BIOBRIEF
Lateral and Vertical Bone Regeneration with Simultaneous Soft Tissue Augmentation

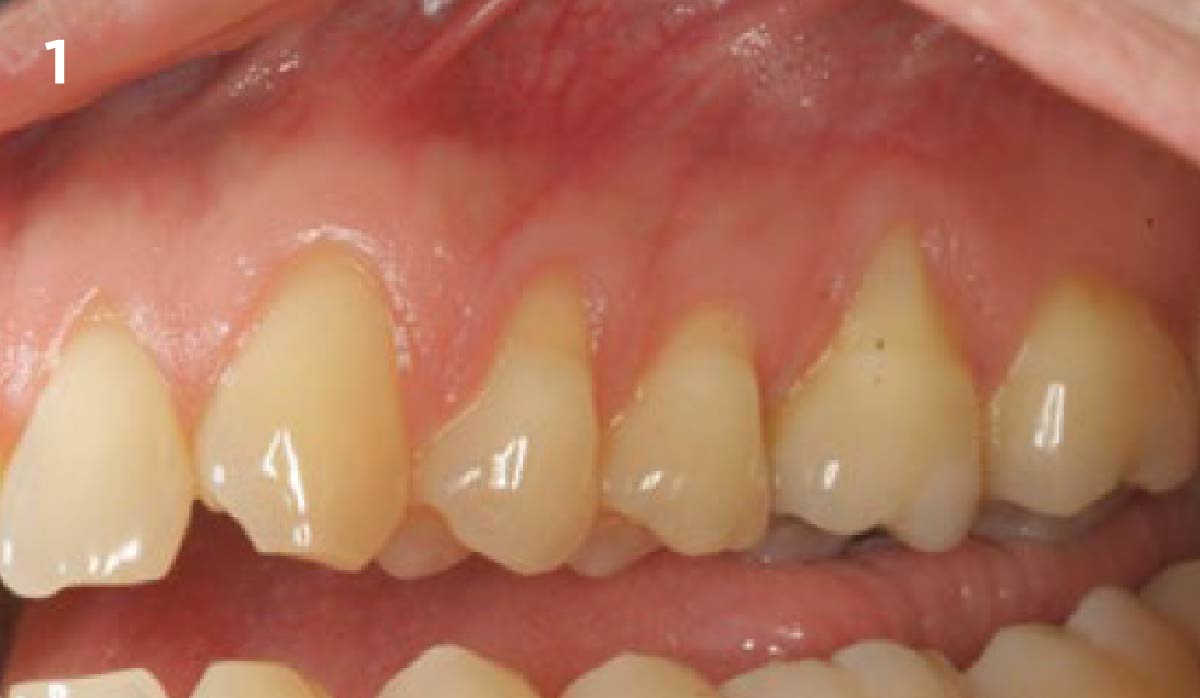
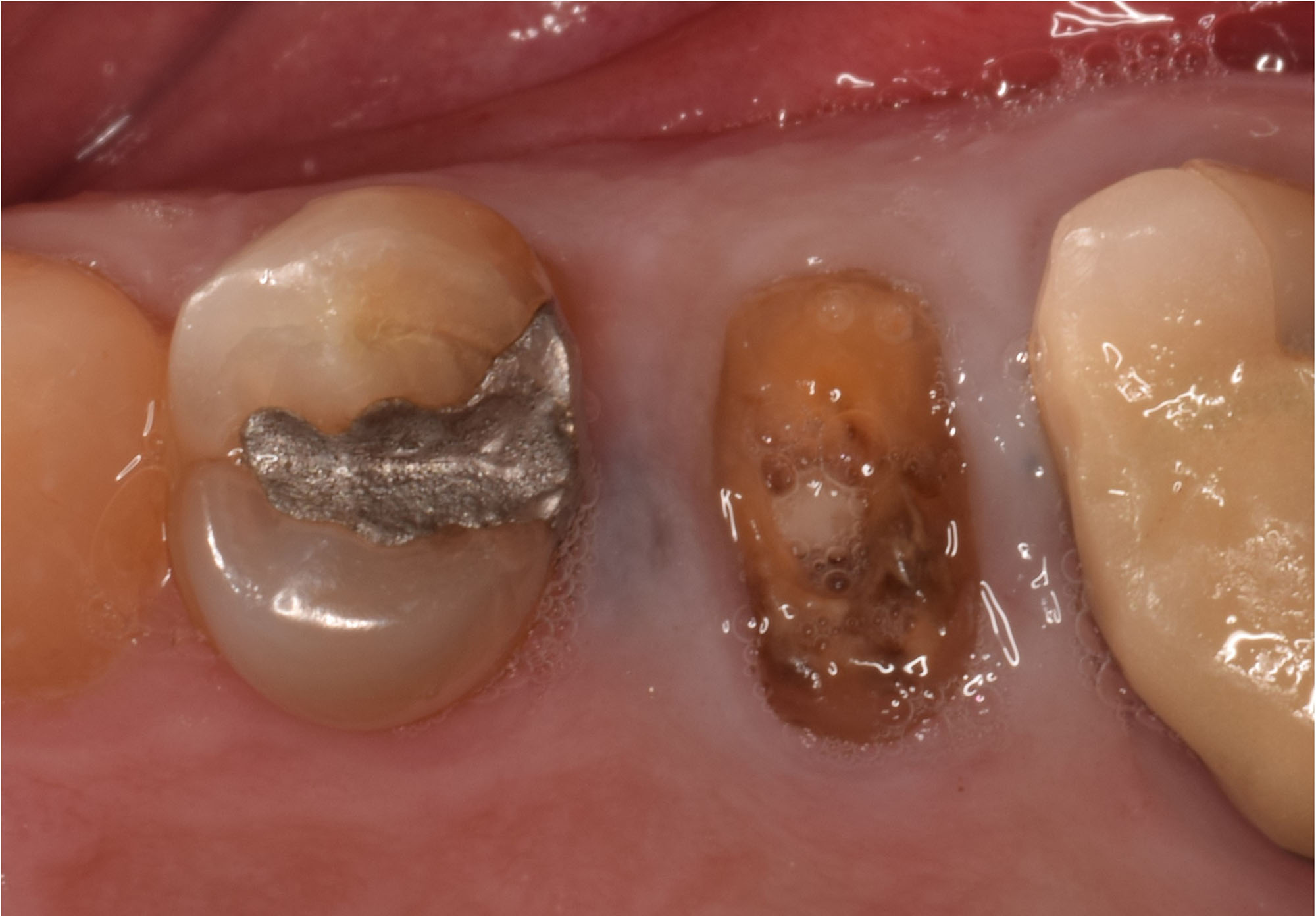
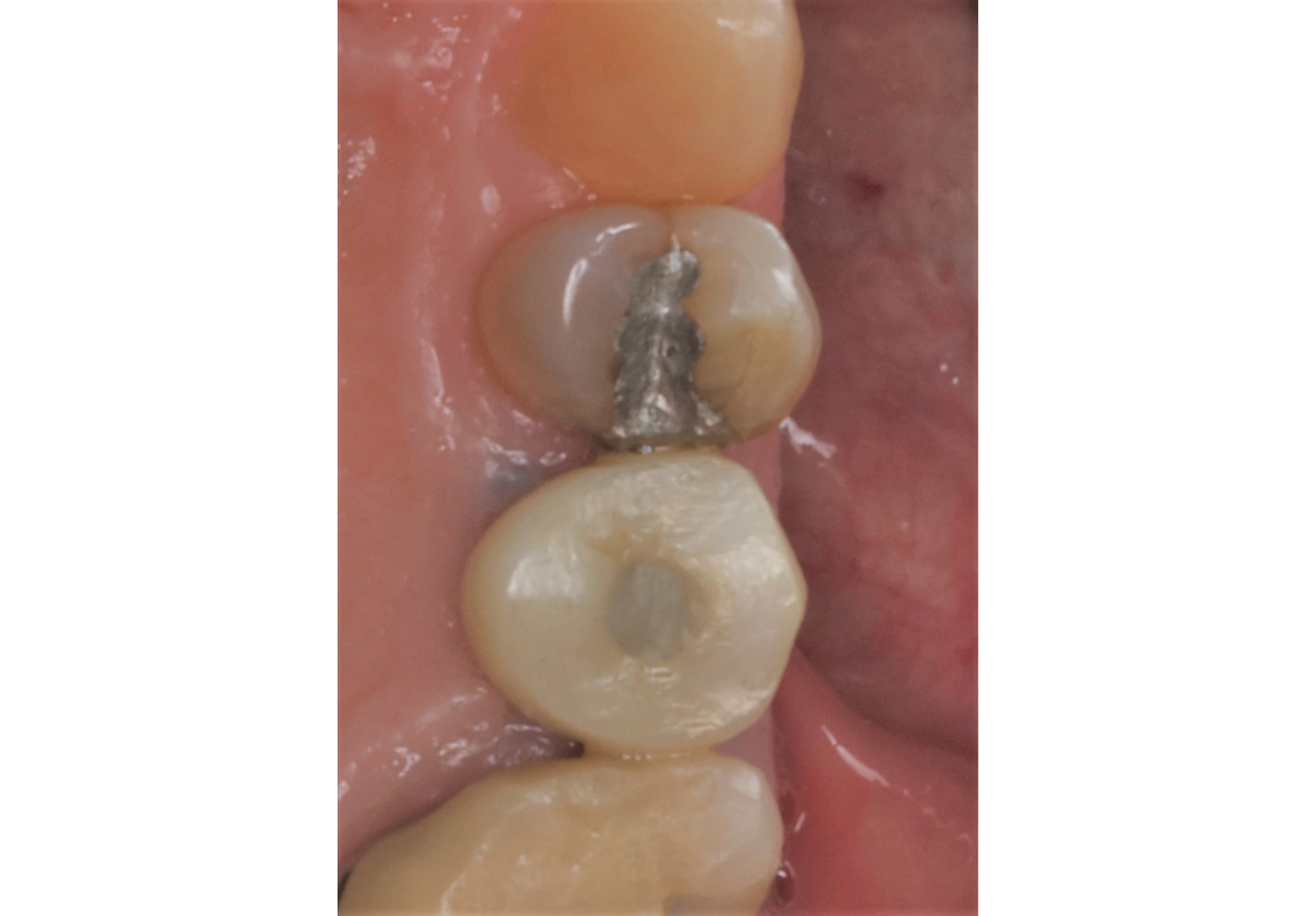
THE SITUATION
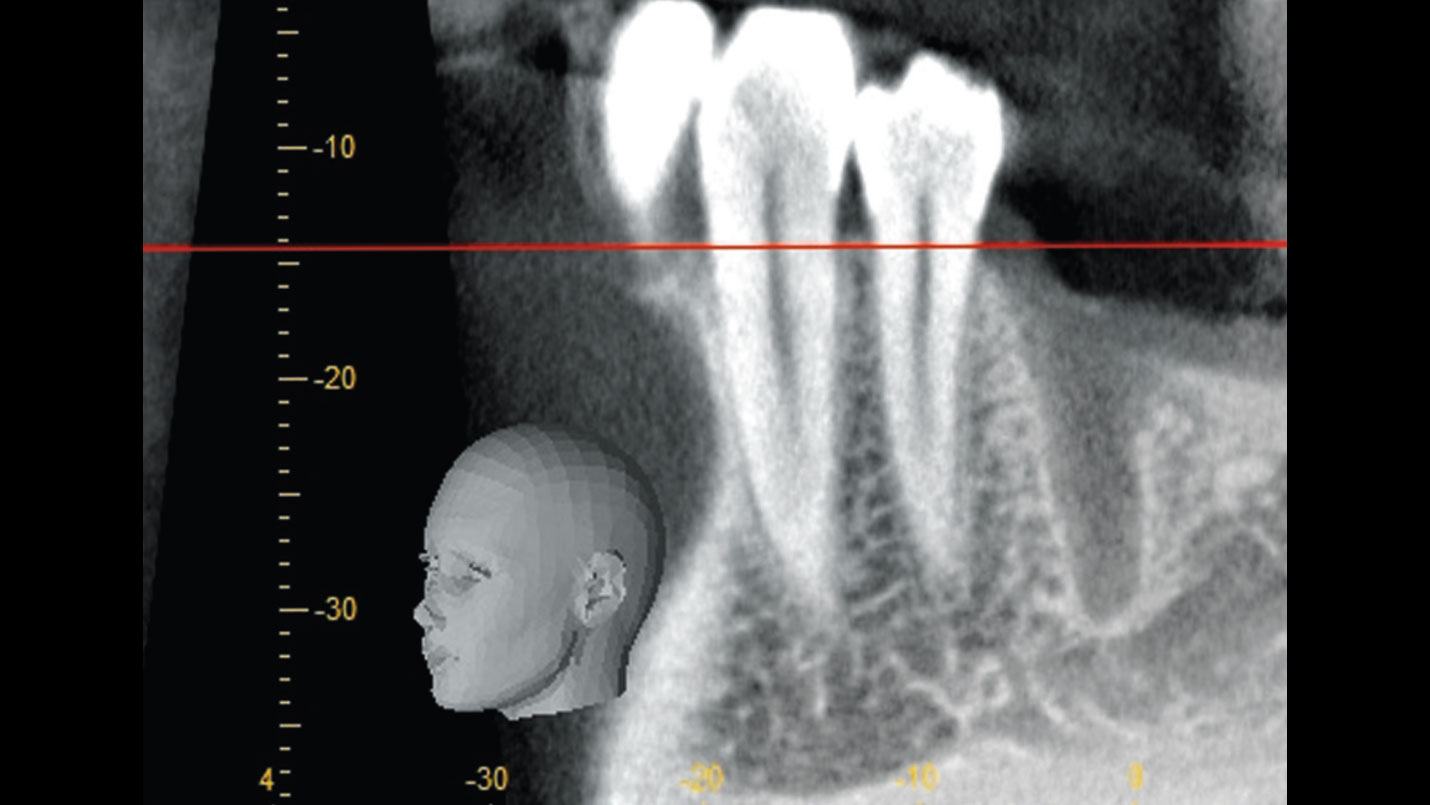
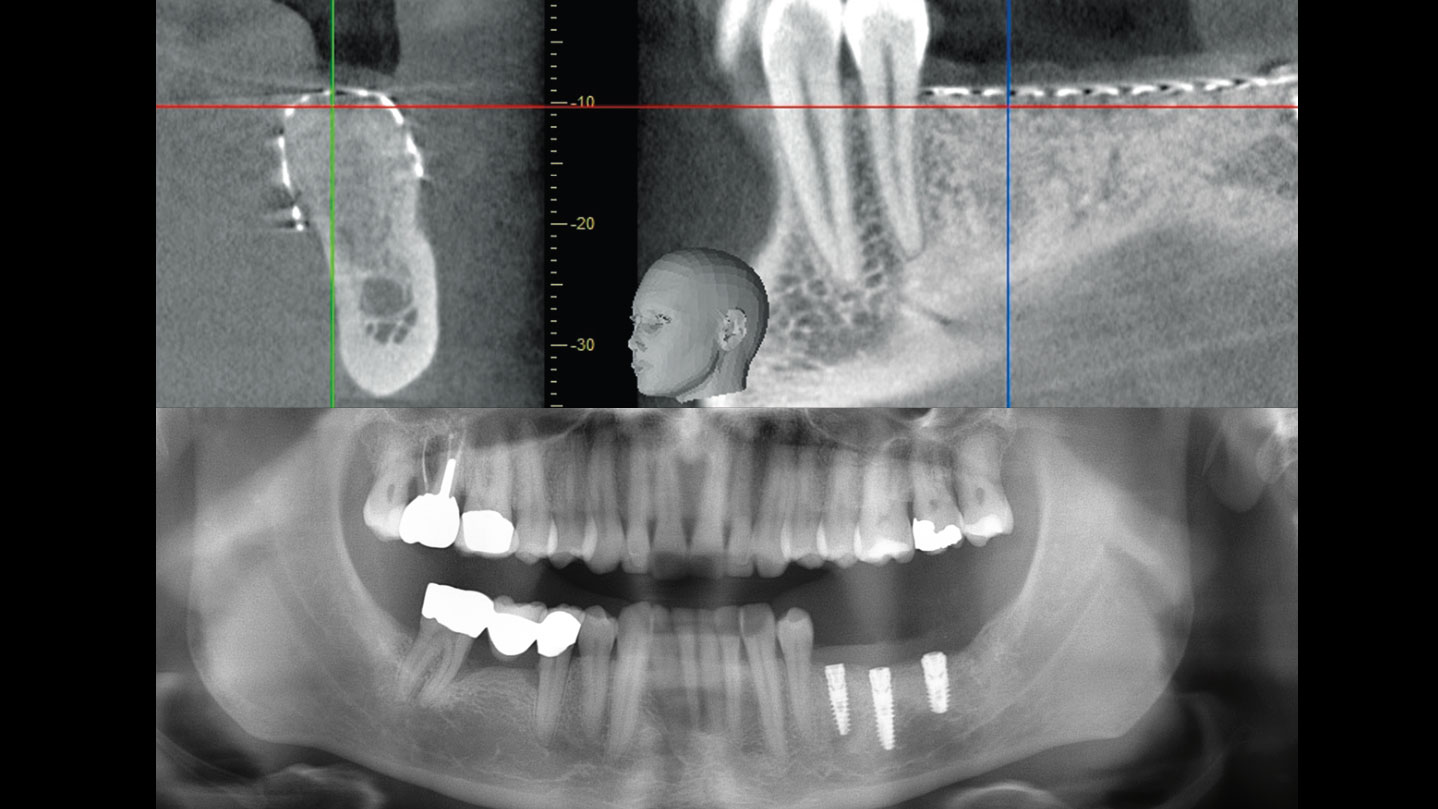
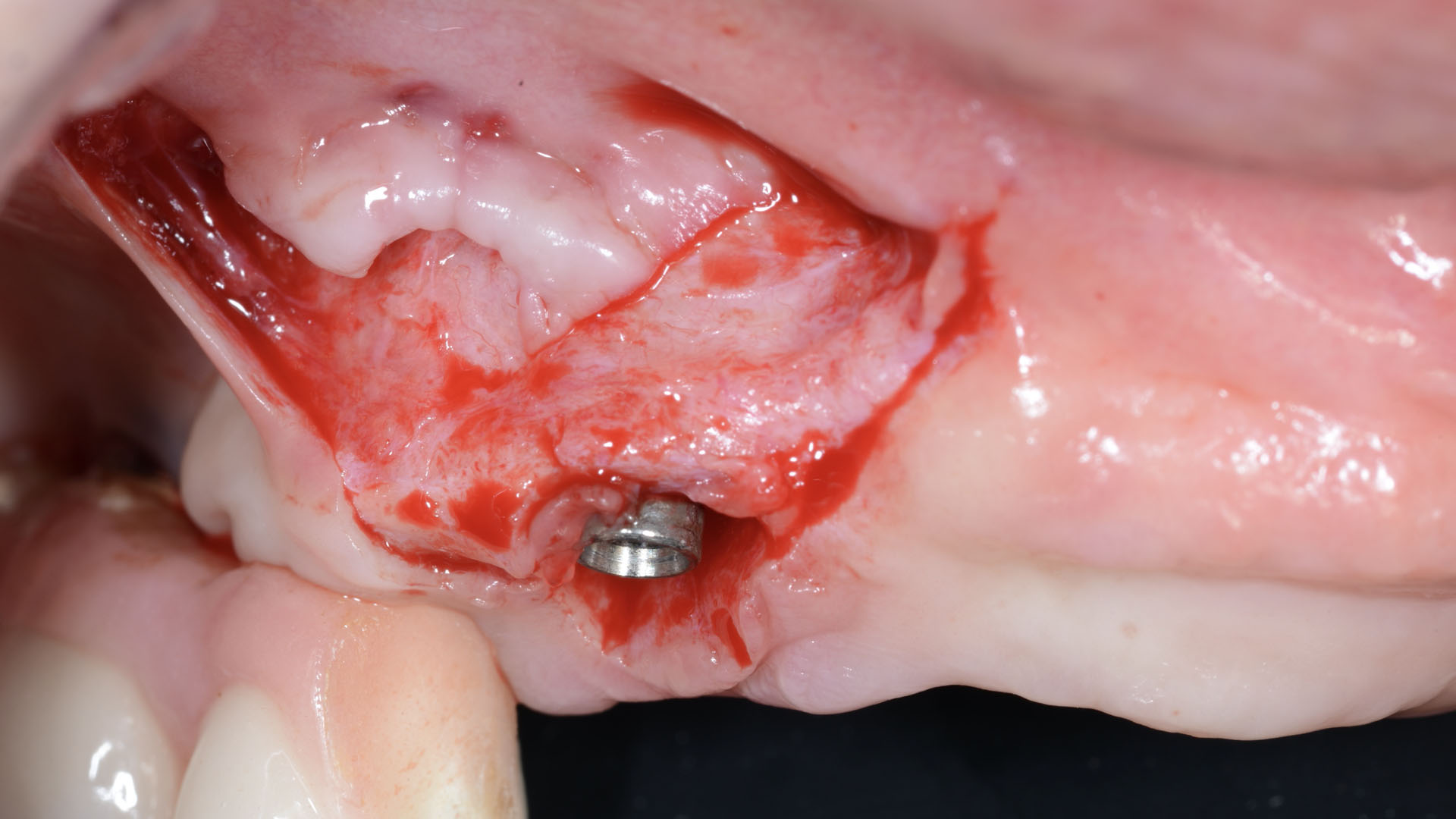
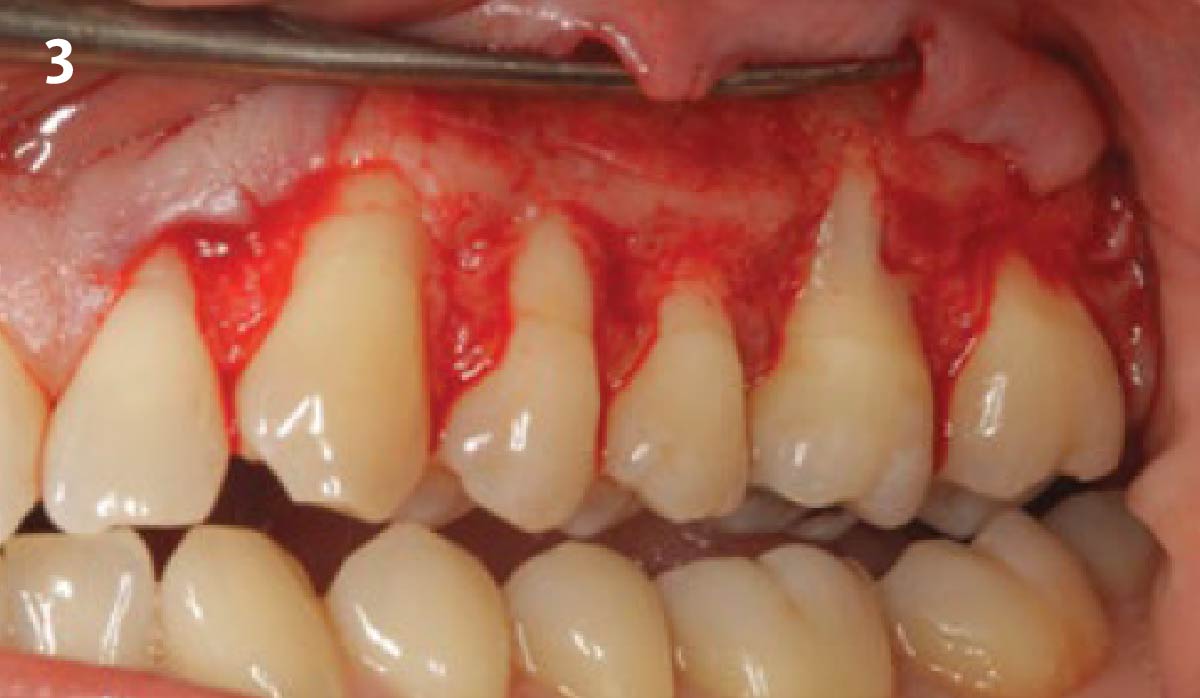
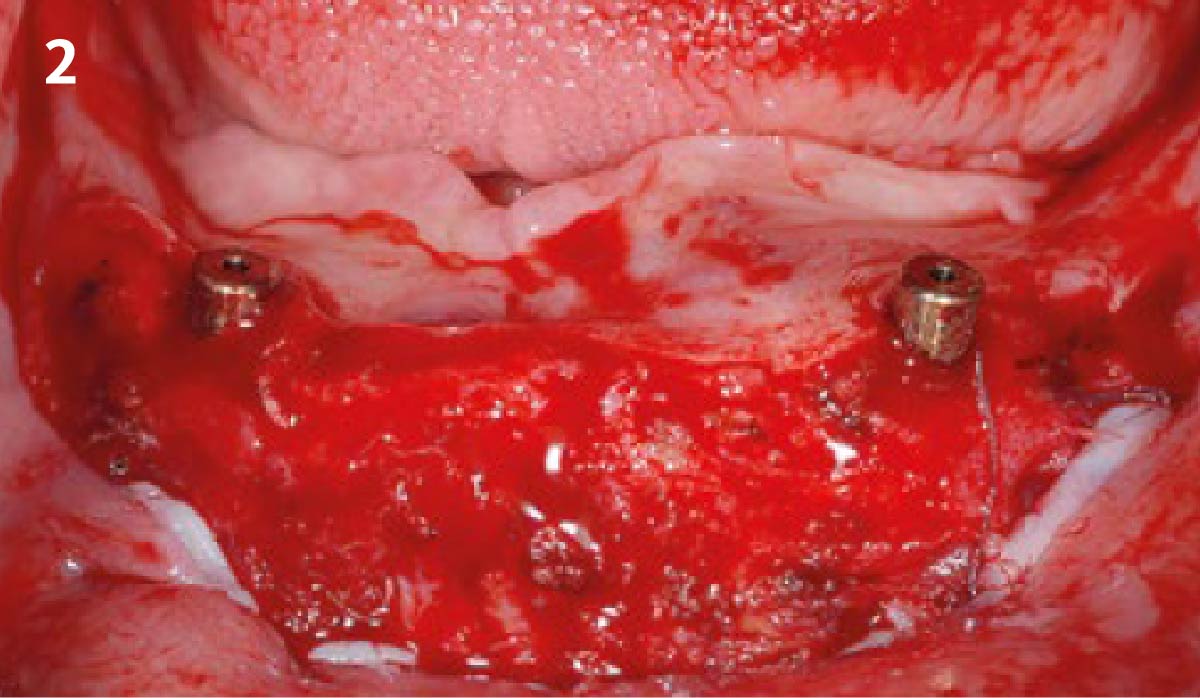
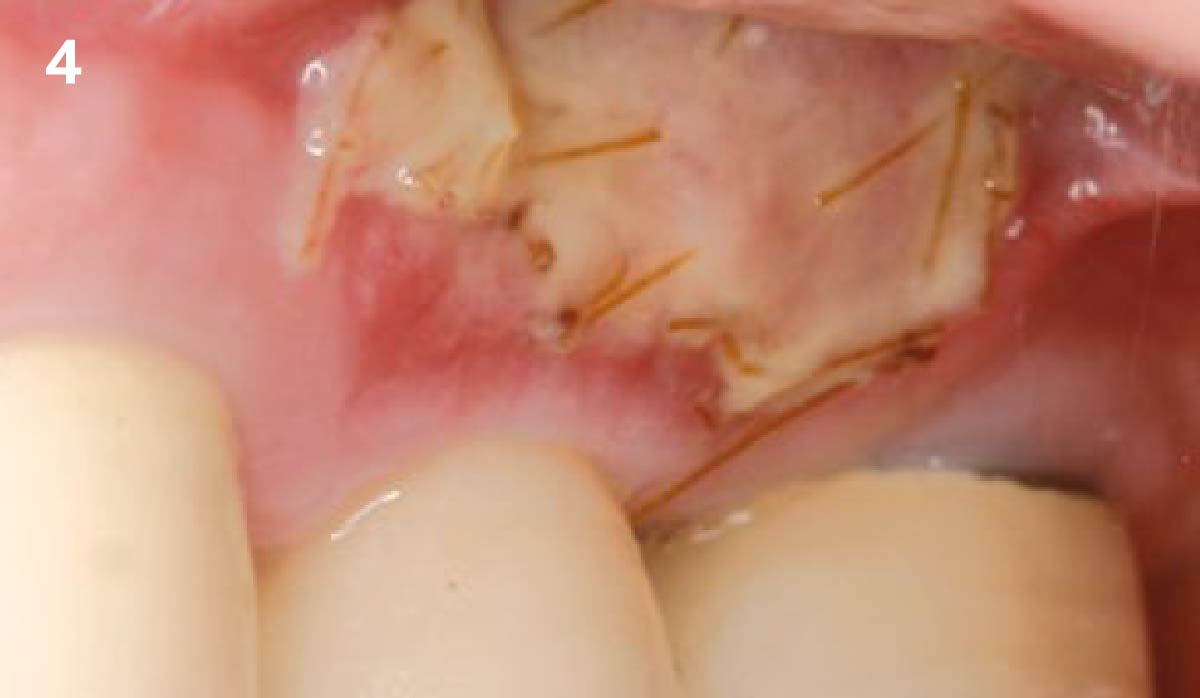
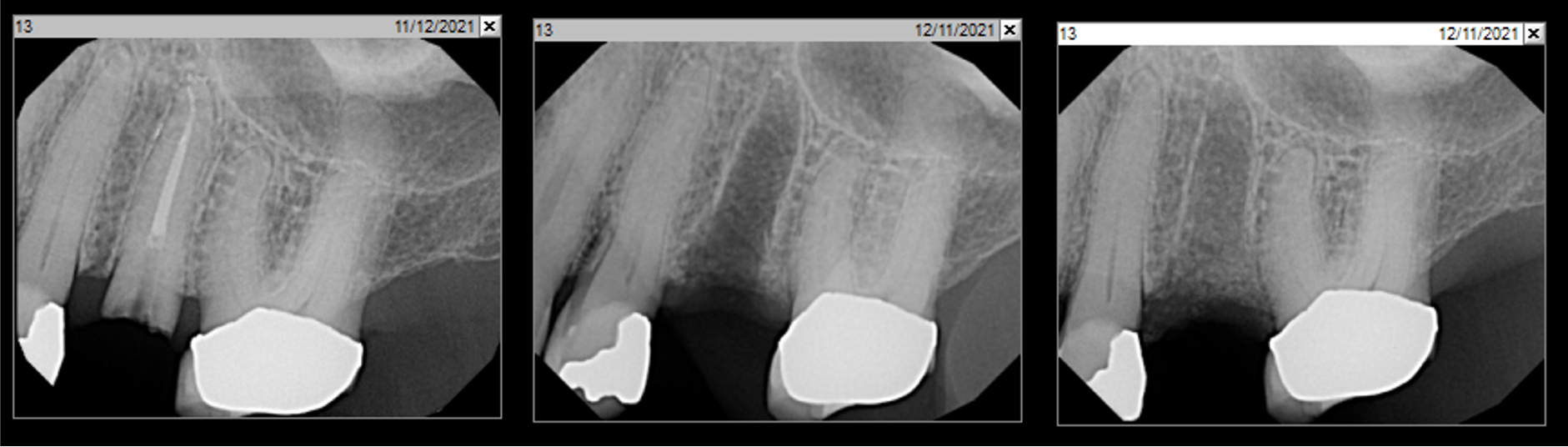
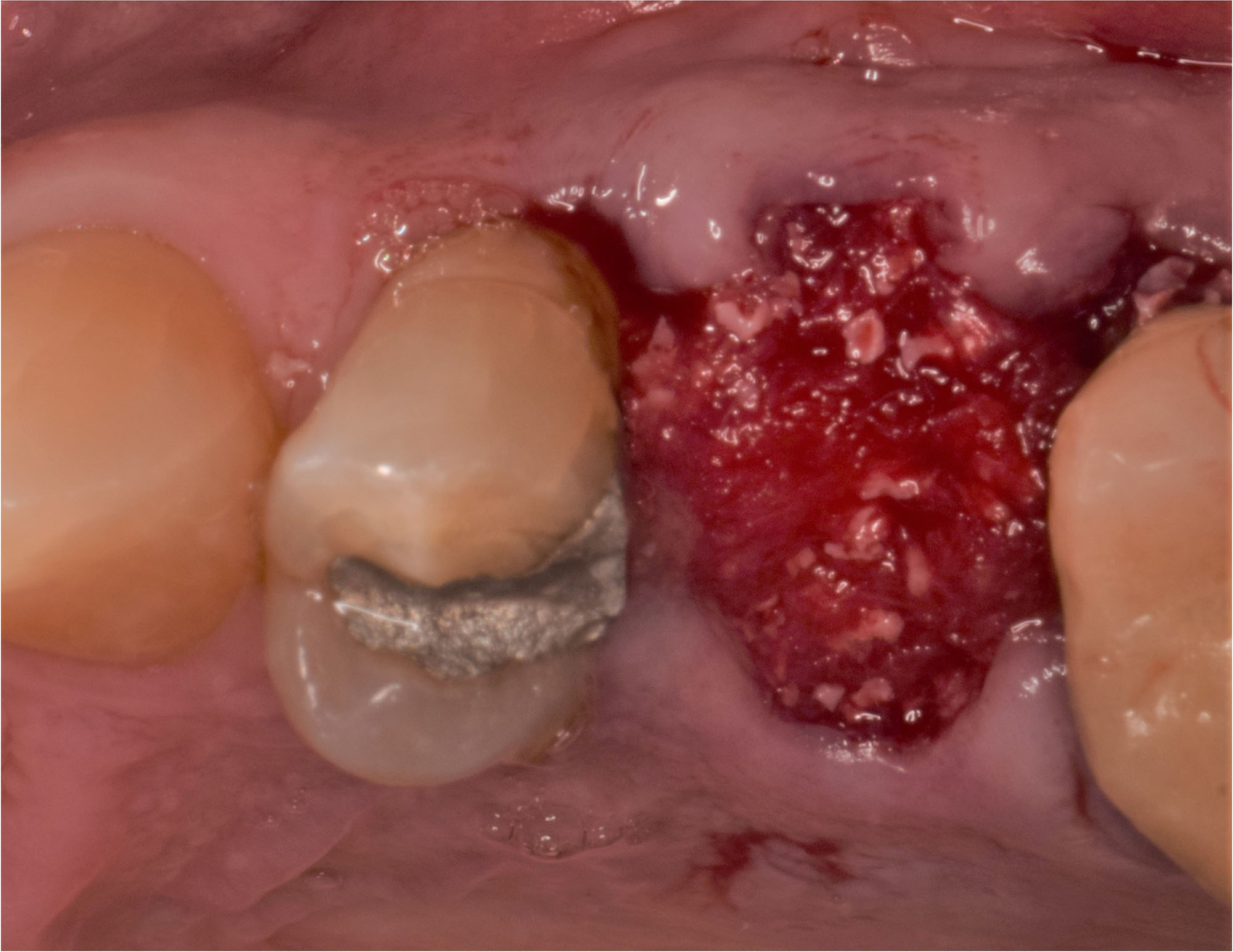
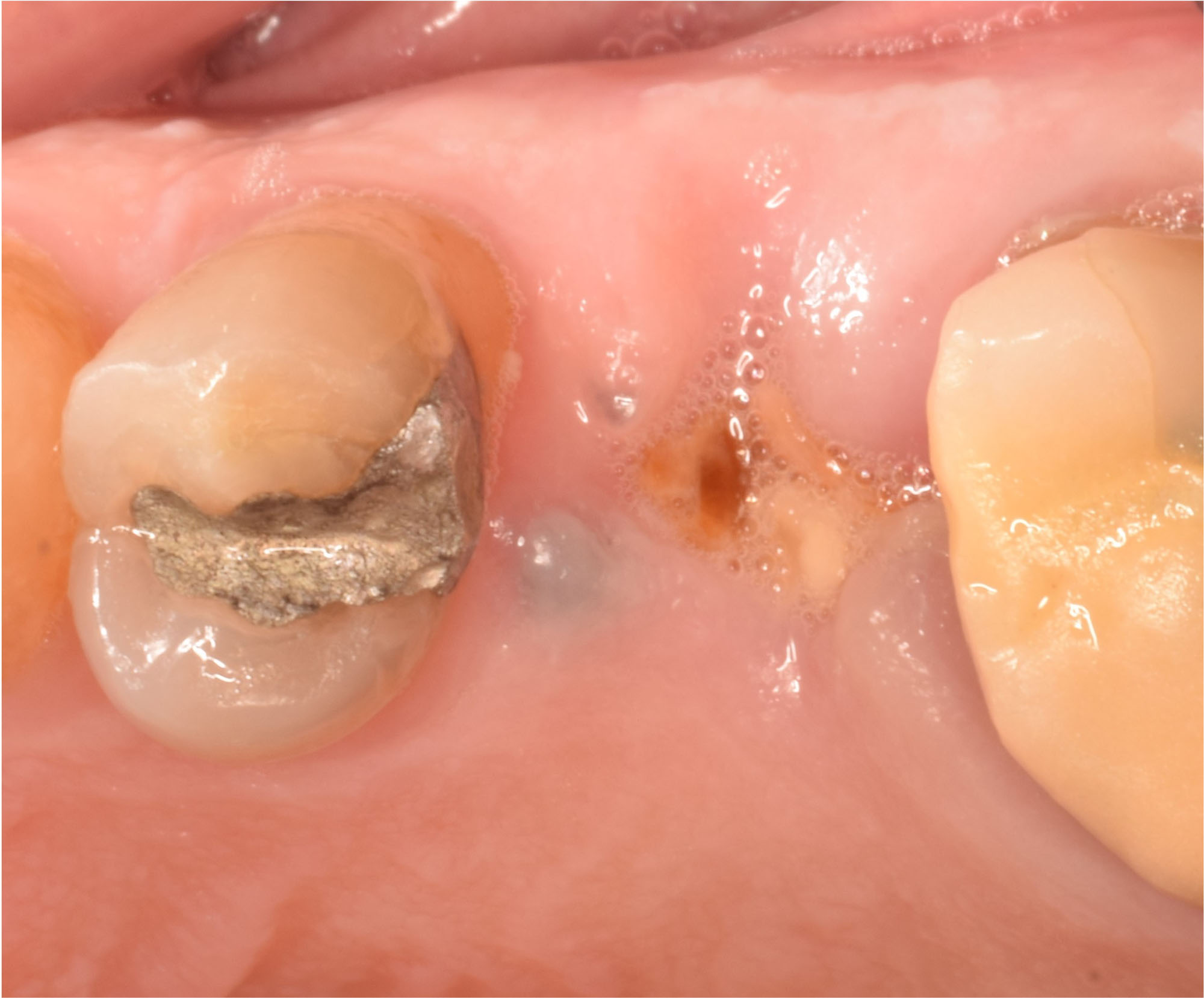
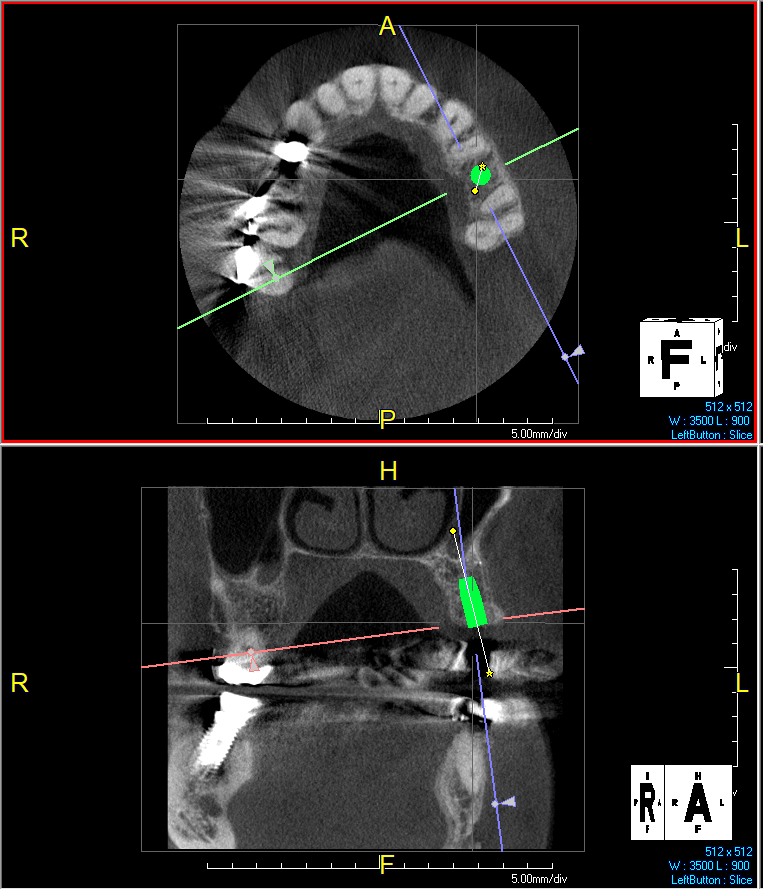
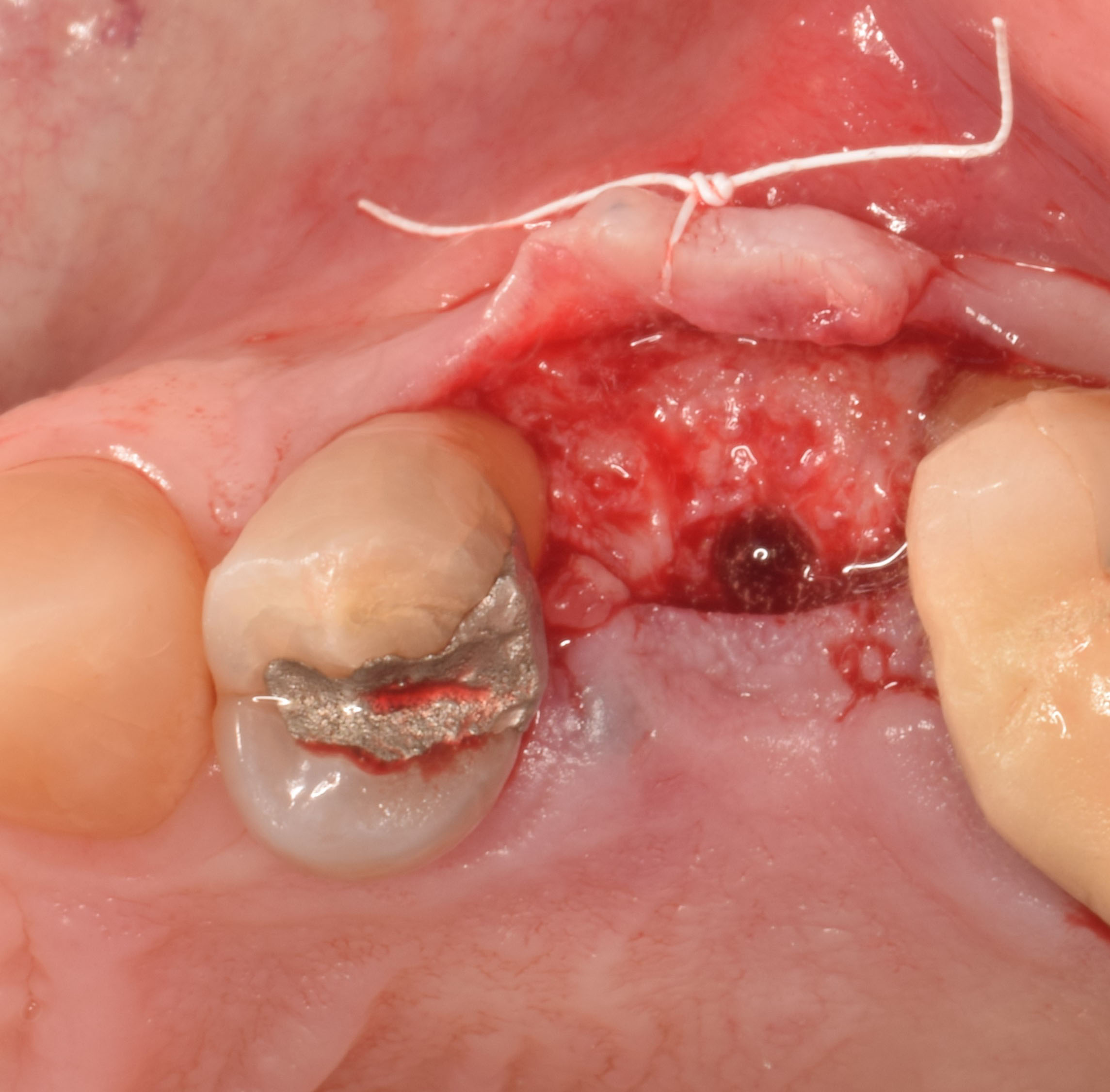
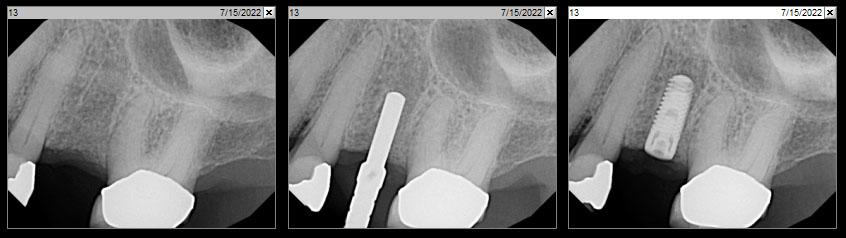
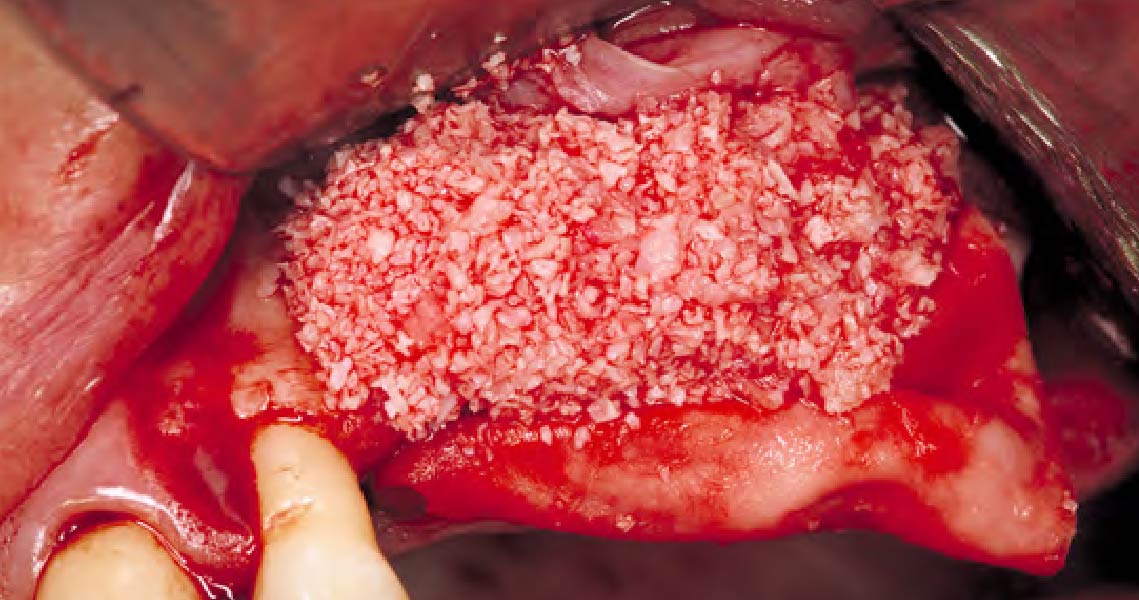
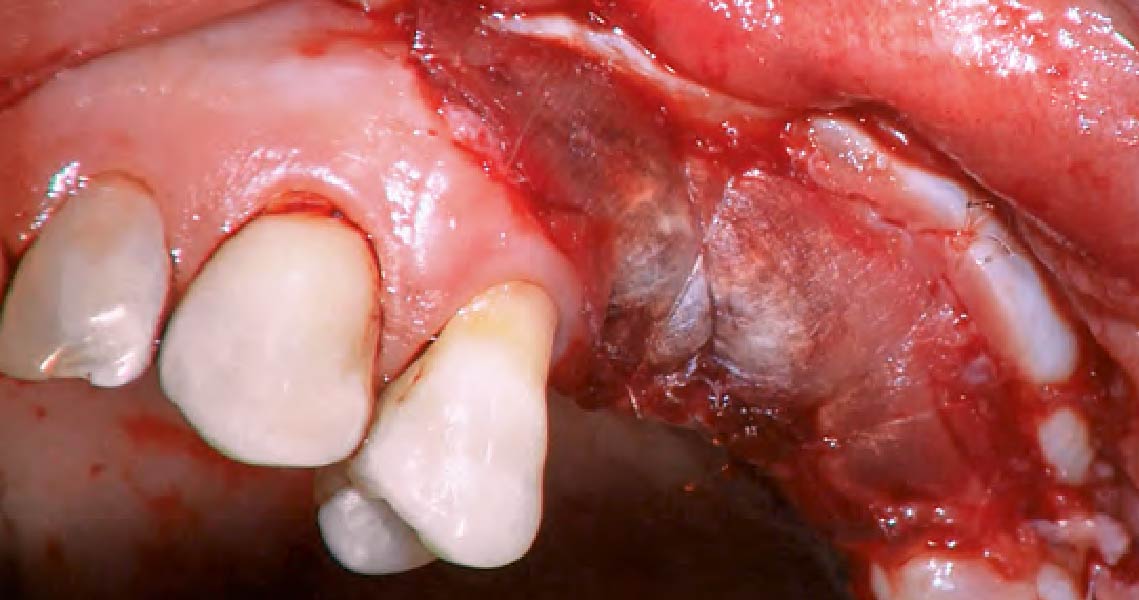
After extraction of the periodontally damaged tooth #20 the preoperative Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) imaging shows reduced vertical bone volume in the area of tooth #s 18 – 20. A lateral and vertical bone regeneration was necessary.
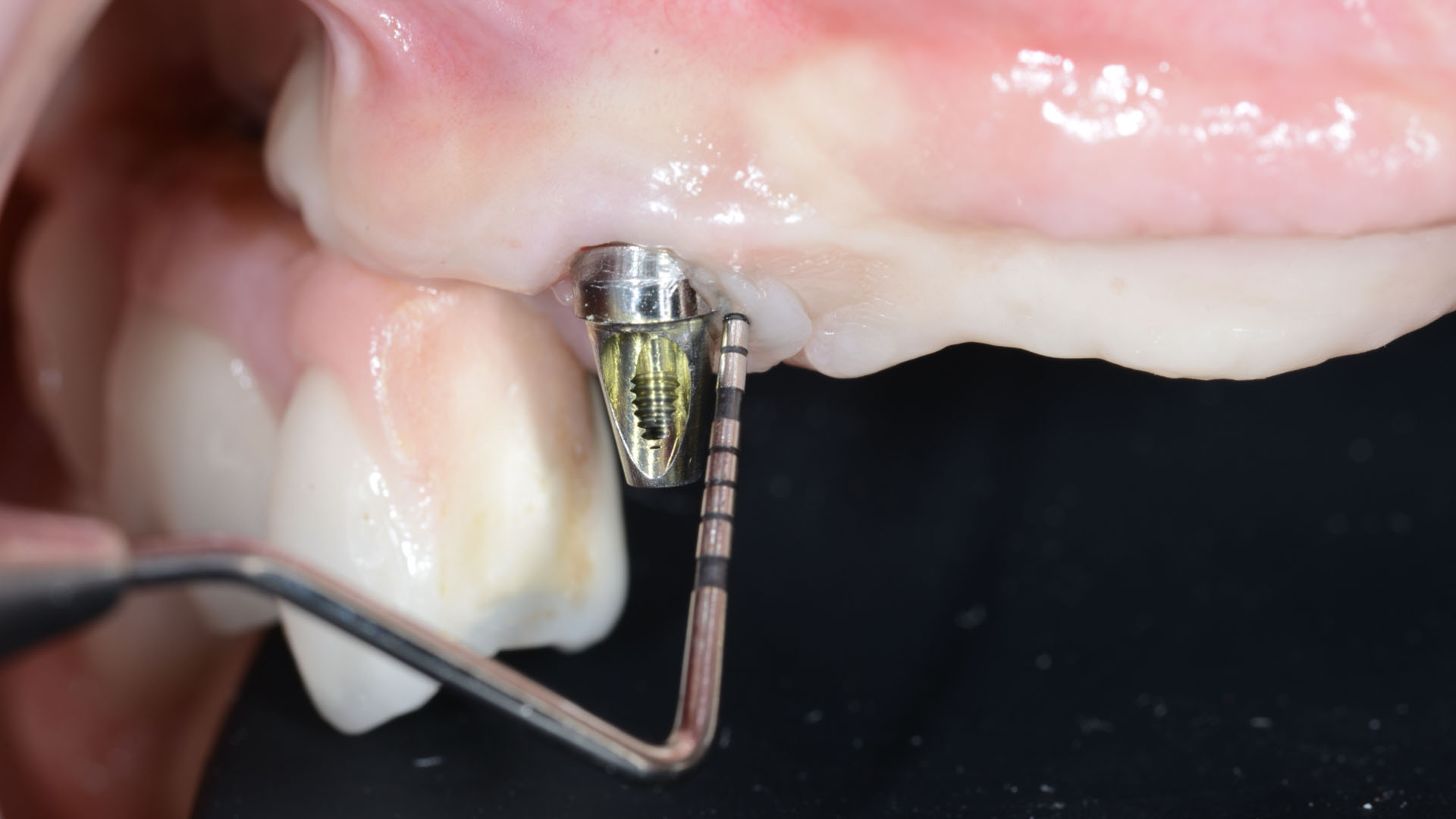
The goal of treatment was a late implant placement after bone regeneration and creation of stable periimplant soft tissue for long-term implant preservation.
THE RISK PROFILE
| Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient’s health | Intact immune system | Light smoker | Impaired immune system |
| Patient’s esthetic requirements | Low | Medium | High |
| Gingival biotype | Thick – “low scalloped” | Medium – “medium scalloped” | Thin – “high scalloped” |
| Infection at implant sight | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone height at adjacent tooth | ≤ 5 mm from contact point | 5.5 – 6.5 mm from contact point | ≥ 7 mm from contact point |
| Width of tooth gap | 1 tooth (≥ 7 mm) | 1 tooth (≤ 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft-tissue anatomy | Intact | Compromised | |
| Bone anatomy of the alveolar ridge | No defect | Horizontal defect | Vertical defect |
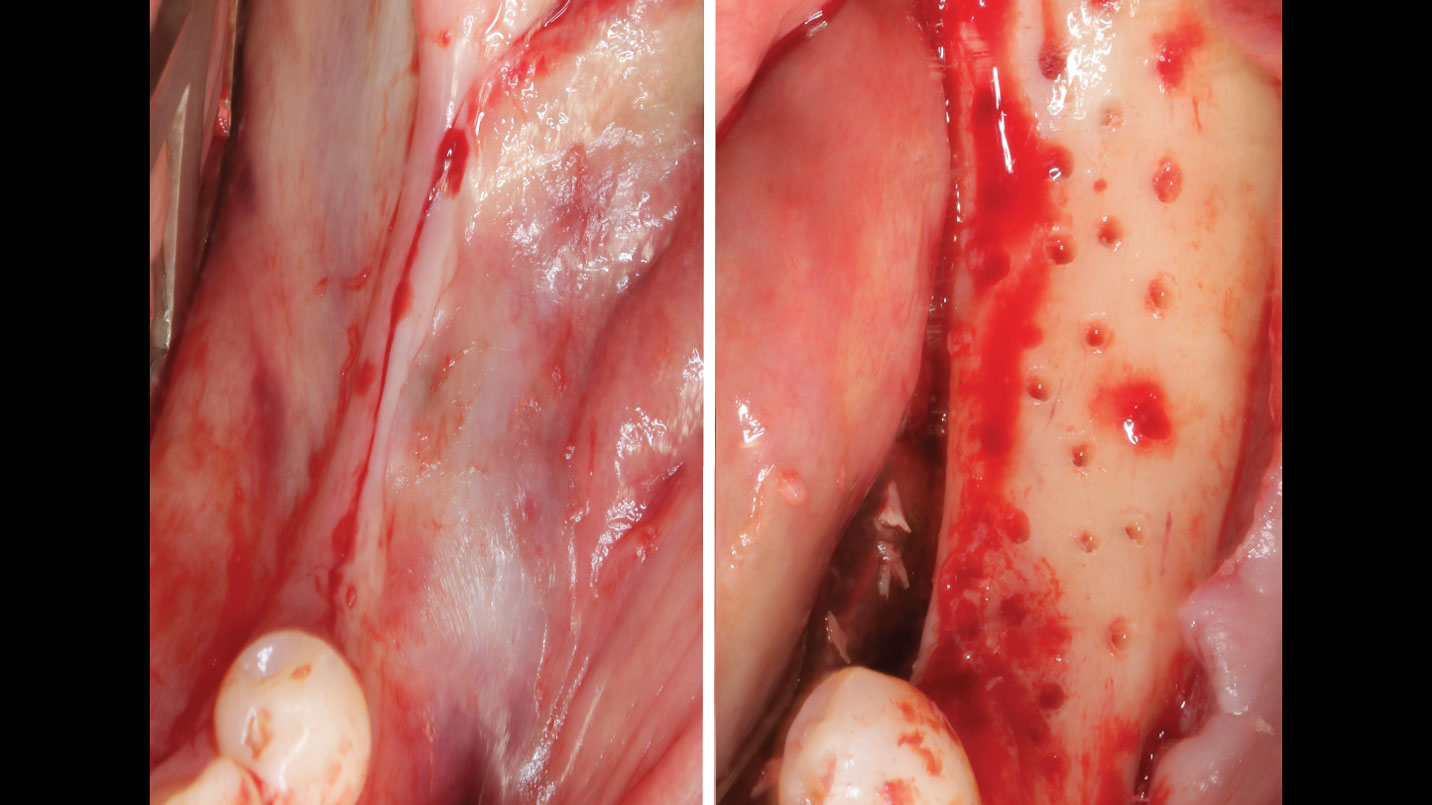
Additional Risk Factors: Roots were divergent, and intra-radicular bone (septal bone) was excellent, with more than 5 mm of remaining apical bone to achieve optimal primary stability.
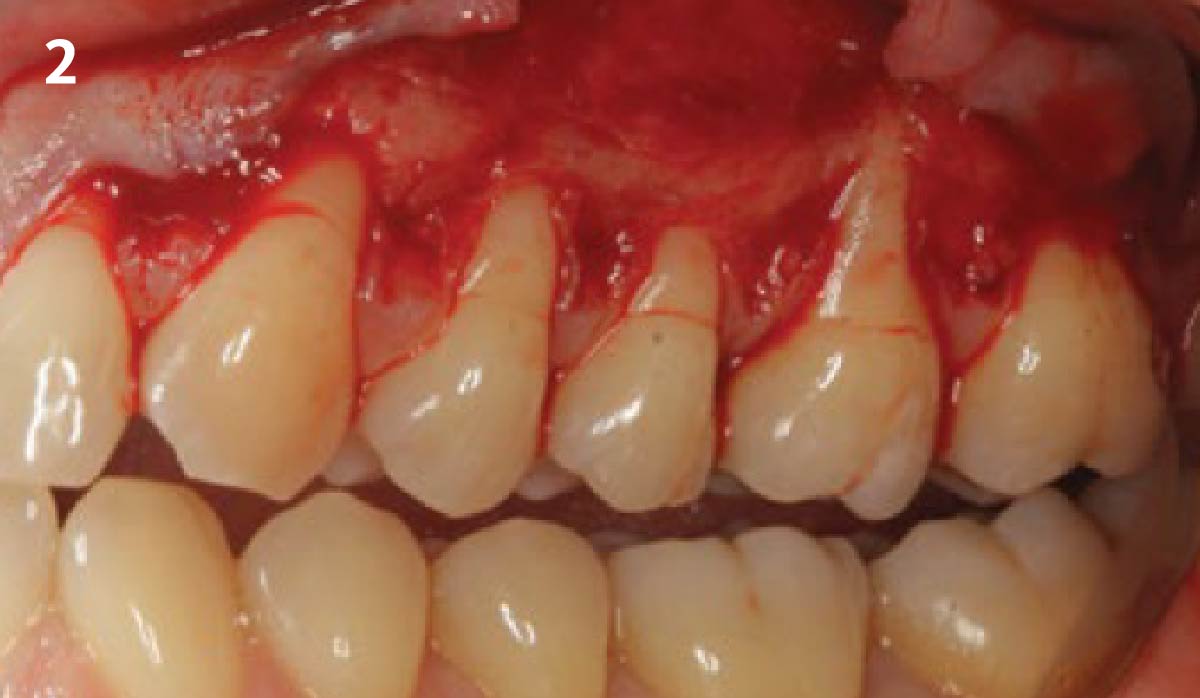
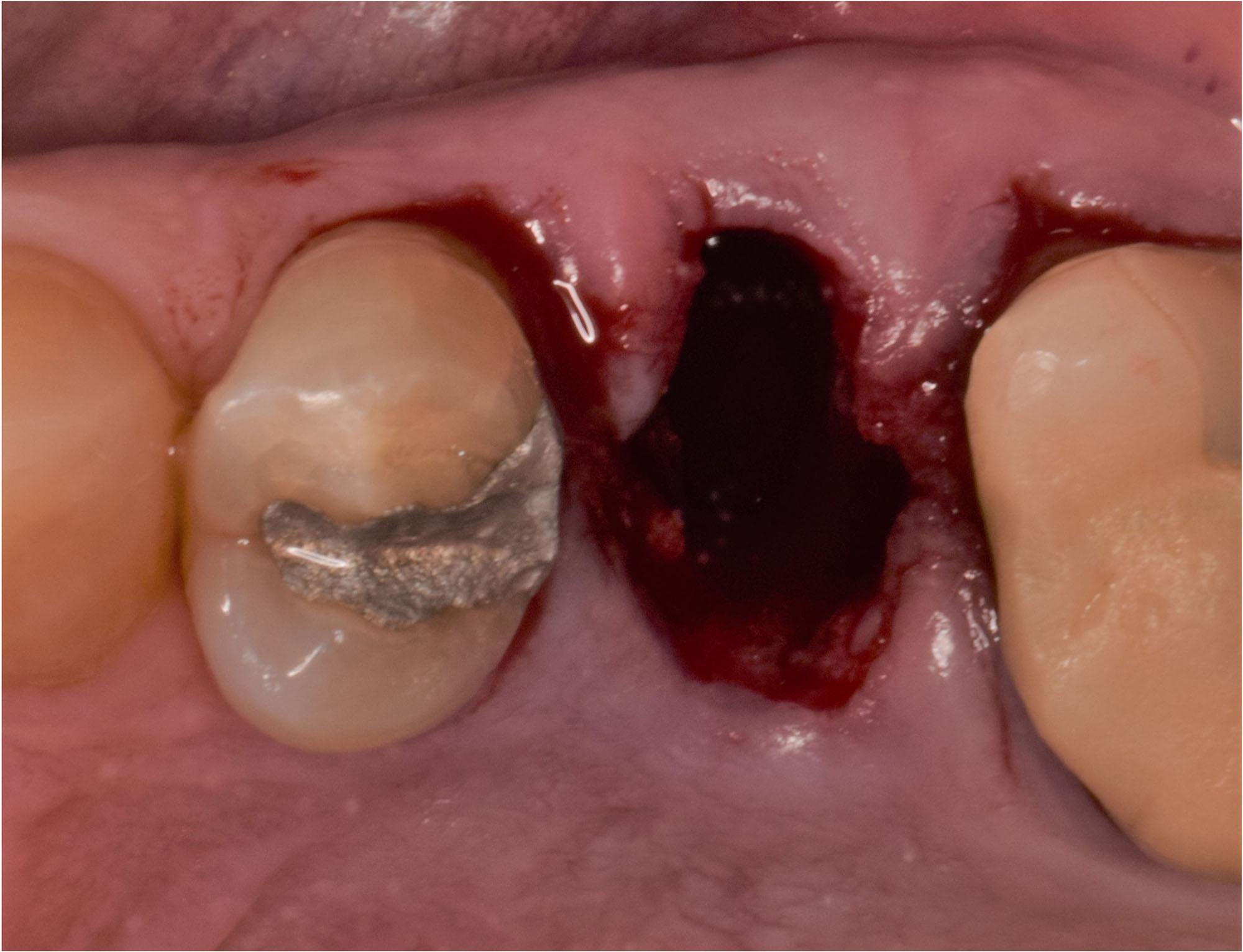
THE APPROACH
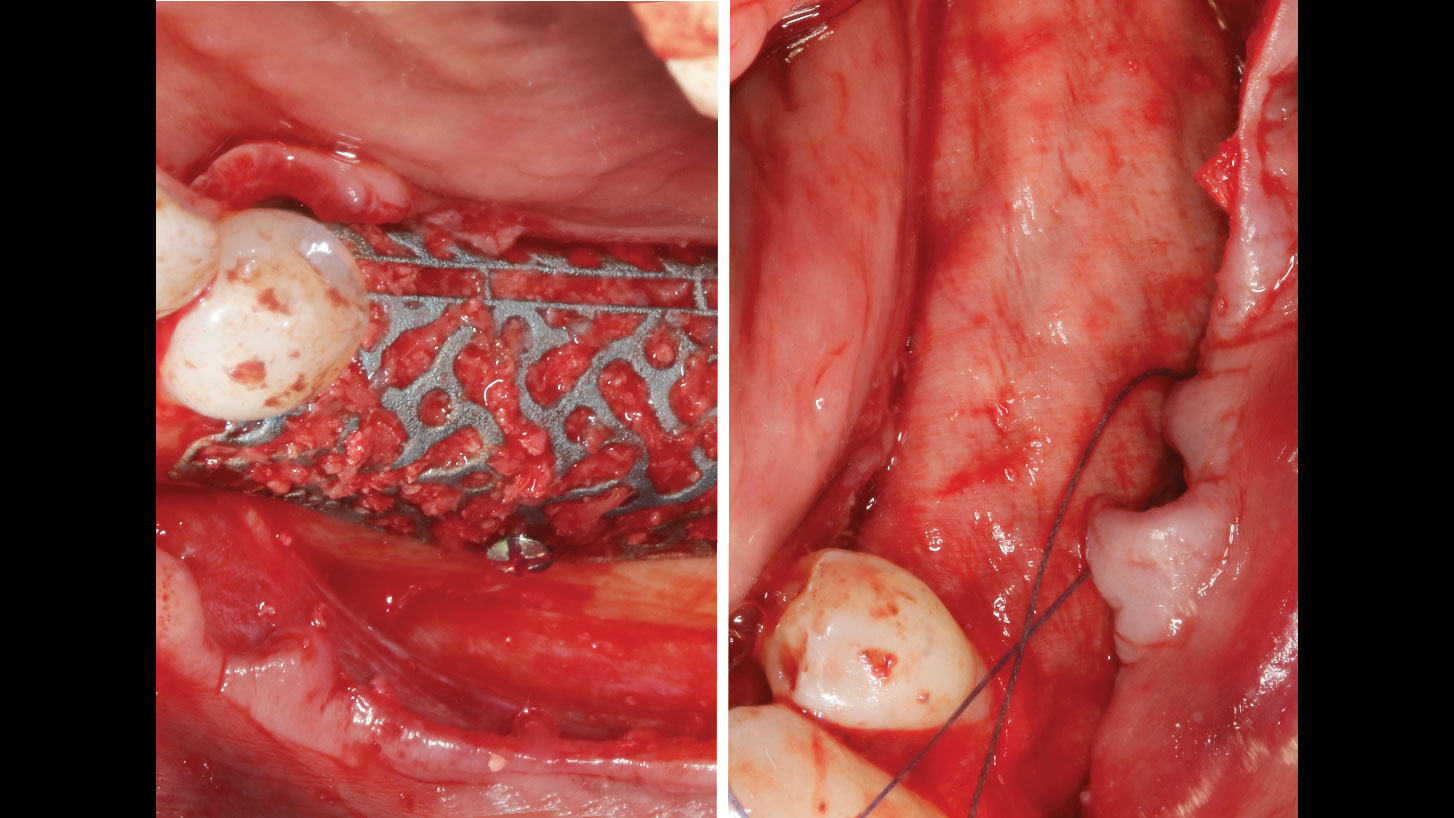
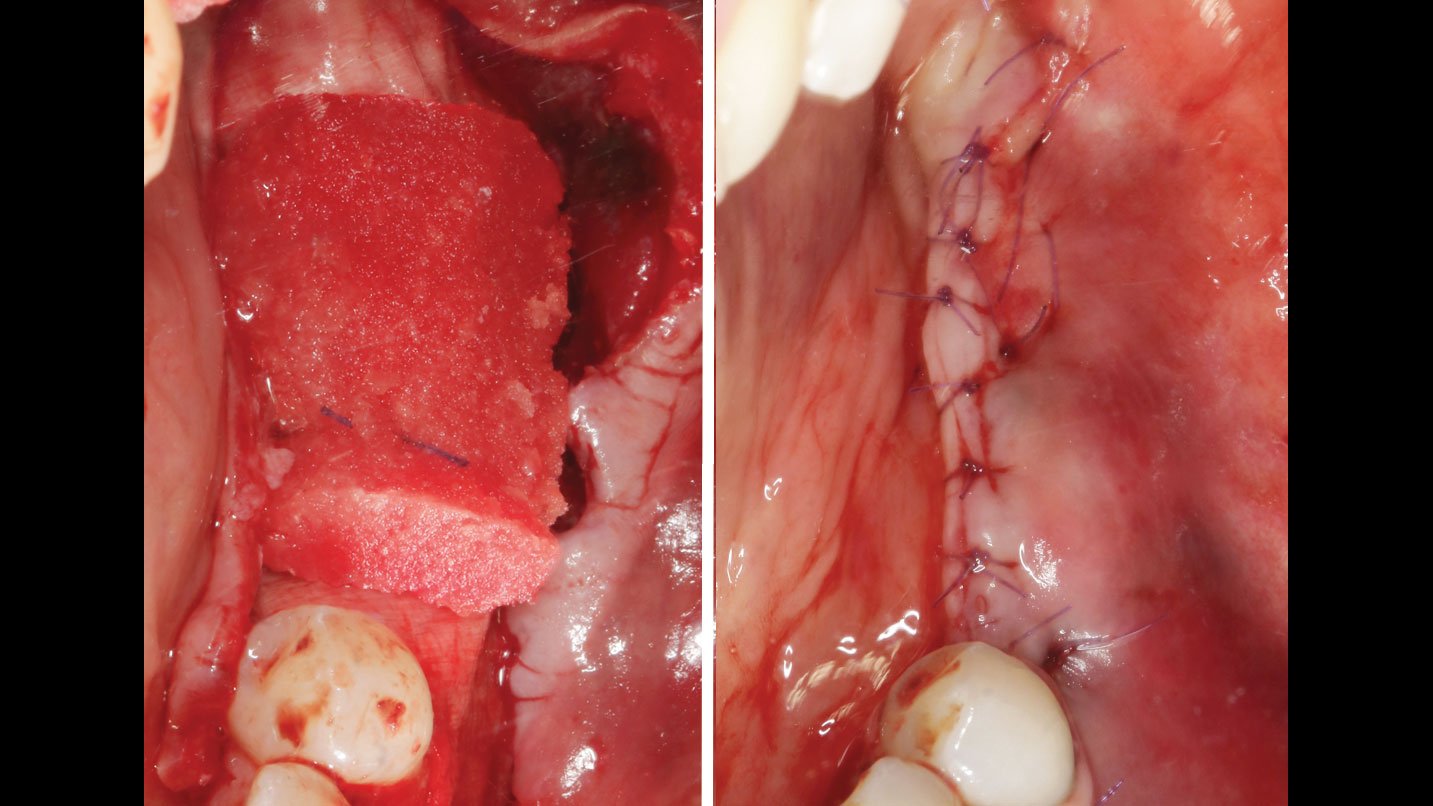
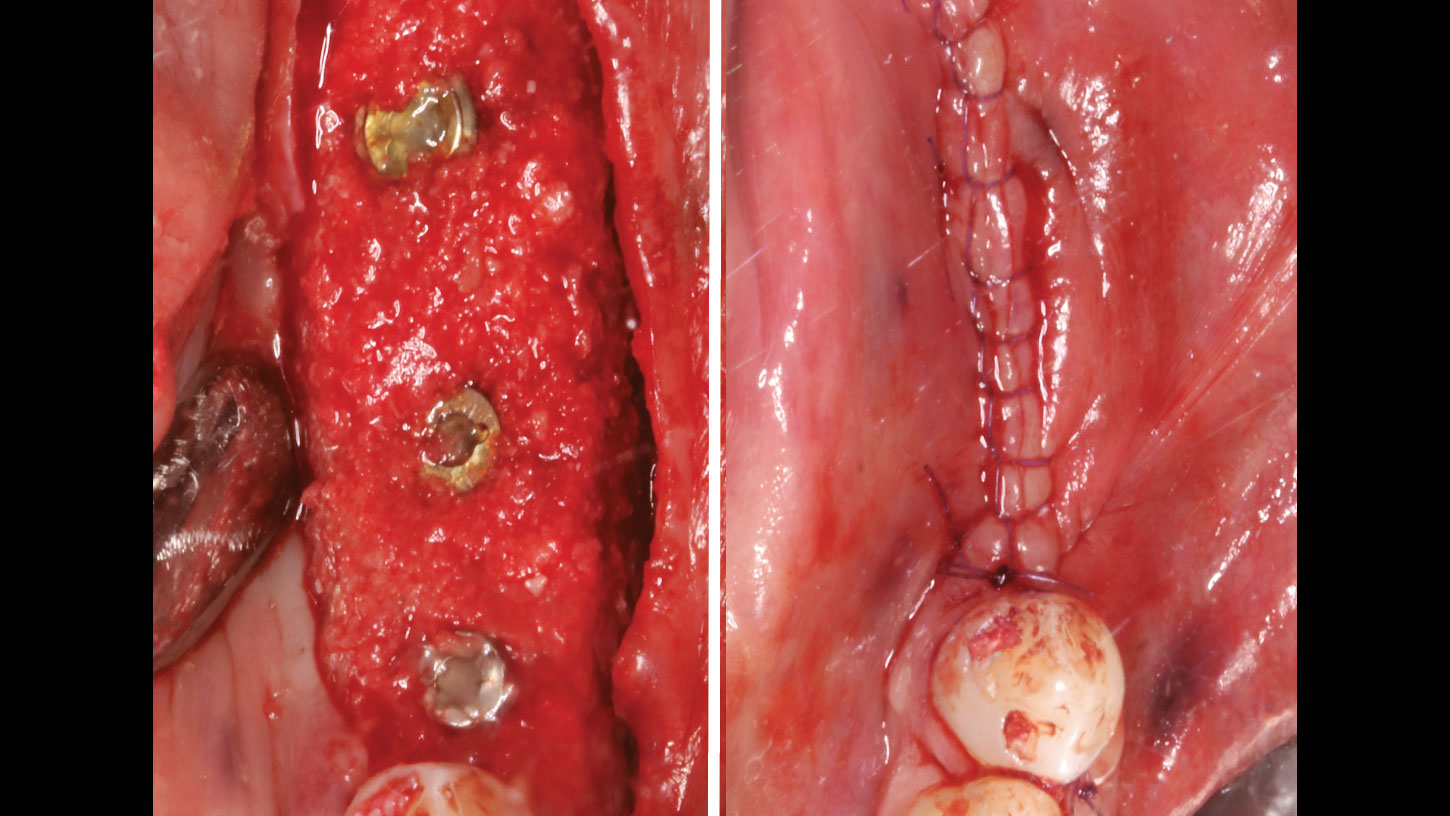
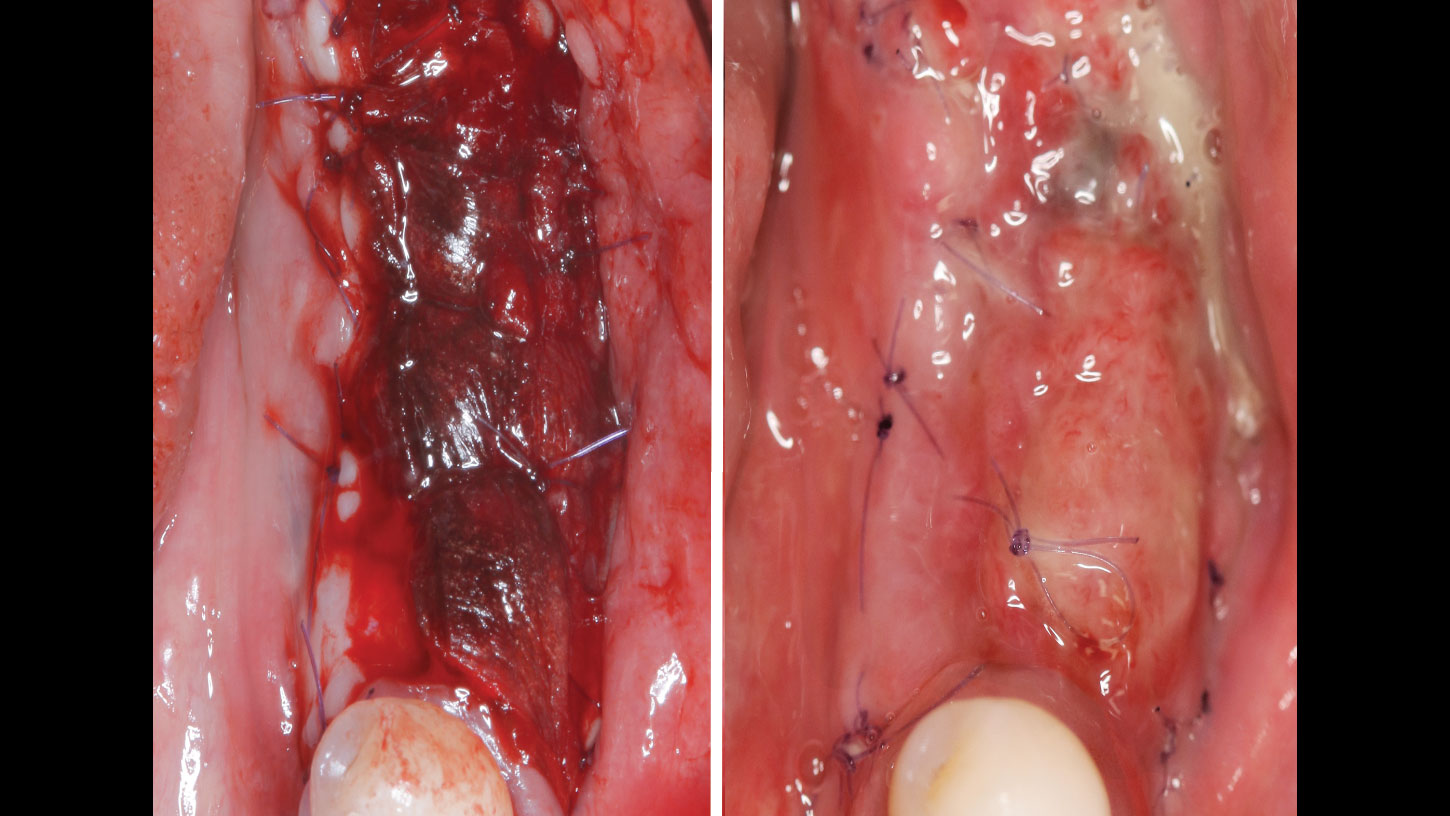
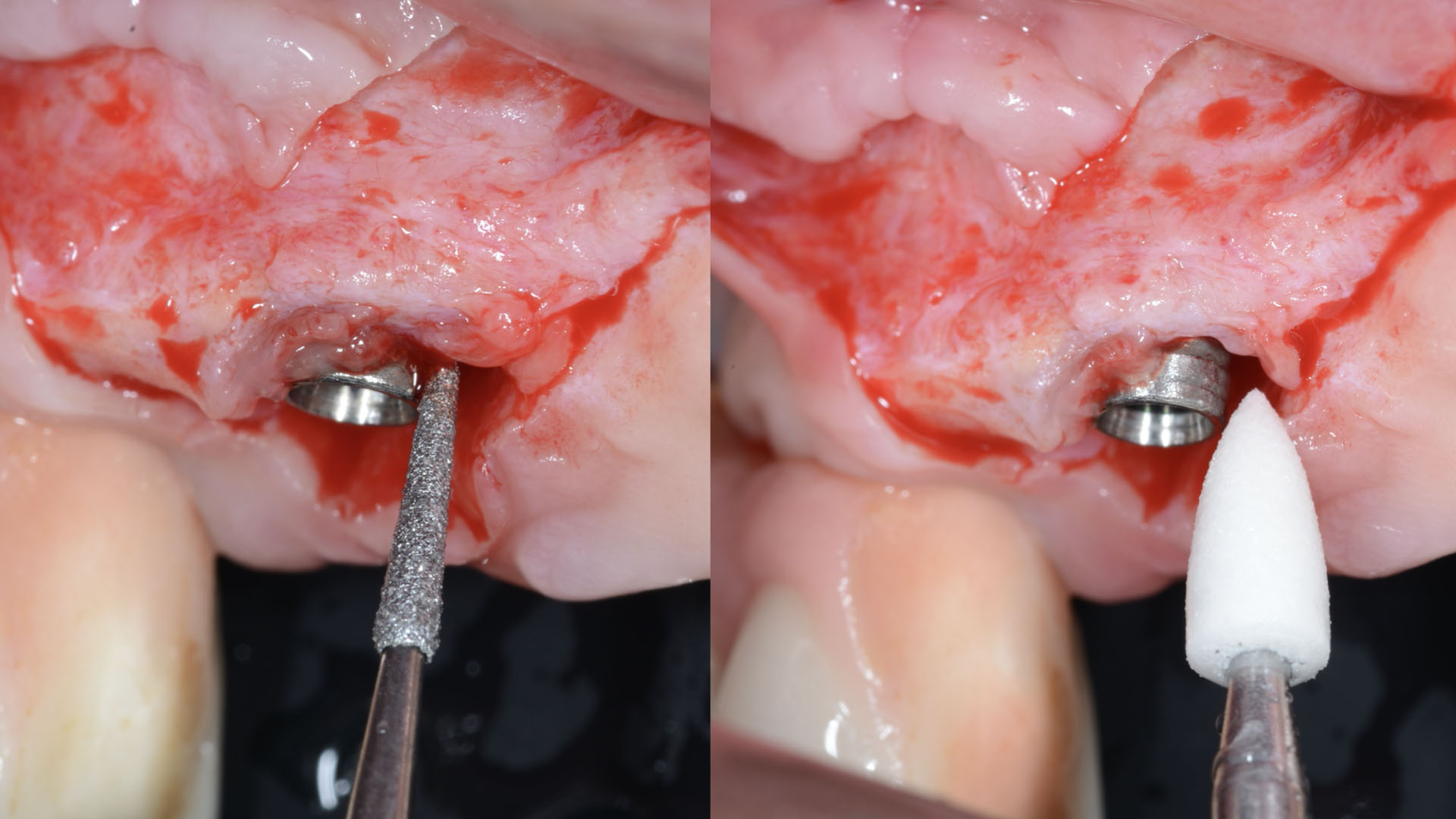
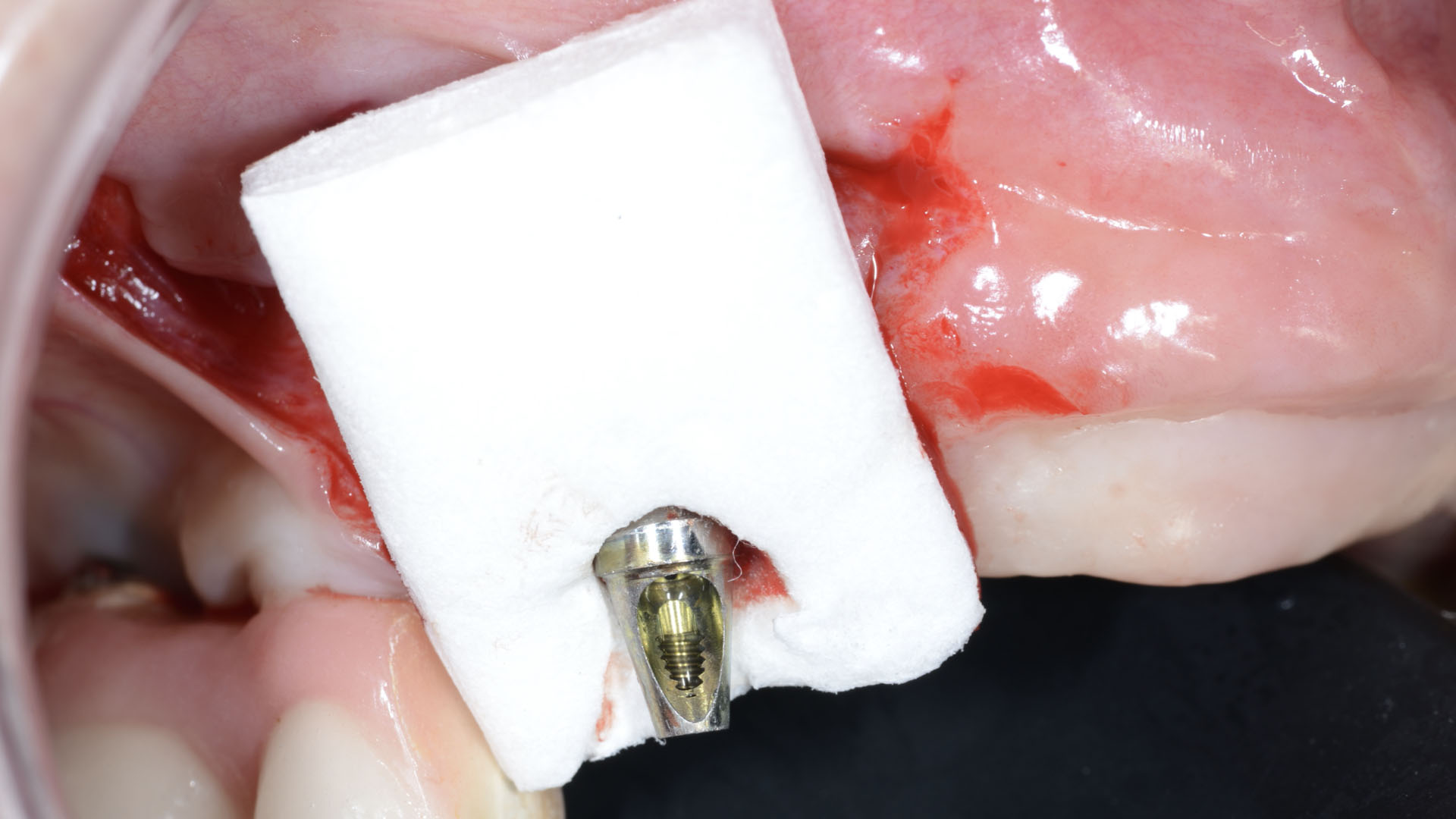
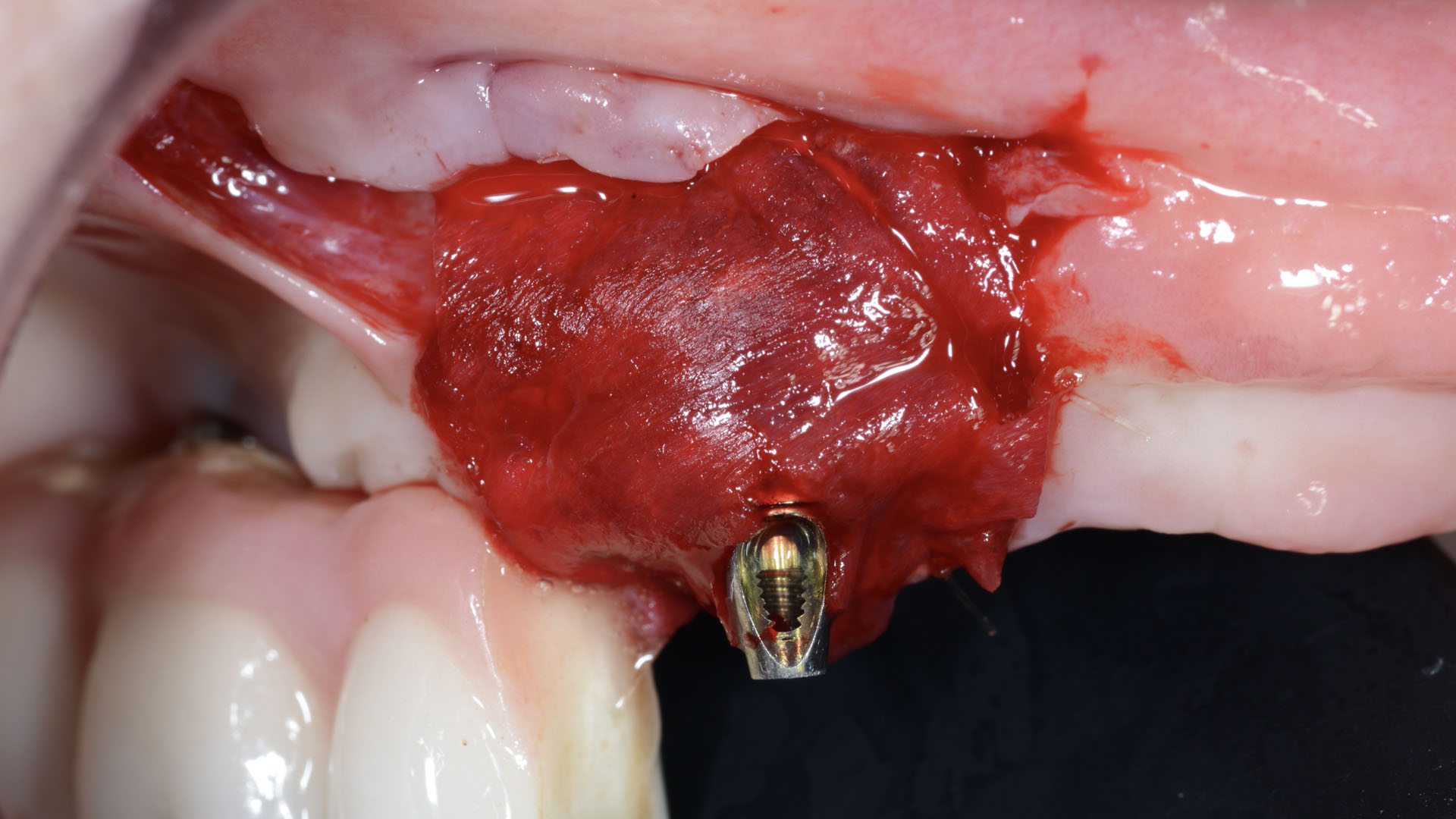
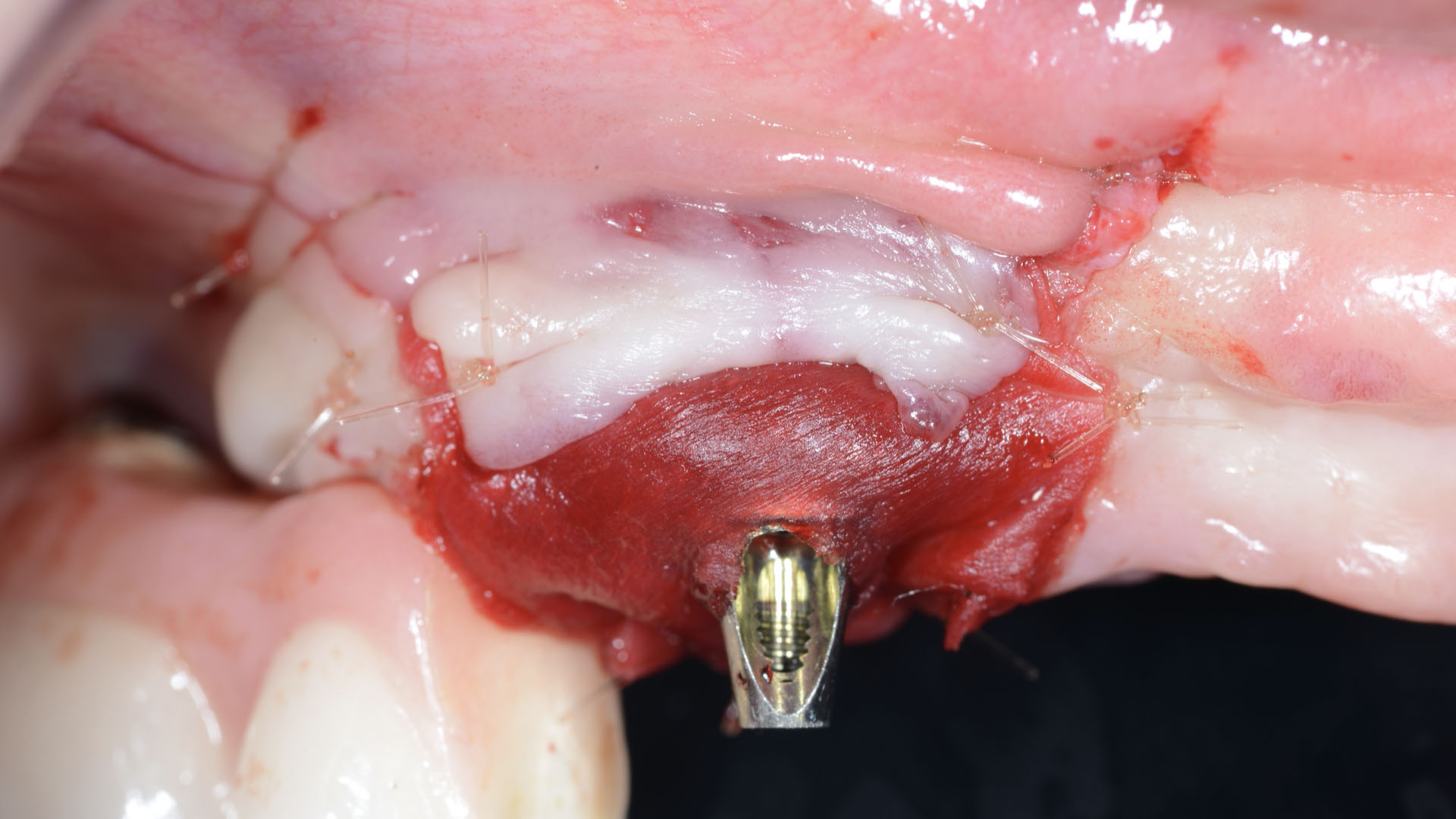
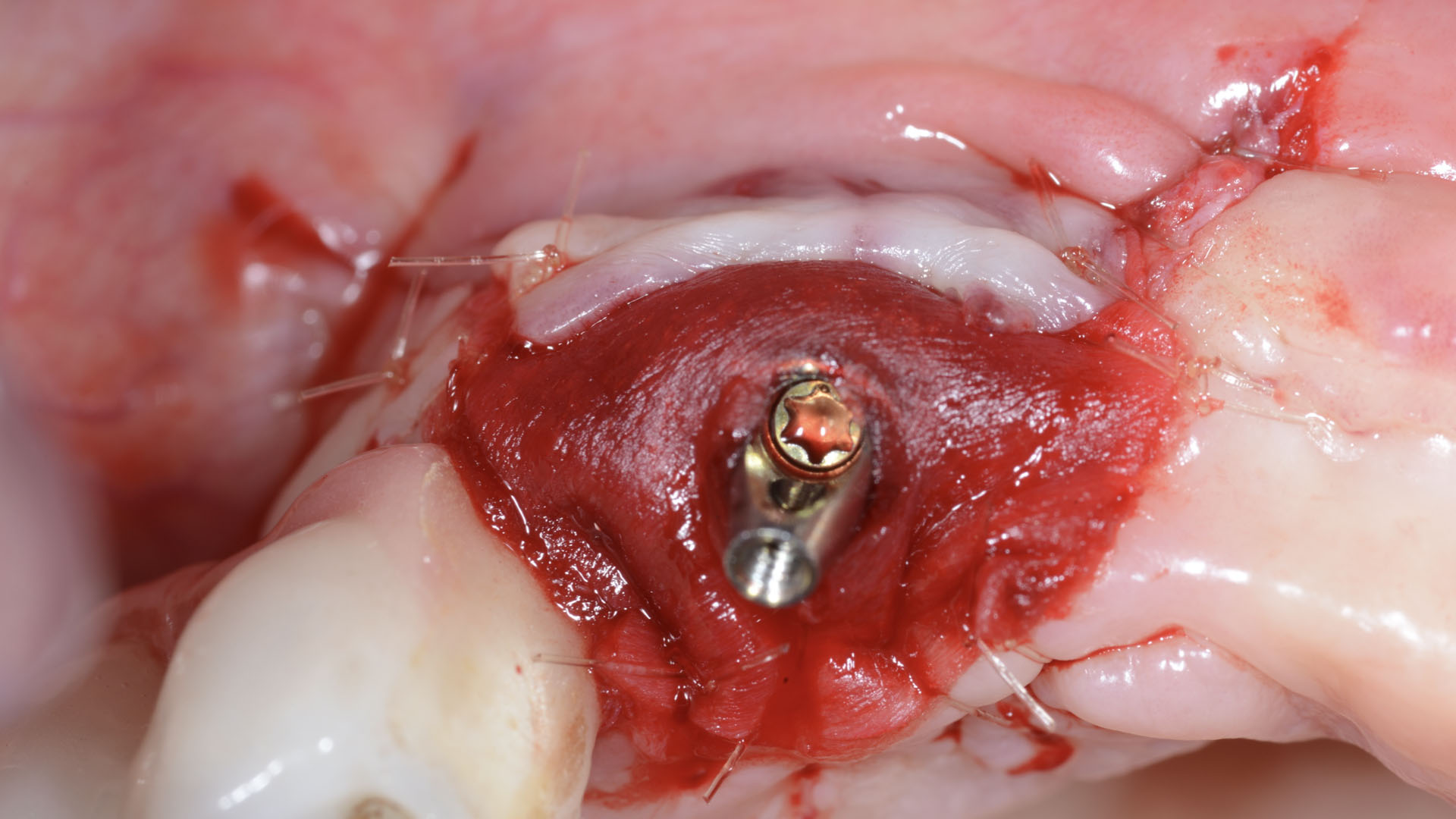
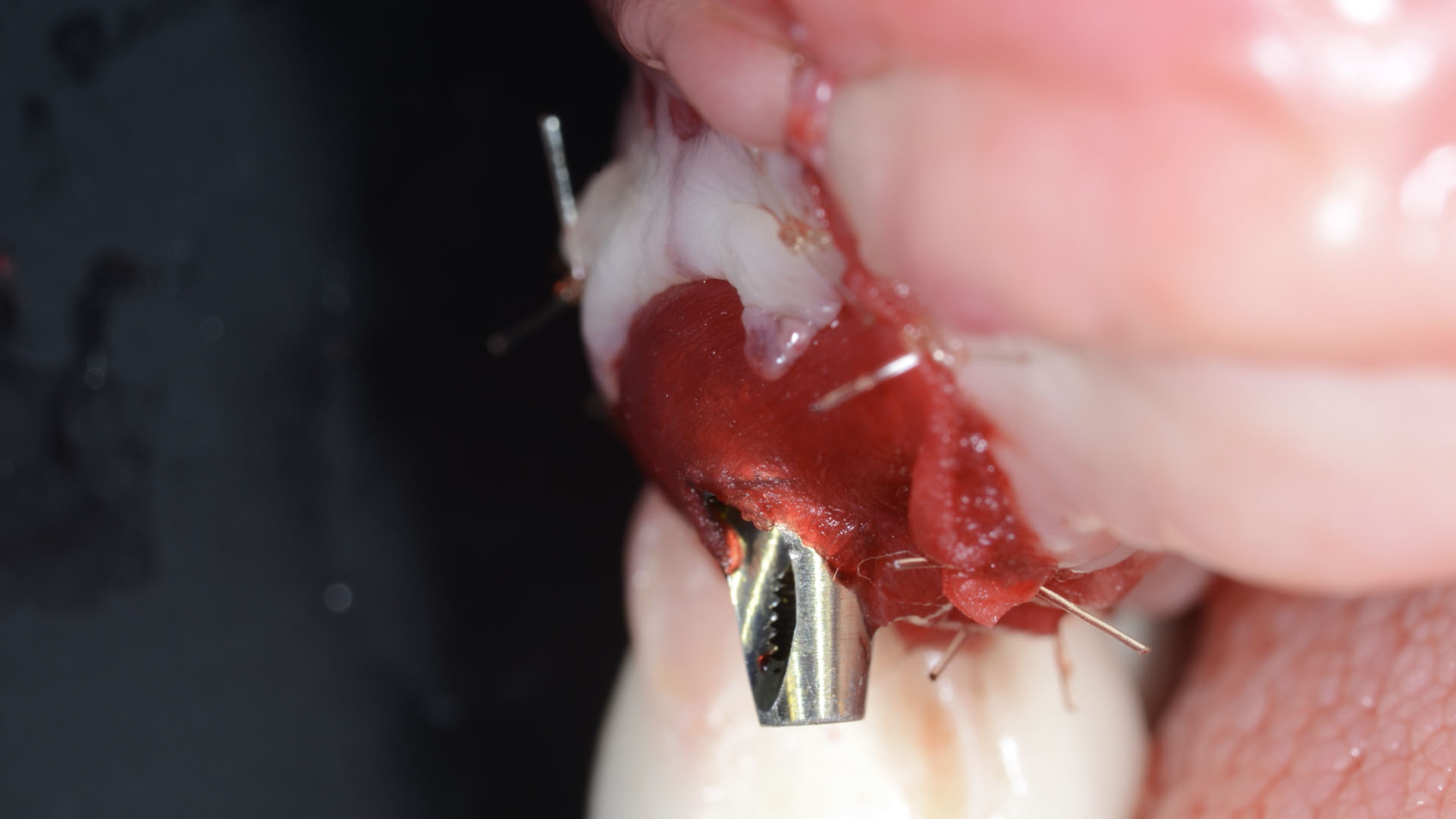
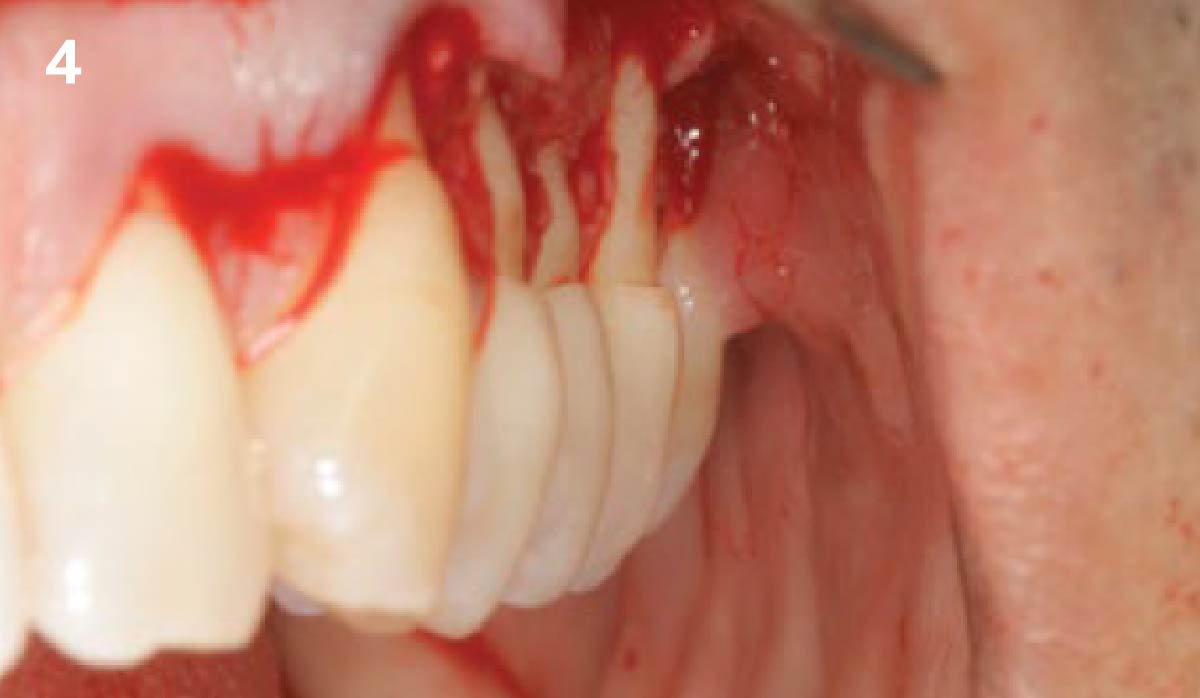
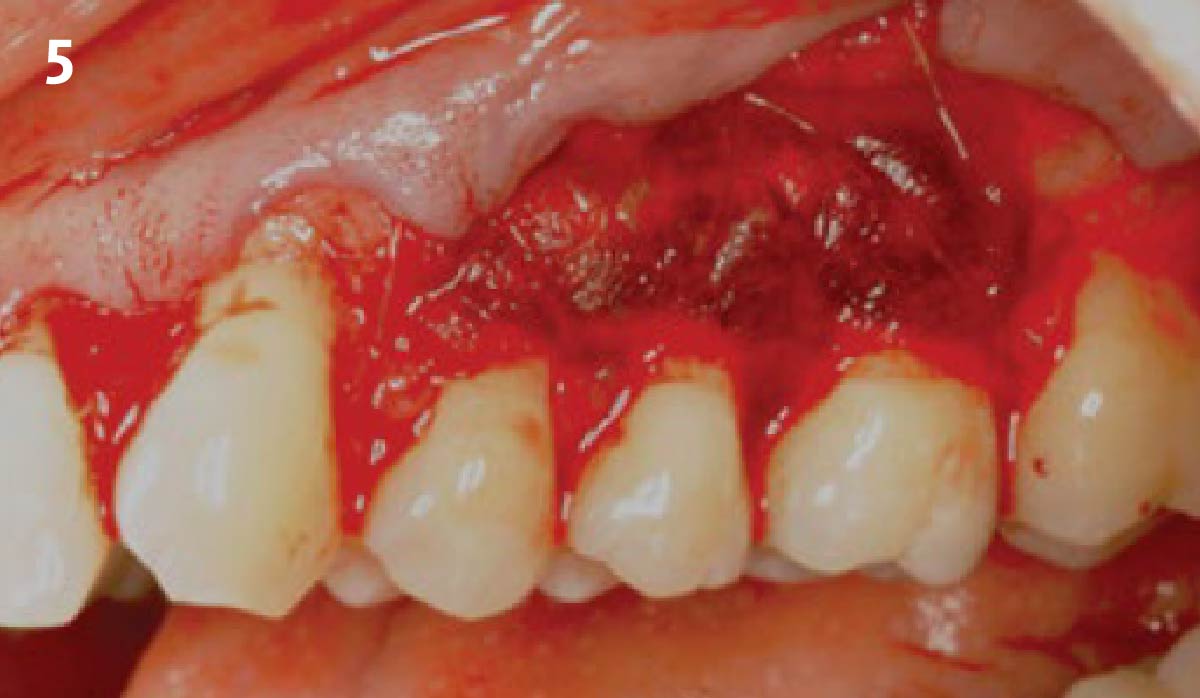
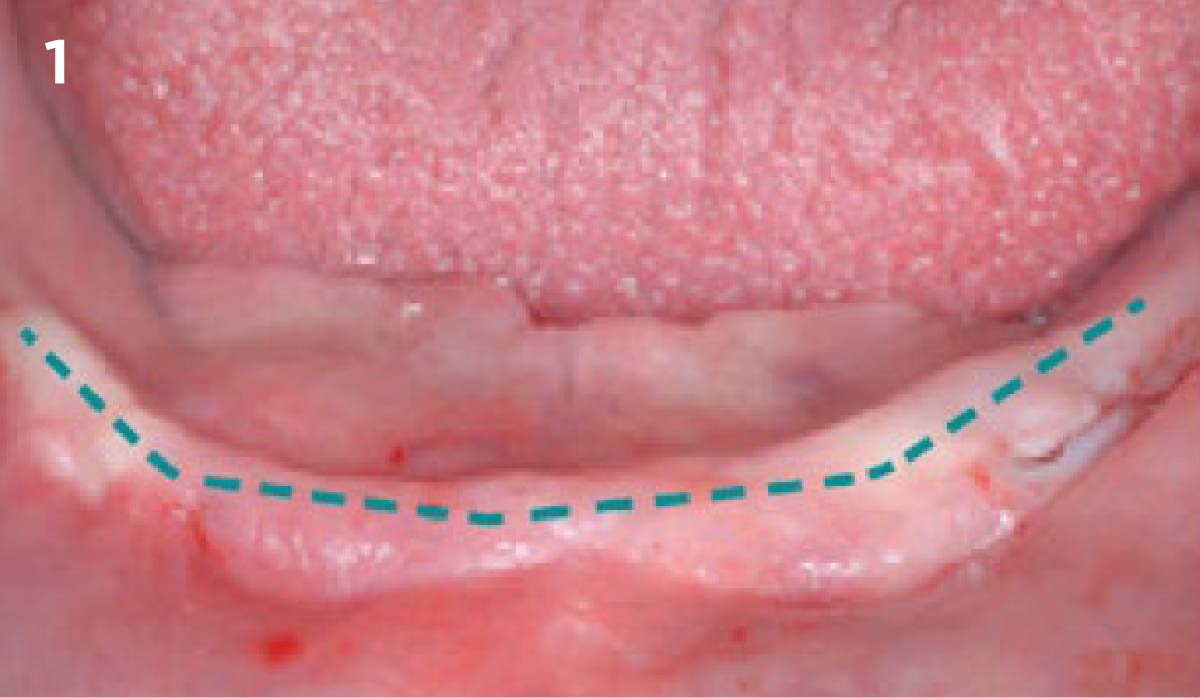
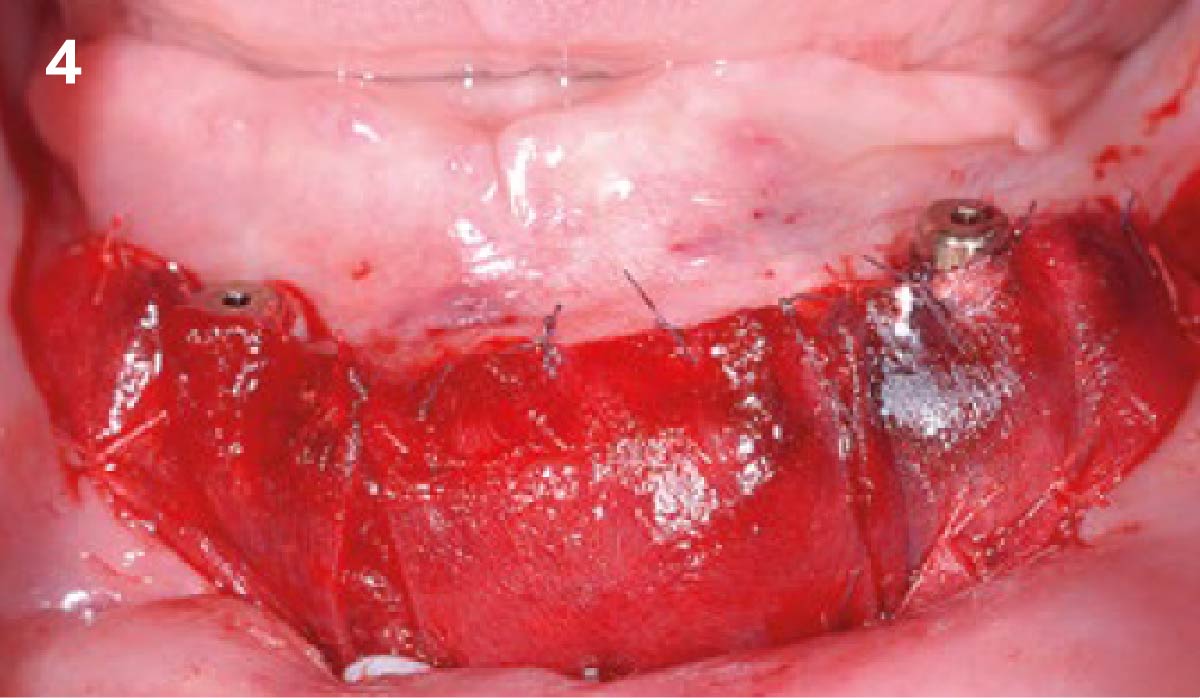
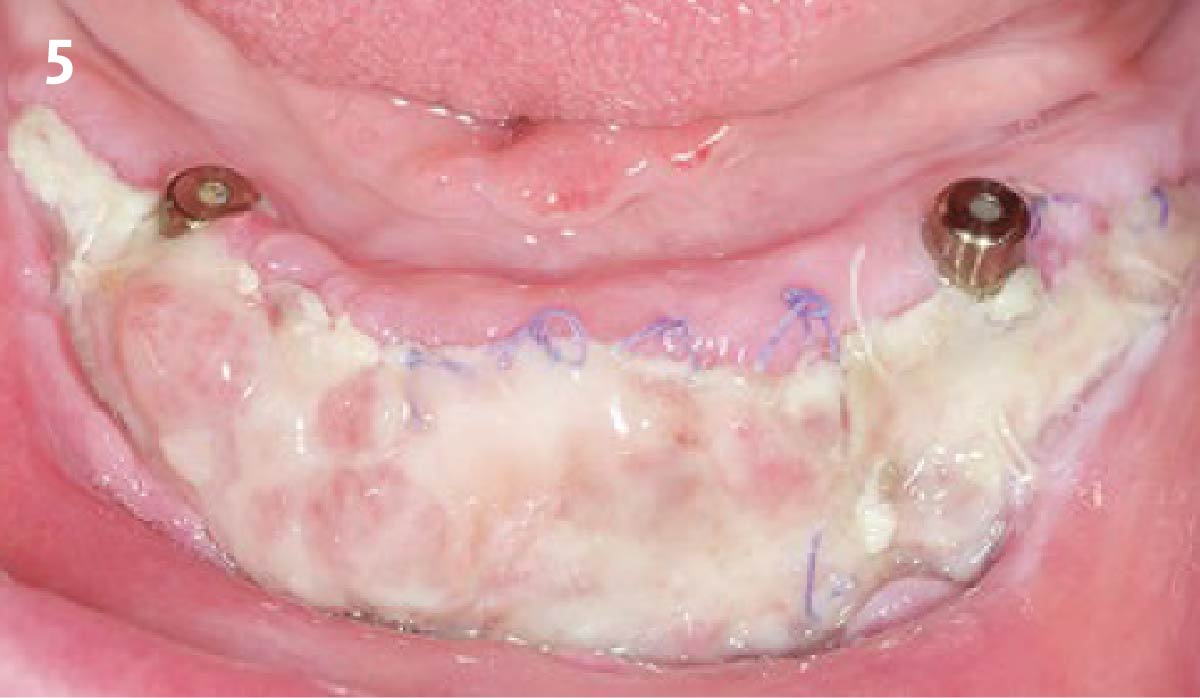
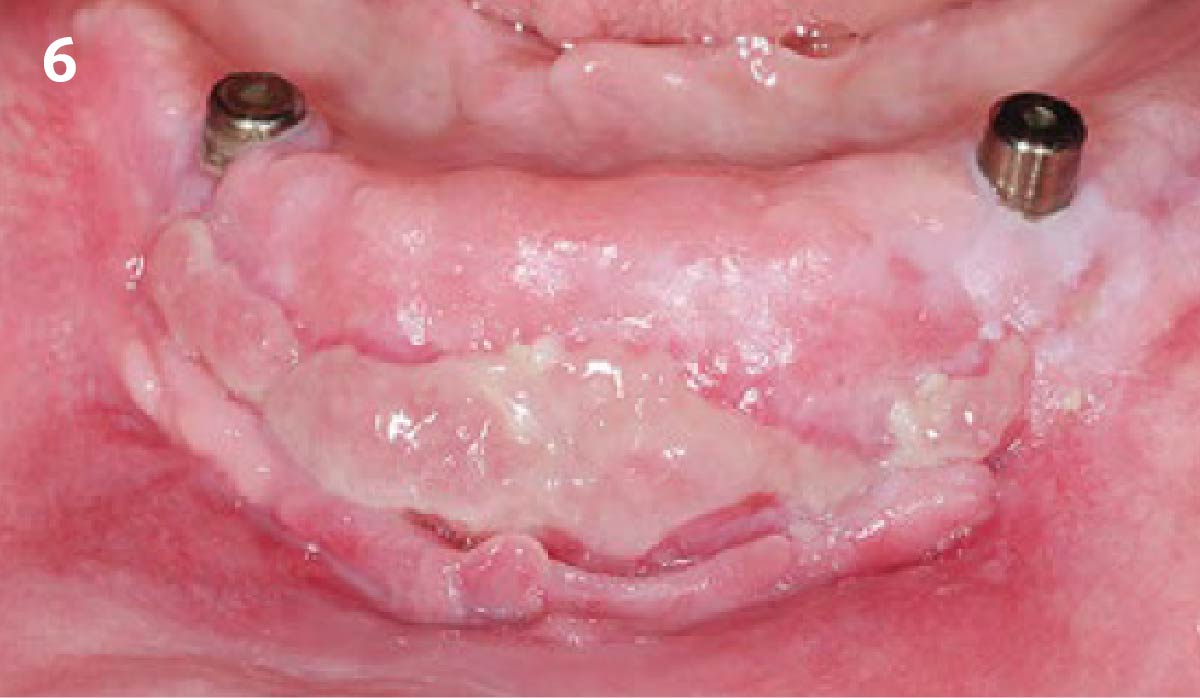
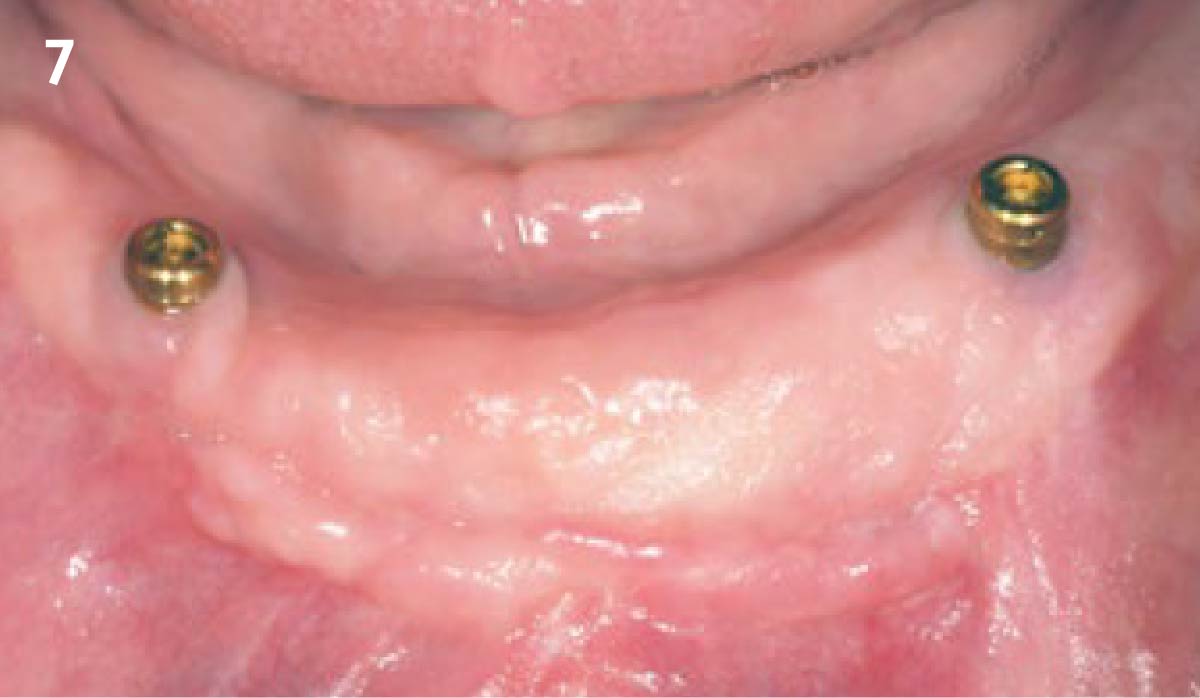
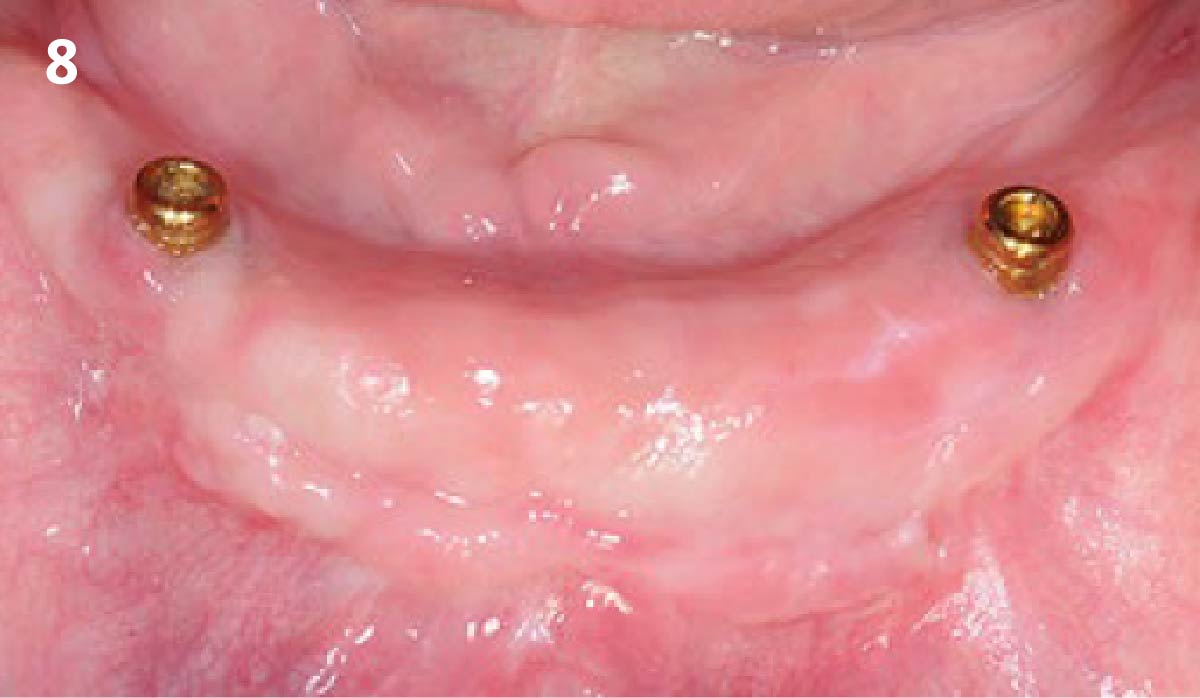
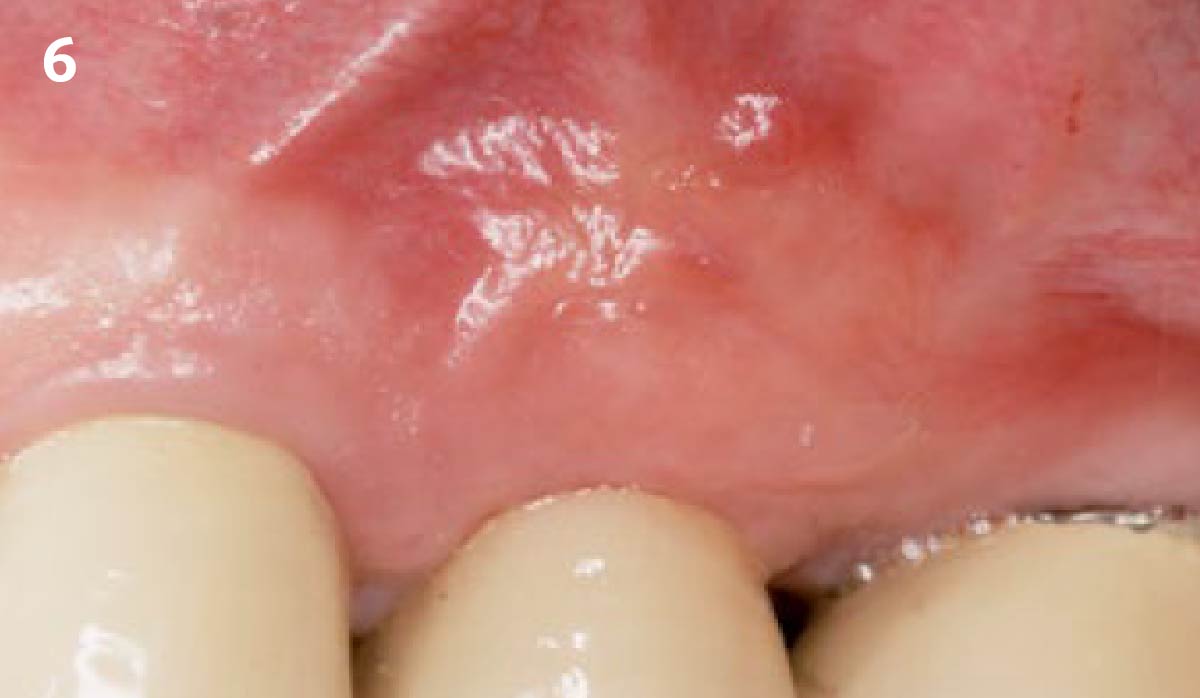
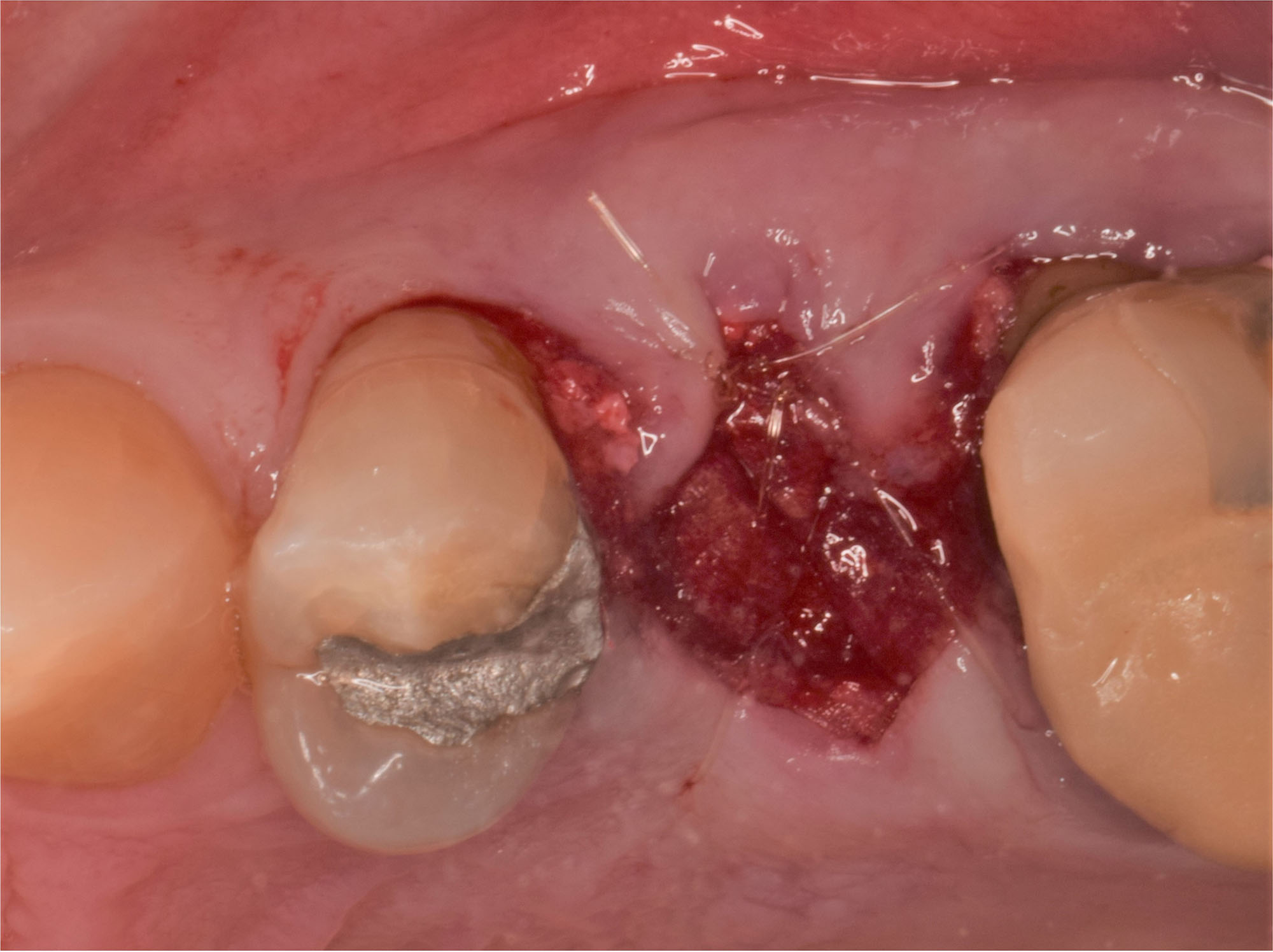
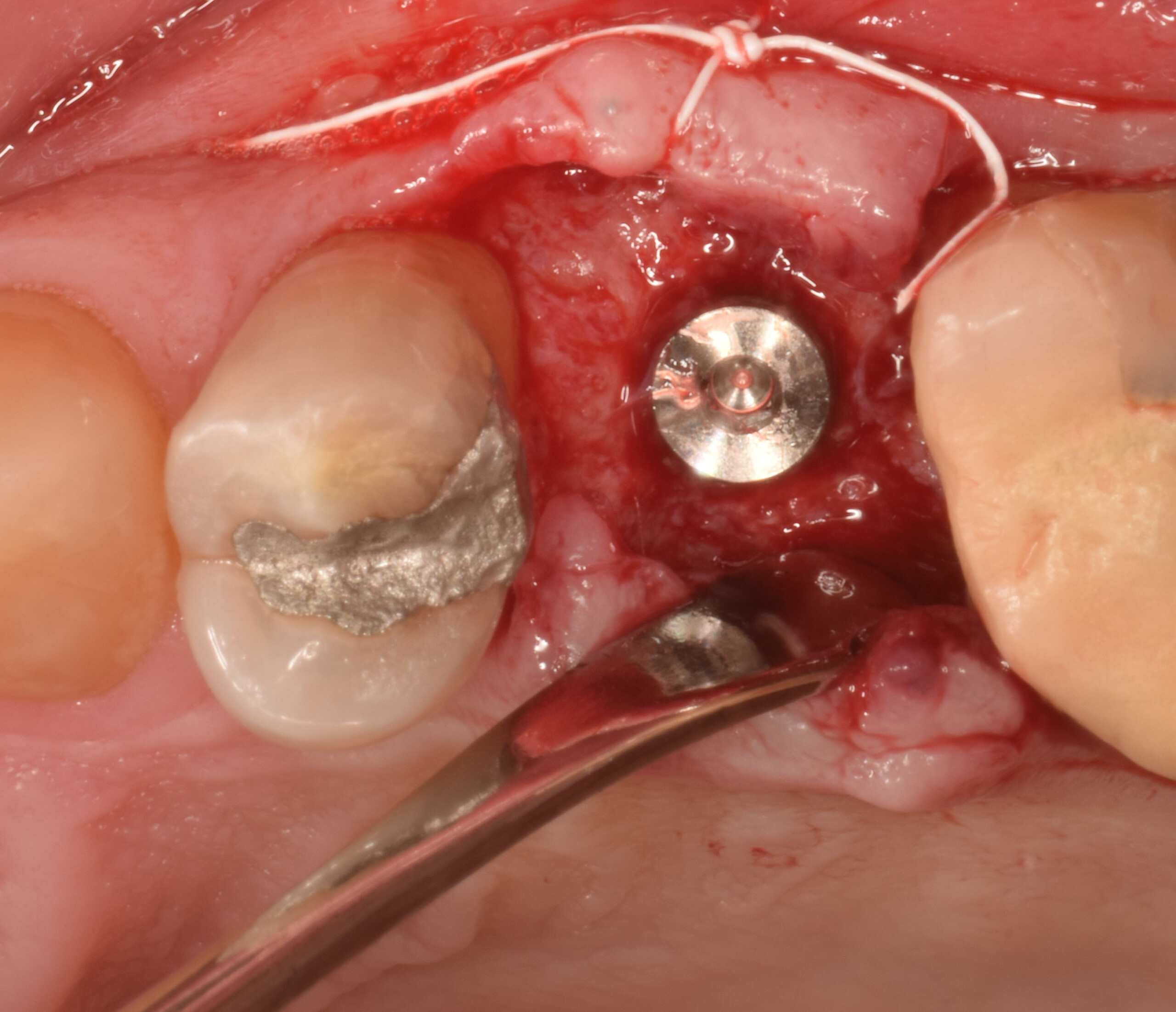
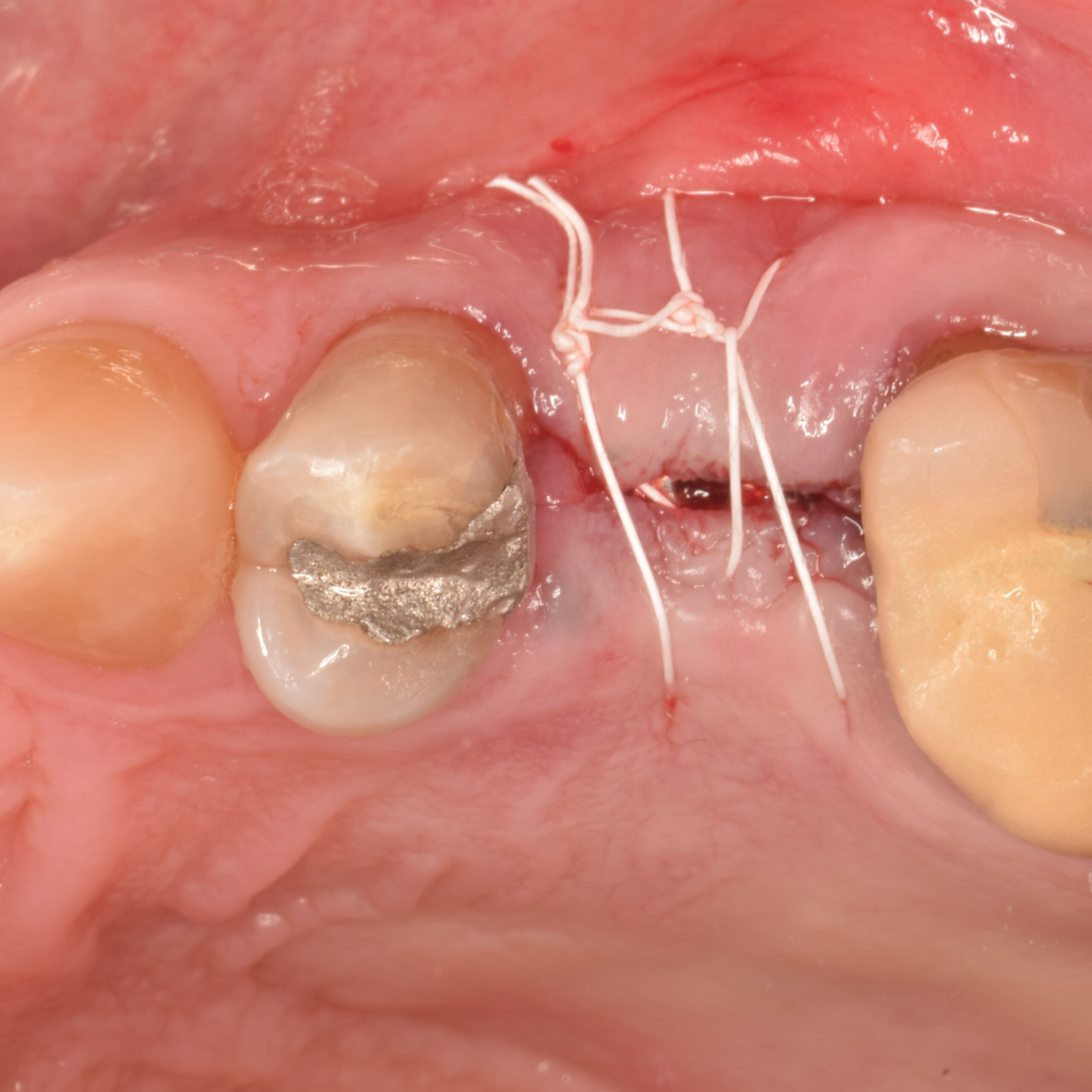
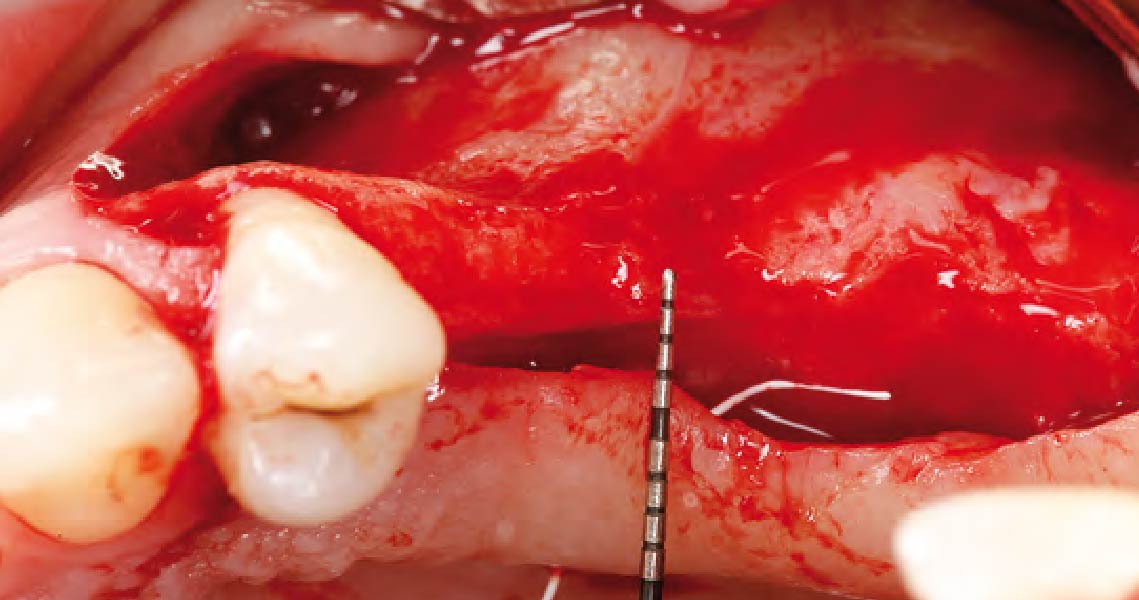
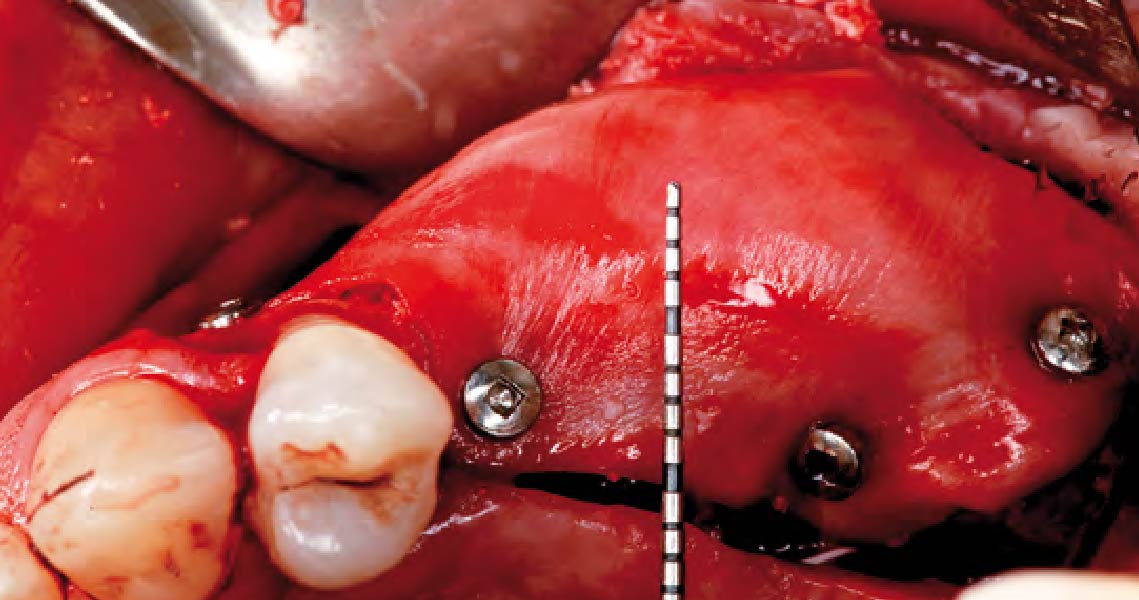
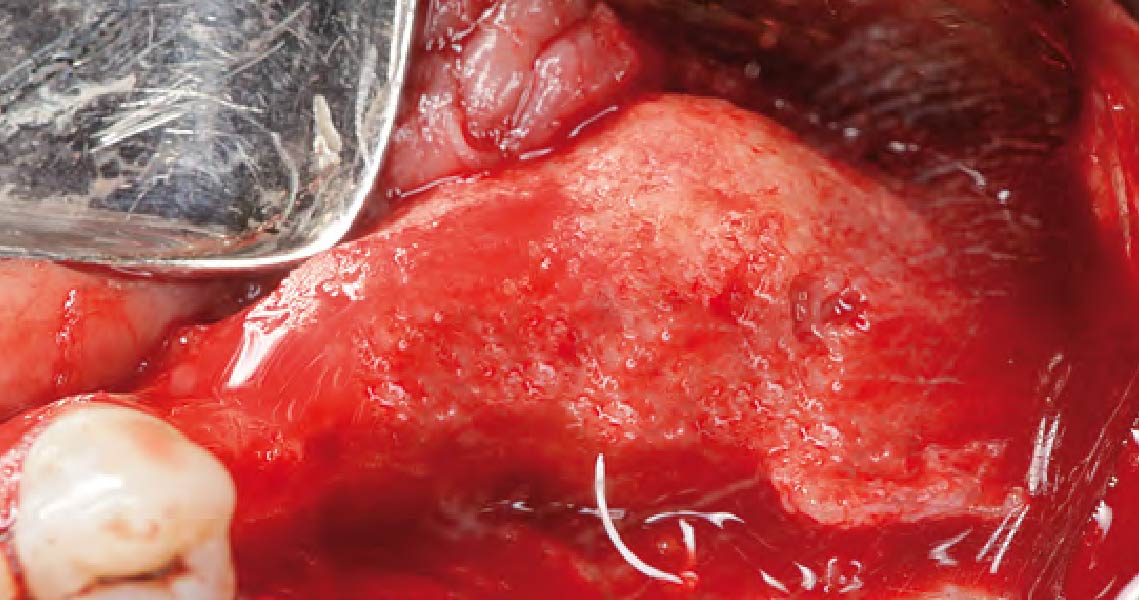
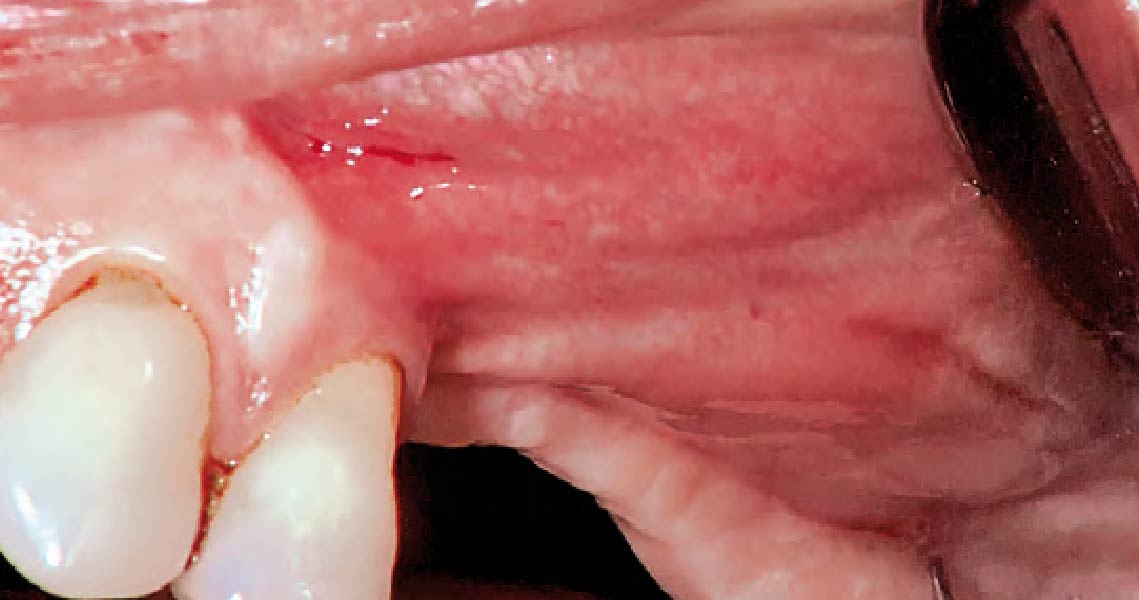
A customized bone regeneration procedure utilizing Yxoss CBR®. Followed by coverage of the graft with Geistlich Bio-Gide® for the purpose of Guided Bone Regeneration (GBR). Soft tissue thickening using Geistlich Fibro-Gide®. Delayed implantation into the augmented tissue. A vestibuloplasty with Geistlich Mucograft® for the regeneration of keratinized mucosa.
“Using the Geistlich Fibro-Gide® matrix enabled concurrent augmentation of hard
— Arnd Lohmann, MSc
and soft tissues without any postoperative complications. At the same time, the soft
tissue thickening facilitated floor of the mouth surgery and vestibuloplasty.”
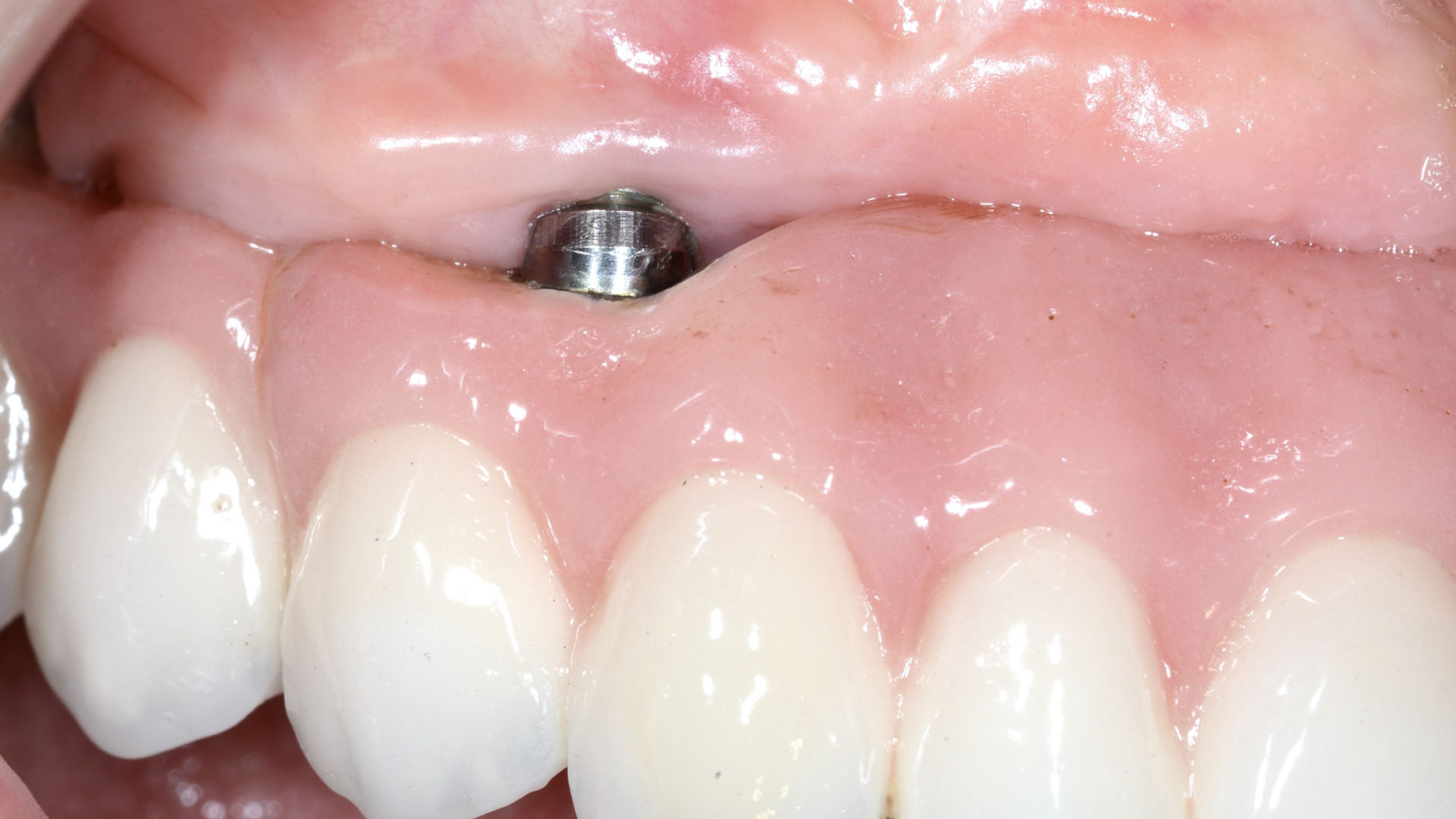
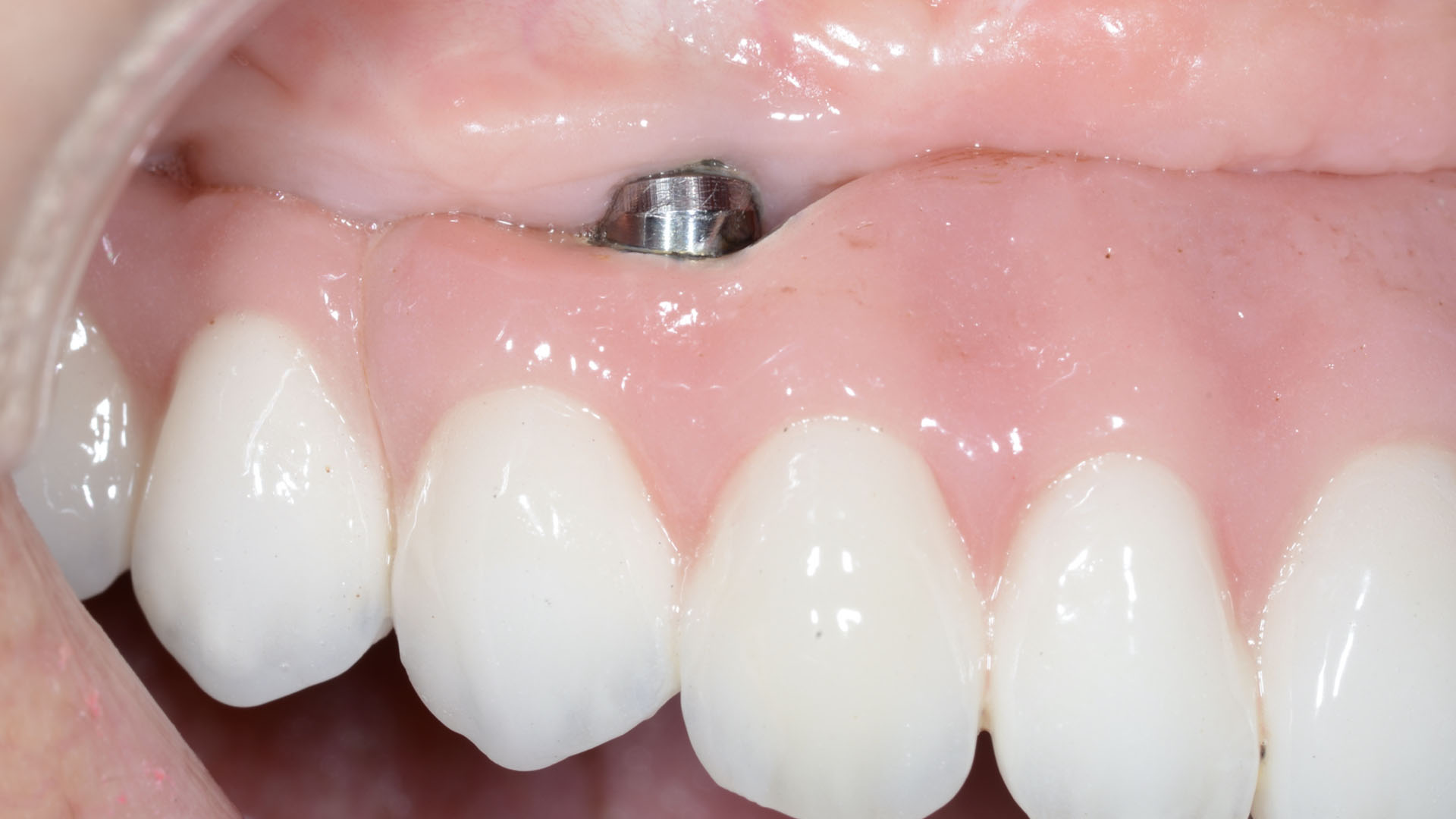
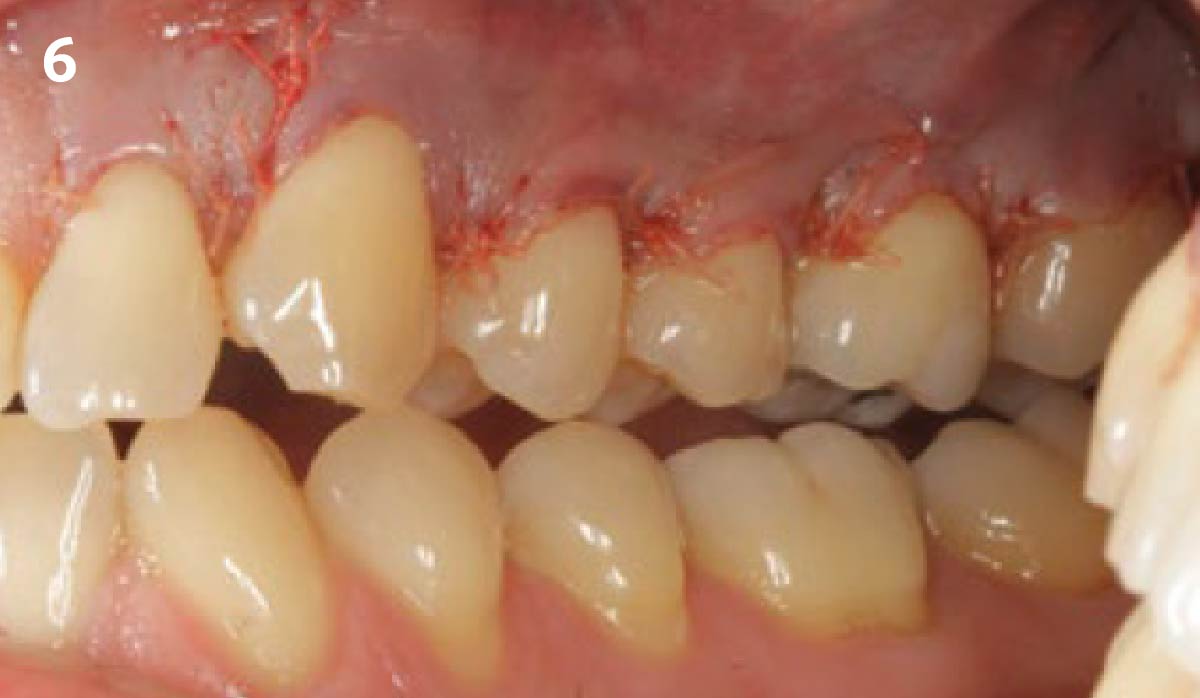
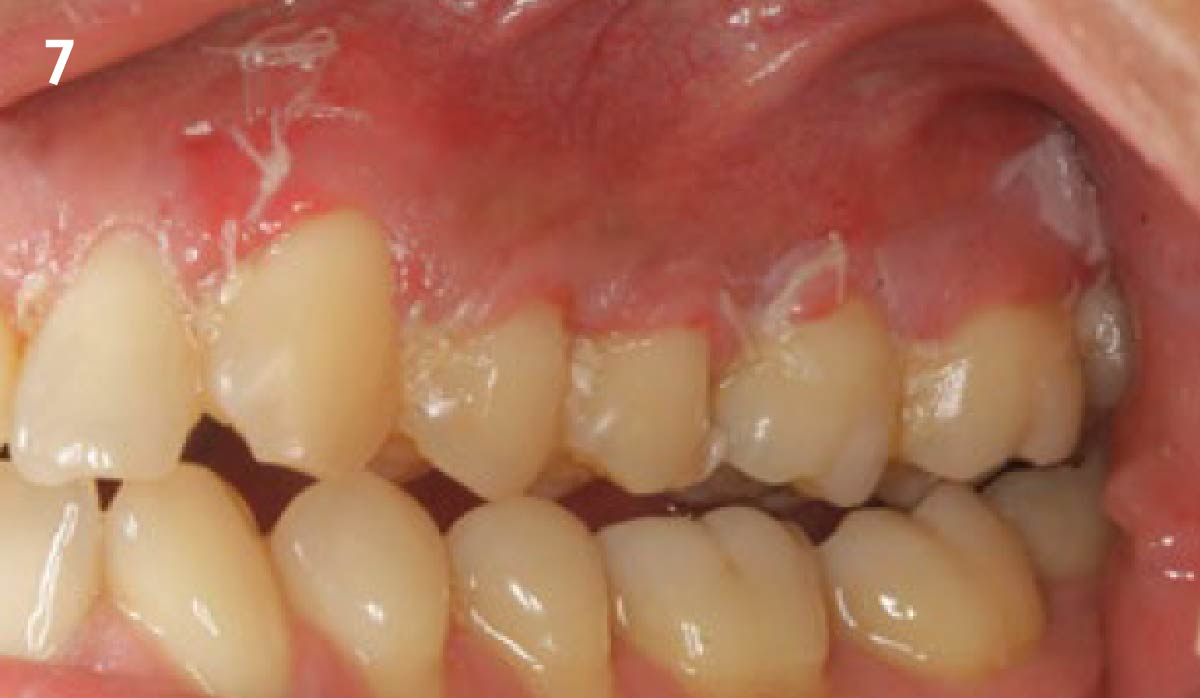
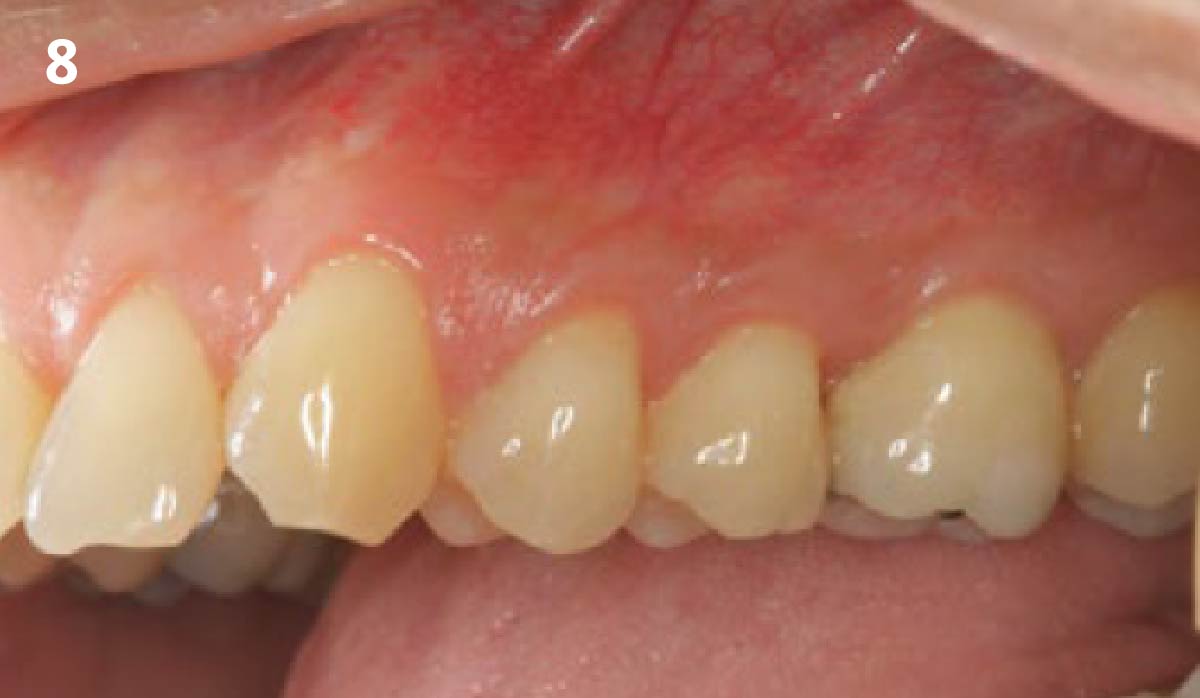
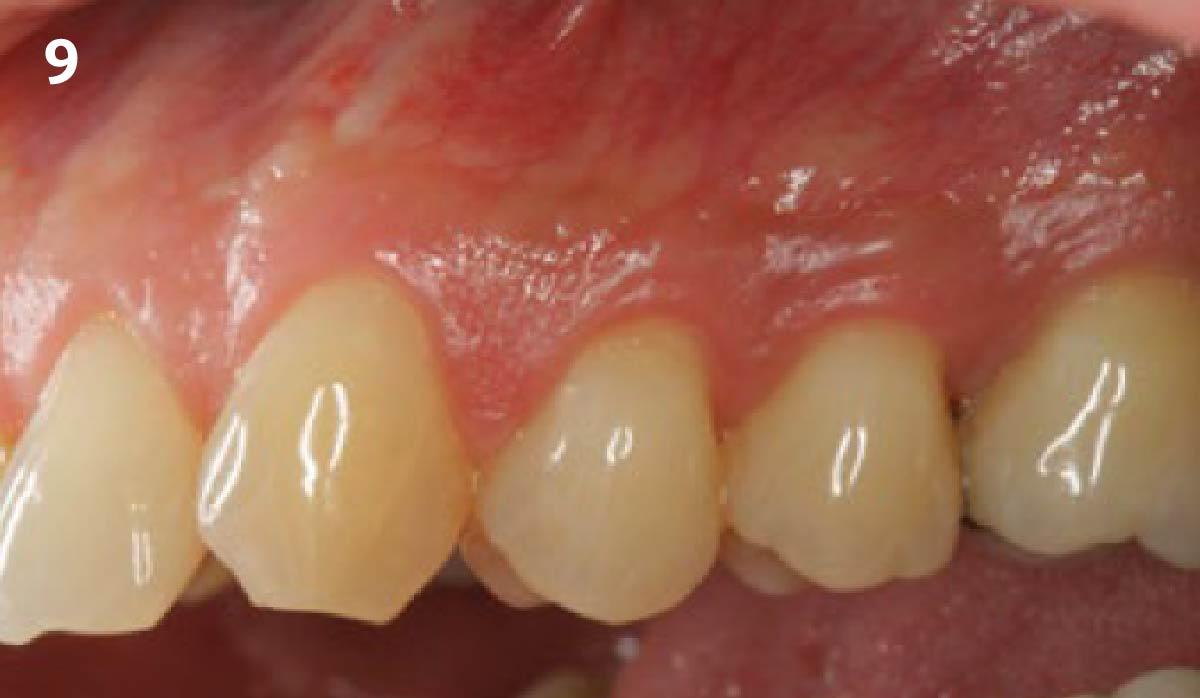
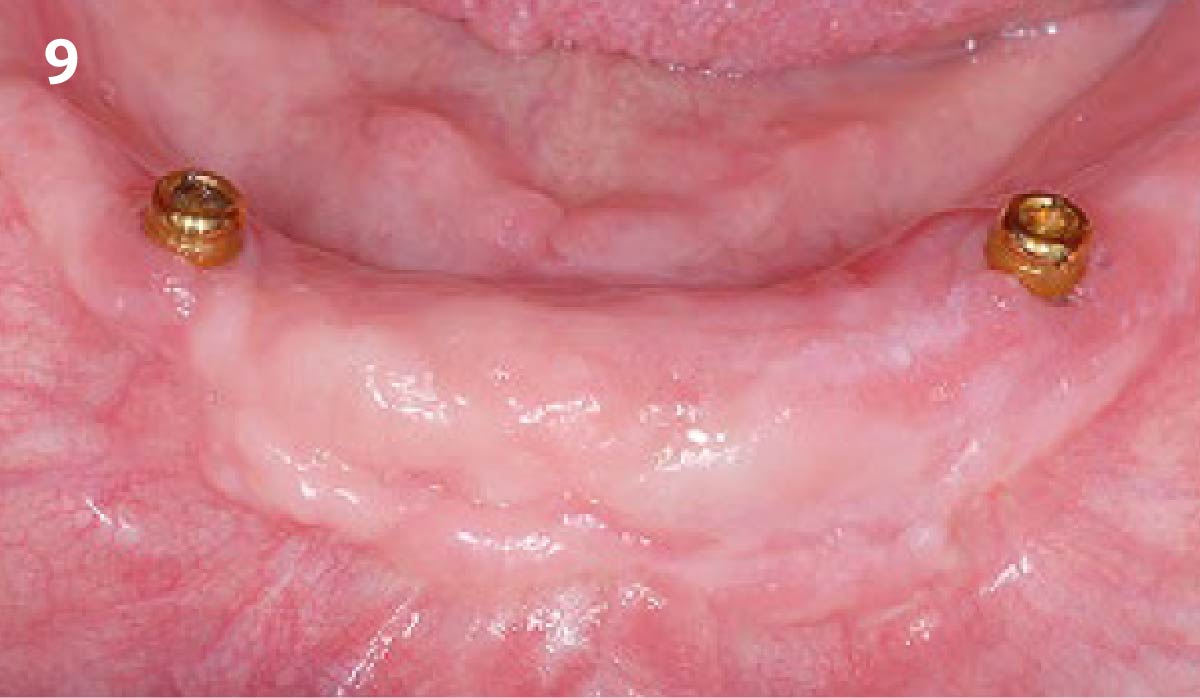
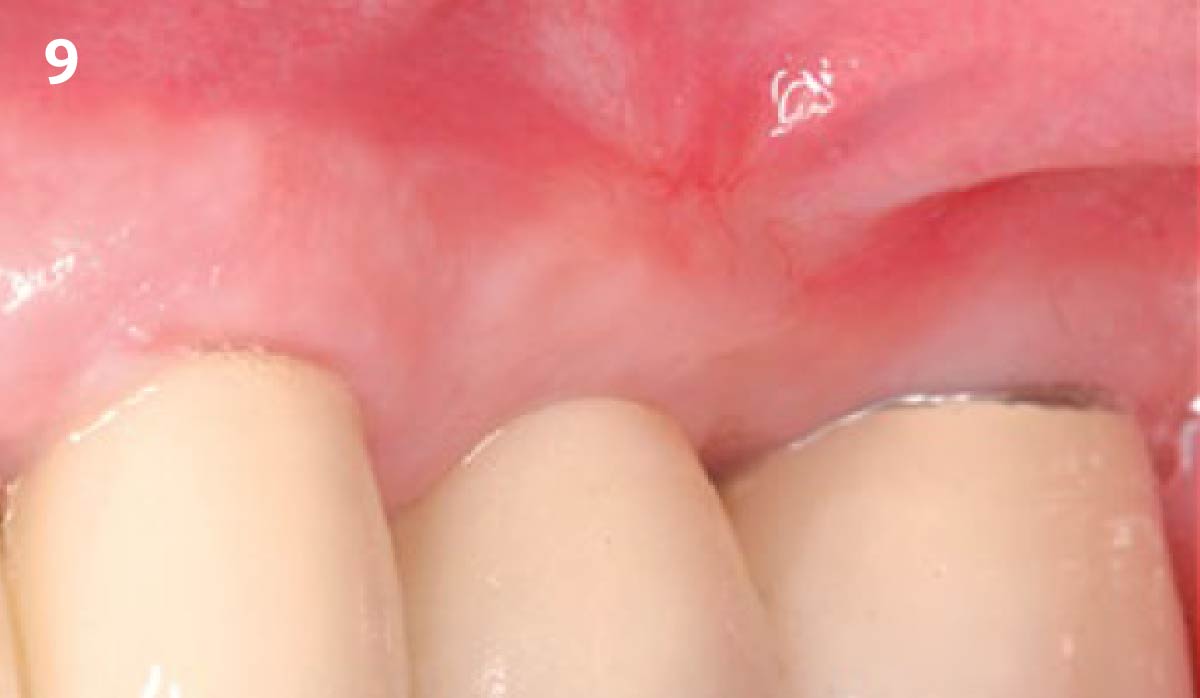
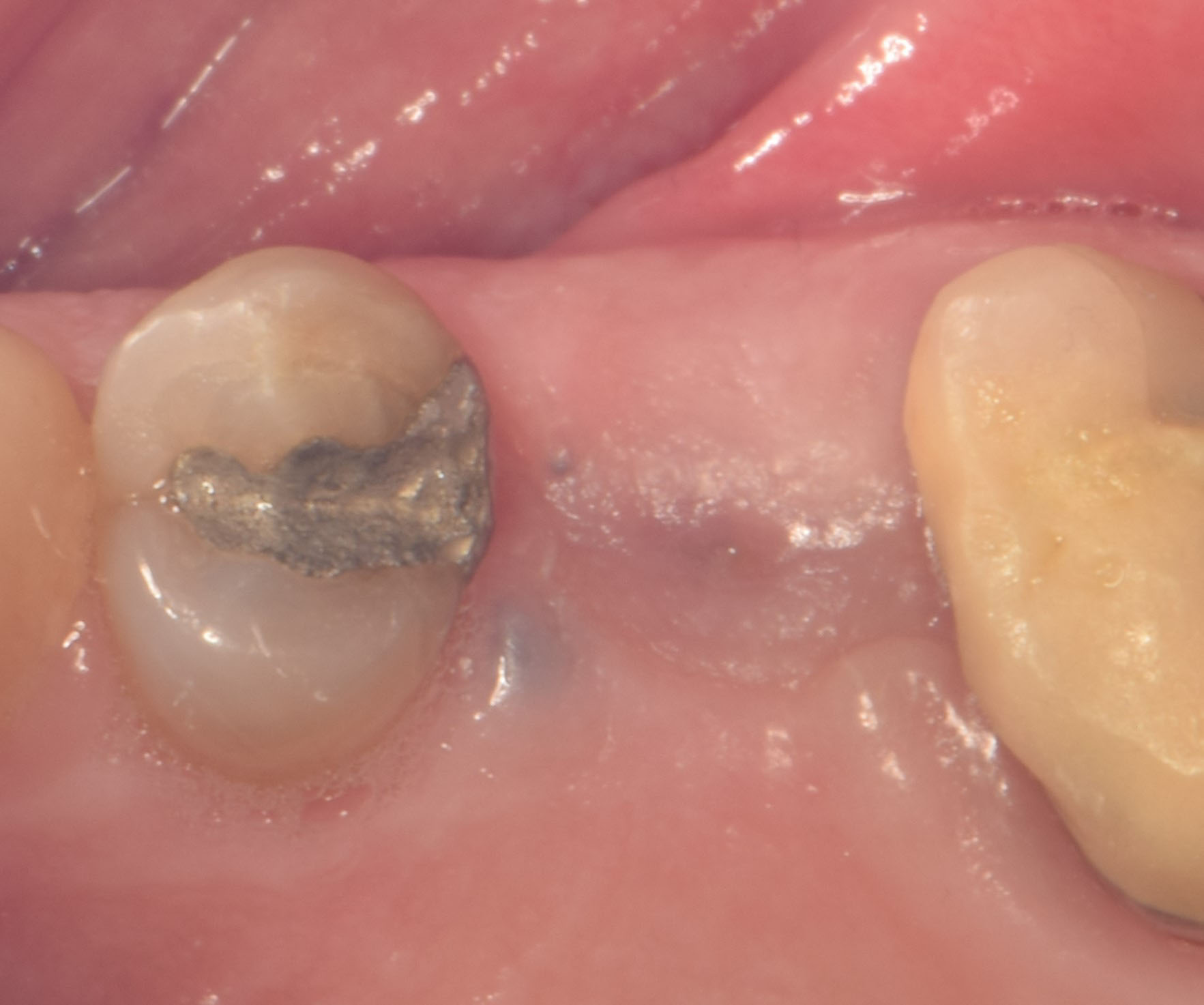
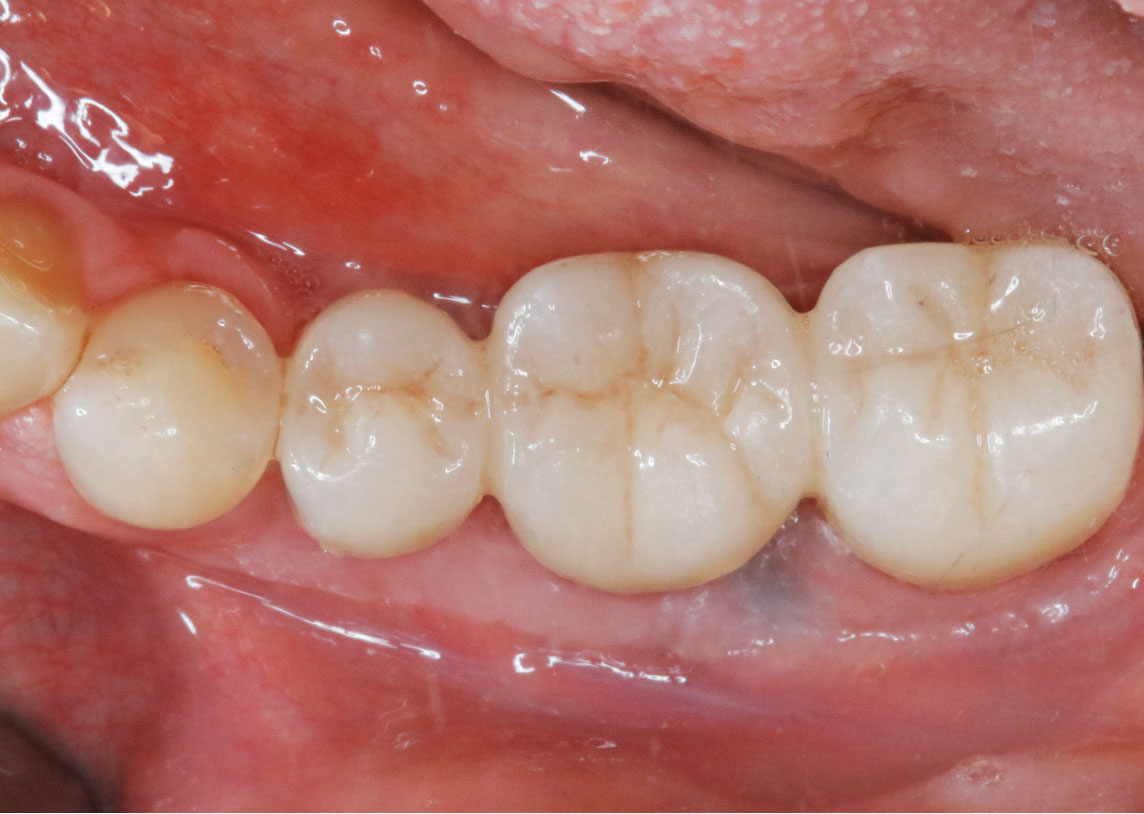
THE OUTCOME
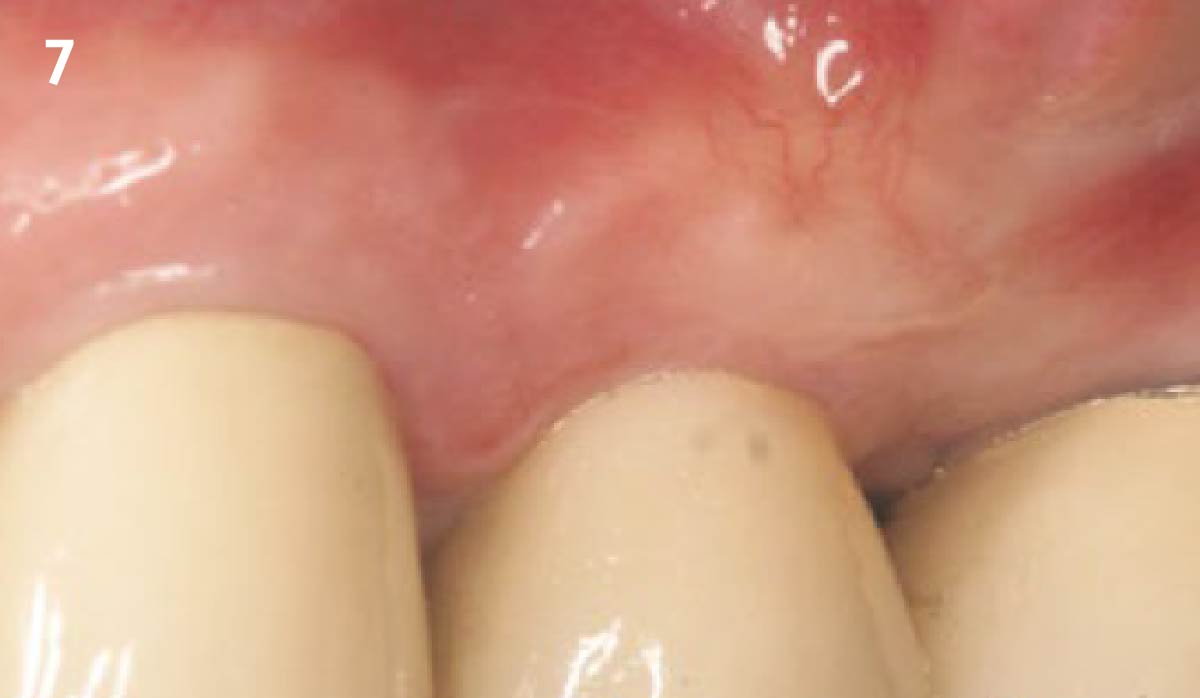
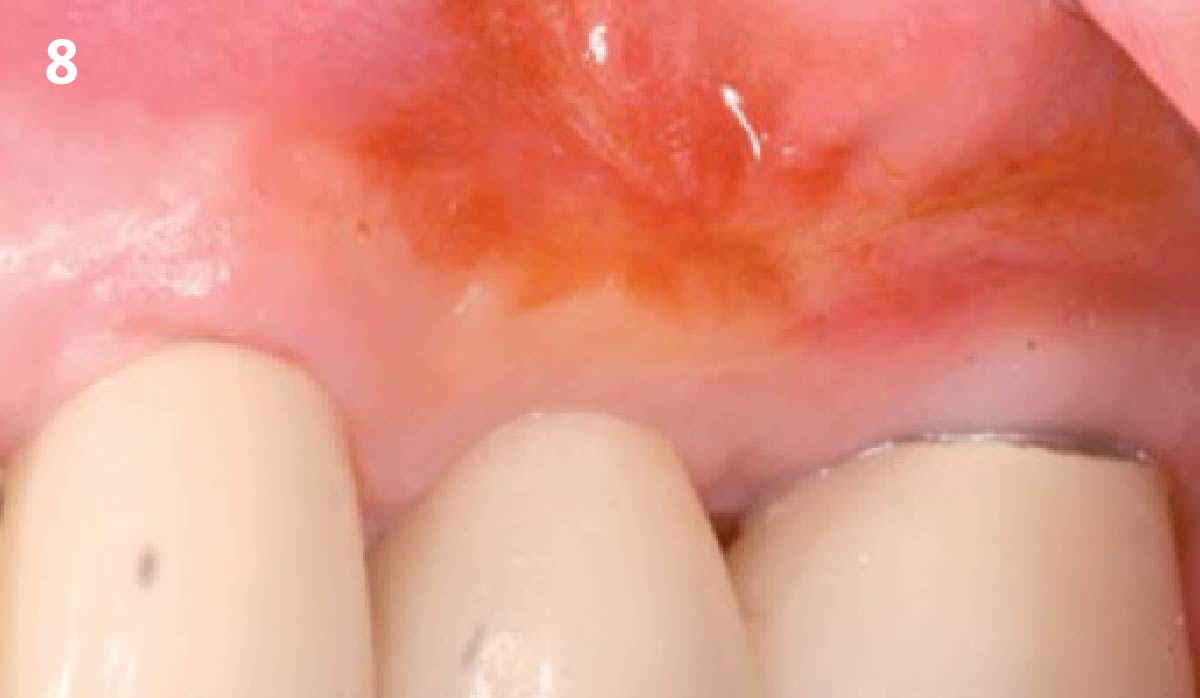
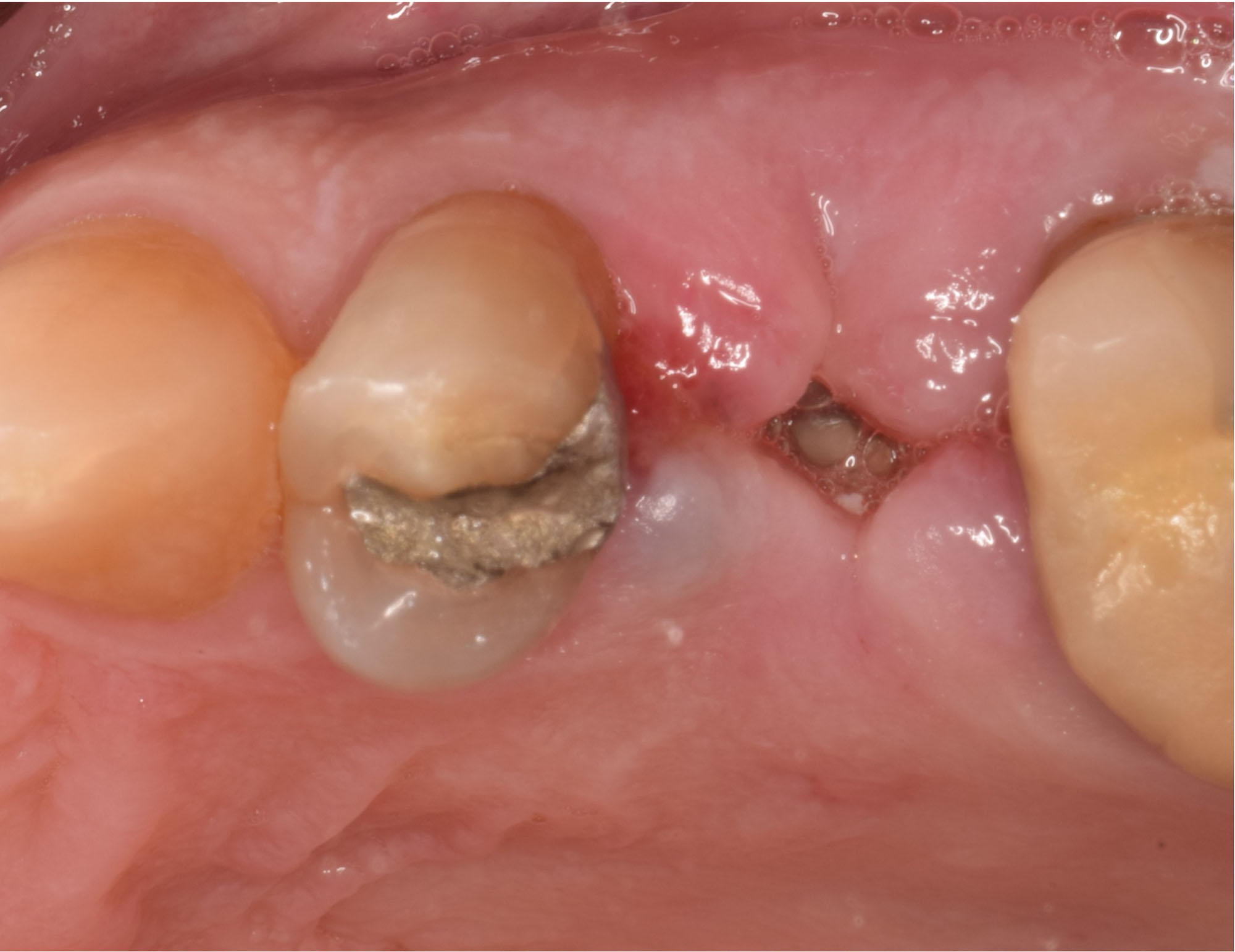
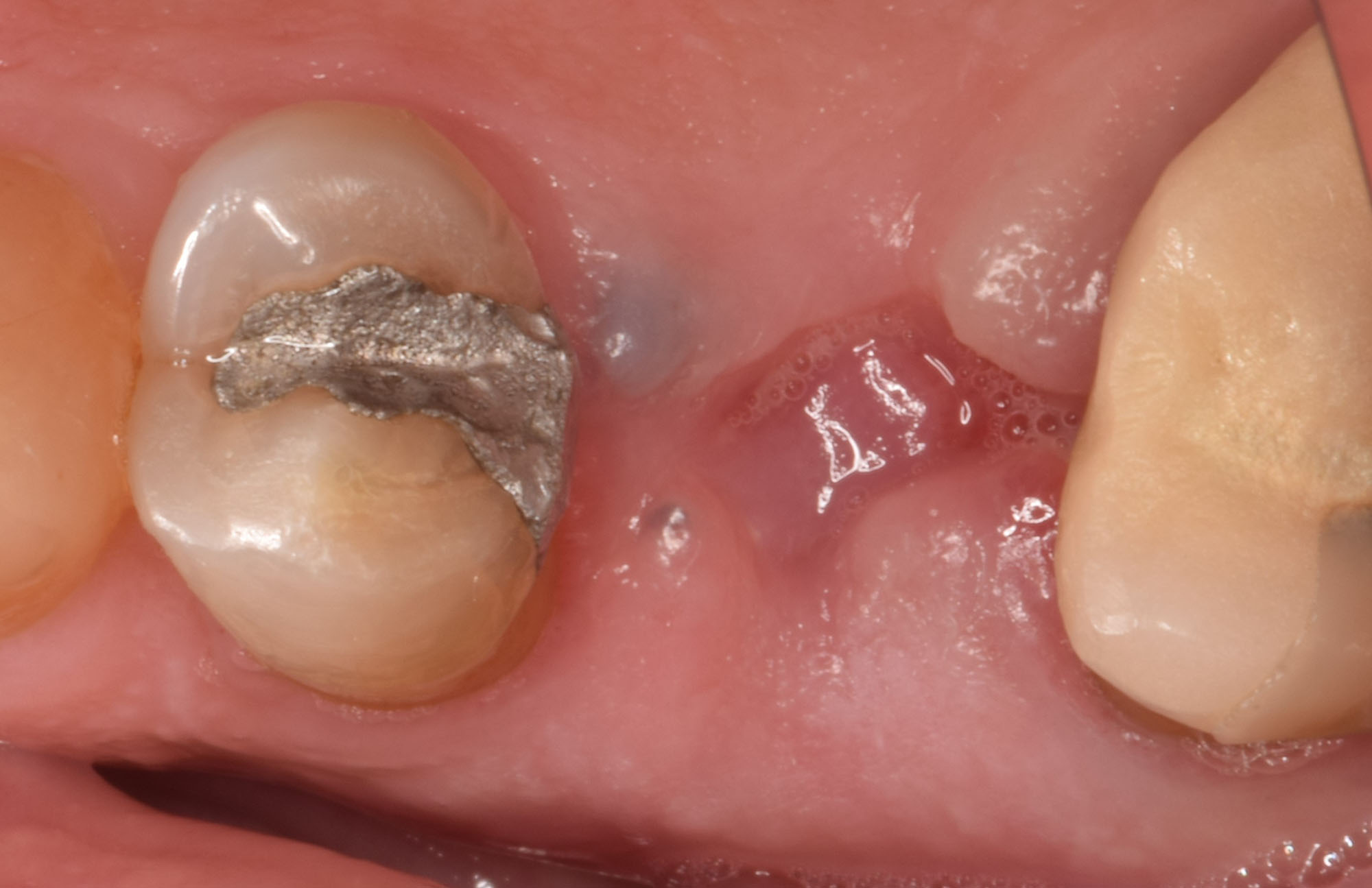
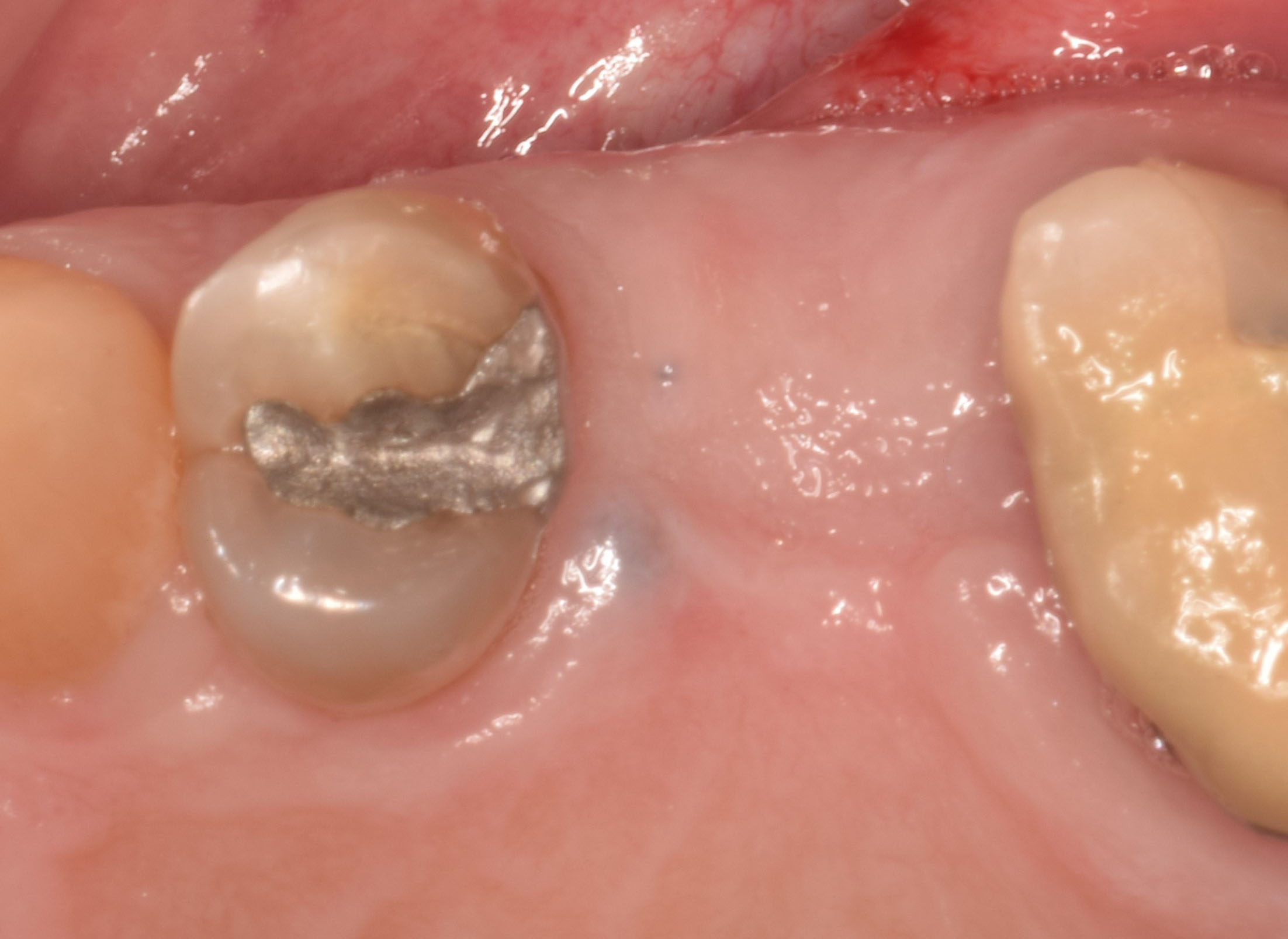
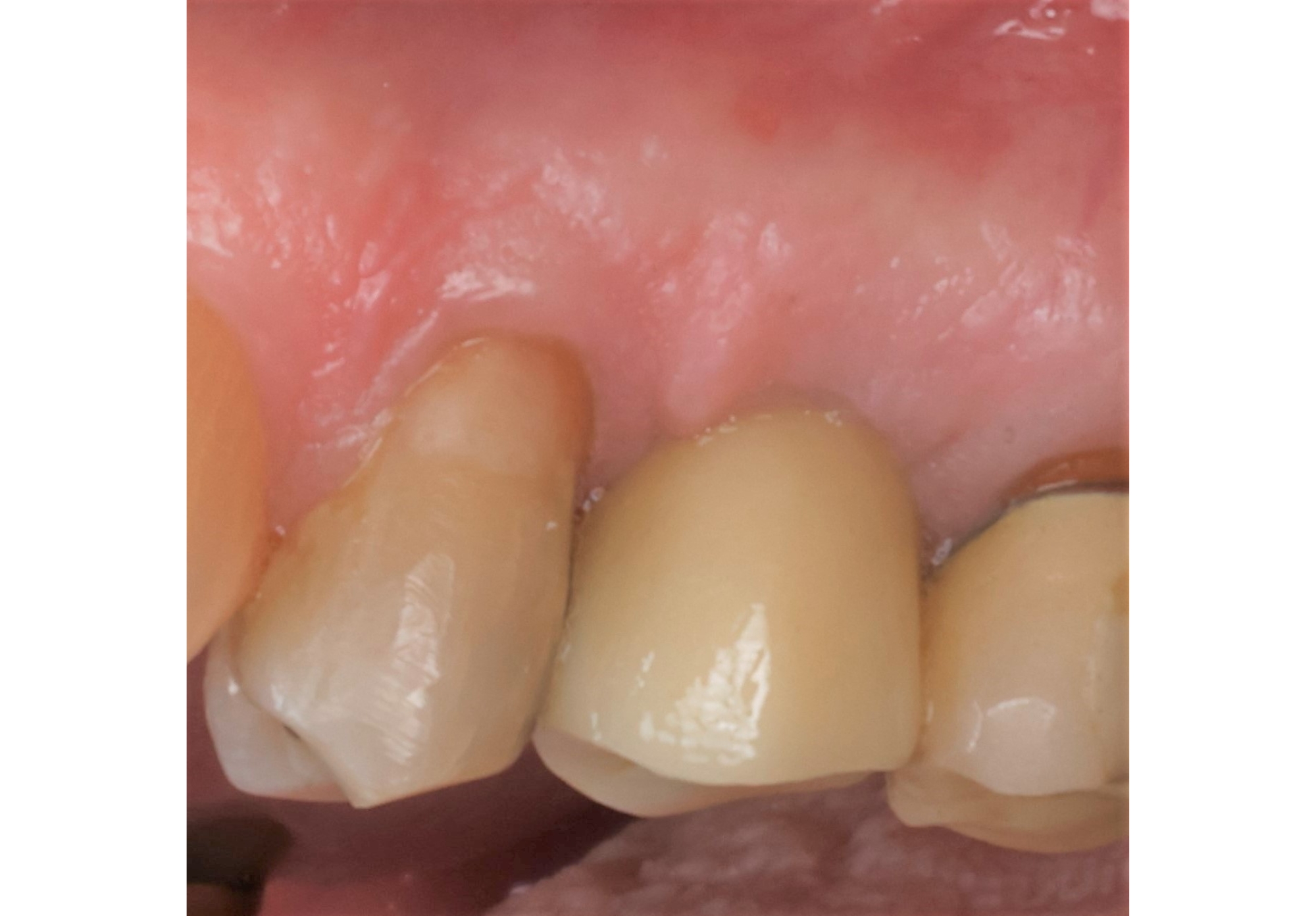
Treatment resulted in approximately 5 mm of vertical bone regeneration. The potential occurrence of a dehiscence associated with a wound opening and exposure of Yxoss CBR® was able to be prevented with Geistlich Fibro-Gide®.
On one hand, the quality of the peri-implant soft tissue was improved by the
soft tissue thickening with Geistlich Fibro‑Gide® and, on the other, by increasing the width of keratinized mucosa with Geistlich Mucograft®. The treatment method chosen resulted in a reduced invasiveness and morbidity by avoiding a donor site for sourcing a transplant.

Arnd Lohmann, MSc
Dr. Arnd Lohmann is a recognized specialist in implantology and periodontology. He earned his dental license in Hamburg in 2002, completed his doctorate in 2003, and has been a partner at a private practice in Bremen since then.
With a Master of Science in Implantology (2007), he specializes in dental implantology and bone augmentation. He is an active speaker at national and international congresses, leads the Bremen study group of the German Society of Oral Implantology (DGOI), and is a member of DGOI, DGZI, and DGI. His practice is equipped with state-of-the-art technology, ensuring high-quality patient care.