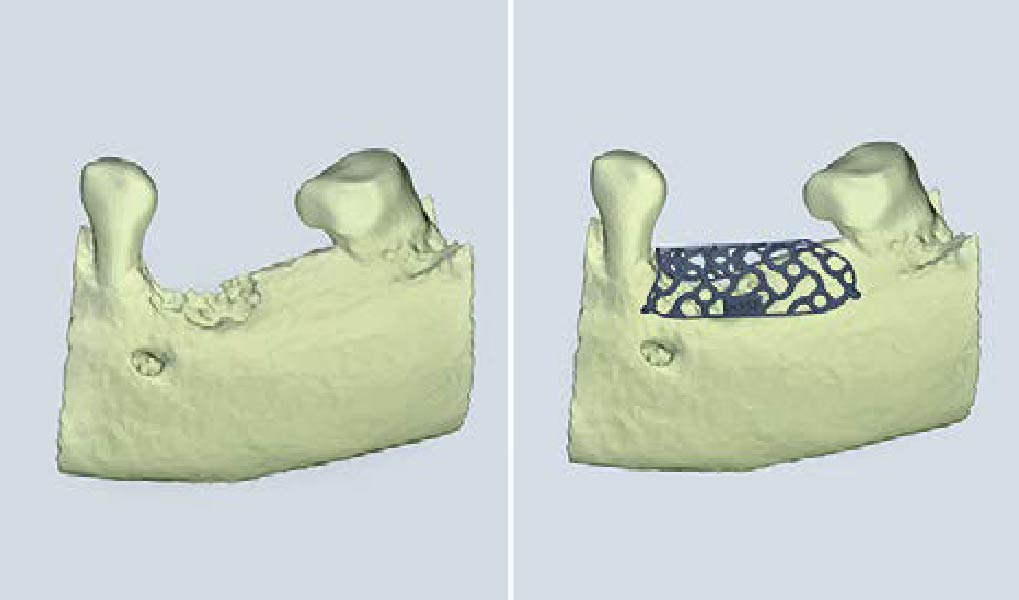
The main goal was to obtain a horizontal and vertical reconstruction of the deficient alveolar bone in order to allow safe and prosthetically-guided implant placement. Reconstruction was obtained by means of a customized titanium mesh, Yxoss CBR®, in combination with a mixture of autologous bone chips harvested from the mandibular ramus and bovine bone mineral, Geistlich Bio-Oss®.
The 3-dimensional reproduction of the left edentulous area permits the production of a precise and customized Ti-mesh.
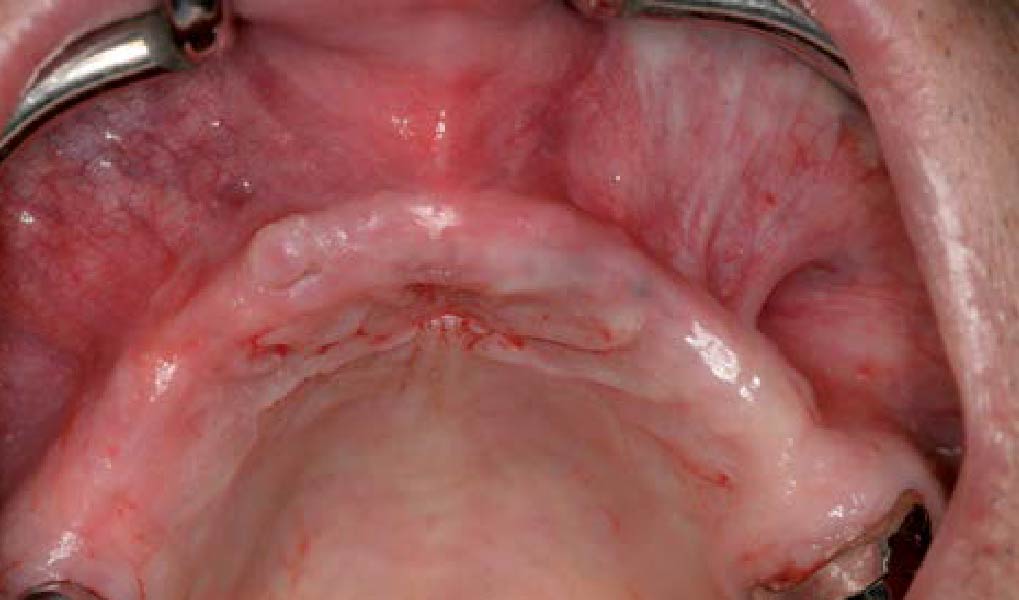
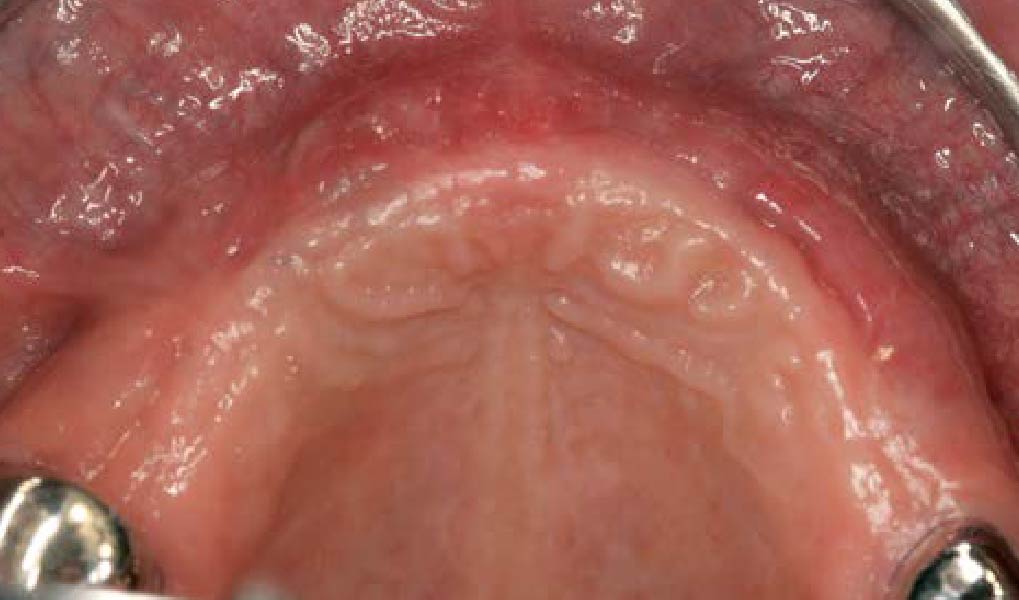
THE OUTCOME
Post-operative recovery of this patient was uneventful, no complications such as dehiscence or late exposure of the customized mesh, with complete correction of the initial defect. The Yxoss CBR® allowed an easy and faster reconstruction thanks to the precision of the prefabricated mesh filled with autologous chips, Geistlich Bio-Oss® and Geistlich Bio-Gide®.

Matteo Chiapasco, D.D.S., M.D.
Graduated in Medicine and specialized in Maxillofacial Surgery at the University of Milan, Italy. Professor, Unit of Oral Surgery, University of Milan; Associate Professor, Loma Linda University, Los Angeles, California, USA.

Grazia Tommasato, D.D.S., M.S.C.
Graduated in Dentistry in 2013, specialized in Oral Surgery at the University of Milan magna cum laude. PhD student and a medical consultant of the Clinical Unit of Oral Surgery (“G. Vogel” Clinic, Milan).

WEBINAR

WEBINAR

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE
CLINICAL CHALLENGE:
- The planning of the patient’s case takes local and general patient-specific risk factors into consideration according to the principles of backward planning for implant positioning.
AIM/APPROACH:
- Highlights step-by-step the important procedures to regenerate the bone (horizontal and vertical) with the 3-D printing technology, Yxoss CBR®.

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE
CLINICAL CHALLENGE:
- Insufficient alveolar ridge height for implant placement and proximity to the alveolar nerve
- Autologous bone harvesting is associated with patient discomfort
AIM/APPROACH:
- Interpositional grafting with Geistlich Bio-Oss® Block for vertical augmentation
- Alveolar ridge volume preservation and minimizing patient morbidity

CLINICAL CASE
CLINICAL CHALLENGE:
- Severely atrophied alveolar ridge with insufficient bone volume for implant placement
- High complication rates and patient discomfort associated with large augmentations when using autologous bone grafts
AIM/APPROACH:
- 3-dimensional augmentation of alveolar ridge by the fence technique for implant placement
- At the same time reducing complication rates and patient discomfort

CLINICAL CASE
CLINICAL CHALLENGE:
- Insufficient alveolar ridge width for implant placement
- Autologous bone is subject to resorption and may lead to loss of volume
AIM/APPROACH:
- Ridge Split procedure in combination with Geistlich Bio-Oss® and Geistlich Bio-Gide® for horizontal augmentation
- Preservation of the alveolar ridge volume

CLINICAL CASE
CLINICAL CHALLENGE:
- Insufficient alveolar ridge width for implant placement
- Donor site morbidity after autologous bone block harvesting and resorption of autologous bone
AIM/APPROACH:
- Horizontal alveolar ridge augmentation with Geistlich Bio-Oss® and Geistlich Bio-Gide®
- Minimizing autologous bone harvesting and resorption protection

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE
CONCLUSIONS:
- Geistlich Mucograft® with a keratinized tissue strip was utilized to increase vestibular depth and gain additional keratinized tissue.
- Augmentation of severely atrophied alveolar ridge provided sufficient bone for implant placement 8 months following augmentation.