NEW EBOOK: How to Master Bone Regeneration with Digital Innovation. Download Today!
Author: Evan Schwarz

BIOBRIEF
Mandibular Alveolar Ridge Split with Delayed Implant Placement
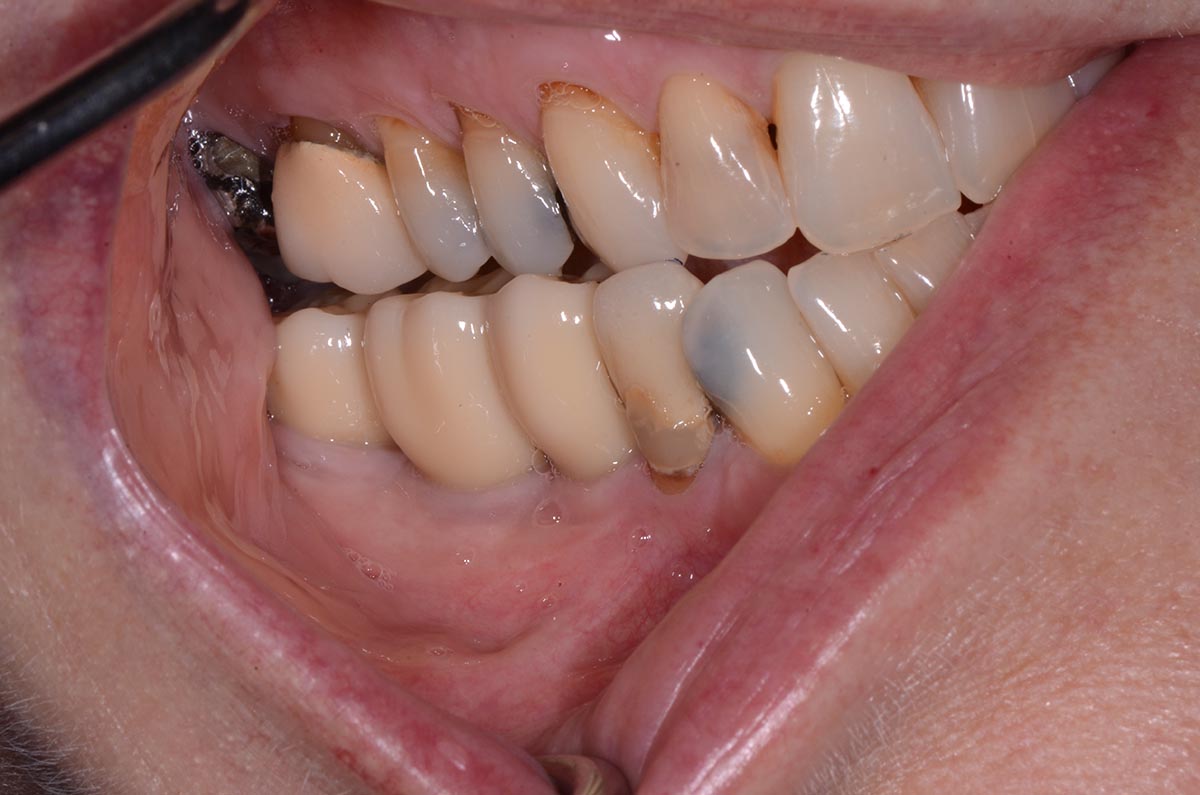

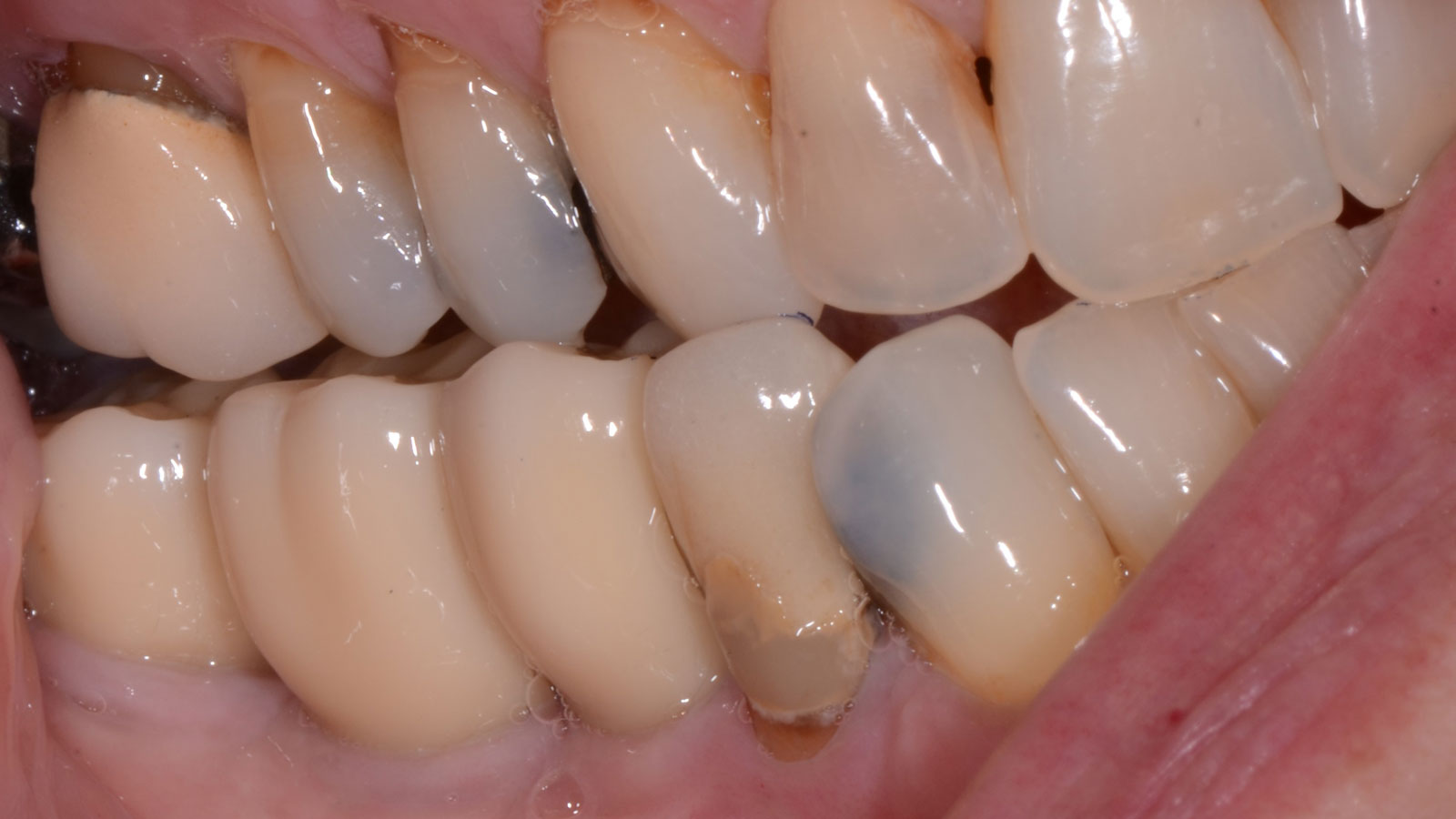
THE SITUATION
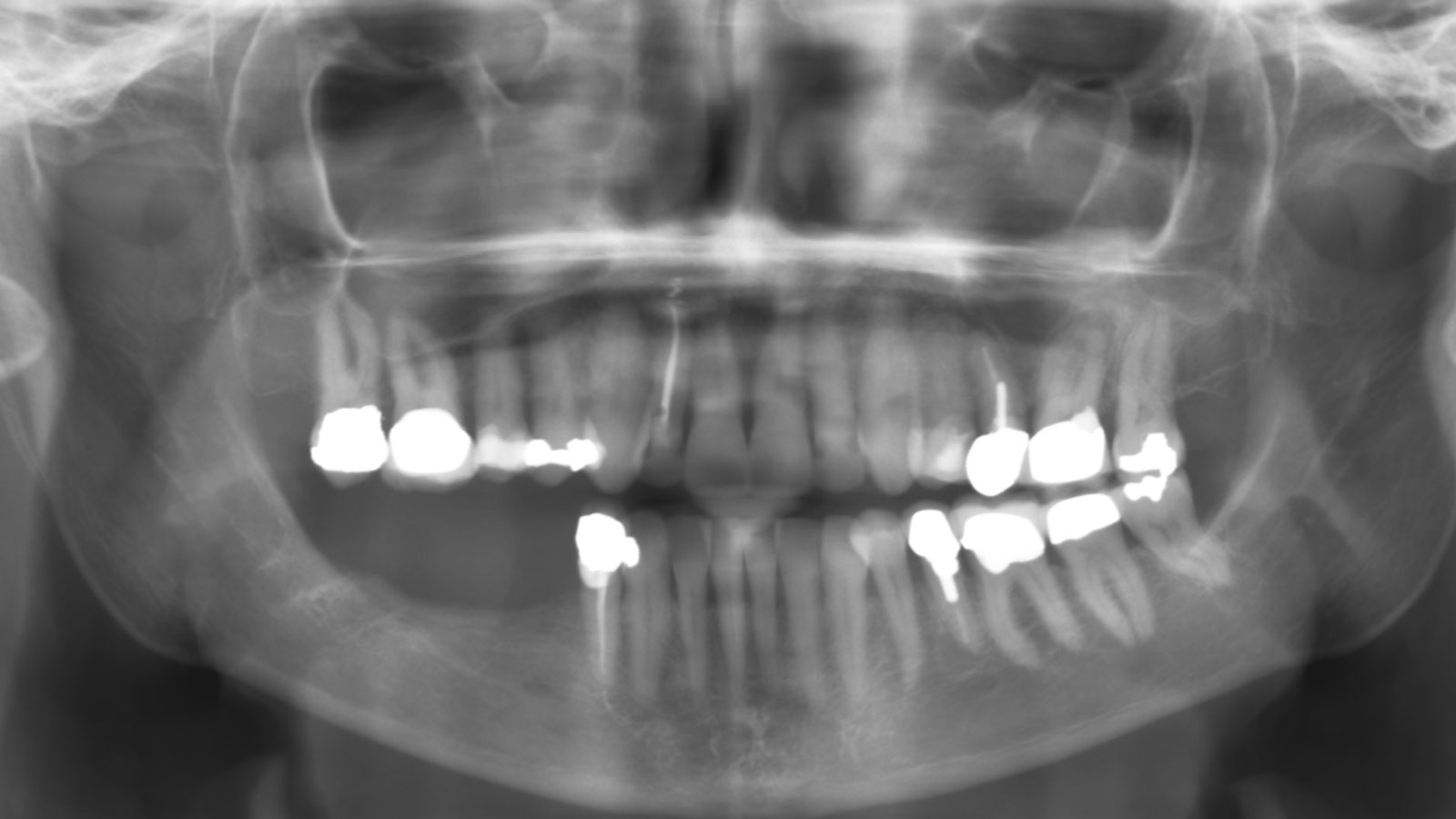
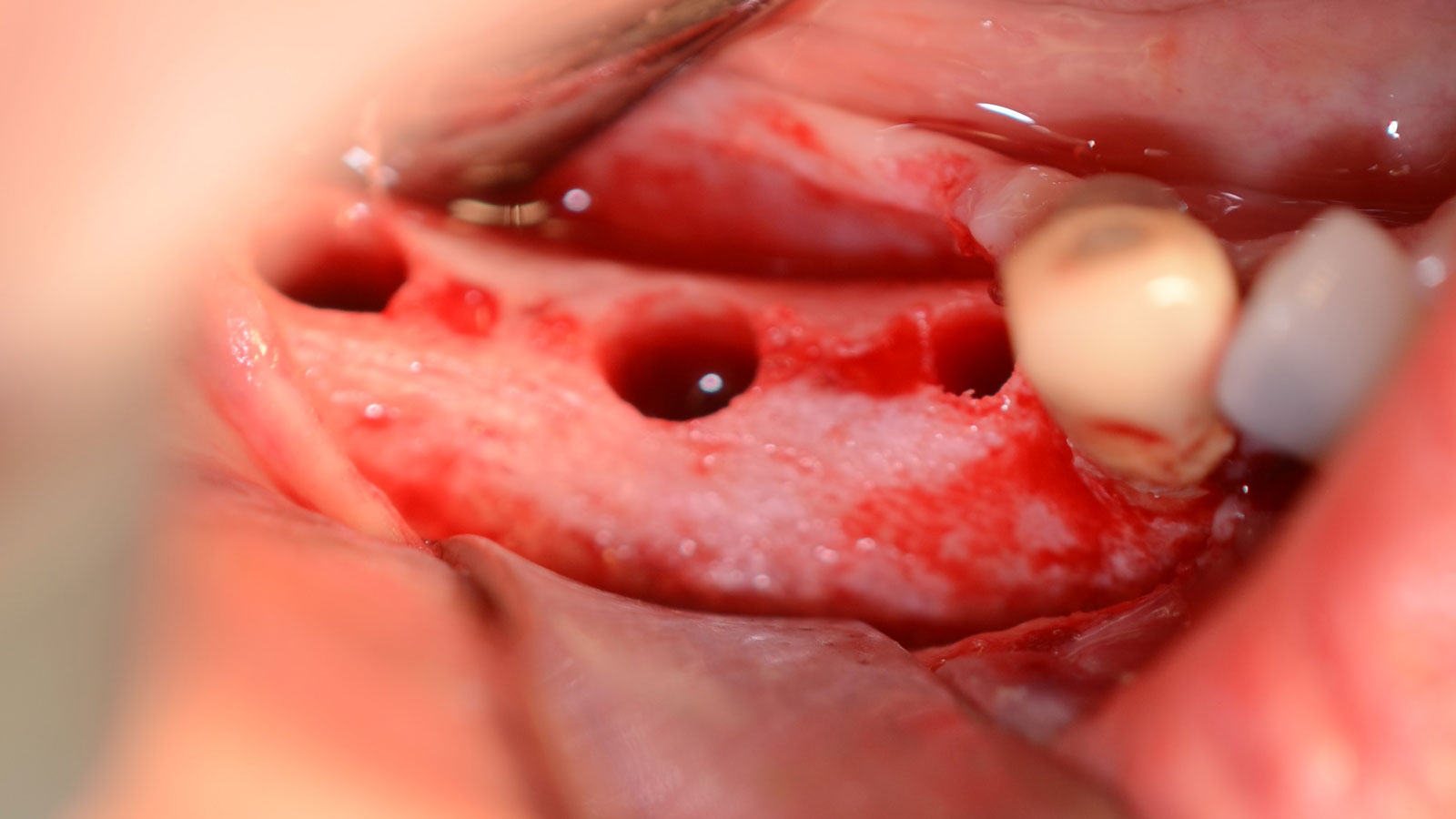
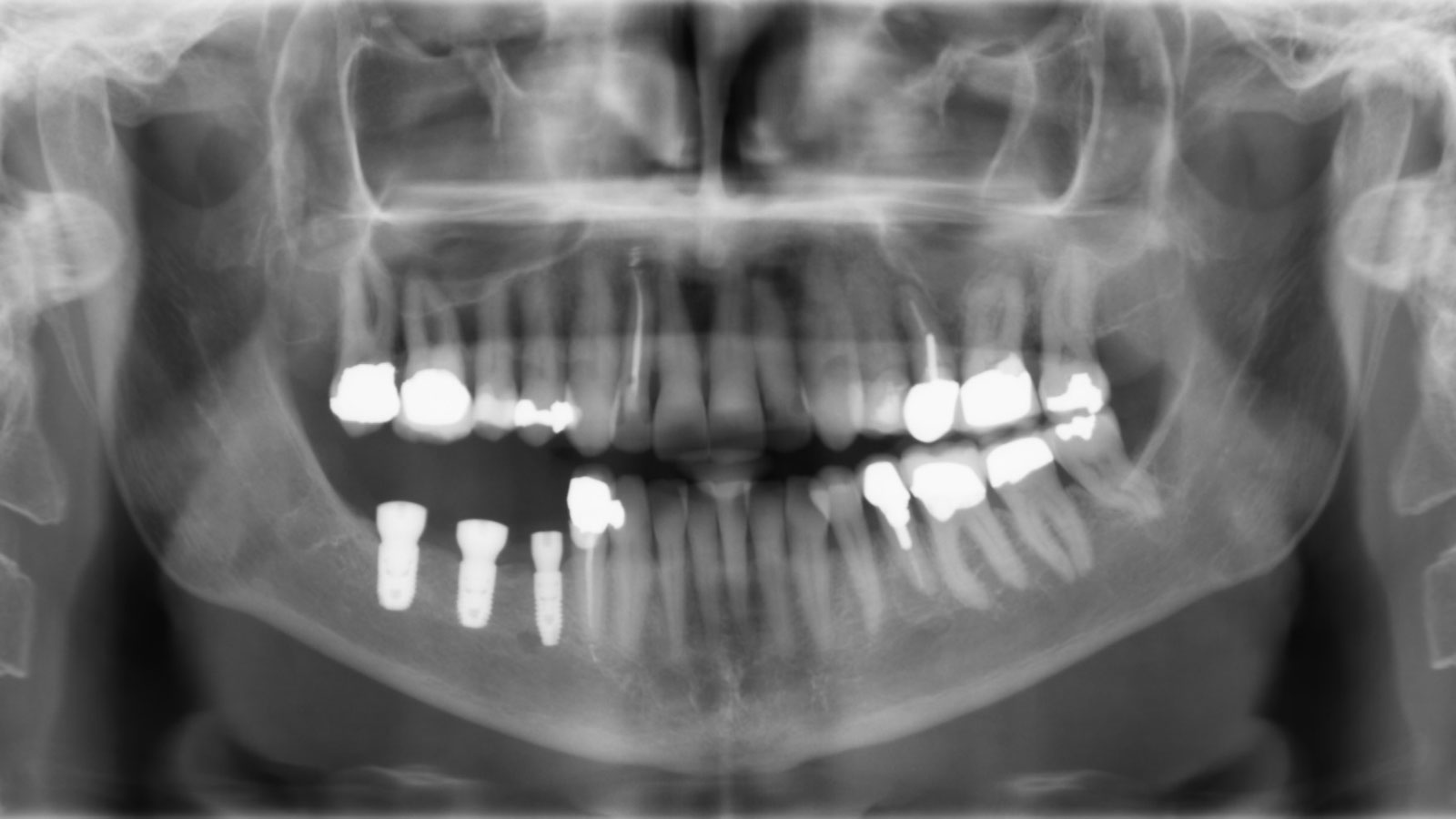
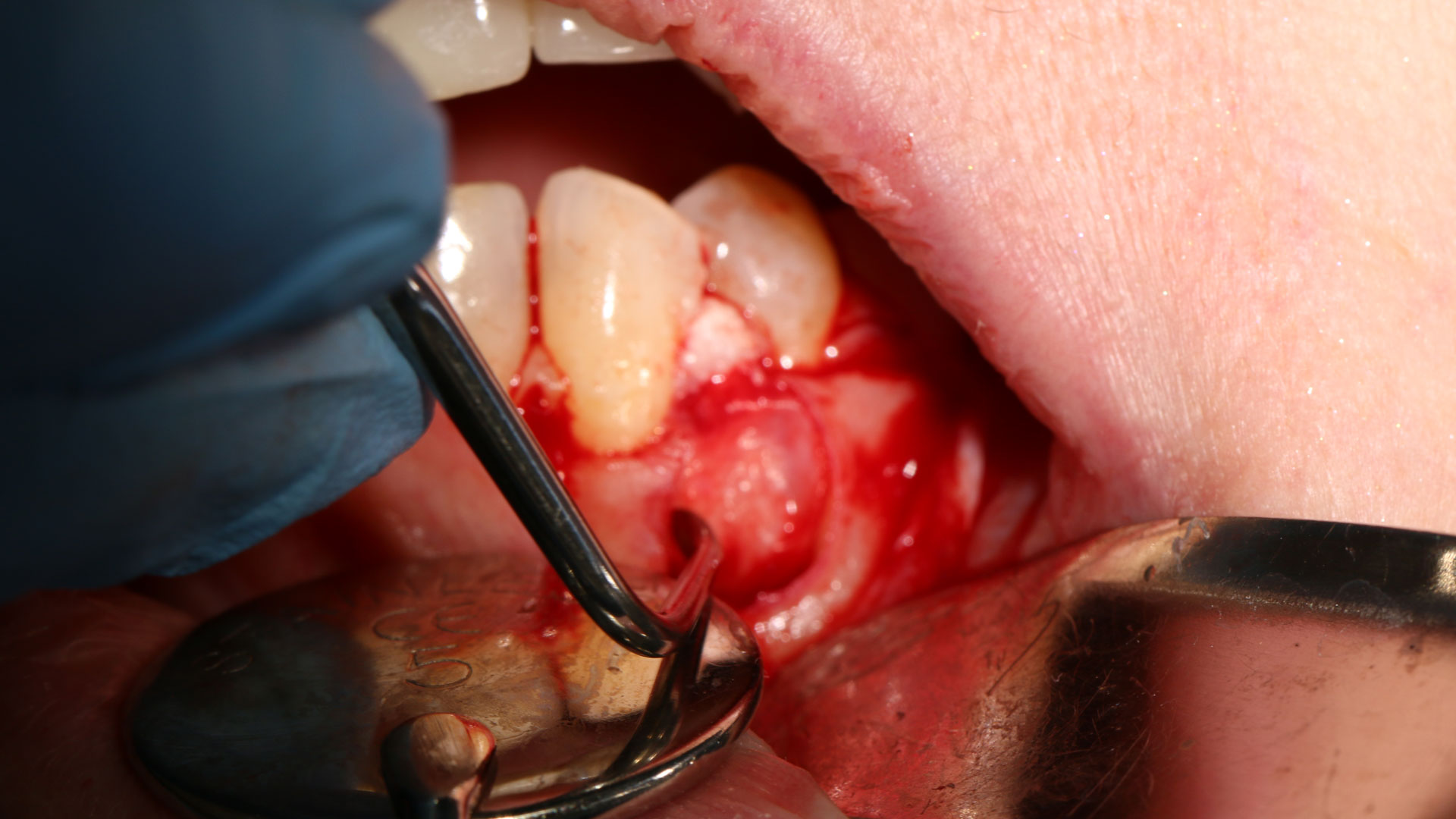
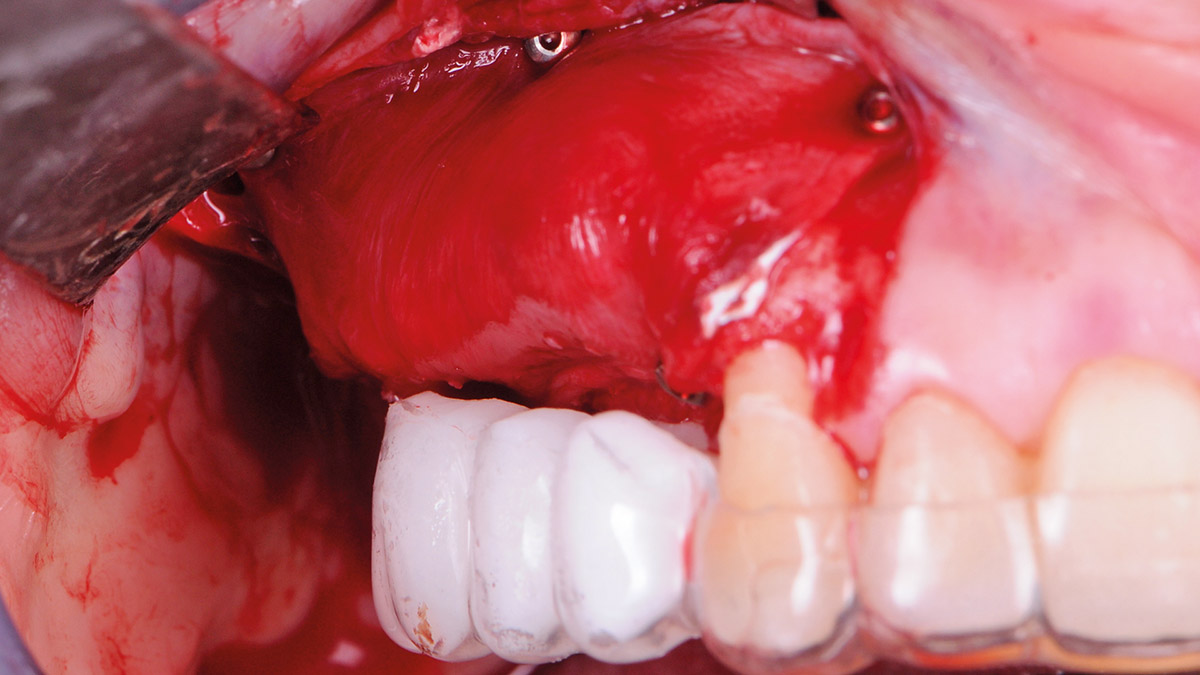
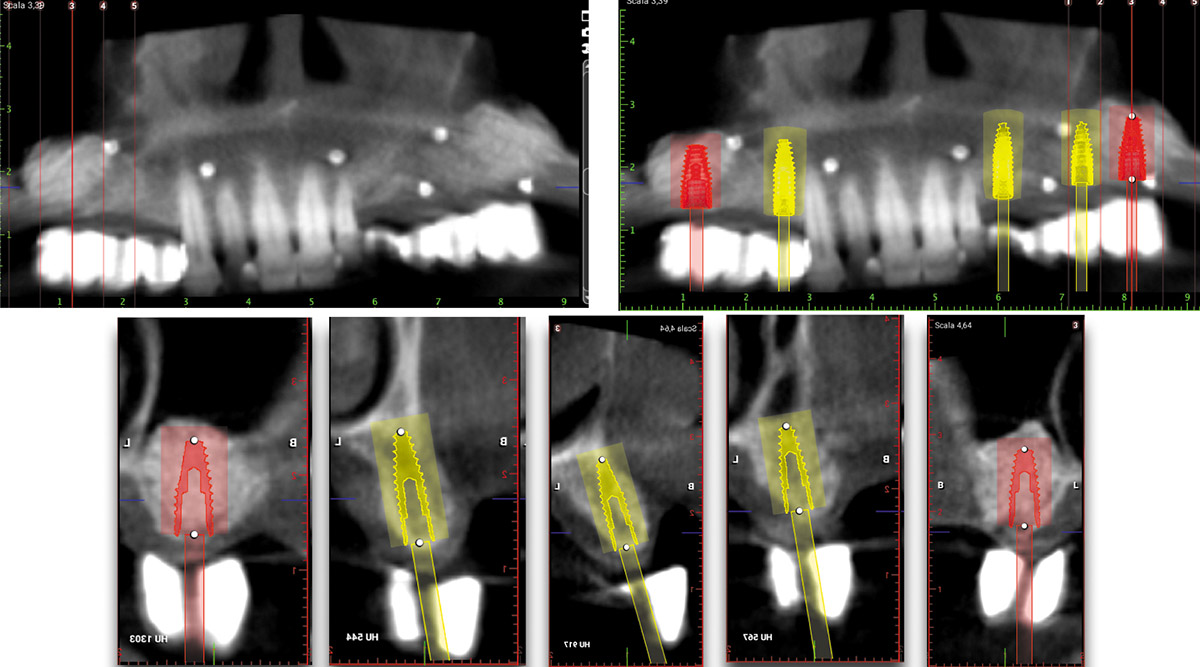
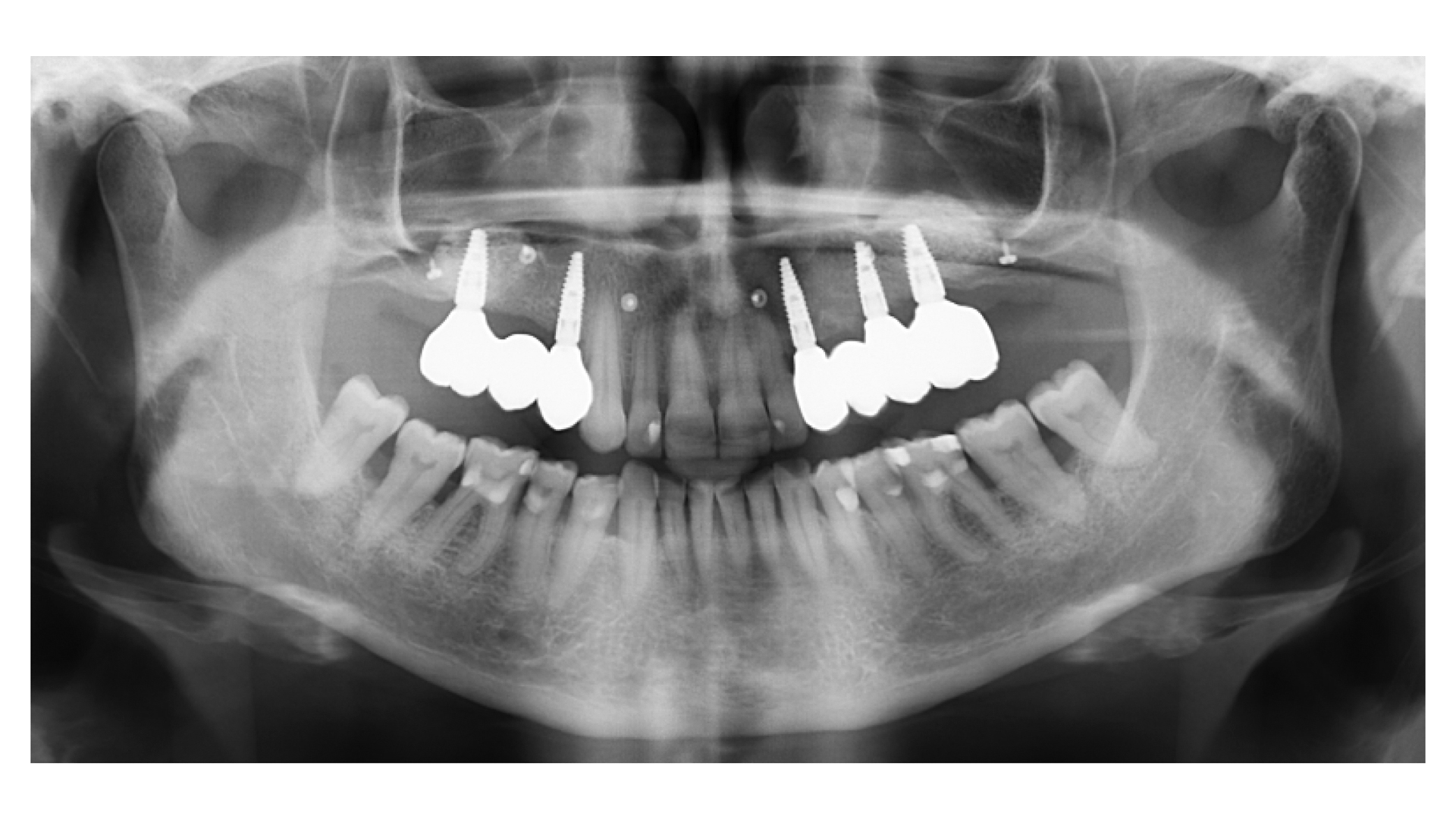
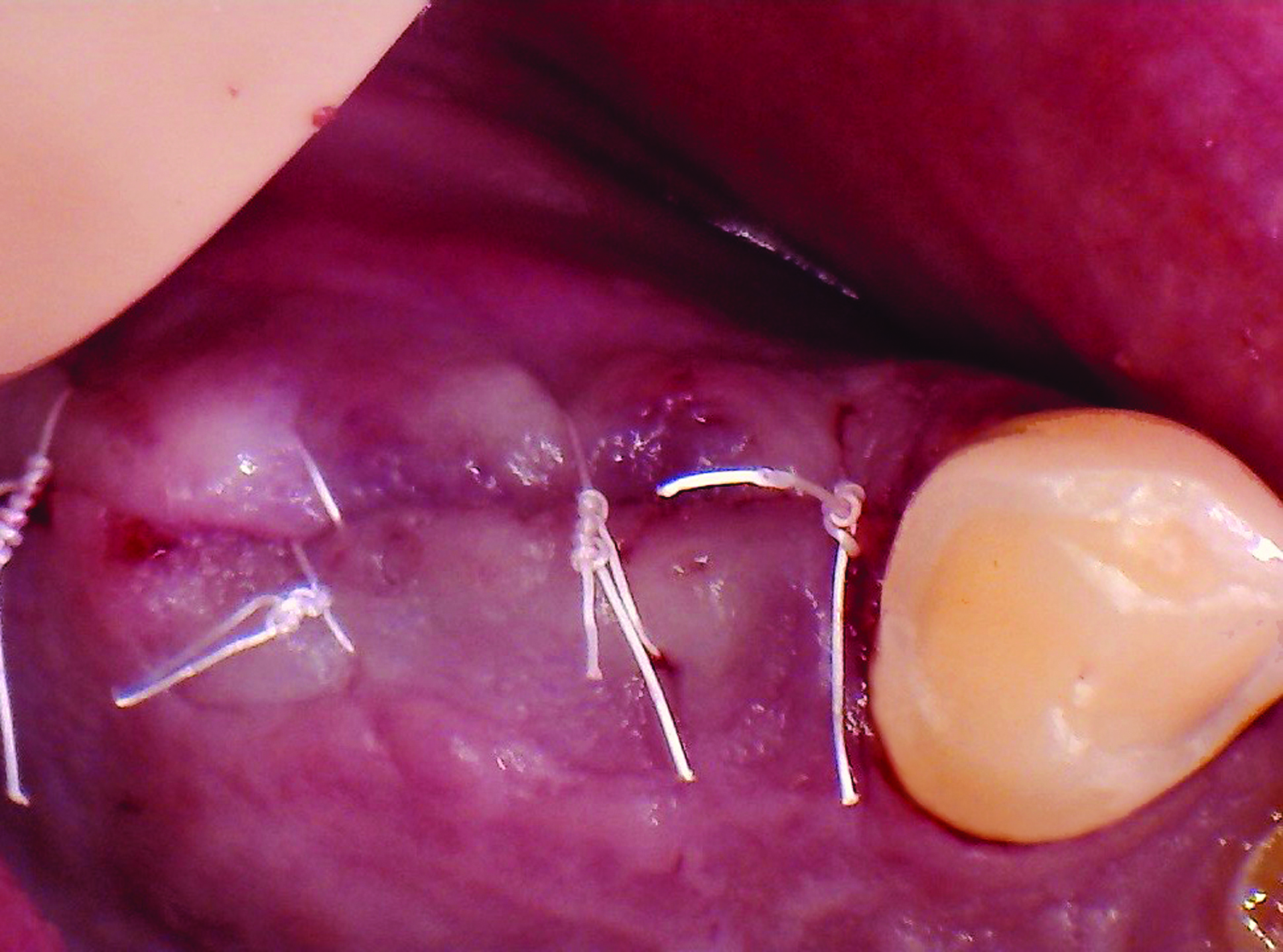
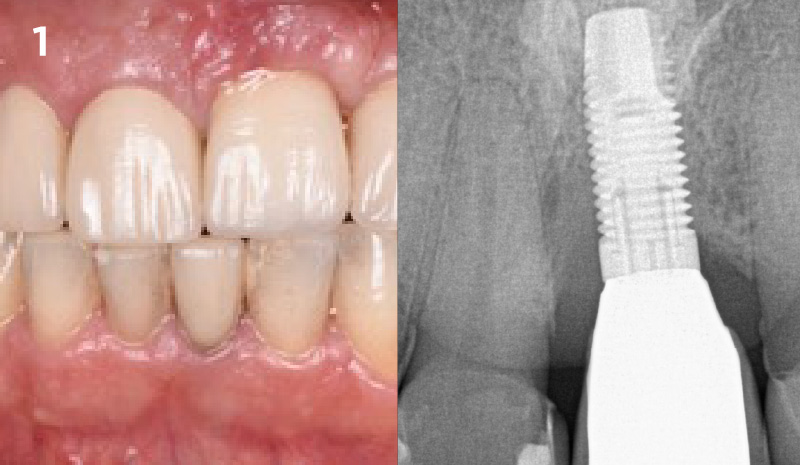
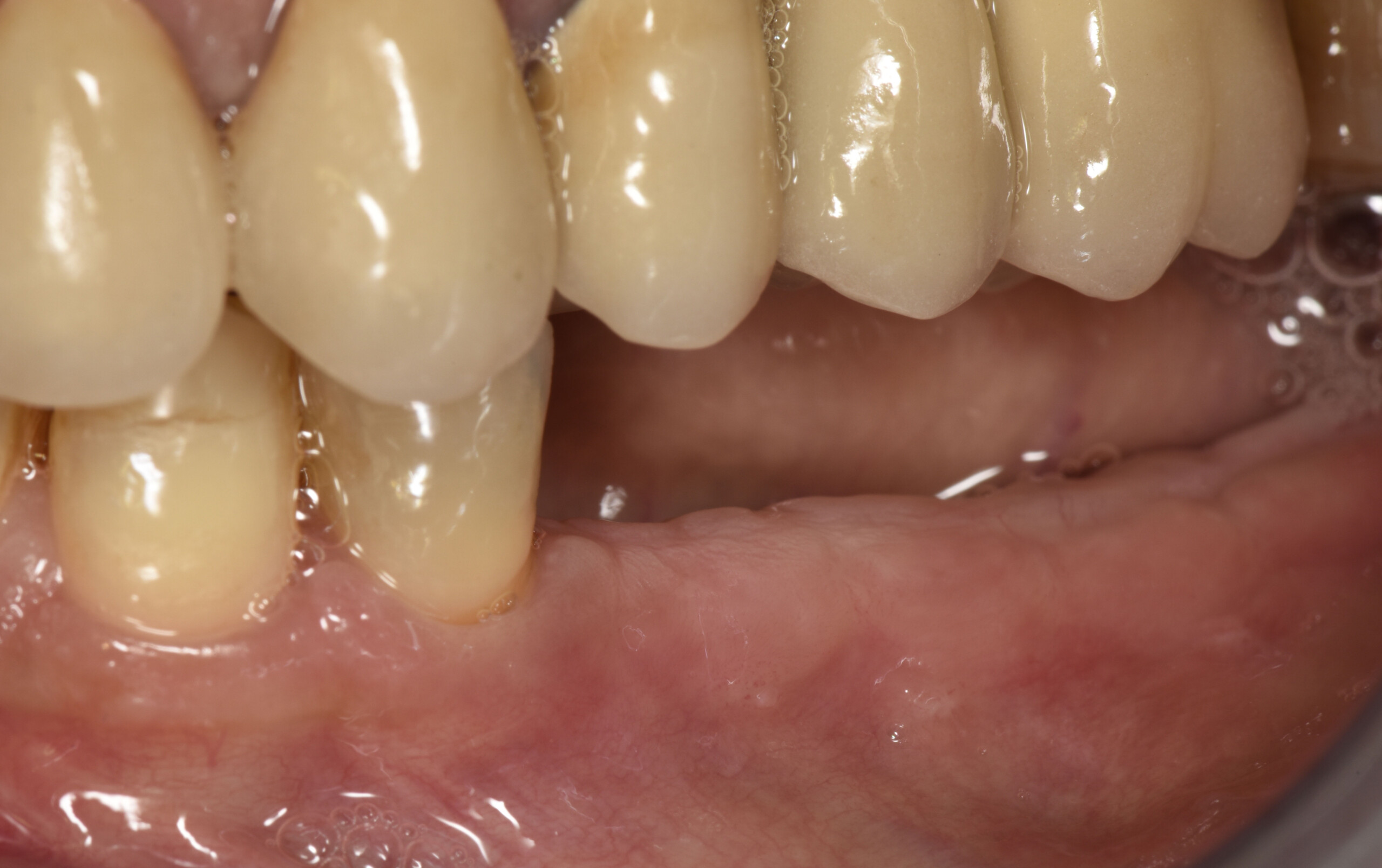
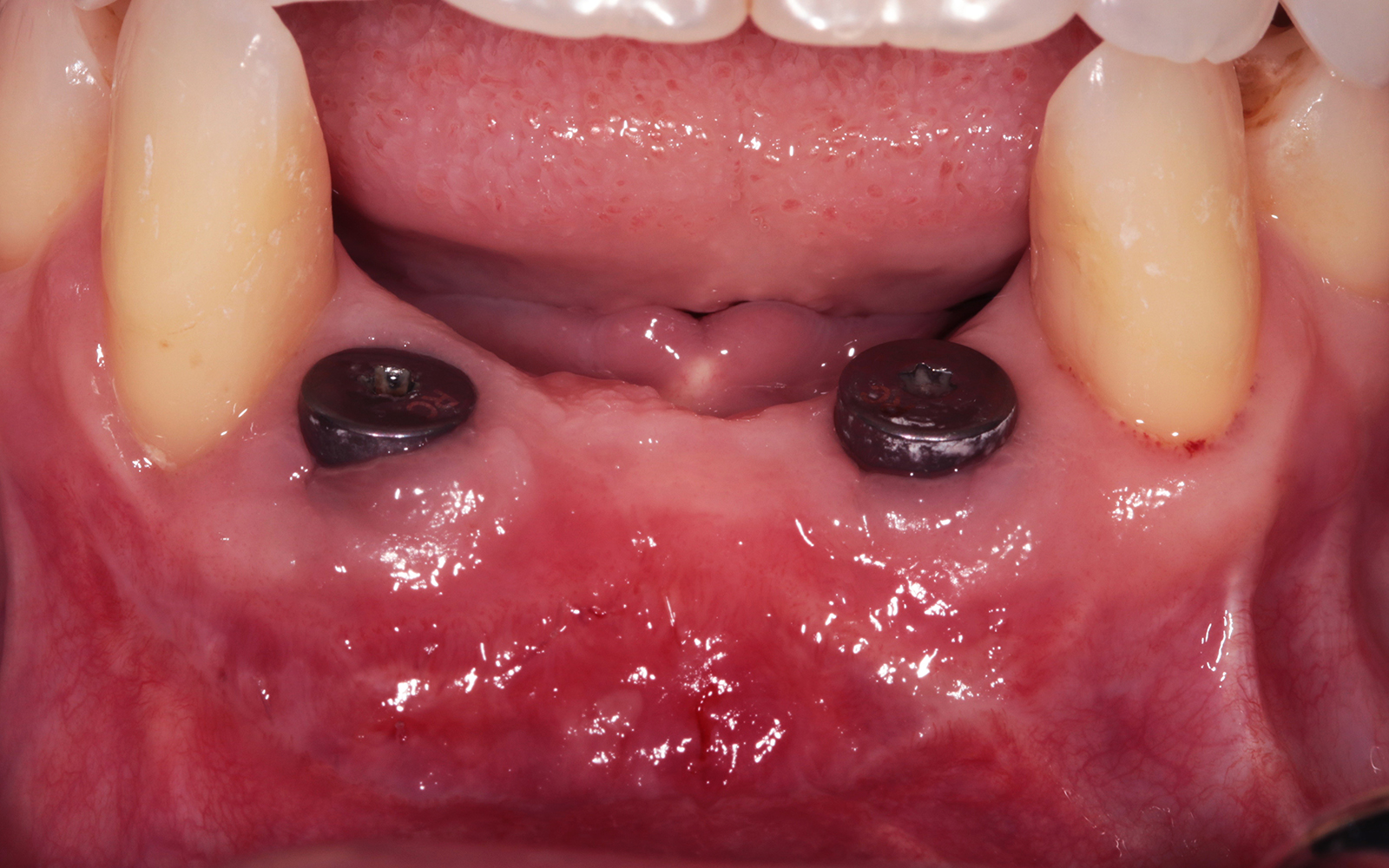
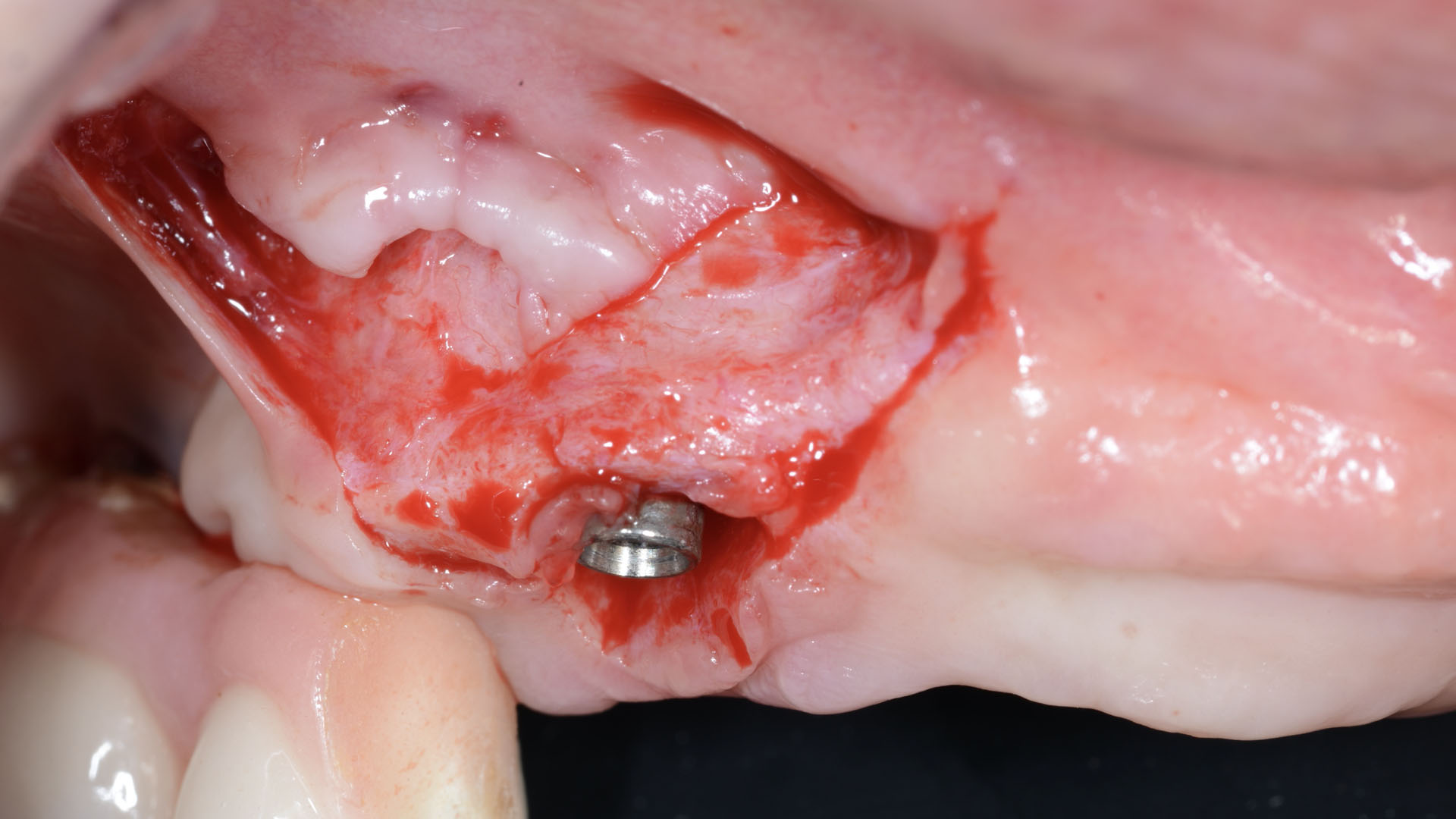
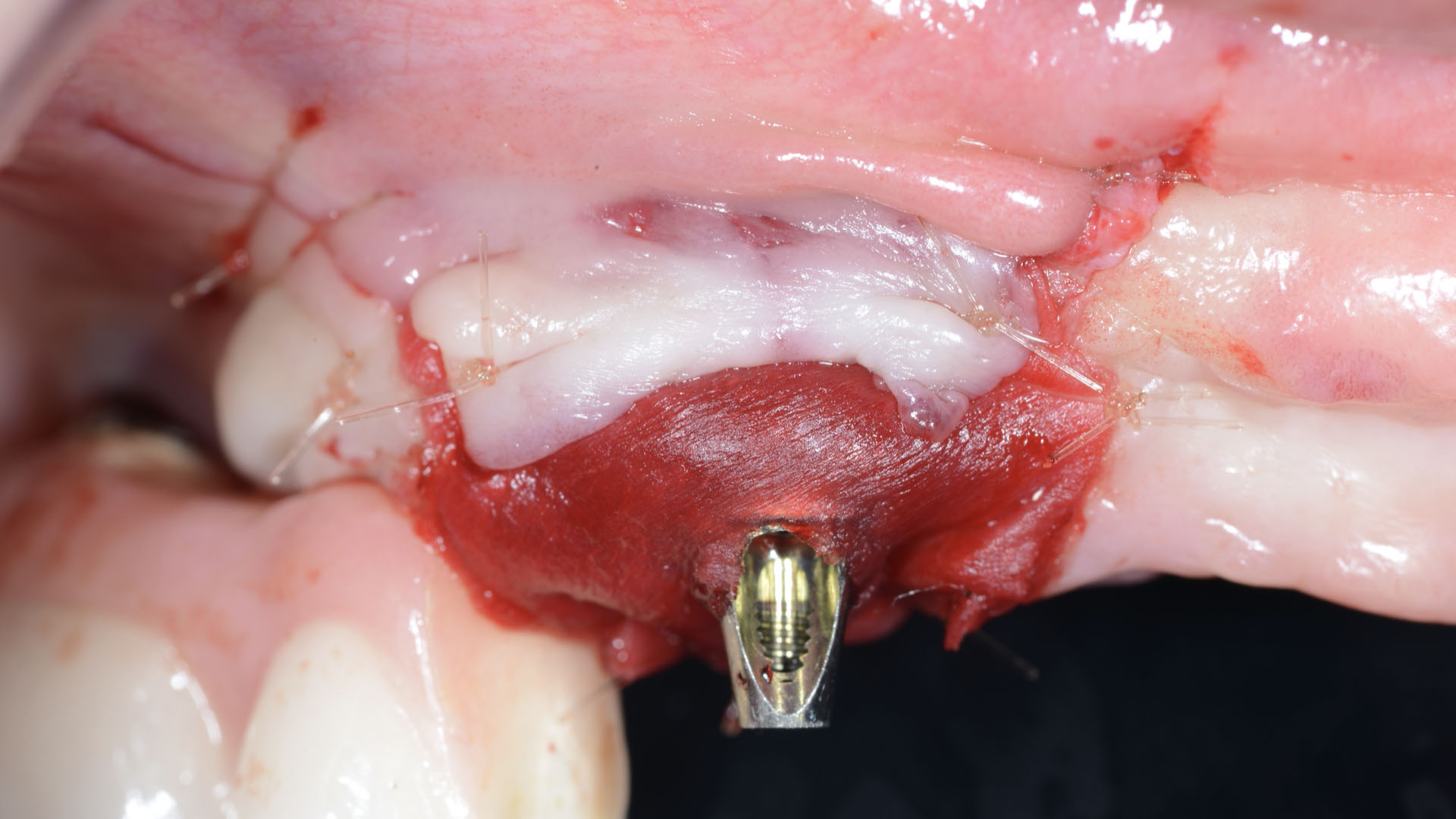
A healthy (ASA 1) non-smoker 63-year-old female presented to my office with Kennedy Class II partial edentulism in the mandibular right posterior quadrant for several years. She denied removable options and wanted dental implants to individually replace her missing teeth. The clinical and radiographic evaluation revealed atrophic mandibular bone height and width at site #’s 29, 30 & 31. The edentulous site required engineering prior to the placement of conventional dental implants and prosthetics.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system/Non-smoker | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
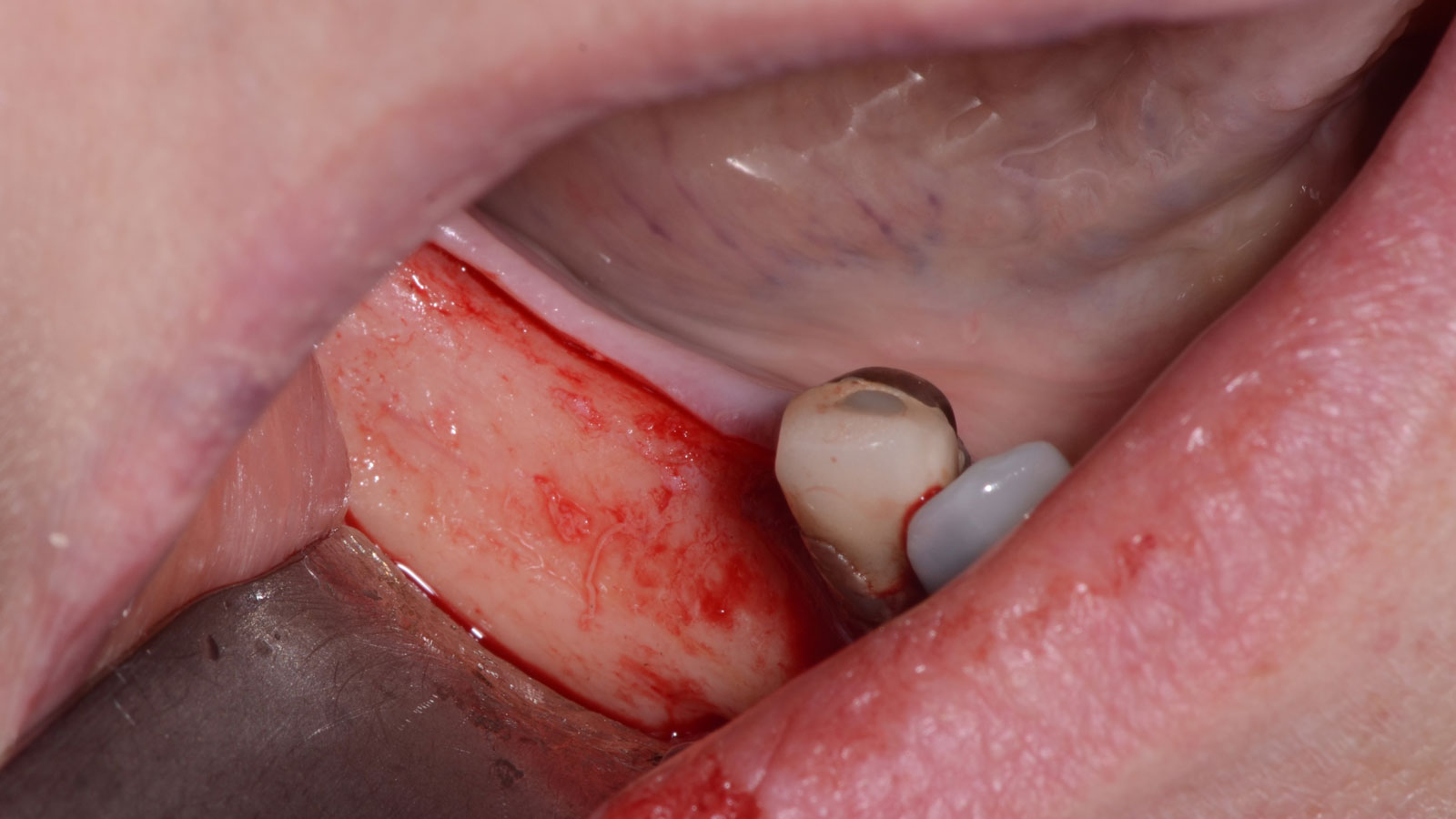
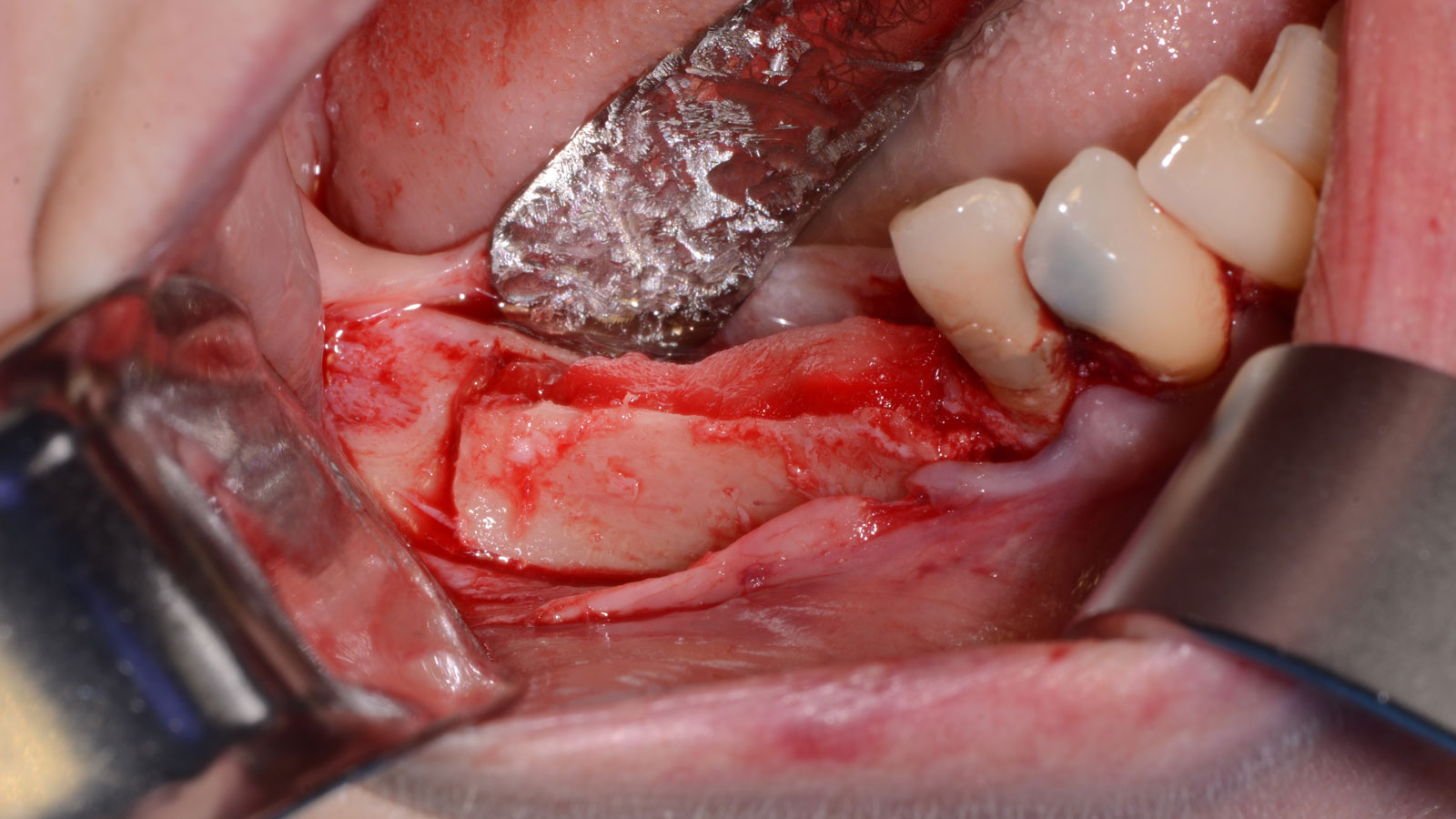
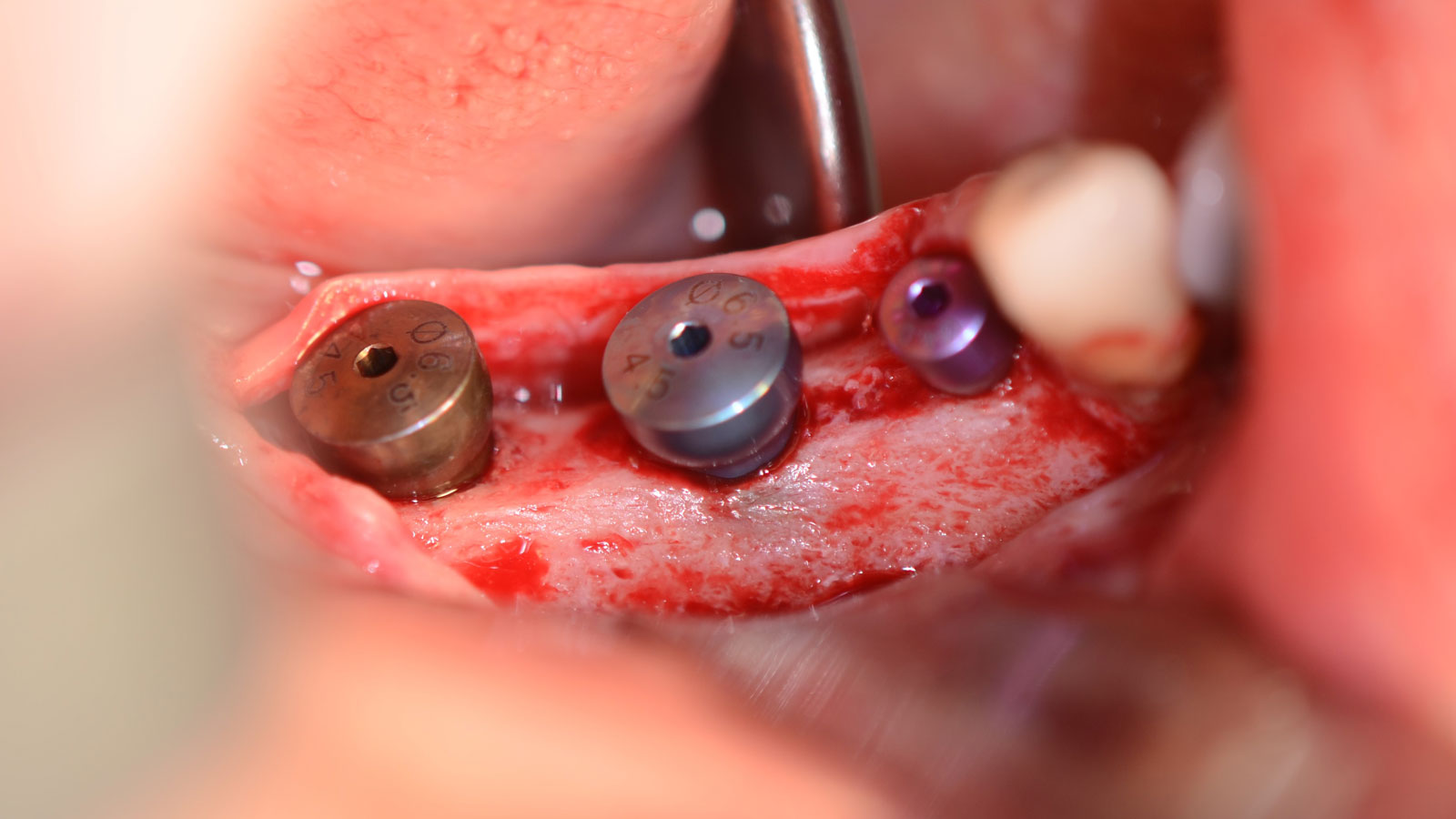
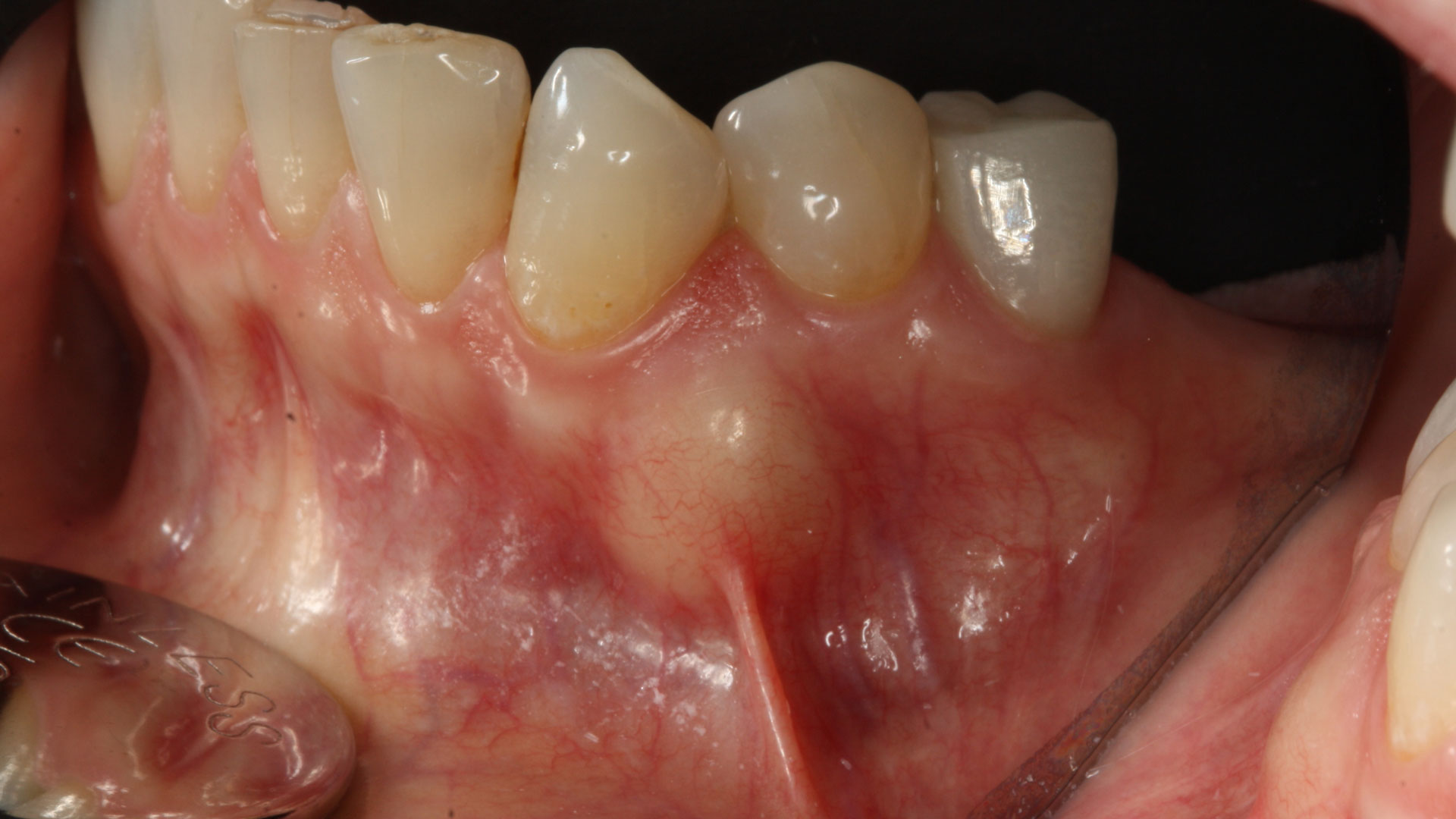
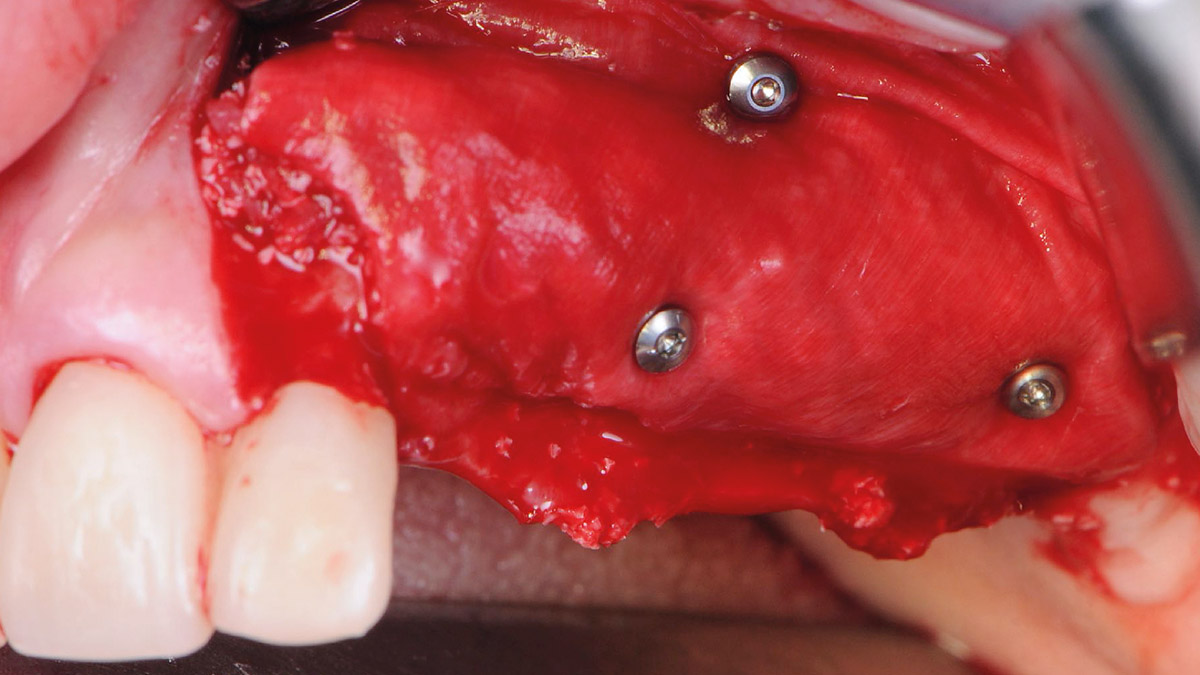
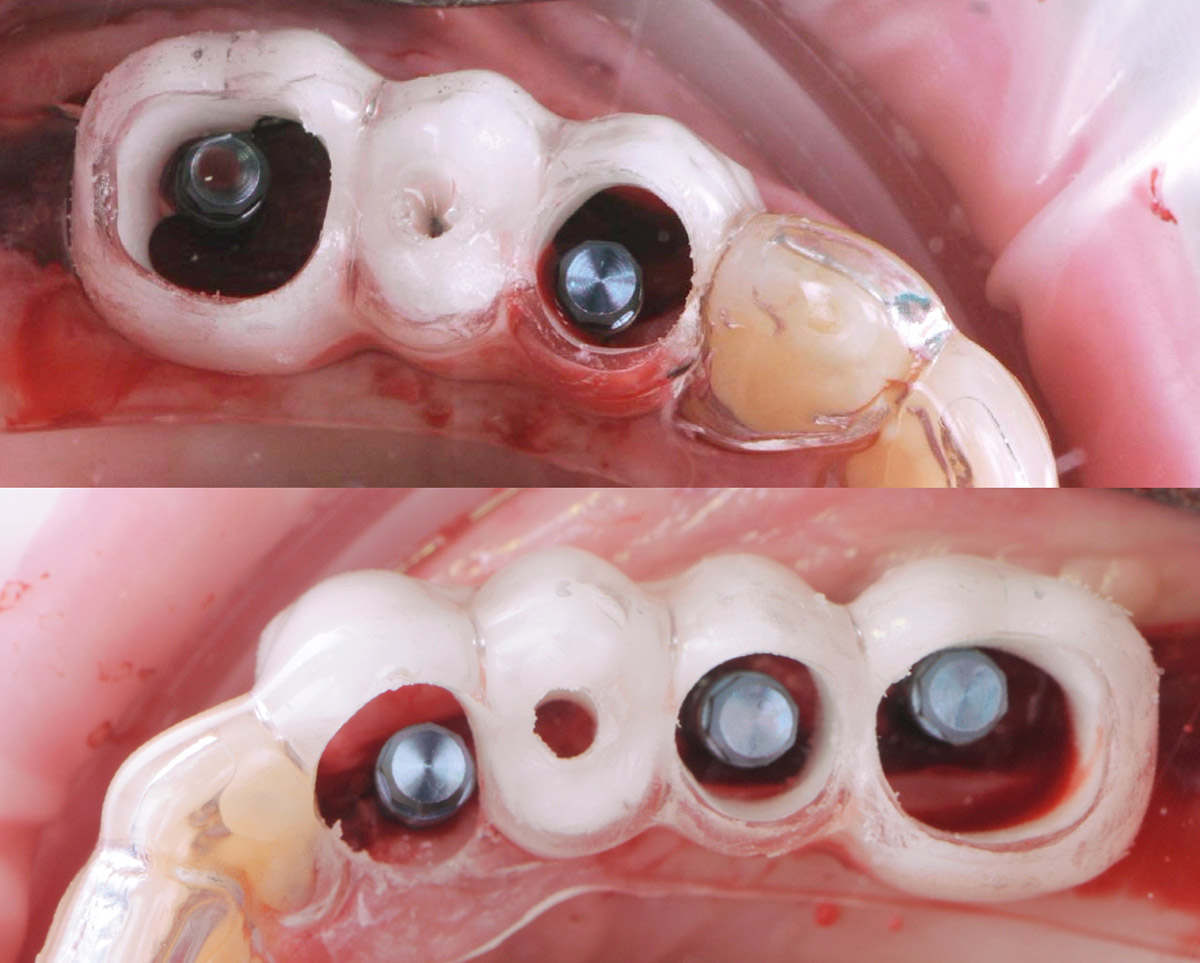
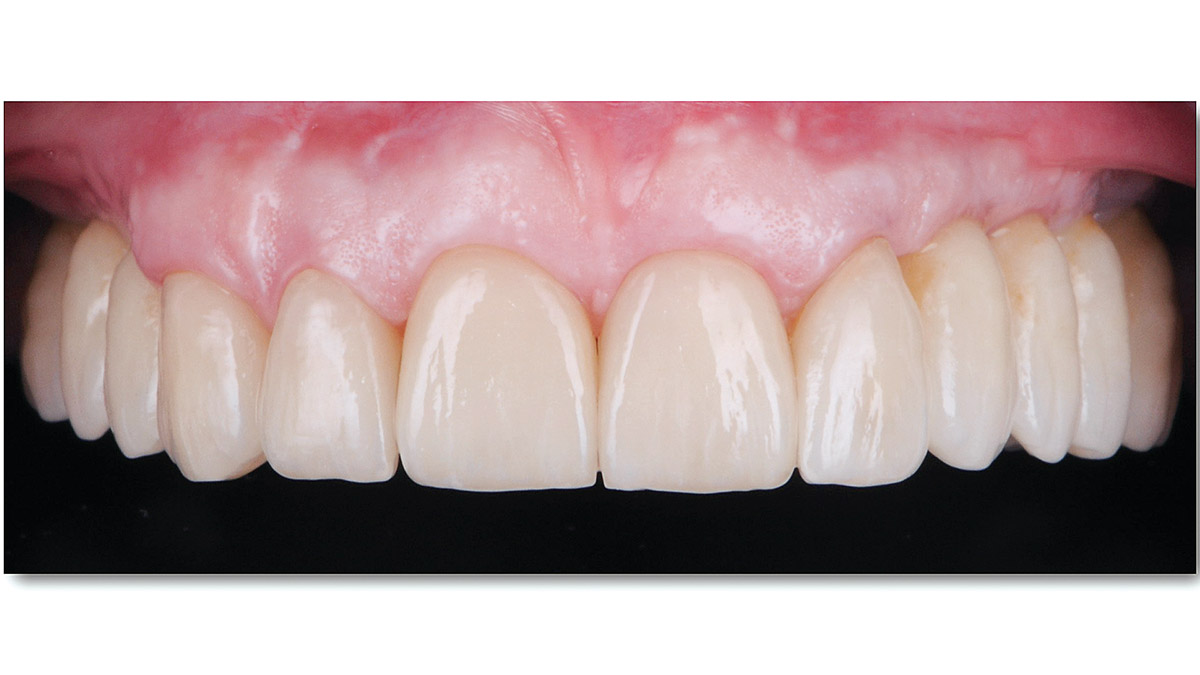
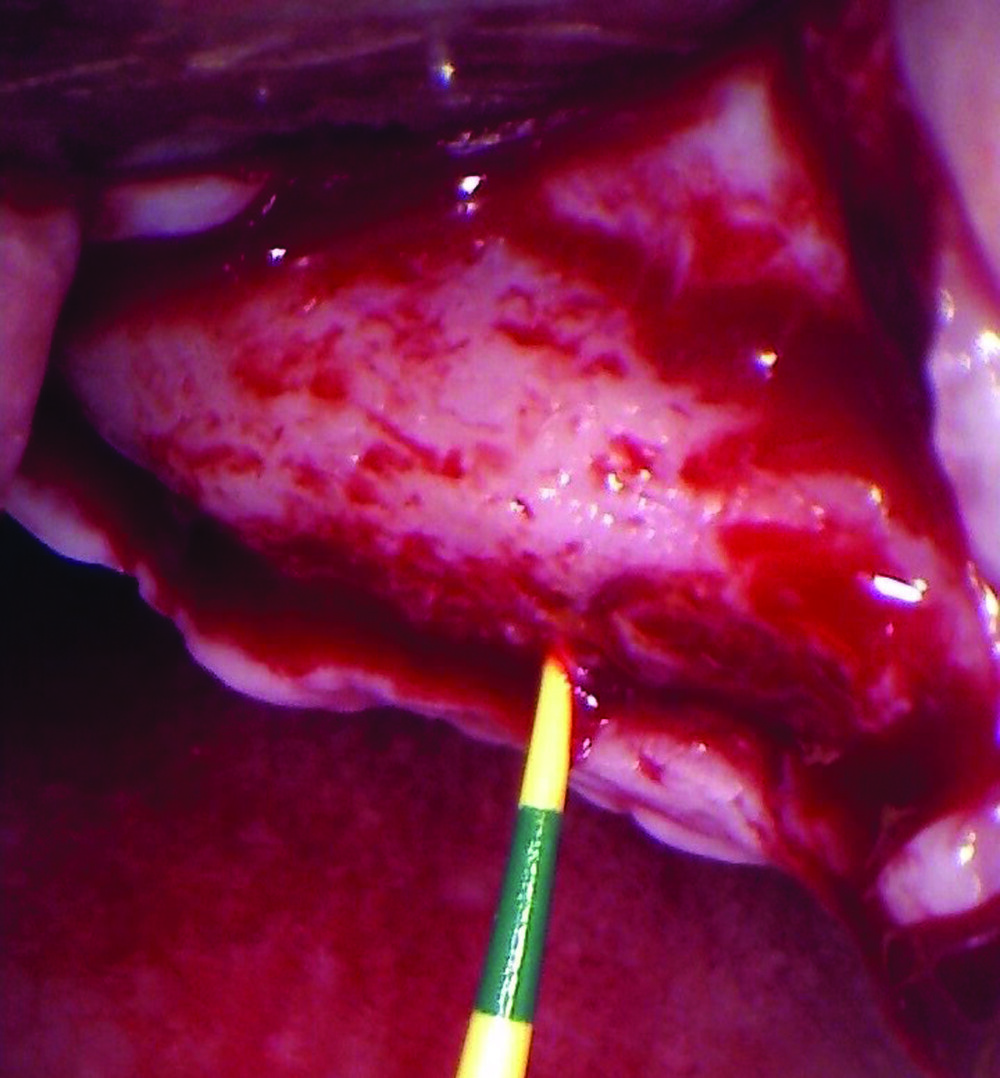
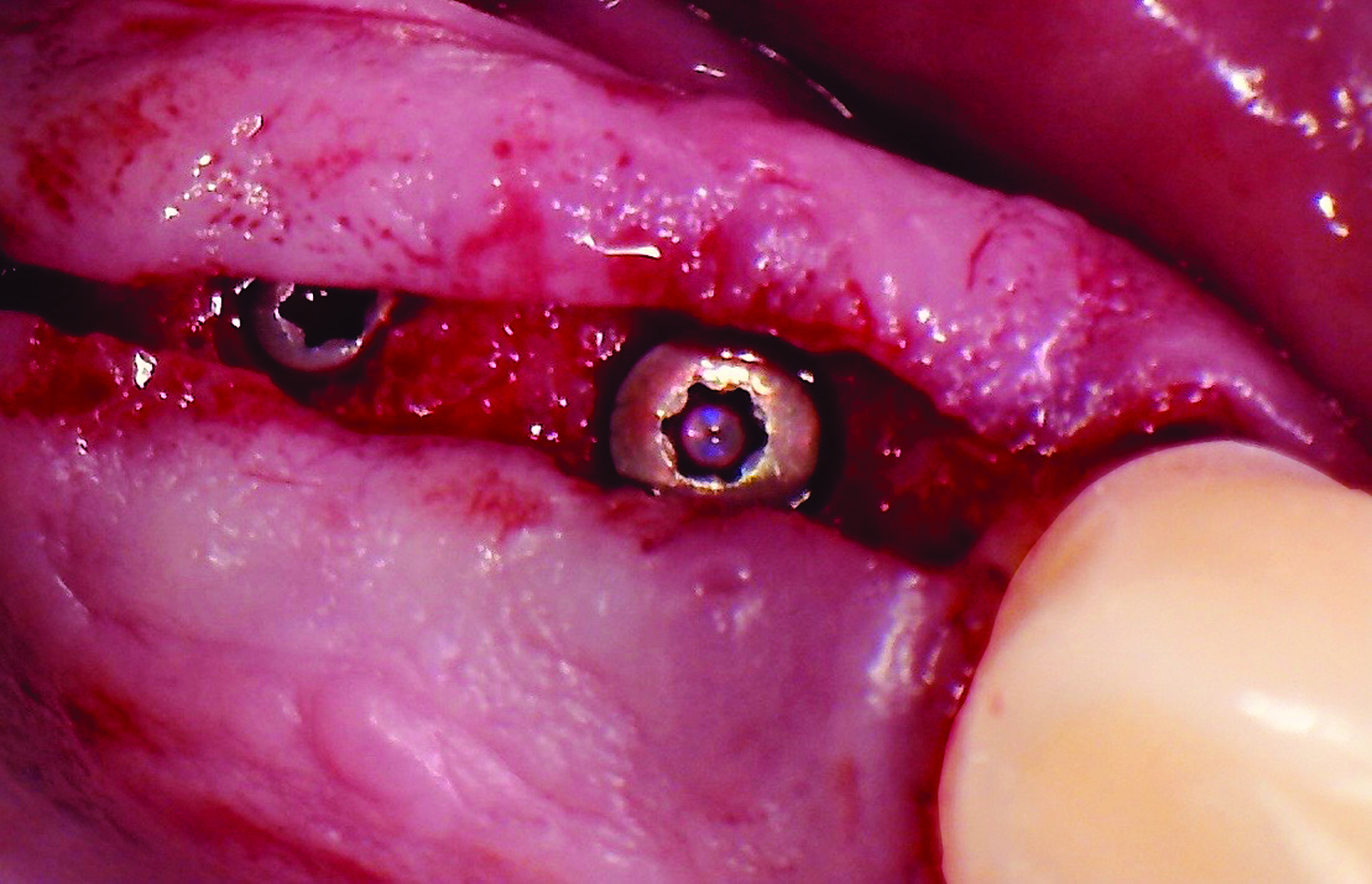
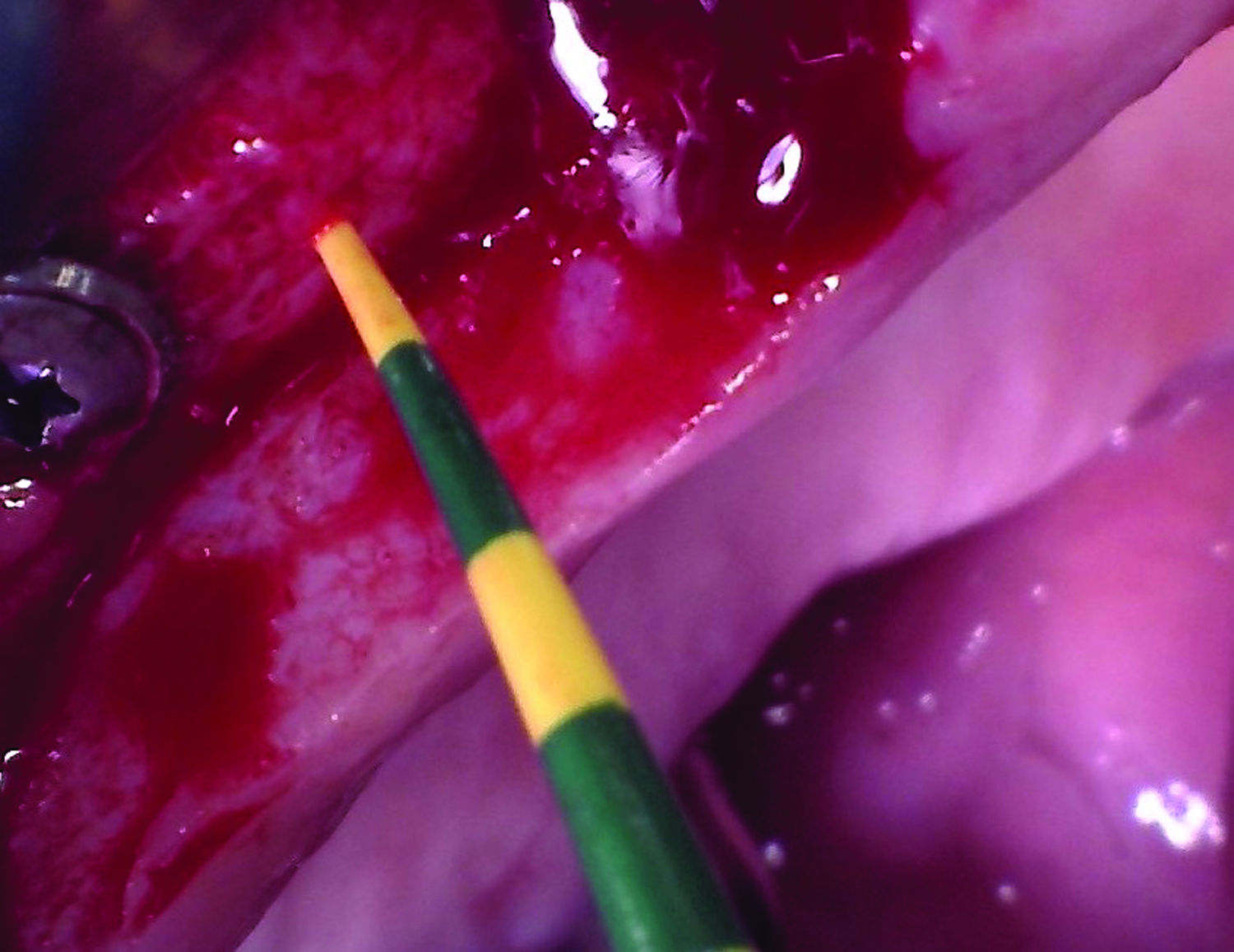
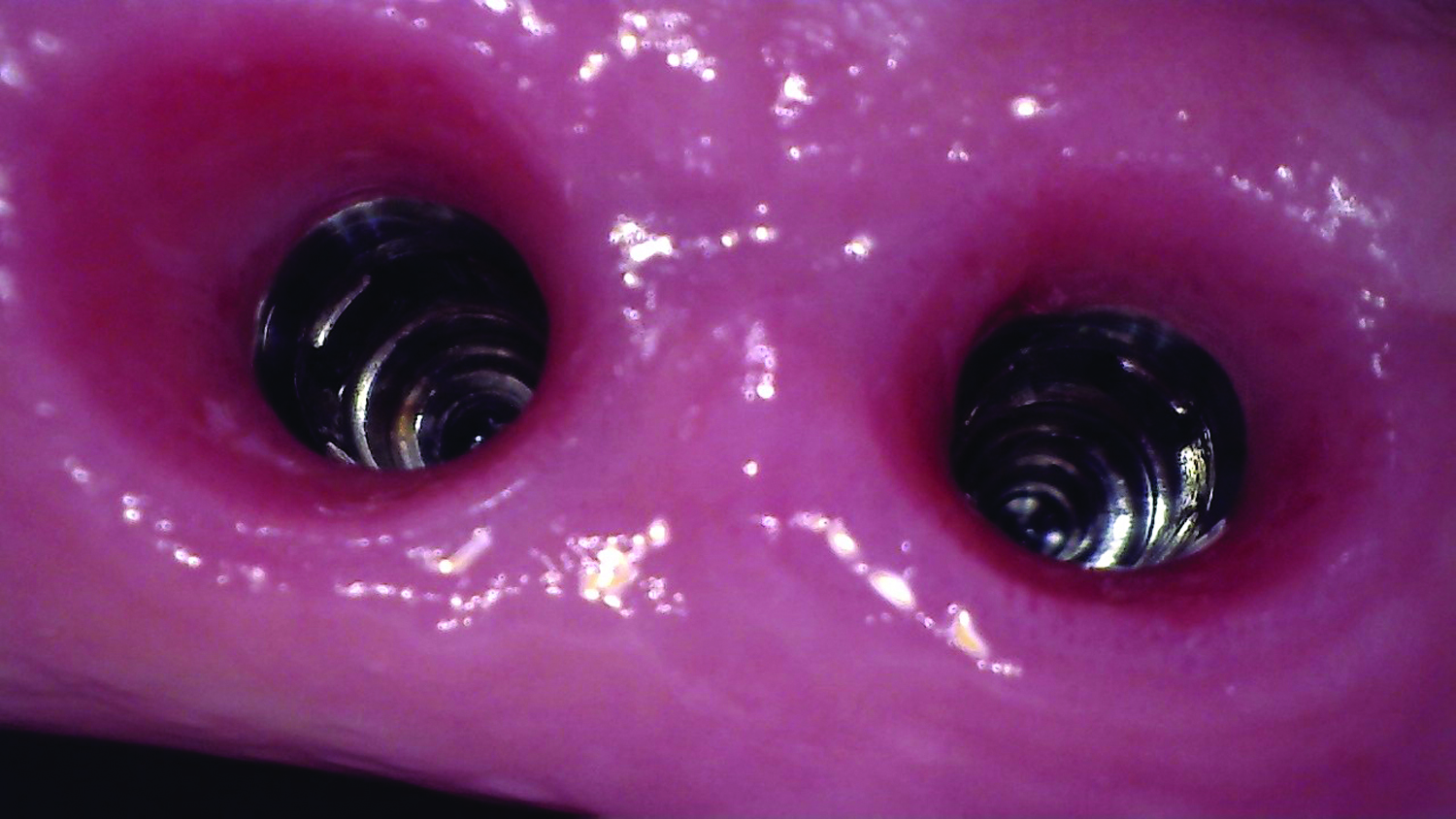
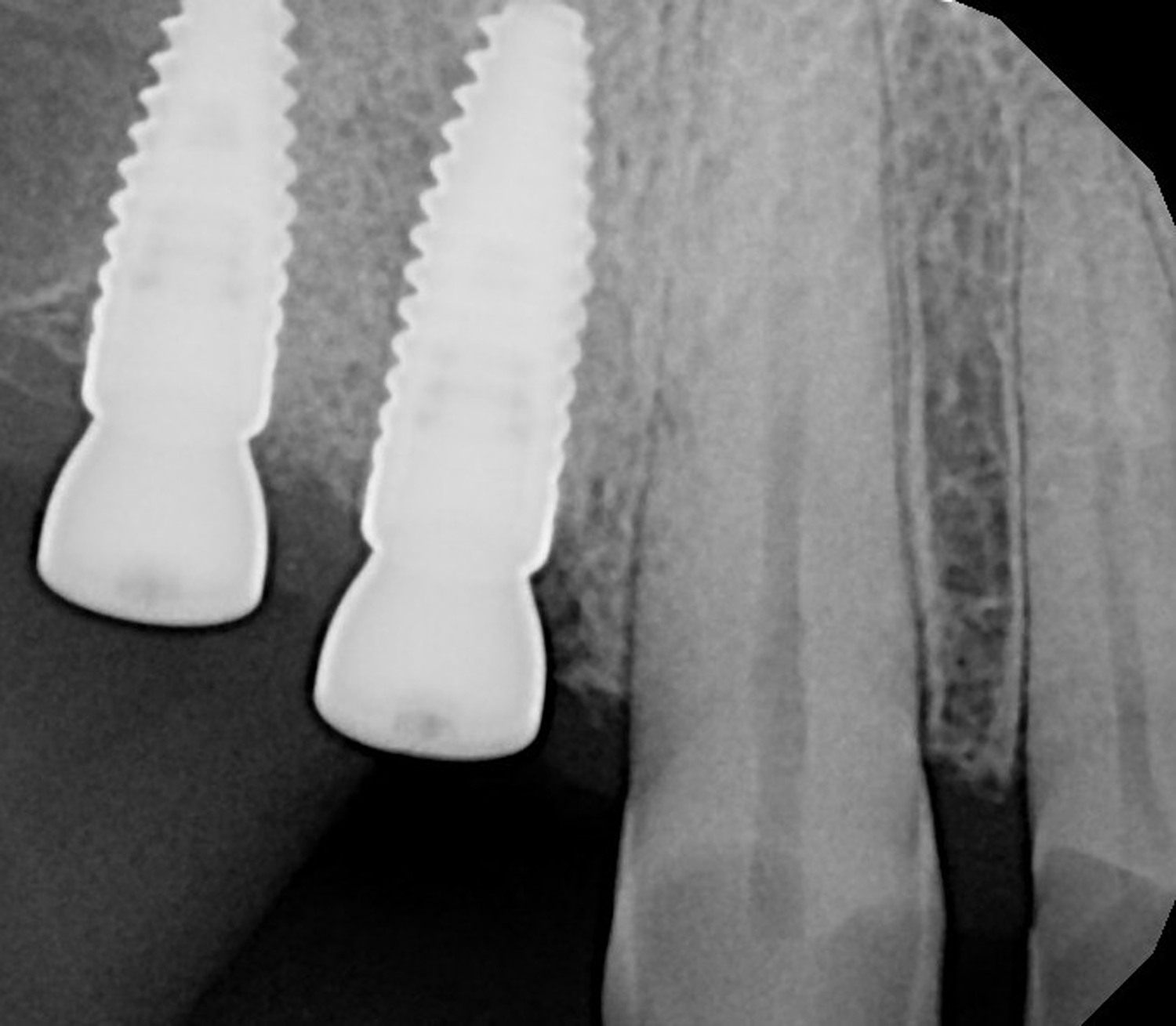
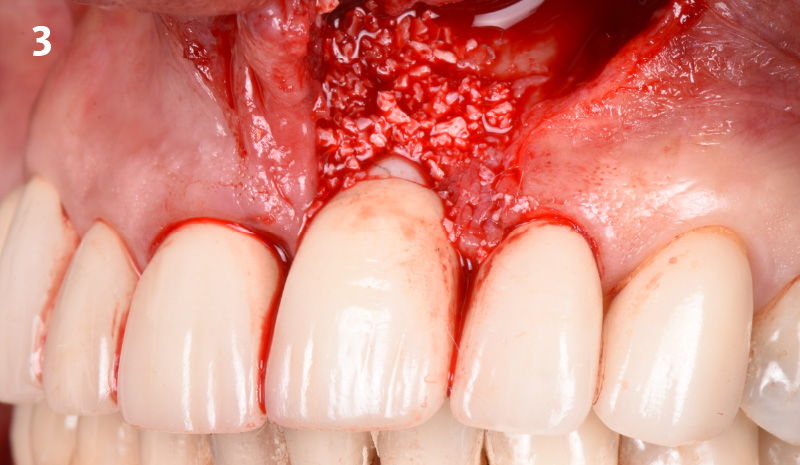
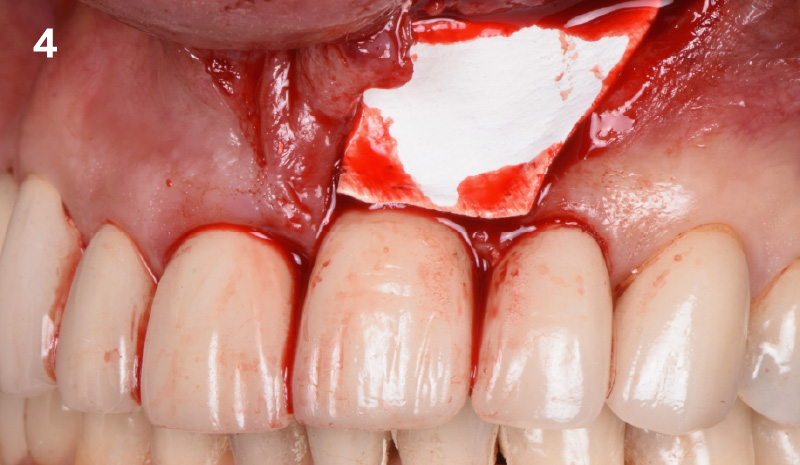
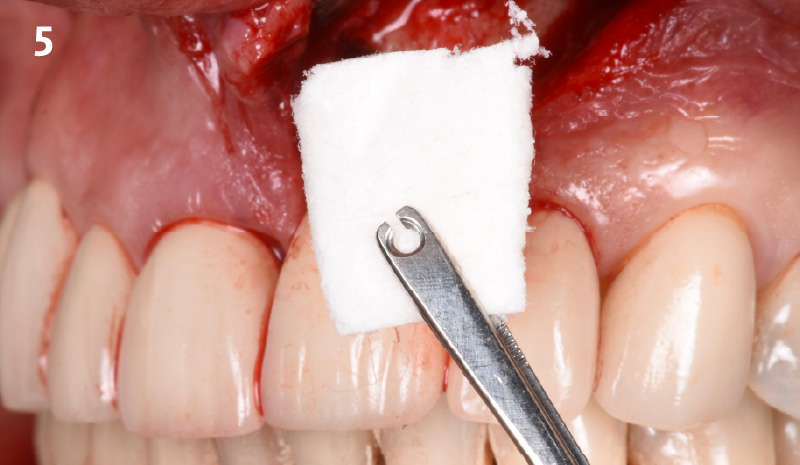
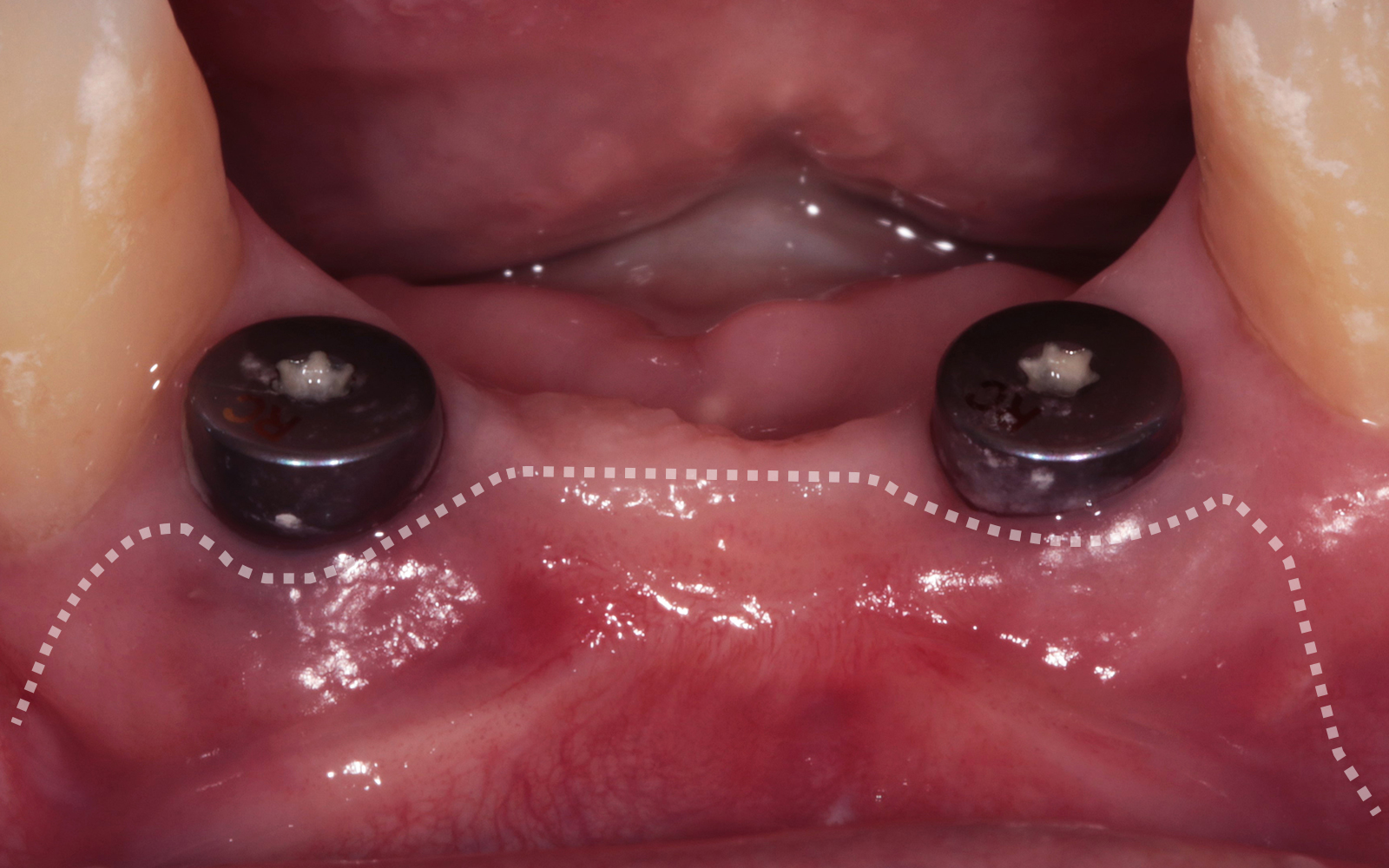
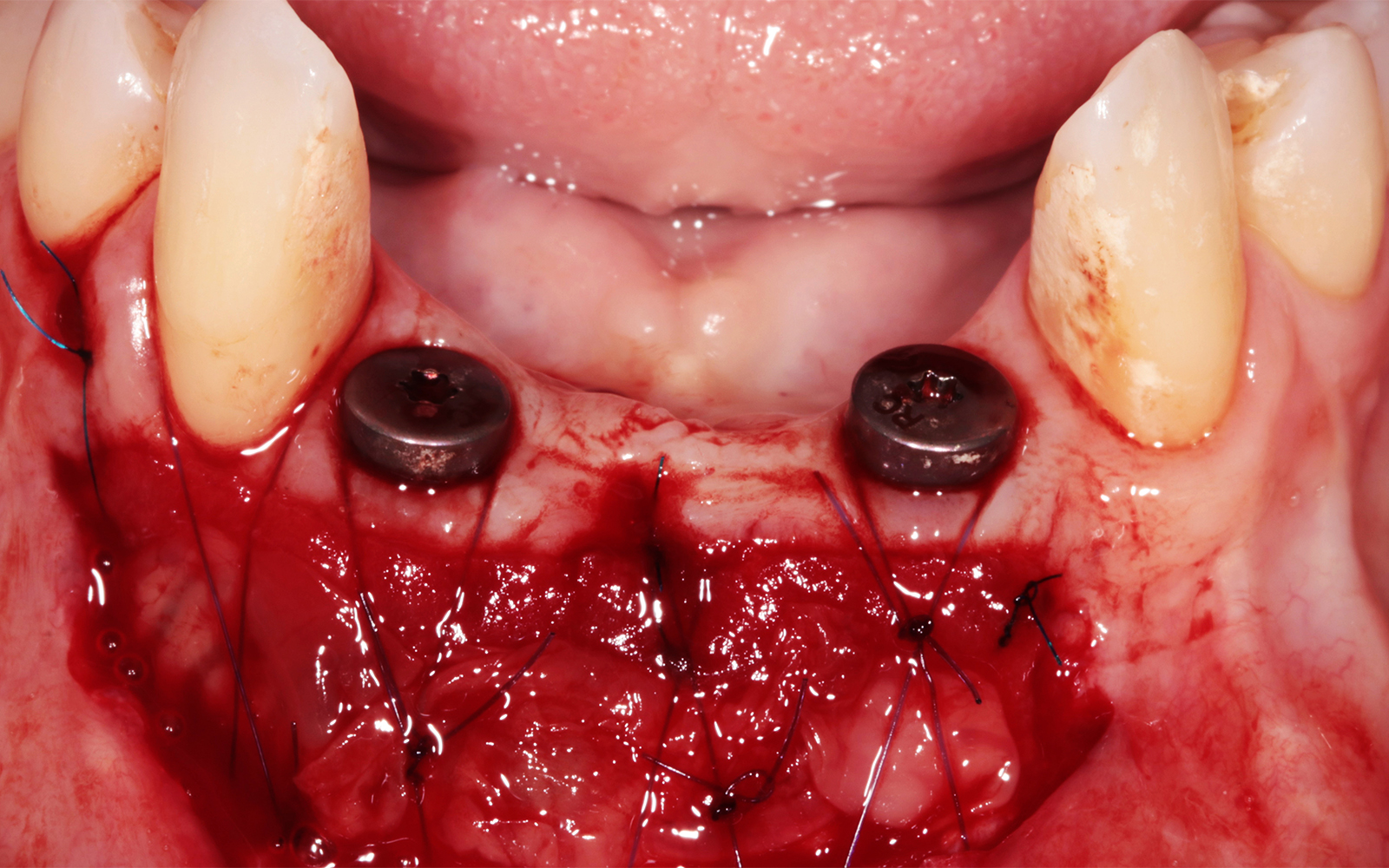
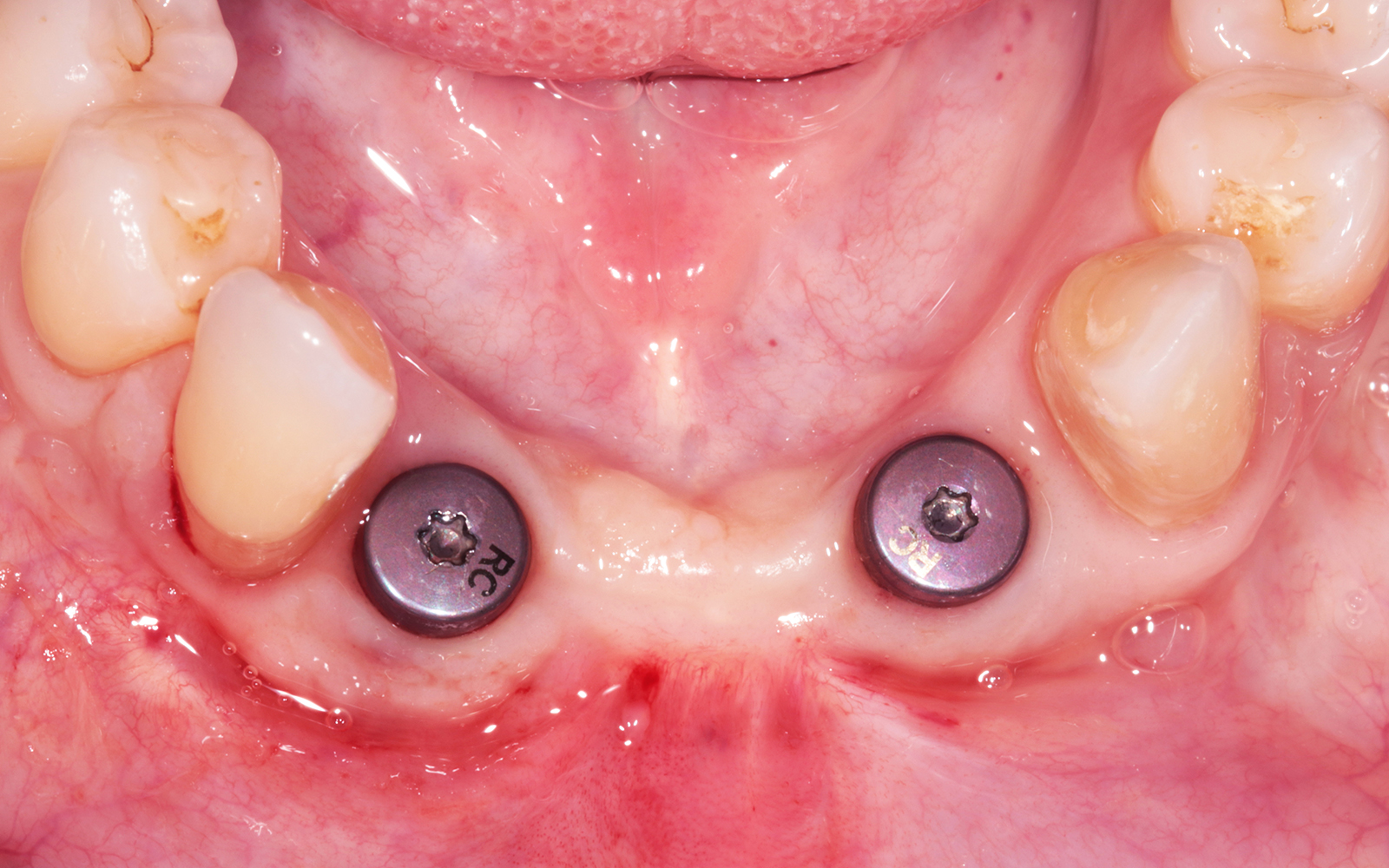
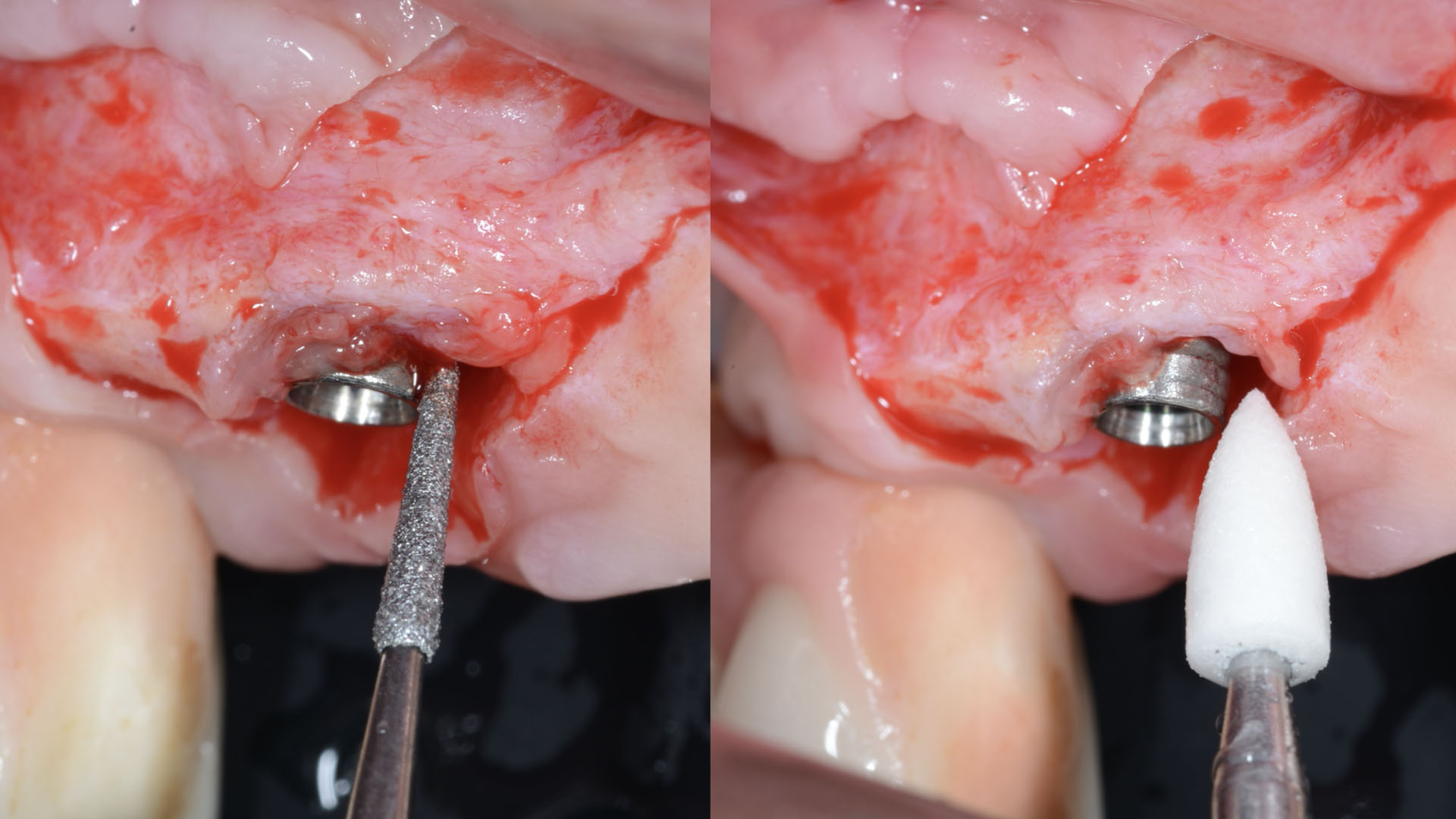
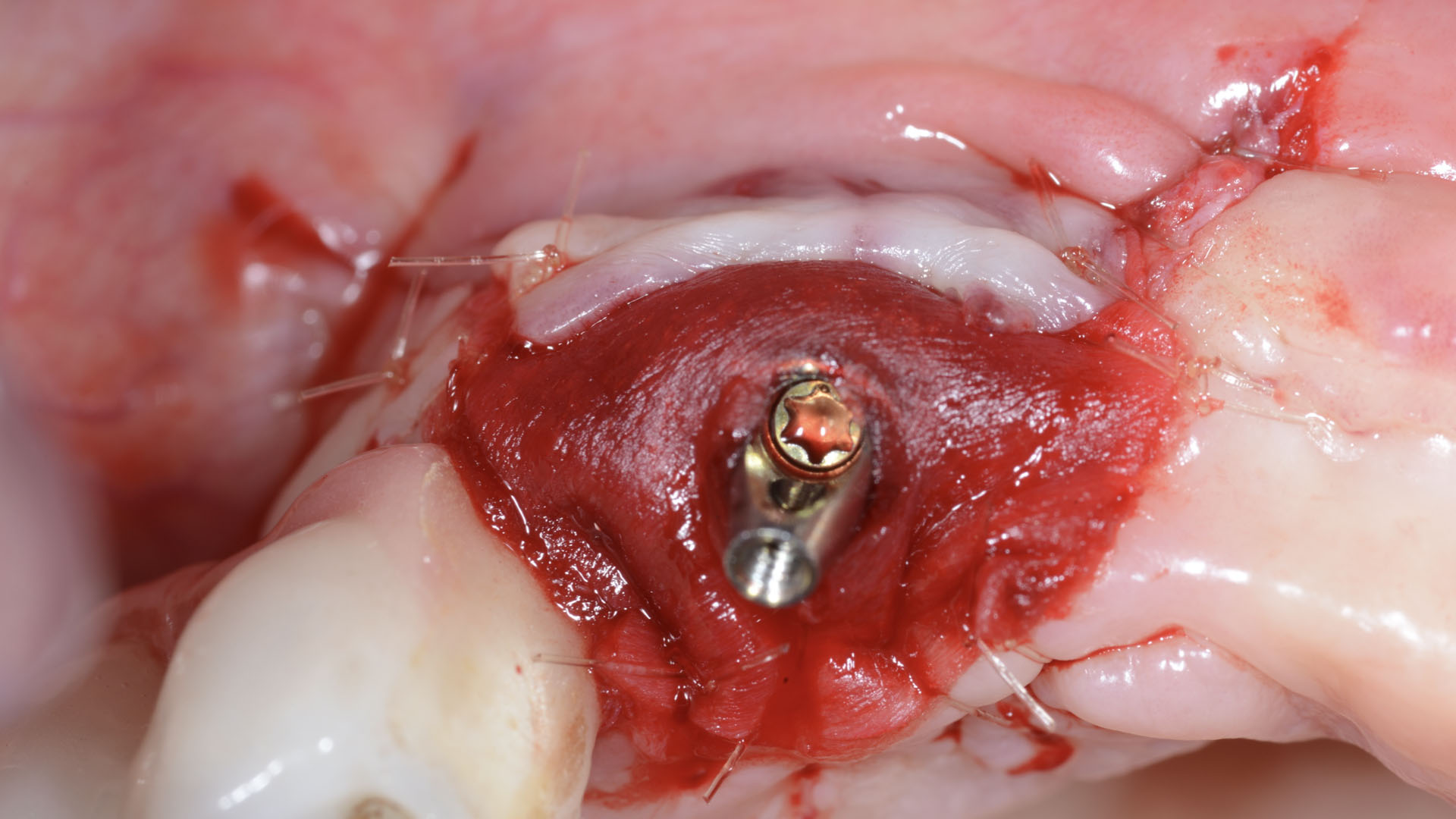
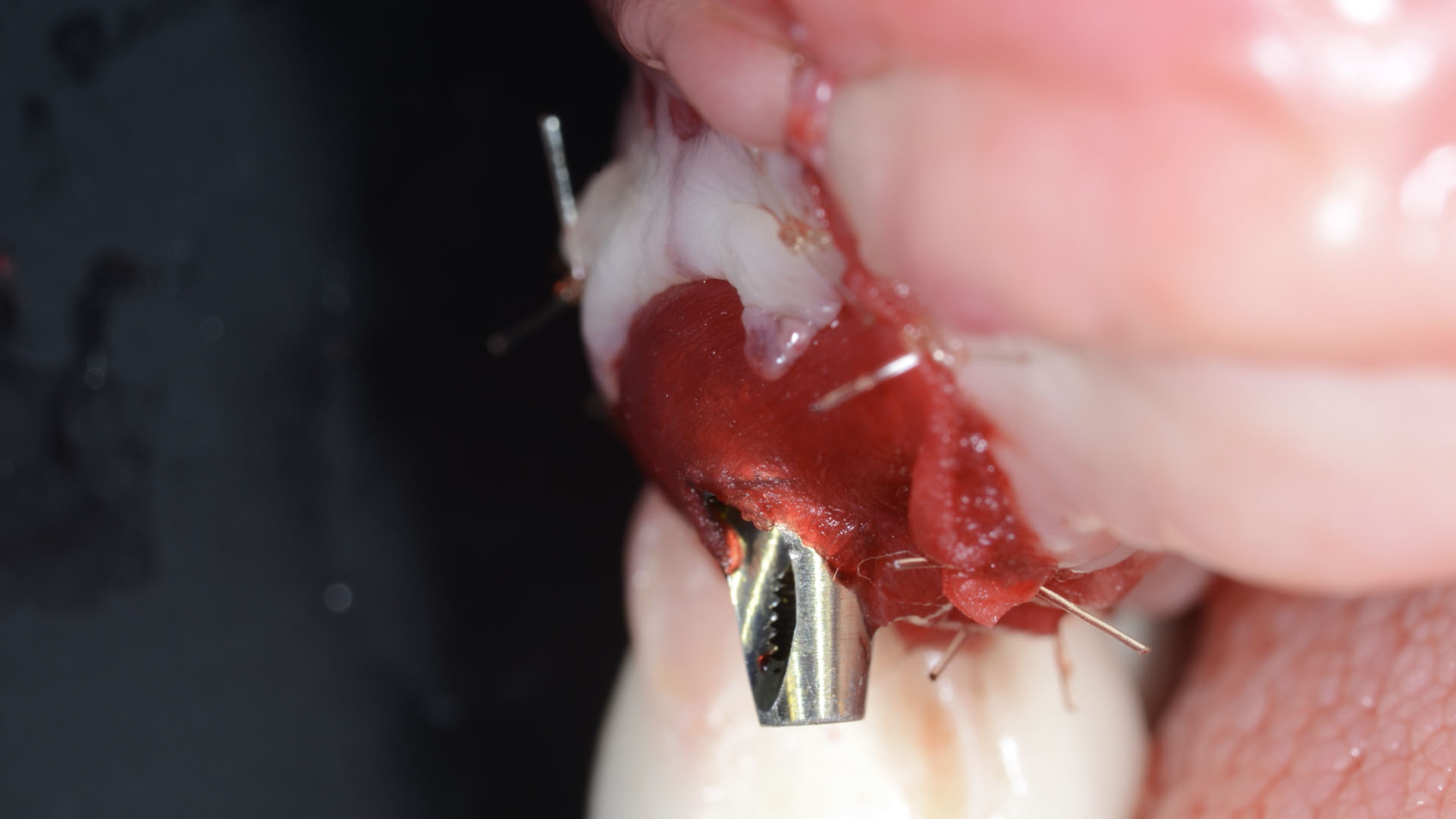
The goal is to provide adequate soft and hard tissue at edentulous site #’s 29, 30 & 31 in order to place dental implants and restore a stable balanced occlusion.
“The hard and soft tissue of the edentulous posterior mandible were inadequate to rehabilitate with dental implants.”
— Dr. Gregory Santarelli
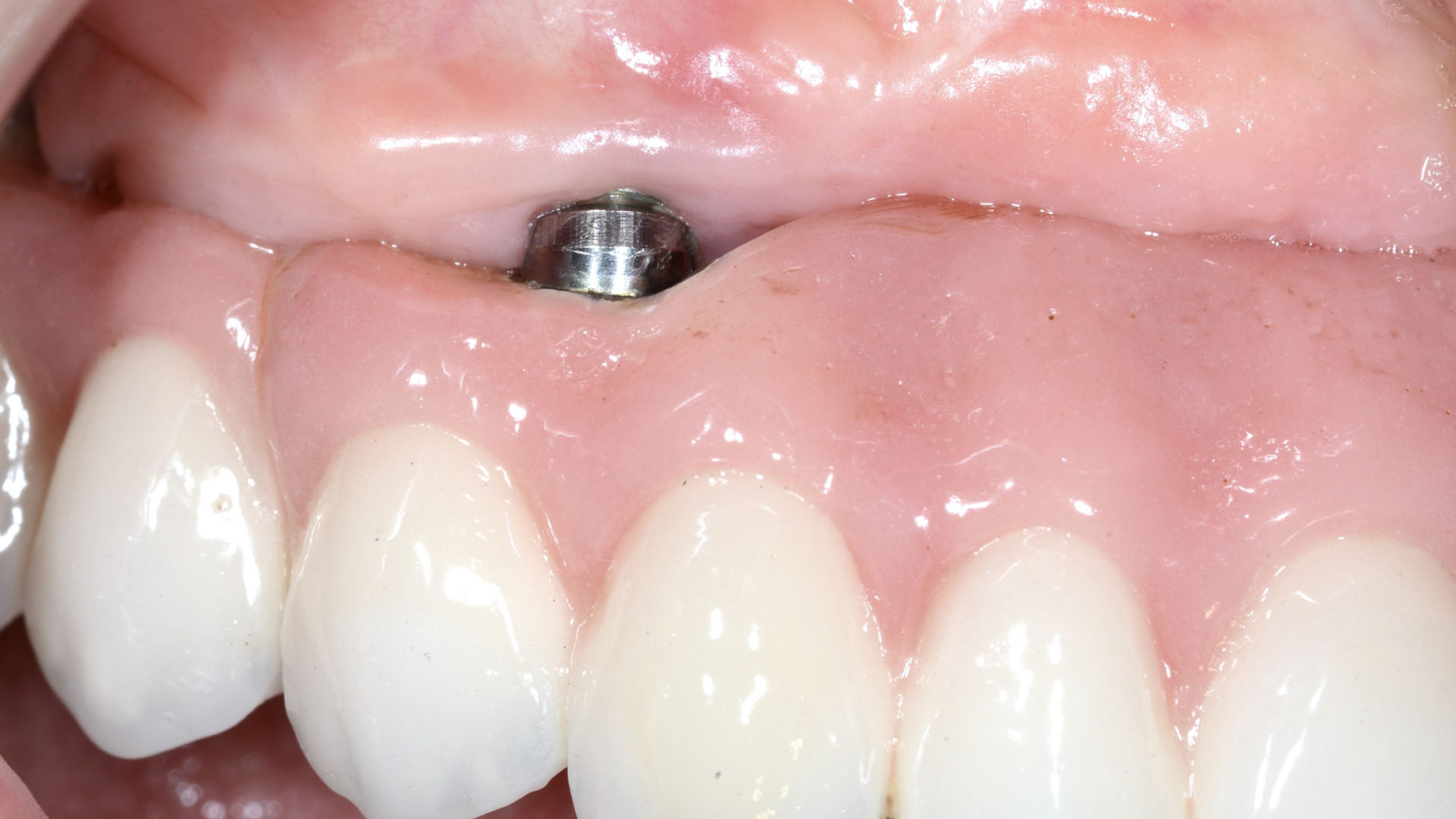
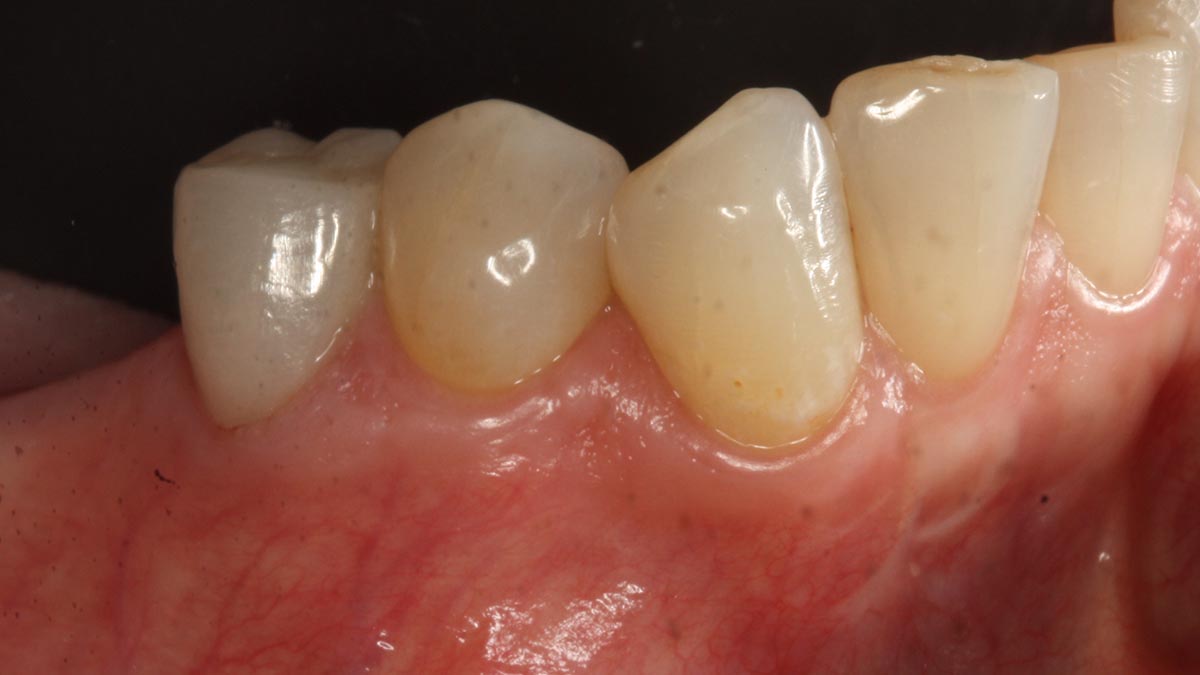
THE OUTCOME
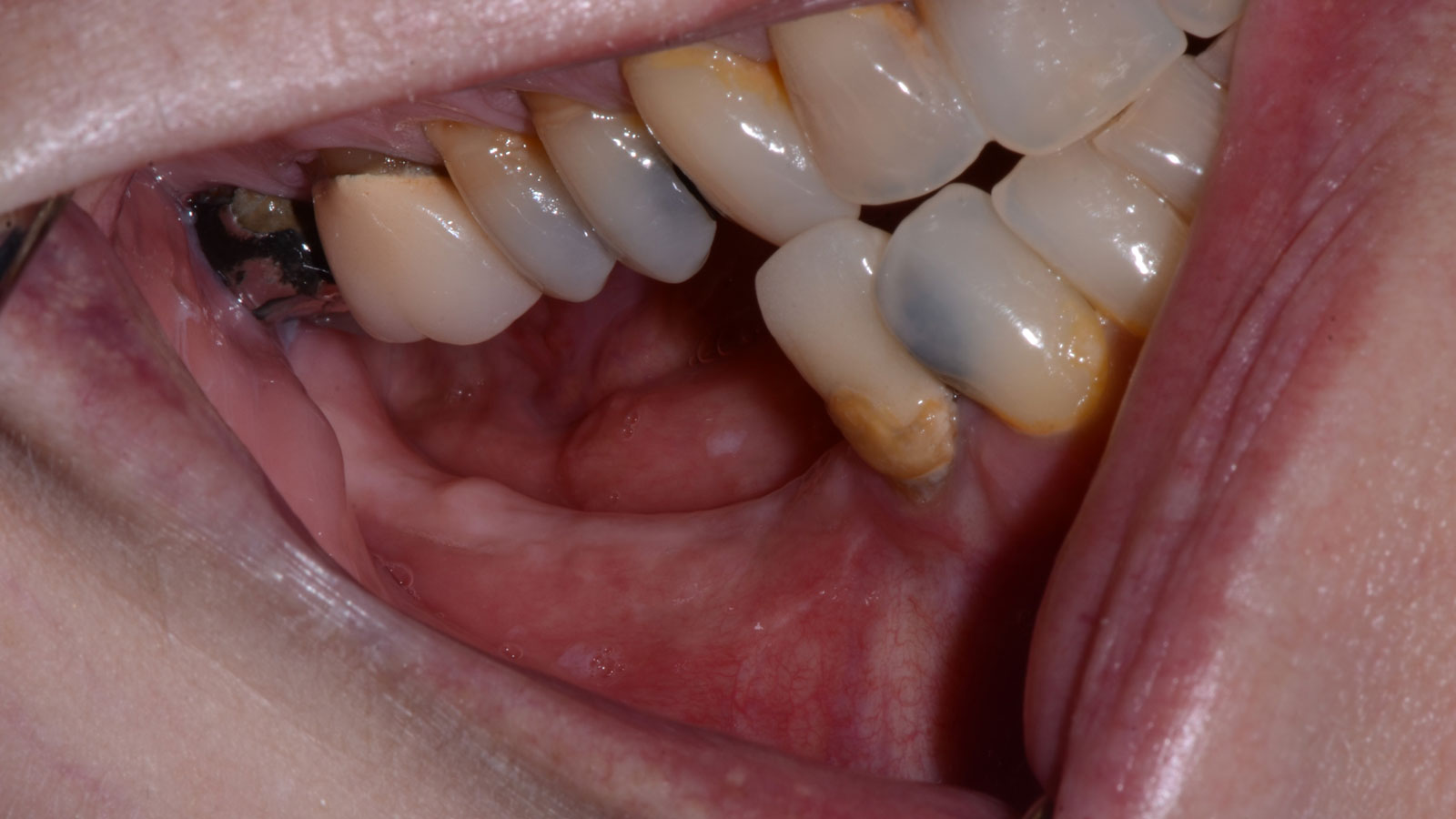
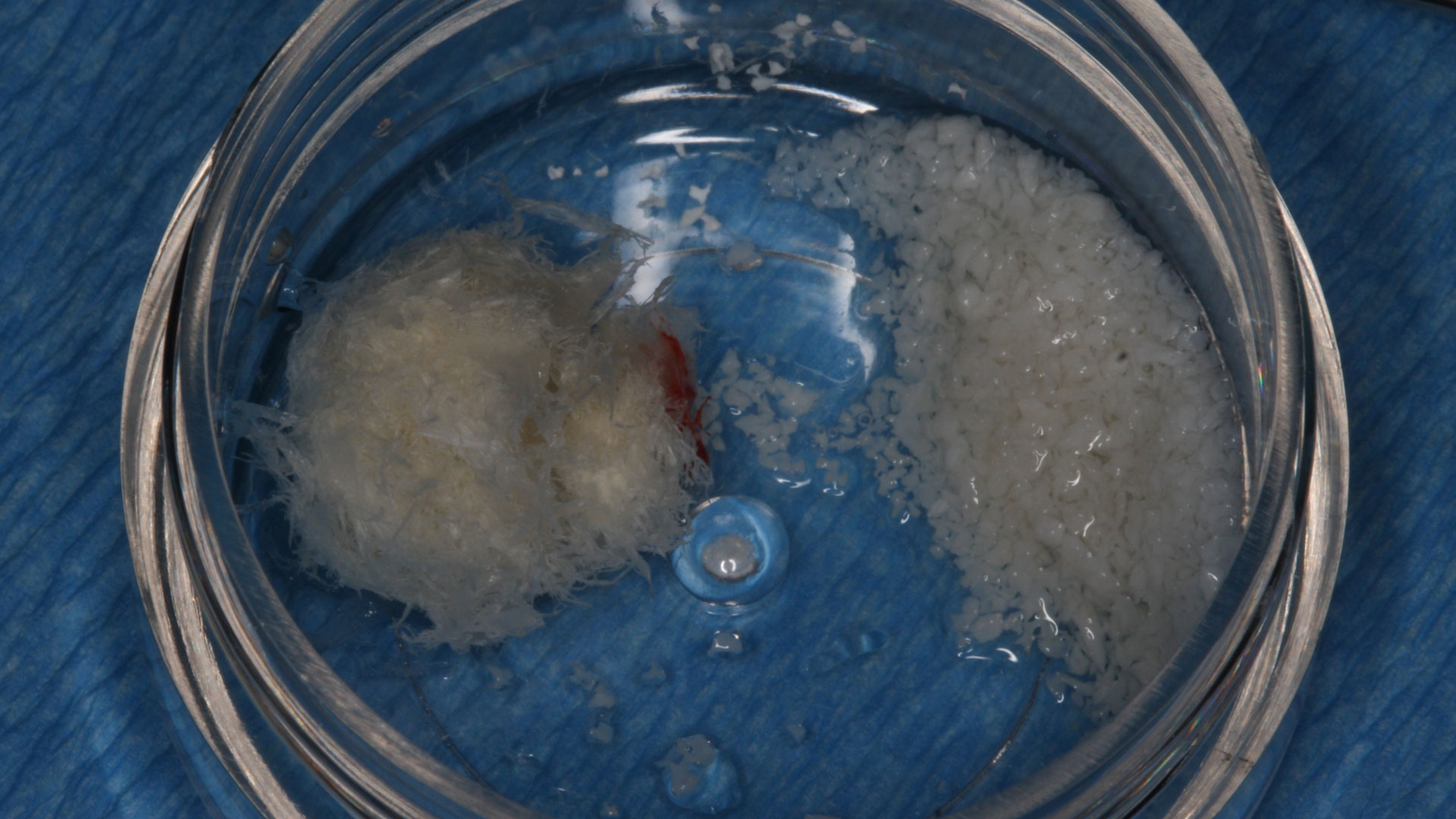
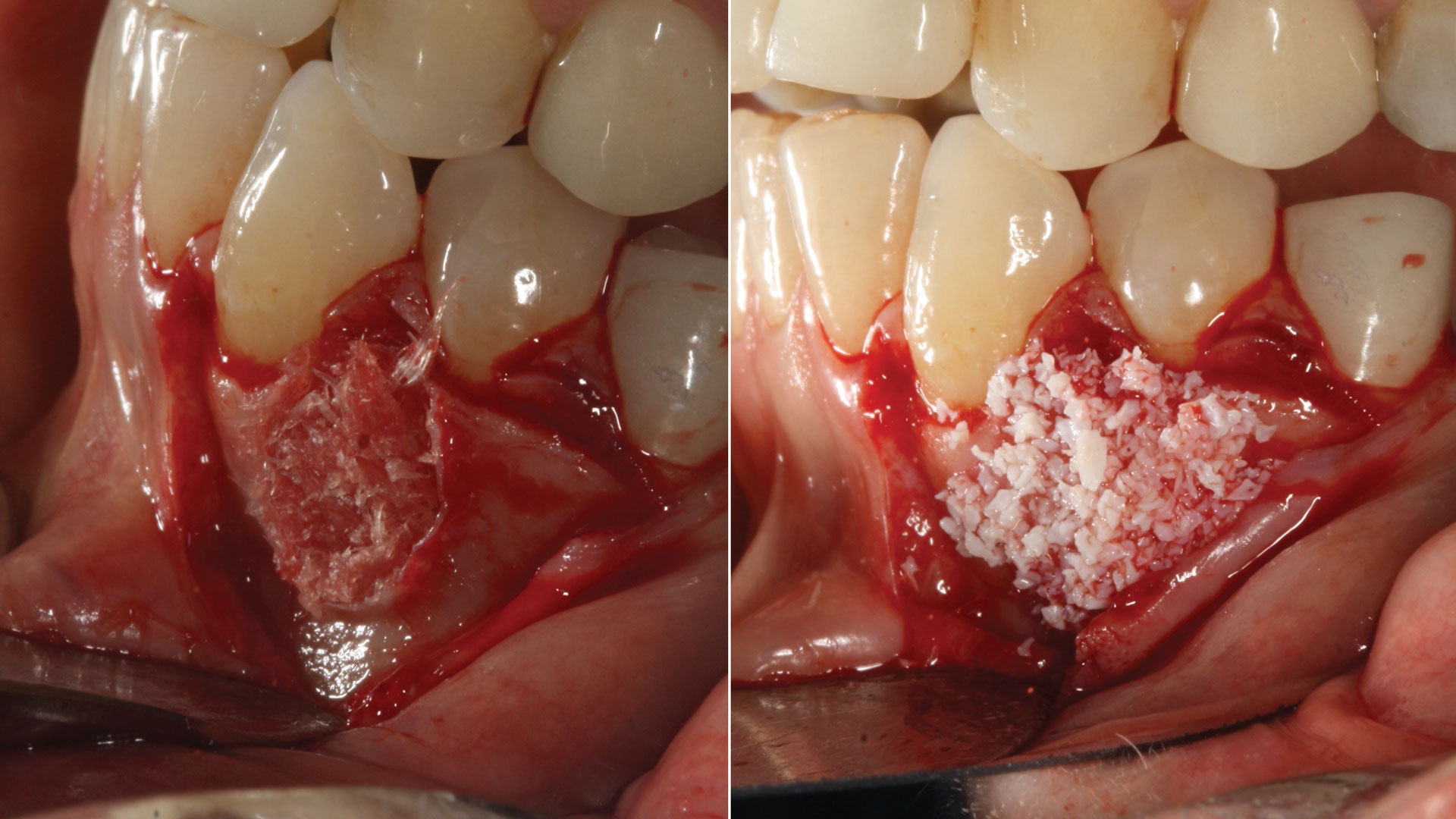
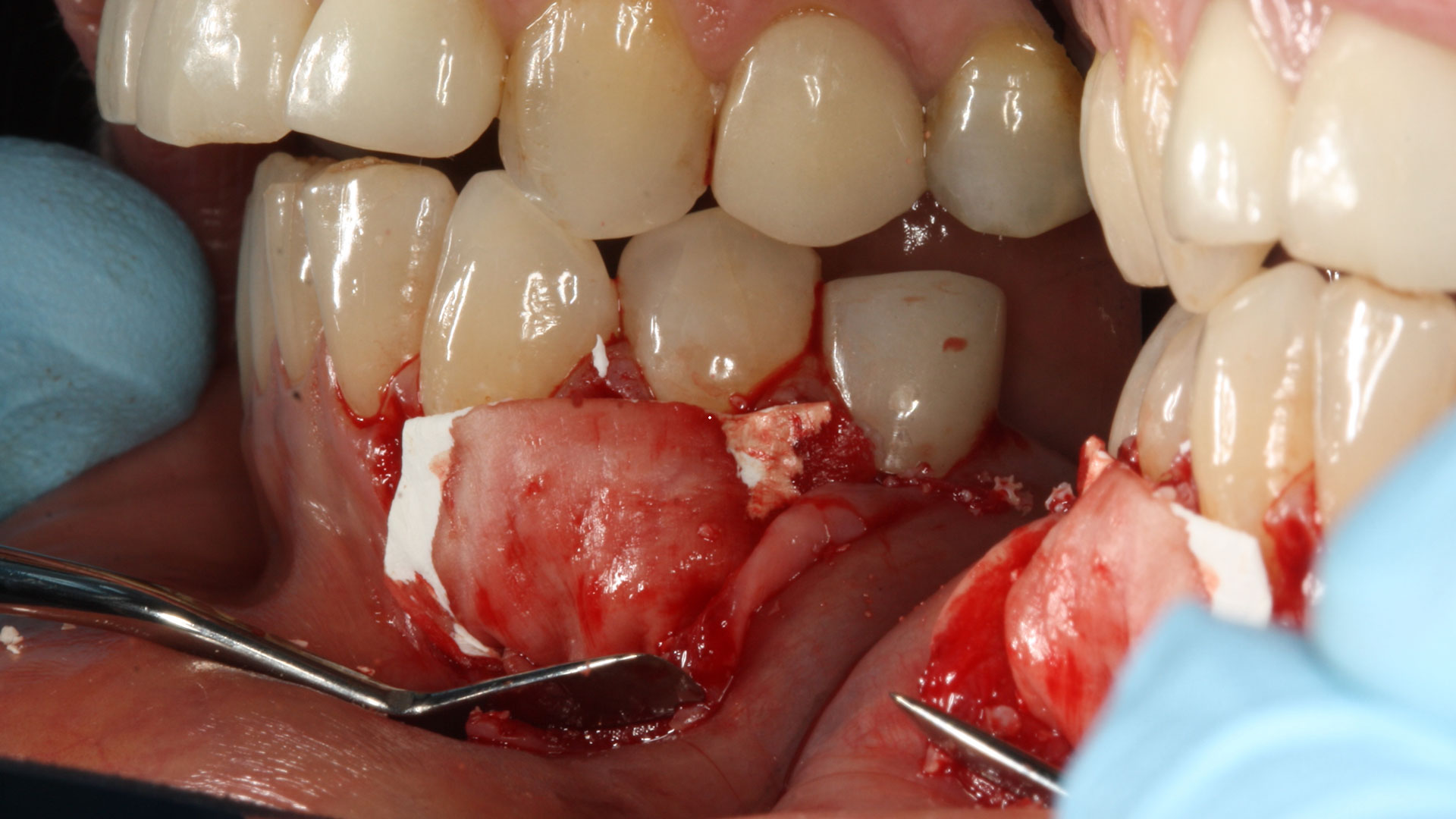
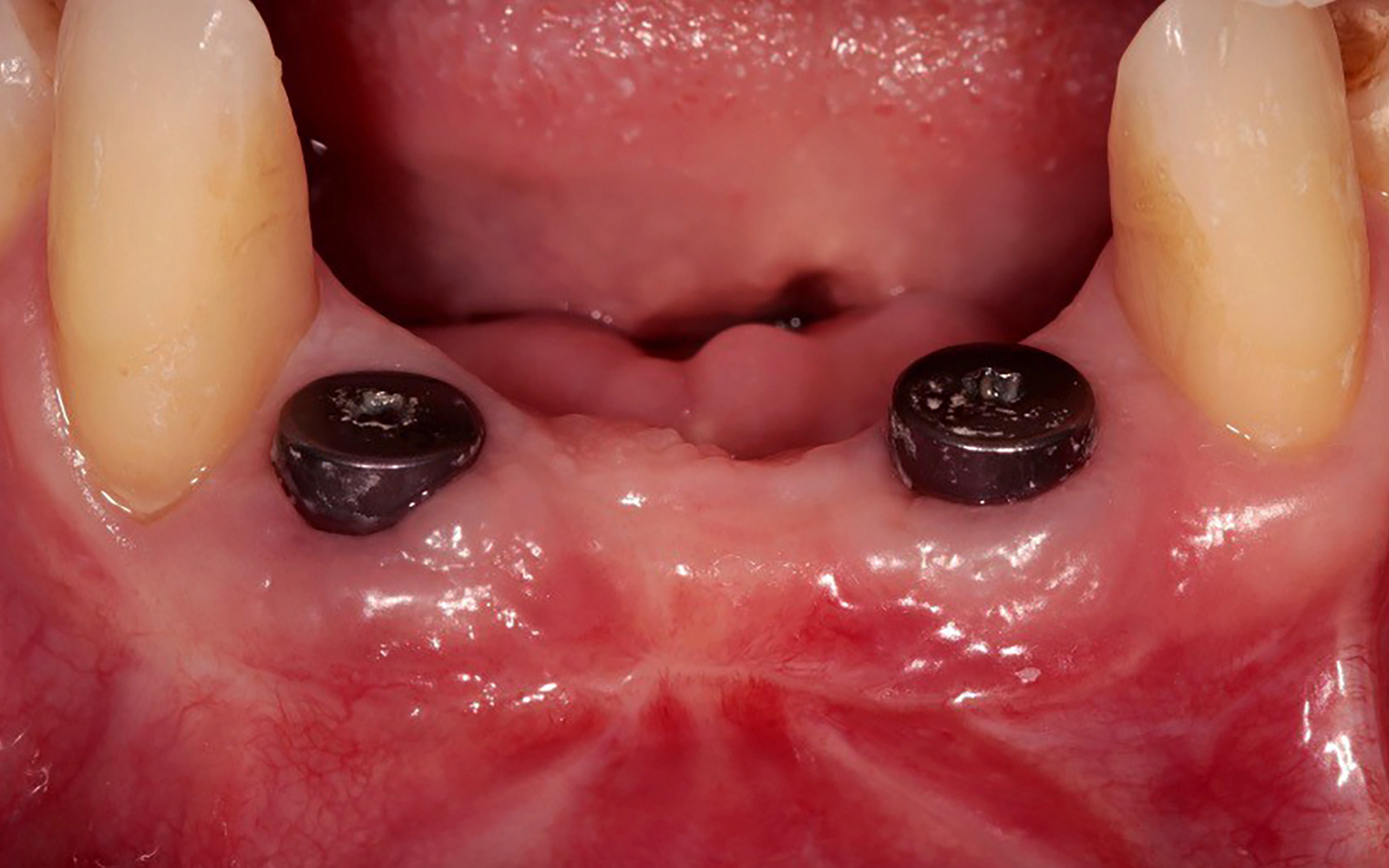
The patient summarized this challenging case very well – “I never imagined I would have fixed teeth again.” Geistlich Bio-Oss® and Geistlich Mucograft® allowed for retention of the hard and soft tissue volume to achieve our final result and for maintenance of the final prosthesis.

Gregory A. Santarelli, DDS
Dr. Santarelli earned his DDS degree in 1998 from the University School of Dentistry, Milwaukee, WI, after graduating with his B.S. in Biology from Arizona State University (Tempe, AZ). In 1999, he completed his General Practice Residency at the University of Iowa Hospital and Clinics, and went on to an Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Internship at the Medical College of Virginia (Richmond, VA) as well as an Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Residency Program, Christiana Care Health System (Wilmington, DE).
After completing his formal training in 2004, Dr. Santarelli’s work experience includes the Bankor Hospital for Children, Cambodia (2003), Adjunct Clinical Professor, University of Marquette, School of Dentistry, Department of Oral Sugery, Marquette, WI (2005), and Oral Surgery Associates of Milwaukee, Milwaukee, WI (2004-2005). He now maintains a private practice in Kenosha, WI with his partner Dr. Deno Tiboris.
Dr. Santarelli performs numerous hard/soft tissue regeneration surgeries in preparation for dental implants and is actively involved in clinical research with The McGuire Institute (iMc).

BIOBRIEF
Odontogenic Keratocyst Management

THE SITUATION
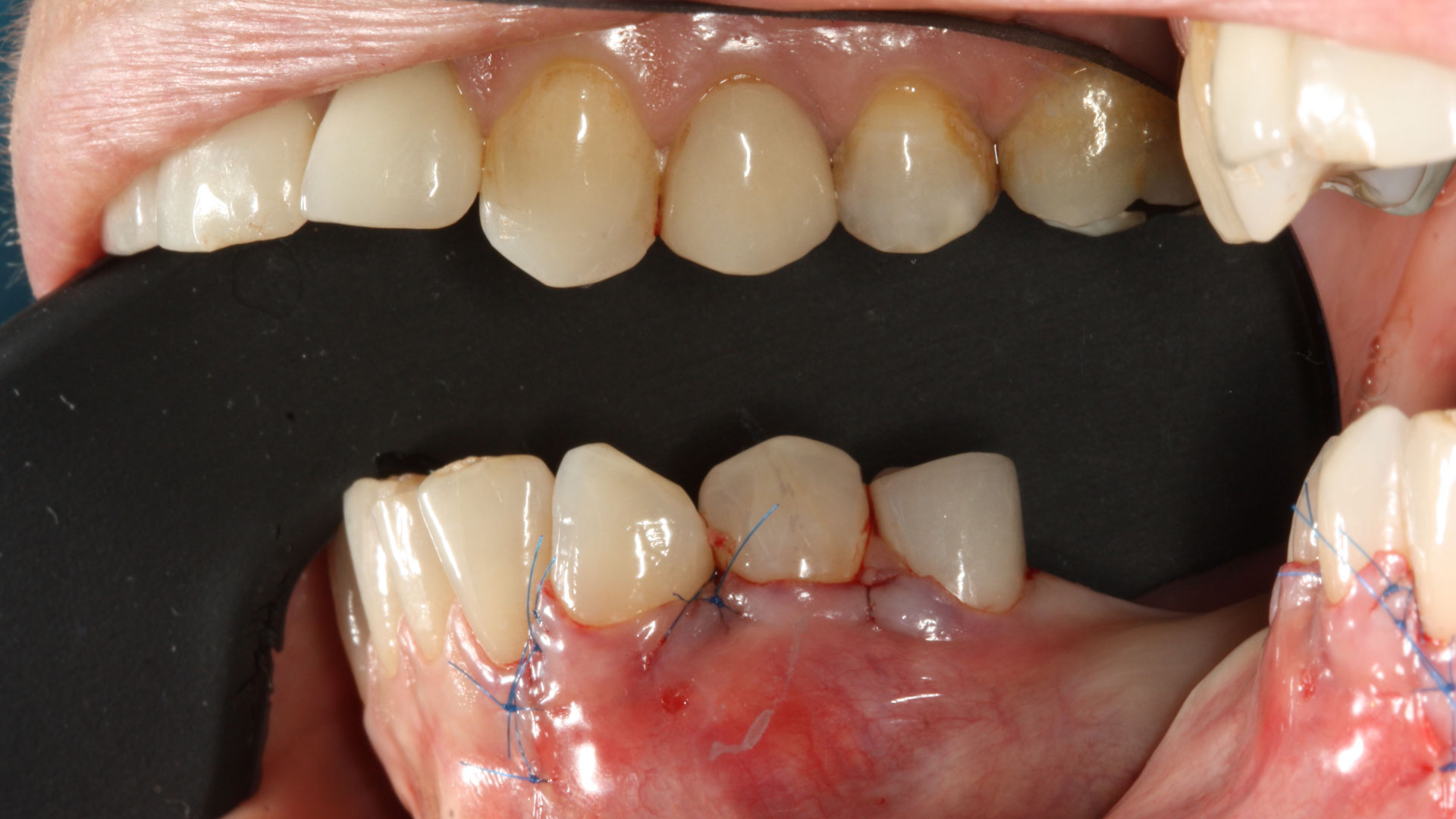
A 60-year-old-heathy Caucasian female presented with the chief complaint: “I noticed a bump on my lower left teeth since last year.” An examination revealed a stable periodontium except for enlarged gingival tissue between #21-22 measuring 10x8x5mm, well-defined borders, depressible, non-painful, and vital teeth without displacement. The treatment plan included flap surgery, excisional biopsy, GTR #21-22 (Diff Dx: Lateral periodontal cyst (LPC), Odontogenic Keratocyst (OKC), Benign Fibro-Osseous lesion (BFOL).
Guided Tissue Regeneration (GTR) using Geistlich Bio-Oss® and vallos®f was performed and covered with a resorbable collagen membrane (Geistlich Bio-Gide®).
Primary closure was completed using non-resorbable sutures. Follow-up at 2, 4 weeks, 3, 6 months showed stable periodontium without re-occurrence. The pathology report indicated OKC and the area is monitored annually.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
The treatment goal was to excise the lesion around #21-22 and stabilize the periodontium. Sulcular incisions #20-22 with vertical incision #22 MF were performed. Upon full thickness flap reflection, the lesion was removed (excisional biopsy). The defect extended #21M-#22D with complete facial bone loss. It was a wide 1-2 bony wall defect measuring 10x8x5mm. GTR procedure using Geistlich Bio-Oss® and vallos®f and Geistlich Bio-Gide® for the collagen membrane were employed. Primary closure was obtained using 6-0 prolene suture.
“Excisional biopsy and guided tissue regeneration is indicated to treat the pathology (#21-22 area) and stabilize the periodontium.”
— Dr. Bassam Kinaia
THE OUTCOME
Complete excision of pathology and biopsy followed by GTR using vallos®f internally for maximum osteogenic/osteoinductive potential and Geistlich BioOss® externally for space maintenance showed excellent radiographic bone fill and stable periodontium.

Bassam Kinaia, DDS, MS, DICOI
Dr. Kinaia is the Associate Director of the Graduate Periodontology Program at the University of Detroit Mercy (UDM). He is also the former Director of the Periodontology Program at UDM in Michigan and Boston University Institute for Dental Research and Education in Dubai. He is a Diplomate of the American Academy of Periodontology (AAP) and International Congress of Oral Implantology (ICOI). He received a certificate of Excellence from the AAP in recognition of teaching-research fellowship.

BIOBRIEF
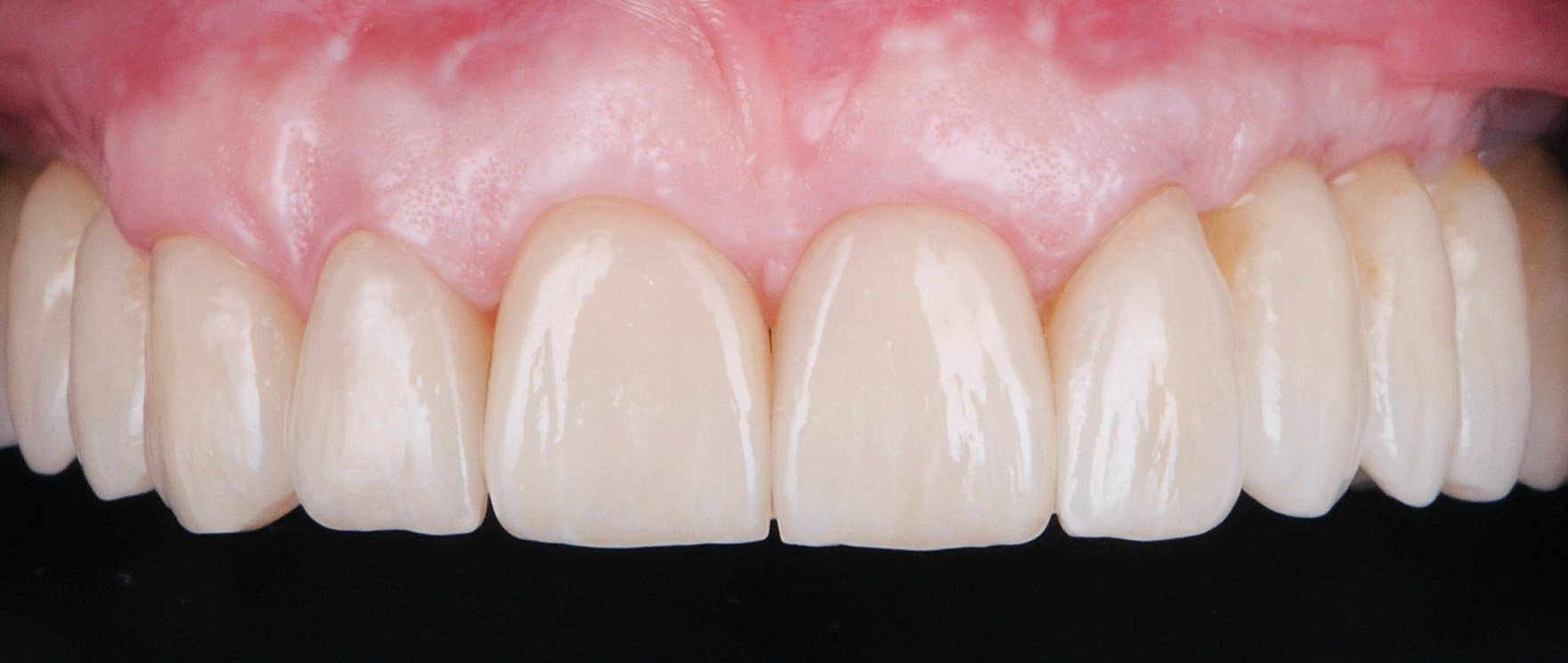
Prosthetically Guided Regeneration (PGR) in the Posterior Maxilla

THE SITUATION
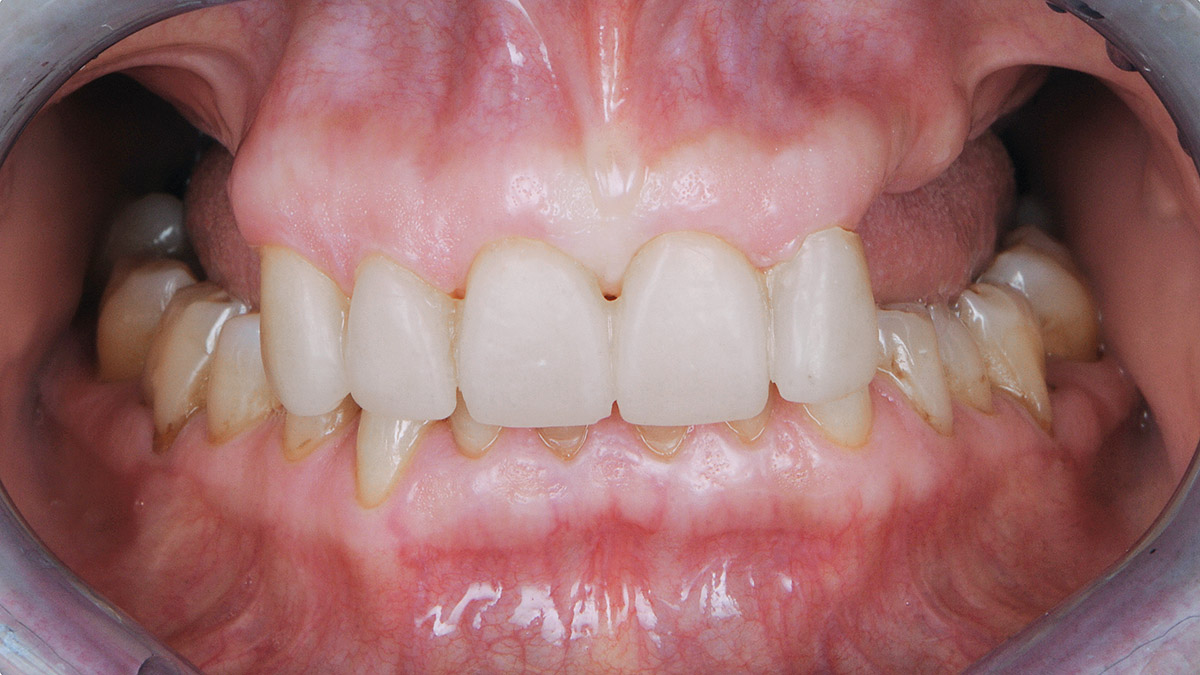
The 60-year-old female patient’s chief complaint was represented by unsatisfactory esthetics and function, related to loss of multiple maxillary teeth. Her request focused on improving esthetics and function by means of a fixed reconstruction.
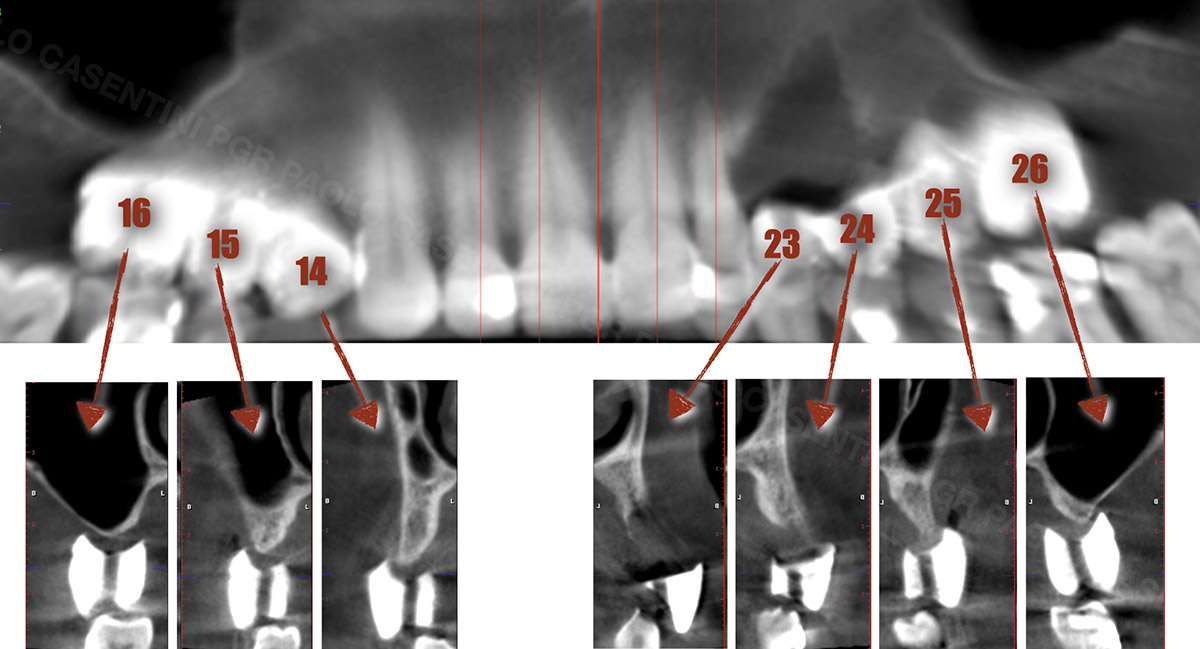
The patient presented five residual anterior maxillary teeth (from 6 to 10) that could be maintained. After preliminary periodontal diagnosis and treatment, specific diagnostic steps for implant treatment demonstrated inadequate bone volume for implant placement.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system Non-smoker | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
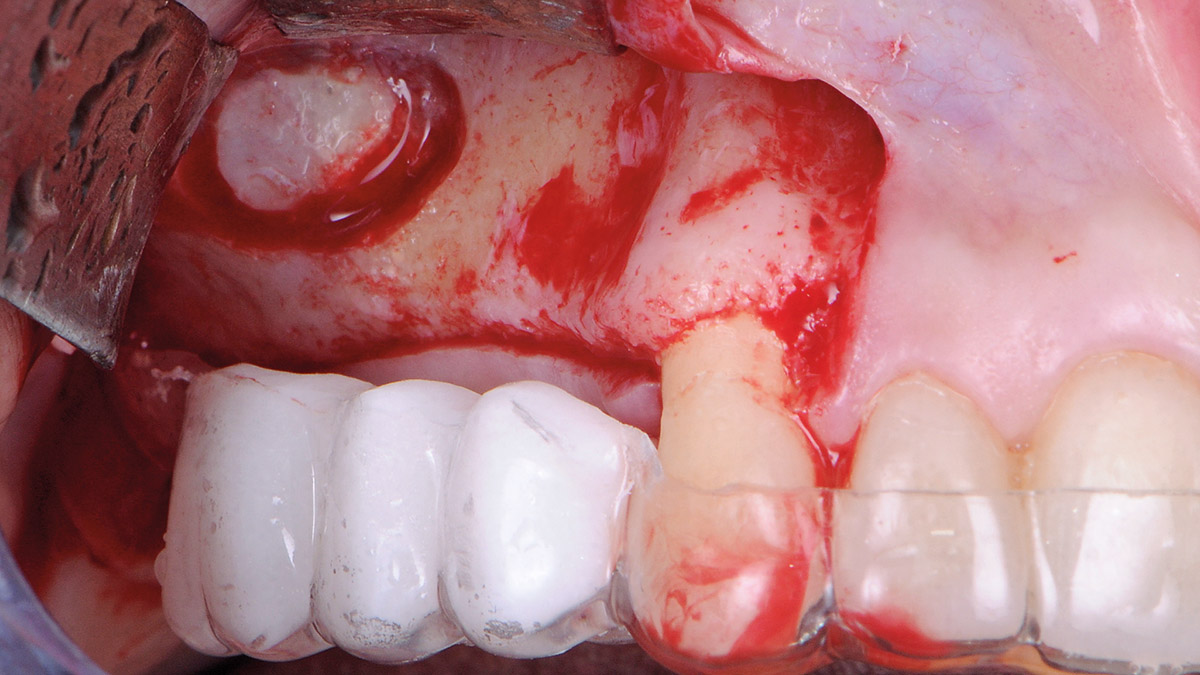
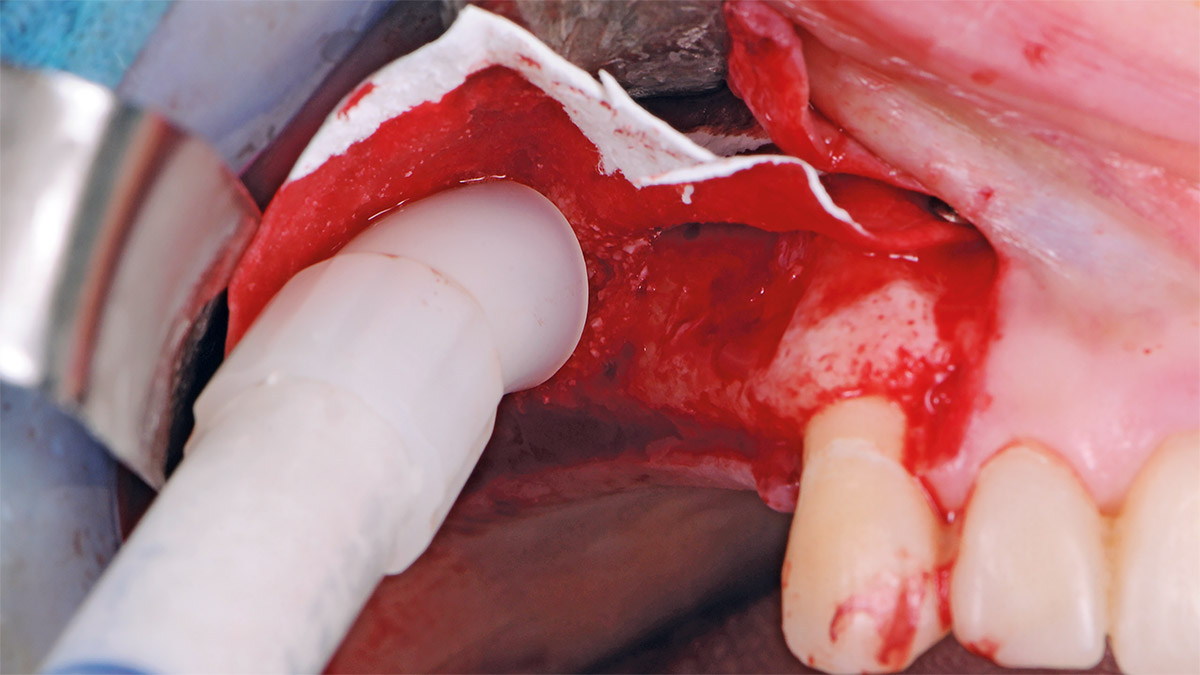
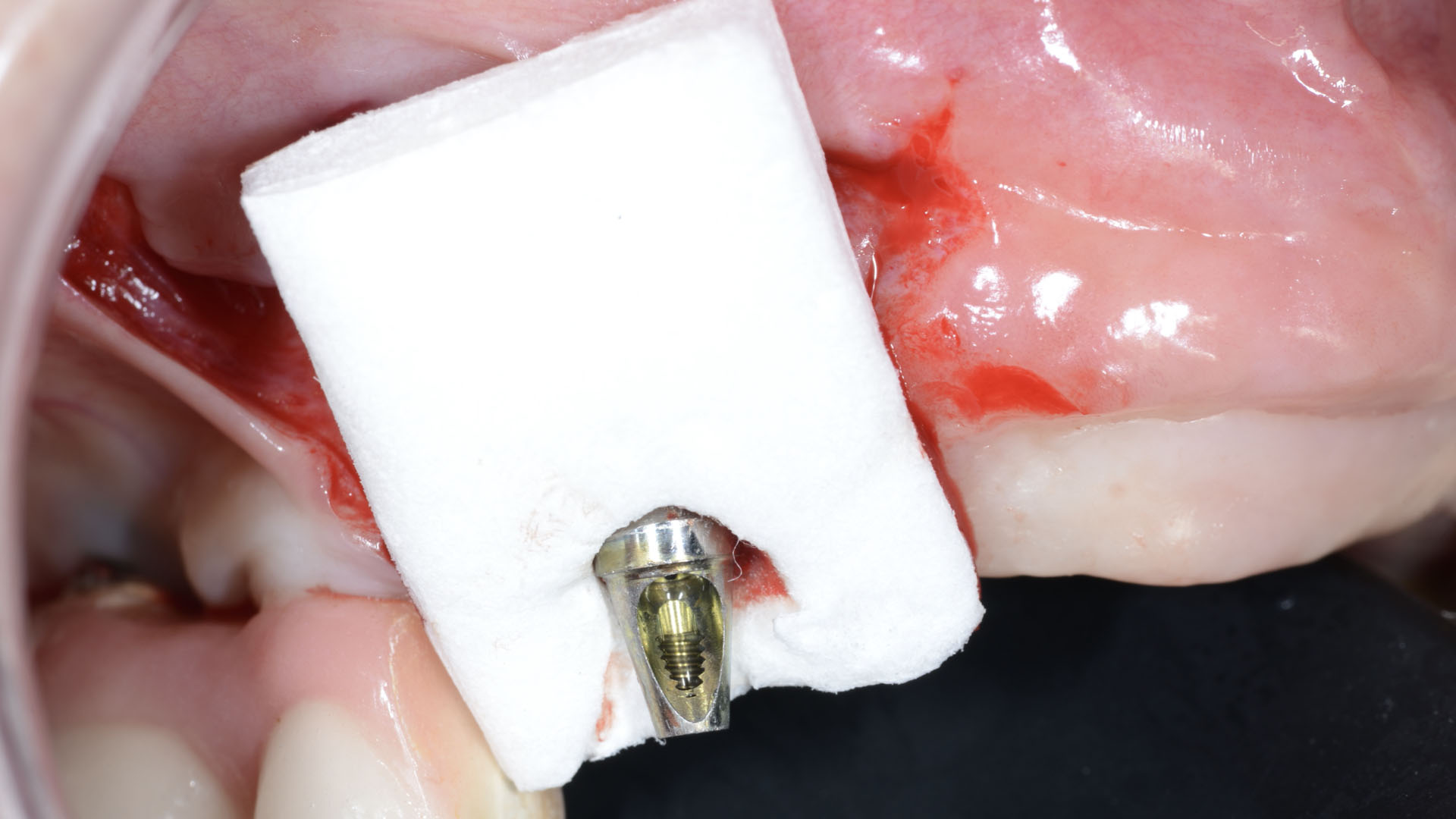
Bi-lateral sinus lift with Geistlich Bio-Oss Pen® and horizontal bone augmentation with a 1:1 mix of autogenous bone and Geistlich Bio-Oss® were performed six months prior to implant placement, following a Prosthetically Guided Regenerative (PGR) approach. The augmented sites were protected with Geistlich Bio-Gide® stabilized with titanium pins. The template utilized for radiographic diagnosis and GBR was then used to guide the implants’ placement.
Using a diagnostic template during the GBR procedure helps to highlight the presence of bone defects in relationship to the restorative plan and future position of implants.
THE OUTCOME
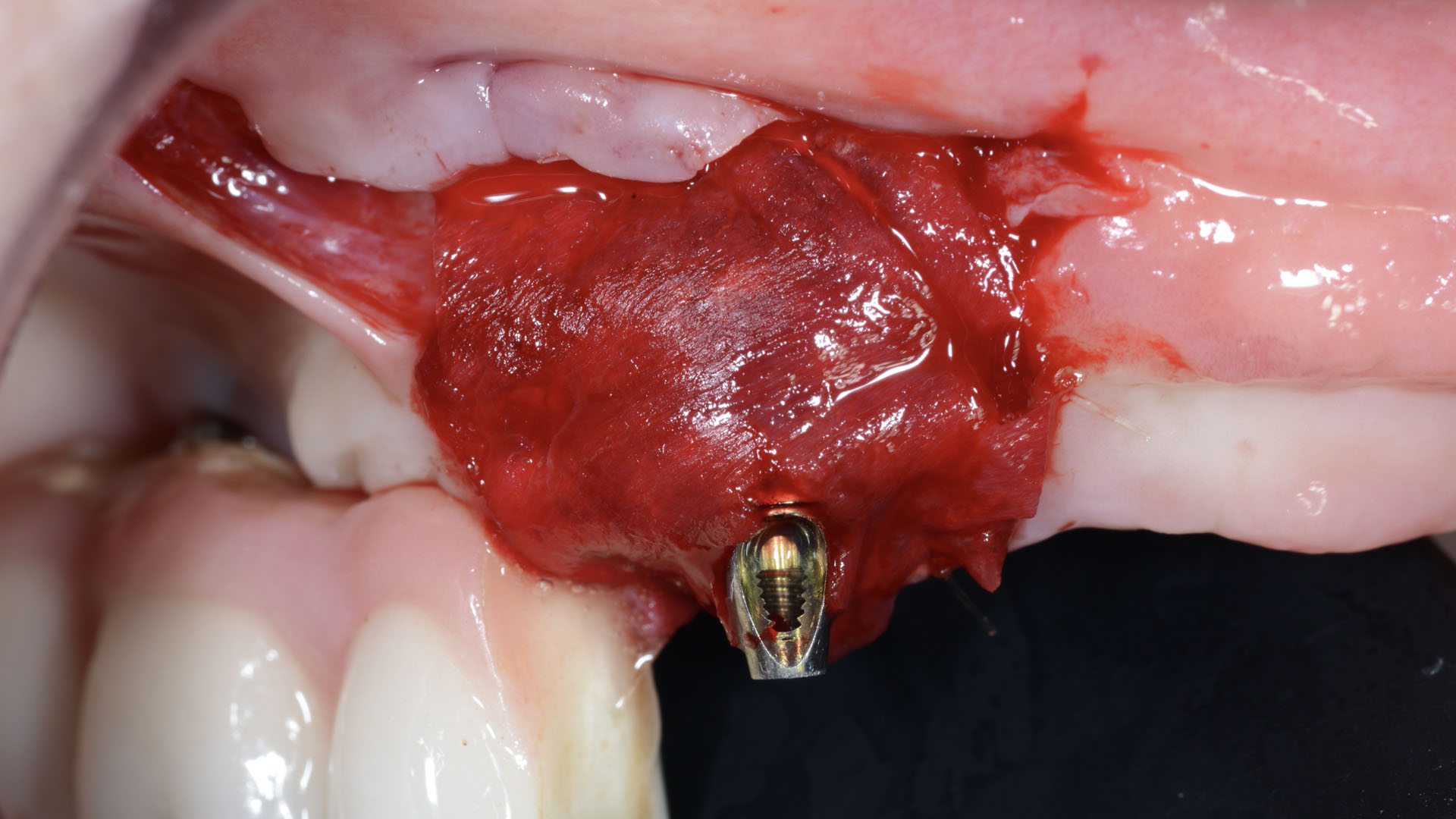
After a healing period of six months, adequate bone volume was achieved for the placement of five implants. Geistlich Fibro-Gide® was also used to optimize soft tissue volume at the buccal aspect of implants.
Implants were early loaded with a temporary screw-retained fixed prostheses six weeks after placement. The final prosthetic reconstruction included ceramic veneers of the frontal residual teeth and zirconium-ceramic screw-retained fixed prostheses on implants.


Paolo Casentini, DDS
Graduated in Dentistry at the University of Milan, Fellow and Past Chairman of the Italian section of ITI, Active member Italian Academy of Osseointegration. Co-author of 10 textbooks including ITI Treatment Guide volume 4, translated in eight languages, and “Pink Esthetic and Soft Tissues in Implant Dentistry” translated in five languages. His field of interest is advanced implantology in complex and esthetically demanding cases. He has extensively lectured in more than 40 countries.

BIOBRIEF
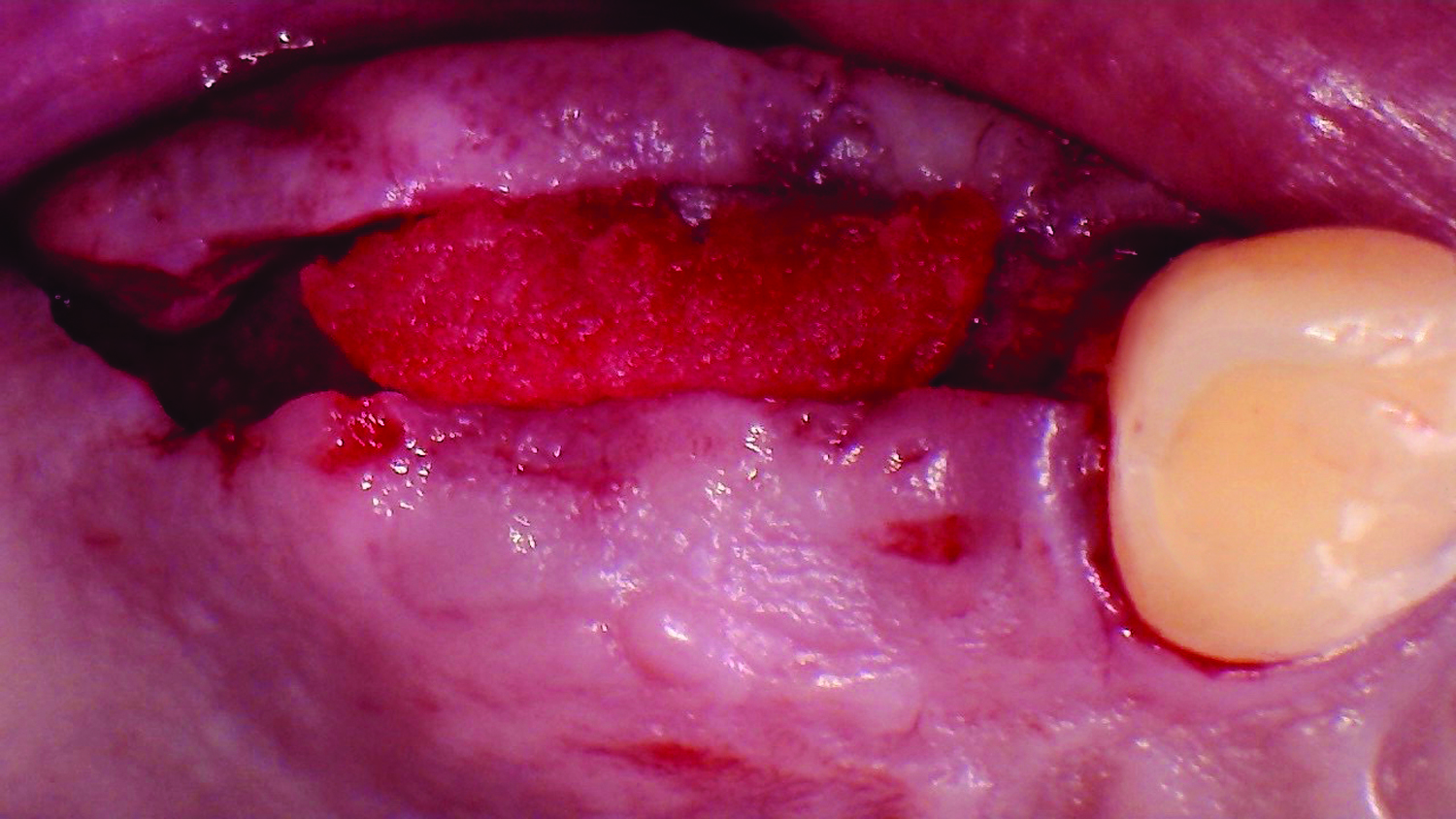
Avoiding Post-Implant Placement and Long Term Crestal Bone Resorption by Thickening Vertical Soft Tissue

THE SITUATION
Our patient is a 60-year-old caucasian male that had just finished a large ridge augmentation in the area of #4 and #5. We used the sausage technique for the ridge augmentation and yielded excellent bone volume in this area. However, as we began the 2nd stage implant placement procedure, we noticed, as is frequently seen following a large ridge augmentation, very thin vertical soft tissue over the crest of the bone. We know that inadequate soft tissue thickness will lead to compromised vasculature and transfer of oxygen and nutrients to the bone which can absolutely lead to a loss of crestal bone surrounding the implants.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
Note: Bone was augmented prior to this case report due to a severe horizontal defect.
THE APPROACH
Our goal here is to create increased vertical soft tissue thickness over the crest of the implant site. Following implant placement and placement of the cover screws, we used Geistlich Fibro-Gide® over the implants and then layed it over the crest and buccal aspect. Following the placement of Geistlich Fibro-Gide®, we gently released the full thickness flap so that we can achieve tension-free primary closure over the site.
The use of Geistlich Fibro-Gide® is a wonderful alternative to using a connective tissue graft to thicken vertical soft tissue, which will help minimize crestal bone loss around implants.
THE OUTCOME
The soft tissue that will now surround the implant site is thick and healthy due to the use of Geistlich Fibro-Gide® at the time of implant placement. This is a simple technique and only requires a minimal amount of flap release to achieve tension-free primary closure over the site. The results are phenomenal and will be beneficial for the stability of the crestal bone surrounding the implants for years to come.

Tamir Wardany, D.D.S.
Dr. Wardany is a graduate of Meharry Medical College School of Dentistry in Nashville, TN. After completion of a dental implant fellowship through State University of New York Stonybrook, he continues to spend extensive time in Europe training under Dr. Istvan Urban in the field of advanced bone and soft tissue regeneration.
He is a Diplomate of the American Board of Implantology, and lectures extensively on the topic of bone regeneration. He maintains a referral based surgical implant practice in San Francisco and Sacramento, California.

BIOBRIEF
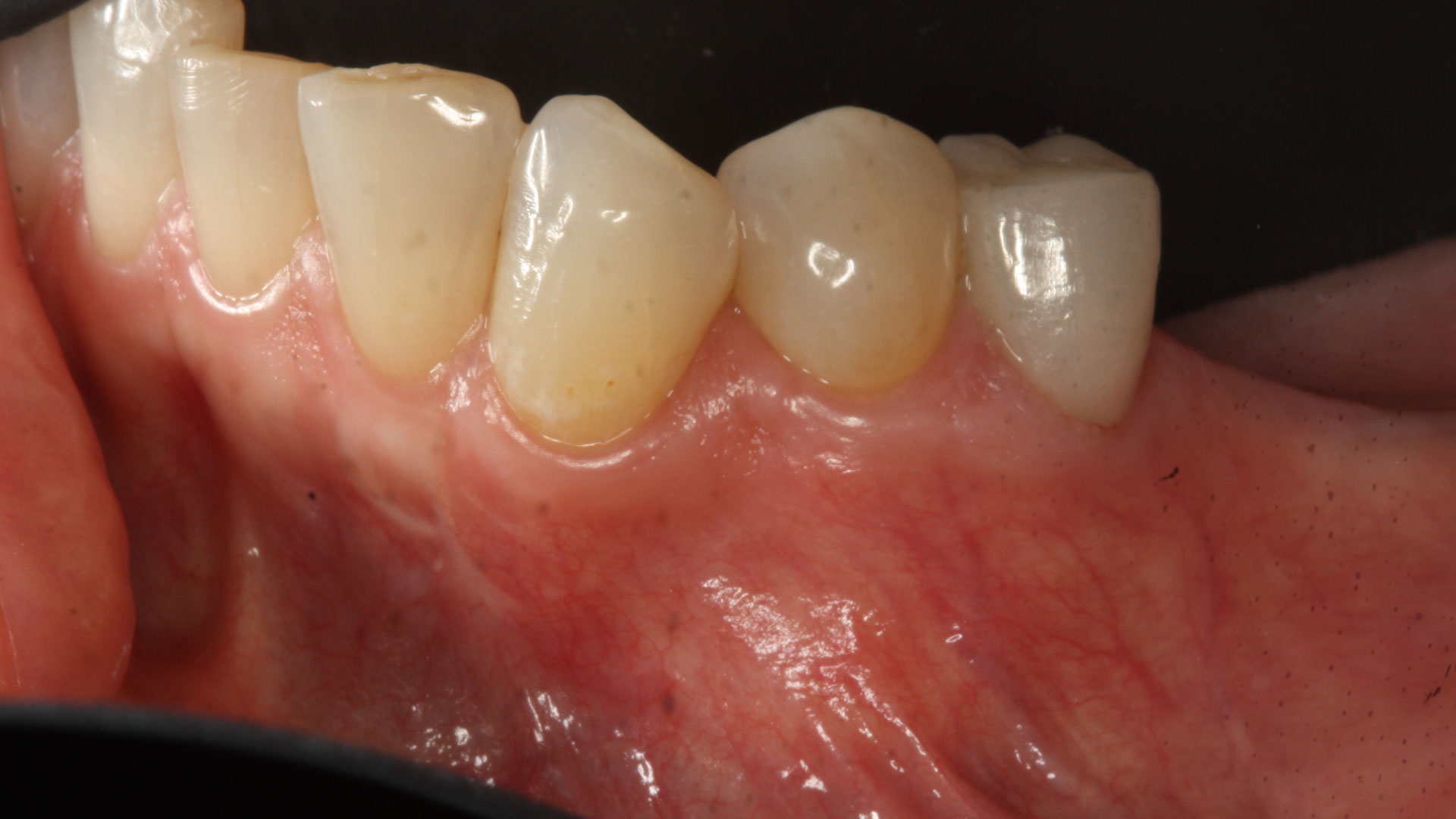
A Regenerative Approach to Peri-implantitis
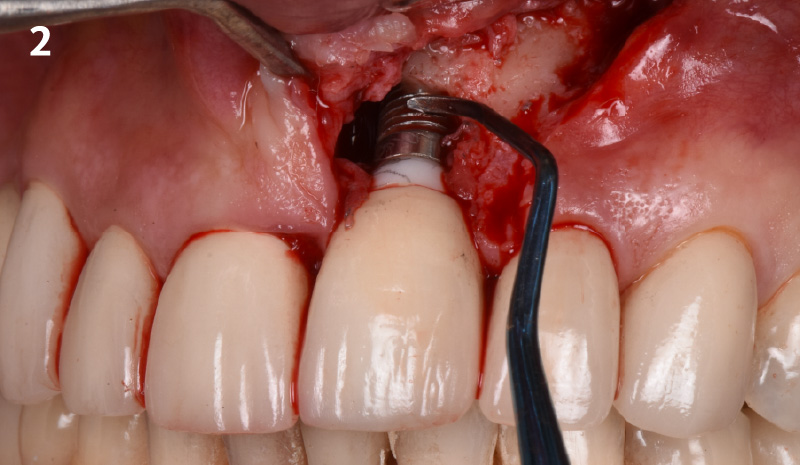

THE SITUATION
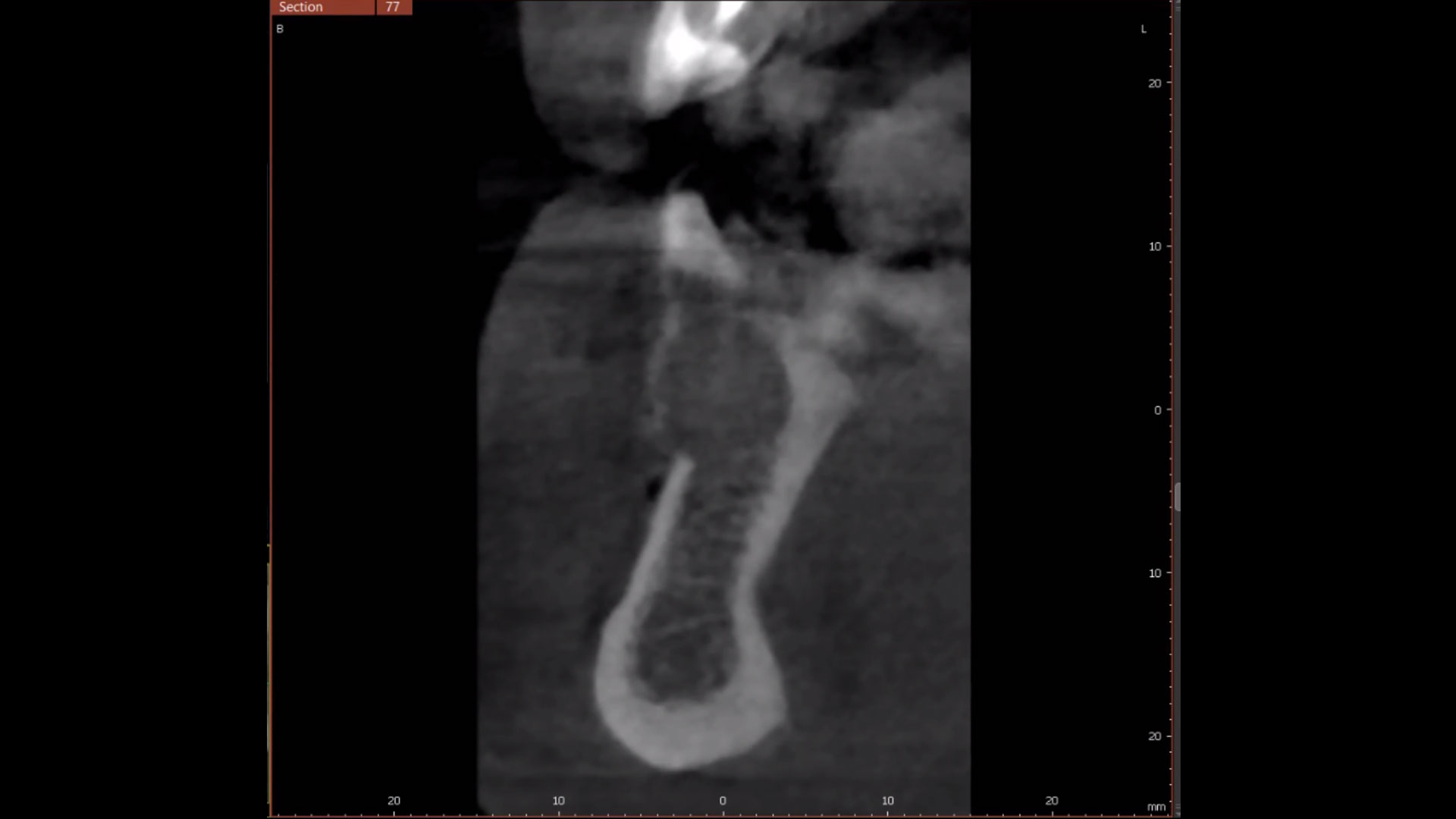
A 55-year-old man was referred to me by his general dentist. Upon initial clinical and radiographic findings, failing implant #9 showed signs of peri-implantitis that included BoP, Suppuration, 9+mm PD and radiographic bone loss affecting both the implant and the natural adjacent tooth. Patient stated that although his gums bleed, he does not have any pain. Gingival erythema was also found.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
Note: Peri-implantitis on implant #9 migrating to the mesial portion of root #8
THE APPROACH
The clinical goals were to eliminate the peri-implant infection, restore hard and soft-tissues and have long-term success. The technique utilized was a systematic regenerative approach to eliminate the underlying cause of the peri-implantitis infection and restore hard and soft-tissues to prior health.
Geistlich Fibro-Gide® has the capacity to enhance the soft-tissue during a bone regenerative approach.
THE OUTCOME
My observation at the 1.5 year follow-up shows the elimination of peri-implantitis and complete peri-implant health was achieved showing a reduction in BOP, PD and most importantly soft tissue thickness stability. Radiographically, crestal bone shows no signs of progressive pathological loss and has maintained adequate volume.
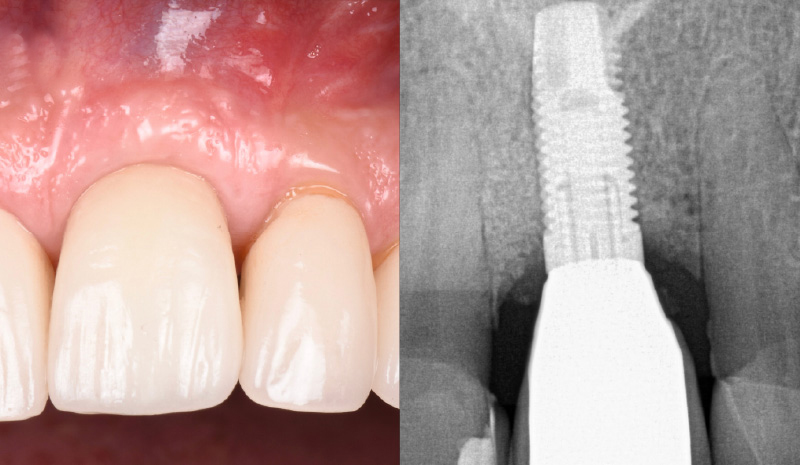

Hector L. Sarmiento, D.M.D., MSc.
Dr. Hector Sarmiento was awarded his D.M.D. degree by the University of Rochester. He is uniquely trained in both maxillofacial surgery and periodontics. He is a professor in the maxillofacial surgery department of trauma and reconstructive unit at the Regional Hospital in Mexico and is an Assistant Clinical Professor in periodontics at the University of Pennsylvania. Along with his periodontal degree, he also received his masters in oral biology from the University of Pennsylvania. Dr. Sarmiento is an international and national lecturer and has published numerous articles in peer reviewed journals and textbooks. His research focus includes infected dental implants such as peri-implantitis, sinus complications as well as bone biology. Dr. Sarmiento maintains his private practice in the upper east side of Manhattan in NYC.

BIOBRIEF
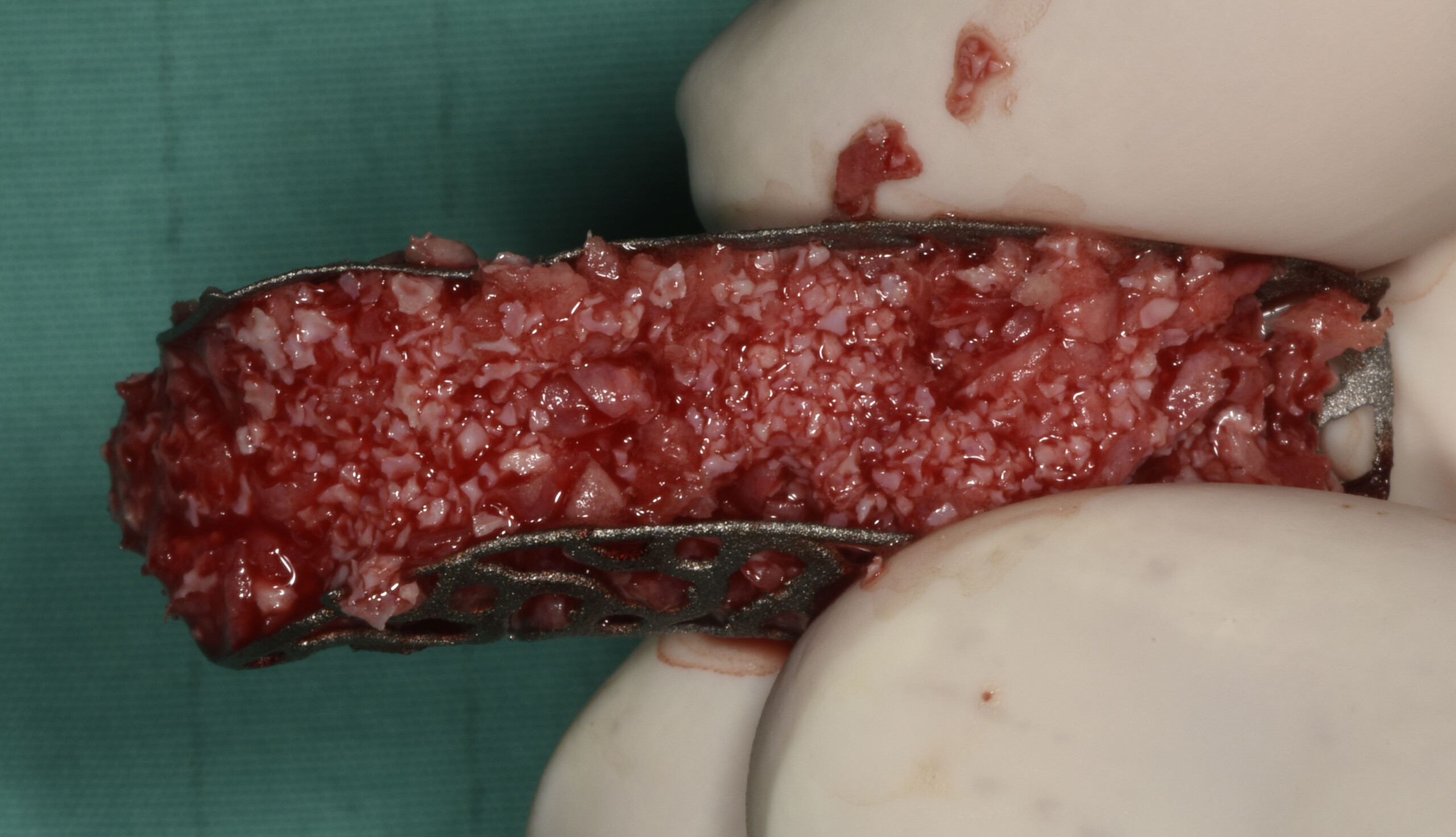
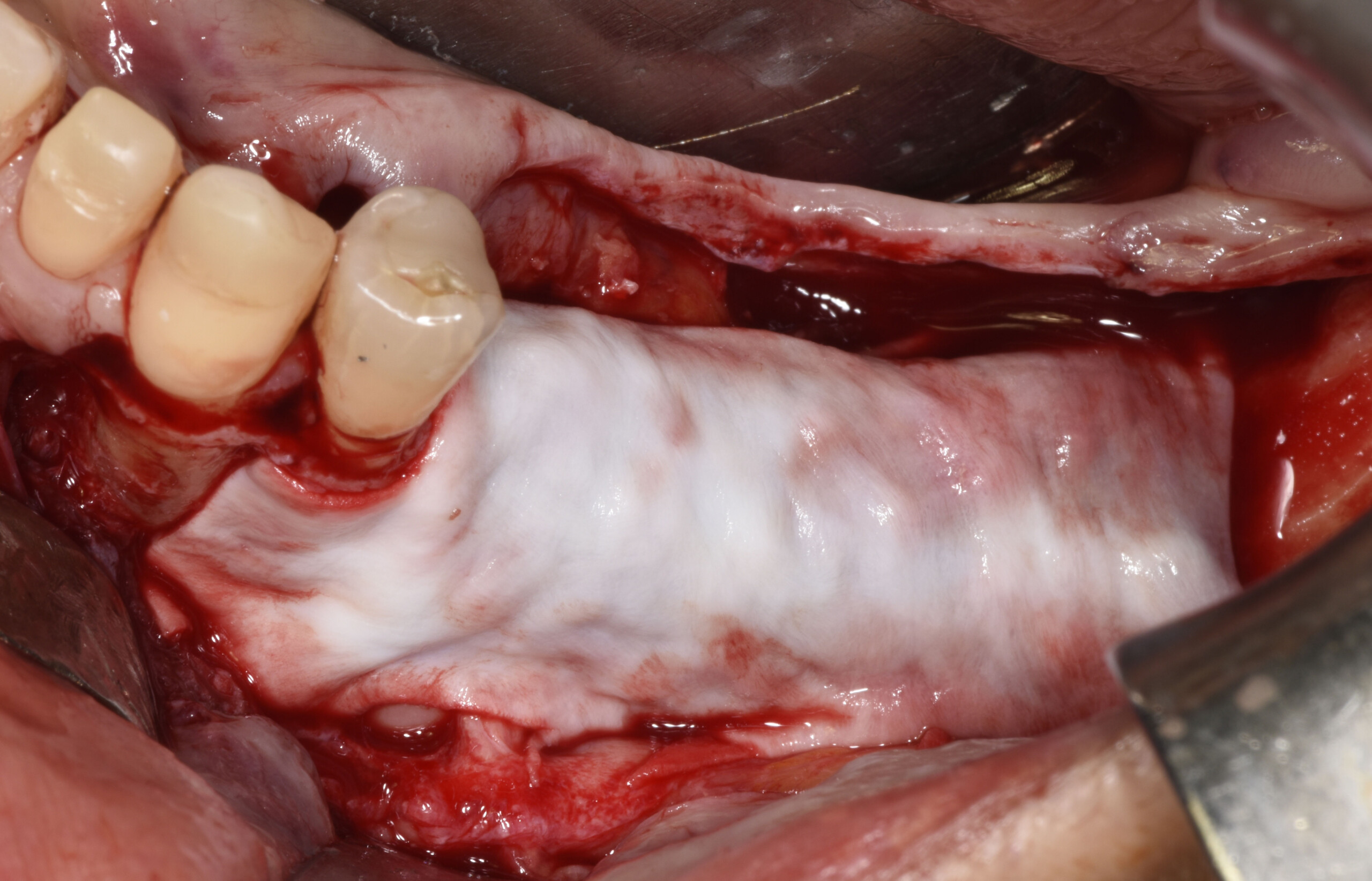
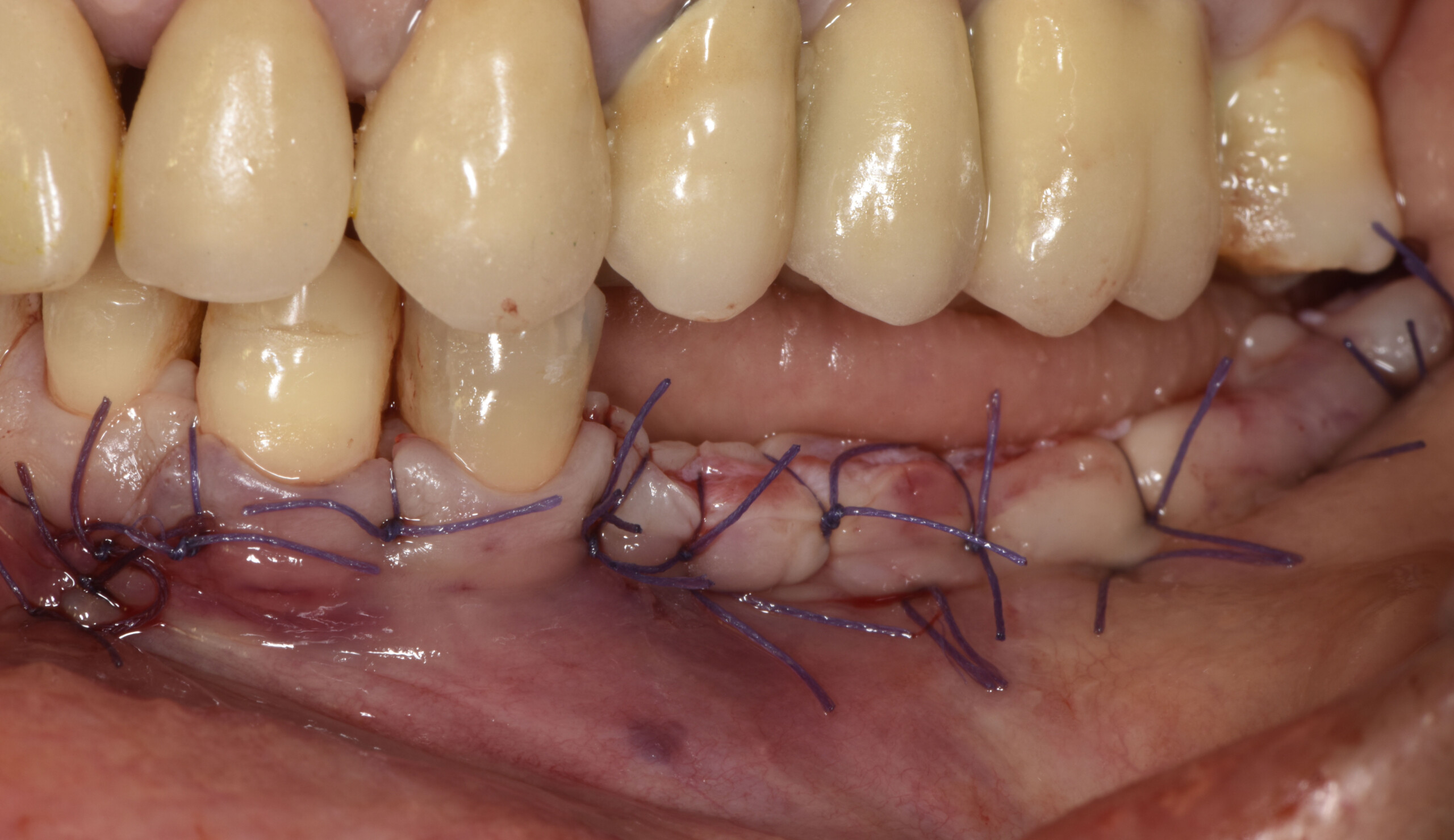
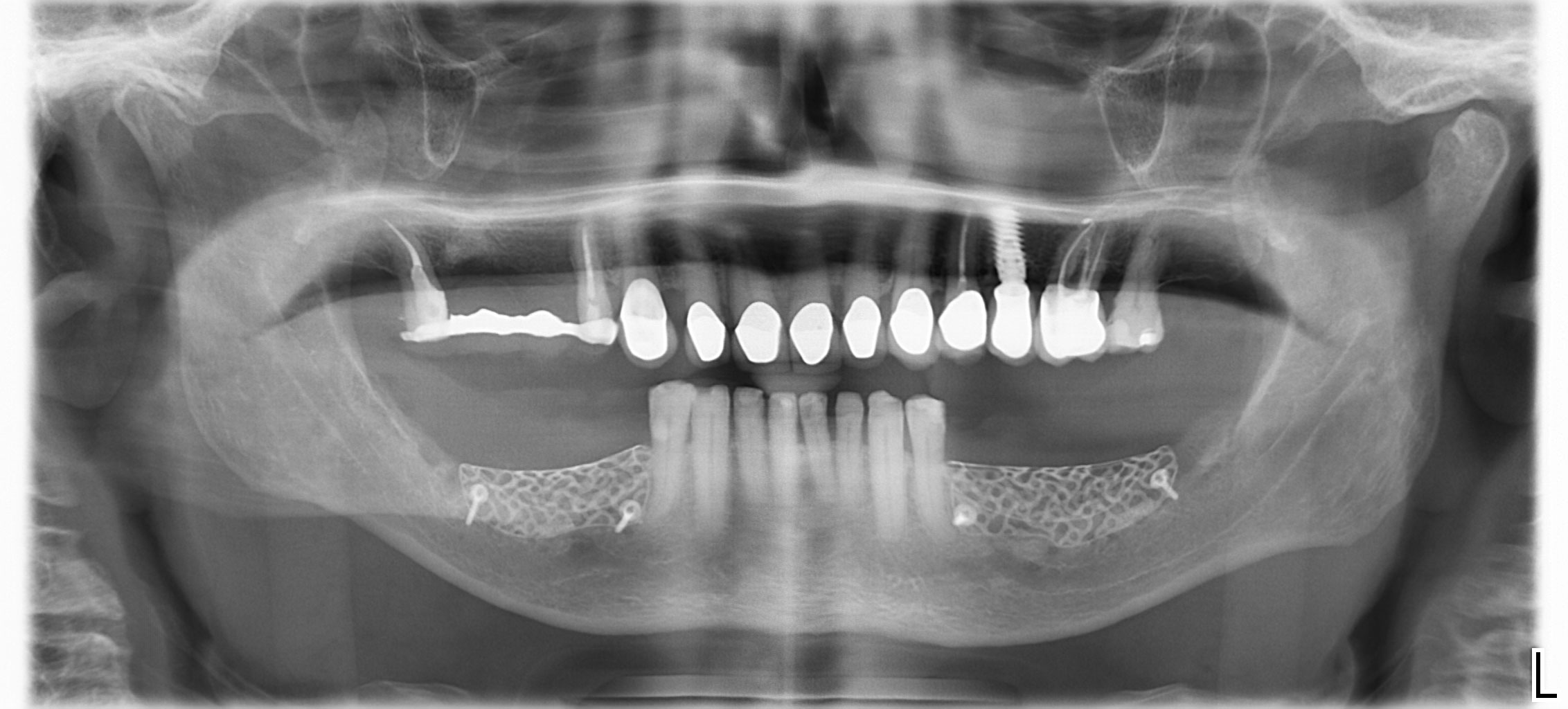
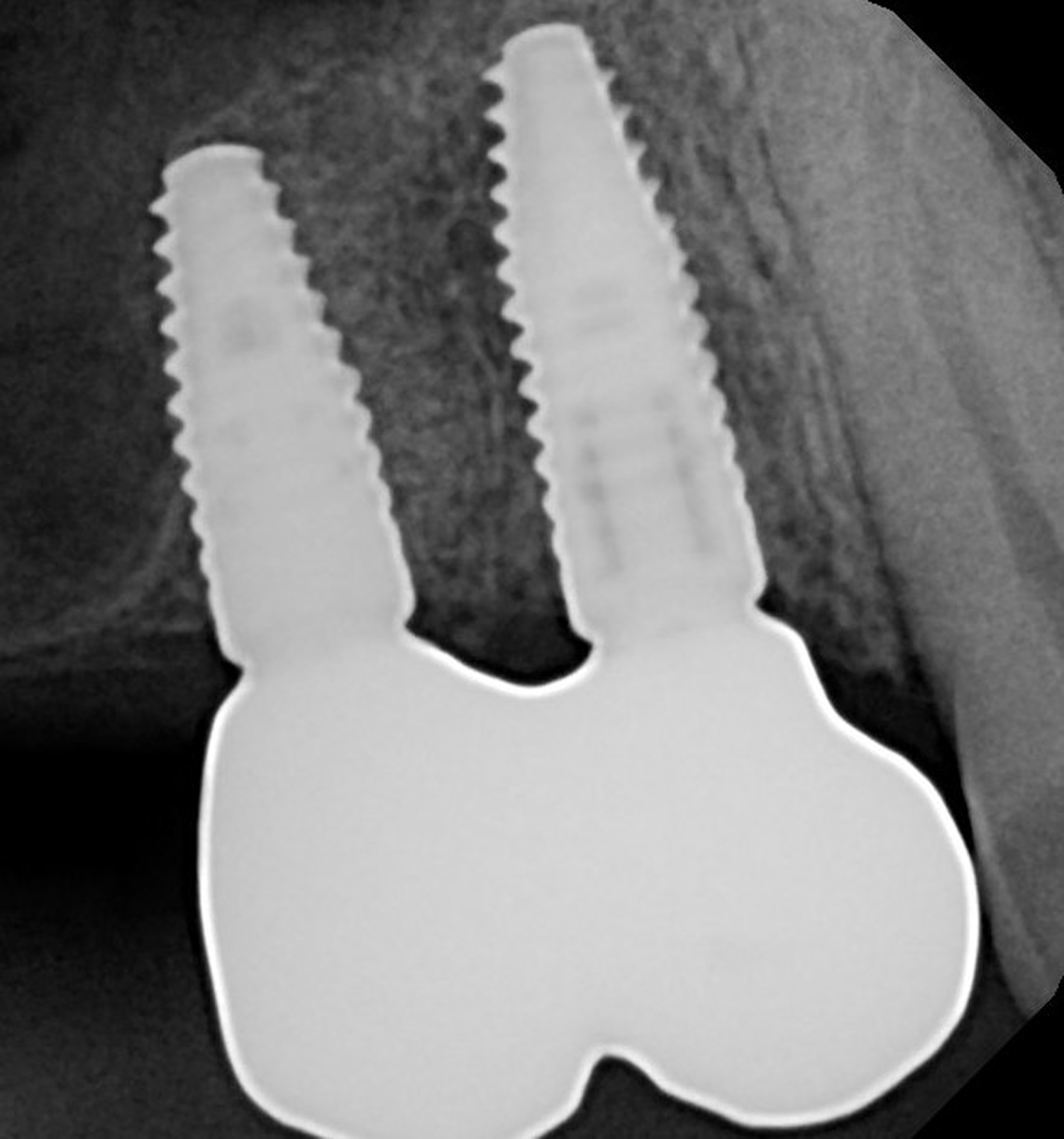
3D Bone Augmentation Using Customized Titanium Mesh in Conjunction with Autogenous Bone and Bovine Bone Material Granules
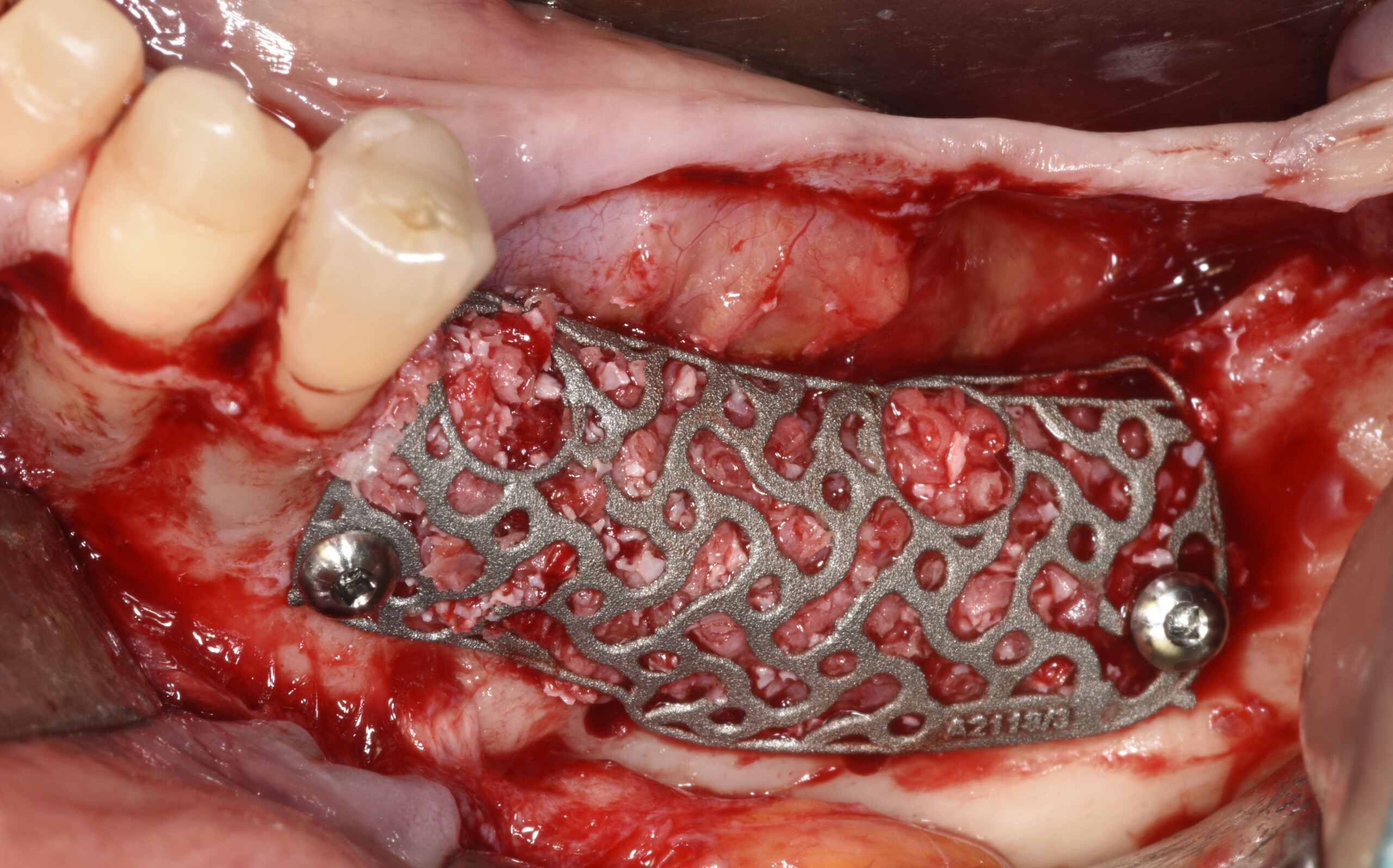


THE SITUATION
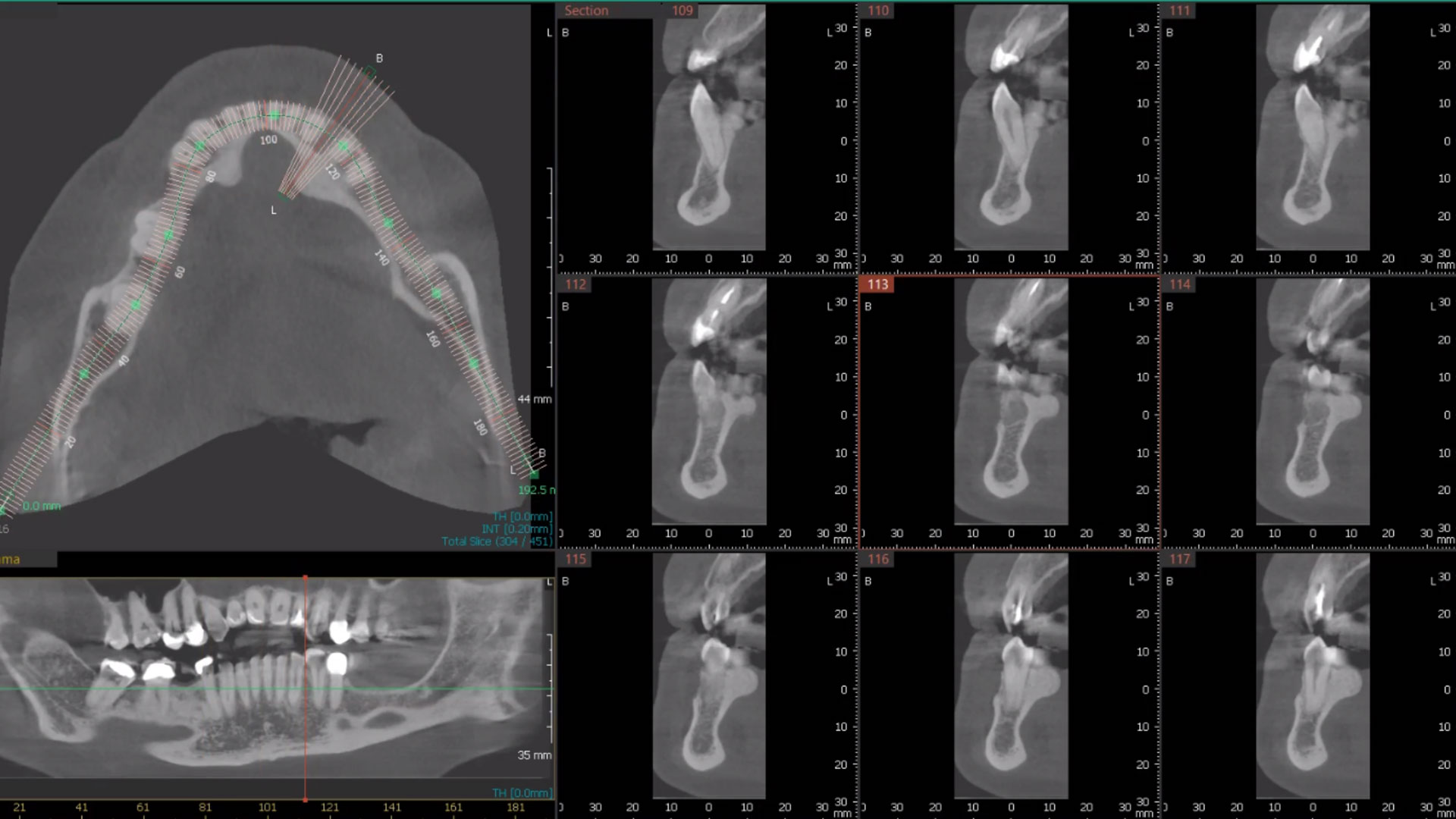
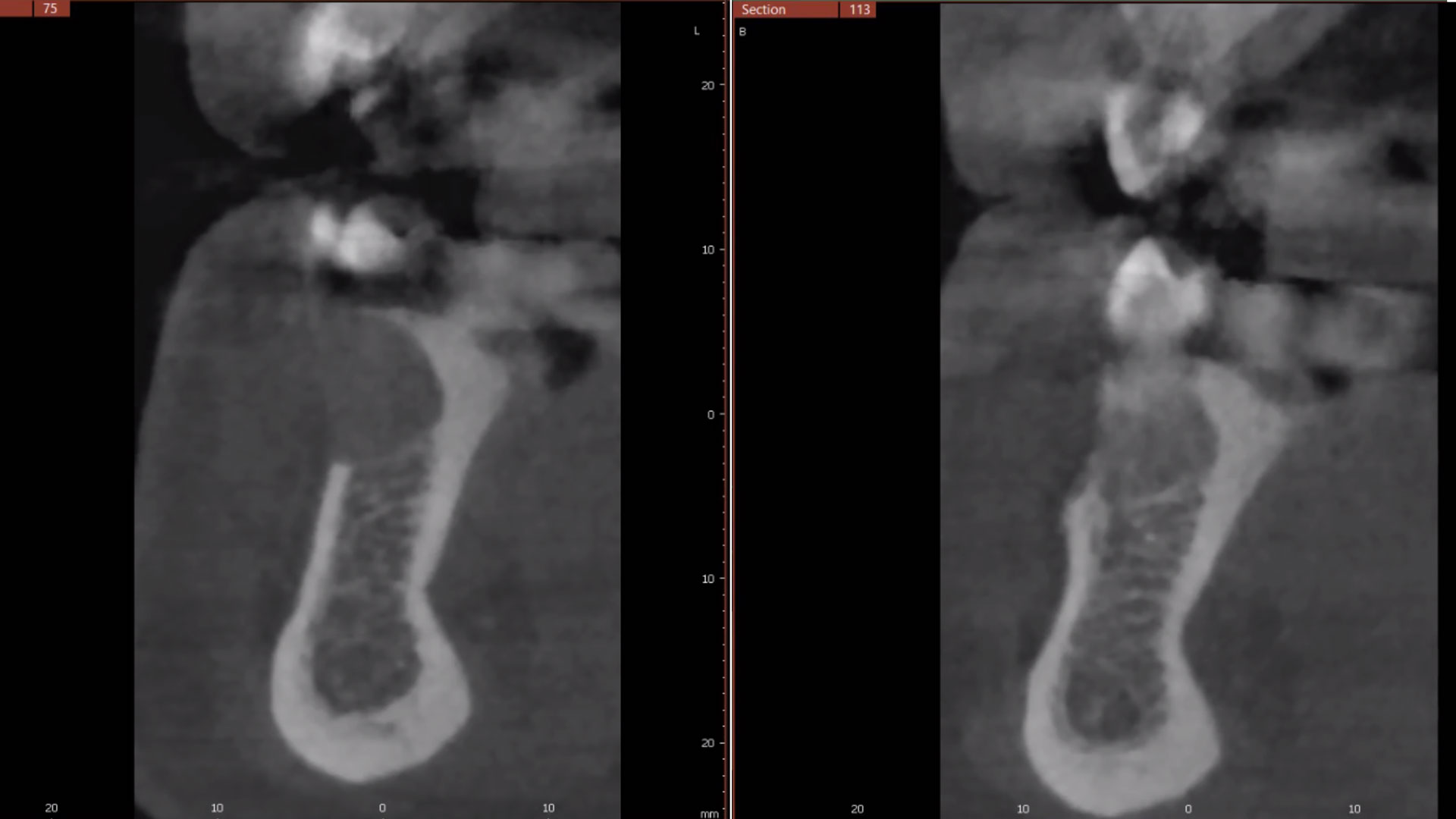
A 75-year-old systemically healthy female came to our attention presenting with absent mandibular second bicuspids and molars and requiring a fixed rehabilitation supported by implants as she refused a removable solution. The clinical and radiographic evaluation showed a relevant vertical and horizontal bone atrophy of such an extent that short or narrow implants were not considered a reliable option. The patient smoked <10 cigarettes per day.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
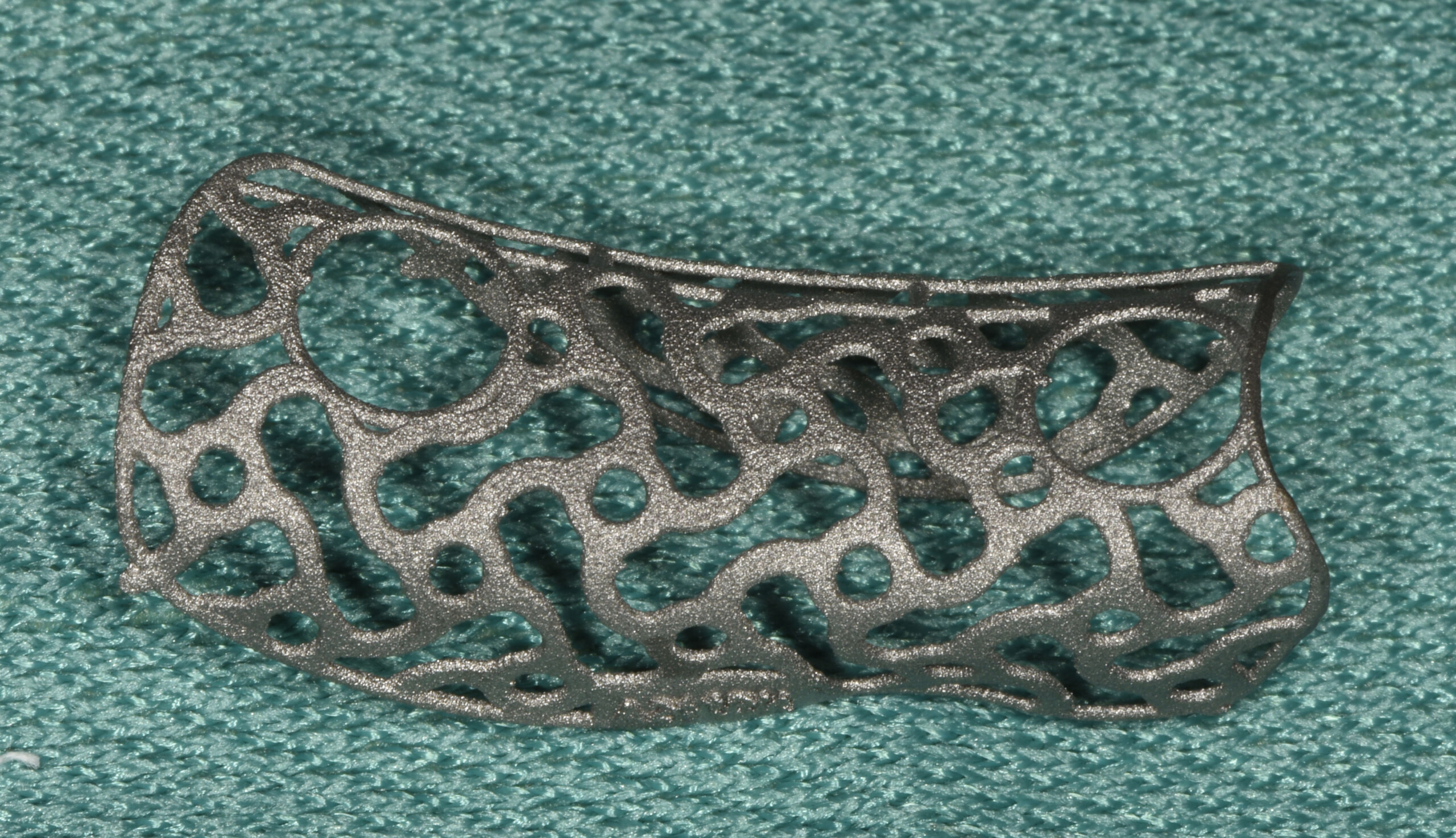
The main goal was to obtain a horizontal and vertical reconstruction of the deficient alveolar bone in order to allow safe and prosthetically-guided implant placement. Reconstruction was obtained by means of a customized titanium mesh, Yxoss CBR®, in combination with a mixture of autologous bone chips harvested from the mandibular ramus and bovine bone mineral, Geistlich Bio-Oss®.
The 3-dimensional reproduction of the left edentulous area permits the production of a precise and customized Ti-mesh.
THE OUTCOME
Post-operative recovery of this patient was uneventful, no complications such as dehiscence or late exposure of the customized mesh, with complete correction of the initial defect. The Yxoss CBR® allowed an easy and faster reconstruction thanks to the precision of the prefabricated mesh filled with autologous chips, Geistlich Bio-Oss® and Geistlich Bio-Gide®.

Matteo Chiapasco, D.D.S., M.D.
Graduated in Medicine and specialized in Maxillofacial Surgery at the University of Milan, Italy. Professor, Unit of Oral Surgery, University of Milan; Associate Professor, Loma Linda University, Los Angeles, California, USA.

Grazia Tommasato, D.D.S., M.S.C.
Graduated in Dentistry in 2013, specialized in Oral Surgery at the University of Milan magna cum laude. PhD student and a medical consultant of the Clinical Unit of Oral Surgery (“G. Vogel” Clinic, Milan).

BIOBRIEF
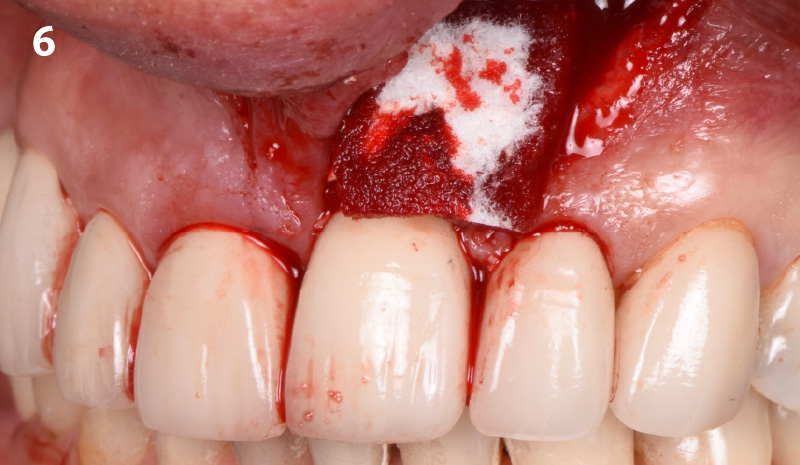
Enhance Periodontal Phenotype with Geistlich Mucograft® for Soft Tissue Augmentation
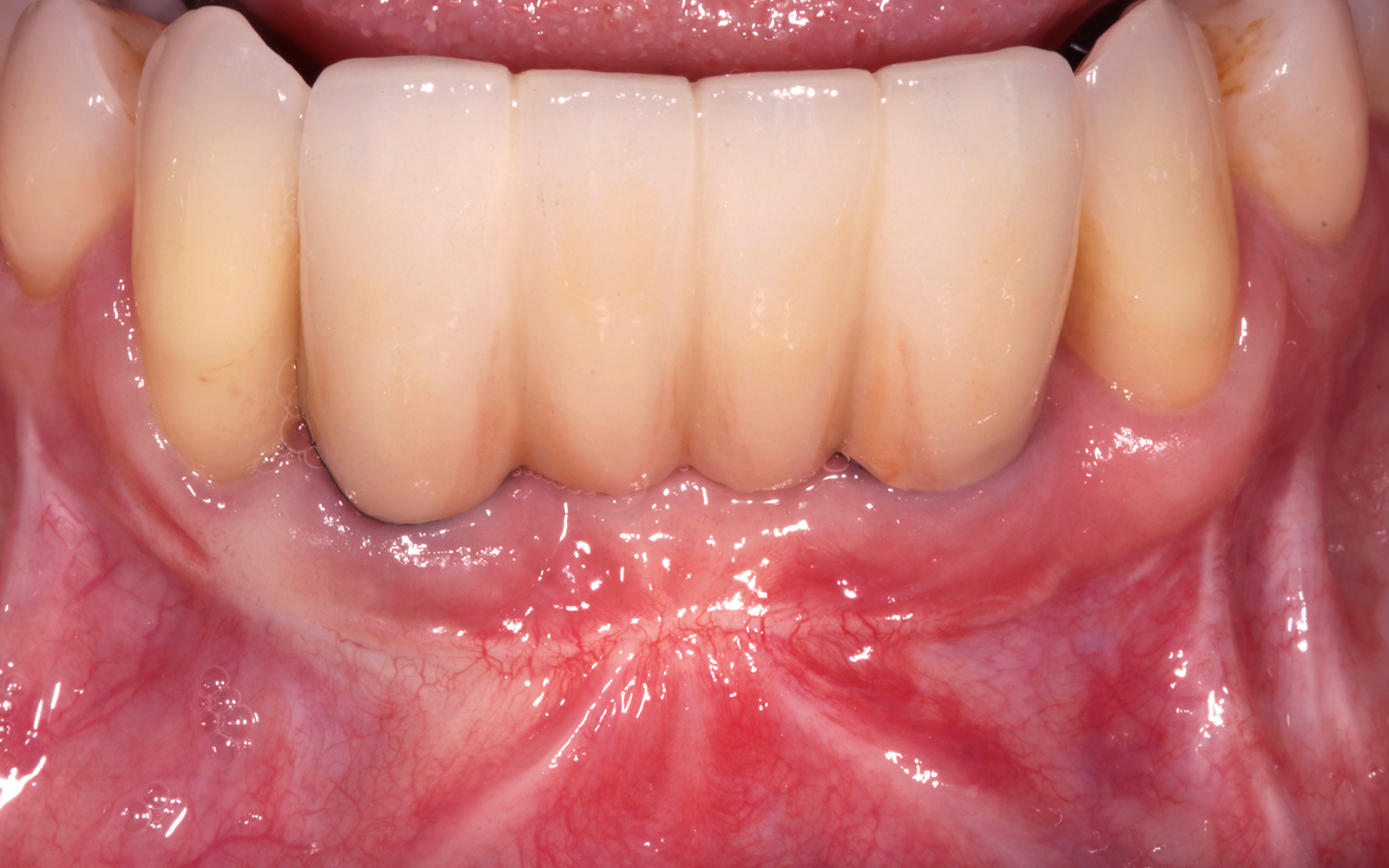

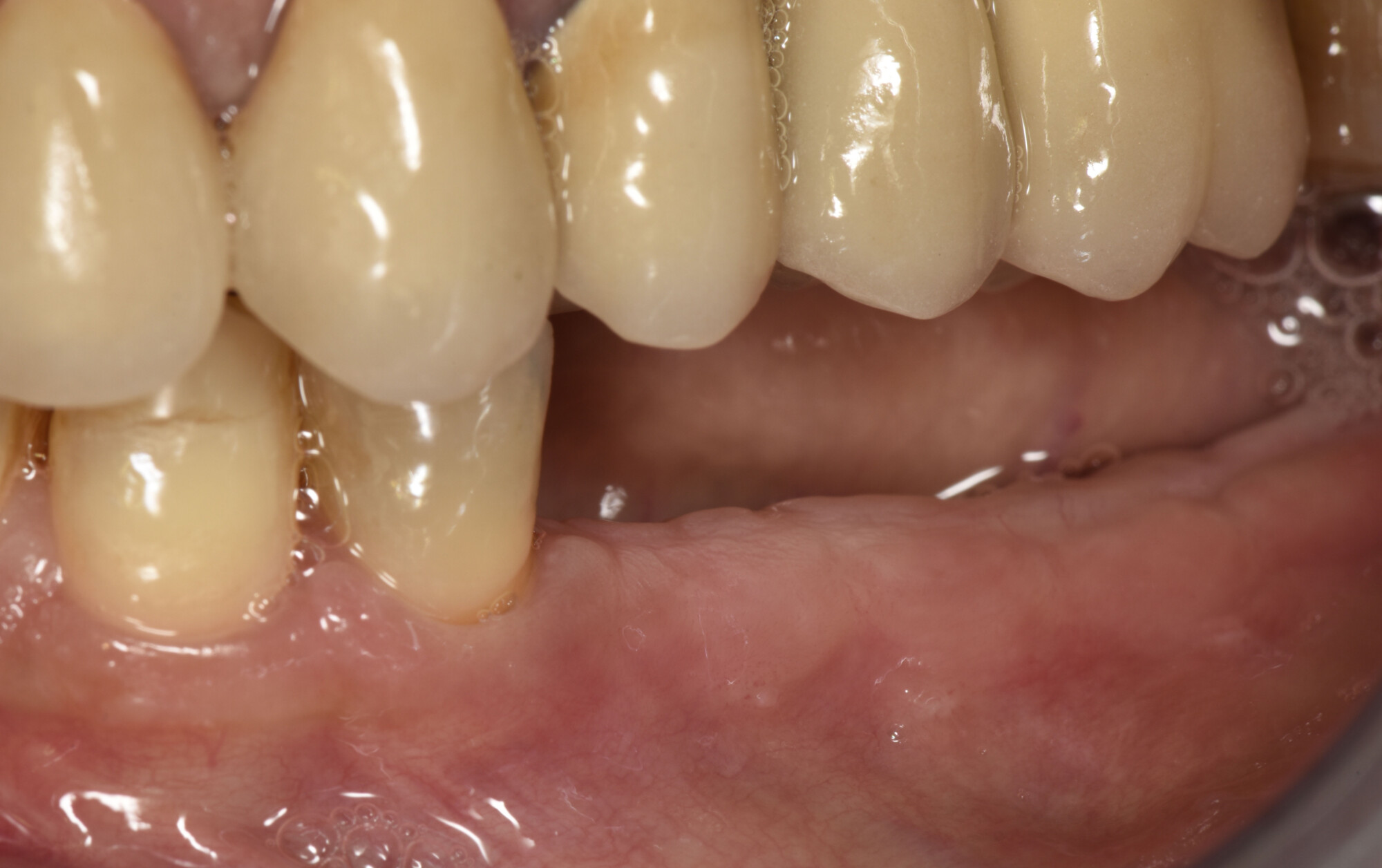
THE SITUATION
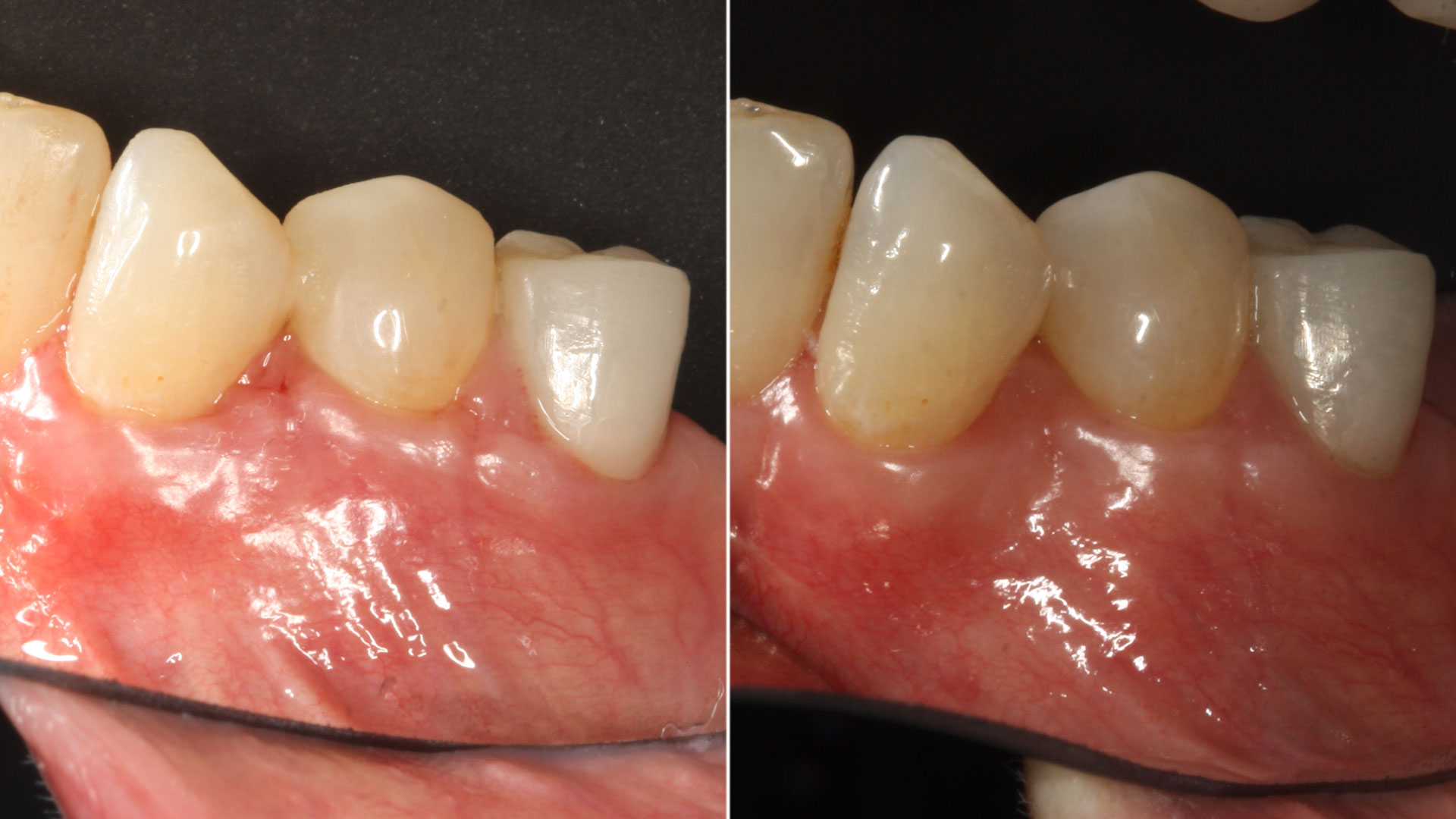
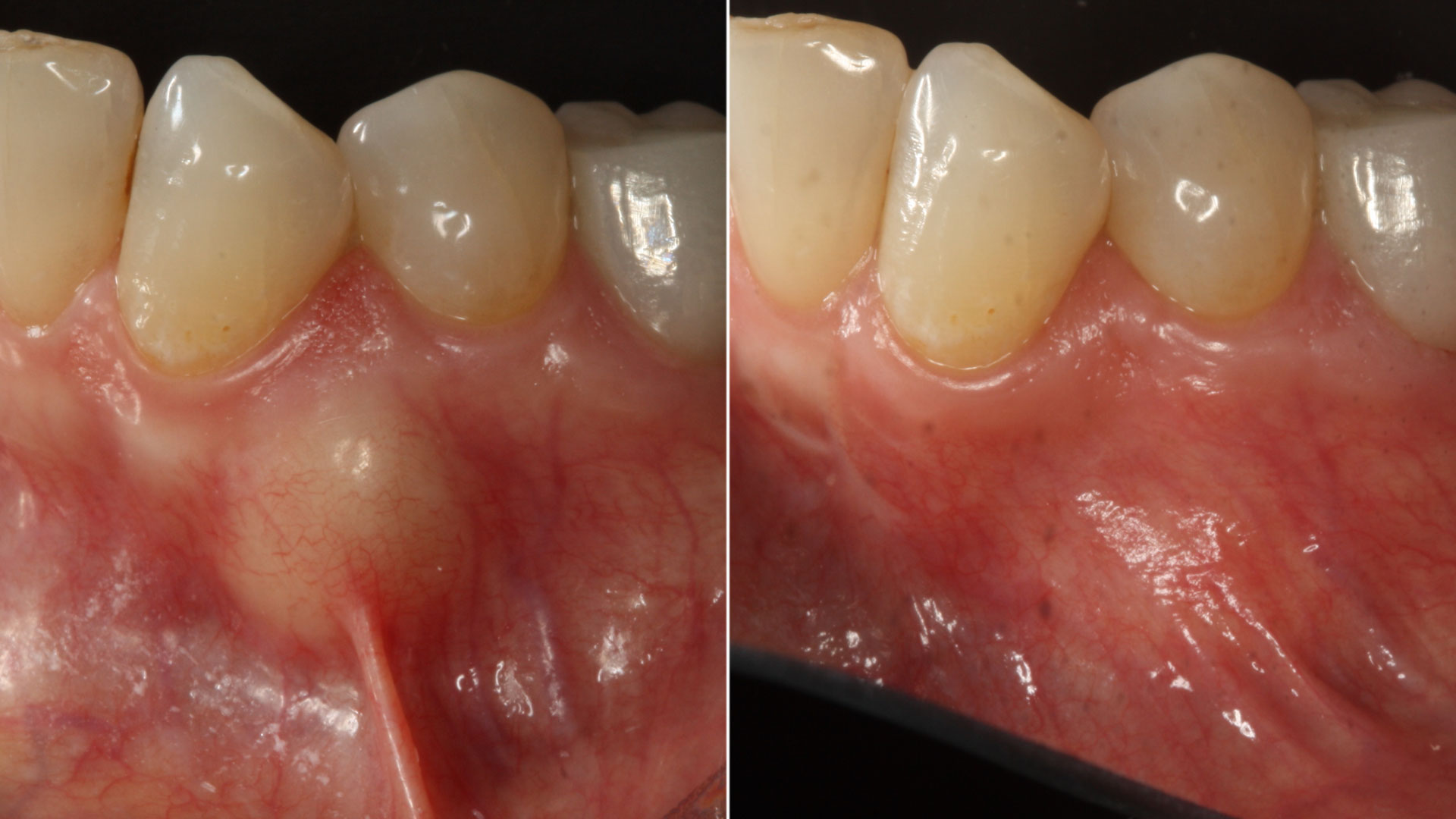
A healthy, non-smoking, 37- year-old female presented for second stage surgery at implant sites #23 and #26. Limited keratinized tissue width and gingival thickness can be appreciated in the edentulous ridge, and the patient can be classified as having a thin periodontal phenotype. Additionally, the patient states she experiences sensitivity, and the tissue feels “tender” when brushing. The patient hopes to address her needs in a minimally invasive manner.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system Non-smoker | Light smoker | Impaired immune system Heavy smoker |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
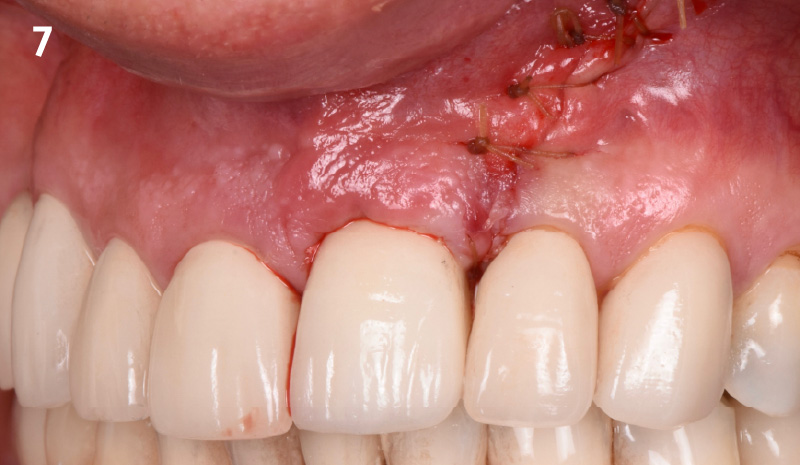
The aim of treatment was to enhance the existing periodontal phenotype from that of one which is thin, with limited keratinized tissue, to one that is thick and maintains an adequate band of attached keratinized tissue. Geistlich Mucograft® was used in conjunction with a PRF membrane, in order to provide optimal wound healing, due to its chemotactic and angiogenic properties.
A viable option that allows for reduced patient morbidity, adequate functional necessity, and ideal esthetics.
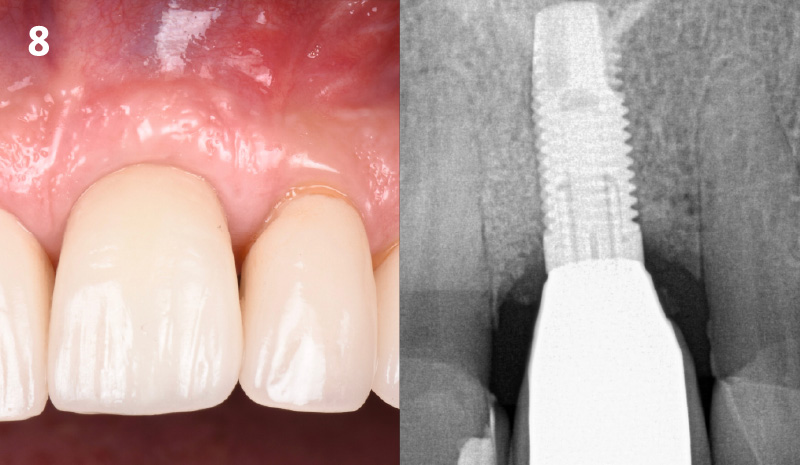
THE OUTCOME
Dual application of platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) and a xenogenic collagen matrix, Geistlich Mucograft®, led to successful augmentation of the edentulous ridge. At one-year, the tissues appear healthy, and an increased keratinized tissue width and gingival thickness can be appreciated. By using this soft tissue alternative, the patient was able to avoid post-operative morbidity from a second surgical site, and the chief complaint was addressed.


Allison Rascon, D.D.S., M.S.
Dr. Allison Rascon was born and raised in Miami, Florida. She received her Bachelor of Science in Biomedical and Health Sciences from the University of Central Florida. She received her DDS from New York University, where she graduated with honors in Periodontics and was inducted into the Omicron Kappa Upsilon National Dental Honor Society in 2020. She then went on to receive a Certificate in Periodontics and Master of Science in Oral Biology from the University of Pennsylvania. Currently, she is board-eligible by the American Academy of Periodontology. She is an active member of the AAP, AO, OF, and ADA. Aside from her active participation in organized dentistry, she is also passionate about her research in periodontal and peri-implant regeneration. Dr. Rascon was a recipient of the George J. Coslet Memorial Scholarship in 2021 and 2022. During her residency, she was awarded the Best Oral Clinical Presentation Award at the Academy of Osseointegration Annual Meeting in 2022 and was the recipient of the Northeastern Society of Periodontists Tannenbaum/ Schoor Resident School Competition Award for 2023. Currently, Dr. Rascon works in private practice in Manhattan, NY.

BIOBRIEF
Clinical Efficacy of Geistlich Mucograft® in Regeneration of Oral Mucosa Combined with the Surgical Treatment of Peri-implantitis in Implants with Lack of Keratinized Tissue
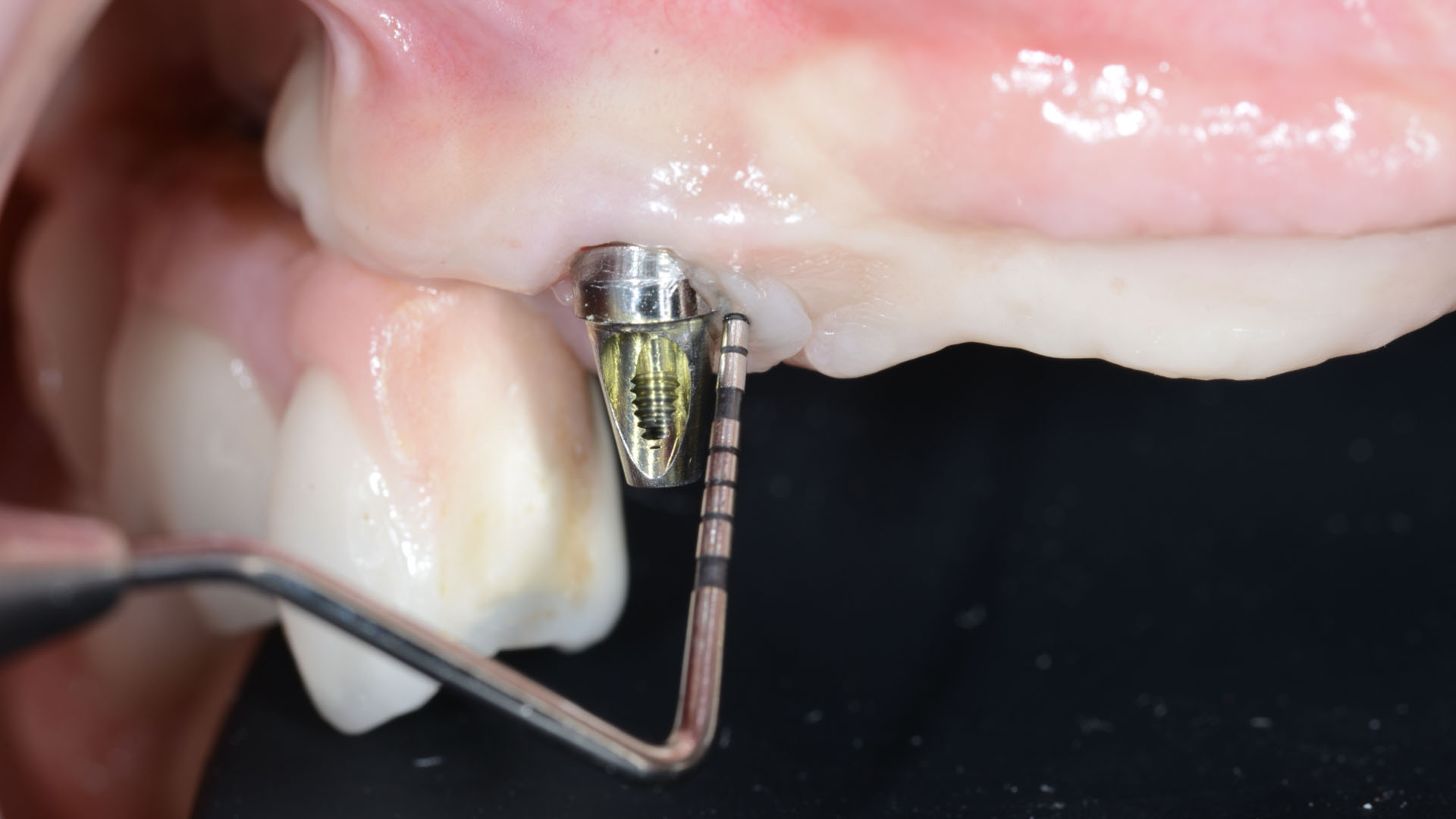


THE SITUATION
Adult patient, non-smoker and without relevant systemic history, attends to clinic referring peri-implant tissue inflammation, bleeding and brushing discomfort around her implant in the upper jaw. Clinically peri-implant pocket depth > 5 mm, bleeding and suppuration on probing were observed. Furthermore, the implant presented < 2 mm of keratinized mucosa and radiographic horizontal bone loss.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system Non-smoker | Light smoker | Impaired immune system Heavy smoker |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
Intrasulcular incision was made and a mucosal partial thickness flap was raised. The recipient site was prepared by sharp disection in order to create a periosteal bed free of any muscle attachment. Peri-implant granulation tissue was removed and implantoplasty was performed. Finally, Geistlich Mucograft® was used to support the gain of keratinized tissue. Thus, the collagen matrix was sutured with the resulting flap apically at the base of the newly created vestibulum.
Absence of > 2 mm of keratinized mucosa was associated with peri-implant soft-tissue inflammation, bleeding and discomfort on brushing.
THE OUTCOME
After two years follow-up, the successful outcome can be observed in terms of clinical peri-implant parameters, gain of keratinized mucosa without significant graft shrinkage and stability of vertical position of the mucosal margin.
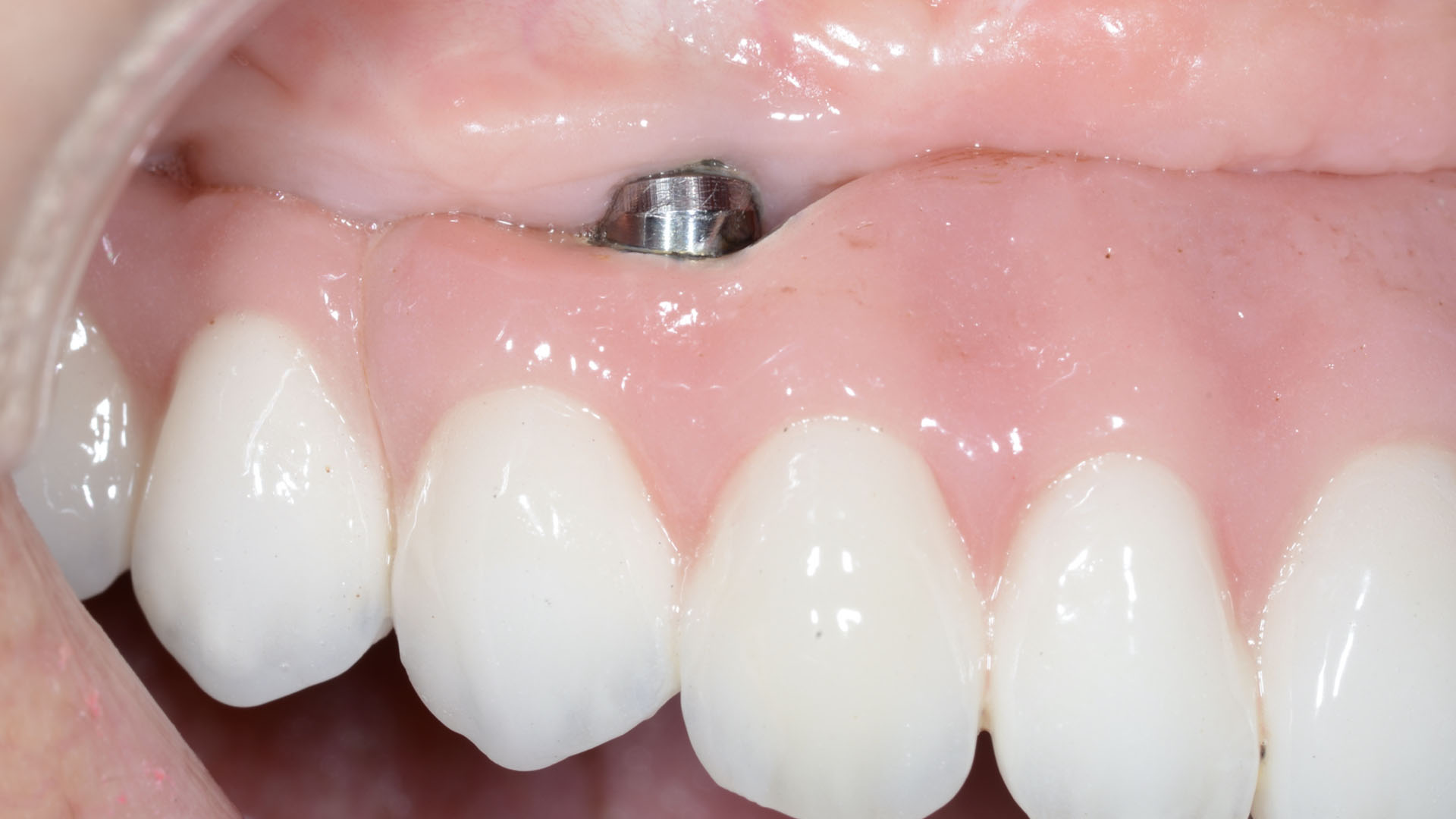

Dr. Alberto Ortiz-Vigón
- DDS from the University of the Basque Country
- MSc and PhD in bone regeneration from the University Complutense of Madrid (UCM)
- Master in Periodontology and Implant dentistry from the EFP
- Research fellowship at the University of Gothenburg
- MBA from the Deusto Business School
- Assistant professor and clinical researcher at UCM and ThinkingPerio Research
- PerioCentrum Clinic in Bilbao
- Co-founder of ARC Healthtech Innovation Holding
- Socially engaged & NGO co-founder of Smile is a Foundation

Dr. Erik Regidor Correa
- DDS from the University of the Basque Country
- MSc from the U. of the Basque Country
- Master in Periodontology and Implant Dentistry U. of the Basque Country
- PhD student in the U. of the Basque Country
- Assistant professor and clinical researcher ThinkingPerio Research

VIDEO