BIOBRIEF
Horizontal Ridge Augmentation with a Layered Allograft-Xenograft Approach


THE SITUATION
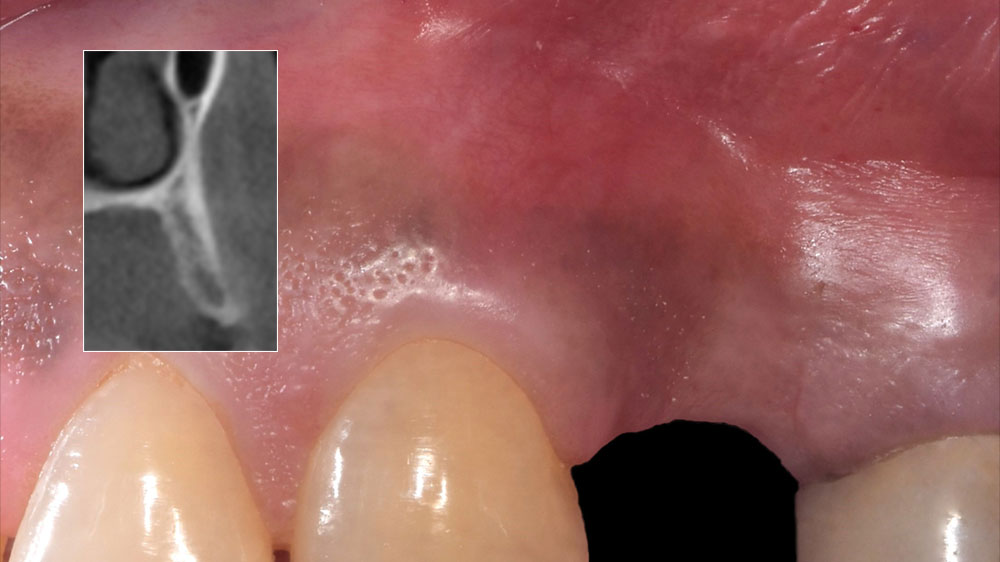
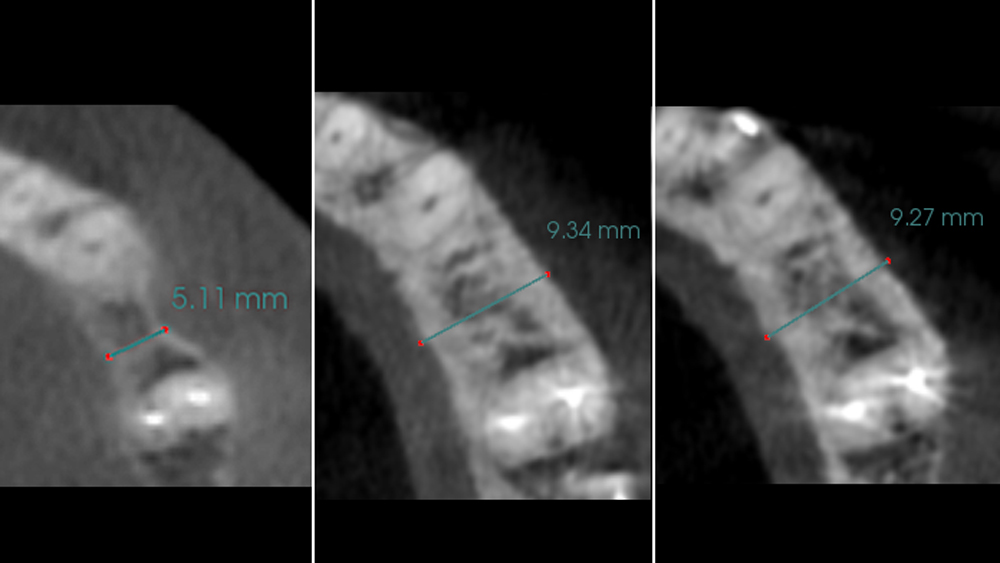
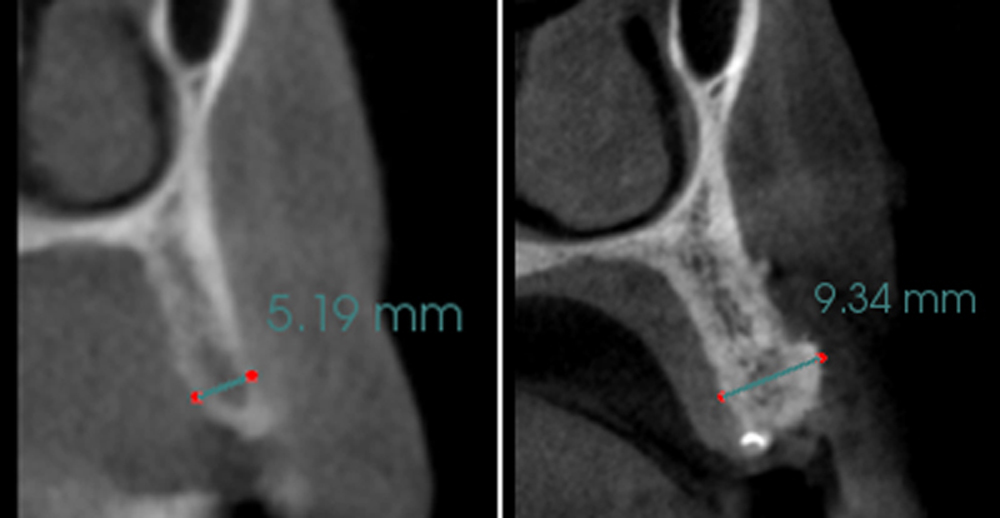
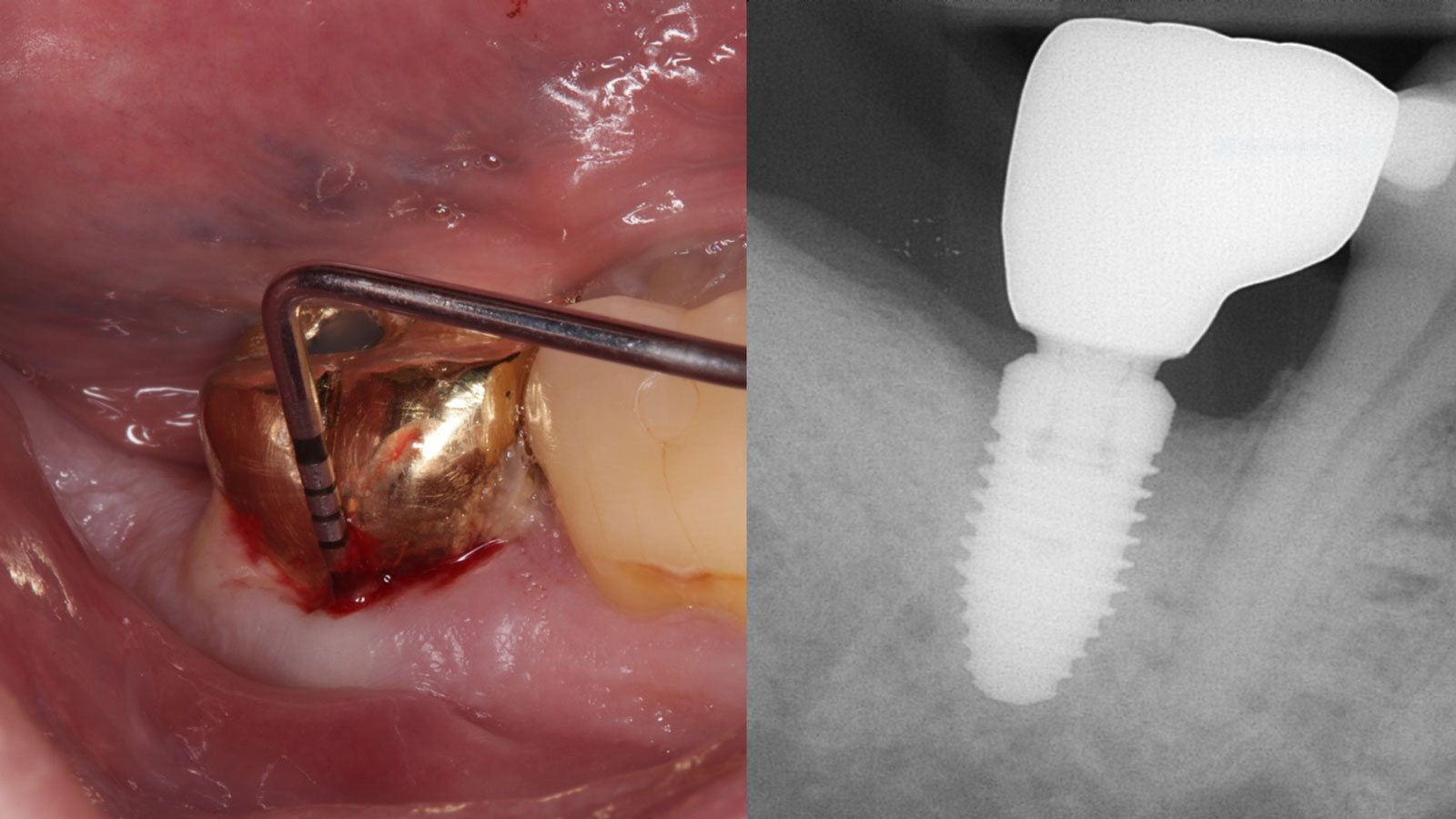
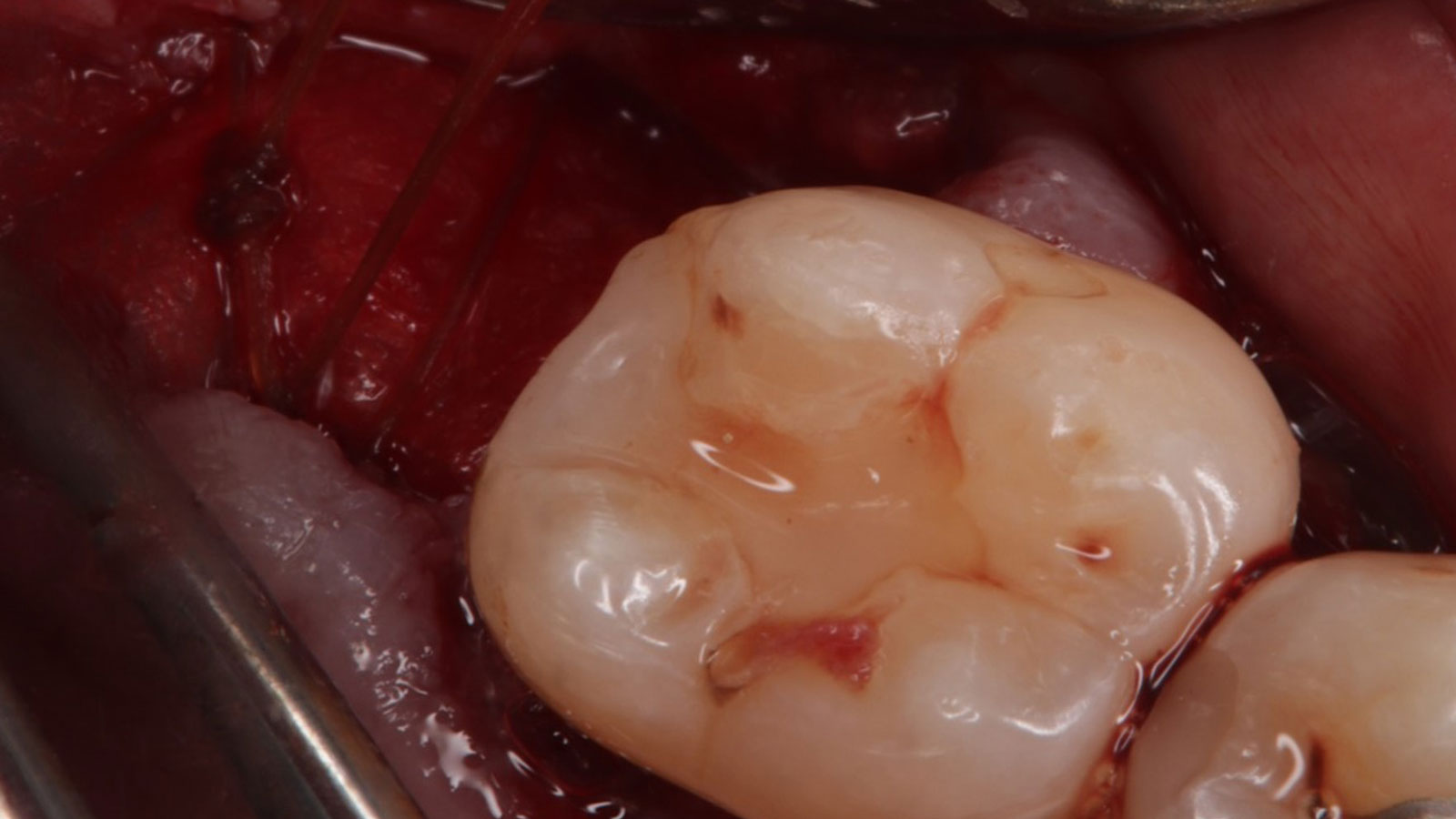
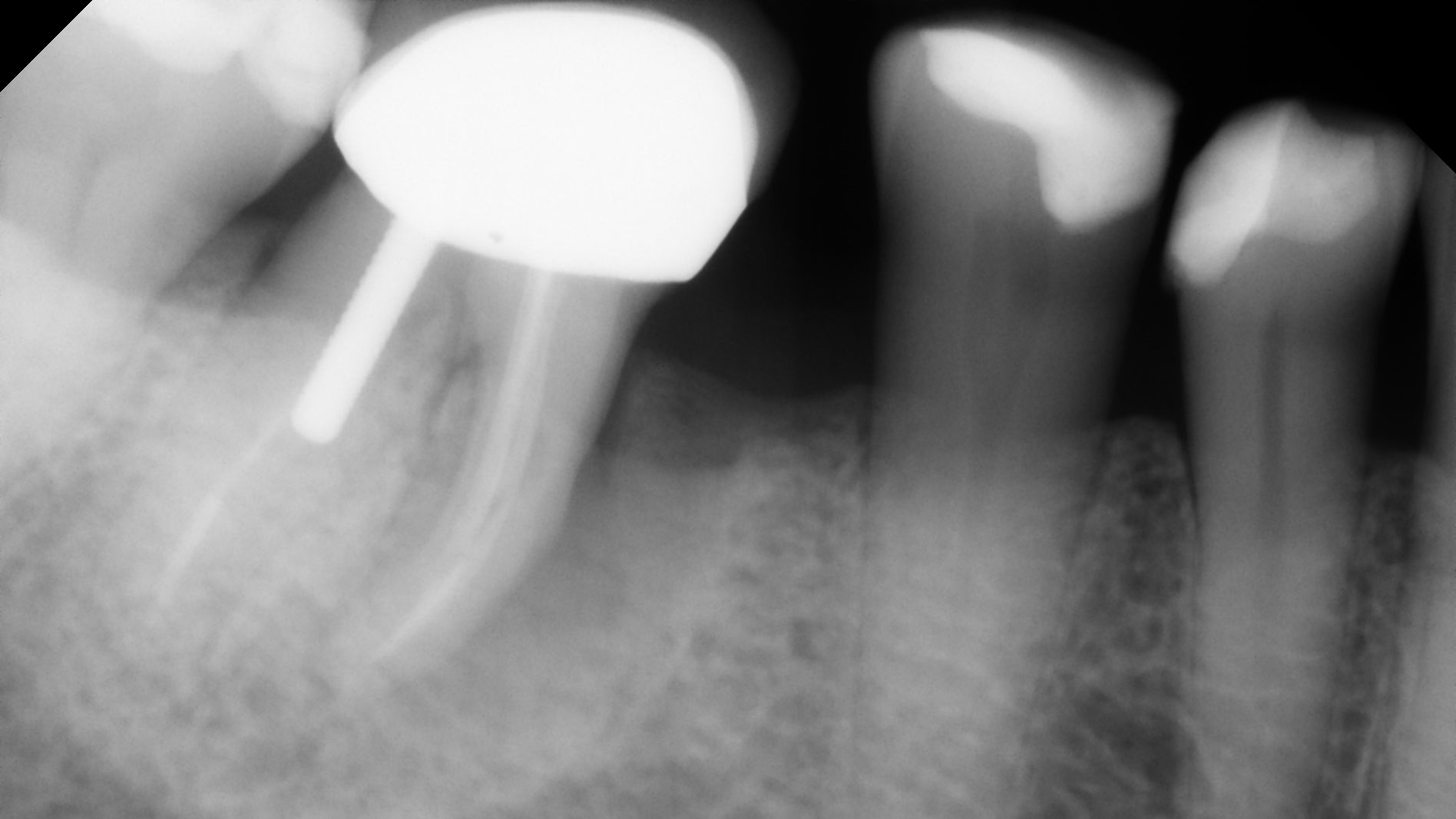
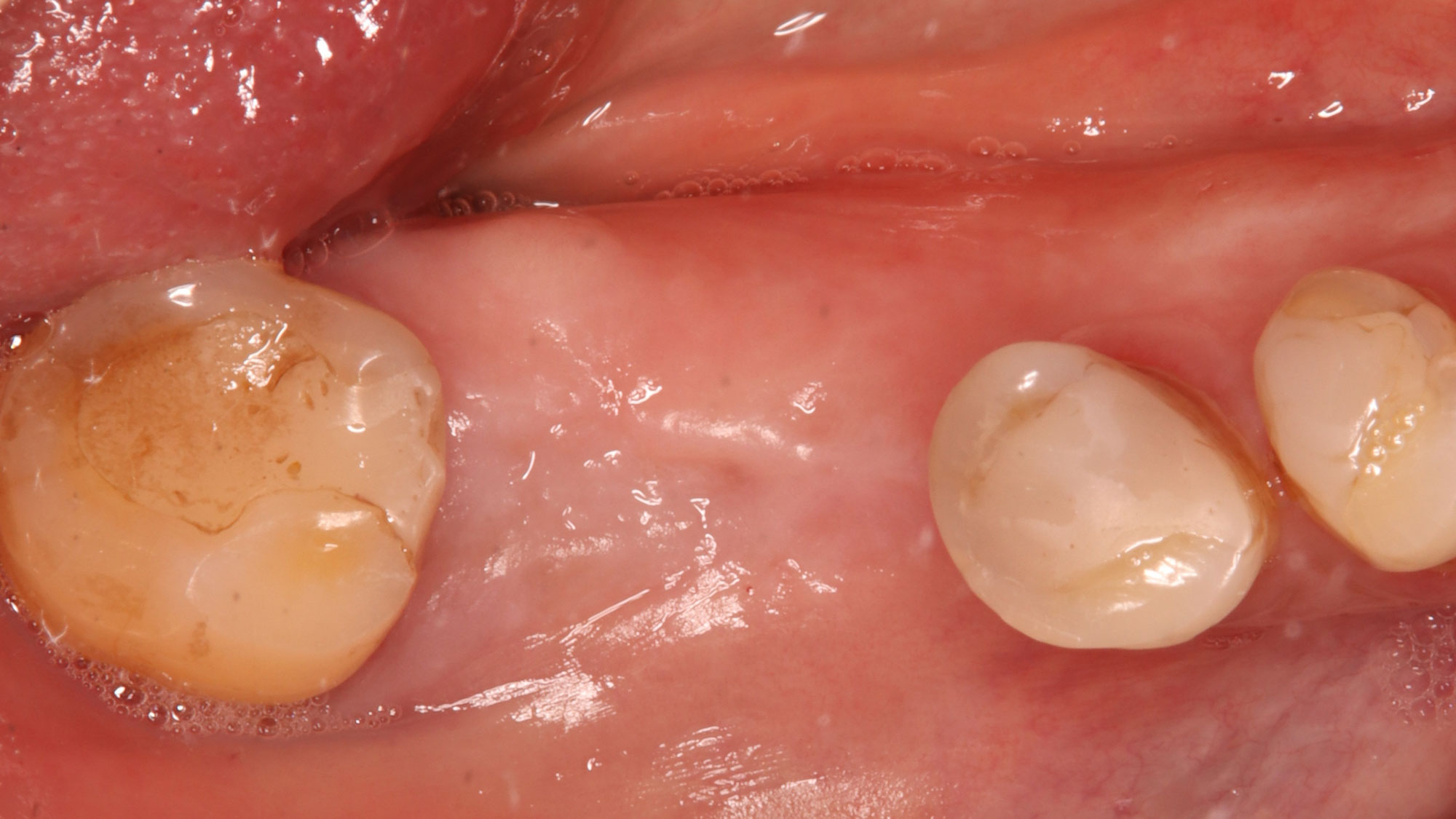
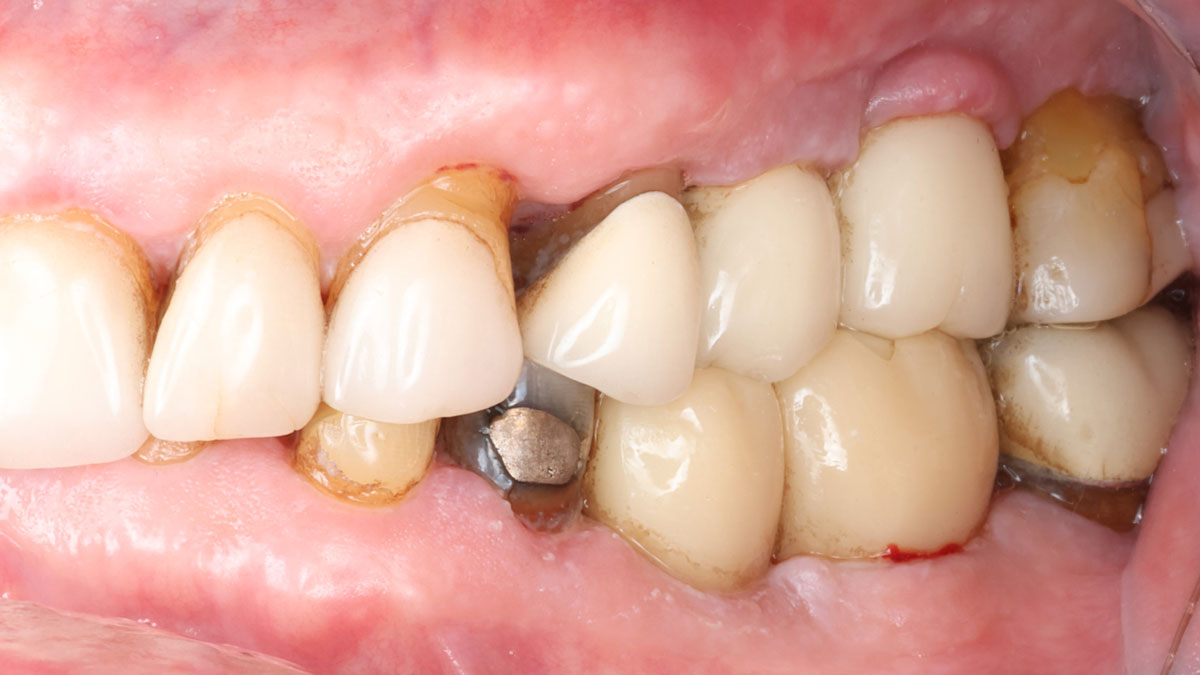
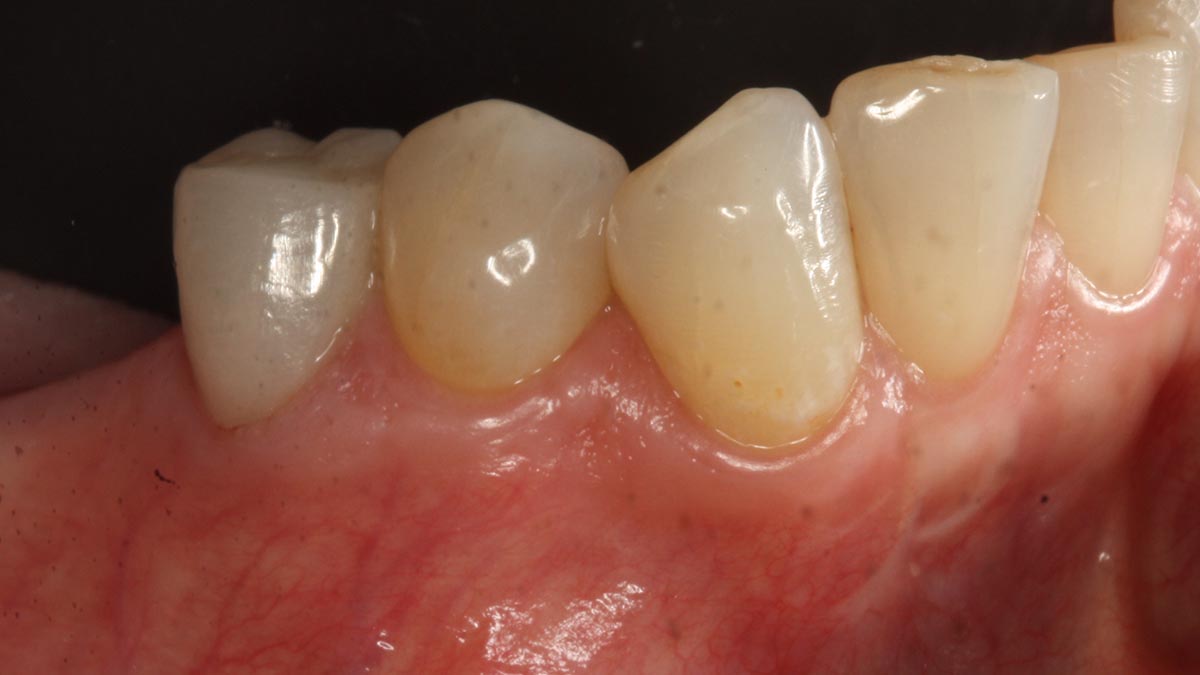
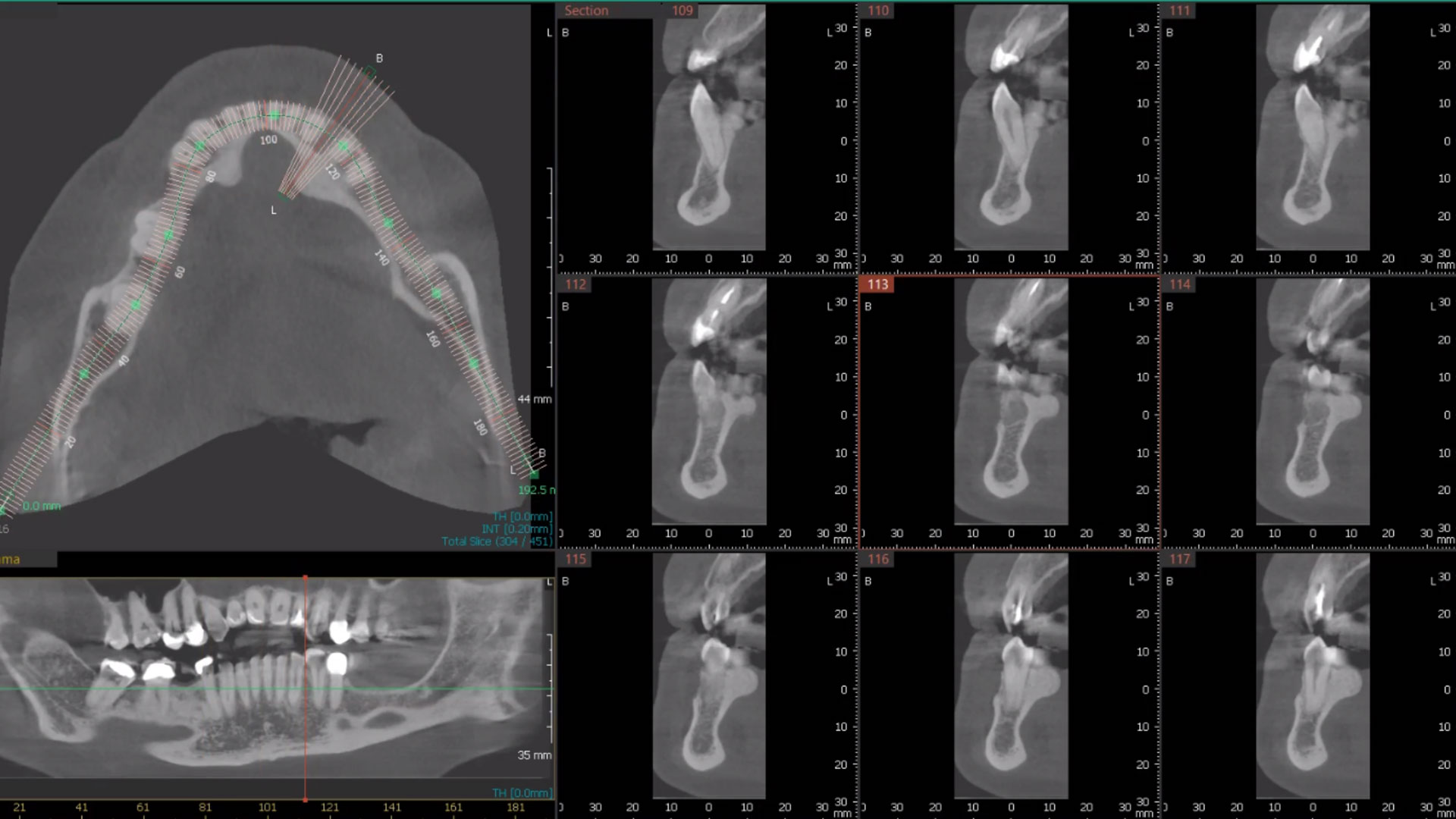
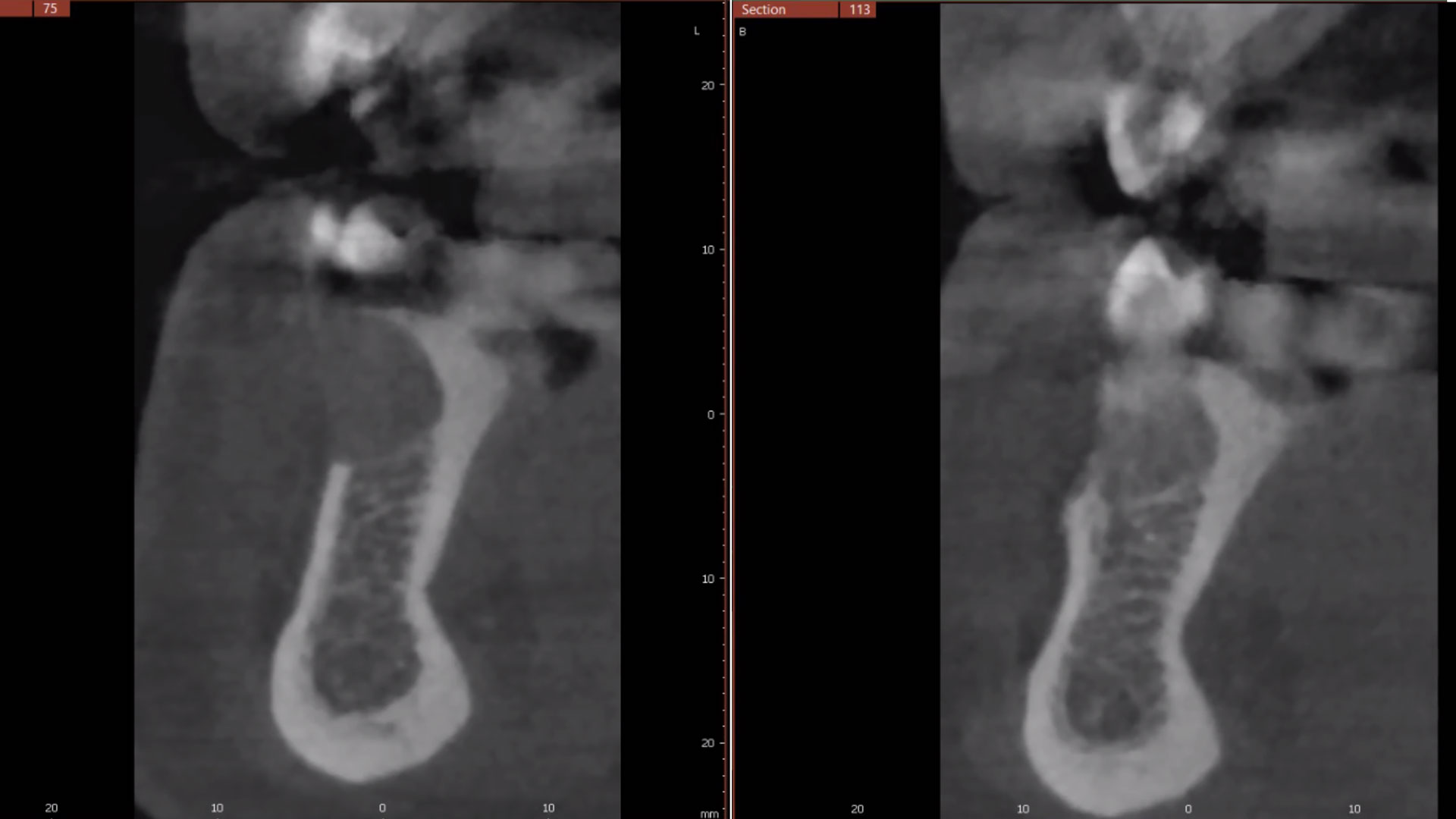
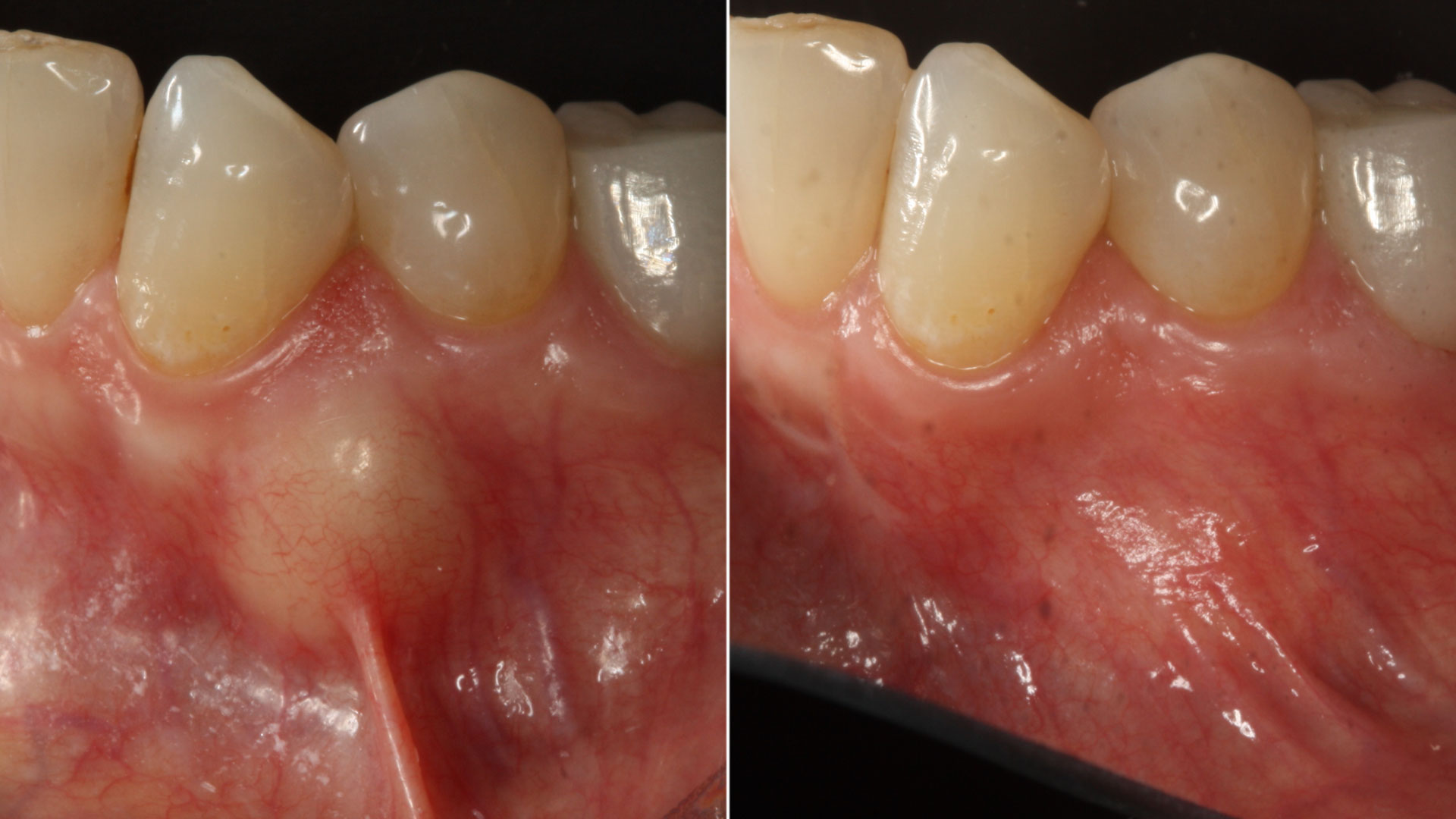
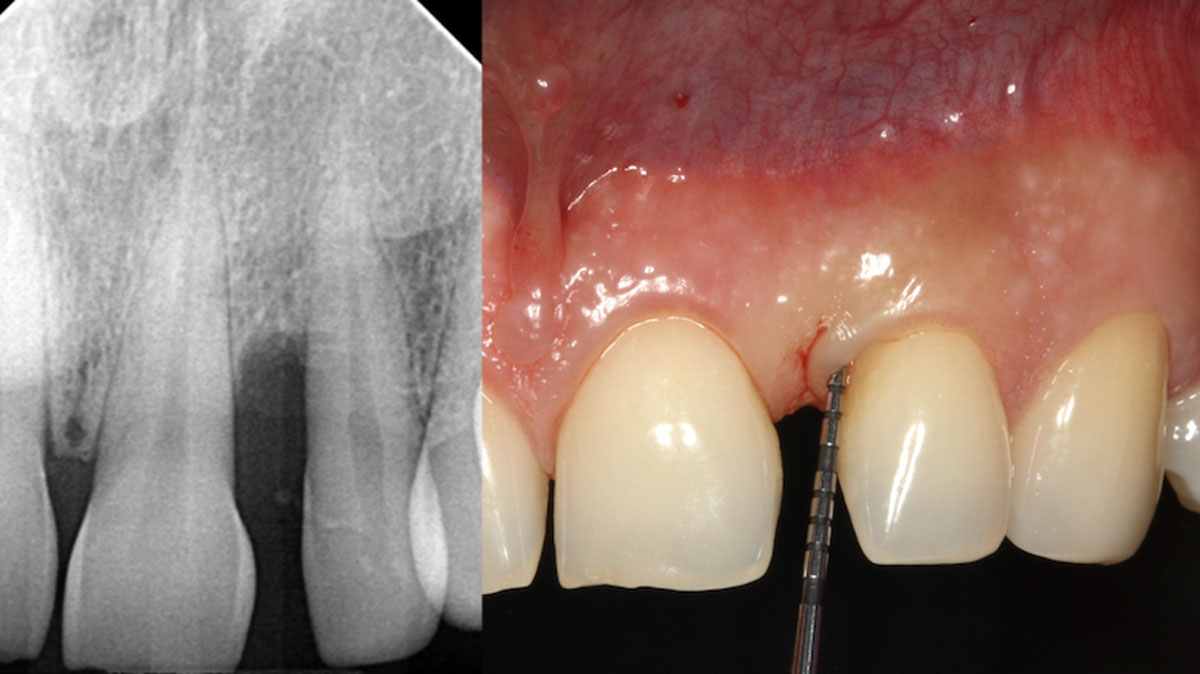
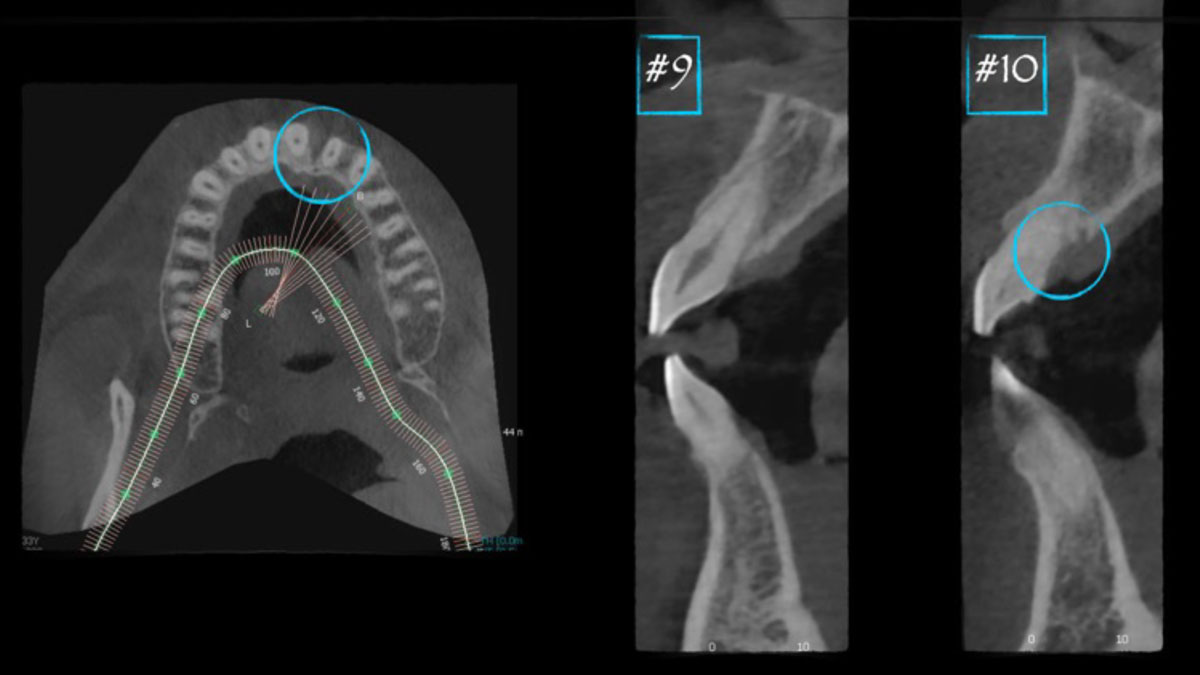
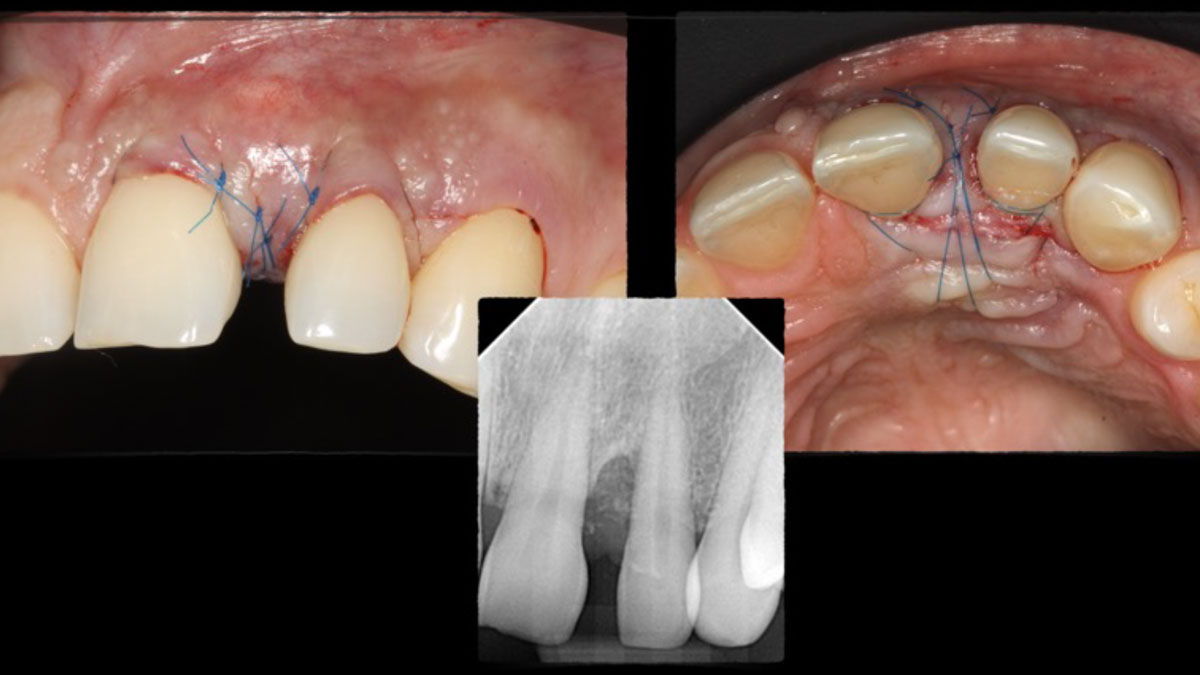
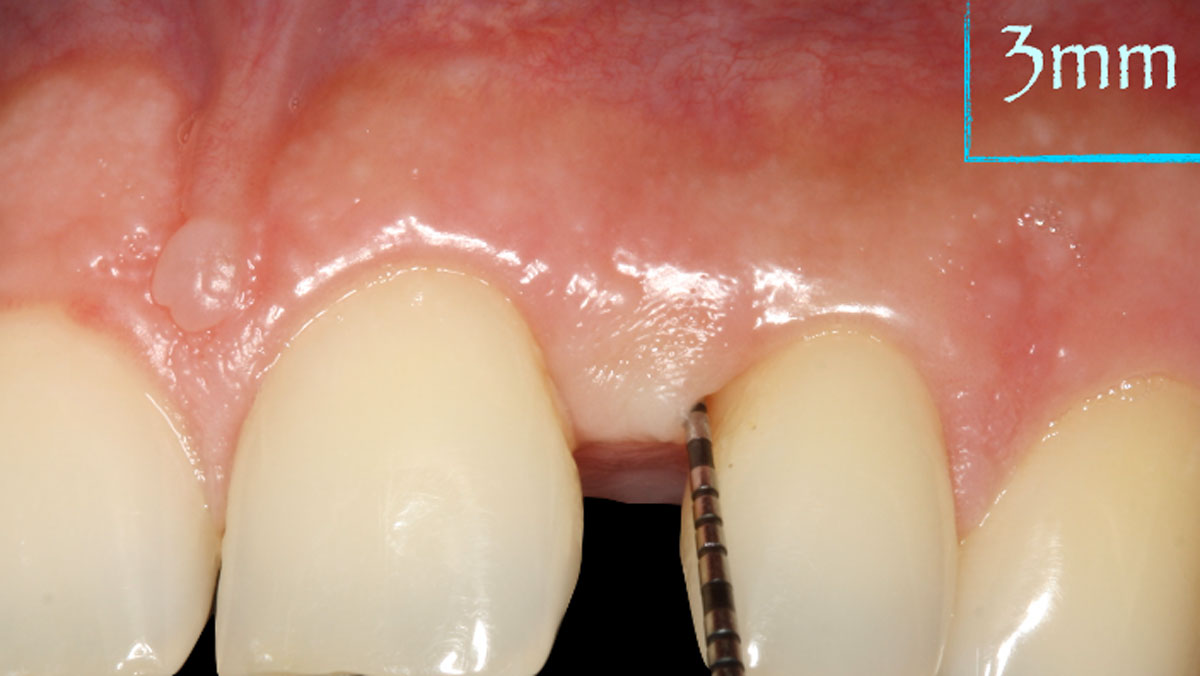
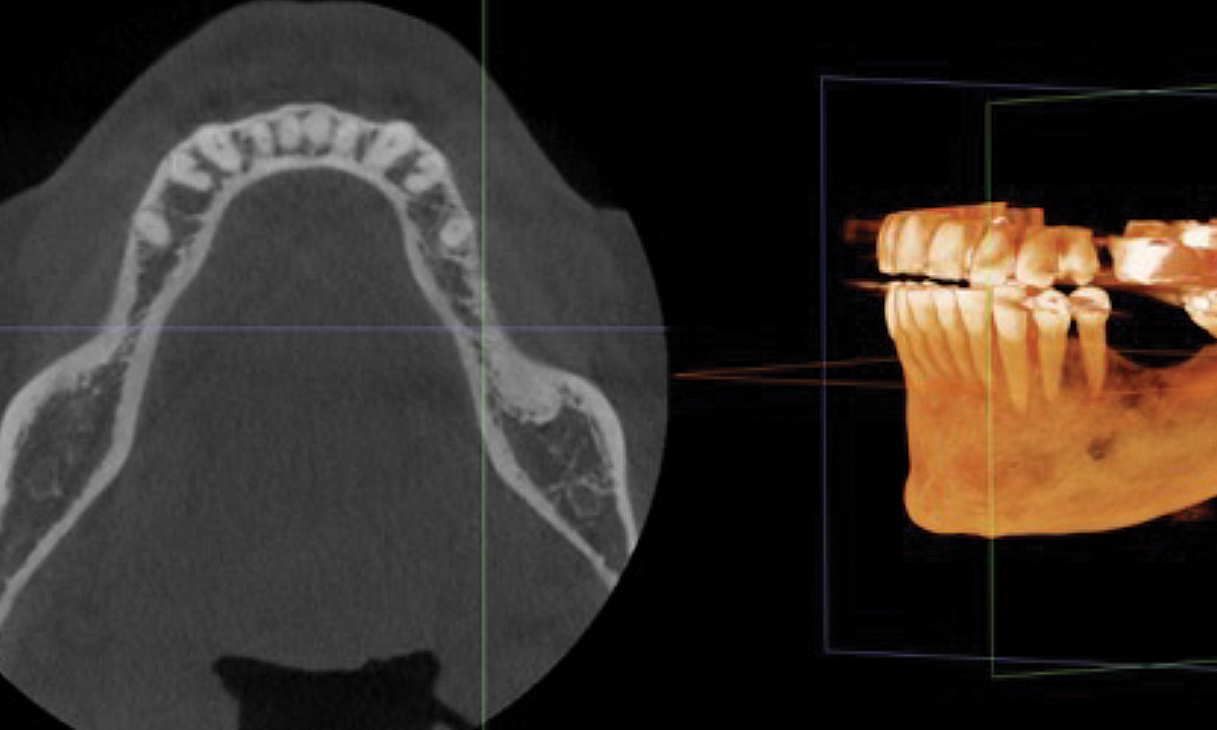
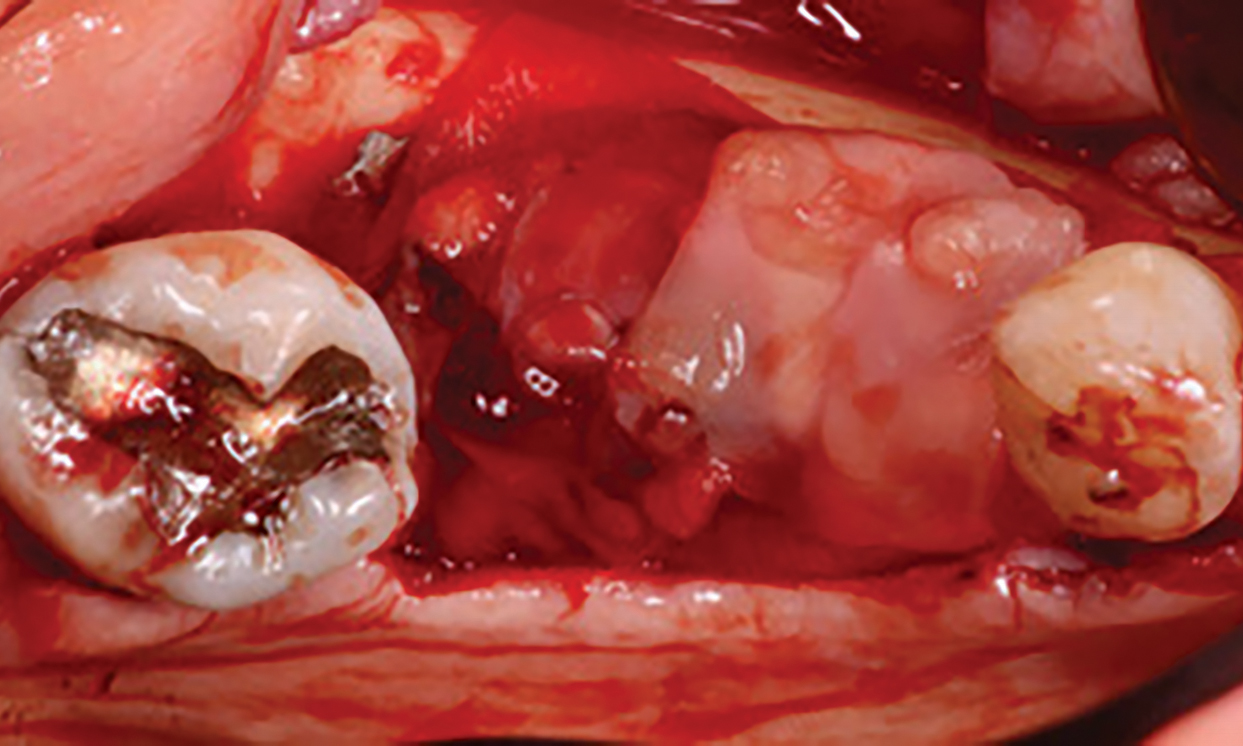
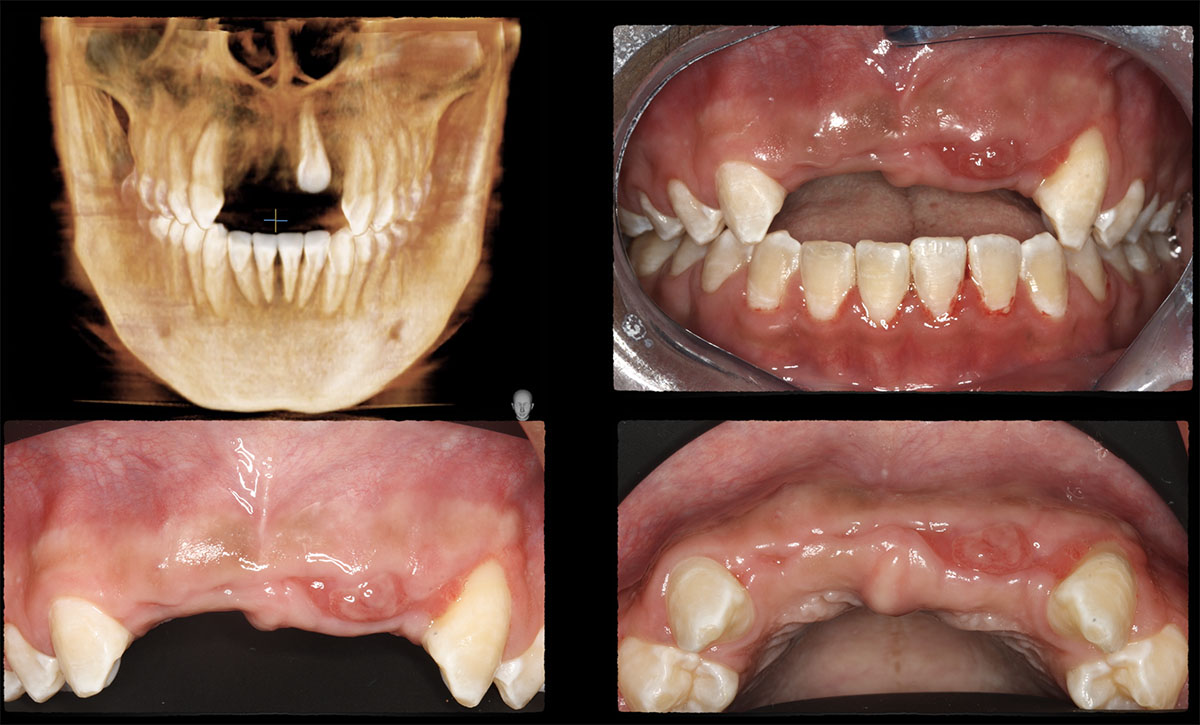
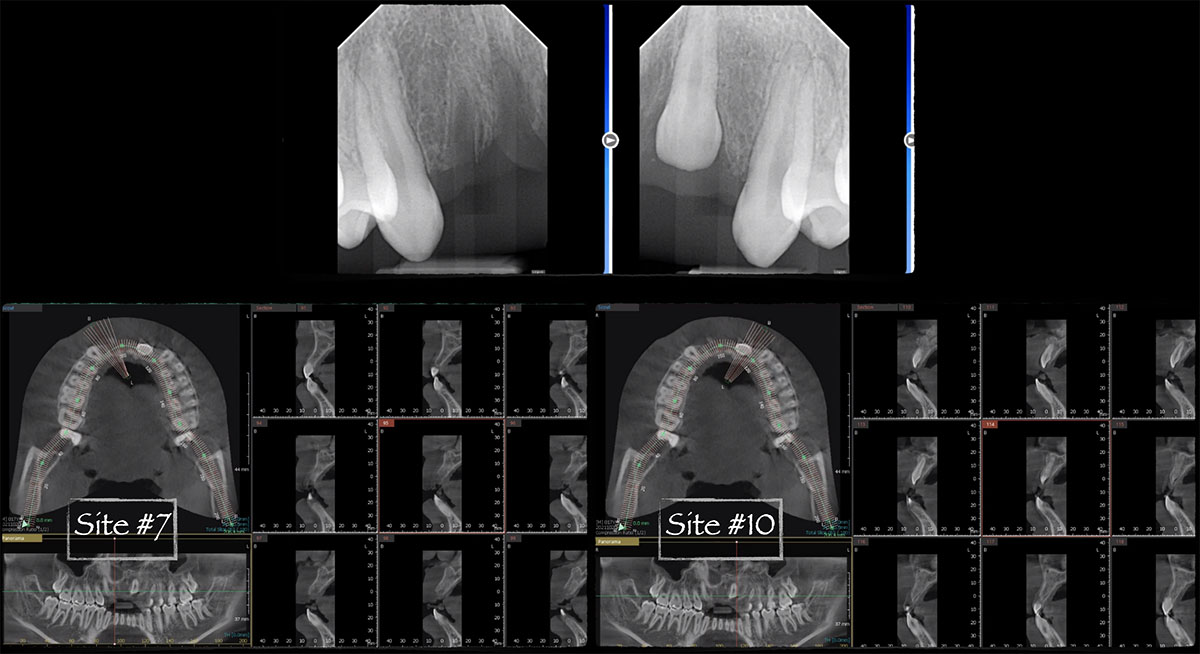
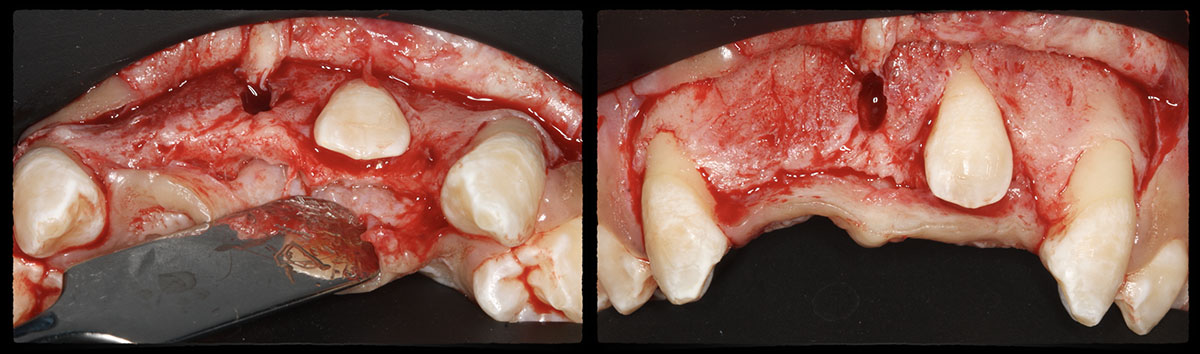
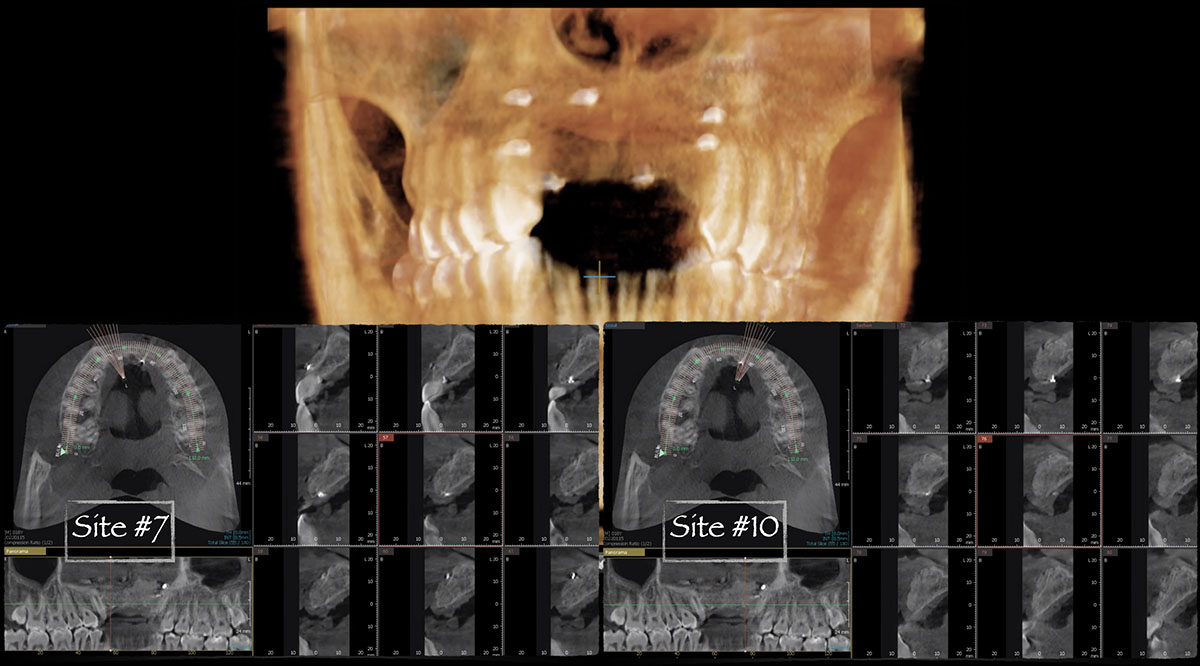
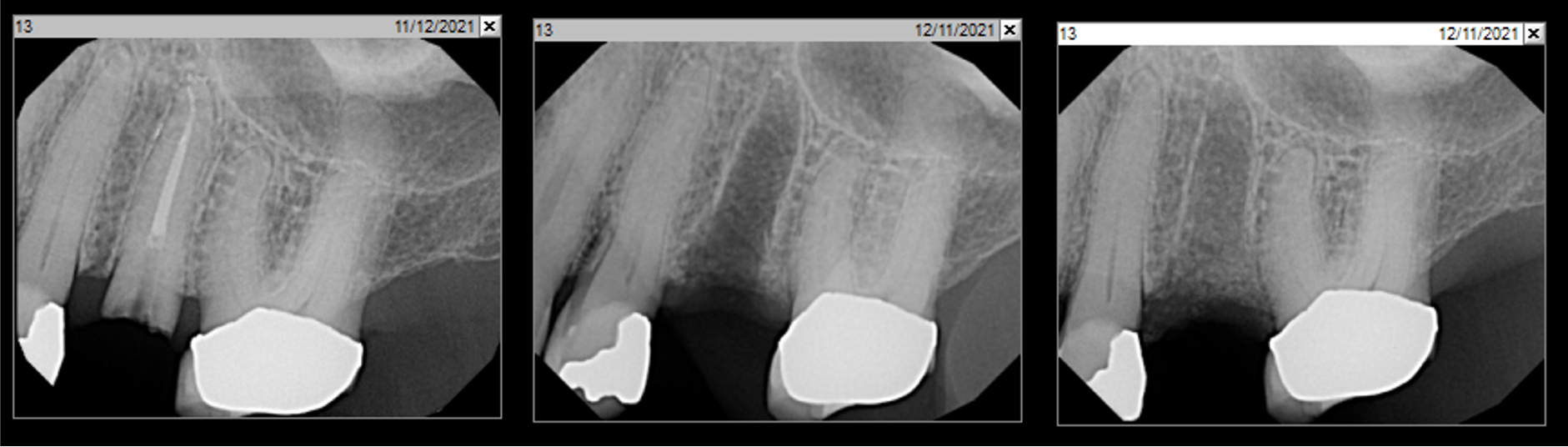
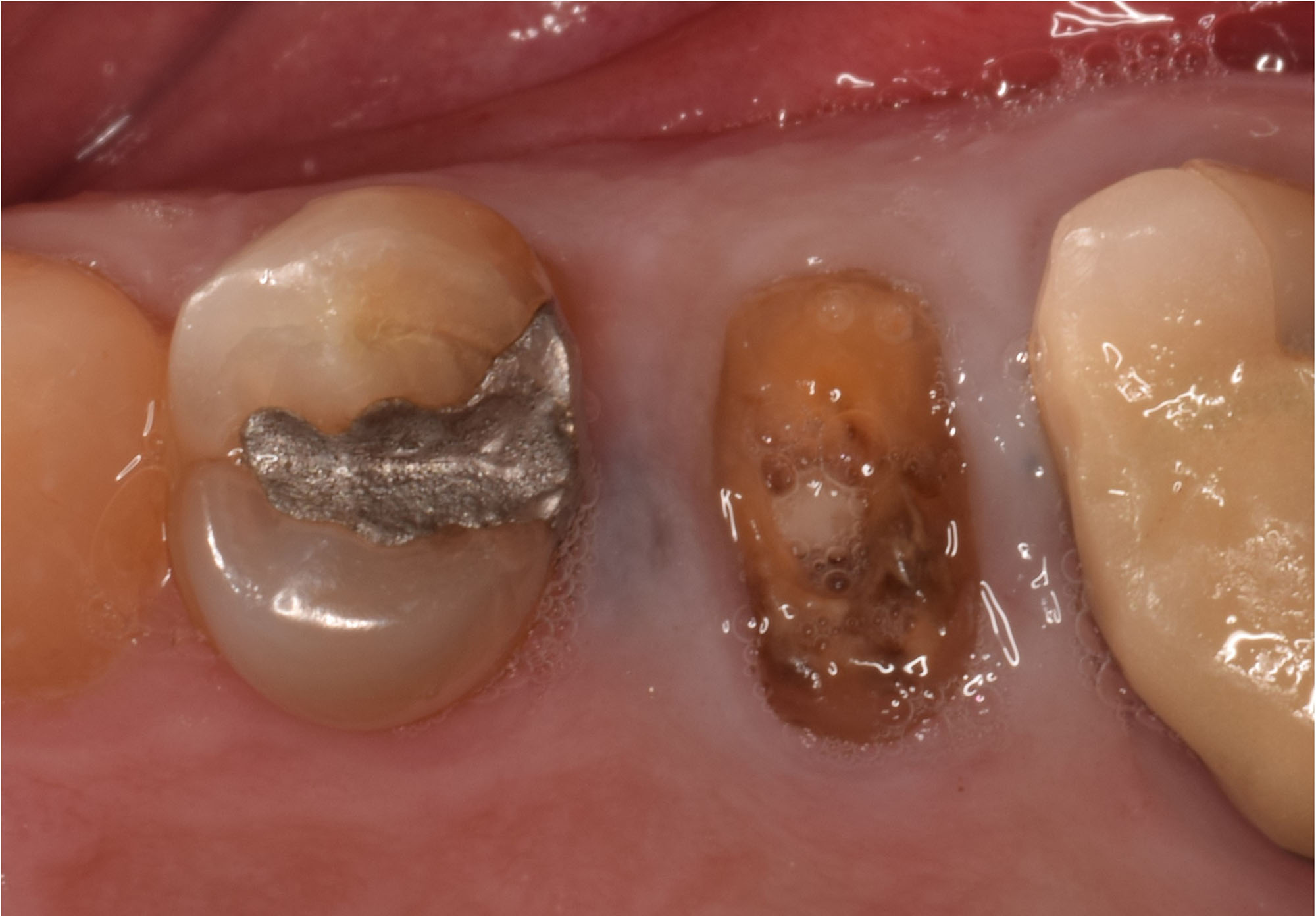
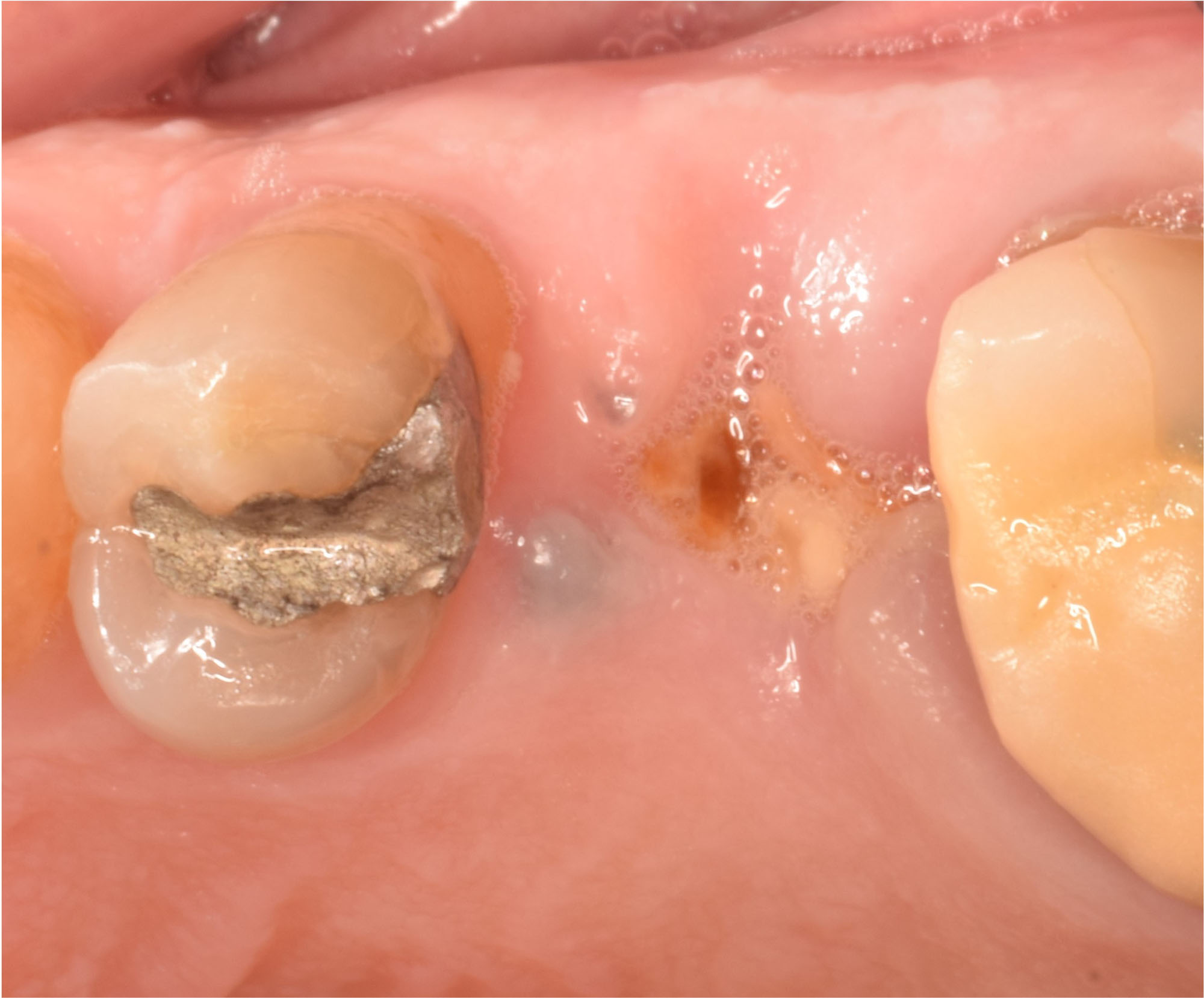
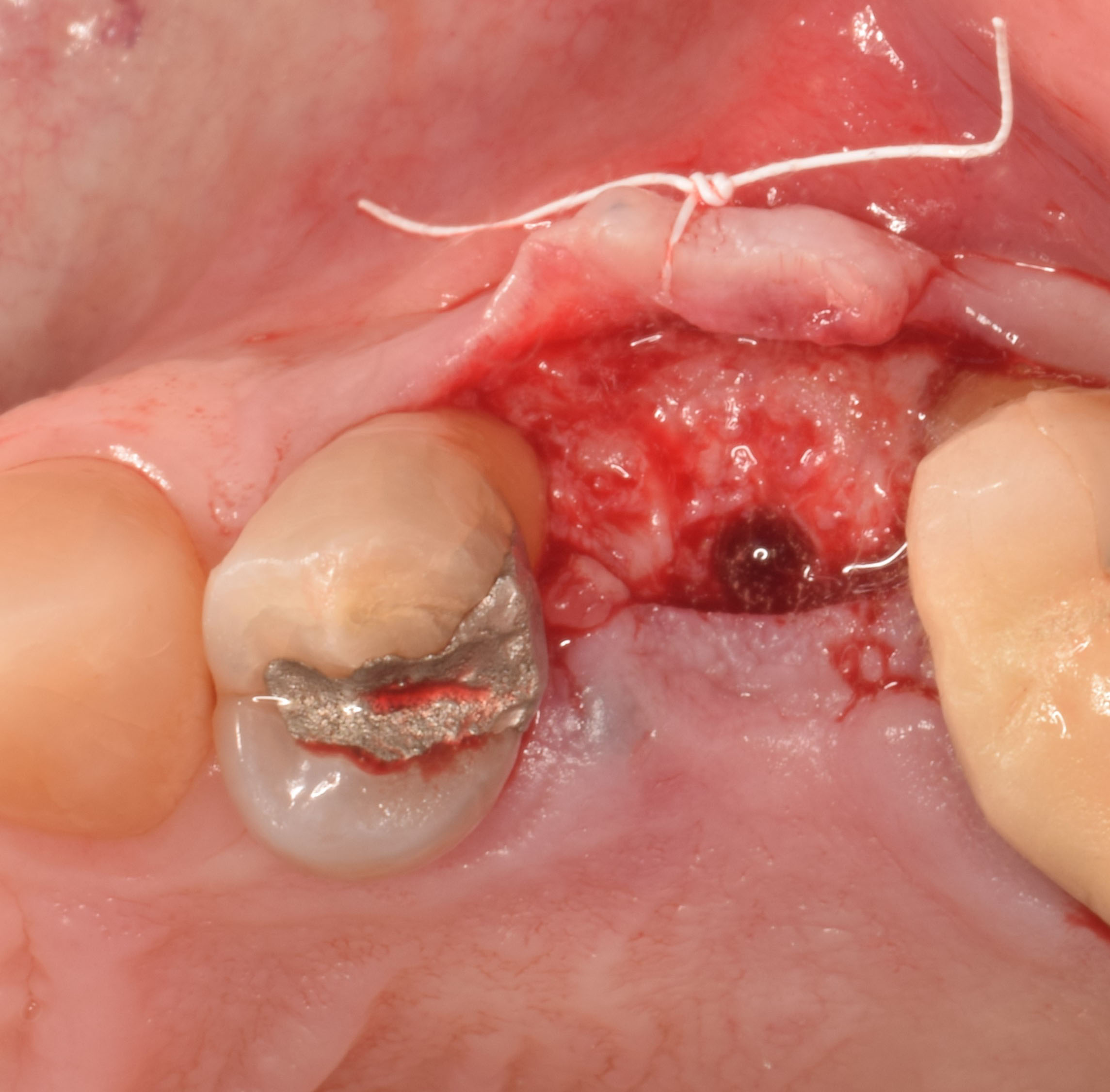
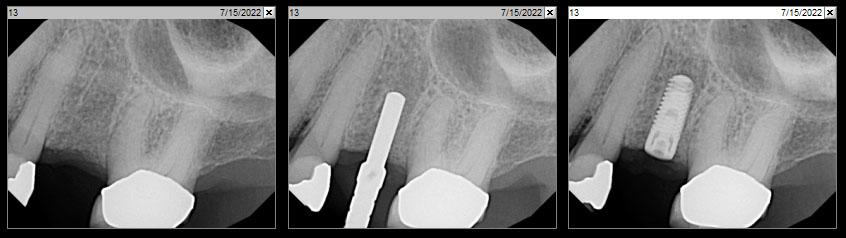
The patient presented to the clinic for a dental implant in the tooth #12 location. Clinical evaluation revealed a ridge deficiency. A Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) scan was taken, confirming insufficient ridge width for implant placement. As a result, the site was treatment planned for horizontal ridge augmentation.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Restorative status of adjacent tooth | Intact | Restored | |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
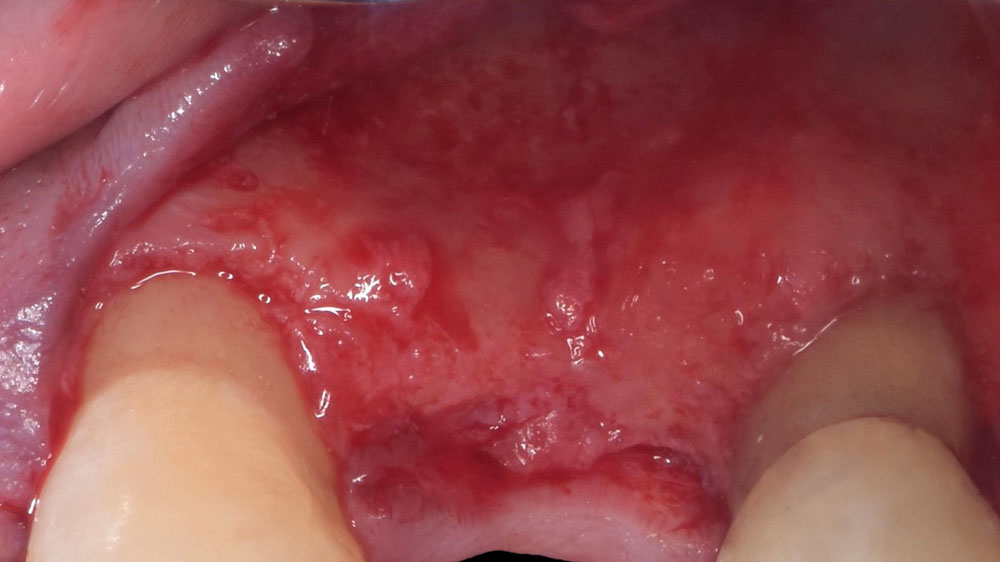
THE APPROACH
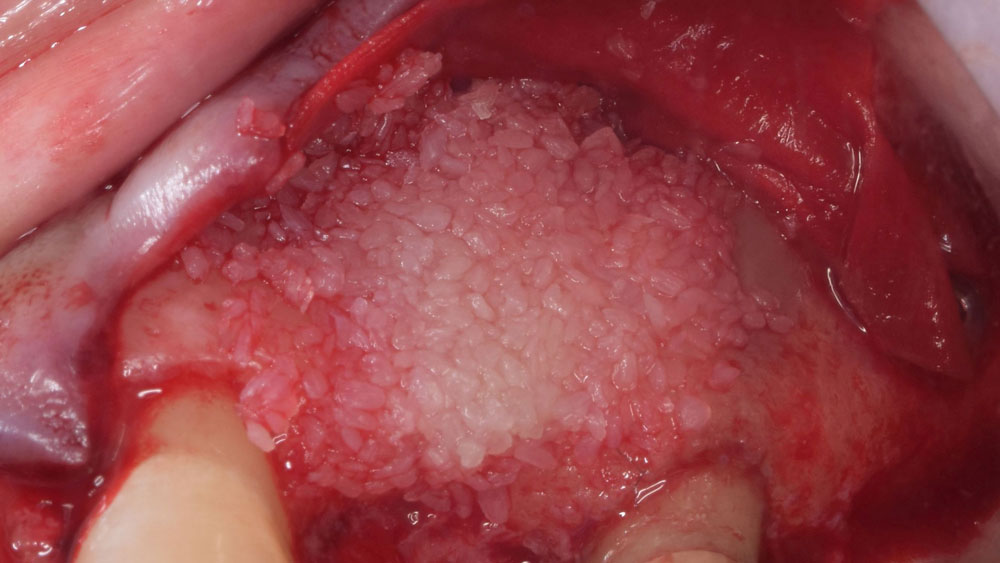
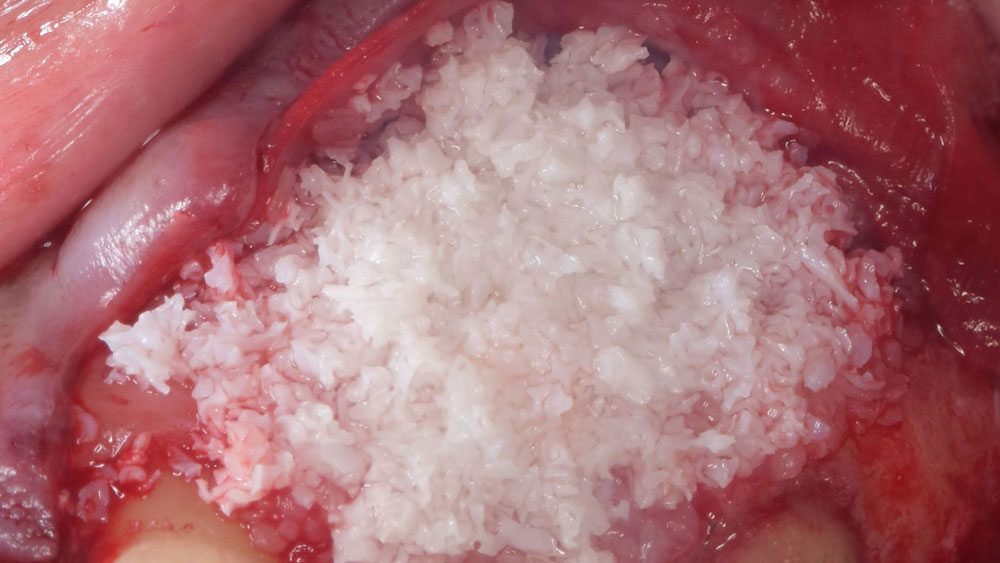
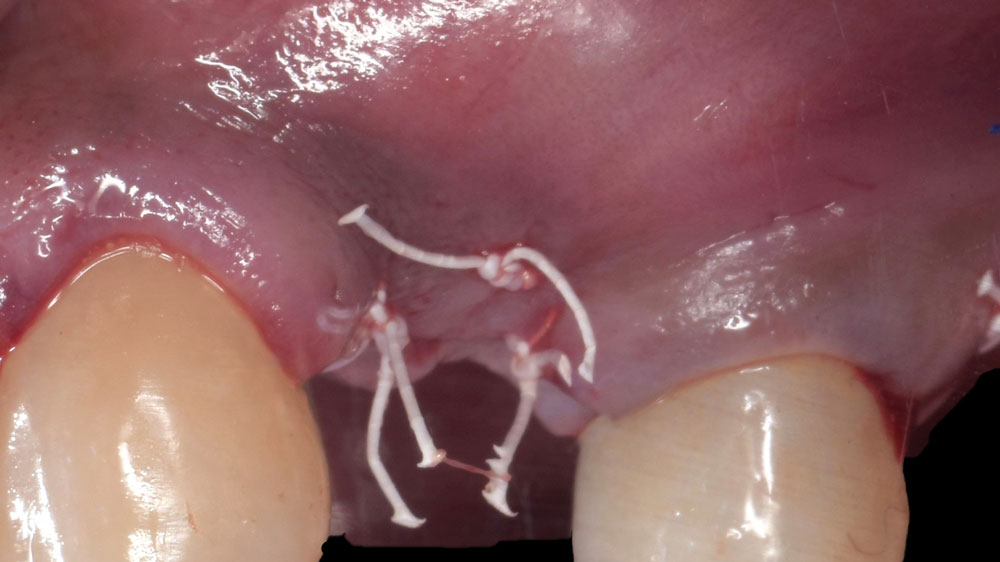
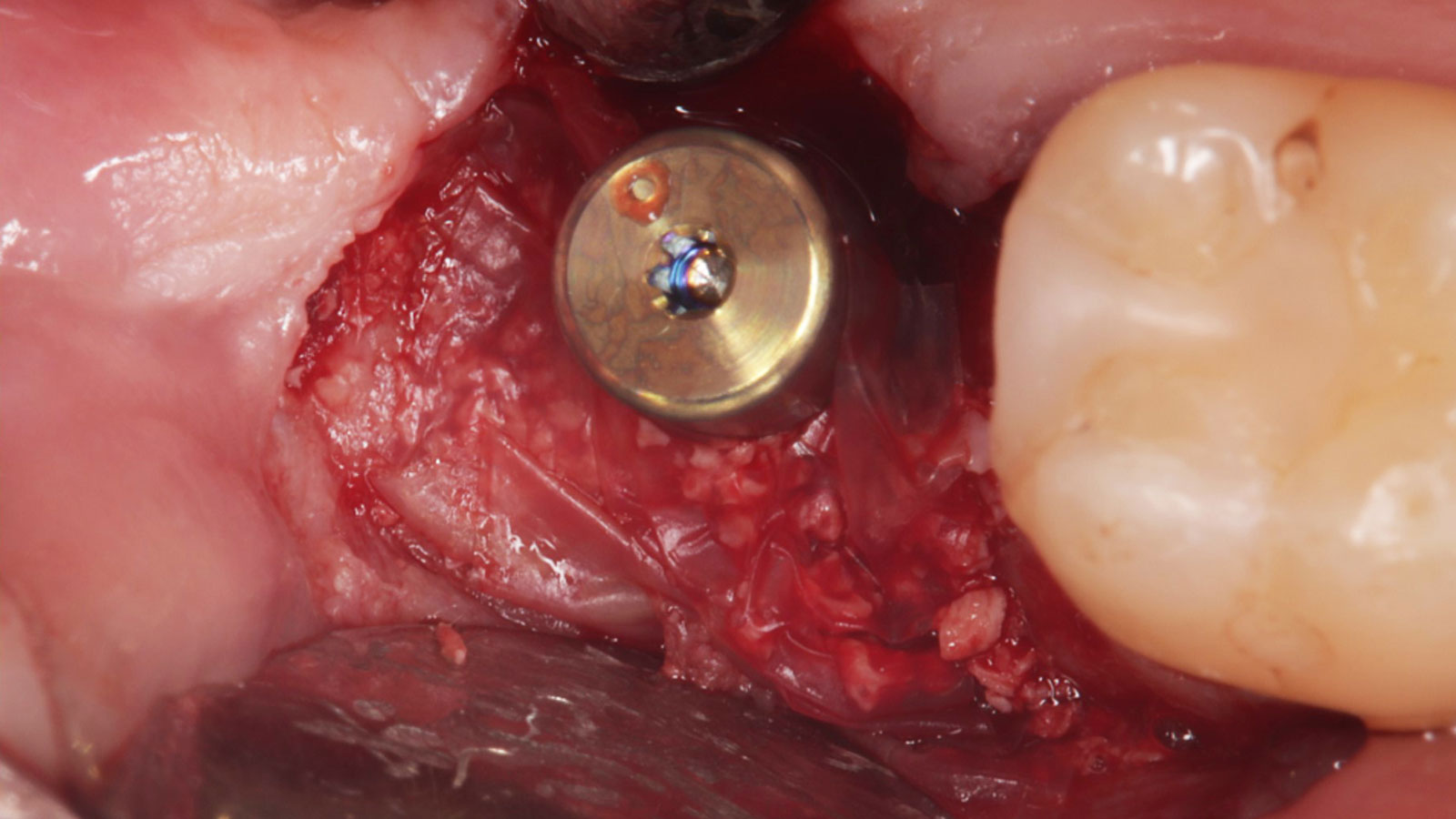
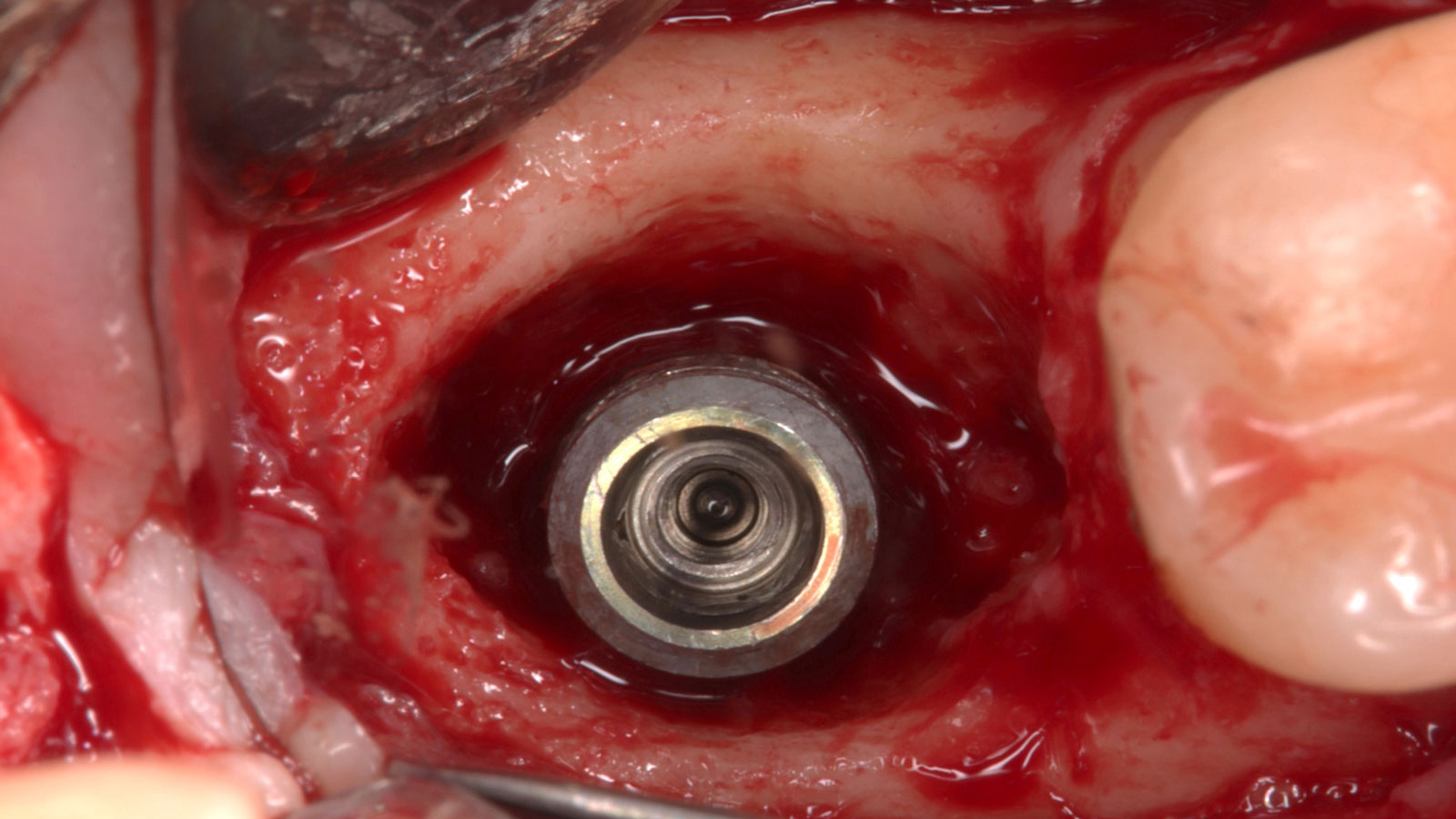
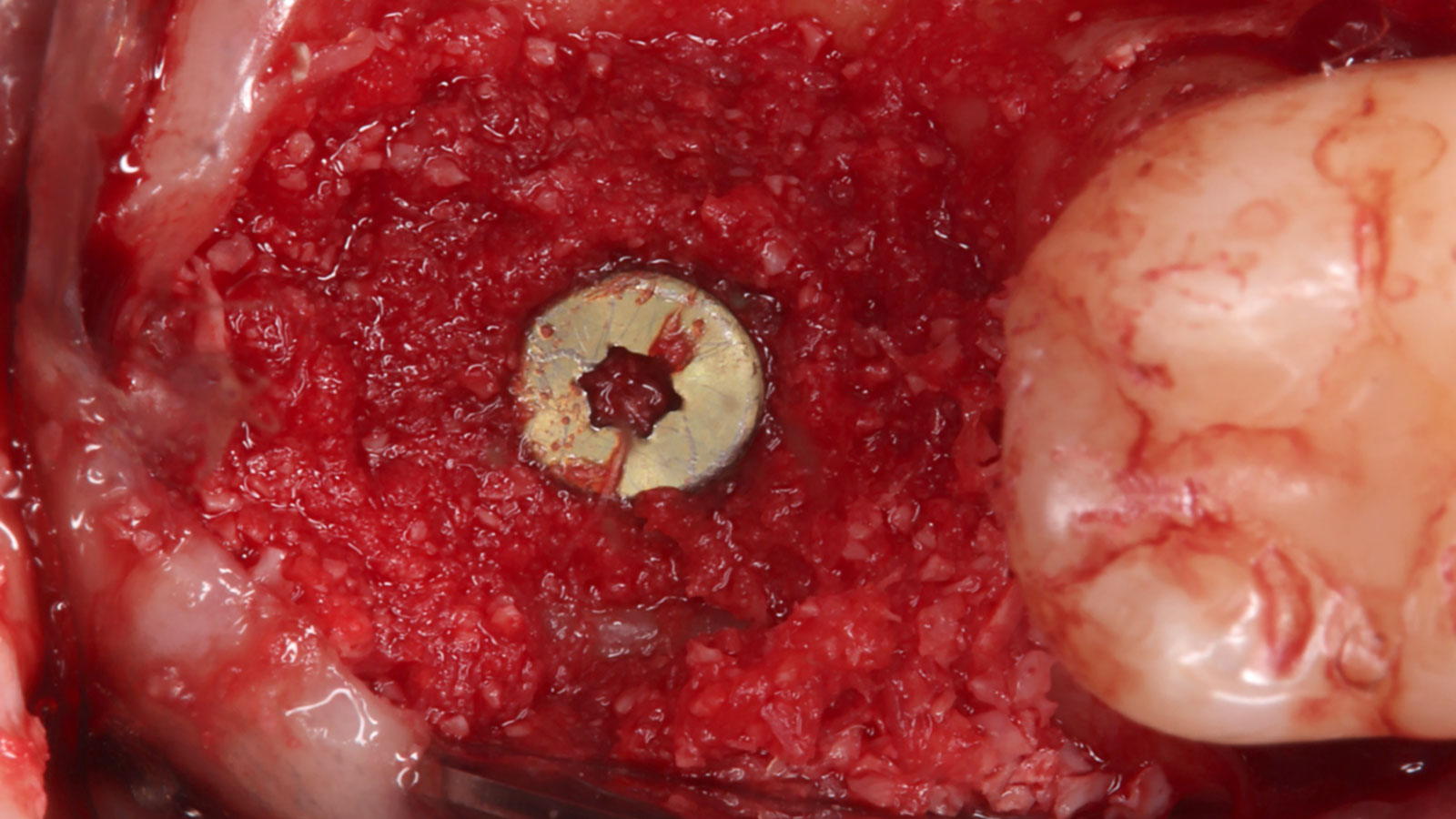
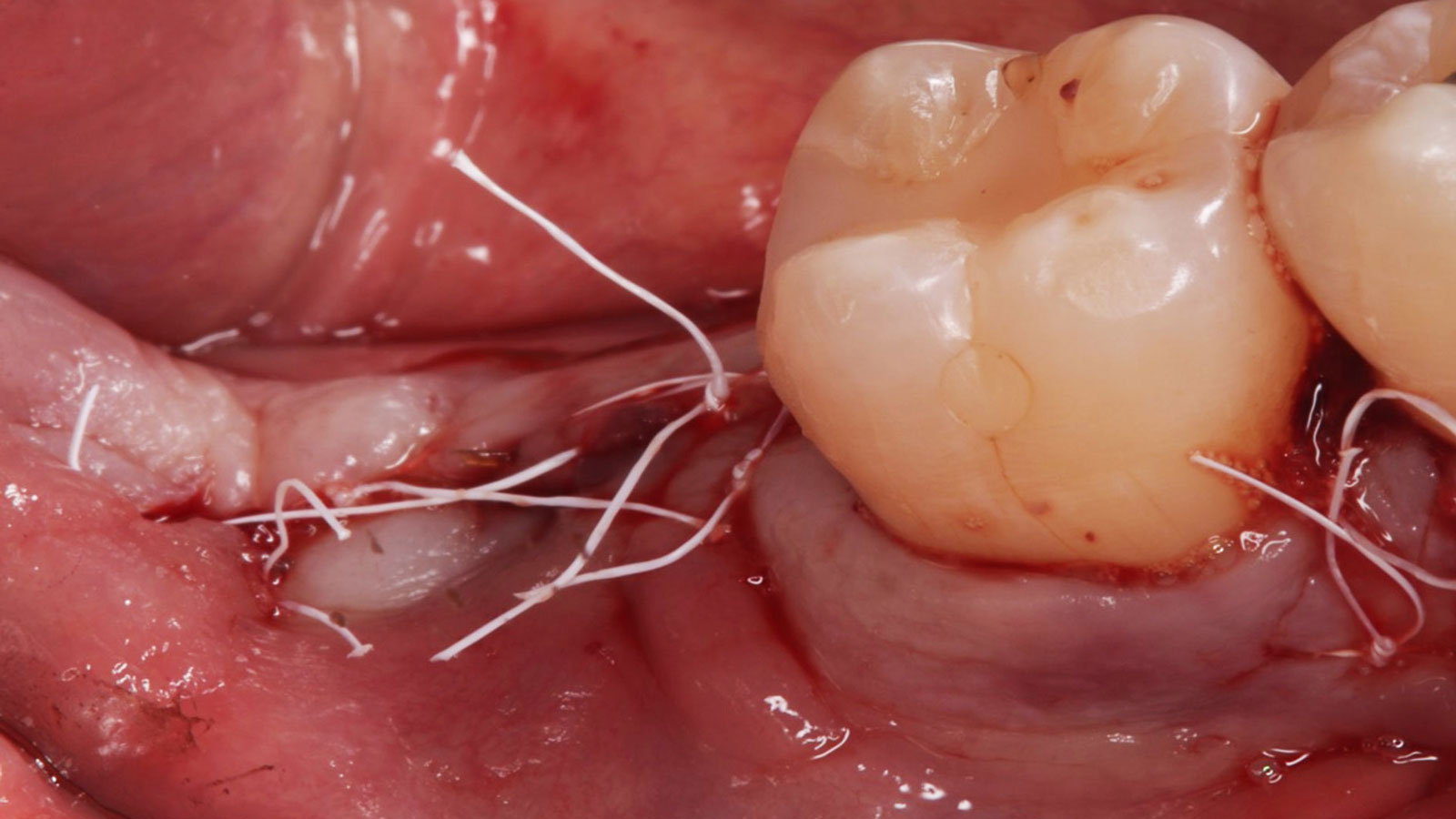
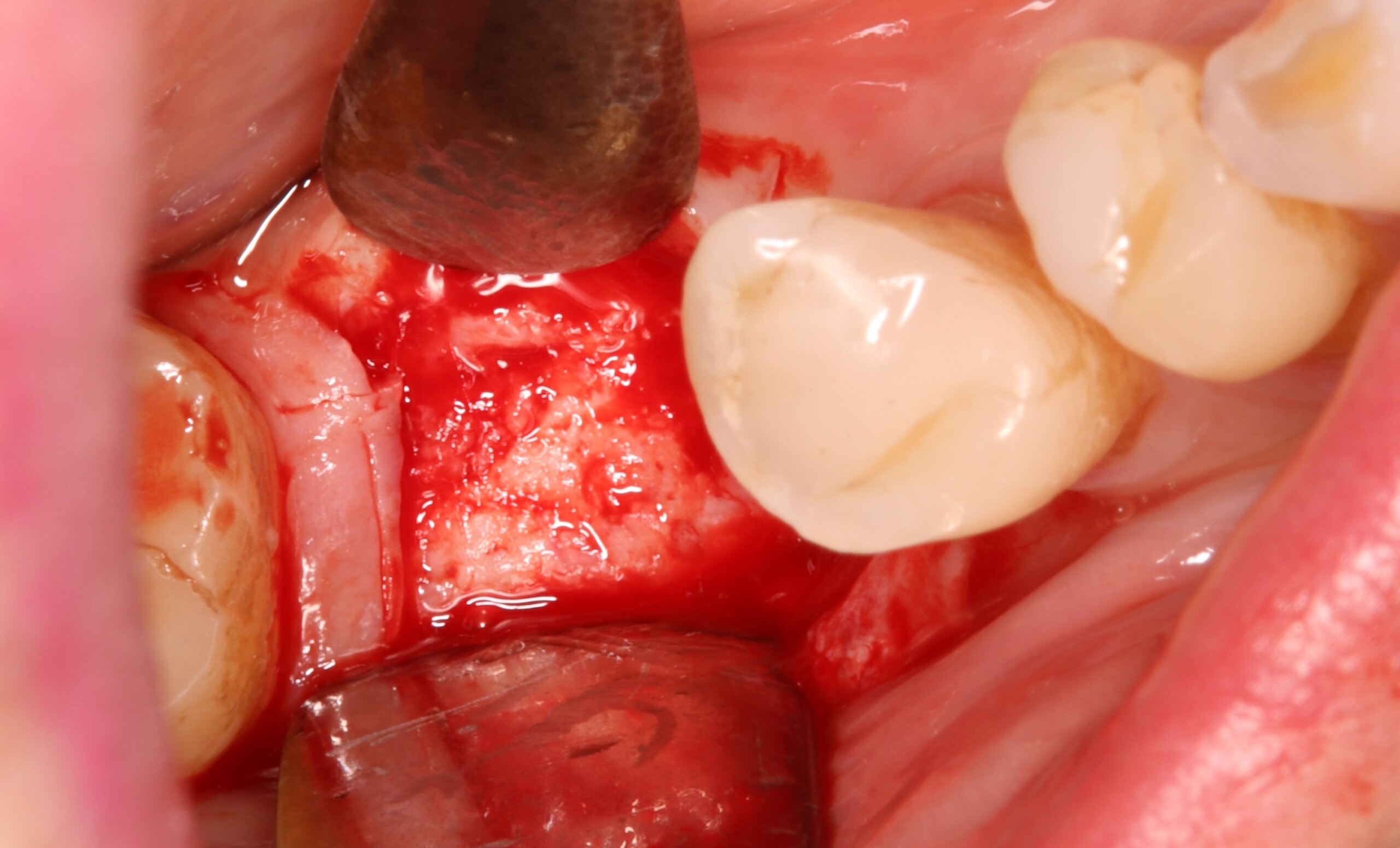
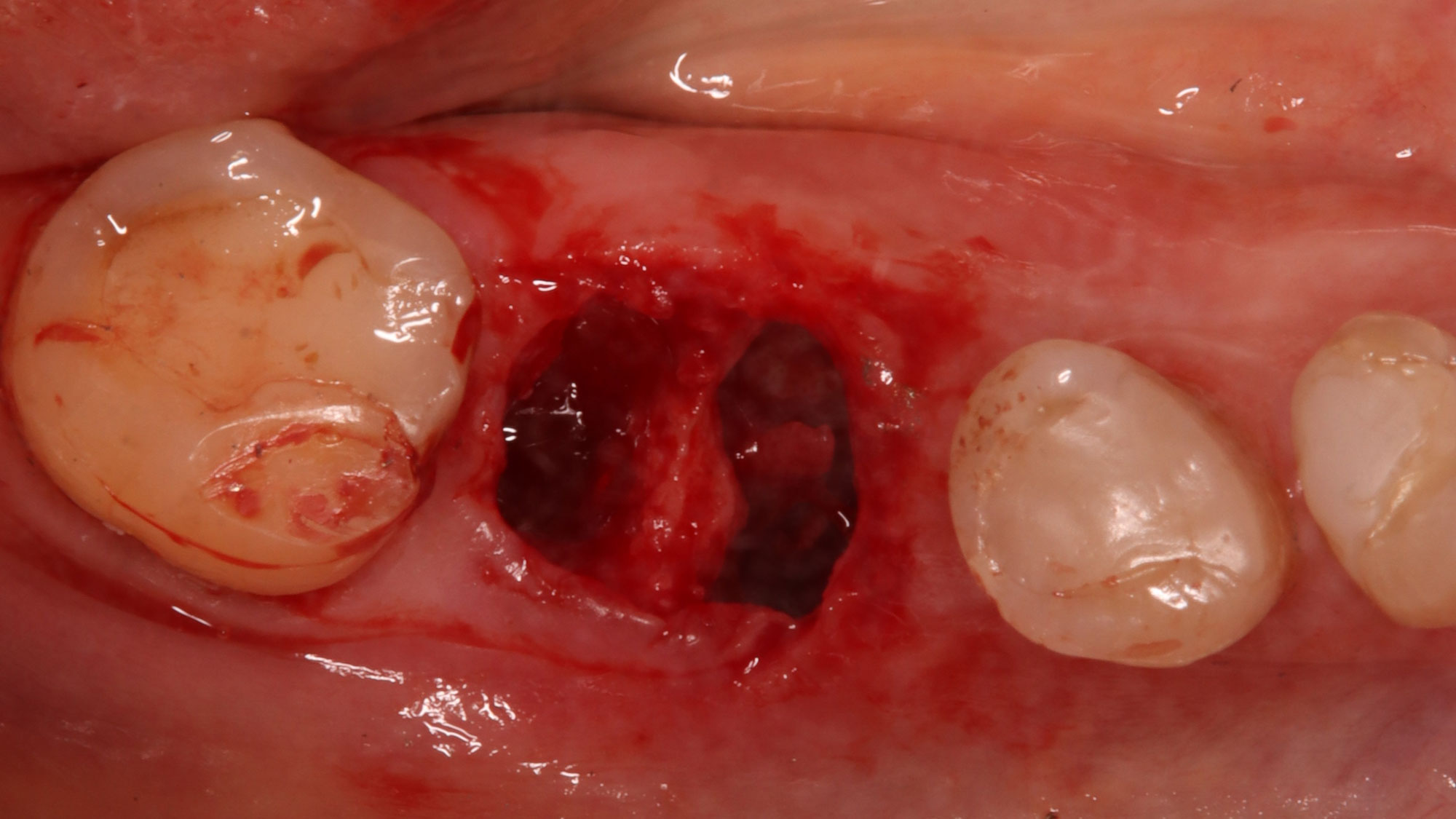
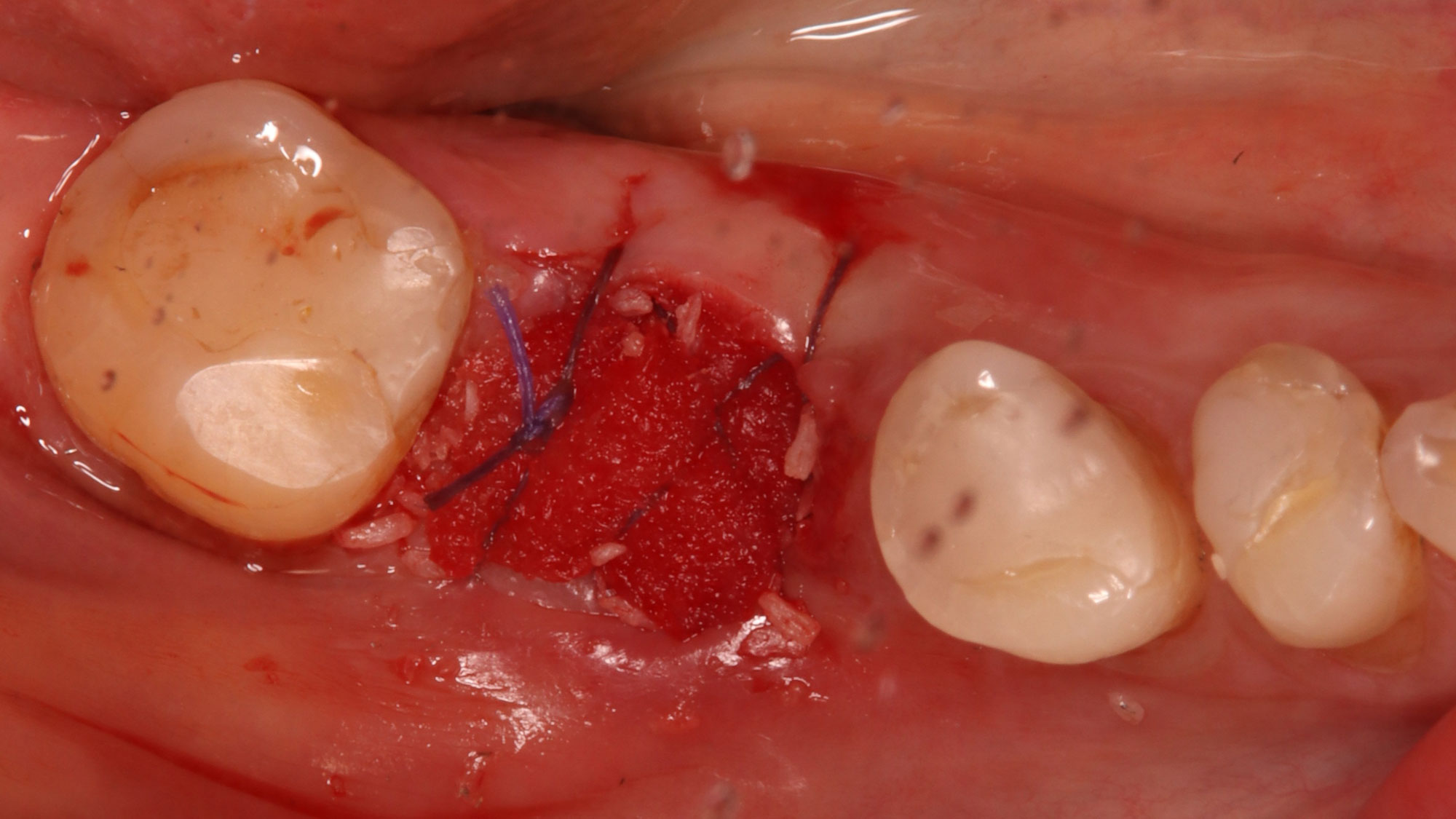
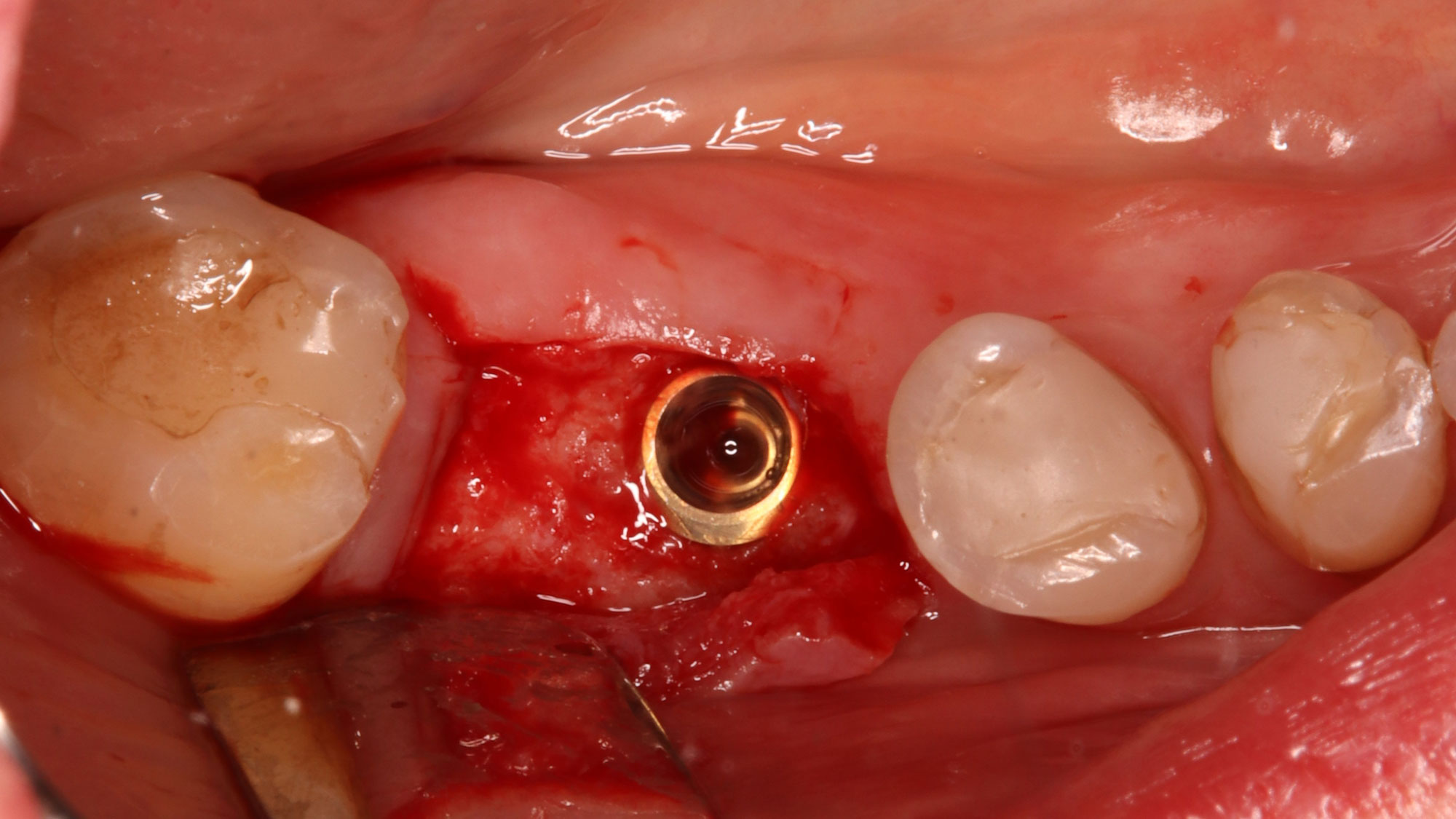
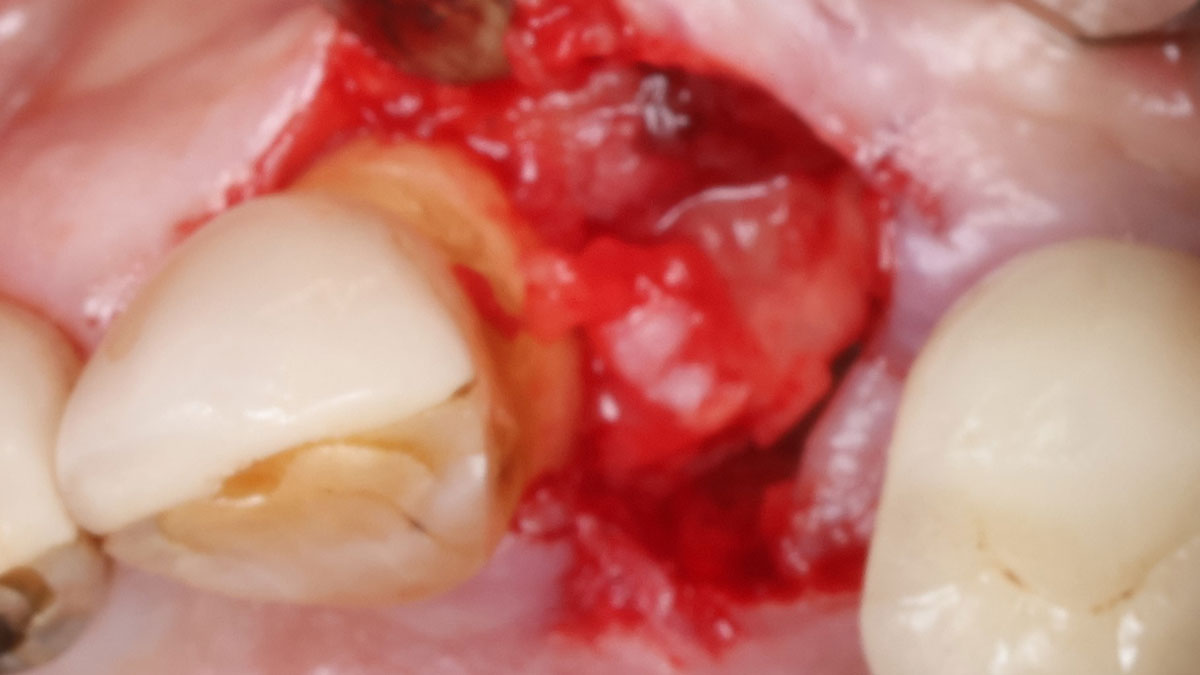
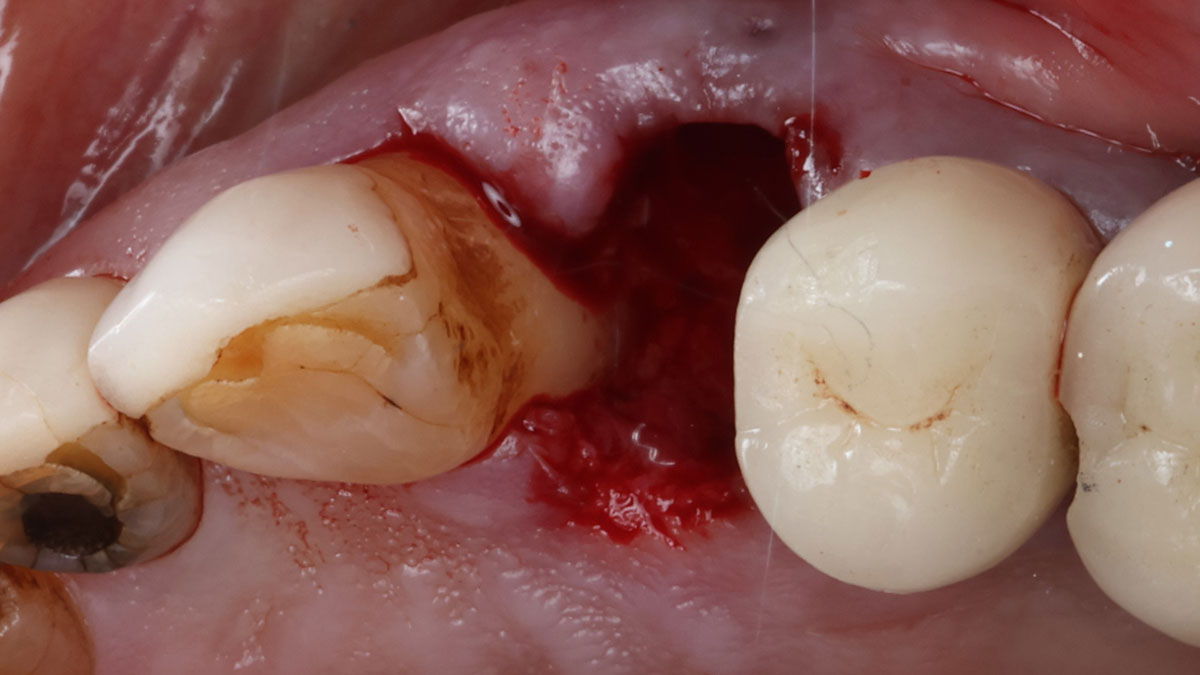
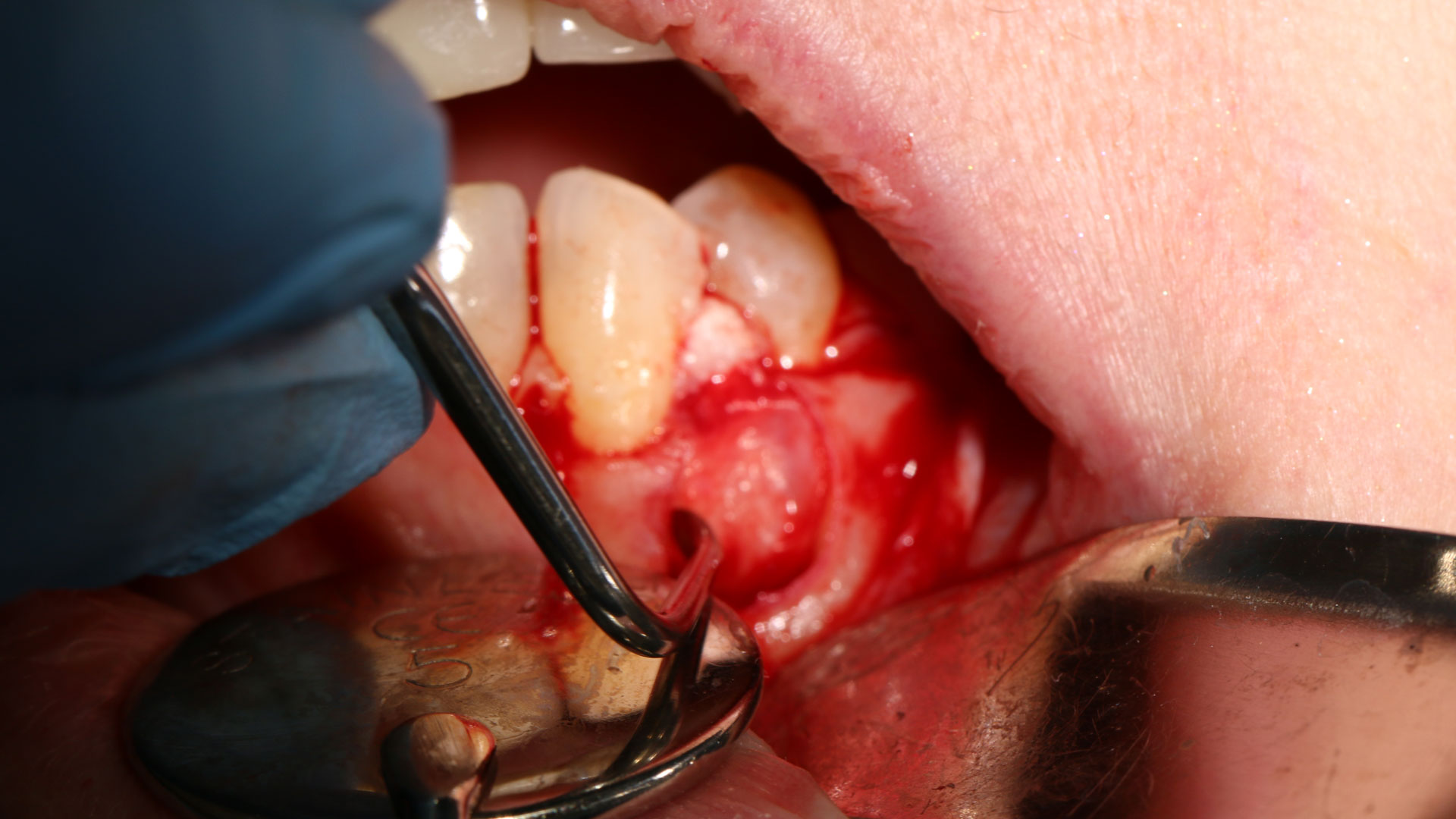
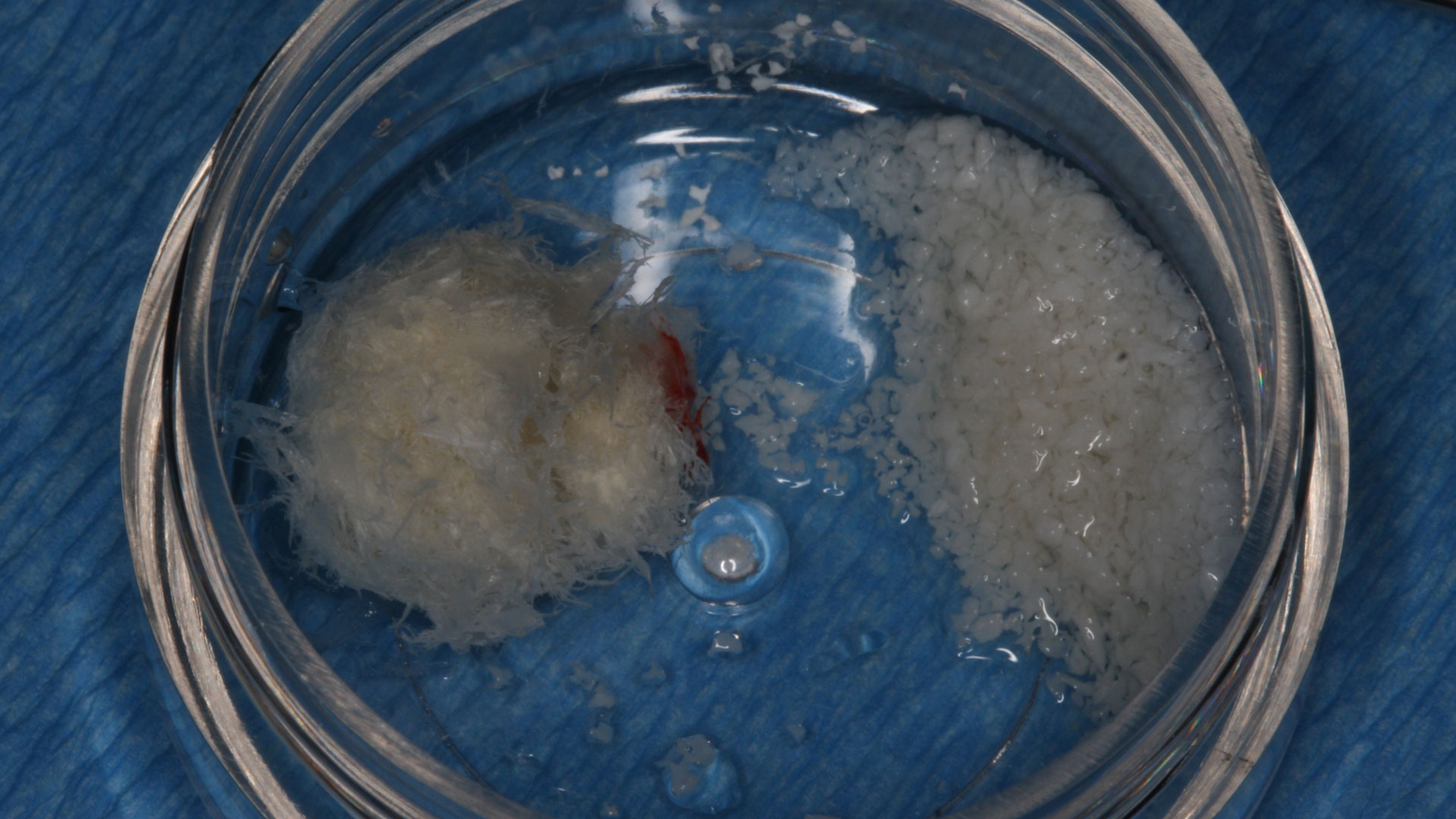
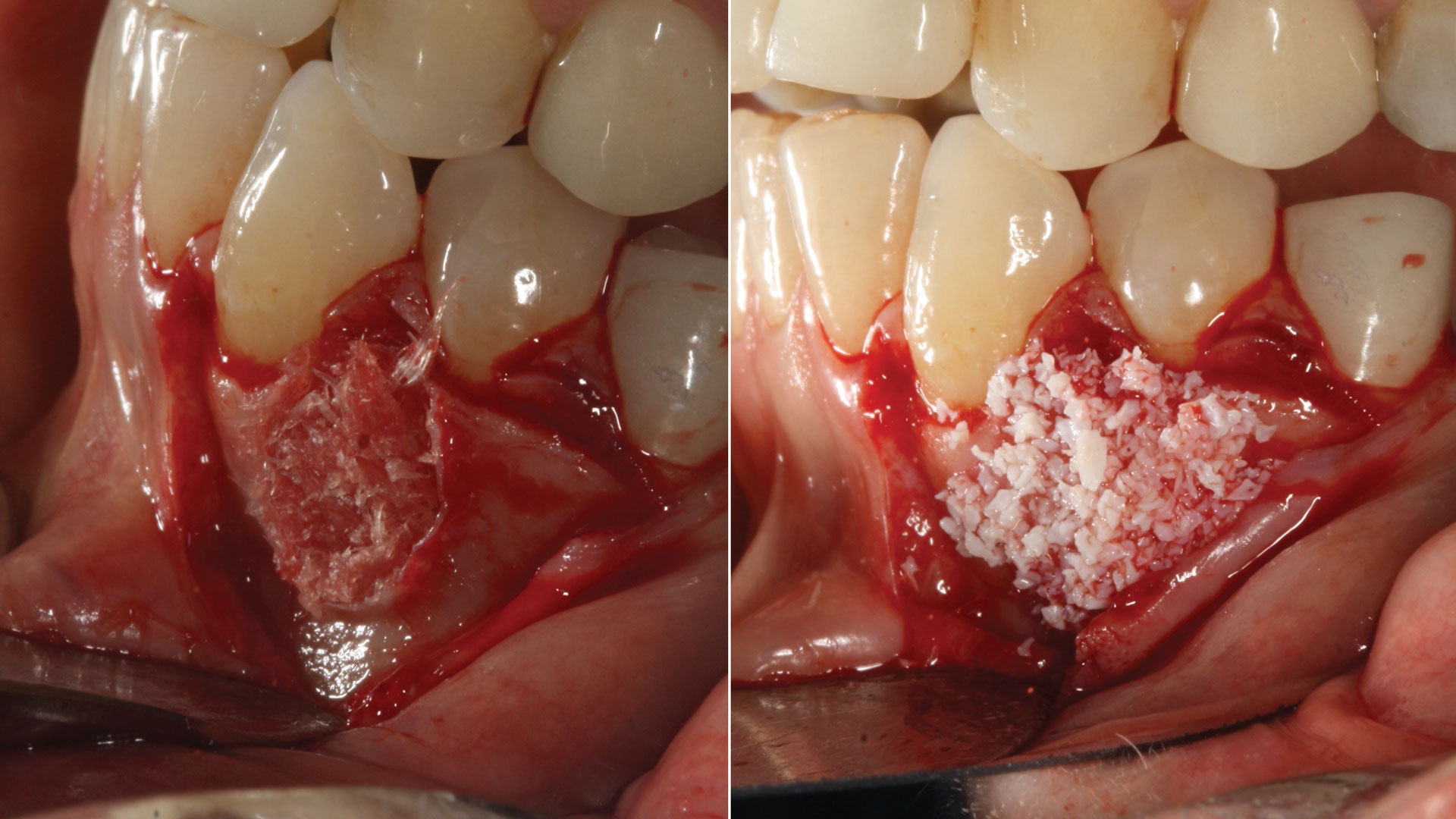
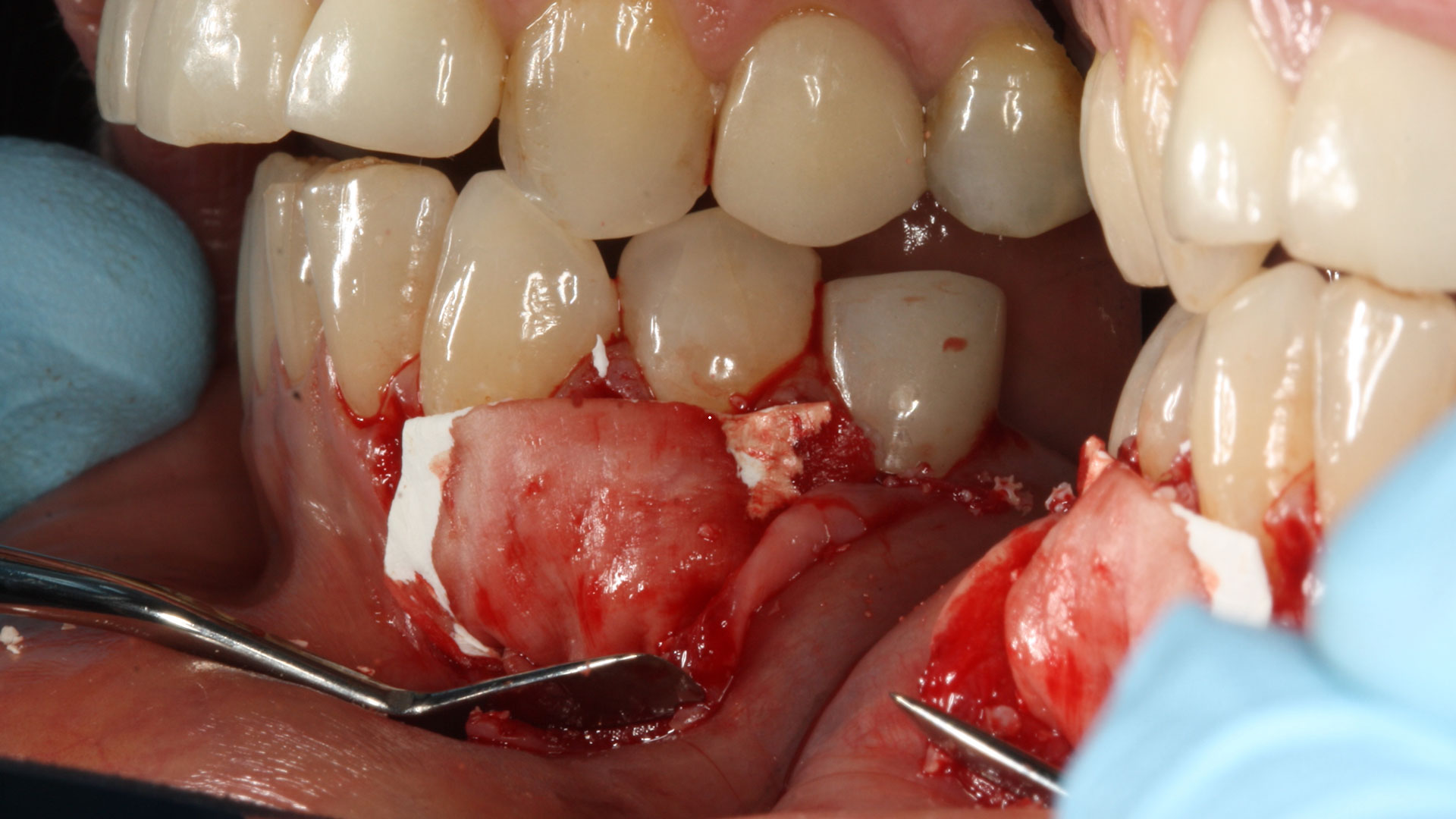
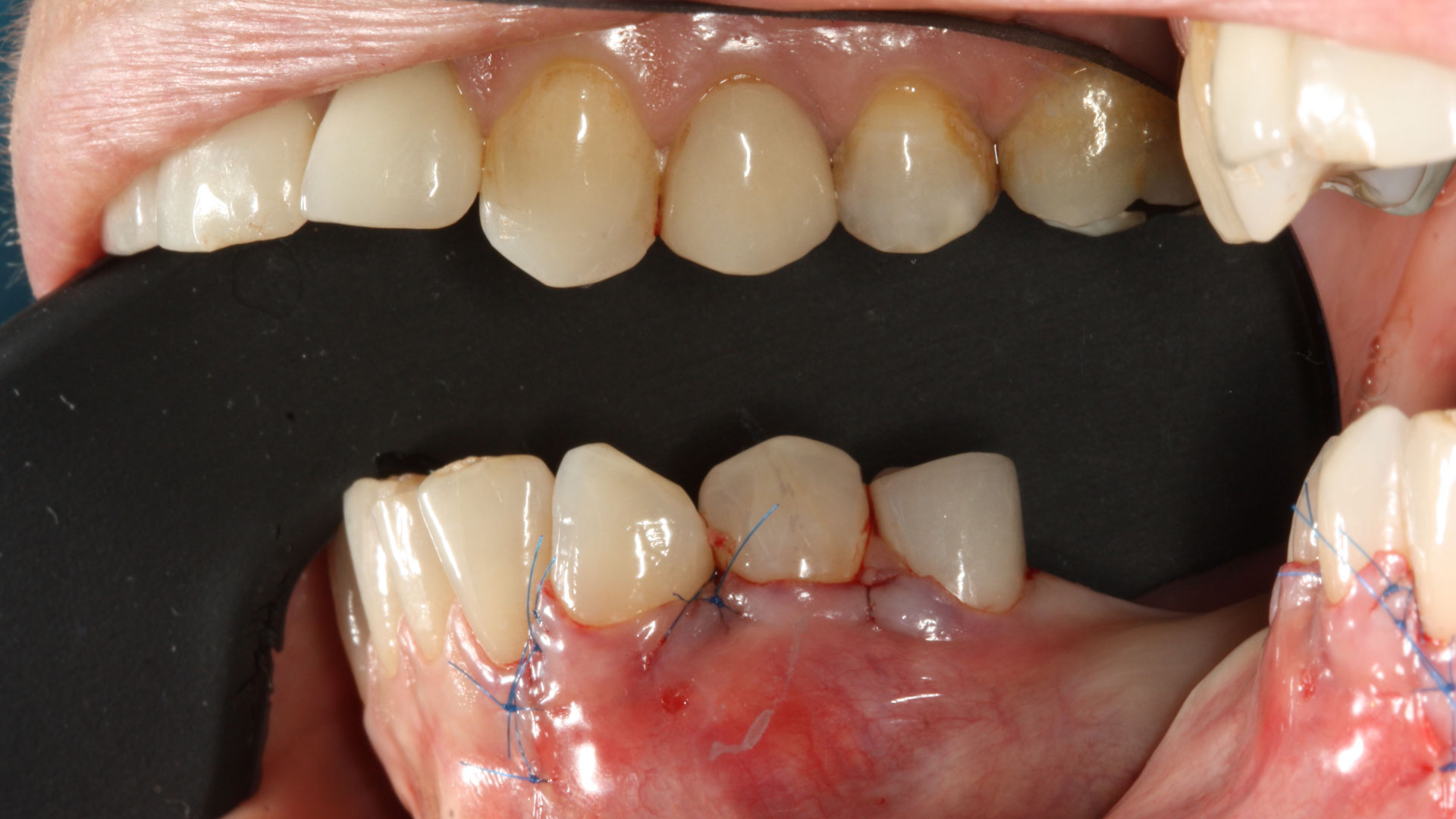
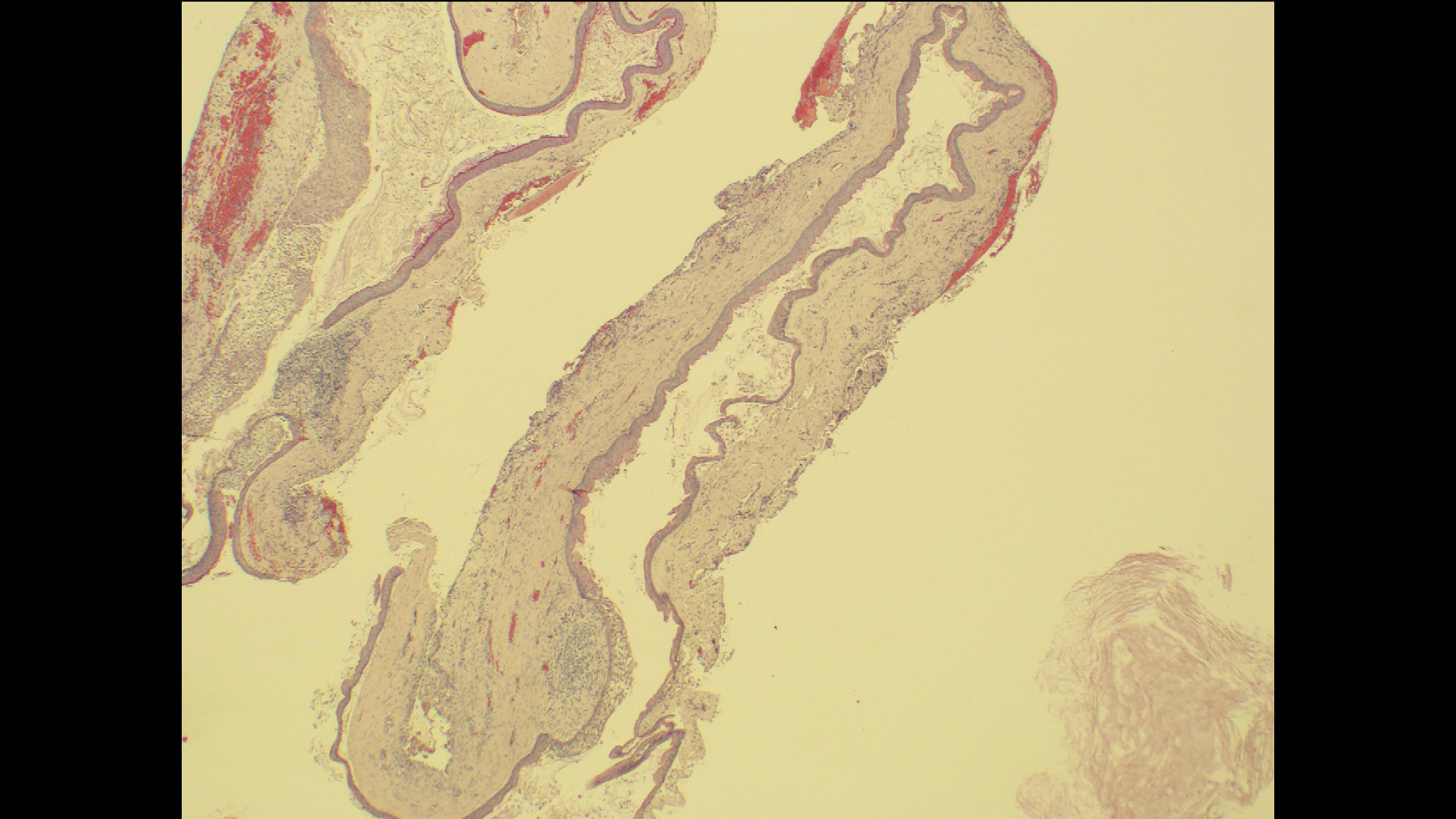
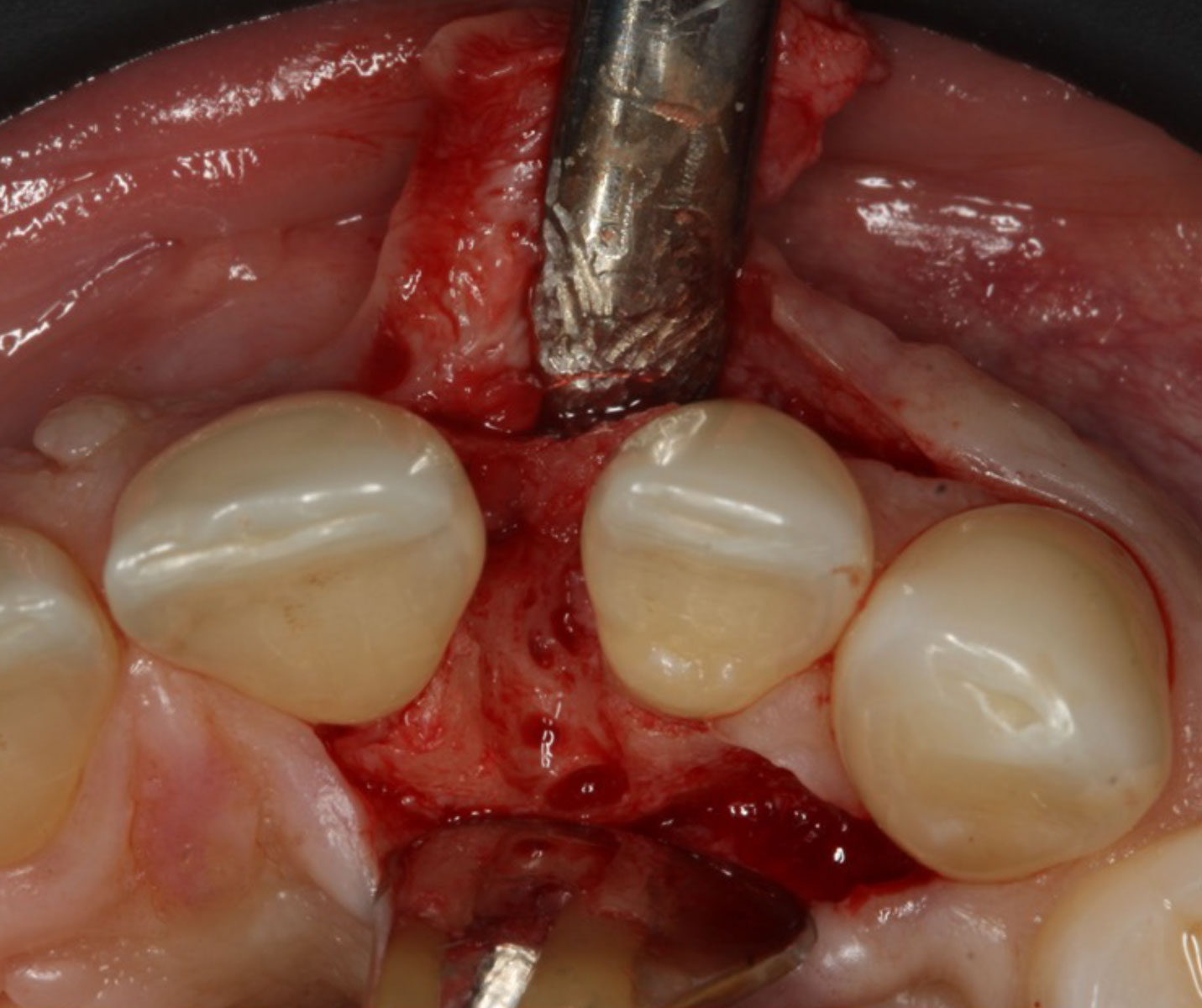
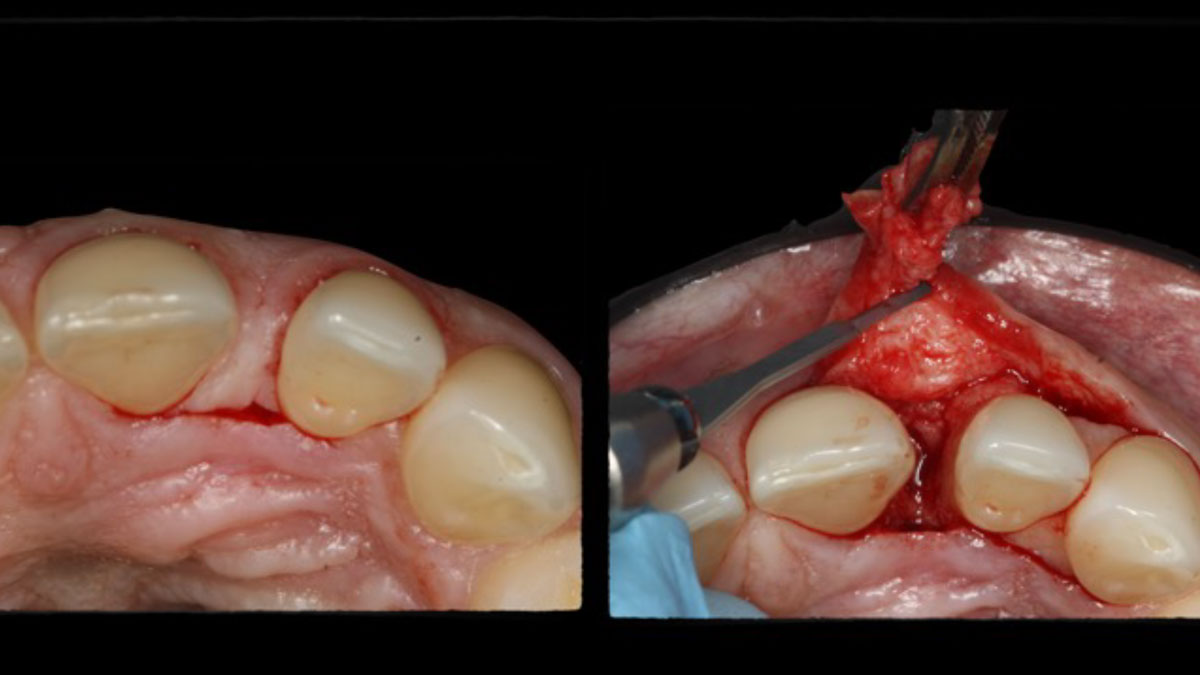
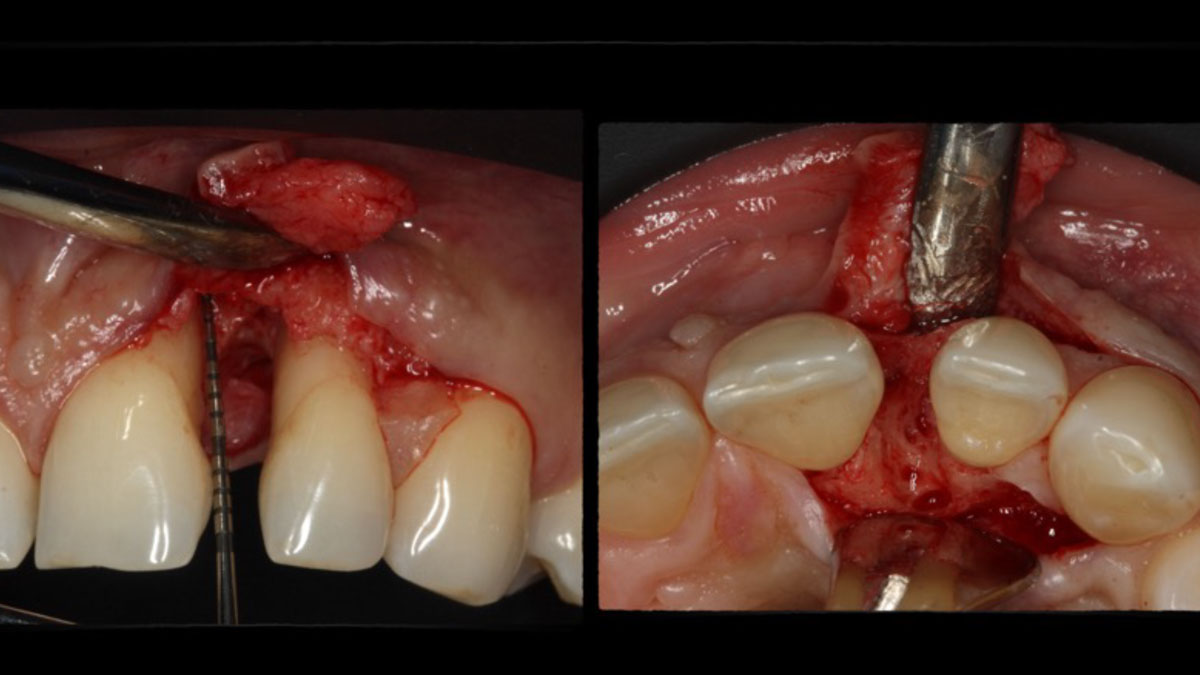
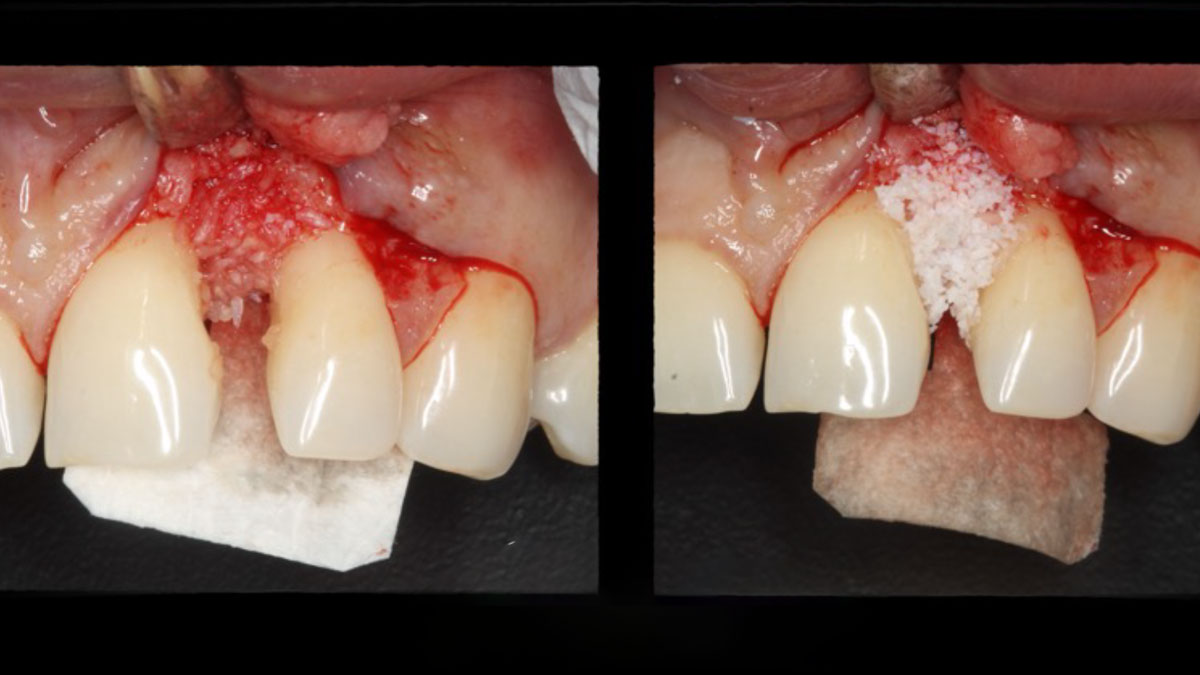
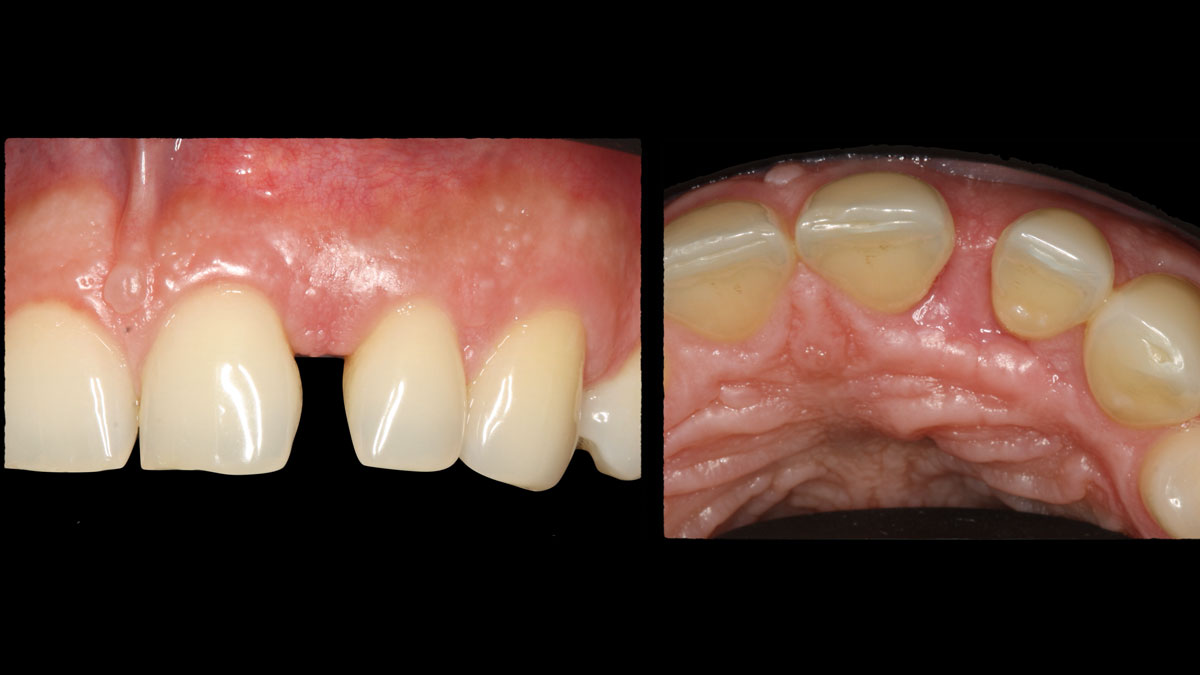
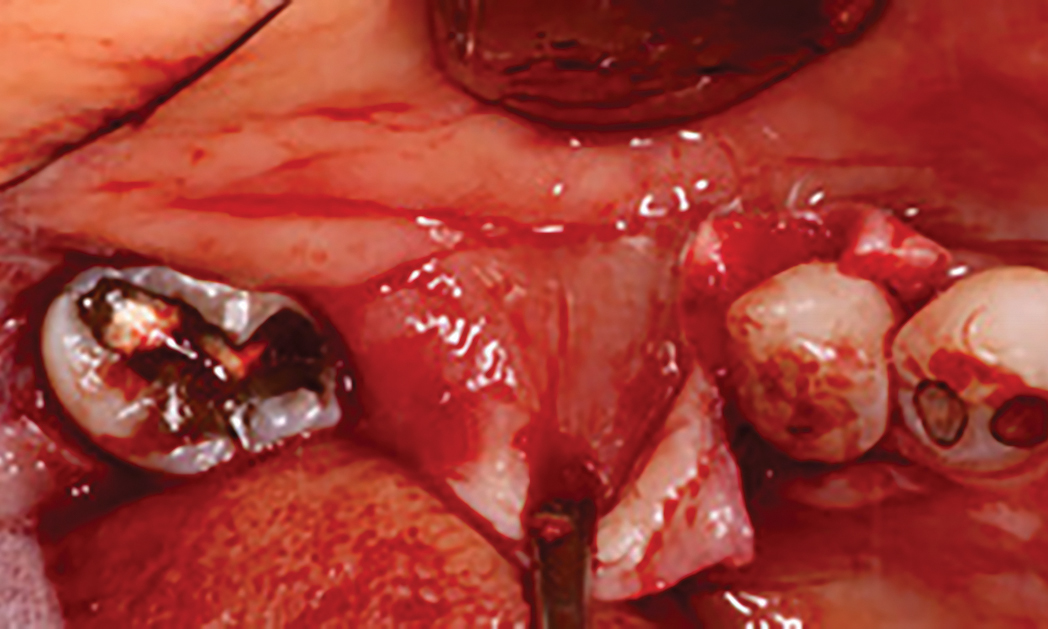
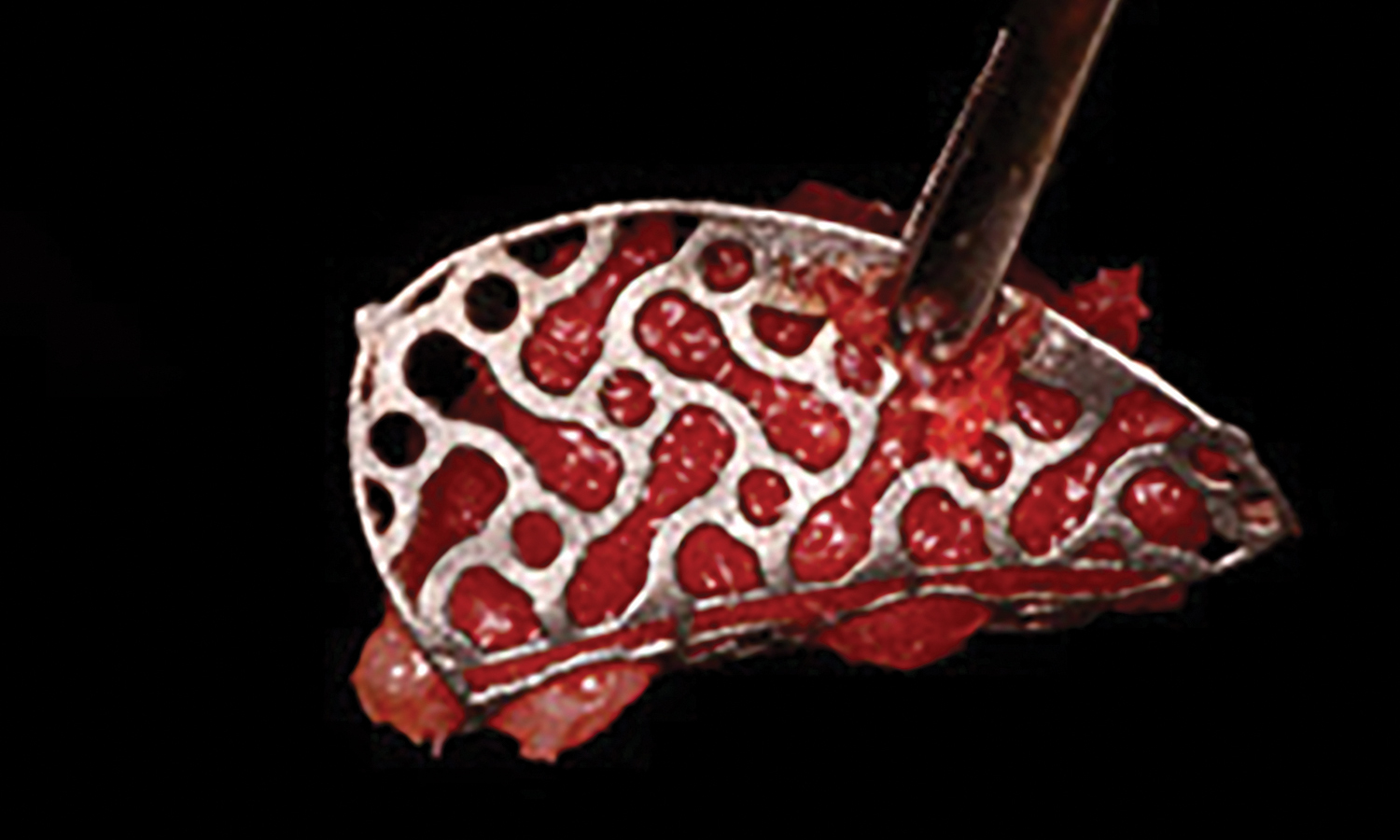
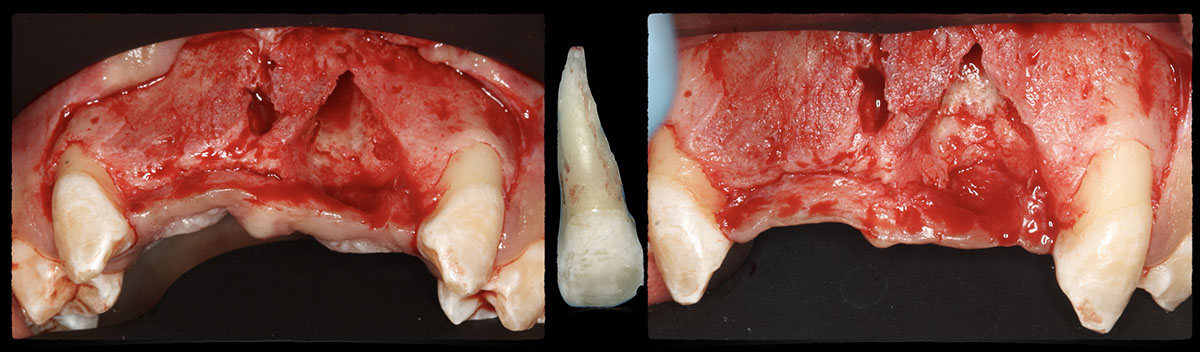
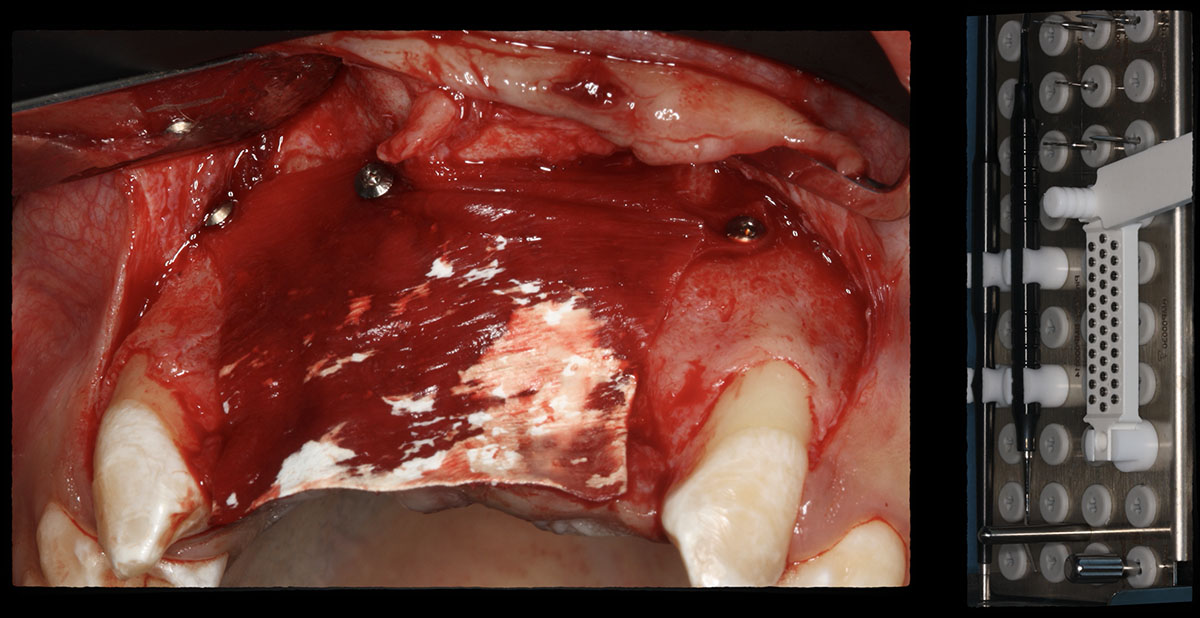
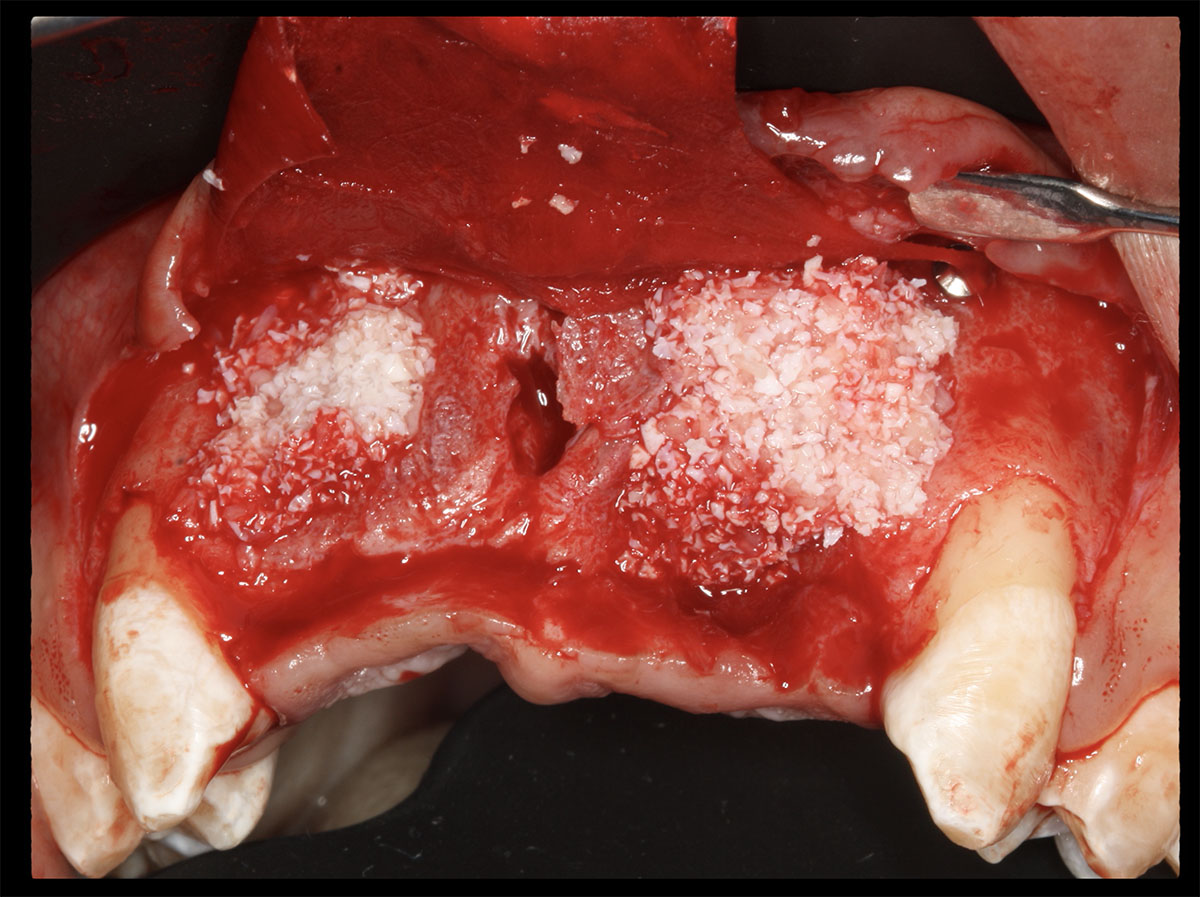
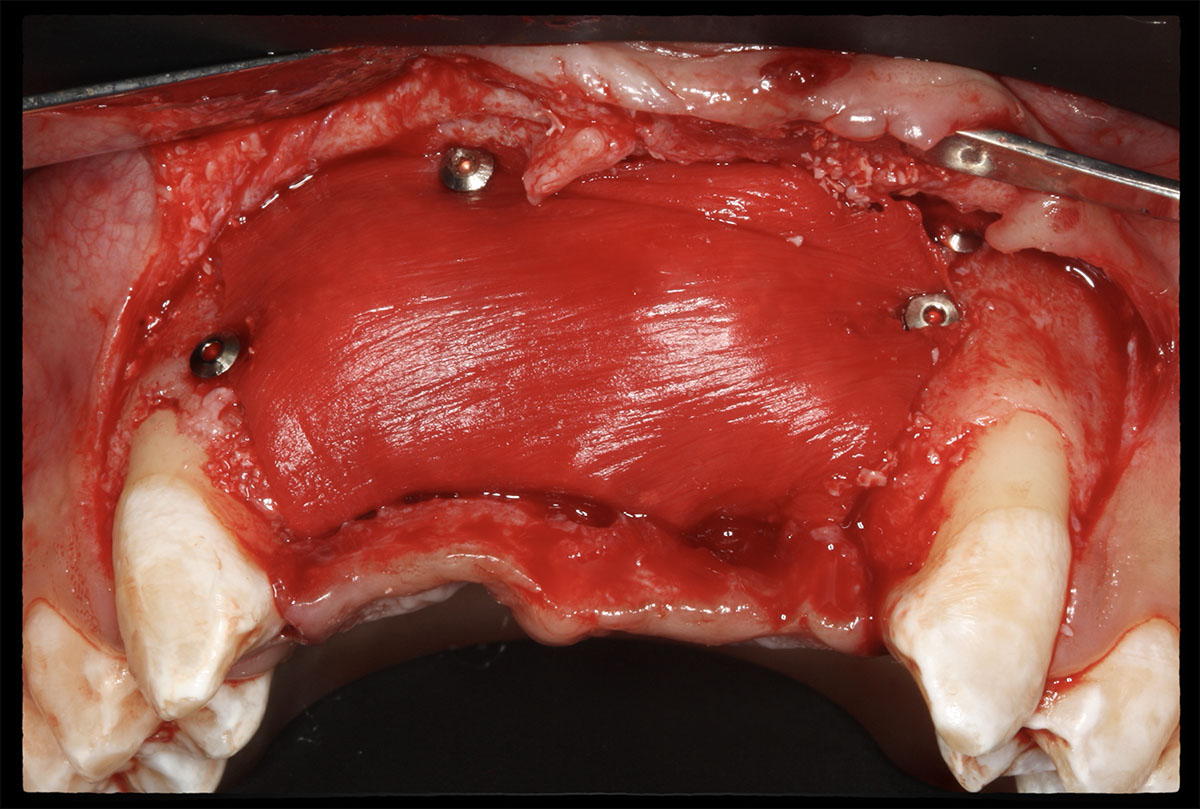
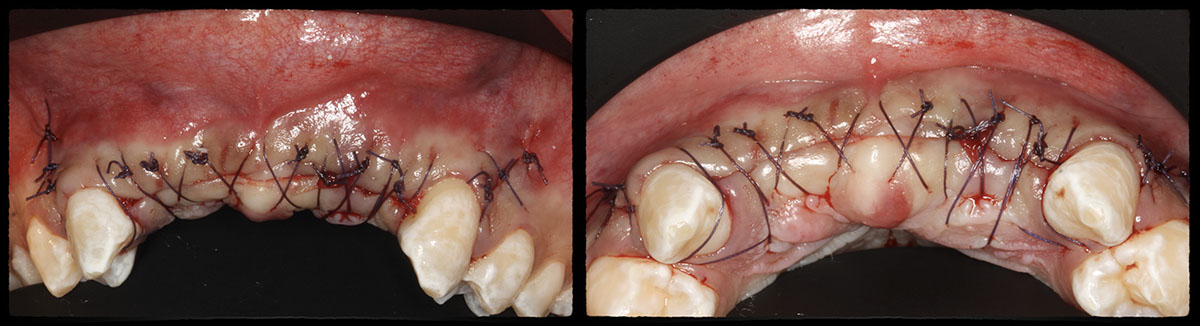
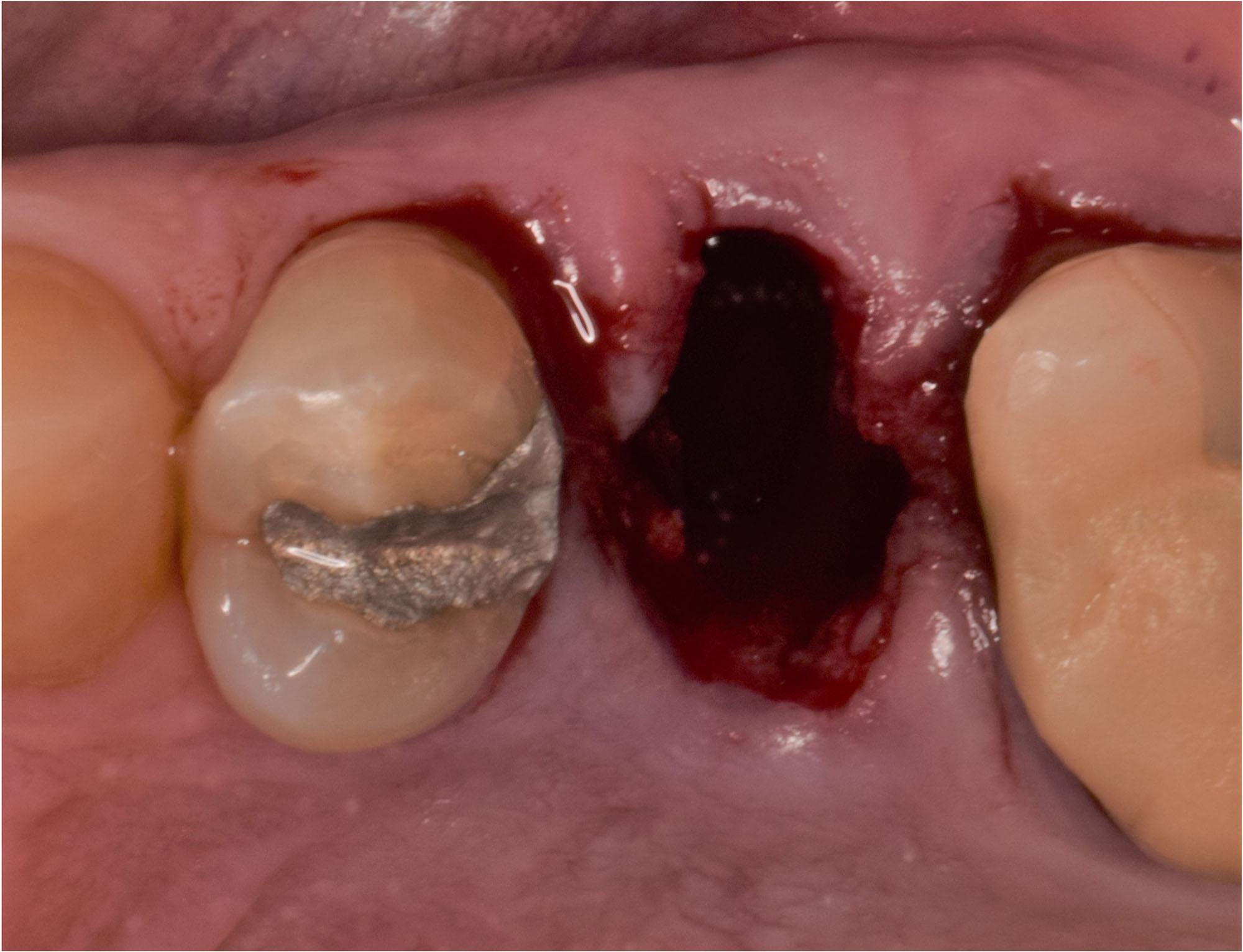
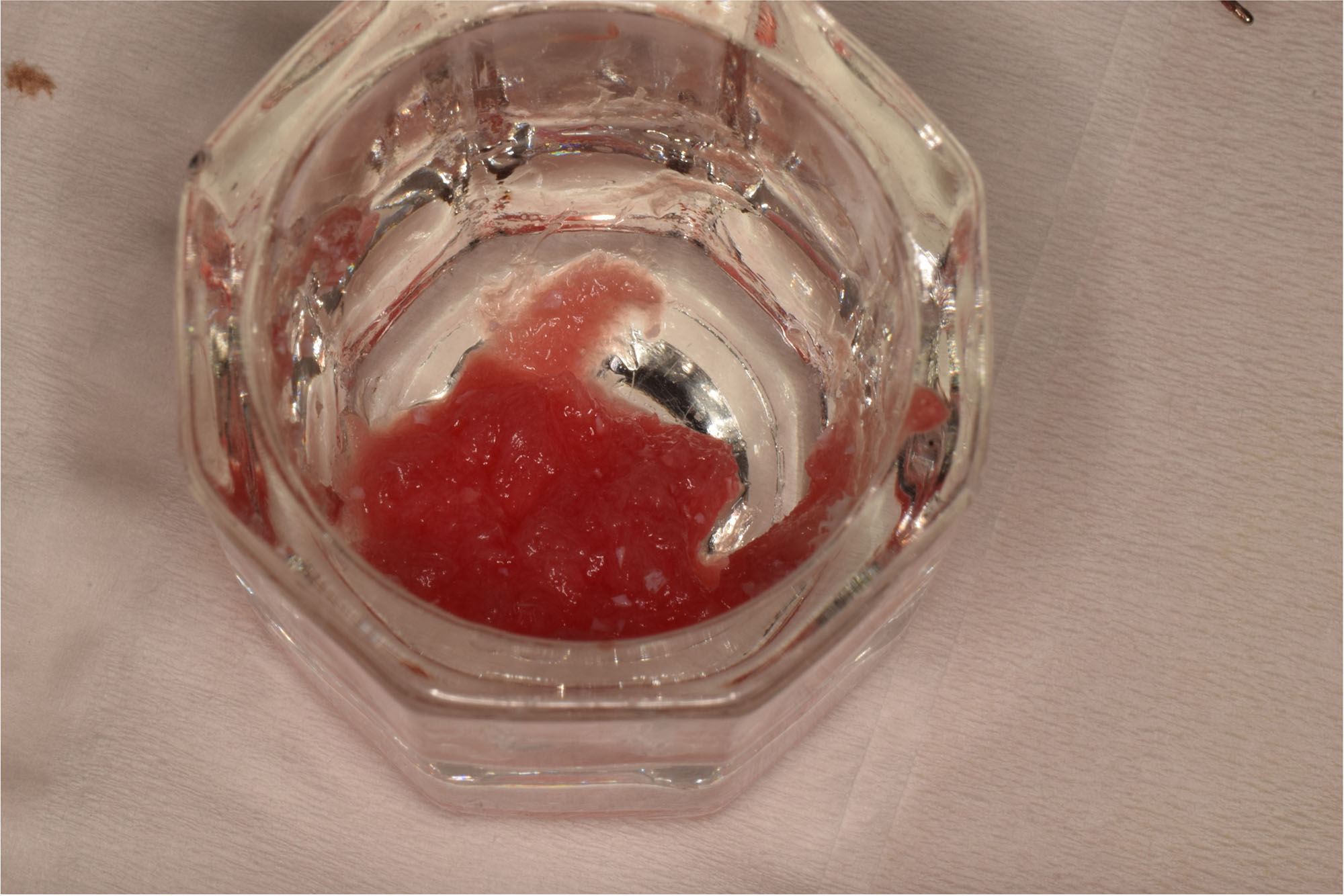
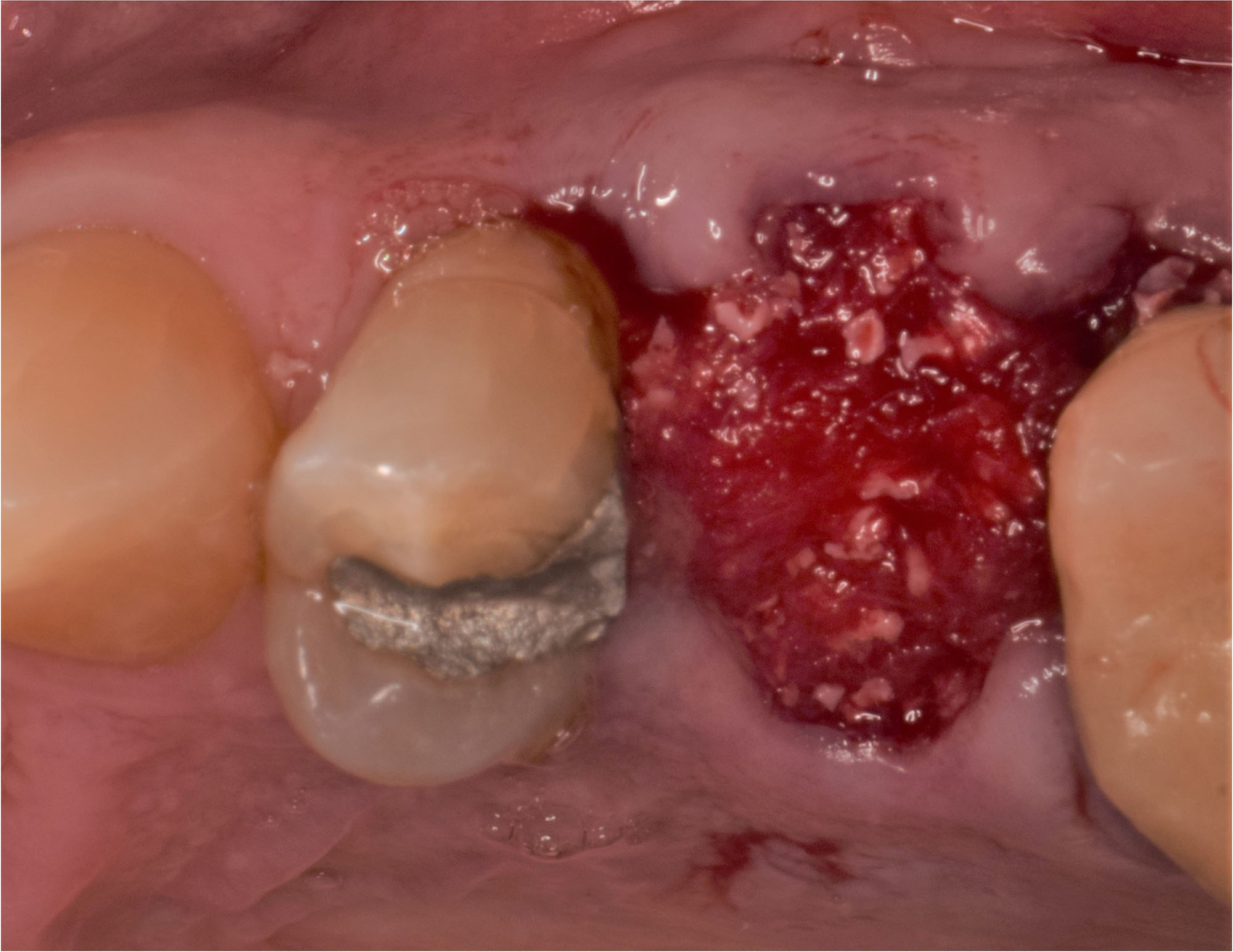
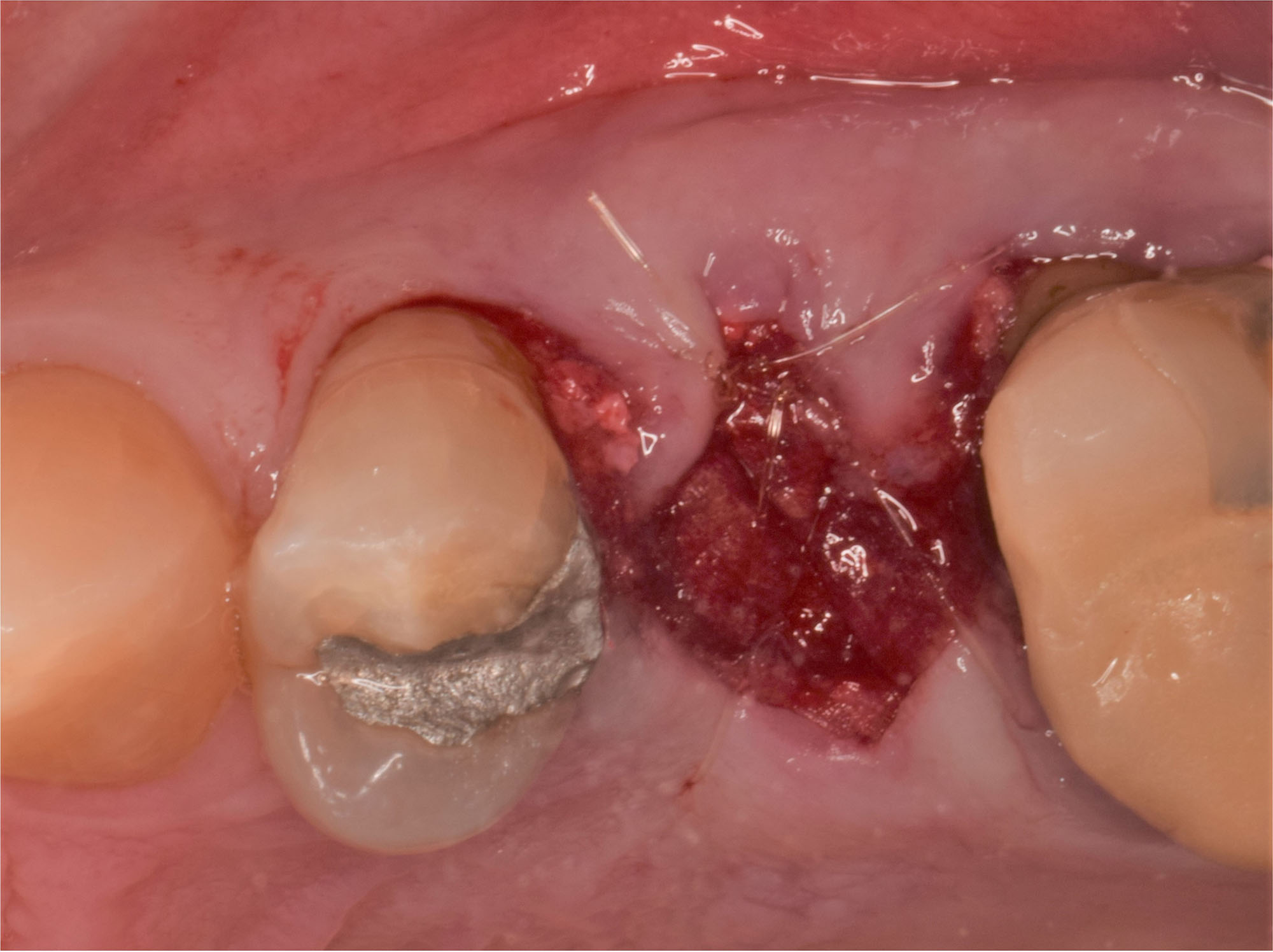
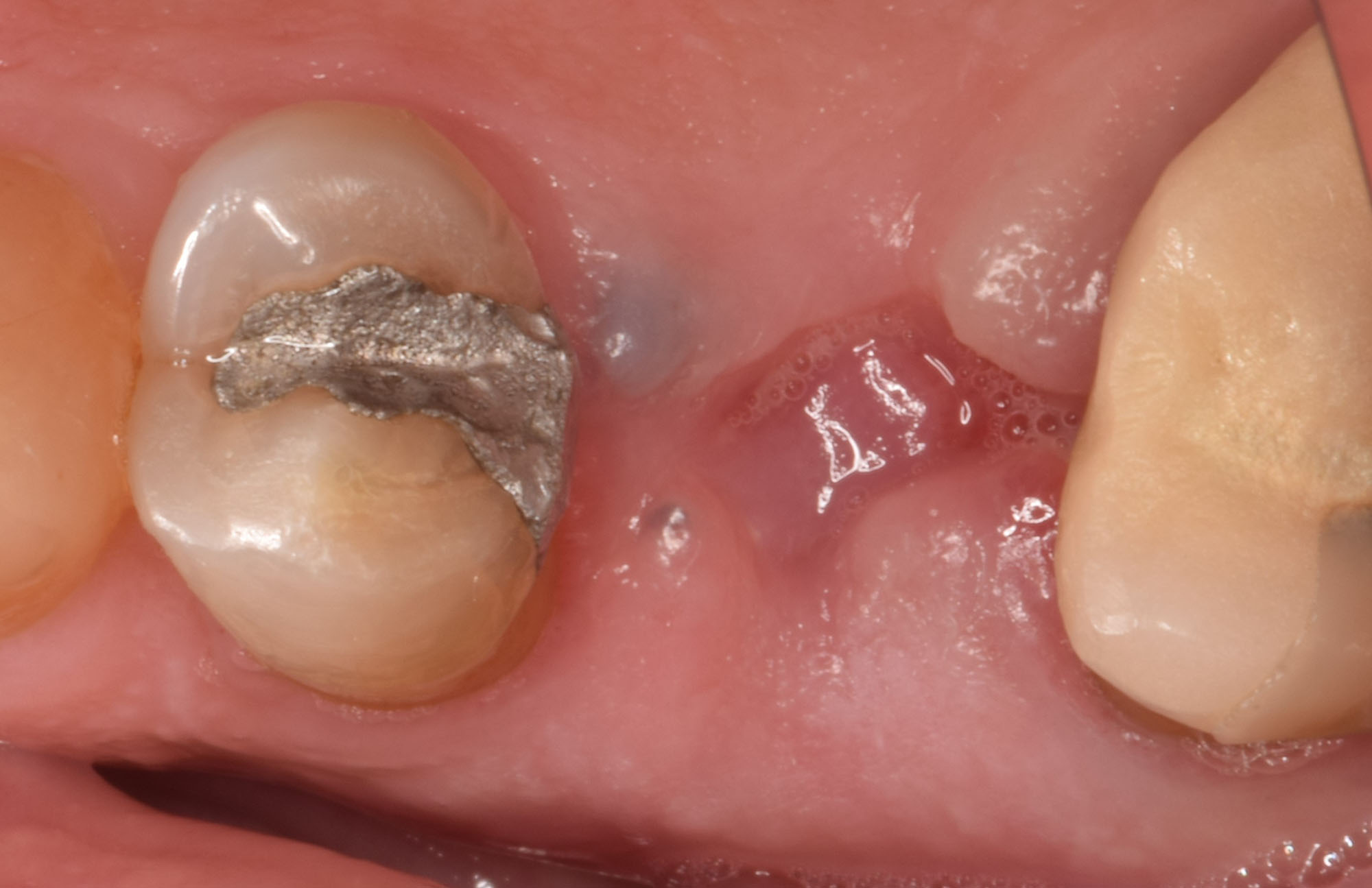
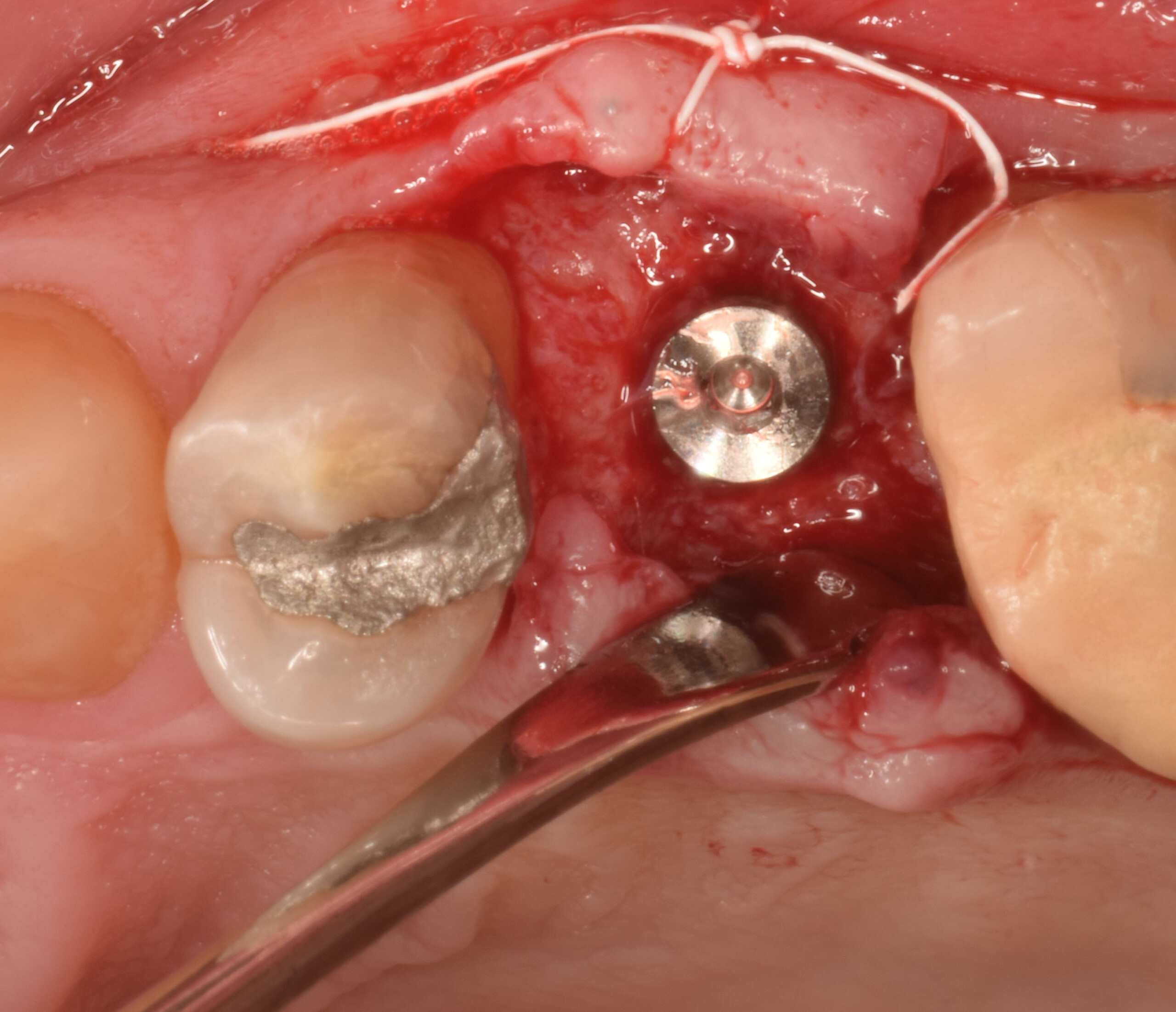
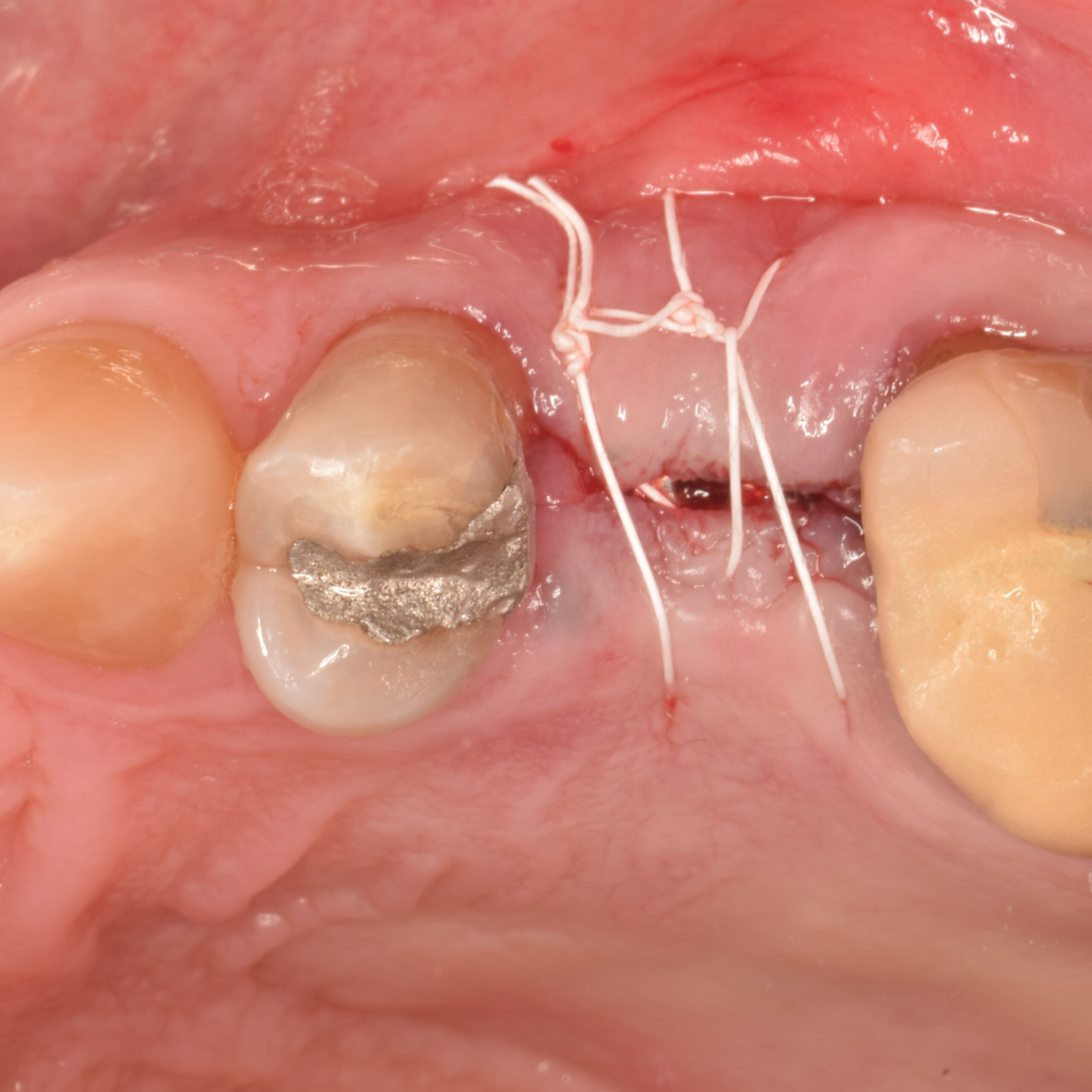
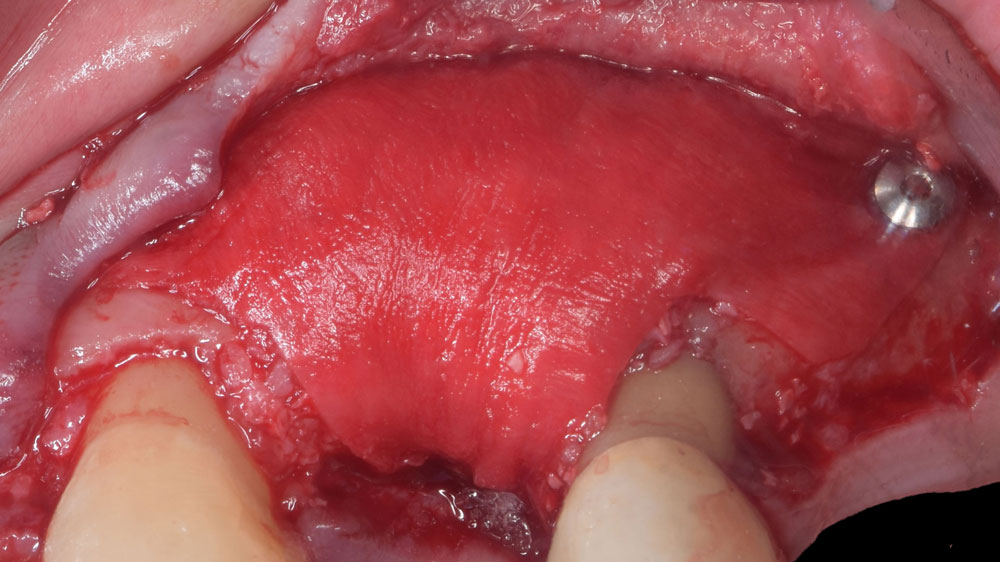
Horizontal ridge augmentation was performed using a horizontal layering technique. An inner layer of demineralized freeze-dried bone allograft (DFDBA), featuring vallos® demineralized cortical particles (to promote osteoinduction), was followed by an outer layer of deproteinized bovine bone, Geistlich Bio-Oss® (to maintain space and volume). The graft was contained with a native bilayer collagen membrane, Geistlich Bio-Gide®, and secured with titanium pins (tacks).
“By horizontally layering two distinct bone graft materials—Geistlich Bio-Oss® and vallos®—this approach was designed to tailor the regenerative environment, harnessing the unique osteoinductive potential of the allograft and the long-term space-maintaining properties of the xenograft to optimize both early bone formation and dimensional stability.”
— Eswar Kandaswamy, BDS, MS
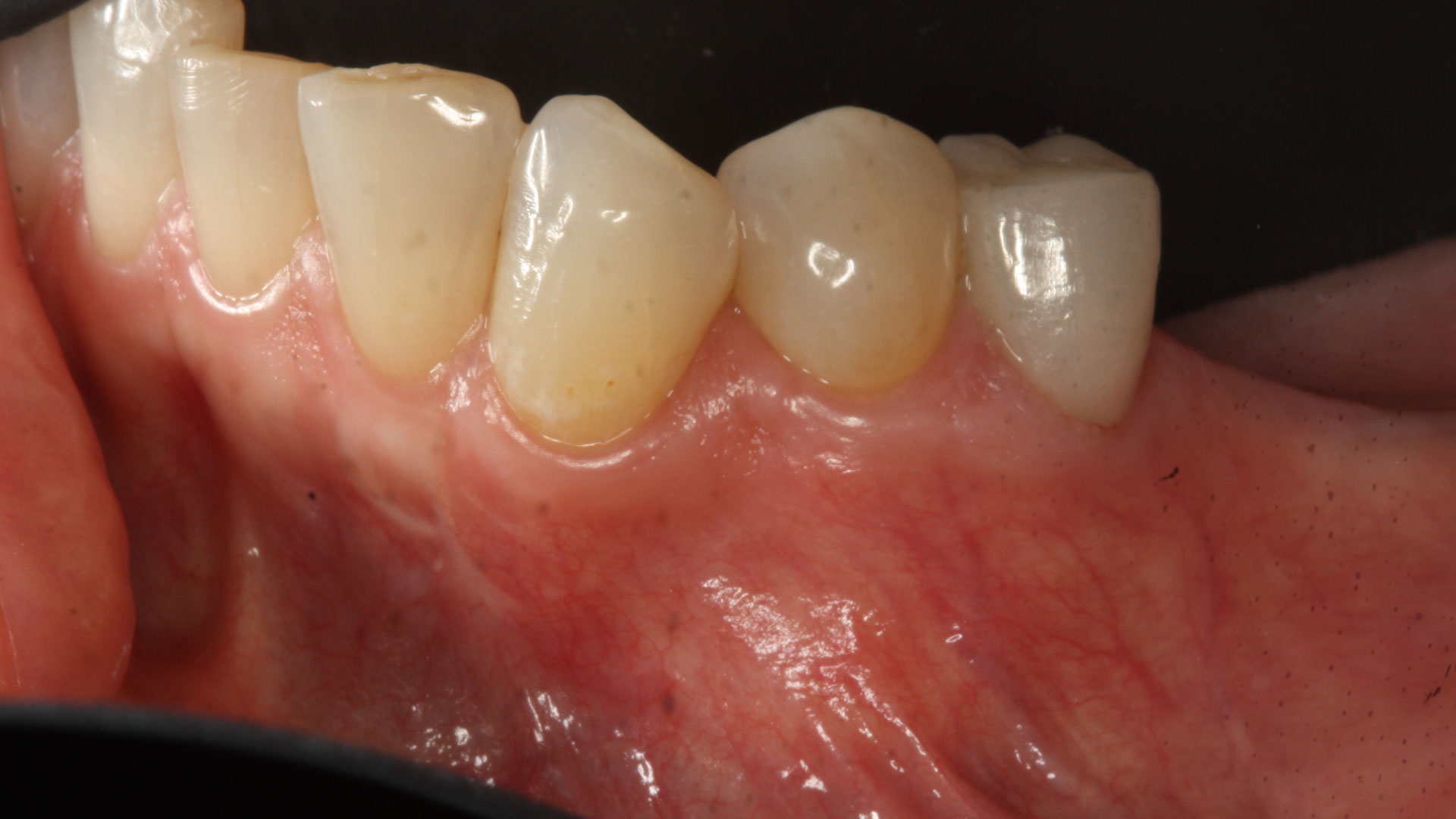
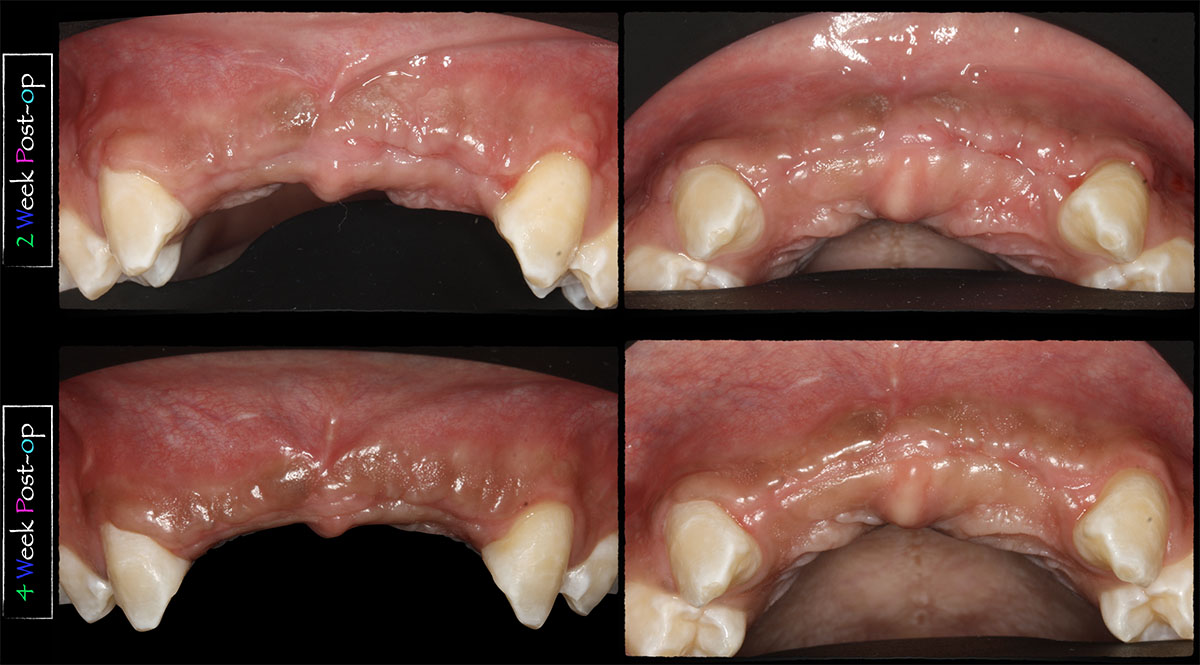
THE OUTCOME
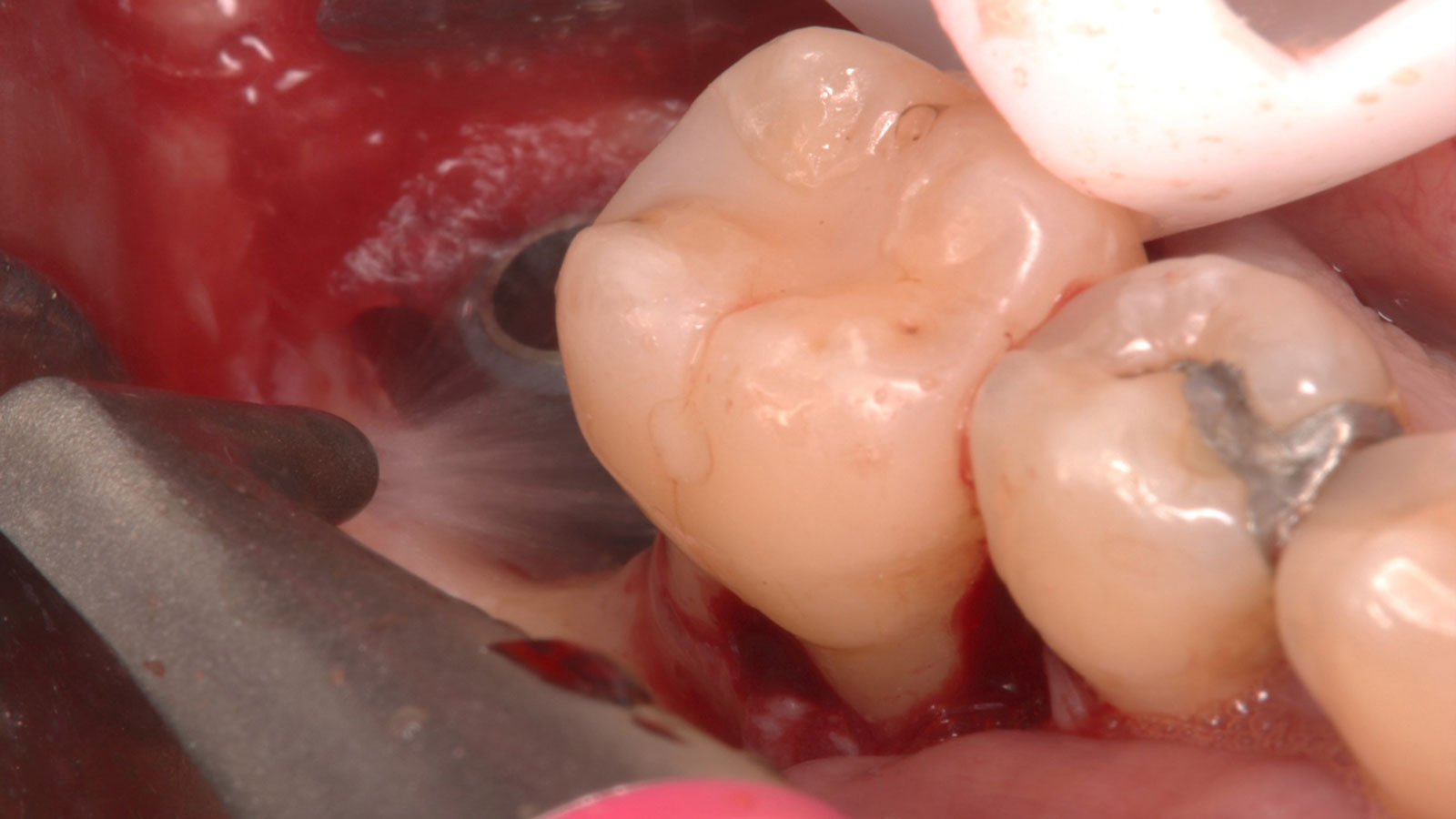
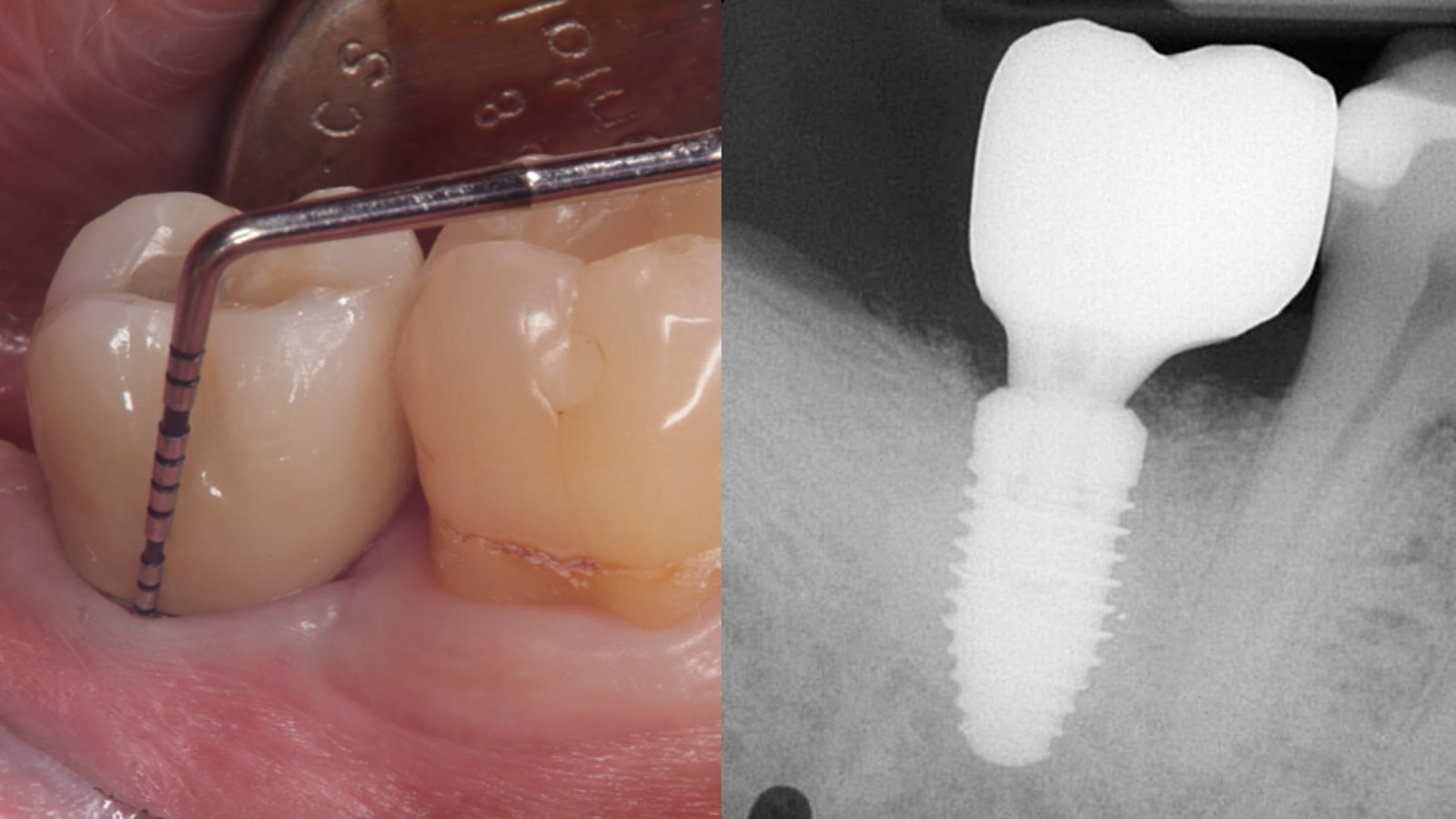
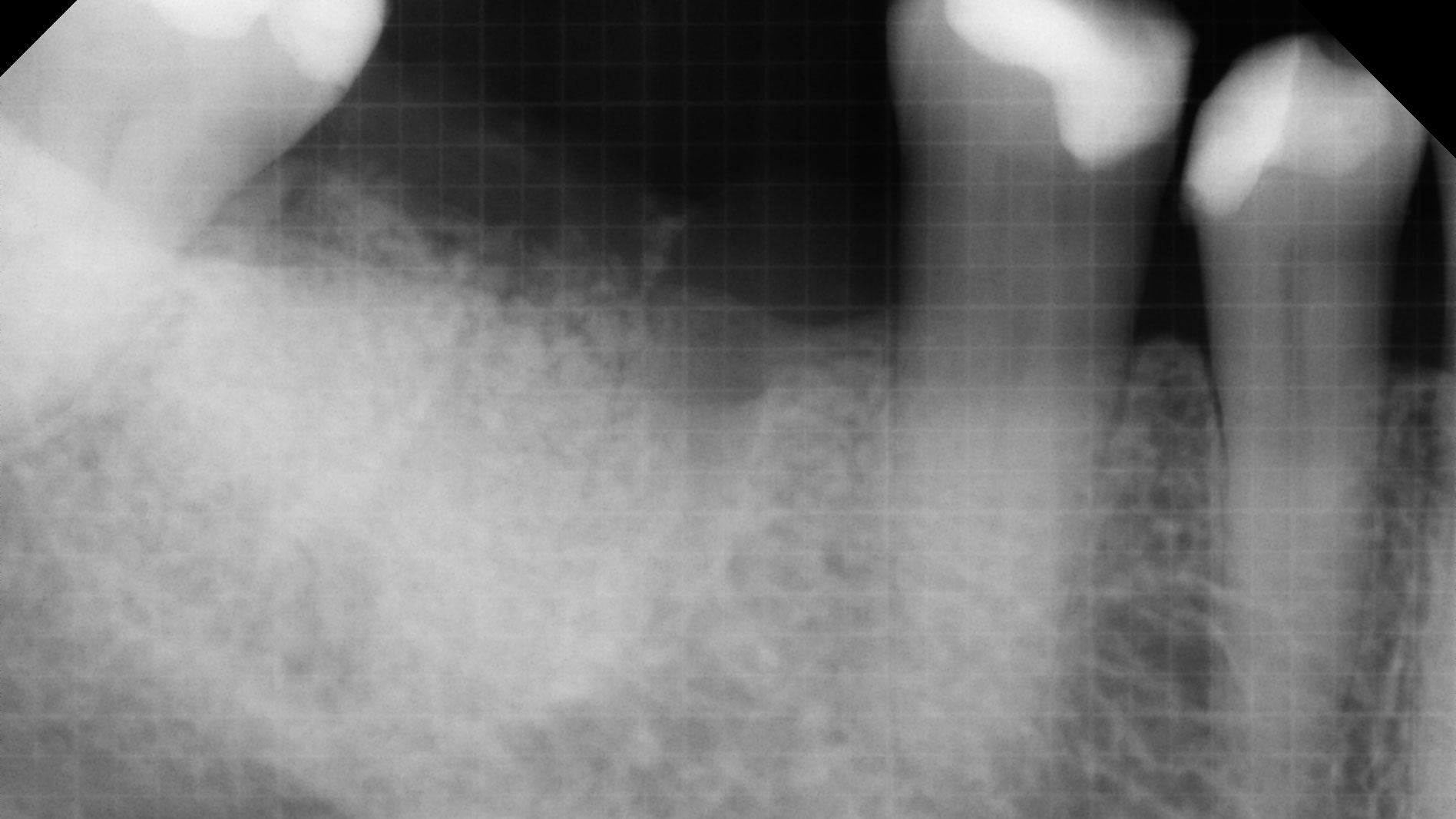
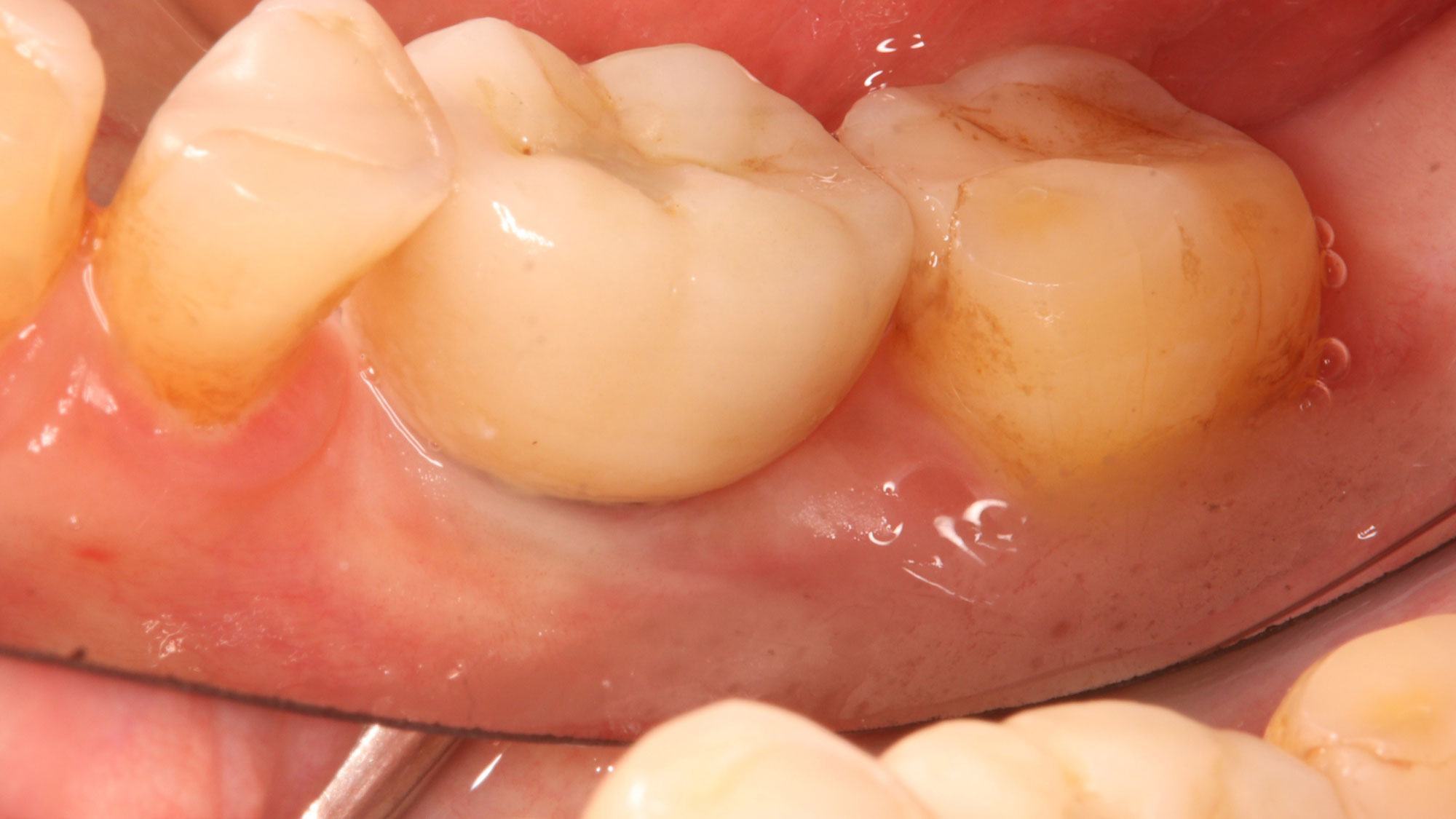
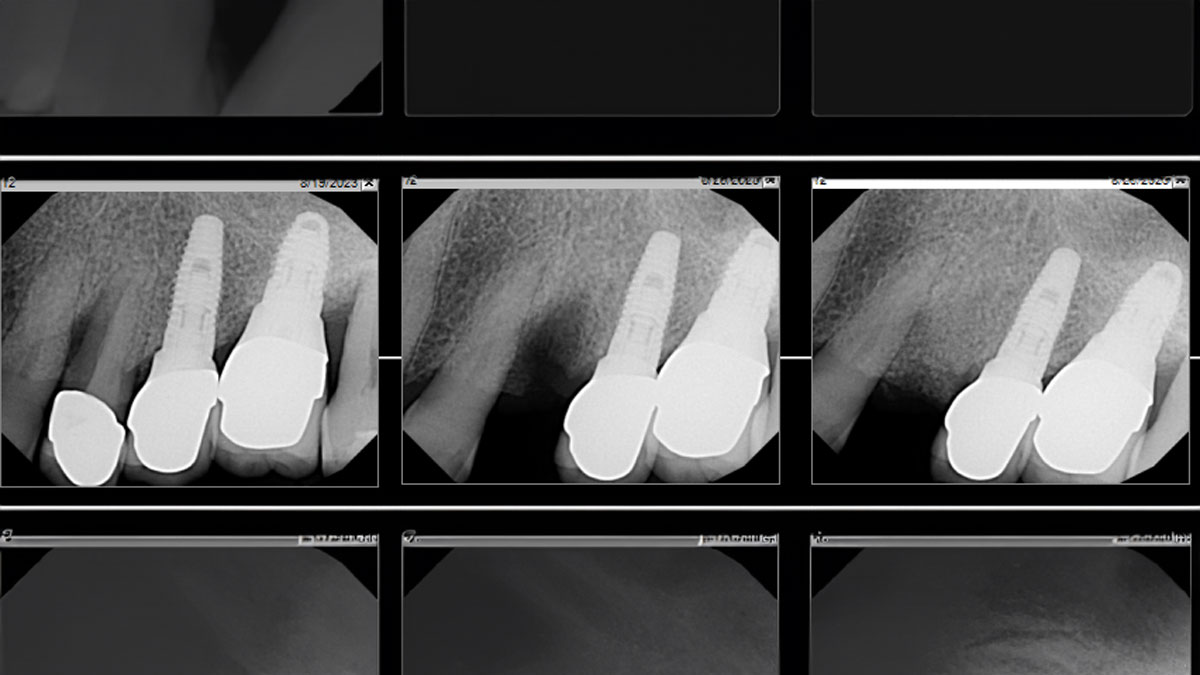
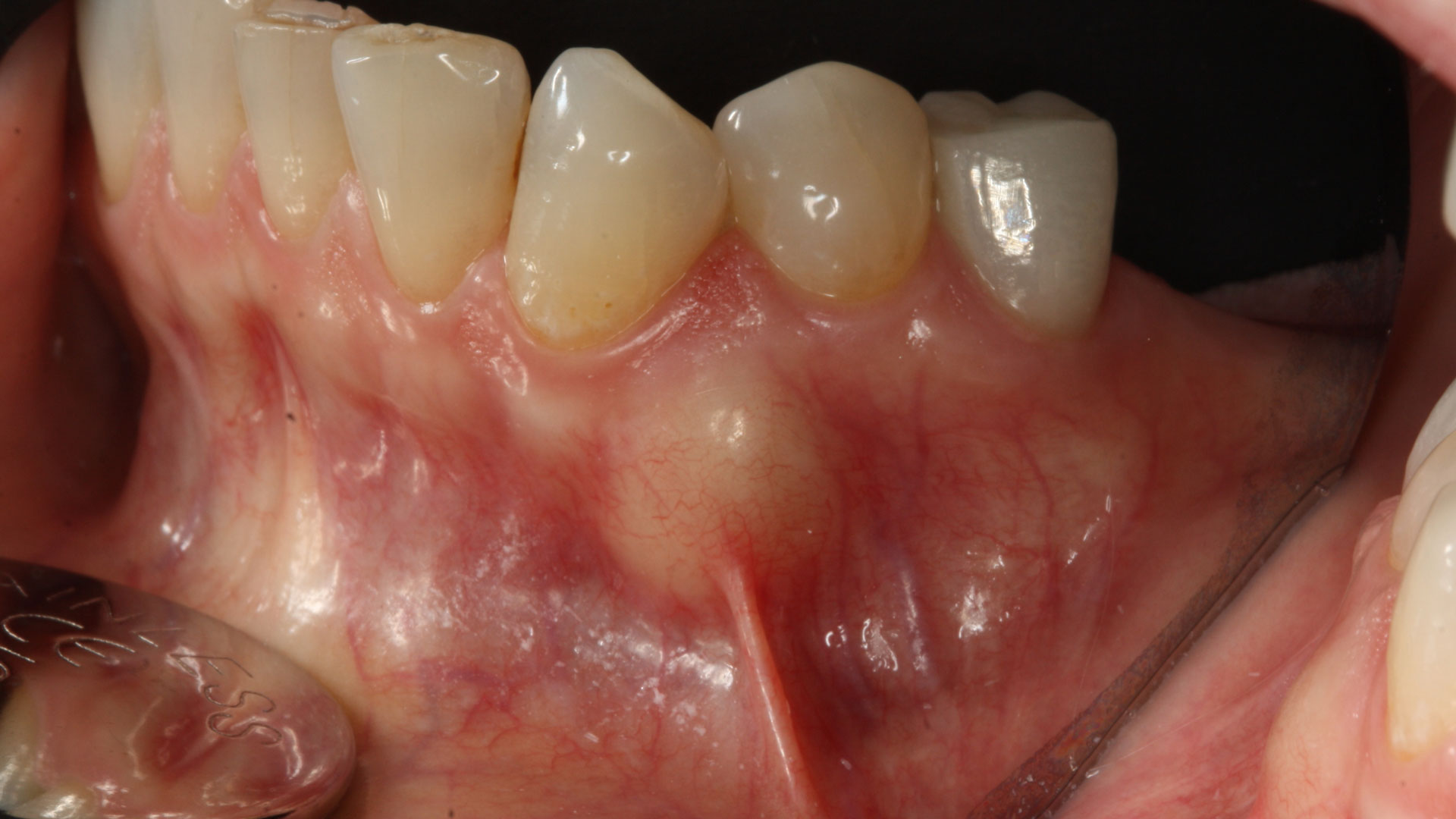
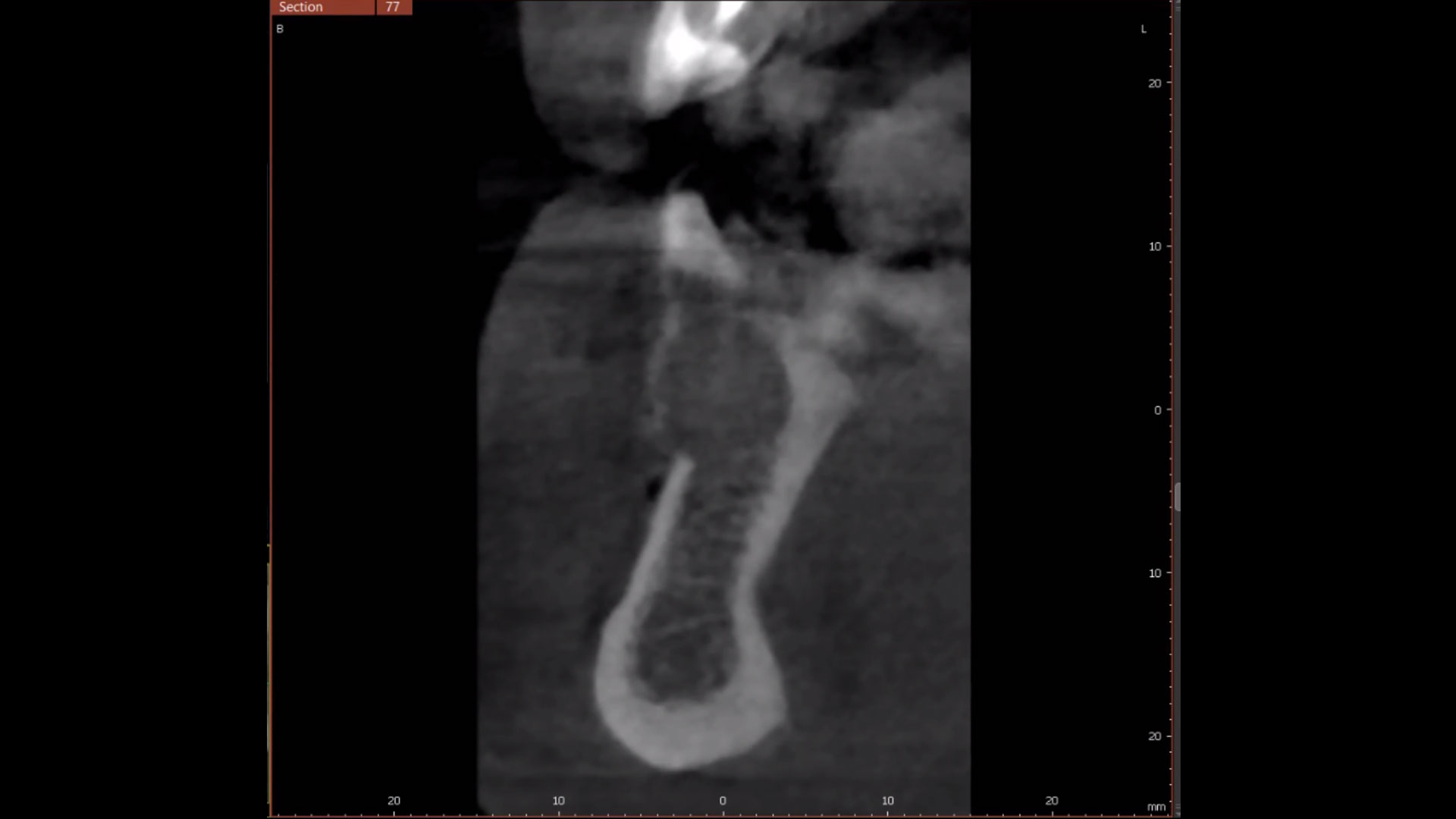
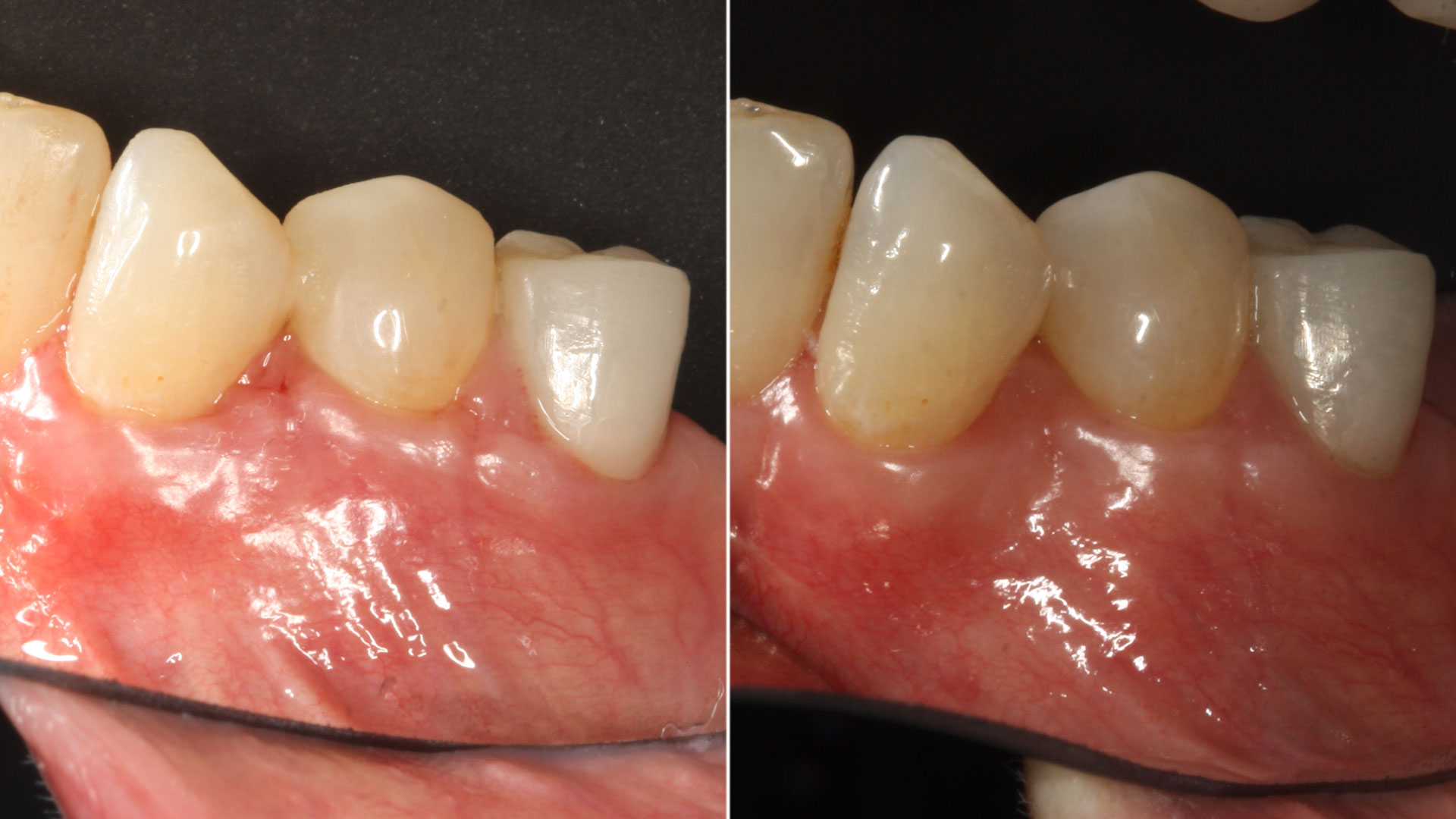
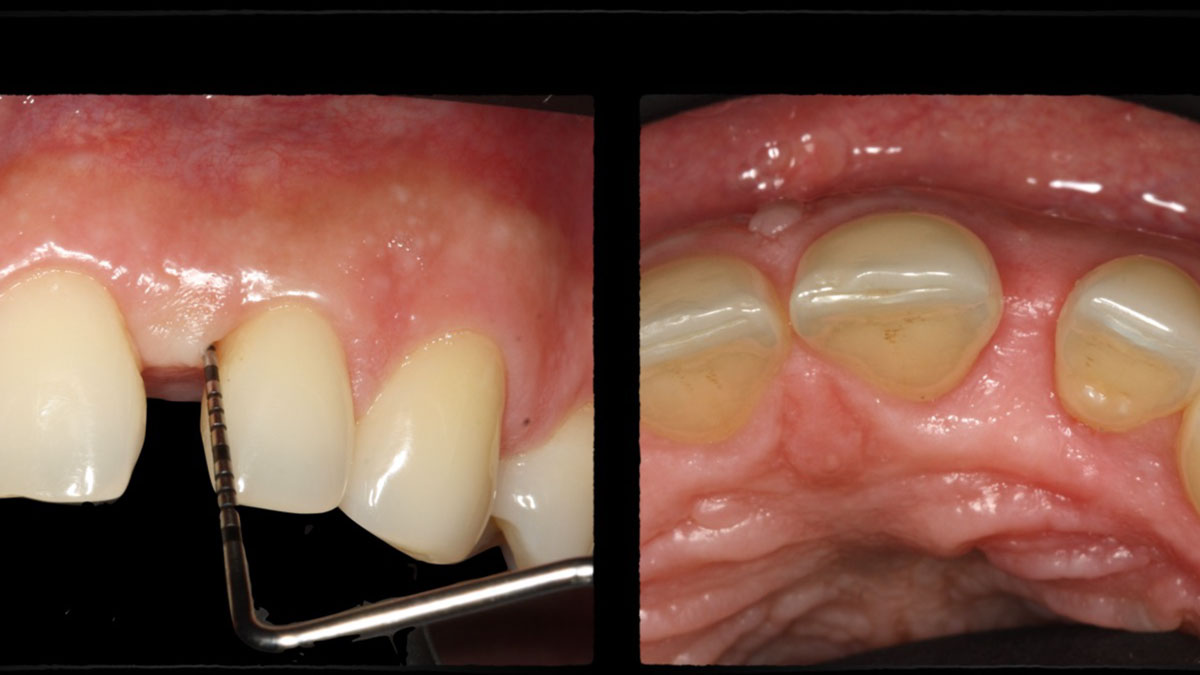
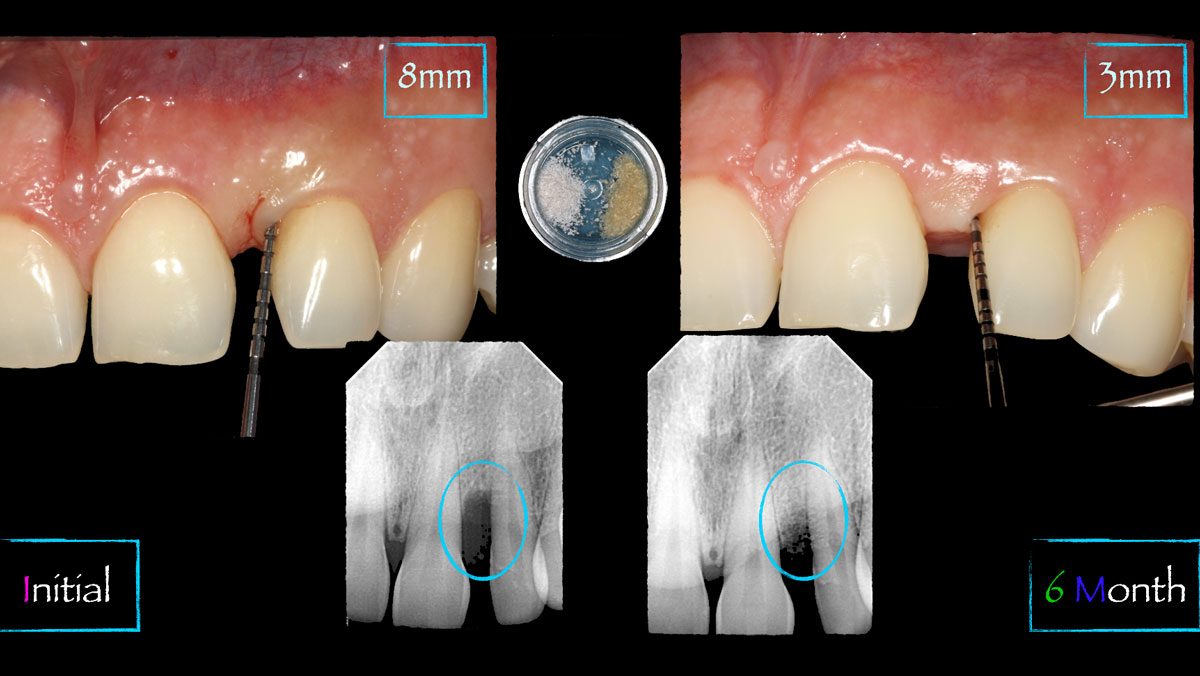
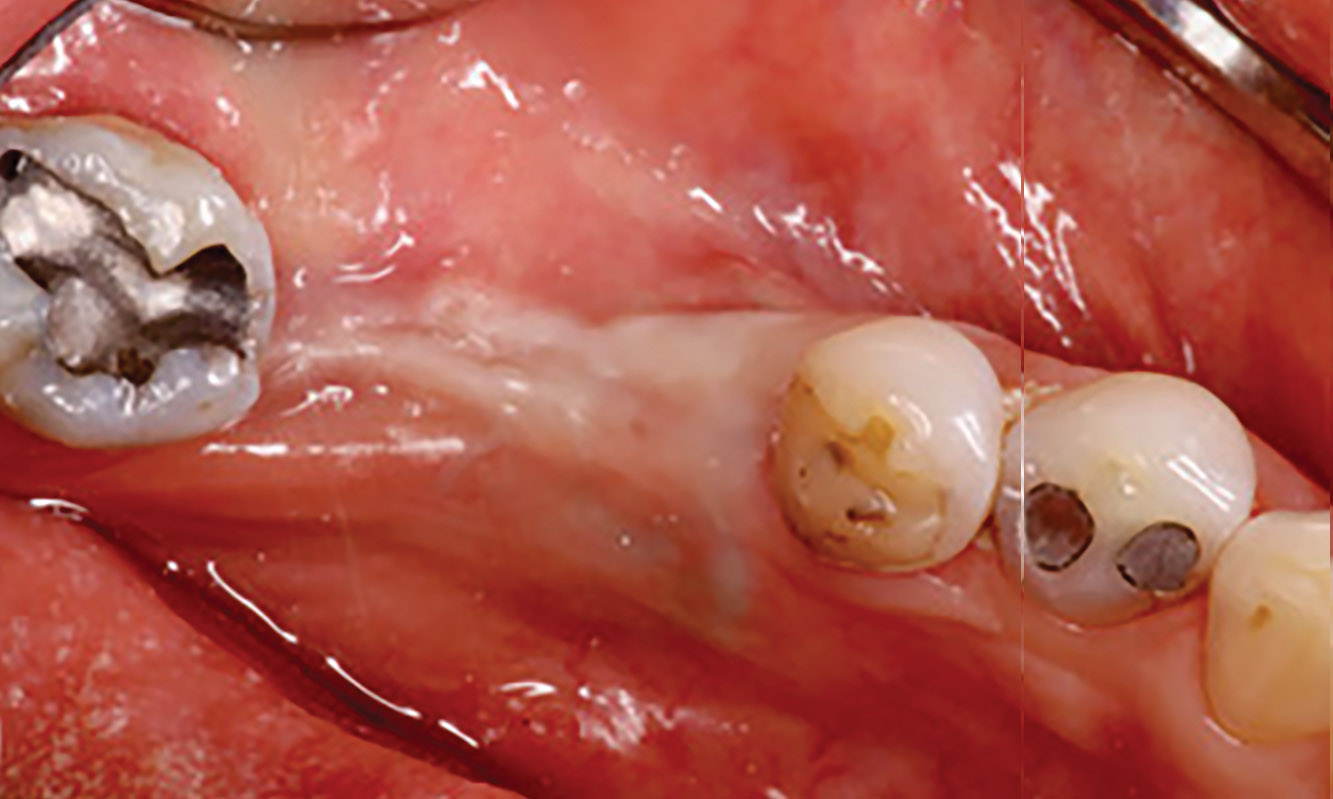
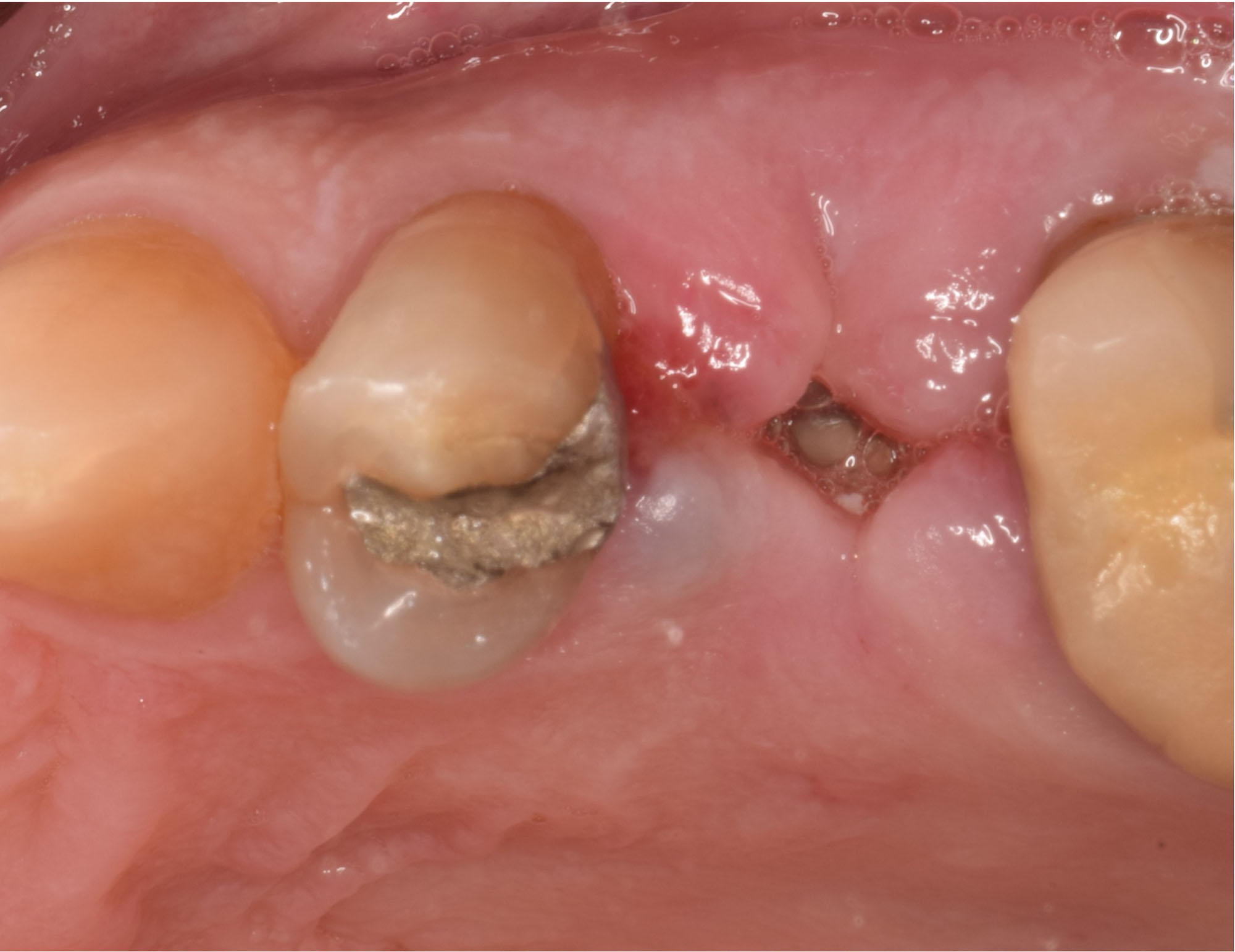
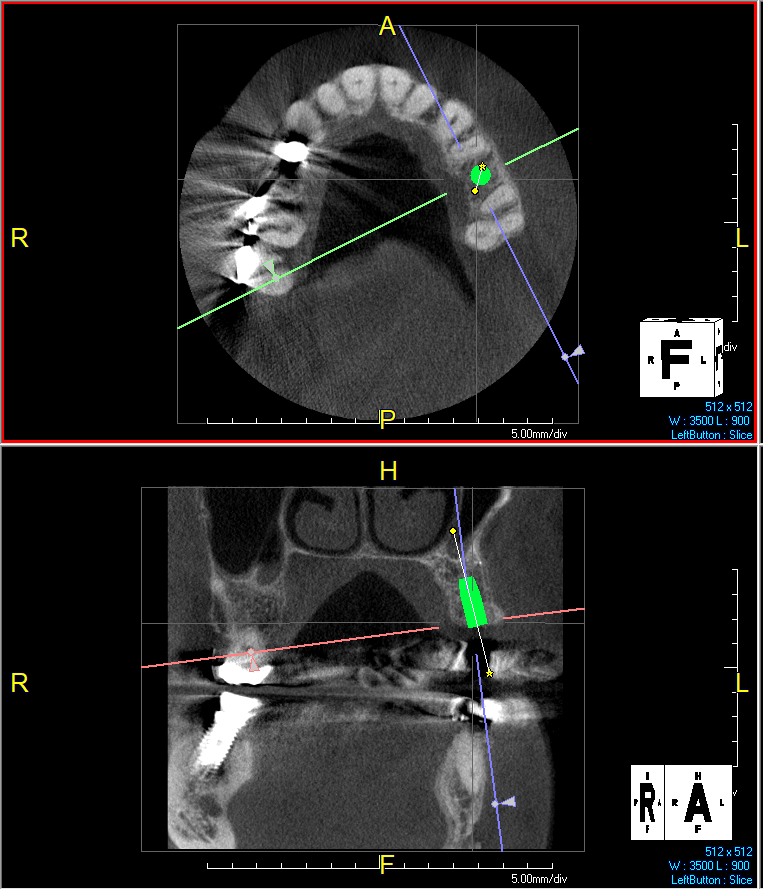
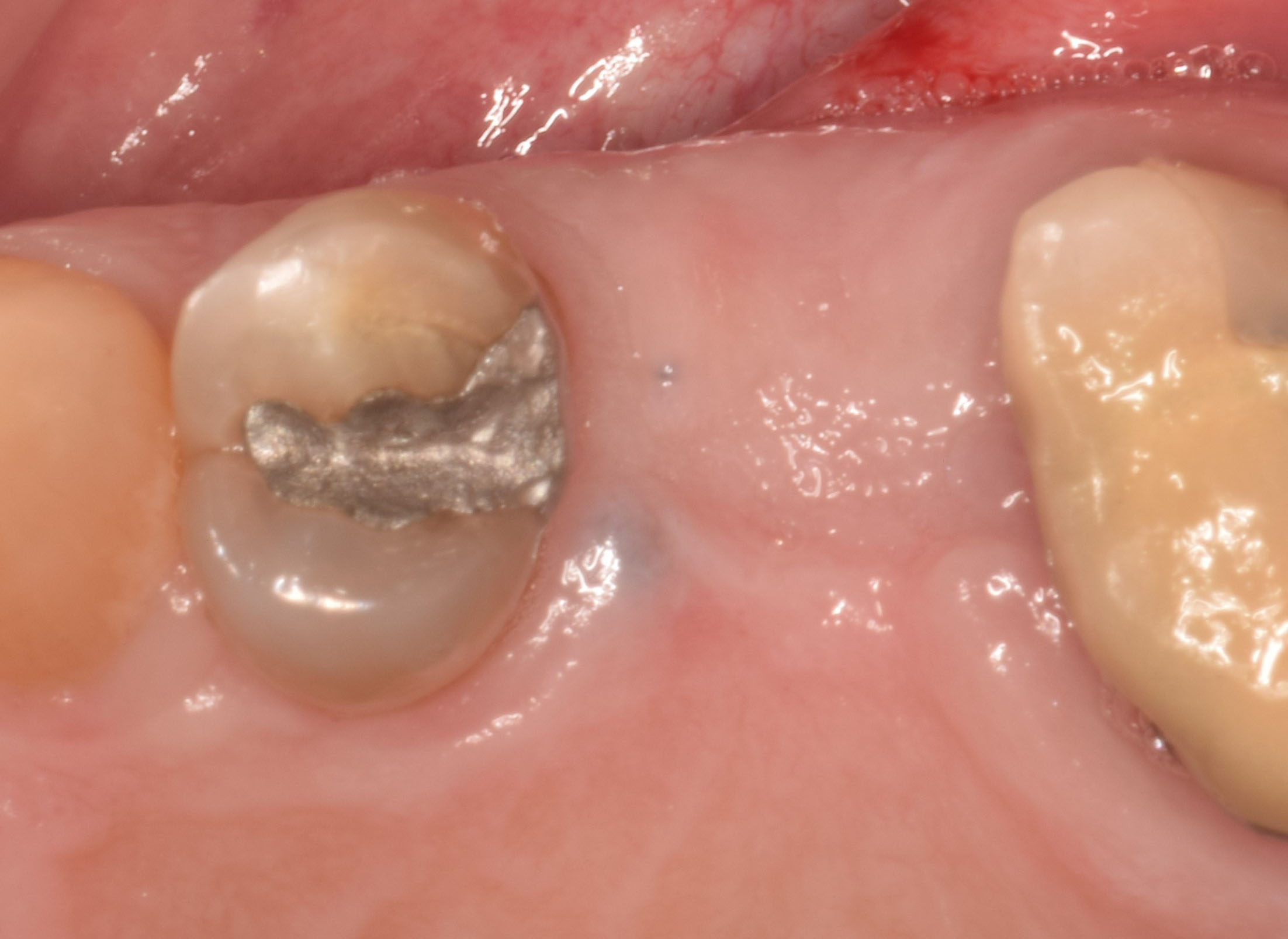
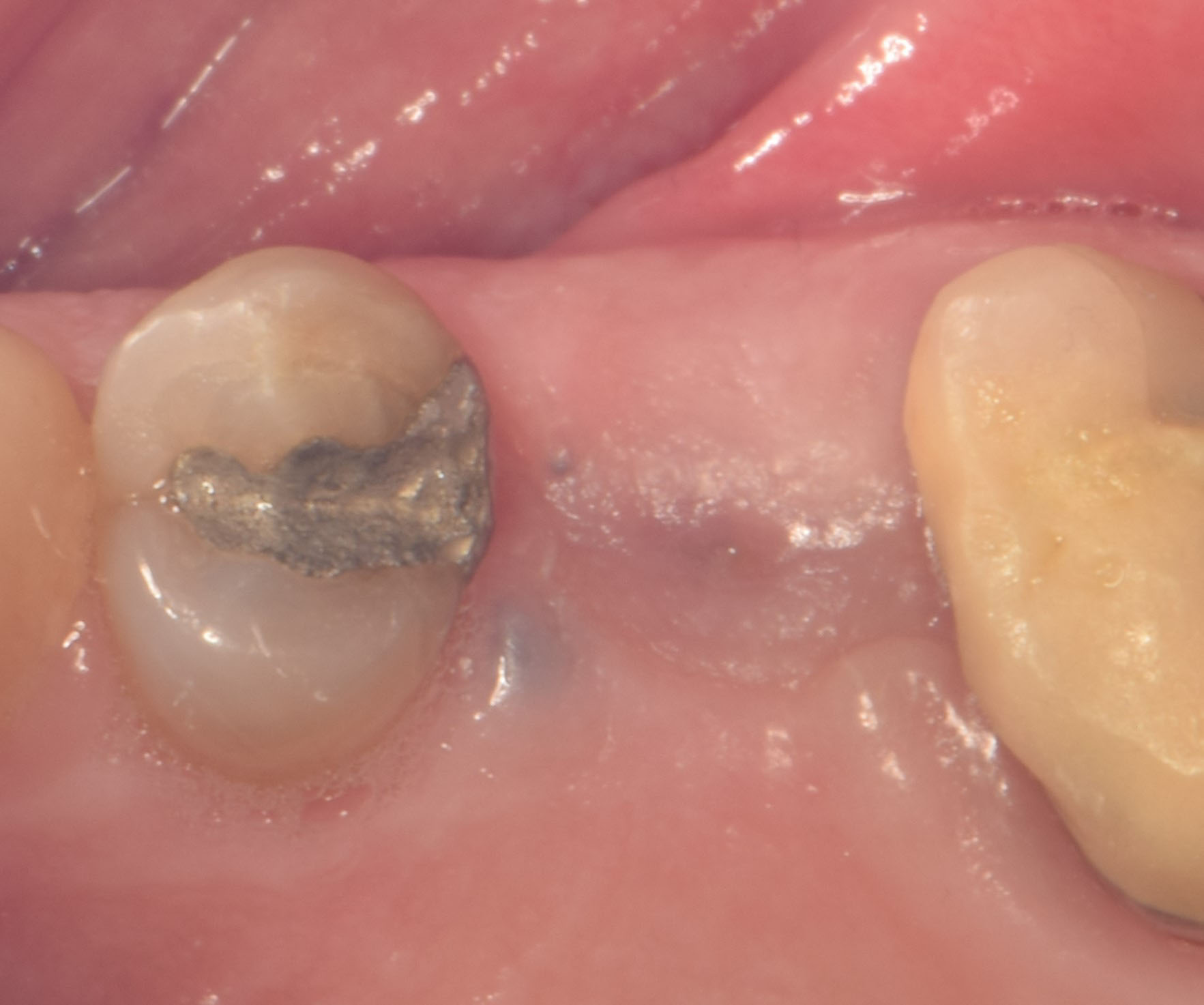
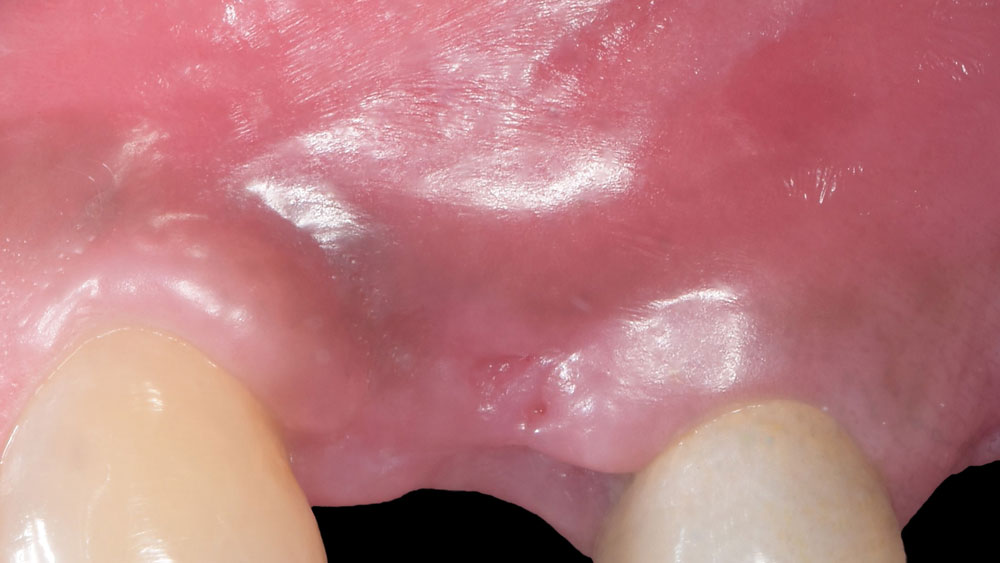
The 6-month post-operative CBCT evaluation demonstrated sufficient ridge width for restoratively driven implant placement, a result achieved through the utilization of vallos® and Geistlich Bio-Oss® bone graft materials.

Eswar Kandaswamy, BDS, MS
Dr. Eswar Kandaswamy, BDS MS, is an Assistant Professor at Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center, School of Dentistry. He earned his Dental Degree from Sri Ramachandra University, India, and practiced general dentistry for two years. He then completed his specialty training in Periodontics and a Master of Science at The Ohio State University.

Amber Kreko, DDS
Dr. Amber Kreko, DDS is a third-year Periodontics resident at Louisiana State University School of Dentistry, soon to earn her Master of Science. With a foundation in dental hygiene and six years of clinical practice in Southeast Louisiana,she returned to LSU for her DDS. Her comprehensive background enriches her approach to periodontal care. Upon graduation, she will transition to private practice.