New Product! Buy 5 Geistlich Bio-Gide® Forte, Get 1 Free! Use code FORTE. Check it out!
Treatment Solution: GBR Procedure

BIOBRIEF
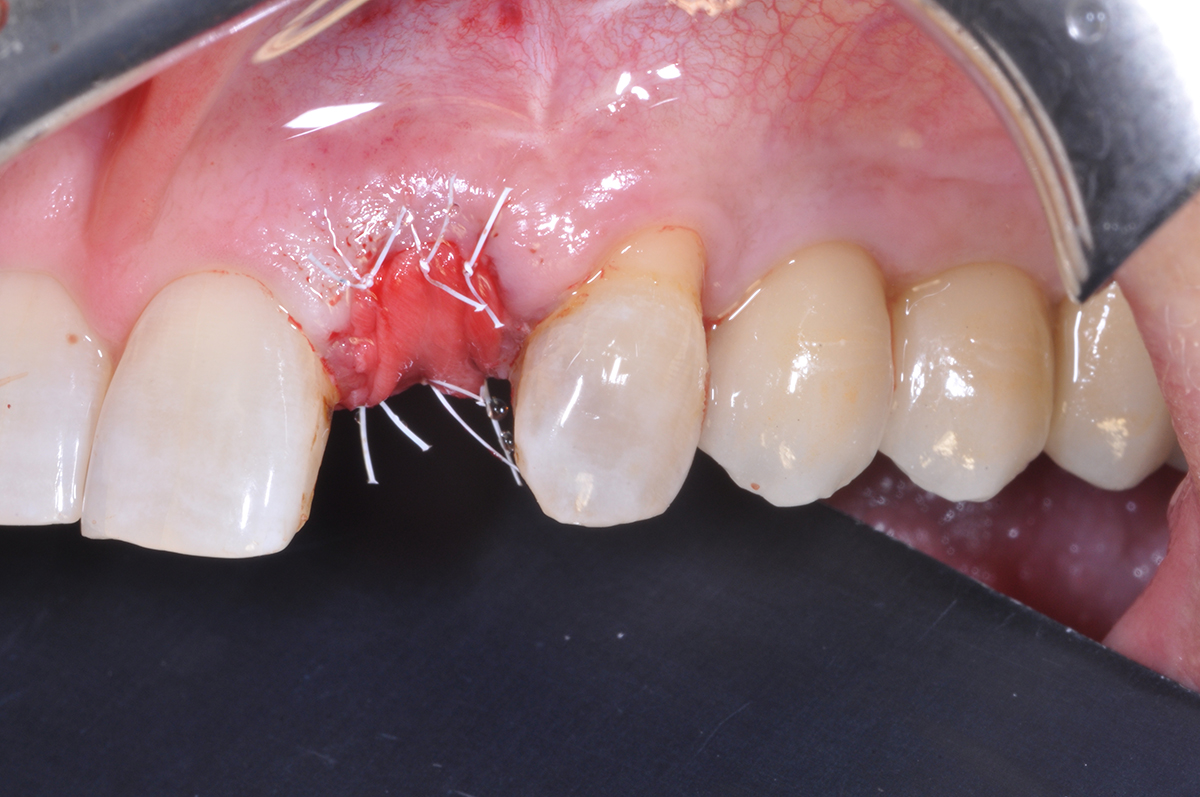
Bone Grafting and Immediate Implant Placement in the Maxillary First Molar Region


THE SITUATION
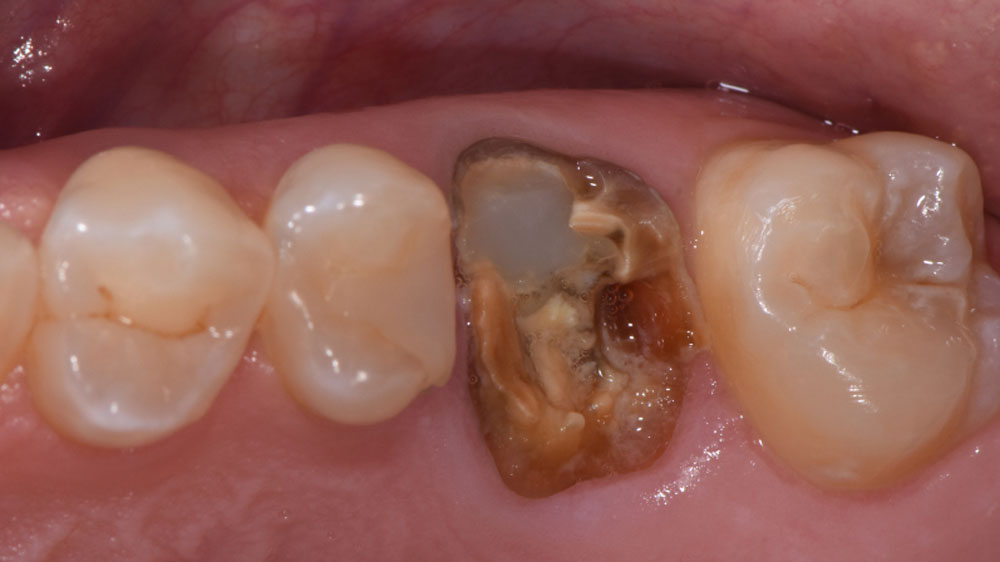
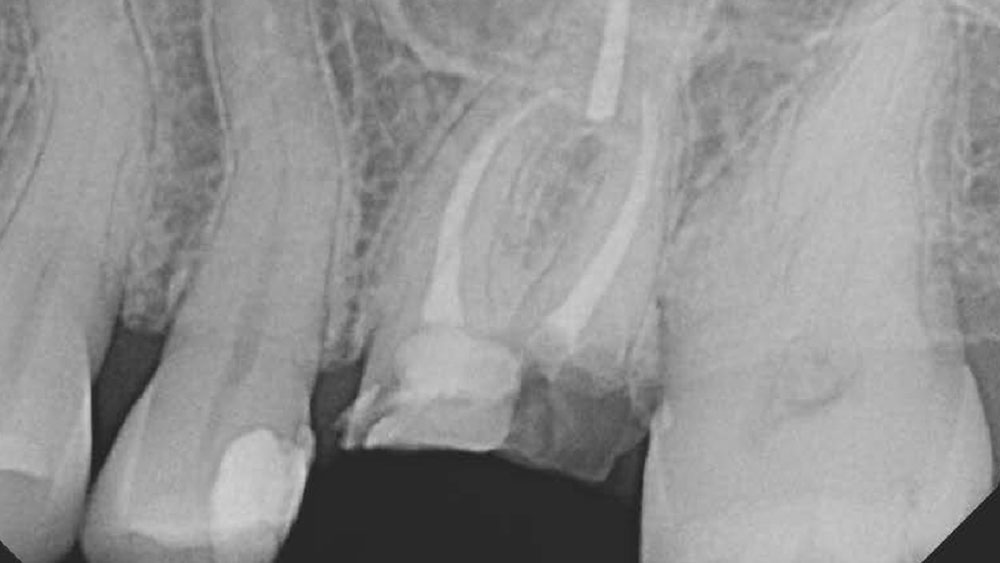
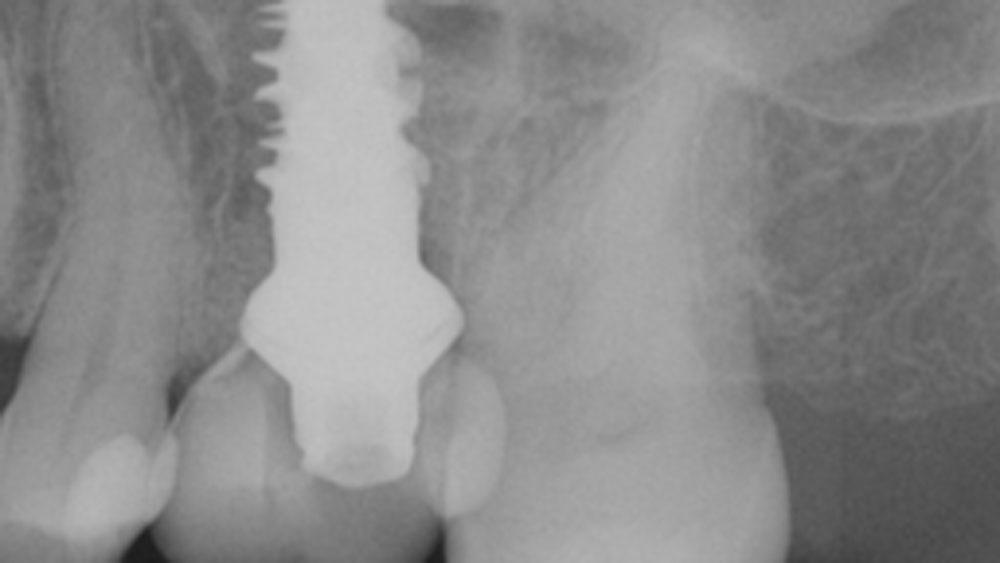
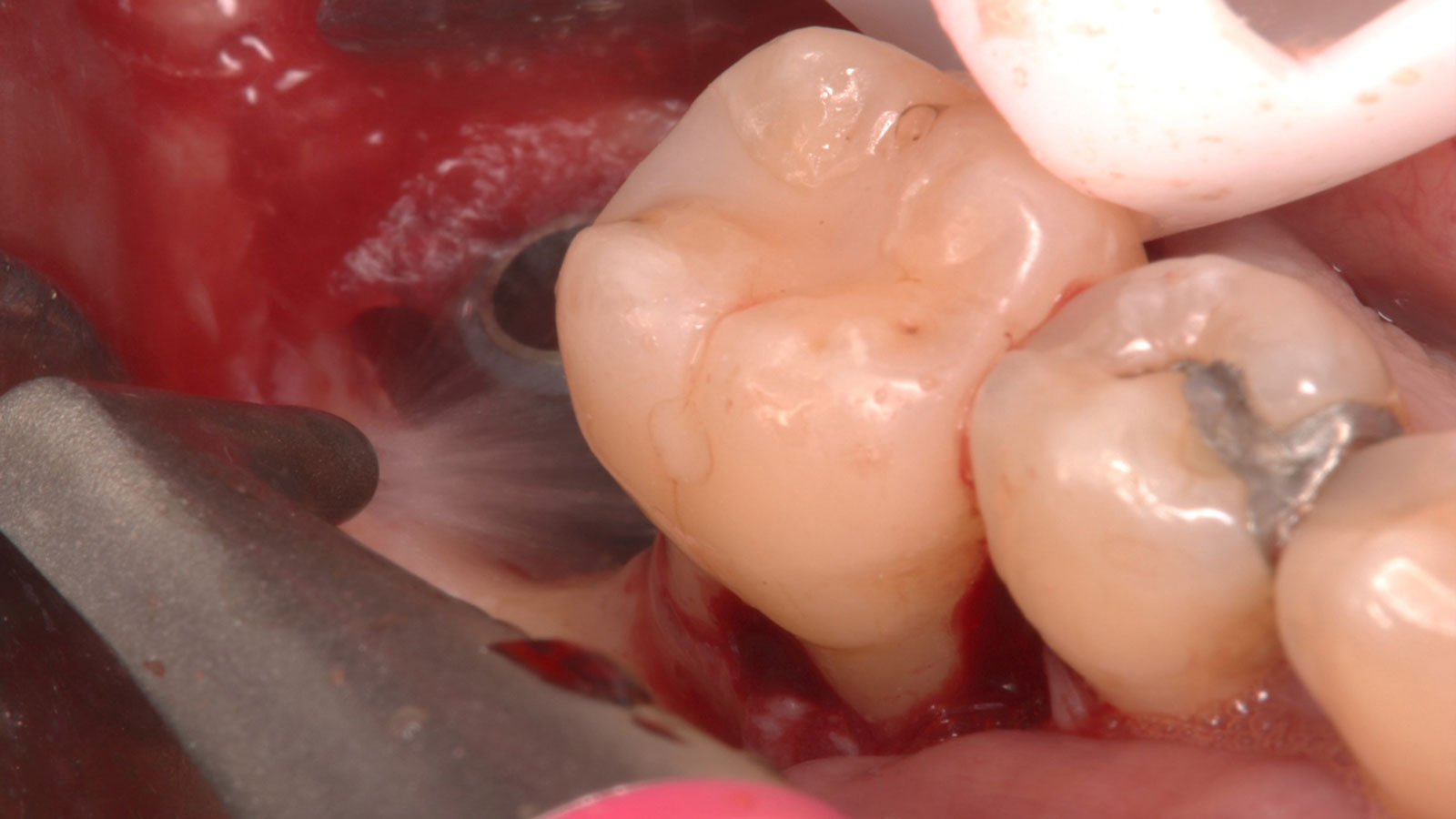
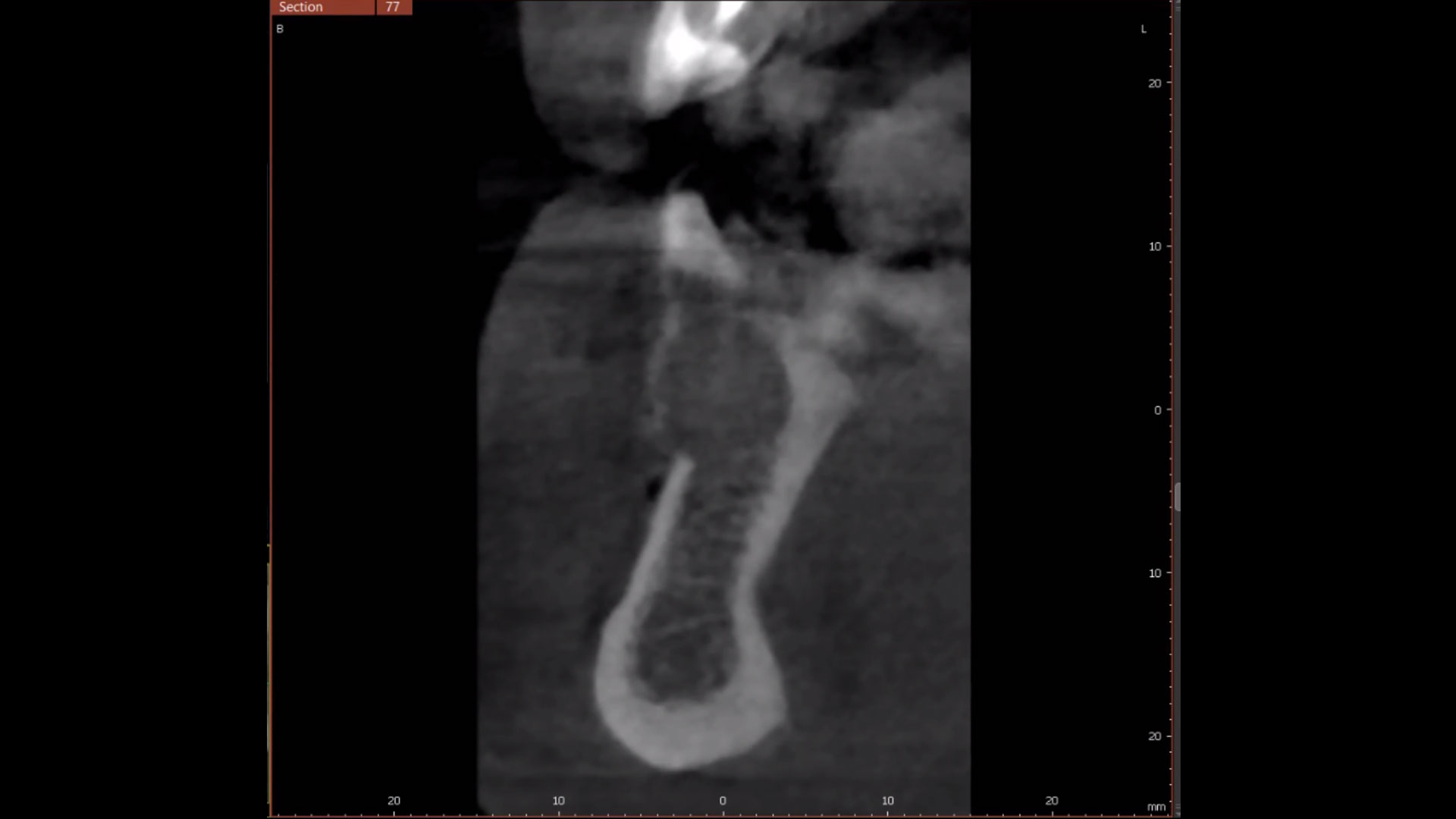
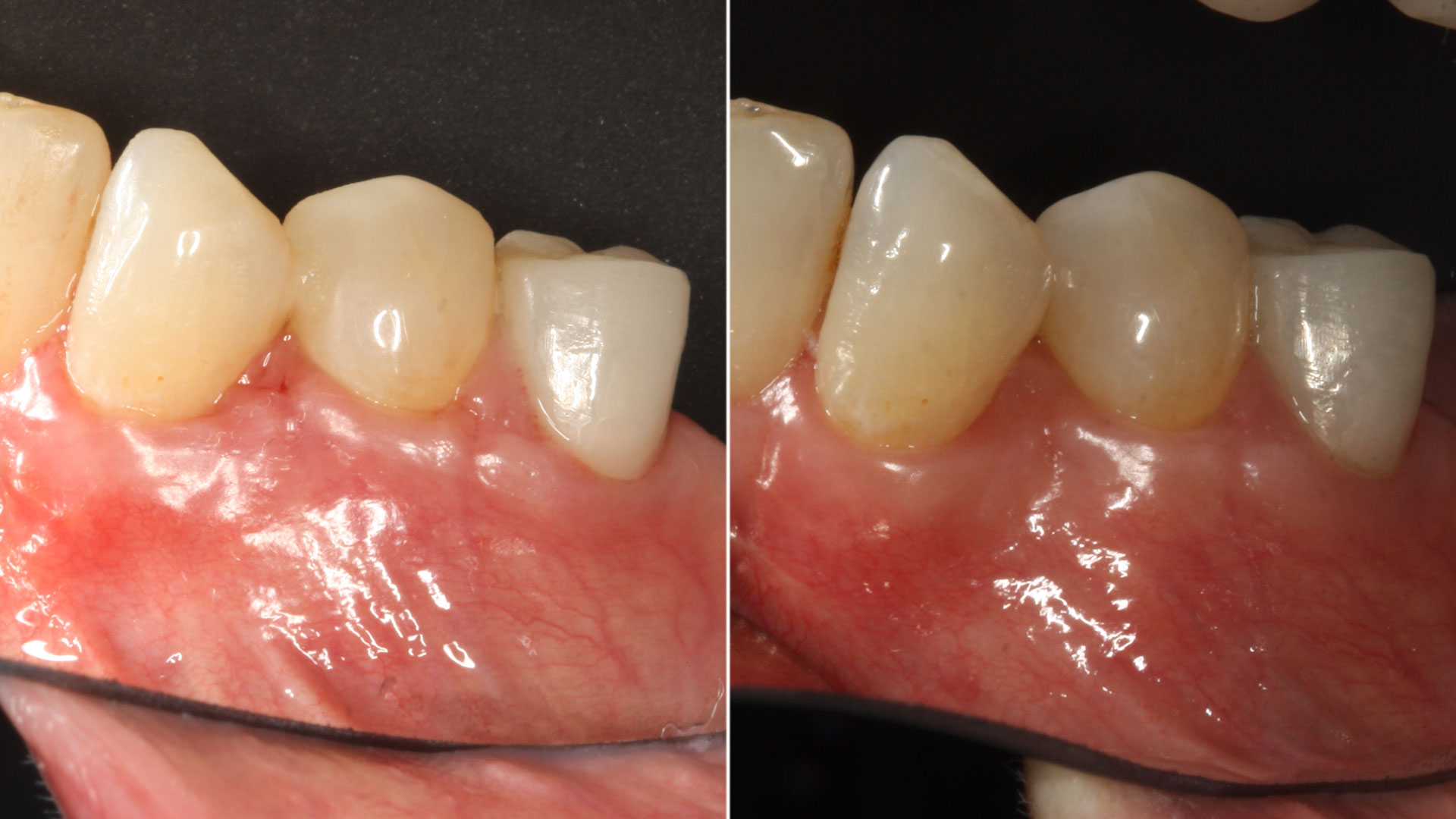
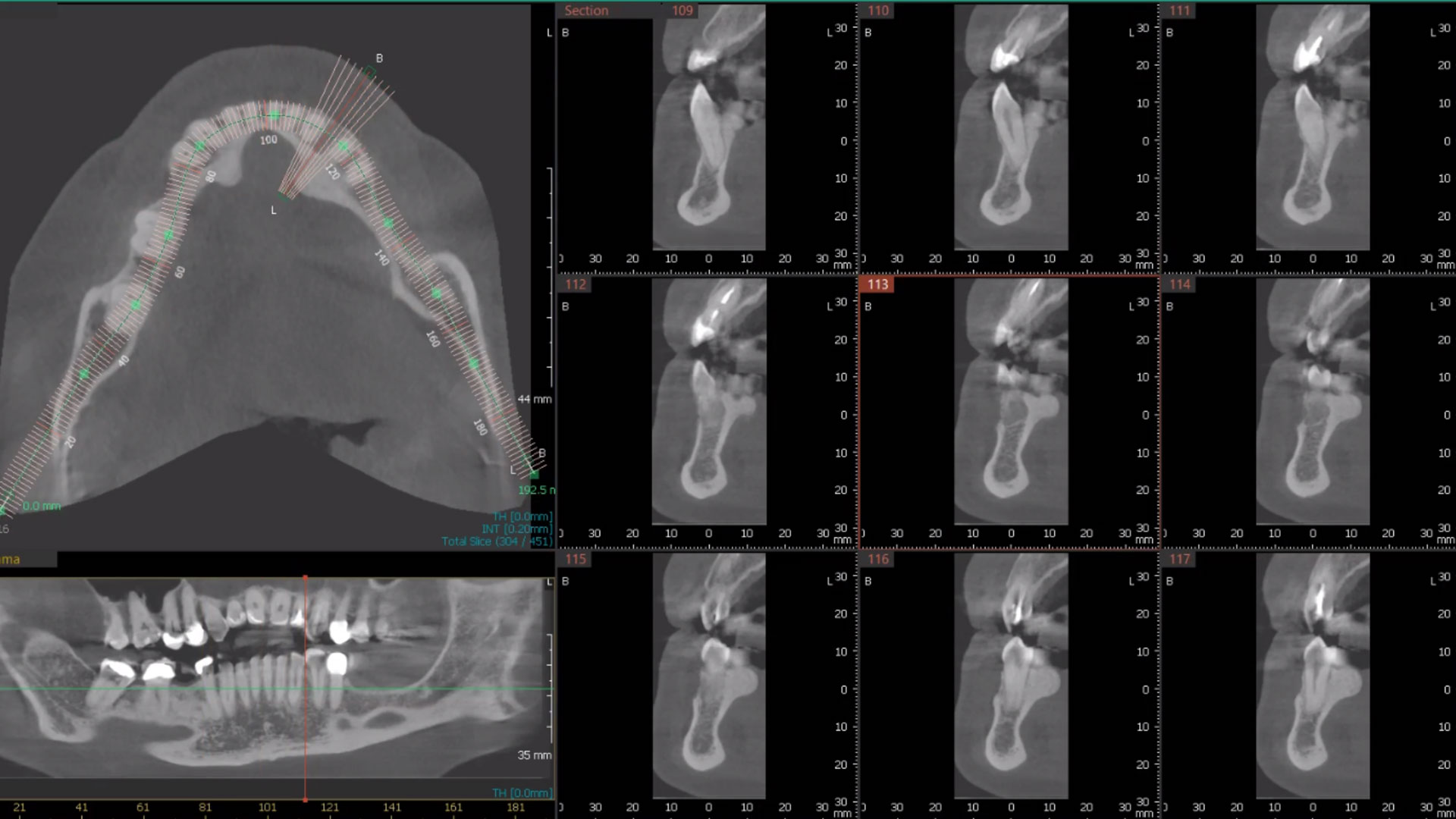
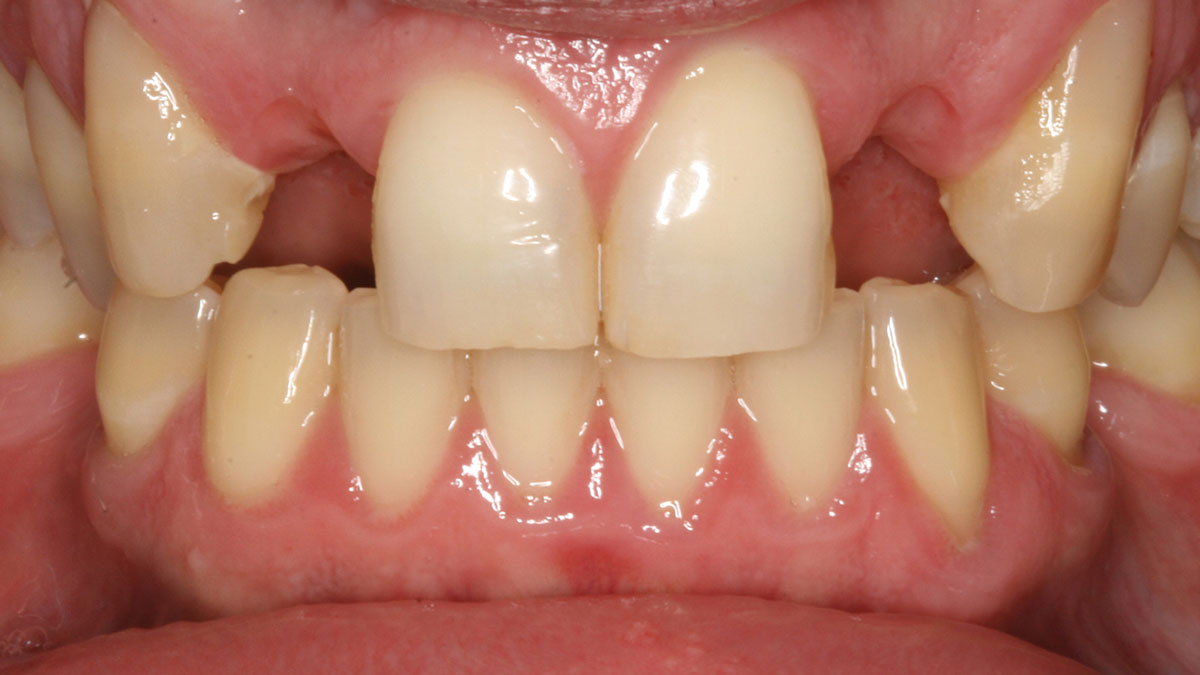
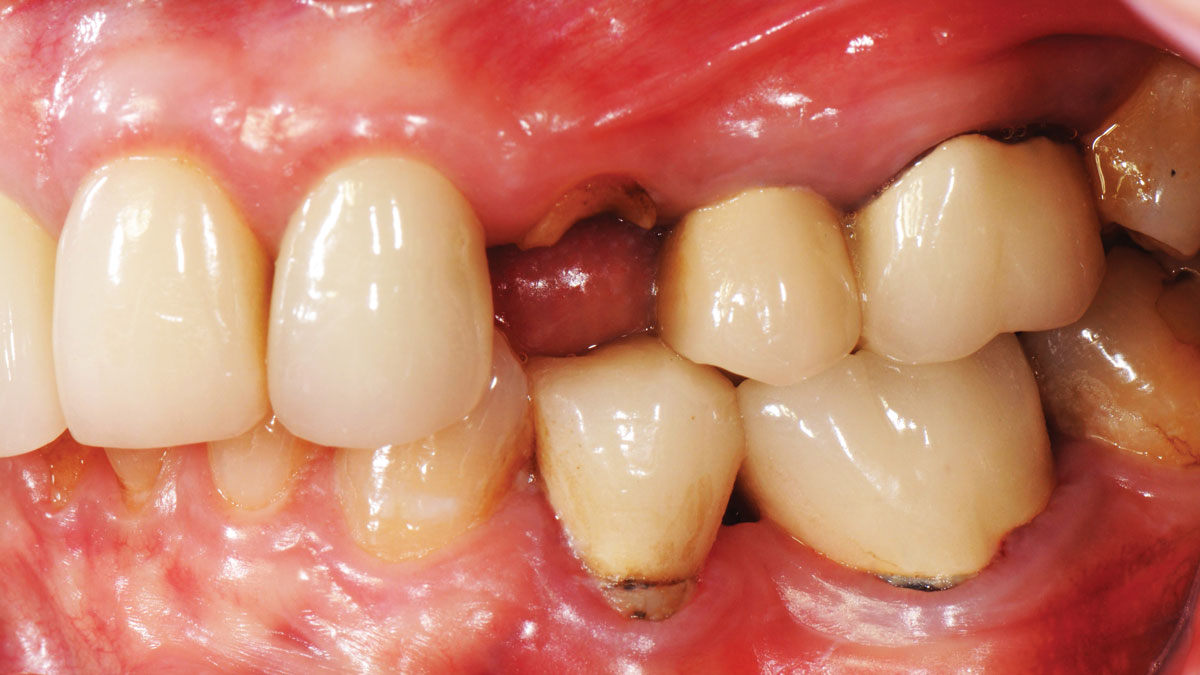
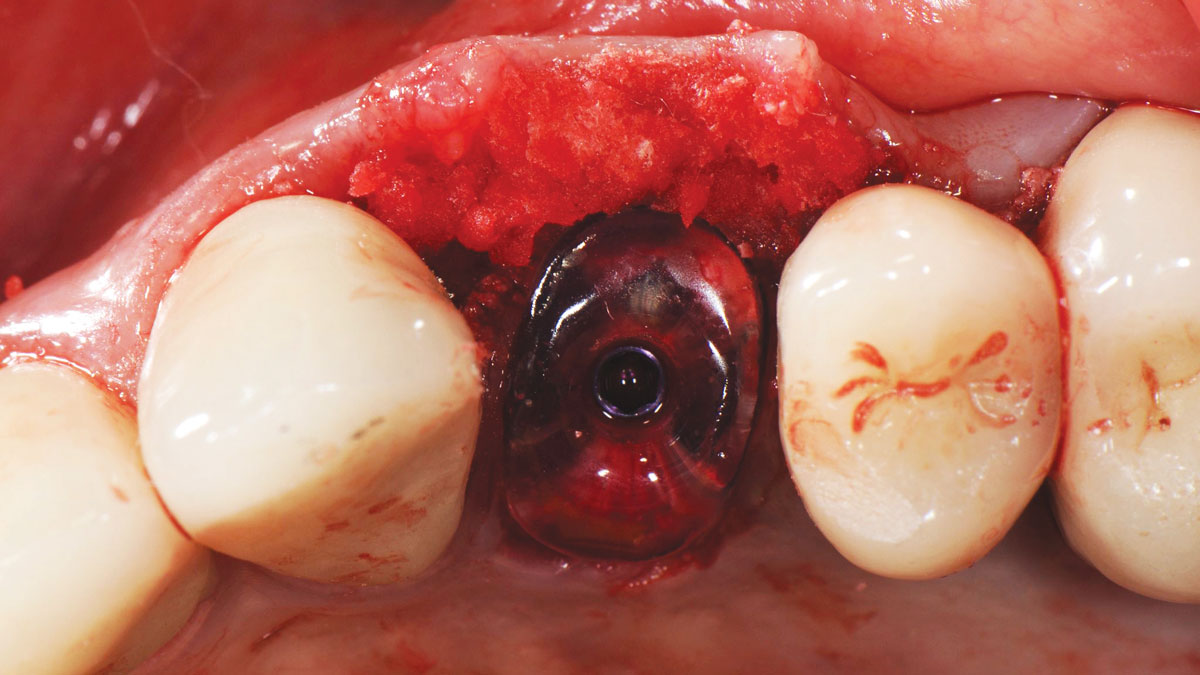
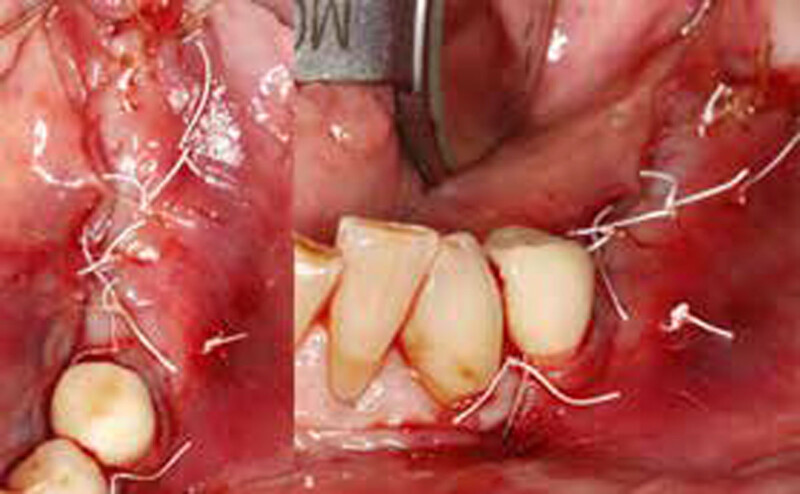
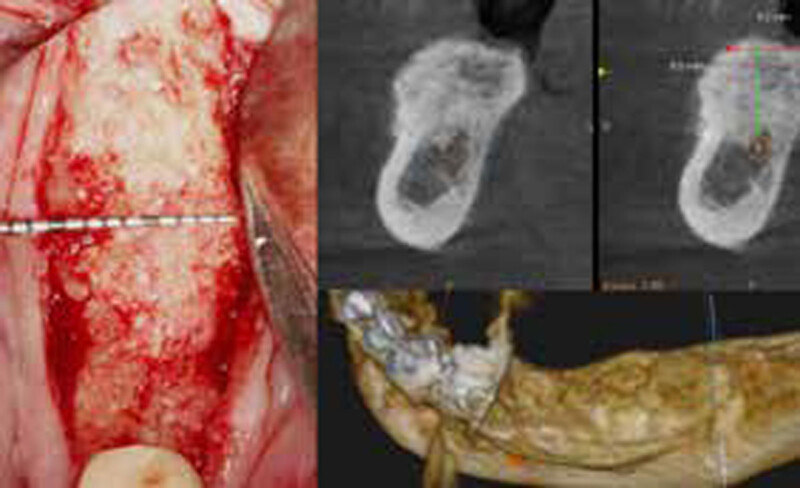
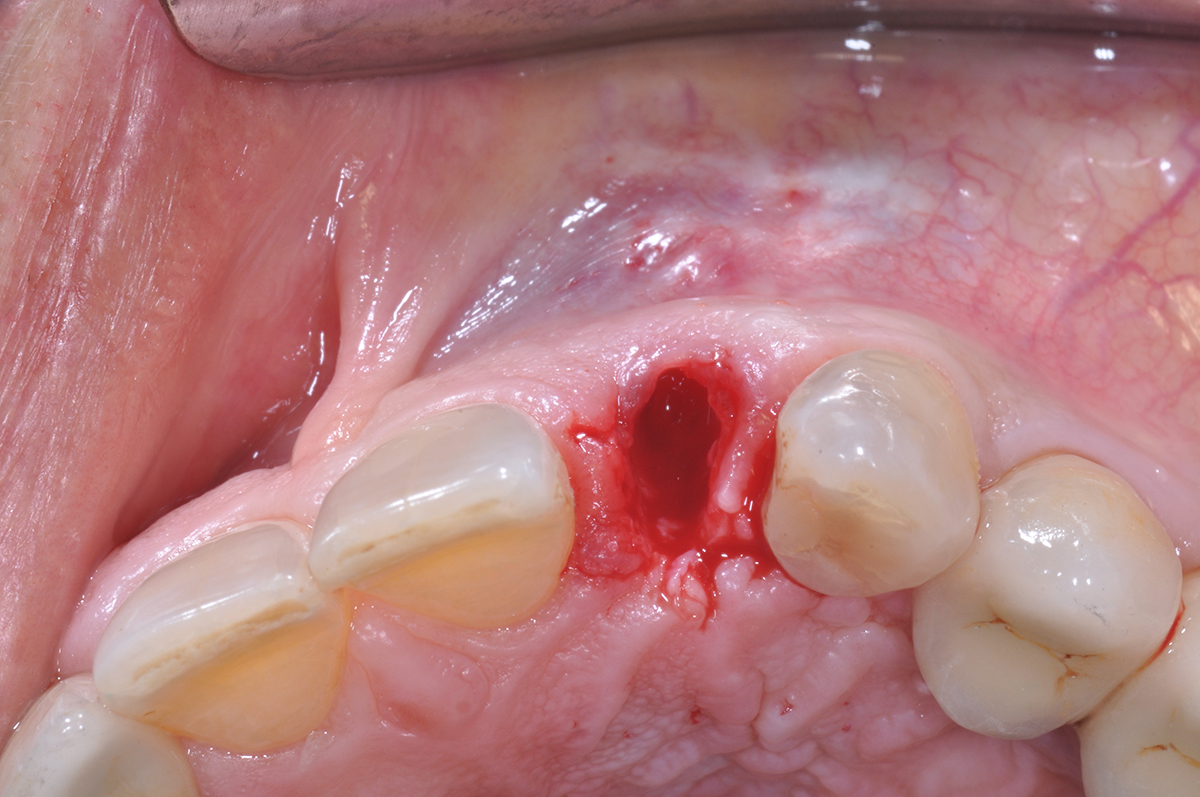
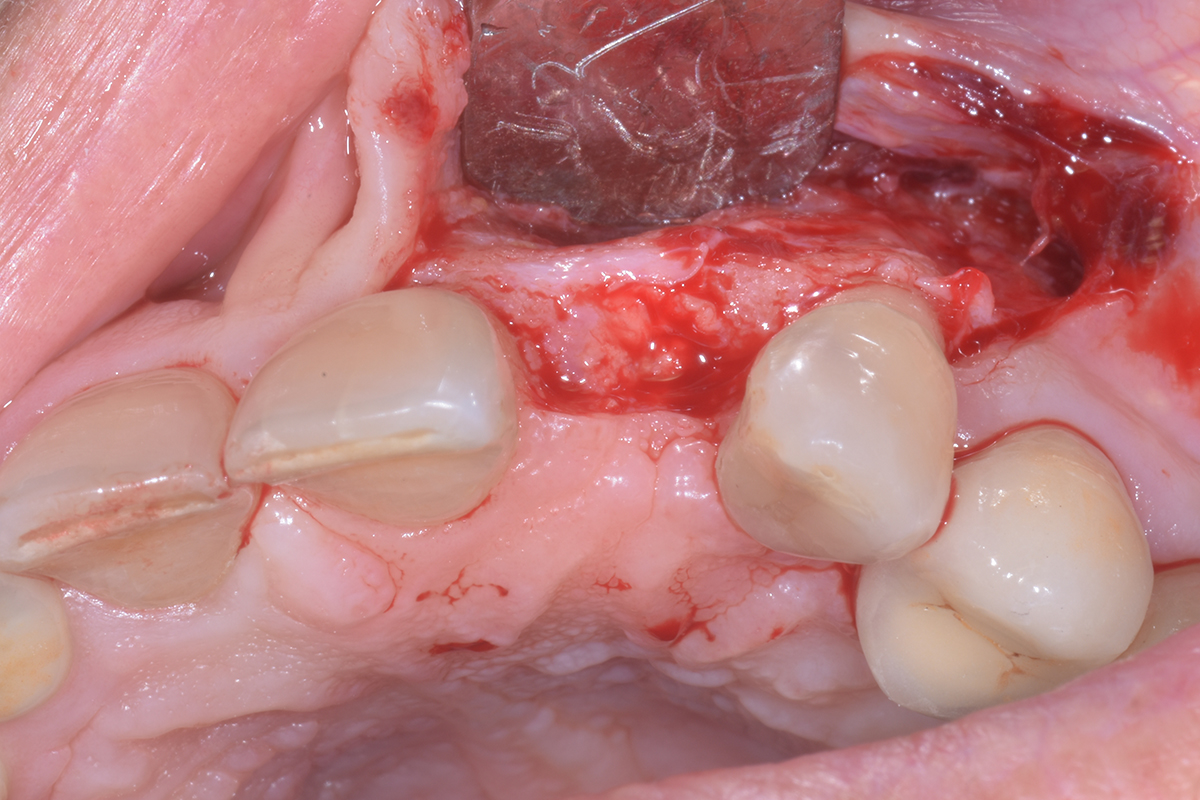
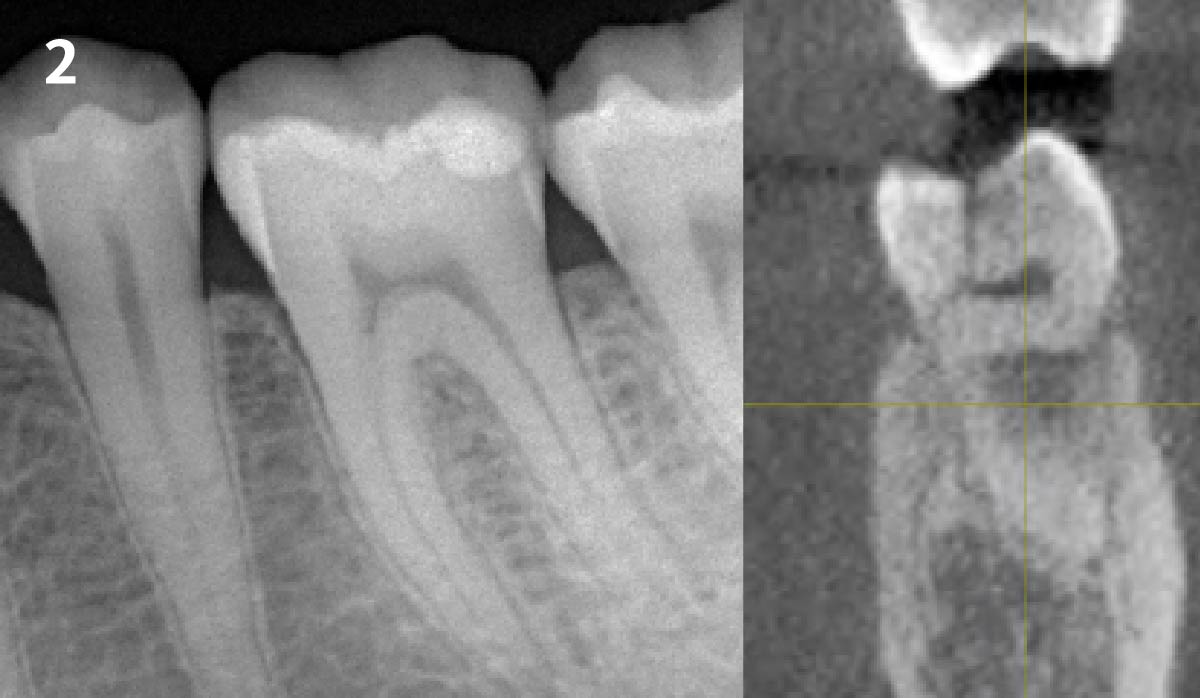
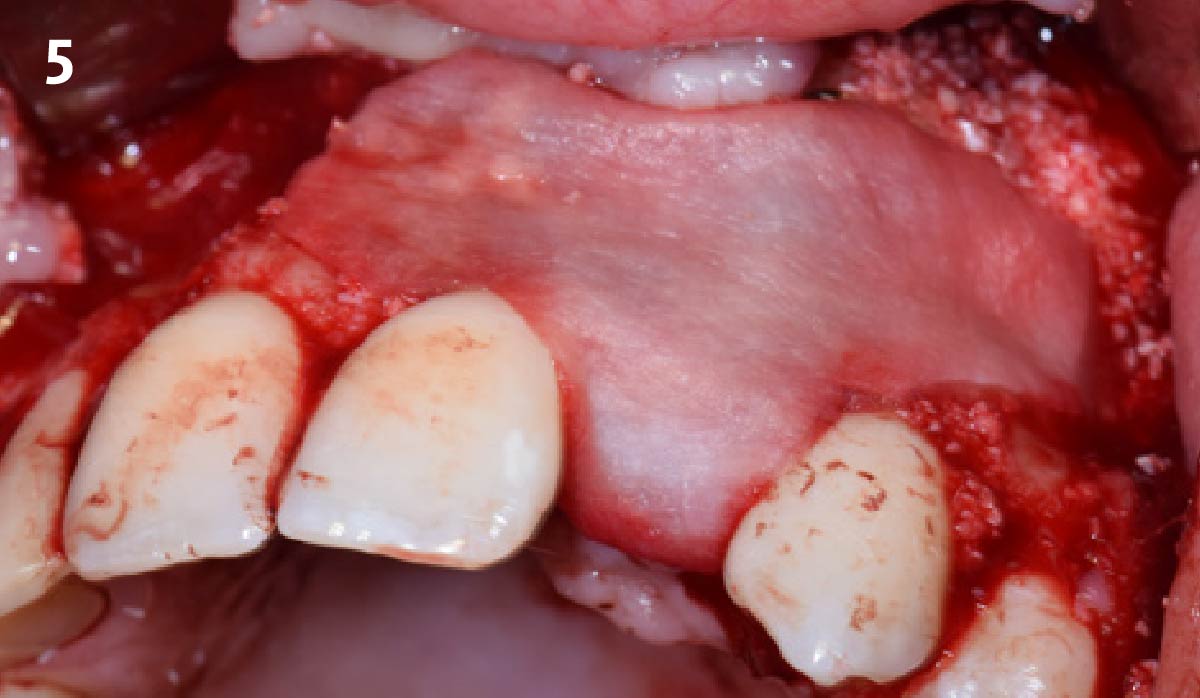
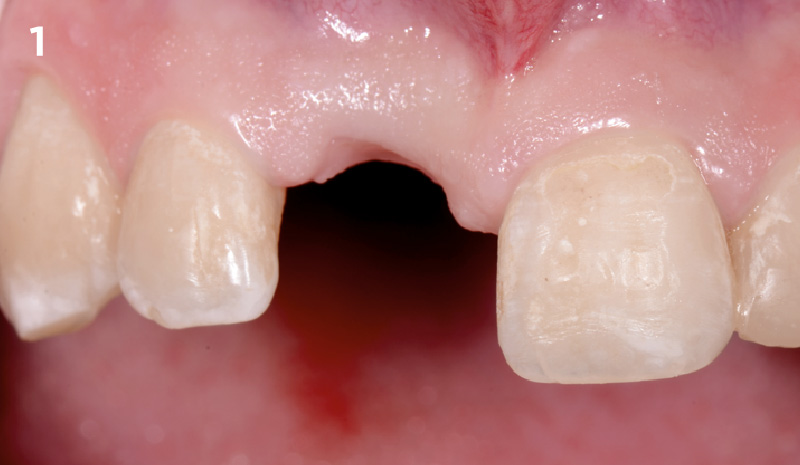
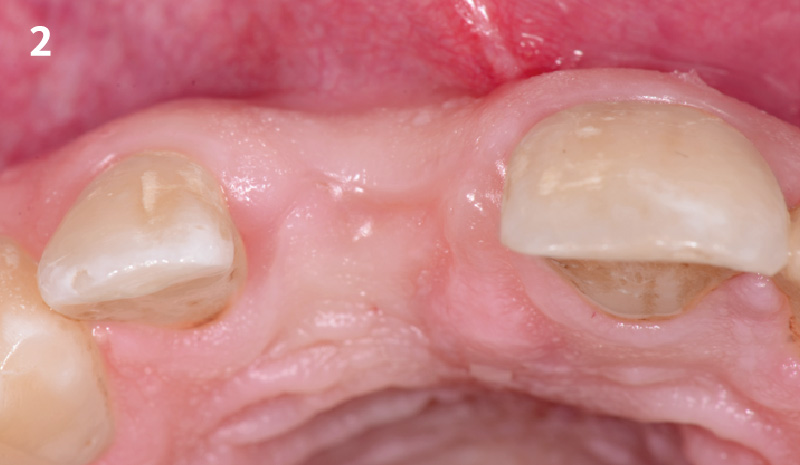
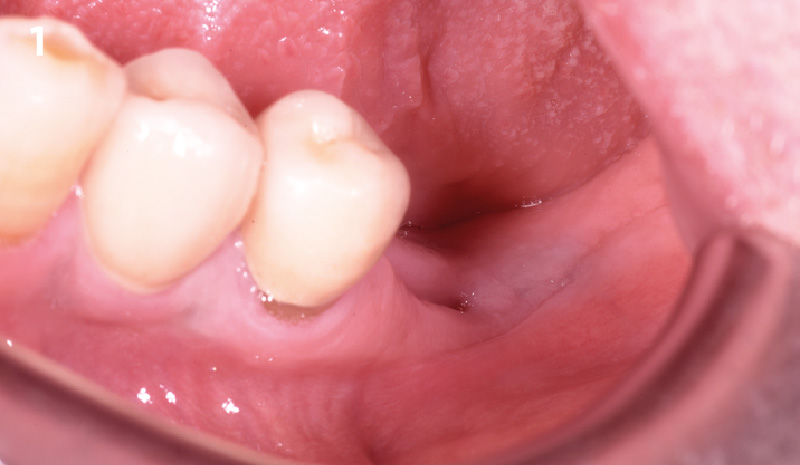
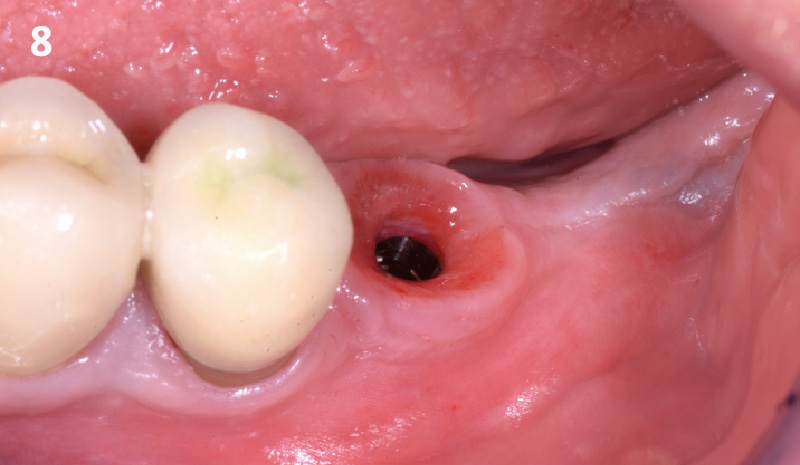
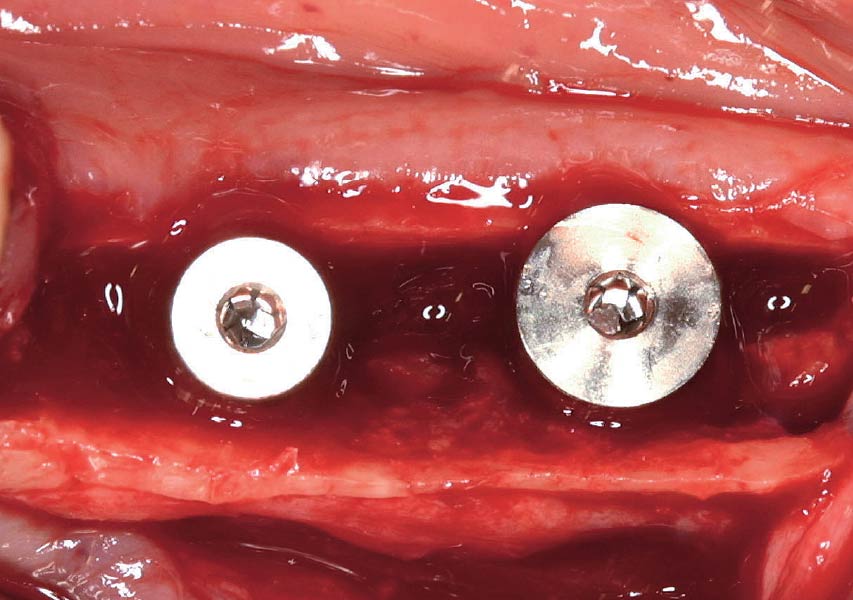
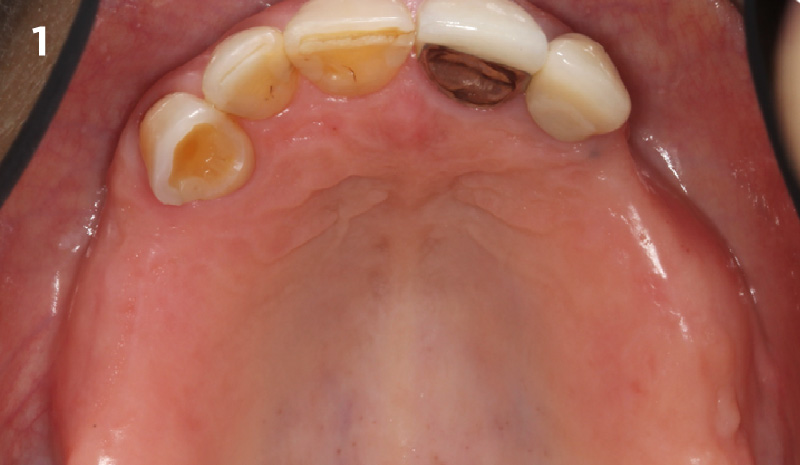
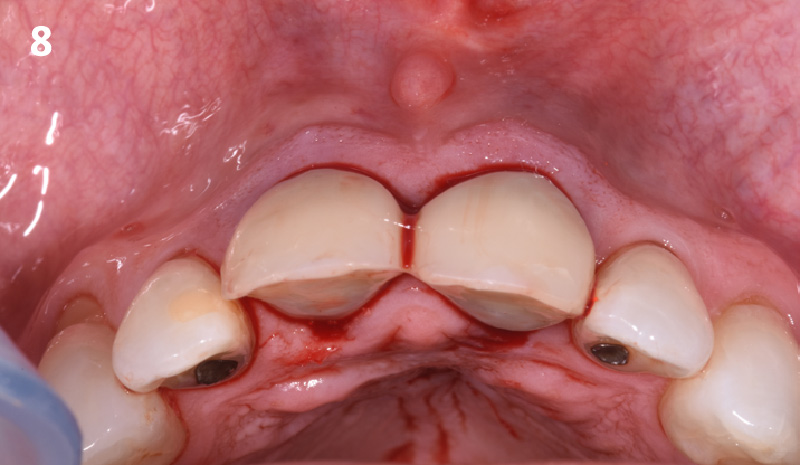
Patient presented with unrestorable left maxillary first molar. After data collection with Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) and intra-oral scanning, and clinical examination, the situation was considered favorable for minimally traumatic extraction and immediate implant placement.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
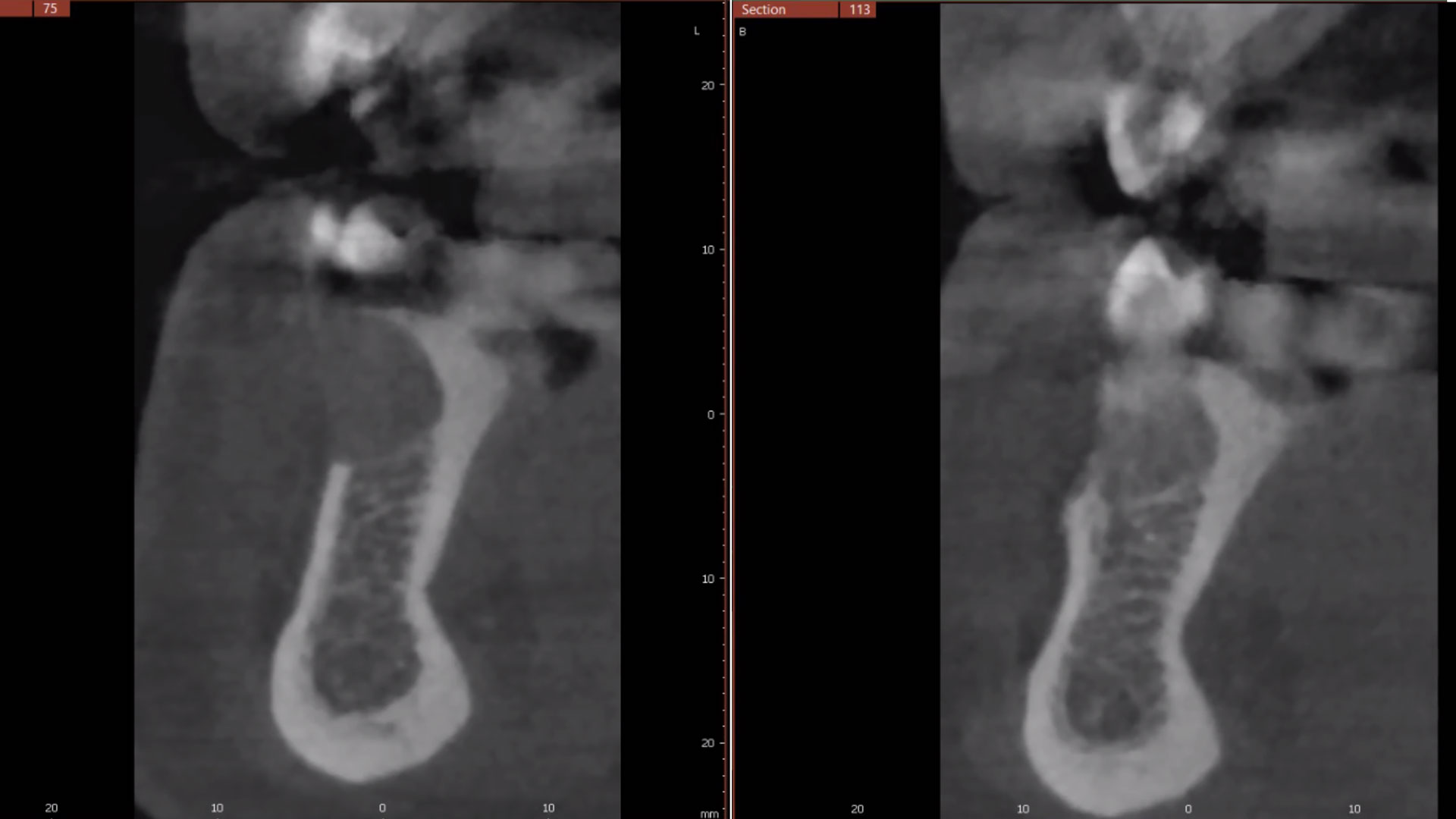
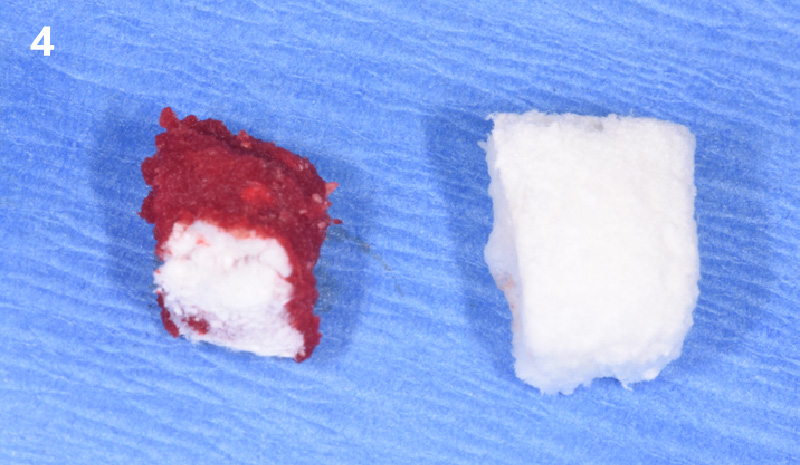
Additional Risk Factors: Roots were divergent, and intra-radicular bone (septal bone) was excellent, with more than 5 mm of remaining apical bone to achieve optimal primary stability.
THE APPROACH
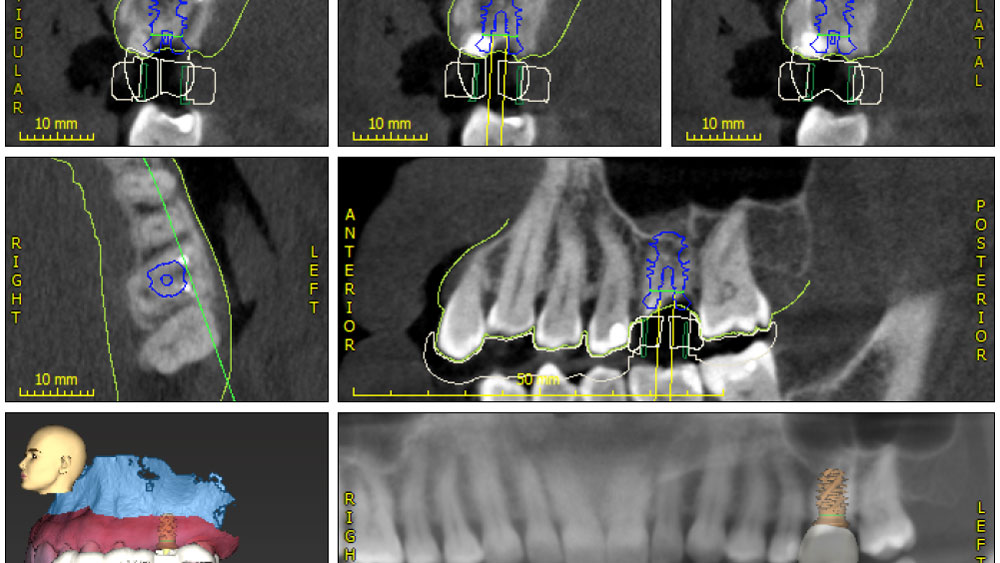
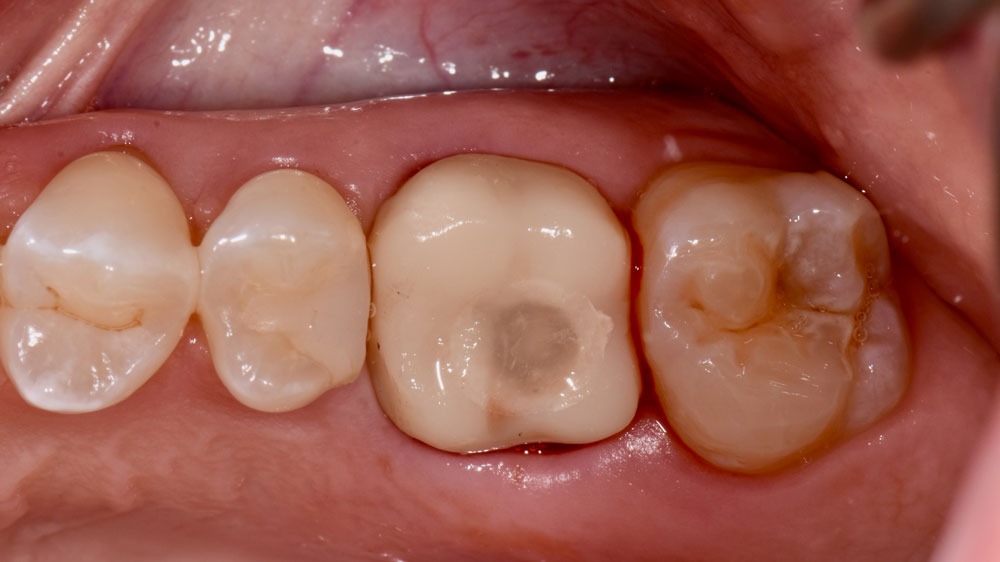
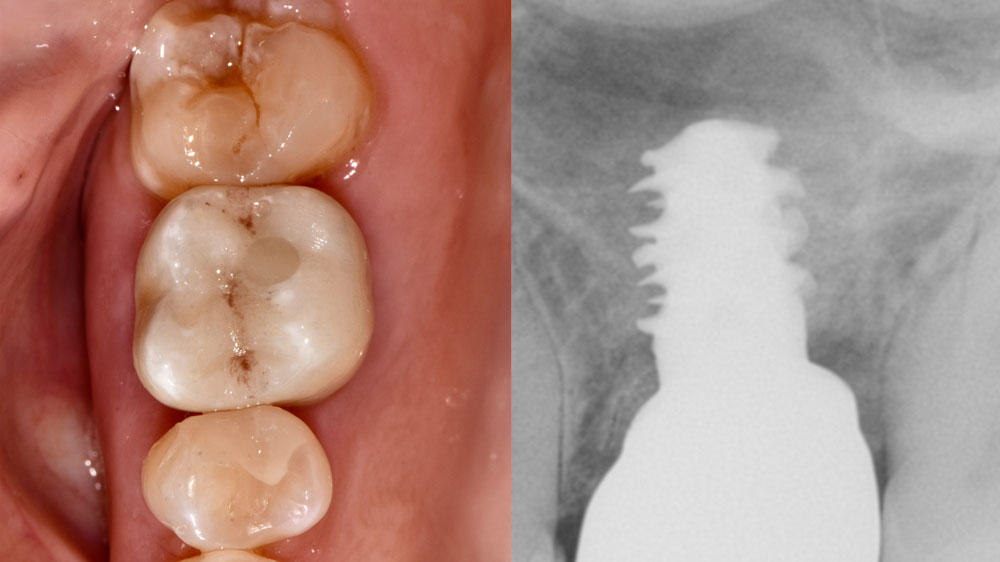
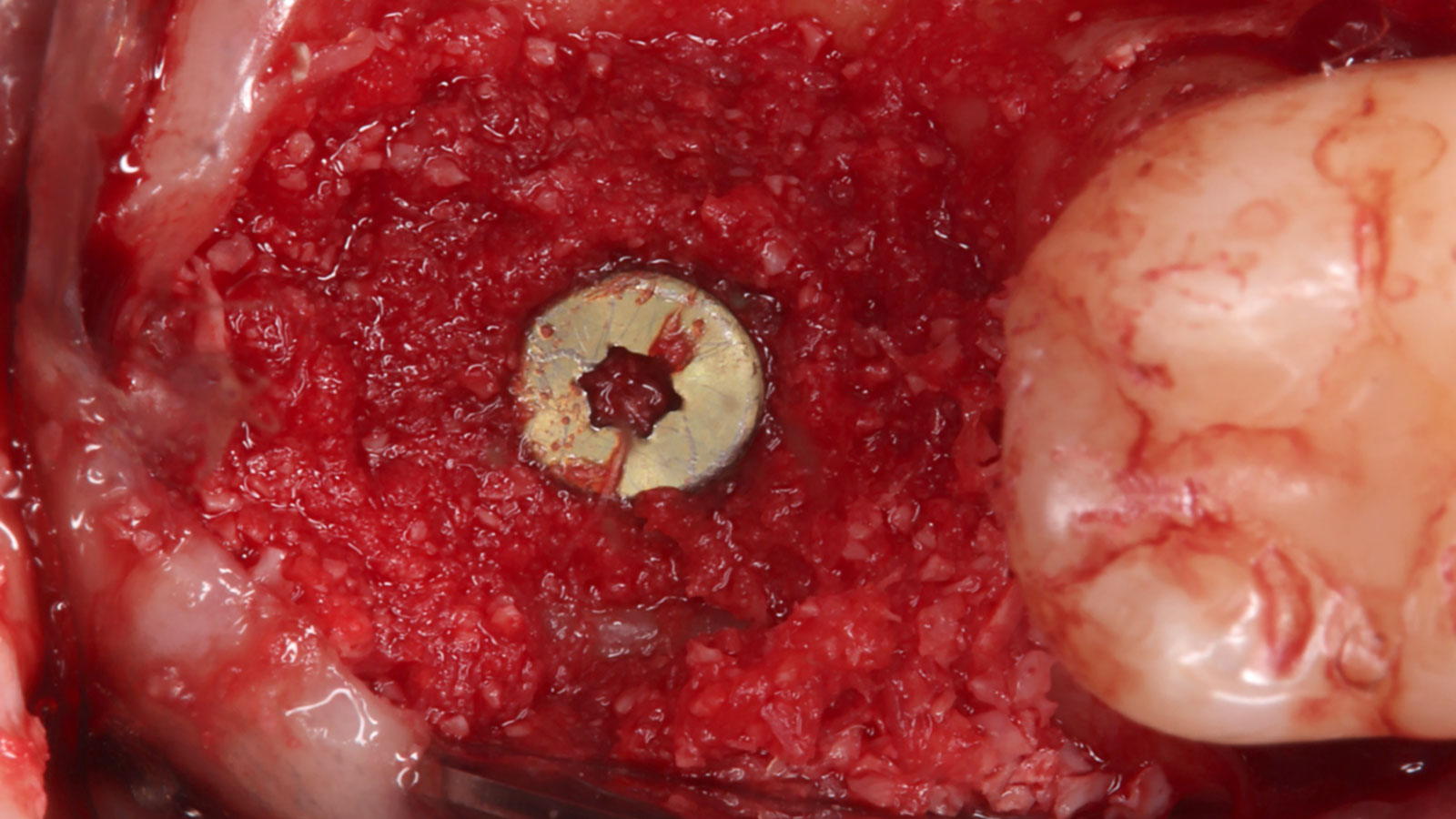
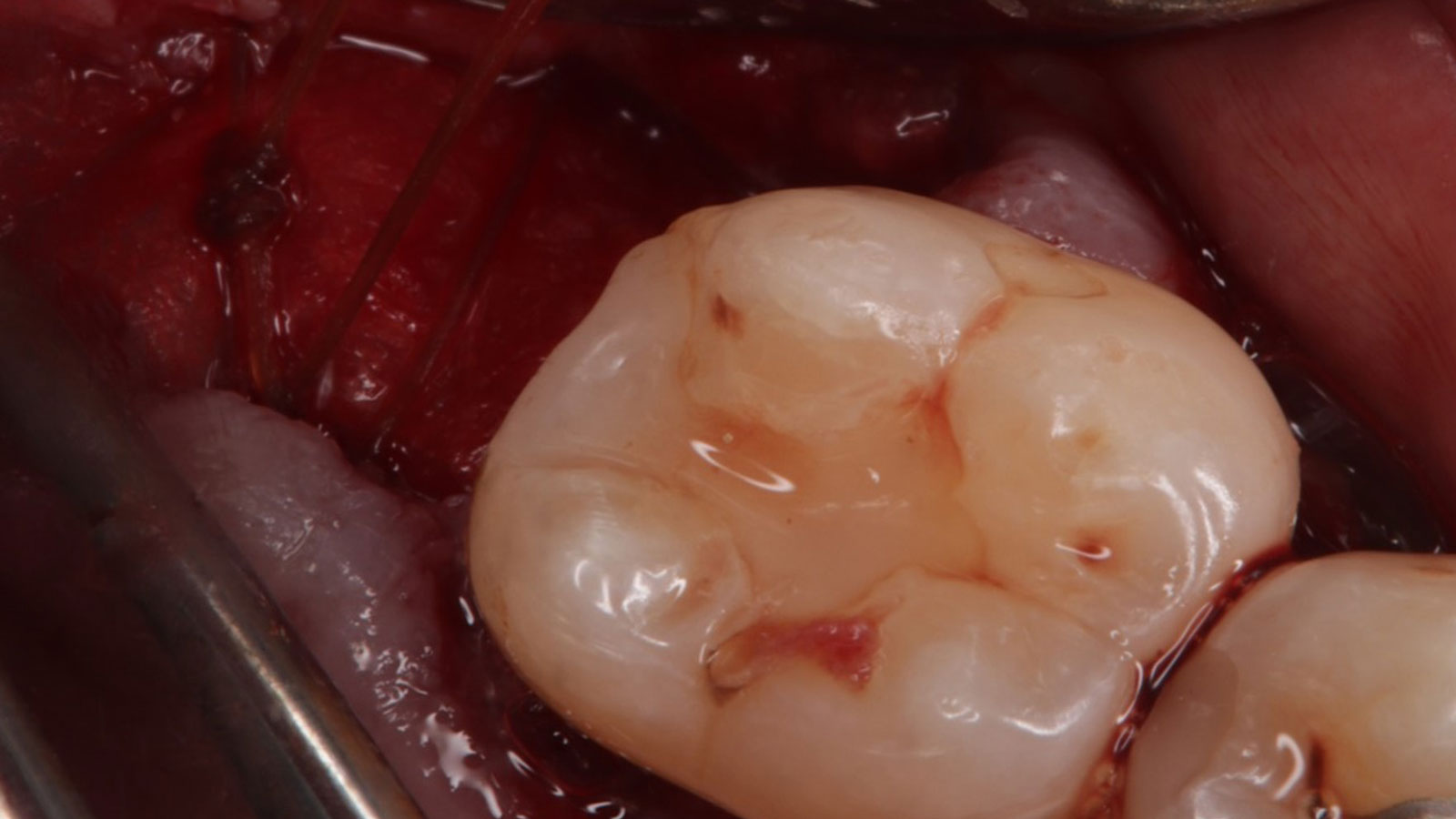
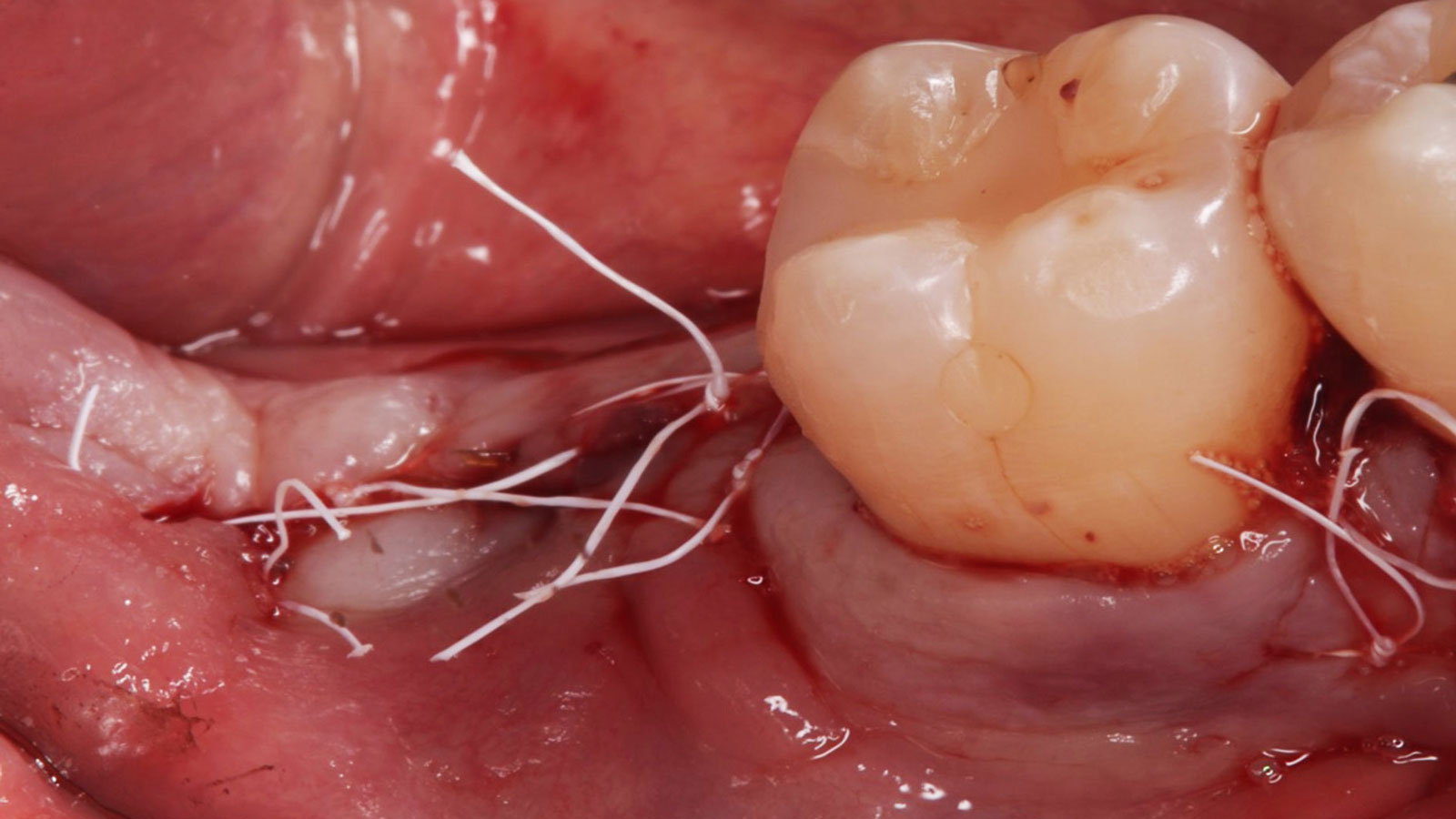
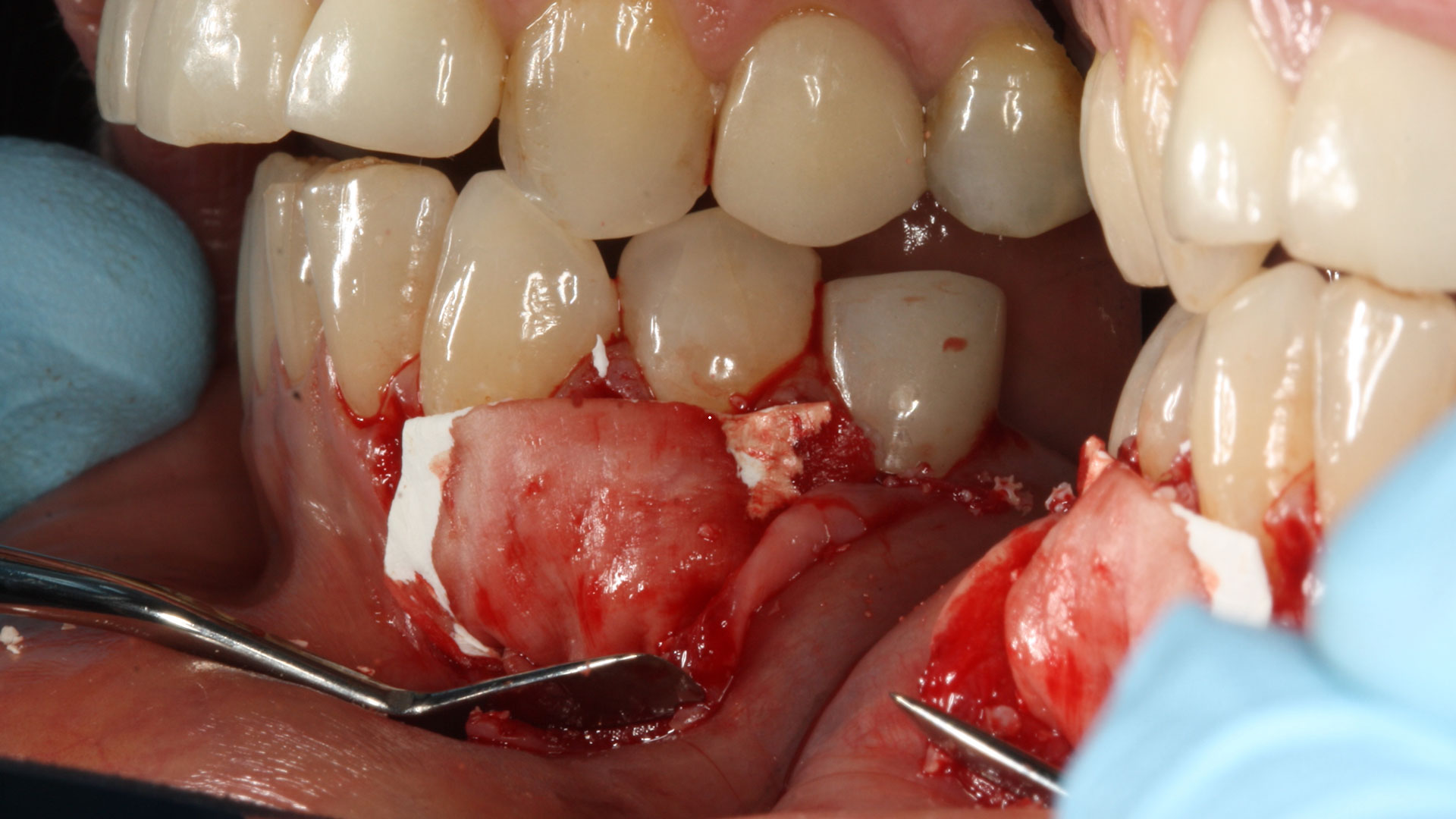
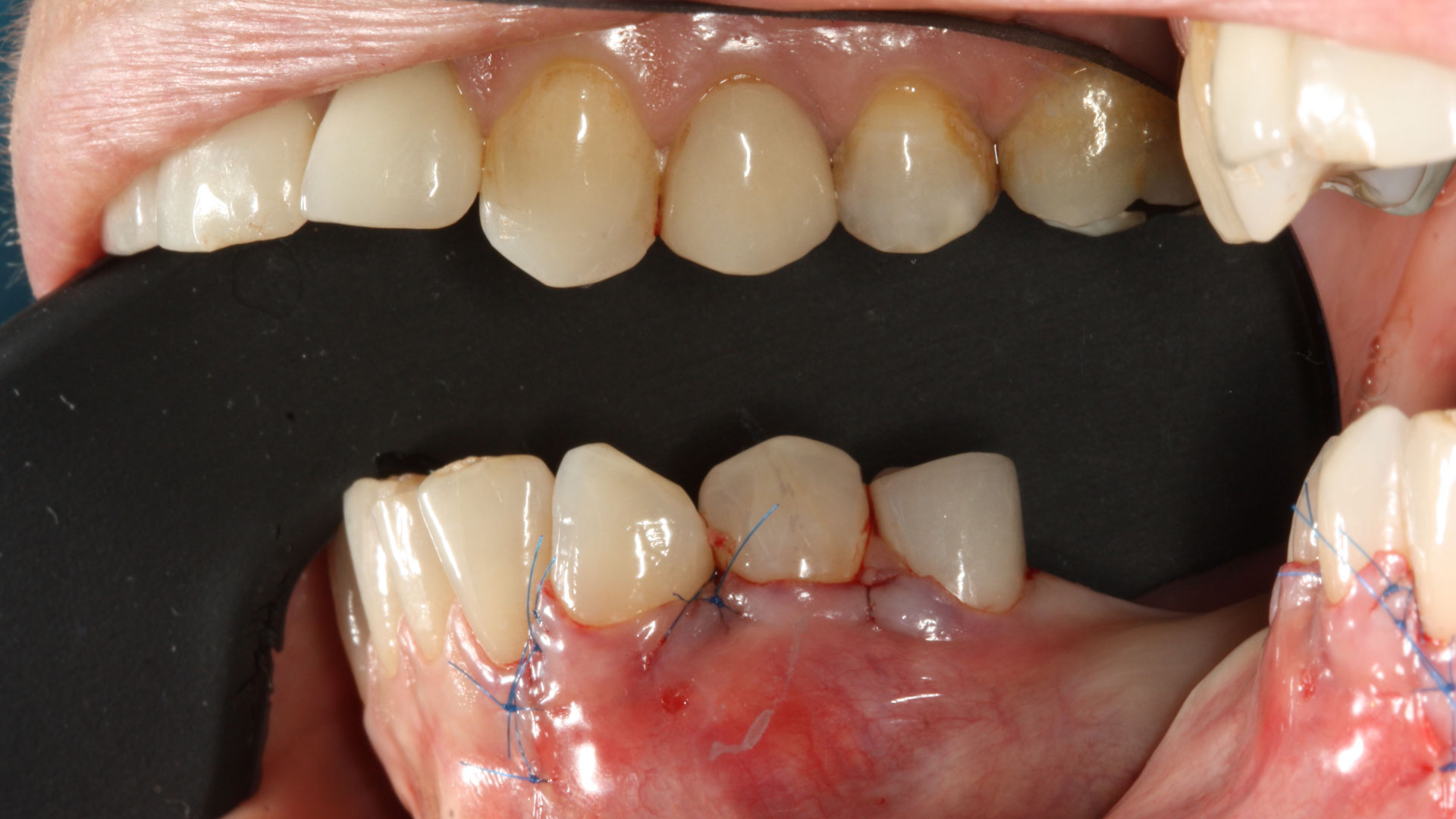
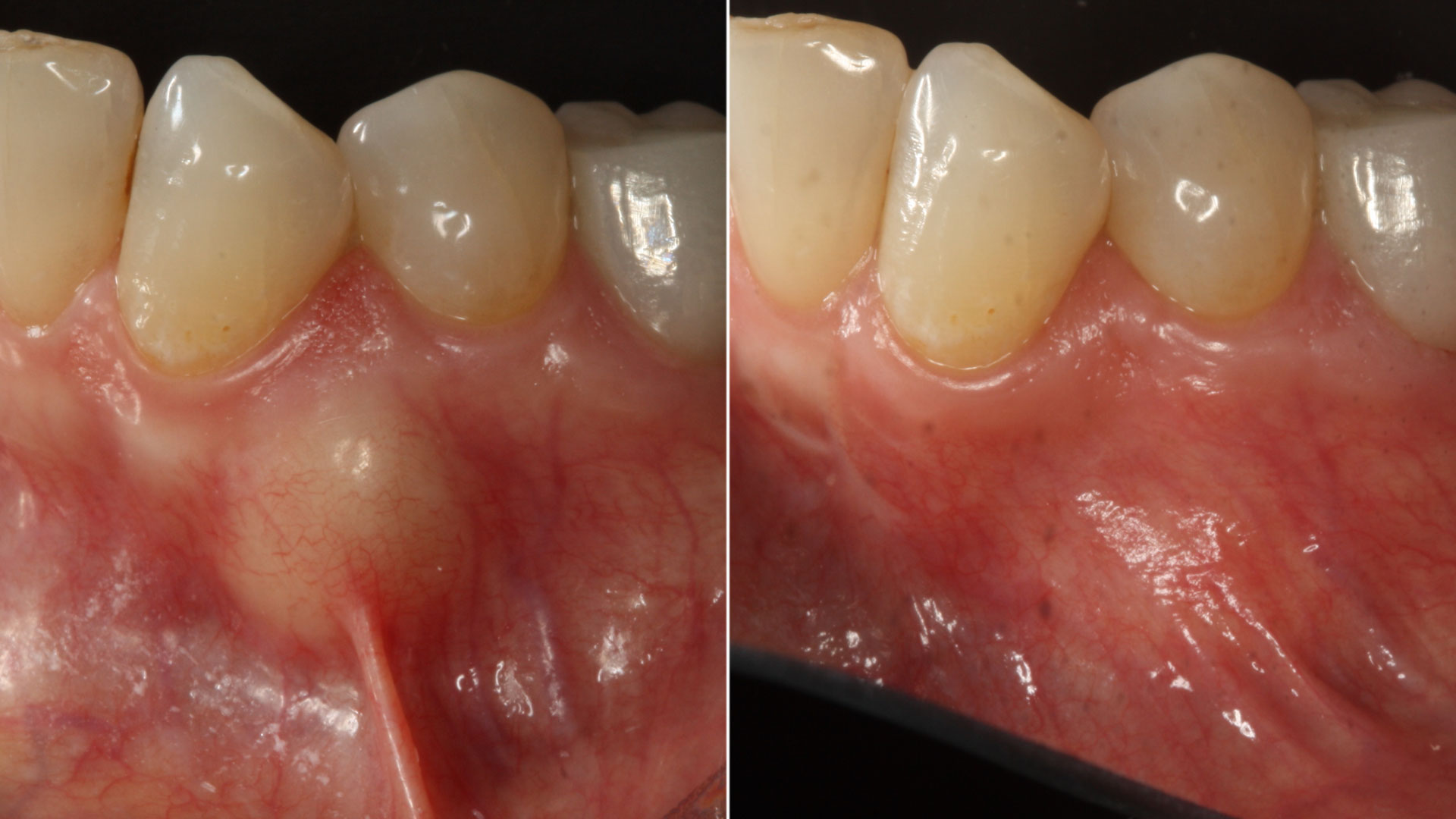
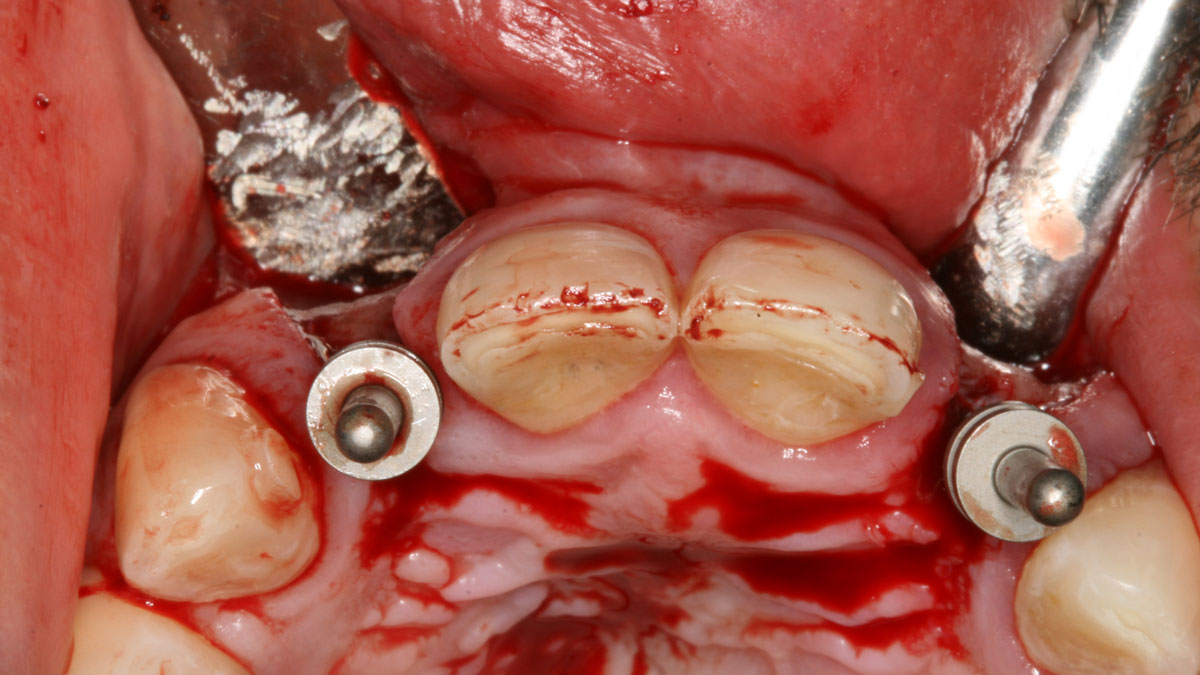
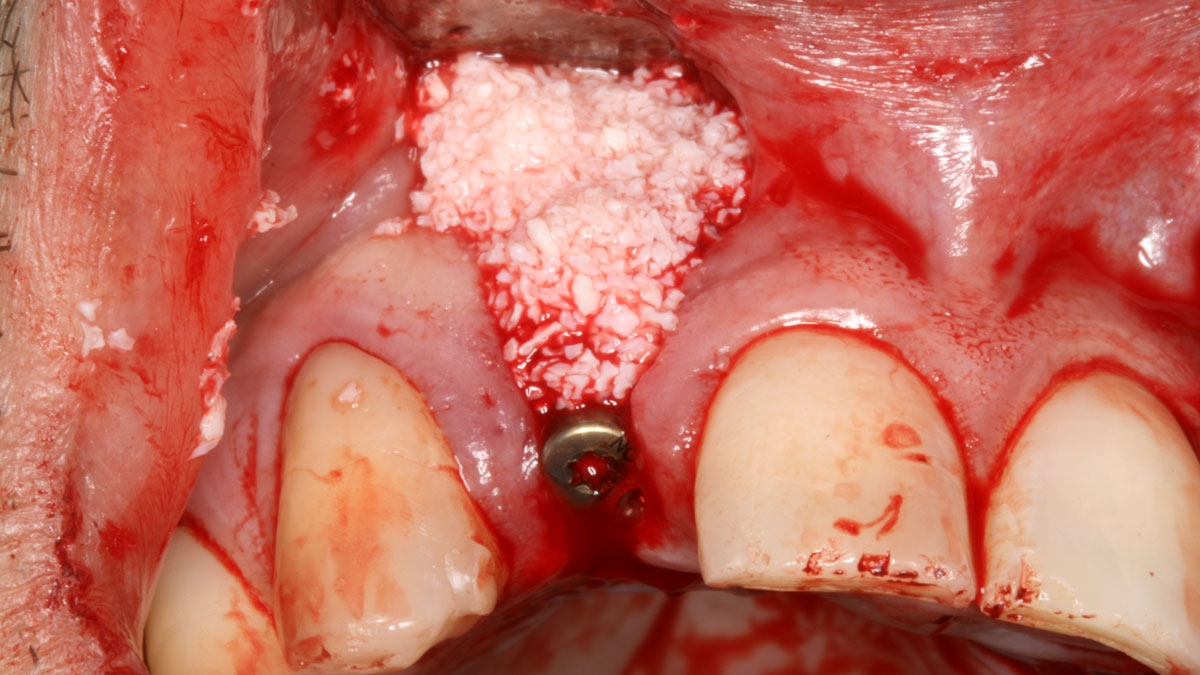
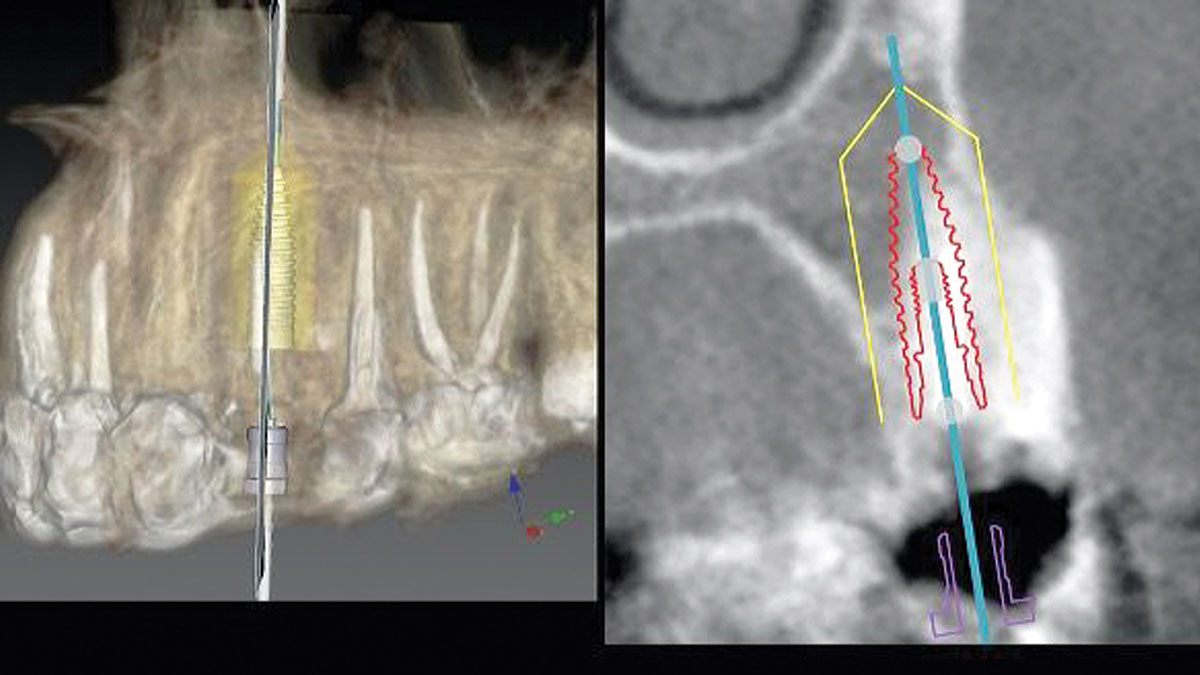
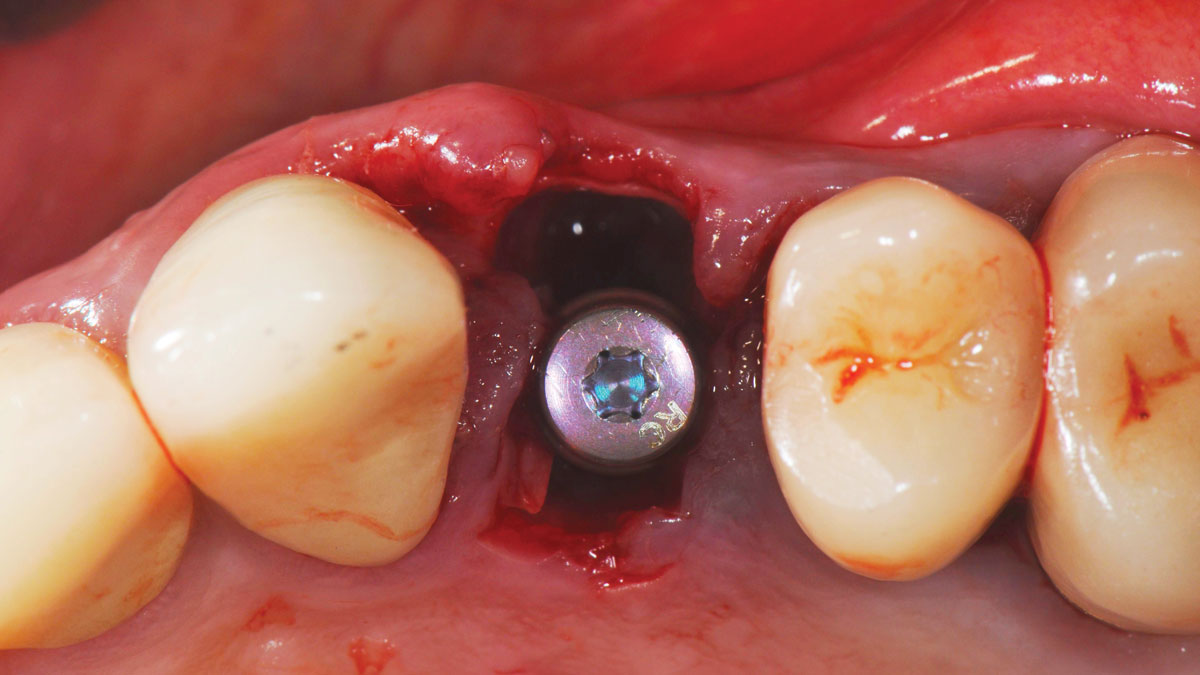
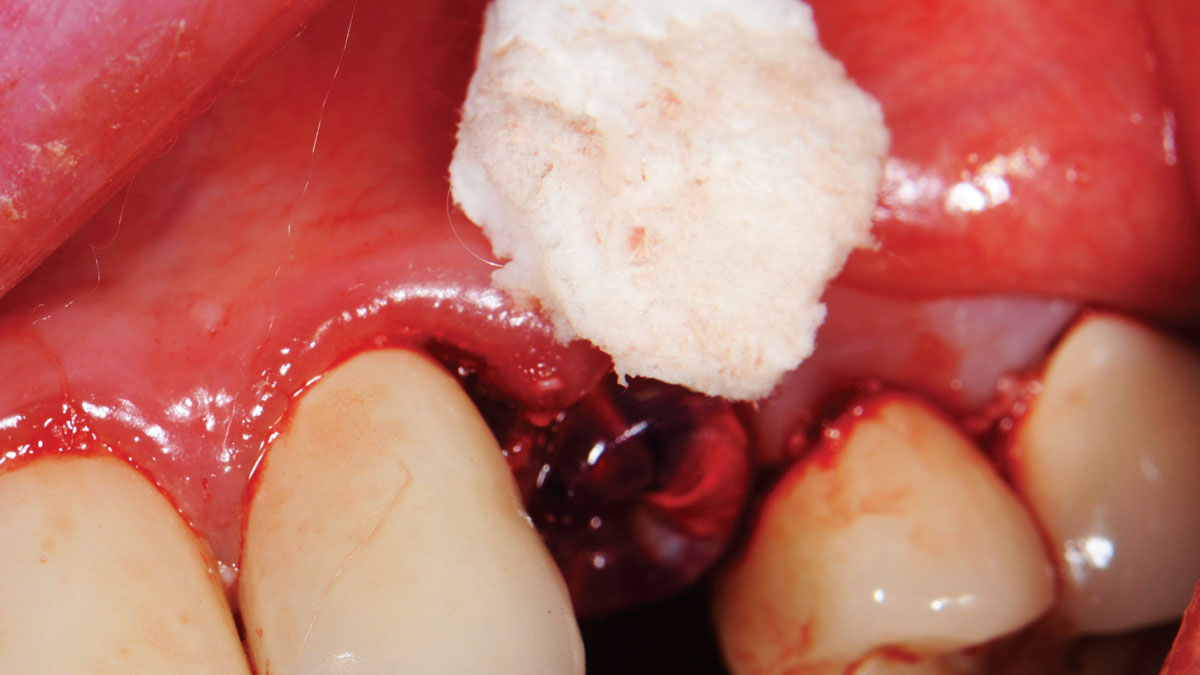
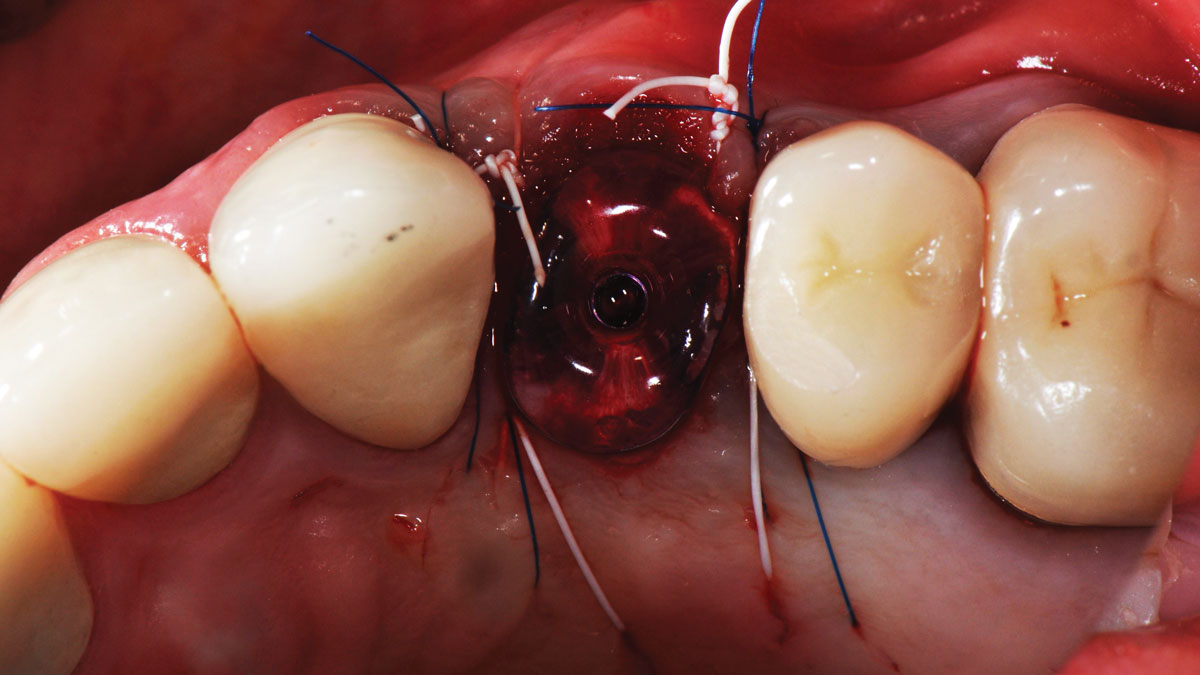
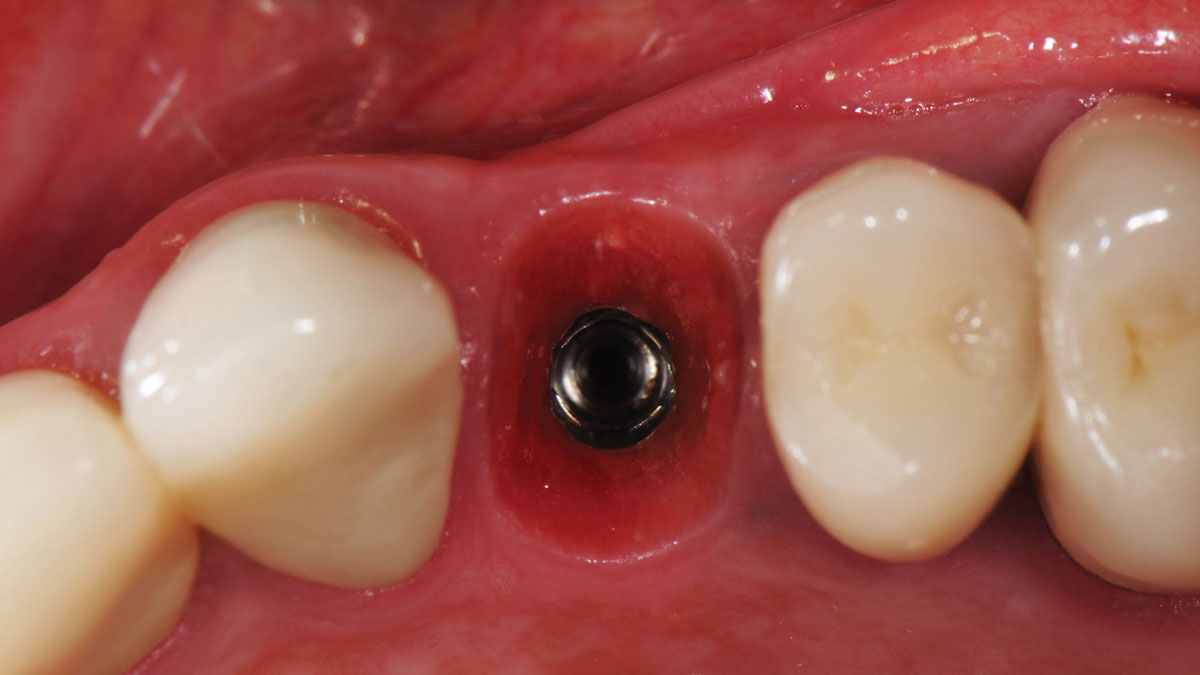
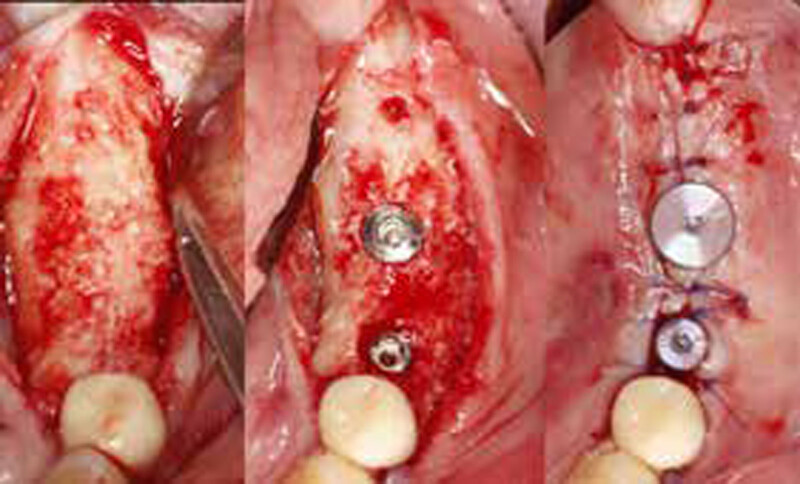
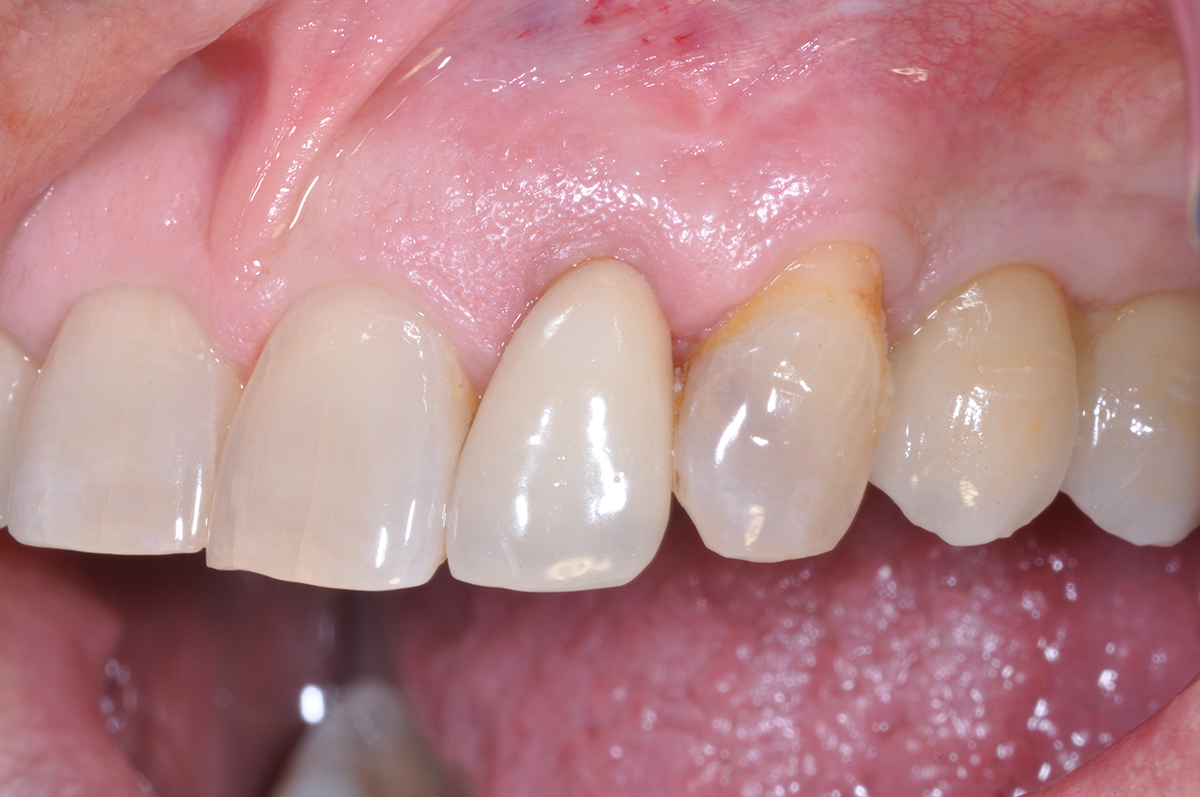
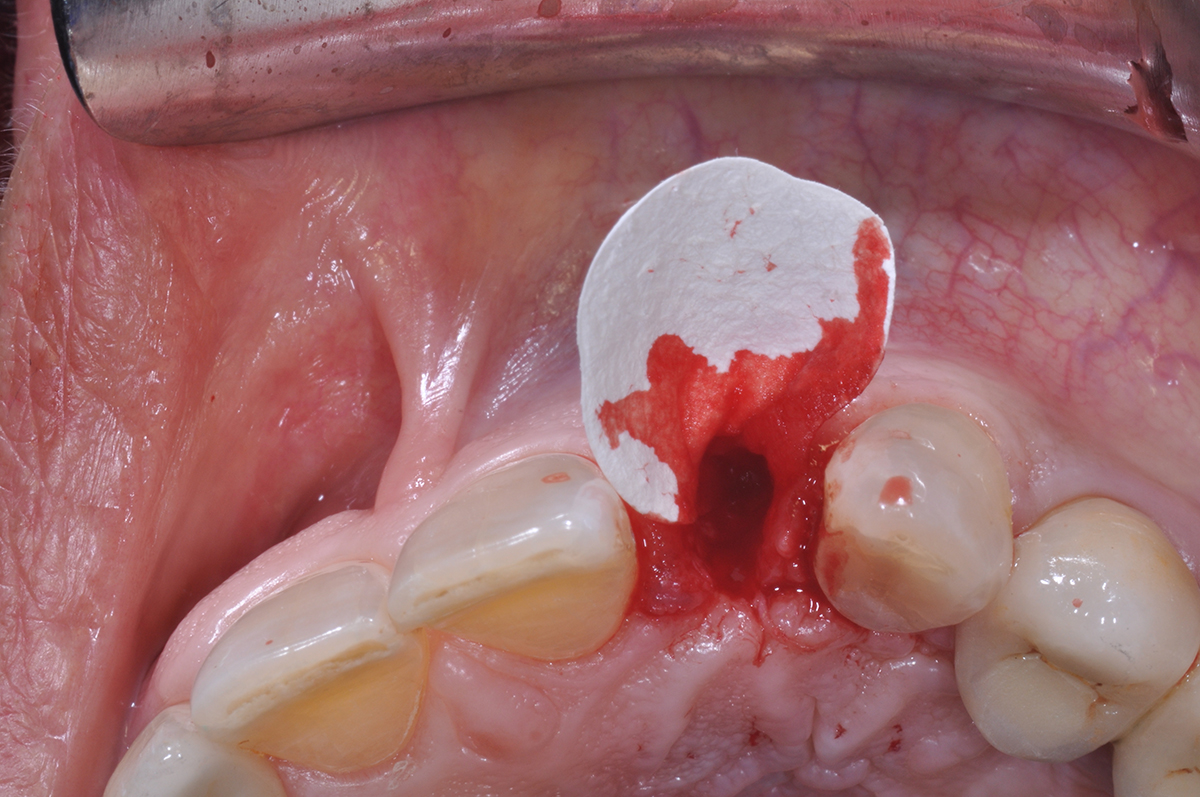
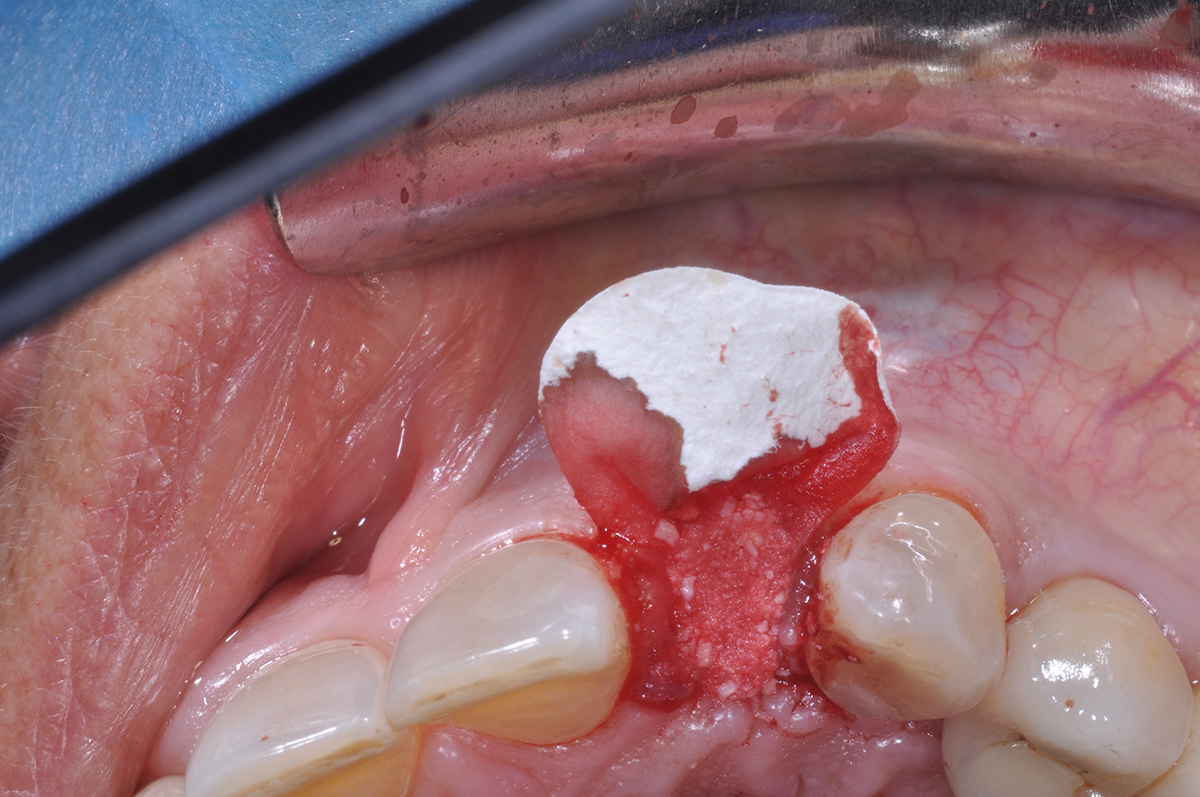
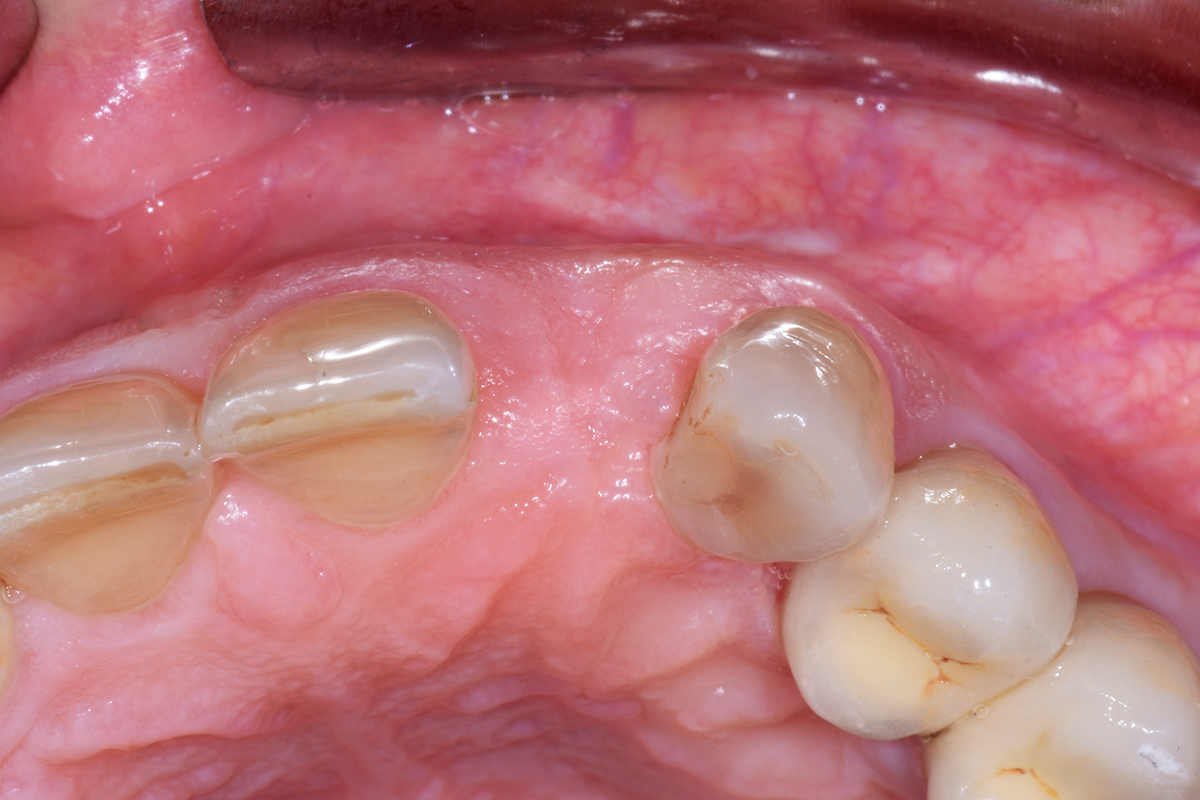
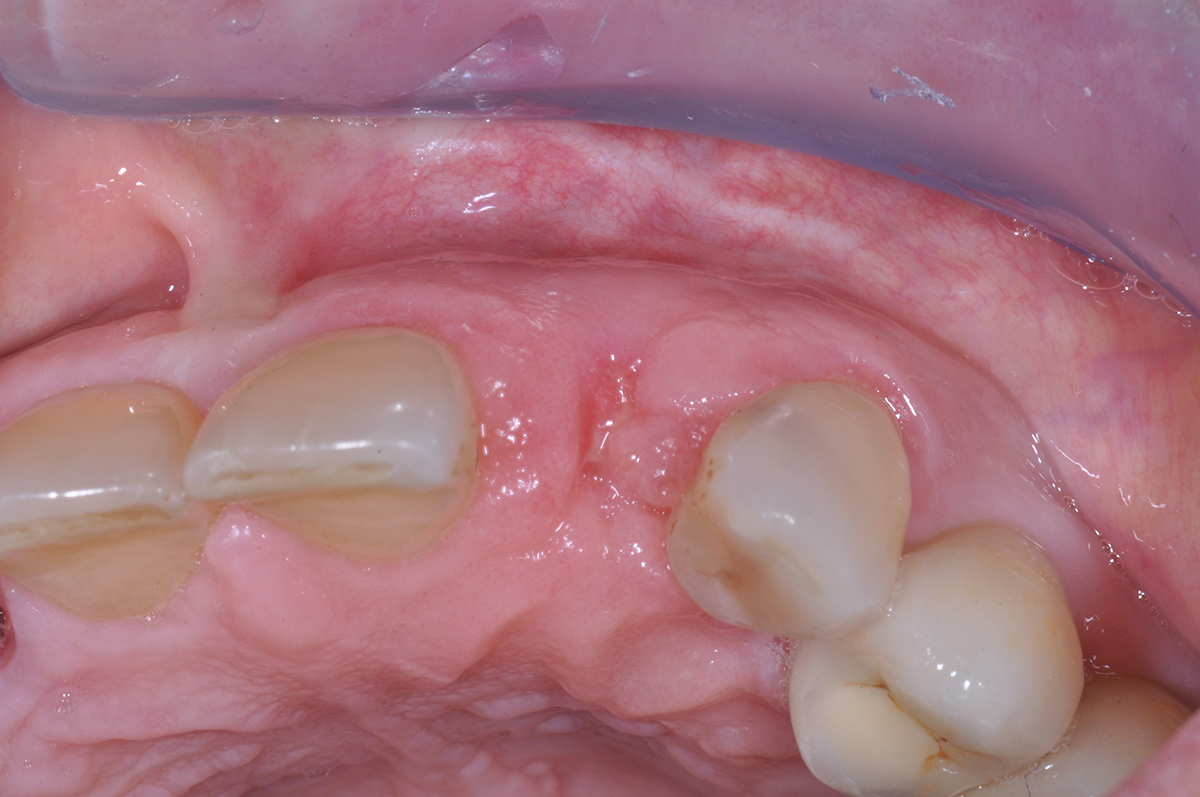
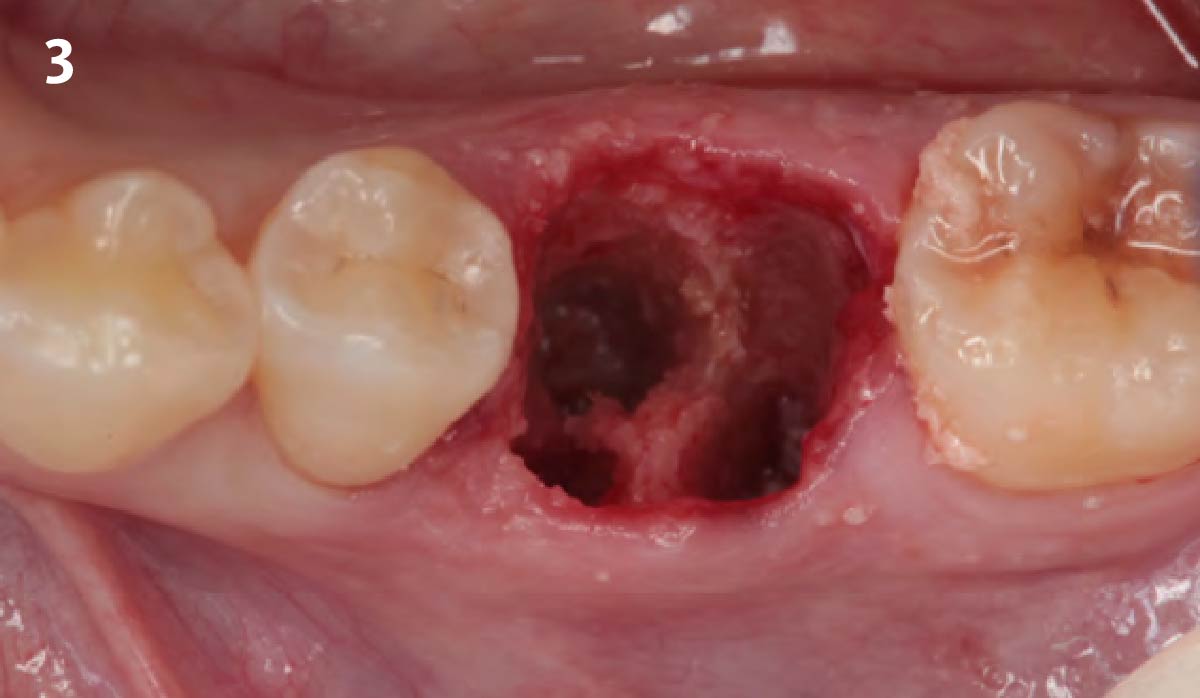
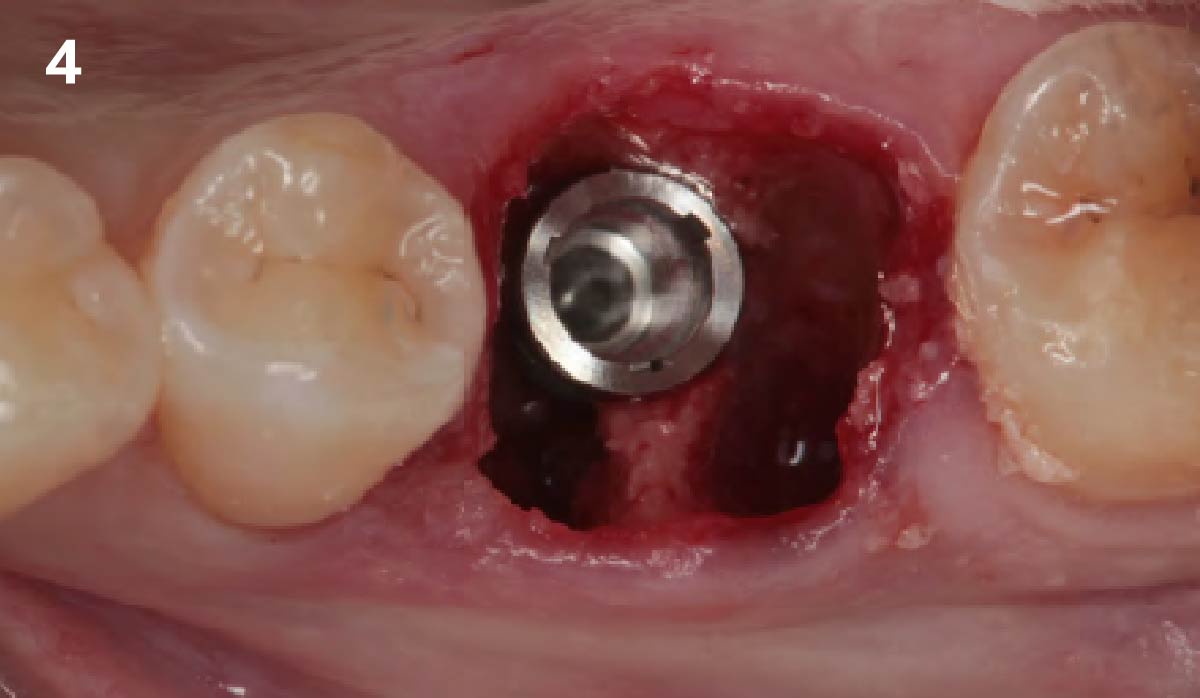
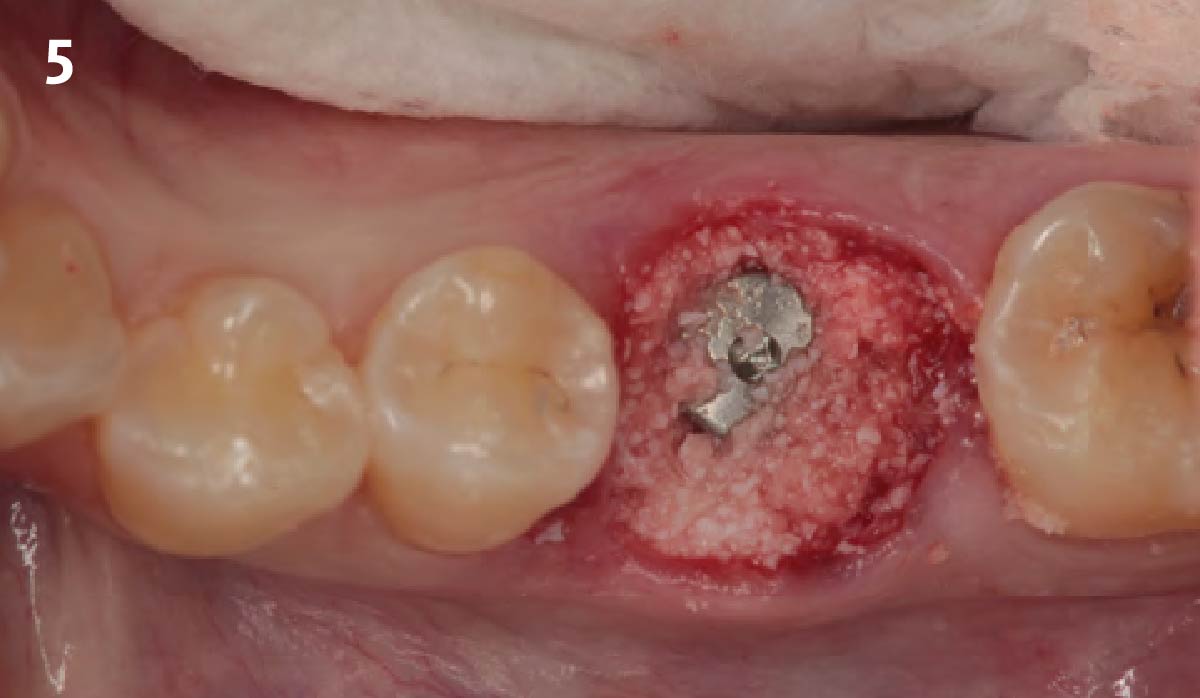
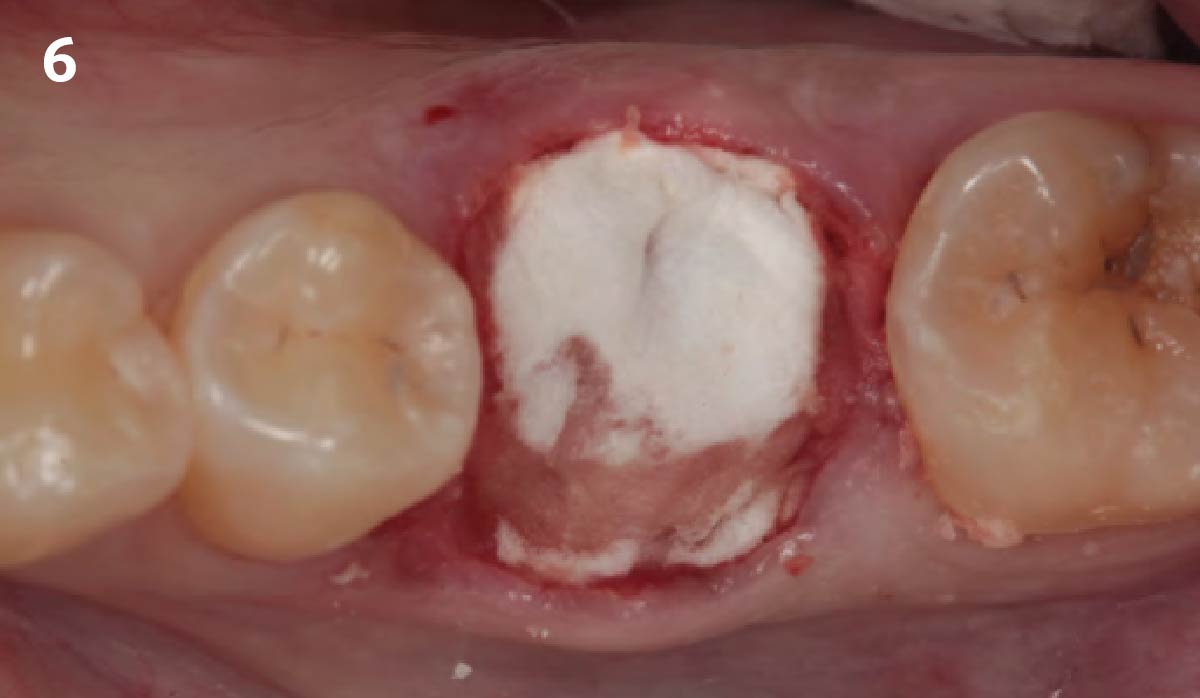
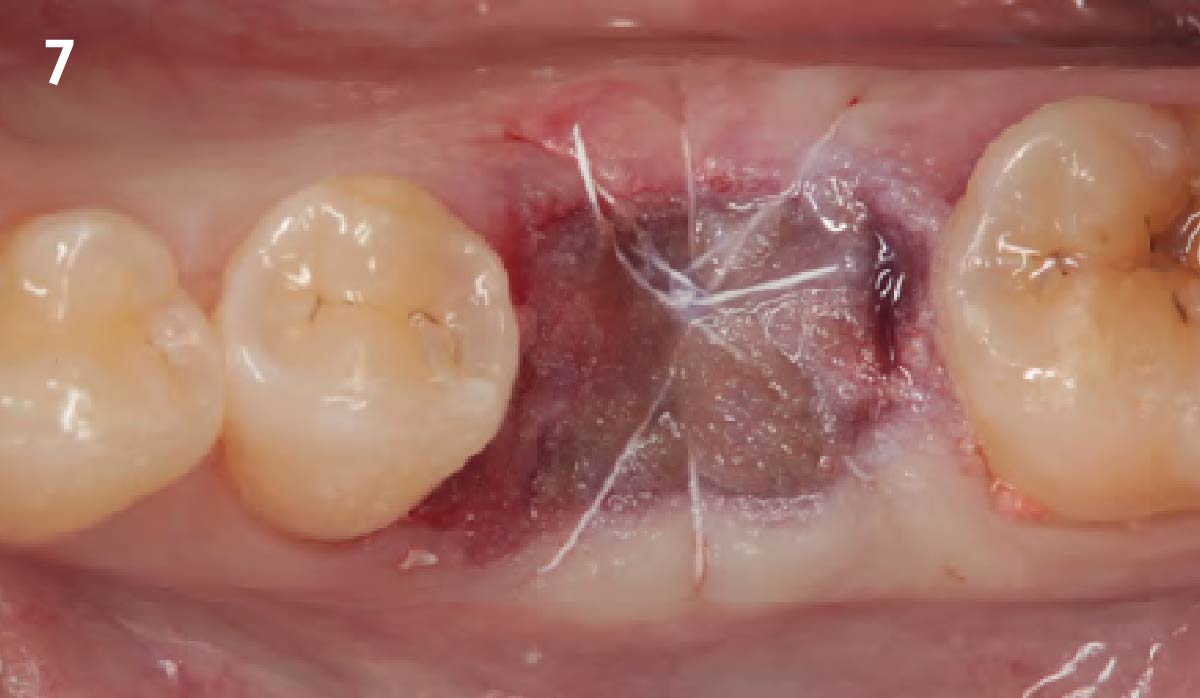
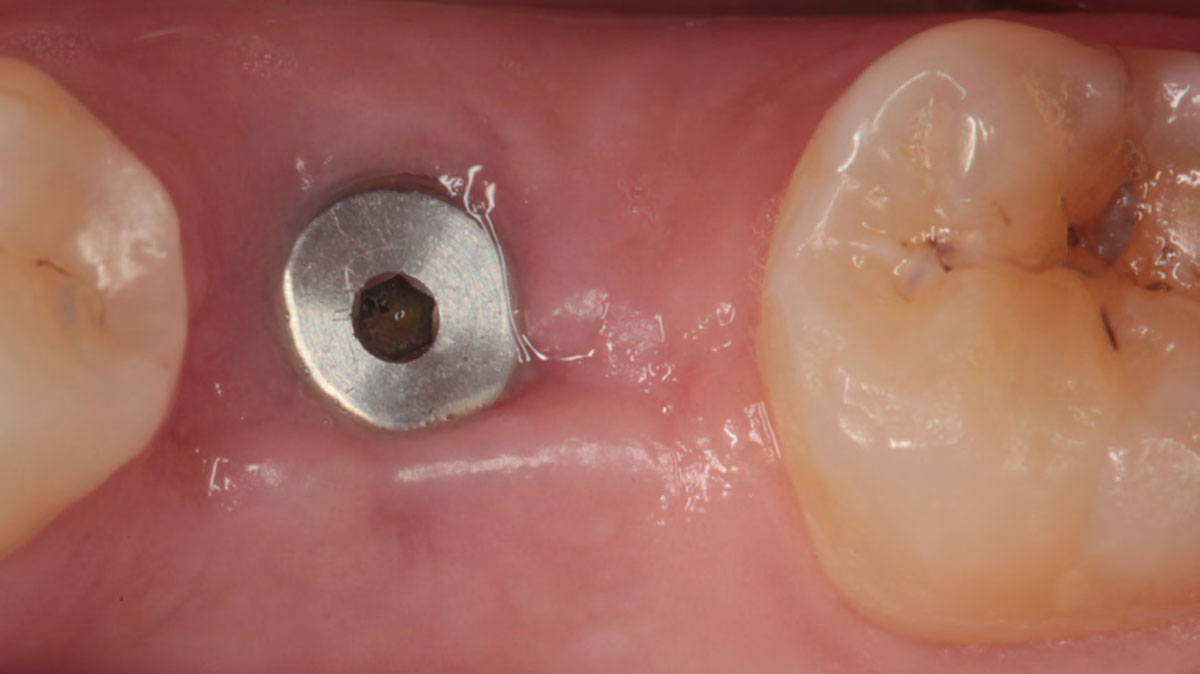
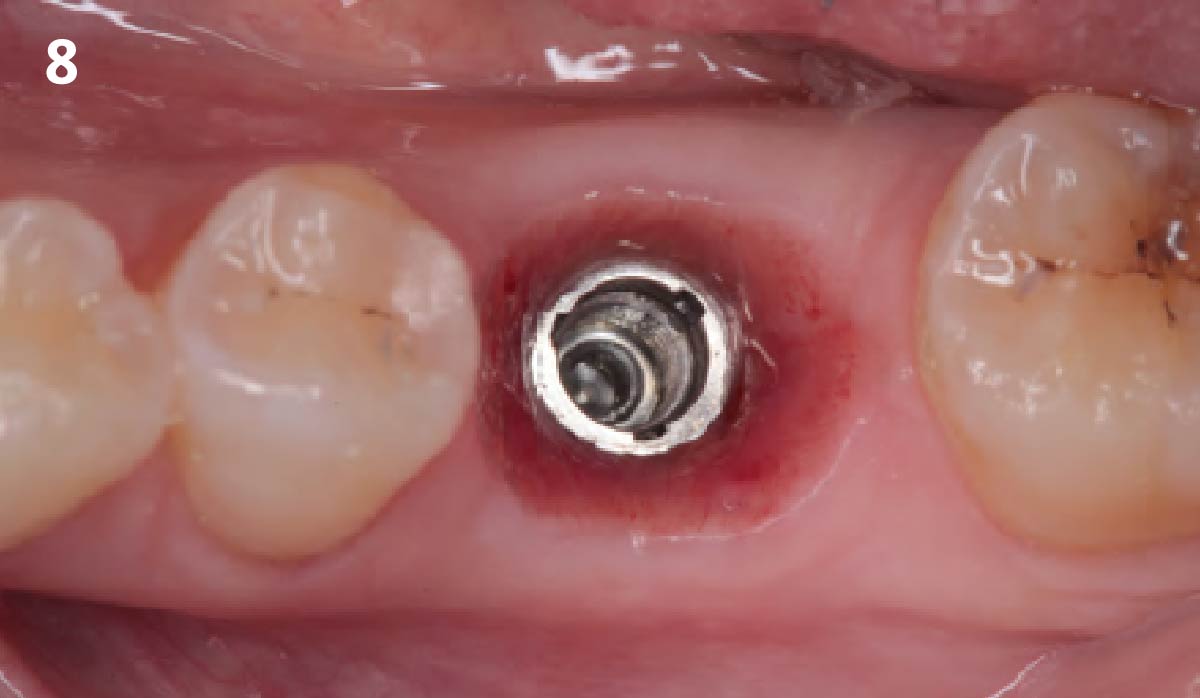
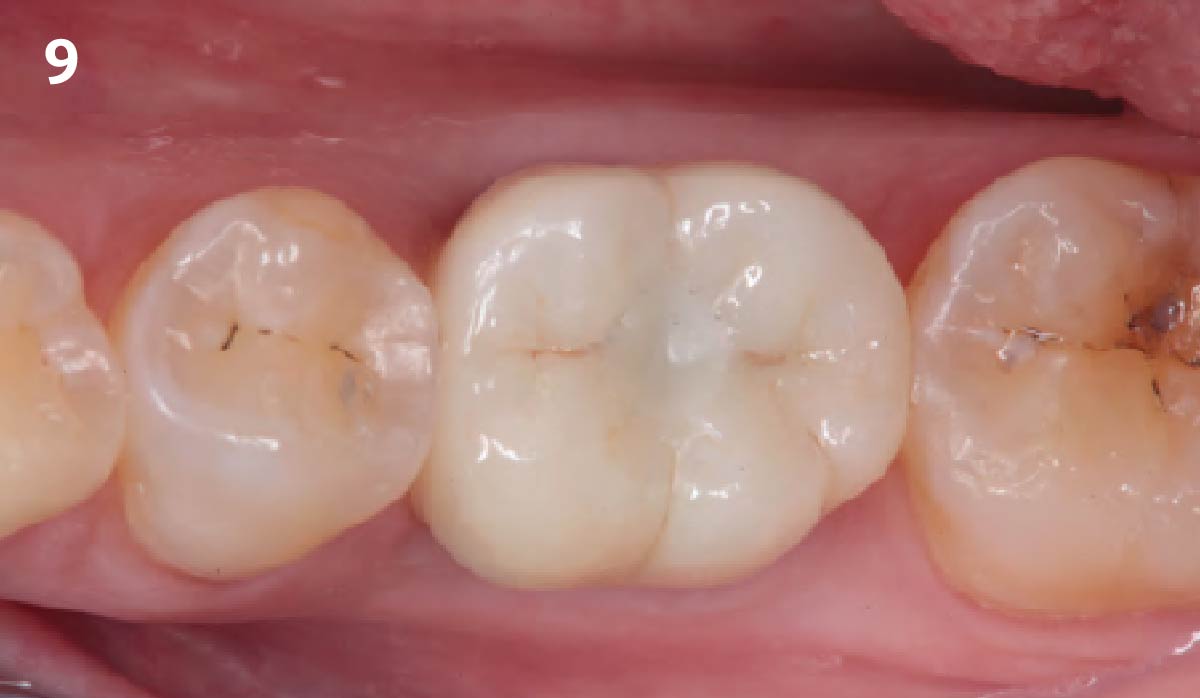
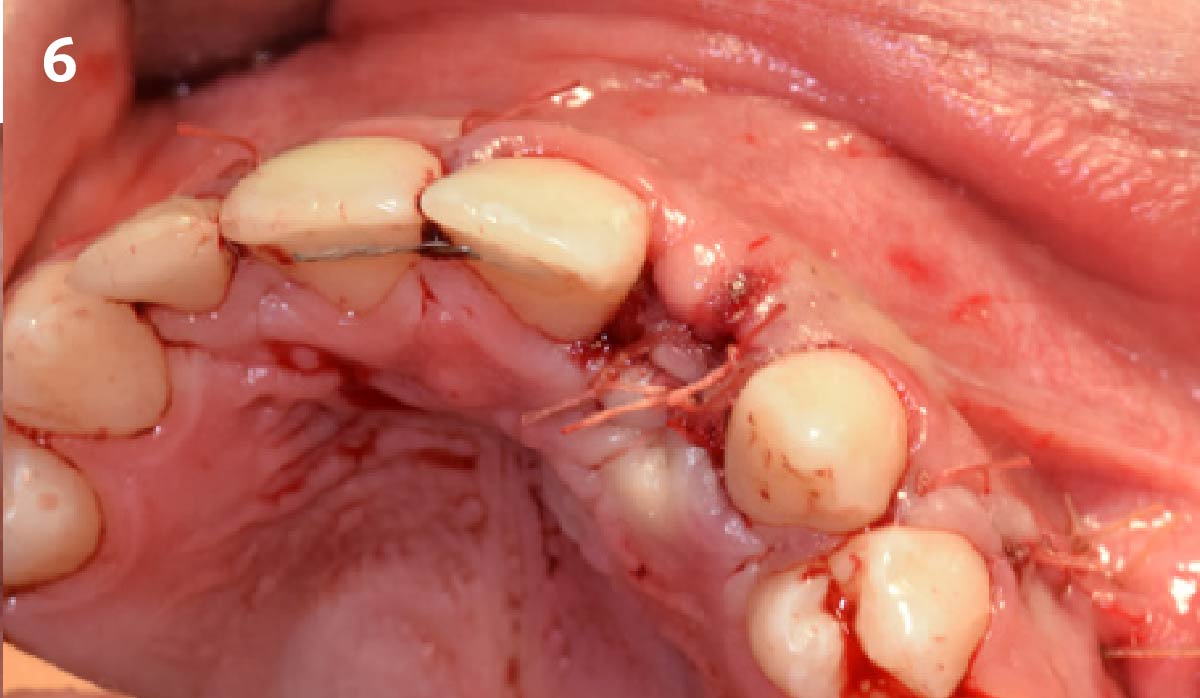
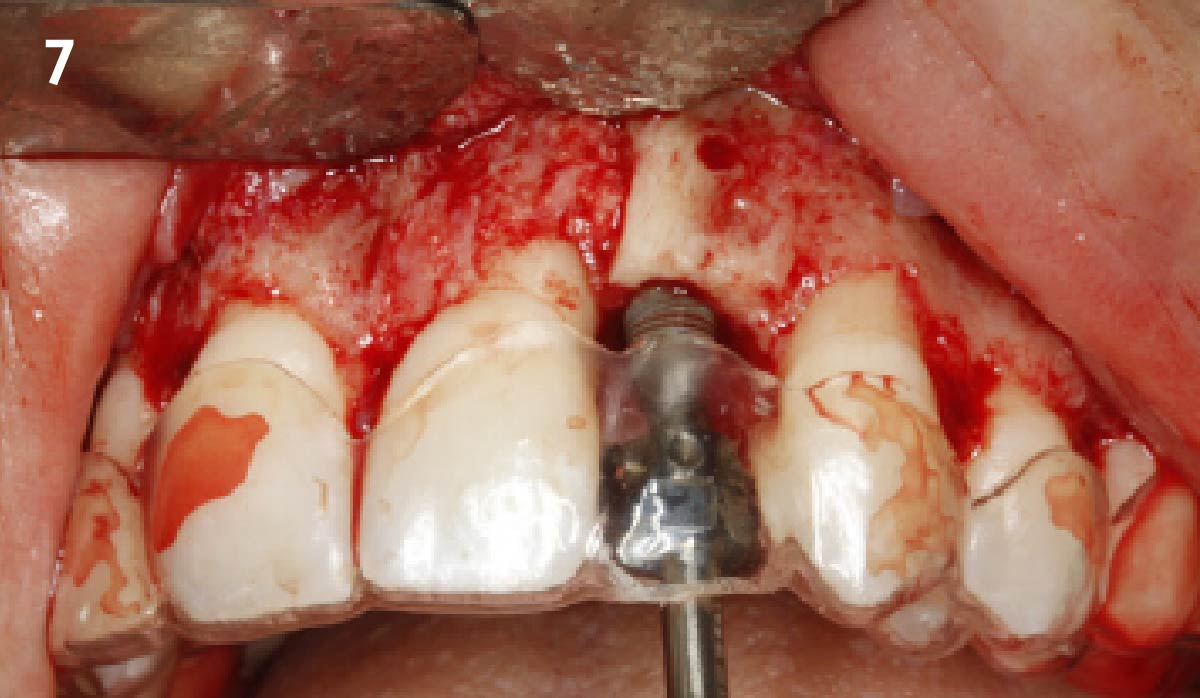
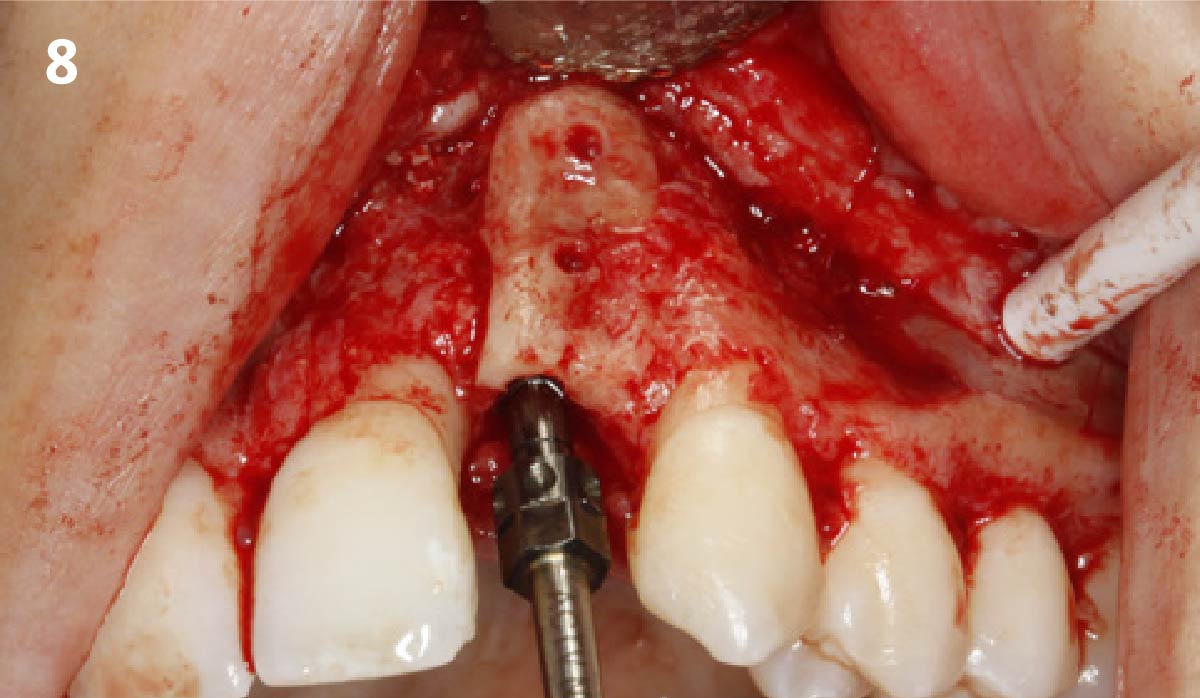
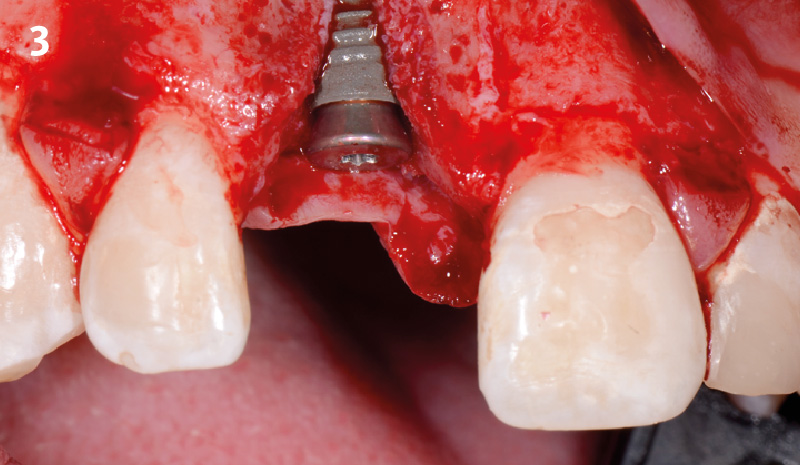
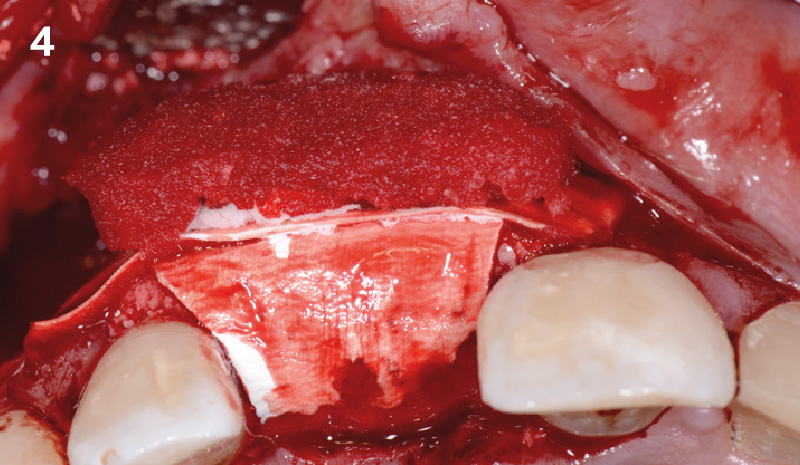
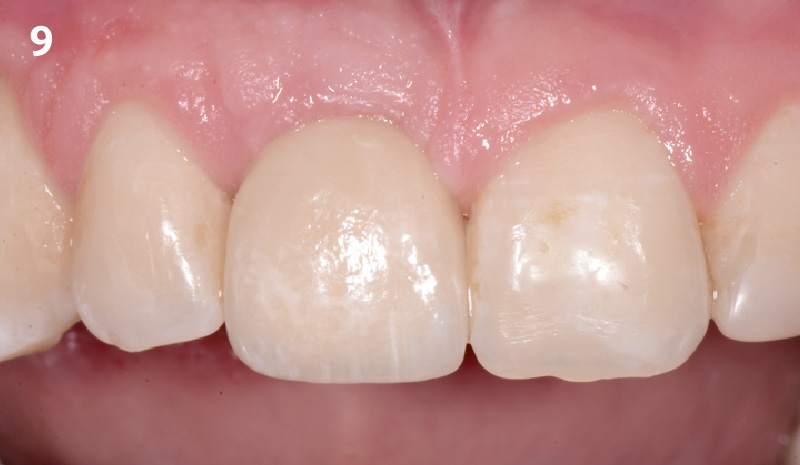
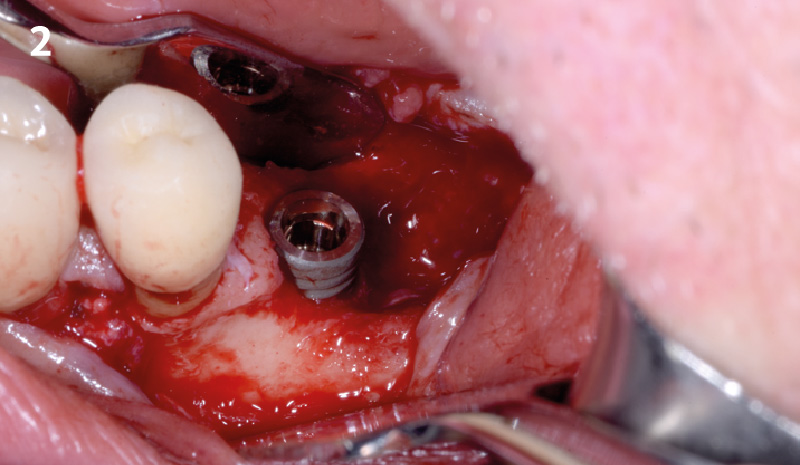
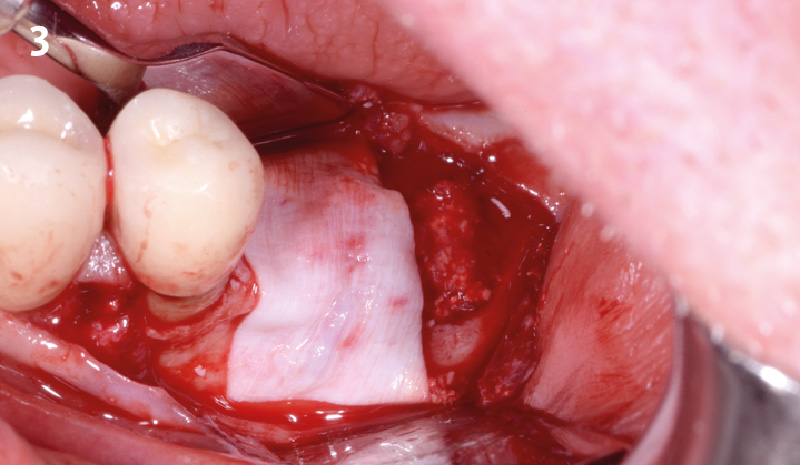
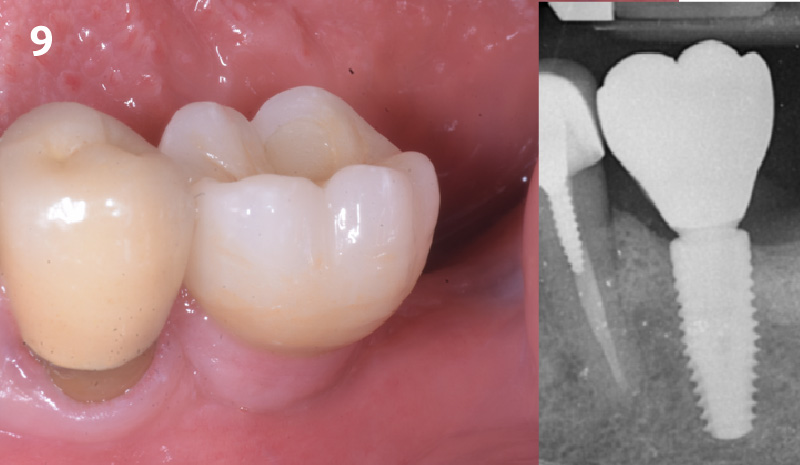
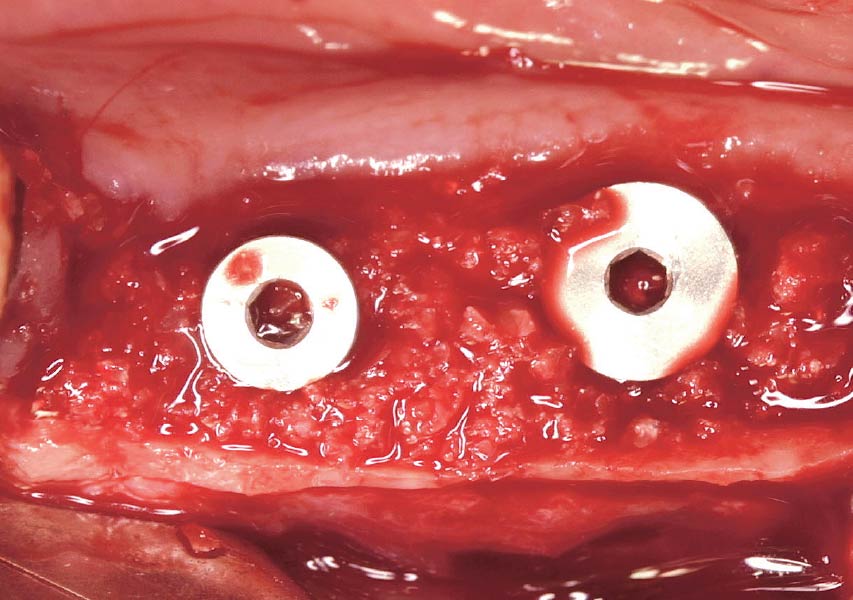
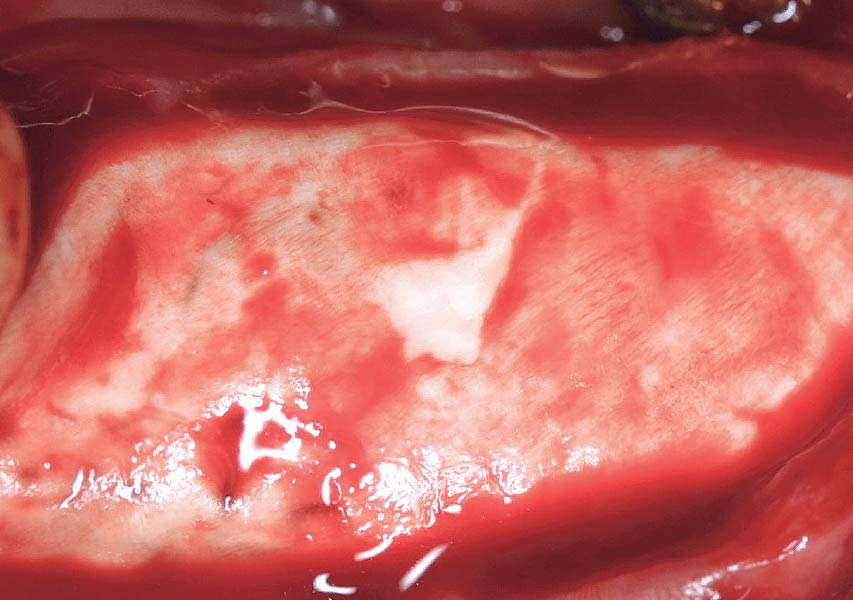
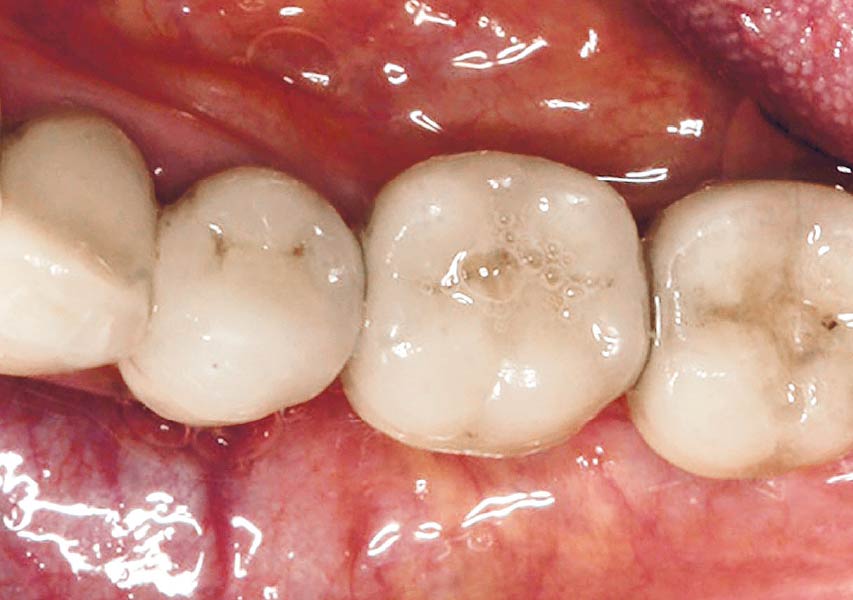
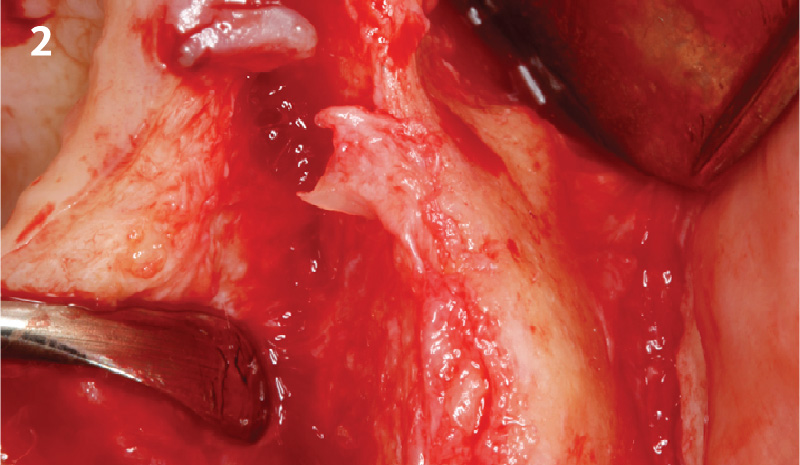
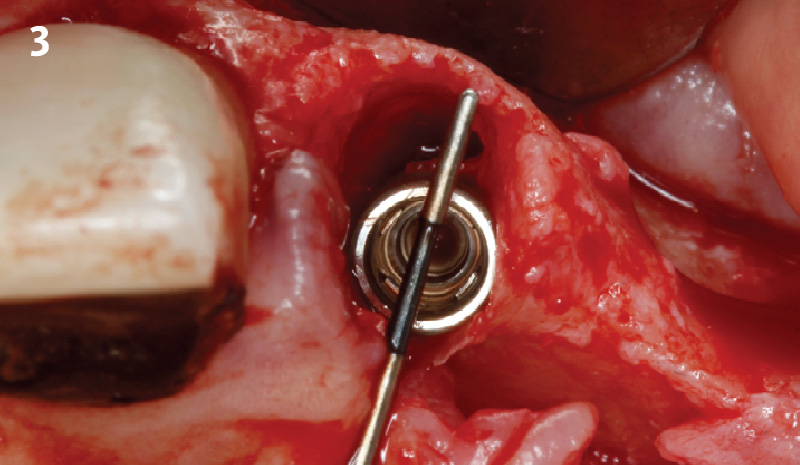
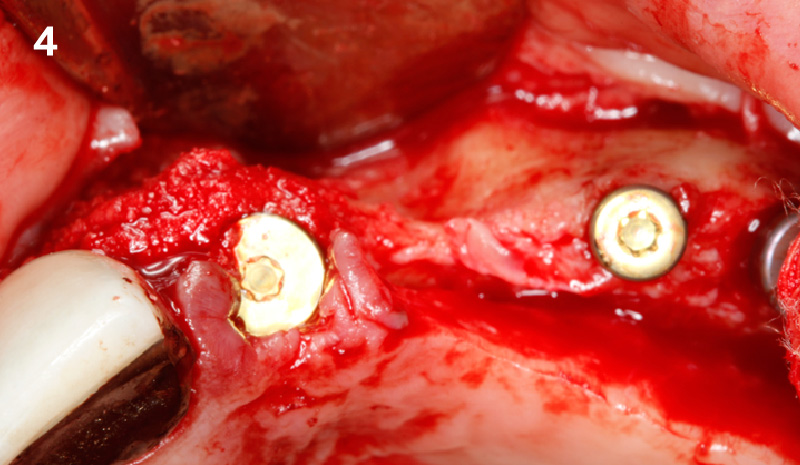
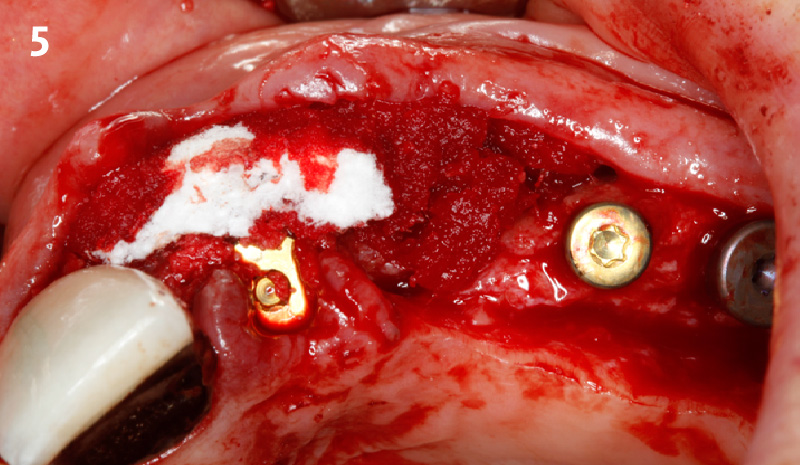
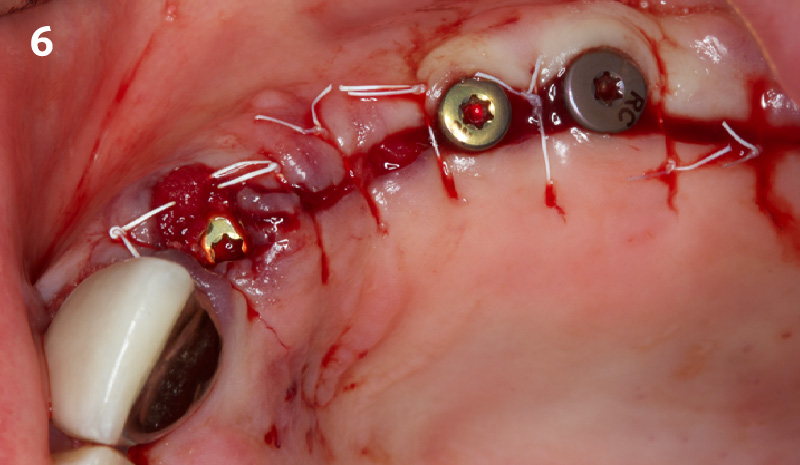
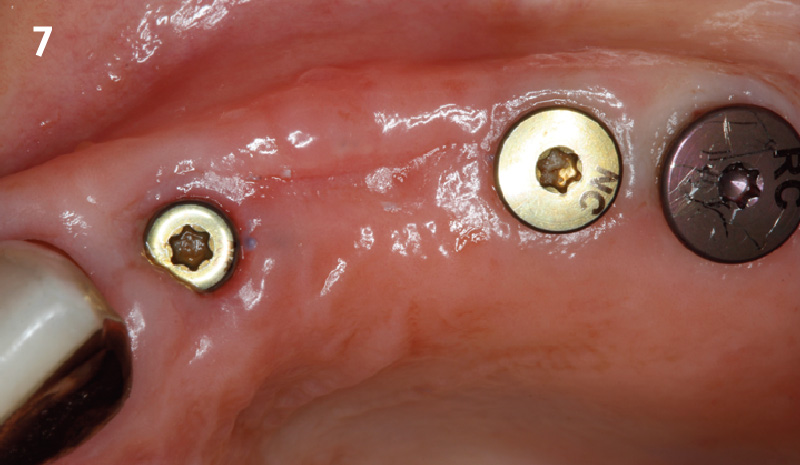
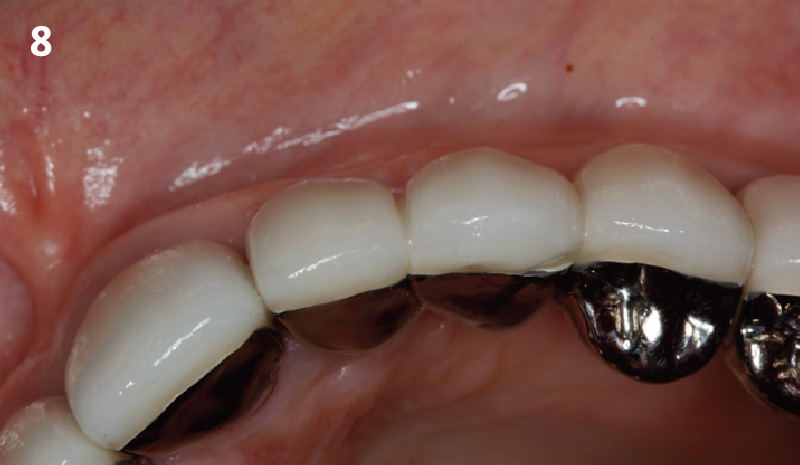
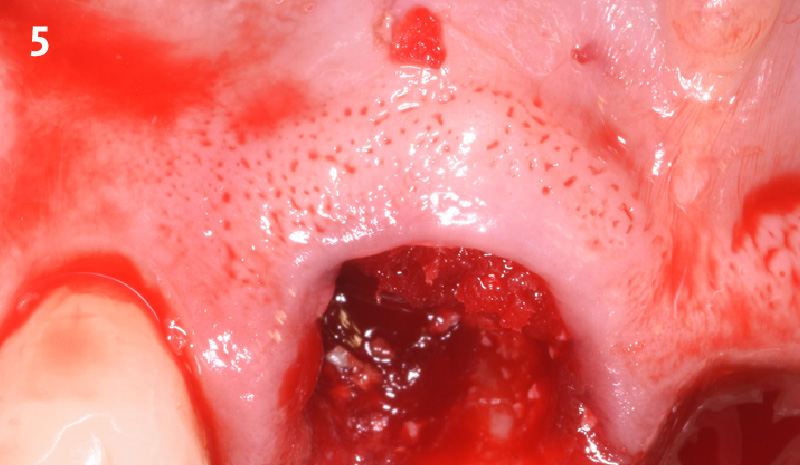
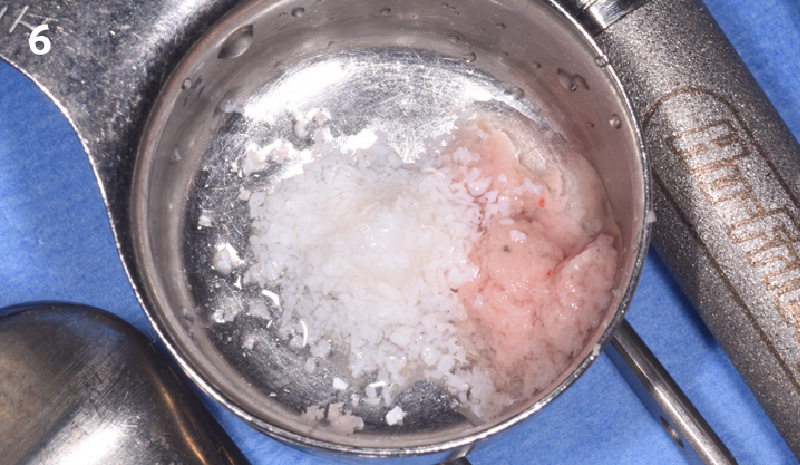
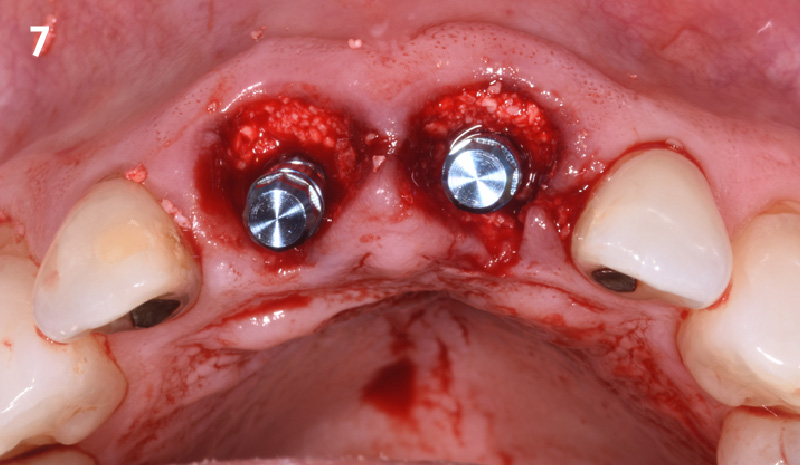
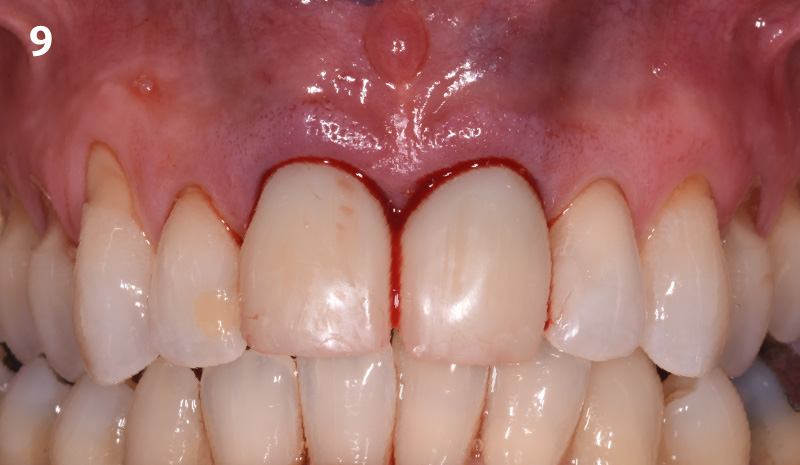
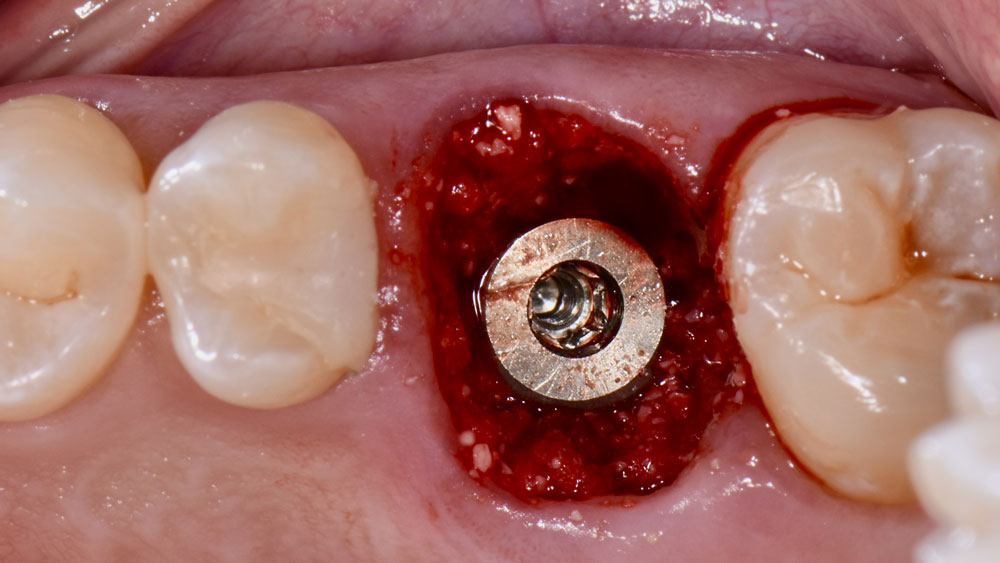
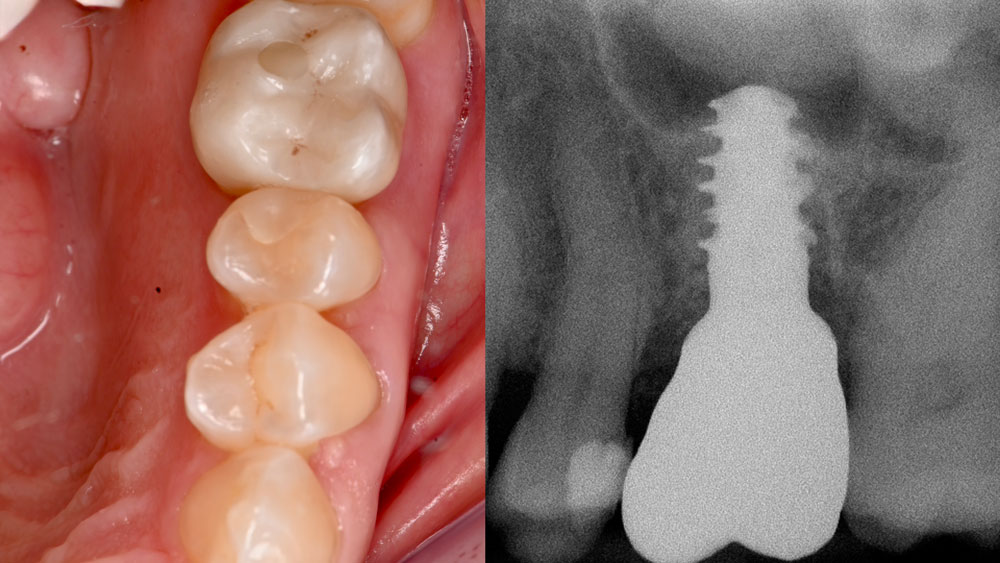
A fully guided approach was utilized, with an immediate provisional Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM) crown. Alveolar socket gaps were grafted with Geistlich Bio-Oss Collagen®, after implant placement. The provisional crown was used also as a socket seal, optimizing healing. After 3 months, a final ceramic crown was delivered. A one-year and a three-year follow-up show excellent clinical contour of the alveolar bone, and integration of the implant.
“Immediate implant placement and loading in molars is a feasible technique, with excellent long-term outcomes, if case selection is adequate, treatment planning is optimized by digital technology, and proper surgical and restorative techniques are applied.”
— Waldemar D. Polido, DDS, MS, PhD
THE OUTCOME
This case shows a three-year follow-up of an immediate implant placement, using Geistlich Bio-Oss Collagen® as a graft material on the gap. Careful tissue management, minimally traumatic extraction, and proper planning, including guided implant surgery can optimize treatment outcomes.

Waldemar D. Polido, DDS, MMS, PhD
Dr. Polido is an Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon with MS and PhD degrees from the PUCRS School of Dentistry in Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil. He completed his residency in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery at The University of Texas, Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, Texas. Currently, Dr. Polido is a Clinical Professor of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery at the Indiana University School of Dentistry. He is also the Co-Director of the Center for Implant, Esthetic, and Innovative Dentistry at Indiana University School of Dentistry in Indianapolis.

Wel-Shao Lin, DDS, FACP, PhD, MBA
Dr. Lin is a tenured Professor and Chair of Prosthodontics at Indiana University School of Dentistry. He earned his DDS from Chung-Shan and Surgical Implant Fellowship at the University of Rochester (2010). He holds a PhD in Educational Leadership (2020) and an MBA in Healthcare Administration (2022) and is currently pursuing a Master’s Intelligence. Dr. Lin specializes in dental implants, digital dentistry, and AI applications, with over 120 peer-reviewed publications. A Diplomate of the American Board of Prosthodontics and Fellow of ITI and ACP, he also serves as an associate editor for the Journal of Prosthodontics and maintains a clinical practice at Indiana University.

BIOBRIEF
Prosthetic-Surgical Approach to Regenerative Treatment for Peri-Implantitis
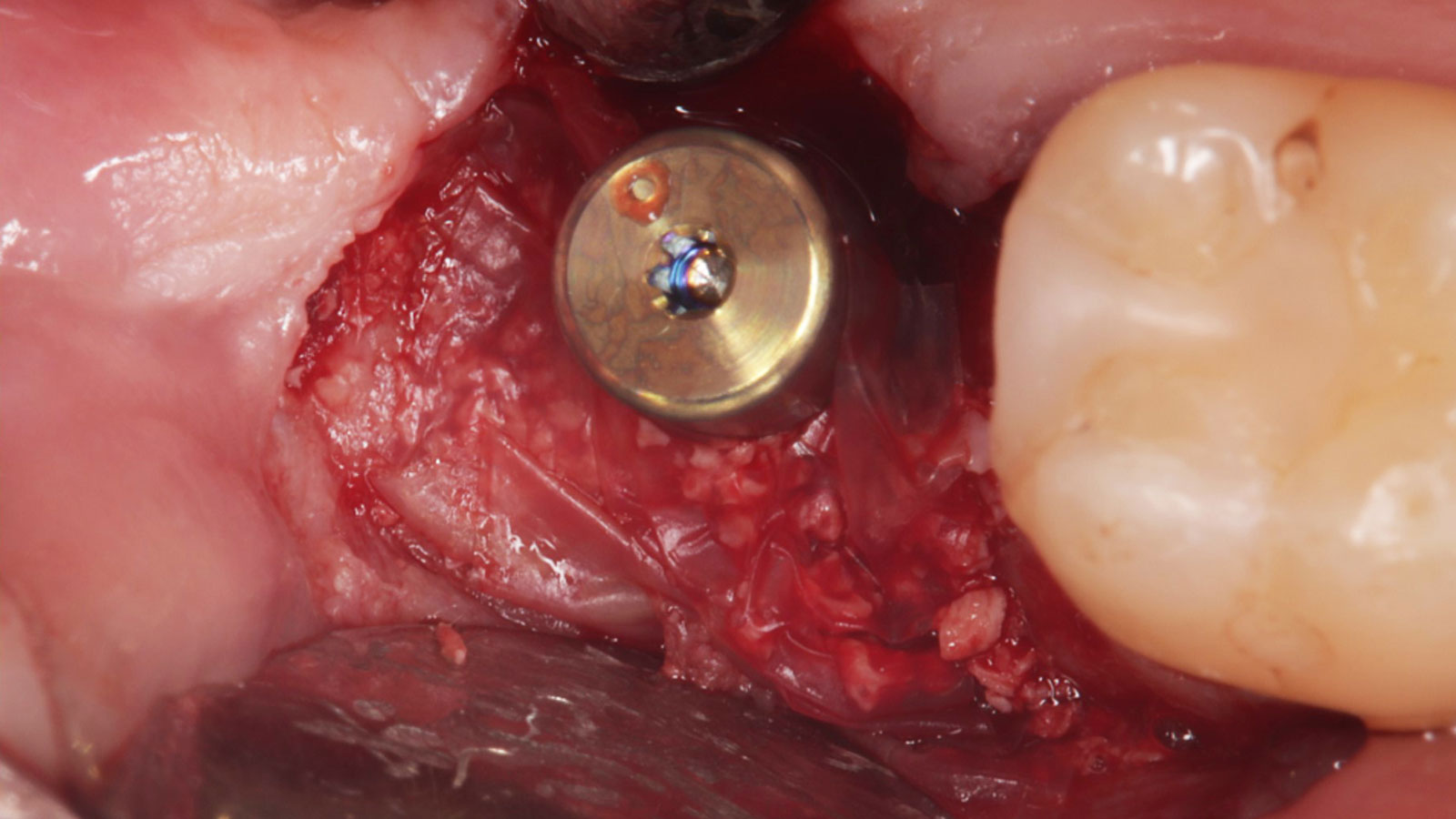


THE SITUATION
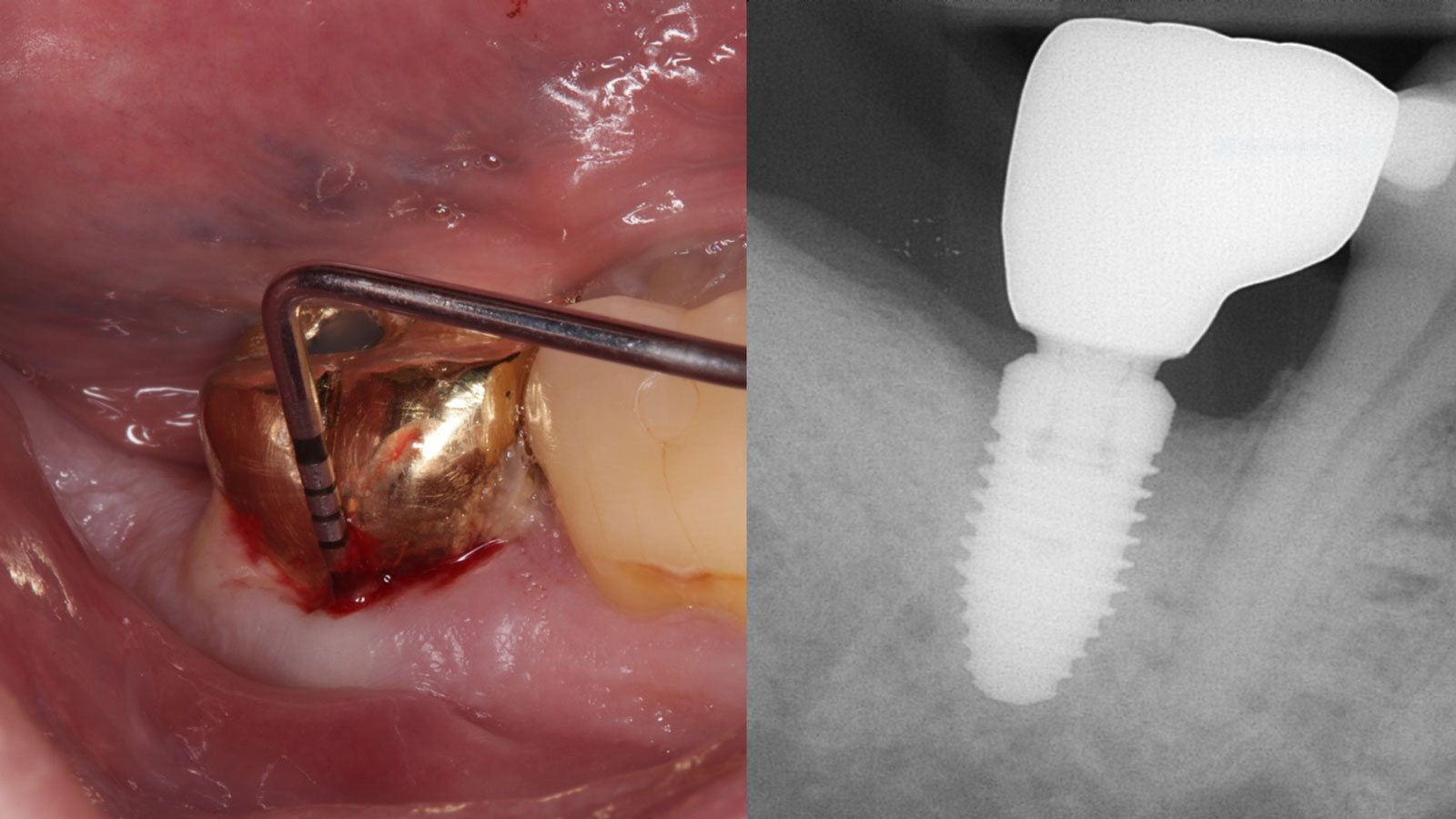
A 68-year-old male patient, who received an implant in tooth position #31 about 8 years prior, presented for an examination. He reports bleeding during brushing around the implant and some discomfort. Clinically, there was severe vertical bone loss, profuse bleeding on probing, and deep probing depths, but no pain. The condition was diagnosed as peri-implantitis according to the 2018 classification.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
Additional Risk Factors: The patient exhibited bleeding on probing and deep pocket depths. He also reported occasional marijuana use and was inconsistent with periodontal maintenance and oral hygiene visits.
THE APPROACH
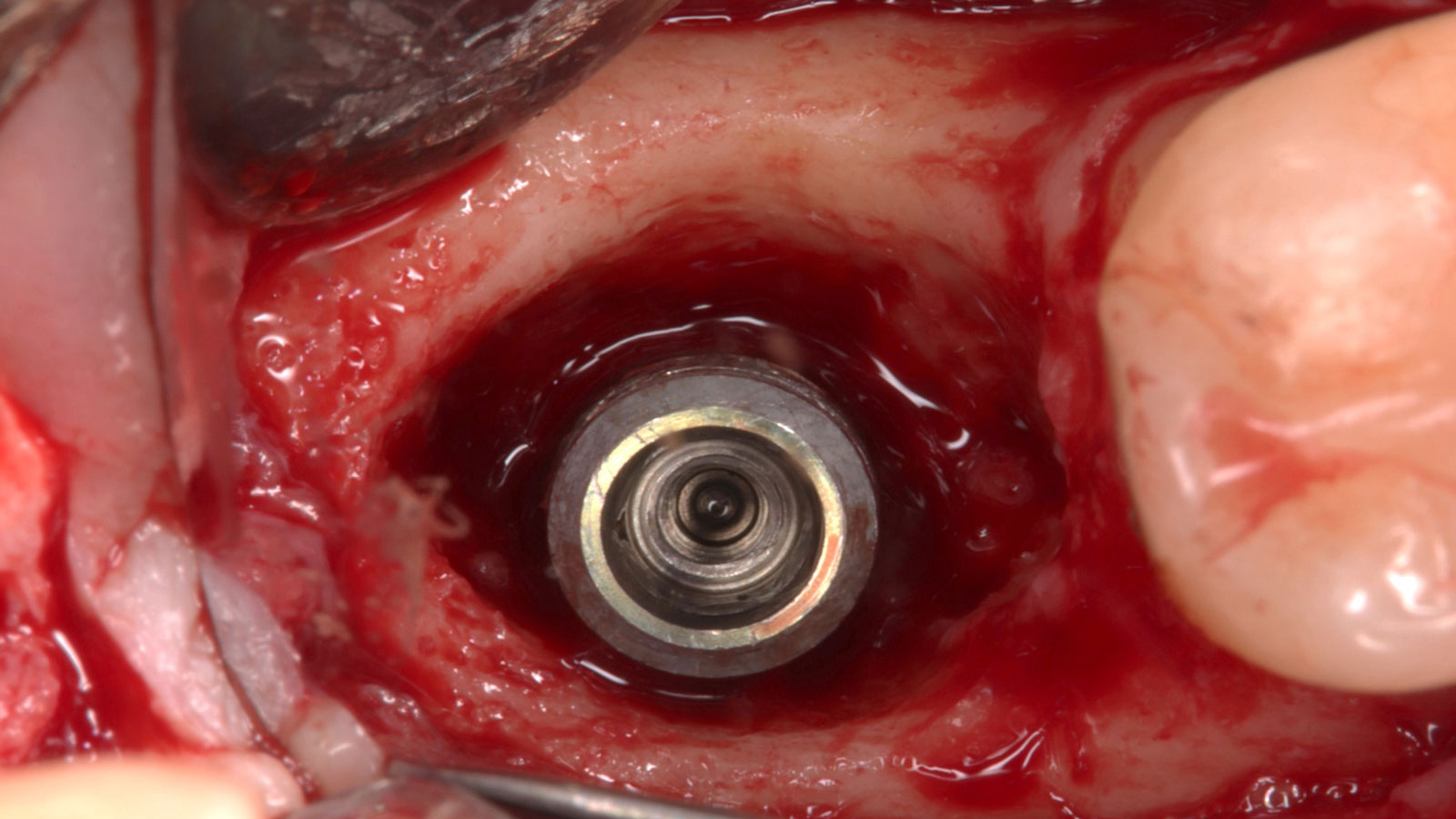
The treatment goals were to eliminate peri-implant infection, regenerate lost hard and soft tissues, and ensure long-term implant stability. A closed regenerative approach was utilized, including crown removal, thorough implant decontamination with Perioflow®, an airpolishing technology, application of the correct bone grafting materials (Geistlich Bio-Oss®, vallos® and GEM 21S®), enclosed healing, and fabrication of a new crown to facilitate hygiene.
“The implant presented with significant bone loss, deep probing depths, and bleeding on probing, placing it at risk of failure and requiring intervention to preserve function and longevity.”
— Andrea Ravidà, DDS, MS, PhD
THE OUTCOME
At the two-year follow-up, clinical and radiographic assessments showed disease resolution, complete bone gain, and stable peri-implant tissues. Probing depths were within healthy ranges, and no bleeding on probing was observed, confirming the long-term success of the treatment.
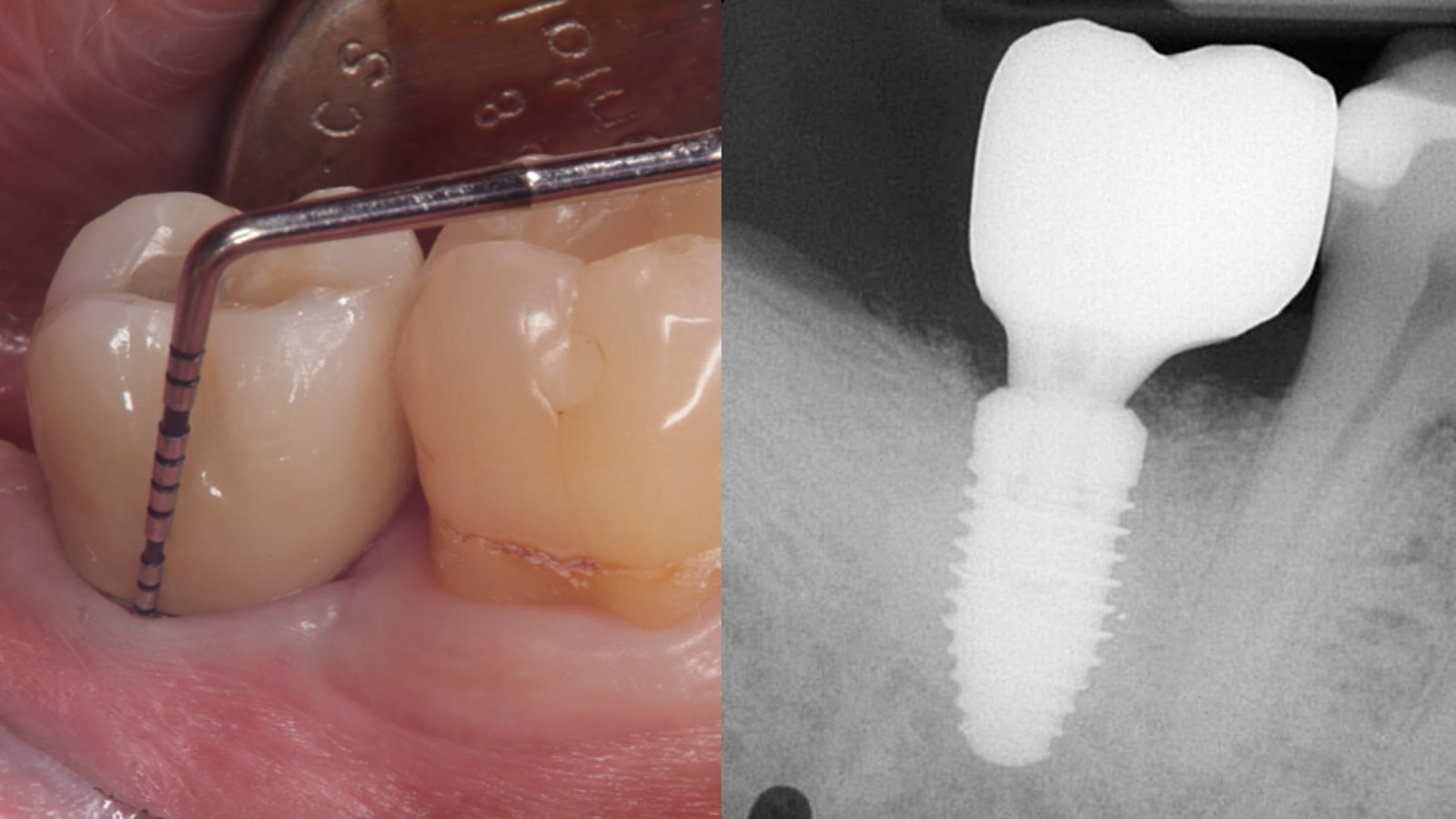

Andrea Ravidà, DDS, MS, PhD
Dr. Andrea Ravidà is the Director of the Graduate Periodontics Program in the department of Periodontics at the University of Pittsburgh. He conducts clinical research focusing on peri-implantitis, periodontitis and short implants. He has published more than 70 peer-reviewed articles and conference abstracts/presentations related to periodontics and implant therapy. He is section editor of the International Journal of Oral Implantology and the Journal of Translational Medicine.

Anu Viswanathan DDS, MDS
Dr. Anu Viswanathan is a Diplomate of the American Board of Periodontology and Implant Dentistry. She earned her Doctor of Dental Surgery degree from the University of Colorado School of Dental Medicine in 2019. Dr. Viswanathan completed a Certificate in Periodontics and earned a Master of Dental Science at the University of Pittsburgh School of Dental Medicine. She also obtained a Certificate in IV Sedation. Dr. Viswanathan is currently in private practice in Shoreline, Connecticut.
Sorry, you do not have permission to view this content.
Sorry, you do not have permission to view this content.
Sorry, you do not have permission to view this content.
Sorry, you do not have permission to view this content.
Sorry, you do not have permission to view this content.

BIOBRIEF
Odontogenic Keratocyst Management
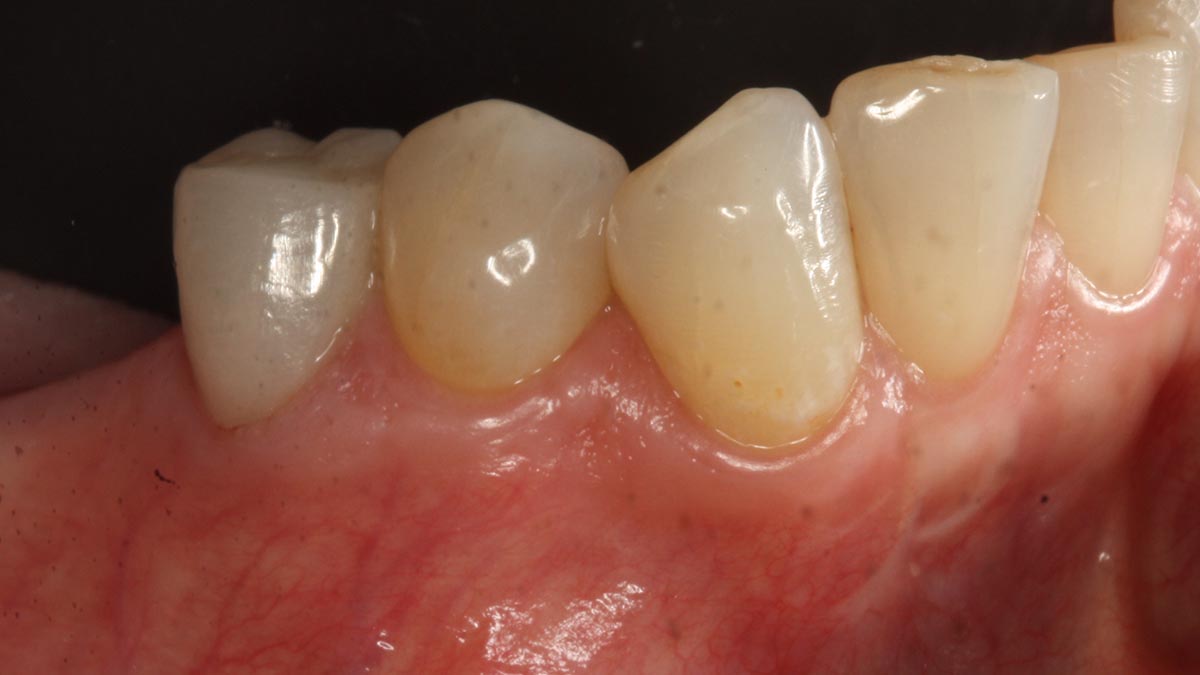

THE SITUATION
A 60-year-old-heathy Caucasian female presented with the chief complaint: “I noticed a bump on my lower left teeth since last year.” An examination revealed a stable periodontium except for enlarged gingival tissue between #21-22 measuring 10x8x5mm, well-defined borders, depressible, non-painful, and vital teeth without displacement. The treatment plan included flap surgery, excisional biopsy, GTR #21-22 (Diff Dx: Lateral periodontal cyst (LPC), Odontogenic Keratocyst (OKC), Benign Fibro-Osseous lesion (BFOL).
Guided Tissue Regeneration (GTR) using Geistlich Bio-Oss® and vallos®f was performed and covered with a resorbable collagen membrane (Geistlich Bio-Gide®).
Primary closure was completed using non-resorbable sutures. Follow-up at 2, 4 weeks, 3, 6 months showed stable periodontium without re-occurrence. The pathology report indicated OKC and the area is monitored annually.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
The treatment goal was to excise the lesion around #21-22 and stabilize the periodontium. Sulcular incisions #20-22 with vertical incision #22 MF were performed. Upon full thickness flap reflection, the lesion was removed (excisional biopsy). The defect extended #21M-#22D with complete facial bone loss. It was a wide 1-2 bony wall defect measuring 10x8x5mm. GTR procedure using Geistlich Bio-Oss® and vallos®f and Geistlich Bio-Gide® for the collagen membrane were employed. Primary closure was obtained using 6-0 prolene suture.
“Excisional biopsy and guided tissue regeneration is indicated to treat the pathology (#21-22 area) and stabilize the periodontium.”
— Dr. Bassam Kinaia
THE OUTCOME
Complete excision of pathology and biopsy followed by GTR using vallos®f internally for maximum osteogenic/osteoinductive potential and Geistlich BioOss® externally for space maintenance showed excellent radiographic bone fill and stable periodontium.
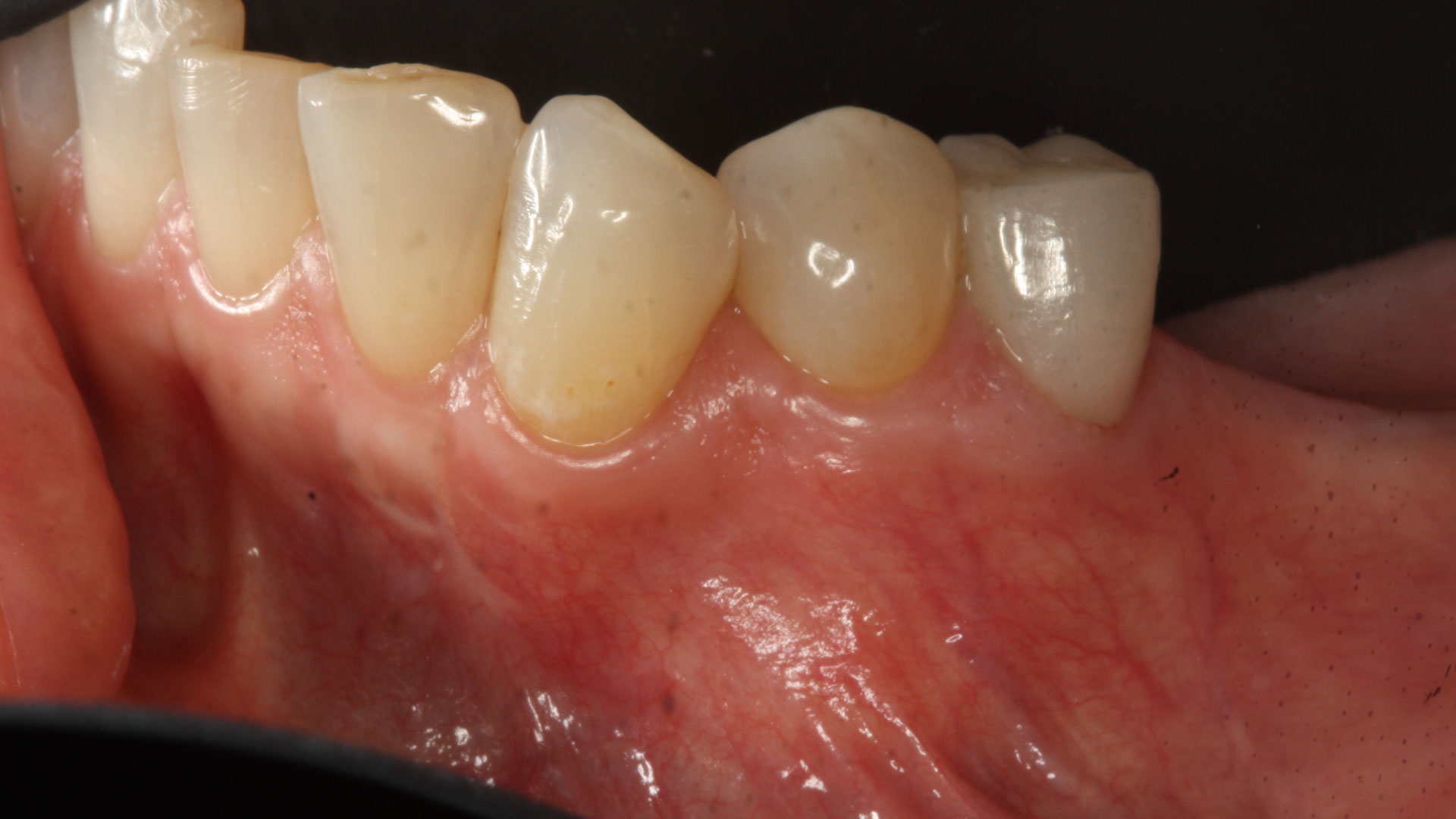

Bassam Kinaia, DDS, MS, DICOI
Dr. Kinaia is the Associate Director of the Graduate Periodontology Program at the University of Detroit Mercy (UDM). He is also the former Director of the Periodontology Program at UDM in Michigan and Boston University Institute for Dental Research and Education in Dubai. He is a Diplomate of the American Academy of Periodontology (AAP) and International Congress of Oral Implantology (ICOI). He received a certificate of Excellence from the AAP in recognition of teaching-research fellowship.

BIOBRIEF
Successful Implant Placement and Horizontal Augmentation for Bilateral Congenitally Missing Maxillary Incisors
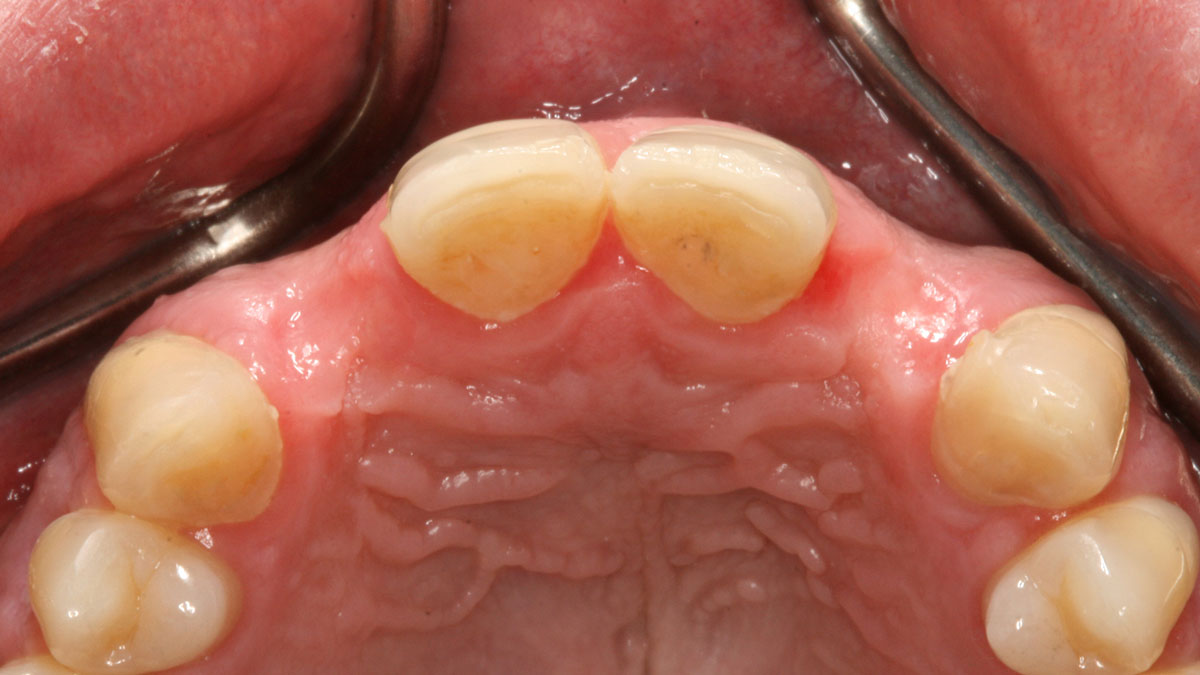

THE SITUATION
A 30-year-old male patient was referred to me with bilateral congenitally missing lateral incisors in the maxilla. The referring general dentist had previously made a resin-bonded bridge which was successful for a few years but had frequent debondings. Clinical examination revealed lack of ridge contour but the CBCT revealed existence of adequate width for placement of narrow-diameter implants with additional bone grafting and contour augmentation. The existing bone anatomy precluded placement of implants for screw-retained restorations without a pre-surgical lateral ridge augmentation procedure. The patient accepted a treatment plan for placement of two narrow-diameter implants and simultaneous bone grafting and contour augmentation followed by restoration with zirconia cement-retained crowns.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Compromised | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
My treatment goals were to preserve the existing soft-tissue architecture, especially the interdental papilla, mesial and distal to the lateral incisors, improve the facial contour at the lateral incisor sites by bone grafting with a low substitution biomaterial, and harmonize esthetics and function with optimal implant-supported restorations.
“The patient had failed resin-bonded bridges with deficient contours for bilateral congenitally missing lateral incisors.”
THE OUTCOME
Single-stage implant placement with bilateral papilla-sparing incision design and simultaneous contour augmentation using a mixture of Geistlich Bio-Oss® autologous bone chips and Geistlich Bio-Gide®.
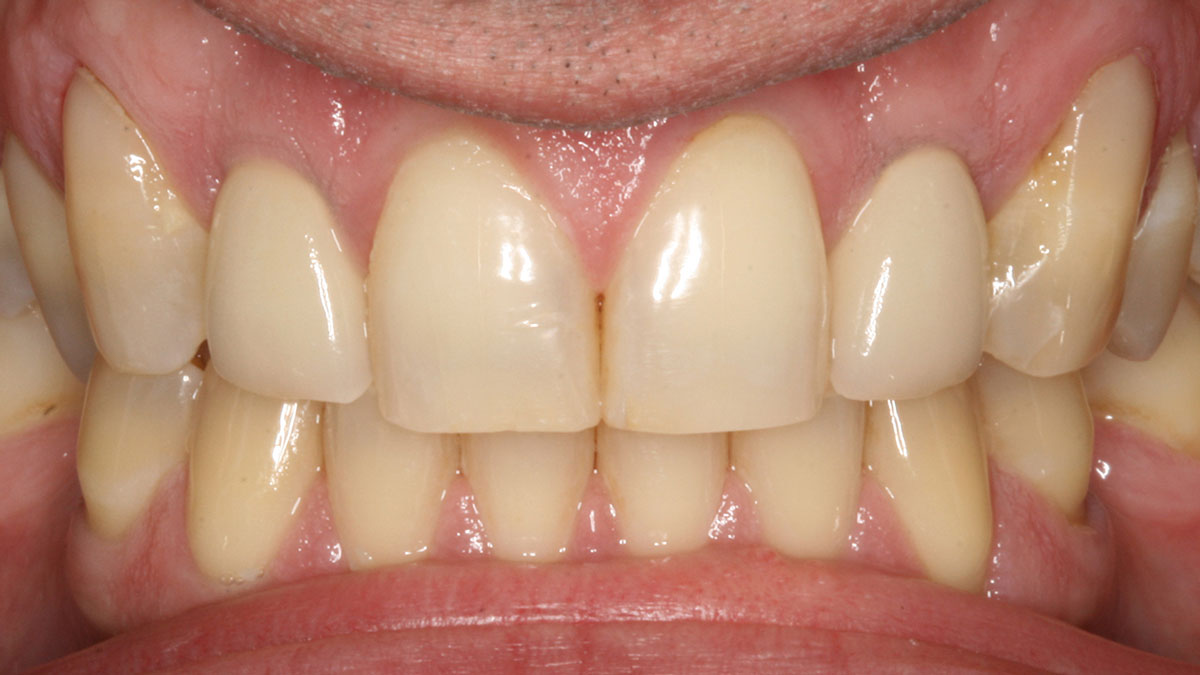

Dr. Avinash Bidra
Dr. Bidra is a Board Certified Maxillofacial Prosthodontist and Director of the Prosthodontics Residency Program at UCONN School of Dental Medicine. He has extensive surgical experience and maintains a part-time private practice restricted to Implant Surgery and Prosthodontics in Meriden, CT. He has lectured at national and international meetings, as well as published extensively in international scientific journals. He has invented prosthetic components and is a co-inventor of a new implant design.

BIOBRIEF
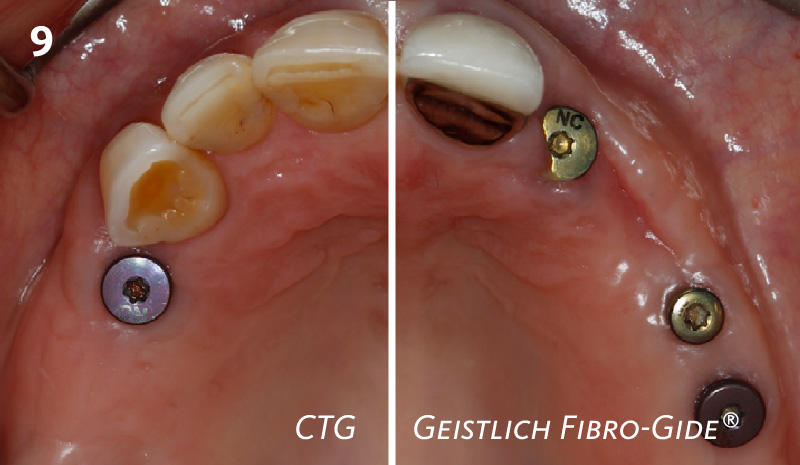
Phenotype Conversion Using Geistlich Fibro-Gide® for Immediate Implants in the Esthetic Zone
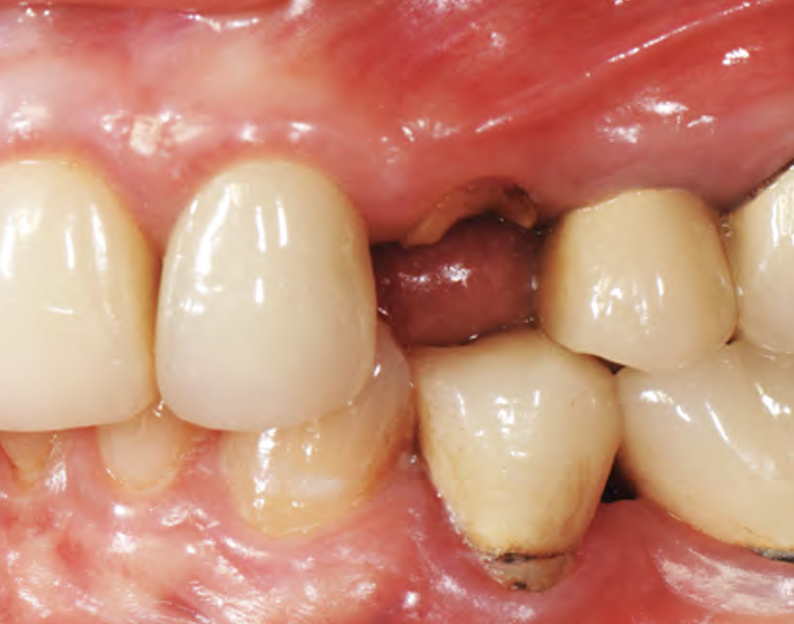

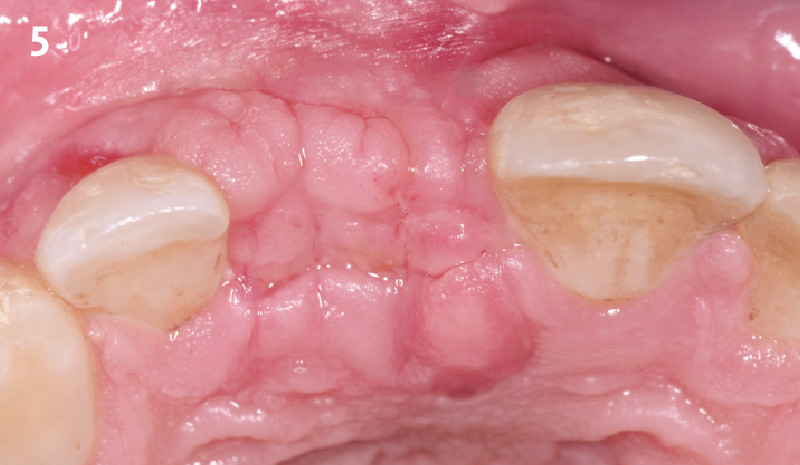
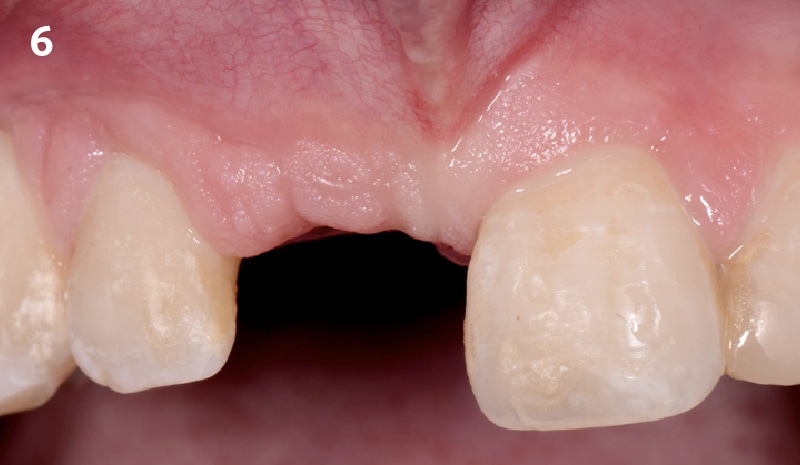
THE SITUATION
A healthy non-smoking 50-year-old female patient who desires a single tooth solution to replace a non-restorable tooth, #12. A root fracture at the level of the palatal post was diagnosed in a root canaled tooth. Maintaining esthetics of the adjacent teeth is important as they are also restored with single full coverage porcelain crowns. Lastly, treatment time reduction and a minimally invasive surgical technique are desired by the patient for reduced downtime and post-operative morbidity.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
Facial Bone Wall Phenotype: High Risk (<1mm)
Esthetic Risk Profile (ERP) = Medium (summary of above)
THE APPROACH
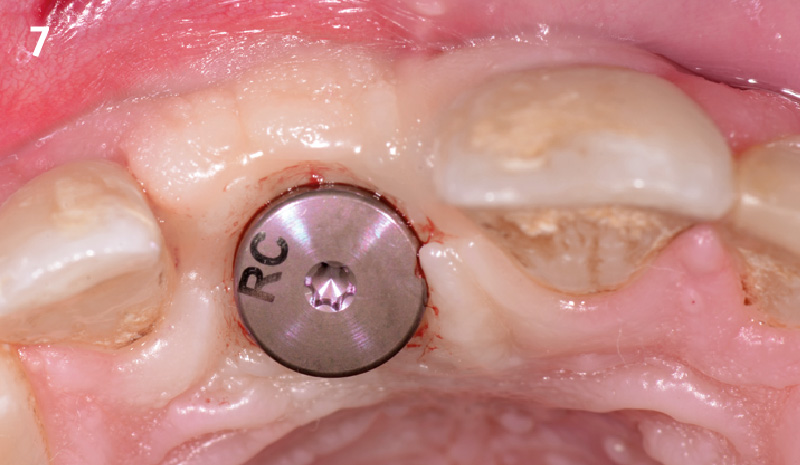
A minimally invasive surgical removal of tooth #12 with maintenance of the buccal plate and leaving a 3mm buccal gap. The implant will be placed one mm below the level of the intact buccal plate with an anatomically correct surgical guide template to provide for a screw-retained solution. The gap will be filled with Geistlich Bio-Oss Collagen® to maintain the bone buccal to the implant, and a palate free approach utilizing Geistlich Fibro-Gide® for soft tissue thickening to accomplish “phenotype conversion.” The long-term surgical goal is >2-3mm thickness of both hard and soft tissue buccal to the implant.
“High esthetic demands were the primary concern with this case. They were addressed with the diagnostic tools of clinical photos, a site specific CBCT to evaluate the buccal wall status, and summing the findings with patient expectations gathered using the Esthetic Risk Assessment (knee-to-knee; eye-to-eye) which is used along with our consent agreement to treatment.”
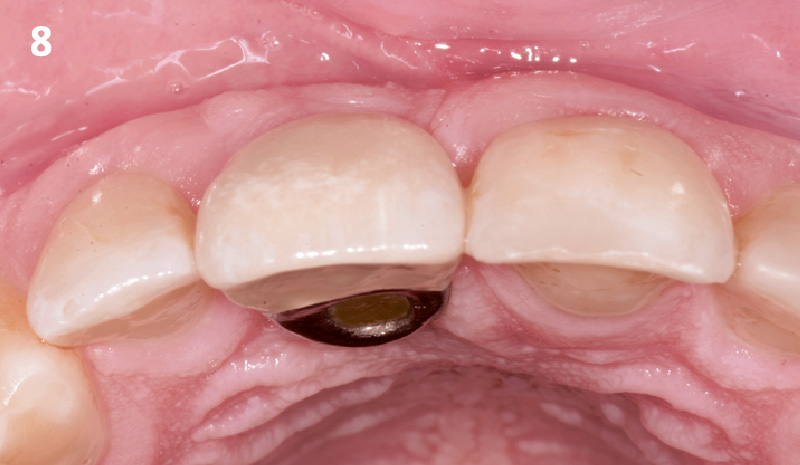
THE OUTCOME
Minimally invasive surgery for buccal wall maintenance, virtually planning the buccal gap and implant width, using a xenograft in the buccal gap with phenotype conversion using a volume stable collagen matrix in conjuction with immediate contour management, allows for the best chance for papillae fill interproximally and maintenance of the mid-buccal gingival margin long-term.
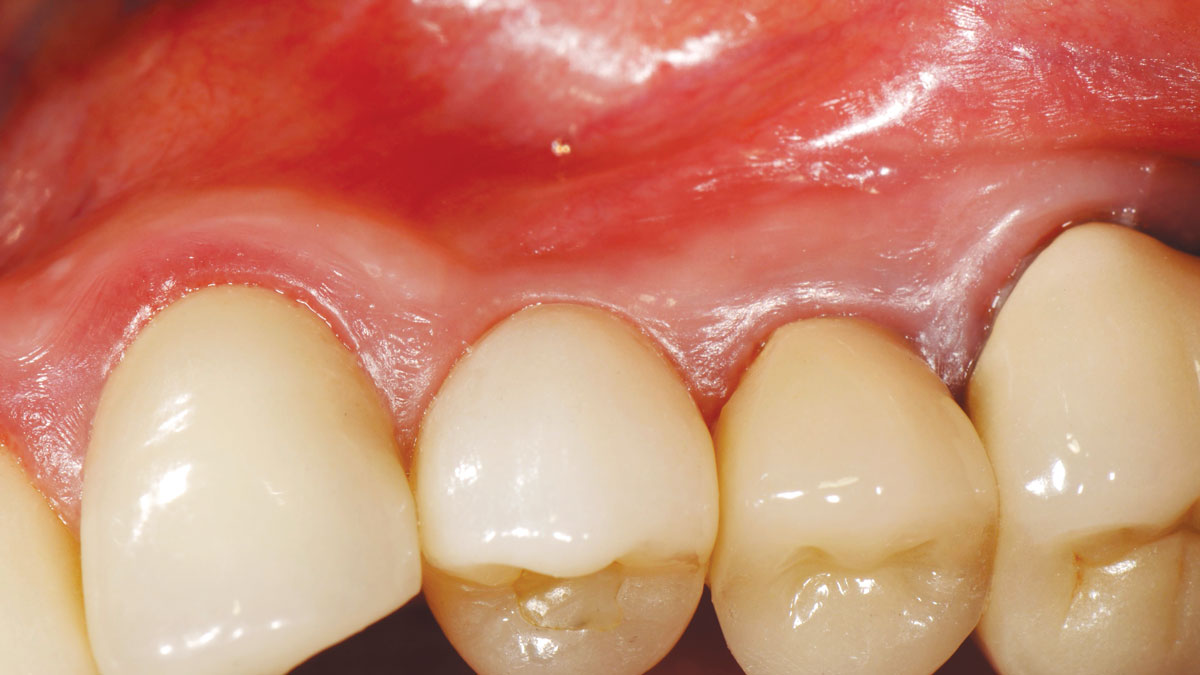

Dr. Robert A. Levine
Robert A. Levine DDS is a board-certified periodontist at the Pennsylvania Center for Dental Implants and Periodontics in Philadelphia. He is a Fellow of the International Team for Dental Implantology (ITI), College of Physicians in Philadelphia, International Society of Periodontal Plastic Surgeons and the Academy of Osseointegration. He has post-graduate periodontology and implantology teaching appointments at Temple University in Philadelphia, UNC in Chapel Hill and UIC in Chicago and has over 80 scientific publications.

BIOBRIEF
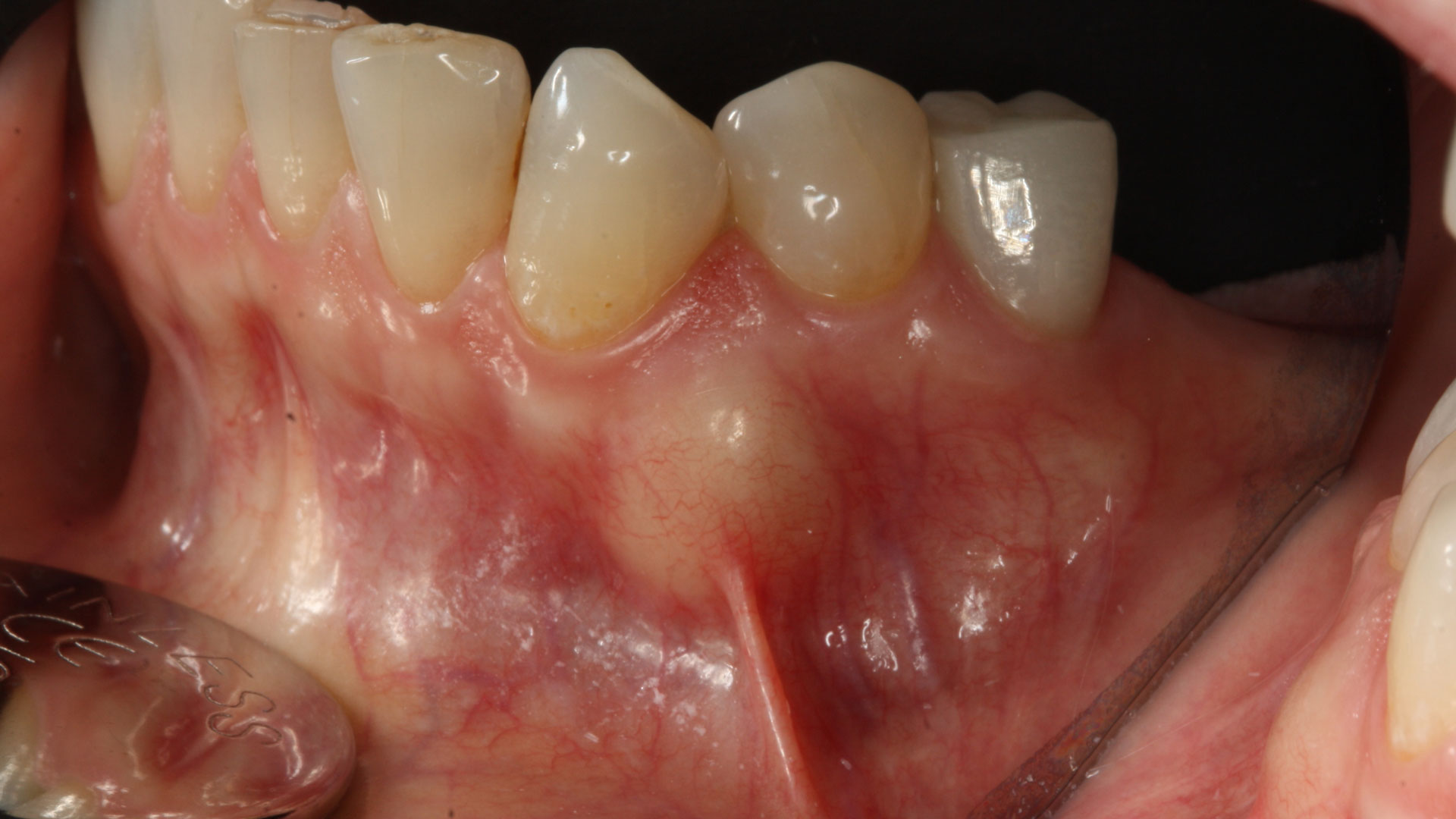
Horizontal Ridge Augmentation in the Posterior Mandible of a 90-Year-Old Female
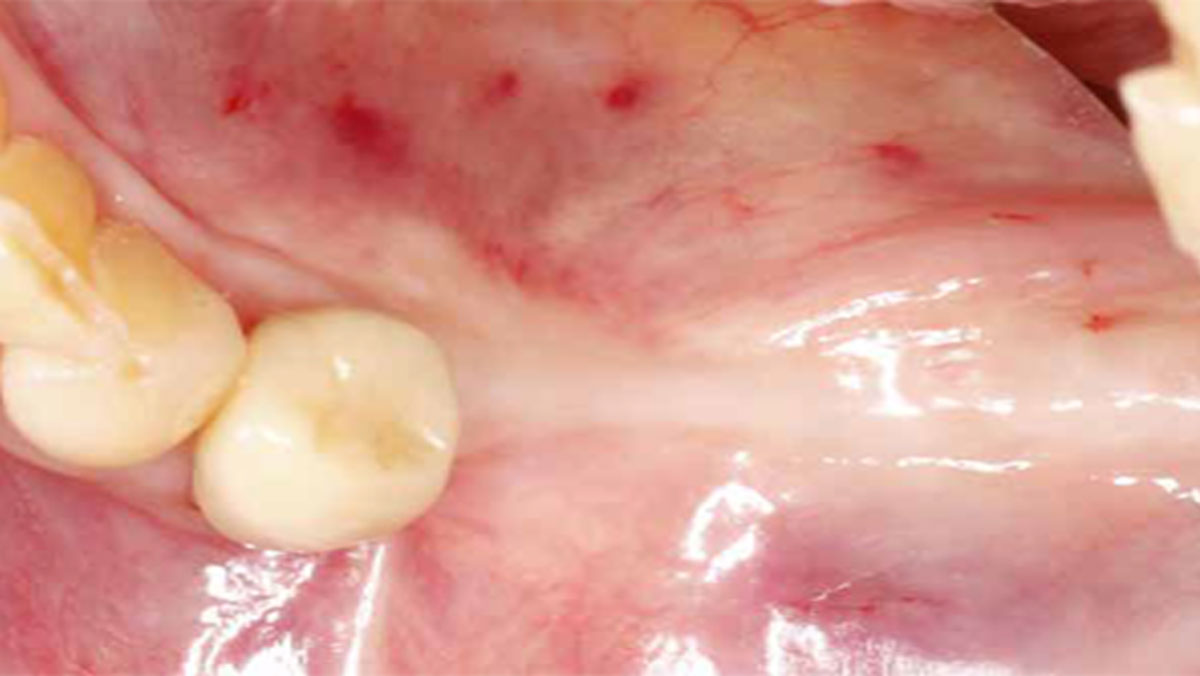

THE SITUATION
A 90-year-old female presented requesting dental implants be placed in the left mandibular posterior region. Her chief complaint was increased drooling and difficulty chewing on only one side. She lost her bridge one year prior to her visit and firmly stated that she did not want to wear a partial denture. The clinical exam and CBCT showed that there was a horizontal alveolar ridge deficiency that precluded the implants from being placed in a restoratively desirably position. Therefore, a horizontal ridge augmentation was done using multiple layers of Geistlich Bio-Gide® Compressed over a 1:1 ratio of autogenous bone and Geistlich Bio-Oss® xenograft.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
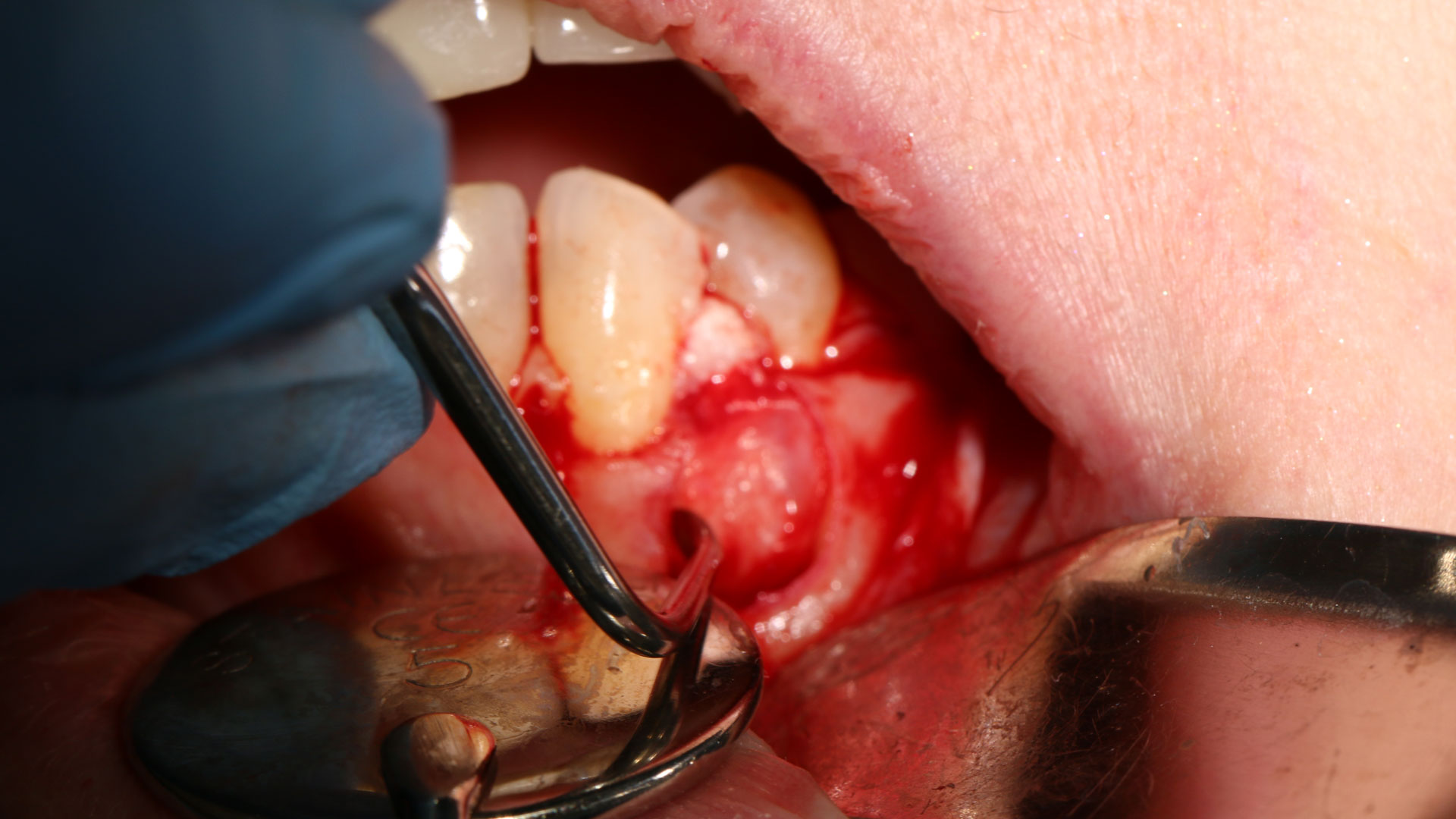
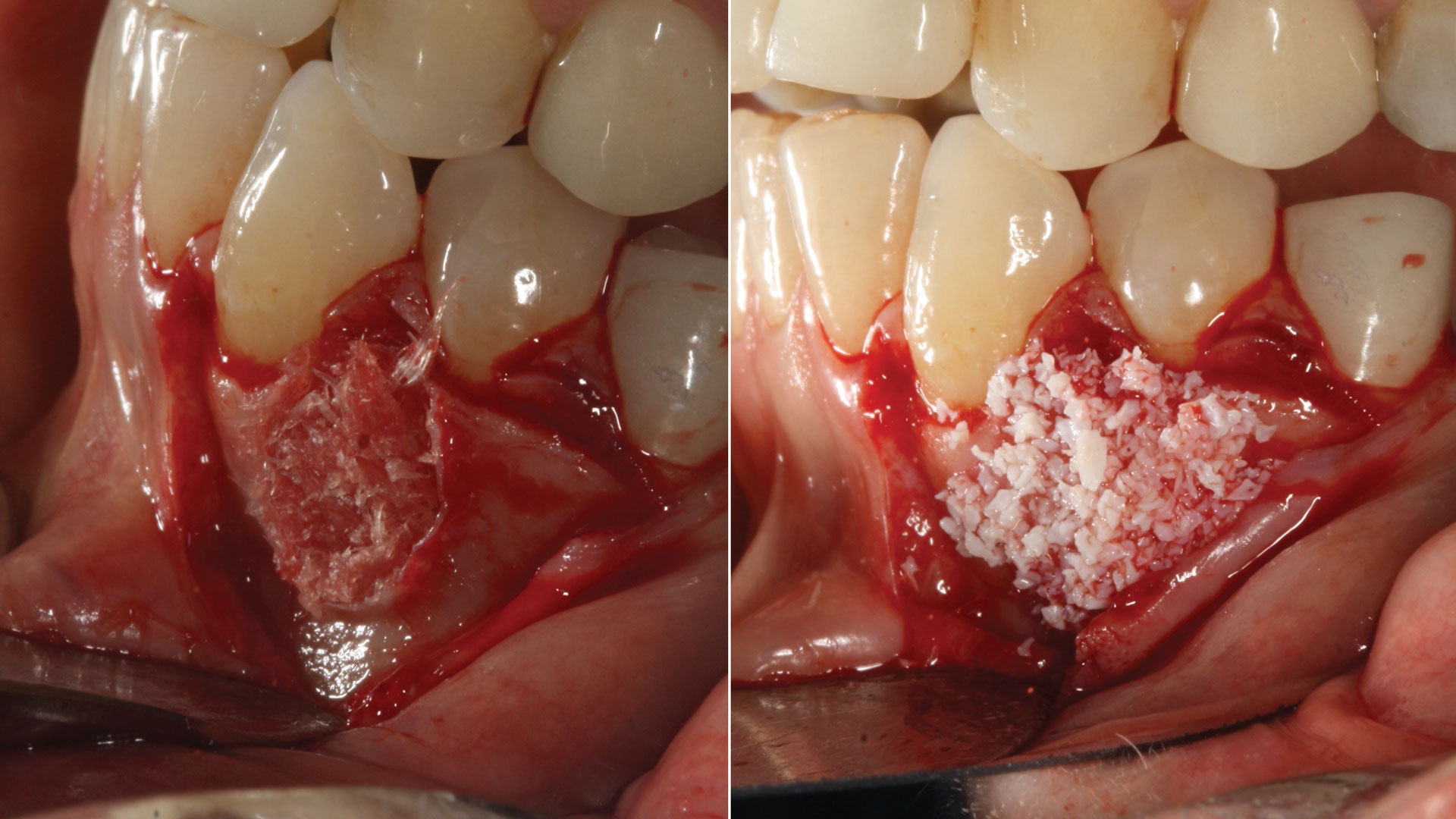
THE APPROACH
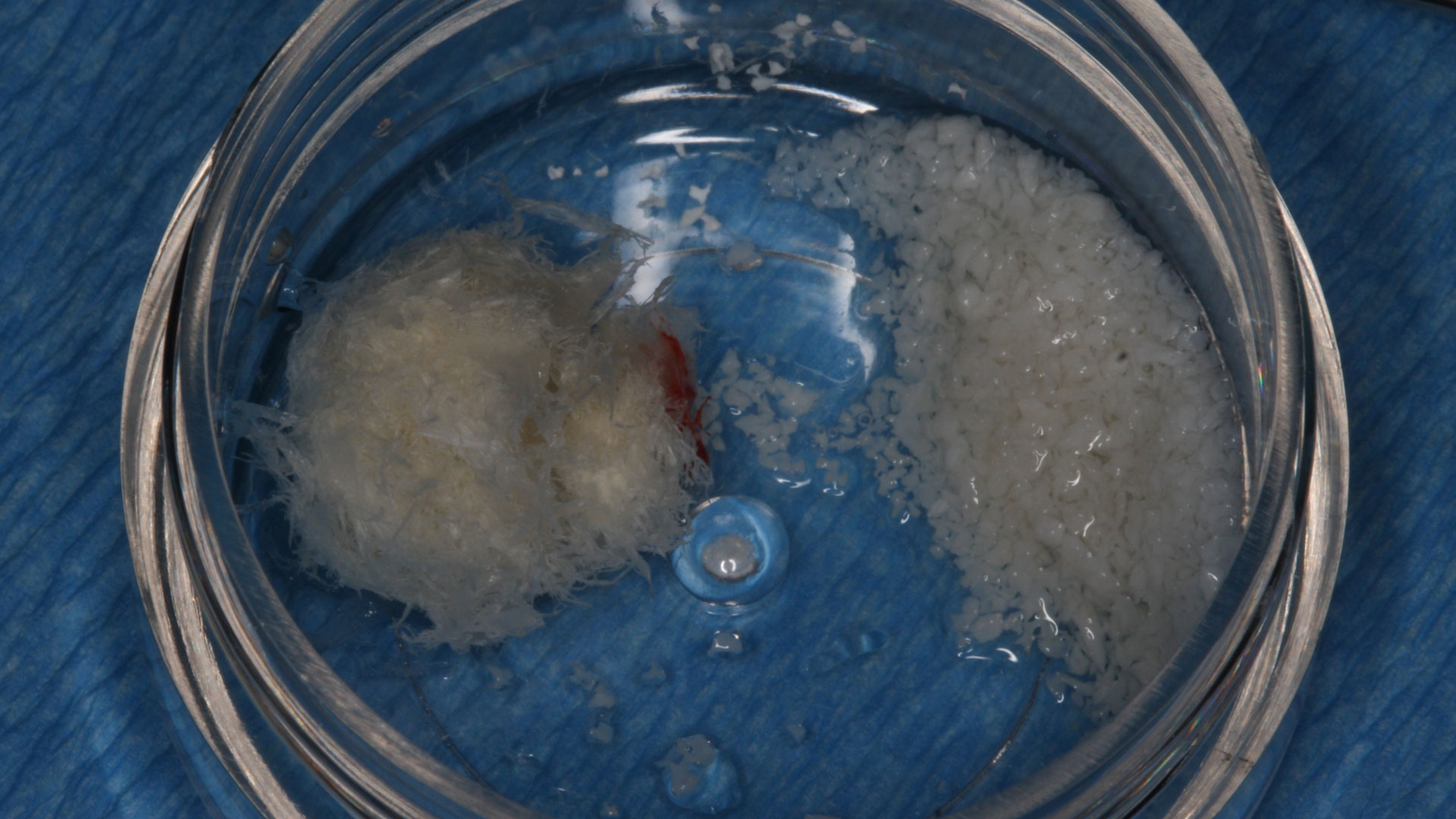
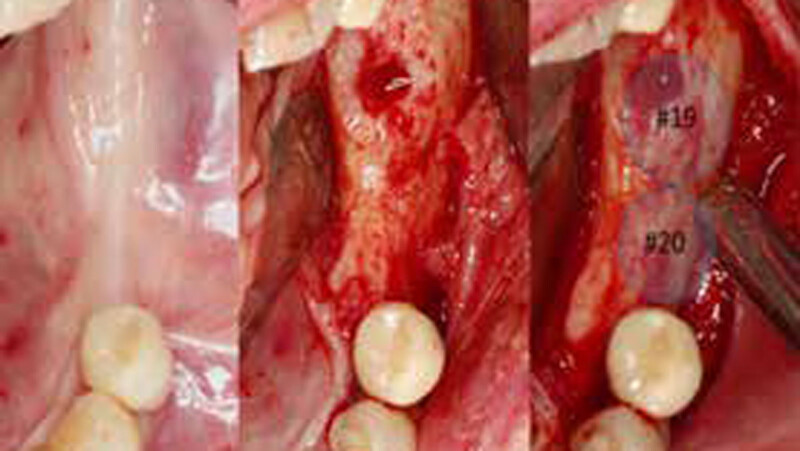
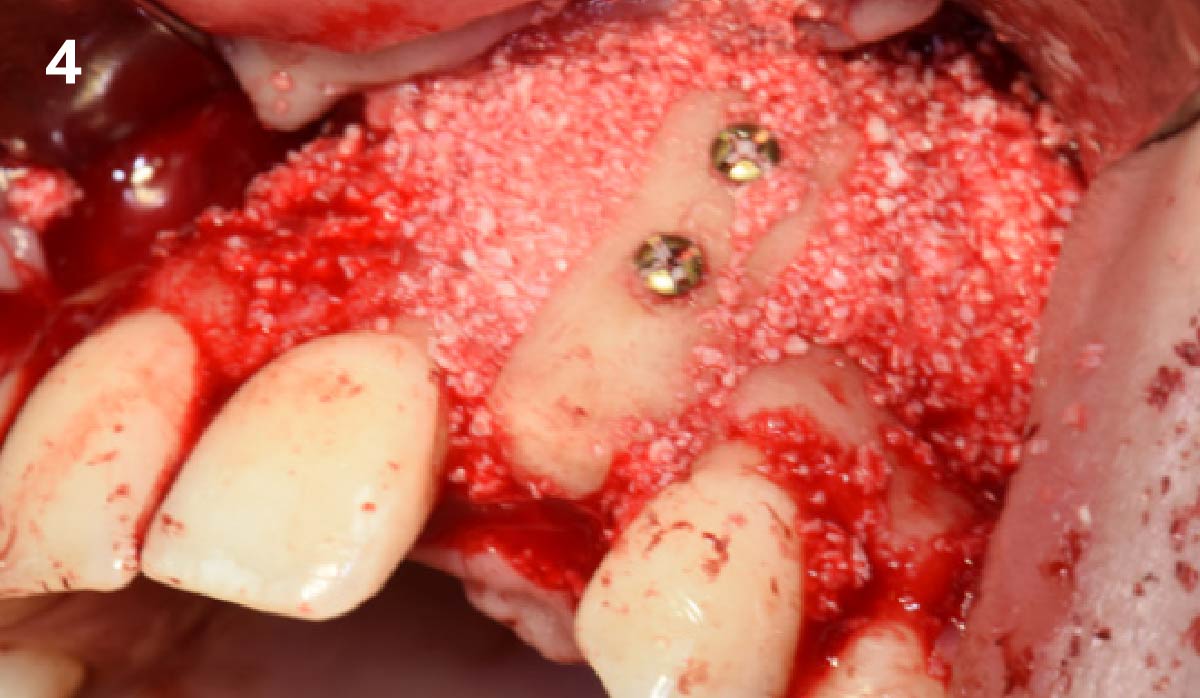
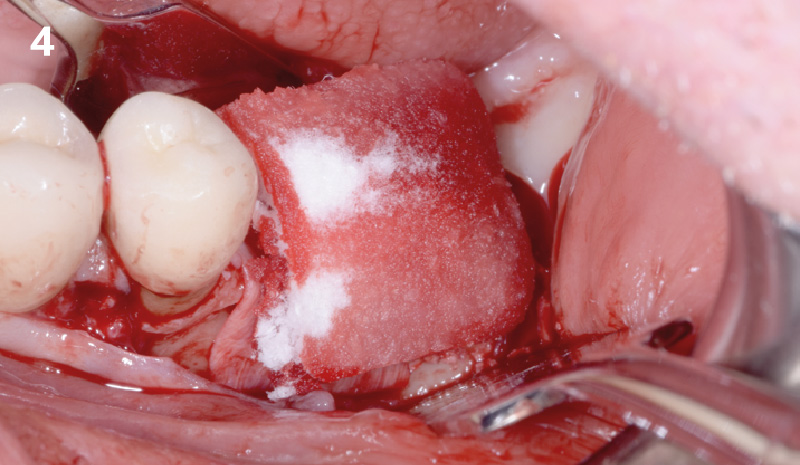
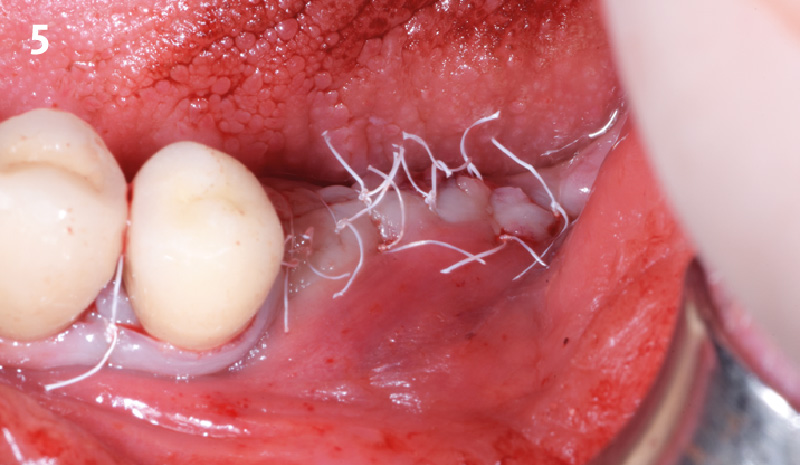
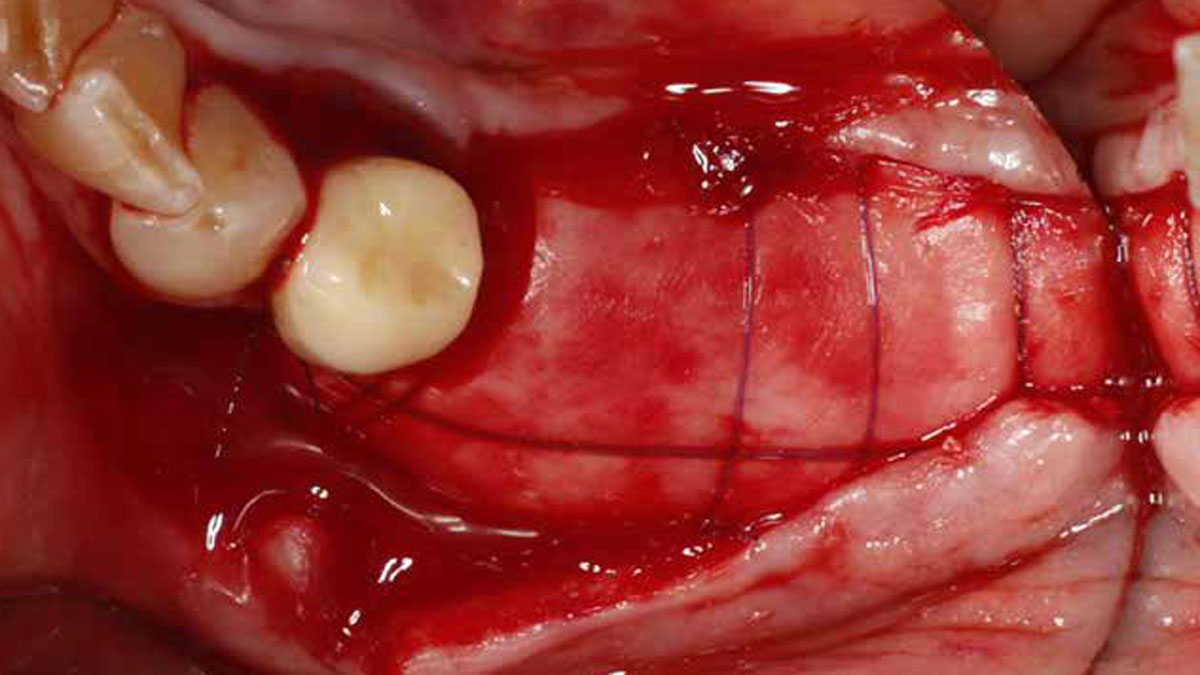
The treatment goal was to gain adequate horizontal bone dimension to allow for prosthetically-driven implant placement. Guided bone regeneration was performed in which autogenous bone was mixed with Geistlich Bio-Oss® xenograft in a 1:1 ratio. PRF was used to create “sticky bone” and was covered by multiple layers of Geistlich Bio-Gide® Compressed. The membrane was stabilized with periosteal biting stabilizing sutures. Tension-free primary closure was achieved and the grafted site was allowed to heal for 8 months prior to the implant surgery for #19 and #20.
“A predictable ridge augmentation procedure was needed to help our 90-year-old patient avoid having nutritional deficiencies due to lack of proper chewing ability and also to improve her quality of life.”
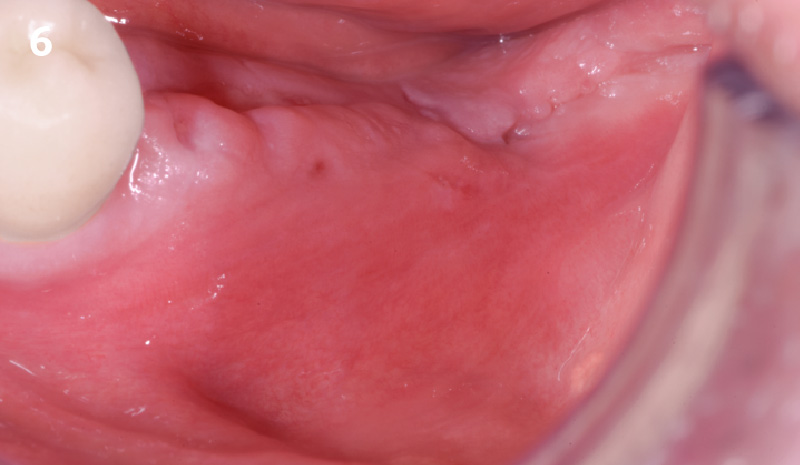
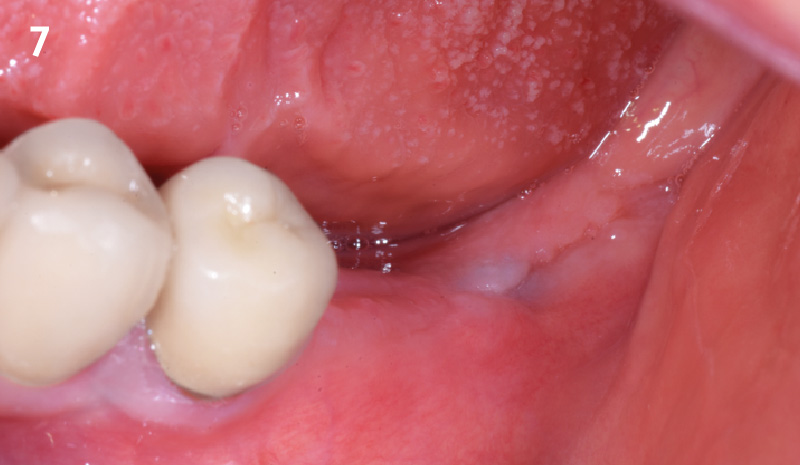
THE OUTCOME
The horizontal ridge augmentation procedure resulted in adequate bone for implant therapy as evidenced by the CBCT scan and re-entry surgery. With a sufficient quantity of good quality regenerated bone, implants for #19 and #20 were placed using a surgical guide based on a diagnostic wax up. Our 90-year-old patient is very happy to be able to chew efficiently again.

Dr. John Kim
Dr. Kim, originally from Fairfax, VA, received his DMD from Harvard School of Dental Medicine. He completed his residency and received his M.S. in Periodontics at UNC School of Dentistry at Chapel Hill. Dr. Kim is a Diplomate of the American Board of Periodontology and actively speaks as an expert on guided bone regeneration, implant therapy, soft tissue grafting, and managing complications domestically and internationally. He is also an adjunct faculty at UNC Adams School of Dentistry.

BIOBRIEF
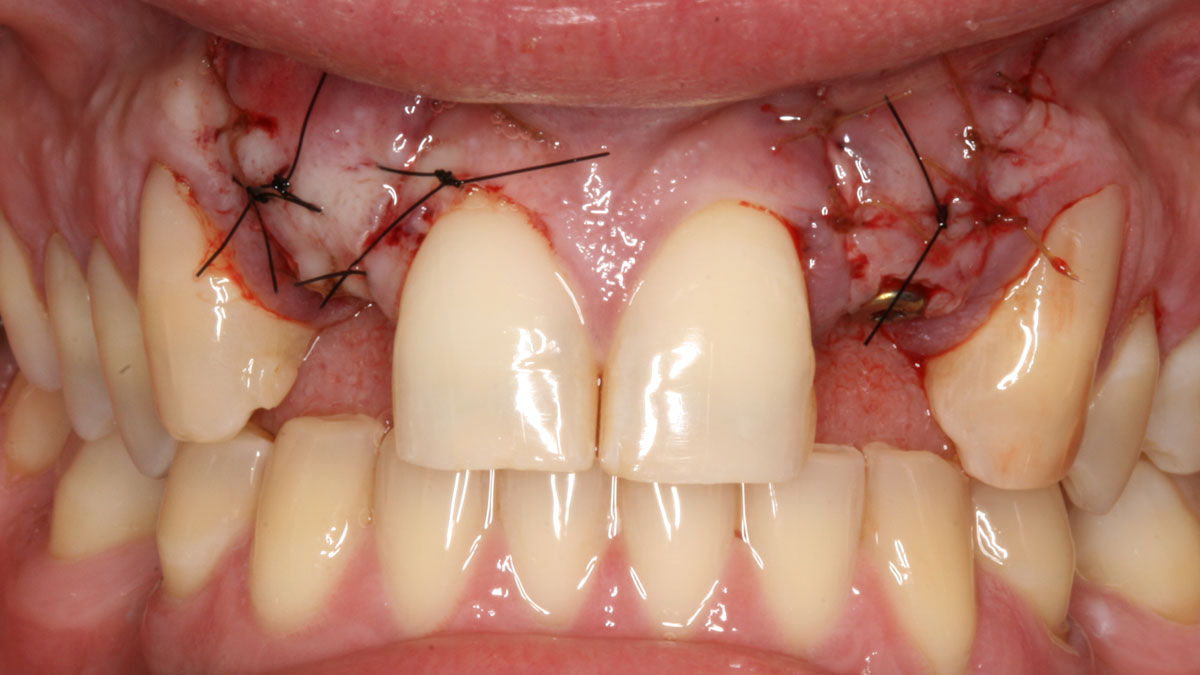
Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor
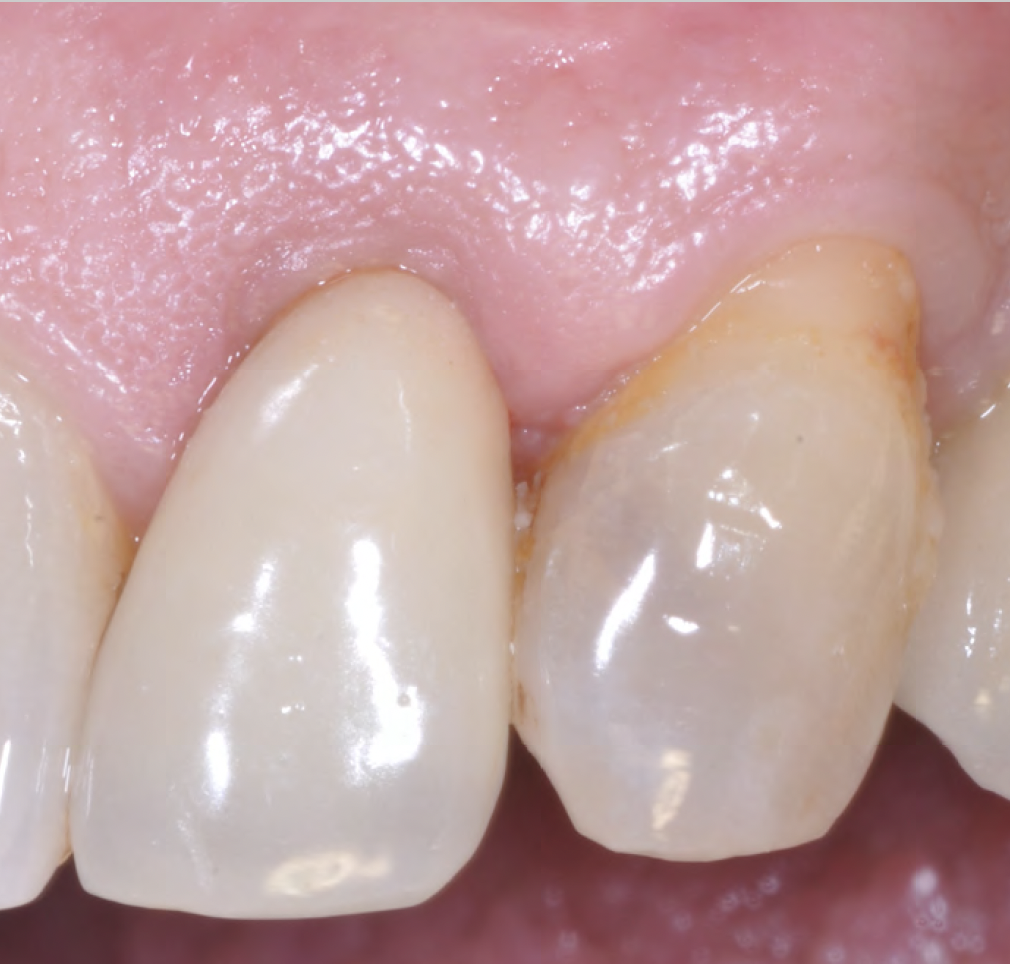

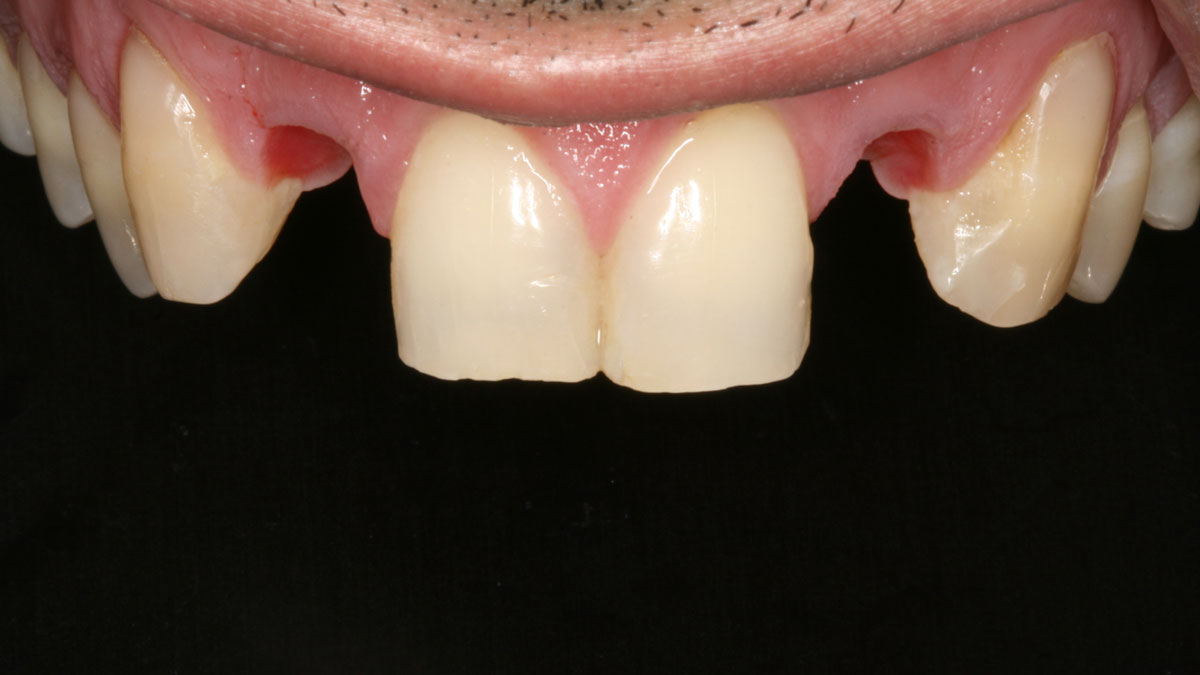
THE SITUATION
An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure on the maxillary left lateral incisor. The patient‘s request was to have a definitive implant-supported single crown. The clinical situation revealed recession of the free gingival margin, while the CBCT evaluation showed the missing buccal bone plate, which contra-indicated an immediate implant placement. The treatment plan included a staged approach with a ridge augmentation procedure at the time of tooth extraction, in order to recreate the buccal bone plate and reduce the gingival recession. By moving the free gingival margin, keratinized tissue was gained through an open-healing approach.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system Non-smoker | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
The treatment goals were to improve the soft-tissue levels and regenerate the buccal bone plate. After performing a flapless extraction procedure, a specifically designed resorbable bilayer collagen membrane, Geistlich Bio-Gide® Shape, was inserted into the socket with the long wing in contact with the buccal surface and the smooth, compact upper layer facing outward. The alveolus was then grafted with Geistlich Bio-Oss Collagen®. The three smaller wings of the membrane were folded on top of the graft material and sutured to the surrounding soft-tissue, allowing for open-healing.
“The patient had a failing crown with compromised soft tissue and requested a single crown rehabilitation with improved esthetics.”
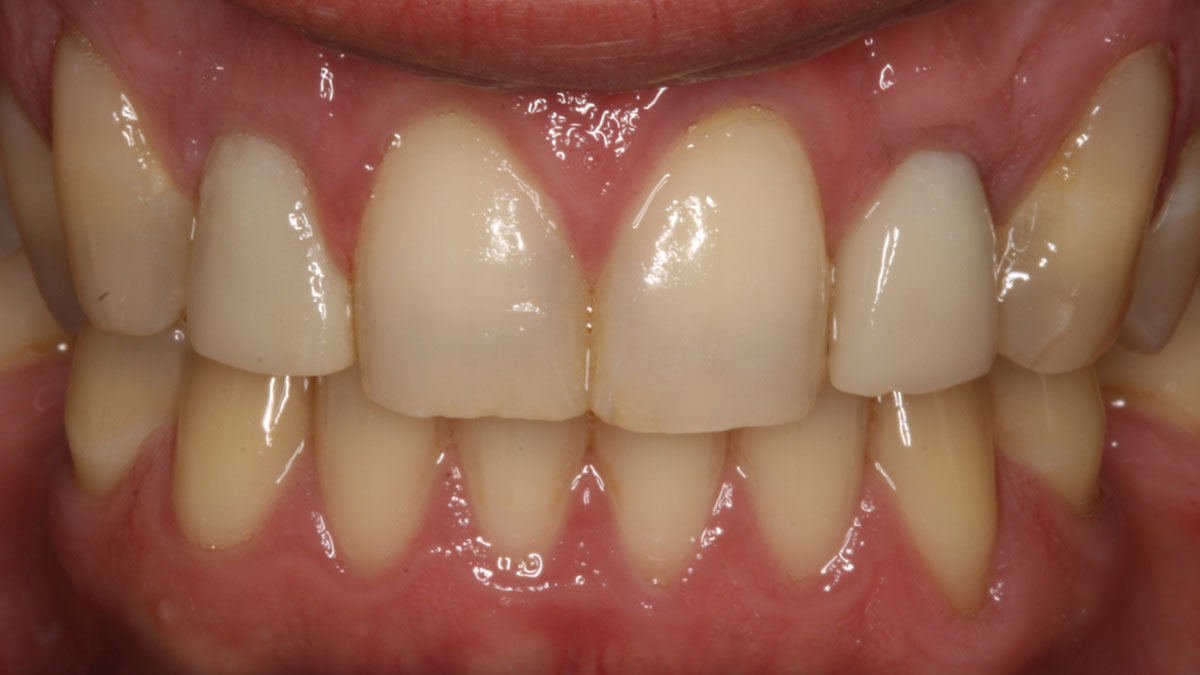
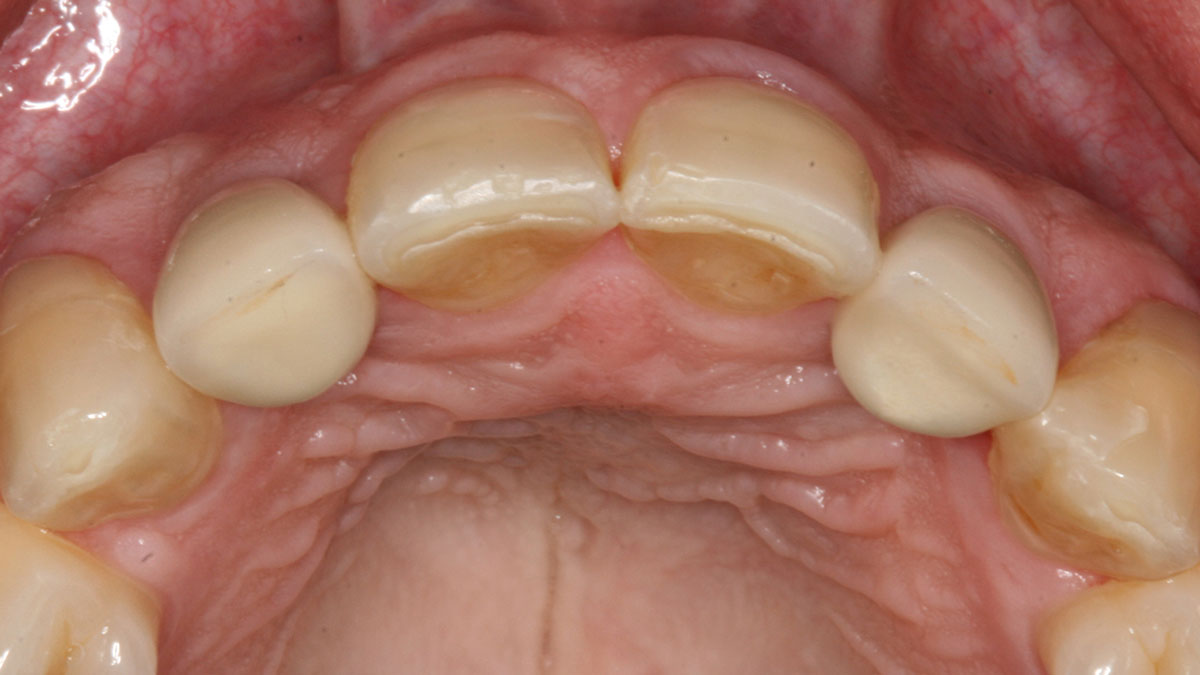
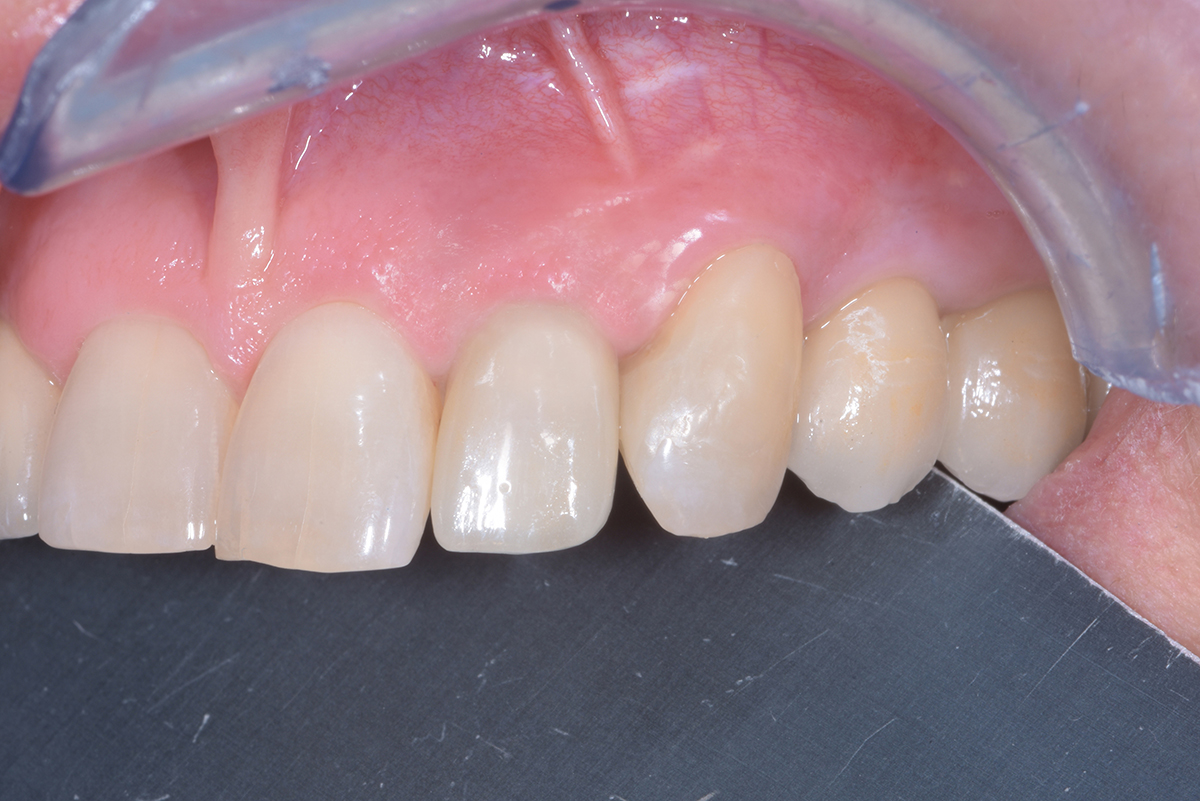
THE OUTCOME
This case demonstrates how it is possible to improve the clinical and esthetic situation that was presented at baseline. Despite missing the buccal bone plate and the recession of the free gingival margin, the ridge augmentation procedure performed with the combination of Geistlich Bio-Gide® Shape and Geistlich Bio-Oss Collagen® was able to create a positive volume of the ridge, allowing for a prosthetically guided implant placement.

Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli
Periodontist – PRoED, Institute for Professional Education in Dentistry, Torino
Doctor of Dentistry and Certificate in Periodontology from the University of Torino, Italy.
Active member of the Italian Society of Periodontology, European Federation of Periodontology, Italian Academy of osseointegration and Academy of osseointegration. International member of the American Academy of Periodontology. Scientific Director of Institute for Professional Education in Dentistry (PRoED), Torino. Member of the Editorial Board of The International Journal of Periodontics and Restorative Dentistry. Private practice in Torino, Italy.

BIOBRIEF
Immediate Mandibular Molar Transition
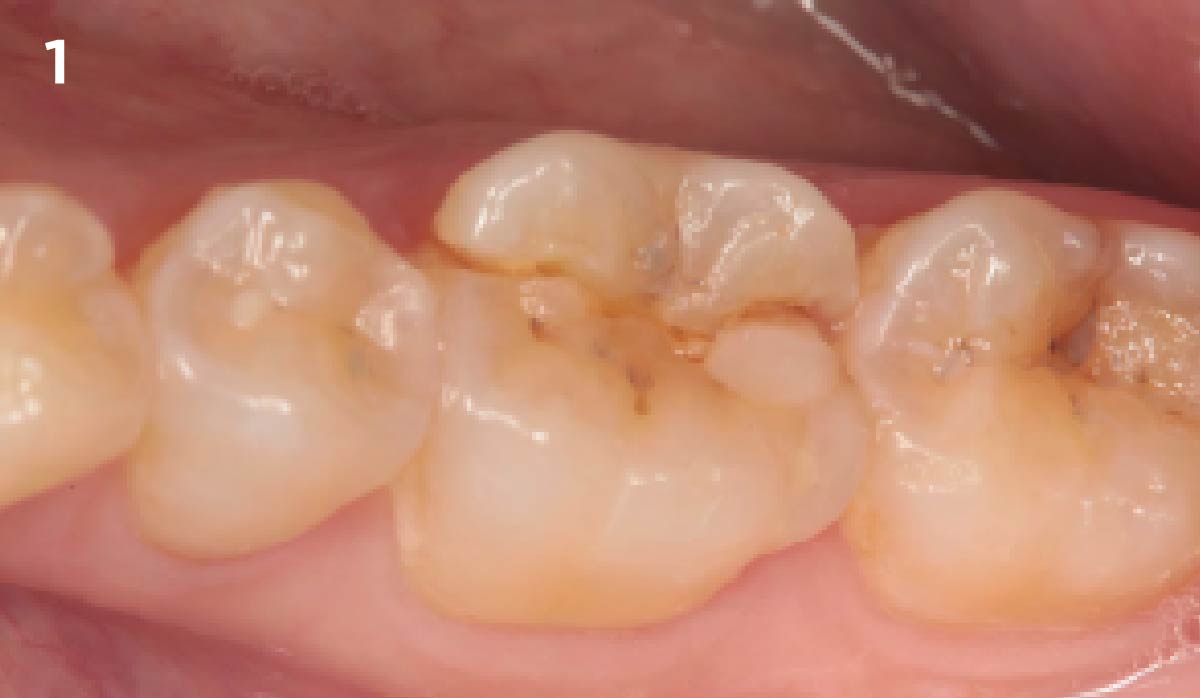

THE SITUATION
The case here is typical enough, a failing mandibular molar with a vertical sub-osseous fracture. Traditionally, the replacement process can take three or more surgical exposures (extraction and regeneration), (implant placement), (second stage exposure) and more than a year of therapy.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system Non-smoker | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
Immediate molar replacement requires atraumatic removal of the fractured tooth, careful socket debridement and development of a channel for an ideally positioned implant. The implant then needs to be placed down in the bone channel with the implant platform positioned just below the socket walls. It needs to be stable. Channel deficiency augmentation is achieved with Geistlich Bio-Oss Collagen® which is covered with a collagen matrix, Geistlich Mucograft® with the edges tucked under the gingival margins and sealed over with tissue glue.
“The patient desires an implant placement for a fractured mandibular molar, as fast as possible.”
– Dr. Peter Hunt
THE OUTCOME
This single stage replacement protocol has proven to be simple, safe and highly effective providing the socket is fully degranulated and the implant is stable and not loaded in the early healing stages. It works well when a gingiva former is immediately placed into the implant instead of a cover screw, Geistlich Bio-Oss Collagen® is packed around the implant to fill the residual socket, then covered with a Geistlich Mucograft® and sutured. There is no need for flap advancement to cover over the socket.
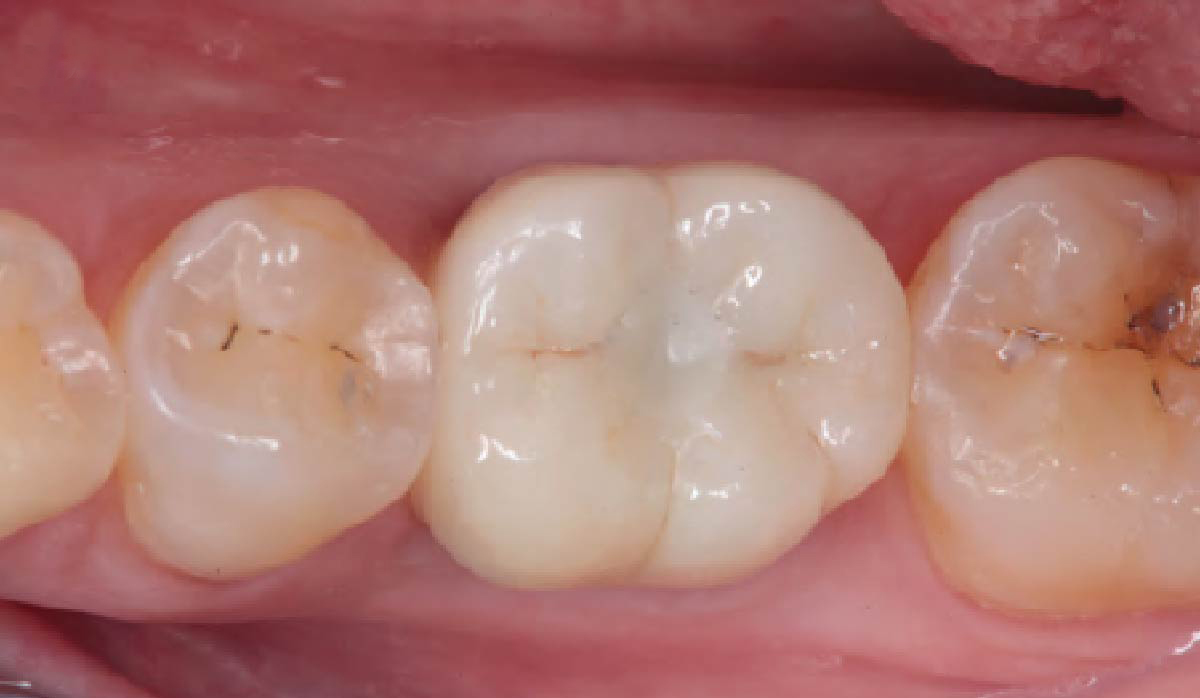

Dr. Peter Hunt
After graduate training on an Annenberg Fellowship at the University of Pennsylvania, dr. hunt helped start up the University of the Western Cape dental School in Cape Town, South Africa. he returned to the University of Pennsylvania where in time he became Clinical Professor of Periodontics. later he helped start up Nova Southeastern‘s dental School where he was Professor of Restorative dentistry, Post Graduate director and director of Implantology. he has had a private practice in Philadelphia focusing on implant and rehabilitation dentistry since 1981.

BIOBRIEF
Ramal Bone Graft for Congenitally Missing Maxillary Lateral Incisor
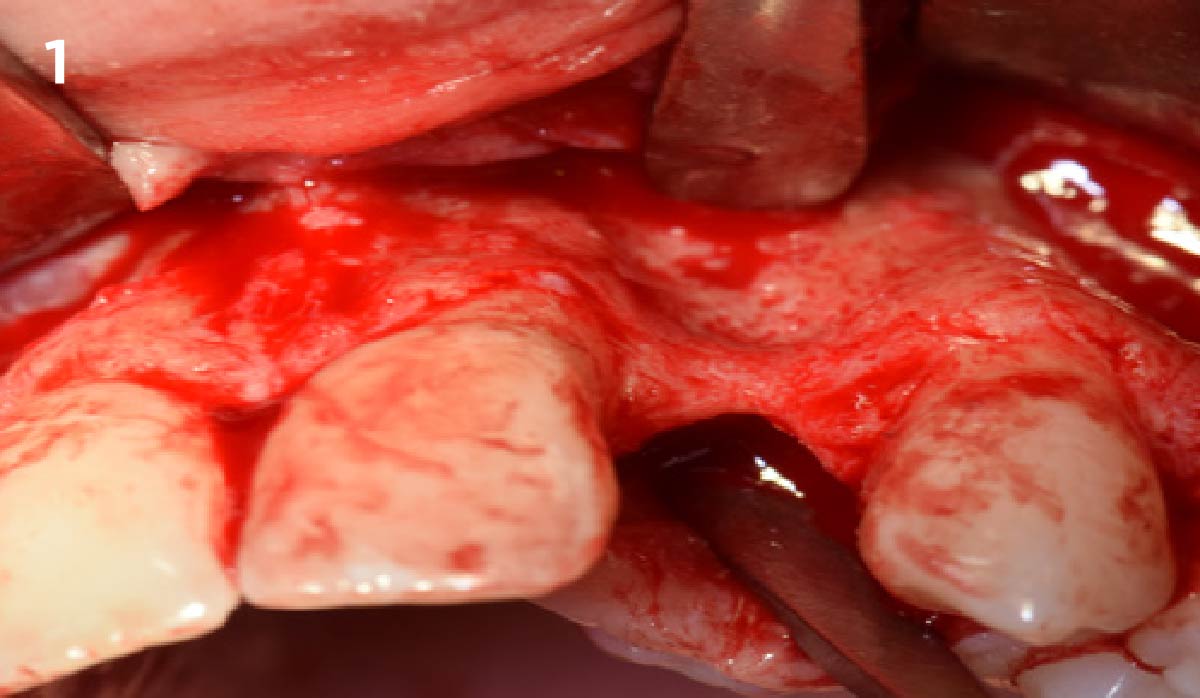

THE SITUATION
An 18-year-old female presented with a congenitally missing tooth #10. The patient previously sought care by another provider and had undergone guided bone regeneration with allograft and subsequent implant placement with additional grafting at the time of implant placement. The implant ultimately failed and was removed prior to my initial consultation. An examination revealed maximal incisal opening, within normal limits, missing #10 with 6 mm ridge width. In addition there was a significant palpable cleft-like depression on the facial aspect of the ridge, adequate attached tissue but reduced vertical height in relation to adjacent dentition and attached tissue. Previous surgeries resulted in extensive fibrous tissue with scarring at site #10. Plan: A ramal bone graft is indicated at the congenitally missing site #10 with Geistlich Bio-Oss® and Geistlich Mucograft® matrix utilized for ridge augmentation prior to secondary implant placement.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system Non-smoker | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
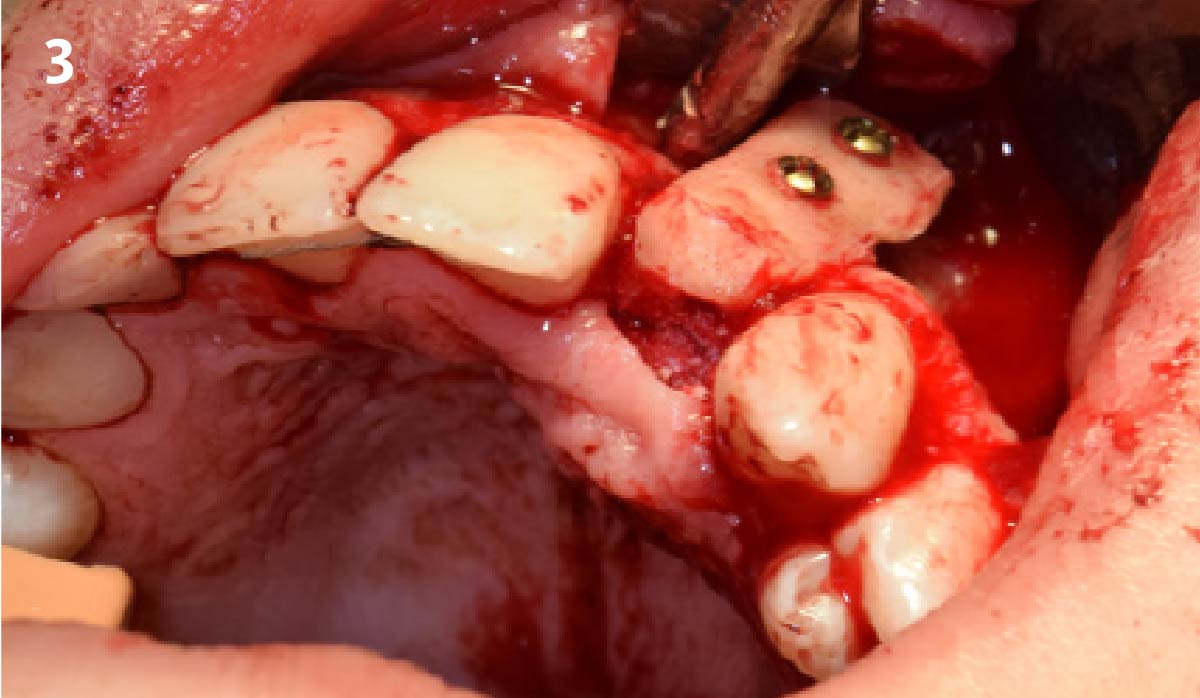
The goals for this patient are to reconstruct the osseous foundation and provide a matrix for improvement with the overlying soft tissue. Specifically, a coordinated multidisciplinary plan was established with the restoring dentist, periodontist and oral surgeon. A plan for idealized anterior cosmetic prosthetic restoration was established. Sequencing of treatment was established. Surgical phase one included a ramal bone graft to site #10 and Essix type temporary prosthesis for immediate post-operative phase followed by a temporary Maryland bridge. Surgical phase two included implant placement and simultaneous crown lengthening and osteoplasty. This stage was done with immediate provisionalization.
“This is a young patient with a congenitally missing incisor that has high esthetic concerns and has had multiple failed surgical attempts that is now presenting for definitive management.”
THE OUTCOME
This case was dependent upon adequate hard-tissue reconstruction combined with soft-tissue manipulation to eliminate scar tissue and provide esthetic recontouring. Obtaining an adequate autogenous graft combined with Geistlich Bio-Oss® at the periphery of the onlay graft is essential for anterior-posterior and vertical augmentation. Utilizing a Geistlich Mucograft® matrix at the ridge crest to help contain the particulate graft and improve the soft-tissue profile for subsequent immediate provisionalization and re-contouring of the surrounding soft tissue played a significant role in the esthetic success.
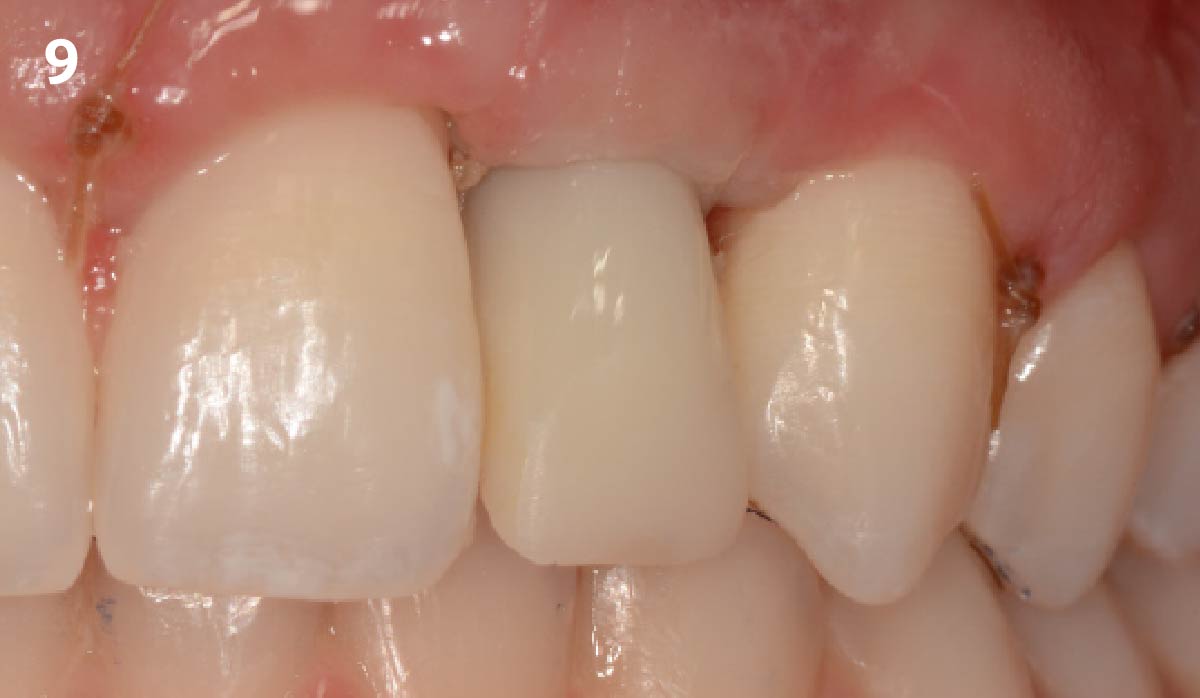

Dr. Richard E. Bauer, III
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon – University of Pittsburgh
Richard E. Bauer, III, DMD, MD is a graduate of the University of Pittsburgh Schools of Dental Medicine and Medicine. Dr. Bauer completed his residency training in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center. Dr. Bauer has served on multiple committees for the American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery (AAOMS). He is a full-time faculty member and Residency Program Director at the University of Pittsburgh in the department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and his practice is focused on dental implants and corrective jaw surgery. He has been active in research with focus on bone regeneration and virtual applications for computer assisted planning and surgery.

WEBINAR

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE
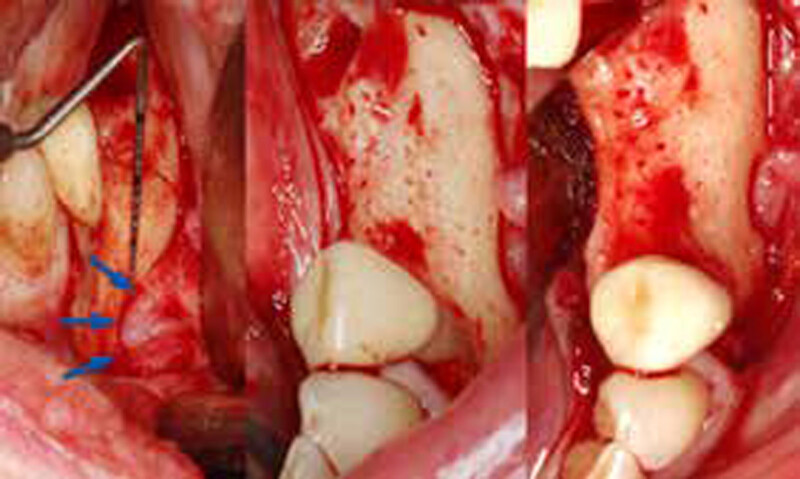
CLINICAL CHALLENGE:
- Insufficient alveolar ridge width for implant placement
- Autologous bone is subject to resorption and may lead to loss of volume
AIM/APPROACH:
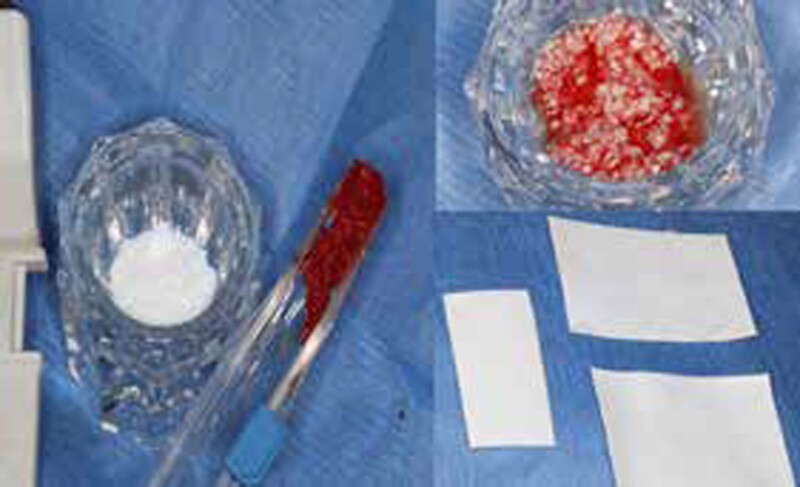
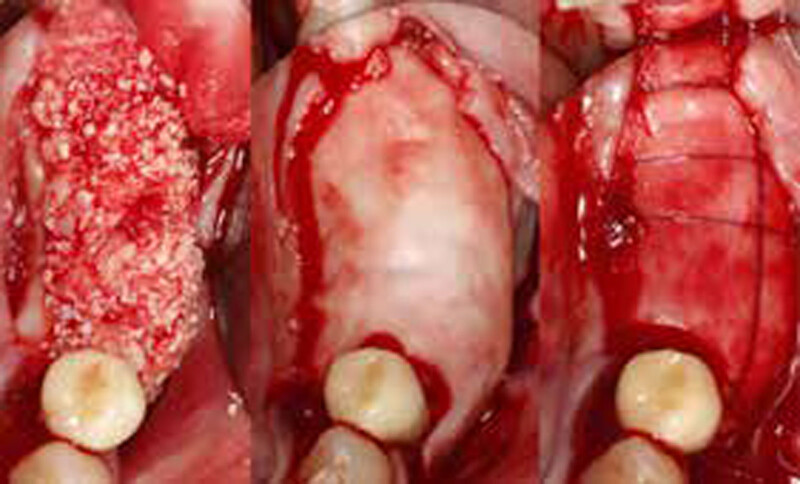
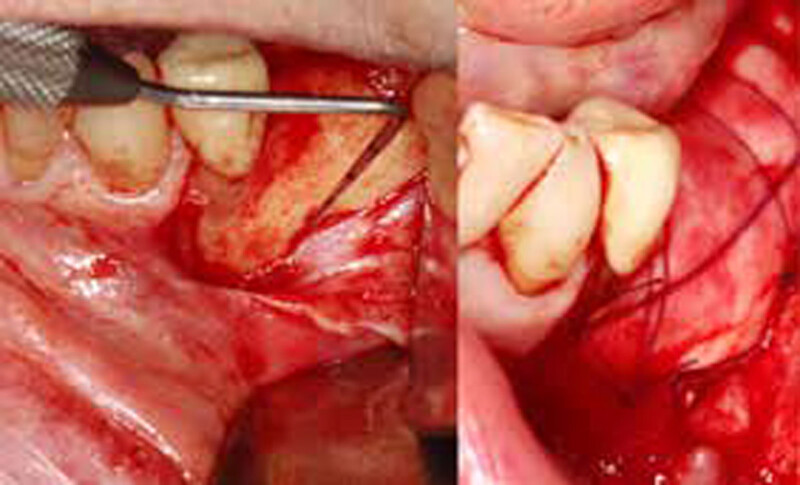
- Ridge Split procedure in combination with Geistlich Bio-Oss® and Geistlich Bio-Gide® for horizontal augmentation
- Preservation of the alveolar ridge volume

CLINICAL CASE