NEW EBOOK: How to Master Bone Regeneration with Digital Innovation. Download Today!
Therapeutic Area: Ridge Preservation

BIOBRIEF
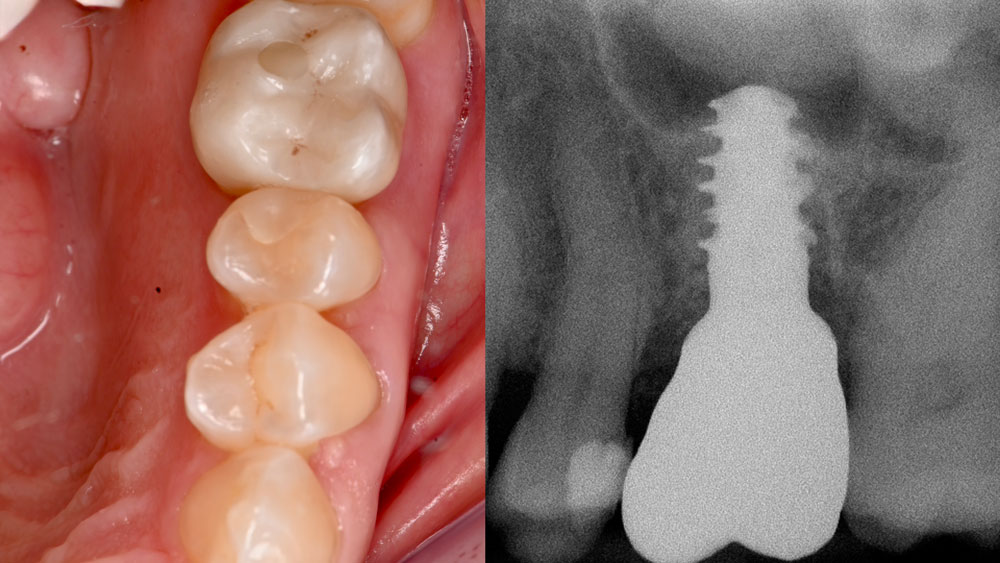
Bone Grafting and Immediate Implant Placement in the Maxillary First Molar Region


THE SITUATION
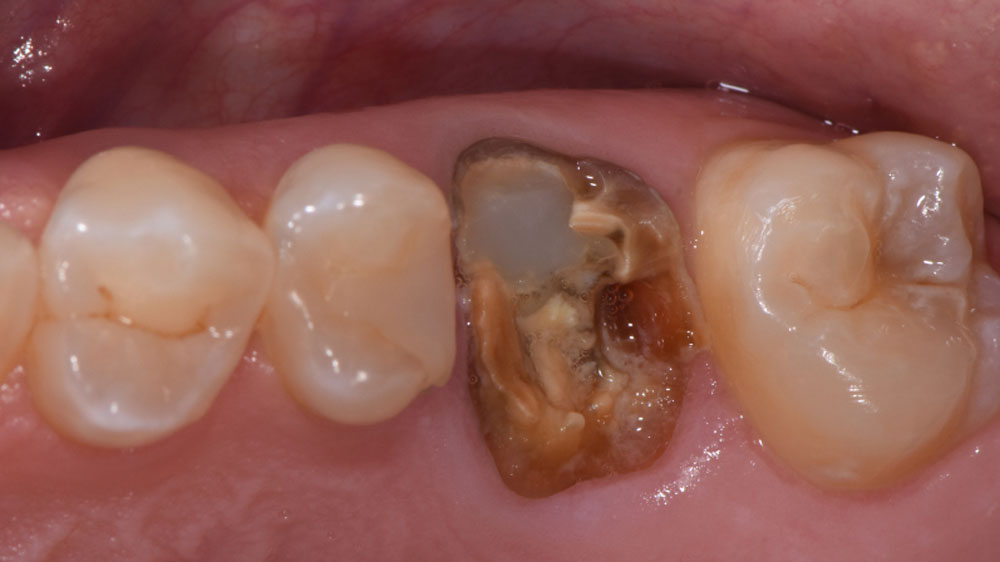
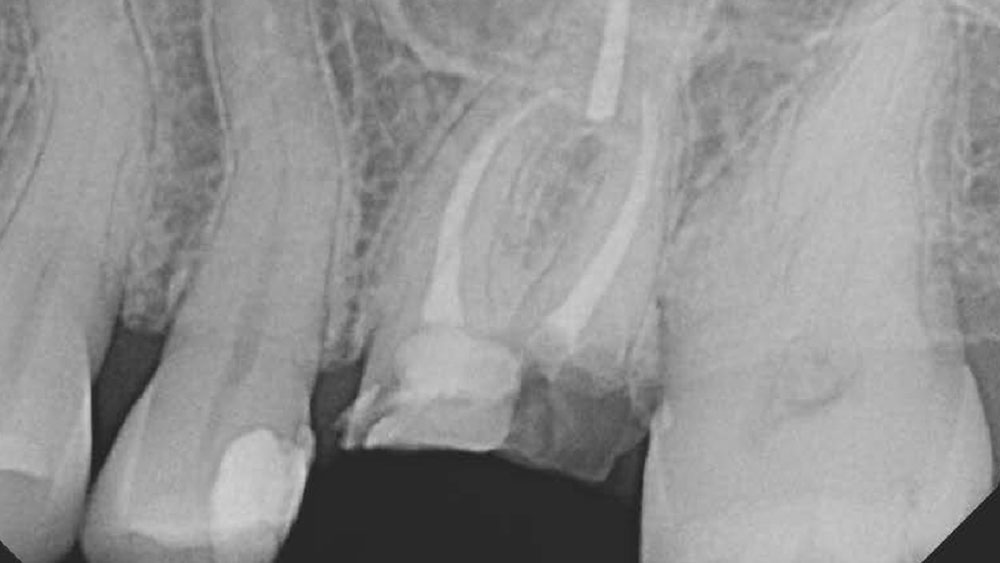
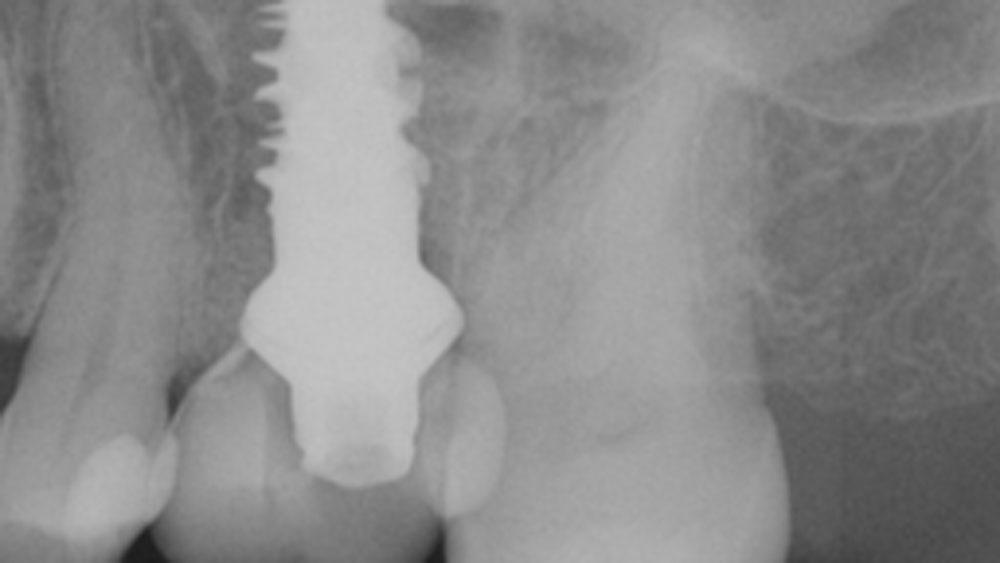
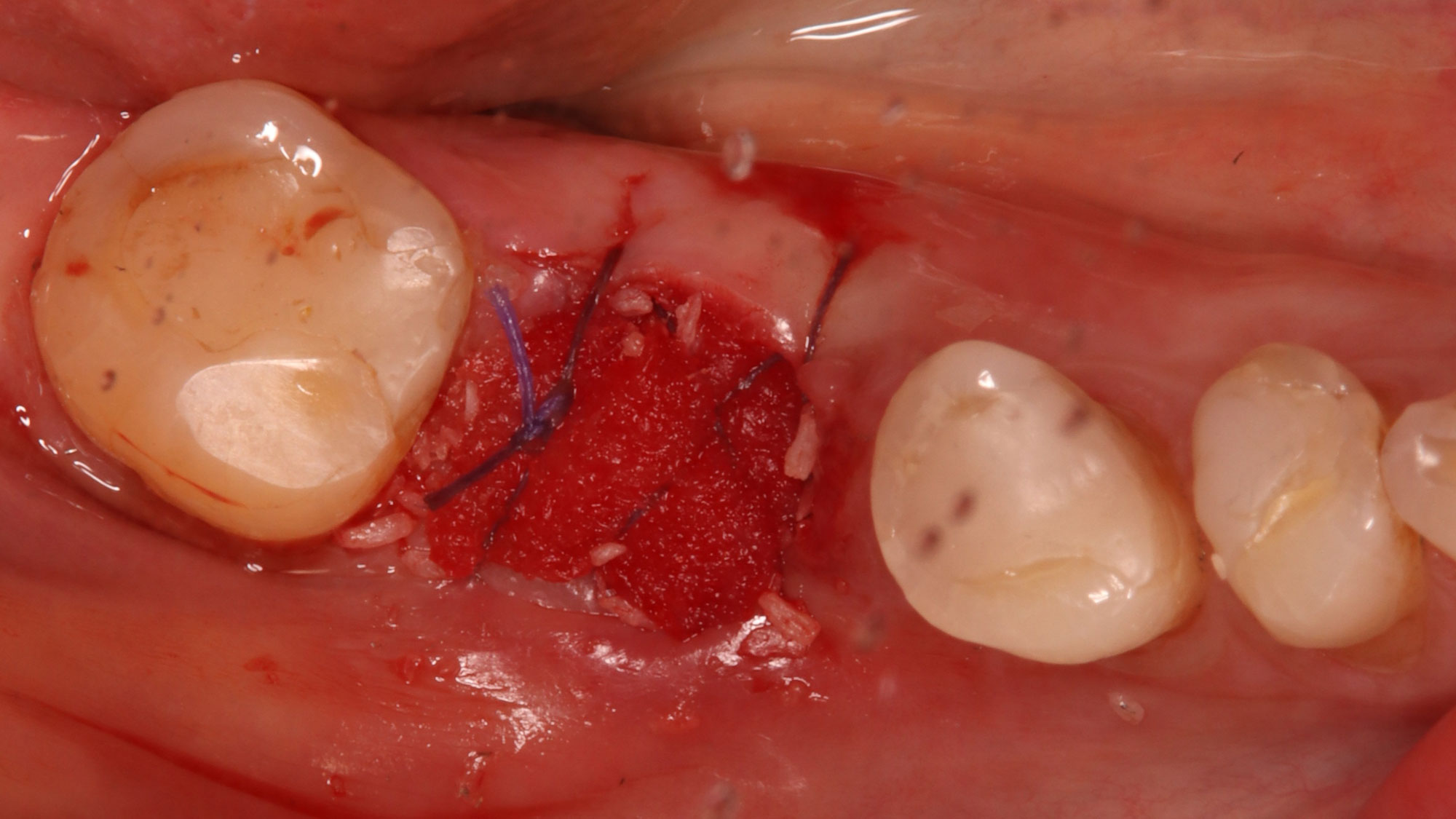
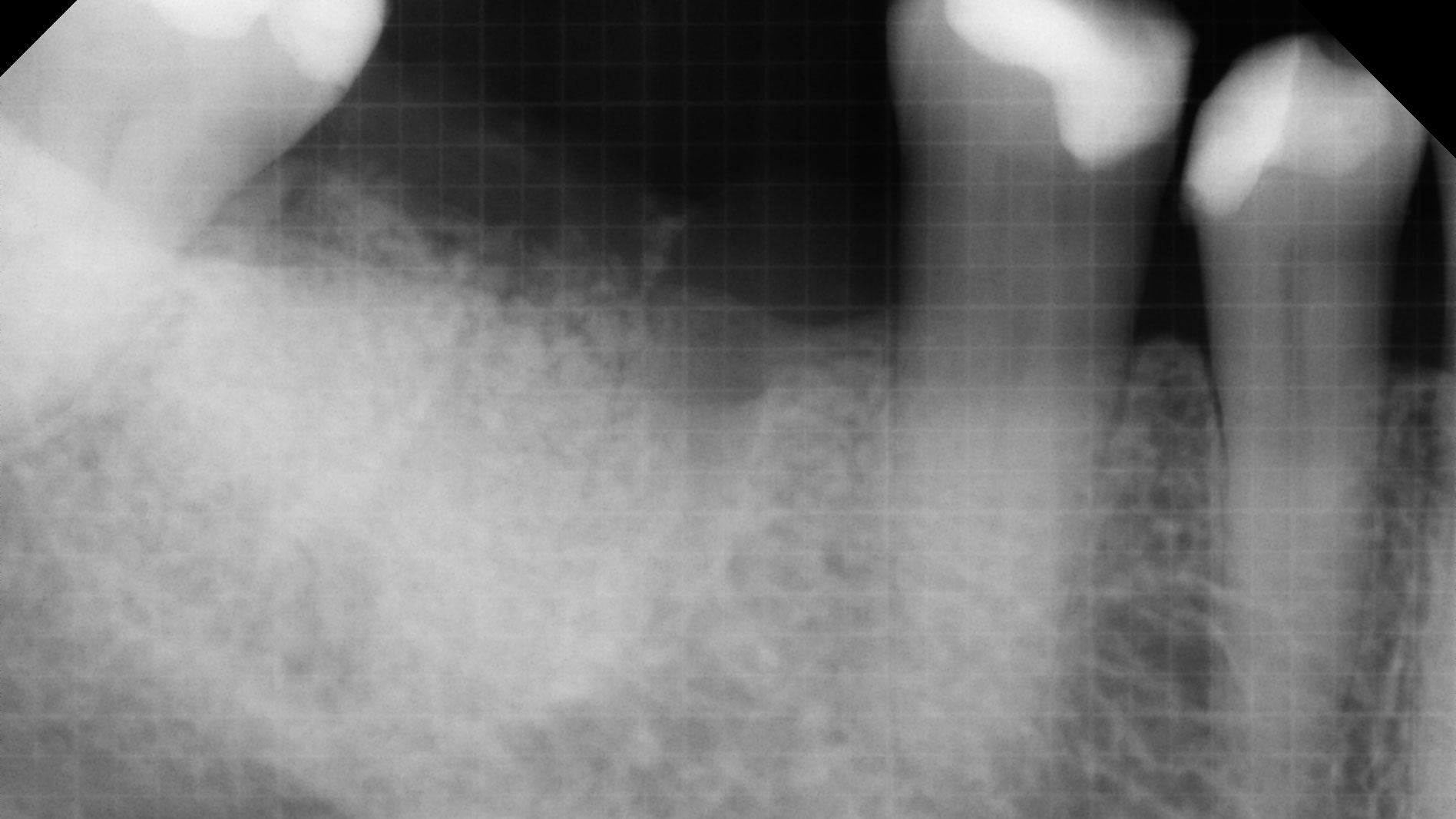
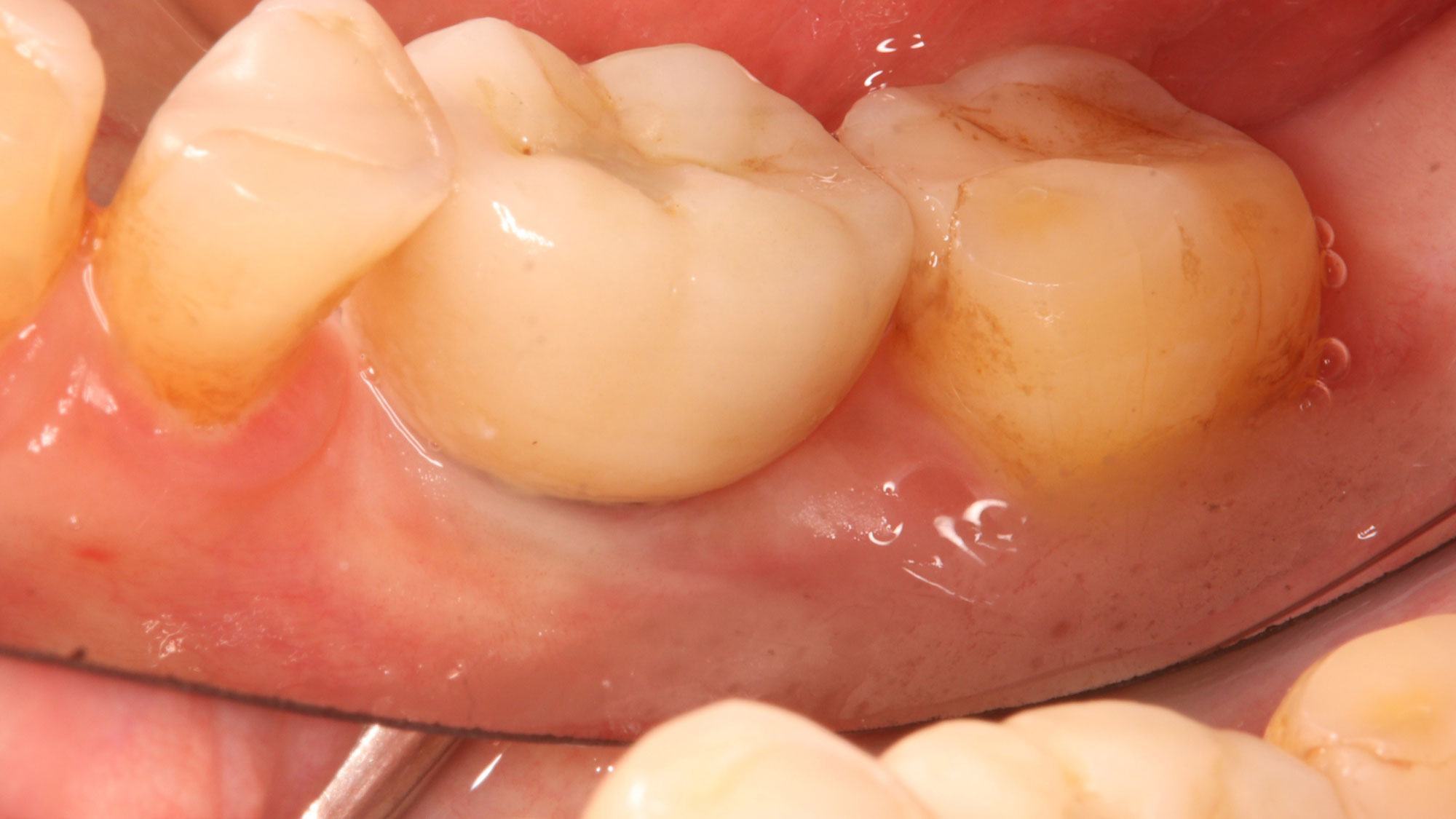
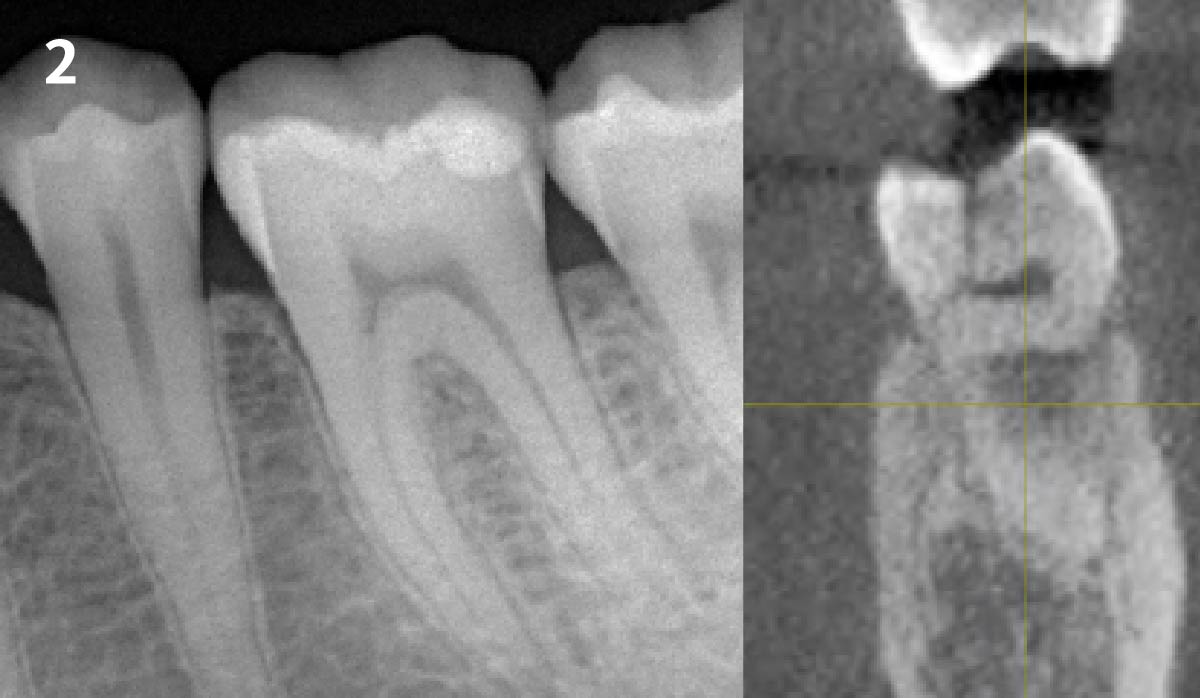
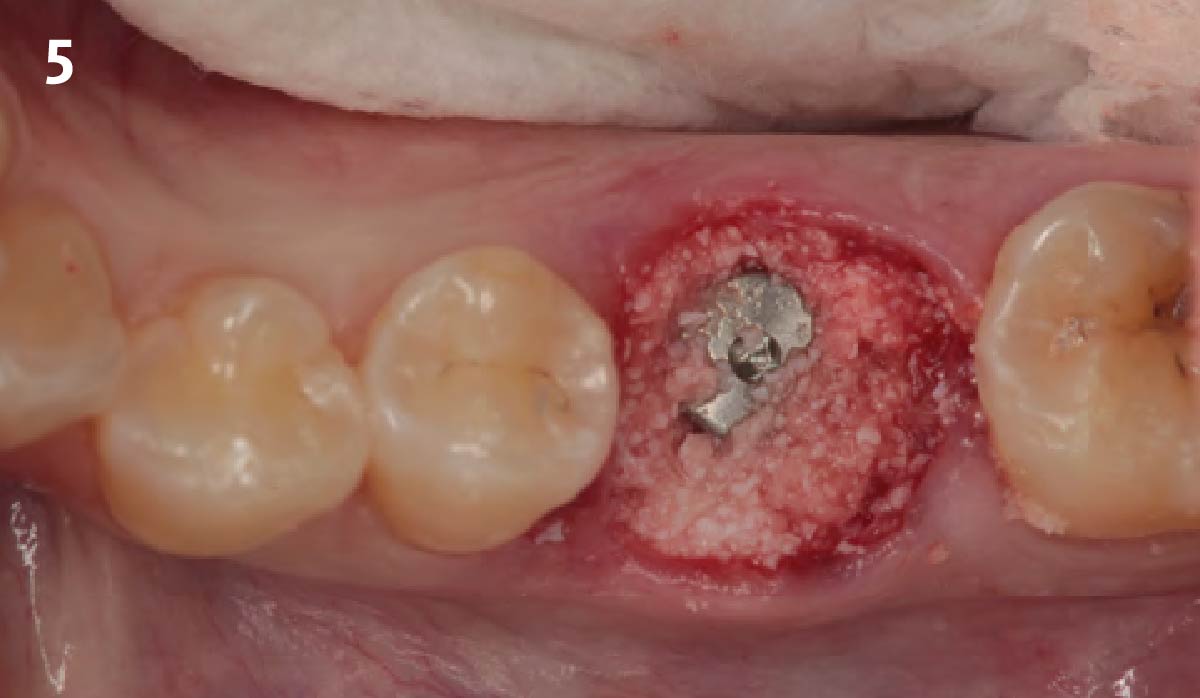
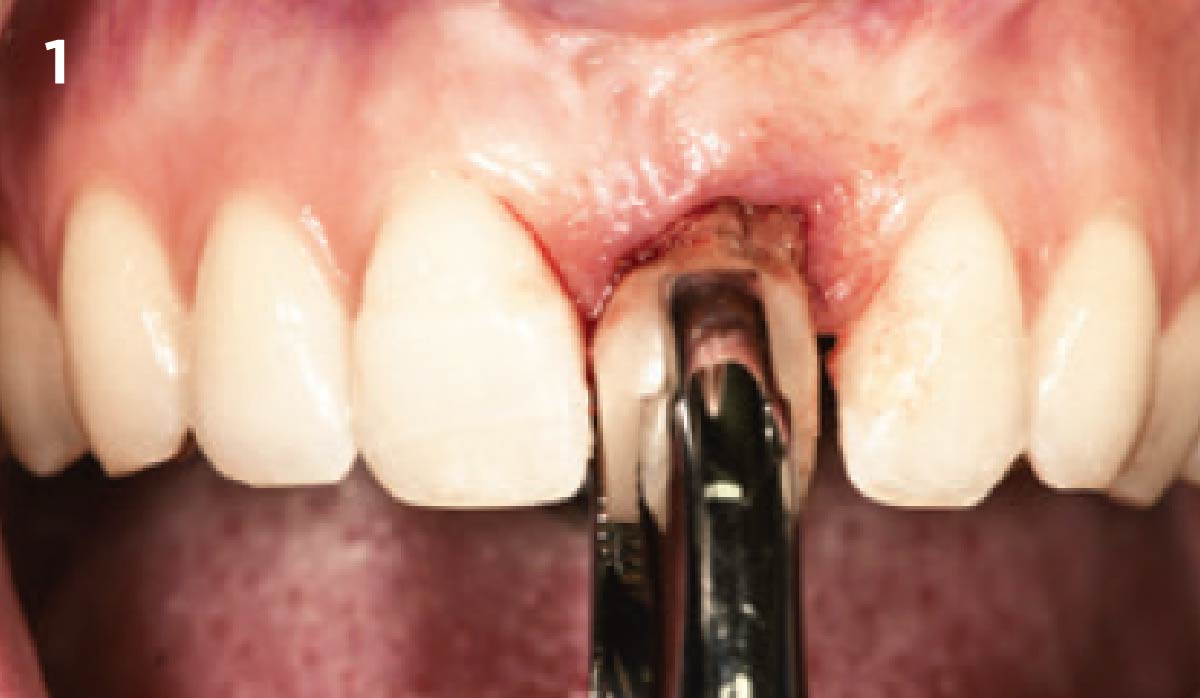
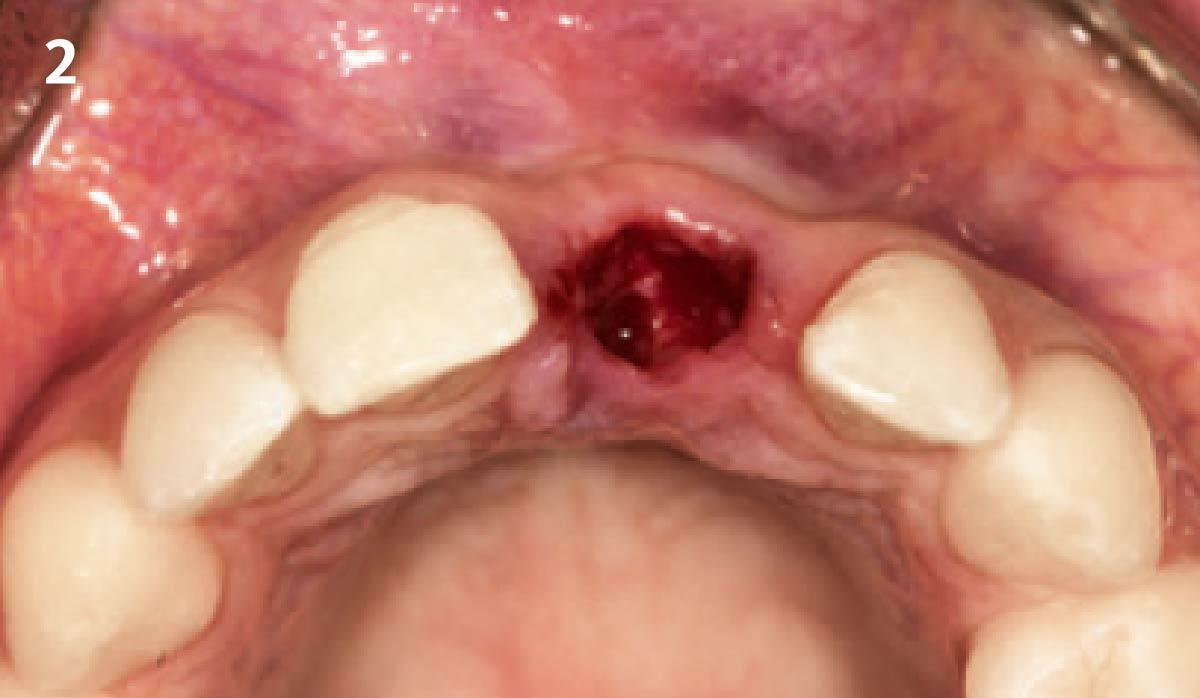
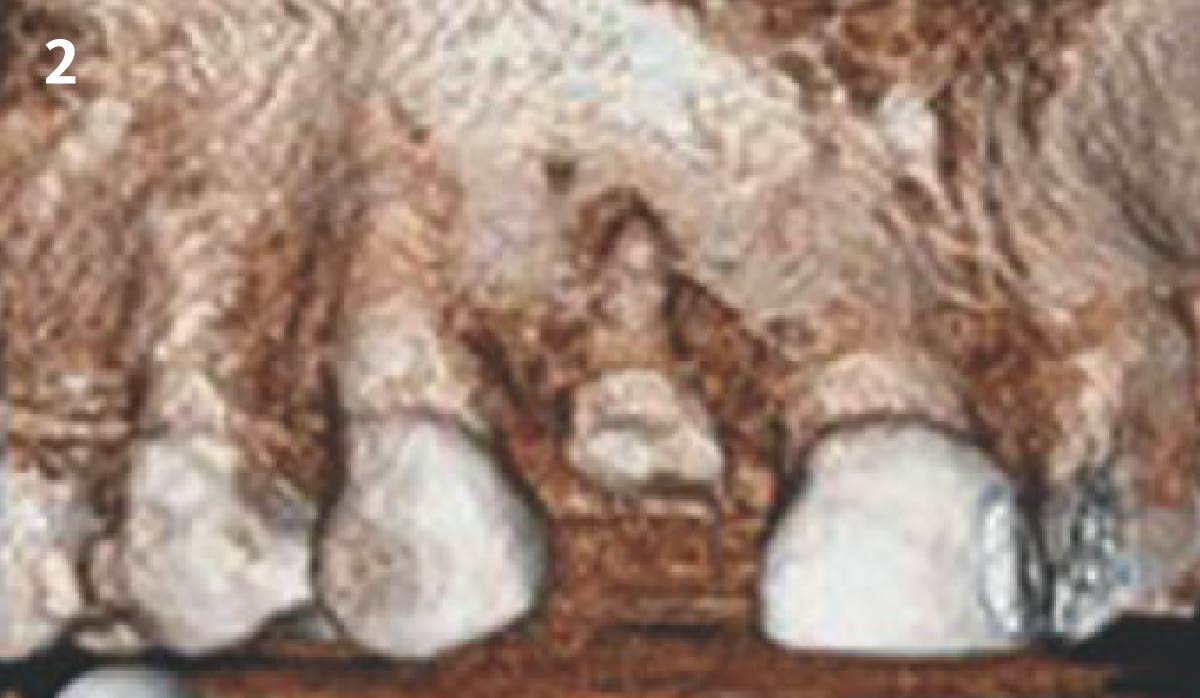
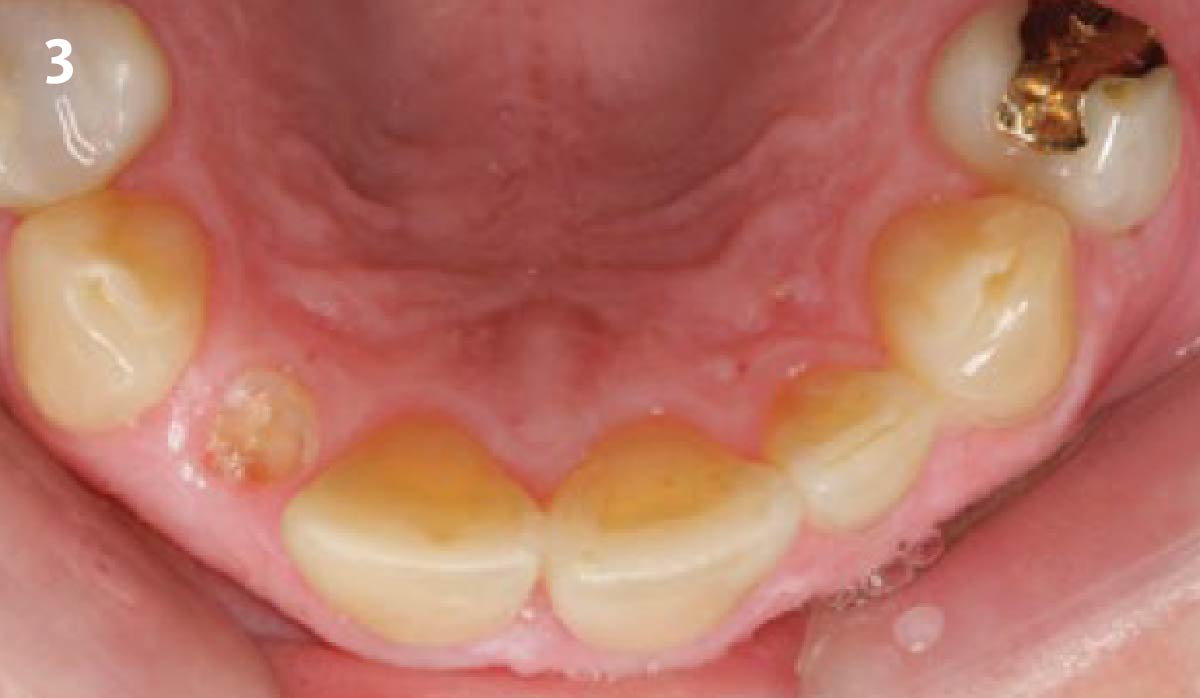
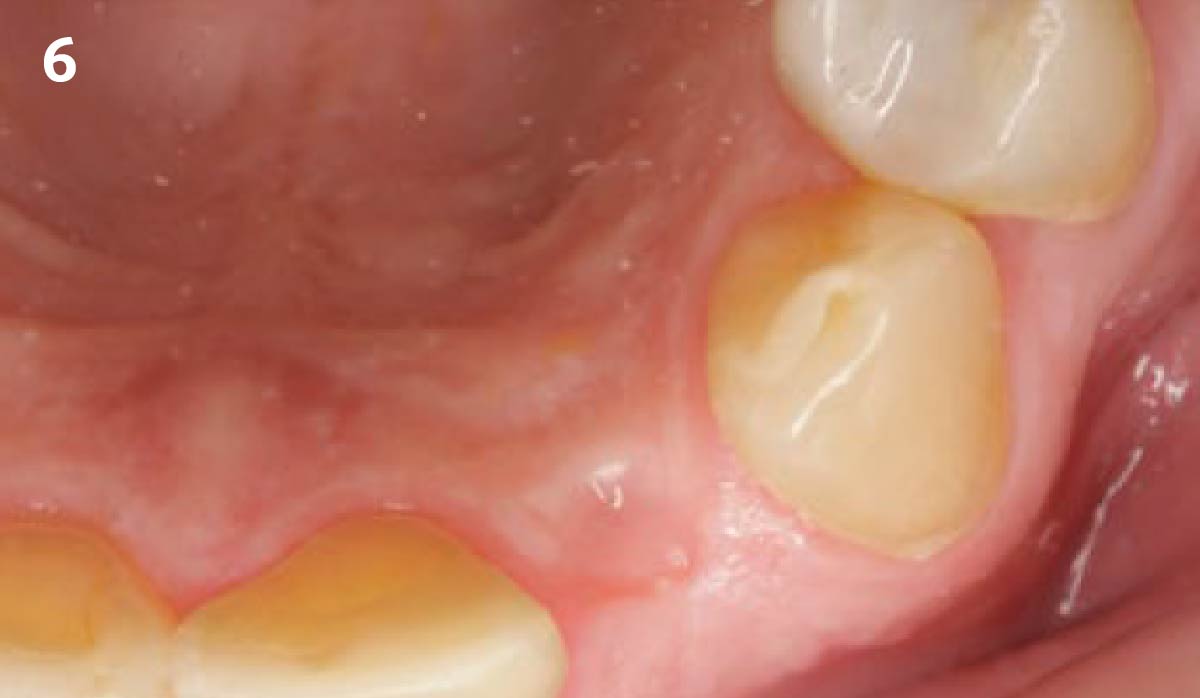
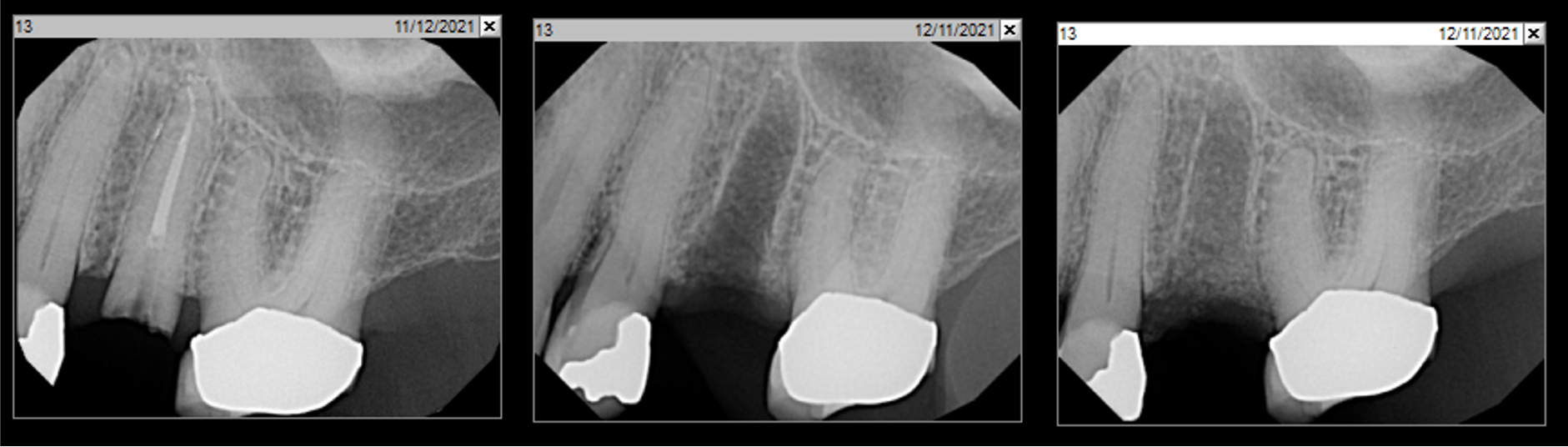
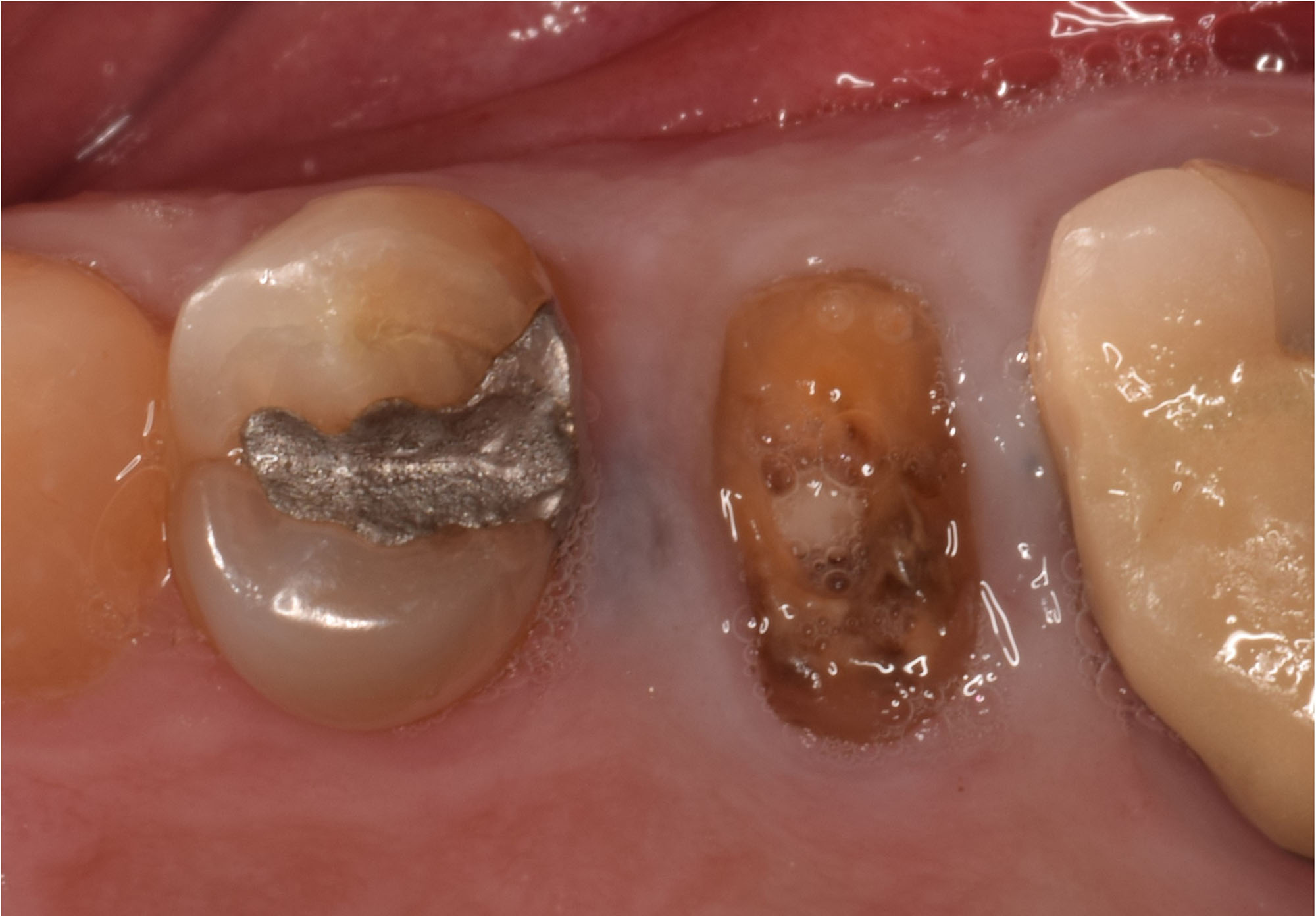
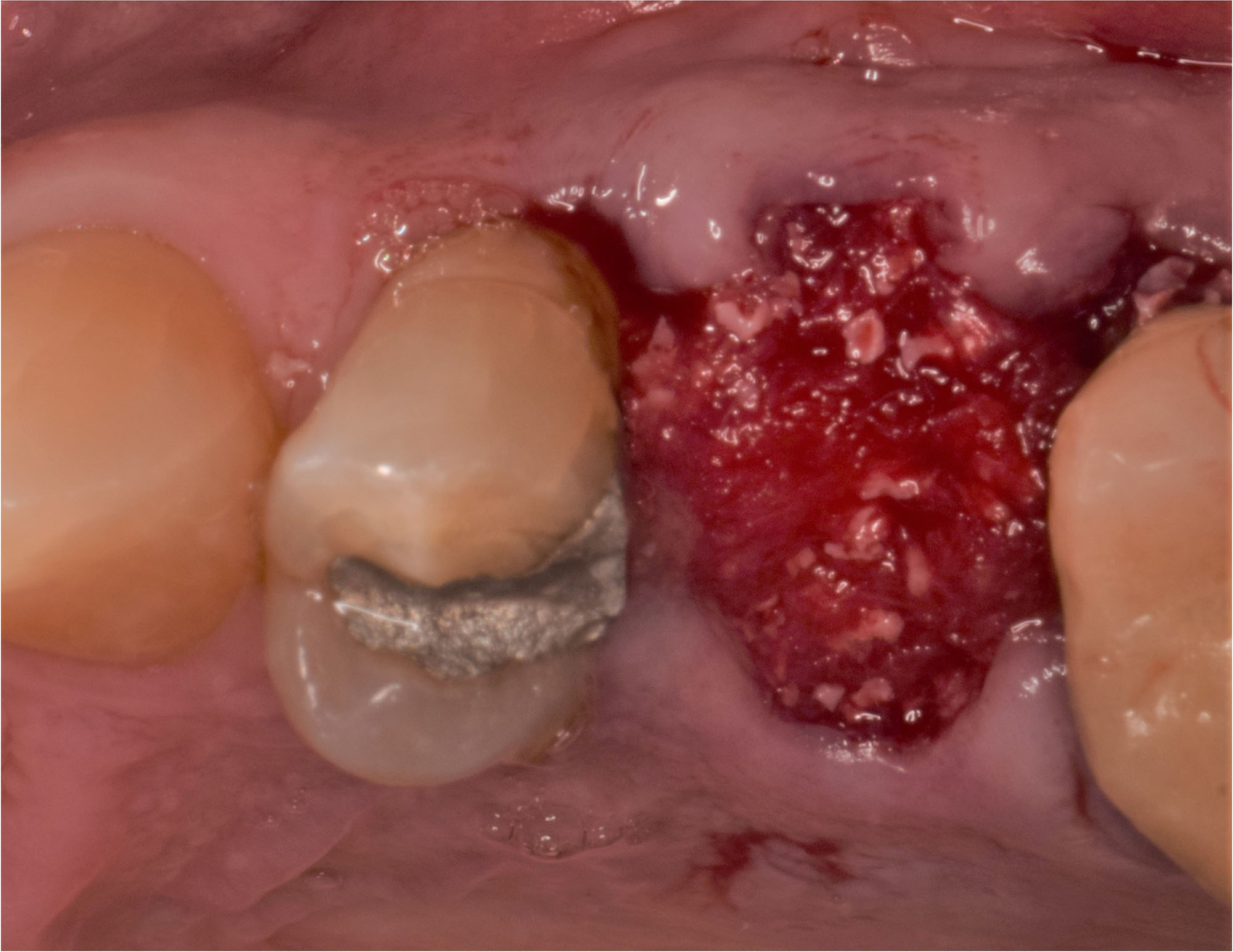
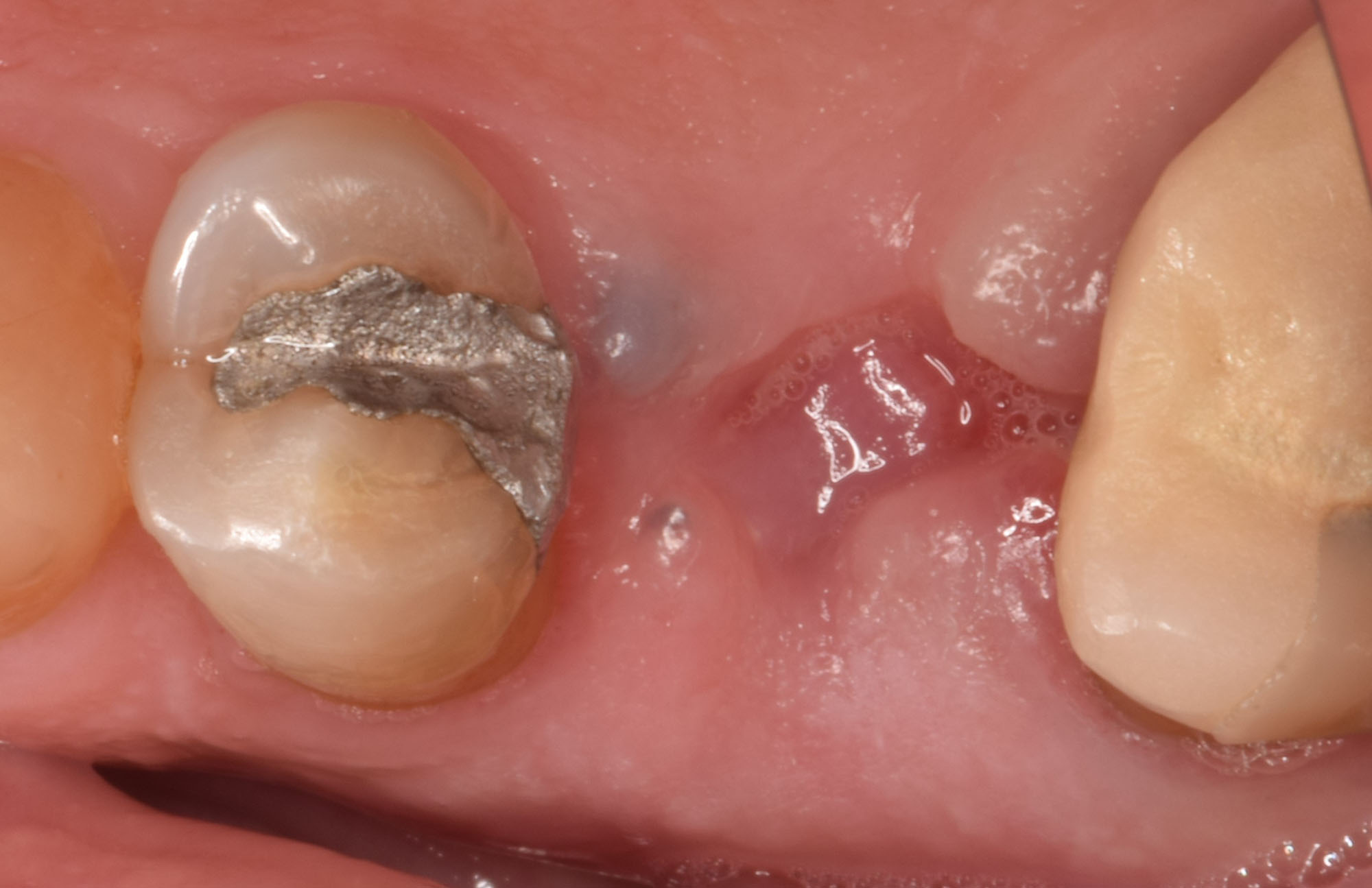
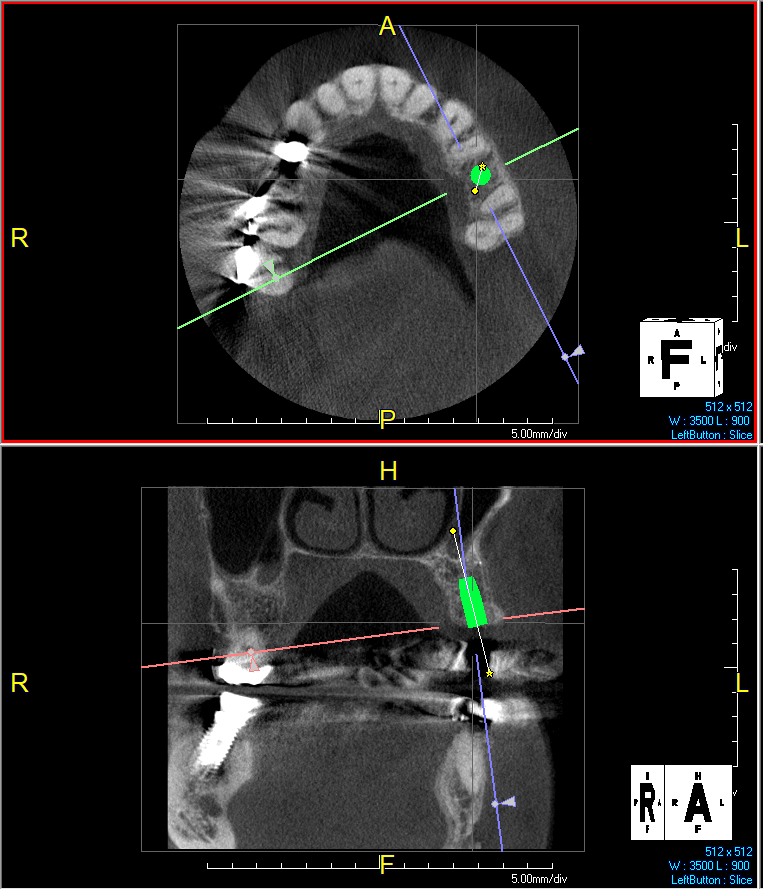
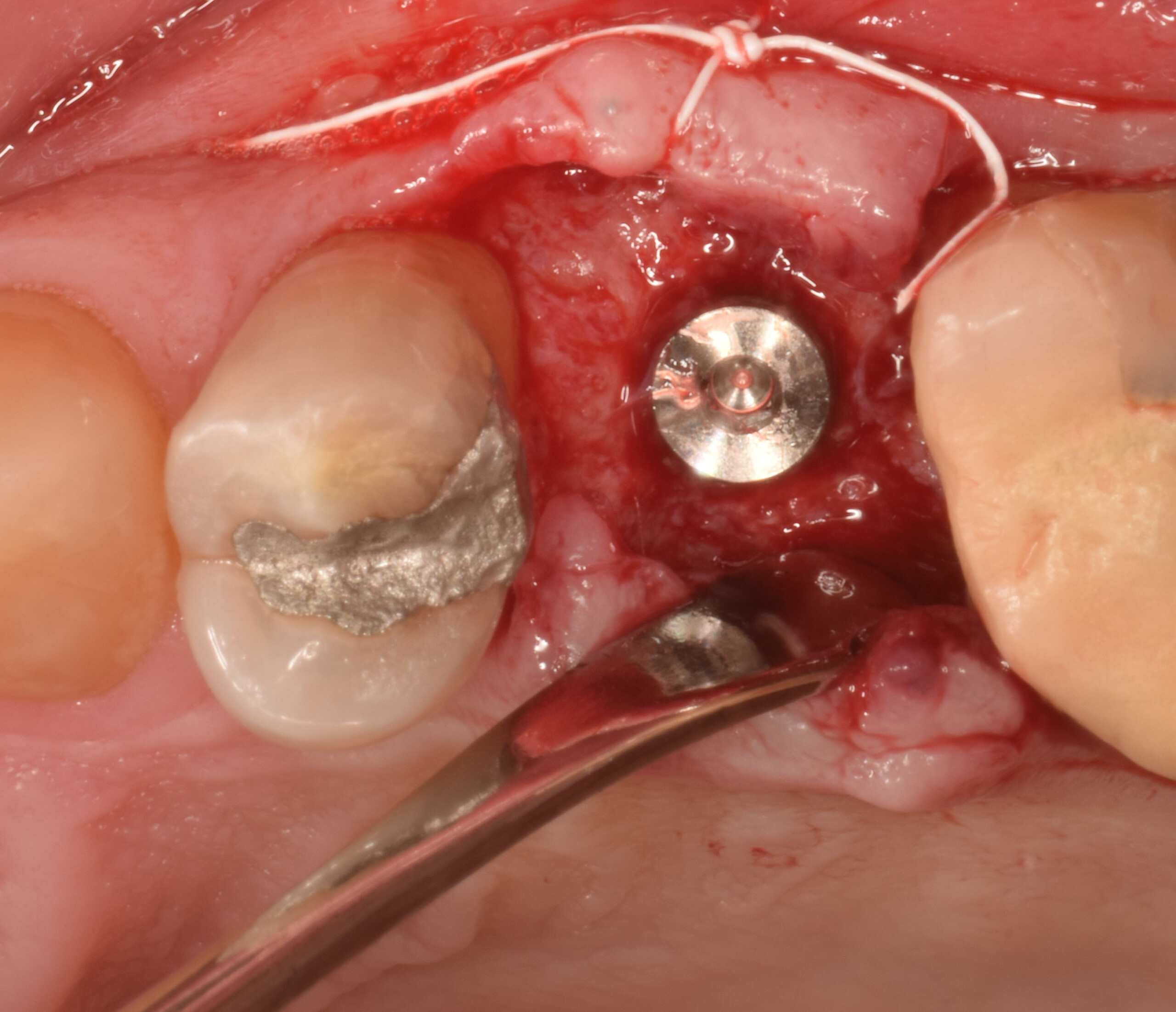
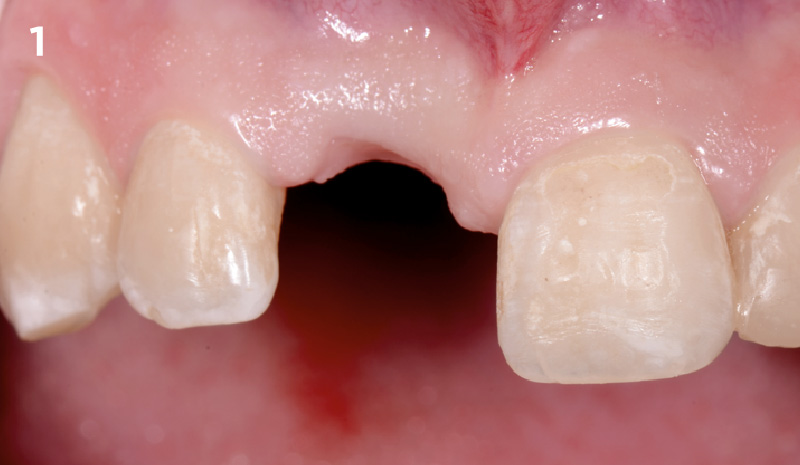
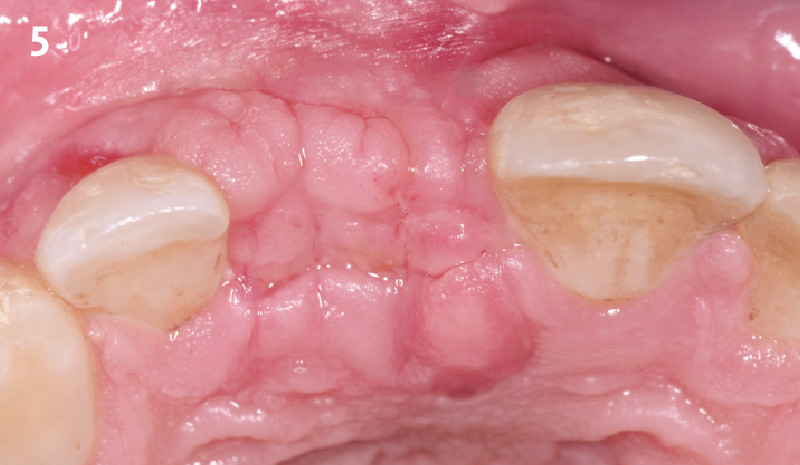
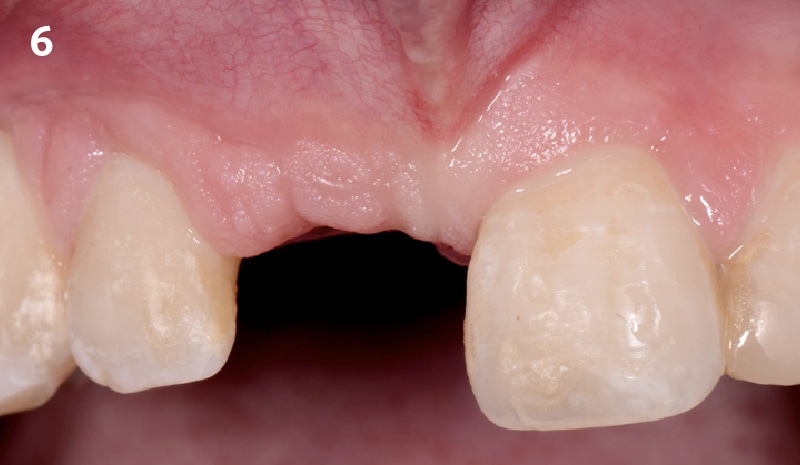
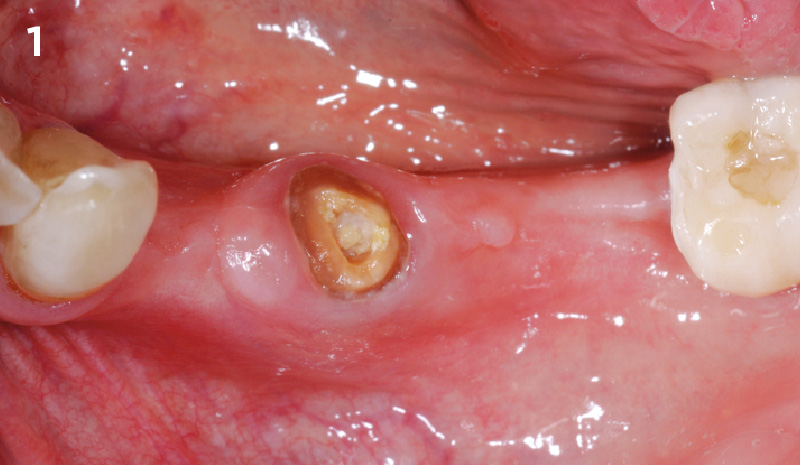
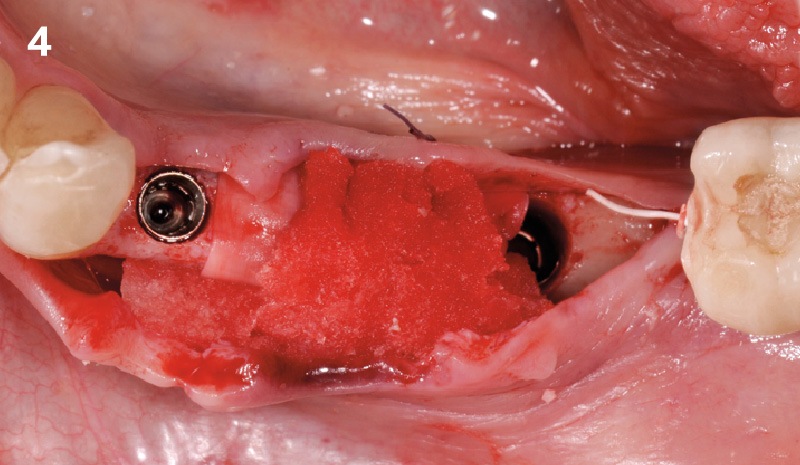
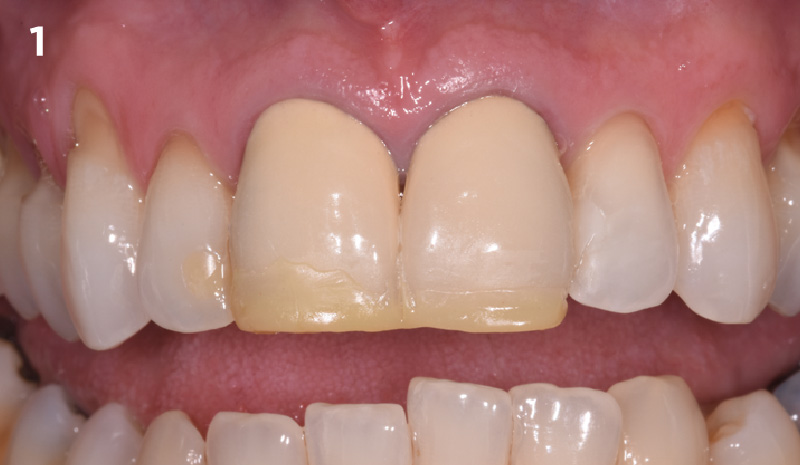
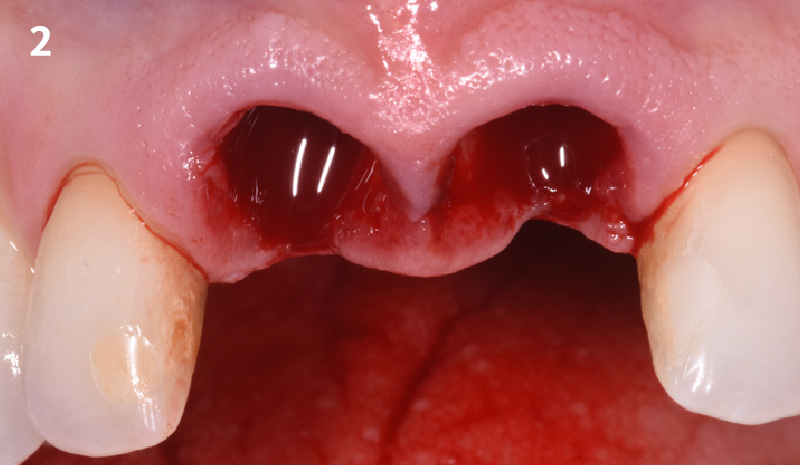
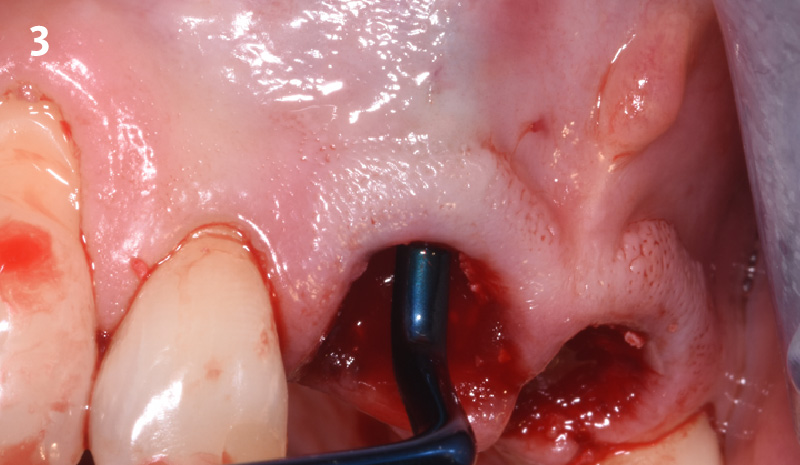
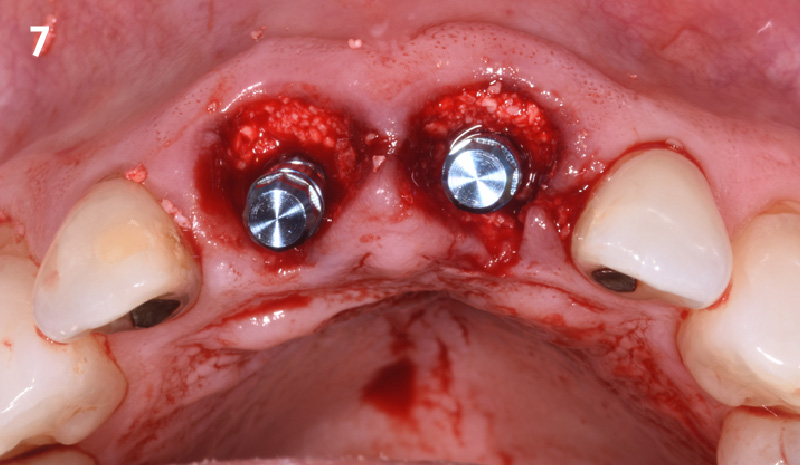
Patient presented with unrestorable left maxillary first molar. After data collection with Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) and intra-oral scanning, and clinical examination, the situation was considered favorable for minimally traumatic extraction and immediate implant placement.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
Additional Risk Factors: Roots were divergent, and intra-radicular bone (septal bone) was excellent, with more than 5 mm of remaining apical bone to achieve optimal primary stability.
THE APPROACH
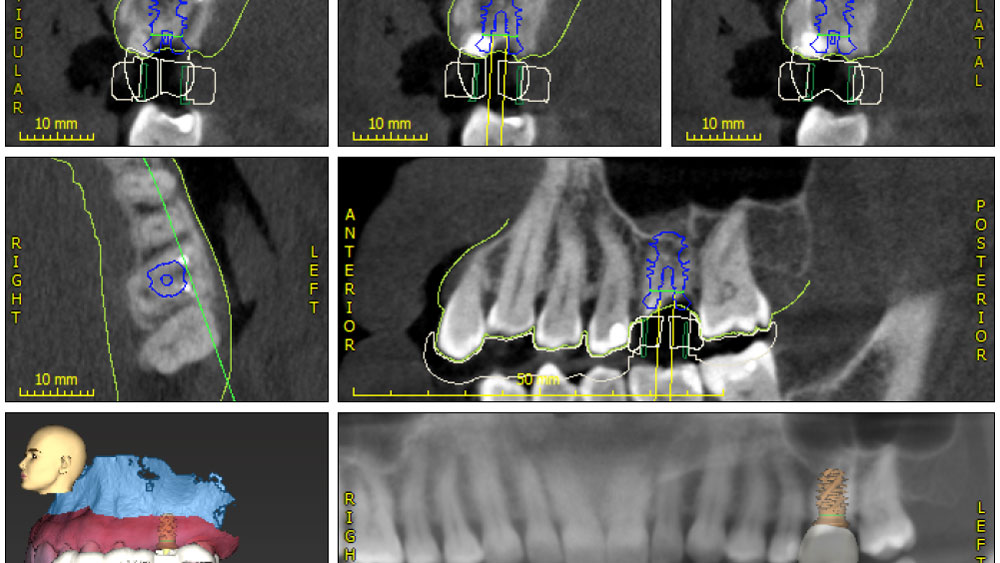
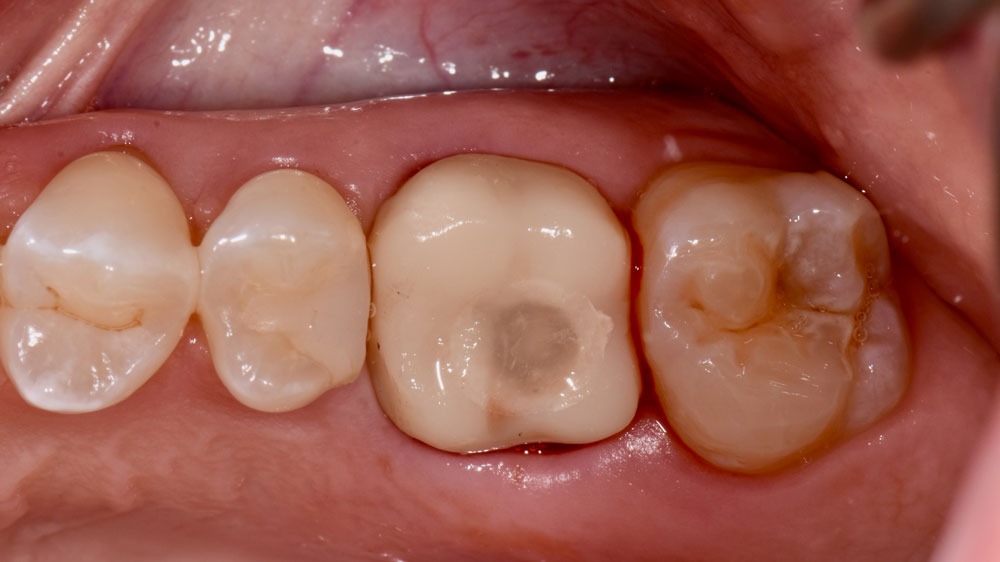
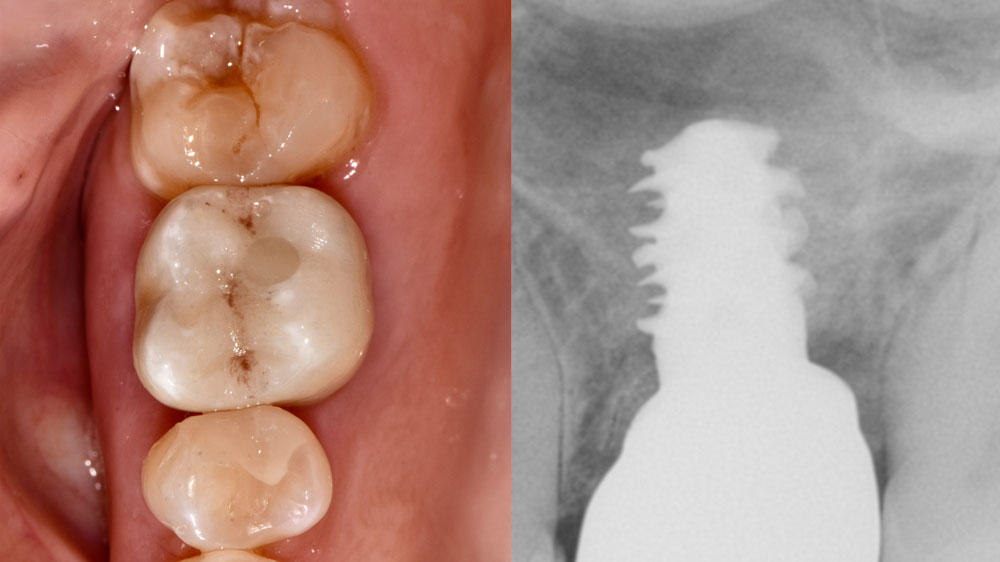
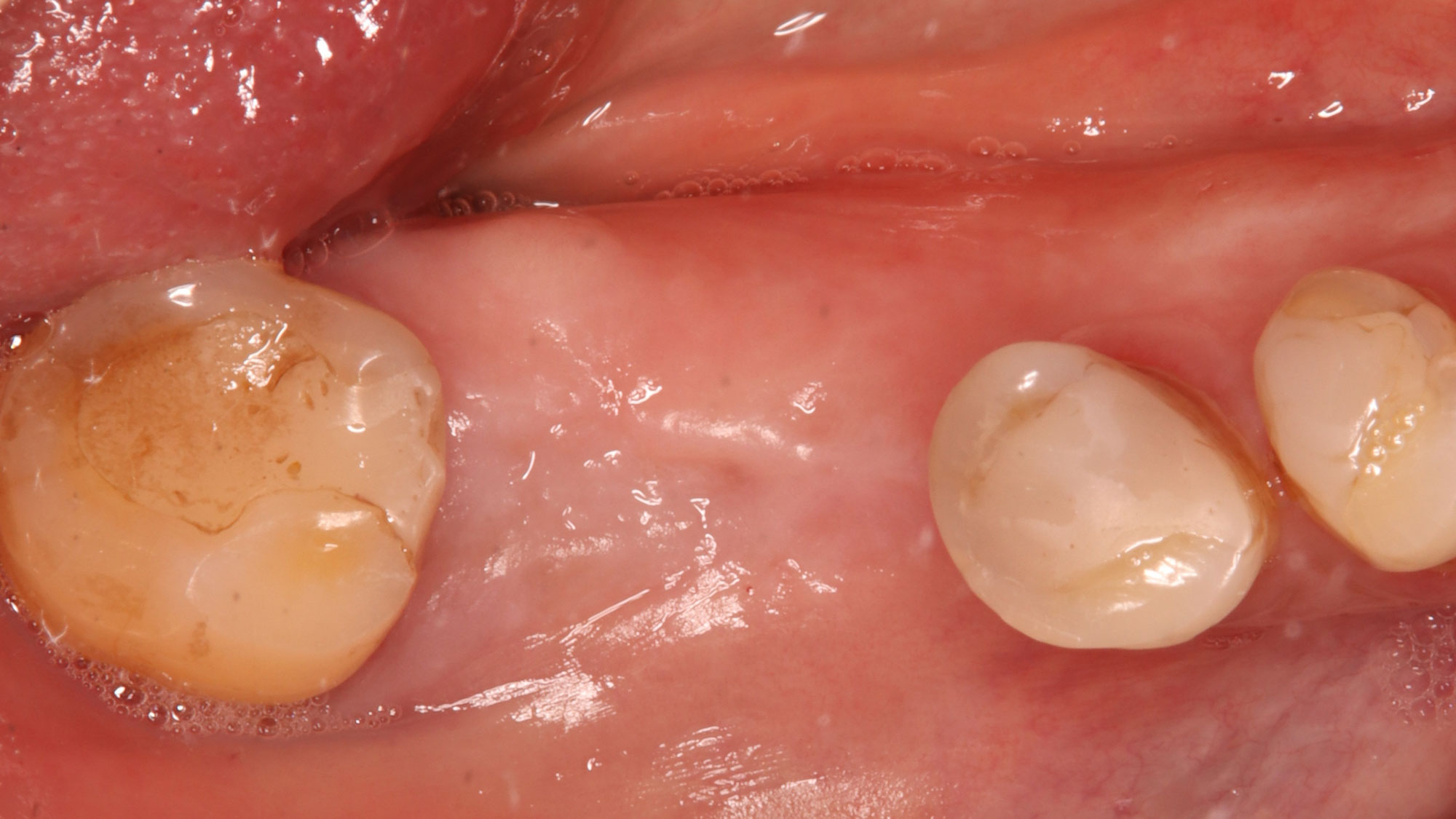
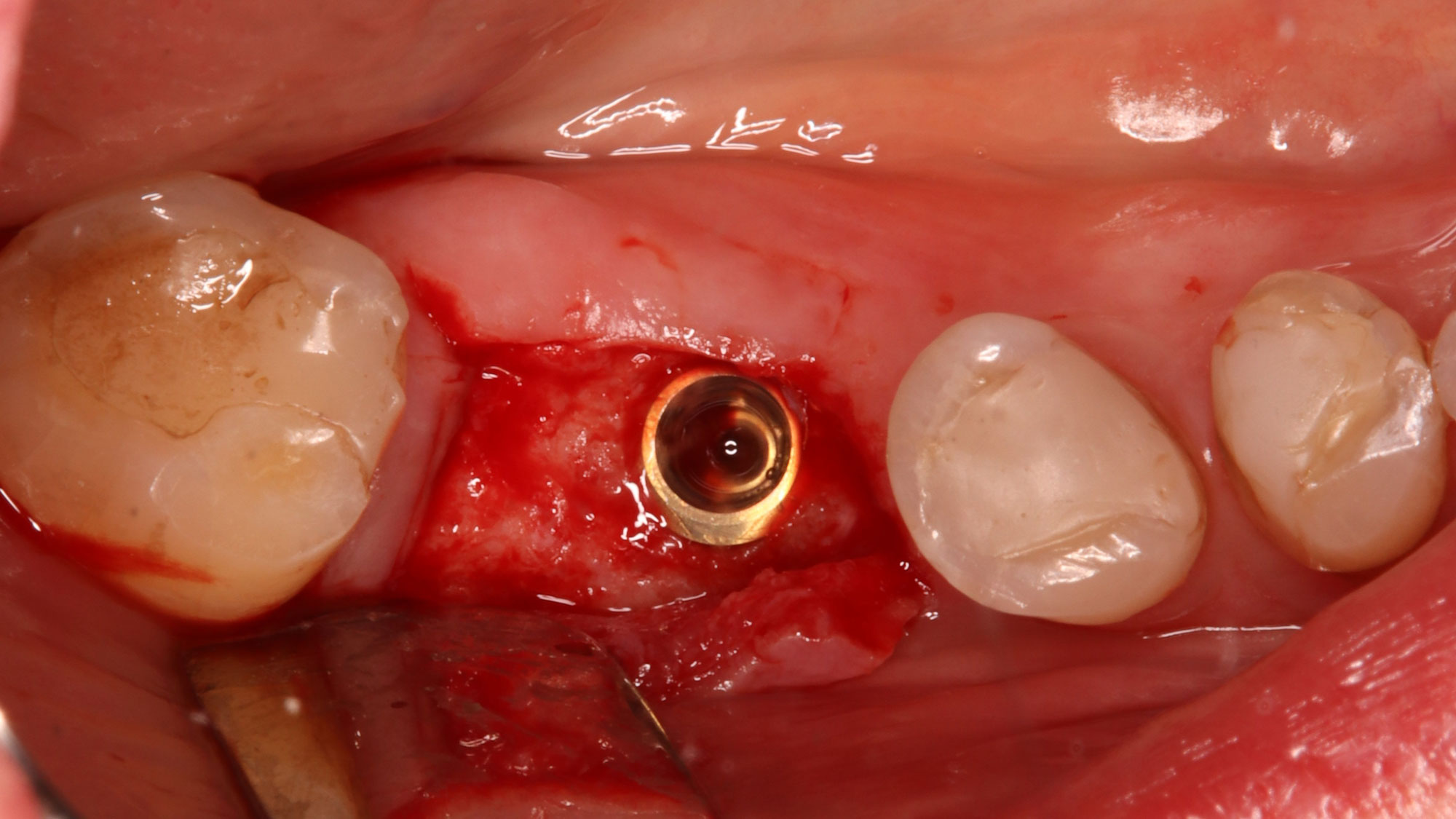
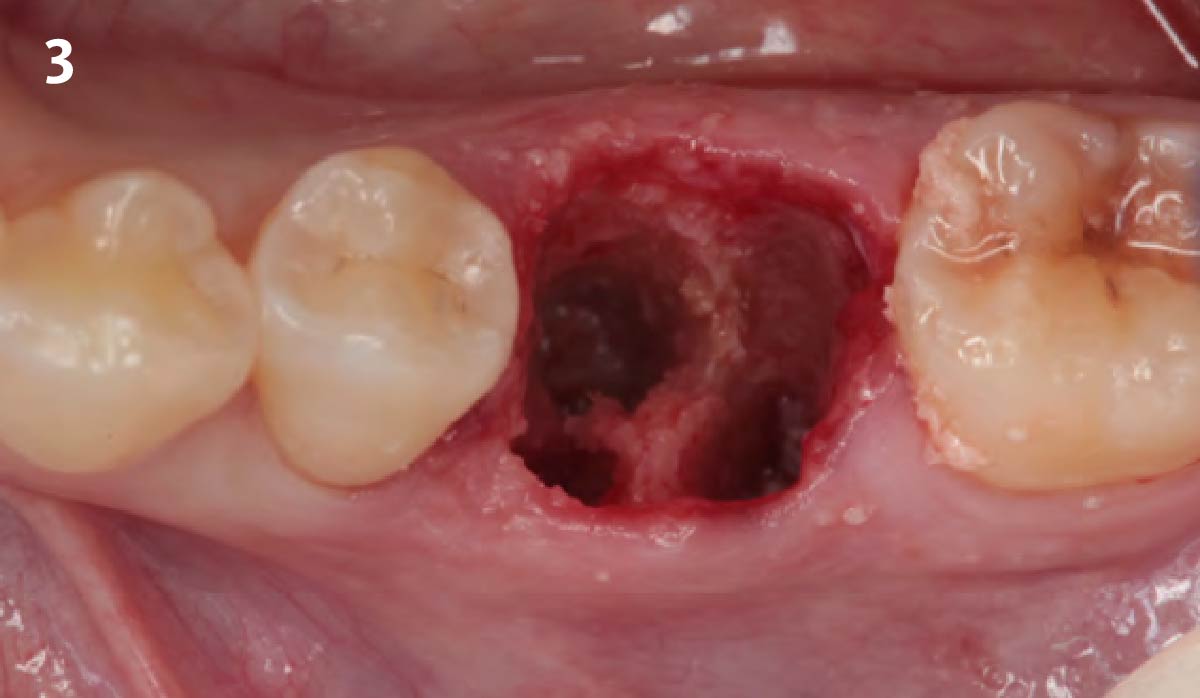
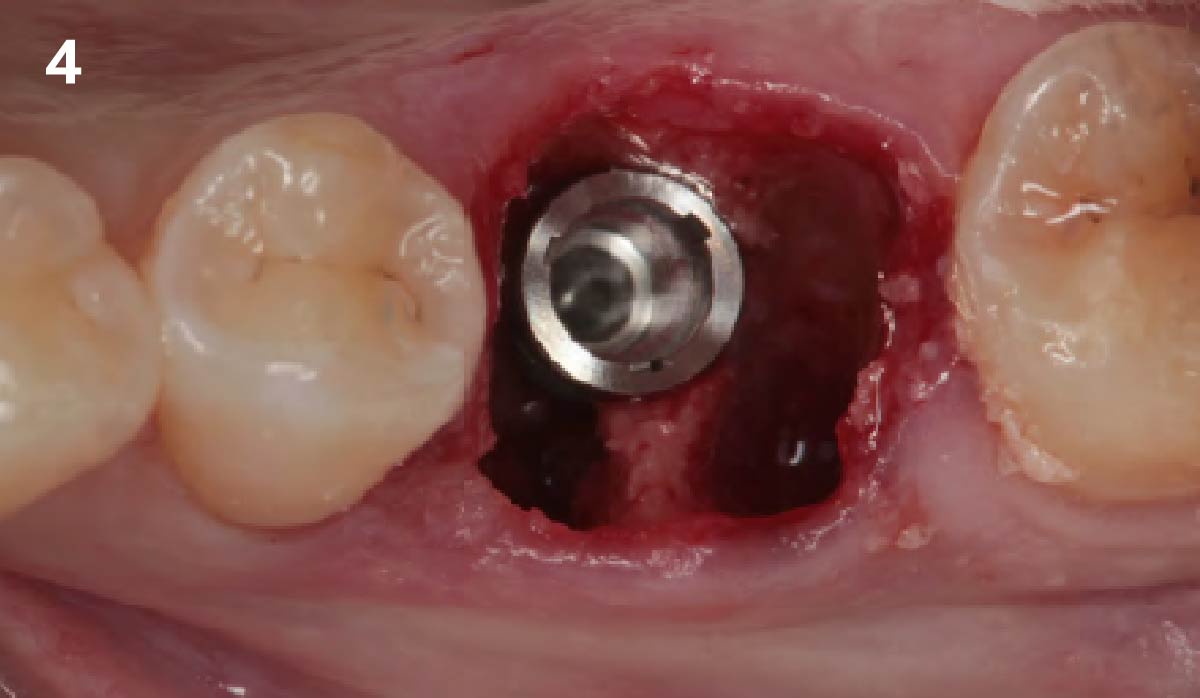
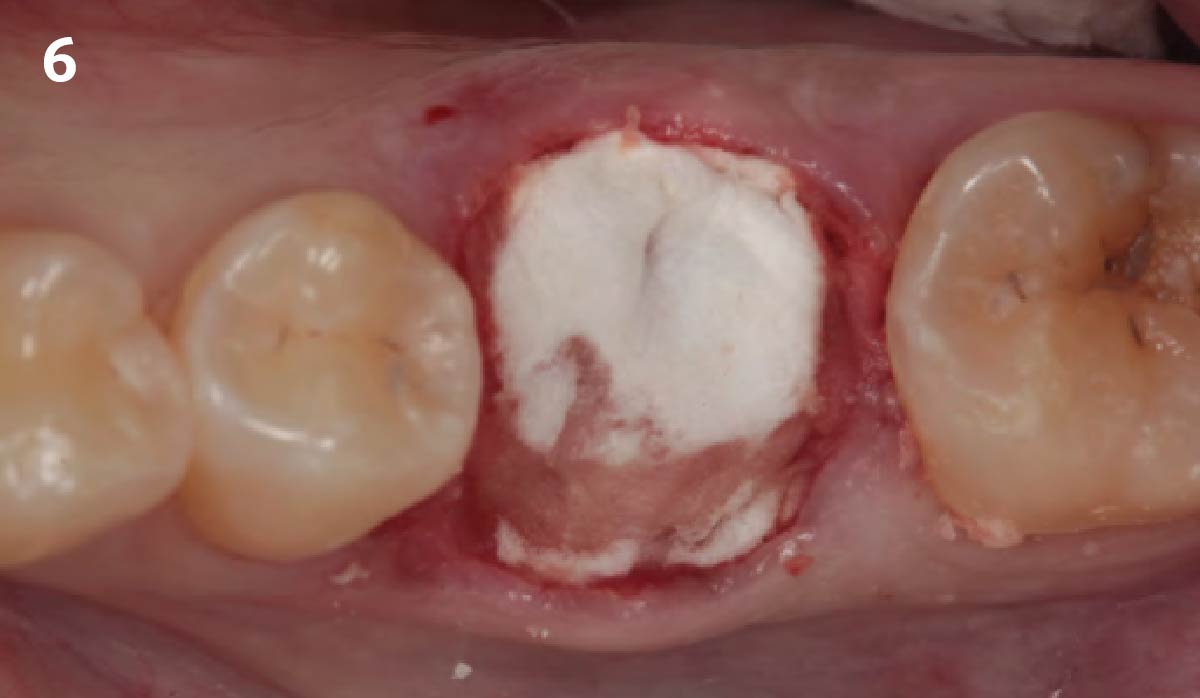
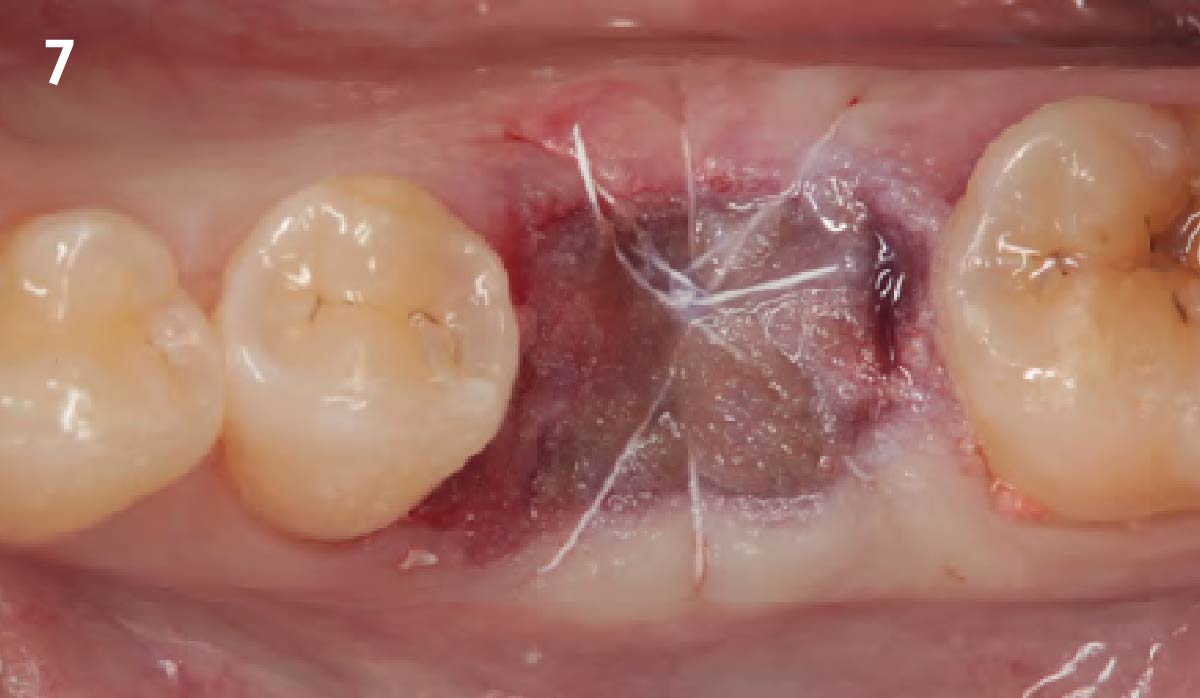
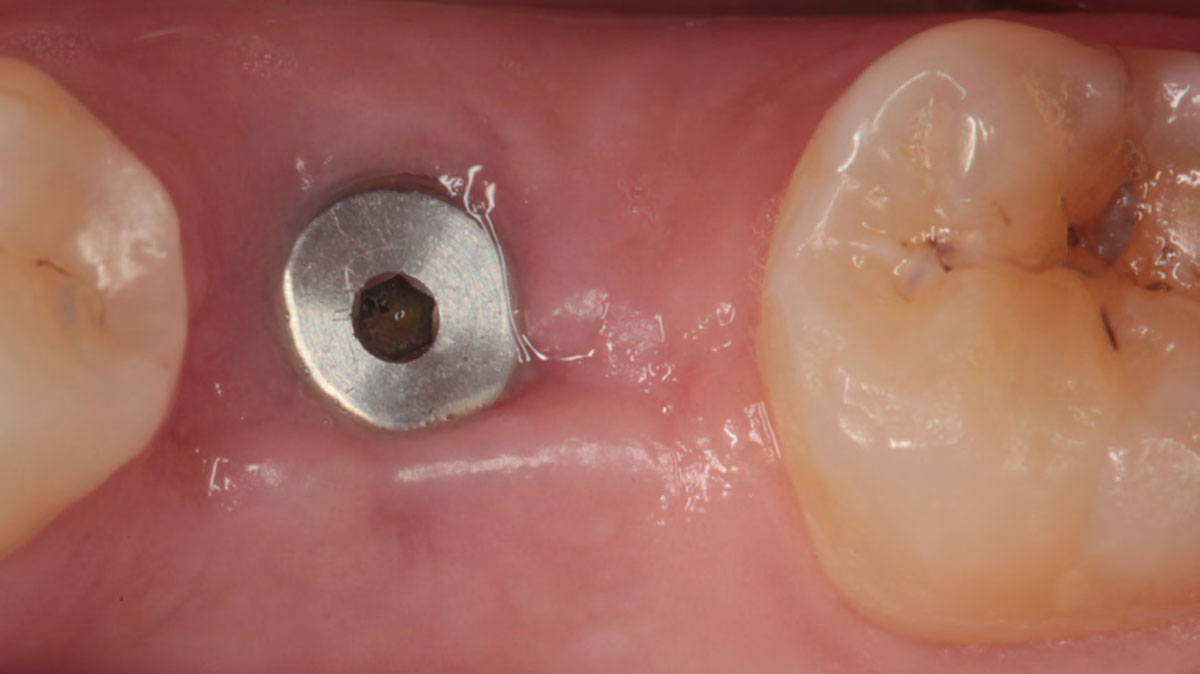
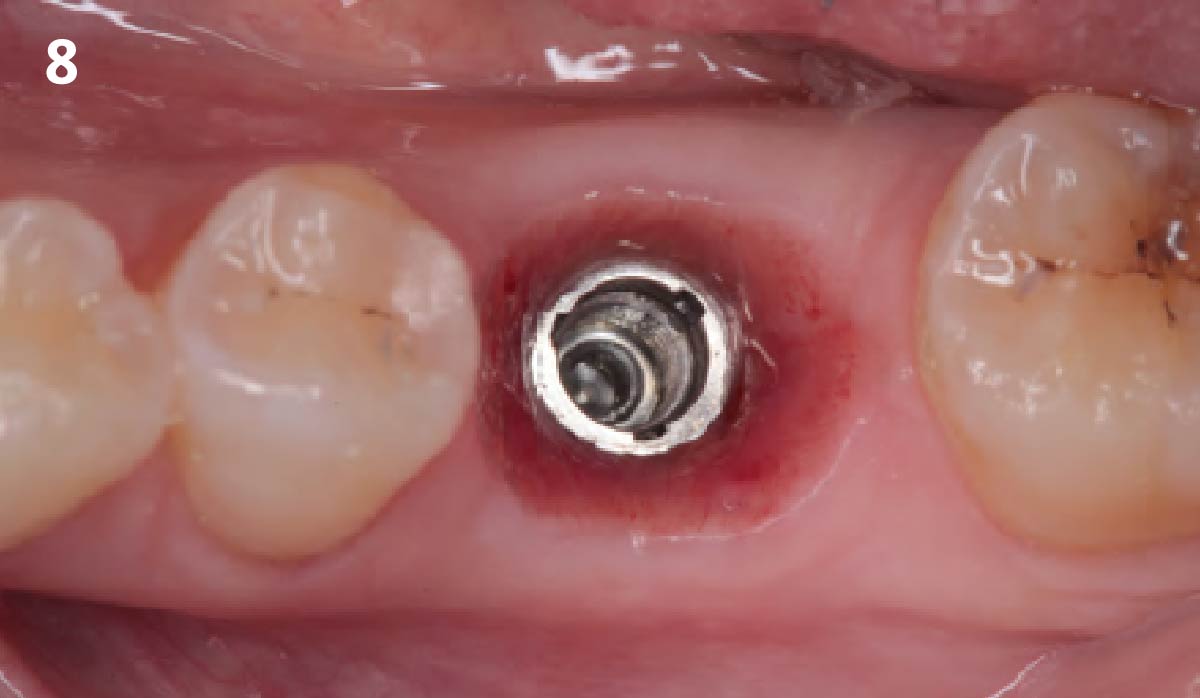
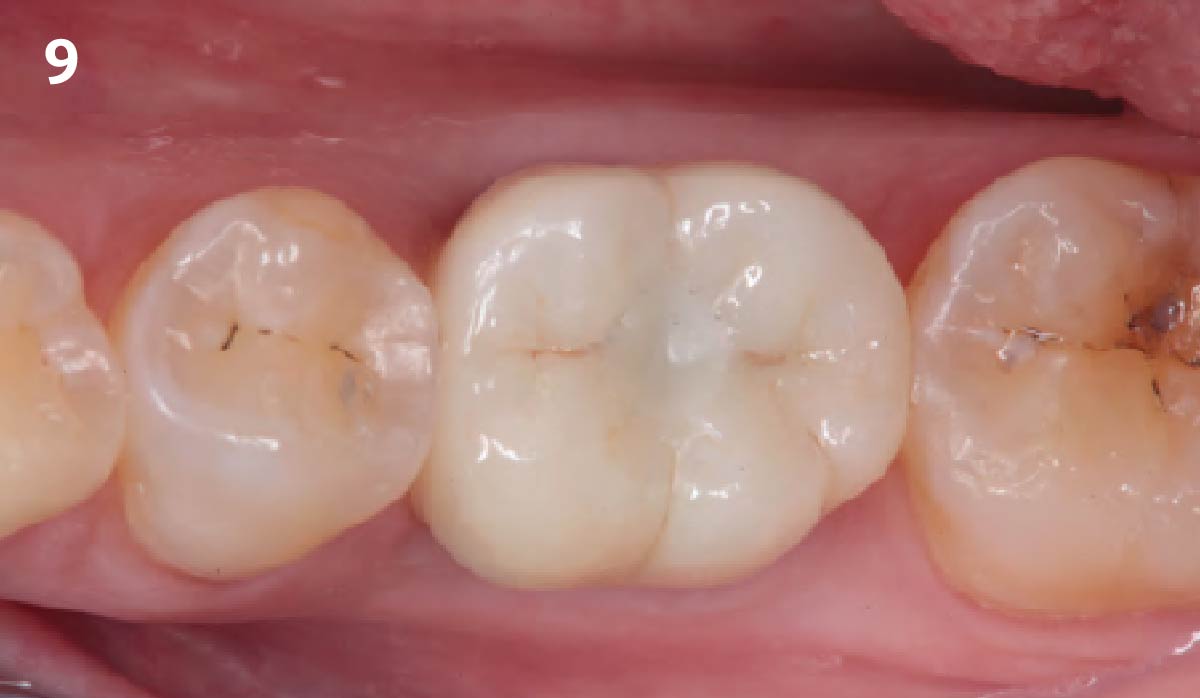
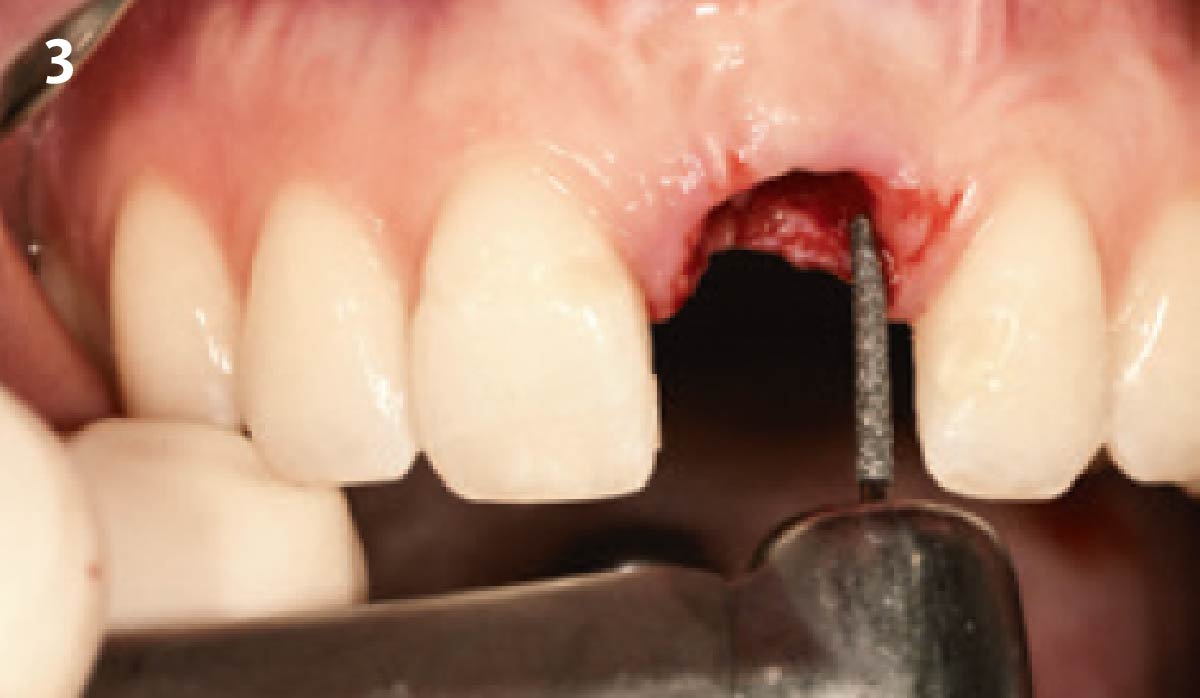
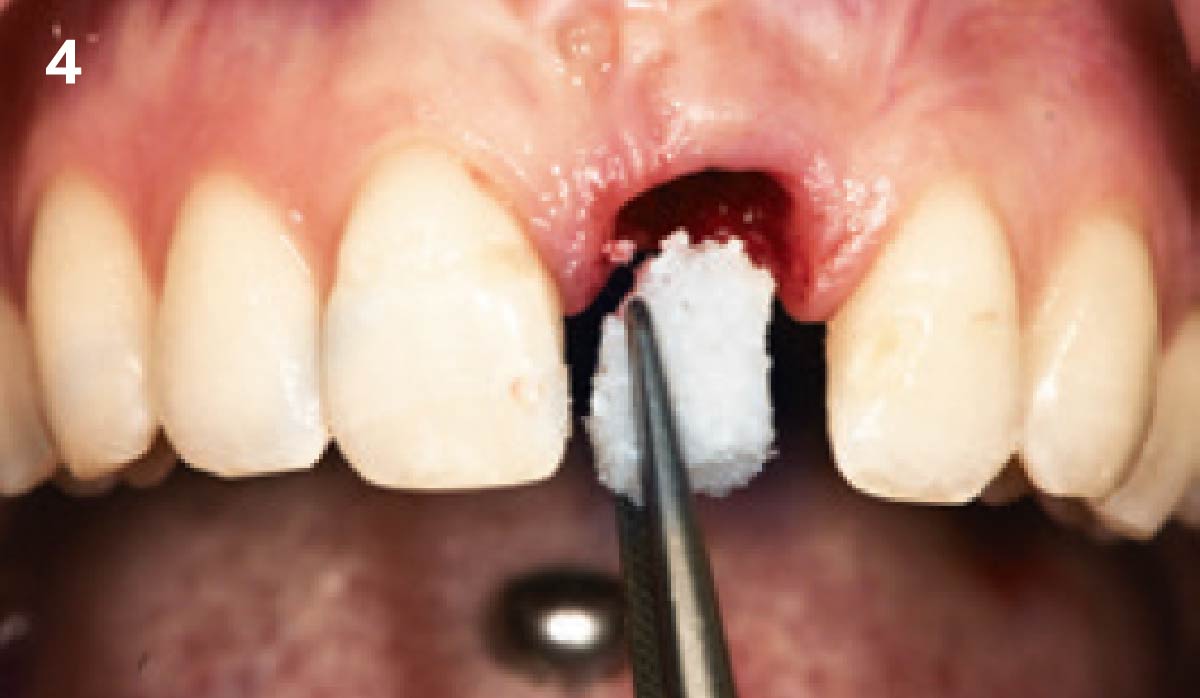
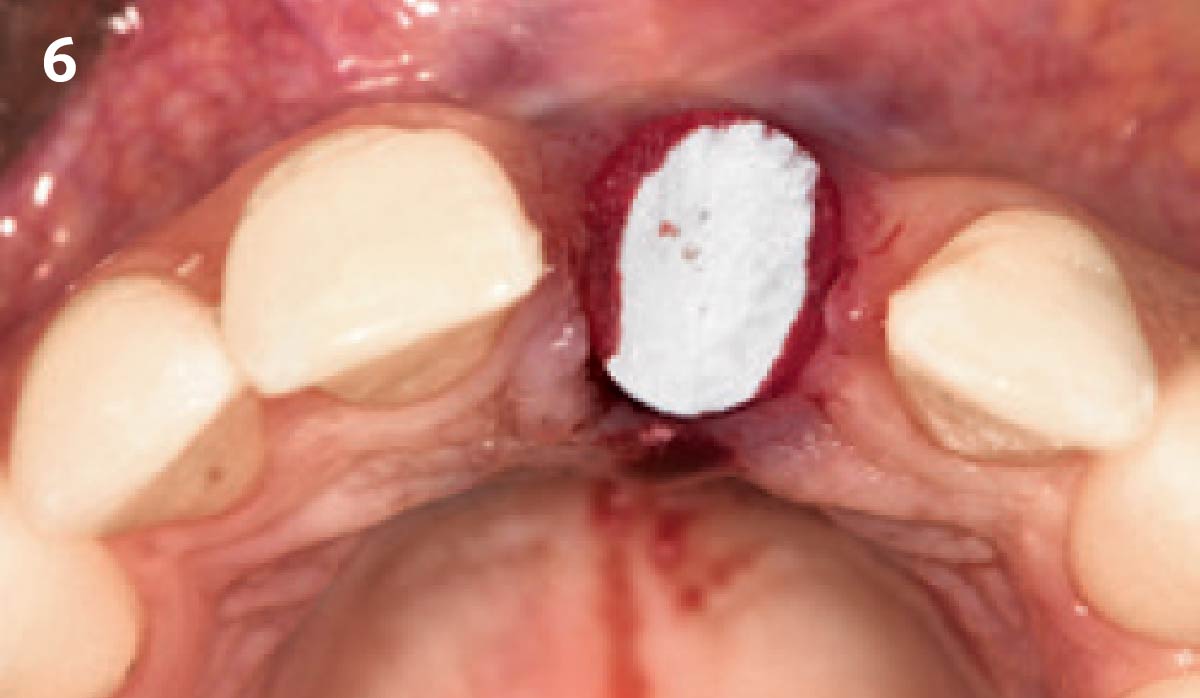
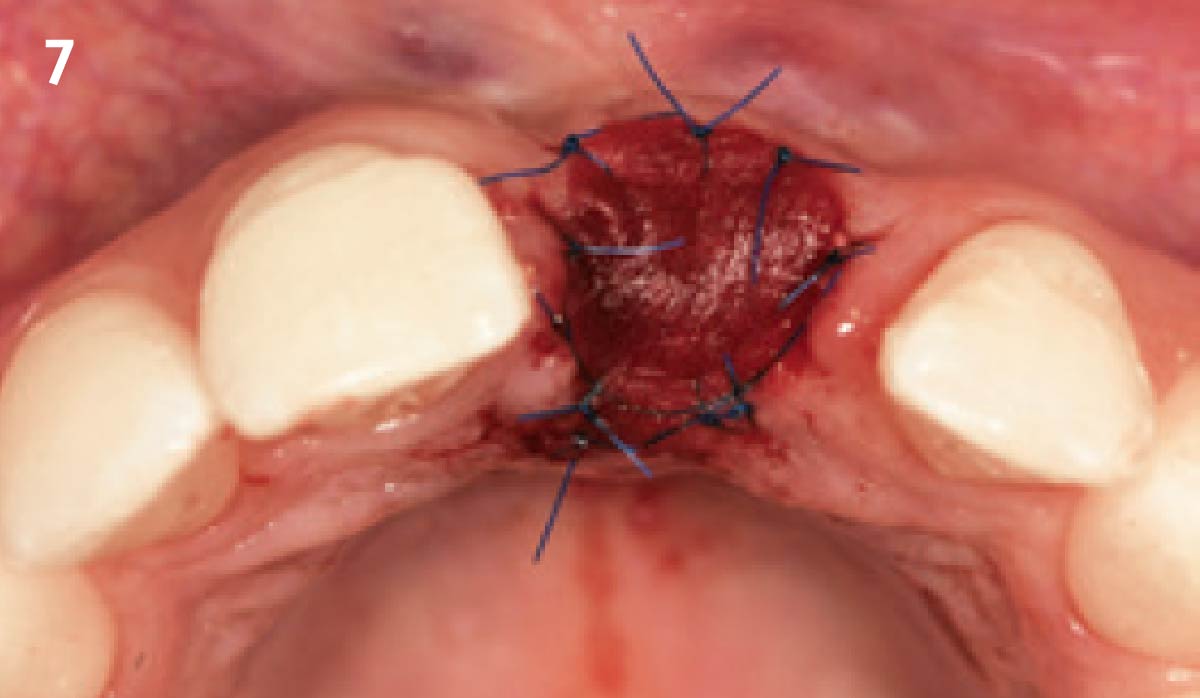
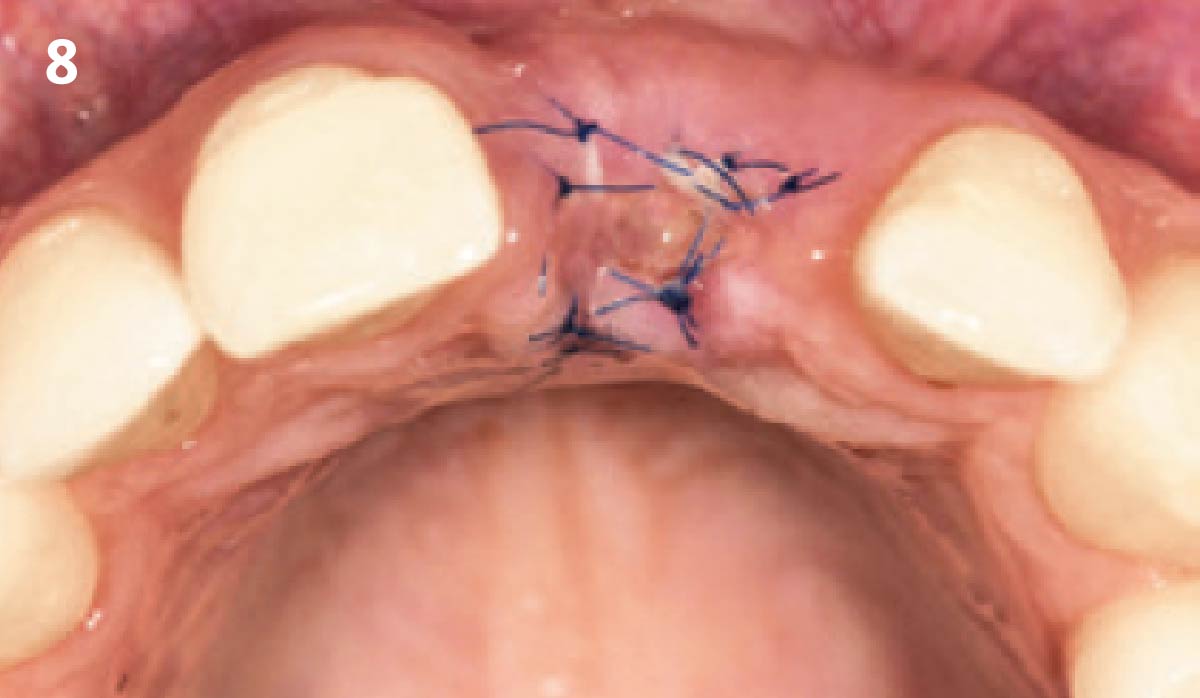
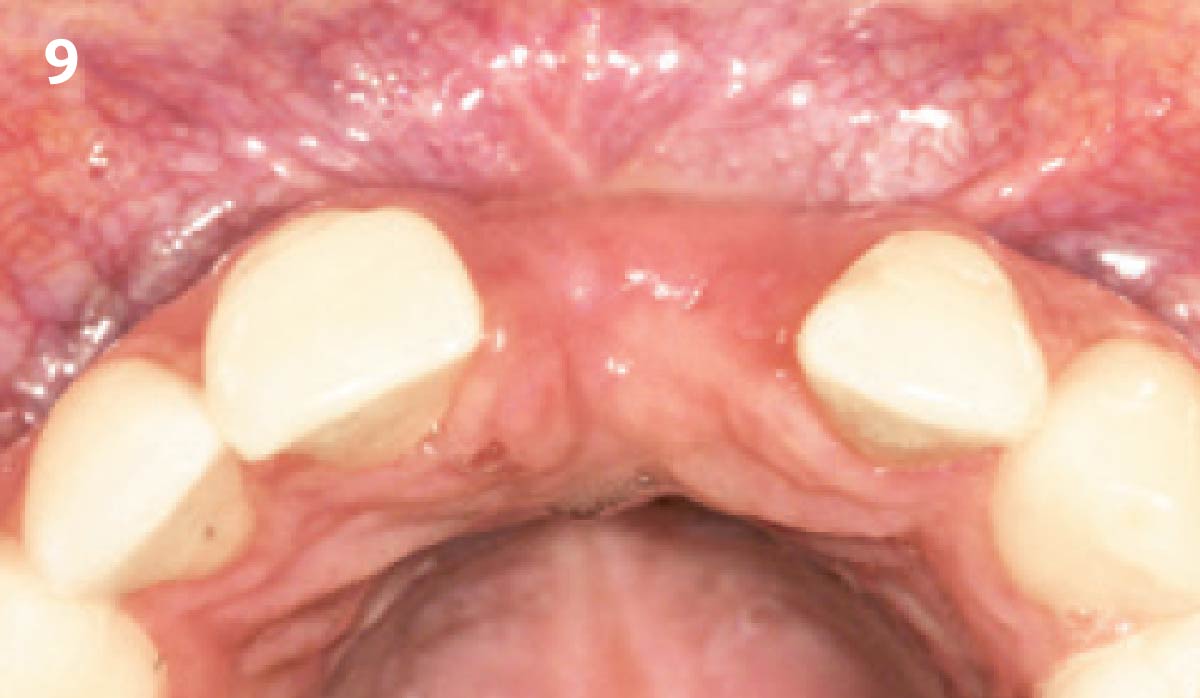
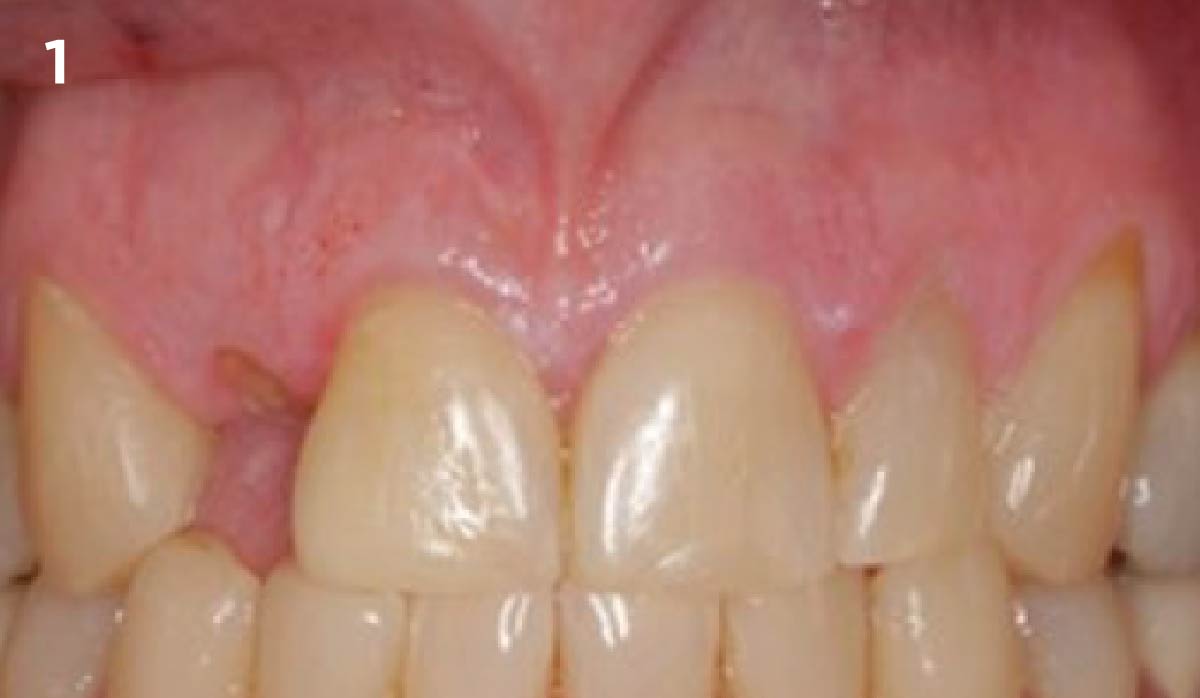
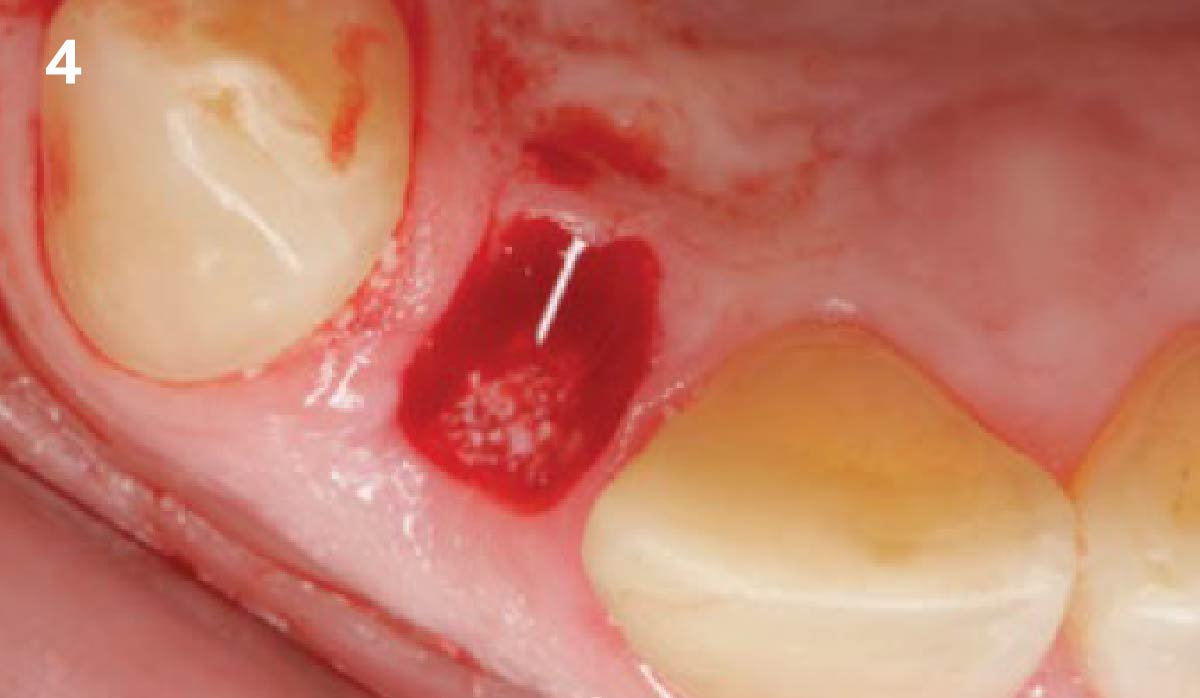
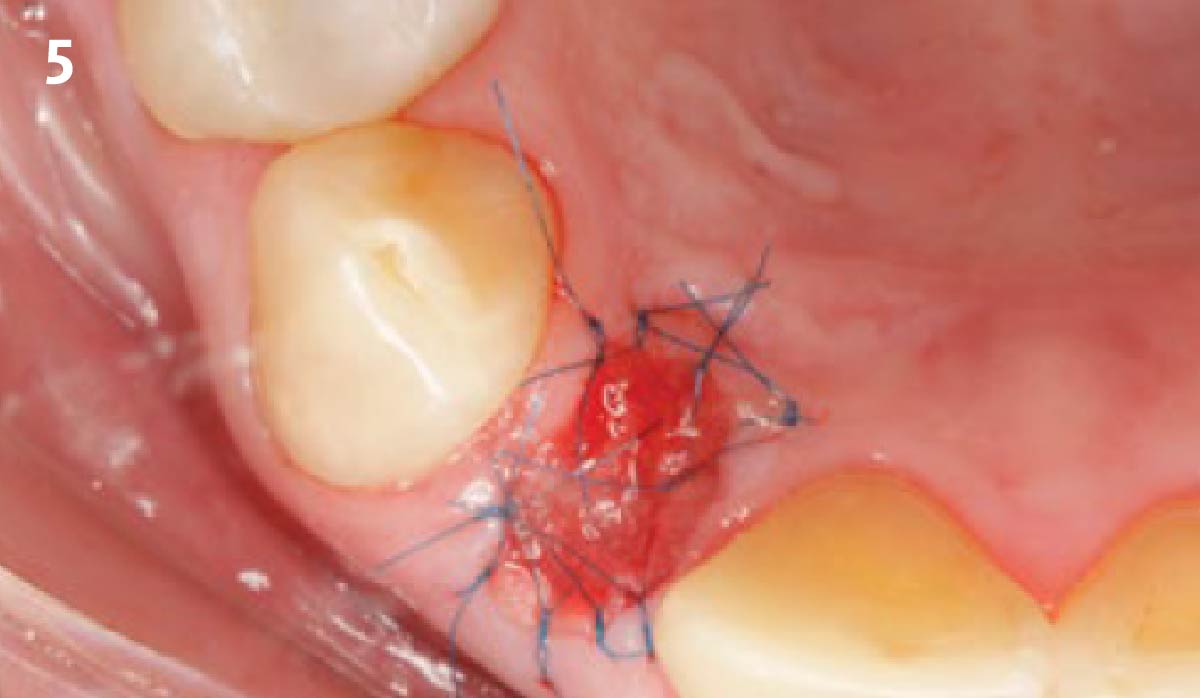
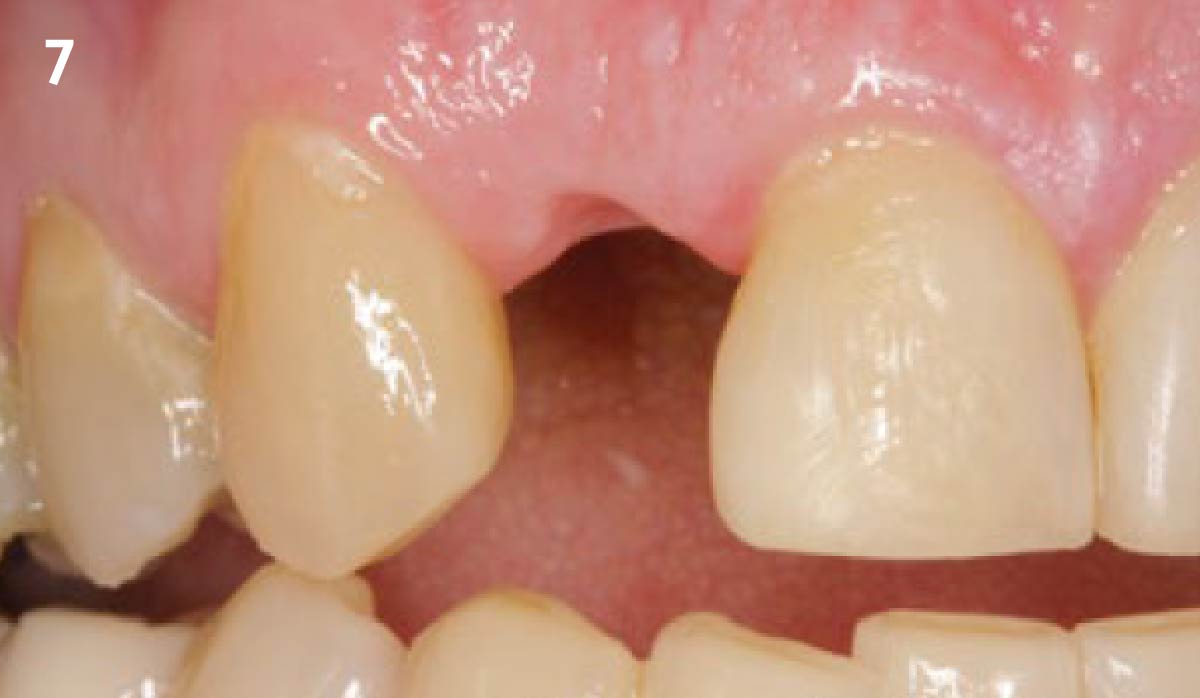
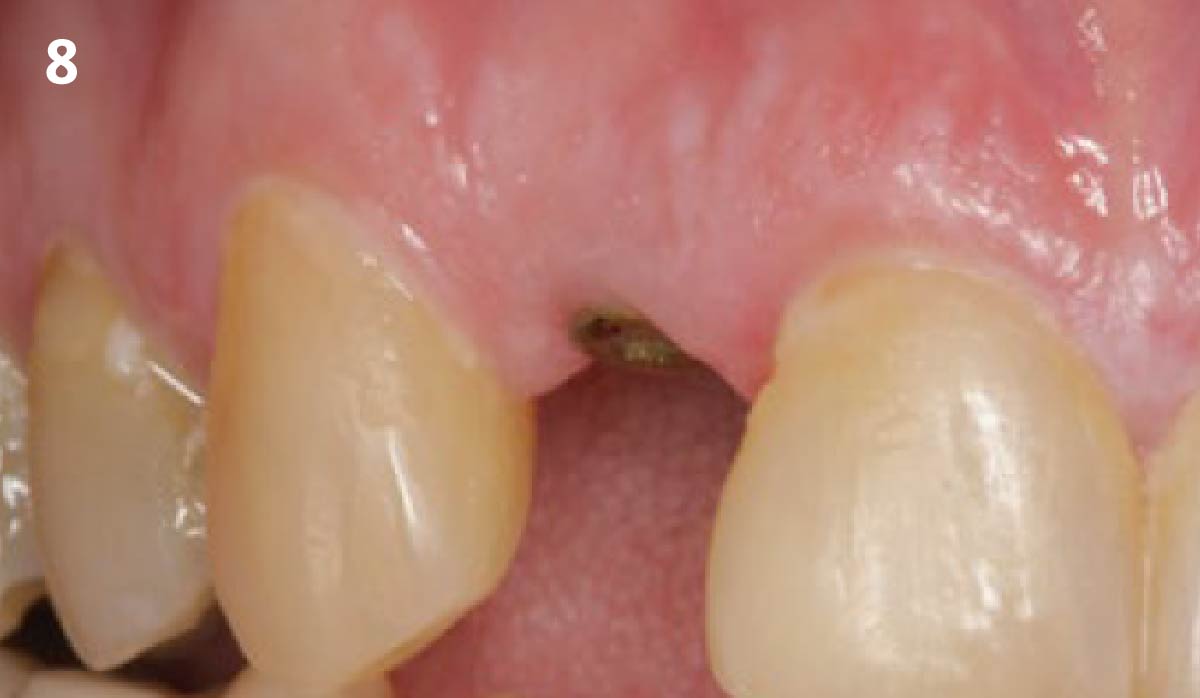
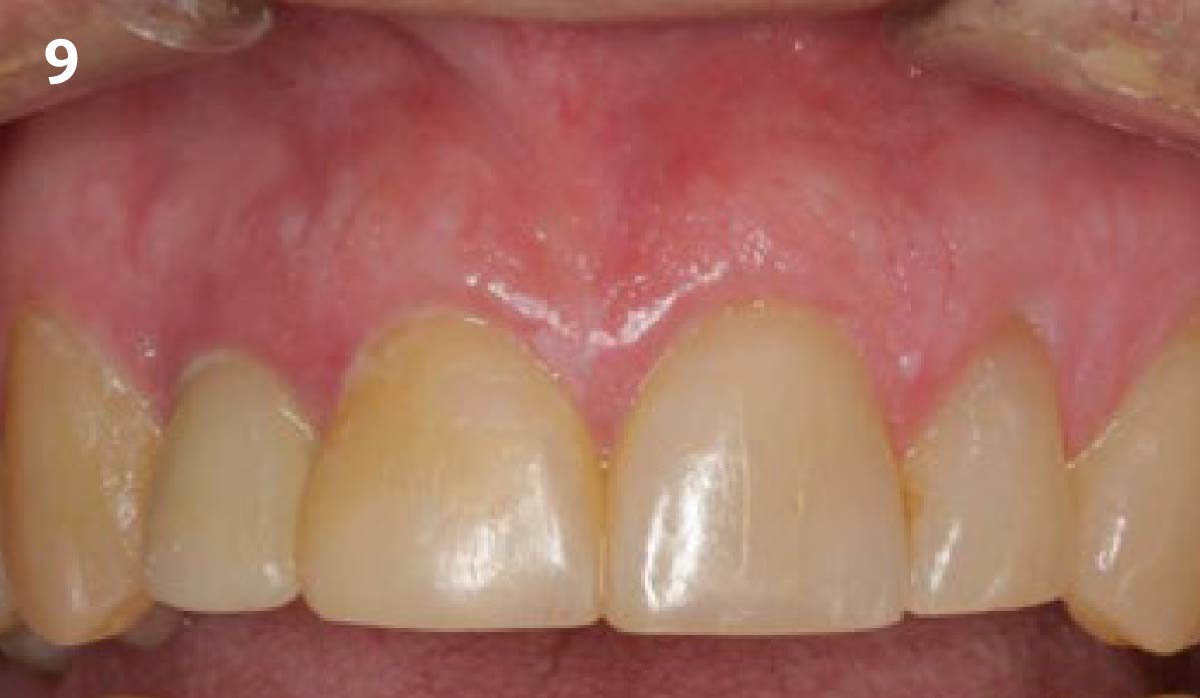
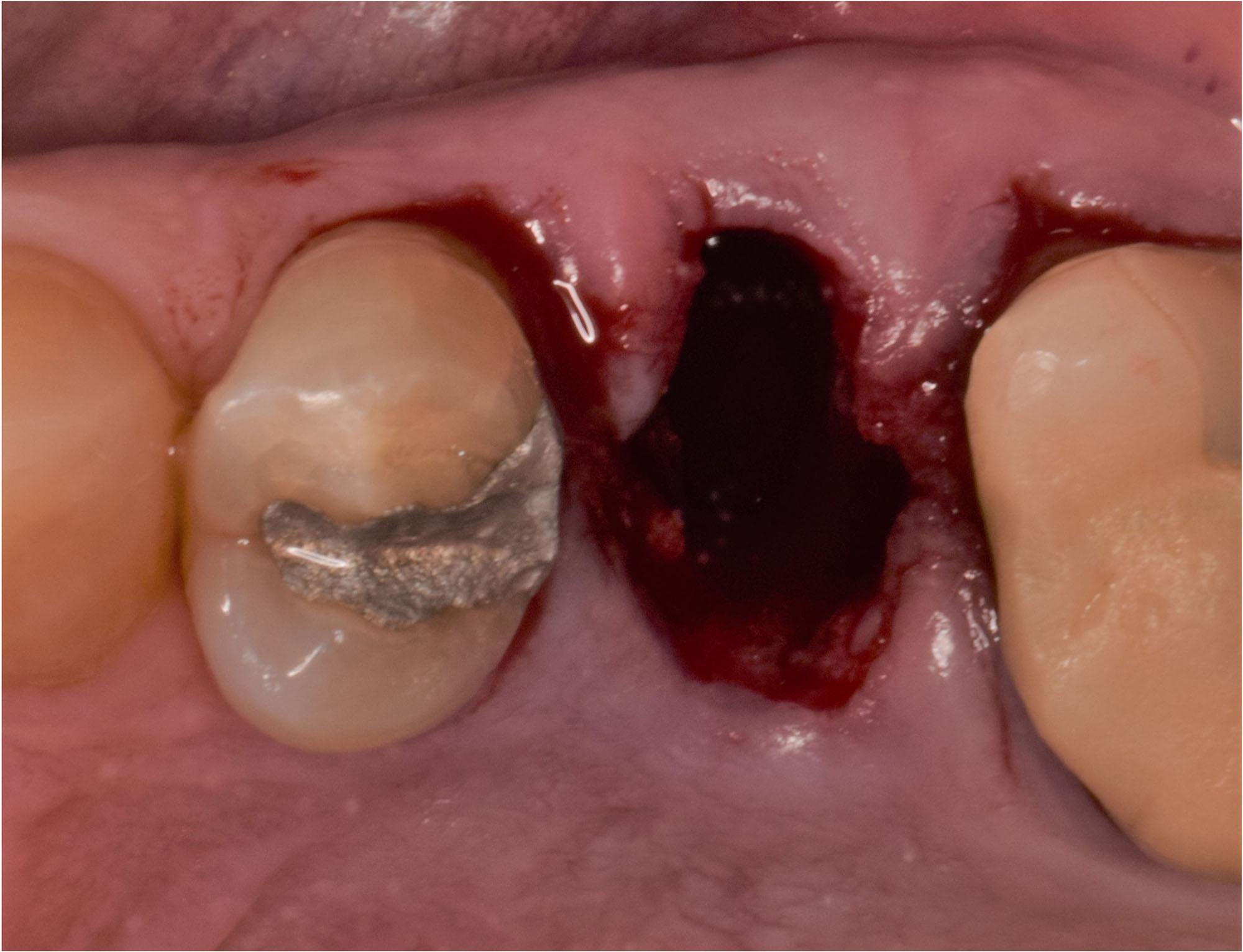
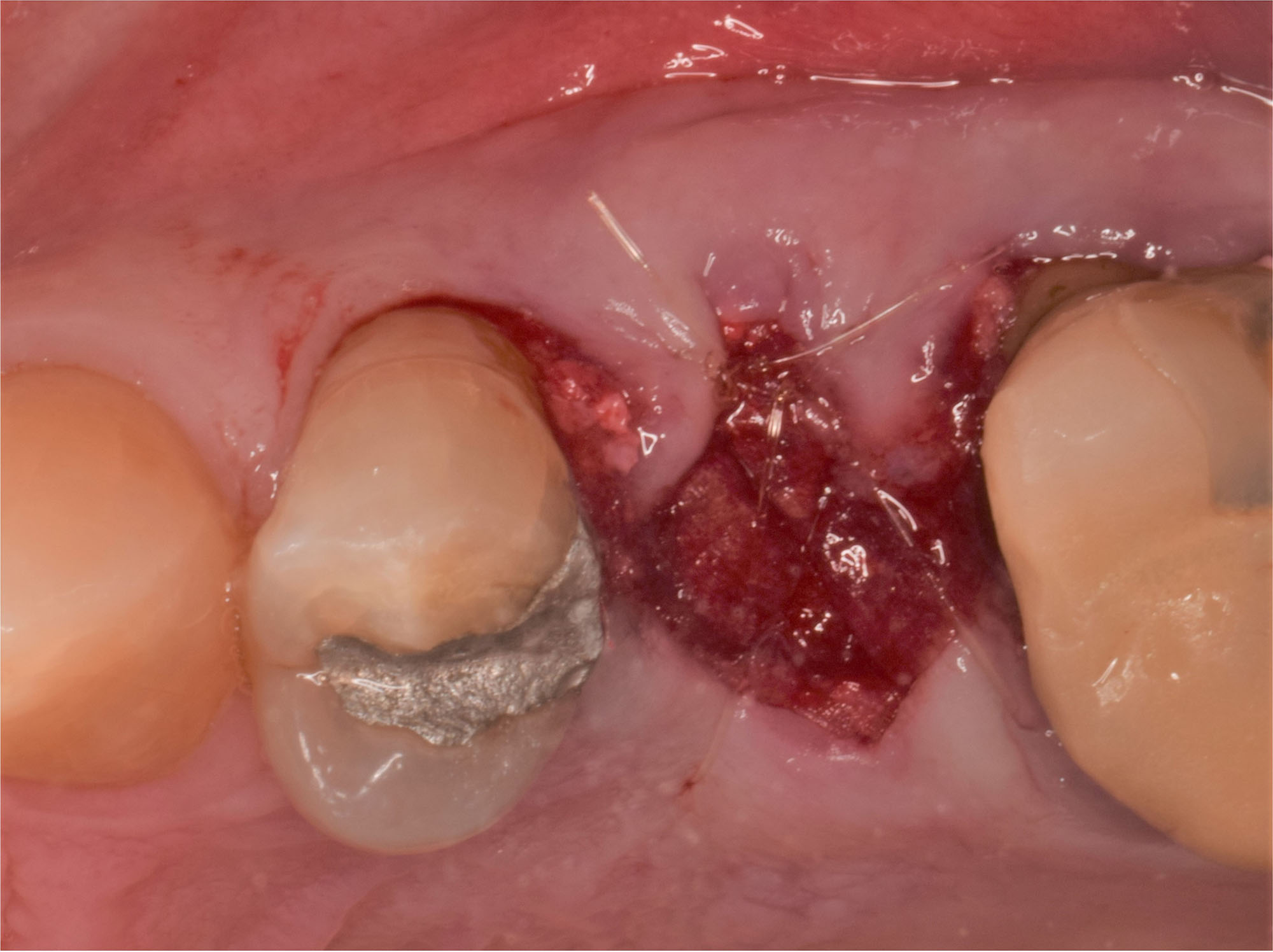
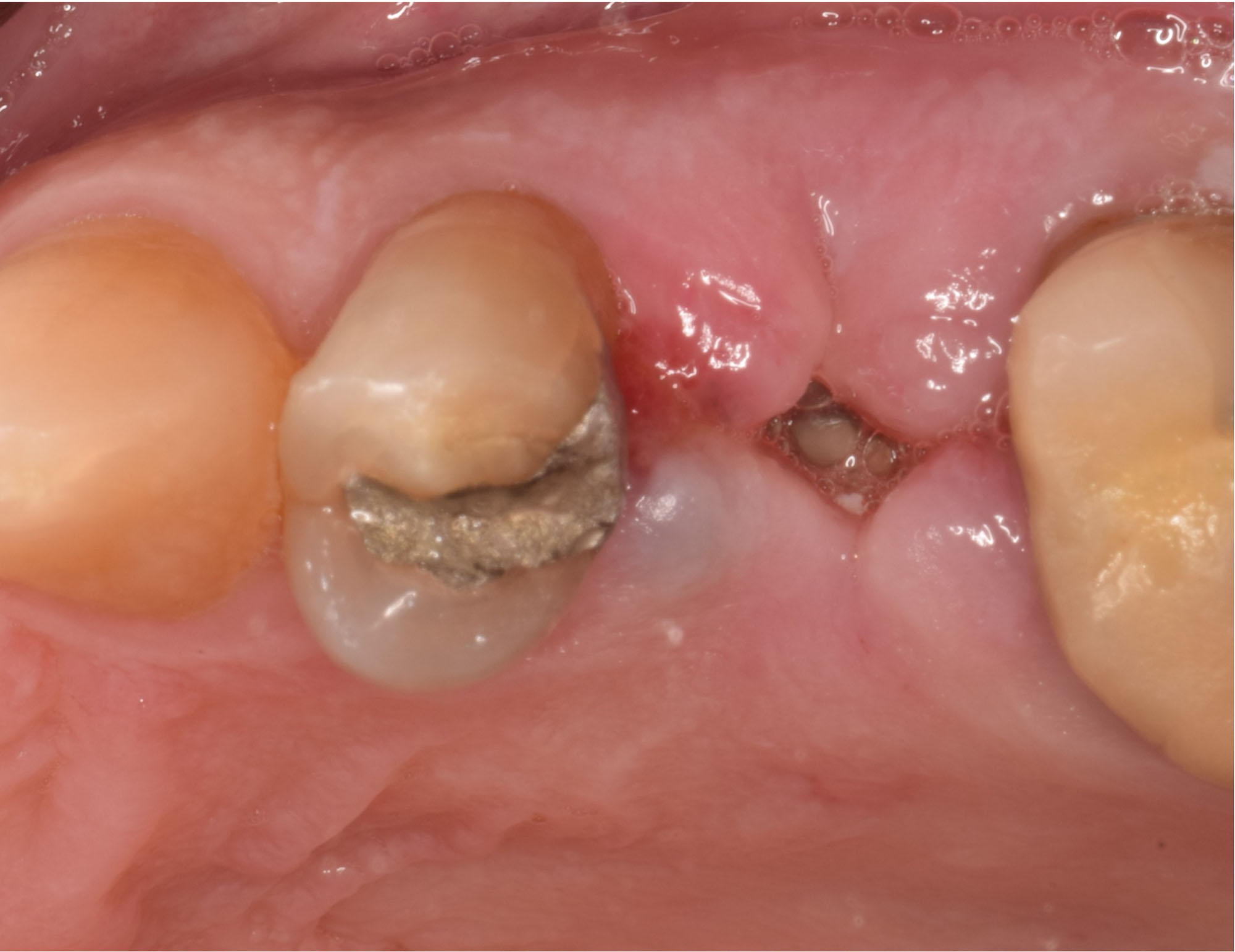
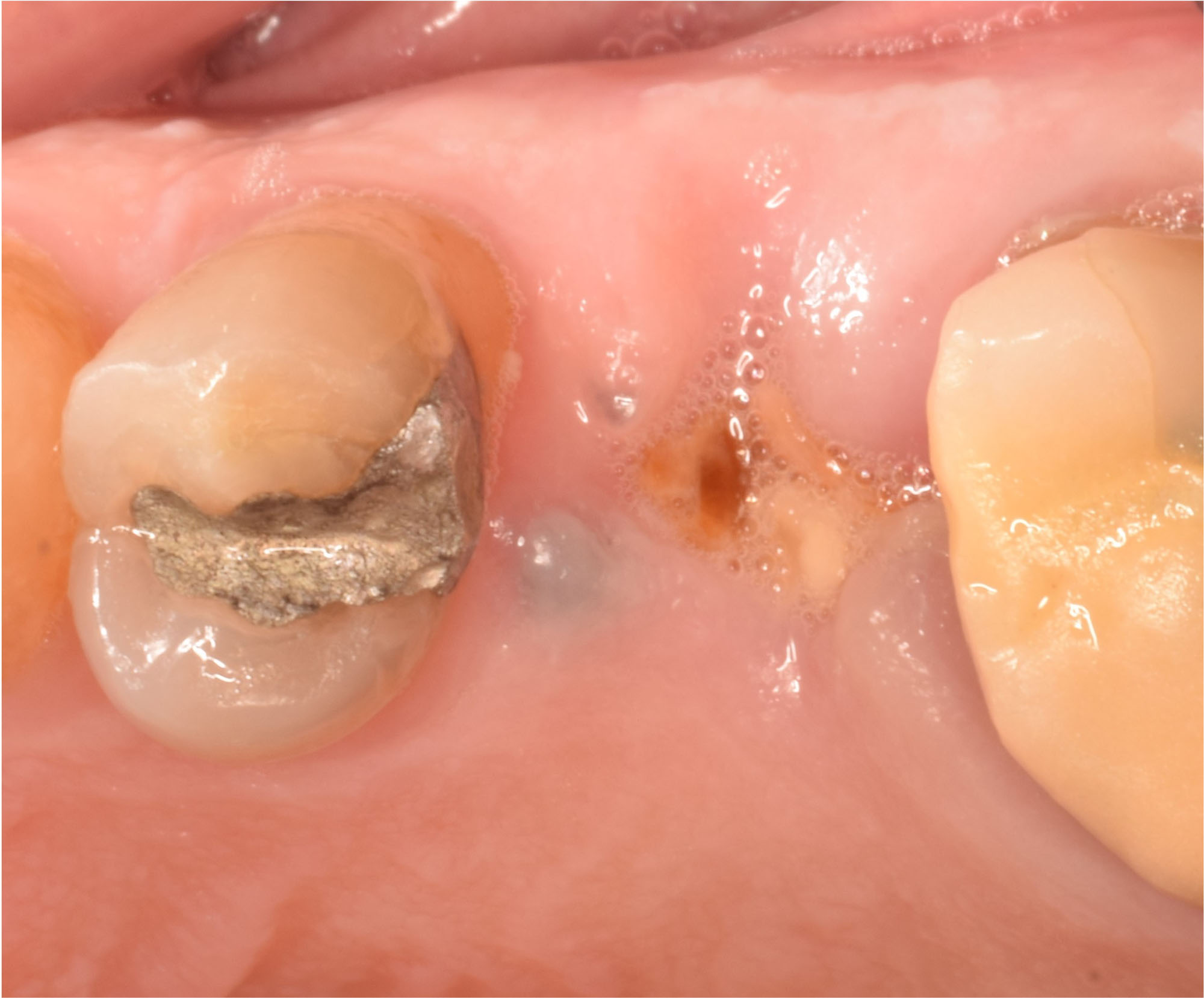
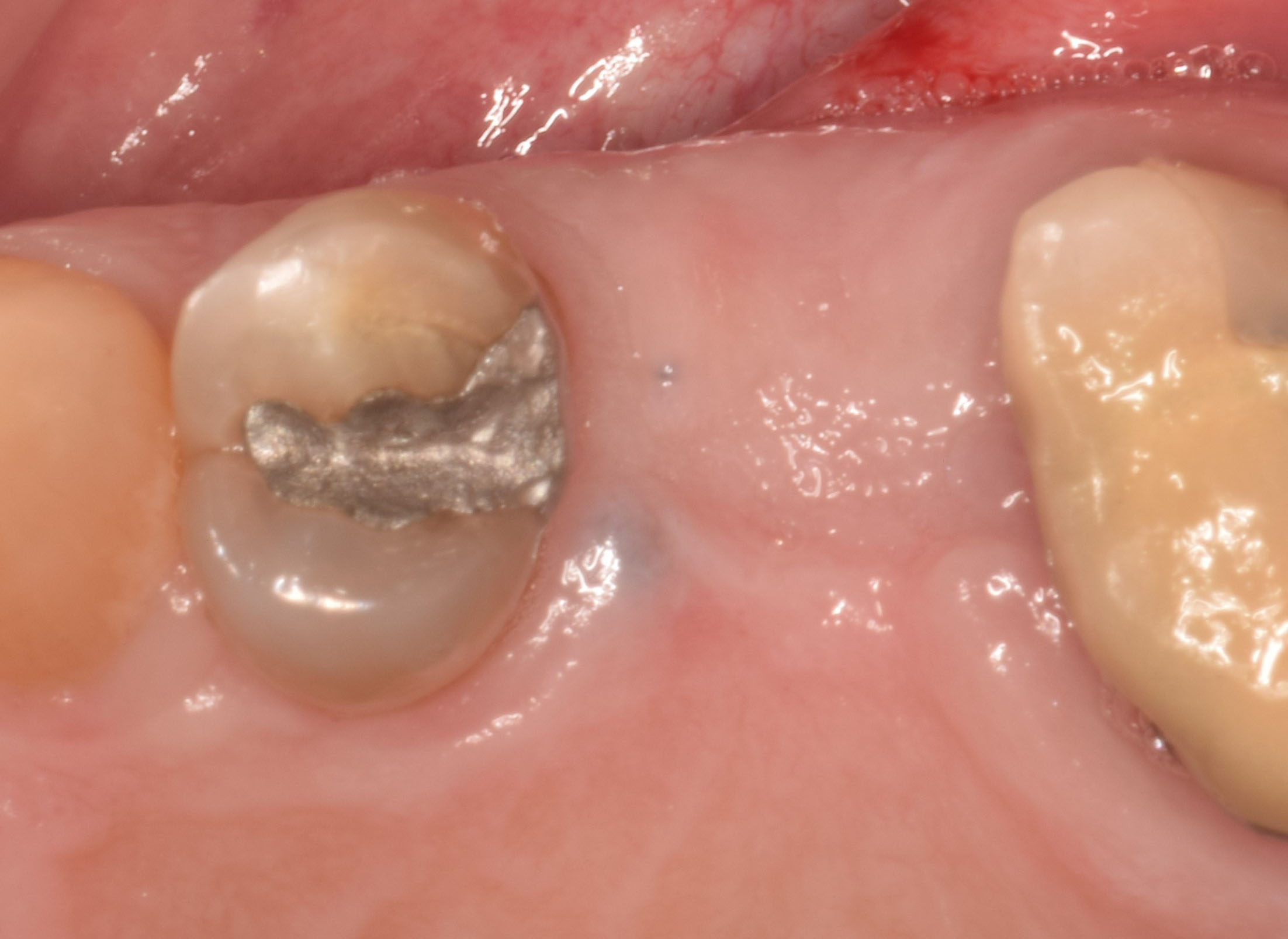
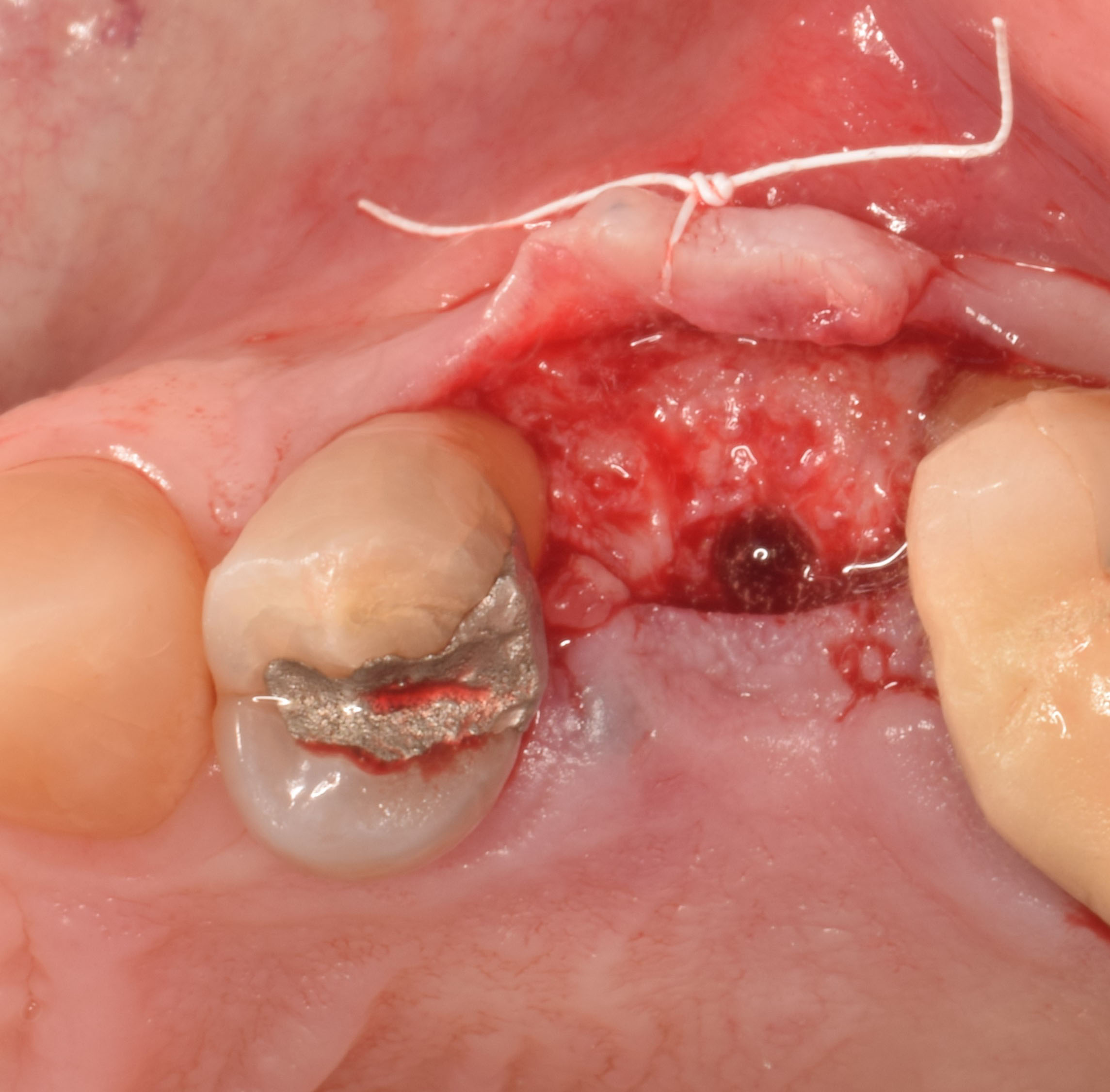
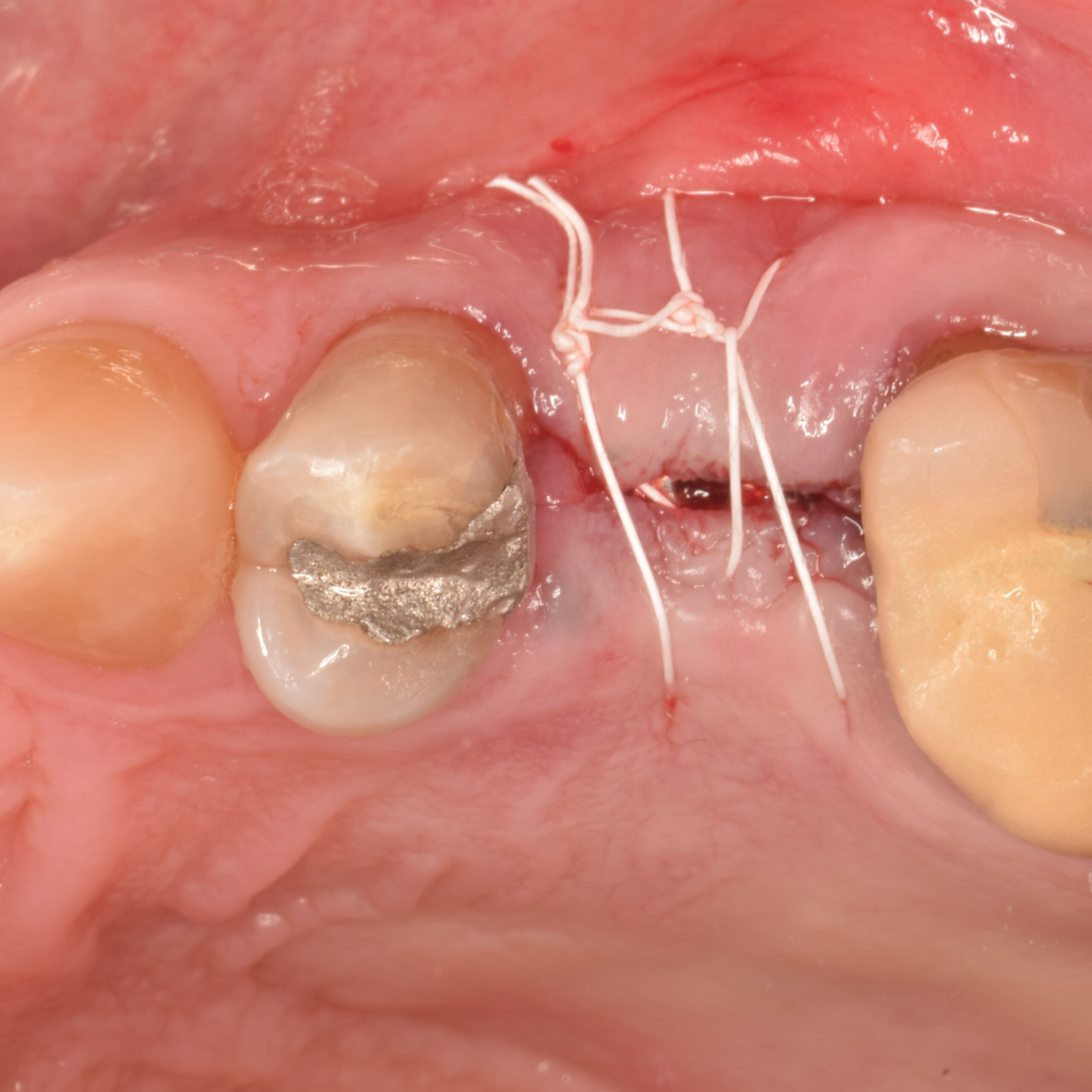
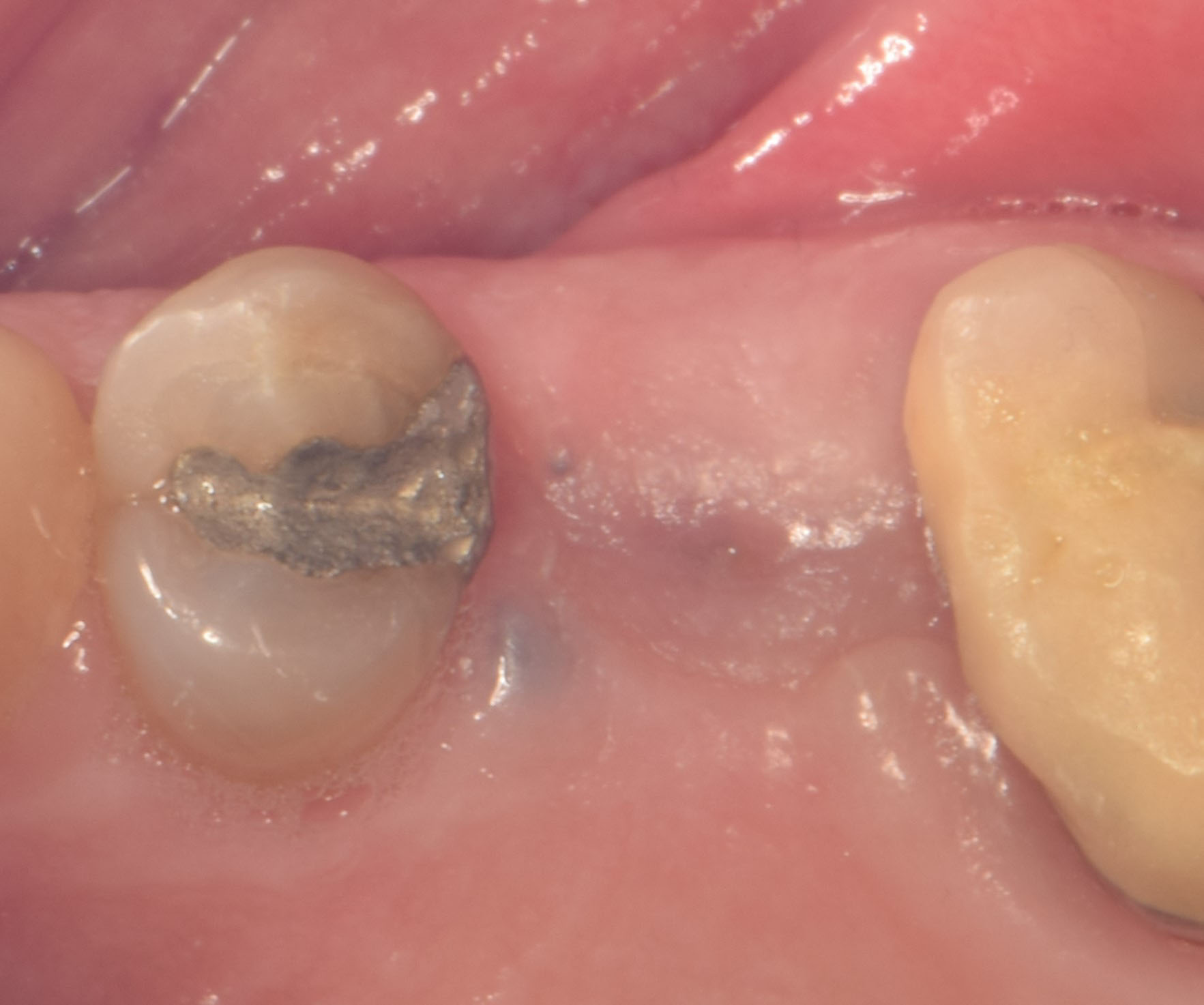
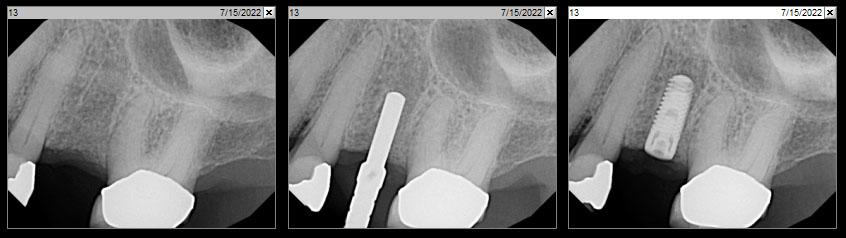
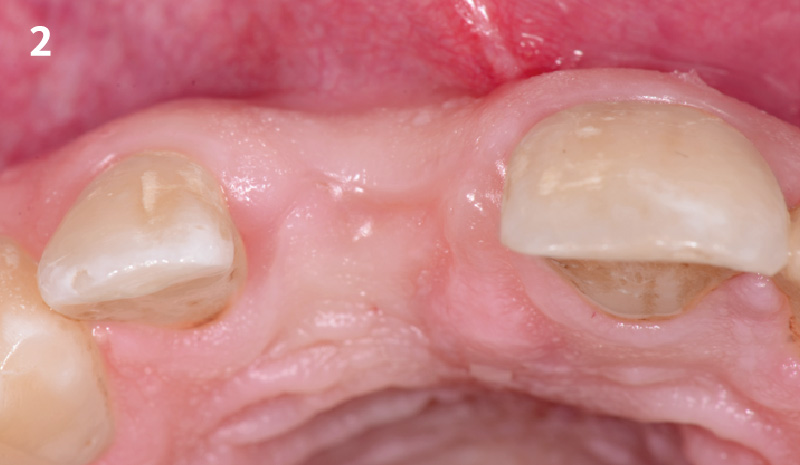
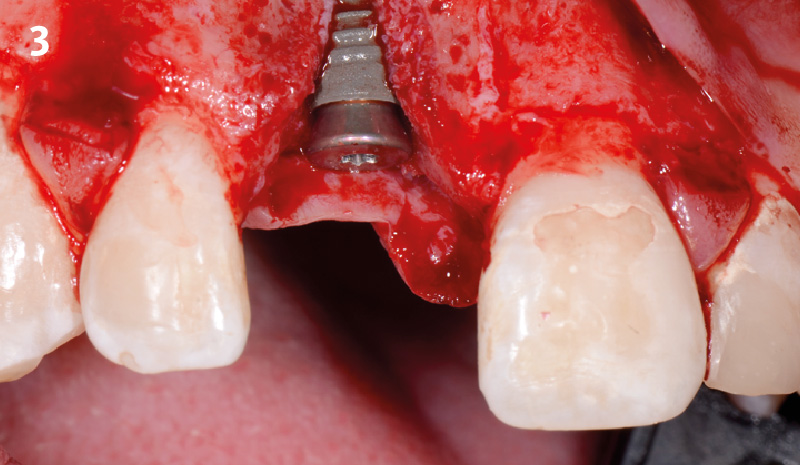
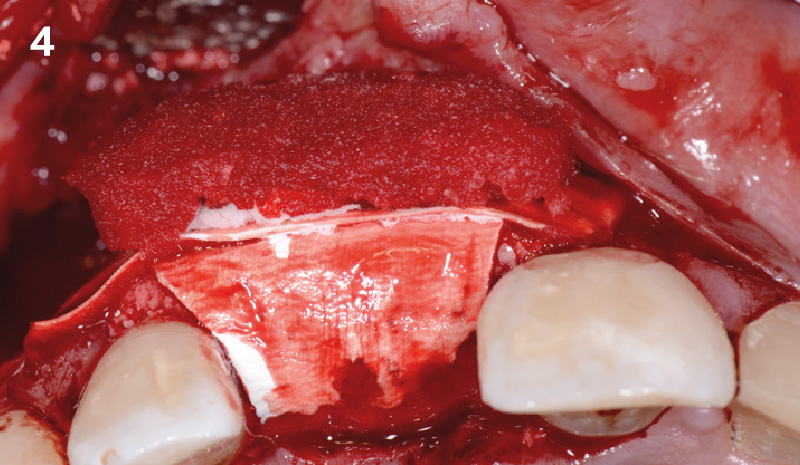
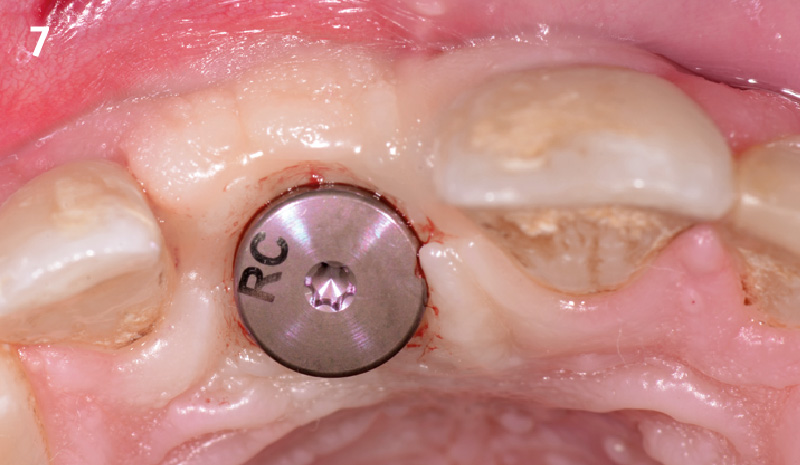
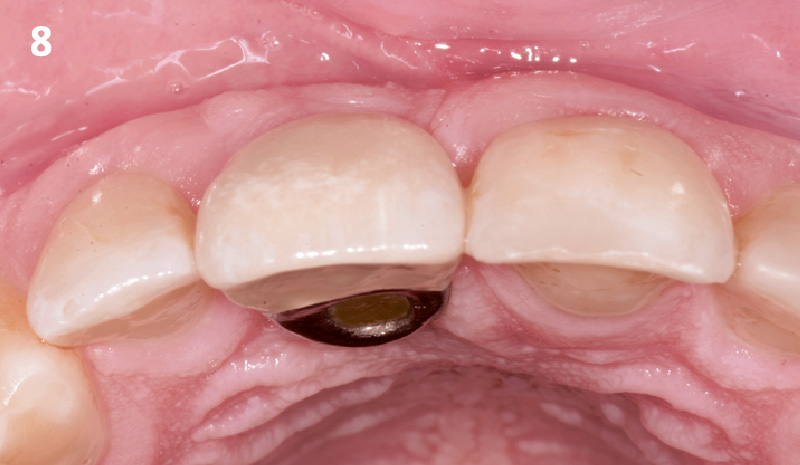
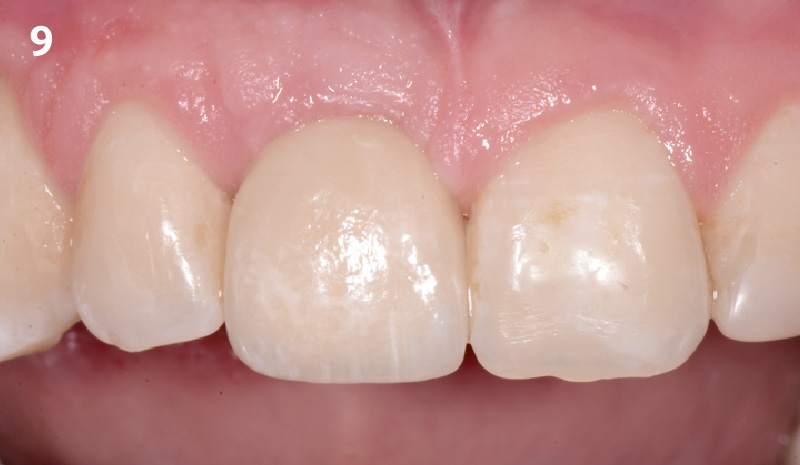
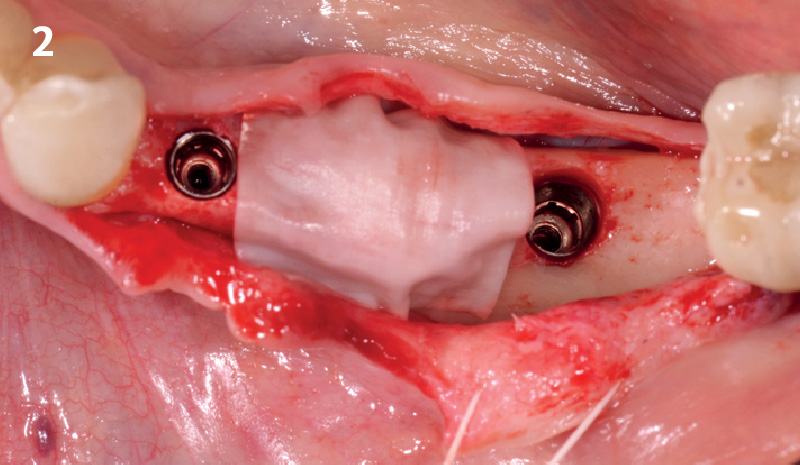
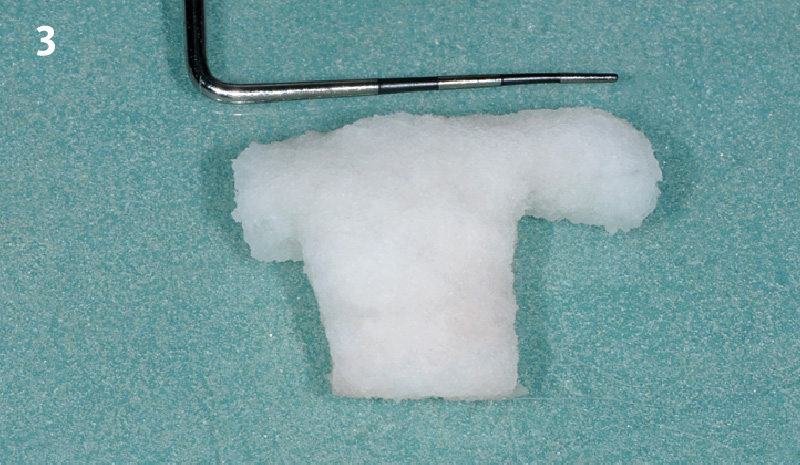
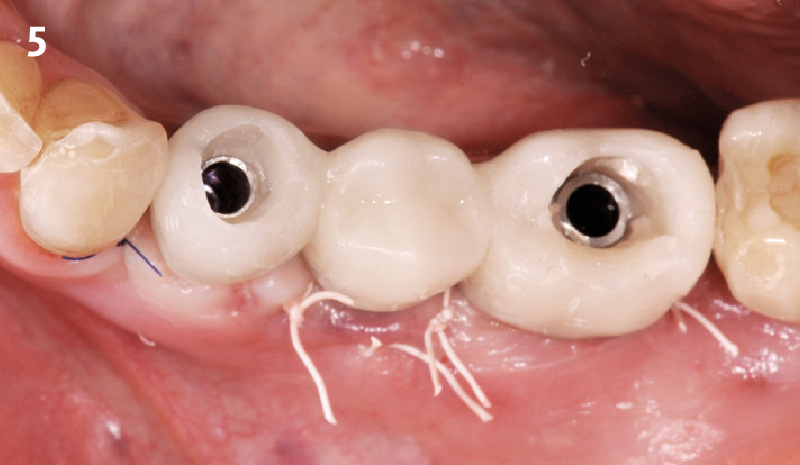
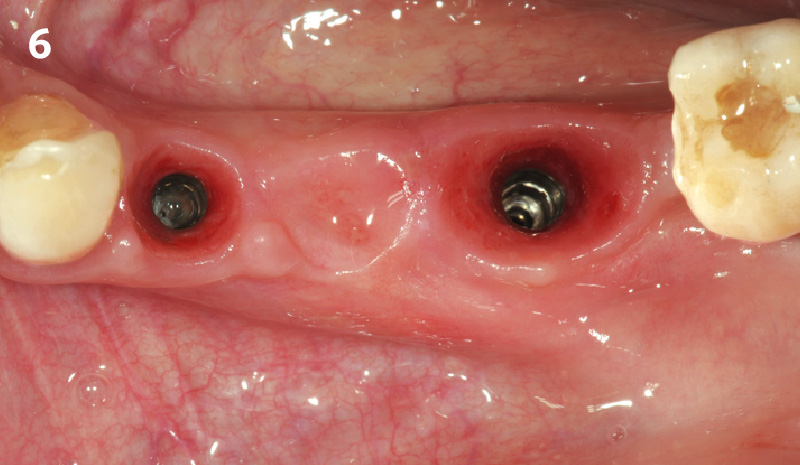
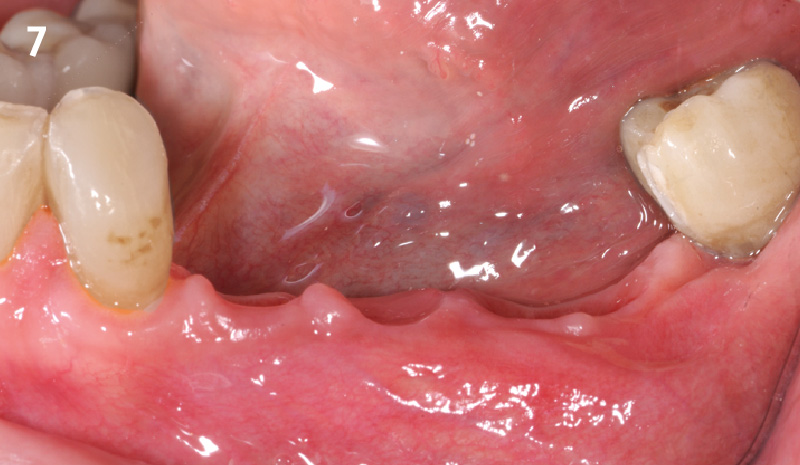
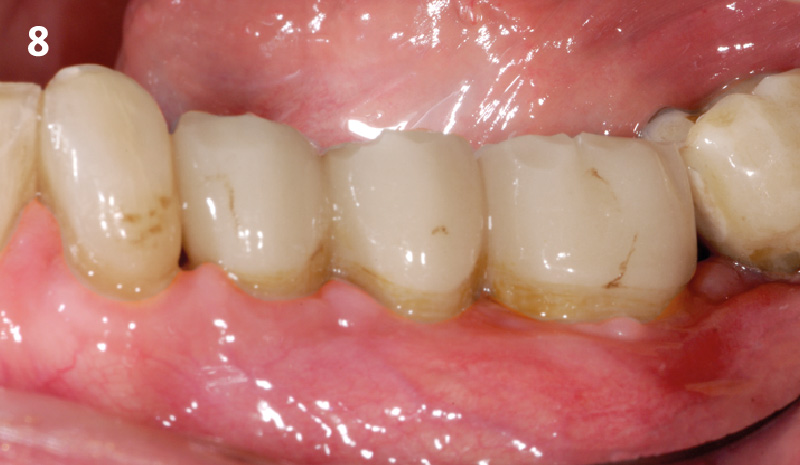
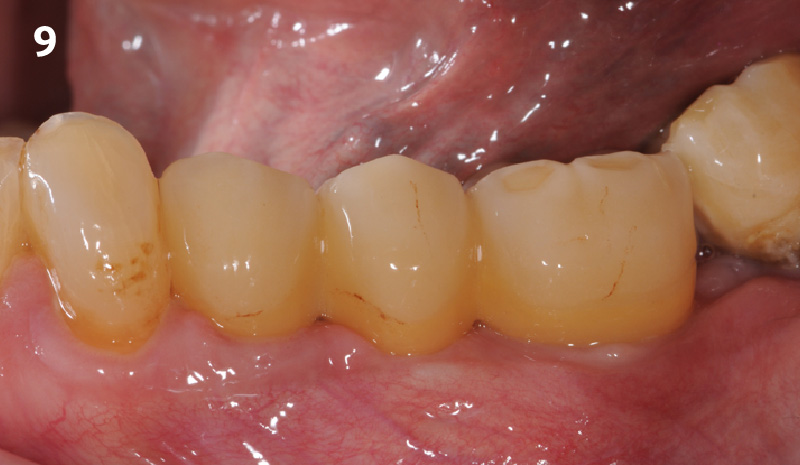
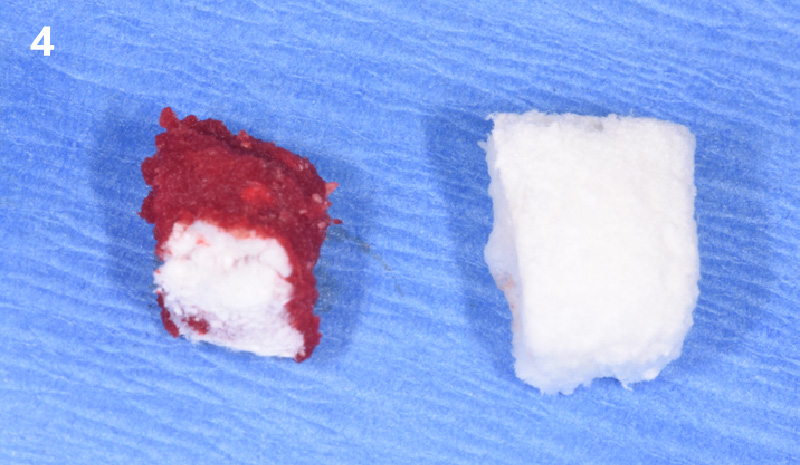
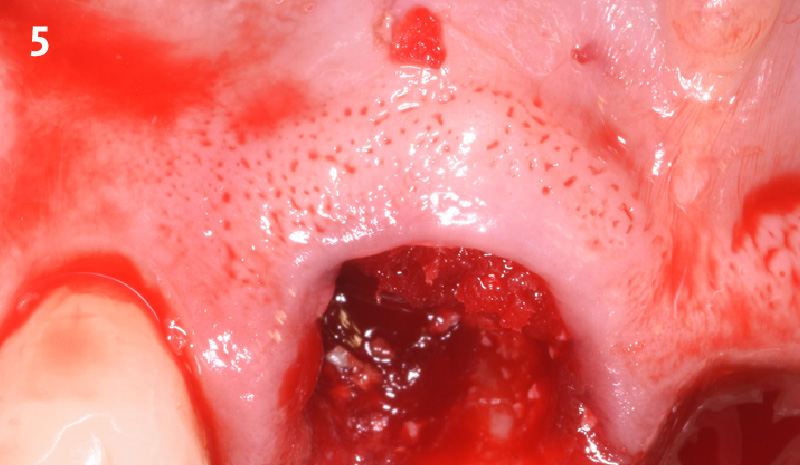
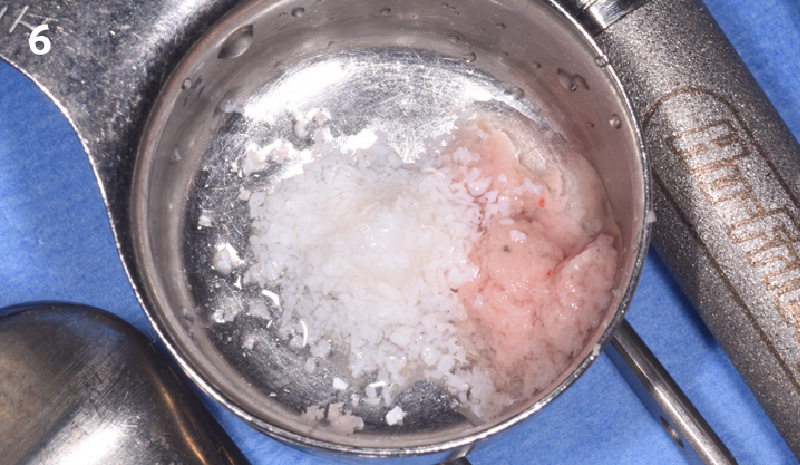
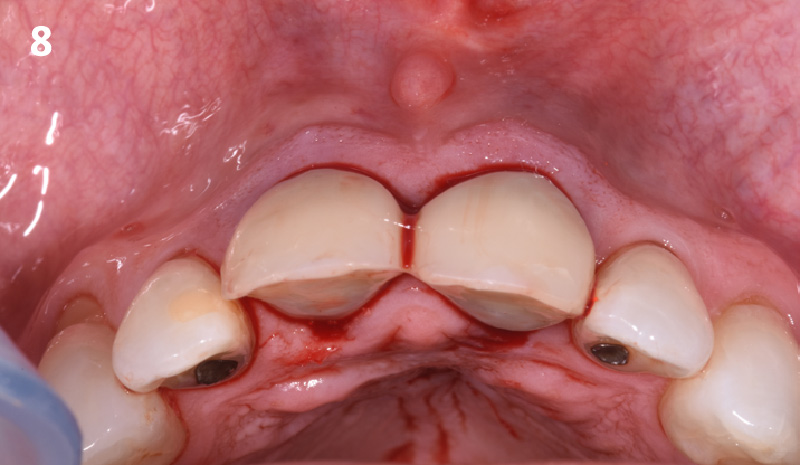
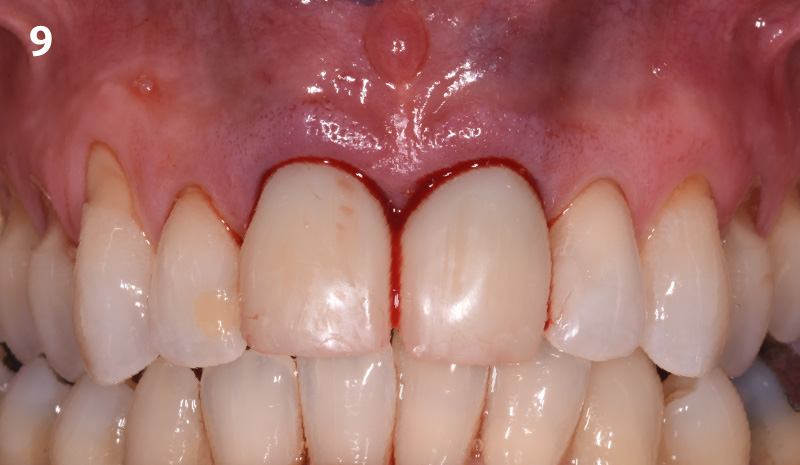
A fully guided approach was utilized, with an immediate provisional Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM) crown. Alveolar socket gaps were grafted with Geistlich Bio-Oss Collagen®, after implant placement. The provisional crown was used also as a socket seal, optimizing healing. After 3 months, a final ceramic crown was delivered. A one-year and a three-year follow-up show excellent clinical contour of the alveolar bone, and integration of the implant.
“Immediate implant placement and loading in molars is a feasible technique, with excellent long-term outcomes, if case selection is adequate, treatment planning is optimized by digital technology, and proper surgical and restorative techniques are applied.”
— Waldemar D. Polido, DDS, MS, PhD
THE OUTCOME
This case shows a three-year follow-up of an immediate implant placement, using Geistlich Bio-Oss Collagen® as a graft material on the gap. Careful tissue management, minimally traumatic extraction, and proper planning, including guided implant surgery can optimize treatment outcomes.

Waldemar D. Polido, DDS, MMS, PhD
Dr. Polido is an Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon with MS and PhD degrees from the PUCRS School of Dentistry in Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil. He completed his residency in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery at The University of Texas, Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, Texas. Currently, Dr. Polido is a Clinical Professor of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery at the Indiana University School of Dentistry. He is also the Co-Director of the Center for Implant, Esthetic, and Innovative Dentistry at Indiana University School of Dentistry in Indianapolis.

Wel-Shao Lin, DDS, FACP, PhD, MBA
Dr. Lin is a tenured Professor and Chair of Prosthodontics at Indiana University School of Dentistry. He earned his DDS from Chung-Shan and Surgical Implant Fellowship at the University of Rochester (2010). He holds a PhD in Educational Leadership (2020) and an MBA in Healthcare Administration (2022) and is currently pursuing a Master’s Intelligence. Dr. Lin specializes in dental implants, digital dentistry, and AI applications, with over 120 peer-reviewed publications. A Diplomate of the American Board of Prosthodontics and Fellow of ITI and ACP, he also serves as an associate editor for the Journal of Prosthodontics and maintains a clinical practice at Indiana University.

WEBINAR

BIOBRIEF
Alveolar Ridge Preservation with vallos® Mineralized Cortico-Cancellous Allograft
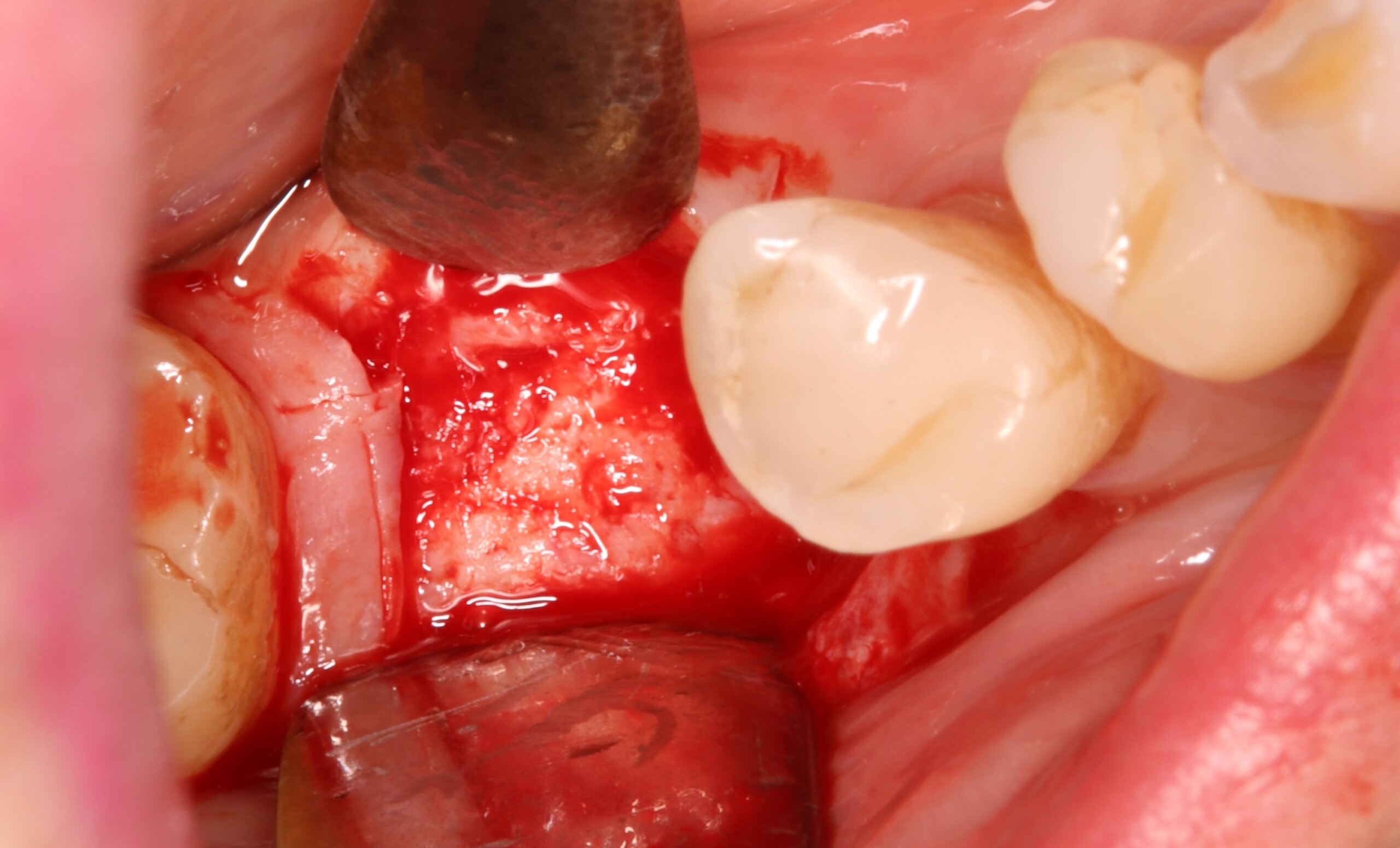


THE SITUATION
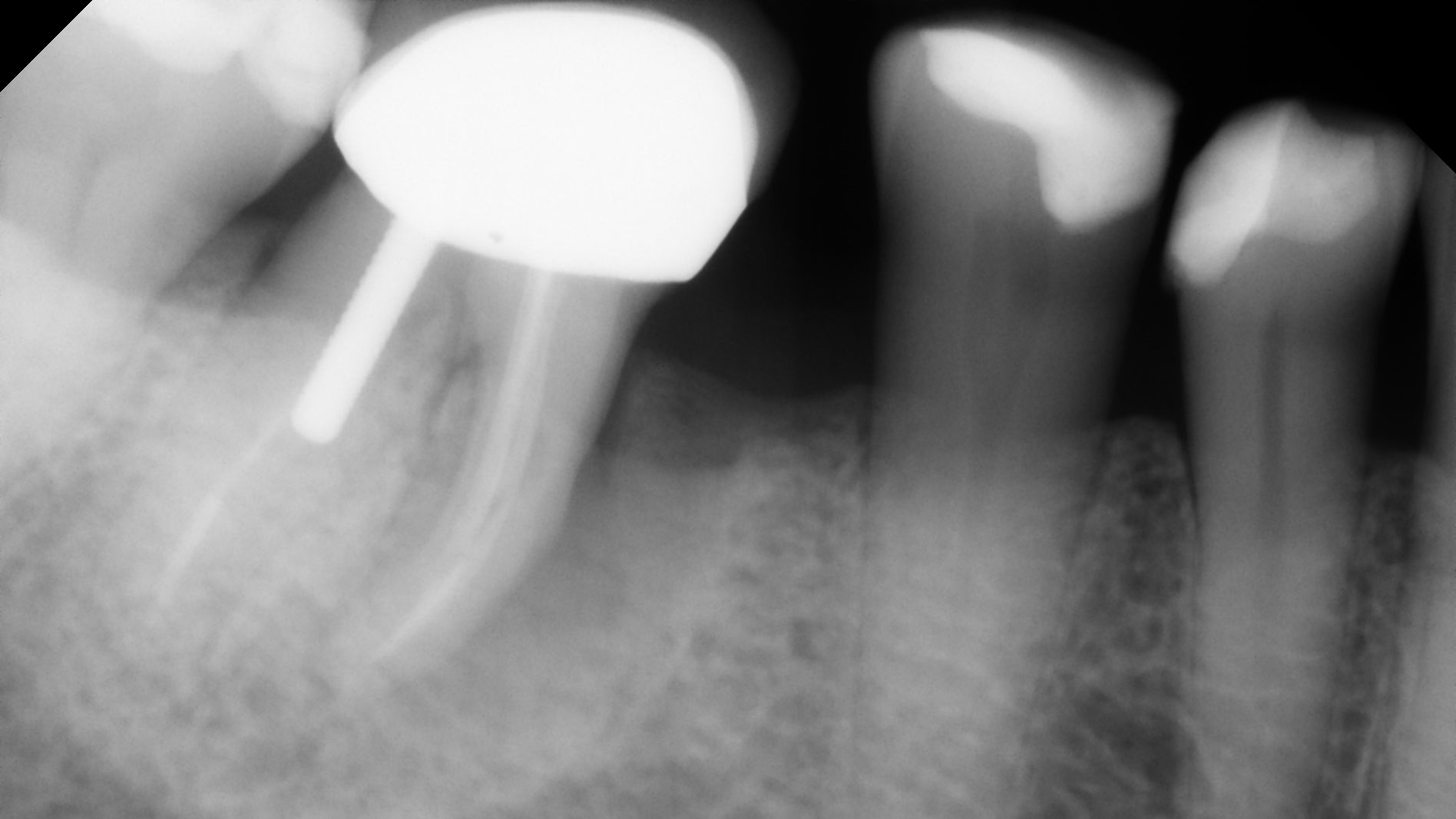
A 68 year old female patient was referred from her general dentist for persistent minor discomfort on #31, suspected endo-perio lesion. Upon the examination, deep probing depth and grade 1 mobility were noted. Radiographic interpretation indicating a large J shaped lesion and possible root fracture. Patient had missing #30 and #32 has been mesially drifted and left a restorative space more than > 13 mm mesio-distally.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system/Non-smoker | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
A successful treatment outcome comes with proper selection of the technique and materials. In order to facilitate an implant supported restoration in the site with > 13mm mesio-distal space, a staged approach was selected, with alveolar ridge preservation (ARP) performed using an atraumatic extraction technique and vallos® mineralized cortico-cancellous bone allograft chosen as the material.
“Ensuring atraumatic extraction techniques, regardless of whether it’s in the anterior or posterior regions, is crucial for preserving the integrity of both hard and soft tissues. Equally important is the selection of biomaterials that not only offer structural support but also possess bone regeneration properties.”
— Dr. Hanae Saito
THE OUTCOME
The planned treatment of replacing a tooth with a dental implant in the regenerated alveolar ridge was achieved. By employing secondary intention healing following ARP and utilizing a lingual paracrestal incision, adequate keratinized tissue was preserved on the buccal side of the implant-supported restoration.
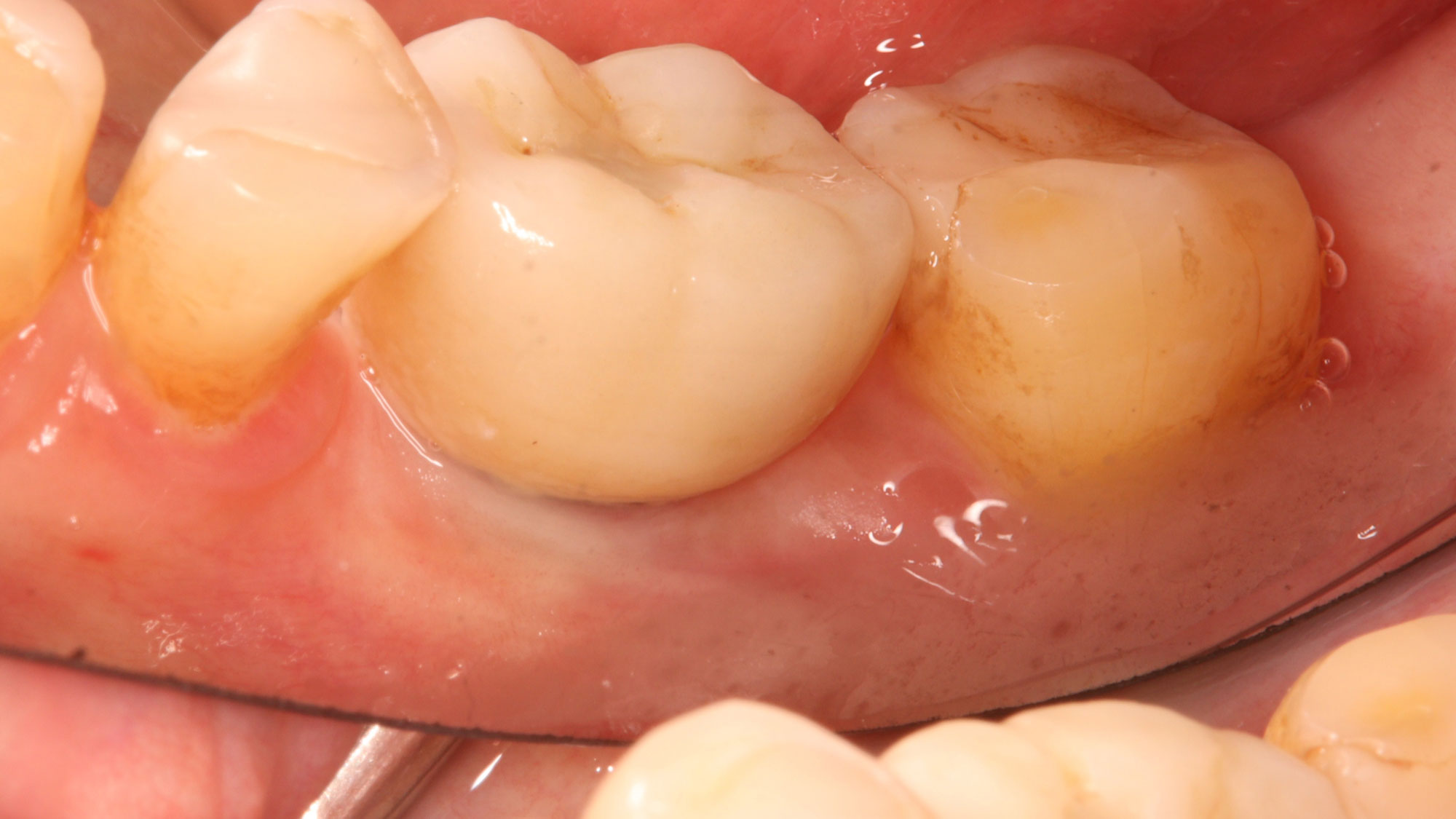

Hanae Saito, DDS, MS, CCRC
Hanae Saito, DDS, MS, CCRC serves as a clinical associate professor and oversees the Dual Perio-Pros program and predoctoral periodontal education within the Division of Periodontics, at the University of Maryland School of Dentistry. She is a Diplomate of the American Board of Periodontology. Dr. Saito obtained a Master of Science in Clinical Research and a certificate in Periodontics from New York University College of Dentistry. Additionally, she operates a faculty practice focused on periodontology and implant dentistry.

Andrew Tong, DDS
Andrew Tong, DDS earned his Bachelor of Science degree from the University of Maryland at College Park in 2015 before completing his Doctor of Dental Surgery (D.D.S) degree at the University of Maryland School of Dentistry in 2019. Following this, he undertook a General Practice Residency at the Newark Beth Israel Medical Center in New Jersey from 2019 to 2020. Dr Tong now practices general dentistry at Tong Dental Care in Gaithersburg, MD. Concurrently, he is pursuing a Master’s degree in Periodontics at the University of Maryland School of Dentistry.
Sorry, you do not have permission to view this content.
Sorry, you do not have permission to view this content.
Sorry, you do not have permission to view this content.

BIOBRIEF
Immediate Mandibular Molar Transition
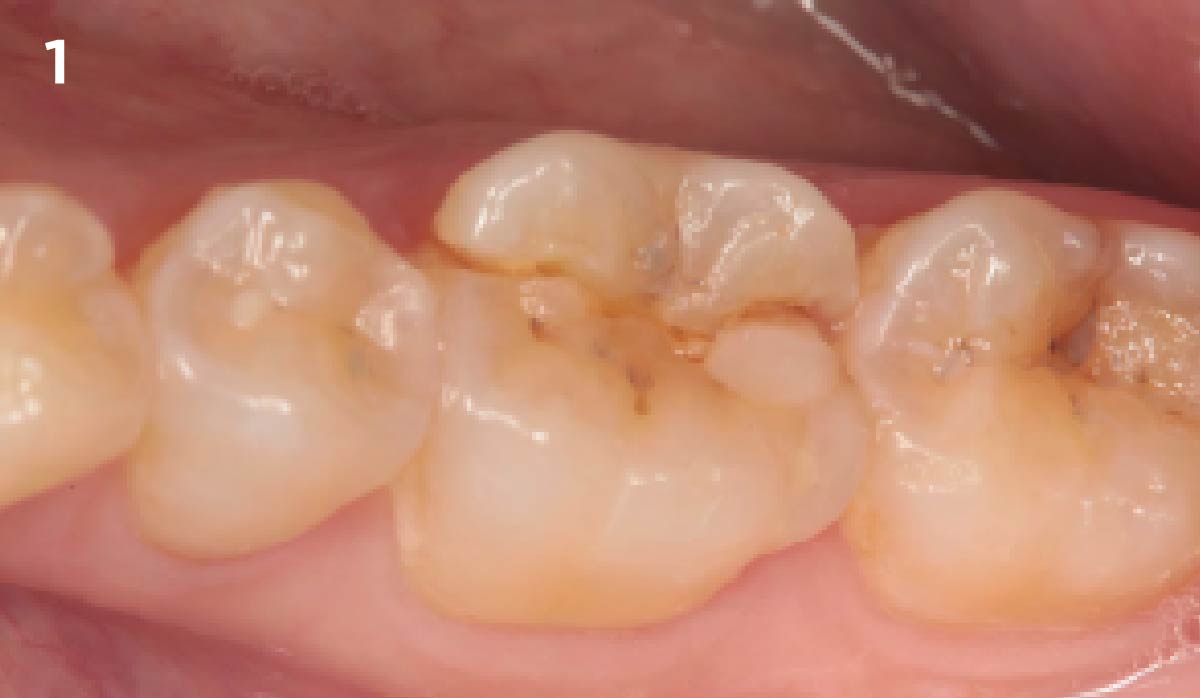

THE SITUATION
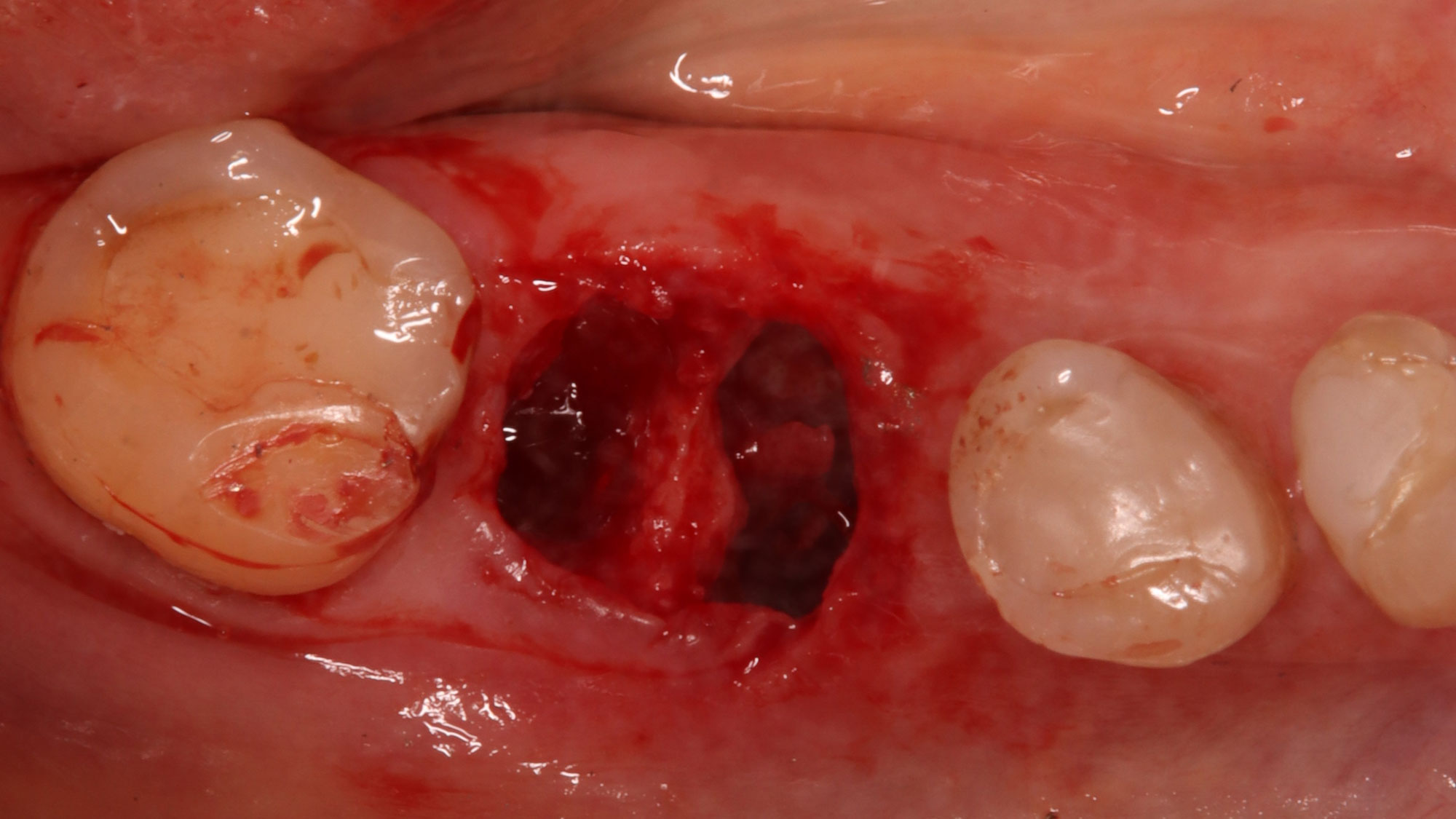
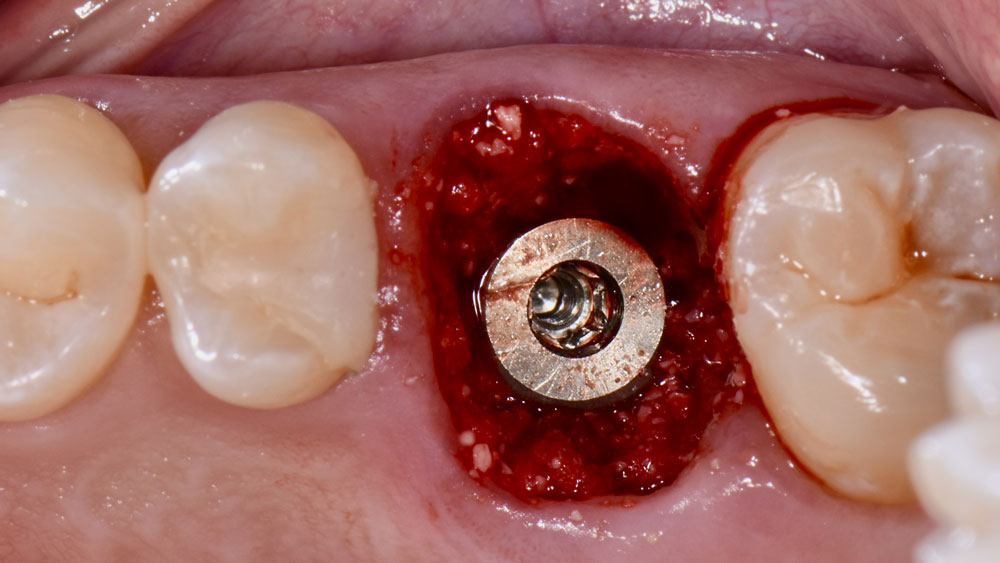
The case here is typical enough, a failing mandibular molar with a vertical sub-osseous fracture. Traditionally, the replacement process can take three or more surgical exposures (extraction and regeneration), (implant placement), (second stage exposure) and more than a year of therapy.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system Non-smoker | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Height of smile line | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Shape of dental crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth site | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
THE APPROACH
Immediate molar replacement requires atraumatic removal of the fractured tooth, careful socket debridement and development of a channel for an ideally positioned implant. The implant then needs to be placed down in the bone channel with the implant platform positioned just below the socket walls. It needs to be stable. Channel deficiency augmentation is achieved with Geistlich Bio-Oss Collagen® which is covered with a collagen matrix, Geistlich Mucograft® with the edges tucked under the gingival margins and sealed over with tissue glue.
“The patient desires an implant placement for a fractured mandibular molar, as fast as possible.”
– Dr. Peter Hunt
THE OUTCOME
This single stage replacement protocol has proven to be simple, safe and highly effective providing the socket is fully degranulated and the implant is stable and not loaded in the early healing stages. It works well when a gingiva former is immediately placed into the implant instead of a cover screw, Geistlich Bio-Oss Collagen® is packed around the implant to fill the residual socket, then covered with a Geistlich Mucograft® and sutured. There is no need for flap advancement to cover over the socket.
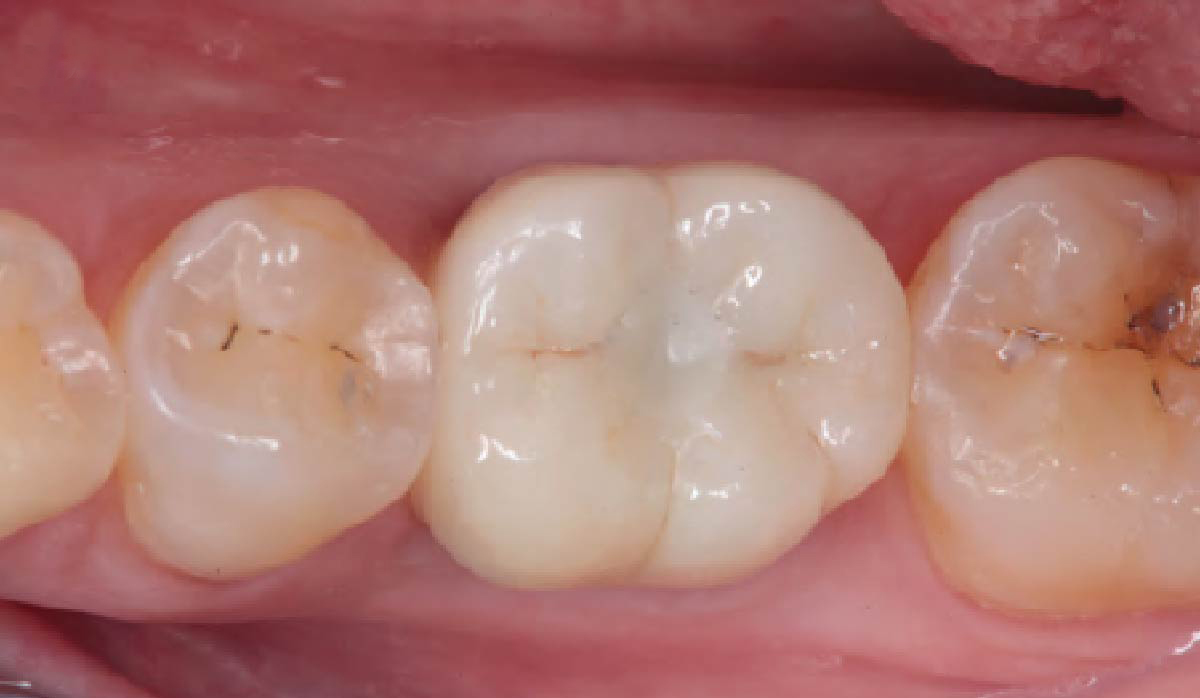

Dr. Peter Hunt
After graduate training on an Annenberg Fellowship at the University of Pennsylvania, dr. hunt helped start up the University of the Western Cape dental School in Cape Town, South Africa. he returned to the University of Pennsylvania where in time he became Clinical Professor of Periodontics. later he helped start up Nova Southeastern‘s dental School where he was Professor of Restorative dentistry, Post Graduate director and director of Implantology. he has had a private practice in Philadelphia focusing on implant and rehabilitation dentistry since 1981.

WEBINAR

WEBINAR

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE

CLINICAL CASE